Page 1

6212-I1 4-Port Router
User’s Guide
Document No. 6212-A2-GB23-00
September 2005
Page 2

Copyright 2005 Paradyne Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
Notice
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language in any form or
by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the express
written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without
obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new
release to this manual.
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for any help needed. For additional
information concerning warranty, sales, service, repair, installation, documentation, training, distributor locations, or
Paradyne worldwide office locations, use one of the following methods:
Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com. (Be sure to register your warranty at
www.paradyne.com/warranty.)
Telephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to speak with a company
representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-795-8004
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them to Technical Publications,
Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773, or send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include the
number and title of this document in your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you are
willing to provide additional clarification.
Trademarks
Acculink, ADSL/R, Bitstorm, Comsphere, DSL the Easy Way, ETC, Etherloop, FrameSaver, GranDSLAM, GrandVIEW,
Hotwire, the Hotwire logo, iMarc, Jetstream, MVL, NextEDGE, Net to Net Technologies, OpenLane, Paradyne, the
Paradyne logo, Paradyne Credit Corp., the Paradyne Credit Corp. logo, Performance Wizard, ReachDSL, StormPort,
TruePut are registered trademarks of Paradyne Corporation.
Connect to Success, Hotwire Connected, JetFusion, JetVision, MicroBurst, PacketSurfer, Quick Channel, Reverse
Gateway, Spectrum Manager, and StormTracker are trademarks of Paradyne Corporation.
All other products or services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or
registered service marks of their respective owners.
A September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 3
!
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product or included in the manual.
2. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for ventilation. To ensure reliable operation of the product and to
protect it from overheating, these slots and openings must not be blocked or covered.
3. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord and do not locate the product where persons will walk on the power
cord.
4. Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or removing covers may expose you to dangerous high
voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
5. General purpose cables are used with this product for connection to the network. Special cables, which may be
required by the regulatory inspection authority for the installation site, are the responsibility of the customer. Use a
UL Listed, CSA certified, minimum No. 24 AWG line cord for connection to the Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
network.
6. When installed in the final configuration, the product must comply with the applicable Safety Standards and
regulatory requirements of the country in which it is installed. If necessary, consult with the appropriate regulatory
agencies and inspection authorities to ensure compliance.
7. A rare phenomenon can create a voltage potential between the earth grounds of two or more buildings. If products
installed in separate buildings are interconnected, the voltage potential may cause a hazardous condition. Consult
a qualified electrical consultant to determine whether or not this phenomenon exists and, if necessary, implement
corrective action prior to interconnecting the products.
8. Input power to this product must be provided by one of the following: (1) a UL Listed/CSA certified power source
with a Class 2 or Limited Power Source (LPS) output for use in North America, or (2) a certified transformer, with a
Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) output having a maximum of 240 VA available, for use in the country of
installation.
9. In addition, since the equipment is to be used with telecommunications circuits, take the following precautions:
— Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
— Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations.
— Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the
network interface.
— Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
— Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of
electric shock from lightning.
— Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
CE Marking
When the product is marked with the CE mark on the equipment label, a supporting Declaration of Conformity may be
downloaded from the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com. Select Library → Technical Manuals →
CE Declarations of Conformity.
FCC Part 15 Declaration
An FCC Declaration of Conformity may be downloaded from the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com.
Select Support -> Technical Manuals -> Declarations of Conformity.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
The authority to operate this equipment is conditioned by the requirement that no modifications will be made to the
equipment unless the changes or modifications are expressly approved by the responsible party.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 B
Page 4

This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference
to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice to Users of the United States Telephone Network
The following notice applies to versions of the modem that have been FCC Part 68 approved.
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules and the requirements adopted by the Administrative Council for
Terminal Attachment (ACTA). On the bottom side of this equipment is a label that contains, among other information, a
product identifier in the format US:AAAEQ##TXXXX. If requested, this number must be provided to the Telephone
Company.
This equipment is intended to connect to the Public Switched Telephone Network through a Universal Service Order
Code (USOC) type RJ11C jack. A plug and jack used to connect this equipment to the premises wiring and telephone
network must comply with the applicable FCC Part 68 rules and requirements adopted by the ACTA. A compliant
telephone cord and modular plug is provided with this product. It has been designed to be connected to a compatible
modular jack that is also compliant.
The Ringer Equivalence Number (or REN) is used to determine the number of devices that may be connected to a
telephone line. Excessive RENs on a telephone line may result in the devices not ringing in response to an incoming
call. In most but not all areas, the sum of RENs should not exceed five (5.0). To be certain of the number of devices that
may be connected to a line, as determined by the total RENs, contact the local Telephone Company. The REN for this
product is part of the product identifier that has the format US:AAAEQ##TXXXX. The digits represented by ## are the
REN without a decimal point. For example, 03 represents a REN of 0.3.
If the modem causes harm to the telephone network, the Telephone Company will notify you in advance that temporary
discontinuance of service may be required. But if advance notice is not practical, the Telephone Company will notify the
customer as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised of your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you believe it is
necessary.
The Telephone Company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations or procedures that could affect the
operation of the equipment. If this happens, the Telephone Company will provide advance notice in order for you to
make necessary modifications to maintain uninterrupted service. If trouble is experienced with the modem, refer to the
repair and warranty information in this document.
If the equipment is causing harm to the telephone network, the Telephone Company may request that you disconnect
the equipment until the problem is resolved.
The user may make no repairs to the equipment.
Connection to party line service is subject to state tariffs. Contact the state public utility commission, public service
commission or corporation commission for information.
If the site has specially wired alarm equipment connected to the telephone line, ensure the installation of the modem
does not disable the alarm equipment. If you have questions about what will disable alarm equipment, consult your
Telephone Company or a qualified installer.
C September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 5

Notice to Users of the Canadian Telephone Network
NOTICE: This equipment meets the applicable Industry Canada Terminal Equipment Technical Specifications. This is
confirmed by the registration number. The abbreviation IC before the registration number signifies that registration was
performed based on a Declaration of Conformity indicating that Industry Canada technical specifications were met. It
does not imply that Industry Canada approved the equipment.
NOTICE: The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) for this terminal equipment is labeled on the equipment. The REN
assigned to each terminal equipment provides an indication of the maximum number of terminals allowed to be
connected to a telephone interface. The termination on an interface may consist of any combination of devices subject
only to the requirement that the sum of the Ringer Equivalence Numbers of all the devices does not exceed five.
If your equipment is in need of repair, contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor
directly.
!
CANADA - EMI NOTICE:
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian interference-causing equipment regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du règlement sur le matérial brouilleur du
Canada.
Japan Notices
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for
Interference from Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this is used near a radio or
television receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use
the equipment according to the instruction manual.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 D
Page 6

E September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 7

Contents
About This Guide
1 Introduction
Document Purpose and Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . v
Document Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . v
Product-Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Front Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2 Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Connecting the Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Configuring Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Windows ME . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Windows 95 and Windows 98 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Windows NT 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Logging in to Your Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
3 Device Information
Status Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
WAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
LAN Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
WAN Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
ATM Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
ADSL Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
ADSL BER Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 i
Page 8

Contents
ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
4 Quick Setup
Quick Setup with Auto-Connect Enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Quick Setup with Auto-Connect Disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
5 Advanced Setup
WAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Local Area Network (LAN) Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
NAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Port Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
DMZ Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Firewall. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Port Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
Quality of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-16
Routing – Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-17
Routing – Static Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-18
Routing – RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-19
DNS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
Dynamic DNS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
ADSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-21
DSL Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-23
Tone Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
Add Function – ATM PVC Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Connection Type Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
WAN Setup - Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Remove Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Finish Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Virtual Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
IP Filtering – Outgoing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
IP Filtering – Incoming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
Firewall – MAC Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
Parental Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-14
Modulation Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-22
Phone Line Pair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-22
Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-22
ii September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 9

6 Diagnostics
7 Management
Contents
Testing the DSL Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Saving and Restoring the Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Backing Up Configuration Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Restoring Configuration Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Restoring Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
View System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
Configure System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
SNMP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Internet Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
Access Control – Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Access Control – IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Access Control – Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
Update Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
Reboot Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
A Specifications
Index
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
iii
Page 10

Contents
iv September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 11
About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
This guide contains detailed information about the 6212-I1 router. It is intended for
all users of the router.
Document Summary
Section Description
Chapter 1, Introduction Describes the features of the router.
Chapter 2, Hardware
Installation and PC Setup
Chapter 3, Device Information Explains how to use the web interface to obtain
Chapter 4, Quick Setup Describes the Quick Setup configuration process.
Chapter 5, Advanced Setup Describes configuration of the advanced router
Chapter 6, Diagnostics Describes the test screen.
Chapter 7, Management Describes the management functions of the router,
Appendix A, Specifications Lists the specifications of the router.
Index Lists key terms, concepts, and sections in alphabetical
A master glossary of terms and acronyms used in Paradyne documents is
available online at www.paradyne.com. Select Support → Technical Manuals →
Technical Glossary.
Shows how to connect the router and set up your PC to
manage the router.
statistics and other information about the router.
features.
including backing up and restoring configuration
settings, viewing the system log, configuraing access
control, and upgrading software.
order.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 v
Page 12

