Page 1

COMSPHERE
UALFLOW
D
DATA SERVICE UNITS
MODELS 3615 AND 3616
USER’S GUIDE
Document No. 3615-A2-GB20-40
July 1999
Page 2

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
COMSPHERE
DualFlow Data Service Units
Models 3615 and 3616
User’s Guide
3615-A2-GB20-40
5th Edition (July 1999)
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new release to this manual.
United States
FCC Registration number: AW292J-61661-DD-N
PSTN Ringer Equivalence number (REN): DBM option 0.7B
Canada
V.32 Dial Backup Module
Certification number: 230 3684 A
DOC Load number: 7
2-Wire Switched 56 DBM
Certification number: 230 5870 A
DOC Load number: 0
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for any help needed. For additional information
concerning warranty, sales, service, repair, installation, documentation, training, distributor locations, or Paradyne worldwide office
locations, use one of the following methods:
• Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com. (Be sure to register your warranty there. Select
Technical Support → Warranty Registration.)
• Telephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to speak with a company representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them to Technical Publications, Paradyne Corporation,
8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773, or send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include the number and title of this document in
your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you are willing to provide additional clarification.
Trademarks
All products and services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks or registered service marks of their
respective owners.
Printed on recycled paper
COPYRIGHT 1999 Paradyne Corporation. All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system,
or translated into any human or computer language in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties
without the express written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Avenue North, P.O. Box 2826, Largo, Florida 33779-2826.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability
or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents
hereof without obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
A July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 3
!
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product or
included in the manual.
2. This product is intended to be used with a 3-wire grounding type plug – a plug which
has a grounding pin. This is a safety feature. Equipment grounding is vital to ensure
safe operation. Do not defeat the purpose of the grounding type plug by modifying
the plug or using an adaptor.
Prior to installation, use an outlet tester or a voltmeter to check the ac receptacle for
the presence of earth ground. If the receptacle is not properly grounded, the
installation must not continue until a qualified electrician has corrected the problem.
If a 3-wire grounding type power source is not available, consult a qualified
electrician to determine another method of grounding the equipment.
3. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for ventilation. To ensure reliable
operation of the product and to protect it from overheating, these slots and openings
must not be blocked or covered.
4. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord and do not locate the product where
persons will walk on the power cord.
Safety Instructions
5. Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or removing covers may
expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to
qualified service personnel.
6. General purpose cables are provided with this product. Special cables, which may be
required by the regulatory inspection authority for the installation site, are the
responsibility of the customer.
7. When installed in the final configuration, the product must comply with the applicable
Safety Standards and regulatory requirements of the country in which it is installed. If
necessary, consult with the appropriate regulatory agencies and inspection
authorities to ensure compliance.
8. A rare phenomenon can create a voltage potential between the earth grounds of two
or more buildings. If products installed in separate buildings are interconnected, the
voltage potential may cause a hazardous condition. Consult a qualified electrical
consultant to determine whether or not this phenomenon exists and, if necessary,
implement corrective action prior to interconnecting the products.
In addition, if the equipment is to be used with telecommunications circuits, take the
following precautions:
– Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
– Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed
for wet locations.
– Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has
been disconnected at the network interface.
– Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
– Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm.
There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
– Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
B3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 4
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Notices
! ! ! ! !
!
! !!
Government Requirements
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) requires that instructions pertaining to
connection to the telephone network be included in the installation and operation manual. Specific
instructions are listed in this section.
Notice to Users of the Digital Data Service
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules. On the bottom of the equipment is a label
or silk-screened text that contains, among other information, the FCC registration number and
Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) for this equipment. If requested, please provide this
information to your telephone company.
The REN is useful to determine the quantity of devices you may connect to your telephone line
and still have all of those devices ring when your number is called. In most, but not all areas, the
sum of the RENs of all devices should not exceed 5. T o be certain of the number of devices you
may connect to your line, as determined by the REN, you should call your local telephone
company to ascertain the maximum REN for your calling area.
If your DSU causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company may discontinue your
service temporarily . If possible, they will notify you in advance. But if advance notice is not
practical, you will be notified as soon as possible. You will be advised of your right to file a
complaint with the FCC.
C July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 5

Safety Instructions
If your DSU causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company may discontinue your
service temporarily . If possible, they will notify you in advance. But if advance notice is not
practical, you will be notified as soon as possible. You will be advised of your right to file a
complaint with the FCC.
Your telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures
that could affect the proper operation of your equipment. If so, you will be given advance notice so
as to give you an opportunity to maintain uninterrupted service.
The DBM cannot be used on public coin-operated telephone service provided by the telephone
company . Connection to party-line service is subject to state tariffs. (Contact the state public utility
commission, public service commission, or corporation commission for information.)
No repairs may be performed by the user. Should you experience difficulty with this equipment,
refer to the Equipment Warranty and Support section of Chapter 1.
For Digital Data Service (DDS) installations, inform the local telephone company of the
appropriate network channel interface code for the service you desire.
DDS
Interface
Code
04DU5-24 2400
04DU5-48 4800
04DU5-96 9600
04DU5-19 19,200
04DU5-56 56,000
04DU5-64 64,000
Data Rate
(bps)
The DDS Service Order Number is 6.0Y. The jack configurations required are RJ48S for the
Model 3615 DSU and RJ48T for the Model 3616. With an RJ48T configuration, you must specify
the number of data lines you require. Refer to the Technical Specifications section of Chapter 1 for
V.32 DBM jack information.
After the telephone company has installed the requested jack, you can connect the DSU with the
appropriate cable (provided). An FCC-compliant telephone cord and modular plug is provided
with this equipment. This equipment is designed to be connected to the telephone network or
premises wiring using a compatible modular jack that is Part 68 compliant.
D3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 6

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
E July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 7

Table of Contents
Preface
About This Guide vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Use This Guide vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Related Documents viii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reference Documents viii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. About Your DualFlow DSU
Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard Features 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DBM Features 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T echnical Specifications 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Warranty and Support 1-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
Overview 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Before You Begin 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Change Hardware Straps 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Where to Place the DSU 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the DSU 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Network 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the DSU to a Router 2-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Addressing the Unit 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Operation and Testing Connections 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
Overview 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Before You Begin 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Change Hardware Straps 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the DSU 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Network 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting the DSU to a Router 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Addressing the Unit 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Operation and Testing Connections 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
i3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 8

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
4. Operating the DualFlow DSU
5. Unit Configuration
Appendices
Overview 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DCP and SDCP Operation 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Menu Structure 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Branch 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backup Branch 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T est Branch 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Branch 4-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Branch 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Message Branch 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using the DCP to Set Configuration Options 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Option T ables 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glossary
Index
A. DSU Menu A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B. Configuration Worksheets B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. Status Indicators and Control Panel Messages C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D. Pin Assignments D-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
E. Applications Configurations E-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F. Equipment List F-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ii July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 9

Table of Contents
List of Figures
Figure Page
2-1 Model 3615 DSU Hardware Switch Location 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2 Model 3615 DSU Electrical Connection 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-3 Model 3615 DSU Network Connection 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-4 Model 3615 DSU Dial (PSTN) Network Connection 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-5 Model 3615 DSU Switched 56 kbps Network Connection 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-6 Model 3615 DSU DDS (LADS) 2-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-7 Router Connection 2-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-8 Addressing Example 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1 Model 3616 DSU Switch and Jumper Locations 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2 COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Rear View 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-3 Model 3616 DSU Installation and Circuit Pack Lock 3-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-4 V.35 Adapter Installation 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-5 Addressing Example 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1 Model 3615 DCP 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-2 SDCP and Model 3616 DSU Faceplate 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3 Loopbacks 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-1 Digital Network Connector D-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-2 3600 Hubbing Device (3600-F3-300) D-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-3 Model 3616 DSU 25-Pin EIA-232/25-Pin V.35
Rear Connector Plate (3000-F1-021) D-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-4 V.35 Adapter Plug (3000-F1-511) D-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-5 EIA-232-D Crossover Cable (4951-035F) D-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-6 V.35 Crossover Cable (3211-178F) D-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
E-1 Dial Backup for Received Data Errors (SyBC and SyBT) Application E-2. . . . . . . . . .
E-2 Dial Backup for Exceeded Load Thresholds (SyBC and SyBT) Application E-3. . . . .
E-3 Frame Relay and Simultaneous Diagnostic (DiDg) Application E-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iii3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 10

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table Page
1-1 General Technical Specifications 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-2 DSU T echnical Specifications 1-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-3 V.32 DBM Technical Specifications 1-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-4 4-Wire Switched 56 DBM Technical Specifications 1-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-5 2-Wire Switched 56 DBM Technical Specifications 1-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1 Model 3615 DSU Switch Settings 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2 LADS Connection Distances 2-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1 Model 3616 DSU Switch Settings 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2 Model 3616 DSU Jumper Straps 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1 Identity Descriptions 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-2 Backup Branch Menu Selections 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3 Digital T est Results 4-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-4 End-to-End Test Results 4-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-5 Bit Error Rate T est Results 4-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-6 Directory Entry and Password Characters 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-7 Lead States 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1 DSU Configuration Options 5-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-2 DSU Port Configuration Options 5-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-3 DBM Configuration Options 5-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-4 DBM Port Configuration Options 5-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-5 Diagnostic DBM Configuration Options 5-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-6 Diagnostic General Configuration Options 5-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-7 Backup Configuration Options 5-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-1 DSU Status Indicators C-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-2 SDCP Status Indicators C-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-3 Device Health and Status Messages C-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-4 Expanded Health and Status Messages C-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-5 Subnetwork Health and Status Messages C-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-6 Command Progress Messages C-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-7 Dial Backup Progress Messages C-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-8 Command Error Messages C-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C-9 Dial Backup Error Messages C-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of Tables
iv July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table Page
D-1 Model 3615 – Digital (DDS and 4-Wire Switched 56 kbps)
Network Connector Pin Assignments D-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-2 Model 3615 – Dial (Analog and 2-Wire Switched 56 kbps)
Network Connector Pin Assignments D-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-3 3600 Hubbing Device Pin Assignments D-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-4 3600 Hubbing Device CC IN/DC OUT Jack Pin Assignments D-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-5 EIA-232/V.24 Connector Pin Assignments D-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D-6 V.35 Connector Pin Assignments D-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
v3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 12

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
vi July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 13

Preface
About This Guide
This user’s guide provides the information needed to
install and operate your COMSPHEREr Model 3615 or
3616 DualFlow Data Service Unit (DSU), which is
equipped with a dial backup module (DBM) – either a
V.32 DBM, a 4-wire Switched 56 DBM, or a 2-wire
Switched 56 DBM.
Be sure to read the safety and regulatory information at
the beginning of this guide.
It is assumed that you are familiar with the functional
operation of digital data communications equipment.
How to Use This Guide
This guide provides basic information about your DSU,
how to install it and verify that it is installed and operating
correctly , how to operate the unit and its options, and how
to configure it.
T wo installation chapters are provided, one for the
Model 3615 DualFlow DSU and one for the Model 3616
DualFlow DSU. Select the chapter that applies to your
DSU.
Refer to the following chapters or appendices, as
needed:
Chapter 1 Provides a general overview of
the DualFlow DSU, the unit’s
technical specifications,
equipment warranty and
support services information,
and instructions for equipment
return.
Chapter 3 Provides step-by-step
instructions for installing your
carrier-mounted Model 3616
DualFlow DSU.
Chapter 4 Describes how to operate your
DSU and its DBM.
Chapter 5 Presents the basics of setting
and changing configuration
options and provides
Configuration Option T ables,
which provide the default
(factory-loaded) settings and
describe each configuration
option and its possible settings.
Appendix A Provides a diagram for
navigating the DSU’s menu
structure.
Appendix B Summarizes the configuration
options for you.
Appendix C Lists the DSU’s messages and
identifies when they appear.
Appendix D Shows application
configurations and network
hookups.
Appendix E Provides cable and connector
pin assignments.
Appendix F Equipment List
Glossary
Index
Chapter 2 Provides step-by-step
instructions for installing your
standalone Model 3615
DualFlow DSU.
vii3615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 14

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Related Documents
Other product documentation includes the following:
3000-A2-GA31 COMSPHERE 3000 Series
Carrier, Installation Manual
3000-A2-GB41 COMSPHERE –48 Vdc
Central Office Power Unit,
Installation Guide
6700-A2-GB41 COMSPHERE 6700 Series
Network Management System,
User’s Guide, Security
Manager Feature Supplement
6700-A2-GY31 COMSPHERE 6700 Series
Network Management System,
User’s Guide
6800-A2-GB31 COMSPHERE 6800 Series
Network Management System,
Communications Products
Support Command Reference
Manual
Contact your sales representative for additional product
documentation.
Reference Documents
• AT&T Technical Reference 41458
• AT&T Technical Reference 61330
• AT&T Technical Reference 62310 – 1987
• Bell Canada DCTE Specifications
• Bell Communications Research T echnical
Reference Publication 41028
• ITU-T V.35 (ISO 2593)
• EIA-232-D/V.24 (ISO 2110)
• Integrated Network Corporation Compatibility
Bulletin CB-INC-101
• Northern T elecom NIS S204-2e 1986
• Pacific Bell PUB L-780035-PB/NB
• Pacific Bell PUB L-780036-PB/NB
Paradyne documents are also available on the World
Wide Web at www.paradyne.com. Select Library →
Technical Manuals.
viii July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 15

About Your DualFlow DSU
Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard Features 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DBM Features 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
V.32 DBMs 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switched 56 DBMs 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Specifications 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Warranty and Support 1-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
Overview
The COMSPHEREr DualFlow Data Service Unit
(DSU) provides simultaneous digital data service (DDS)
and backup connections to support Frame Relay and
router-based applications.
The DDS portion provides basic non-rate adapted,
non-diagnostic access using the DSU’s V.35 connector.
The backup portion (either a V.32, 4-wire Switched 56, or
2-wire Switched 56 DBM) provides simultaneous
rate-adapted, diagnostic access to the switched network.
T wo versions are available:
• The standalone Model DualFlow 3615 DSU is
designed for desktop or shelf operation.
• The carrier-mounted (nest- or rack-mounted)
Model DualFlow 3616 DSU is designed for
operation in the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier.
Each DualFlow DSU is equipped with an integral dial
backup module (DBM) for operation over the Public
Switched T elephone Network (PSTN), often referred to as
the dial network, or the Switched 56 kbps digital service.
The following sections describe the DSU’s standard
features, as well as the features of the integral DBMs.
Refer to the appropriate section for DBM feature
information.
Standard Features
The DualFlow DSU offers the following features:
• Multispeed operation. The DSU operates at data
rates of 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 38.4, 56, and 64CC kbps
full-duplex over the DDS network.
• T wo DTE connectors (interfaces) are provided:
EIA-232-D and V.35. Use the EIA-232-D
connector for router-management data or backup;
use the V.35 connector for user data.
• LADS operation. The DSU can operate as a local
area data set (LADS) (sometimes called a
limited-distance modem, or LDM) at 2.4, 4.8, 9.6,
19.2, 38.4, 56, or 64kbps.
• NMS control. The DSU can be controlled by
COMSPHEREr 6700 or 6800 Series NMS. Both
NMSs operate using Advanced Diagnostic protocol
(ADp).
The Model 3615 DSU requires a hubbing device
for connection to the NMS; the Model 3616 DSU is
connected to the NMS through the shared
diagnostic unit (SDU) in the COMSPHEREr
3000 Series Carrier.
T echnical specifications of the DSU and various DBMs
are near the end of this chapter.
1-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 16

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
• Diagnostic Control Panel control. The
Model 3615 DSU is controlled from its diagnostic
control panel (DCP). The diagnostic control panel
for the Model 3616 DSU, called a shared diagnostic
control panel (SDCP), is installed in the
3000 Series Carrier. Both control panels display
information about the DSU on 2-line, 16-character
liquid crystal display (LCD) and through
light-emitting diode (LED) status indicators.
NOTE
Except where a distinction is
made, the term DCP refers to
both types of diagnostic control
DCP
panels, the
For more information about the 3000 Series Carrier or
the SDCP, refer to the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier,
Installation Manual. For more information about the 6700
or 6800 Series NMS, refer to your NMS documentation.
These documents are identified in the Related Documents
section of the Preface, which also provides a telephone
number you can call to order these documents.
or the
SDCP
.
V.32 DBMs
The V.32bis 14.4 kbps dial backup module (referred to
as V.32 DBM throughout this guide) is attached to the
DSU. The V.32 DBM provides the following features:
• Multispeed nondisruptive point-to-point
connections. The DBM provides point-to-point
service over the 2-wire dial network. Backup rates
available are 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 12.0, and 14.4 kbps.
DBM and DDS connections can be active at the
same time.
• Independent operation. Although the DBM is
installed on the DSU, the two are configured
separately and most tests can be run on either
independent of the other (e.g., you can run a test on
the DBM while a test is running on the DSU).
• Security. There are four levels of call setup
security: None, Password, Callback, and Alarm.
With Alarm, the DBM only answers incoming calls
when an alarm is detected on the DDS line.
• Management control. Dial backup can be initiated
from a 6700 or 6800 Series NMS, the DSU’s DCP,
or it can be initiated automatically by the
DSU-DBM.
DBM Features
DualFlow DSUs are ordered with one of the following
features:
• V.32bis 14.4 kbps dial backup module (DBM)
• 2-Wire Switched 56 DBM
• 4-Wire Switched 56 DBM
Refer to the appropriate section for specific DBM
features.
• DTR control setup. When configured for DTR call
control (DTRCallCon: Orig) backup, the
DSU-DBM initiates dial backup when the DTE
raises data terminal ready (DTR) to the DSU-DBM.
• Rate Adaption. With this feature, the DSU-DBM
can adapt its data rate to a low-speed application
while operating over a higher speed switched
circuit.
• Port Async/Sync. The port asynchronous-to-
synchronous feature makes it possible to send
asynchronous data over the synchronous network.
• Nondisruptive Diagnostics. When set up to use
nondisruptive diagnostics, the local DSU-DBM
sends diagnostic data over the dial connection
without interrupting or disrupting customer data.
• Full tributary diagnostics. The DSU-DBM
supports a full complement of diagnostic tests and
commands when a call is established on a backup
line. Diagnostics can be addressed to and sent to a
tributary from a 6700 or 6800 Series NMS
workstation, or from the DCP of a control DSU.
1-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 17

