Page 1

iMarc™ DSL 9783 Router
Installation Instructions
Document Number 9783-A2-GN11-30
May 2003
NOTE: The FrameSaver®
product line has been
renamed to iMarc.
Contents
iMarc DSL 9783 Router Overview ................................................................ 2
Upgrading a Unit to the SLM Feature Set ..................................................... 3
Product Documentation Online ..................................................................... 4
Package Checklist ........................................................................................ 4
Wiring and Cables You May Need ................................................................ 5
Prior to Installing the Router ......................................................................... 6
Installing the Router ...................................................................................... 7
Status LEDs .................................................................................................. 11
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................ 12
Configuration Setup ...................................................................................... 13
Menu Hierarchy ............................................................................................ 16
Verifying that Self-Test Passed ..................................................................... 14
Using the Easy Install Feature ...................................................................... 19
Completing Setup From the NOC ................................................................. 20
Configuring SNMP Trap Managers and Traps .............................................. 21
Setting Up for In-Band Management ............................................................ 21
Verifying the End-to-End Management Path ................................................ 23
Checking That Data is Being Received ........................................................ 23
Checking PVC Connections ......................................................................... 24
Provisioning the Router Interface ................................................................. 24
Important Safety Instructions ........................................................................ 25
Government Requirements ........................................................................... 27
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information ...................................... 28
1
Page 2
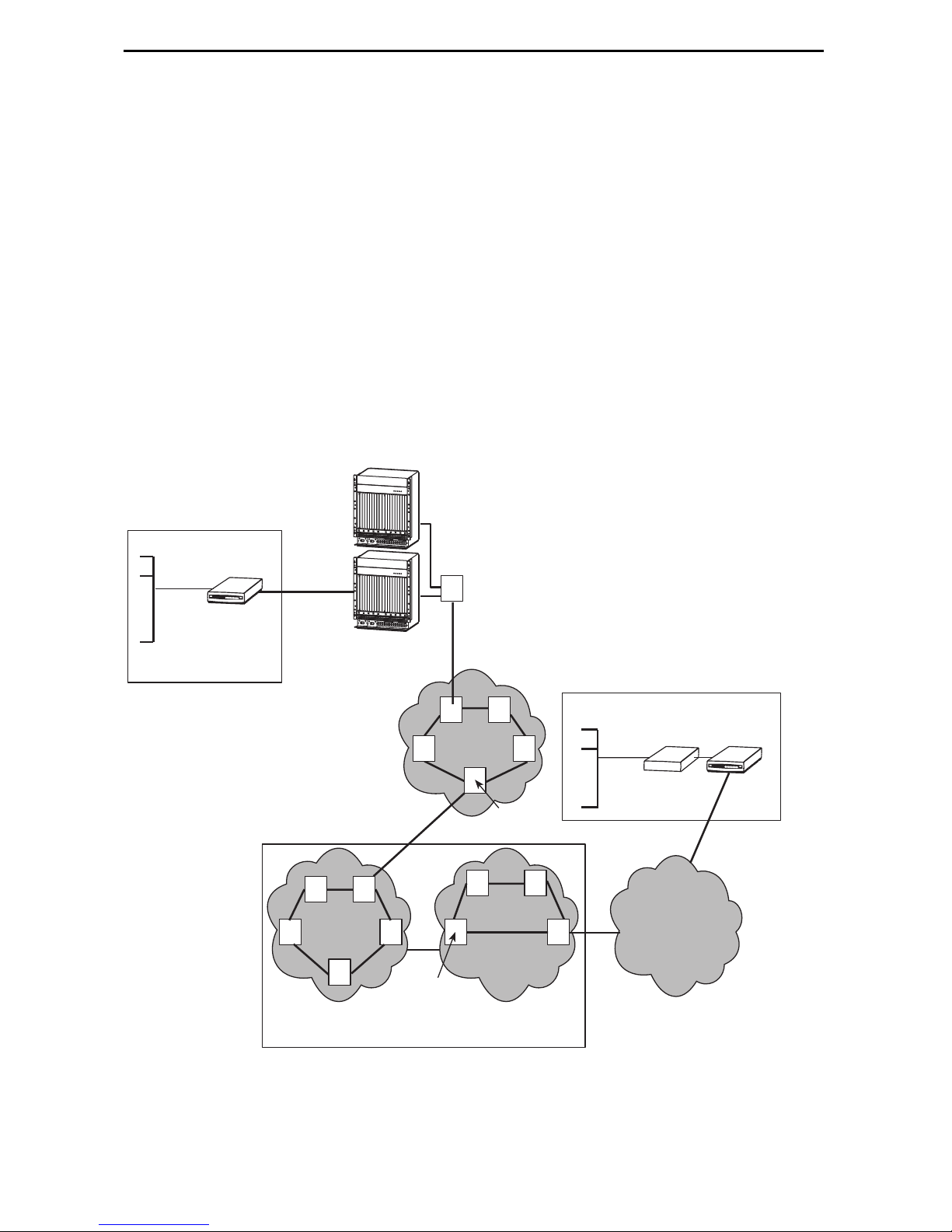
iMarc DSL 9783 Router Overview
The iMarc™ DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) 9783 Router is a component in the iMarc
system. This system allows you to perform end-to-end service level management (SLM)
across a hybrid iMarc DSL/ATM/Frame Relay network. Service providers can isolate
and correct problems remotely from their NOC (Network Operations Center).
The router has an SDSL front end and is a manageable frame relay aware endpoint. It
operates as a bridge or an IP router that connects a DSL link to an Ethernet network.
The iMarc DSL 9783 Router is used for data only and provides corporate LAN access
over traditional twisted-pair copper telephone wiring. Copper pairs run from the central
office (CO) to the customer premises (CP) to create the local loop. The local loop
terminates on the customer premises at the demarcation point in a punchdown block or
network interface device (NID). A typical example of using the iMarc DSL 9783 Router in
a network configuration is shown below.
Central Office
Customer
Premises –
Remote Site
LAN
iMarc
DSL
Bridge/Router
Endpoint
DSL
Copper
Loop
GranDSLAMs
Access
Network
AT M
Switches
P
O
W
E
R
E
N
T
R
Y
M
O
D
U
L
E
L
C
E
L
F
T
O
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
P
O
A
W
E
R
E
N
T
R
Y
M
O
D
U
L
E
R
I
G
H
T
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
A
N
E
B
48V RTN
L
E
F
T
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
A
R
I
G
H
T
U
N
48V NEG
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
B
48V RTN
48V NEG
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
P
O
W
ER
M
U
S
T
BE
D
IS
C
O
NN
E
C
TE
D
AT TH
BE
E
S
F
O
O
UR
RE
C
R
E
E
M
OV
IN
G
O
R
IN
S
W
T
A
A
L
R
LI
N
NG
I
N
TH
G
!
P
IS
OW
PW
E
R
R
E
M
N
U
TR
ST
Y
B
M
E
OD
D
IS
U
C
LE
ON
N
E
CT
E
D
A
T
T
H
E
B
S
E
FO
OU
R
R
E
C
R
E
E
MO
V
IN
G
O
R
IN
S
TAL
LI
NG
T
H
IS
PW
R
E
N
TR
Y
M
O
DU
LE
B
C
L
O
P
O
W
E
R
E
N
T
R
Y
M
O
D
U
L
E
L
C
E
L
F
T
O
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
P
A
O
W
E
R
E
N
T
R
Y
M
O
D
U
L
E
R
I
G
H
T
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
A
N
E
B
48V RTN
L
E
F
T
U
N
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
A
R
I
G
H
T
U
N
48V NEG
I
T
:
L
I
N
E
B
48V RTN
48V NEG
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
PO
W
E
R
M
U
S
T
B
E
D
IS
C
O
N
N
EC
T
ED
A
T
T
H
E
B
E
SO
F
O
U
R
R
E
C
R
E
E
M
O
V
IN
G
O
R
IN
S
W
TA
A
L
R
L
N
I
N
I
N
G
G
T
H
!
P
IS
O
P
W
W
E
R
R
E
M
N
U
T
S
R
T
Y
B
M
E
O
D
D
I
S
U
C
L
E
O
N
N
E
C
T
E
D
A
T
T
H
B
E
S
E
F
O
O
U
R
R
E
C
R
E
E
M
O
V
IN
G
O
R
IN
S
T
A
L
L
I
N
G
T
H
IS
P
W
R
E
N
T
R
Y
M
O
D
U
L
E
B
C
L
O
Hotwire
DSL
AT M
NNI(s)
P
O
W
E
R
A
L
A
R
M
S
F
a
nBA
M
a
j
o
r
M
i
n
C
K
S
E
R
IA
L
A
C
M
C
C
A
L
A
R
M
L
A
N
2
/
W
A
N
S
4
L
O
T
6
8
A
1
0
1
2
1
4
S
E
R
I
A
L
A
L
A
R
M
1
3
C
K
S
M
5
C
M
7
9
B
11
13
P
O
W
E
R
A
L
A
R
M
S
A
B
F
a
n
M
a
j
o
r
M
i
n
C
K
S
E
R
I
A
L
A
C
M
C
C
A
L
A
R
M
L
A
N
2
/
W
A
N
S
4
L
O
T
6
8
A
1
0
12
1
4
S
E
R
I
A
L
A
L
A
R
M
1
35
C
K
S
M
C
M
7
9
B
1
1
1
3
o
r
1
6
18
1
5
1
7
o
r
1
6
18
1
5
1
7
Services
FR/ATM
IWF
Aggregation
Switch
(Optional)
AT M
AT M
Switches
FR Network
FR
Switches
Customer Premises –
HQ Site
iMarc
LAN
Endpoint
Router
TDM
Access
Network
Frame Relay NSP’s Network
ATM – Asynchronous Transfer Mode
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line
FR – Frame Relay
HQ – Headquarters
2
03-17412
IWF – Interworking Function
LAN – Local Area Network
NSP – Network Service Provider
TDM – Time Division Multiplexer
Page 3