About This Guide
Product-Related Documents
Complete documentation for Paradyne products is available online at
www.paradyne.com. Select Support → Technical Manuals.
To order a paper copy of a Paradyne document, or to speak with a sales
representative, please call 1-727-530-2000.
vi September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 13

Introduction
Introduction
Features
1
Congratulations on becoming the owner of a 6212 ADSL router.
This User’s Guide will show you how to set up the router, and how to customize its
configuration to get the most out of this product.
The 6212 router has the following features:
Built-in ADSL modem which offers G.Dmt, G.lite, T1.413, ADSL2, Annex L,
and ADSL2+ to meet different linking speeds from your ISP.
Four 10/100BaseT Ethernet ports to provide Internet connectivity to all
computers on your LAN.
Easy-to-use configuration program accessible through a standard web
browser.
System Requirements
In order to use the 6212 ADSL router for Internet access, you must have the
following:
ADSL service subscription from your ISP
A PC with:
— An Ethernet 10/100BaseT network interface card
— A processor equivalent to or faster than a Pentium II 133 MHz
— 32 MB RAM or greater
— Windows 95b, 98, 98SE, 2000, ME, NT, or XP (Note: Windows 95 requires
the installation of the Winsock program, not included.)
— (Optional) An Ethernet hub or switch, if you wish to connect the router to
several computers on an Ethernet network.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 1-1
Page 14

1. Introduction
Parts List
— For system configuration using the supplied web-based program: a web
browser such as Internet Explorer Version 6.0 or later. Netscape is not
supported.
In addition to this document, your 6212 ADSL router should come with the
following:
6212 ADSL router
Power adapter
Ethernet cable (RJ45, straight-through type)
Phone cable (RJ11)
1-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 15
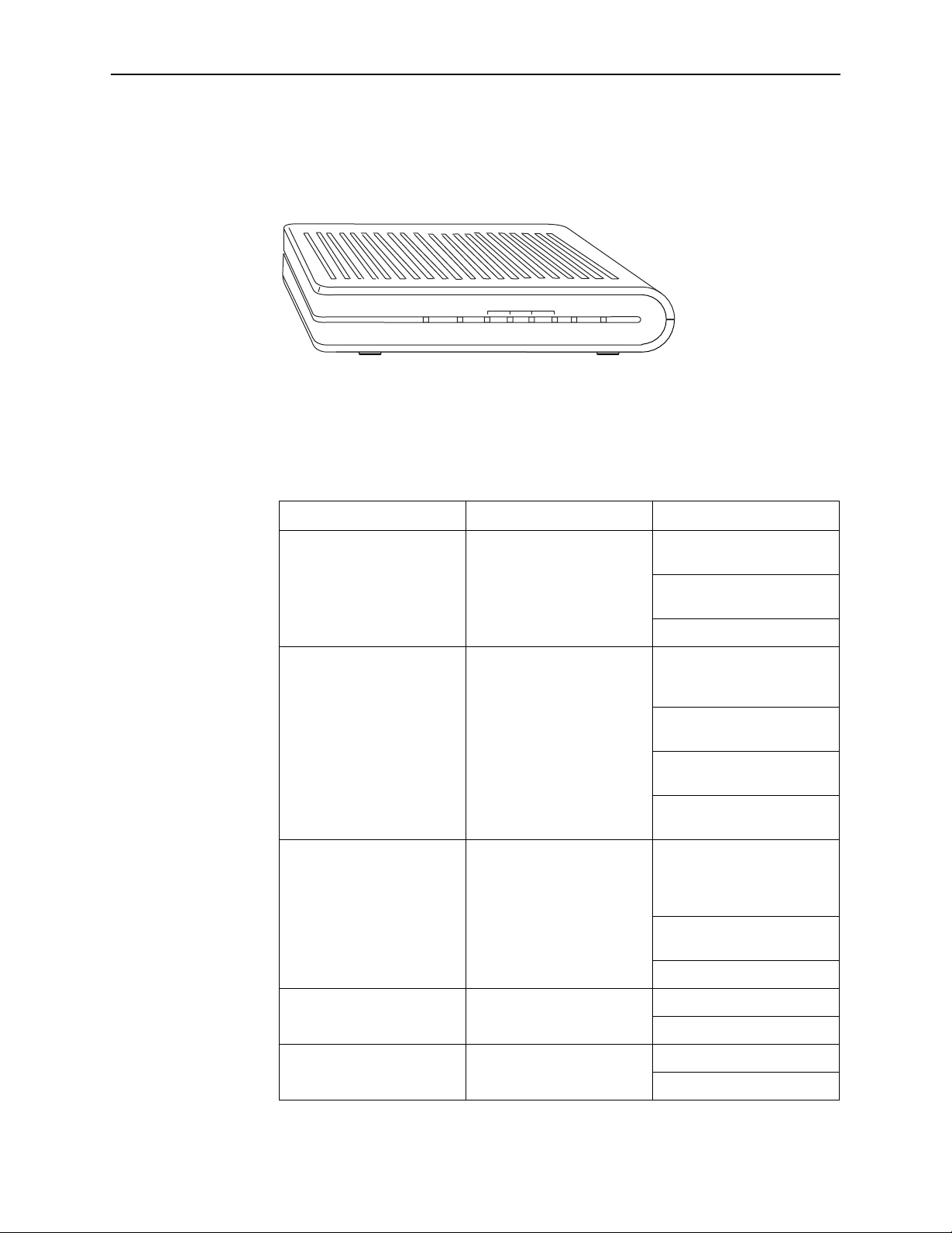
Front Panel
1. Introduction
The front panel contains LED indicators that show the status of the unit.
xDSL LINK
xDSL ACT ALARM POWER
4LAN
32 1
05-17710
Figure 1-1. Front Panel LEDs
Table 1-1. Front Panel Label and LEDs
Label Color Function
xDSL LNK Green On: ADSL link is
established.
Flashing: ADSL link is
established and active.
Off: No ADSL link.
xDSL ACT Green Off: No PPP connection is
established or the
connection is not used.
Blinking: a PPP connection
is being attempted.
Solid: A PPP connection is
established.
Flickering: There is activity
over the link.
LAN 1–4 Green On: The Ethernet interface
is successfully connected to
a device through the LAN
port.
Flashing: Data transfer at
LAN connection
ALARM Red On: ADSL is not connected.
POWER Green On: Unit is powered on.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
Off: No LAN link
Off: ADSL is connected.
Off: Unit is powered off.
1-3
Page 16
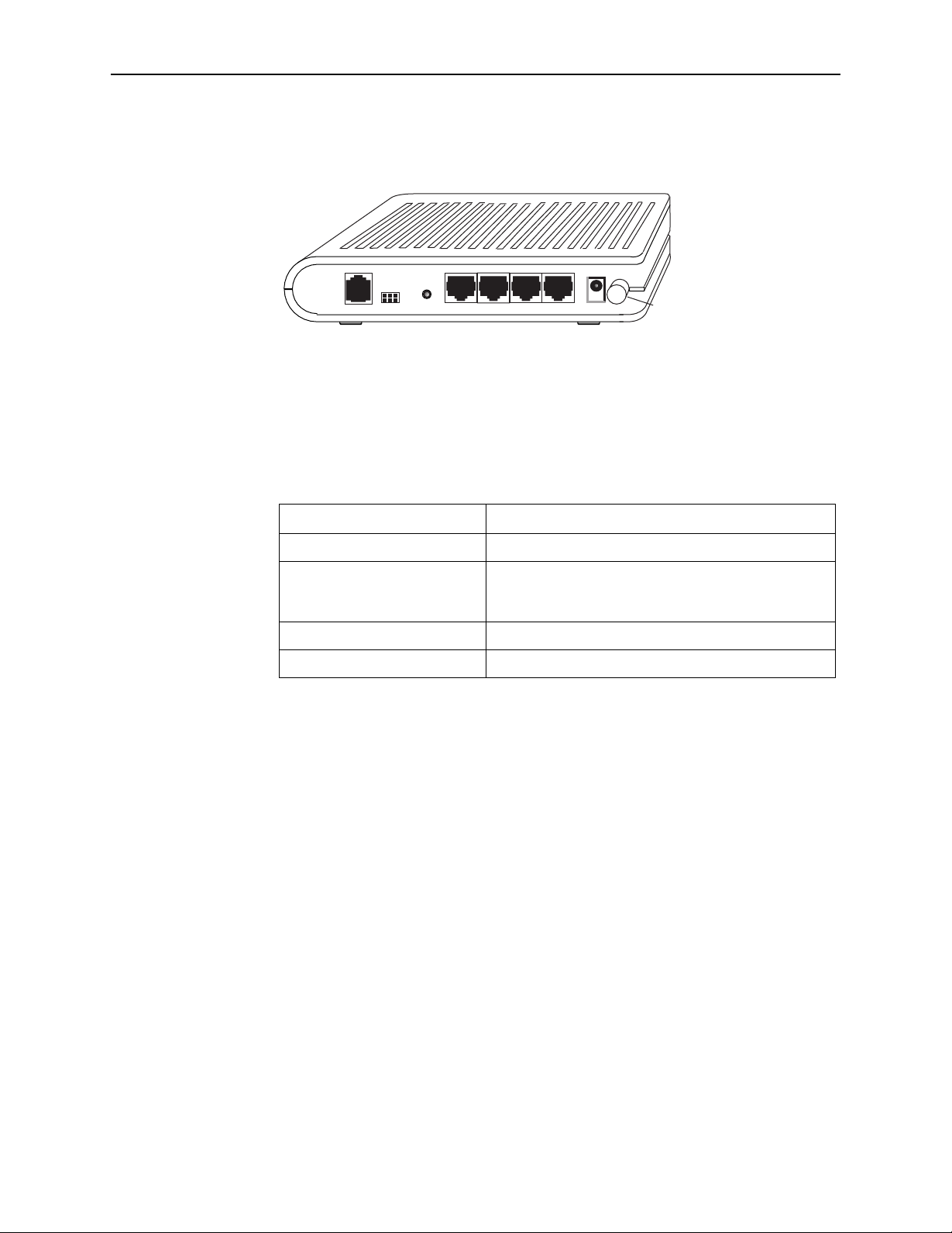
1. Introduction
Rear Panel
RESET
LINE
CONSOLE
DEFAULT
LAN 1
LAN 2 LAN 3 LAN 4
POWER
05-17711
Power
Switch
Figure 1-2. Back Panel
The rear panel contains the ports for the router's data and power connections.
Table 1-2. Rear Panel Labels and Connectors
Label Function
LINE Connects to your ADSL line
LAN 1–4 Connects the router to Ethernet devices on your LAN,
such as your PC's Ethernet port, or the uplink port on a
hub or switch
RESET/DEFAULT To reset the router to its default settings
POWER Connects to the supplied power adapter
1-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 17

Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Overview
This chapter provides basic instructions for connecting the router to a computer or
a LAN and to the Internet using DSL. The first part provides instructions to set up
the hardware, and the second part describes how to prepare your PC for use with
the router.
It is assumed that you have already subscribed to DSL service with your Internet
service provider (ISP).
2
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 2-1
Page 18

2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Connecting the Hardware
Shut down your PC and any other equipment before connecting it to the router. To
connect your router:
Procedure
1. Verify that the router’s power switch is in the Off (outward) position. Verify that
any PCs and other LAN devices you will attach (such as hubs or switches) are
turned off.
2. Use the provided modular phone cable to connect the LINE jack of the router
to your RJ11 wall jack.
3. Use the provided Ethernet cable to connect your computer to the router.
Attach one end of the Ethernet cable to one of the LAN ports on the back of
the router and connect the other end to the Ethernet port or Network Interface
Card (NIC) in your PC.
Connect any other PCs, hubs, and switches to the remaining LAN ports. Either
a crossover or a straight-through Ethernet cable can be used: the router
determines the type of signal required.
4. Connect the cylindrical power plug into the POWER connector on the back of
the device. Next:
— If you have a wall-mount adapter, plug the AC adapter into a wall outlet or
a power strip.
— If you have a table-top adapter, use the AC power cord to connect the
adapter to a wall outlet or power strip.
The supplied power adapter may look different than the one illustrated here.
2-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 19
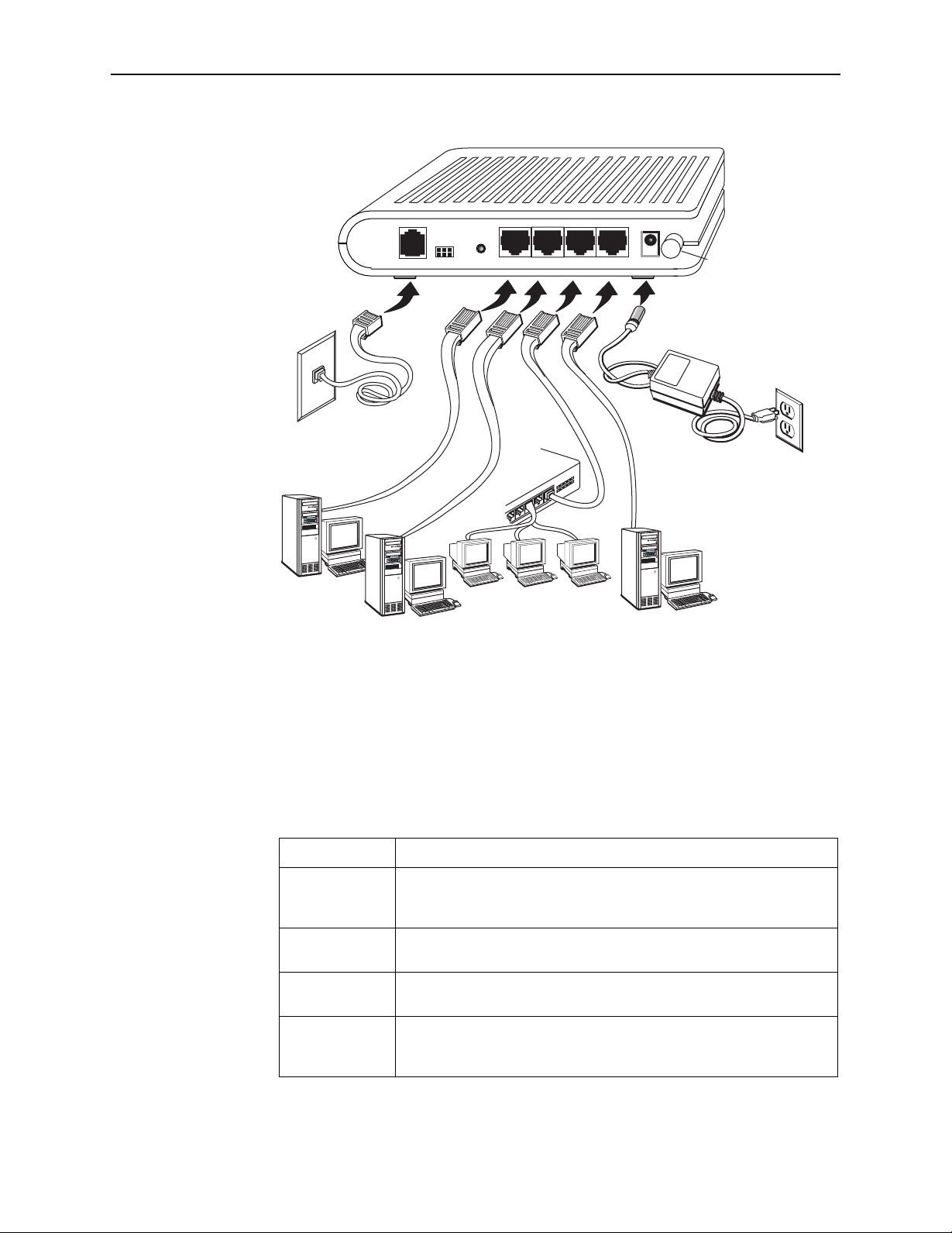
LINE
CONSOLE
RESET
DEFAULT
LAN 1
LAN 2 LAN 3 LAN 4
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
05-17712
Power
Switch
POWER
Figure 2-1. Hardware Installation
5. Turn on your PC and any other LAN devices, such as hubs or switches.
6. Turn on the router using its power switch.
7. Verify that the router's LEDs are illuminated as shown in Ta bl e 2 -1 .
Table 2-1. LED Indicators
This LED . . . Should be:
POWER Solid green to indicate that the device is turned on. If this light is not
on, check if the power adapter is attached to the router and plugged
into an AC power source.
STATUS Solid green to indicate that the router can communicate with your ISP
via ADSL, or flashing when the router is trying to connect to your ISP.
ACTIVITY Flashing when the device is sending or receiving data over the ADSL
connection.
LAN Solid green to indicate that the device can communicate with your PC
via Ethernet, or flashing when the router is sending or receiving data
over Ethernet.
If the LEDs are illuminated as expected, the router is working properly.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
2-3
Page 20
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Configuring Your Computer
Before you can access the router over the LAN you have to configure your PC's
TCP/IP address to be 192.168.1.x (where x is any number between 3 and 254),
with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Your router's default IP address is
192.168.1.1.
If you know the version of Windows that you use, go to the appropriate section
below to learn how to set the IP address of your PC. To determine the version of
Windows running on your PC, click on the Windows Start button, then click on
Run... in the Start menu. Type winver in the Open selection box and click on OK.
Figure 2-2. Windows Run Dialog
The Windows version is displayed.
Figure 2-3. Windows Version