About Your DualFlow DSU
Switched 56 DBMs
The Switched 56 DBM is attached to the DSU and
offers dial backup capability through the Switched
56 kbps digital service. The Switched 56 DBM offers the
following features:
• Nondisruptive point-to-point connections. The
DBM sends its line data to the EIA-232 port, which
is not used for DDS data. DBM and DDS
connections can be active at the same time.
• Independent operation. Although the DSU and
Switched 56 DBM are functionally integrated, they
are configured separately and can run most tests
independently (e.g., you can run a test on the DBM
while a test is running on the DSU).
• Network compatibility. The Switched 56 DBM,
either the 2-wire or 4-wire version, provides service
over compatible Switched 56 kbps switched
services, such as AT&T’s ACCUNETr Switched
56 kbps Service, MCI’s 56 kbps Switched Digital
Service, Northern T elecom’s DataPatht service,
and US SPRINT’s VPN56 using either dedicated
2-wire or 4-wire access, or local exchange carrier
2-wire or 4-wire switched access. This DBM
operates at 56 kbps full-duplex, and uses
proprietary rate adaption to support data rates of
less than 56 kbps.
• Security. The Switched 56 DBM offers four levels
of call setup security: None, Password, Callback,
and Alarm. Alarm allows the DBM to only answer
incoming calls when there is a Facility Alarm on
the DDS line.
• DTR control setup. When configured for DTR call
control (DTRCallCon: Orig) backup, the
DSU-DBM initiates dial backup when the DTE
raises data terminal ready (DTR) to the DSU-DBM.
• Management control. Dial backup functions can
be controlled from a 6700 or 6800 Series NMS, the
DSU’s DCP, or automatically by the DSU-DBM.
• Rate Adaption. With this feature, the DSU-DBM
can adapt its data rate to a low-speed application
while operating over a higher speed switched
circuit.
• Port Async/Sync. The port asynchronous-to-
synchronous feature makes it possible to send
asynchronous data over the synchronous network.
• Nondisruptive Diagnostics. When set up to use
nondisruptive diagnostics, the local DSU-DBM
sends diagnostic data over the dial connection
without interrupting or disrupting customer data.
• Full tributary diagnostics. The DSU-DBM
supports a full complement of diagnostic tests and
commands when a call is established on a backup
line. Diagnostics can be addressed to and sent to
tributaries from a 6700 or 6800 Series NMS
workstation, or from the DCP of a control DSU.
Technical Specifications
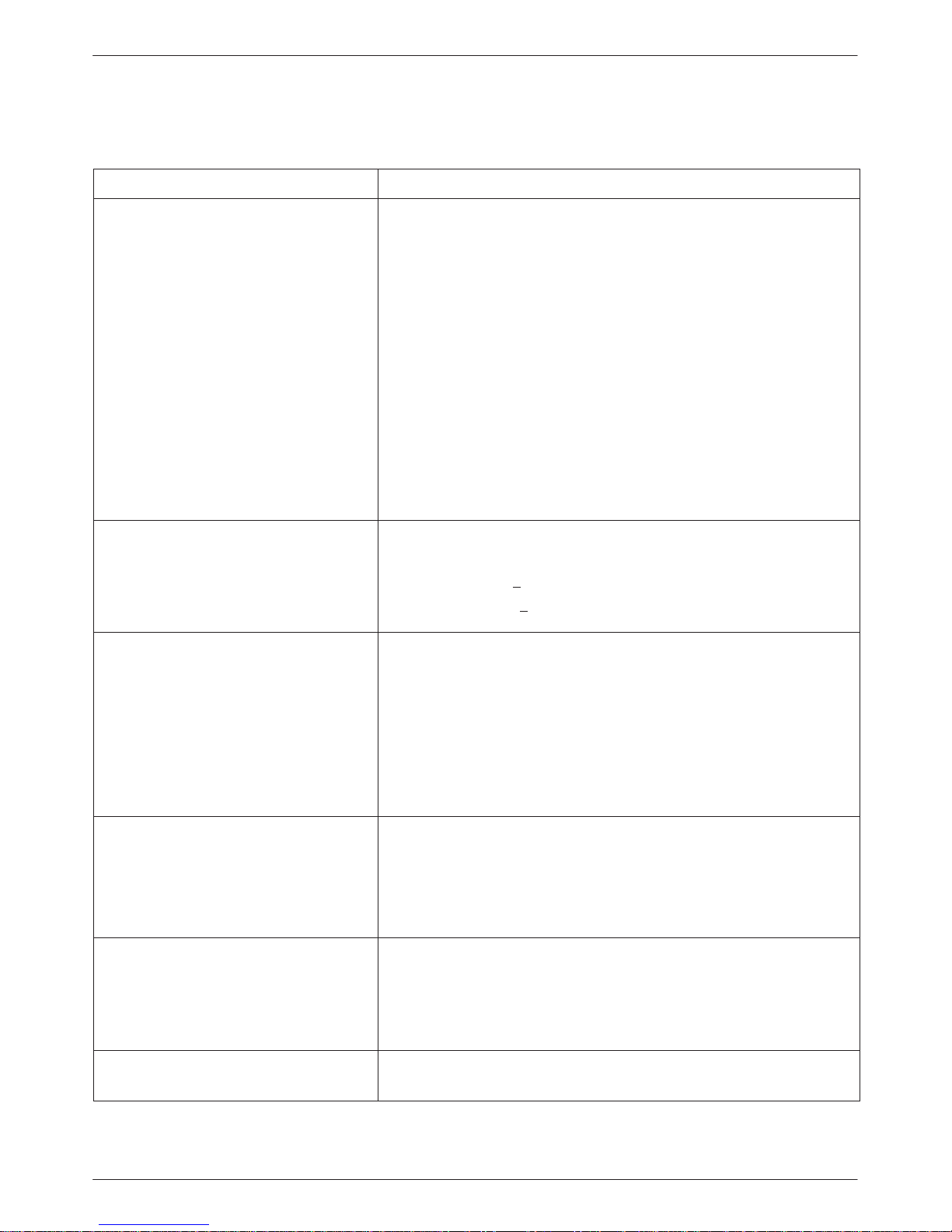
T ables 1-1 through 1-5 list the technical specifications
for the following:
• General specifications that apply to all DualFlow
DSUs, regardless of the type of DBM installed
(Table 1-1)
• Specifications for the Model 3615 and 3616 DSU
only (T able 1-2)
• Specifications for the V.32 DBM (Table 1-3)
• Specifications for the 4-Wire Switched 56 DBM
(Table 1-4)
• Specifications for the 2-Wire Switched 56 DBM
(Table 1-5)
1-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 18
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Specifications Criteria
APPROVALS
FCC Part 15
FCC Part 68
UL
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU,
3000 Series Carrier
CSA
Safety
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU,
3000 Series Carrier
Emissions
Bell Canada
Table 1-1
General Technical Specifications
Class A digital device
AW292J-61661-DD-N
Listed UL 1950, second edition
Recognized Component UL 1950, second edition
Certified CSA 22.2, No. 950-M89
Certified Component CSA 22.2, No. 950-M89
CSA 108.8 – M1983, Class A digital apparatus
“DCTE Specifications,” July 1989, Issue 1
AC POWER REQUIREMENTS
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
3000 Series Carrier (16 DualFlow DSUs,
plus SDU and fan module)
DTE INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
25-pin D-subminiature connector
34-pin connector
3616 DualFlow DSU with
25-Pin V.35 Interface
Uses a Rear Connector Plate with two
25-pin D-subminiature connectors.
ENVIRONMENT
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Relative Humidity
Shock and Vibration
HEAT DISSIPATION (MAX.) AT 115 VAC
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
3000 Series Carrier (16 DualFlow DSUs
plus SDU and fan module)
24 Vac (CT), 60 HZ ± 3 (0.115 amp, 9.5 watts at 115 Vac)
24 Vac (CT), 60 Hz +3 (0.080 amp, 8.0 watts at 115 Vac)
90—132 Vac, 60 Hz +3 (1.650 amp, 165 watts at 115 Vac)
EIA-232-D/ITU-T V.24 (ISO 2110)
ITU-T V.35 (ISO 2593)
EIA-232-D/ITU-T V.24 (ISO 2110)
ITU-T V.35 (ISO 2593)
(A V.35 adapter is required to use the V.35 connector . The adapter
provides an interface between the DSU’s 25-pin D-type connector and the
DTE cable’s V.35 connector.)
32° to 122° F (0° to 50° C)
–4° to 158° F (–20° to 70° C)
5%—95% (noncondensing)
Withstands normal shipping and handling
29.00 Btu/hr
27.30 Btu/hr
563.00 Btu/hr
NMS COMPATIBILITY
1-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
COMSPHEREr 6700 Series NMS, Release 4.0 or greater
COMSPHEREr 6800 Series NMS, Release 4.1.5 or greater
Page 19
About Your DualFlow DSU
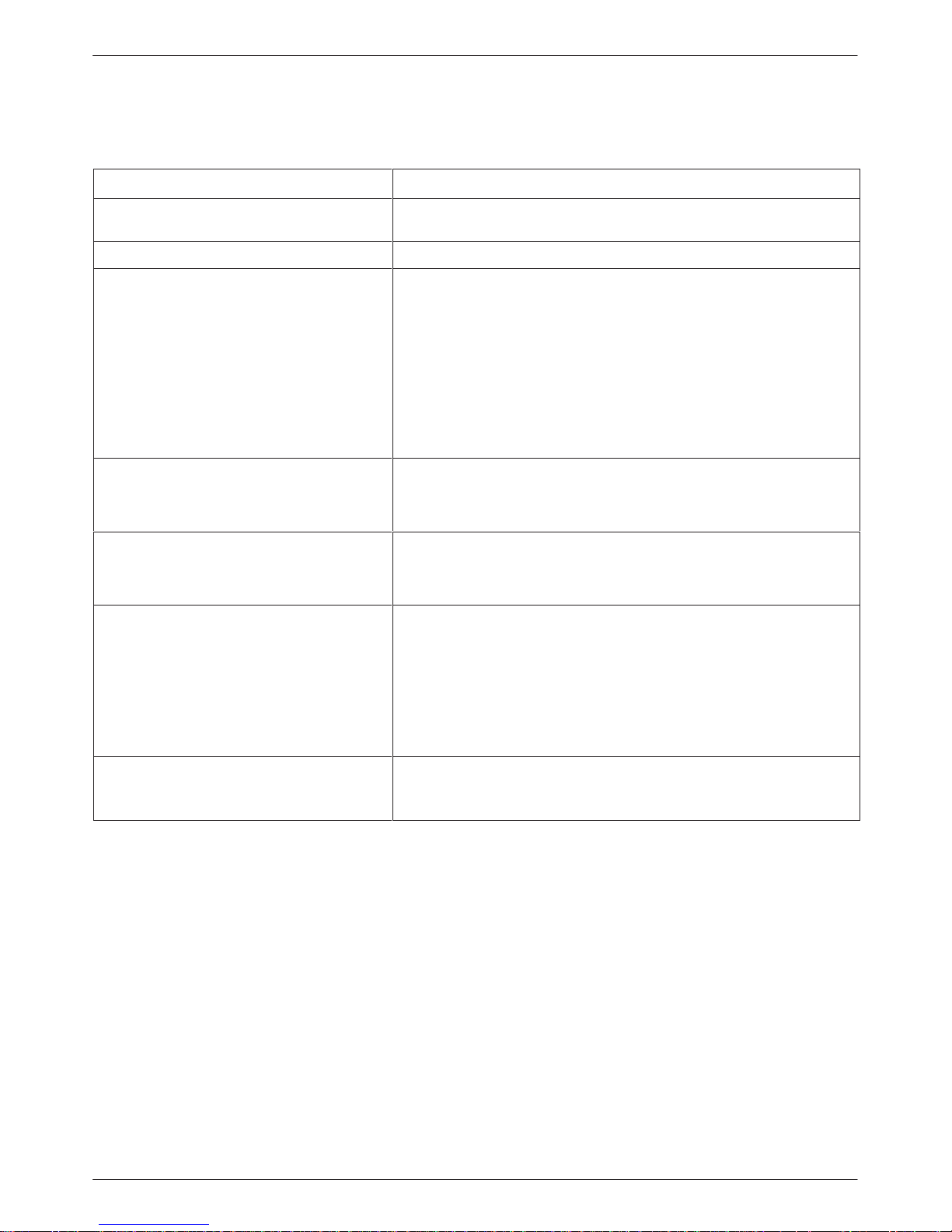
Table 1-2
DSU Technical Specifications
Specifications Criteria
APPLICATION Full- or half-duplex data transmission via point-to-point DDS network, or
local area data channel
COMMUNICATION LINE Leased or private 4-wire DDS line
DATA RATES
Digital Services (DDS, ASDS)
LADS
When timing is external (provided by the
DTE), the DTE’s clock must be within these
ranges.
DDS NETWORK INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 38.4, 56, and 64CC kbps
2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 38.4, 56, and 64 kbps
64 kbps 11 bps
56 kbps 9 bps
38.4 kbps 4 bps
19.2 kbps 5 bps
9.6 kbps 1 bps
4.8 kbps 0 bps
2.4 kbps 0 bps
8-pin modular jack, USOC RJ48S
(One or two) 50-pin connector, USOC RJ48T
DIAGNOSTIC INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
NETWORK COMPATIBILITY
ANSI T1.410 – 1992 and
A T&T Technical Reference 62310 – 1987
Integrated Network Corporation
Compatibility Bulletin CB-INC-101, and
Pacific Bell publications
PUB L-780035-PB/NB and
PUB L-780036-PB/NB
DSU COMPATIBILITY
Primary Channel
Requires 3600 Hubbing Device which provides two 8-pin modular jacks
Via the SDU in the COMSPHEREr 3000 Series Carrier
2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 56, and 64CC kbps
19.2 kbps loop at levels of +6, 0, or –10 dBm
All Paradyne digital products and other products that are compliant with
A T&T Technical Reference 62310 – 1987
1-53615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 20
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 1-3
V.32 DBM Technical Specifications
Specifications Criteria
RINGER EQUIVALENCE NUMBER (REN) DBM option 0.7B
APPLICATION Full- or half-duplex data transmission via analog 2-wire dial network,
point-to-point
MODULATION AND FREQUENCY At 14.4 and 12 kbps: ITU-T V.32bis, 1800 Hz
At 4.8 and 9.6 kbps: ITU-T V.32, 1800 Hz
At 2.4 kbps: ITU-T V.22bis, 2400 Hz
COMMUNICATION LINE 2-wire analog (PSTN) line
PORT RATES Async or Sync rates: 14.4, 12.0, 9.6, 9.2, 8.4, 7.2, 4.8, 4.4, 4.0, 2.4, 2.0,
DATA RATES 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 12, 14.4 kbps
DBM COMPATIBILITY If Call Setup is set for Callback or Password security, then the device is
APPROVALS
DOC
Certification (PSTN)
Load Number
RECEIVE VF INTERFACE
Dynamic Range
V.32 2-wire PSTN
Impedance
SWITCHED NETWORK INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
and 1.2 kbps
Other asynchronous rates (e.g., 150, 300, 600, and 1800 bps) can be
obtained through oversampling
Asynchronous rates support ITU-T V.14 extended rate range at
8 to 12 bits per character, including the
percent overspeed/underspeed compensation at 10 bits per character)
compatible with a 3600 Series V.32 DBM only.
If Call Setup is set for Alarm or None, then
used.
Also, V.22bis at 2.4 kbps can be used.
230 3684 A
7
–43 to –10 dBm
600 Ω
6-pin modular jack
Permissive: USOC RJ11C
8-pin modular jack
Programmable: USOC RJ45S
start
and
stop
any
V.32 modem can be
bit (+2.3, –2.5
3616 DualFlow DSU
TRANSMIT VF INTERFACE
Signal Level
V.32 2-wire Dial (PSTN)
Impedance
1-6 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
(One or two) 50-pin connector
Permissive: USOC RJ21X
Programmable: USOC RJ27X
Permissive: –9 dBm
Programmable: –12 to 0 dBm (set by a resistor in the telco jack)
600 Ω
Page 21
About Your DualFlow DSU
Table 1-4
4-Wire Switched 56 DBM Technical Specifications
Specifications Criteria
APPLICATION Full- or half-duplex data transmission via 56 kbps switched services
compatible with A T&T, MCIr, and US SPRINTr using 4-wire switched
access to a local exchange carrier (LEC) or an inter-exchange carrier
(IEC)
COMMUNICATION LINE A dedicated 4-wire access or a local exchange carrier 4-wire switched
access
PORT RATES Async or Sync rates: 56, 48, 38.4, 32, 28.8, 19.2, 18.8, 18.0, 16.8, 14.4,
12.0, 9.6, 9.2, 8.4, 7.2, 4.8, 4.4, 4.0, 2.4, 2.0, and 1.2 kbps
Other asynchronous rates (e.g., 150, 300, 600, and 1800 bps) can be
obtained through oversampling
Asynchronous rates support ITU-T V.14 extended rate range at
start
and
stop
8 to 12 bits per character, including the
percent overspeed/underspeed compensation at 10 bits per character)
bit (+2.3, –2.5
DATA RATES 56 kbps
(Note that the 4-wire Switched 56 DBM or 3600 Series DBM-S
uses proprietary rate adaption to support data rates of less than
56 kbps.)
DBM COMPATIBILITY If Call Setup is set for Callback or Password security, then the
device is compatible with a 3600 Series Switched 56 DBM only .
If Call Setup is set for Alarm or None, then any Switched 56 kbps
terminal interface unit (TIU) can be used.
SWITCHED 56 KBPS
NETWORK INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
NETWORK COMPATIBILITY A T&T Technical References 41458 and 61330
8-pin modular jack, USOC SJA56
(One or two) 50-pin connector, USOC SJA57
1-73615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 22
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 1-5
2-Wire Switched 56 DBM Technical Specifications
Specifications Criteria
APPLICATION Full- or half-duplex data transmission via 56 kbps switched services
compatible with A T&T, US SPRINTr, and MCIr using DataPatht 2-wire
switched access to a local exchange carrier (LEC) or an interexchange
carrier (IEC)
COMMUNICATION LINE A dedicated 2-wire access or a local exchange carrier 2-wire switched
access
PORT RATES Async or Sync rates: 56, 48, 38.4, 32, 28.8, 19.2, 18.8, 18.0, 16.8, 14.4,
12.0, 9.6, 9.2, 8.4, 7.2, 4.8, 4.4, 4.0, 2.4, 2.0, and 1.2 kbps
Other asynchronous rates (e.g., 150, 300, 600, and 1800 bps) can be
obtained through oversampling
Asynchronous rates support ITU-T V.14 extended rate range at
8 to 12 bits per character, including the
percent overspeed/underspeed compensation at 10 bits per character)
start
and
stop
bit (+2.3, –2.5
DATA RATES 56 kbps
uses proprietary rate adaption to support data rates of less than
56 kbps.)
DBM COMPATIBILITY If Call Setup is set for Callback or Password security, then the device is
compatible with a 3600 Series Switched 56 DBM only .
If Call Setup is set for Alarm or None, then any Switched 56 kbps
terminal interface unit (TIU) can be used.
SWITCHED 56 KBPS
NETWORK INTERFACE
3615 DualFlow DSU
3616 DualFlow DSU
APPROVALS
DOC
Certification Number
Load Number
NETWORK COMPATIBILITY
6-pin modular jack, USOC SJA48
(One or two) 50-pin connector
230 5870 A
0
Northern Telecom NIS S204-2e 1986
Equipment W arranty
and Support
(Note that the 2-wire Switched 56 DBM or 3600 Series DBM-D
• Via Telephone: Call our automated call system to
receive current information via fax or to speak with
a company representative.
If you experience trouble with this equipment, please
contact your sales or service representative (as
appropriate) for repair or warranty information. If the
product needs to be returned to the company service
center for repair, contact them directly for return
instructions using one of the following methods:
• Via the Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide
Web site at http://www .paradyne.com
1-8 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Page 23

Installing the Model 3615
Overview 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Before you Begin 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Change Hardware Straps 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Where to Place the DSU 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the DSU 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power-up Routine 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Network 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the NMS 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Dial (or PSTN) Network 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Switched 56 kbps Network 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the DDS (or LADS) Network 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting the DSU to a Router 2-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Addressing the Unit 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tributary DSU Addressing 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Operation and Testing Connections 2-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying DBM Operation 2-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Network Addresses 2-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying the Network 2-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Other Tests 2-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview
The Model 3615 DualFlow DSU is designed for
desktop operation and is delivered ready to connect to the
network. It is configured as a tributary DSU for operation
at 56 kbps on a point-to-point circuit.
Installation consists of the following steps, which
should be performed in the order listed.
DualFlow DSU
Although the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU is designed
for desk or table-top operation, you can order an
ACCULINKr 3100 Series CSU wall-mount adapter if
you want to mount the DSU on a wall, an equipment
shelf, a 19-inch RS-310-C or 23-inch AT&T
DATAPHONEr equipment cabinet. Refer to Appendix F
to order the adapter.
2
• Physical installation
• Hardware straps
• Electrical connection
• Network diagnostic connection
• Software configuration
• DDS network (or LADS) connection
• Dial network (or PSTN) connection
• Router connection
• Verification testing
Before You Begin
Your installation site should be clean, well-lighted,
well-ventilated, and free from environmental extremes.
A dedicated grounded ac outlet that is protected by a
circuit breaker should be installed within 6 feet of the
DSU’s planned location. The outlet should be capable of
supplying 90 to 132 Vac 60 Hz (U.S. and Canada). At the
branch site, the circuit must be capable of supplying a
minimum of 2 amperes at 115 Vac. Refer to the T echnical
Specifications section in Chapter 1 for additional power
requirements.
2-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 24
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
CAUTION
The ac transformer contains a
3-wire grounding-type plug
which has a grounding pin.
This is a safety feature. Do
not defeat the purpose of the
grounding plug by modifying
it or by using an adapter.
Prior to installation, use an
outlet tester to check the ac
receptacle for earth ground. If
the power source does not
provide a ground connection,
consult an electrician to
determine another method of
grounding the DSU before
proceeding with the
installation.
Before connecting the DSU, you need to contact the
telephone company to coordinate your installation before
connecting the DSU to the DDS or Switched 56 kbps
network. The DSU can only be operated at the data rate
for which access to the DDS network is provided. In
addition, the DSU must be connected to the dial network.
Refer to the notice at the front of this guide to ensure
compliance with FCC, Bell Canada, and Canadian DOC
rules.
No on-site assembly of the DSU is required. However,
installation should not proceed if any of the following is
missing:
• A power cord with table-top ac transformer
• A 14-ft cable for connection to the DDS network,
with an 8-pin RJ48S modular plug on each end
• A 14-ft cable for connection to the permissive dial
network, with a 6-pin RJ11C modular plug on each
end (feature number 3600-F3-503)
For programmable services, the following dial
interface cable should have been ordered.
• Programmable (RJ45S) – an 8-pin modular plug at
each end (feature number 4400-F1-
For Canadian purchasers, an 8-pin RJ48S connector is
on one end while a 6-pin connector is on the other is
required (order feature number 3000-F1-006).
54x)
Contact your service representative if any of these
items is missing from the shipping container, or to order
the programmable dial interface cable.
Since your DualFlow DSU is equipped with a DBM,
you may need to change the DSU’s hardware straps before
installing the DSU.
How to Change
Hardware Straps
HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
FOR
ST ATIC-SENSITIVE DEVICES
This product is designed to protect
sensitive components from damage
due to electrostatic discharge (ESD)
during normal operation. When
performing installation procedures,
however, take proper static control
precautions to prevent damage to
equipment. If you are not sure of the
proper static control precautions,
contact your nearest sales or service
representative.
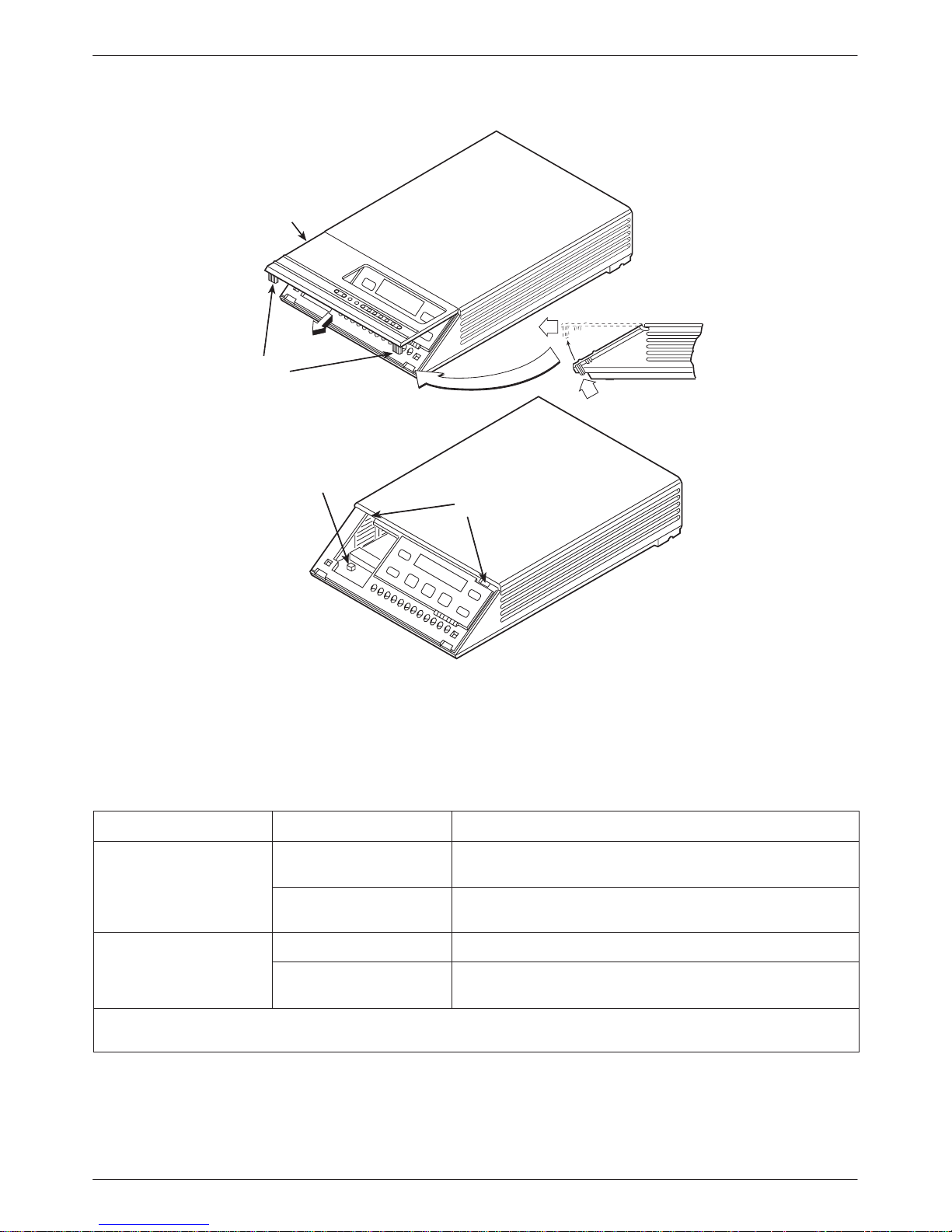
The Model 3615 DSU has a switch located behind its
diagnostic control panel (DCP). This switch contains two
straps, one that controls the permissive or programmable
connection for the DBM, and one that controls the
frame-to-signal grounds. Table 2-1 shows the DSU’s
switch settings. Refer to Figure 2-1 and follow these steps
if you need to change one of these straps.
" Procedure
1. With your thumbs under the edge of the front
bezel, firmly press upward to lift the bezel from
the tabs securing it in place.
2. Swing the front bezel up and set the bezel aside.
3. Refer to Table 2-1 to determine which switch
needs to be changed. Then, using a small
instrument, carefully change the position of the
switch.
4. Reinsert the front bezel’s hinge tabs into position
and swing the bezel down. Snap the bezel back
into place.
2-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 25
FRONT BEZEL
COMSPHERE 3615
SNAP
TABS
Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
SWITCH 1
HINGE TAB
LOCATIONS
496-14499-01
Figure 2-1. Model 3615 DSU Hardware Switch Location
Table 2-1
Model 3615 DSU Switch Settings
Switch Position Switch Setting Function
ON
(default)
S1-1
Off Programmable V.32 DBM transmit level between –12 dBm and
Permissive V.32 DBM transmit output level of –9 dBm
0 dBm
S1-2
ON is to the rear as you face the front of the DSU.
Off is to the front.
ON Frame ground (FG) connected to signal ground (SG)
Off
FG connected to SG through 100 ohm resistor
(default)
2-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 26
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Where to Place the DSU
As mentioned earlier, the DSU must be placed within
6 feet of a dedicated grounded ac outlet that is protected
by a circuit breaker.
The distance between the DSU and its DTE must be
within EIA-232-D/V.24 limits, or V.35 limits if operating
the DSU at speeds greater than 19.2 kbps.
• For the EIA-232 connector, the typical maximum
distance is 50 feet at speeds less than or equal to
19.2 kbps. If a longer distance is needed, use high
quality , low capacitance cable and ensure that the
effective shunt capacitance of the circuit (measured
at the DSU and including the capacitance of the
cable and the DTE) does not exceed
2500 picofarads, as specified in EIA-232-D.
• For the V.35 connector, the maximum distance
recommended between the DSU and the DTE is
nominally 1000 feet.
Allow 1 to 2 feet of clearance around the DSU for
access and cable connections during installation.
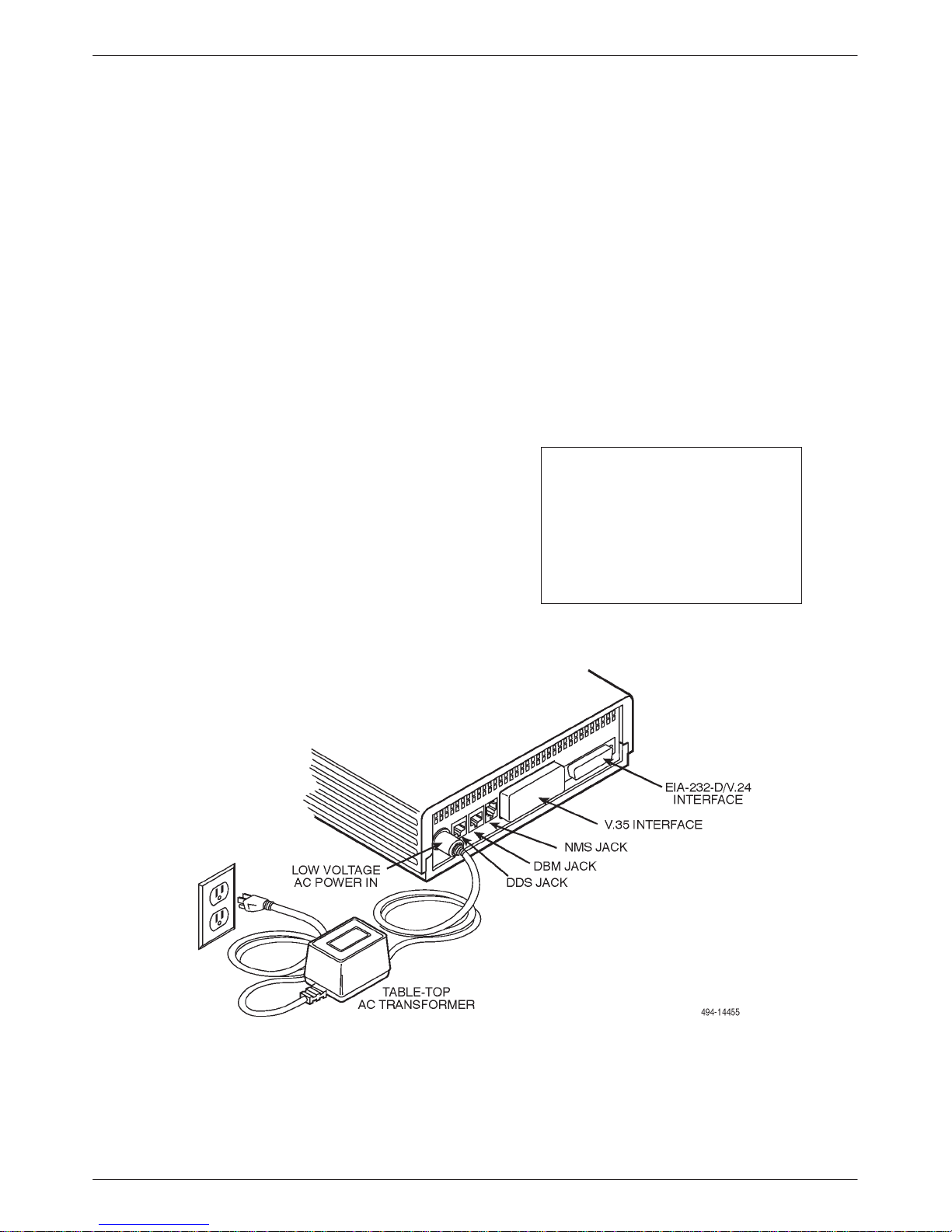
Installing the DSU
Before installing the DSU, label the circuit breaker that
protects the ac wall outlet, and make sure that it is set to
ON. T o proceed with the installation:
" Procedure
1. Place the DSU in its planned location. Make sure
the ventilation slots are not blocked.
2. At the rear of the DSU (Figure 2-2), insert the ac
transformer, circular plug into the interface labeled
POWER.
3. Plug the ac transformer’s 3-prong plug into the ac
wall outlet.
CAUTION
Only use the power
transformer designed for the
Model 3615 DSU. Using other
transformers may result in
personal injury or damage to
the equipment.
Figure 2-2. Model 3615 DSU Electrical Connection
2-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 27

Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
Power-Up Routine
When power is applied, the DSU:
• Runs a Device T est on itself and the DBM.
During the tests, all indicators on the DCP light
briefly and the message Power-Up Tests appears
on the liquid crystal display (LCD).
• Displays the results of each test momentarily as
Pass, Fail, or Abrt. (Abrt indicates that the Device
T est was aborted because a network loopback was
in progress during the power-up procedure.) These
tests take about 20 seconds to complete.
If the DSU or DBM fails this test, follow these steps.
Refer to Appendix A as you perform the procedures
described in this guide. Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for
additional examples and procedures.
" Procedure
1. Press the key to return to the top-level menu.
2. Select Local (F1 key).
3. Press the
(Configuration) branch into view.
4. Press the function key directly below Confg.
5. Press the F1 key to select Opts (Configuration
Options).
The Load from screen appears.
key to scroll the Confg
7. Press the F1 key to SAVE the selected
configuration.
The Save to screen appears.
8. Save the selected configuration to Activ (F1 key).
9. Press the
then select Local again.
10. Select Test (F3).
The Run Test on screen appears.
11. Select the device that Failed: the DSU or DBM.
12. Press the F2 key to run the Device Test again.
The device should pass.
13. Should the device fail, contact your service
representative (see Equipment Warranty and
Support section in Chapter 1).
key to return to the top-level menu,
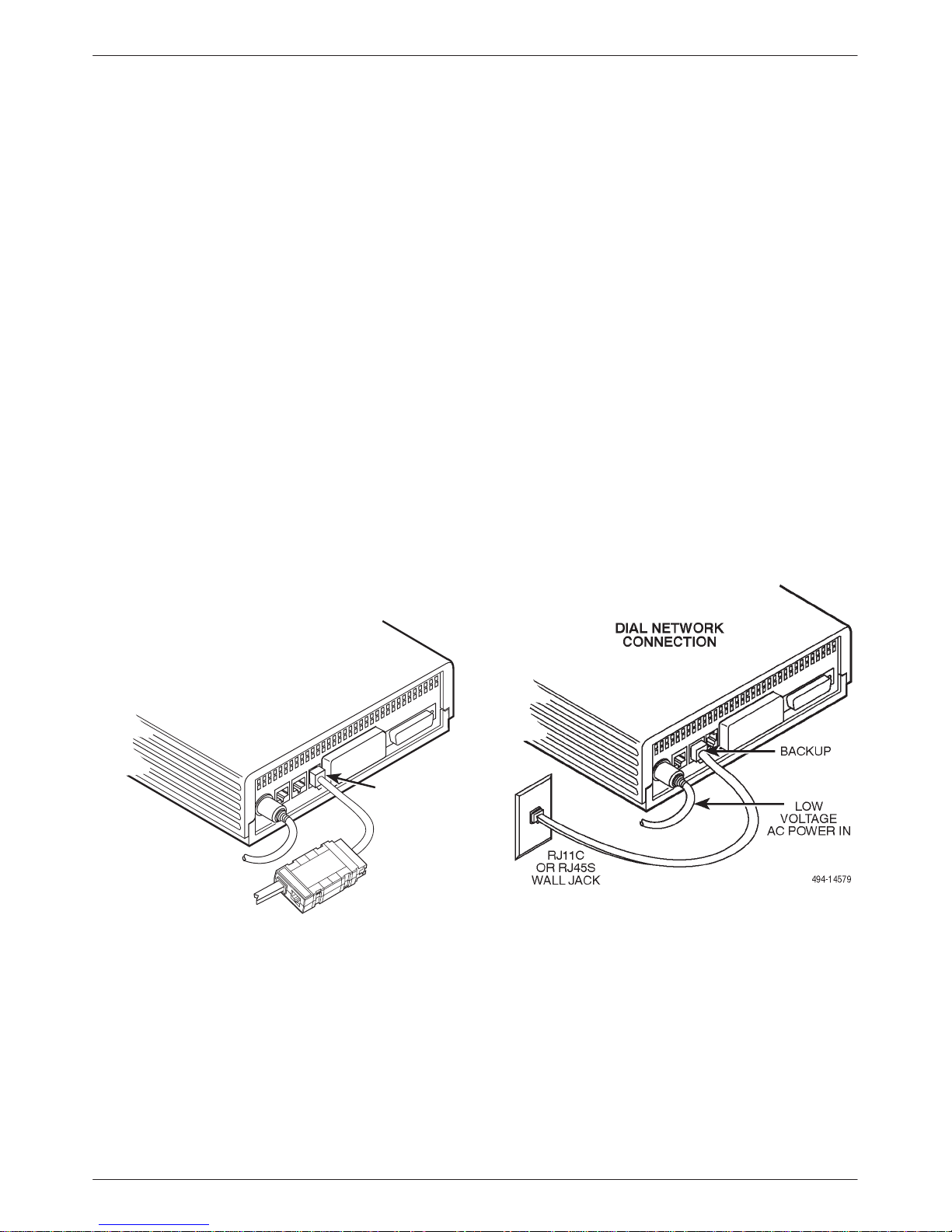
Connecting to the Network
The DSU provides three interfaces (often called jacks).
One jack connects the DSU to the 6700 or 6800 Series
NMS, one connects the DSU to the dial (or public
switched telephone network – PSTN) network, and one
connects the DSU to the DDS network. Follow the
appropriate procedure when making your network
connections.
6. Press the
configurations into view, and select the
appropriate configuration.
• SyBC (Synchronous Backup for a Control
DSU) for a control when the router controls
backup.
• SyBT (Synchronous Backup for a Tributary
DSU) for a tributary when the router controls
backup.
• DiDg (Dial Diagnostics) for asynchronous
router-management data to be sent over the
EIA-232 port via the DBM connection and user
data over the V.35 port via the DDS
connection.
key to bring the factory-loaded unit
2-53615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 28
COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Connecting to the NMS
A 3600 Hubbing Device is required to connect the
control DSU to the 6700 or 6800 Series NMS. When
connected to the NMS, the DSU can be controlled and
configured from the NMS rather than from the DCP
alone.
" Procedure
1. Plug the 4-pin modular plug of the 3600 Hubbing
Device (Figure 2-3) into the DSU jack labeled
CC/DC.
2. Plug one end of an M6BJ cable into the hubbing
device jack labeled CC IN/DC OUT .
3. Plug the other end of the 6-pin M6BJ cable into
the 6-pin end of the 873A adapter.
4. Plug the D-type end of the 873A adapter into the
appropriate 6700 or 6800 Series NMS jack.
Refer to your COMSPHERE 6700 or 6800 Series NMS
documentation to control and configure the DSU from the
NMS.
Connecting to the Dial (or PSTN) Network
If your DSU is equipped with a V.32 DBM, refer to
Figure 2-4 as you follow these steps.
" Procedure
1. Plug either end of the dial (analog) interface cable
into the DSU jack labeled BACKUP.
• Permissive service – telephone cord with 6-pin
modular RJ11C plug
• Programmable service – telephone cord with
8-pin RJ45S plug
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the modular
jack provided by the telephone company, USOC
RJ11C (permissive) or USOC RJ45S
(programmable).
3. If your site has programmable service, verify that
the DSU’s hardware strap S1-1 is switched to the
OFF position.
NMS NETWORK
CONNECTION
LOW VOLTAGE
AC POWER IN
TO
NMS (873A)
3000HUBBING DEVICE
MODEL #3000-F3-300
Figure 2-3. Model 3615 DSU
NMS Connection
HUBBING
DEVICE
CC/DC
496-14576a
Figure 2-4. Model 3615 DSU
Dial (PSTN) Network Connection
2-6 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 29
Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
Connecting to the
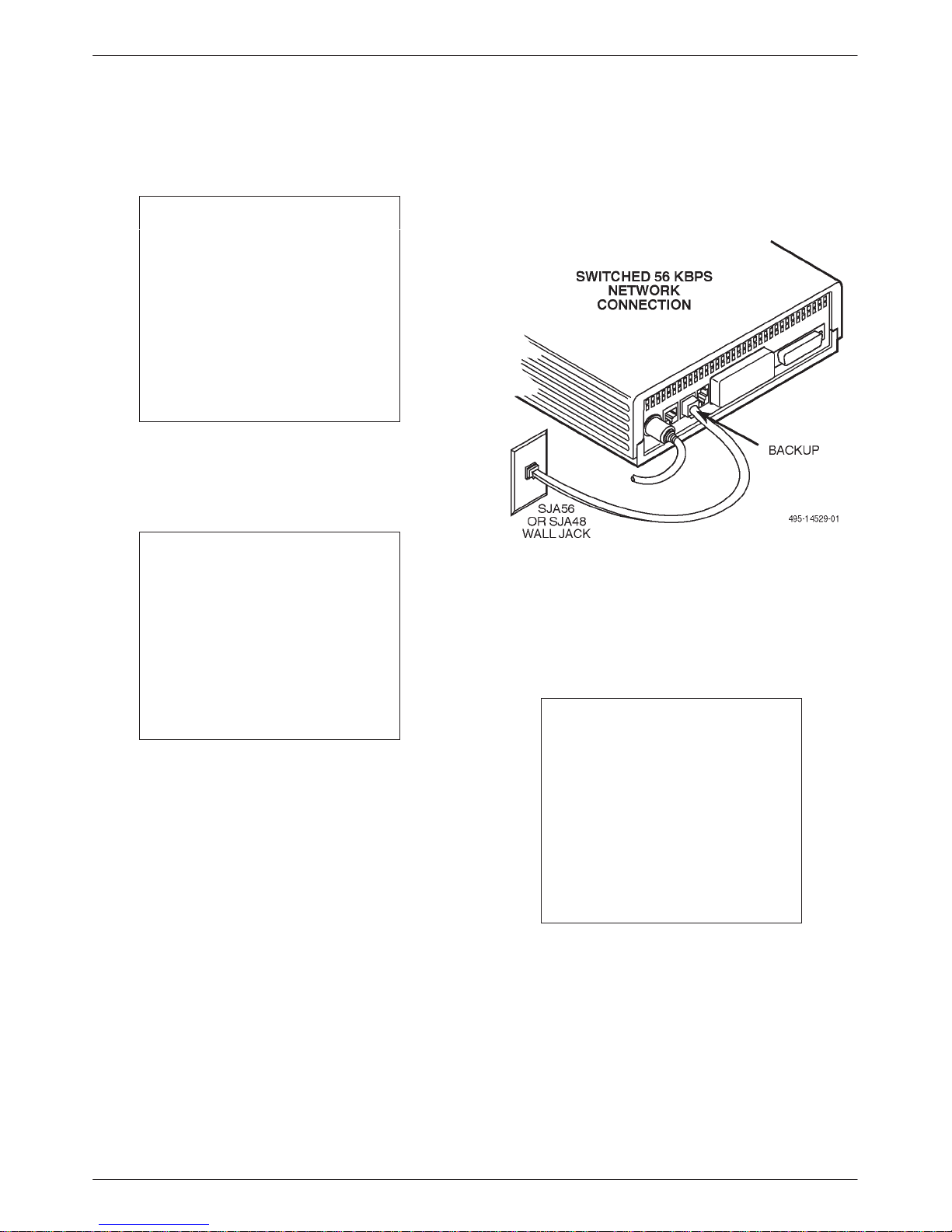
Switched 56 kbps Network
NOTE
Before connecting the DSU to
the Switched 56 kbps network,
ensure that approved primary
protectors have been installed
on the circuit in accordance with
Article 800 of the National
Electric Code, NFPA 70, in the
United States and Section 60 of
the Canadian Electric Code,
Part 1, in Canada.
If the DSU is equipped with a 4-wire Switched
56 DBM, an 8-pin cable is provided; if a 2-wire
Switched 56 DBM, a 6-pin cable is provided.
WARNING
Do not insert the 2-wire
Switched 56 kbps plug into an
RJ11C jack. This type of jack
is intended for analog public
switched telephone network
(PSTN) devices. Doing so may
cause equipment damage and
harm to the telephone
network.
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the modular
jack provided for the Switched 56 kbps network
connection.
Figure 2-5. Model 3615 DSU
Switched 56 kbps Network Connection
Connecting to the DDS (or LADS) Network
NOTE
T o make a physical connection to the Switched 56 kbps
network, refer to Figure 2-5 as you follow these steps.
" Procedure
1. Plug either end of the Switched 56 kbps network
interface cable into the DSU jack labeled
BACKUP.
• For the 2-wire Switched 56 DBM, use the
6-pin cable.
• For the 4-wire Switched 56 DBM, use the
8-pin cable.
Before connecting the DSU to
the DDS network, ensure that
approved primary protectors
have been installed on the
circuit in accordance with Article
800 of the National Electric
Code, NFPA 70, in the United
States and Section 60 of the
Canadian Electric Code, Part 1,
in Canada.
Refer to Figure 2-6 as you follow these steps.
2-73615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 30

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Data Rate
" Procedure
1. Plug the DDS network interface cable into the
DSU jack labeled LINE.
• U.S. – select either end of the cable
• Canada – select the 8-pin end
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the modular
jack (USOC RJ48S) provided by the circuit
provider.
If the remote DSU is also connected to the network, the
DSU’s green OK indicator lights and the Alrm indicator
goes off. The Health and Status screen no longer displays
a No Signal message.
If connecting the DSU to a LADS network, there are
distance limitations that govern the use of DSUs on the
network. T able 2-2 summarizes these limitations.
Figure 2-6. Model 3615 DSU DDS (LADS)
Network Connection
Data Rate
(kbps)
2.4 20.0 mi
(32.2 km)
4.8 19.4 mi
(31.2 km)
9.6 15.2 mi
(24.5 km)
1
19.2
38.4 1 1.2 mi
56 9.2 mi
64 9.2 mi
1
Power level is –10 dBm.
1 1.8 mi
(19.0 km)
(18.0 km)
(14.8 km)
(14.8 km)
Table 2-2
LADS Connection Distances
Wire Gauge (AWG)
19 22 24 26
16.6 mi
(26.7 km)
12.7 mi
(20.5 km)
9.7 mi
(15.6 km)
7.5 mi
(12.1 km)
6.5 mi
(10.5 km)
5.4 mi
(8.7 km)
5.4 mi
(8.7 km)
12.7 mi
(20.5 km)
9.6 mi
(15.4 km)
7.3 mi
(1 1.7 km)
5.7 mi
(9.2 km)
4.6 mi
(7.4 km)
3.8 mi
6.2 km)
3.8 mi
(6.2 km)
9.4 mi
(15.1 km)
7.1 mi
(1 1.5 km)
5.6 mi
(9.0 km)
4.2 mi
(6.8 km)
3.2 mi
(5.1 km)
2.8 mi
(4.5 km)
2.8 mi
4.5 km)
2-8 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 31

Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
Connecting the DSU
to a Router
The DualFlow DSU transmits user data through its
V.35 interface and diagnostic or user data through its
EIA-232-D/V.24 interface. Cabling is based upon the
preset configuration (SyBC, SyBT, or DiDg) selected in
the Opts subbranch (Config branch).
Figure 2-7 shows the DualFlow DSU’s rear panel.
Refer to this figure as you connect the DSU to the router.
Appendix E shows examples common to the DSU-torouter application configurations.
" Procedure
1. Connect the plug end of the router’s V.35 cable to
the DSU’s V.35 connector.
Tighten the two holding screws.
V .35
INTERFACE
2. Connect the other end of the router’s V.35 cable to
the router’s primary serial port.
Tighten any holding screws.
3. Connect the plug end of the router’s EIA-232
cable to the DSU’s EIA-232-D/V.24 connector.
Tighten any holding screws.
4. Connect the other end of the router’s EIA-232
cable to the router:
• If the DSU is to be configured using the SyBC
• If the DSU is to be configured using the DiDg
Tighten any holding screws.
EIA-232-D/V.24
INTERFACE
or SyBT configuration, connect to the router’s
secondary serial port.
configuration, connect to the router’s console
port.
DiDg CONFIGURATION:
TO ROUTER
CONSOLE PORT
(ROUTER-MANAGEMENT
DATA)
SyBC OR SyBT
CONFIGURATION:
TO ROUTER
SECONDARY SERIAL PORT
(BACKUP OR OVERFLOW
DATA)
DSU
CC
LOW
VOLTAGE
AC POWER
IN
TO NMS
(CONTROL
DEVICE
ONLY)
3000HUBBING DEVICE
MODEL #3000-F3-300
Figure 2-7. Router Connection
TO ROUTER
PRIMARY SERIAL PORT
(USER DATA)
496-14498-01
2-93615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 32

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Addressing the Unit
A unique address must be assigned to each control and
tributary DSU in your network. You can assign an address
within the range of 1 through 255.
NOTE
Do not assign the number 192
as a network address. This
number is reserved as a
broadcast address.
The DBM requires a separate address, which is
automatically assigned by the DSU. The address assigned
a DBM is the DSU’s address, plus 1 (e.g., if the DSU’s
address is 1, the assigned DBM address will be 2).
NOTE
The numbers 191 and 255
cannot be assigned to a DSU
that has a DBM. However,
addresses can be assigned in
any order; they do not have to
be sequential.
It is recommended that only
odd-numbered
assigned to DSUs so that
even-numbered addresses
reserved for DBMs
addresses be
are
.
Tributary DSU Addressing
Tributary DSU addresses are user-definable. The
control DSU accesses its tributary via an active backup
connection by specifying the tributary’s address.
The 6700 or 6800 Series NMS accesses the DSU via its
network address. To access a tributary DSU, the NMS
first addresses the control, then the tributary. An address
issued from the NMS takes the format of control
channel/control DBM network address/tributary network
address. This is called link-level network addressing.
Figure 2-8 shows an example of DSU and DBM
addressing, as well as link-level network addressing.
Refer to Chapter 4 to learn how to set the DSU’s
network address.
Verifying Operation and
Testing Connections
Verification testing should be performed after any
installation.
After installing and configuring the circuit (including
control and tributary DSUs, the DDS network, the DBMs
and their dial connections), perform the following series
of tests from the control DSU to verify network operation
(using either the DCP or NMS).
Next, test the tributary DBM for dial tone, and verify
that the DSU can place and receive calls.
2-10 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Figure 2-8. Addressing Example
Page 33

