Paradyne 7612 SNMP DSU User Manual

MODEL 7612 SNMP DSU
WITH INTERNAL ETHERNET LAN ADAPTER
USER’S GUIDE
Document No. 7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997

Copyright 1997 Paradyne Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
Notice
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language in any form
or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the
express written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Avenue North, P.O. Box 2826, Largo,
Florida 33779-2826.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without
obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new
release to this manual.
Trademarks
All products and services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks or registered
service marks of their respective owners.
Warranty, Sales, and Service Information
Contact your sales or service representative directly for any help needed. For additional information concerning
warranty, service, repair, spare parts, installation, documentation, or training, use one of the following methods:
Via the Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide W eb site at http://www.paradyne.com
Via Telephone: Call our automated call system to receive current information via fax or to speak with a
company representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— International, call 727-530-2340
Printed on recycled paper
A
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Contents
About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Document Summary vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Product-Related Documents viii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 About the DSU
Model 7612 SNMP DSU Features 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Typical SNMP DSU Configurations 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Management Capabilities 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Management Information Base (MIB) Support 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Panel Interface Connections 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
Accessing the ATI 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting to the Terminal Port 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main Menu 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Screen Format Types 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
What Affects Screen Displays 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Screen Work Areas 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Navigating the Screens 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keyboard Keys 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Screen Function Keys 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switching to the Screen Function Key Area 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ending an ATI Session 2-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
i

Contents
3 Configuring the DSU
Entering Device and System Information 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Name 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Fields 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Identity Information 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuring the DSU 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Option Areas 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Saving Configuration Options 3-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Security
Overview 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Creating a Login 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Deleting a Login 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A TI Access 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Effective Access Level 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Controlling SNMP Access 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assigning SNMP Community Names and Access Types 4-6. . . . . . . . . .
Limiting SNMP Access through the IP Addresses of
the Managers 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 IP Addressing
Selecting an IP Addressing Scheme 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IP Addressing Scheme Examples 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IMC Connection – Same Subnet 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using Routers to Route DSU Management Data 5-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assigning IP Addresses and Subnet Masks 5-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Monitoring the DSU
What to Monitor 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DSU LEDs 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System LEDs 6-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network LEDs 6-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Port LEDs 6-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Screen Commands 6-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System and Test Status 6-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Self-Test Results 6-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Status Messages 6-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ii
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

7 T esting
Contents
Network Interface Status 6-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Performance Statistics 6-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ethernet Port Status 6-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Management Protocol Statistics 6-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Detecting Problems 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tests Available 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Tests 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CSU or External Network Loopback 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DSU or Internal Network Loopback 7-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Send V.54 Up/Down Sequences 7-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
511 Test Pattern for the Network 7-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Data Port Tests 7-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local Loopback 7-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
511 Test Pattern for the DTE 7-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lamp Test 7-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ending an Active Test 7-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Loopbacks 7-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Reset 7-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 Messages and Troubleshooting
Overview 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuring SNMP Traps 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Messages 8-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting 8-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A Configuration Option Tables
Overview A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Options Menu A-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Interface Options Menu A-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Data Port Options Menu A-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ethernet Port Options Menu A-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Terminal Port Options A-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Telnet Session Options A-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Menu A-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General SNMP Management Options A-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP NMS Security Options A-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Traps Options A-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
iii

Contents
B Worksheets
Overview B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Worksheets B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C MIB Descriptions
Overview C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MIB II – RFC 1213 and RFC 1573 C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Group C-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interfaces Group C-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Extension to Interface Table (ifXTable) C-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interface Stack Group C-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interface Test Table C-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Generic Receive Address Table C-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IP Group C-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ICMP Group C-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCP Group C-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UDP Group C-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Group C-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Group C-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RS-232-Like MIB, RFC 1659 C-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Number of RS-232-Like Ports Object C-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Port Table Objects C-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Asynchronous Port Table Objects C-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Synchronous Port Table Objects C-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Signal Table Objects C-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output Signal Table Objects C-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ethernet-Like MIB, RFC 1643 C-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Enterprise MIB C-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Configuration Variable (pdn-common 7) C-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DDS Interface Specific Definitions, pdn-dds (pdn-interfaces 2) C-18. . . . .
Device Security, pdn-security (pdn-common 8) C-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Traps, pdn-traps (pdn-common 9) C-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Device Control, pdn-control (pdn-common 10) C-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

D Standards Compliance for SNMP Traps
Overview D-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Trap: warmStart D-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Trap: authentificationFailure D-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Traps: linkUp and linkDown D-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Traps: enterpriseSpecific D-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
E Cables and Pin Assignments
Overview E-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Terminal Port (EIA-232) Connector E-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Port (V.35) Connector E-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard EIA-232-D Crossover Cable E-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard Null-Modem Cable E-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10BaseT Connector E-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modular RJ48S DDS Network Interface Connector E-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contents
F Technical Specifications
Glossary
Index
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
v

About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
This guide contains information needed to set up, configure, and operate the
Model 7612 DSU and is intended for installers and operators.
Document Summary
Section Description
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Chapter 4
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 8
About the DSU.
management capabilities with a typical configuration
example.
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface.
accessing the user interface and navigating the screens.
Configuring the DSU.
device and system identification and configuring the DSU.
Security.
the effective access levels, and controlling SNMP access.
IP Addressing.
examples.
Monitoring the DSU.
screens, and network statistics.
Testing.
setup.
Messages and Troubleshooting.
SNMP traps, device messages, and troubleshooting.
Presents procedures for creating a login, setting
Provides details about available tests and test
Describes the DSU features and SNMP
Provides instructions for
Provides procedures for establishing
Provides details regarding IP addresses with
Describes the LEDs, DSU status
Provides information on
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
vii