2-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 21
Windows XP
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
1. In the Windows task bar, click on the Start button, and then click on Control
Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network Connections icon.
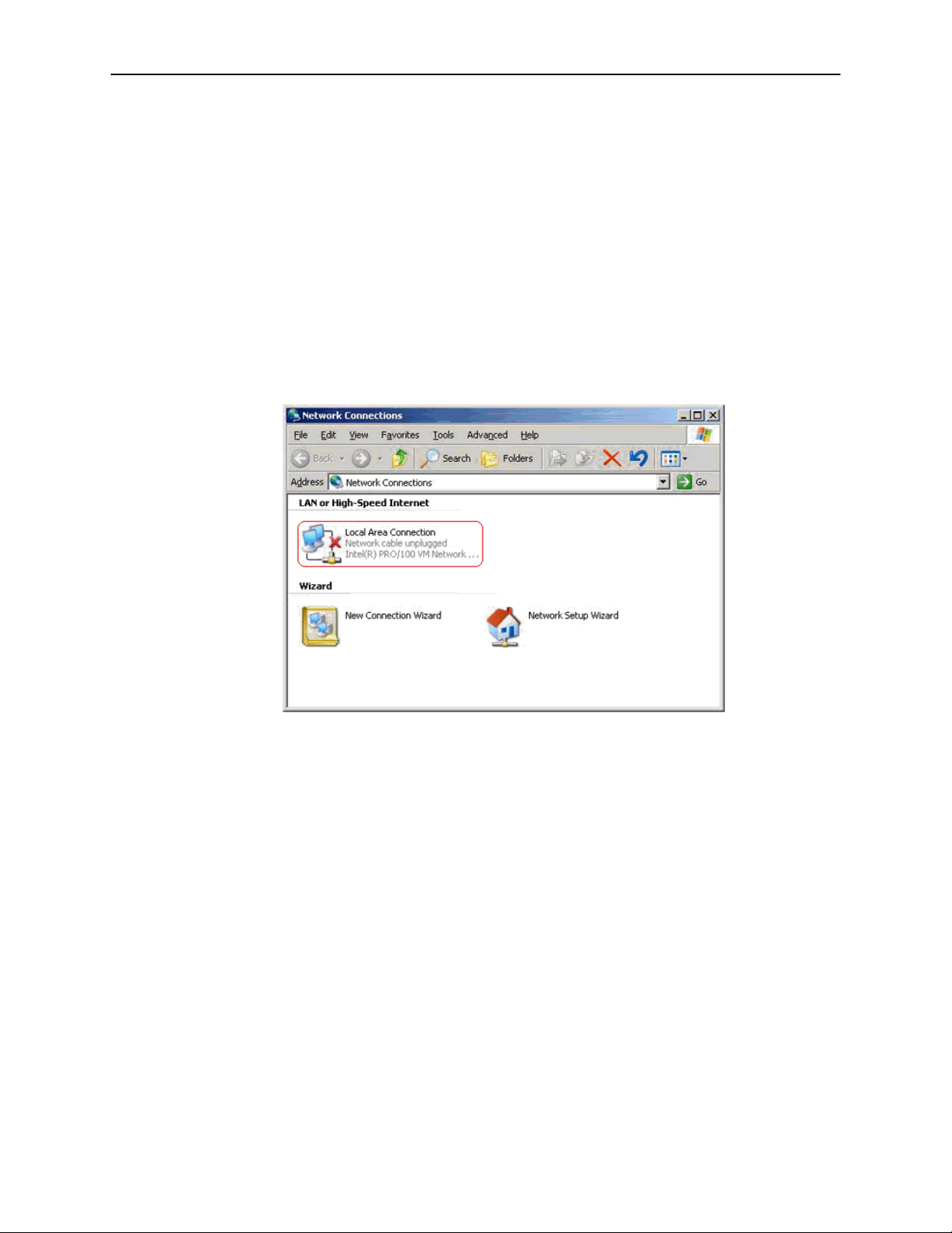
3. In the LAN or High-Speed Internet window, right-click on the icon
corresponding to your network interface card (NIC), and select Properties.
(Often this icon is labeled Local Area Connection). The Local Area Connection
dialog box displays with a list of currently installed network items.
4. Ensure that the check box to the left of the item labeled Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) is checked, and click on Properties.
Figure 2-4. Network Connections (Windows XP)
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
2-5
Page 22
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Figure 2-5. Local Area Connection Properties (Windows XP)
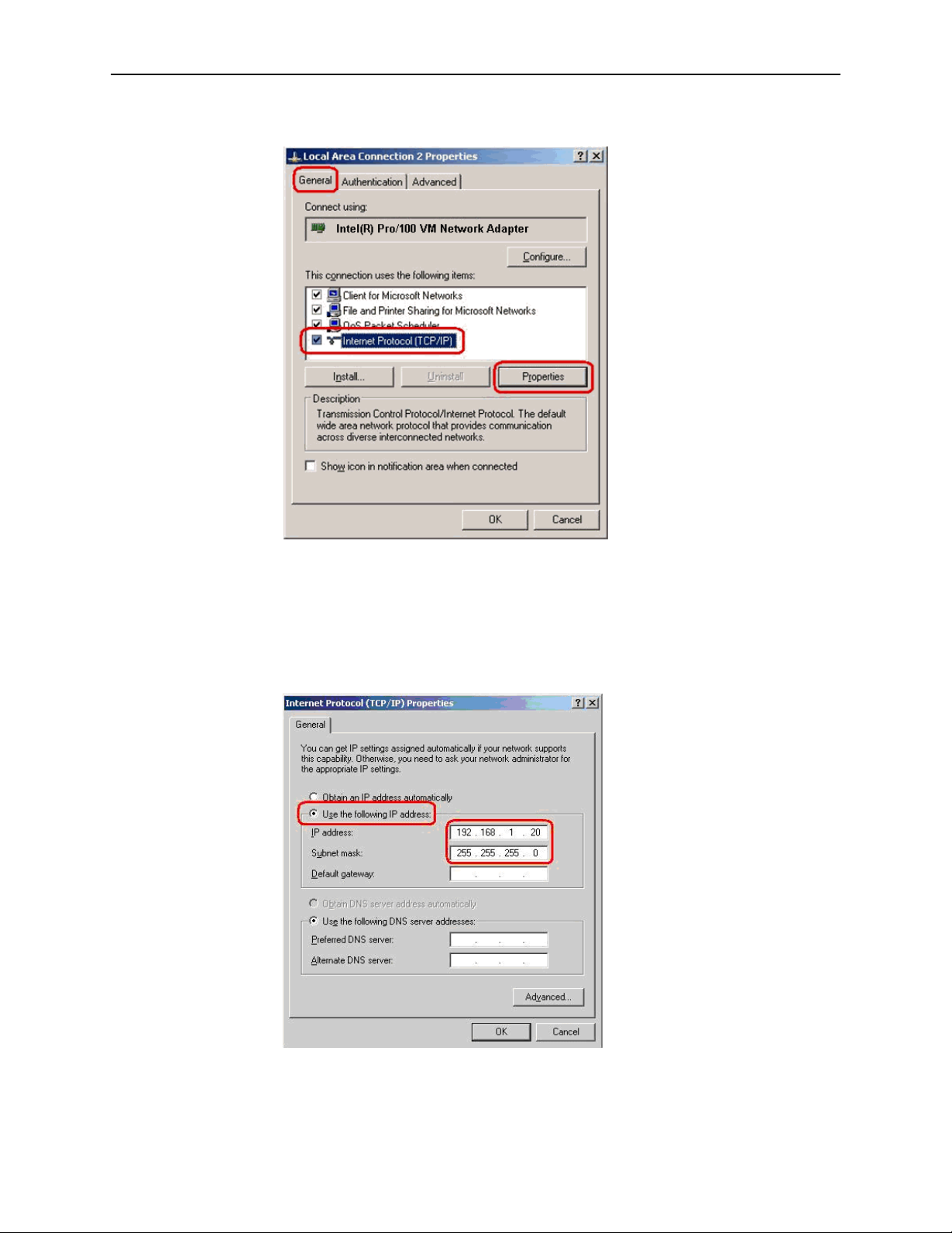
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click on the radio
button labeled Use the following IP address. Type an address between
192.168.1.3 and 192.168.1.254 in the IP Address field (192.168.1.20 is shown
here as an example) and 255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask field.
Figure 2-6. TCP/IP Properties (Windows XP)
6. Click on OK twice to confirm your changes, and close the Control Panel.
2-6 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 23

Windows 2000
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
1. In the Windows task bar, click on the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click on Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click on the Local Area
Connection icon, and then select Properties.
The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box display a list of currently
installed network components. If the list includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP),
the protocol has already been enabled; skip to Step 10.
4. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not appear as an installed component, click
on Install.
5. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select Protocol, and then
click on Add.
6. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Network Protocols list, and then click
on OK.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 2000 installation CD
or other medium. Follow the instructions to install the files.
Windows ME
7. If prompted, click on OK to restart your computer with the new settings.
8. After restarting your PC, double-click on the Network and Dial-up Connections
icon in the Control Panel.
9. In Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click on the Local Area
Connection icon, and then select Properties.
10. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP), and then click on Properties.
11. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click on the radio
button labeled Use the following IP address. Type an address between
192.168.1.3 and 192.168.1.254 in the IP Address field and 255.255.255.0 in
the Subnet Mask field.
12. Click on OK twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the
Control Panel.
1. In the Windows task bar, click on the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click on Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click on the Network
icon, and then select Properties.
The Network Properties dialog box displays a list of currently installed network
components. If the list includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), the protocol has
already been enabled; skip to Step 11.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
2-7
Page 24

