Paradyne 5620-A2-GN11-30 User Manual

Hotwire 5620 RTU Customer Premises
Installation Instructions
Document Number 5620-A2-GN11-30
August 2000
Contents
What Does the Hotwire 5620 RTU Do? 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the DSL Access Wiring 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the Hotwire 5620 RTU 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status LEDs 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting 13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Increasing the Number of End-User Systems 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cables & Connectors 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Important Safety Instructions 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
What Does the Hotwire 5620 RTU Do?
The Hotwire 5620 RTU (Remote Termination Unit) is a component in the Hotwire
RADSL Access System and interoperates with the Hotwire 8373, 8374, or 8510 DSL
Card in the DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) system. This system
provides high-speed Internet or corporate LAN access over traditional twisted-pair
copper telephone wiring.
Copper pairs run from the central office (CO) to the customer premises (CP) to create
the local loop. The local loop terminates on the customer premises at the demarcation
point in a punchdown block or network interface device (NID).
Optional POTS Splitter
An optional POTS (plain old telephone service) splitter can be installed to block out the
DSL signal and allow the POTS frequencies to pass through. At the customer
premises, the 5620 RTU and a telephone can function simultaneously over the same
pair of copper wires when either:
A Hotwire 5030 or 5038 POTS Splitter is installed near the demarcation point for all
telephones on the same POTS line as DSL,
A Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Filter is installed on each telephone on the same
POTS line as DSL.
or
1
NOTES:
In this document:
— End-user system is used to represent any host with an Ethernet connection.
— Service provider is used to represent any Internet Service Provider (ISP) or
remote LAN access provider.
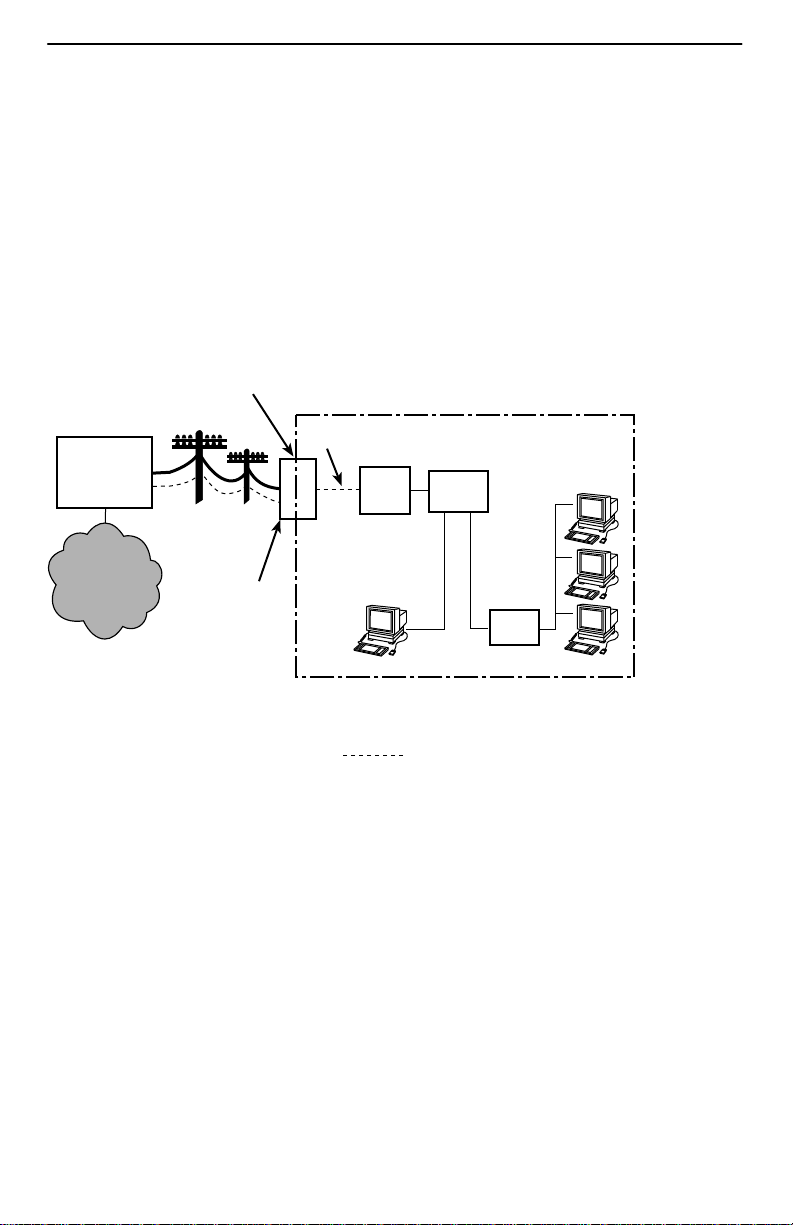
DSL Access without a POTS Splitter
When the Hotwire 5620 RTU is installed without a POTS splitter , the DSL line is used
for data only and does not provide telephone services.
