Page 1

TM
Hotwire 5446 RTU Customer Premises
Installation Instructions
Document Number 5446-A2-GN10-60
May 1999
Before You Begin
The Hotwire 5446 RTU (Remote Termination Unit) interoperates with the Hotwire 8546
DSL Card in the DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) system.
An optional POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) splitter is available for the Hotwire
5446 RTU. When a POTS splitter is installed, the telephone and 5446 RADSL (Rate
Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line) RTU can function at the same time over the same pair
of copper wires. In order to confirm the RTU installation, the POTS splitter should be
installed first.
To install a POTS splitter, refer to the appropriate POTS splitter document:
Document Number Document Title
5030-A2-GN10
5038-A2-GN10
Contact your sales or service representative to order additional product documentation.
Paradyne documents are available on the World Wide Web at www.paradyne.com.
Select
Library → Technical Manuals.
Hotwire 5030 POTS Splitter Customer Premises
Installation Instructions
Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter Customer
Premises Installation Instructions
Wiring and Cables Needed
The following wiring and standard connectors are used with this product:
New or existing unshielded twisted-pair wiring (CA T3 or better). The CAT3 wiring
must meet EIA/TIA-568 specifications with 24 AWG (.5 mm) or 26 A WG (.4 mm).
Standard RJ1 1 wall jack.
Standard Ethernet 8-pin, non-keyed modular plug for a PC or workstation. An
Ethernet straight-through or crossover cable is used. Refer to
5446 RTU,
After the RTU is installed and powered on, there are additional requirements in order to
utilize the DSL and Ethernet connections. Refer to
page 16.
page 8, for Ethernet cable details.
Hotwire 5446 RTU IP Setup
1
Installing the Hotwire
,
Page 2