About This Guide
Section Description
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E
Appendix F
Glossary Defines acronyms and terms used in this document.
Index Lists key terms, acronyms, concepts, and sections in
Product-Related Documents
Document Number Document Title
Configuration Option Tables.
options, default settings, and possible settings.
Worksheets.
settings, and possible settings to use for planning.
MIB Descriptions.
supported by the DSU.
Standards Compliance for SNMP Traps.
trap compliance details.
Cables and Pin Assignments.
interface details.
Technical Specifications.
specifications, clock rates, and LADS connection distances.
alphabetical order.
Contains all the configuration options, default
Provides an overview of the MIB objects
Contains all configuration
Contains SNMP
Contains connector and
Contains physical and regulatory
7612-A2-GN10
To order additional product documentation, refer to
Information
on page A at the beginning of this User’s Guide.
Model 7612 SNMP DSU with Internal Ethernet LAN
Adapter Startup Instructions
Warranty, Sales, and Service
viii
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10
About the DSU
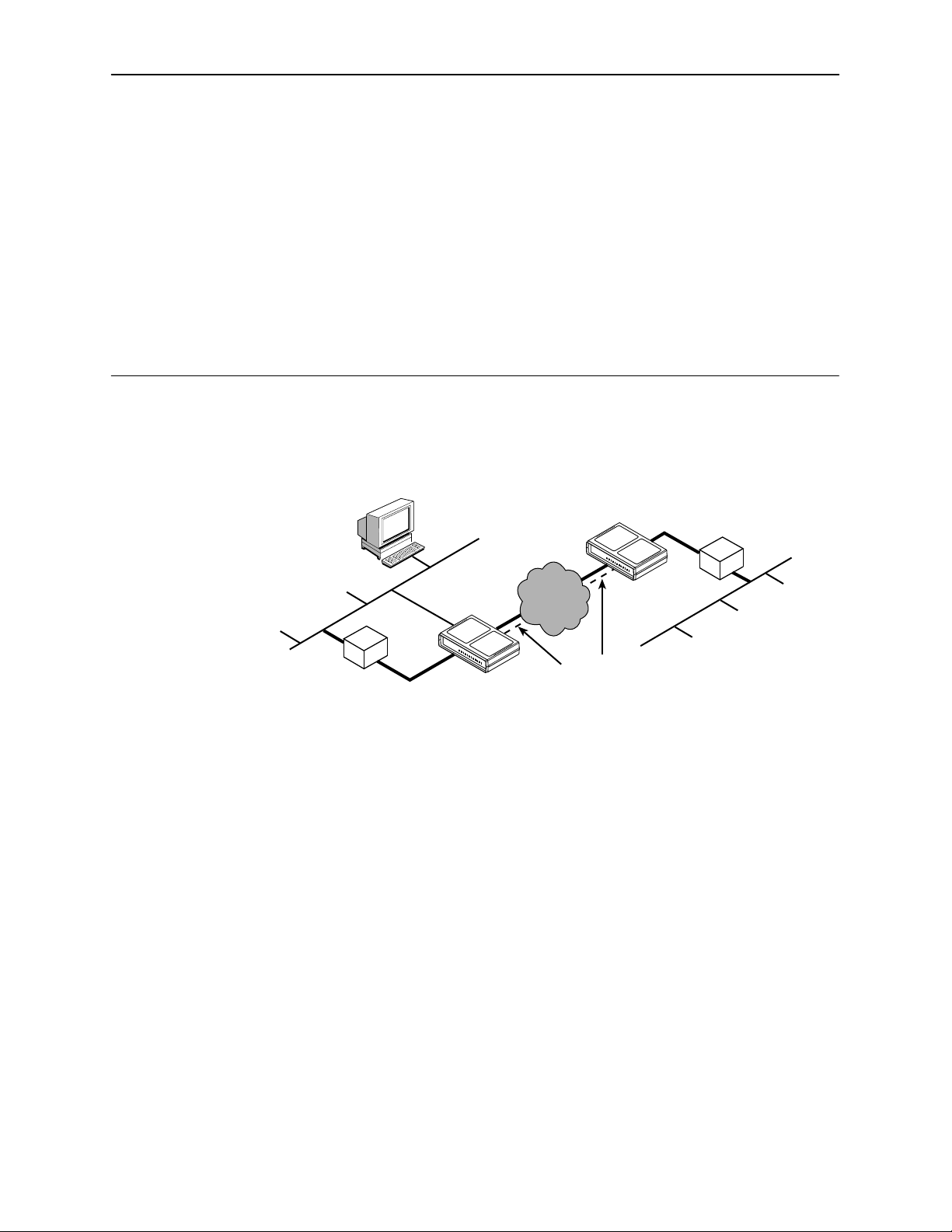
Model 7612 SNMP DSU Features
1
NMS
LAN A
Router
The Model 7612 SNMP DSU provides an interface between the customer
premises equipment (CPE) and a DDS network. Its features include:
Integral LAN Adapter. Connects the DSU directly to an Ethernet LAN.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Management. Provides
network management via an industry-standard SNMP management system.
In-band Management Channel (IMC). Provides remote management via
SNMP or Telnet session capability over the DDS network.
ASCII Terminal Interface (ATI). Provides a menu-driven VT100-compatible
interface for configuring and managing the DSU locally or remotely by Telnet
session or external modem.
10BaseT
Connection
SNMP DSU
with LAN
Adapter
Digital
Network
SNMP DSU
Data
In-Band
Management
Channel
Router
LAN B
497-15279
7612-A2-GB20-10
Local Management. Provides local management via an:
— Asynchronous terminal connection through the Terminal port
— NMS connection through the 10BaseT port
November 1997
1-1