Demarcation
Point
Central
Office
(CO)
Local Loop
Service
Provider
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line RTU – Remote Termination Unit
NID – Network Interface Device New Wiring Connections
Punchdown
Block or NID
Customer Premises (CP)
POTS/DSL
DSL
Jack
Ethernet
Crossover
Cable
RTU
or
End-user
Systems
Ethernet
Cable
Hub
00-16725
2
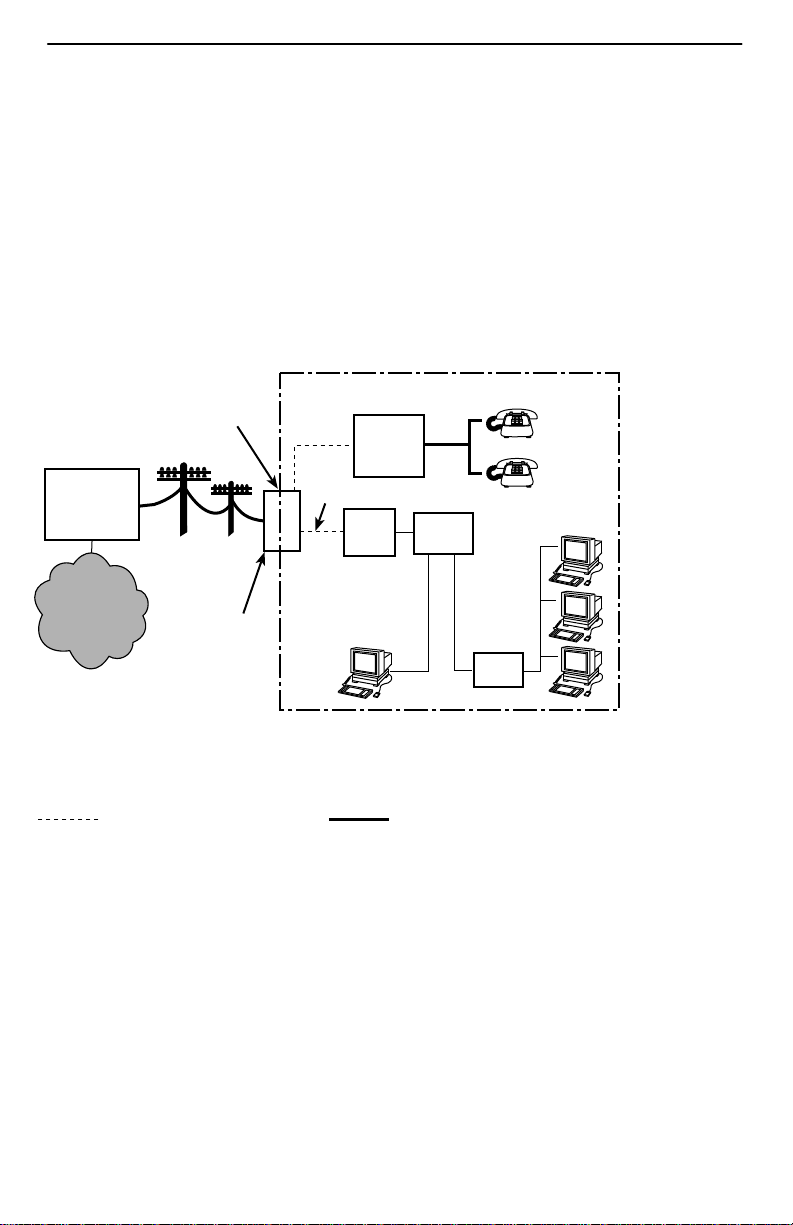
DSL Access with a Hotwire 5030 or 5038 POTS Splitter
When a Hotwire POTS splitter is used at both ends of the local loop, wiring is
connected:
From the demarcation point to the CP POTS splitter, and
From the demarcation point to the DSL jack.
