Page 1

COMSPHERE
3821
Document No. 3821-A2-GB20-40
P
LUS
MODEM
USER’S GUIDE
January 1999
Page 2

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
COMSPHERE
3821
Plus
Modem
User’s Guide
3821-A2-GB20-40
5th Edition (January 1999)
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new release or a limited
revision of this manual.
For the 3821Plus modem the USOC for Permissive mode is RJ21X. The Canadian equivalent to the USOC is CA21A. For single line
connection to an analog private line, an adapter cable should be used to facilitate connection to a JM8 jack. The Canadian equivalent is
CA40A.
FCC Registration number: (See label on modem)
Ringer Equivalence number (REN): (See label on modem)
Canadian Certification number: (See label on modem)
Canadian DOC Load number: (See label on modem)
Warranty, Sales, and Service Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for any help needed. For additional information
concerning warranty, sales, service, repair, installation, documentation, training, distributor locations, or Paradyne worldwide office
locations, use one of the following methods:
• Via the Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at http://www.paradyne.com
• Via Telephone: Call our automated call system to receive current information via fax or to speak with a company representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Trademarks
All products and services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks or registered service
marks of their respective owners.
Printed on recycled paper
COPYRIGHT 1999 Paradyne Corporation. All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system,
or translated into any human or computer language in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties
without the express written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Avenue North, P.O. Box 2826, Largo, Florida 33779-2826.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability
or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents
hereof without obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
A January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 3
!
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product or included in
the manual.
2. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for ventilation. To ensure reliable operation of the
product and to protect it from overheating, these slots and openings must not be blocked or covered.
3. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord and do not locate the product where persons will
walk on the power cord.
4. Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or removing covers may expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
5. General purpose cables are provided with this product. Special cables, which may be required by the
regulatory inspection authority for the installation site, are the responsibility of the customer.
6. When installed in the final configuration, the product must comply with the applicable Safety
Standards and regulatory requirements of the country in which it is installed. If necessary, consult
with the appropriate regulatory agencies and inspection authorities to ensure compliance.
In addition, if the equipment is to be used with telecommunications circuits, take the following
precautions:
— Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
— Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed
for wet locations.
— Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has
been disconnected at the network interface.
— Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
— Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
— Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
Safety Instructions
B3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 4

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Notices
!
C January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 5

Safety Instructions
Government Requirements and Equipment Return
Certain governments require that instructions pertaining to modem connection to the public switched telephone network be included in
the installation and operation manual. Specific instructions are listed in the following sections.
United States
Notice to Users of the Public Switched Telephone Network
1. This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules. On the circuit card is a label that contains, among other information,
the FCC registration number and ringer equivalence number (REN) for this equipment.
2. Page A of this manual contains the Universal Service Order Codes (USOC) associated with the services on which the
equipment is to be connected.
3. The Ringer Equivalence (REN) is used to determine the quantity of devices which may be connected to the telephone line.
Excessive RENs on the telephone line may result in the devices not ringing in response to an incoming call. In most, but not
all areas, the sum of the RENs should not exceed five (5.0). To be certain of the number of devices that may be connected to
the line, as determined by the total RENs, contact the telephone company to determine the maximum RENs for the calling
area.
4. If the modem causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company will notify you in advance that temporary
discontinuance of service may be required. But if advance notice is not practical, the telephone company will notify the
customer as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised of your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you believe it is
necessary.
5. The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures that could affect the
operation of the equipment. If this happens, the telephone company will provide advance notice in order for you to make the
necessary modifications in order to maintain uninterrupted service.
6. If you experience trouble with this equipment, please contact your sales or service representative (as appropriate) for repair or
warranty information. If the product needs to be returned to the company service center for repair, contact them directly for
return instructions using one of the following methods:
• Via the Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at http://www.paradyne.com
• Via Telephone: Call our automated call system to receive current information via fax or to speak with a company
representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside of U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
If the trouble is causing harm to the telephone network, the telephone company may request that you remove the equipment
from the network until the problem is resolved.
7. The user is not authorized to repair or modify the equipment.
8. This equipment cannot be used on public coin service provided by the telephone company. Connection to Party Line Service
is subject to state tariffs. (Contact the state public utility commission, public service commission or corporation commission
for information.)
9. The Telephone Consumer Protection Act of 1991 makes it unlawful for any person to use a computer or other electronic
device to send any message via a telephone fax machine unless such a message clearly contains, in a margin at the top or
bottom of each transmitted page, or on the first page of the transmission, the date and time it is sent, and an identification of
the business, or other entity, or other individual sending the message, and the telephone number of such business, or other
entity, or individual.
In order to program this information, follow the steps outlined in the manual supplied with your fax software.
10. An FCC compliant telephone cord with modular plugs may be provided with this equipment. This equipment is designed to
be connected to the telephone network or premises wiring using a compatible modular jack which is Part 68 compliant.
D3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 6
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Canada
Notice to Users of the Canadian Public Switched Telephone Network
The Canadian Department of Communications label identifies certified equipment. This certification means that the equipment meets
certain telecommunications network protective, operational and safety requirements. The Department does not guarantee the equipment
will operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is permissible to be connected to the facilities of the local
telecommunications company. The equipment must also be installed using an acceptable method of connection. In some cases, the
company’s inside wiring associated with a single line individual service may be extended by means of a certified connector assembly
(telephone extension cord). The customer should be aware that compliance with the above conditions may not prevent degradation of
service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized Canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs
or alterations made by the user to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to
request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of the power utility, telephone line and internal
metallic water pipe system, if present, are connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
The Load Number for this equipment is listed on a label on the modem. The Load Number (LN) assigned to each terminal device
denotes the percentage of the total load to be connected to a telephone loop which is used by the device to prevent overloading. The
termination on a loop may consist of any combination of devices subject only to the requirement that the total of the Load Numbers of
all devices does not exceed 100.
If your equipment is in need of repair, refer to page A in the front of this document for contact information.
United Kingdom
Ringer Equivalence Number
The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) is a customer guide indicating approximately the maximum number of items of apparatus that
should be connected simultaneously to the telephone line. The sum of the RENs should not exceed four. This value includes any
BT-provided instrument which may be assumed to have a REN of 1 unless marked otherwise. The REN of this modem is 1.
Connection to Leased Lines
If any other apparatus, including cable or wiring, is connected between the apparatus and the point of connection to any speechband
circuit, then all that other apparatus shall comply with the following:
1. The overall transmission characteristics of all that other apparatus shall be such as to introduce no material effect upon the
electrical conditions presented to one another by the apparatus and the speechband circuit; and
2. All that other apparatus shall comprise only:
(i) apparatus approved for the purpose of connection between the apparatus and a speechband circuit; and
(ii) cable or wiring complying with a code of practice for the installation of equipment covered by this part of BS 6328 or
such other requirements as may be applicable.
E January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 7