About the DSU
Remote Management. Provides remote management:
— Using an external modem through the Terminal port
— Using SNMP or Telnet through the 10BaseT port or the IMC
DDS Operation. Operates at 56 kbps and 64 kbps CC (clear channel).
LADS (Local Area Data Set) Operation. Operates as a limited-distance
modem at 56 kbps and 64 kbps full-duplex.
Autorating of Line Rate. Establishes the line rate from the network receive
signal and automatically adjusts to the detected line rate.
Data Port Rates. Automatically adjusts to the DDS or LADS operating rates.
Diagnostics. Provides the capability to diagnose device and network
problems and perform tests, including digital loopbacks, pattern tests, and
self-test.
Device and Test Monitoring. Provides the capability of tracking and
evaluating the unit’s operation, including health and status, and error-rate
monitoring.
Two Customer-Specified Configuration Storage Areas. Allows quick
access to alternate sets of configuration options.
Security. Provides multiple levels of security, which help prevent
unauthorized access to the DSU.
1-2
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10
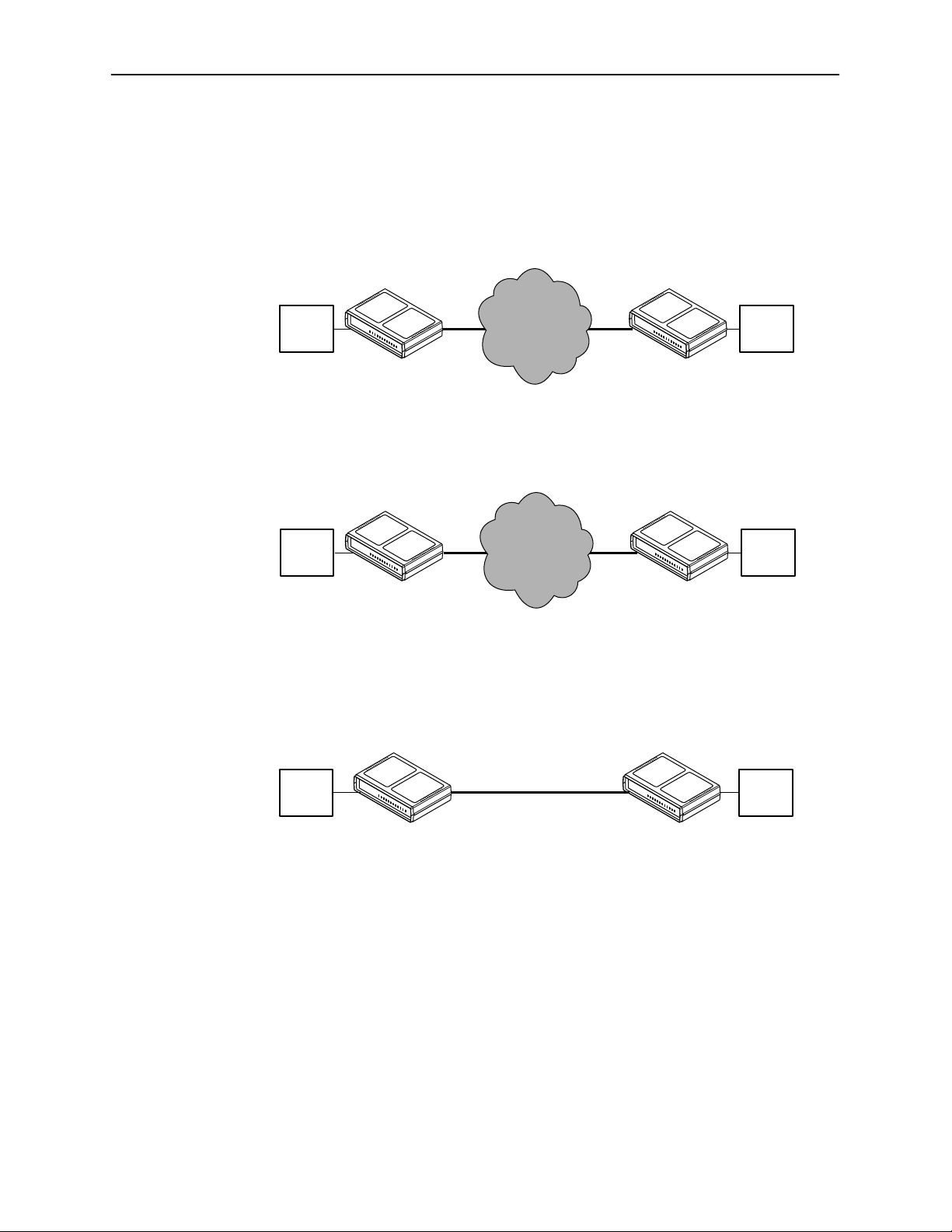
Typical SNMP DSU Configurations
1
The following illustration shows a typical LAN/WAN interconnection application for
the DSU. The routers connected to the DSU at each location provide the LAN
interconnection.
About the DSU
Digital
Data
Network
DDS
SNMP
DSU
Router
497-15274
Router
DDS
SNMP
DSU
The SNMP DSU can also be used in a frame relay network.
Frame
Relay
Network
DDS
SNMP
DSU
Router
497-15275
Router
DDS
SNMP
DSU
Two SNMP DSUs can be connected back-to-back to act as Local Area Data Sets.
Table F-3 in Appendix F,
Technical Specifications
, shows the maximum distances
for LADS applications.
7612-A2-GB20-10
Router
SNMP
DSU
November 1997
56 kbps
or
64 kbps
SNMP
DSU
Router
497-15276-0
1-3
About the DSU
SNMP Management Capabilities
The DSU supports SNMP Version 1, and can be managed by any
industry-standard SNMP manager and accessed using SNMP by external SNMP
managers.
Management Information Base (MIB) Support
The following MIBs are supported:
MIB II (RFC 1213 and RFC 1573) – Defines the general objects for use with
a network management protocol in TCP/IP internets and provides general
information about the DSU. MIB II is backward-compatible with MIB I.
RS-232-Like MIB (RFC 1659) – Defines objects for managing RS-232-type
interfaces (e.g., V.35, RS-422, RS-423, etc.) and supports the synchronous
data port on the DSU.
Ethernet-like MIB (RFC 1643) – Defines objects for managing Ethernet-like
interfaces (e.g., 10BaseT).
Enterprise MIB – Supports configuration, status, statistics, and tests.
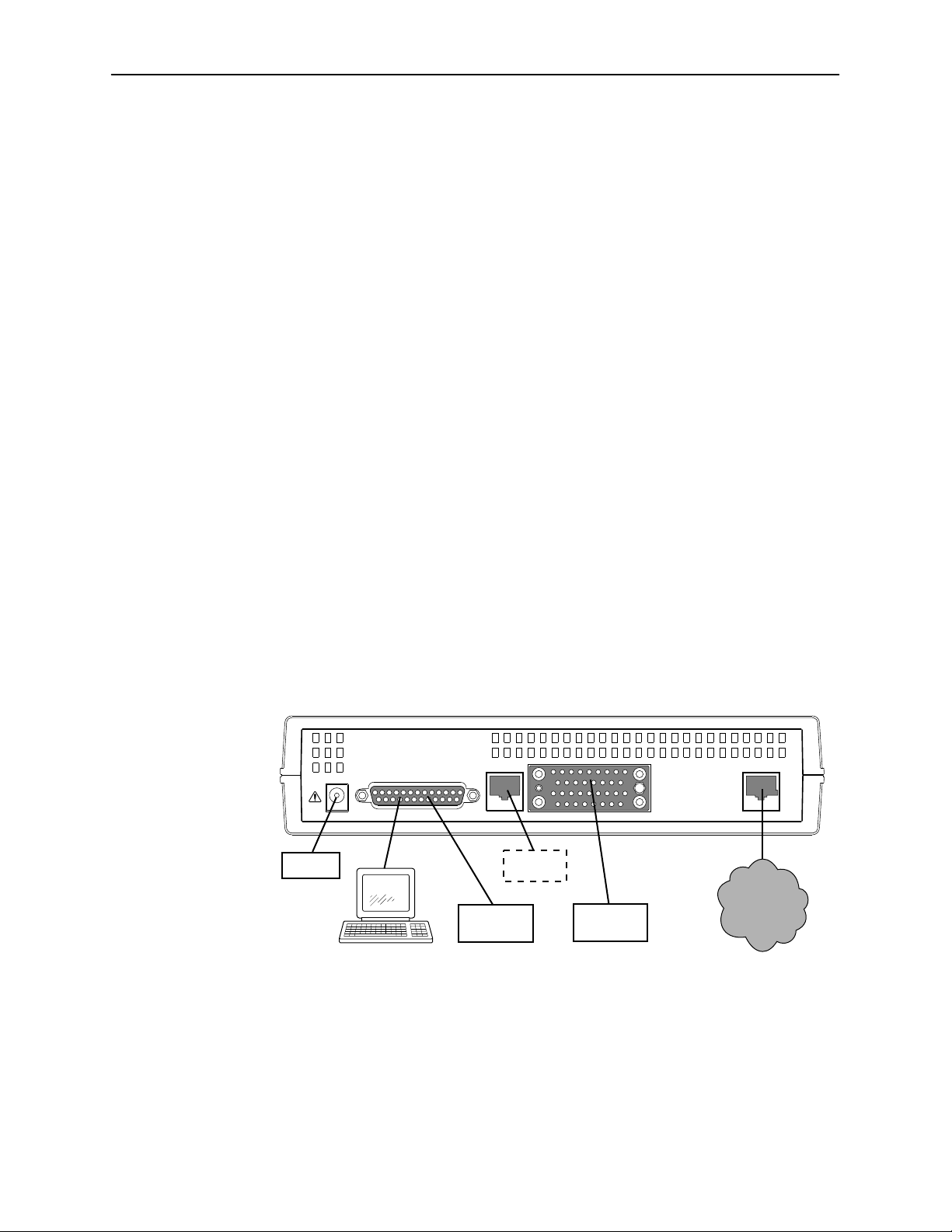
Rear Panel Interface Connections
The following illustration shows the physical interfaces of the DSU. Information
about the installation of the DSU is contained in the
Internal Ethernet LAN Adapter Startup Instructions
POWER
Power
TERMINAL
or
Terminal
10BaseT
Modem
LAN
Model 7612 SNMP DSU with
.
NETWORK
Network
DTE
D
T
E
497-15272
1-4
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
Accessing the ATI
You can communicate with the ASCII Terminal Interface (ATI) using one of the
following methods:
Direct connection through the Terminal port.
Dialing in through an external modem to the Terminal port.
Telnet session through the 10BaseT port.
2
Telnet session through the In-band Management Channel (IMC).
NOTE:
Only one ATI session can be active at a time, and another user’s session
cannot be forced to end. To automatically log out a user due to inactivity,
enable the Inactivity Timeout option (see Table A-5, Terminal Port Options,
and Table A-6, Telnet Session Options.
The user interface is idle until activated. Press Return to activate the user
interface. Security can limit ATI access several ways. To setup security or a login
ID, refer to Chapter 4,
Connecting to the Terminal Port
Verify that the settings of the device that you connect to the Terminal port match
these factory-loaded option default settings:
Data rate set to 9.6 kbps.
Character length set to 8.
Parity set to None.
Stop Bits set to 1.
Security
.
7612-A2-GB20-10
To change the Terminal Port settings, refer to Table A-5, Terminal Port Options.
November 1997
2-1
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
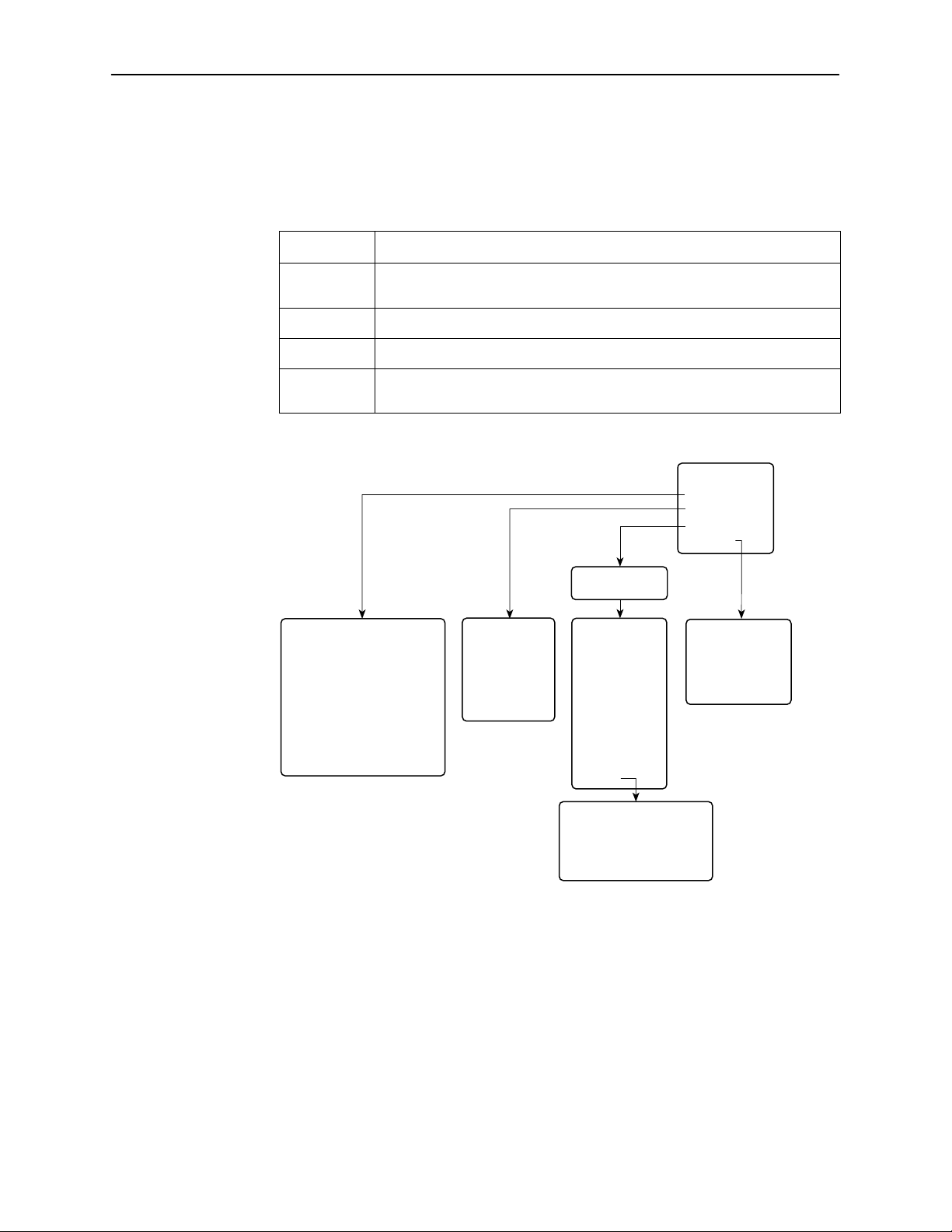
Main Menu
Entry to all of the DSU’s tasks begins at the Main Menu screen, which has four
menus or branches.
Select . . .
To . . .
Status View diagnostic tests, network status of interfaces, statistics, LEDs, and
DSU identity information.
Test Select and cancel tests for the DSU’s interfaces.
Configuration Display and edit the configuration options.
Control Control the user interface for device naming and login administration, or
to initiate a power-up reset of the DSU.
MAIN MENU
Status
Test
Configuration
Control
Load Configuration
from . . .
Status
• System and Test Status
• Network Interface Status
• Network Performance Statistics
• Ethernet Port Status
• Management Protocol Statistics
• Display LEDs
• Identity
Test
• Network T ests
• Data Port Tests
• Lamp Test
• Abort All Tests
Configuration
Edit/Display
• System
• Network
• Data Port
• Ethernet Port
• Terminal Port
• Telnet Session
• SNMP
Control
• Device Name
• Administer Logins
• Reset Device
2-2
November 1997
SNMP Options
• General SNMP Management
• SNMP NMS Security
• SNMP Traps
97-15306
7612-A2-GB20-10
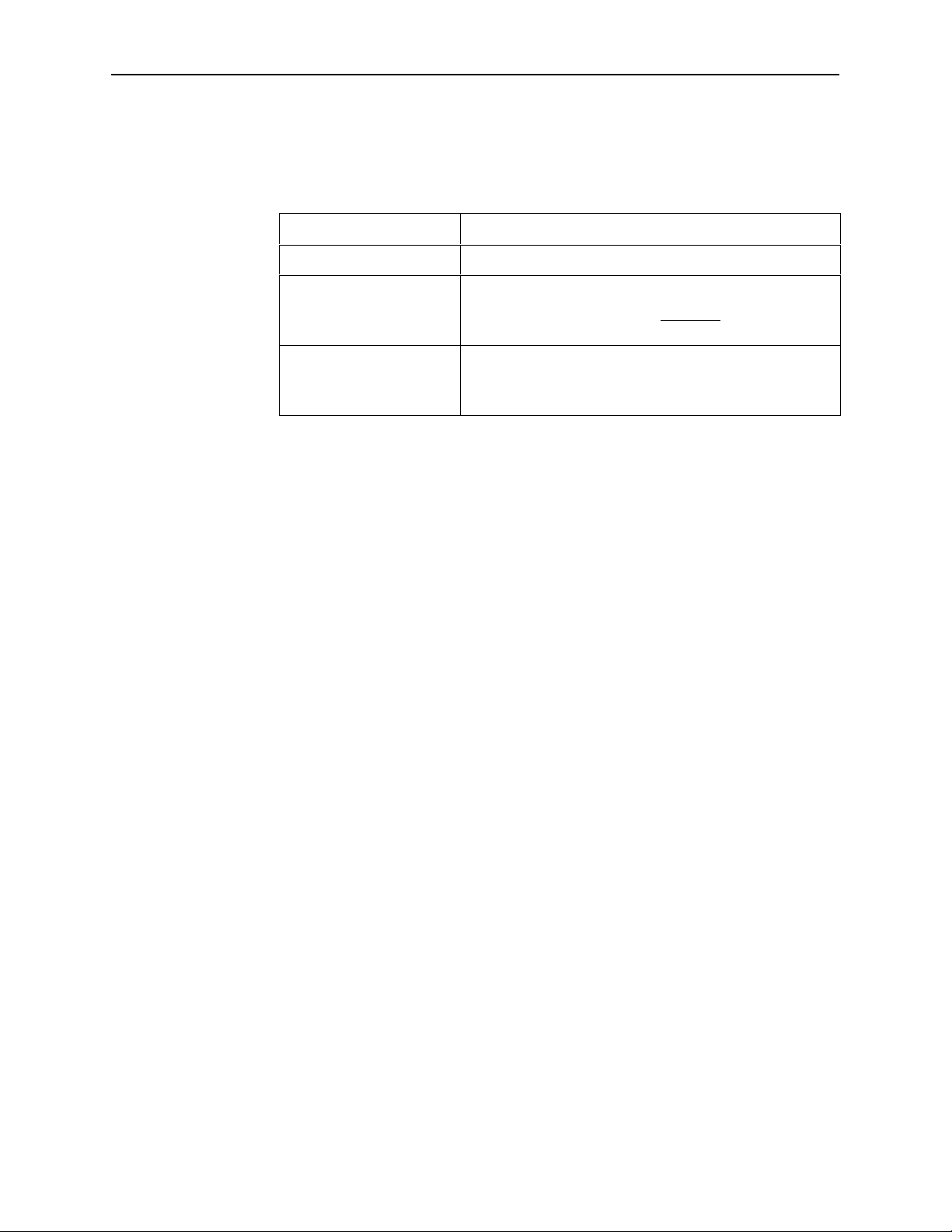
Screen Format Types
Three types of screen formats are available on the ATI.
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
Use the screen format . . .
Menu selection Display a list of available functions for user selection.
Input Add or change information on a screen.
Display Display configuration information and results from
What Affects Screen Displays
What appears on the screens depends on the:
Current configuration – How the DSU is currently configured.
Effective security access level – An access level that is typically set by the
system administrator for each interface and each user.
Data selection criteria – What you entered in previous screens.
To . . .
Input or edit fields that have an Underline
or selection. See
performance and DSU-specific tests.
Display-only fields that have no underline in the field value.
Screen Work Areas
in the field value
on page 2-4
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
2-3

Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
Screen Work Areas
There are two user work areas:
Screen area – Provides the menu path, access level, menus, and input fields
above the dotted line.
The menu path appears as the first line on the screen. In this manual, the
menu path is presented as a menu selection sequence with the names of the
screens:
Main Menu→Configuration→Load Configuration From→
Edit
Screen function key area – Provides functions available below the dotted
line based upon screen selection and access level. See
Screen Function Key Area
Menu Path
main/configuration/edit/term
Device Name: Node A Model: 7612
→
Terminal Port
Switching to the
on page 2-7.
Screen
Function
Keys
Field V alue
Choices and
ATI messages
TERMINAL PORT OPTIONS
Data Rate (Kbps): 9.6
Character Length: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Monitor DTR: Enable
Login Required: Enable
Port Access Level: Level 1
Inactivity Timeout: Enable
Disconnect Time(minutes): 5
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
S
ave
Select: 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 14.4, 19.2, 28.8, 38.4 No Signal
Input Fields
ainMenu Exit
System Alarm
Messages
2-4
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Navigating the Screens
You can navigate the screens by:
H Using keyboard keys
H Using screen function keys
H Switching between the two screen work areas
Keyboard Keys
Use the following keyboard keys to navigate within the screen.
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
To . . .
Move cursor between the screen area and the screen function
keys area below the dotted line at the bottom of the screen
Return to the previous screen Esc
Move cursor to the next field on the screen Tab
Accept entry or display valid options on the last row of the screen
when pressed before entering data or after entering invalid data
Move cursor one position to the left Ctrl-k
Select the next valid value for the field Spacebar
Delete character that the cursor is on Delete (Del)
Move cursor up one field within a column on the same screen Up Arrow or Ctrl-u
Move cursor down one field within a column on the same screen Down Arrow or Ctrl-d
Move cursor one character to the right if in edit mode Right Arrow or Ctrl-f
Move cursor one character to the left if in edit mode Left Arrow or Ctrl-b
Redraw the screen display , clearing information typed in but not
yet entered
Press . . .
Ctrl-a
Return (Enter)
Ctrl-l
7612-A2-GB20-10
" Procedure
To make a menu or field selection:
1. Press the tab key or the arrow keys to position the cursor on a menu or field
selection. Each selection is highlighted as you press the key to move the
cursor from position to position.
2. Press Return. The selected menu or screen appears.
3. Continue Steps 1 and 2 until you reach the screen you want.
November 1997
2-5
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
The current setting or value appears to the right of the field name. The valid
choices for the field are displayed in the screen function area. You can enter
information into a selected field by typing in the first character or characters of a
field value or command.
If a field is blank and the Field Values screen area displays valid selections, press
the spacebar and the first valid value for the field will appear. Continue pressing
the spacebar to scroll through other valid values.
Screen Function Keys
All screen function keys located below the dotted line operate the same way
(upper- or lowercase) throughout the screens.
For the screen
function . . .
Clear C or c Clear status messages for one-time events.
ClrStats C or c Clear statistics and refresh the screen.
Select . . . And press Return to . . .
Delete L or l Delete data.
Exit E or e Terminate the async terminal session.
MainMenu M or m Return to the Main Menu screen.
New N or n Enter new data.
PgDn D or d Display the next page.
PgUp U or u Display the previous page.
Refresh R or r Update screen with current information.
ResetMon R or r Reset an active Monitor 51 1 test counter to zero.
Save S or s Save information.
2-6
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10
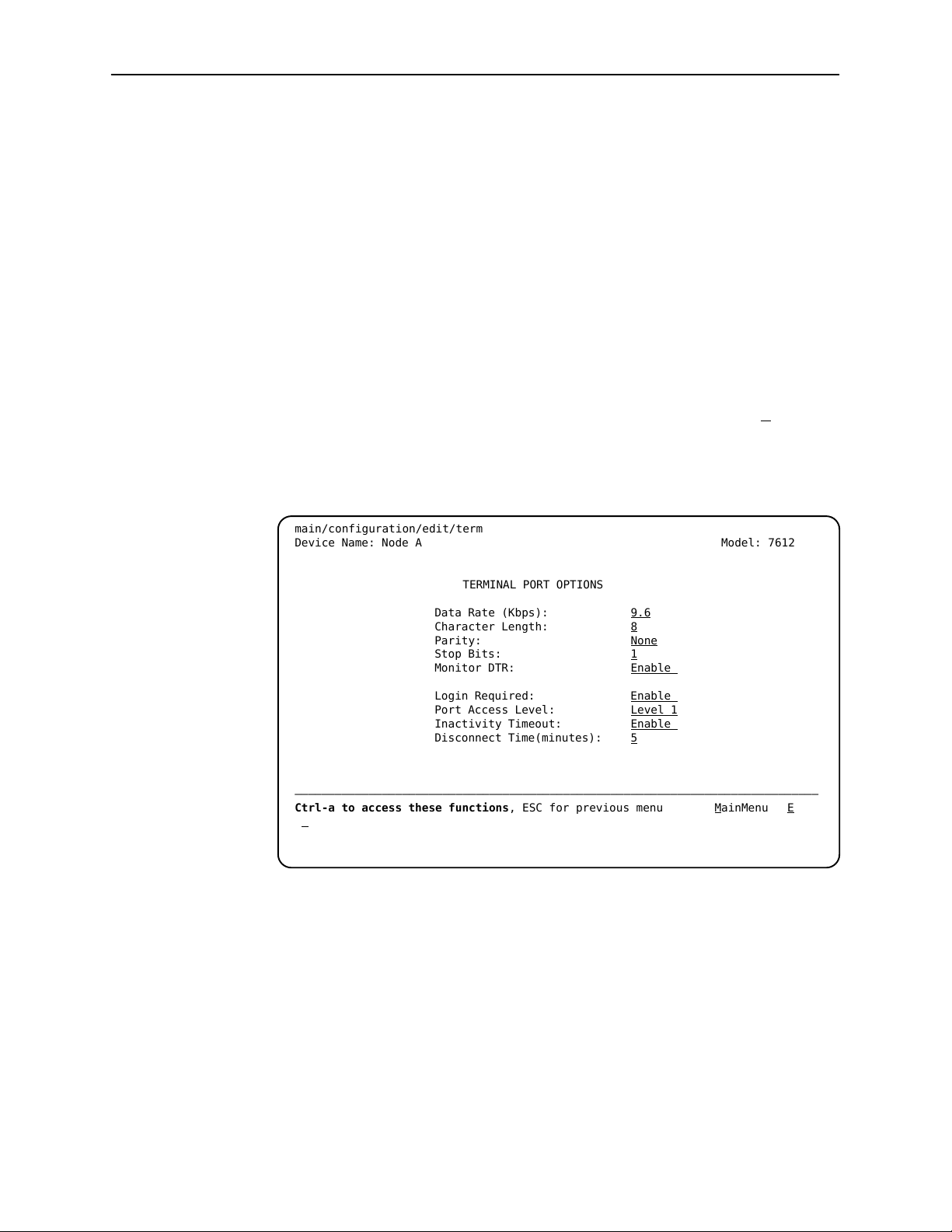
Switching to the Screen Function Key Area
Selecting Ctrl-a allows you to switch between the two screen work areas to
perform all screen functions.
Procedure
To access the screen function area below the dotted line:
1. Press Ctrl-a to switch from the screen area to the screen function key area
below the dotted line. The available selections for the first input field appear
on the last line as shown below.
2. Select either the function’s designated (underlined) character or press the tab
key until you reach the desired function key.
Example:
To save the changes you have made on this screen, enter s or S (Save).
3. Press Return. The function is performed.
4. To return to the screen area above the dotted line, press Ctrl-a again.
Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
main/configuration/edit/term
Device Name: Node A Model: 7612
TERMINAL PORT OPTIONS
Data Rate (Kbps): 9.6
Character Length: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Monitor DTR: Enable
Login Required: Enable
Port Access Level: Level 1
Inactivity Timeout: Enable
Disconnect Time(minutes): 5
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
S
ave
ainMenu Exit
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
2-7