Package Checklist
Verify that your package contains the following:
-
Model 5446 Remote Termination Unit (RTU)
-
DSL interface cable with RJ11 connectors
-
Power cord with power transformer
Refer to
Be sure to register your warranty at www.paradyne.com. Select
Warranty Registration
Cables & Connectors,
.
page 17, for standard pin numbers.
Service & Support
→
What Does the Hotwire 5446 RTU Do?
The Hotwire 5446 RTU is a component in the Hotwire RADSL Access System. This
system provides high-speed Internet or corporate LAN access over traditional
twisted-pair copper telephone wiring.
A POTS splitter blocks out the DSL signal and allows the POTS frequencies to pass
through. At the customer premises, the RADSL RTU and a telephone can function
simultaneously over the same pair of copper wires when either:
H A Hotwire 5030 or 5038 POTS Splitter is installed near the demarcation point for all
telephones on the same POTS line as DSL,
H A Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Filter is installed on each telephone on the same
POTS line as DSL.
DSL Access with a Hotwire 5030 or 5038 POTS Splitter
Copper pairs run from the central office (CO) to the customer premises (CP) to create
the local loop. The local loop terminates on the customer premises at the demarcation
point in a punchdown block or network interface device (NID).
The Hotwire 5030 POTS splitter is designed for outdoor or indoor installation. The
Hotwire 5038 POTS Splitter is designed for indoor use only .
When a Hotwire POTS splitter is used at both ends of the local loop, wiring is
connected:
H From the demarcation point to the CP POTS splitter, and
H From the demarcation point to the DSL jack.
or
NOTES:
In this document:
— End-user system is used to represent any PC with an Ethernet connection and
DSL-based service.
— Network Service Provider (NSP) is used to represent any Internet Service
Provider (ISP) or remote LAN access provider.
2
Page 3
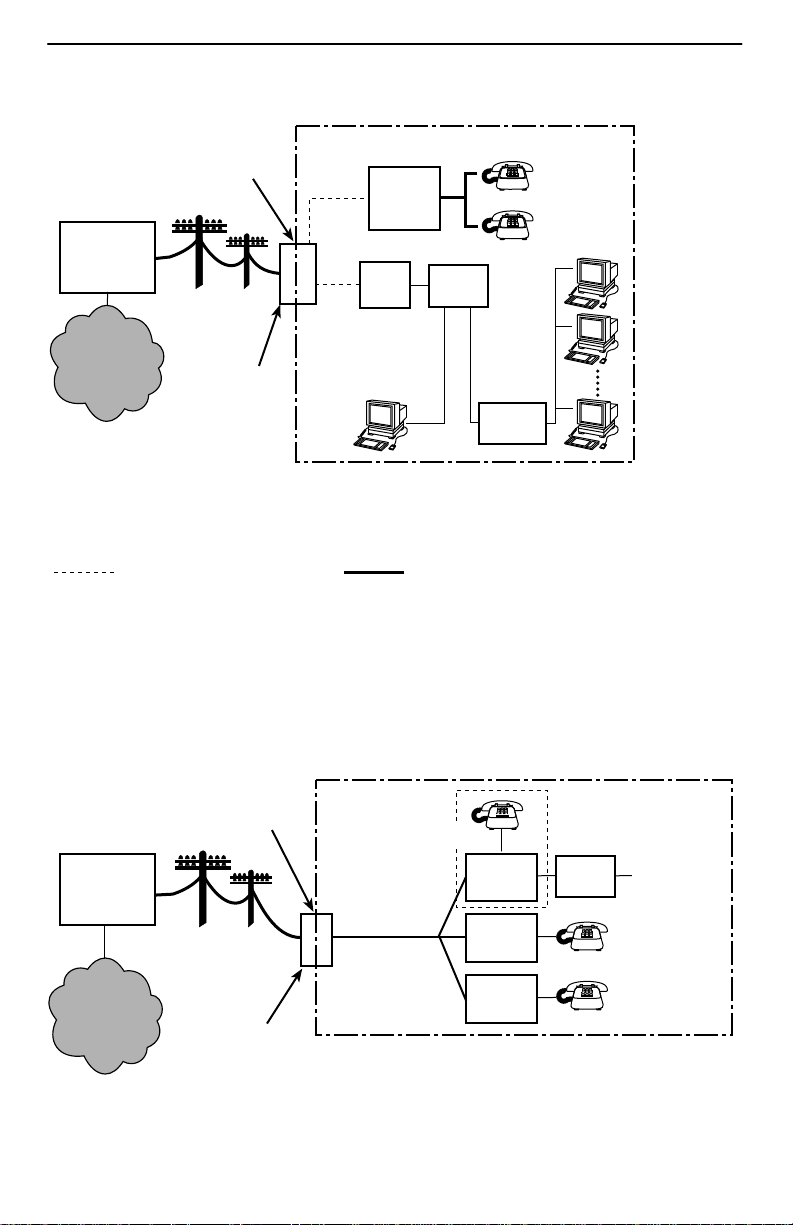
Customer Premises (CP)