The Hotwire 5030 POTS Splitter is designed for outdoor or indoor installation. The
Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter is designed for indoor use only .
Customer Premises (CP)
Demarcation
Point
POTS
CP
POTS
Splitter
Central
Office
(CO)
Service
Provider
Local Loop
Punchdown
POTS/DSL
DSL
Jack
Ethernet
Crossover
Cable
RTU
or
End-user
Systems
Ethernet
Cable
Block or NID
Hub
00-16726
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
NID – Network Interface Device RTU – Remote Termination Unit
New Wiring Connections Existing Wiring (POTS)
3
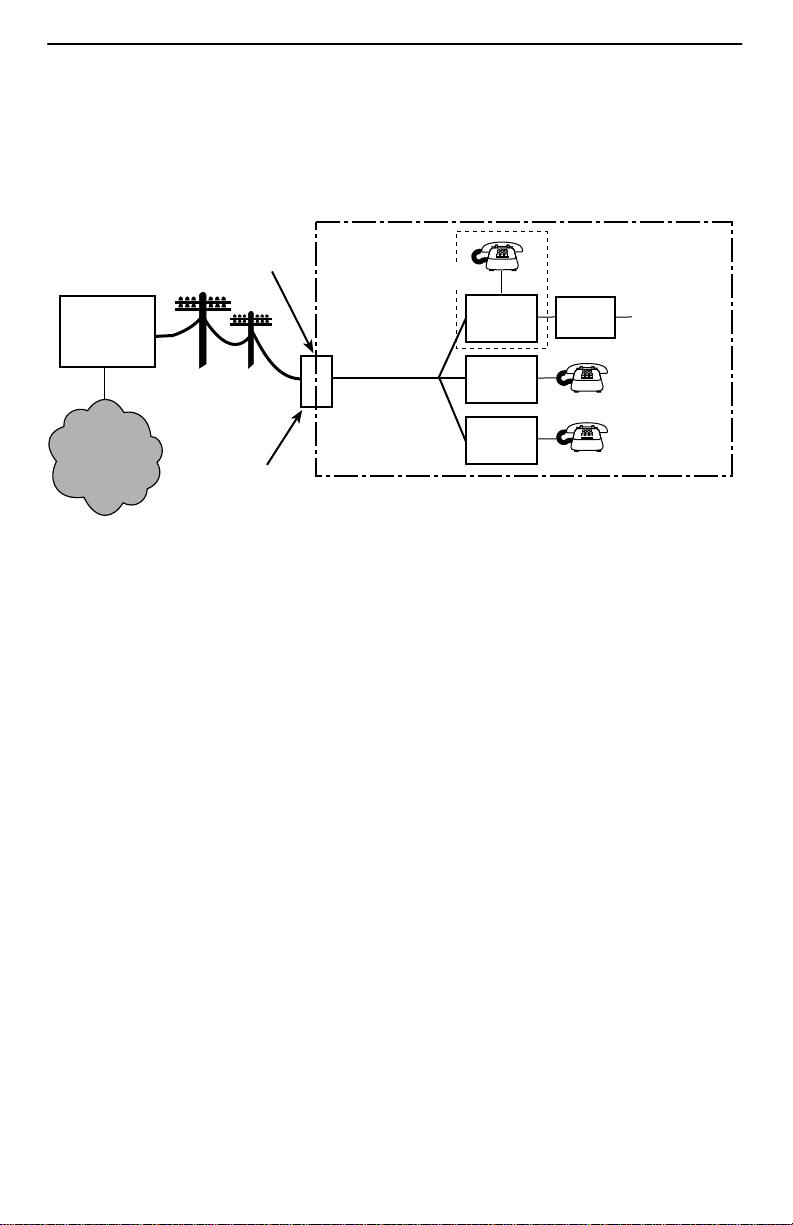
DSL Access with a Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter
When a Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter is used, one 5038 Distributed POTS
Splitter is installed as a phone filter for each telephone on the same POTS line as DSL.
Customer Premises (CP)
Demarcation
Point
Central
Office
(CO)
POTS/DSL
Local Loop
Optional
POTS
Splitter
POTS
Splitter
RTU
To End-user
Systems
Service
Provider
Punchdown
Block or NID
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
NID – Network Interface Device RTU – Remote Termination Unit
POTS
Splitter
00-16727
Product-Related Documents
To install a POTS splitter, refer to the appropriate POTS splitter document:
Document Number Document Title
5030-A2-GN10
5038-A2-GN10
Contact your sales or service representative to order additional product documentation.