Installing the Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
Verifying DBM Operation
A backup connection must be established to verify that
the switched network is functioning. Then, perform the
Digital T est by selecting the DBM path.
" Procedure
1. Select Local (F1).
2. Select Bckup (F2).
3. Select Dial to establish a dialed call to the
tributary.
Refer to Chapter 4 for the procedure for entering
telephone numbers.
4. Press the
to the dial circuit.
5. Press the key twice.
6. Select Test (F3).
7. Select DBM (F2).
8. Select DT (F3).
9. Select Start (F1).
10. Select the amount of time you want the test to run
in hours: minutes: seconds (hh:mm:ss).
• Press the
cursor to the digit to be changed.
key, then select Cnnct to switch
or key to move the blinking
11. Select Enter (F3). Please wait appears as the
DBM runs the test.
12. When Command Complete appears, press the
key.
13. Select Displ (F1) to display the results of the test.
14. Press the
key to scroll through the test results.
Verifying Network Addresses
Access the DSU’s identity (ID) subbranch for the
tributary DSU to ensure that the DSU is properly
addressed. Refer to Chapter 5 for an example using the
DCP, if needed.
" Procedure
1. Select Remot (Remote branch).
2. Enter the tributary’s network address.
3. Select Stat (Status branch).
4. Press the
5. Select ID.
6. Press the key until Network Addr appears.
7. Verify that the correct address has been entered.
key until ID appears.
• Press the F1 ( ) key to increment the digit
(1 through 9).
• Press the F2 ( ) key to decrement the digit.
2-113615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 34

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Verifying the Network
Perform a Health and Status check on the DDS circuit
to ensure that the network is functioning.
" Procedure
1. Select Local (F1).
2. Select Stat (F1).
3. Select H/S (F1).
4. Select Devic (F1).
5. Press the
6. Select Local (F1).
7. Select Bckup (F2).
8. Select DrBU to drop the backup call.
No error messages should appear. Refer to
Appendix C, the Device Health and Status Messages
section, should there be a problem with the DDS Line.
key to return to the top-level menu.
Other Tests
The following lists the tests available on your DSU.
Refer to the Test Branch section of Chapter 4 for further
test information, as well as more detail on how to
configure and operate the DSU. Refer to Appendix A to
determine how best to access each test.
• Device Test (Devic)
• Local Loopback (LL) – DSU only
• DTE Loopback (DTE)
• Digital Loopback (DL)
• Remote Digital Loopback (RL) – DBM only
• Bilateral Loopback
• Digital Test (DT) – DBM only
• End-to-End Test (EE) – DBM only
• Bit Error Rate Test (BERT)
• Lamp Test (Lamp)
2-12 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 35

Installing the Model 3616
Overview 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Before you Begin 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Change Hardware Straps 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the DSU 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power-up Routine 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Network 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the NMS 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Dial (or PSTN) or Switched 56 kbps Network 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the DDS (or LADS) Network 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting the DSU to a Router 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Addressing the Unit 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tributary DSU Addressing 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Operation and Testing Connections 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
To Connect the SDCP to a DSU 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Network Addresses, the Network, and DBM Operation 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Other Tests 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview
A Model 3616 DualFlow DSU is designed for
installation in a COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, which
supplies power and provides the interfaces for connecting
to the DDS or dial networks. Up to 16 DSUs can be
installed in the carrier. Refer to the COMSPHERE
3000 Series Carrier, Installation Manual for additional
carrier and installation information.
The DSU is delivered ready to install in the carrier. It is
configured as a control DSU for operation at 56 kbps on a
point-to-point circuit.
DualFlow DSU
Installation of the DSUs and carrier-related equipment
consists of the following steps, which should be
performed in the order listed.
• Hardware straps
• DSU physical installation
• Network diagnostic connection
• Software configuration
• DDS network (or LADs) connection
• Dial network (or PSTN) connection
3
A rear connector plate, shipped with the DSU, is
installed onto the rear of the carrier. The rear connector
plate contains two connectors: a 25-pin EIA-232-D/V.24
connector and a 25-pin V.35 connector. Once installed, the
DSU can be removed from the front of the carrier without
disconnecting the DTE cables.
• Router connection
• Verification testing
3-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 36

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Before You Begin
The COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier should already
be installed properly and be operational, with a
functioning shared diagnostic control panel (SDCP). An
SDCP (installed in the carrier) is required for installation
and maintenance of the Model 3616 DSU. For installation
information, see the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier,
Installation Manual.
A fan module may also be needed to dissipate heat.
Refer to the Fan Module Installation section in Chapter 3
of the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Installation
Manual to determine whether a fan is required.
The distance between your DTE and the DSU must be
within EIA-232-D/V.24 or V.35 limits.
• For the EIA-232 connector, the maximum
recommended distance is 50 feet. If operating at
56 kbps the maximum distance is 34 feet for
shielded cable, and 68 feet for unshielded cable.
When a Switched 56 DBM is installed, ensure that
the effective shunt capacitance of the circuit
(measured at the DSU and including the
capacitance of the cable and the DTE) does not
exceed 1250 picofarads.
• For the V.35 connector, the recommended
maximum distance between a DTE and DSU is
nominally 1000 feet.
Contact the telephone company to coordinate your
installation before connecting the DSU to the DDS,
Switched 56 kbps, or dial network. The DSU can only
operate at the data rate for which access to the DDS or
dial network is provided. Refer to the notice at the front of
this guide to ensure compliance with FCC, Bell Canada,
and Canadian DOC rules.
How to Change
Hardware Straps
HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
FOR
ST ATIC-SENSITIVE DEVICES
This product is designed to protect
sensitive components from damage
due to electrostatic discharge (ESD)
during normal operation. When
performing installation procedures,
however, take proper static control
precautions to prevent damage to
equipment. If you are not sure of the
proper static control precautions,
contact your nearest sales or service
representative.
The Model 3616 DSU has several hardware straps that
control the permissive or programmable connection when
a DBM is installed, the T est Mode Indication leads, and
the external interface leads (used with a –48 Vdc Central
Office Power Unit).
Refer to Figure 3-1 to locate the switch and jumper
locations. If a V.32 DBM is installed, refer to Table 3-1 to
determine which switch needs to be changed, if any. Refer
to Table 3-2 to determine whether these jumper straps
need to be changed.
3-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 37

Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
S1-1
Figure 3-1. Model 3616 DSU Switch and Jumper Locations
Table 3-1
Model 3616 DSU Switch Settings
Switch Position Switch Setting Function
ON
(default)
Off Programmable V.32 DBM transmit level between –12 dBm and
ON Frame ground (FG) connected to signal ground (SG)
S1-2
ON is to the rear as you face the front of the DSU.
Off is to the front.
Off
(default)
Permissive V.32 DBM transmit output level of –9 dBm
0 dBm
FG connected to SG through 100 ohm resistor
3-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 38

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Strap
Designation
J12 Left V.35 Test Mode Indication:
J13 Left EIA-232-D Test Mode Indication:
J20 Left Alarm Monitoring (used with the –48 Vdc Central Office Power Unit):
State of
Jumper Strap
Table 3-2
Model 3616 DSU Jumper Straps
Left — Enables V.35 Test Mode Indication (Pins 1 and 2).
This is the factory default.
Right — Disables V.35 Test Mode Indication (Pins 2 and 3).
Left — Enables EIA-232-D Test Mode Indication (Pins 1 and 2).
This is the factory default.
Right — Disables EIA-232-D Test Mode Indication (Pins 2 and 3).
Left — Disables the –48 Vdc alarm monitoring function
(Pins 1 and 2).
Right — Enables the –48 Vdc alarm monitoring function
(Pins 2 and 3); the NMS adapter cable is being used for alarm
monitoring.
This is the factory default.
Function
J21 Right Alarm Monitoring (used with the –48 Vdc Central Office Power Unit):
Left — Enables control of alarm monitoring via the NMS adapter
cable (Pins 1 and 2); the NMS adapter cable is being used for alarm
monitoring.
Right — Disables control of alarm monitoring via the NMS adapter
cable (Pins 2 and 3); a standard EIA-232 cable or the NMS adapter
cable is being used for the diagnostic channel.
This is the factory
default.
3-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 39

Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
Installing the DSU
Prior to installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU,
install a rear connector plate onto the rear of the
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier (Figure 3-2). Only
after this procedure can the DSU be installed or
de-installed by simply removing it from the carrier.
" Procedure
1. At the rear of the carrier, set the tab on the rear
connector plate into one of the slotted grooves on
the carrier’s backplane. Loosely fasten the screws.
Make sure the rear connector plate uses the same
slot position intended for the DSU.
2. Loosely fasten the screw attached to the rear
connector plate, allowing for slight adjustment
that may be needed when installing the DSU.
3. Change any default hardware strap settings that
may be required before installing the DSU.
Figure 3-2. COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Rear View
3-53615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 40

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
4. Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the screw
holding the circuit pack lock and rotate the lock to
the open position (Figure 3-3). Open the latch.
5. At the front of the carrier, hold the DSU vertically
with the latch on its faceplate in the open position.
Then, insert the circuit card into the top and
bottom circuit card guides for the slot that
contains the rear connector plate.
Slide the DSU into the slot, aligning the circuit
card with the rear connector plate until the
connectors seat firmly into the back of the carrier.
Press the faceplate latch to secure the DSU into
the carrier, rotate the circuit pack lock into the
closed position (Figure 3-3), and tighten the screw.
6. Return to the rear of the carrier and tighten the
rear connector plate screw.
Figure 3-3. Model 3616 DSU Installation and Circuit Pack Lock
3-6 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 41

Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
7. At the rear of the carrier, connect the appropriate
router cable (EIA-232-D or V.35) to the rear
connector plate. For an EIA-232-D interface
cable, connect the EIA-232-D cable to the top
DTE connector on the rear connector plate.
For the 25-pin V.35 interface, a V.35 adapter is
shipped with the unit. To connect a V.35 Interface
Cable to the 25-pin V.35 connector, refer to
Figure 3-4 and perform the following steps:
a. Connect the 25-pin end of the DSU’s V.35
adapter to the bottom DTE connector of the
rear connector plate. Tighten the thumbscrews
on each side of the adapter.
b. Connect the V.35 cable to the 34-pin end of
the V.35 adapter. Tighten the screws on each
side of the cable connector.
8. The installed DSU is connected to the DDS
network through the 50-pin connectors at the rear
25-Pin Connector
Thumbscrews
of the carrier. These interfaces are specified in the
USOC RJ48T, and the pin assignments are shown
in Appendix D. Proper network connection to the
DDS facility or to the network channelterminating equipment must be made at the far
end of the cable.
9. If the network line and remote DSU are installed
and tested, do a Remote Loopback – a T est Pattern
test.
10. If the Front Panel test switch strap is to be
disabled, slide the DSU slightly out of the carrier,
open switch S3-1, then reseat the DSU into the
carrier. Do this now.
11. Circuit ID information can be written on the cover
plate under the appropriate slot number.
V.35 Adapter
V.35 Cable
Figure 3-4. V.35 Adapter Installation
99-16298
3-73615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 42

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Power-Up Routine
When power is applied, the DSU:
• Runs a Device T est on itself and the DBM.
During the tests, all indicators on the DCP light
briefly and the message Power-Up Tests appears on
the liquid crystal display (LCD).
• Displays the results of each test momentarily as
Pass, Fail, or Abrt. (Abrt indicates that the Device
Test was aborted because a network loopback was
in progress during the power-up pr ocedure.) These
tests take about 20 seconds to complete.
If the DSU or DBM fails this test, follow the procedure
below . Refer to Appendix A as you perform the
procedures described in this guide. Refer to Chapters 4
and 5 for additional examples and procedures.
" Procedure
1. Press the key to return to the top-level menu.
2. Select Local (F1 key).
3. Press the
(Configuration) branch into view.
key to scroll the Confg
7. Press the F1 key to SAVE the selected
configuration.
The Save to screen is displayed.
8. Save the selected configuration to Activ (F1 key).
9. Press the
then select Local again.
10. Select the Test branch (F3).
The Run Test on screen appears.
11. Select the device that Failed, the DSU or DBM.
12. Press the F2 key to run the Device Test again.
The device should pass.
13. Should the device fail, contact your service
representative (see Chapter 1).
key to return to the top-level menu,
Connecting to the Network
Network connections are provided through the
3000 Series Carrier. Refer to Figure 3-2 as you read the
following sections and set up your network connections.
4. Press the function key directly under Confg.
5. Press the F1 key to select Opts (Configuration
Options).
The Load from screen appears.
6. Press the
configurations into view, and select the
appropriate configuration.
• SyBC (Synchronous Backup for a Control
DSU) for a control when the router controls
backup.
• SyBT (Synchronous Backup for a Tributary
DSU) for a tributary when the router controls
backup.
• DiDg (Dial Diagnostics) for asynchronous
router-management data to be sent over the
EIA-232 port via the DBM connection and user
data over the V.35 port via the DDS
connection.
key to bring the factory-loaded unit
Connecting to the NMS
A Model 3616 DualFlow DSU is set up for network
diagnostic connection through the shared diagnostic unit
(SDU), which is installed in Slot 0 of the carrier. Refer to
the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Installation
Manual to set up the network diagnostic connection.
For connection of the DSU, see Appendix E of this
guide. For pin assignments, see Appendix D.
Connecting to the Dial (or PSTN) or
Switched 56 kbps Network
Connection to the dial network (or public switched
telephone network – PSTN) or Switched 56 kbps network
for the carrier-mounted Model 3616 DSU is through a
network interface module (NIM) that is installed onto the
carrier’s backplane (see Figure 3-2). Refer to the
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Installation Manual
for additional information or to install the NIM.
3-8 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 43

Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
Connecting to the
DDS (or LADS) Network
NOTE
Before connecting the DSU to
the DDS network, ensure that
approved primary protectors
have been installed on the
circuit in accordance with Article
800 of the National Electric
Code, NFPA 70, in the United
States and Section 60 of the
Canadian Electric Code, Part 1,
in Canada.
If connecting the DSU to a LADS network there are
distance limitations that govern the use of DSUs on the
network. T able 2-2 in Chapter 2 summarizes these
limitations.
The DDS network interface is provided by two RJ48T
50-pin connectors on the back of the carrier (refer back to
Figure 3-2, DDS Interface). Each connector serves eight
contiguous slots in the carrier: one for Slots 1 through 8
and one for Slots 9 through 16.
Appendix E provides connectivity diagrams should you
need further assistance in connecting the DSU to the
network.
For the 25-pin V.35 connector, use a V.35 adapter
(feature number 3000-F1-510). The adapter provides the
interface between the 25-pin V.35 D-type connector and a
V.35 router cable.
Appendix E provides connectivity diagrams should you
need further assistance.
The DualFlow DSU transmits user data through its
V.35 interface, and diagnostic or user data through its
EIA-232-D/V.24 interface. Cabling is based upon the
preset configuration (SyBC, SyBT, or DiDg) selected in
the Opts subbranch (Config branch).
" Procedure
1. Install the V.35 adapter as described in Step 7 of
the Installing the DSU section of this chapter.
2. Connect the plug end of the router’s V.35 cable to
the V.35 adapter.
Tighten the two holding screws.
3. Connect the other end of the router’s V.35 cable to
the router’s primary serial port.
Tighten any holding screws.
4. Connect the plug end of the router’s EIA-232
cable to the DSU’s EIA-232-D/V.24 connector.
Tighten any holding screws.
5. Connect the other end of the router’s EIA-232
cable to the router:
Connecting the DSU
to a Router
The rear connector plate provides the router interface
for the Model 3616 DSU. Each rear connector plate
contains two DB25 (or 25-pin D-type) connectors. The
top connector is an EIA-232-D/V.24 (ISO 2110)
connector. The bottom connector is a ITU-T V.35
(ISO 2593) connector.
• If the DSU is to be configured using the SyBC
or SyBT configuration, connect to the router’s
secondary serial port.
• If the DSU is to be configured using the DiDg
configuration, connect to the router’s console
port.
Tighten any holding screws.
3-93615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 44

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Addressing the Unit
A unique address must be assigned to each control and
tributary DSU in your network. You can assign an address
within the range of 1 through 255.
NOTE
Do not assign the number 192
as a network address. This
number is reserved as a
broadcast address.
The DBM requires a separate address, which is
automatically assigned by the DSU. The address assigned
a DBM is the DSU’s address, plus 1 (e.g., if the DSU’s
address is 1, the assigned DBM address will be 2).
NOTE
The numbers 191 and 255
cannot be assigned to a DSU
that has a DBM. However,
addresses can be assigned in
any order; they do not have to
be sequential.
It is recommended that only
odd-numbered addresses
assigned to DSUs so that
even-numbered addresses
reserved for DBMs.
be
are
Tributary DSU Addressing
Tributary DSU addresses are user-definable. The
control DSU accesses its tributary via an active backup
connection by specifying the tributary’s address.
The 6700 or 6800 Series NMS accesses the DSU via its
network address. To access a tributary DSU, the NMS
first addresses the control, then the tributary. An address
issued from the NMS takes the format of control
channel/control DBM network address/tributary network
address. This is called link-level network addressing.
Figure 3-5 shows an example of DSU and DBM
addressing, as well as link-level network addressing.
Refer to Chapter 4 to learn how to set the DSU’s
network address.
3-10 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Figure 3-5. Addressing Example
Page 45

Installing the Model 3616 DualFlow DSU
Verifying Operation and
Testing Connections
Perform verification testing after any installation.
After installing and configuring the circuit (including
control and tributary DSUs, the DDS network, the DBMs
and their dial connections), perform a series of tests from
the control DSU to verify network operation (using either
the SDCP or NMS).
To Connect the SDCP to a DSU
For the carrier-mounted Model 3616 DSU, the SDCP
must first be reconnected to the DSU. Once connected, the
SDCP operates like a DCP.
" Procedure
1. Press the Select key (refer to Figure 3-2).
A screen similar to the following appears.
Carr:Slot: 1: 01 A
1:02A
On the second line
• Press the F1 key (↑) to increment the number
that the cursor is on.
• Press the F2 key (↓) to decrement the number.
• Press the
and keys to move the cursor
one position to the left or right, to change either
the carrier or slot number.
• Press the F3 key to toggle between DSUs, to
switch from 1:01A to 1:02A in this example.
(In our example, the previously accessed DSU
was located in Slot 2 of Carrier 1.)
2. Press the Select key on the SDCP again.
The SDCP accesses the DSU in Carrier 1, Slot 1.
The top-level menu (your starting point) of the
carrier-mounted DSU is displayed.
1:01A DSU 9.6 C
Local Remot
F1
F2
F3
F1 F2
F3
The cursor is usually positioned under the second
position of the slot number (1:01 ).
In this example, the first line shows
• 1 indicates Carrier 1 (Carr)
• 01 indicates the DSU in Slot 1
• A is reserved for future use
From the first line of this example, you can see
that this is a carrier-mounted DSU (1:01A instead
of Port1) that is located in Carrier 1, Slot 1, is
operating as a DSU (i.e., not as a DBM), at
9.6 kbps, and is configured as a control (C).
From the second line you can see that there are no
NMS messages (no Msg branch over the F3 key)
waiting to be read and cleared.
Also note that the SDCP indicator on the selected
DSU’s faceplate, Front Panel, is lit.
3-113615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 46

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Verifying Network Addresses, the Network,
and DBM Operation
Establish a backup connection and perform a Digital
T est over the backup connection to ensure that the
switched network is functioning. Access the DSU’s
identity (ID) subbranch for the tributary DSU to ensure
that the DSU is properly addressed.
Verify that no alarms appear in the Device Health and
Status subbranches. Refer to the Verifying Operation and
T esting Connections section of Chapter 2 for procedures
that lead you through each of these procedures.
Other Tests
The following lists the tests available on your DSU.
Refer to the Test Branch section of Chapter 4 for further
test information, as well as more detail on how to
configure and operate the DSU. Refer to Appendix A to
determine how best to access each test.
• Device Test (Devic)
• Local Loopback (LL) – DSU only
• DTE Loopback (DTE)
• Digital Loopback (DL)
• Remote Digital Loopback (RL) – DBM only
• Bilateral Loopback
• Digital Test (DT) – DBM only
• End-to-End Test (EE) – DBM only
• Bit Error Rate Test (BERT)
• Lamp Test (Lamp)
3-12 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 47

Operating the DSU
Overview 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DCP and SDCP Operation 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keypad 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Menu Structure 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Top-Level Menu 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Branch 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Health and Status 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Health and Status 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expanded Health and Status 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Subnetwork Health and Status 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Status 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Quality 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Identity 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Terminal Power 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backup Branch 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dial Backup Operation 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuring the Unit for Dial Backup 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Understanding Operating Modes 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Backup 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Placing a Backup Call 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Dial Backup Termination 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Branch 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abort 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Test 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Loopback 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local Loopback 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Loopback 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Loopback 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Digital Loopback 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bilateral Loopback 4-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Test 4-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
End-to-End Test 4-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bit Error Rate Test 4-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lamp Test 4-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Branch 4-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Selecting an Application Configuration 4-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Options 4-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Poll List 4-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Displaying the Poll List 4-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Changing the Poll List 4-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Acquiring the Poll List 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Directory 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering a Telephone Number 4-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Phone 4-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Address 4-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assigning an Address 4-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
4-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 48

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Control Branch 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Control 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LEDs 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Leads 4-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Displaying External Leads 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Changing External Leads 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reporting External Lead Changes to NMS 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Message Branch 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview
A DualFlow DSU can be managed from its control
panel, or from a COMSPHEREr 6700 or 6800 Series
NMS. This chapter describes how to manage the DSU
using the control panel. Refer to the appropriate NMS
documentation to understand how to manage the unit from
the NMS.
The DSU’s menus are organized as a branching
hierarchy , sometimes referred to as a menu tree. Refer to
Appendix A as you perform the procedures described in
this guide to help you quickly learn more about your
DSU.
DCP and SDCP Operation
There are two types of control panels, one for each
DSU model.
• The standalone Model 3615 DualFlow DSU
(Figure 4-1) is controlled from its diagnostic
control panel (DCP).
• The carrier-mounted (nest- or rack-mounted) Model
3616 DualFlow DSU (Figure 4-2) is controlled
from a shared diagnostic control panel (SDCP). The
SDCP is mounted onto the COMSPHEREr 3000
Series Carrier to control multiple units.
NOTE
Throughout this guide, DCP
refers to either control panel,
DCP
or
SDCP
, except where a
distinction is made.
KEYPAD
COMSPHERE 3615
4-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
LCD
DISPLAY
OK
NETWORK/DEVICE
ALARM
Figure 4-1. Model 3615 DCP
Alrm
TEST
MODE
F1 F2
Dial TXD RXD RTS DSR
104
103
DTE STATUS INDICATORS
DIAL
BACKUP
105
F3
CTSTest
106
107
LSD
DTR
108
496-14469-01
109
Page 49