The iMarc DSL 9783 CSU/DSU is available in two feature sets:
Basic diagnostic feature set provides basic frame relay and diagnostic capability.
Service Level Management (SLM) provides basic features, plus reporting and
monitoring.
Refer to the iMarc SLV Technical Description for a list of iMarc DSL features, and the
capabilities provided by each feature set.
Upgrading a Unit to the SLM Feature Set
Full Service Level Management (SLM) capability can be activated in units that have the
basic diagnostic feature set at any time. This is an optional feature that adds real-time
and historical network performance monitoring and SLA (Service Level Agreement)
reporting capabilities to your iMarc unit and network. To activate SLM, order a Feature
Activation Certificate. You can order the certificate for a single unit or for many units.
OpenLane SLM Release 5.3 or above is required to schedule activation of SLM features
in units, and to manage the number of activations remaining on the certificate.
OpenLane also provides a Certificate Summary Report to assist you in the management
of the certificate.
When the Feature Activation Certificate arrives, add the Activation Certificate Number to
your OpenLane SLM application’s database. Activations can occur at any time, for as
many units as desired, until no activations remain for the certificate.
Contact your sales representative for additional information.
3
Page 4

Product Documentation Online
Complete documentation for this product is available at www.paradyne.com.
Select Support → Technical Manuals → iMarc IP/Frame Relay Devices.
Select the following documents:
iMarc SLV Technical Description (9000-A2-GB30)
iMarc SLV Configuration Reference (9000-A2-GB31)
iMarc SLV SNMP Reference (9000-A2-GB32)
iMarc SLV Operations Guide (9000-A2-GB33)
iMarc SLV Router Command Line Interface (9000-A2-GB34)
To order a paper copy of a Paradyne document, or to speak with a sales representative,
please call 1-727-530-2000.
Package Checklist
In addition to these instructions, verify that your package contains the following:
❑ iMarc DSL 9783 Router
❑ Power cord with power transformer
❑ Tie wrap for power cord strain relief
❑ DSL network access cable with 8-pin connectors – U.S. models only
❑ Ferrite choke – International models only
Be sure to register your warranty at www.paradyne.com/warranty.
4
Page 5
Wiring and Cables You May Need
The following wiring and cables are used with this product, which uses standard
interface connectors:
❑ Standard connectors: An 8-pin modular (similar to RJ48C) or 6-pin modular
(similar to RJ11) wall jack for the DSL network connection.
❑ DSL wiring: Unshielded twisted-pair wiring (CAT3, or better). The CAT3 wiring must
meet EIA/TIA-568 specifications with 24 AWG (.5 mm) or 26 AWG (.4 mm).
❑ Ethernet wiring: Shielded twisted-pair wiring (CAT5, or better). The CAT5
wiring must meet EIA/TIA-568 specifications with 24 AWG (.5 mm) or
26 AWG (.4 mm).
Contact your sales representative to order Paradyne cables.
Interface
Connection Cables
COM port to a PC
or asynchronous
terminal
ETHERNET port
to a NIC on a PC
or an Ethernet hub
NETwork to the
DSL wall jack
DB25-to-DB25:
Standard EIA-232 straight-through cable —
DB25-to-DB9:
DB25-to-8-pin modular adapter
8-pin modular-to-DB9 cable
(14 feet – 4.3 m)
For connection to a PC NIC:
Standard Ethernet crossover cable —
For connection to an Ethernet Hub:
Standard Ethernet straight-through cable —
Standard straight-through DSL network cable
with 8-pin modular connectors – similar to an
RJ48C-toRJ48C cable (20 feet – 6.1 m).
Cable supplied for use in the U.S.
Feature
Number
3100-F1-920
3100-F2-550
3100-F1-500
Standard DSL network cable with
6-pin connectors – similar to an RJ11 cable
—
5
Page 6