Safety Instructions
This modem is suitable for connection to BT circuits with signalling at a nominal frequency of 2280 Hz and may be connected to
multipoint or point-to-point circuits. The apparatus does not require signalling or otherwise use the frequency range 0–200 Hz.
No d.c. interaction is intended between the modem and the telephone network.
This apparatus may be directly connected to a speechband circuit or connected to a relevant branch system for speechband circuits.
All European Countries
Safety Notice
Interconnection circuits between this modem and any other equipment should be such that the equipment continues to comply with the
requirements of EN41003 for TNV (Telephone Network Voltage) circuits and EN60950 for SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage) circuits
after making connection between circuits.
Japan
Notices
This equipment is classified in the 1st Class category. When used in a residential
area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio interference may be caused to radios and
TV receivers, etc. VCCI-1
Restrictions
Due to JATE (Japan Approvals Institute for Telecommunications Equipment) regulations, only 3 attempts to dial a number are
permitted in a 3-minute period. If a fourth attempt is made to dial the same number, the modem returns the ERROR return code. This
restriction applies to the number dialed from the command line or from a directory. An occurrence of the restriction is canceled when a
different number is dialed, or when 3 minutes have elapsed.
F3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 8

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
This page intentionally left blank.
G January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 9

Table of Contents
Preface
Objectives and Reader Assumptions v. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Use This Manual v. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Related Documents vi. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. Introduction
Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Features 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Indicators 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SDCP Operation 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. 3821
Plus
Modem Installation
Overview 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3821Plus Installation 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install Communications Software 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Select Factory Configuration Options 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. SDCP Menus
Menu Structure 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modem Status Messages 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modem Select Branch 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Quick Configuration Display 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Call Setup Branch 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Branch 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T est Branch 3-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configure Branch 3-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Branch 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Automatic Firmware Download 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Branch 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security Branch 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
i3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 10

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
4. AT Commands and S-Registers
5. Fax Operation
6. Remote Access
Overview 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Modes 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Command Guidelines 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AT Command List 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
S-Register List 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Recovering AT Commands 4-26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Initialization Strings 4-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fax Operation 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Access 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7. Security
Overview 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Password T ypes 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Originate Security 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Answer Security 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Callback Security 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security Branch 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security Configuration Options 7-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A. SDCP Menu Tree
Overview A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B. Result Codes
Overview B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. Troubleshooting
Overview C-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Automatic Firmware Download C-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ii January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 11

D. Technical Specifications
E. Pin Assignments
EIA-232-E Pin Assignments E-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
JM8 to RJ11 Crossover Cable E-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
NIM Cable Pin Assignments E-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F. ITU-T V.25bis Dialing Commands and Responses
Overview F-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Call Request Commands F-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Call Response F-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Call Answer Commands F-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Program Normal (PRN) F-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Request List of Stored Numbers (RLN) F-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List Stored Number
Response (LSN) F-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Command Response F-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
G. Equipment List
H. Country-Specific Configuration Options
Configuration Options by Country H-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glossary
Index
iii3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 12

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
This page intentionally left blank.
iv January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 13

Preface
Objectives and Reader
Assumptions
This guide describes how to install the 3821Plus circuit
card and operate the 3821Plus modem. It is intended for
all users of the 3821Plus modem.
Each 3821Plus card comprises three modems. In
general this guide refers to the 3821Plus modem with
regard to operation and the 3821Plus card with regard to
installation. The term 3800Plus refers to all the modems
in the 3800Plus series, including the 3810Plus, 3811Plus,
3820Plus, 3821Plus, and 3825Plus.
How to Use This Manual
Chapter 1 provides information about 3821Plus
hardware and software features, including the front panel
and status indicators.
Chapter 2 provides instructions for installing the card,
selecting factory configuration options, recovering the
ability to use AT commands, and using AT command
initialization strings.
Chapter 3 shows the options menus available from the
Shared Diagnostic Control Panel (SDCP).
Chapter 4 provides instructions for displaying and
changing AT commands and S-registers. These commands
control all aspects of the modem’s operation.
Chapter 5 provides general information about fax
modem operation.
Chapter 6 shows how to use the SDCP of a
COMSPHERE modem to access and control a remote
3800Plus modem.
Chapter 7 describes the security features of the
3821Plus modem, including AT commands and SDCP
controls used to set security configuration options.
Appendix A shows the menu trees available from the
SDCP.
Appendix B lists result codes produced by the modem.
Appendix C provides instructions for performing
diagnostic tests when data communications problems
occur, and explains the Automatic Firmware Download
process.
Appendix D lists the technical specifications of the
3821Plus modem.
Appendix E provides cable pin assignments.
Appendix F provides V.25bis dialing information.
Appendix G provides an equipment list.
Appendix H shows configuration options whose
validity or default values vary according to country code.
The Glossary provides a description of terms used
throughout this guide.
v3821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 14

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Related Documents
3000-A2-GA31 COMSPHERE 3000 Series
Carrier Installation Manual
3980-A2-GB30 COMSPHERE 3800Plus
Modems, User’s Guide
6700-A2-GY31 COMSPHERE 6700 Series
Network Management System,
User’s Guide
6800-A2-GE26 COMSPHERE 6800 Series
Network Management System,
User’s/System Administrator’ s
Guide
Contact your sales or service representative to order
additional product documentation.
Paradyne documents are also available on the World
Wide Web at:
http://www .paradyne.com
Select Service & Support → Technical Manuals
vi January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 15