Using the ASCII Terminal Interface
Ending an ATI Session
Use the Exit function key from any screen to terminate the session.
Procedure
To end an ATI session:
1. Press Ctrl-a to go to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
2. Save changes if you have altered your configuration.
3. Select E
xit and press Return. The User Interface Idle screen appears.
2-8
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10
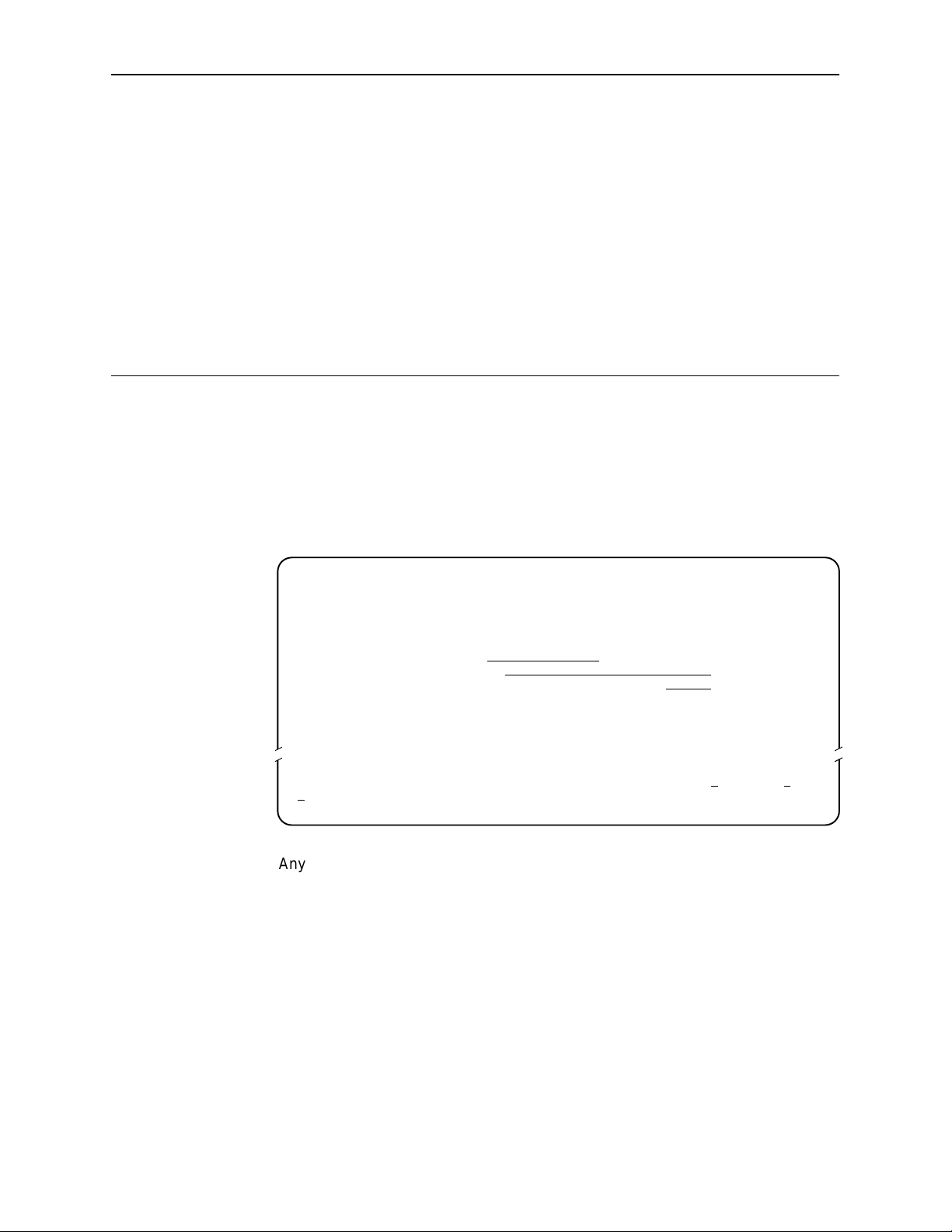
Configuring the DSU
Entering Device and System Information
Use the Device Name screen to input DSU device and SNMP system entries. To
access the Device Name screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu→Control→Device Name
main/control/device name
Device Name: Model: 7612
3
DEVICE NAME
Device Name: NE815378
System Name: lllQJ98-001
System Location: Bldg. A412, 2nd Floor, Left cabinet
System Contact: Joe Smith 800-555-5555 pager 888-555-5555 Clear
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
S
ave
Any printable ASCII characters are valid entries for all the Device Name screen
inputs. ASCII printable characters include:
Numeric 0–9
Upper or lower case A–Z
Space
All standard keyboard symbols
Clear
Clear
Clear
ainMenu Exit
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
3-1