Demarcation
CP
POTS
Splitter
DSL
Jack
Ethernet
Crossover
Cable
RTU
or
End-user
Systems
Ethernet
Cable
Hub or
Central
Office
(CO)
Network
Service
Provider
(NSP)
Point
Local Loop
Punchdown
Block or NID
POTS
DSL
Router
98-16105
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
NID – Network Interface Device RTU – Remote Termination Unit
New Wiring Connections Existing Wiring (POTS)
DSL Access with a Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter
When a Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS Splitter is used, one 5038 Distributed POTS
Splitter is installed as a filter for each telephone on the same POTS line as DSL.
Customer Premises (CP)
Demarcation
Point
Optional
Central
Office
POTS
Splitter
RTU
To End-user
Systems
(CO)
Network
Service
Provider
(NSP)
POTS/DSL
Local Loop
Punchdown
Block or NID
POTS
Splitter
POTS
Splitter
98-15815-01
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
NID – Network Interface Device RTU – Remote Termination Unit
3
Page 4
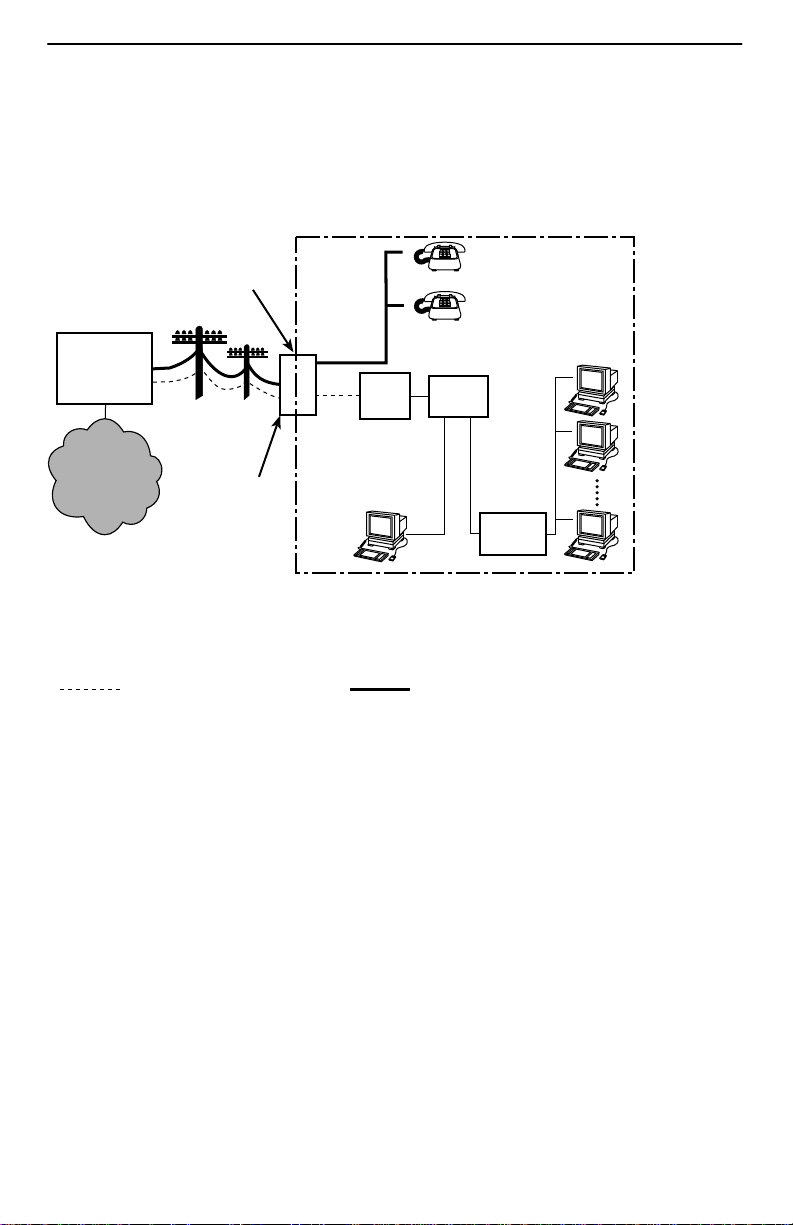
DSL Access without a POTS Splitter
When the Hotwire 5446 RTU is installed without a POTS splitter , a second telephone
wiring pair is needed for DSL access.
Customer Premises (CP)
Demarcation
Point
End-user
Systems
Central
Office
(CO)
Local Loop
POTS
DSL
DSL
Jack
RTU
Network
Service
Provider
(NSP)
Punchdown
Block or NID
Ethernet
Crossover
Cable
or
Ethernet
Cable
Hub or
Router
98-16104
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
NID – Network Interface Device RTU – Remote Termination Unit
New Wiring Connections Existing Wiring (POTS)
4
Page 5
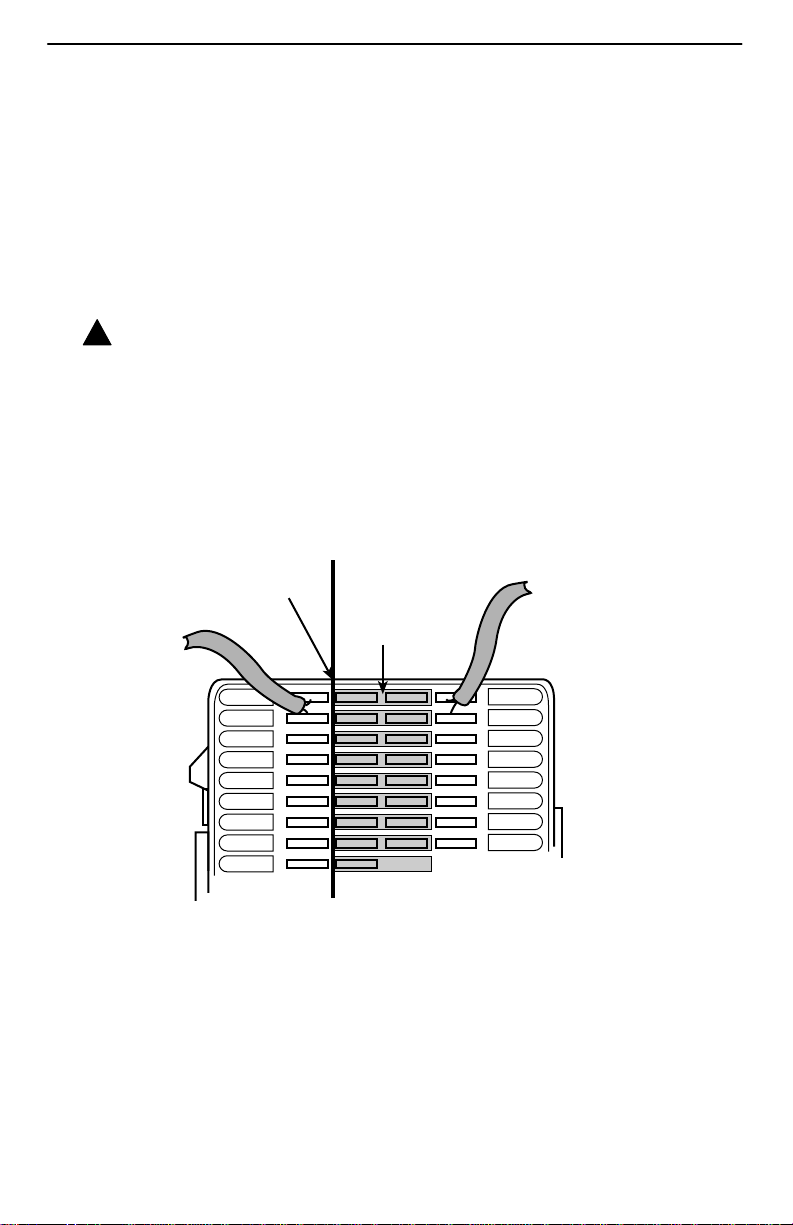
Installing the DSL Access Wiring
The local loop terminates at the punchdown block or NID. Wiring must be connected
from the customer premises side of the punchdown block or the NID to an RJ1 1 jack.
Typically, the punchdown block is installed in commercial locations and the NID is
installed in residential locations.
Pr ocedure
1. Access the punchdown block or NID.