Operating the DSU
CARRIER SLOTS 1–16
SDU12345678910111213141516
Select
OK Alarm BckUp Test EC
F1 F2 F3
COMSPHERE 3000
SELECT
KEY
INDICATORS
OK Alarm BckUp Test EC
NETWORK
DEVICE
ALARM
DIAL
BACKUP
STATUS
TEST
MODE
ERROR
CORRECTION
KEYPAD
Status
OK
Alrm
Test
Dial
103
TXD
104
RXD
105
RTS
106
CTS
107
DSR
108
DTR
109
LSD
Front Panel
Multirate
DSU
3616
LCD DISPLAY
NETWORK/
DEVICE ALARM
TEST MODE
DIAL BACKUP
DTE
STATUS
INDICATORS
SDCP
INDICATOR
496-14470-01
Figure 4-2. SDCP and Model 3616 DSU Faceplate
Both control panels have a 2-line, 16-character liquid
crystal display (LCD) and a keypad, through which you
can
• Monitor the unit’s health and status
• Initiate dial backup
• Initiate diagnostic tests
• Load or change the unit’s configuration, or how it
will operate
• Display or change the status of the general purpose
external DTE leads.
The DCP’s LCD displays the result of any command
initiated from the DCP.
Refer to Appendix C to understand the meaning of
DCP status indicators.
4-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 50

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Keypad
There are seven keys on the DCP of the standalone
Model 3615, and eight on the SDCP for the carriermounted Model 3616 DSU. The additional key, the Selec t
key, connects the SDCP to a specific DSU located in a
specific carrier and slot within the carrier.
F1 F2
• The key returns you to the top-level menu, and
terminates any work in progress.
• The key returns you to the previous display,
one level up from the current display. It can also be
used to terminate a data entry display without
making a change.
• The and keys scroll menus or other
displays to the left or right, respectively.
On status and test result displays, the
keys scroll additional information into view.
F3
and
Top-Level Menu
The top-level menu is the starting point for all DSU
operations. You can always return to this point from
anywhere in the menu by pressing the key. Pressing
this key immediately terminates any operation or work in
progress. Refer to Appendix A as you read about the
branches and subbranches.
The standalone Model 3615 DualFlow DSU indicates
whether the DDS or DBM line interface is being
monitored. The carrier-mounted Model 3616 DualFlow
DSU displays the DSU’s carrier and slot location in the
cabinet.
When there are simultaneous DSU (V.35) and Dial
(232) connections (e.g., as in a Dial Diagnostic – DiDg
configuration), the top-level screen toggles between two
displays every 10 seconds, displaying the status of each of
the two ports, the EIA-232-D port for the router
management or user data and the V.35 port for the user
data.
232 DBM 9.6 C
Local Remot
F1
F2
F3
On data entry displays, these keys move the cursor
one character to the left or right to allow entry of
one digit or character at a time.
• Function keys (F1, F2, or F3) select the item
displayed directly above the key.
Additional information on operating the DSU’s keypad
can be found in the procedures used to install and verify
operation of the DSU in Chapters 2 and 3, the procedure
for editing configuration options in Chapter 5, and the
various procedures scattered throughout this chapter.
Menu Structure
The menu is your map through the DSU’s various
functions. The following sections describe each branch
and subbranch, and provide procedures for operating
certain features. Appendix A shows the complete menu
and describes the DSU’s branches and subbranches. (The
menu is also included on the Reference Card that comes
with this guide.)
V.35 DSU 56 C
Local Remot
F1
F2
F3
Status Branch
The Status (Stat) branch reports on the health and
status of the DSU, DBM, the DTE interfaces, the quality
of the dial connection, the identity of the DSU (model
number, serial number, etc.), and the terminal’ s power
(where it checks the presence of voltage on the DTE’s
RTS lead).
4-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 51

Operating the DSU
Health and Status
The Health and Status (H/S) subbranch displays the
health and status of the DSU, as well as the DBM. It
automatically scans for DSU and line conditions that are
not within normal limits.
There are three types of Health and Status messages:
• Devic (Device Health and Status)
• Expan (Expanded Health and Status)
• Subn (Subnetwork Health and Status)
All alarm and status conditions are displayed for the
specified DSU at the time the option is selected. For a
local DSU, the alarm and status conditions are updated
every 2 seconds; for a remote DSU, the alarm and status
conditions are not updated.
Refer to Appendix C for a complete listing of these
messages.
Device Health and Status
Device Health and Status (Devic) reports health and
status information for a selected DSU. If five minutes
elapse without a key being pressed, the Device Health and
Status screen is redisplayed.
• When the digital circuit is the active link,
— The first line displays a running
normal-operation timer (hh:mm:ss).
— The second line displays the DSU’s operating
rate and can also display one or more of the test
or alarm messages.
• An asterisk ( * ) appears at the far right to indicate
NMS activity.
If the right arrow (→) appears to the right of Expanded
H/S, there is more than one message. Press the
key to
see the next message.
Subnetwork Health and Status
Subnetwork Health and Status (Subn) displays status
information from a DSU’s subnetwork (all DSUs and
DBMs assigned to that DSU’s active poll list). The
downstream network addresses and current statuses are
listed. T o page through tributary addresses:
• Press the F1 key (↑) for the next highest network
address.
• Press the F2 key (↓) for the next lowest network
address.
No PList appears if no DSUs are being monitored
downstream.
This status information is only available through the
local branch and only when DBM Diag Type is set to
NonD.
DTE Status
The DTE status subbranch provides a snapshot status
of the local or remote unit’s external DTE interface.
• For the local DSU status, the display is sampled
and updated every 2 seconds.
• For the remote DSU status, only one set of states is
returned based upon a monitoring period of
approximately 3 seconds.
The DTE interface statuses are displayed in sets. Use
the
or key to scroll each set of lead statuses into
view .
• A right arrow (→) appears just before the asterisk
if there is more than one message. Press the
to see the next message.
Expanded Health and Status
Expanded Health and Status (Expan) only appears
during automatic dialing, and only if an expanded health
and status message has been generated. It retrieves Health
and Status information for the local DSU after an
automatic backup or DTR-controlled backup attempt has
failed, or when there is a disconnect after a successful
connection.
key
If both a backup connection and the DDS line are
active a selection screen appears first.
• Select V.35 to monitor the V.35 interface (for user
data).
• Select 232 to monitor the EIA-232-D interface (for
router-management or user data).
4-53615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 52

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Circuit Quality
Circuit Quality (CircQ) shows the level and quality of
the signal being received from the network by the DBM.
This subbranch is only available for a V.32 DBM.
" Procedure
1. Press the key to scroll ID into view.
2. Press the function key (F1, F2, or F3) directly
below the selection. One field at a time is
displayed.
Identity
Identity (ID) displays a listing of the DSU’s model and
serial numbers, the equipment installed (DBM), software/
firmware versions, the network address, the DDS or
3. Press the
display (screen) at a time.
T able 4-1 lists the Identity information provided about
the DSU and its equipment.
DSU’s rate, and the DBM’s rate.
Table 4-1
Identity Descriptions
Description Information Displayed
Model: 3615 or 3616.
S#: Unit serial number.
DSU SW ver: Software/firmware version residing on the DSU.
Netwrk Addr: Unit’s network address.
key to display the information, one
DSU Rate: V alue set for DSU
does not appear if a DBM has its DBM
DBM SW ver:
(
Switched 56 DBM only
DBM Rate: V alue set for DBM
DBMtype:
App Modul: ASPEN. Appears when the Single-Port Async/Sync feature is installed.
App Modul: CISC or 64CC.
xxx yy.y z
)
Software/firmware version residing on the Switched 56 DBM.
Type of DBM installed:
xxx
can be either
V (V.32 DBM),
4wS (4-wire Switched 56 DBM), or
2wS (2-wire Switched 56 DBM).
yy.y
indicates the DBM’s maximum speed.
z
designates whether the
DBM Primary Core option was enabled.
(A P indicates Primary Core is enabled.)
Only appears when a DBM is installed.
CISC when the Clear Channel with Integrated Secondary Channel chip is present.
64CC when the CISC chip is not present.
Rate(Kbps)
Rate(Kbps)
configuration option; the DSU’s aggregate speed. This
Primary Core
configuration option; the DBM’s aggregate speed.
configuration option set to Yes.
4-6 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 53

Operating the DSU
Terminal Power
Terminal Power (TPwr) displays the status of the
EIA-232 or V.35 interface (connector). The DSU checks
the state of the RTS lead to determine when the DTE is
ON to report the following:
• When the voltage is approximately less than –3V or
greater than +3V for both the EIA-232 and V.35
interfaces.
— If power is detected, the second line displays
On.
— If no power is detected, the second line displays
Off.
Backup Branch
The Backup (Bckup) branch controls dial backup
operation. The following sections explain dial backup
operation.
Dial Backup Operation
The DualFlow DSU with dial backup capability can
provide backup for a point-to-point circuit operating at
56 kbps or below. Appendix E shows some typical
DualFlow configurations.
Backup is controlled primarily by software
configuration options in the DBM, DBM Port, and Backup
option sets. The unit can be configured so that backup can
be either automatic or manual. Manual backup can be
controlled from either the DSU’s control panel, or a 6700
or 6800 Series NMS.
Backup begins with configuring the unit.
Configuring the Unit for Dial Backup
The following configuration options should be set,
whether initiating backup manually or automatically.
DBM Option Set:
• AutoAnswer – Select Enab.
When enabled, this option set allows the DBM to
answer an incoming call. (Enab is the factoryloaded default setting.)
• Call Setup – Set call setup security level:
None – No call setup security is required.
(None is the default.)
Password – Originating and receiving DBMs
exchange passwords before the DBMs can
complete the connection. There must be an
incoming password (RxPwd) and an outgoing
password (TxPwd) set up. Select Pswrd when
the DiDg application configuration is being
used.
Callback – Both DBMs must exchange
passwords and a Backup Directory pointer
must be sent before a call can be initiated.
There must be an incoming password (RxPwd)
and an outgoing password (TxPwd) set up, and
the originator’s local telephone number (Phone
subbranch) must be stored in the answering
DBM’s Backup Directory.
Alarm – No security is to be used at the
control DBM, and the DBM only answers
incoming calls when there is a facility alarm.
If the control DSU is to initiate the call, set the
control for Pswrd and the tributary for Cllbk.
If the tributary DSU is to initiate the call, set the
control for Cllbk and the tributary for Pswrd.
Backup Option Set (none of these need to be set
for manual backup):
• Auto Bckup – Select Enab.
When enabled, the DSU will automatically initiate
dial backup when the DDS line is down. Up to
10 attempts will be made.
If both the control and tributary DSUs are
configured for automatic backup, NtwkT imOut
should be set to different values so that the control
and tributary DSUs do not try to place a call at the
same time.
On a point-to-point circuit, it is best that only one
end performs automatic backup. It is possible to
trigger the backup for single-direction network
failures only detected at the remote DSU. The
remote DSU must have RTS Control set to FrcOn.
4-73615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 54

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
NOTE
Auto Backup
and
Auto Restor
should not be enabled if
DTRCallCon
is enabled (set to
Orig or Ansr).
• Bckup Dir – Select the call directory identifier
(1 to 10) stored in the DBM’s Backup Directory for
the telephone number to be dialed.
• AutoRestor – Select Enab.
When enabled, the DBM automatically restores
data to the DDS circuit when service is restored and
the amount of time set in RestoreTimOut has
expired.
• NtwkTimOut – Set the amount of time that the
DDS circuit must be out of service before a backup
attempt is made: from 0:00 (minutes:seconds) to
29:59 (the default is 0:20).
• RestorTimOut – Set the amount of time that the
DDS circuit must be back in service before
automatic restoration is attempted: from 1 to
60 minutes (the default is 5 minutes).
• MultiCall – Select Disab.
When enabled, instead of following the normal
calling cycle, the DBM cycles through all dial
strings contained in its Backup Directory until a call
attempt is successful.
Do not enable MultiCall unless more than one
telephone number is in the Backup Directory and
each successive (i.e., 1, 2, 3, etc.) telephone number
is different from the previous entry. Directory
entries should be unique.
Understanding Operating Modes
The Backup branch controls operation of the Dial
Backup function. The DualFlow DBM has three modes of
operation:
• In Idle mode, there is no dialed connection. The
DDS circuit is active and carrying user data.
• In Standby mode, the unit has a dialed connection
to another DBM or compatible dial backup unit, but
has not connected line data to the DBM’s DTE port.
• In Dial Backup mode, the dialed circuit is active
and carrying user data and diagnostics.
• TriesTimeOut – Specify the overall time limit
during which a DBM attempts to establish a dial
backup call when Auto Bckup is enabled or when
raising DTR initiates a call attempt: from 1 to 60
minutes (the default is 15 minutes).
Backup Branch Menu Selections
Current
Backup Mode
Idle Bkup
Standby Disc
Dial Backup DrBU
Backup
Command
Dial
→Cnnct
→StnBy
Dial out, establish, and switch to dialed link (Dial Backup mode).
Dial out and establish dialed link (Standby mode).
Disconnect dialed link (Idle mode).
Connect the DBM line data to DBM’s DTE port (Dial Backup mode).
Disconnect dialed link and switch to private line (Idle mode).
Disconnect the DBM line data from DBM’s DTE port (Standby mode).
T able 4-2 lists the Backup branch operating modes and
explains the effects of each backup command.
Table 4-2
Effect
4-8 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 55

Operating the DSU
Manual Backup
You can control each step of a backup attempt by
following one of these procedures.
Placing a Backup Call
T o place a backup call:
" Procedure
1. Go to the Bkup option set under the Confg branch
and set Auto Bckup to Disab.
2. Select Bckup (Backup branch) to select a
telephone number from the Backup Directory.
3. Select Dial, the Backup Dir screen is displayed
identifying the Backup Directory indicator.
If the telephone number in the Backup Directory is
the number you want to dial, go to Step 5.
4. Select another telephone number to call:
• Press the F1 key (↑) to increment the directory
indicator (e.g., 1 to 2).
Abort
The Abort selection allows you to abort a test that is
running. The DSU cannot run any other test until the test
in progress is aborted.
There are two types of selections to abort a test:
• Selective terminates whatever test is in progress at
the local DSU.
• Subn (Subnetwork) only displays for the DBM
branch. This selection terminates all tests running
on the remote DSU or DBM.
After selecting either Selective or Subn, the test is
terminated and the DCP displays the message Command
Complete.
Device Test
The Device (Devic) Test uses a test pattern generator
built into the DSU. When testing the DBM, the DBM must
be in Idle mode, with no call in progress before running a
Device Test.
• Press the F2 key (↓) to decrement the indicator
(e.g., 2 to 1).
5. Select Dial (F2); the DBM places the call.
6. Once the dialed call has been established, select
Cnnct to switch data to the dialed connection.
Manual Dial Backup Termination
• If in Standby mode, select Disc.
• If in Dial Backup mode, select DrBU.
Test Branch
The Test branch provides extensive testing capabilities
for the DSU, the DDS circuit, the DBM, and the backup
circuit. Most tests can be run simultaneously on the DSU
and DBM. When the tributary DSU receives a test request
from the control DSU, it aborts any locally initiated test in
progress.
Running a test can affect your application data or may
cause your application session to be dropped depending
upon front-end processor, time-out parameters, etc. since
no data or acknowledgment messages will be transmitted
while the test is in progress.
NOTE
On power-up, the DSU sends
out polls to verify that a DBM is
installed. It then initiates a
Device Test on itself and the
DBM. The results of the tests
appear momentarily on the
DCP’s LCD.
Loopback
The Loopback (Lpbk) branch displays four loopbacks:
• Local Loopback (LL) – DSU only
• DTE Loopback (DTE)
• Digital Loopback (DL)
• Remote Digital Loopback (RL) – DBM only
Figure 4-3 shows where each loopback occurs on the
circuit. Refer to the figure as you read about loopbacks.
4-93615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 56

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
NOTE
To abort a loopback on the
tributary DSU from the NMS,
establish a dial connection with
the control DSU, then issue a
subnetwork abort command
from the NMS to the control.
Local Loopback
Only available to a DSU, Local Loopback (LL) is
session-disruptive; that is, performing the test will disrupt
data. It permits the DTE or router to run a test to
determine whether the DTE or router connection to the
DSU and the DSU itself are functioning properly. The
DSU must be connected to the DTE or router, but the
network connection to the DSU is not required.
While the DSU is in Local Loopback, any data
transmission by the DTE or router is returned as received
data. An operator can send a test pattern and verify correct
reception of the test. The DSU does not monitor this
testing.
NOTE
If the NMS is to abort the Local
Loopback, the tributary’s DBM
must be in Standby mode. If in
Dial Backup mode and the NMS
Abort
issues the
command will not be
recognized. The loopback will
have to be aborted from the
DSU’s control panel.
command, the
DTE Loopback
DTE Loopback (DTE) loops back the data path at the
DTE interface without affecting operation of the other
port. This loopback is used to verify that the DTE or
router connection and the cable are good.
Digital Loopback
Digital Loopback (DL) allows manual testing of the
remote end of the circuit. Data coming in is immediately
transmitted back. For example, a Digital Loopback may
be required in order to complete an external bit error rate
test (BERT) from the remote DSU. The local DSU
receives test data, loops it back to the transmitter before
the DSU’s DTE interface, and returns it to the network.
Digital Loopback can also be initiated by receiving a
V.54 pattern to go into Digital Loopback. Enable
configuration options V.54 Lpbk (V.54 Loopback) in the
DSU option set, and RespondRDL (Respond to Remote
Digital Loopback).
Remote Digital Loopback
Only available to the DBM, the Remote Digital
Loopback (RL), sometimes referred to as RDL, typically
supports testing using an external device, like a protocol
analyzer that is connected to the local DSU’s DTE
interface. A test message from the external device is
looped back from the receiver to the transmitter in the
remote DBM and returned to the local DBM.
In Remote Digital Loopback, the local DBM (control
or tributary) puts the remote DBM into Digital Loopback.
DTE
DTE
(ROUTER)
4-10 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
DSU
COMSPHERE 3610
LL
NETWORK
Figure 4-3. Loopbacks
DL or
RL on
Aggregate
DL or
RL on a
Port
DSU
COMSPHERE 3610
DTE
(ROUTER)
496-14493a
Page 57

Operating the DSU
When a DBM (control or tributary) originates Remote
Digital Loopback, both the originating DBM and the
targeted DBM enter Test mode. No other test can be run at
the originating DSU or the targeted DSU until the Remote
Digital Loopback is aborted.
The DBM does not generate test results.
NOTE
To activate a V.54 Loopback from
the NMS to a DSU, first enable
V.54 Lpbk
(DSU option set) at
both the control and tributary
DSUs. Then, select
3600 remote-digital at the NMS,
not
V.54-remote-digital.
Bilateral Loopback
Bilateral Loopback (Bilat Lpbk) is a combination of
DTE and Digital Loopbacks operating simultaneously in
the same DSU. Both Bilateral and Digital Loopbacks are
selected from the DSUpt (DSU Port) or DBMpt (DBM
Port) option set.
During the test, the TXD, RXD, and RTS LED
indicators show the states of the leads at the DTE
interface if the DBM port leads are being displayed. At
the conclusion of the test, the local DSU releases the
remote DBM from Digital Loopback.
T o review the results of the test, select Displ (Display)
and press the
key to scroll through the results shown
in Table 4-3.
When the test is over, the top line displays Final
instead of Active.
Table 4-3
Digital Test Results
Results Information Displayed
Time: Running test timer. (The Clr
selection resets the timer to
0:00:00.)
Tot Error: Running count of bits in error;
Max, if the maximum error
count has been reached, the
maximum being 64000. (The
Clr selection resets the counter
to 0.)
Err Secs: Running count of errored
seconds. (The Clr selection
resets the counter to 0.)
NOTE
If
Bilat Lpbk
is enabled,
requesting a Remote Digital
Loopback or Digital Test will
automatically initiate a DTE
Loopback, as well.
Digital Test
Only available to a DBM, the Digital T est (DT) checks
the functionality of a pair of DBMs. This test is run on the
DBM over the backup connection to a remote DBM for
point-to-point testing.
The remote DBM is placed in Digital Loopback, then
the local DBM transmits the 511-bit test pattern over the
network to the remote DBM for an operator-specified
length of time.
End-to-End Test
Only available to the DBM, the End-to-End (EE) Test
analyzes a control and a tributary DBM, and the network
circuit between them in both directions independently. It
transmits fixed packets (or blocks) of data between the
DBMs When an End-to-End T est is run, diagnostic data
may be disrupted.
T o view the results of the test, select Displ (Display)
and press the
in Table 4-4.
When the test is over, the top line displays Final
instead of Active.
key to scroll through the results shown
4-113615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 58

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 4-4
End-to-End Test Results
Results Reported By
Time: Local and remote DBM Running test timer. (The Clr selection resets the timer to 0:00:00.)
Tot Block: Local and remote DBM Number of blocks completed. (The Clr selection resets the counter to 0.)
Rx Blk err: Local and remote DBM Number of incoming blocks with errors detected, indicating a fault in the
Tx Blk err: Local and remote DBM Number of blocks with errors detected at the remote DSU, indicating a
Rx TimOuts: Local DBM only Number of blocks that were not received or acknowledged by the
1
Local
refers to the test initiator.
1
incoming transmission path. (The Clr selection resets the counter to 0.)
fault in the outgoing transmission path. (The Clr selection resets the
counter to 0.)
remote DSU or DBM. (The Clr selection resets the counter to 0.)
Information Displayed
Bit Error Rate Test
The Bit Error Rate T est (BERT) is a session-
disruptive test that transmits a 511-bit pattern. It analyzes
the network circuit. It can monitor the results by putting
the remote DSU or DBM into Digital Loopback and
checking the returned pattern for errors, or by
simultaneously executing a BERT in the local DSU.
The test continues until aborted from the DCP or NMS.
If nondisruptive diagnostics are in effect (if Diag Type
is set to NonD), diagnostic data can be disrupted.
To display the results of the test, press F2 to select
Displ. The results are shown in Table 4-5. To clear the
results of the test and clear the counters to zero, press F3
to select Clr.
Table 4-5
Bit Error Rate Test Results
Results Information Displayed
Time: Running test timer. (The Clr
selection resets the timer to
0:00:00.)
Tot Error: Running count of bits in
error; Max, if the maximum error
count has been reached, which
is 64000. (The Clr selection
resets the counter to 0.)
Err Secs: Running count of errored
seconds. Errored second is at
least one error is detected during
a 1-second time period. (The Clr
selection resets the counter to
0.)
4-12 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 59

Operating the DSU
Lamp Test
The Lamp Test is a local test of the status indicators
(LEDs) and liquid crystal display (LCD) on the DSU’s
control panel (both models). Any indicator that does not
flash is not functional.
Note that if all LEDs are functioning, all the indicators
on the Model 3615 DCP are flashing steadily. In a
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, the indicators on the
SDCP remain ON. The LCD on the DCP or SDCP
alternately flashes solid blocks, moving from position to
position on the display until the test is aborted.
Pressing any key except the
portion of the Lamp T est and return you to the DSU Test
menu so you can abort the test. Once aborted, the LCD
and LEDs stop flashing.
key will stop the LCD
Configuration Branch
The Configuration (Confg) branch allows you to
configure or customize the DSU and its DBM to fit your
site’s requirements, to enter and change telephone
numbers, and to specify the mode for viewing or editing
configuration options.
• Synchronous Backup for a Tributary DualFlow
DSU (SyBT) – Sends user data over the DDS
connection via the V.35 port, and configures the
DBM for synchronous user-data transfer during
Bandwidth on Demand or backup situations. This
configuration also configures the DualFlow DSU to
answer calls only when DTR on the EIA-232 port is
active, and to disconnect when DTR transitions
from active to inactive (DTRCallCon: Ansr). Used
for a tributary device.
• Dial Diagnostics (DiDg) – Sends user data over the
DDS connection via the V.35 port, and configures
the DBM for asynchronous router-management
data and for disruptive diagnostics.
Select the appropriate configuration based upon how
the unit will be used within your network. All
configurations support simultaneous DDS and DBM
connections. The difference is in how the DBM
connection is used.
Refer to the Application Configurations in Appendix E
for examples using these three configurations. Refer to the
DSU’s menu in Appendix A as you follow these steps.
" Procedure
1. Select Confg (Configuration branch).
Selecting an Application Configuration
The DSU is shipped from the factory with three
common applications already configured. All you have to
do is select the appropriate application and load the preset
configuration into the unit. These configurations include:
• Synchronous Backup for a Control DualFlow DSU
(SyBC) – Sends user data over the DDS connection
via the V.35 port, and configures the DBM for
synchronous user-data transfer during Bandwidth
on Demand or backup situations. This configuration
also configures the DualFlow DSU to dial when
DTR on the EIA-232 port transitions from inactive
to active, and to disconnect when DTR transitions
from active to inactive (DTRCallCon: Orig). Used
for a control device.
2. Press the F1 key to select Opts (Configuration
Options subbranch).
The Load from screen appears.
3. Press the
configuration into view.
By referencing the menu in
Appendix A, you will see that
pressing the key is often
more efficient.
4. Make your selection: SyBC, SyBT, or DiDg, and
press the function key (F1, F2, or F3) directly
below the desired configuration.
The Edit/Save screen appears.
or key to scroll the desired
NOTE
4-133615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 60