Configuring the DSU
Device Name
System Fields
The Device Name entry appears on all ATI screens. The input on this screen is
displayed on the Identity screen. Refer to
The three System entry fields are alphanumeric and provide 127 characters for
each field. The System entries appear on the Identity display as shown in the
next section. The SNMP System entry fields are:
System Name: The general SNMP system name.
System Location: The physical location of the SNMP-managed device.
System Contact: Identification information, such as contact name, phone
number, or mailing address.
Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
Select S
appears at the bottom of the screen.
ave and press Return. When Save is complete, Command Complete
Identity Information
on page 3-3.
3-2
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Identity Information
The Identity screen provides identification information about the DSU.
To access the Identity screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu→Status→Identity
main/status/identity
Device Name: NE815378 Model: 7612
Configuring the DSU
IDENTITY
System Name: lllQJ98-001
System Location: Bldg. A412, 2nd Floor, Left cabinet
System Contact: Joe Smith 800-555-5555 pager 888-555-5555
Serial Number: 1234567
Model Number: 7612-A1-201
Software Revision: 01.00.00
Hardware Revision: 2048-80A
Ethernet MAC Address: 00:E0:39:00:00:00
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
Press arrow
keys to view
additional
information
ainMenu Exit
To view information on the three System entries beyond the 40 characters on the
screen, place the cursor on the first or last character and press the left or right
arrow.
In addition to the System information entered on the Device Name screen, the
Identity screen shows:
Serial Number: The unique serial number of the unit.
7612-A2-GB20-10
Model Number: The model number of the unit.
Software Revision: The revision level of the firmware in the unit.
Hardware Revision: The revision level of circuit card assembly.
Ethernet MAC Address: The Media Access Control address of the Ethernet
port, assigned at the time of manufacture.
November 1997
3-3