Paradyne documents are available on the World Wide Web at www.paradyne.com.
Select
Library → Technical Manuals → Hotwire DSL & MVL Systems.
Hotwire 5030 POTS Splitter Customer Premises
Installation Instructions
Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter Customer
Premises Installation Instructions
4

Package Checklist
Verify that your package contains the following:
Model 5620 Remote Termination Unit (RTU)
DSL interface cable with RJ1 1 modular plugs
Power cord with power transformer
Wiring and Cables You Need
The following wiring and standard connectors are used with this product:
Standard RJ1 1 wall jack for the DSL cabling.
DSL cabling: New or existing unshielded twisted-pair wiring (CA T3 or better). The
CAT3 wiring must meet EIA/TIA-568 specifications with 24 AWG (.5 mm) or
26 AWG (.4 mm).
Ethernet cabling: Standard Ethernet 8-pin, non-keyed modular plug for a PC or
workstation. An Ethernet straight-through or crossover cable is used. Refer to
Installing the Hotwire 5620 RTU
on page 9 for Ethernet cable details.
Refer to
Cables & Connectors
on page 14 for standard pin numbers.
5
Installing the DSL Access Wiring
The local loop terminates at the punchdown block or NID. Wiring must be connected
from the customer premises side of the punchdown block or the NID to an RJ1 1 jack.
Typically, the punchdown block is installed in commercial locations and the NID is
installed in residential locations.
Procedure
1. Access the punchdown block or NID.
2. Disconnect the DSL access pair from the local loop.
!
WARNING:
Do not continue unless the DSL access line from the local loop has been
disconnected at the NID or punchdown block. Refer to
Instructions
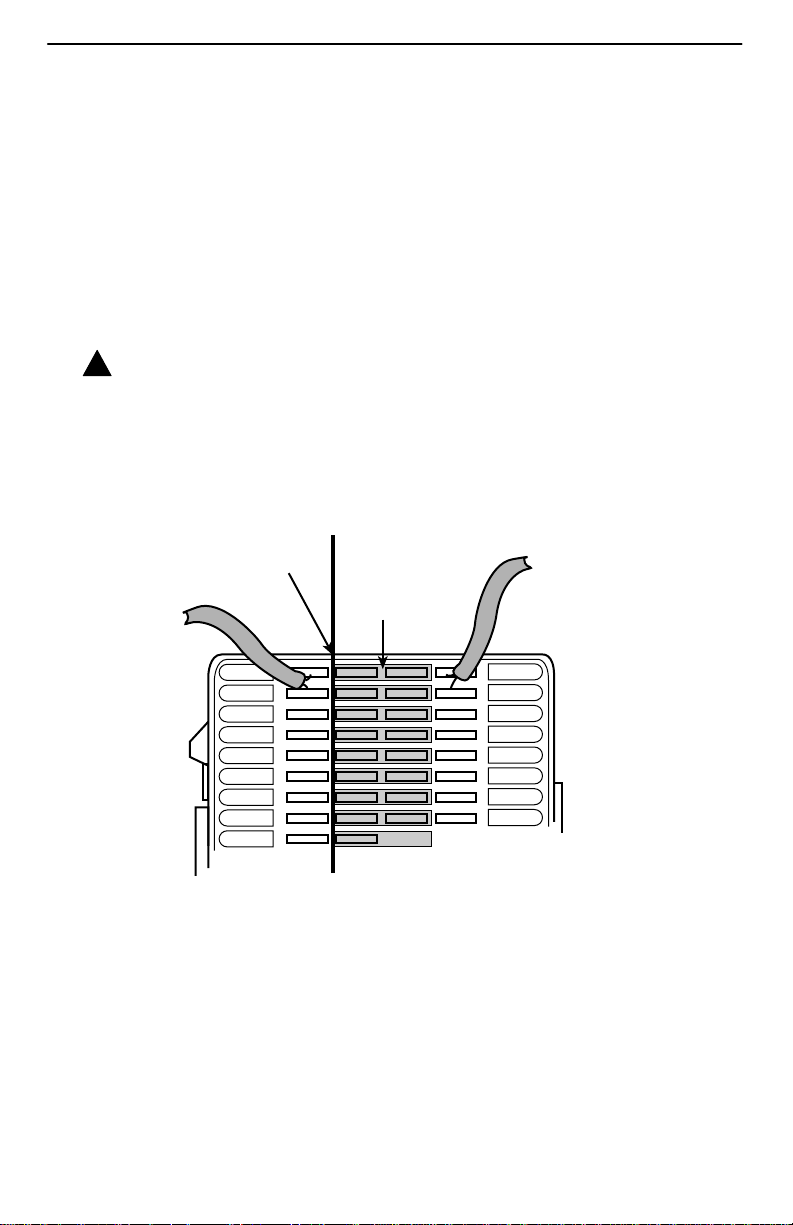
A punchdown block is used without a POTS splitter in the following example.
on page 19.