Introduction
Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Features 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Status Indicators 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SDCP Operation 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LCD 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keypad 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
Overview
The 3821Plus is a member of the COMSPHERE
3800 Series Modem product line. The 3821Plus card
comprises three modems, permitting as many as
48 modems to be installed in a single 3000 Series Carrier.
Each is a software-definable high-speed modem that
offers reliable asynchronous and synchronous operation
over dial or two-wire leased-line networks.
Features
The 3821Plus modem has a wide variety of features,
including:
• Dial-Line Modulations: ITU-T V.34 (up to
33,600 bps), V.32terbo (19,200 and 16,800 bps),
ITU-T V.32bis (up to 14,400 bps), V.32 (up to
9600 bps), V.22bis (2400 bps), V.22 (1200 bps),
V.21 (300 bps), Bell 212A (1200 bps), and
Bell 103J (300 bps).
• T wo-wire Leased-Line Modulations: ITU-T V.34
(up to 33,600), V.32terbo (19,200 and 16,800 bps),
V.32bis (14,400, 12,000, 9600, 7200, and
4800 bps), V.32 (9600 and 4800 bps), and V.22bis
(2400 bps).
• Class 1 and Class 2 Group III Fax modulations:
ITU-T V.17 (14,400, 12,000, 9600, 7200 bps),
V.29 (9600, 7200 bps) and V .27ter (4800,
2400 bps).
• Convenient migration to new or optional features
through software downloading.
• ITU-T V.42bis and MNP Class 5 data compression.
• Virtual error-free data integrity with ITU-T V.42
and MNP Levels 2–4 error control.
• Asynchronous dial DTE data rates from 300 bps to
115,200 bps.
• Optional Enhanced Throughput Cellular (ETC),
which improves reliability and speed over cellular
links.
• Compatibility with the industry de facto standard
AT Command set.
• High-speed transmission using asynchronous,
synchronous, or UNIX devices over full- or
half-duplex dial networks or 2-wire leased lines.
• Supported under the COMSPHERE 6700 or
6800 Series Network Management System (NMS).
• Compatibility with standalone COMSPHERE
3800Plus, 3800, and 3900 Series modems’ Remote
Access Mode, which allows users to view the
configuration options of a 3821Plus modem from a
remote Diagnostic Control Panel (DCP) or Shared
Diagnostic Control Panel (SDCP).
1-13821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 16
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
• Storage of up to 10 telephone numbers to directory
locations.
• Originate Security and three Answer Security
modes.
• Callback Security with telephone directory index or
telephone number.
• T wo factory-defined configurations and two
user-defined configuration areas.
Diag
Diag
Status
Status
OK
Alrm
In
Out
Alrm
Alrm
Alrm
Mod
Mod
Mod
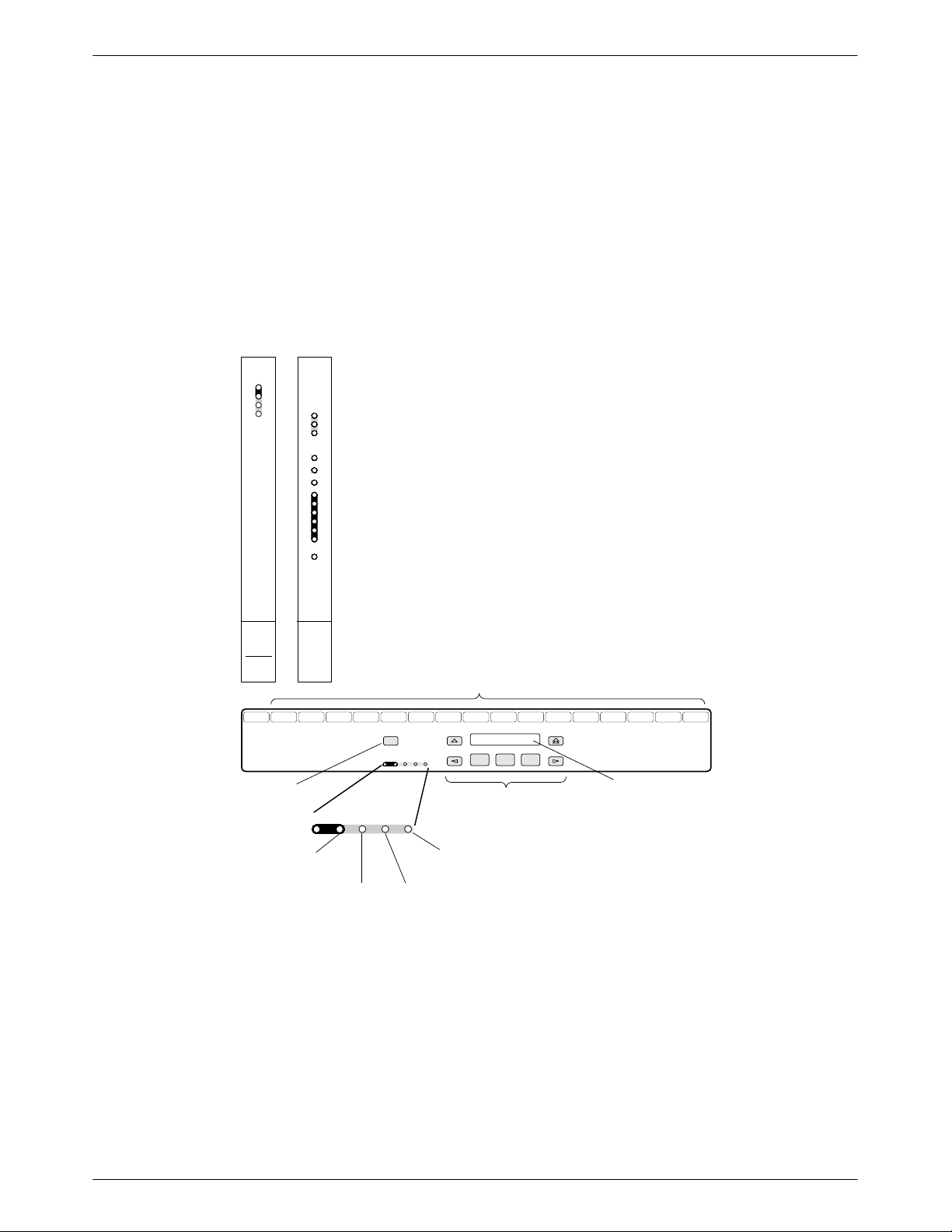
Front Panel
A
B
C
A
B
C
TXD
RXD
CD
RI
DTR
OH
Status Indicators
The status indicators on a 3821Plus circuit card