!
WARNING:
Do not continue unless the DSL access line from the local loop has been
disconnected at the NID or punchdown block. Refer to
Instructions,
2. Disconnect the DSL access pair from the local loop.
A punchdown block is used without a POTS splitter in the following example.
page 20.
Important Safety
Punchdown Block
Demarcation Point
DSL
Access
from Local
Loop
Customer Premises
Bridge Clip
ABCD
Wiring to
DSL Jack
97-15348
5
Page 6
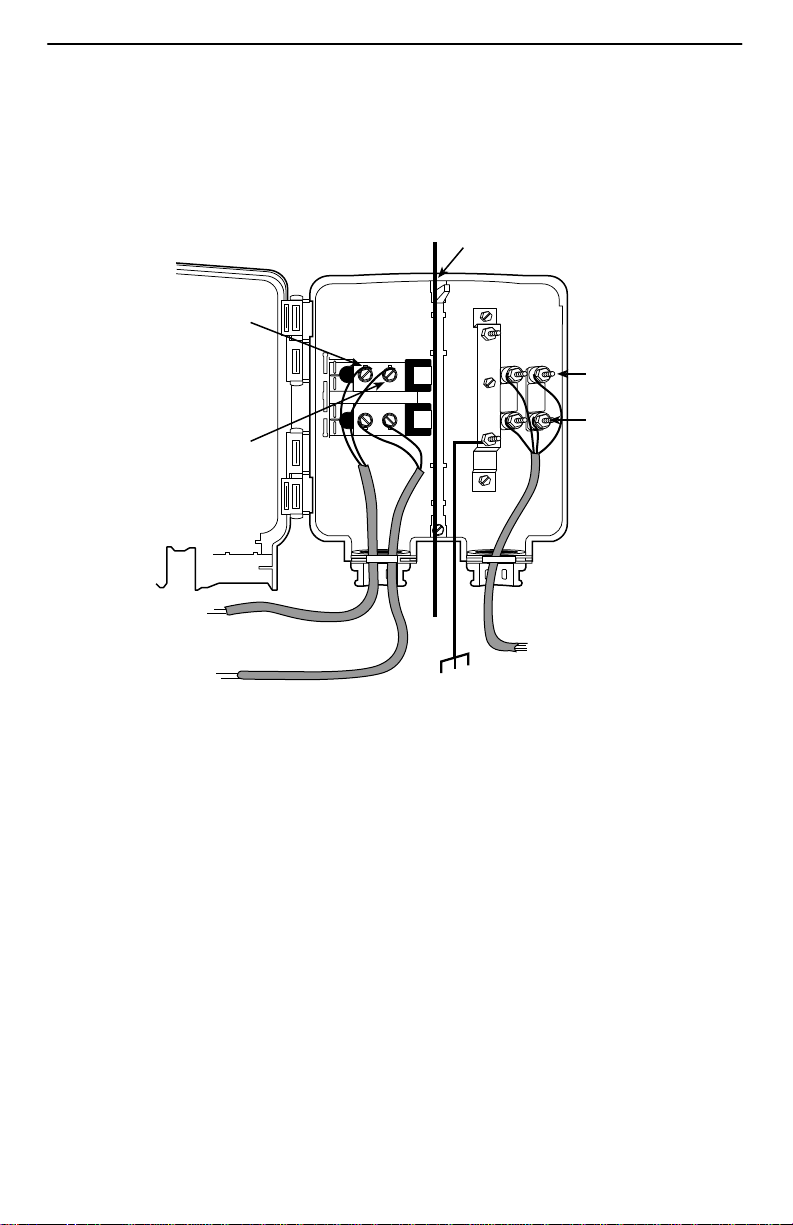
3. Locate the DSL pair of T1/R1 connectors on the customer premises side of the NID
or punchdown block. Attach the wiring that will be connected to the DSL jack. In the
following example, a NID is used without a POTS splitter. It includes an existing
POTS line and a second pair installed for DSL access.
Telephone Network Interface Device (NID)
Customer Premises
Demarcation Point
Tip
T1
(Green)
DSL Pair
Wiring to
DSL Jack
Existing POTS
Wiring to
Telephone
Ring
R1
(Red)
Ground
POTS Pair
DSL/POTS
Access from
Local Loop
97-15438-01
6
Page 7
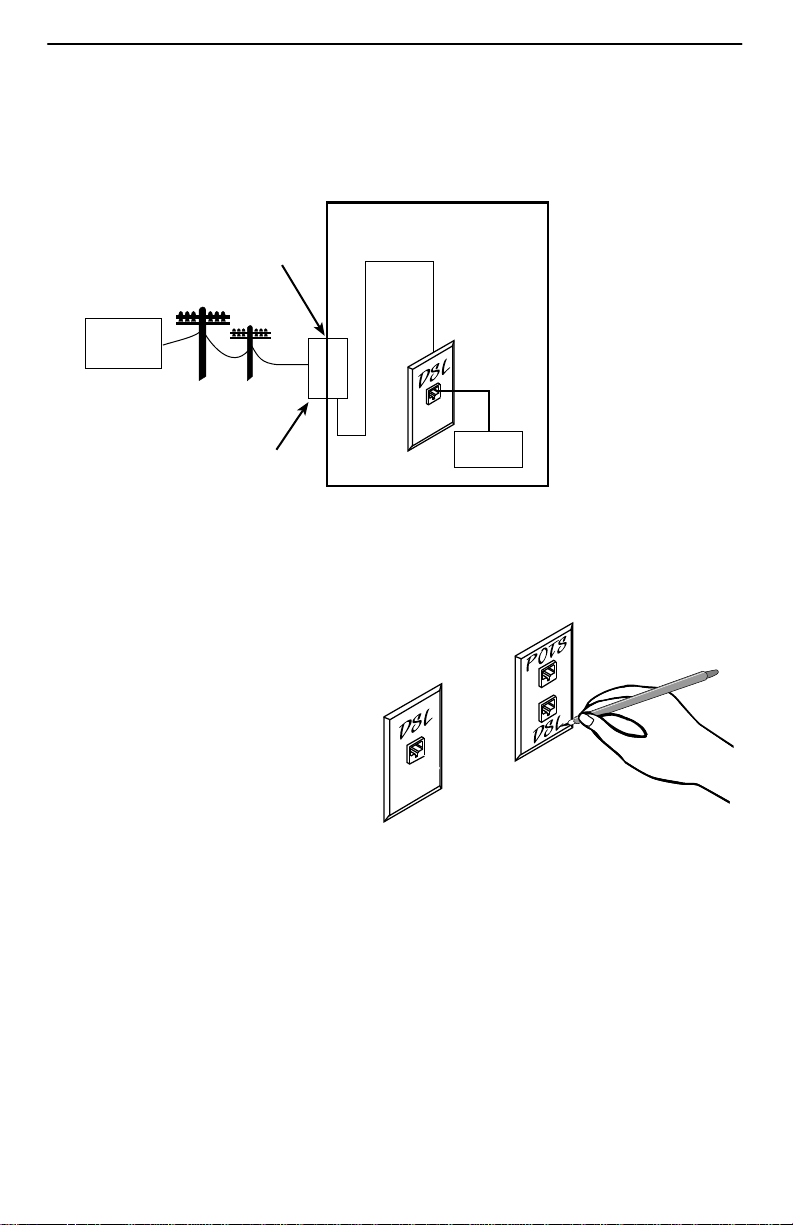
The 5446 RTU connects to the local loop via wiring from the demarcation point to an
RJ11 wall jack. The DSL twisted-pair wiring from the local loop terminates at a new or
existing wall jack. It may be necessary to install a standard single RJ11 jack or replace
a single jack with a double RJ1 1 jack.
Customer Premises
Demarcation Point
Central
Office
POTS/DSL
Local Loop
Punchdown
Block or NID
DSL
Twisted-pair
Wiring
DSL
RJ11
Jack
RTU
97-15343-02
Procedure
1. Wiring can be run from the
punchdown block or NID to a
new or existing wall jack. Match
the pair colors on both ends.
2. Label the DSL jack.
3. Reconnect the DSL access pair
at the punchdown block or NID.
Refer to
Access Wiring
both terminal screws with a flatblade screwdriver.
The RJ1 1 6-pin jack uses the center two pins. For pin assignments, refer to
Connectors
Installing the DSL
, page 5. Tighten
, page 17.
RJ11 Wall Jack
or
7
97-15300a
Cables &
Page 8