Configuring the DSU
Configuring the DSU
Configuration option settings determine how the DSU operates. Use the DSU’s
Configuration branch to display or change configuration option settings.
Configuration Option Areas
The DSU is shipped with factory settings in all configuration option areas. You
can find default information by:
Referring to Appendix A,
Worksheets
Accessing the Default Factory Configuration branch of the DSU menu.
The DSU offers four sets of configuration option settings located in the following
areas. The first three sets match the Default Factory Configuration options set
until modified and saved by the user.
If the factory default settings do not support your network’s configuration,
customize the configuration options for your application.
Configuration Option Area
Current Configuration The DSU’ s active set of configuration options.
Customer Configuration 1 Use to set up and store a set for future use.
Customer Configuration 2 Use to set up and store a second set for future use.
Default Factory Configuration A read-only configuration area containing the
.
Configuration Option Tables,
Configuration Option Set
factory-default configuration options.
or Appendix B,
3-4
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options
To display the configuration options, you must first copy one configuration option
set into the edit area.
" Procedure
To load a configuration option set into the configuration edit area:
1. Follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu→Configuration→Load Configuration From
2. Select one of the four configuration option areas listed in the table in
Configuration Option Areas
3. Press Return. The selected configuration option set is loaded and the
Configuration Edit/Display menu screen appears.
No configuration edits are allowed when the effective access level is 2 or 3.
Configuration is read-only and allows viewing only of configuration option
settings. If the effective access level is not 1:
Configuring the DSU
on page 3-4.
H The last line of the Load Configuration From screen reads:
n
Access Level is
H The S
Refer to Chapter 4,
ave prompt will not appear on any screens.
, Configuration is read-only
Security
.
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
3-5