2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
4. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not appear as an installed component, click
on Add.
5. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select Protocol, and then
click on Add.
6. Select Microsoft in the Manufacturers box.
7. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Network Protocols list, and then click
on OK.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows Me installation CD or
other media. Follow the instructions to install the files.
8. If prompted, click on OK to restart your computer with the new settings.
9. After restarting your PC, double-click on the Network and Dial-up Connections
icon in the Control Panel.
10. In Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click on the Network icon,
and then select Properties.
11. In the Network Properties dialog box, select TCP/IP, and then click on
Properties.
12. In the TCP/IP Settings dialog box, click on the radio button labeled Use the
following IP address. Type an address between 192.168.1.3 and
192.168.1.254 in the IP Address field and 255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask
field.
13. Click on OK twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the
Control Panel.
Windows 95 and Windows 98
1. In the Windows task bar, click on the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click on Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network icon.
The Network dialog box displays a list of currently installed network
components. If the list includes TCP/IP, the protocol has already been
enabled. Skip to step 9.
3. If TCP/IP does not appear as an installed component, click on Add. The Select
Network Component Type dialog box appears.
4. Select Protocol, and then click on Add.
The Select Network Protocol dialog box appears.
5. Click on Microsoft in the Manufacturers list box, and then click on TCP/IP in
the Network Protocols list box.
6. Click on OK to return to the Network dialog box, and then click on OK again.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 95/98 installation CD.
Follow the instructions to install the files.
7. Click on OK to restart the PC and complete the TCP/IP installation.
2-8 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 25

Windows NT 4.0
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
8. After restarting your PC, open the Control Panel window, and then click on the
Network icon.
9. Select the network component labeled TCP/IP, and then click on Properties.
If you have multiple TCP/IP listings, select the listing associated with your
network card or adapter.
10. In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click on the IP Address tab.
11. Click in the radio button labeled Use the following IP address. Type an address
between 192.168.1.3 and 192.168.1.254 in the IP Address field and
255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask field.
12. Click on OK twice to confirm and save your changes. You will be prompted to
restart Windows. Click on Yes.
1. In the Windows NT task bar, click on the Start button, point to Settings, and
then click on Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel window, double click on the Network icon.
3. In the Network dialog box, click on the Protocols tab.
The Protocols tab displays a list of currently installed network protocols. If the
list includes TCP/IP, the protocol has already been enabled. Skip to Step 9.
4. If TCP/IP does not appear as an installed component, click on Add.
5. In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, select TCP/IP, and then click on
OK.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows NT installation CD or
other medium. Follow the instructions to install the files.
After all files are installed, a window appears to inform you that a TCP/IP
service called DHCP can be set up to dynamically assign IP information.
6. Click on Yes to continue, and then click on OK, if prompted, to restart your
computer.
7. After restarting your PC, open the Control Panel window, and then double-click
on the Network icon.
8. In the Network dialog box, click on the Protocols tab.
9. In the Protocols tab, select TCP/IP, and then click on Properties.
10. In the Microsoft TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click on the radio button labeled
Use the following IP address. Type an address between 192.168.1.3 and
192.168.1.254 in the IP Address field and 255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask
field.
11. Click on OK twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the
Control Panel.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
2-9
Page 26
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
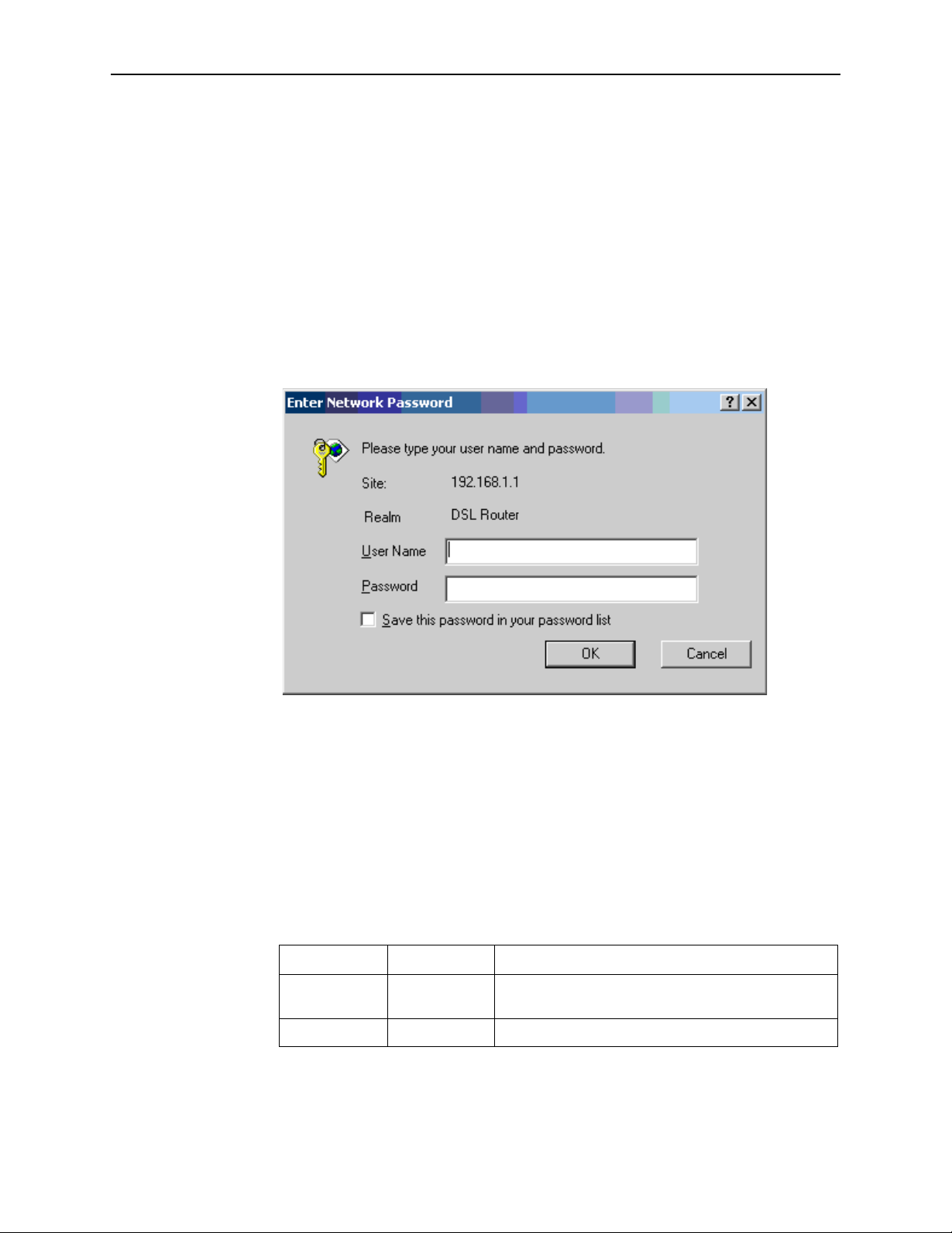
Logging in to Your Router
This section shows how to connect to the router's web interface, configure
settings, and observe some statistics of your Internet connection.
1. Open your Web browser, and type the following URL in the address/location
box, and press Enter:
http://192.168.1.1
This is the default IP address for the LAN port on the router.
A login screen appears.
Figure 2-7. Login Screen
If you have problem connecting to the router, verify that your PC is properly
configured within the subnet of the router's default IP address 192.168.1.1.
Setup is described in Configuring Your Computer on page 2-4.
2. Enter your user name and password, and then click on OK to display the home
page of the router's web interface. There are two default user name and
password combinations:
Table 2-2. Default User Names and Passwords
User Name Password Capability
user user Can display device status, but cannot change or save
configuration options.
admin admin Can perform all functions.
You can change the passwords at any time.
2-10 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 27

The home page is shown in Figure 2-8.
2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
Figure 2-8. Web Interface Home Page
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
2-11
Page 28

2. Hardware Installation and PC Setup
2-12 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 29

Device Information
Status Summary
Display the general status report for the router by clicking on Summary under
Device Info (Figure 3-1).
3
Figure 3-1. Status Summary
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 3-1
Page 30

3. Device Information
WA N
Display the WAN status report from the by clicking on WAN under Device Info
(Figure 3-3).
Figure 3-2. WAN Status
When a WAN connection is configured, the screen looks like Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3. WAN Status with WAN Connection
3-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 31