Installing the Hotwire 5446 RTU
Place the Hotwire 5446 RTU on a flat surface with clearance for the rear connectors.
Procedure
1. Use the supplied RJ1 1 6-pin interface cable for the DSL connection. Insert one end
of the cable into the jack labeled DSL. Insert the other end into the wall jack labeled
DSL.
Hotwire RTU
POWER
ETHERNET
DSL
Jack
If the Hotwire 5446 RTU is installed on the same line as POTS, a Hotwire 5038
Distributed POTS Splitter can be used as a filter. One 5038 Distributed POTS
splitter is installed as a filter for each telephone, as shown below. To install the
Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS splitter, refer to
Splitter Customer Premises Installation Instructions.
DSL
97-15300-01
Hotwire 5038 Distributed POTS
Customer
Premises (CP)
POTS Splitter
POTS Splitter
Distributed
LINE DSL
PHONE
Line from
RJ11 Wall Jack
LINE DSL
PHONE
Distributed
Distributed
POTS Splitter
PHONE
Hotwire
RTU
LINE DSL
Line from
RJ11 Wall Jack
98-15813
8
Page 9

2. Use an 8-pin Ethernet cable for the Ethernet connection. Insert one end of the
cable into the jack labeled ETHERNET.
Use a straight-through cable and connect the other end to an Ethernet hub, or
Hotwire RTU
Ethernet
Line
POWER
ETHERNET
DSL
Ethernet
Hub
Ethernet
Cable
97-15303-01
Use an Ethernet crossover cable and connect the other end to a PC with an
Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC) or router.
Hotwire RTU
Ethernet
Line
POWER
PC with Ethernet
ETHERNET
DSL
Network Interface
Card
Ethernet
Cable
For RTU cable pin assignments, refer to
9
Cables & Connectors
97-15303b
, page 17.
Page 10