Configuring the DSU
Saving Configuration Options
When changes are made to the configuration options, the changes must be
saved to take effect. The S
when the user has an effective access level of 1. All other effective access levels
have read-only permission.
Procedure
To save configuration options changes:
1. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
ave key and Save Configuration To screen appear
2. Select S
3. Select one of the three configuration option areas on the screen and press
Return. When Save is complete, Command Complete appears in the
message area at the bottom of the screen.
ave and press Return. The Save Configuration To screen appears.
NOTE:
If you attempt to leave the edit session without saving your changes, a Save
Configuration screen appears requiring a Yes or No response.
If you select . . .
Yes Save Configuration To screen appears.
No Main Menu appears and changes are not saved.
Then the . . .
3-6
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Security
Overview
4
The DSU provides several ways to control access to the ATI through option
settings. You can:
Enable the Login Required option to require a Login ID for the:
— Terminal Port
— Telnet Session via the IP interfaces (the 10BaseT port or the IMC)
Limit the access using:
— Port Access Level option of 1, 2, or 3 for the Terminal port
— Session Access Level option of 1, 2 or 3 for the Telnet Session
Refer to Table 4-1, Effective Access Levels.
Disable the access using:
— In-Band Management Channel Rate (bps) option for the IMC
— Ethernet Port Use option
— Telnet Session option
Refer to
SNMP security is handled through Community Names with access levels and
IP address validation. Refer to
Preventing access to the ATI by setting the In-Band Management Channel Rate
or Ethernet Port Use options to Disable also inhibits SNMP management over
those interfaces.
ATI Access
on page 4-3.
Controlling SNMP Access
on page 4-6.
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
4-1

Security
Creating a Login
Logins apply to Terminal port access and Telnet access to the ATI. Six login
ID/password combinations are available. Each Login ID and Password must be
unique and include an access level.
For additional information regarding the ATI access using the Login Required
option, refer to
ATI Access
on page 4-3
.
Procedure
To create a login record:
1. Follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu→Control→Administer Logins
2. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
3. Select N
4. Create the login by entering the following fields.
On the Administer
Logins screen, for the . . .
Login ID 1 to 10 ASCII printable characters
Password 1 to 10 ASCII printable characters
Access Level Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3
ew and press Return.
Enter . . .
NOTE:
Assign at least one Level 1 Access Level. Full access is necessary to
make configuration option changes and administer logins. If there is no
effective Access Level 1, refer to
5. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
Select S
6. When Save is complete, Command Complete appears at the bottom of the
screen. Select:
—N
ave and press Return.
ew to add another login record
Device Reset
in Chapter 7,
Testing
.
4-2
—M
ainMenu to go to the Main Menu
xit to end the ATI session
—E
November 1997
7612-A2-GB20-10

Deleting a Login
Procedure
"
To delete a login record:
1. Follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu→Control→Administer Logins
2. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
Security
A TI Access
3. Select PgU
until you find the one to be deleted.
4. Once the correct record is displayed, select Del
5. To complete the delete action, select S
When the deletion is complete, Command Complete appears at the bottom of
the screen. The number of login pages/records reflects one less record, and
the record following the deleted record appears.
Access to the ATI is available through either the Terminal port or a Telnet session.
Access to the ATI through the Terminal port can be limited. Refer to Table A-5,
Terminal Port Options, to:
H Enable Login Required.
H Assign a Port Access Level of 1, 2, or 3.
The ATI can be accessed remotely through a Telnet Session via either the
10BaseT port or the IMC. The DSU provides several methods for limiting access
to the ATI through a Telnet session.
p or PgDn and press Return to page through login pages/records
ete and press Return.
ave and press Return.
7612-A2-GB20-10
H Refer to Table A-6, Telnet Session Options, to:
— Enable Login Required.
— Assign a Telnet Session Access Level of 1, 2, or 3.
— Disable Telnet access completely.
H To prevent the 10BaseT port and IMC from supporting a Telnet session you
can also:
— Set the Ethernet Port Use option to Disable. Refer to Table A-4, Ethernet
Port Options.
— Disable the IMC using the In-Band Management Channel Rate (bps)
option. Refer to Table A-2, Network Interface Options.
Preventing access to the ATI by setting the In-Band Management Channel Rate
or Ethernet Port Use options to Disable also inhibits SNMP management over
those interfaces.
November 1997
4-3
 Loading...
Loading...