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
T o view the configuration loaded:
" Procedure
1. Select an option set (e.g., DSU – F2 key).
2. Press the F1 key (Next) to scroll through each
configuration option’s default (factory-loaded)
setting.
The option sets (DSU, DSU Port, DBM, etc.)
scroll from the last to the first (e.g., Diag
BkupSAVEDSUDSU Port, etc.).
3. Select Prev (press the
then select it).
4. Press the
key to return to the Edit/Save
screen.
You can select another option set to view, or you
can proceed.
Refer to Chapter 5, Configuring the Unit, for an
example showing you how to edit (change)
configuration options.
5. Select Save (F1).
key to display Prev,
Poll List
The Poll List (PList) subbranch maintains or changes
the DBM’s poll list. A control DBM’s poll list includes
the tributary DSU and DBM one level downstream, and
only a control can acquire a poll list.
You can display, clear, change, or acquire a poll list. If
you select Clr (Clear) from the Poll List screen, all
network addresses are erased from the DBM’s poll list.
PList is only available from the Local branch, and only
to a control DBM configured for nondisruptive
diagnostics (Diag Type is set to NonD).
Displaying the Poll List
T o display each of the network addresses included in
the DSU’s poll list:
" Procedure
1. Select PList (F2).
2. Select Displ (F1). The following screen appears:
The Save to screen appears.
6. Select Activ (F1).
The selected application’s configuration is saved
to the DSU’s Active operating area, and the
Command Complete message appears.
Configuration Options
The Configuration Options (Opts) subbranch allows
you to save, copy, and/or change configuration options.
Refer to Chapter 5, Configuring the Unit. Chapter 5
fully explains the Opts subbranch, and provides an
example of changing configuration options.
Addr: 2 Acti ve
F1
F2
F3
The number after Addr (in this example, 2) is the
network address of the poll list member. The
member is identified as either Active or Skip
(identified via the Change Poll List function).
3. Press the F1 or F2 key to display additional
addresses.
4. Press the
key to return to the Poll List screen.
4-14 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 61

Operating the DSU
Changing the Poll List
T o change the poll list (e.g., add network address 3):
" Procedure
1. Select Chang (F3).
Poll List:
Displ Clr Chang
F1
2. Select Activ (F1).
Chng Poll List:
Activ Delet Skip
F1
3. Press the F1 key to increment network address 2.
F2
F2
F3
F3
T o delete a network address (e.g., 3) from the poll list:
" Procedure
1. Select Delet (F2).
Chng Poll List:
Activ Delet Skip
F1
2. Select Enter (F3).
Address: 3
F1
In this example, 3 was just added, so it is the
address displayed. If another address needs to be
deleted, change the network address displayed as
previously shown.
F2
F2
F3
Enter
F3
Address: 2
Enter
F1
F2
F3
4. Select Enter (F3).
Address: 3
Enter
F1
F2
F3
The address is added to the poll list. The control
determines the round trip delay, then sends that
information to the tributary DSU.
5. Press the
key to return to the Chng Poll List
screen.
Make 3 Acti ve:
Command Complete
The tributary DSU associated with the address is
removed from the poll list.
D el 3 frPList:
F2
F3
Command Complete
F1
F1
F2
F3
4-153615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 62

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Acquiring the Poll List
A call must be established before this procedure can be
performed (refer to the Backup Branch section earlier in
this chapter).
T o automatically generate a poll list if a control:
" Procedure
1. Press the key to display Acq.
Poll List:
Displ Clr Chang
F1
2. Select Acq (F1).
You can stop the process and keep the poll list as it
has been generated by selecting Abort.
Poll List:
Acq Displ Clr
F1
Acquir Poll List:
Abort
F1
F2
F2
F2
F3
F3
F3
Directory
The DSU’s dial backup Directory (Dir) can store up to
ten telephone numbers (dial strings) so the DBM can call
other DBMs. Directory entries are numbered from 1 to 10.
Each dial string in the directory can be up to 36 characters
in length. Refer to T able 4-6 for numbers and characters
that can be used.
When the dial string or changes are complete, enter an
underscore ( _ ) to the immediate right of the last
character; this ends the dial string field.
Table 4-6
Directory Entry and Password Characters
Character
0—9 Dialing digit (These are the only
, (comma) In a dial string: a 2-second pause
( ) (space) Space (readability character)
1
characters accepted by the
Switched 56 DBM.)
*
# Tone-dialing character#
t Tone dial
p Pulse dial
w Wait for dial tone
ť Delimiter, separating telephone
Tone-dialing character*
number and callback directory
pointer (for use with callback
security)
at the beginning of a password;
suppresses display of all following
characters (invisible mode)
Use
2
2
2
3
Acquir Poll List:
Command Complete
F1
F2
Otherwise, all tributary addresses have been
acquired.
4-16 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
F3
_ (underscore) Required character for
end-of-string marker
(erases end-of-line)
1
The colon (:) character should not be entered from the
NMS.
2
Not supported by Switched 56 DBMs.
3
Space is not used for directory entries.
NOTE
Do not load duplicate telephone
numbers into the Directory;
telephone numbers should be
unique.
Page 63

Operating the DSU
Entering a Telephone Number
For the following example, add a dial string (telephone
number) to Backup Directory 1. The number to be entered
is 555-1234.
T o add or change a telephone number:
" Procedure
1. Select Local.
2. Press the
branch).
3. Select Confg.
4. Select Dir if entering a telephone number into the
Backup Directory.
Press the
entering the local DSU’s telephone number. This
telephone number is entered similarly to entering
a number into Dir.
5. Select Chang (F1) to add or change a telephone
number.
The Enter Dir screen appears.
key to display Confg (Configuration
key to display then select Phone if
For numeric screens, the following applies:
— Press the F1 key (↑) to increment the digit.
— Press the F2 key (↓) to decrement the digit.
— Press the
or keys to move the
blinking cursor one position to the left or
right.
— Press the F3 key (Undo) to restore the number
as it was first displayed so you can start over.
Refer to T able 4-6 to see all available directory
and password entry characters.
7. Press the F1 key until the number 5 appears.
8. Press the
key to move to the next position.
9. Repeat the process until all numbers in the
telephone number have been entered.
1 : 5 5 5 1 2 3 4
Undo
F1
F2
F3
Press the F1 key (↑) to increment the Directory
entry indicator (the default is 1). For this example,
assume that you are entering your first directory
entry.
6. Select Load (F2).
The Directory entry appears on the first line; the
cursor is positioned in the first position of the
currently empty Directory.
1 :
Undo
F1
F2
F3
If the number had been entered previously, that
number would appear on the first line, following
the colon (:).
NOTE
A dial string cannot have any
separating characters or spaces
(i.e., 555-1234 or 555 1234).
Other valid characters
can be
interspersed as needed : *, #, t,
p, w, and comma (,).
10. Press the key to return to the Enter Dir
screen.
11. Press the F3 key to Save the entry.
12. Verify that the number was loaded by pressing the
key again and selecting Load (F2).
The telephone number should appear as entered, or you
can repeat the procedure to edit/correct your entry.
4-173615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 64

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Phone
The local telephone number (Phone) feature stores the
local DBM’s telephone number if a DBM is installed.
Refer to T able 4-6 to see all available telephone
number characters.
Network Address
The network address (Addr) is the network address of
the local DSU. It is only available from the Local branch.
The DSU’s network address is a number in the range of
1 to 254 if the DSU has a DBM installed. The DBM
automatically acquires an address equal to the DSU’s
plus 1.
Assigning an Address
The Addressing the Unit sections of the installation
chapters, Chapters 2 and 3, provide guidelines for
assigning an address to the DSU based upon its position in
the network – control or tributary. Follow the steps below
to assign a network address to a DSU. Refer to the menu
in Appendix A, if necessary.
" Procedure
1. Press the
2. Select Local.
3. Select Confg (Configuration branch) from the
menu.
(Press the
press the function key (F3) directly below the
branch name to select it.)
key to return to the top-level menu.
key to scroll Confg into view , then
5. Select Load.
Net Address appears, with the current network
address displayed. (The DSU is shipped with its
network address set to 254.)
6. Change the DSU’s network address by moving the
blinking cursor and incrementing or decrementing
the digits (1 through 9).
— Press the
1 position to the right.
— Press the
1 position to the left.
— Press the F1 (↑) key – increments the digit
by 1 (e.g., 1, 2, 3, ...).
— Press the F2 (↓) key – decrements the digit
by 1 (e.g., 1, 2, 3, ...).
7. Press the
screen when finished entering the DSU’s address.
8. Select Save (F2).
The DSU displays the address assigned along with
a Command Complete message.
If an error was made in entering the address:
key – moves the cursor
key – moves the cursor
key to return to the Net Address
" Procedure
1. Press the
screen.
2. Re-select Addr, and re-edit the address.
3. Select Save again.
key to return to the Configure
4. Press the
then select Addr.
4-18 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
key until Addr (Address) appears,
Page 65

Operating the DSU
Control Branch
The Control (Ctrl) branch allows you to enable or
disable the DSU’s transmitter, as well as the DBM’s, and
to display or change the status of the general purpose
external DTE leads. A DBM can be disabled if it is
addressed from the Remote branch.
Transmitter Control
The Transmitter Control (TxCtl) selection allows you
to enable or disable the DSU’s or DBM’s transmitter
(DDS core).
When the DSU transmitter is disabled, the following is
possible:
• When a DSU is disabled, it responds to tests.
Aborting a test clears the test but the unit remains
disabled.
• A DSU in test clears the test when a disable (or
enable) command is received.
• If an enable command is executed to a control from
the NMS or the local DCP, all disabled tributaries
are enabled; all tributaries in test are restored to
Data mode.
LEDs
The LEDs selection is only available from the Local
branch. This selection allows you to monitor the port at
any given time. When selected, the port’s lead activity is
reflected in the DCP circuit designation status indicators
(TXD, RXD, etc.) on the faceplate of the Model 3616
DSU, or on the DCP of the Model 3615 DSU.
External Leads
The External Leads (ExtL) selection allows you to
display the state of four general-purpose leads on the
EIA-232-D/V.24 port interface: Pins 12 and 13 for output
(control leads) and Pins 19 and 23 for input (alarm leads).
When the configuration option Ext Leads (External
Leads) is set to ExtLd (DBM Port option set), you can
change the state of the two output leads from the DCP or
NMS. When CCN by EL (CCN by External Leads) is
enabled (DBM Port option set), the control DSU reports
changes in the four leads to the NMS as part of its health
and status poll response.
T able 4-7 describes the meaning of the state of each
input or output lead.
When the local DBM is disabled, the DBM does not
originate or answer any calls until enabled.
Symbol Meaning
Off (below text line)
ON (above text line)
Changing
?
NOTES:
Input leads A and B:
Off ( ) when voltage on lead is less than +.8V.
) when voltage on lead is more than +2.2V.
ON (
Output leads are either ON or Off:
When output is set to Off (
When output is set to ON (
Indicates an illegal value
), –12V is applied to lead.
), +12V is applied to lead.
Table 4-7
Lead States
4-193615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 66

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Displaying External Leads
The Display (Displ) selection allows you to view the
external lead states. When Display is selected, the
External Leads status report appears showing the current
status of the general-purpose external leads on the
EIA-232-D/V.24 interface.
Changing External Leads
The Change (Chang) selection allows you to change
the state of the two output leads (for example, to change a
lead to signal a console operator or to reset a remote
computer). Leads can be changed from the NMS.
After the leads are set, press the F2 key to save the
leads in the specified state.
Reporting External Lead Changes to NMS
Changing either the output leads or the input leads
changes the DSU’s health and status message.
If the DSU is polled by the NMS, the NMS reports a
change configuration notification (CCN) event. The NMS
operator can then issue a CCN Display command to
determine what caused the event.
• If the event was caused the state of the external
leads, select Displ (F1) to see the current states of
the leads.
Message Branch
The Messages (Msgs) branch of the top-level menu
allows the DBM to receive messages from the NMS. It
only appears when there is a message waiting. Both
control and tributary DSUs can receive messages.
T o receive messages:
" Procedure
1. Press the F3 key (Msgs).
2. Select Read (F1).
3. If the message is less than 16 characters in length,
the entire message is displayed.
If the message is greater than 16 characters, press
the
key to scroll additional lines of the
message onto the screen.
T o clear (delete) messages:
" Procedure
1. Press the F3 key (Msgs).
2. Select Clear (F2).
The message is deleted, and Msgs no longer
appears over the F3 key.
• If a positive (+) voltage is detected in either one of
the input leads, an external leads alarm is also
reported.
4-20 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 67

Operating the DSU
Front Panel (DCP) Security
NOTE
This page can be removed to
prevent unauthorized persons
from learning about the security
access levels and their
selection.
The Model 3615 diagnostic control panel (DCP) and
Model 3616 shared diagnostic control panel (SDCP) have
two levels of security access, as shown in T able 4-8.
Table 4-8
Security Access Levels
Security
Access Level
Unlock All
Lock Local branch only:
Functions Available
S Status branch
S Configuration branch:
Display only (no changes)
S Control branch:
Display External Leads only
(no changes)
If the security has not been set on the DCP before, the
following appears:
FP Access: ? ? ?
Lock Unlock Save
F1
F2
F3
T o select the security level:
" Procedure
1. Press the
top-level menu.
2. Press the
three seconds. The following menu appears:
3. Select the security level:
Lock – To restrict access
key to ensure that you are at the
and keys simultaneously for
FP Access: Unlock
Lock Unlock Save
F1
F2
F3
The DualFlow DSUs are shipped from the factory with
the security level set to Unlock. When the DCP is locked,
only the Local branch appears on the control DSU and no
settings can be changed or saved.
Unlock – To provide full access
Press the appropriate function key (F1 or F2).
4. Select Save (F3).
4-213615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 68

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
4-22 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 69

Unit Configuration
Overview 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using the DCP to Set Configuration Options 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Editing Configuration Options 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Saving Configuration Options 5-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Example Using the DCP 5-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Option Tables 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Understanding the Tables 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5
Overview
After the DSU has been installed and any necessary
hardware switches or jumpers have been set, the software
configuration options must be set. Configuration options
are set via the DCP by accessing the Configuration
(Confg) branch of the menu (refer to the menu in
Appendix A).
There are eight configuration option areas within the
DSU:
• The Active area (Activ) contains the DualFlow
DSU configuration options currently being used.
• The Remote area (Remt) allows a selected
DualFlow DSU’s or DBM’s configuration options
to be retrieved so they can be displayed, edited,
and/or saved back to the selected DSU or DBM,
another DSU or DBM, or the local DSU or DBM.
The remote configuration option sets that can be
retrieved are Activ, Usr1, Usr2, and Usr3.
• The User 1 area (Usr1) is a customer-defined set of
stored configuration options. By having these
predetermined option sets stored, they can be
loaded rapidly as operating requirements change.
• The User 2 area (Usr2) is functionally the same as
Usr1, providing further flexibility when creating
configurations for various applications.
• The User 3 area (Usr3) is another customer-defined
option set.
NOTE
The next three option sets,
SyBC, SyBT, and DiDg, are
read-only storage areas;
changes cannot be saved to
these option sets.
• The factory-loaded configuration for the
Synchronous Backup application for a control DSU
is stored in the SyBC area.
• The factory-loaded configuration for the
Synchronous Backup application for a tributary
DSU is stored in the SyBT area.
• The factory-loaded configuration for the Dial
Diagnostic application is stored in the DiDg area.
NOTE
A DualFlow DSU cannot
configure a non-DualFlow DSU
remotely.
5-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 70

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Selection of Activ , Usr1, Usr2, Usr3, SyBC, SyBT, or
DiDg from the Load from menu brings a complete set of
configuration option into the working buffer. Once loaded,
the Edit/Save submenu appears (shown below).
Edit/Save:
SAVE DSU DSUpt
F1
F2
F3
Using the DCP to
Set Configuration Options
Any one of the following 6 configuration option sets
can be selected: DSU, DSU Port, DBM, DBM Port,
Diagnostic (DBM and General), and Backup. The
configuration options can be edited and then saved to the
Activ , Usr1, Usr2, or Usr3 storage areas.
In addition, an example is included to illustrate DCP
operation.
Editing Configuration Options
T o edit or change configuration options:
" Procedure
1. Select Local, or Remot (Remote) and the remote
DSU’s network address.
2. Select Confg (Configuration branch).
Press the
the function key (F1, F2, or F3) directly below
Confg.
key until Confg appears, then press
5. Select the option set (e.g., DSU, DSUpt, DBM,
etc.) to be edited.
The first configuration option within that set
appears. Page through each configuration option
within the set as follows:
a. Press the F1 key to go to the Next
configuration option. These configuration
options scroll or wrap around (e.g. first, then
last; or last, then first).
b. To return to the previous configuration option,
press the
Prev appears over the F1 key.
c. Select Prev by pressing the F1 key.
As you edit configuration options, be aware of the
following:
• The first line of each configuration option identifies
the option and its current setting.
If configuration data has been corrupted, ??? will
appear in place of the current value. If this occurs,
reset all configuration options, along with the
network address. Check the Backup Directory
entries, the poll list, and the DSU’s local telephone
number, as well.
• The second line displays all values that are
available for selection – three at a time, one above
each function key.
— Press the
selections into view.
— Press the function key (F1, F2, or F3) directly
below a value to select it.
— Select Next to proceed to the next option.
key instead of selecting Next.
or key to scroll other
3. Select Opts (Configuration Options).
4. Select storage area (Activ, Remt, Usr1, etc.) from
the Load from screen.
If the unit is a control and you select Remt, enter
the network address of the remote DSU.
5-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
— Select Prev to return to a previous option.
— Press the
submenu or screen, and select the next option
set to be edited.
key to return to the Edit/Save
Page 71

Unit Configuration
Saving Configuration Options
CAUTION
Be extremely careful when
saving configuration options to
avoid saving them to the wrong
location.
T o save edited configuration options:
" Procedure
1. From any configuration option in any option set,
press the key to return to the Edit/Save
submenu.
2. Press the F1 key below SAVE.
3. Select area (Activ, Remt, Usr1, etc.) on the
Save to screen.
• If Activ is selected, your changes take effect
immediately.
Example Using the DCP
In this example, load the configuration options stored
in the DiDg area. Change RTS Cntrl (in the DSU Port
option set) from FrcOn to DTE. Then, save the changes to
the Usr1 area and return to the top-level menu.
" Procedure
Press the DCP keys indicated by the shading.
V.35 DSU 56 C
Local Remot
F1
F2
Local Mode:
Stat Bckup Test
F1
F2
F3
F3
• If Usr1, Usr2, or Usr3 is selected, your changes
are stored for future use.
• If the unit is a control and Remt is selected, the
complete set of configurations (all option sets
available to the unit) are sent to the tributary
and saved to its Activ area.
Remember that you cannot save to the factoryloaded configuration areas.
Local Mode:
Bckup Test Confg
F1
F2
F3
Configure:
Opts PollL Dir
F1
F2
F3
Load from:
Activ Remt Usr1
F1
F2
F3
5-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 72

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Load from:
DiDg Activ Remot
F1
F2
F3
Edit/Save:
SAVE DSU DSUpt
F1
F2
F3
DTE Port: V.35
Next V.35 Prev
F1
F2
F3
RTS Cntrl: FrcOn
Next FrcOn DTE
Edit/Save:
SAVE DSU DSUpt
F1
F2
F3
Save to:
Activ Remot Usr1
F1
F2
F3
Save to: Usr1
Please wait . . .
F1
F2
F3
Save to: Usr1
Command Complete
F1
F2
F3
RTS Cntrl: DTE
Next FrcOn DTE
F1
F2
F3
F1
F2
F3
V.35 DSU 56 C
Local Remot
F1
F2
F3
5-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 73

Unit Configuration
Configuration Option Tables
This section contains a table for each option set that
can be found under the Configuration (Confg) branch, in
the order in which it appears in the menu.
This chapter includes the following option set tables:
• DSU Configuration Options (Table 5-1)
• DSU Port Configuration Options (T able 5-2)
• DBM Configuration Options (Table 5-3)
• DBM Port Configuration Options (T able 5-4)
• Diagnostic DBM Configuration Options (T able 5-5)
• Diagnostic General Configuration Options
(Table 5-6)
• Backup Configuration Options (T able 5-7)
Understanding the Tables
Refer to the appropriate tables when configuring the
DSU. Each configuration option is segmented into three
sections: the option as it appears on the DCP, an
explanation of the option, then the values that can be
selected or set.
Each table shows each configuration option as it is
displayed. As you refer to these tables, be aware of the
following:
• The first line shows each configuration option as
it appears on the DCP, followed by a colon (:), then
the default setting (the value set at the factory).
• The second line shows all selectable values, which
can be viewed on the DCP by scrolling to the left or
right using the
The first selection is always Next, which allows
you to go to the next configuration option in the set.
The last selection is always Prev, which allows you
to go back to the previous configuration option.
Possible selections wrap around so you can
immediately press the
saving key presses.
or key.
key to display Prev,
An explanation of the configuration option and its
selectable values follow, which includes:
• The full or unabbreviated name of the configuration
option, followed by a brief explanation of its
purpose or function.
• The selectable values for the configuration option,
which are listed with guidelines for when each
should be selected.
5-53615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 74