3. Insert the power cord’s round end into the jack labeled POWER. Plug the
transformer into an AC outlet.
Hotwire RTU
Power
Jack
POWER
or
ETHERNET
DSL
Transformer
or
98-15836
The RTU hardware installation is now complete. When the power cord is installed, the
RTU goes through a power-on self-test.
Power-On
When power is applied, the RTU performs self-diagnostics and the PWR LED is on. The
self-diagnostics includes a power-on self-test. During the power-on self-test, all of the
LEDs turn on for one second.
Power – green
Alarm – red
Test – yellow
Digital Subscriber Line – green
Ethernet Link – green
TST
Refer to
5446
TM
Troubleshooting,
ALMPWR
DSL
page 14, for LED indications requiring action.
10
ETHERNET
97-15317
Page 11

Optional RTU Wall Placement
The Hotwire 5446 RTU is designed for tabletop placement. The RTU can also be
mounted on a wall. To mount an RTU, you will need:
-
Three slotted-head #6 self-threading screws with molly bolts
-
Drill and 3/16” drill bit for the molly bolts
-
Screwdriver
A template with the dimensions for the three screws is provided. See
Template
on page 12.
RTU Hardware
" Pr ocedure
To mount the RTU:
1. Use a drill to install the plastic anchors (molly bolts).
2. Use a screwdriver to install the screws. Do not install the screws flush with the wall.
Leave enough clearance to hang the RTU housing from the screws.
Wall
Fasteners
Hotwire
RTU
11
98-16170
Page 12

RTU Hardware Template
5.43"
Front
(LEDs)
7.55"
To Bottom
Hole
12
98-16171
Page 13

Status LEDs
All of the LEDs turn on and off during the power-on self-test. After a successful self-test,
the LEDs should appear as indicated in BOLD in the Condition column below.
LED Condition Status
PWR ON RTU has power.
ALM OFF
ON
TST OFF
ON
DSL Fast
blinking
Slow
blinking
ON
OFF
ETHERNET ON
OFF
No active alarms.
An alarm condition exists.
No active tests.
The TST LED is on during the power-on self-test and
during a test initiated by the NSP.
RTU is establishing the active DSL link. The LED blinks
on and off about five times per second.
The DSL link is up and the RTU is establishing the active
PPP link. The LED blinks on and off every two seconds.
The DSL/PPP link is ready to transmit and receive data.
The DSL link has not been established.
The Ethernet 10BaseT connection to the Ethernet hub or
PC is active.
No Ethernet 10BaseT device is detected.
13
Page 14

Troubleshooting
LED Symptom Action
All LEDs are on. If the LEDs remain on after ten minutes, the RTU is not
ALM LED remains
on.
ALM and TST
LEDs are blinking.
DSL LED is off. Verify that the DSL cable is securely installed on both ends.
DSL LED continues
to blink after the
power-on self-test.
DSL LED is on and
there is no data
transmission.
DSL and Ethernet
LEDs are on and
there is no data
transmission.
Ethernet LED is off.
PWR LED is off.
functional. Contact the NSP.
The power-on self-test may have failed. Unplug the unit and
reapply power. If the alarm light is still on, contact the NSP.
Firmware download may be in progress. If firmware download
is not in progress or the LEDs remain on after ten minutes,
contact the NSP.
If the problem continues, contact the NSP.
The RTU is attempting to establish the DSL link or adjusting the
rate of the DSL line due to line conditions. If the DSL LED
continues to blink for more than ten minutes, contact the NSP.
The DSL link has been established but there is no data
transmission. Verify the Ethernet connection. If the problem
persists, contact the NSP.
Verify that your IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
have been entered correctly in the end-user system.
From the end-user system, use the PC PING utility to ping the
5446 RTU’s IP address.
If no response to the ping, use the PC ARP (Address
Resolution Protocol) utility to verify the IP address and physical
address (MAC address) from the end-user system to the 5446
RTU. If the problem continues, contact the NSP.
Verify that the Ethernet 10BaseT cable is securely installed at
both ends, and at least one PC is connected and powered on.
Verify that the correct straight-through or crossover cable is
installed. Refer to
Check that the power cord is securely installed on both ends.
Installing the Hotwire 5446 RTU,
page 8.
If no LEDs are on, the power supply may be defective. Test the
outlet to verify power. If the problem persists, contact the NSP.
If other LEDs are on, the PWR LED may be burned out. Unplug
the unit and reapply power; watch all the LEDs during the
power-on self-test to verify that the PWR LED is functioning.
TST LED is on. A test initiated by the NSP may be active. Wait five minutes. If
the TST LED does not go off, contact the NSP.
14
Page 15