Prior to Installing the Router
These Installation Instructions assume that the virtual circuits at the DSLAM have
already been configured. Provisioning of these circuits can be simplified by using the
OpenLane SLM (Service Level Management) system, as indicated in Provisioning Data
Circuits in OpenLane.
Provisioning Data Circuits in OpenLane
Use the OpenLane SLM system’s Provision Circuit screen to add new circuits that start
at the iMarc DSL endpoint and traverse the SCM and ATM line card in the Hotwire
GranDSLAM, and the default VC sets (from 1 to 4). A group of 250 VCs can be allocated
to each line card, which can be assigned to any port on the card. These custom
connections carry the frame relay traffic.
Note that before the custom cross-connects are configured, the Maximum VCI
number for the uplink VP to be used by these custom connections must be
specified on the Max VCI per VPI screen, and the apply changes executed.
For ATM line cards, custom connections can be used to expand the number of VCs
connected to the card. Each of the 250 VCs can be cross-connected from any VC
on the uplink to any port on the line card.
The following information is collected by the Provision Circuit process:
Uplink VPI/VCI
Slot number and Port number of the DSL connection
Traffic Profile
DSL link VPI/VCI
Frame relay DLCI (provided by NSP)
Frame relay CIR, B
A Circuit ID is then applied to the newly defined circuit, and stored in both the router and
the OpenLane SLM system.
, Bc (provided by NSP)
e
6
Page 7
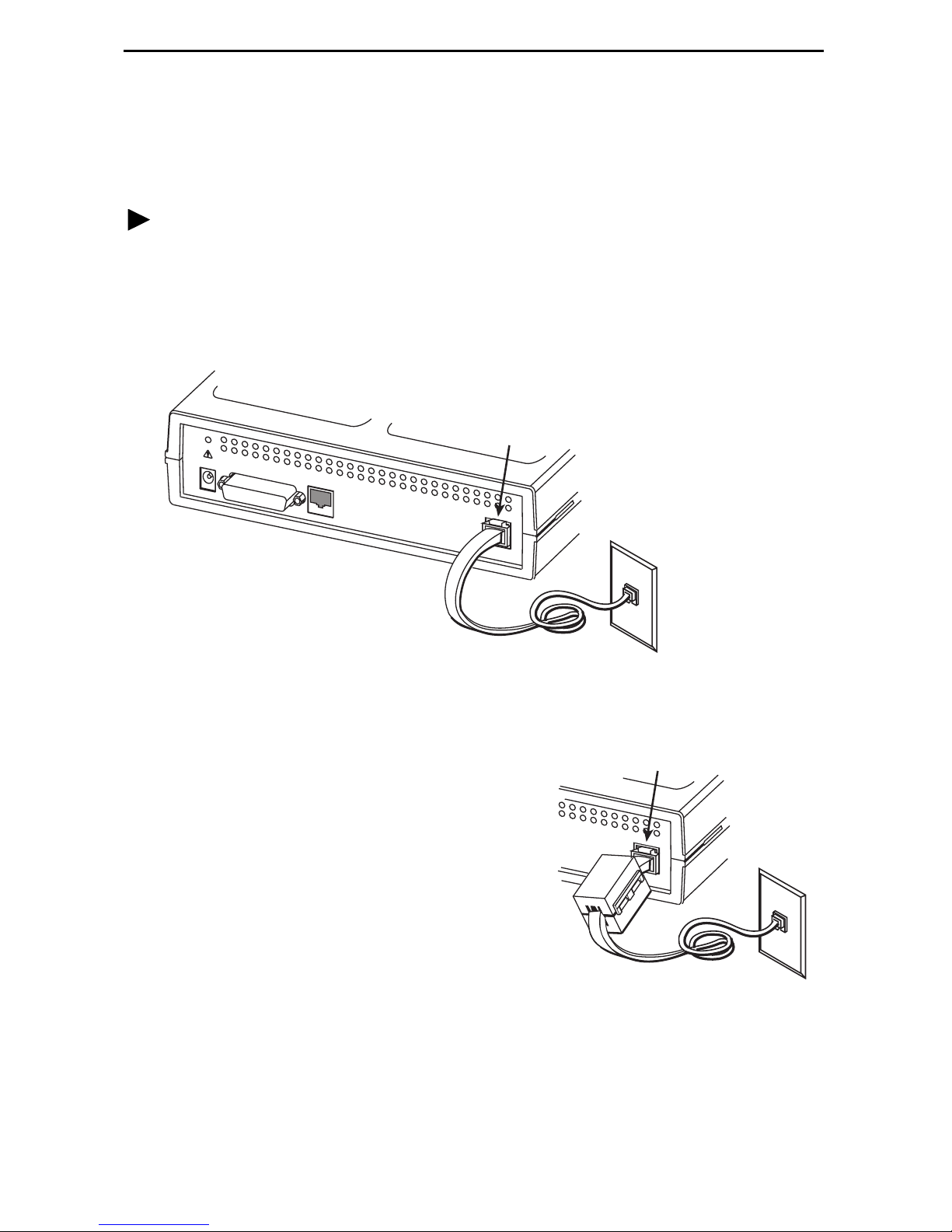
Installing the Router
Place the iMarc DSL 9783 Router on a flat surface, with clearance for the rear
connectors.
Procedure
1. Use the supplied 8-pin DSL network cable (for use in the U.S.), or a 6-pin DSL
network cable (using connectors similar to RJ11), as applicable, for the DSL