continuously provide information on the modem’s
operating condition. The status indicators for the
3821Plus card are located on its faceplate, the SDCP, and
the Shared Diagnostic Unit (SDU) faceplate (Figure 1-1).
The 3821Plus card has 13 Light Emitting Diodes
(LEDs). These LEDs are listed and described in T able 1-1.
SDU
3821
Plus
CARRIER SLOTS 1–16
SDU12345678910111213141516
Select
OK Alarm BckUp Test EC
SELECT
KEY
OK Alarm BckUp Test EC
NETWORK
DEVICE
ALARM
STATUS
INDICATORS
DIAL
BACKUP
ERROR
CORRECTION
TEST
MODE
Figure 1-1. Optional SDCP, 3821
F1 F2 F3
KEYPAD
Plus
Faceplate, and Optional SDU
COMSPHERE 3000
LCD
496-14802-01
1-2 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 17
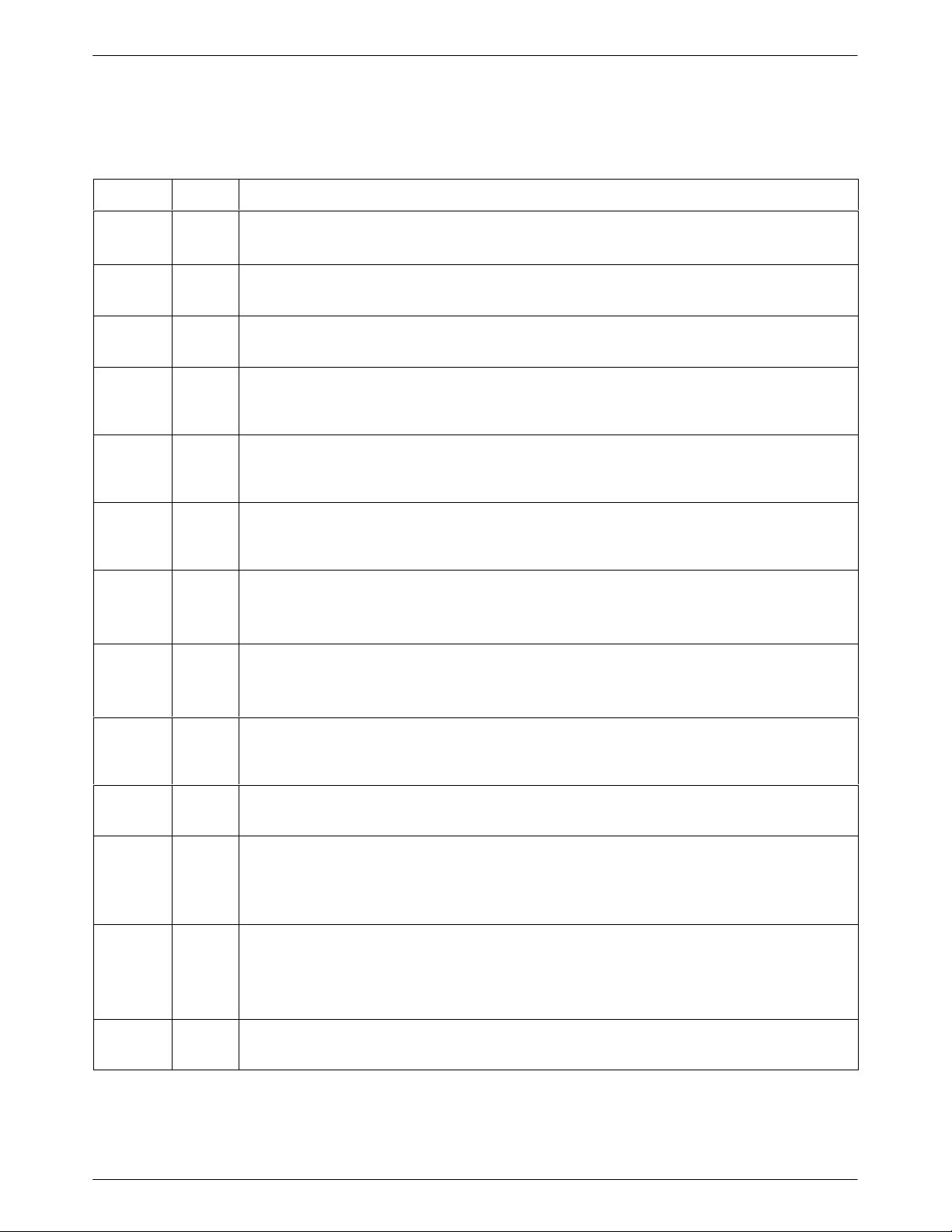
Table 1-1
3821
Plus
Introduction
LEDs
Label
ALRM A red Alarm A
ALRM B red Alarm B
ALRM C red Alarm C
Mod A green Modem A
Mod B green Modem B
Mod C green Modem C
TXD green Transmit Data
Color Indicates
ON: Modem A has detected a problem with its operation.
ON: Modem B has detected a problem with its operation.
ON: Modem C has detected a problem with its operation.
ON: The status of Modem A is reflected by the TXD, RXD, CD, RI, DTR, and OH LEDs. If the
Front Panel LED is ON, Modem A is connected to the SDCP.
ON: The status of Modem B is reflected by the TXD, RXD, CD, RI, DTR, and OH LEDs. If the
Front Panel LED is ON, Modem B is connected to the SDCP.
ON: The status of Modem C is reflected by the TXD, RXD, CD, RI, DTR, and OH LEDs. If the
Front Panel LED is ON, Modem C is connected to the SDCP.
ON: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is receiving data from the DTE to transmit.
The TXD and RXD LEDs blink for 5 seconds after a modem is selected using NMS or the SDCP.
RXD green Receive Data
ON: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is transferring received data to the DTE.
The TXD and RXD LEDs blink for 5 seconds after a modem is selected using NMS or the SDCP.
CD green Carrier Detect
ON: The modem has detected a valid modulation carrier signal and is capable of transferring
received data to the DTE.
RI green Ring Indicate
Cycling ON and Off: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is receiving a ring signal.
DTR green Terminal Ready
ON: The DTE connected to the modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED has turned ON the
DTR (Data Terminal Ready) signal, or the modem is configured to ignore DTR.
Off: The DTR signal of the modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is Off.
OH green Off-Hook
ON: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is off-hook and set for Dial.
Off: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is on-hook and set for Dial.
Cycling ON and Off: The modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED is set for leased line operation.
Front
Panel
amber Front Panel
ON: The SDCP is connected to the modem indicated by the A, B, or C LED.
1-33821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 18