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-1
DSU Configuration Options
Rate(Kbps): 56
Next 64CC 64L 56 38.4 19.2 9.6 4.8 2.4 Prev
DSU Rate
and tributary DSUs must be set to the same value.
64CC — 64 kbps Clear Channel (on a 72 kbps circuit) with 3600 Series DSUs at both ends of the circuit.
64L — 64 kbps LADS operation.
TxClkSource: DDS
Next Int RXC Ext DDS Prev
Transmit Clock Source
Int — Internal clock source. Timing is taken from the DSU.
RXC — Receive clock source. The DSU generates its transmit timing from the receive data signal. This choice is
Ext — External clock source. The DSU is timed by the external Transmit Timing lead.
DDS — DDS Network. This source is used when the DSU is connected to a DDS network and the network
19.2 PowrLvl: +6
Next +6 0 –10 Prev
19.2 kbps Power Level
only appears when
+6 — For DDS network service.
0 — For alternate DDS service.
–10 — For LADS operation.
. Data rate (in kbps) on the digital circuit. Must be set to match the speed of the DDS circuit. Both the control
. Specifies the transmit timing source for the DSU.
provided for LADS configurations. It differs from the DDS selection during tests.
provides the timing.
. Selects the appropriate power level, in dBm, for operation at 19.2 kbps. This configuration option
Rate(Kbps)
is set to 19.2.
64KScramblng: Off
Next On Off Prev
64 kbps Scrambling
suppresses the possible simulation of network control codes by application data. This configuration option must be the
same at both the local and remote DSUs. This configuration option only appears when
On — Enables data scrambling.
Off — Disables data scrambling.
64KLatchLpbk: On
Next On Off Prev
64 kbps Latching Loopback
Channel operation. This configuration option only appears when Rate(Kbps) is set to 64CC.
On — DSU responds to the network latching loopback command. ON is required for compliance with AT&T
Off — DSU ignores the network latching loopback command.
V.54 Lpbk: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
V .54 Loopback
configurations.
Enab — This configuration option should be enabled if the remote DTE generates V.54 loopback sequences or if
Disab — This configuration option should not be enabled if the remote DTE does not support V.54 loopback
. Controls the data scrambler used with 64 kbps Clear Channel operation. Data scrambling
Rate(Kbps)
. Controls the DSU’s response to the network latching loopback sequence on 64 kbps Clear
Technical Reference 62310 – 1987.
. Enables ITU-T V .54 Loopback operation. This configuration option is supported for point-to-point
the DualFlow DSU is communicating with a non-AT&T DSU that supports V.54signaling.
sequences or other DSUs do not support V.54 signaling.
is set to 64CC.
5-6 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 75

Unit Configuration
Table 5-2
(1 of 3)
DSU Port Configuration Options
DTE Port: V.35
Next V.35 Prev
DTE Port
V.35 — For all available rates at distances up to 1000 feet.
RTS Cntrl: FrcOn
Next FrcOn DTE Prev
Request-to-Send Control
set to FrcOn, the DSU internally forces the RTS lead ON; if set to DTE, the DSU sends control mode idle (CMI)
whenever RTS is Off, and data mode idle (DMI) when RTS is ON.
For point-to-point configurations with nondisruptive diagnostics, or rate adaption, this configuration option is forced ON
internally.
FrcOn — The DSU keeps the internal RTS ON continuously, regardless of whether RTS at the DTE interface is ON
DTE — The DSU responds to RTS from the DTE.
CTS Cntrl: Std
Next Std =RTS Delay FrcOn Prev
Clear-to-Send Control
Std — CTS is normally controlled by the DTE’s RTS lead; however, the CTS lead can be affected by the
=RTS — RTS Control must be forced on (RTS Cntrl is set to FrcOn). In point-to-point configurations where RTS
Delay — CTS does not go Off in response to a network alarm condition or CMI. CTS goes Off only after a
FrcOn — Keeps CTS on as long as the DSU has power.
. Forces user data over the V.35 interface.
. This configuration option determines how the DSU will function with respect to the RTS lead. If
or Off.
. Controls the behavior of the CTS lead.
response to abnormal conditions, such as no signal or test mode, as determined by configuration options
RTS Cntrl, and Circ Assur.
Cntrl is forced ON, CTS Cntrl can also be forced ON if the DTE interfaces require no delay between RTS
Cntrl and CTS Cntrl (0 ms), but does not require an RTS-to-CTS transition.
successful backup connection is established.
AntiStream:Disab
Next Chang Prev
Antistreaming
constantly turned ON) by clamping the RTS lead of the tributary DSU.
If the tributary DTE turns ON RTS longer than the time specified for the Antistreaming configuration option, the tributary
DSU turns on its alarm indicator and clamps RTS to Off. Although the tributary DTE is not allowed to send, the DSU can
still respond to commands and is capable of being tested or disabled.
Upon detecting that RTS is no longer turned ON, the DSU turns Off its alarm and resets the streaming timer, and allows
the DTE to send data once again.
This configuration option only has an effect at a DSU configured with RTS Control set to DTE. It is disabled when RTS
Control is set to FrcOn.
Chang — Set timer to Disab, or to any value from 1 to 100 second(s) in increments of 1. When Disab is selected,
. Antistreaming provides circuit protection against a streaming DTE (a defective DTE that has its RTS lead
streaming terminal detection is not provided.
5-73615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 76

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-2
(2 of 3)
DSU Port Configuration Options
LSD Lead: Std
Next Std Delay FrcOn Prev
Line Signal Detect Lead
Std — LSD lead goes Off in response to a control mode idle (CMI) signal from the DDS network or DDS failure.
Delay — LSD does not go Off in response to a network alarm condition or CMI. LSD goes Off only after a
FrcOn — Keeps LSD on as long as the DSU has power.
DSR FrcOn: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
successful backup connection is established.
Data Set Ready Forced On
Enab — DSR remains ON as long as the device is working, regardless of tests and network alarms.
Disab — DSR functions as an active lead reflecting various test and alarm conditions and other options.
SystemStat: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
System Status
from the network.
Enab — Network alarm turns Off DSR.
Disab — Network alarm does not affect DSR.
. Controls the behavior of the DSR lead in response to a No Signal, Out-of-Service, or Out-of-Frame alarm
. Controls behavior of the Line Signal Detect lead.
. Provides the ability to override any other options controlling the Data Set Ready lead.
DSR on Tst: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Data Set Ready On in Test
Enab — DSR is ON continuously during testing, allowing a DTE that relies on DSR being ON to send test
Disab — DSR is Off during testing.
Circ Assur:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Circuit Assurance
RTS and RTS Cntrl is set to FrcOn, this configuration option is ignored.
A DDS Facility Alarm condition turns Off the CTS lead, regardless of the Circuit Assurance setting.
Enab — The DSU will turn Off the CTS lead if the DSU receives control mode idle (CMI) from the network.
Disab — The DSU is not affected by the receipt of CMI.
RespondRDL:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
messages to the DSU.
. Controls behavior of the CTS lead in response to a data signal from the network. If CTS Cntrl is set to
Respond to Remote Digital Loopback
Enab — Performs a Digital Loopback.
Disab — Ignores the Loopback command.
. Controls the behavior of the DSR lead during testing.
. Determines whether the DSU responds to a V.54 Remote Loopback request.
5-8 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 77

Unit Configuration
Table 5-2
(3 of 3)
DSU Port Configuration Options
LL by DTE: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Local Loopback by DTE
DSU is the active device. Whenever this lead is ON, the Local Loopback overrides any other diagnostic tests run by the
network.
Enab — The DTE forces the DSU into Local Loopback when the signal on Pin L is turned ON. Local Loopback
ends when the signal is dropped.
Disab — The DTE will not initiate Local Loopback in response to the signal on Pin L.
Bilat Lpbk:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Bilateral Loopback
Enab — When enabled, DTE Loopback occurs whenever a Digital Loopback occurs.
Disab — Disables Bilateral Loopback.
DTR Alarm: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Data Terminal Ready Alarm
30 seconds. The DCP displays
Enab — If DTR lead turns Off for 30 seconds, the DSU generates an alarm.
Disab — Regardless how long the DTR lead is Off, no alarm is generated.
. Controls using Pin L of the V.35interface by the DTE to initiate a Local Loopback when the
. If this configuration option is enabled, a DTE Loopback occurs when a Digital Loopback occurs.
. Causes the DSU to generate an alarm if DTR over the V.35 port is Off for more than
DTR Alarm
and reports the alarm to the NMS.
Table 5-3
(1 of 4)
DBM Configuration Options
Rate(Kbps): 9.6
Next 14.4 12.0 9.6 4.8 2.4 Prev
DBM Rate
14.4 — V.32bis modulation. This rate is not displayed for a 12.0 kbps DBM.
12.0 — V.32bis modulation.
9.6 — V.32bis modulation.
4.8 — V.32bis modulation.
2.4 — V.22bis modulation.
PrtSp(Kbps): 9.6 for V.32 DBM, 56 for Switched 56 DBM
Next 56 48 38.4 32 28.8 19.2 18.8 18.0 16.8 14.4 12.0 9.6 9.2
8.4 7.2 4.8 4.4 4.0 2.4 2.0 1.2 Disab Prev
Port Speed
only be displayed when a Switched 56 DBM is installed; 14.4 kbps will not be displayed for a 12.0 kbps DBM.
56 to — Selects the port speed. When a V.32 DBM is installed and the DiDg configuration is loaded the
1.2 default is 9.6 kbps. When a Switched 56 DBM with SyBC or SyBT configuration, the default is 56 kbps.
Disab — Sets the port speed to 0.
. Initial data rate (in kbps) for dial backup calls.
. If this value is set to less than the DBM rate, the DBM performs rate adaption. Rates above 14.4 kbps will
Only appears for a V.32 DBM.
5-93615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 78

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-3
(2 of 4)
DBM Configuration Options
TxClkSource: Int for a control DBM, RXC for a tributary DBM
Next Int RXC Ext Prev
Transmit Clock Source
Int — Internal clock source. The local DBM provides the timing. This source is used primarily in point-to-point
RXC — Receive clock source. This source is used primarily in multipoint tributary applications.
Ext — External clock source. This source is used primarily in applications where the connected DTE must
CarrLossDisc: Yes
Next Yes No Prev
applications.
provide the timing, such as when a 3616 V.32 DBM with its DBM
Yes and where timing is received from the digital bridge.
Carrier Loss Disconnect
signal becomes unacceptable.
Yes — Call is terminated upon loss of carrier.
No — For factory testing only. Never set Carrier Loss Disconnect to No. Doing so will cause an off-hook line
Auto Retrain:Yes
Next Yes No Prev
condition, resulting in excessive telephone charges.
Automatic Retrain
unacceptable.
Yes — Retraining is initiated automatically.
No — Retraining is not initiated automatically; however, the DBM will respond to a retrain request from a remote
Only appears for a V.32 DBM.
modem.
. Source of timing for the DBM.
. Controls whether the V.32 DBM terminates a call when the receive signal carrier is lost or the
. Controls the automatic start of a retrain sequence by the DBM when received signal quality becomes
Only appears for a V.32 DBM.
Primary Core
configuration option set to
Single Rate: No
Next Yes No Prev
Single Rate
must be set to Yes if rate adaption or non-disruptive diagnostics are enabled.
If Rate(Kbps) is set to 2.4, the DBM can only talk to a 2.4 kbps modem, regardless of the Single Rate setting. (Will only
train at 2.4 kbps.)
Yes — The DBM operates only at the rate for which it is configured.
No — The DBM will adjust its rate downward to correct a mismatch.
AutoAnswer: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Automatic Answer
Enab — DBM answers incoming calls.
Disab — DBM does not answer incoming calls.
. Determines whether the DBM will adjust its rate to resolve a rate mismatch with a remote DBM. Single Rate
Only appears for a V.32 DBM.
. Controls whether the DBM answers incoming calls.
5-10 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 79

Unit Configuration
Table 5-3
(3 of 4)
DBM Configuration Options
Call Setup:None
Next None Pswrd Cllbk Alarm Prev
Dial Backup Call Setup
selections use a proprietary password exchange to ensure that the DBM does not route line data to the DBM’s DTE
interface. If security fails, the call is disconnected. These password exchanges only work between 3600 Series DBMs.
None — No security. Outgoing calls have no security. For incoming calls, if the calling device is not a 3600 Series
DBM, an answering DBM with Call Setup set to None will automatically switch from Standby to Dial
Backup mode after the time-out period has expired.
Pswrd — Intermediate security level. The originating and answering DBMs must exchange valid passwords to
establish a call.
Cllbk — Highest security level. The originating and answering DBMs exchange passwords and disconnect; the
answering DBM calls the originator back with a second exchange of passwords.
Alarm — Causes a DBM to answer incoming calls only when the DSU reports a Facility Alarm. No security
checking is performed. This feature is for customers that provide data services to other customers that
may not have non-3600 Series DBMs.
RxPwd:
Next Chang Prev
Receive Password
remote DBM’s TxPwd). The maximum password length is 10 characters. The default, *, is a wildcard meaning “any
character string.”
Chang — Enter up to 10 characters for the receive password. An underscore ( _ ) to the immediate right of the last
password character is required for passwords of fewer than 10 characters in length. To make the
password invisible to the DCP, enter a comma ( , ) as the first character.
. Establishes the security level on call setup attempts. The Password and Callback security
. The password that the DBM expects to receive from a remote DBM (must be the same as the
When Call Setup is set to None or Alarm, this configuration option will not appear
.
TxPwd:
Next Chang Prev
Transmit Password
RxPwd). The maximum password length is 10 characters. The default is a null password.
None or Alarm, this configuration option will not appear
Chang — Enter up to 10 characters for the receive password. An underscore ( _ ) to the immediate right of the last
Dial T est:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Dial Test
Test Failure alarm in its health and status. A Dial Test occurs once every 60 minutes until a failure occurs. Then, the test
repeats every minute until the network recovers.
If enabled, the V.32 DBM periodically tests receipt of dial tone, the 4-wire Switched 56 DBM goes off-hook and checks
for receipt of a data mode idle (DMI) signal burst (referred to as
goes off-hook and checks for receipt of a proceed-to-select message from the switch.
Enab — Enables the Dial Test.
Disab — Disables the Dial Test.
. When enabled, the DBM periodically checks for a signal or dial tone. If the test fails, the DSU reports a Dial
. The password that the DBM sends to a remote DBM (must be the same as the remote DBM’s
When Call Setup is set to
.
password character is required for passwords of fewer than 10 characters in length. To make the
password invisible to the DCP, enter a comma ( , ) as the first character.
winkback detection
), and the 2-wire Switched 56 DBM
5-113615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 80

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-3
(4 of 4)
DBM Configuration Options
Primary Core:No
Next Yes No Prev
DBM Primary Core
Switched 56 DBM.
Yes — Enables the Primary Core so the unit operates like a 3600 Series DBM-V, DBM-S, or DBM-D.
No — Disables the Primary Core so that the DSU function is active.
DTRCallCon:Orig for SyBC, Ansr for DiDg and SyBT configurations
Next Orig Ansr Disab Prev
Data Terminal Ready Call Control
DBM originates a backup. When set to Ansr, the DBM only answers a backup call when DTR is active. The DTR lead is
ignored when DTRCallCon is disabled.
. When enabled, the DSU is disabled and the DBM is enabled so that it functions as a V.32 DBM or
No is the factory-set (default) setting for a
DualFlow DSU.
. DTRCallCon uses the state of the DTR lead to control backup. When set to Orig, the
Orig — DTR lead is used for
when DTR is raised based upon the number stored in the Backup Directory specified by the Backup Dir
configuration option, and drops the call when DTR goes low. The DBM will try to call the number ten
times, or until
(
A phone number must have been entered into the Backup Directory. If a call cannot be completed, check
outgoing
T riesTimeOut
Expanded Health and Status messages
Ansr — DTR lead is used for
Disab — Disables DTR Call Control; the state of the DTR lead is ignored.
EchoCancel:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Echo Cancel
network is US SPRINTr or when the network has echo cancellers. Disable this configuration option if the DBM is
interfaced to an AT&T Switched 56 kbps 4-wire service facility.
Enab — Enables Echo Cancel.
Disab — Disables Echo Cancel.
Remot DBM:4-wire
Next 2-wire 4-wire Prev
Remote Dial Backup Module
process completion time can be determined. This configuration option only appears for a 2-wire Switched 56 DBM with
EchoCancel
2-wire — Originating remote DBM is a 2-wire Switched 56 DBM, so the process completes in 460 milliseconds.
4-wire — Originating remote DBM is a 4-wire Switched 56 DBM, so the process completes in 3.85 seconds.
Msg Clamp: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Message Clamping
from the remote DBM.
Enab — Received Data (RXD) is held to MARK and LSD is turned Off during diagnostic exchanges. This prevents
Disab — DSU passes diagnostic messages to the DTE interface. Use the Disable setting if the remote DSU is
goes low or will not answer an incoming call if DTR is low.
. This configuration option is only displayed for a Switched 56 DBM and is required if the Switched 56 kbps
. Specifies the identity of the far-end Switched 56 DBM so the appropriate dial backup
enabled. If unsure of whether the remote DBM is 2-wire or 4-wire, select 4-wire.
. Controls behavior of the data leads when disruptive diagnostic tests and commands are received
diagnostic messages from reaching the DTE interface.
configured for switched RTS (RTS Control is set to DTE).
incoming
calls. When Orig is selected, the DBM originates (dials out) a backup call
expires. If Multicall is also enabled, the DBM uses the multiple calling cycle.
.)
calls. When Ansr is selected, the DBM drops a backup call when DTR
5-12 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 81

Unit Configuration
Table 5-4
(1 of 3)
DBM Port Configuration Options
DTE Port: 232
Next 232 V.35 Prev
DTE Port
Primary Core
232 — For the EIA-232-D connector, the maximum cable length from the DBM to the router is 34 feet with
V.35 — Only appears if Primary Core (DBM option set) is set to Yes. For the V.35 connector, all rates are
RTS Cntrl: FrcOn for DiDg, DTE for other configurations
Next FrcOn DTE Prev
Request-to-Send Control
FrcOn — The DBM keeps the internal RTS ON continuously, regardless of whether RTS at the DTE interface is ON
DTE — The DBM responds to RTS from the router.
CTS Cntrl: Std
Next Std =RTS FrcOn Prev
Clear-to-Send Control
Std — CTS is normally controlled by the router’s RTS lead; however, the CTS lead can be affected by the
=RTS — CTS follows RTS.
FrcOn — CTS remains ON as long as the DSU has power.
. Selects which DTE port will be used for DBM data. This configuration option is forced to 232 (EIA-232) unless
is set to Yes.
shielded cable and 68 feet with unshielded cable when operating at 56 kbps.
available for distances up to 1000 feet.
. This configuration option determines how the DBM will function with respect to the RTS lead.
or Off. FrcOn should be used when the DBM is connected to the console port of a router since the router
does not support RTS signalling.
. Controls the behavior of the CTS lead.
response to abnormal conditions, such as no signal or test mode.
AntiStream:Disab
Next Chang Prev
Antistreaming
constantly turned ON) by clamping the RTS lead of the tributary DBM.
If the tributary DTE turns ON RTS longer than the time specified for the Antistreaming configuration option, the tributary
DBM turns on its alarm indicator and clamps RTS to Off. Although the tributary DTE is not allowed to send, the DBM can
still respond to commands and is capable of being tested or disabled.
Upon detecting that RTS is no longer turned ON, the DBM turns Off its alarm and resets the streaming timer, and allows
the DTE to send data once again.
This configuration option only has an effect at a DBM configured with
Chang — Set timer to Disab, or to any value from 1 to 100 second(s) in increments of 1. When Disab is selected,
LSD Lead: Std
Next Std FrcOn Prev
Line Signal Detect Lead
Std — LSD lead goes Off in response to a loss of carrier or a switched network failure.
FrcOn — Keeps LSD on as long as the DBM has power.
. Antistreaming provides circuit protection against a streaming DTE (a defective DTE that has its RTS lead
RTS Cntrl
streaming terminal detection is not provided.
. Controls behavior of the Line Signal Detect lead.
set to DTE.
5-133615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 82

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-4
(2 of 3)
DBM Port Configuration Options
DSR FrcOn: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Data Set Ready Forced On
Enab — DSR remains ON as long as the device is working regardless of tests and network alarms.
Disab — DSR functions as an active lead reflecting various test and alarm conditions and other options.
DSR on Tst: Enab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Data Set Ready On in Test
Enab — DSR is ON continuously during testing, allowing a DTE that relies on DSR being ON to send test
messages to the DBM.
Disab — DSR is Off during testing.
RespondRDL: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Respond to Remote Digital Loopback
Enab — Performs a Digital Loopback.
Disab — Ignores the Loopback command.
RL by DTE: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Remote Digital Loopback by DTE
DTE or router to initiate a Remote Digital Loopback.
NOTE: Use of Pin 18 or Pin L is determined by the DBM’s
Enab — The DTE or router forces the DBM to request a Remote Digital Loopback when the signal on Pin 21 or
Pin N is turned ON. Remote Digital Loopback ends when the signal is dropped.
Disab — The DTE or router cannot initiate Remote Digital Loopback.
. Provides the ability to override any other options controlling the Data Set Ready lead.
. Controls the behavior of the DSR lead during testing.
. Determines whether the DBM responds to a V.54 Remote Loopback request.
. Allows Pin 21 of the EIA-232-D/V.24 interface or Pin N of the V.35 interface by the
DTE Port
configuration option.
Bilat Lpbk: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Bilateral Loopback
Enab — When enabled, DTE Loopback occurs whenever a Digital Loopback occurs.
Disab — Disables Bilateral Loopback.
Ext Leads: Rate
Next ExtLd Rate RPowr Prev
External Leads
These leads can be controlled and monitored from the DCP or a 6700 or 6800 Series NMS.
ExtLd — Enables Pins 12 and 13 as output (control) and Pins 19 and 23 as input (alarm) leads. When enabled,
Rate — Pin 12 on the port is turned Off to indicate that the DBM is in fallback mode. If the port does not fall back
RPowr — Functions similarly to ExtLd, but the inputs report power failure or fan alarms when a redundant power
5-14 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
. If this configuration option is enabled, a DTE Loopback occurs when a Digital Loopback occurs.
. Controls the general-purpose leads on the EIA-232-D/V.24 interface except when Rate is selected.
Pins 12 and 13 output +12V when ON and –12V when Off. Pins 19 and 23 recognize voltages from +2.2V
to +12V as ON (reported as an External alarm) and –12V to +.8V as Off.
and remain at the same speed, then the fallback feature in the DCE or router connected to that port
should not be enabled.
supply is installed in the COMSPHEREr 3000 Series Carrier.
Page 83

Unit Configuration
Table 5-4
(3 of 3)
DBM Port Configuration Options
CCN by EL: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Configuration Change Notification by External Leads
event. This configuration option only has an effect if
Enab — Change in state of a general-purpose lead signals CCN to the NMS.
Disab — General-purpose lead changes do not set a CCN event.
DTR Alarm: Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Data Terminal Ready Alarm
displays
Enab — If DTR lead turns Off for 30 seconds, the DSU generates an alarm.
Disab — Regardless how long the DTR lead is Off, no alarm is generated.
Async→Sync: Enab for DiDg, Disab for SyBC and SyBT configurations
Next Enab Disab Prev
DTR Alarm
and reports the alarm to the NMS.
Asynchronous-to-Synchronous Conversion
Enab — Configures the DBM as asynchronous (asynchronous-to-synchronous conversion takes place).
Disab — Configures the DBM as synchronous.
AsyncBit/Char: 8 for DiDg configuration
Next 6 7 8 9 10 Prev
Asynchronous Bits per Character
stop bits. This configuration option only applies to the Dial Diagnostic (DiDg) configuration.
6 to 10 — Selects the asynchronous bits per character. When Stop Bits is set to 2, 10 will not be displayed.
. Causes the DSU to generate an alarm if DTR is Off for more than 30 seconds. The DCP
. Sets the DBM port for asynchronous or synchronous operation.
. Specifies the length of a character, including the parity bit but excluding the start and
. Controls using the general-purpose output leads to set a CCN
Ext Leads
is set to ExtLd.
Stop Bits: 1 for DiDg configuration
Next 1 2 Prev
Stop Bits
Dial Diagnostic (DiDg) configuration.
1 to 2 — Selects the number of stop bits to be used. When the AsyncBit/Char configuration option is set to 10, 2
Overspeed: 2.3 for DiDg, not applicable for other configurations
Next 1.0 2.3 Prev
Overspeed
only displayed when the Async→Sync configuration option is enabled.
1.0 — Selects the basic overspeed range. Basic range provides 1.0% overspeed in the DTE or router
2.3 — Selects the overspeed percentage for extended range. Extended range provides 2.3% overspeed in the
. Specifies the number of stop bits in an asynchronous character. This configuration option only applies to the
will not be displayed.
. Selects the overspeed range of the asynchronous-to-synchronous converter. This configuration option is
asynchronous data rate.
DTE or router asynchronous data rate.
5-153615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 84