connection. Insert one end of the cable into the jack labeled NET on the router.
Insert the other end into the wall jack for DSL data communications.
DSL 9783 Router
NET
POW
ER
COM
ETHERNET
For domestic models, go to Step 3 on page 8.
2. For certain international models, a ferrite
choke has been provided. Place the ferrite
choke on the network cable, as close as
possible to the rear panel.
Close the two halves around the cable
and snap the latch shut.
NET
DSL
Network
00-16878
NET
NET
DSL
Network
Ferrite
Choke
01-16944
7
Page 8
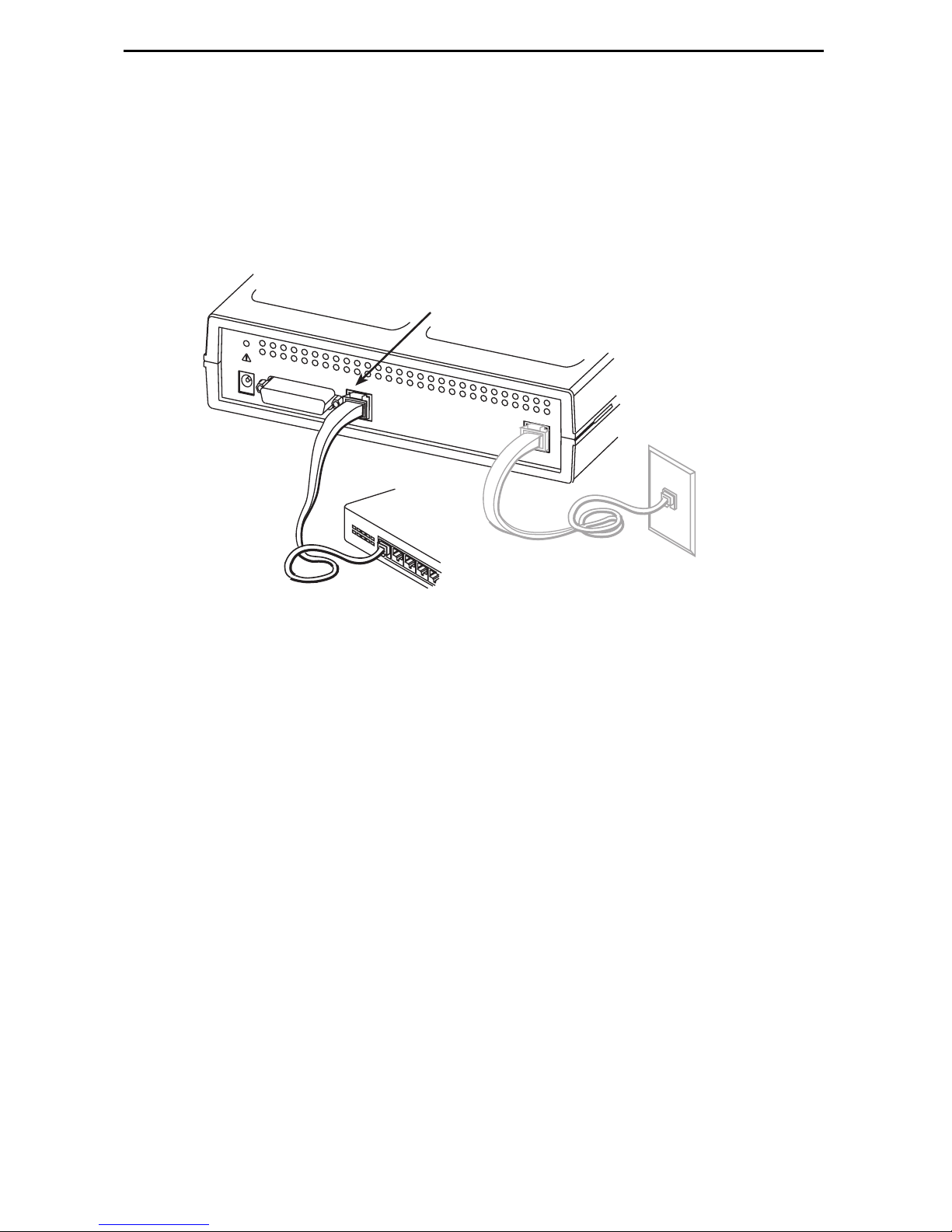
3. Use an 8-pin Ethernet cable for the Ethernet connection. Insert one end of the cable
into the jack labeled ETHERNET.
— Use a straight-through cable to connect the other end of the cable to an
Ethernet hub. Do not connect to the hub’s optional Uplink connection with a
straight-through cable; the Uplink connection requires an Ethernet crossover
cable.
DSL 9783 Router
ETHERNET
POW
ER
COM
ETHERNET
NET
Ethernet
Straight-Through
Cable
Hub
00-16879
– or –
— Use an Ethernet crossover cable to connect to a PC with an Ethernet Network
Interface Card (NIC) installed or a hub’s Uplink connection.
8
Page 9
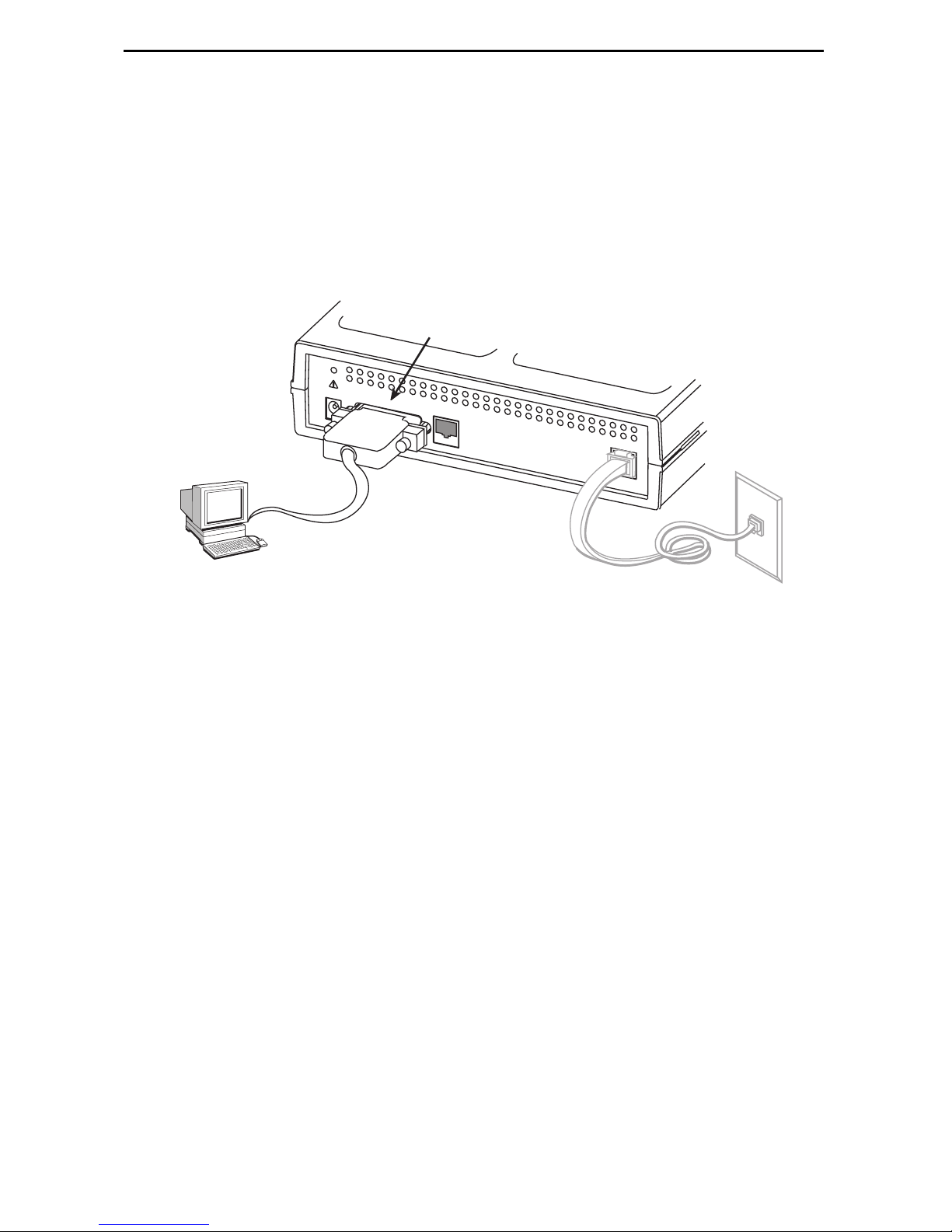
4. Use a VT100-compatible asynchronous terminal or PC to set up management
access to the unit. Insert the DB25 end of the EIA-232 cable into the router’s COM
port. Tighten the screws on each side of the connector. Insert the other end into the
terminal or PC.
The terminal or PC’s configuration must be compatible with the router’s. Refer to
the procedure on page 13 of Configuration Setup. If connecting an external modem
to the COM port, use a standard crossover cable.
DSL 9783 Router
COM
Por t
POW
ER
COM
ETHERNET
VT100
Terminal
NET
00-16876
9
Page 10