Hotwire 5446 RTU Next Hop Router Support
The Hotwire 5446 RTU now includes support for next hop routers and a default
gateway .
The following illustration includes a router and a default gateway . The maximum of 32
end-user systems applies to end-user systems directly connected to the 5446 RTU
(with or without a hub) and end-user systems connected to routers. Any connections to
a default gateway are not included in the 32 systems.
Customer Premises (CP)
End-user
Systems
End-user
Systems
DSL/POTS
5446 RTU
TM
TST
ALMPWR
ETHERNET
DSL
Hub Hub
Router
Default
Gateway
Hub
98-16091
15
Page 16

Hotwire 5446 RTU IP Setup
The Hotwire 5446 RTU hardware installation is now complete. Additional steps are
required by the NSP to utilize the DSL and Ethernet connections.
Network Service Provider Example
The ISP:
Assigns and sets up the RTU IP address and subnet mask.
Assigns the IP address and subnet mask for each end-user system connected to
the 5446 RTU.
To configure the end-user system, the following is used:
IP address
Subnet mask
Default gateway*
*In most cases, the 5446 RTU is the upstream default gateway for all connected
end-user systems. The other option is to connect a router between the 5446 RTU
and the end-user system.
Example using TCP/IP Network Settings with Windows 95:
Set up the network configuration. Use the network settings in the Windows environment
to enter the default gateway , IP address, and subnet mask.
1. To configure the end-user system, from the Control Panel window, select:
Network → Configuration → TCP/IP
2. From the TCP/IP Properties window, select Gateway and enter the 5446 R TU’s
IP address.
3. From the IP Address
window, enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask. Select OK.
NOTE:
Any application supported by the NSP should now start up.
16
Page 17

Increasing the Number of End-User Systems
A single end-user system is attached to the Hotwire 5446 RTU by using an Ethernet
crossover cable. To increase the number of end-user systems, connect all end-user
systems to an Ethernet hub using straight-through Ethernet cable. Refer to
Hotwire 5446 RTU,
The initial IP address for the first end-user system remains in effect when the end-user
system is reconnected. All new end-user systems must be configured by the NSP.
Coordinate additional IP addresses and subnet masks with the NSP.
The 5446 RTU can support up to 32 end-user systems using static or dynamic IP
addressing. The number of end-user systems can be increased on the network with the
use of subnets utilizing static addresses or connecting to a default gateway . Verify any
planned changes with the NSP.
page 8.
Installing the
Cables & Connectors
Use standard twisted-pair CA T3 or better cables.
This section is reference information.
The DSL interface connector uses a 6-pin,
non-keyed modular plug.
RJ11 6-Pin Connector
Pin # Function
1 & 2 Not used
3 DSL Ring
4 DSL Tip
DSL
Cable
6-Pin
RJ11 Plug
Pin #6
Pin #1
5 & 6 Not used
98-15304-01
17
Page 18

The Ethernet interface connector uses an 8-pin, non-keyed modular plug.
— To connect to an Ethernet hub, use the straight-through connection.
8-Pin Straight-Through Connection
Pin # Function
Ethernet
Cable
1 10BaseT TX D+
2 10BaseT TX D–
8-Pin
3 10BaseT RX D+
Plug
4 & 5 Not used
6 10BaseT RX D–
7 & 8 Not used
Pin #8
Pin #1
— To connect the RTU directly to a PC with an Ethernet NIC card, use an
Ethernet crossover cable.
8-Pin Ethernet Crossover Cable
Function Pin # FunctionPin #
10BaseT TX D+
10BaseT TX D–
1
2
1
10BaseT TX D+
2
10BaseT TX D–
98-16055a
10BaseT RX D+
Not Used
Not Used
10BaseT RX D–
Not Used
Not Used
3
4
5
6
7
8
3
10BaseT RX D+
4
Not Used
5
Not Used
6
10BaseT RX D–
7
Not Used
8
Not Used
97-15316
18
Page 19

Hotwire 5446 RTU Technical Specifications
Item Specification
Height x Width x Depth 1.43″ x 6.00″ x 8.75″ (3.64 cm x 15.24 cm x 22.23 cm)
Weight 1 lb. 1 oz. (0.48 kg)
Power
Class 2 Transformer normal
service input voltage range
Approvals
FCC Part 15
CISPR 22
Safety Certifications
Physical Environment
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Relative humidity
Shock and vibration
Heat Dissipation 40.9 Btu/hr. (max.) at nominal input voltage
Interface Connectors
DSL Interface
Ethernet Type II Frame
*
Technical Specifications subject to change without notification.
Input: 100 Vac (+10%), 50 Hz;
Output: 18 Vdc nominal, minimum 0.8A
Class B Subpart B digital device
Class B
Refer to equipment’s label for approvals on product
32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
–4° F to 158°F (–20°C to 70°C)
5% to 95% (noncondensing)
Withstands normal shipping and handling
RJ11 6-pin
10BaseT 8-pin
*
120 V ac (+
230 V ac (+
10%), 60 Hz; or
10%), 50/60 Hz
19
Page 20