Important Safety
Punchdown Block
Demarcation Point
DSL
Access
from Local
Loop
Customer Premises
Bridge Clip
ABCD
Wiring to
DSL Jack
97-15348
6
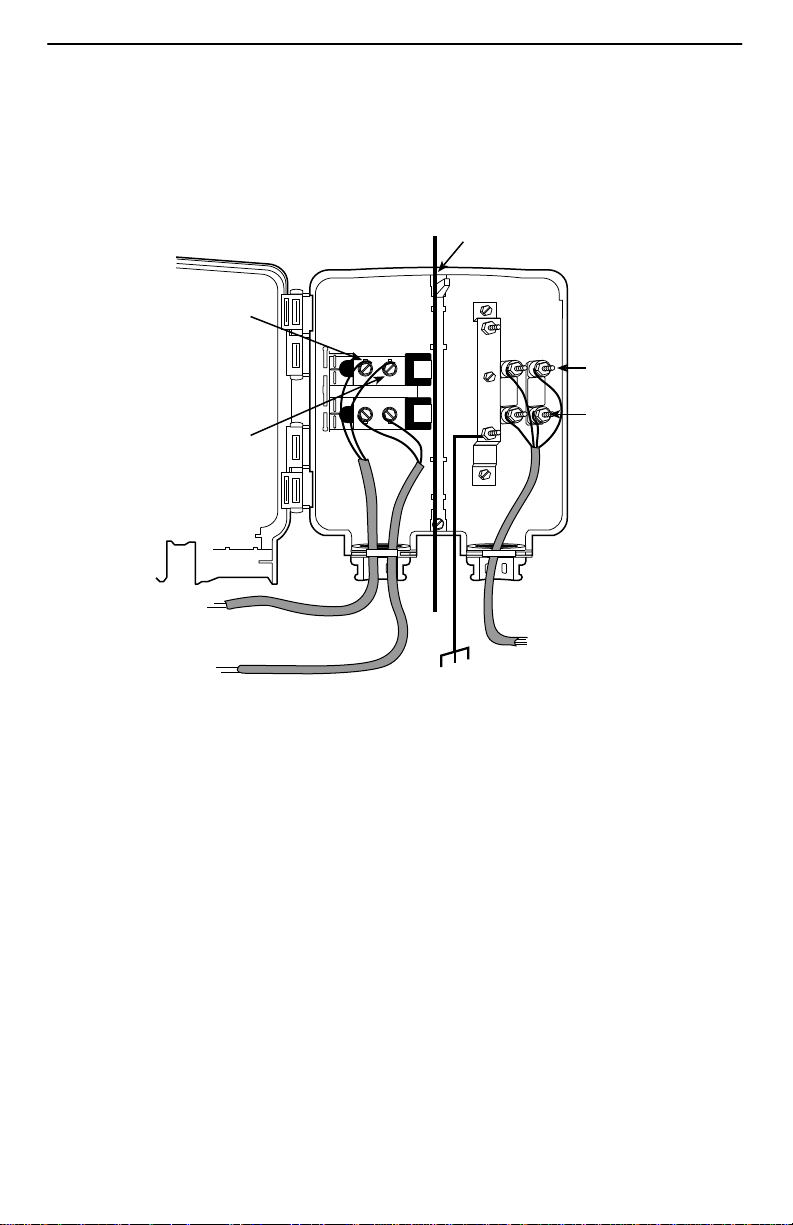
3. Locate the DSL pair of T1/R1 connectors on the customer premises side of the
NID or punchdown block. Attach the wiring that will be connected to the DSL jack.
In the following example, a NID is used without a POTS splitter. It includes an
existing POTS line and a second pair installed for DSL access.