5. Insert the supplied power cord’s round end into the jack labeled POWER. Plug the
transformer into an AC outlet.
Install the supplied tie wrap for strain relief, as shown.
Grounded
Power
Outlet
Tie
Wrap
Power
Jack
POW
ER
COM
ETHERNET
NET
03-17401
Installation of the hardware is now complete. When the power cord is installed, the
router goes through a power-on self-test.
Power-On
When power is applied, the router performs self-diagnostics and the PWR LED is on.
The self-diagnostics include a power-on self-test where all of the LEDs are on.
System OK – green
Alarm – red
Test – yellow
ATM – green/yellow
DSL – green
Ethernet Port – green
R
DSL
SDSL
SLV
Refer to Status LEDs on page 11 for information about the LEDs. Refer to
Troubleshooting on page 12 for LED indications requiring action.
OK
ALM
9783
ROUTER
TEST
NetworkSystem
AT M
DSL
OK
Por t
03-17400
10
Page 11

Status LEDs
After a successful self-test, the LEDs should appear as indicated in BOLD in the
Condition column below.
LED Condition Status
System LEDs
OK ON The router has power.
ALM ON
OFF
TEST ON
OFF
Network LEDs
ATM ON – Green
ON – Yellow
DSL Blinking
ON
OFF
Port LED
OK ON
An alarm condition exists.
No alarms have been detected by the router.
The router is performing the power-on self-test, or a test
initiated by the service provider is currently active.
No tests are active.
ATM mode is active and cell delineation is in sync.
ATM mode is active and there is loss of cell delineation.
The router is in start-up or is retraining. The LED blinks on
and off about five times per second.
The DSL link is ready to transmit and receive data.
No DSL link has been established, or the link is down.
The Ethernet port is transmitting and receiving data.
OFF
Self-diagnostics have not been completed successfully.
11
Page 12