!
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product or
included in the manual.
2. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for ventilation. To ensure reliable
operation of the product and to protect it from overheating, these slots and
openings must not be blocked or covered.
3. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord and do not locate the product
where persons will walk on the power cord.
4. Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or removing covers may
expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to
qualified service personnel.
5. General purpose cables are used with this product for connection to the network.
Special cables, which may be required by the regulatory inspection authority for the
installation site, are the responsibility of the customer. Use a UL Listed, CSA
certified, minimum No. 24 AWG line cord for connection to the Digital Subscriber
Line (DSL) network.
6. When installed in the final configuration, the product must comply with the
applicable Safety Standards and regulatory requirements of the country in which it
is installed. If necessary , consult with the appropriate regulatory agencies and
inspection authorities to ensure compliance.
7. A rare phenomenon can create a voltage potential between the earth grounds of
two or more buildings. If products installed in separate buildings are
interconnected, the voltage potential may cause a hazardous condition. Consult a
qualified electrical consultant to determine whether or not this phenomenon exists
and, if necessary , implement corrective action prior to interconnecting the products.
8. Input power to this product must be provided by one of the following: (1) a UL
Listed/CSA certified power source with a Class 2 or Limited Power Source (LPS)
output for use in North America, or (2) a certified transformer, with a Safety Extra
Low Voltage (SELV) output having a maximum 240 VA available, for use in the
country of installation.
9. In addition, since the equipment is to be used with telecommunications circuits,
take the following precautions:
— Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
— Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically
designed for wet locations.
— Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone
line has been disconnected at the network interface.
— Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
— Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm.
There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
— Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
20
Page 21

Declaration of Conformity
This Declaration of Conformity is made by Paradyne Corporation pursuant to Parts 2
and 15 of the Federal Communications Commission’s Rules. This compliance
information statement pertains to the following products:
Trade Name: Hotwire
Model Number: 5446-A3-200
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
The name, address, and telephone number of the responsible party is given below:
Paradyne Corporation
8545 126th Avenue North
Largo, FL 33773-1502
Phone: (727) 530-2000
The authority to operate this equipment is conditioned by the requirement that no
modifications will be made to the equipment unless the changes or modifications are
expressly approved by Paradyne Corporation.
Japan
Notices
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for
Interference from Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this is used near a radio or
television receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use
the equipment according to the instruction manual.
21
Page 22

CE Marking
When the product is marked with the CE mark, this demonstrates full compliance with
the following European Directives:
Directive 73/23/EEC – Council Directive of 19 February 1973 on the harmonization
of the laws of the member states relating to electrical equipment designed for use
within states relating to electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage
limits, as amended by Directive 93/68/EEC.
Directive 89/336/EEC – Council Directive of 3 May 1989 on the approximation of
the laws of the member states relating to Electro-Magnetic Compatibility (EMC), as
amended by Directive 93/68/EEC.
Canada EMI Warnings
!
WARNING:
To Users of Digital Apparatus in Canada:
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
interference-causing equipment regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du
règlement sur le matérial brouilleur du Canada.
Notice to Users of the Canadian Telephone Network
The Industry Canada label identifies certified equipment. This certification means that
the equipment meets telecommunications network protective, operational and safety
requirements as prescribed in the appropriate Terminal Equipment Technical
Requirements document(s). The Department does not guarantee the equipment will
operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is permissible to be
connected to the facilities of the local telecommunications company . The equipment
must also be installed using an acceptable method of connection. The customer should
be aware that compliance with the above conditions may not prevent degradation of
service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be coordinated by a representative designated by
the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the user to this equipment, or
equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to request
to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of
the power utility , telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system, if present, are
connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
CAUTION:
Users should not attempt to make such connections themselves, but should
contact the appropriate electric inspection authority , or electrician, as
appropriate.
22
Page 23

The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) assigned to each terminal device provides an
indication of the maximum number of terminals allowed to be connected to a telephone
interface. The termination on an interface may consist of any combination of devices
subject only to the requirement that the sum of the Ringer Equivalence Numbers of all
the devices does not exceed 5.
If your equipment is in need of repair, refer to
Information.
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for
any help needed. For additional information concerning warranty , sales, service, repair,
installation, documentation, training, distributor locations, or Paradyne worldwide office
locations, use one of the following methods:
H Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com.
(Be sure to register your warranty there. Select
Registration
H T elephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to
speak with a company representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
.)
Service & Support →Warranty
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them
to Technical Publications, Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773,
or send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include the number and title of this
document in your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you
are willing to provide additional clarification.
Trademarks
All products and services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks,
registered trademarks or registered service marks of their respective owners.
Copyright E 1999 Paradyne Corporation
23
 Loading...
Loading...