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-5
Diagnostic DBM Configuration Options
Diag Type: Disr
Next NonD Disr None Prev
Diagnostic Type
set consistently for all Dualflow DBMs on the same circuit.
NonD — Nondisruptive Diagnostics. An in-band secondary channel transport is derived to carry diagnostics data
Disr — Disruptive Diagnostics. The same (primary) channel that carries user-transmitted data between the
None — No diagnostic communications with remote devices; only local diagnostics are allowed.
2nd Ch(bps): 400
Next 100 400 800 1200 1600 Prev
In-band Secondary Channel Diagnostic T ransport Speed (in bps)
(nondisruptive diagnostics) is selected and there is no excess bandwidth available for in-band secondary channel
transport operation. (This configuration option only appears when DiagType = NonD.)
The selection entered here allocates DBM port bandwidth to the in-band secondary channel transport. For example, both
the DBM port speed and the backup line speed are 9.6 kbps, and the Diagnostic Type entered is NonD and the In-band
Secondary Channel Diagnostic Transport Speed entered is 400. The resulting DBM port speed is 9.2 kbps. (Refer to the
following list for valid diagnostic speeds.)
If the DBM Rate(Kbps) is equal to
Port Speed: Valid diagnostic speeds are:
1.2 100, 400
2.0 100, 400
2.4 100, 400, 800
4.0 100, 400, 800
4.8 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
7.2 100, 400, 800, 1200
8.4 100, 400, 1600
9.6 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
12.0 100, 400, 800, 1200
14.4 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
16.8 100, 400, 800, 1200
18.0 100, 400, 1200
19.2 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
28.8 100, 400, 800
32 100, 400, 800, 1200
38.4 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
48 100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
56 100, 400, 800, 1200
. Defines the diagnostic interaction between the control and tributary DBMs in Backup mode. It must be
between the control and the tributary DBMs.
control and the tributary DBMs also carries diagnostic data. This mode should be selected for
compatibility with earlier releases that use session-disruptive diagnostics.
. Determines the DBM’s port speed when NonD
5-16 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 85

Unit Configuration
Table 5-6
Diagnostic General Configuration Options
Position: Cntrl for SyBC, Trib for DiDg and SyBT configurations
Next Cntrl Trib Prev
Network Position
Cntrl — Control
Trib — Tributary
RemoteDiag:Enhan
Next V.54 Enhan Prev
Remote Diagnostics
V.54 — The V.32 DBM generates a ITU-T V.54 loopback sequence. This selection does not appear for a
Enhan — The V.32 DBM uses enhanced 3600e protocol and the Switched 56 DBM uses Br56. Both the control and
Link Delay: 0s
Next 0s 1s 2s 5s 10s 20s 50s Prev
Link Delay
downstream. This configuration option does not appear when Diag Type (Diagnostic DBM option set) is set to Disr and
Position is set to Trib (DiDg and SyBT configurations);
control.
. Determines the DSU’s position in the network, and defines its test and diagnostic capabilities.
. Determines the type of loopback message generated by a DBM.
Switched 56 DBM.
tributary must be set for Enhan.
. Controls the additional time (in seconds) that a control DBM will wait for a response from a device one level
this configuration option only appears for a DBM configured as a
NOTE: If diagnostic time-outs are occurring during polling, increase the link delay to the next higher value.
0s to 50s — Sets the time the DBM will wait for a downstream device response.
Packet Delay: 0s
Next 0s 1s 2s 5s Prev
Packet Delay
configuration option only appears for a DBM configured as a control
NOTE: Must be used when the DualFlow DSU’s diagnostic channel operates over packet switch, satellite
0s to 5s — Sets the time the DBM will wait for the NMS.
. Controls the time (in seconds) that a control DBM will wait for a packet to complete from an NMS.
.
communications, or other facilities that provide extended throughput delays.
This
5-173615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 86

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table 5-7
(1 of 2)
Backup Configuration Options
Auto Bckup:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Automatic Backup
detection of No Signal or Out-of-Service codes, or excessive bipolar violations. (Automatic dial attempts begin after the
Network Time-out expires.)
NOTE: The backup connection is made through the EIA-232 port.
Enab — Upon detecting a failure of the DDS network, the DSU waits for a period equal to DDS Timeout, and if the
Disab — No automatic attempt is made to establish a dial backup connection.
Backup Dir: 1
Next Chang Prev
Backup Directory
display shows the identifier of the current default dial string to be used to set up a dial backup call for automatic backup
as described in the Auto Bckup configuration option, or when the backup command is received from the DCP or the
NMS.
Chang — Produces a data entry display for changing the directory entry identifier.
BckupOnCMI:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Backup on Control Mode Idle
condition as a facility alarm to trigger automatic dial backup. Configuration option
Enab — Upon detecting CMI for 250 to 500 milliseconds from the network, the DSU attempts to establish a dial
Disab — No attempt is made to establish a dial backup connection if CMI is detected.
. Controls automatic initiation of a call setup attempt upon failure of the DDS network, defined as
DDS network is still down, it attempts to establish a dial backup connection to the number specified by
the Backup Directory pointer after the Network Time-out expires.
. The DBM can store 10 dial strings or telephone numbers, identified by the numbers 1 through 10. This
. This configuration option determines whether the DSU treats a control mode idle (CMI)
Auto Bckup
backup connection to the router after the DDS Time-out expires. When enabled, CMI will also generate a
Facility Alarm (FA). Do not use this configuration option if the DSU is configured to generate CMI.
must be enabled.
AutoRestor:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Automatic Restoration
determines that the DDS circuit has been returned to service.
DTRCallCon
When
Enab — Restoral of the DDS circuit triggers automatic restoration (after the Restoration Time-out expires).
Disab — Restoral of the DDS circuit does not trigger automatic restoration. Disable when
NtwkTimOut: 0:20 for a control DSU, 01:00 for a tributary DSU
Next Chang Prev
Network Time-out
sequence is made. This configuration option only has an effect if
. Controls whether the DSU automatically terminates the dial backup call when the DSU
is enabled (set to Orig or Ansr), disable
. Length of time the DDS network must remain out of service before the dial backup call attempt
AutoRestor
Auto Bckup
.
is set to Enab.
DTRCallCon
is enabled.
When configured for
nondisruptive diagnostics or rate adaption, this configuration option must be set to greater than or equal to 20 seconds.
Chang — Calls up a data entry display for changing the current value which can range from 1 second to
30minutes. The cursor has two positions: a minutes field with a range of 0 to 29, and a seconds field with
a range of 00 to 59.
5-18 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 87

Unit Configuration
Table 5-7
(2 of 2)
Backup Configuration Options
RestorTimOut: 5m
Next Chang Prev
Restoration Time-out
attempted. This configuration option only has an effect at a DSU configured with Automatic Restoration enabled.
Chang — Calls up a data entry display for changing the current value, with a range of 1 to 60 minutes.
TriesT imeOut:15m
Next Chang Prev
Call Attempts Time-out
configuration option only has an effect if
whether MultiCall is enabled (multiple calling cycle) or disabled (normal calling cycle).
Only 10 call attempts are made for the normal calling cycle. If a call attempt is in progress and the timer expires, the call
attempt will not be aborted.
Chang — Calls up a data entry display for changing the current value, with a range of 1 to 60 minutes.
MultiCall:Disab
Next Enab Disab Prev
Multiple Calls
each valid dial string in the directory , or selects the normal calling cycle. This configuration option only has an effect if
Auto Bckup
Enab — The DBM makes one attempt to call the dial string in the directory pointed to in the Backup Directory
Disab — The normal calling cycle is used: three call attempts, a 5-minute wait, three more call attempts, another
NOTE: Multicall must not be enabled unless successive telephone numbers in the Backup Directory are different. In
. Selects the multiple calling cycle in which the DBM steps through the Backup Directory , attempting to call
is set to Enab or if
addition, duplicate telephone numbers should be avoided. These precautions prevent the DBM from making
excessive call attempts to the same telephone number.
. Length of time the DDS network must be back in service before automatic restoration is
. Sets an overall time limit for dial backup call attempts upon failure of the DDS network. This
Auto Bckup
DTRCallCon
configuration option (default is the first dial string in the directory). If the attempt fails, the DBM makes an
attempt to call the next dial string in the directory , and so on until either a call is completed or the DBM
cycles through all the dialed strings in the Backup Directory , ignoring blank entries. The DBM then waits
five minutes and begins the calling cycle again until the TriesTimeOut period expires.
5-minute wait, etc., until the TriesTimeOut period expires.
is set to Orig.
is set to Enab, or if
DTRCallCon
is set to Orig, regardless of
5-193615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 88

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
5-20 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 89

DSU Menu
Overview A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Menu Structure A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Top-Level Menu A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local/Remote Menu Subbranches A-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
Overview
This menu is your map through the DSU’s various
functions and pathways. Compare it against the menus
that appear as you move through procedures. You will
learn to quickly access where you want to go on the menu
when operating the DSU.
Menu Structure
The DSU’s operation is represented as menu selections
that branch downward from its starting point, the top-level
menu, like the roots of a tree. The menu is sometimes
referred to as a menu tree.
Top-Level Menu
The top-level menu is the starting point for all DSU
operations. You can always return to this point from
anywhere in the menu by pressing the key. Pressing
this key immediately terminates any operation or work in
progress.
The following shows an example of the top-level menu
for a standalone Model 3615 DSU that is configured as a
control operating at 9.6 kbps, with an NMS message
waiting.
232 DBM 9.6 C
Local Remot Msg
F1
The following information is displayed:
Line 1 – Source of the information being displayed
–DSU’s current function or mode (In this
example, the unit is operating as a DBM,
not as a DSU.)
–DSU’s data rate
–DSU’s network designation (Here the
DSU is a control.)
If this display was for a Model 3616 (a
carrier-mounted DSU), the carrier (nest or
rack) and slot numbers would appear
instead of port interface (e.g., Carrier 2
and Slot 16 would appear as 2:16).
F2
F3
Line 2 – Menu selections, one appearing directly
over each function key (F1 and F2).
Continued on Page A-4.
A-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 90

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
A-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 91

DSU Menu
A-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 92

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Continued from Page A-1.
If both DDS and dial connections have been made,
then every 10 seconds the top-level menu screen
alternates status information between the DDS and dial
ports (V.35 for the DDS line and active DBM port for the
dial line).
V.35 DSU 56 C
Local Remot Msg
F1
F2
F3
In the example above, the top-level menu is displaying
the status of the DDS port interface.
Press a function key to select one of the following
branches:
• Local branch
• Remote (Remot) branch – Only available to a DSU
configured as a control or a point-to-point tributary
with a dial connection.
• Messages (Msgs) branch – Only appears when a
message from the NMS is waiting. Once the
message is cleared, this branch no longer appears.
Local/Remote Menu Subbranches
The Local branch menu has five subbranches; the
Remote branch menu has four:
• The Status (Stat) branch provides reports on the
health and status of the DSU and DBM, the DTE
interface, the identity of the DSU and DBM, the
status of the connected DTE’s EIA-232 and V.35
interfaces, and if there is a dialed connection, the
quality of the dial network circuit.
• The Backup (Bckup) branch controls operation of
the dial backup feature. This branch is only
available from the Local branch.
• The Test branch provides extensive testing
capabilities for the DSU; the DDS circuit; the
DBM; and the backup circuit, if there is a backup
call established.
NOTE
If the Test branch does not
appear, the DSU is in Display
mode (values can be read, but
not changed).
Only authorized persons can
change configuration option
values for the DSU. Contact your
System Administrator
for further
information.
• The Configuration (Confg) branch allows you to
customize DSU software configuration options, to
enter and change telephone numbers, and to change
the DSU network address.
• The Control (Ctrl) branch allows you to display
and change external leads, and enable or disable the
DSU or DBM.
Each selection leads to a functional subbranch of the
menu.
Only three menu selections appear at a time, one over
each function (F1, F2, F3) key. Press the
and
keys to scroll backward or forward through menu
selections.
• Press the key to go to the previous
screen/menu display.
• Press the key to return to the starting point –
the top-level menu.
Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for additional DCP operation
information.
A-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 93

Configuration Worksheets
Overview B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Instructions B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
Overview
The Configuration Worksheet summarizes the DSU’s
software configuration options and the selections that can
be set for each. The Configuration Option T ables in
Chapter 5 provide further explanation of each
configuration option should you need to change settings,
as well as an example showing how to change or edit
these options.
Refer to the Configuration Option Tables section,
Chapter 5, when configuring the unit, or when more
detailed configuration information is needed.
Instructions
Configuration Worksheets can be used for reference, or
they can be used to record changes made to the DSU’s
configuration options or to record the configurations
saved to the Usr1, Usr2, or Usr3 storage areas.
1. Complete the information at the top of each
worksheet first.
If you have a Model 3615 (standalone) DSU, enter
your site in the location field.
If you have a Model 3616 (carrier-mounted) DSU,
enter the DSU’s carrier and slot location. Also,
make a copy for each DSU.
2. Circle the appropriate setting(s) – either all of the
configuration option changes, or only those
changed from their factory-loaded (default)
settings.
3. Store the worksheets so they will be available
when needed.
B-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 94

DualFlow DSU Configuration Worksheet (1 of 2)
Date:_____________________________________________ Location:____________________________________________
Local Phone No: ( j )_____________________________
Device:___________________________________________ Local Addr:__________________________________________
Serial No:_________________________________________ Tributary Network Addr:________________________________
DSU Value
Rate(Kbps) 64CC, 64L, 56, 38.4, 19.2, 9.6, 4.8, 2.4
TxClkSource Int, RXC, Ext, DDS
19.2 PowrLvl + 6, 0, –10
64KScramblng On, Off
64KLatchLpbk On, Off
V.54 Lpbk Enab, Disab
Hardware Straps Value
DDD Interface * Permissive, Programmable
Frame Ground/
Signal Ground
Connected, Disconnected
Test Mode Indication Enabled, Disabled
{ V.32 DBM only *Switched 56 DBM only
{{ Only if Call Setup set to Pswrd ** 2-wire Switched 56 DBM only
DSU Port (V.35) Value
DTE Port V.35
RTS Cntrl FrcOn, DTE
CTS Cntrl Std, =RTS, Delay, FrcOn
AntiStream
(Chang)
Disab (1–100 sec)
LSD Lead Std, Delay, FrcOn
DSR FrcOn Enab, Disab
SystemStat Enab, Disab
DSR on Tst Enab, Disab
Circ Assur Enab, Disab
RespondRDL Enab, Disab
LL by DTE Enab, Disab
Bilat Lpbk Enab, Disab
DTR Alarm Enab, Disab
DBM Value
Rate(Kbps){
14.4, 12.0, 9.6, 4.8, 2.4
PrtSp(Kbps) 56, 48, 38.4, 32, 28.8, 19.2, 18.8, 18.0,
16.8, 14.4, 12.0, 9.6, 9.2, 8.4, 7.2, 4.8, 4.4,
4.0, 2.4, 2.0, 1.2, Disab
TxClkSource{
Int, RXC, Ext
CarrLossDisc{
Yes, No
Auto Retrain{
Yes, No
Single Rate{
Yes, No
AutoAnswer Enab, Disab
Call Setup None, Pswrd, Cllbk, Alarm
RxPwd{{
(Chang)
(up to 10 digits)
TxPwd{{
(Chang)
(up to 10 digits)
Dial Test Enab, Disab
Primary Core Yes, No
DTRCallCon Orig, Ansr, Disab
EchoCancel * Enab, Disab
Remot DBM ** 2-wire, 4-wire
Msg Clamp Enab, Disab
Page 95

DualFlow DSU Configuration Worksheet (2 of 2)
DBM Port (232) Value
DTE Port
232, V.35}
RTS Cntrl FrcOn, DTE
CTS Cntrl Std, =RTS, FrcOn
AntiStream
(Chang)
Disab (1 to 100 sec)
LSD Lead Std, FrcOn
DSR FrcOn Enab, Disab
DSR on Tst Enab, Disab
RespondRDL Enab, Disab
RL by DTE Enab, Disab
Bilat Lpbk Enab, Disab
Ext Leads ExtLd, Rate, RPowr
CCN by EL Enab, Disab
DTR Alarm Enab, Disab
Async→Sync
Enab, Disab
AsyncBit/Char 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Stop Bits 1, 2
Overspeed 1.0, 2.3
{ V.32 DBM only
{{{ Only if Diag Type set to NonD
} Only if Primary Core set to Yes
}} Only at the Control
Diagnostic DBM V alue
Diag Type NonD, Disr, None
2nd Ch(bps){{{
100, 400, 800, 1200, 1600
Diagnostic General Value
Position Cntrl, Trib
RemoteDiag
V.54{, Enhan
Link Delay }}
0s, 1s, 2s, 5s, 10s, 20s, 50s
Packet Delay }}
0s, 1s, 2s, 5s
Backup Value
Auto Bckup Enab, Disab
Backup Dir
(Chang)
(1–10)
BckupOnCMI Enab, Disab
AutoRestor Enab, Disab
NtwkTimOut
(Chang)
min and sec (1 to 30 min)
RestorTimOut
(Chang)
min and sec (1 to 60 min)
TriesTimeOut
(Chang)
min and sec (1 to 60 min)
MultiCall Enab, Disab
Backup Directory Dial String
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Page 96

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
B-4 March 1999 3615-A2-GB20-30
Page 97

Status Indicators and
Control Panel Messages
Overview C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Indicators C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Panel Messages C-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Format C-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Health and Status Messages C-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Progress Messages C-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Error Messages C-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview
This appendix describes the status indicators on the
DSU’s control panel, the diagnostic control panel (DCP)
for a Model 3615 and the shared diagnostic control panel
(SDCP) for the Model 3616.
Informational messages that may appear on the control
panel while a command is executing, or when a command
is prevented from executing, are also described.
C
Status Indicators
Status indicators provide information on the current
operating condition of the DSU. The status indicators of
the Model 3615 DSU appear on the DCP’s faceplate. The
status indicators for the carrier-mounted Model 3616 DSU
are spread across the the faceplate of the DSU, the SDCP,
and the faceplate of the shared diagnostic unit (SDU), if
installed. Refer to the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier
Installation Manual for SDU status indicator information.
The DSU DCP and SDCP status indicators are described
in Tables C-1 and C-2.
C-13615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 98

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table C-1
DSU Status Indicators
Label Color Description
OK Green Health and status indicator: DSU operation is normal. (The DSU has not
detected any of the faults listed under Alrm, below.)
This indicator flashes two times per second if a message from the NMS is
present.
Alrm Red Health and status indicator:
There is a fault in the local or remote DSU, DBM, or DDS facility , or there is a
corrupted configuration.
The following alarms at the local or remote DSU cause the Alrm status
indicator on the affected DSU to light:
Configuration Corrupt
Device Fault
Dial Tone Test Failure
DTR Alarm
Facility Alarm
MUX Failure
No Response
Redundant Power Alarm
Streaming Terminal
Subnetwork Alarm
Out-of-Frame Threshold
Out-of-Service
T est Yellow Active device (DSU or DBM) is either performing a test or other DSUs or DBMs
are in Test mode.
1
Dial Yellow DBM is active
Rapid flashing: Call setup in progress
Slow flashing: Call established but in Standby mode
Steady ON: Backup call established and active
TXD, RXD, RTS,
CTS, DSR, DTR,
LSD
Front Panel
(Model 3616 only)
1
The DSU or DBM is automatically put into Test mode when a remote DSU or DBM is performing a disruptive test (e.g., a
Green Internal lead states at the DSU/DTE interface
Control circuit active or
Data circuit SPACE(ing).
Yellow DSU is currently selected at the SDCP.
.
)
time
(The SDCP addresses one DSU at a
(circuit designations)
:
Local Loopback (LL) at the control DSU. A DSU or DBM in Test mode has its DTE interface turned Off).
C-2 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
Page 99

Status Indicators and Control Panel Messages
Table C-2
SDCP Status Indicators
Label Color Description
OK Green Health and status indicator for the selected DSU; mirrors the OK indicator on
the DSU faceplate.
Alrm Red Health and status indicator for the selected DSU; mirrors the Alrm indicator on
the DSU faceplate.
BckUp Yellow Mirrors the BckUp LED on the selected DSU.
Test Yellow Mirrors the Test indicator on the selected DSU.
EC Green Error Correction indicator is for future use by dial network modems.
Control Panel Messages
This section shows the screen format of messages
appearing on the control panel and describes the various
messages.
Three types of messages are included: health and
status, progress, and error messages.
Format
The format of the control panel messages is shown
below .
Command Name
Message
F1
F2
F3
Health and Status Messages
There are three types of health and status messages:
• Device Health and Status messages are described in
T able C-3
• Expanded Health and Status messages are
described in Table C-4
• Subnetwork Health and Status messages are
described in Table C-5
C-33615-A2-GB20-40 July 1999
Page 100

COMSPHERE DualFlow Data Service Units
Table C-3
(1 of 3)
Device Health and Status Messages
Message Condition
CMI Fac Alarm Facility Alarm on CMI (FacAlOnCMI) configuration option is enabled and control mode
idle (CMI) is being received.
Config Corrupt Configuration is corrupt. Reset all configuration options from one of the default
(factory-loaded) option sets stored in the DiDg, SyBC, or SyBT area.
DBM:Device Fail Internal failure is detected in the DBM.
DBM:Disable DBM transmitter is disabled. DBM is in Idle mode, but no calls can be initiated or
answered.
DBM F:
nn.n
DBM:
nn.n
ExternBU
DBMTst:
alarm
mode nn.n
test,init
A DBM facility alarm;
BiplrVio l — Excessive Bipolar Violations
FDHP Lost — High-level communication over the signaling channel switch
OutofServc — Out-of-Service condition (4-Wire Switched 56 DBM only)
No Signal — No signal has been received (Switched 56 DBM only)
indicates the DBM speed;
Standby — A dialed connection is made, but the data is still routed over the DDS
Active — A dialed connection is made, and data has been routed over that line.
nn.n
indicates the external DBU’s speed:
External — Backup is in progress on an
Bkup disabled.)
The DBM is running a test, initiated from
test
is one of the following tests:
BERT — Bit Error Rate Test
BiL — Bilateral Loopback
Dev — Device Test
DL — Digital Loopback
DT — Digital Test
DTE — DTE Loopback
E-E — End-to-End Test
Lamp — Lamp Test
NetL — Network Loopback (Switched 56 DBM only)
RL — Remote Digital Loopback
TM — Test Mode
init
is one of the following initiators:
DCP — Diagnostic Control Panel
DTE — Data Terminal Equipment
NMS — Network Management System
Remt — Remote DSU
alarm
is one of the following network alarms:
has been lost (2-Wire Switched 56 DBM only)
mode
is one of the following:
circuit. The first line shows the dial backup connection time.
init
external
.
DBU. (DDS line is
C-4 July 1999 3615-A2-GB20-40
 Loading...
Loading...