Troubleshooting
LED Symptom Action
All LEDs are on. If the LEDs remain on for more than ten minutes, the router is
not functional. Unplug the router and reapply power. If the
ALM LED is still on, contact the service provider.
ALM LED only
remains on.
ALM and TEST LEDs
are blinking.
ATM Yellow LED
remains on.
DSL LED is off. Verify that the DSL cable is securely installed on both ends.
DSL LED continues
blinking after the
power-on self-test
has completed.
DSL LED is on, but
no data is being
transmitted.
The power-on self-test may have failed. Unplug the router
and reapply power. If the alarm LED is still on, contact the
service provider.
Firmware download may be in progress. If firmware
download is not in progress or the LEDs continue blinking for
more than ten minutes, contact the service provider. Do not
unplug the unit, unless instructed to do so by the service
provider.
There is loss of cell delineation (OCD) due to line
impairments. Contact the service provider.
Unplug the unit and reapply power. If the problem continues,
contact the service provider.
The router is attempting to establish the DSL link, or adjusting
the DSL line rate due to line conditions. If the blinking
continues for more than ten minutes, contact the service
provider.
The DSL link has been established, but there is no data
transmission. Verify the Ethernet connection. If the problem
persists, contact the service provider.
DSL and Port LEDs
are on, but no data is
being transmitted.
Port LED is off. Verify that the Ethernet cable is securely installed at both
System OK LED is off. Check that the power cord is securely installed on both ends.
TEST LED is on. A test initiated by the service provider may be active. Wait ten
DSL and Ethernet links have been established, but there is
no data transmission. If the problem continues, contact the
service provider.
ends, and at least one PC is connected and powered on.
Verify that the correct Ethernet straight-through or crossover
cable is installed. Refer to Step 3 on page 8.
If no LEDs are on, the power supply may be defective. Test
the outlet to verify power. If the outlet has power and the
problem persists, contact your service representative.
If other LEDs are on, the OK LED may be burned out. Unplug
the unit and reapply power, and watch all LEDs as the router
performs its power-on self-test. If the OK LED is functioning,
call your service representative.
minutes. If the LED does not go off, contact the service
provider.
12
Page 13

Configuration Setup
Once the router is installed, it can be accessed locally through the menu-driven user
interface via an asynchronous terminal or PC connection, or remotely via a Telnet
session, and the router’s interfaces can be provisioned. The following provisioning can
be set up:
Frame relay, ATM, and physical layer provisioning – Typically set up by the
CLEC (Competitive Local Exchange Carrier) using the menu-driven user interface
via an ASCII terminal or PC running a terminal emulation program, or a Telnet
session.
Router provisioning, using the CLI – Typically accessed by the frame relay
service provider providing managed router service, or by the end user.
SLM provisioning – Typically set up by the frame relay service provider or
the CLEC.
As soon as the router’s COM port is connected to a terminal or PC, the menu-driven
user interface can be accessed. The terminal or PC’s configuration must be compatible
with the router’s COM port settings.
Procedure
To access the menu-driven user interface:
1. Verify the terminal or PC’s configuration:
— Data Rate is set to 19.2 kbps.
— Character Length is set to 8 data bits.
— Parity is set to None.
— Stop Bits is set to 1.
— Flow Control is set to None.
2. Press Enter to display the Main Menu.
13
Page 14

main 9783-RtrSLV
Device Name: Node A 2/26/2001 00:02
MAIN MENU
Status
Test
Configuration
Control
Easy Install
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Ctrl-a to access these functions, Shift-r to access the Router’s CLI. E
xit
If the Main Menu does not appear, recheck the terminal or PC’s settings, or press Enter
again. Refer to Troubleshooting in the iMarc SLV Operations Guide for other
explanations.
Verifying that Self-Test Passed
To verify that the unit passed its self-test, go to the System and Test Status screen.
Main Menu → Status → System and Test Status
The results of the self-test appear directly under the screen title.
If any failure messages appear, reset the unit by disconnecting, then reconnecting the
power cord. The unit will perform the self-test again. If the failure reappears, call your
service representative for assistance.
14
Page 15

Menu Navigation
The router should operate using the default (factory-set) configuration options. Refer to
the following table for help in navigating the menus.
Press the . . . To . . .
Esc key Go back one screen or menu level. See Menu Hierarchy on
page 16.
Tab key, and
Up (↑), Down (↓ ),
Left (←), Right (→)
Arrow keys
Enter or Return key Complete the menu or option selection.
Spacebar Display the next available setting when changing a
As an example, follow these steps to go to the Configuration Edit/Display menu so you
can start setting up the unit.
Move the cursor from one menu item to the next.
configuration option. All the available settings for an option
appear at the bottom of the screen.
Procedure
To load a configuration for editing:
1. From the Main Menu, press the Tab key twice, or press the down (↓) arrow twice,
so the cursor is on Configuration.
2. Press Enter to select Configuration. The Load Configuration From menu appears.
3. Press Enter to select Current Configuration (the cursor is already on this selection).
The Configuration Edit/Display menu appears.
This sequence of steps would be shown as the menu selection sequence:
Main Menu → Configuration
Procedure
To save configuration changes:
1. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the function keys area at the bottom of the screen.
2. Type s (S
3. Press Enter again to save your changes to the Current Configuration (the cursor is
already on this selection).
To continue configuring the router, press Esc until the Configuration Edit/Display menu
reappears. To return to the Main Menu, press Ctrl-a, type m (M
Enter.
ave) and press Enter. The Save Configuration To menu appears.
ainMenu), and press
15
Page 16

Menu Hierarchy
The Menu Hierarchy shows the organization of the iMarc unit’s screens.
S ta t u s
System and Test
Status
IP Path Connection
Status
PVC Connection
Status
Network Interface
Status
I P R o u t i n g T a b l e Destination
Self-Test Results
Last Reset
Health and Status
Te s t S t a tu s
Device Name
IP Address
Status
Discovery Source
Source Link, DLCI, EDLCI
Primary Destination Link, DLCI,
EDLCI, Status
Operating Rate
Receiver Attenuation
SNR Margin
Mask
Gateway
Hop
Type
Interface
TTL
Performance
Statistics
T r a p E v e n t L o g Number of Trap Events
Display LEDs and
Control Leads
I d e nt i t y System
Service Level Verification
DLCI
Frame Relay
ATM
VCC
Ethernet
Clear All Statistics
Time of Day
Event
NAM
16
Page 17

Te st
Network PVC Tests PVC Loopback
Send Pattern
Monitor Pattern
Connectivity
Configuration
Network ATM
Loopback Tests
IP Ping
Lamp Test
Abort All Tests
System Class of Service Definitions
Network Physical
Virtual Router Ports DLCI Records
PVC Connections Source Link, DLCI, EDLCI
IP Path List Add and Display Static Paths
Management and
Communication
Options
ATM Ping
Service Level Verification
General
Frame Relay
Circuit Records
ATM
Primary Destination Link, DLCI, EDLCI
Node IP
Management PVCs
General SNMP Management
Telnet and FTP Sessions
SNMP NMS Security
SNMP Traps
Ethernet Management
Communication Port
External Modem (Com Port)
17
Page 18