LAN Statistics
3. Device Information
Display LAN statistics by clicking on LAN under Statistics (Figure 3-4).
Figure 3-4. LAN Statistics
WA N S t a t i s t i c s
Display WAN statistics by clicking on WAN under Statistics (Figure 3-5).
Figure 3-5. WAN Statistics
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
3-3
Page 32

3. Device Information
ATM Statistics
Display ATM statistics by clicking on ATM under Statistics (Figure 3-6).
Figure 3-6. ATM Statistics
ADSL Statistics
Display ADSL statistics by clicking on ADSL under Statistics (Figure 3-7).
Figure 3-7. ADSL Status
3-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 33

ADSL BER Test
3. Device Information
The ADSL Bit Error Rate (BER) test determines the quality of the ADSL
connection. The test is performed by transferring idle cells containing a known
pattern and comparing the received data with this known pattern to check for any
errors (Figure 3-8 and Figure 3-9).
Procedure
To run a BER test:
1. Click on the ADSL BER Test button.
2. Select the test duration and click on Start
3. Check the result.
Figure 3-8. ADSL BER Test — Start
Figure 3-9. ADSL BER Test — Result
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
3-5
Page 34

3. Device Information
Route
Obtain the Routing status report by clicking on the Route item under Device Info
(Figure 3-10)
Figure 3-10. Route Information
ARP
Display the ARP status report by clicking on ARP under Device Info (Figure 3-11)
Figure 3-11. ARP Status
3-6 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 35

Quick Setup
Quick Setup with Auto-Connect Enabled
Auto-connect will automatically detect the first usable PVC and automatically
detect PPPoE, PPPoA, and Bridge Protocol (with DHCP Server available). To use
auto-connect:
Procedure
1. Select Quick Setup. The Quick Setup initial screen appears.
4
Figure 4-1. Quick Setup Initial Screen
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 4-1
Page 36

4. Quick Setup
2. Select DSL Auto-Connect, then click on Next. The progress information
screen appears.
Figure 4-2. Detecting Available PVC
Figure 4-3. Detecting available PVC – Available PVC Detected
4-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 37

Quick Setup with Auto-Connect Disabled
Procedure
1. Select Quick Setup. The Quick Setup initial screen appears.
2. Verify that DSL Auto-Connect is not selected. Entry boxes for VPI and VCI
appear when DSL Auto-Connect is not selected.
3. Specify VPI and VCI as directed by your ISP.
4. Quick Setup
Figure 4-4. Specifying VPI and VCI
4. Click on Next. The Connection Type screen appears.
Figure 4-5. Connection Type
5. Select the protocol and encapsulation type required by your ISP.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
4-3
Page 38

4. Quick Setup
6. Click on Next. Further parameters for the selected protocol are presented. For
example, if you selected PPPoA, the PPP Username and Password screen
appears.
Figure 4-6. PPP Username and Password
7. Click on Next. The Network Address Translation Settings screen appears.
Figure 4-7. NAT Settings
4-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 39

4. Quick Setup
8. Enter the settings specified by your ISP and click on Next. The Device Setup
screen appears.
Figure 4-8. Device Setup
9. If desired, configure configure the DSL Router IP address and Subnet Mask
for the LAN interface to correspond to your LAN's IP Subnet. If you want the
DHCP server to automatically assign IP addresses, then enable the DHCP
server and enter the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign
to your computers. Disable the DHCP server if you would like to manually
assign IP addresses.
If you have a second IP address and subnet mask for the LAN interface, click
on the checkbox to configure it.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
4-5
Page 40

4. Quick Setup
10. Click on Next to continue. The WAN Setup Summary screen displays all WAN
settings that you have made. Check that the settings are correct before
clicking on the Save / Reboot button. Clicking on Save / Reboot saves your
settings and restarts your router.
Figure 4-9. WAN Setup - Summary
4-6 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 41

Advanced Setup
WA N
Set up WAN parameters as directed by your ISP.
5
Figure 5-1. WAN Setup Screen
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 5-1
Page 42

5. Advanced Setup
Add Function – ATM PVC Configuration
If you want to add a new rule for the WAN interface, click on the Add button. The
ATM PVC Configuration screen appears. The ATM PVC Configuration screen
allows you to configure an ATM PVC identifier (VPI and VCI) and select a service
category.
Figure 5-2. ATM PVC Configuration Screen
Verify the following values with your ISP before you change them.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) – The valid range is 0 to 255.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier) – The valid range is 32 to 65535.
Service Category – Five classes of traffic defined are defined:
— UBR Without PCR (Unspecified Bit Rate without Peak Cell Rate)
— UBR With PCR (Unspecified Bit Rate with Peak Cell Rate) – UBR service
is suitable for applications that can tolerate variable delays and some cell
loss, such as data transfer, messaging, distribution, and retrieval, and
remote terminal applications such as telecommuting.
— CBR (Constant Bit Rate) – Used by applications that require a fixed data
rate that is continuously available during the connection time. It is
commonly used for uncompressed audio and video information such as
videoconferencing, interactive audio (telephony), and audio and video
distribution and retrieval.
— Non-Realtime VBR (Non-Real-time Variable Bit Rate) – Can be used for
data transfers that have critical response-time requirements such as
airline reservations, banking transactions, and process monitoring.
— Realtime VBR (Real-time Variable Bit Rate) – Used for time-sensitive
applications such as real-time video. Rt-VBR service allows the network
more flexibility than CBR.
5-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 43

Connection Type Screen
1. Select the type of network protocol and encapsulation mode over the ATM
5. Advanced Setup
PVC that your ISP has instructed you to use, then click on Next button.
Figure 5-3. Connection Type Screen
2. Select a connection type and click on Next. In this example, the Bridge Service
screen appears.
Figure 5-4. Bridge Service Screen
3. Enter or select the parameters presented for the service type, and click on
Next. The WAN Setup - Summary screen appears.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-3
Page 44

5. Advanced Setup
WAN Setup - Summary
1. Make sure that the settings on the WAN Setup - Summary screen match the
settings provided by your ISP. If all settings are correct, click on the Save
button to save these settings; if not, click on the Back button to make any
modifications. If you want to change any item after saving, click on the Edit
button to make any modifications.
Remove Function
Figure 5-5. WAN Setup Summary
2. Activate this WAN interface by clicking on the Finish button and further
configuring services over this interface. The router supports up to five WAN
connections.
If you want to delete a connection from the listed WAN setup, click in the Remove
check box next to the item, then click on the Remove button.
Figure 5-6. WAN Setup List
5-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 45

Finish Function
After you change any item in WAN Setup, remember to click on the Finish button to
apply the changes and reboot the system.
Local Area Network (LAN) Setup
You can configure the DSL Router IP address and Subnet Mask for the LAN
interface to conform your LAN's IP Subnet. If you want the DHCP server to
automatically assign IP addresses, then enable the DHCP server and enter the
range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to your computers.
Disable the DHCP server if you would like to manually assign IP addresses.
The Save button only saves the LAN configuration data. The Save/Reboot button
saves the LAN configuration data and reboots the router to make the new
configuration effective.
5. Advanced Setup
Figure 5-7. LAN Setup
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-5
Page 46

5. Advanced Setup
NAT
Virtual Servers
You can configure the Virtual Server, Port Triggering, and DMZ Host when NAT is
enabled.
A virtual server allows you to direct incoming traffic from the WAN side to a specific
IP address on the LAN side. Click on the Add button to add a virtual server.
Figure 5-8. NAT Virtual Server Setup
You can select a Service or make new one. Enter the Server IP Address, then click
on Save/Apply to submit your configuration.
Figure 5-9. Virtual Server Add Screen
5-6 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 47

5. Advanced Setup
On this screen you can view and delete servers. Click in the check box under
Remove and click on the Remove button to delete selected virtual servers.
Figure 5-10. Removing Selected Virtual Servers
Port Triggering
Click the on the Add button to add Port Triggering for your Internet application.
Figure 5-11. Port Triggering Setup Page
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-7
Page 48

5. Advanced Setup
You can select an application every time or create new one for your application.
Then click on Save/Apply to save your settings.
Figure 5-12. Port Triggering Add Page
On this screen you can view and delete applications. Click in the check box under
Remove and click on the Remove button to delete selected applications.
Figure 5-13. Port Triggering List
5-8 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 49

DMZ Host
5. Advanced Setup
You can define the IP address of the DMZ Host on this screen. Enter the IP
address and click on Save/Apply.
Figure 5-14. DMZ Host Setup
Firewall
For security reasons, firewall options can be configured only from the LAN side of
the router.
IP Filtering – Outgoing
The outgoing filter will block the traffic from the LAN side to the WAN side. Click on
Add to create filters.
Figure 5-15. IP Filtering – Outgoing Filter Setup
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-9
Page 50

5. Advanced Setup
Input the filter name, source information (from the LAN side), and Destination
information (from the WAN side). Then click on Save/Apply.
Figure 5-16. IP Filtering - Outgoing Filter Add Page
You can view and delete the outgoing filter settings on this screen.
Figure 5-17. IP Filtering - Outgoing Filter Setup List
5-10 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 51