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
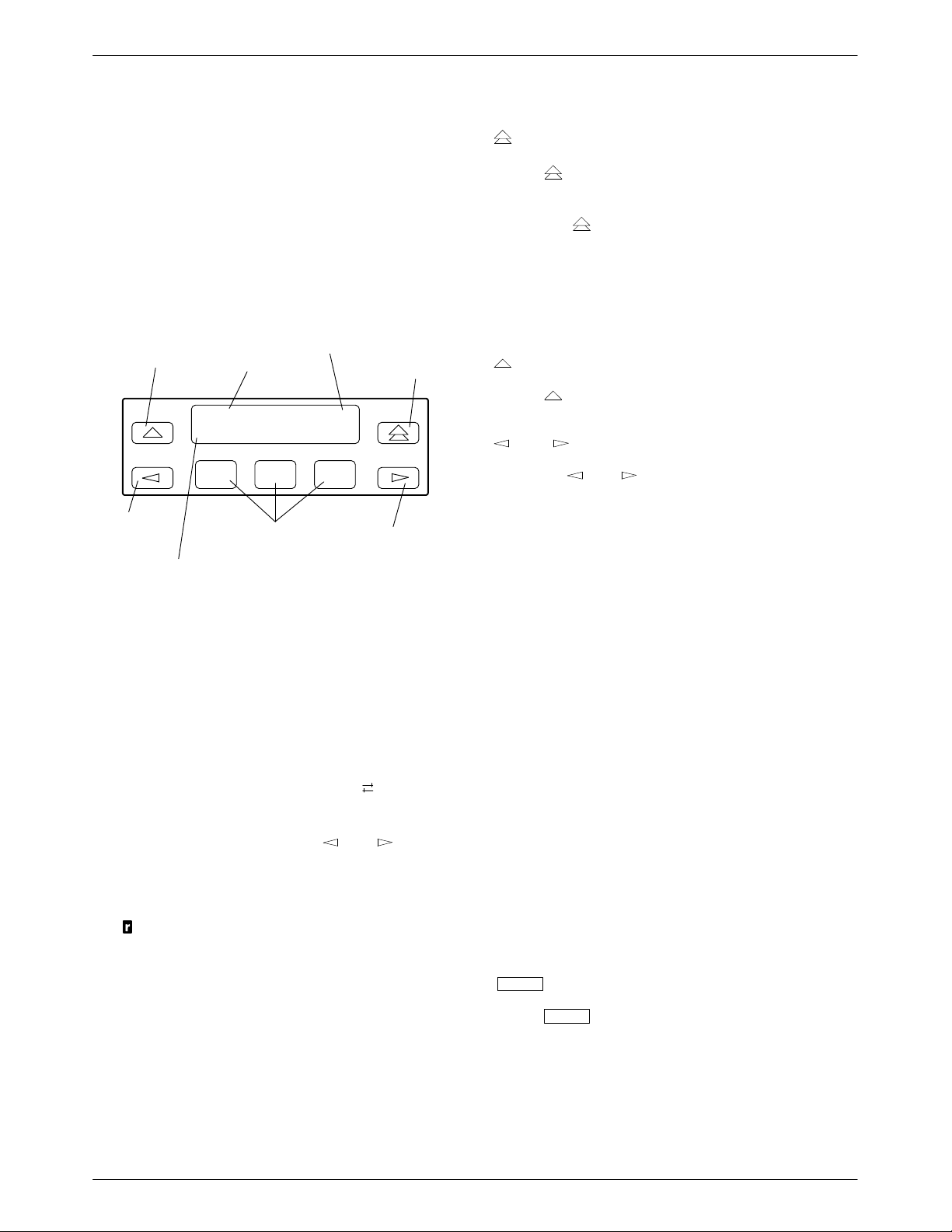
SDCP Operation
Key
The SDCP on the 3000 Series Carrier is the user
interface to all functions used to configure and control the
3821Plus modem. This interface includes the status
LEDs, and a two-line, 32-character Liquid Crystal
Display (LCD) and keypad (Figure 1-2).
MOVES UP
ONE LEVEL
FROM CURRENT
DISPLAY
LCD
TOP
LINE
HIDDEN
CHOICE
INDICATOR
RETURNS
DISPLAY TO
TOP-LEVEL
MENU
Idle:33.6 >
MDMA mdmb mdmc
F3
RIGHT
SCROLL
KEY
LEFT
SCROLL
KEY
LCD BOTTOM LINE
F1
F2
FUNCTION KEYS
Figure 1-2. SDCP Keypad
The key returns you to the Top-Level menu
display from anywhere in the menu tree.
Pressing
while changing configuration options
displays the message Save Straps? Yes No. If No is
selected, changes made to configuration options are not
saved and the T op-Level menu appears. If Yes is selected,
then changes are saved to either Active (Saved),
Customer 1, or Customer 2 configuration areas.
Key
The key moves you up one level in the menu tree.
and
Keys
Use the and keys to move the viewing
window left or right and to scroll the remaining branches
and selections into view. A maximum of three selections
can be displayed at one time.
These keys also allow you to move the cursor one
character to the left or right on data entry displays; for
example, to allow entry of one digit at a time.
F1, F2, F3 Keys
LCD
The LCD consists of a top line and bottom line, with
each displaying a maximum of 16 characters at a time. If
additional information is available than what is currently
displayed, a hidden choice indicator (< or
or >)
appears in the upper right-hand corner of the LCD. The
list of choices does not scroll around to the first choice
when you reach the last choice. The
and keys
allow you to display the other choices.
If a local 3800Plus modem establishes a connection
with a remote 3800Plus modem via the Remote branch,
appears in place of the hidden choice indicator on
then
both modems.
Keypad
The SDCP of the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier
has eight keys.
Function keys select the LCD choice that appears
above the function key; they are labeled F1, F2, and F3. If
a selection spans more than one function key, then any of
those keys choose that selection.
Numerical Scroll Indicators
T o enter a number on the SDCP, such as a telephone
number to be stored in the modem’s directory, use the
function keys F2 () or F3 (). A displayed number is
increased or decreased according to whether the key
associated with the up arrow or the down arrow is pressed.
In other applications, such as password entry, only the up
arrow is displayed, and the displayed numbers can only be
incremented.
The
Key
key is used to connect the SDCP to a card
Select
Select
in a specific slot in the carrier. The Front Panel LED of
the 3821Plus card turns ON when the SDCP is connected
to it.
1-4 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 19