Control
System Information Device Name
System Name, Location, Contact
ATM Location ID
Date
Time
Administer Logins Login ID
Password
Access Level
Easy Install
Change Operating
Mode
Select Software
Release
Reset Device
Back-to-Back Mode
Standard Mode
Current Release
Alternate Release
Switch & Reset
DSLAM Type
Node IP Address
Node Subnet Mask
TS Access
Create Dedicated Network Mgmt Link
Ethernet Port Options Screen
Network 1 DSL Line Rate
Network 1 FRF.8 Encapsulation Mode
18
Page 19

Using the Easy Install Feature
An Easy Install screen is provided for custom configurations, but you are not required to
use it for normal installation. You can configure the router by making selections from the
Configuration Edit/Display menu.
Procedure
1. Select the Easy Install feature.
Main Menu → Easy Install
Easy Install Screen Example
main/easy_install 9783-RtrSLV
Device Name: Node A 2/26/2001 00:01
EASY INSTALL
DSLAM Type: Paradyne
Node IP Address: 000.000.000.000 Clear
Node Subnet Mask: 000.000.000.000
TS Access: VPI,VCI 0,35
Clear
Create a Dedicated Network Management Link
Ethernet Management Options Screen
Network 1 DSL Line Rate (Kbps) AutoRate
Network 1 FRF.8 Encapsulation Mod Transparent
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
19
Page 20

2. If the router will not be connected to a Paradyne DSLAM, change the DSLAM Type.
Other selections are Alcatel (NewBridge), PairGain, and Nokia.
3. Enter the Node IP Address and Subnet Mask.
4. Specify TS Access if a Troubleshooting (TS) DLCI or Virtual Circuit (VC) is being
set up for remote access by the service provider. The default is 0,35.
5. Select Create a Dedicated Network Management Link to set up for permanent
remote access by the NOC. Enter a DLCI, VPI, and VCI at the resulting prompts.
6. Select the Ethernet Management Options Screen to go directly to the Ethernet
Management Options screen. The interface (Status) is already enabled.
— Enter the IP Address (e.g., 10.101.51.253) and Subnet Mask
(e.g., 255.255.255.0) for the Ethernet interface.
— Enter the Default Gateway Address (the IP Address that will be used for
packets without a specified route).
— Press the Esc key to return to the Easy Install screen.
7. Change Network 1 DSL Line Rate (Kbps), if desired. The default is AutoRate.
If a Paradyne DSLAM is used, the default setting is AutoRate. For non-Paradyne
DSLAMs, the AutoRate setting is not valid and the default rate is 784 kbps.
8. Change Network 1 FRF.8 Encapsulation Mode, if desired. The default is
Transparent (data is forwarded without translation), which supports both frame
relay and ATM PVCs, and iMarc proprietary multiplexing.
9. S
ave the configuration and return to the Configuration Edit/Display menu.
Completing Setup From the NOC
Procedure
1. Access the router on the TS Management Link that was set up at the remote site in
Step 5 of Using the Easy Install Feature.
2. Ping the router five times within five seconds. The router automatically provisions
the TS Access VC and accepts the destination IP address of the Ping as its
temporary IP address, which is used on the management VC interface.
3. If necessary, open a Telnet session and configure any specific configuration options
that require input or changes from default settings. Create all customer VCs,
including internal DLCIs and VPI/VCIs on the DSL interface, and cross-connect the
DLCIs to the VCCs.
20
Page 21

Configuring SNMP Trap Managers and Traps
Procedure
To enter SNMP managers and configure traps:
1. Select SNMP Traps.
Main Menu → Configuration → Management and Communication →
SNMP Traps
2. Configure the following:
— Enable SNMP Traps.
— Identify the total Number of Trap Managers.
— Specify the IP address for each NMS Trap Manager to which traps will be sent.
— Specify the Initial Route Destination for each Trap Manager. The default is
AutoRoute.
— Select or disable trap categories, as needed.
ave the configuration.
3. S
Setting Up for In-Band Management
If FRF.8 Encapsulation Mode is set to Translational, remote management of the router
can still be accomplished in-band, as indicated in the following procedure.
The following procedure assumes that the router’s Ethernet interface has already been
assigned an IP address that is in the same subnet as the management IP address
entered in Step 6 on page 20 of Using the Easy Install Feature, and that the router is not
configured for bridging only.
Refer to the iMarc SLV Configuration Reference and iMarc SLV Router Command Line
Interface for additional information.
21
Page 22

Procedure
1. Create a DLCI on the router virtual port.
Configuration → Virtual Router Ports → DLCI Records
Assign the DLCI number that will be used for management on Serial port 0
(Rtr-S0 – e.g., DLCI 900).
2. Create a management PVC using the DLCI just configured on Serial port 0
to connect the management link to the router.
Configuration → Management and Communication → Management PVCs
Using the DLCI 900 example, make the following connection:
— Select Name: Mgmt900
— Intf IP Address: Special, and add the IP address for the Ethernet interface in
Step 6 on page 20 of Using the Easy Install Feature.
— Intf Subnet Mask: Special, and add the Subnet Mask for the Ethernet interface
in Step 6 on page 20 of Using the Easy Install Feature.
— Set DE: Leave at the default, Disable.
— Primary Link: Select Rtr-S0.
— Primary DLCI: Select 900.
3. Return to the M
ain Menu and press Shift-r to access the router’s CLI.
4. From the CLI, enable password and show the router’s configuration.
en
show config
A list of the router’s configuration is shown, most of the configuration already
completed using the default values.
interface serial 0.900
ip unnumbered
frame-relay interface-dlci 900
no bridge-group 1
exit
5. Add the route to the routing table.
config t
ip route 10.101.51.253 255.255.255.255 Serial 0.900
save
exit
6. Ping the Ethernet management interface to verify that the router can be reached.
ping 10.101.51.253
exit
The router is now set up for in-band management.
22
Page 23