IP Filtering – Incoming
Incoming filter filters the traffic from the WAN side to the LAN side. Click on Add to
add incoming filter settings.
Figure 5-18. IP Filtering – Incoming Filter Setup Page
5. Advanced Setup
Enter a filter name, information about the source address (from the WAN side),
and information about the destination address ( to the LAN side). Select the
protocol and WAN interface. Then click on Save/Apply to add the setting.
Figure 5-19. IP Filtering - Incoming Filter Add
You can view and delete the incoming filter settings from this screen.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-11
Page 52

5. Advanced Setup
Figure 5-20. IP Filtering - Incoming Filtering List
Firewall – MAC Filtering
MAC filtering can forward or block traffic by MAC address. You can change the
policy or add settings to the MAC filtering table using the MAC Filtering Setup
screen.
Figure 5-21. IP Filtering - MAC Filtering Setup
If you click on Change Policy, a confirmation dialog lets you verify your change.
Figure 5-22. IP Filtering - MAC Filtering Policy Change Confirmation
5-12 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 53

5. Advanced Setup
If you want to add a setting to the MAC filtering table, enter the Source and
Destination MAC address, and select protocol type, frame direction, and WAN
interface. Then click on Save/Apply to save it.
Figure 5-23. IP Filtering - MAC Filtering Add Page
On this screen you can view and delete MAC filtering rules.
Figure 5-24. IP Filtering - MAC Filtering List
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-13
Page 54

5. Advanced Setup
Parental Control
Use the Parental Control feature to restrict the days and times a particular device
is allowed to access the Internet.
Figure 5-25. Parental Control Screen
To set up parental controls:
1. Click on Add. The Time of Day Restriction screen appears.
Figure 5-26. Parental Control – Time of Day Restrictions
2. Enter a User Name to identify the target of the restrictions.
3. Enter the MAC address of the network adapter to be restricted, and, optionally,
another MAC address.
4. Select the days of the week the restriction is in force.
5. Specify the start and end times the restriction is in force. Use the form hh:mm,
where 23:59, for example, is one minute before midnight.
6. Click on Save/Apply.
5-14 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 55

Port Mapping
5. Advanced Setup
Use the Port Mapping screen to map multiple ports to a PVC and create bridging
groups. Each group will perform as an independent network.
Figure 5-27. Port Mapping
To create a new mapping group:
1. Click on Add. The Port Mapping Configuration screen appears.
Figure 5-28. Creating a Port Mapping Entry
2. Enter a unique Group name.
3. Select interfaces from the available interface list and add them to the grouped
interface list using the arrow buttons to create the required mapping of the
ports.
4. Click on Save/Apply.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-15
Page 56

5. Advanced Setup
Quality of Service
You can configure the Quality of Service to apply different priorities to traffic on the
router.
Figure 5-29. Quality of Service Setup
Click on Add and the Add Network Traffic Class Rule screen appears. To add a
rule:
1. Give a name to this traffic class.
2. Assign a priority level-low, medium, and high-to this traffic class.
3. Select an IP precedence from the range of 0–7.
4. Enter an IP Type of Service from the following selections-
— Normal Service
— Minimize Cost
— Maximize Reliability
— Maximize Throughput
— Minimize Delay
5. Last, enter the traffic conditions for the class such as the protocol (TCP / UDP,
TCP, UDP, or ICMP) to be used.
6. Click on Save / Apply to save the settings.
5-16 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 57

5. Advanced Setup
Figure 5-30. Quality of Service Add Screen
Routing – Default Gateway
You can change the Default Gateway on the Routing - Default Gateway screen. By
default the Enable Automatic Assigned Default Gateway box is checked.
Figure 5-31. Default Gateway Setup
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-17
Page 58

5. Advanced Setup
If you want to specify the default gateway address, then uncheck the box as seen
below. Enter the default gateway address and, optionally, the WAN interface you
will use. Click on Save / Apply to save the settings.
If you add or change the default gateway address, you must reboot the router to
put the new default gateway IP address into effect.
Figure 5-32. Default Gateway Setup
Routing – Static Route
Use the Routing - Static Route screen to add a static route to the routing table.
Figure 5-33. Static Route Setup
5-18 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 59

Routing – RIP
5. Advanced Setup
Enter the route information and click on Save/Apply to make it active. No reboot is
required.
Figure 5-34. Static Route Add
If RIP is enabled, the router operation can be configured as Active or Passive.
Figure 5-35. RIP Setup
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-19
Page 60

5. Advanced Setup
DNS Server
Use the DNS Server screen to request automatic assignment of a DNS or to
specify a primary and secondary DNS.
Dynamic DNS
Figure 5-36. DNS Setup
Use the Dynamic DNS screen to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname,
allowing your router to be easily accessed from anywhere on the Internet.
Figure 5-37. Dynamic DNS
5-20 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 61

To set up a Dynamic DNS entry:
1. Click on Add. The Add Dynamic DNS screen appears.
Figure 5-38. Adding a Dynamic DNS Entry
2. Select a D-DNS Provider from the drop-down list.
3. Enter the Hostname you have selected for the interface.
5. Advanced Setup
ADSL
4. Select the router Interface from the drop-down list.
5. Enter the information you used to register with the dynamic DNS service: for
DynDNS, enter your Username and Password; for TOZ, enter your E-mail
address and Key.
6. Click on Save/Apply.
There are three major items in the ADSL settings.
Figure 5-39. DSL Settings
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-21
Page 62

5. Advanced Setup
Modulation Methods
Phone Line Pair
The following modulation methods are supported by the 6212 ADSL router:
G.dmt Enabled
G.lite Enabled
T1.413 Enabled
ADSL Enabled
Annex L Enabled
ADSL2+ Enabled.
Do not change this setting unless so directed by your ISP.
The 6212 ADSL router supports phone lines on pins 2 and 3 or pins 1 and 4 to
connect your ADSL line. If your phone system uses pins 2 and 3, attach a normal
RJ11 cable to the router and select "Inner pair" on the screen; if your phone
system uses pins 1 and 4, attach the phone with the supplied RJ11 cable and
select "Outer pair" on the screen.
Capability
The following are included under Capability:
Bitswap Enable
SRA (Seamless Rate Adaptation) Enable
Do not change these settings unless so directed by your ISP.
5-22 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 63

DSL Advanced Settings
Do not change the DSL Advanced Settings unless so directed by your ISP. To view
the DSL Advanced Settings screen, click on the Advanced Settings button on the
DSL Settings screen (see Figure 5-39).
There are five test modes between the router and your ISP:
Normal test: Puts the router in a test mode in which it only sends a Normal
signal.
Reverb test: Puts the router in a test mode in which it only sends a Reverb
signal.
Medley test: Puts the router in a test mode in which it only sends a Medley
signal.
No Retrain: In this mode the router will try to establish a connection as in
normal mode, but once the connection is up it will not retrain if the signal is
lost.
L3: Puts the router into the L3 power state.
5. Advanced Setup
Select a test mode and click on Apply. Then click on Tone Selection.
Figure 5-40. DSL Advanced Settings
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
5-23
Page 64

5. Advanced Setup
Tone Selection
To view the ADSL Tone Settings screen, click on the Tone Selection button of the
DSL Advanced Settings screen (see Figure 5-40).
The frequency band of ADSL is split up into 256 separate tones, each spaced
4.3125 kHz apart. With each tone carrying separate data, the technique operates
as if 256 separate modems were running in parallel. The tone range is from 0 to 31
for upstream and from 32 to 255 for downstream.
Do not change these settings unless so directed by your ISP.
Figure 5-41. Tone Settings
5-24 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 65

Diagnostics
Testing the DSL Connection
The diagnostics screen allows you to run diagnostic tests to check your DSL
connection. The screen shows test results for three connections:
Connection to your local network
Connection to your DSL service provider
Connection to your Internet service provider
Use the Test and Test with OAM F4 buttons to retest if necessary.
6
Figure 6-1. Diagnostics
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 6-1
Page 66

6. Diagnostics
6-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 67

Management
Saving and Restoring the Configuration
The configuration of your router can be backed up to a file, and also can be
restored from a file. You can also restore the router to its factory default
configuration.
Backing Up Configuration Settings
To back up your settings, select Management -> Settings -> Backup Settings.
7
Figure 7-1. Back Up Settings Screen
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 7-1
Page 68

7. Management
Verify that you would like to save the file.
Figure 7-2. Backup Settings Upload Confirmation
Select the location where you want to save the file.
Figure 7-3. Backup Settings File Location
7-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 69

Restoring Configuration Settings
To restore saved settings, select Management -> Settings -> Restore User
Settings.
7. Management
Figure 7-4. Restore User Settings Screen
Select the backup file you want to restore and click on Update Settings.
Figure 7-5. Restore Settings File Location
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-3
Page 70