3821
Overview 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3821Plus Installation 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install the Carrier 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install the NIM 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable the NIM 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Attach the DTE Interface Assembly 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install the Circuit Card 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connect the DTE 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install Communications Software 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Select Factory Configuration Options 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Selecting Configurations Using the SDCP 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Selecting Configurations Using AT Commands 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Plus
Modem Installation
2
Overview
This chapter describes how to install the 3821Plus card
and connect both provided and customer-supplied cables
to the modems. In addition, it describes how to configure
3821Plus modems for specific applications.
3821
equipment:
Plus
A typical 3821Plus installation requires the following
• Eight 3821Plus cards
• One DTE interface assembly with 24 ports
• One Network Interface Module (NIM) with a
50-position short ribbon cable
• This user’s guide
• Three DTE (RS-232D) cables or three 8-position
modular cables with six 8-position modular to
DB25 adapters for each 3821Plus card
• One 50-position to network interface cable for each
NIM
Installation
See Appendix G, Equipment List.
If any hardware components are damaged, notify your
sales representative. Return equipment using the
procedures described in the Government Requirements
and Equipment Return section in the front of this guide.
Install the Carrier
The 3821Plus card resides in a COMSPHERE
3000 Series Carrier. The carrier must be installed in a rack
before the modem cards can be installed in the carrier.
The 3821Plus card requires a Shared Diagnostic
Control Panel (SDCP) for control and configuration of
individual modems. It also requires a Shared Diagnostic
Unit (SDU) if the modems will be under control of an
NMS, or if the SDCP is used for more than one carrier.
Instructions for the installation of the SDCP and SDU, as
well as the 3000 Series Carrier and its power supply, can
be found in the COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier
Installation Manual, document number 3000-A2-GA31.
• A 66A-punchdown block or RJ11 gang box
2-13821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 20
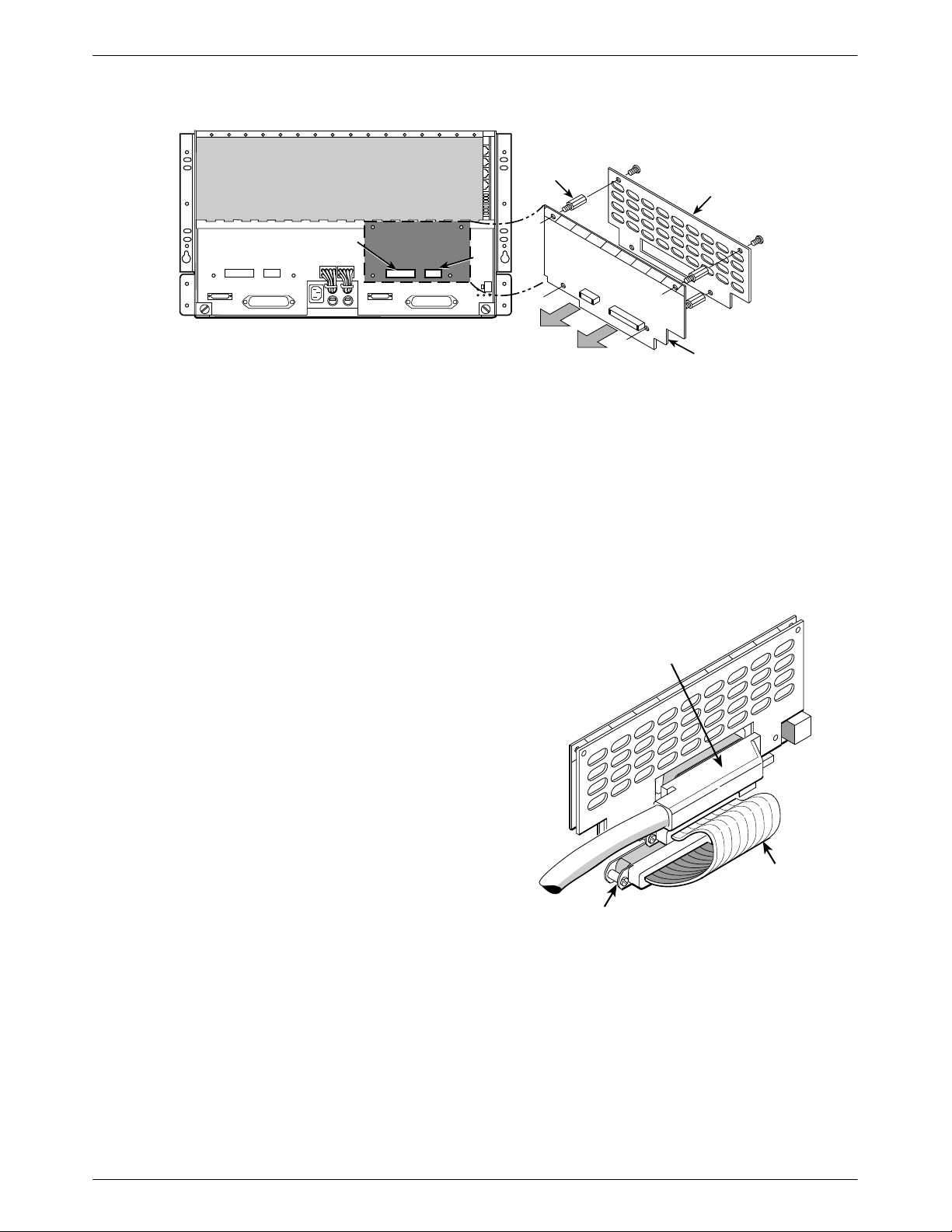
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
STANDOFF
NIM COVER
P24
P26 P25
J2 P22
P20 P19
J1
Figure 2-1. Installing the NIM
Install the NIM
A NIM can be installed on the left or right side of the
back of the 3000 Series Carrier.
" Procedure
1. If you are installing a NIM on the right side of the
carrier, press it onto the connectors P24 and P23. If
you are installing a NIM on the left side of the
carrier, press it onto the connectors P26 and P25.
P21
P23
TO P23
OR P25
TO P24
OR P26
NETWORK
INTERFACE
MODULE
(NIM)
495-14854
A 2-wire leased line connection to a JM8 interface
requires a 6-position to 8-position crossover cable. See
Appendix E.
NETWORK INTERFACE
CABLE
2. Fasten the NIM to the carrier with the four
standoffs provided. See Figure 2-1.
3. Position the NIM cover over the NIM.
4. Fasten the NIM cover in place with the four screws
provided. See Figure 2-1.
Cable the NIM
Connect one end of the short ribbon cable to the 50-pin
connector at the bottom of the NIM. Connect the other
end to P21 (on the right side of the carrier) or P22 (on the
left side of the carrier). See Figure 2-2.
Connect a network interface cable to the 50-pin
connector in the middle of the NIM. Connect the other
end to the dial or leased-line interface. This may be an
RJ11 gang box or a 66A-punchdown block. Wiring for the
50-pin NIM cable is shown in Appendix E.
SHORT
RIBBON
CABLE
P21 or P22
Figure 2-2. Cabling the NIM
495-14798
2-2 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 21