Verifying the End-to-End Management Path
After installation of a remote router, run an ATM Ping test from the Hotwire®
GranDSLAM.
Procedure
To Ping the router:
1. From the Hotwire ATM Line Card’s Main Menu, select the ATM Ping test.
Diagnostics → ATM Ping (D-C)
2. Enter a VPI of 0 and a VCI of 35.
3. Select a Direction of Endpoint, then Start.
4. If the test is successful, select a Direction of Network, then Start.
If both tests are successful, the VC has been tested from end to end.
Checking That Data is Being Received
Procedure
To verify that data is being received:
1. From the router’s Main Menu, select frame relay performance statistics.
Main Menu → Status → Performance Statistics → Frame Relay
2. Repeatedly R
— Verify that the counts for Frames Received and Characters Received under the
Frame Relay Link statistics are increasing.
— Verify that there are no errors under Frame Relay Errors.
If data is not being received or you are receiving errors, check your cable
connections and replace or repair a damaged cable.
3. Return to the Status menu.
efresh the screen to:
23
Page 24

Checking PVC Connections
Check PVC connections to verify that all PVCs, including management PVCs, are
configured and active.
Procedure
To verify PVCs:
1. Select PVC Connection Status from the Status menu.
The PVC Connection Status screen shows all PVC connections, the interface
source and DLCI number of the incoming data linked to the interface, and DLCI
number for the outgoing data. You can also see whether the PVC is active.
2. Verify that each PVC is active.
— If active, the router should be passing data.
— If not active, no data traffic can be carried by the PVC. If the PVC is configured
correctly, the circuit may be down.
Provisioning the Router Interface
The iMarc DSL 9783 Router defaults to bridge mode. Routing without bridging, and
simultaneous routing and bridging, are also options.
Use the bridge command from the router’s CLI to configure the bridge and routing
attributes. Also, enter an Ethernet IP address and a DHCP IP address. Refer to the
iMarc SLV Router Command Line Interface for more information.
24
Page 25

!
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product or
included in the manual.
2. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for ventilation. To ensure reliable
operation of the product and to protect it from overheating, these slots and
openings must not be blocked or covered.
3. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord and do not locate the product where
persons will walk on the power cord.
4. Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or removing covers may
expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to
qualified service personnel.
5. General purpose cables are used with this product for connection to the network.
Special cables, which may be required by the regulatory inspection authority for the
installation site, are the responsibility of the customer. Use a UL Listed, CSA
certified, minimum No. 24 AWG line cord for connection to the Digital Subscriber
Line (DSL) network.
6. When installed in the final configuration, the product must comply with the
applicable Safety Standards and regulatory requirements of the country in which it
is installed. If necessary, consult with the appropriate regulatory agencies and
inspection authorities to ensure compliance.
7. A rare phenomenon can create a voltage potential between the earth grounds of
two or more buildings. If products installed in separate buildings are
interconnected, the voltage potential may cause a hazardous condition. Consult a
qualified electrical consultant to determine whether or not this phenomenon exists
and, if necessary, implement corrective action prior to interconnecting the products.
8. Input power to this product must be provided by one of the following: (1) a UL
Listed/CSA certified power source with a Class 2 or Limited Power Source (LPS)
output for use in North America, or (2) a certified transformer, with a Safety Extra
Low Voltage (SELV) output having a maximum 240 VA available, for use in the
country of installation.
9. In addition, if the equipment is to be used with telecommunications circuits, take the
following precautions:
— Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
— Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically
designed for wet locations.
— Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line
has been disconnected at the network interface.
— Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
— Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm.
There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
— Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
25
Page 26

CE Marking
When the product is marked with the CE mark on the equipment label, this
demonstrates full compliance with the following European Directives:
Directive 73/23/EEC – Council Directive of 19 February 1973 on the harmonization
of the laws of the member states relating to electrical equipment designed for use
within states relating to electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage
limits, as amended by Directive 93/68/EEC.
Directive 89/336/EEC – Council Directive of 3 May 1989 on the approximation of
the laws of the member states relating to Electro-Magnetic Compatibility (EMC), as
amended by Directive 93/68/EEC.
EMI Notices
!
UNITED STATES – EMI NOTICE:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
The authority to operate this equipment is conditioned by the requirements
that no modifications will be made to the equipment unless the changes or
modifications are expressly approved by Paradyne Corporation.
!
CANADA – EMI NOTICE:
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
interference-causing equipment regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du
règlement sur le matérial brouilleur du Canada.
26
Page 27

Government Requirements
Certain governments require that instructions pertaining to connection to the telephone
network be included in the installation and operation manual. Specific instructions are
listed in the following sections.
Notice to Users of the Canadian Telephone Network
The Industry Canada label identifies certified equipment. This certification means that
the equipment meets telecommunications network protective, operational and safety
requirements as prescribed in the appropriate Terminal Equipment Technical
Requirements document(s). The Department does not guarantee the equipment will
operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is permissible to be
connected to the facilities of the local telecommunications company. The equipment
must also be installed using an acceptable method of connection. The customer should
be aware that compliance with the above conditions may not prevent degradation of
service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be coordinated by a representative designated by
the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the user to this equipment, or equipment
malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to request to
disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of
the power utility, telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system, if present, are
connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
CAUTION:
Users should not attempt to make such connections themselves, but should
contact the appropriate electric inspection authority, or electrician, as
appropriate.
The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) assigned to each terminal device provides an
indication of the maximum number of terminals allowed to be connected to a telephone
interface. The termination on an interface may consist of any combination of devices
subject only to the requirement that the sum of the Ringer Equivalence Numbers of all
the devices does not exceed 5.
If your equipment is in need of repair, refer to Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training
Information on page 28.
27
Page 28

Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for
any help needed. For additional information concerning warranty, sales, service, repair,
installation, documentation, training, distributor locations, or Paradyne worldwide office
locations, use one of the following methods:
Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com.
(Be sure to register your warranty at www.paradyne.com/warranty.)
Telephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to
speak with a company representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them to
Technical Publications, Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773, or
send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include the number and title of this document
in your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you are willing
to provide additional clarification.
Trademarks
FrameSaver, Hotwire, and OpenLane are registered trademarks of Paradyne
Corporation. iMarc is a trademark of Paradyne Corporation. All other products and
services mentioned are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or
registered service marks of their respective owners.
"
Copyright © 2003 Paradyne Corporation. Printed in U.S.A.
28
*9783-A2-GN11-30*
 Loading...
Loading...