7. Management
The router will restore settings and reboot to activate the restored settings.
Figure 7-6. Upload in Progress Screen
7-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 71

Restoring Default Settings
Restore Default will erase all current settings and restore the router to factory
default settings.
To restore the router to factory default settings, select Management -> Settings ->
Restore Default.
7. Management
Figure 7-7. Restore Default Settings Screen
Reply OK to the confirmation dialog.
Figure 7-8. Restore Default Confirmation Dialog
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-5
Page 72

7. Management
The router will restore the default settings and reboot.
Figure 7-9. Restore Default Settings Reboot
System Log
The System Log dialog allows you to view the System Log and configure the
System Log options.
Figure 7-10. System Log
7-6 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 73

View System Log
7. Management
Click on the "View System Log" button to check the log file.
Figure 7-11. View System Log
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-7
Page 74

7. Management
Configure System Log
If the log is enabled, the system will log selected events: Emergency, Alert, Critical,
Error, Warning, Notice, Informational, and Debugging. All events above or equal to
the selected log levels will be logged (maintained in the system log file) and
displayed.
If the selected mode is Remote or Both, events will be sent to the specified IP
address and UDP port of a remote system log server. If the selected mode is Local
or Both, events will be recorded in the local memory.
Figure 7-12. System Log Configuration
Select the desired values and click on the "Save/Apply" button to configure the
system log options.
7-8 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 75

SNMP
7. Management
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) allows a management application
to retrieve statistics and status from the SNMP agent in the router. Use the SNMP
screen to set up parameters for SNMP access.
Figure 7-13. SNMP Screen
Select the desired values and click on Save/Apply to configure the SNMP options.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-9
Page 76

7. Management
Internet Time
Use the Internet Time screen to specify whether the router uses Simple Network
Time Protocol (SNTP) to obtain the time of day from NTP servers on the Internet.
To set up the router to obtain time from an NTP server:
1. Select “Automatically synchronize with Internet time servers”. The SNTP fields
appear.
Figure 7-14. Internet Time Screen
2. Select NTP servers.
3. Specify the time zone offset for your router’s location.
4. Click on Save/Apply.
7-10 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 77

Access Control – Services
You can enable or disable some services of your router by LAN or WAN. If no WAN
connection is defined, only the LAN side can be configured.
7. Management
Figure 7-15. Services Setup
Access Control – IP Addresses
Web access to the router can be limited when Access Control Mode is enabled.
The IP addresses of allowed hosts can be added using Access Control -> IP
Address.
Figure 7-16. IP Address Setup
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-11
Page 78

7. Management
To assign the IP address of the management station that is permitted to access
the local management services, enter the IP address in the box and click on the
Save/Apply button.
Figure 7-17. Access Control – IP Address Add Screen
Access Control – Passwords
Use Access Control -> Passwords to change a password. Select an account and
enter the current password and the new password. Then click on Save/Apply.
Figure 7-18. Access Control – Passwords Screen
7-12 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 79

Update Software
7. Management
If your ISP releases new software for this router, follow these steps to perform an
upgrade.
1. Obtain an updated software image file from your ISP.
2. Enter the path to the image file location or click on the "Browse" button to
locate the image file.
3. Click on the Update Software button once to upload the new image file.
Figure 7-19. Update Software
Note
The update process takes about two minutes to complete, and your router will
reboot automatically.
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
7-13
Page 80

7. Management
Reboot Router
Select Management -> Reboot Router to reboot the router using the web interface.
The router will save the current configuration and reboot itself using the new
configuration. The rebooting process takes about two minutes to complete.
Figure 7-20. Reboot Router Screen
7-14 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 81

Specifications
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Table A-1. 6212-I1 Specifications
A
Specification Criteria
Environment Operating Temperature: 32° F to 104° F (0° C to 40° C)
Storage Temperature: –4° F to 149° F (–20° C to 65° C)
Humidity: 5% to 95%, non-condensing
Interfaces DSL Line: RJ11
Ethernet: 10/100BaseT, RJ45
Power 100 VAC, 50 Hz
110 VAC, 60 Hz
220 VAC, 50/60 Hz
Protocol Support ANSI T1.413 (Full Rate ADSL)
ITU G.992.1 (DMT)
ITU G.992.2 (G.lite)
ITU G.992.3 (ADSL2)
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+)
ITU G.994.1 (G.hs)
ITU G.997.1
Size 1.2" High x 6.5" Wide x 4.4" Deep
(3.0 cm High x 16.5 cm Wide x 11.2 cm Deep)
Weight (Shipping) 1.5 lbs (0.7 kg)
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 A-1
Page 82

A. Specifications
A-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 83

Index
A
About This Guide, v
Access Control
IP Addresses, 7-11
Passwords, 7-12
Services, 7-11
ADSL, 5-21
BER Test, 3-5
Statistics, 3-4
Advanced Settings, DSL, 5-23
Advanced Setup, 5-1
ARP, 3-6
ATM
PVC Configuration, 5-2
Statistics, 3-4
B
Backing Up Configuration Settings, 7-1
BER Test, 3-5
Bridge Service, 5-4
Bridging groups, 5-15
C
Cables
Installing, 2-2
Capability, 5-22
CE Marking, B
Configuring
PC, 2-4
System Log, 7-8
Connecting Hardware, 2-2
Connection Type, 5-3
D
Default Gateway, 5-17
Default IP Address, 2-4
Definitions, 1-1
Device Information, 3-1
Diagnostics, 6-1
Dimensions, A-1
DMZ Host, 5-9
DNS, 5-20
Dynamic, 5-20
Document
Feedback, A
Purpose and Intended Audience, v
Summary, v
Domain Name Server, 5-20
Dynamic DNS, 5-20
E
EMI Notice
Canada, D
Japan, D
Environment, A-1
Ethernet
cable, 2-2
F
FCC Part 15 Declaration, B
Features, 1-1
Firewall, 5-9
MAC Filtering, 5-12
Firmware Update, 7-13
Front Panel, 1-3
G
Gateway, Default, 5-17
H
Hardware
Connections, 2-2
Installation, 2-1
I
Important Safety Instructions, B
Installing
Hardware, 2-2
Interfaces, A-1
Internet
Restricting access, 5-14
Internet Time, 7-10
Introduction, 1-1
IP Address
Access Control, 7-11
Of Router, 2-4
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005 IN-1
Page 84

Index
IP Filtering
Incoming, 5-11
Outgoing, 5-9
J
Japan Notices, D
L
LAN
ports, connecting, 2-2
Local Area Network (LAN)
Setup, 5-5
Statistics, 3-3
Logging In, 3-1
M
MAC Filtering, 5-12
Management, 7-1
Mapping ports, 5-15
Modulation Methods, 5-22
N
NAT, 5-6
Network Interface Card, 2-2
Notice
to Users of the Canadian Telephone Network, D
to Users of the United States Telephone Network, C
O
Operating Environment, A-1
P
Parental Control, 5-14
Parts List, 1-2
Password
Access Control, 7-12
Default, 2-10
PC Setup, 2-1
Phone Line Pair, 5-22
Port Mapping, 5-15
Port Triggering, 5-7
Power
Specifications, A-1
Supply, 2-2
Product-Related Documents, vi
Protocols Supported, A-1
PVC
Adding, 5-2
Configuring, 5-2
Detecting, 4-1
Q
Quality of Service, 5-4, 5-16
Quick Setup, 4-1
R
Rear Panel, 1-4
Reboot Router, 7-14
Restoring
Configuration Settings, 7-3
Default Settings, 7-5
Restricting access to Internet, 5-14
RIP, 5-19
Route status, 3-6
Routing
Default Gateway, 5-17
RIP, 5-19
Static Route, 5-18
S
Sales, Service, and Training Information, A
Saving and Restoring Configuration, 7-1
Services
Access Control, 7-11
Shipping Weight, A-1
Size, A-1
SNTP, 7-10
Specifications, A-1
Static Route, 5-18
Statistics
ADSL, 3-4
ATM, 3-4
LAN, 3-3
WAN, 3-3
Status
ARP, 3-6
Route, 3-6
Summary, 3-1
WAN, 3-2
System Log, 7-6
Configuring, 7-8
System Requirements, 1-1
T
Test
BER, 3-5
DSL Connection, 6-1
Time, 7-10
Tone Selection, 5-24
Trademarks, A
IN-2 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
Page 85

Index
U
Update Software, 7-13
User Name, Default, 2-10
V
View System Log, 7-7
Virtual Servers, 5-6
W
WAN, 3-2, 5-1
Setup, 5-4
Statistics, 3-3
Status, 3-2
Warranty, A
Web Interface
Home Page, 2-11
Using, 3-1
Weight, A-1
Windows 2000, 2-7
Windows 95, 2-8
Windows 98, 2-8
Windows ME, 2-7
Windows NT, 2-9
Windows XP, 2-5
6212-A2-GB23-00 September 2005
IN-3
Page 86

Index
IN-4 September 2005 6212-A2-GB23-00
 Loading...
Loading...