3821Plus Modem Installation
Attach the DTE Interface Assembly
The eight-slot DTE interface assembly can be mounted
on the left or the right side of the carrier. If you are
installing only one interface assembly, it must be mounted
on the same side you installed the NIM.
3000 SERIES
CARRIER
TABS
SLOTS
" Procedure
1. Feed the eight tabs at the bottom of the DTE
interface assembly into the slots on the left or right
side of the carrier.
2. Insert the screws provided, but do not completely
tighten them. See Figure 2-3.
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
C
C
C
B
B
C
C
BACKPLATE
ASSEMBLY
B
B
C
C
495-14799
Figure 2-3. DTE Interface Assembly
2-33821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 22
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
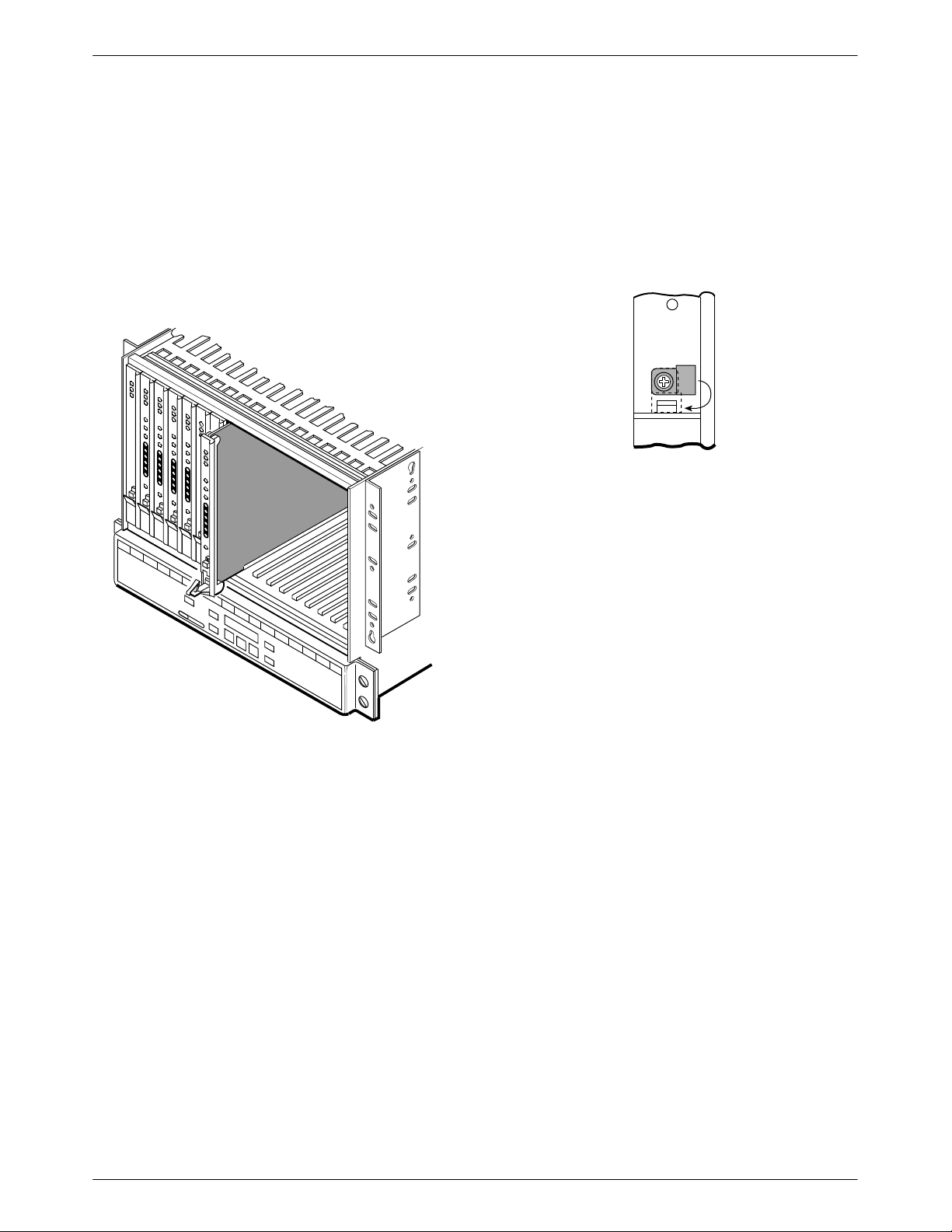
Install the Circuit Card
Slide the 3821Plus card into its slot in the 3000 Series
Carrier. Press firmly until the back edge of the card seats
in the socket of the DTE interface assembly.
Figure 2-4 shows circuit cards in a carrier in which the
NIM and DTE interface assembly were installed on the
right side of the backplane.
" Procedure
1. Turn the circuit pack lock until it is vertical, locking
the 3821Plus card in place. See Figure 2-5.
2. When all cards are installed and locked in place,
tighten the screws on the DTE interface assembly.
Front Panel
495-14800
Figure 2-5. Circuit Pack Lock
495-14797
Figure 2-4. Installing the Card Into the Carrier
Connect the DTE
T o connect the DTE to the modem, you can use two
DB25 to 8-position modular adapters and an 8-pin
RJ45-type modular cable instead of an RS-232 cable with
DB25 connectors. Because of the large number of cables
required for typical 3821Plus installations, the slimmer
modular cable is recommended.
The connectors on the DTE interface assembly are
labeled, from top to bottom, A, B, and C. These markings
show which modem on a card is associated with each
connector.
" Procedure
1. Connect the DB25 adapter or the connector on an
RS-232 DTE cable to one of the DB25 connectors
on the DTE interface assembly. Use a small
screwdriver to fasten the connector to the
backplate.
2. Connect the DB25 adapter or connector on the
cable to the DB25 connector on the DTE. Use a
small screwdriver to fasten the cable to the DTE.
2-4 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 23
3821Plus Modem Installation
Install Communications
Software
A computer commands and controls a modem through
communications software. This software uses the AT
command set to send instructions to the modem. A dumb
asynchronous terminal, however, does not require this
software since it can directly send AT commands.
The 3821Plus can be used with any major
communications software. Refer to your software’s user’ s
guide for installation procedures. For an overview of how
to use AT commands and a list of AT commands
supported by the 3821Plus, refer to Chapter 4, AT
Commands and S-Registers.
Select Factory Configuration
Options
After the modem passes the power-up self-test,
configure it for operation using one of the factory preset
configurations.
The preset configuration gives you a “head start” in
getting your modem operating and reduces the amount of
time required to configure your modem. For a better
understanding of SDCP operation and factory preset
configuration options, refer to Configure Branch in
Chapter 3.
Selecting Configurations Using the SDCP
496-14801-01
The 3821Plus modem has several factory preset