Telephone Network Interface Device (NID)
Customer Premises
Demarcation Point
Tip
T1
(Green)
DSL Pair
Wiring to
DSL Jack
Existing POTS
Wiring to
Telephone
Ring
R1
(Red)
Ground
POTS Pair
DSL/POTS
Access from
Local Loop
97-15438-01
7
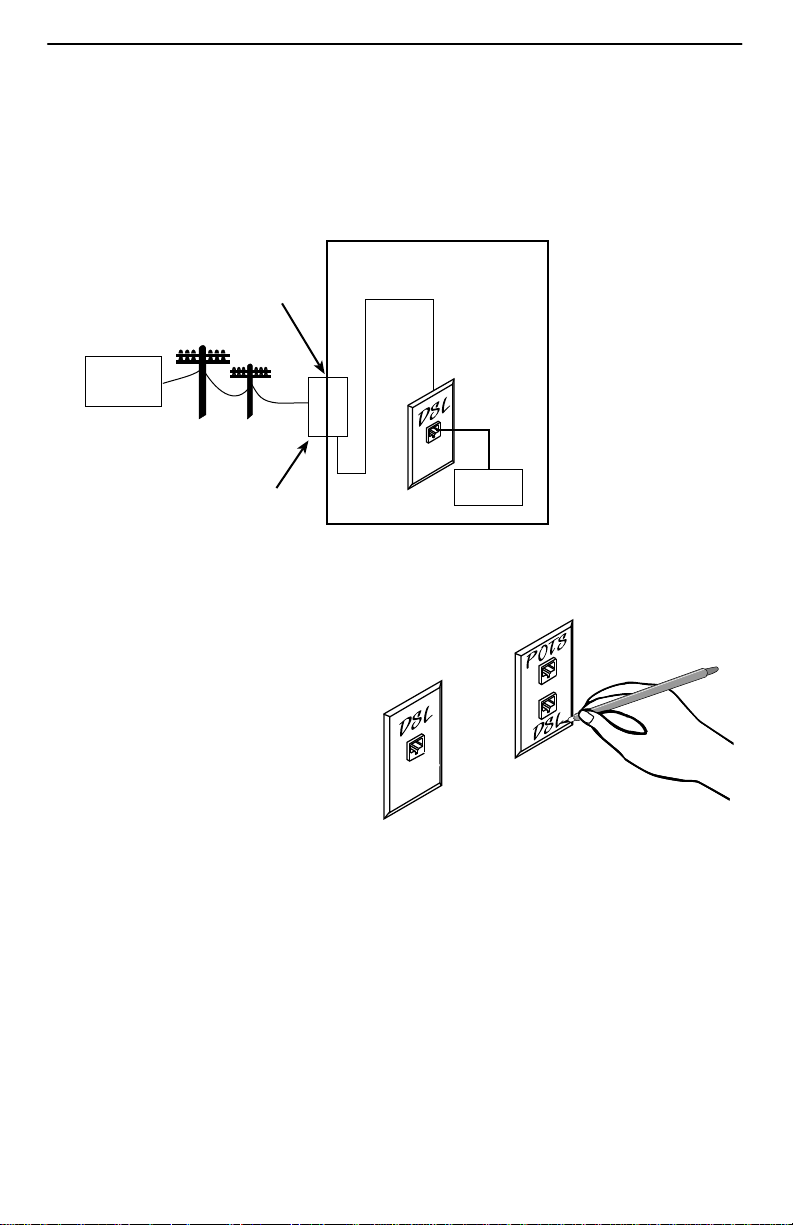
Connecting to the DSL Access Wiring
The Hotwire 5620 RTU connects to the local loop via wiring from the demarcation point
to an RJ1 1 wall jack. The DSL twisted-pair wiring from the local loop terminates at a
new or existing wall jack. It may be necessary to install a standard single RJ11 jack or
replace a single jack with a double RJ1 1 jack.
Customer Premises
Demarcation Point
Central
Office
POTS/DSL
Local Loop
Punchdown
Block or NID
DSL
Twisted-pair
Wiring
DSL
RJ11
Jack
RTU
97-15343-02
Procedure
1. Wiring can be run from the
punchdown block or NID to a
new or existing wall jack. Match
the pair colors on both ends.
2. Label the DSL jack.
3. Reconnect the DSL access pair
at the punchdown block or NID.
Refer to
Wiring
terminal screws with a flat-blade
screwdriver.
The RJ1 1 6-pin jack uses the center two pins. For pin assignments, refer to
Connectors
Installing the DSL Access
on page 6. Tighten both
on page 14.
RJ11 Wall Jack
or
8
97-15300a
Cables &
 Loading...
Loading...