templates that contain the most commonly used
configuration options (straps) for
• Asynchronous Dial (shown as Async Dial on the
SDCP)
• Synchronous Dial (Sync Dial)
• Synchronous Leased (Sync Leased, Answer or
Originate mode)
• UNIX hardware network (UNIX Dial)
If ETC is installed:
• Cellular mobile (Cellular(Mobile))
• Cellular PSTN (Cellular(PSTN))
Your modem is shipped from the factory with the
Async Dial default configuration options stored in
memory . If Sync Dial, Sync Leased, UNIX Dial, or
Cellular is more appropriate for your configuration, then
you must change the factory setting using either the SDCP
or the AT command set as described in the following
sections.
The SDCP’s Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) consists of
two 16-character lines which display modem status,
control functions, and configuration options as well as
indicating your location in the T op-Level menu tree
(Appendix A).
T o change the factory template for each modem using
the SDCP, perform the following steps:
" Procedure
1. At the top level of the menu structure, select
Modem A, B, or C by pressing F1, F2, or F3.
2. Press the
3. Press the function key below Configure to select
the Configure branch.
The LCD now displays Ld EditArea frm.
4. Press the key until Factory comes into view.
Press the F1 key to display the factory preset
configurations.
Factory preset configurations are Async Dial, Sync
Dial, Sync Leased, UNIX Dial, and, if ETC is
installed, Cellular(Mobile), and Cellular(PSTN).
If Sync Leased is selected, you must choose either
Answer or Originate mode.
key until Configure comes into view.
2-53821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 24
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
5. Press the key until the appropriate factory
preset appears on the LCD, and press the
corresponding function key to select your choice.
6. Choose Function appears and displays the Edit and
Save functions.
7. Press the F3 key (Save) to save the new factory
preset configuration to one of three configuration
areas, Active (Saved), Customer 1, or
Customer 2.
(These three configuration areas are nonvolatile
memory locations. Active (Saved) contains the
most recently saved changes to any configuration
options. In the event of power loss, the modem
retrieves these configuration options. Customer 1
and Customer 2 are user-defined configuration
areas.)
The LCD now displays Sav EditArea to.
8. Press the
key until the appropriate
configuration area appears on the LCD, then press
the corresponding function key to select your
choice. (Saving configuration options to the Active
(Saved) configuration area automatically saves
them to the Active (Operating) configuration area.)
The LCD displays Command Complete.
9. The modem is now configured with the selected
factory template. Press the
key to return to the
T op-Level menu.
Refer to Configure Branch in Chapter 3 for more
information regarding default factory configuration
options.
Selecting Configurations Using
AT Commands
495-14829
When using AT commands, the following criteria must
be met:
• Make sure the asynchronous DTE’s communication
software is configured for 10-bit character format
(for example, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit).
• Make sure the DTE (RS-232D) cable is attached to
the DTE connector at the rear of the COMSPHERE
3000 Series Carrier, and to the correct serial
communications port on the asynchronous DTE.
• On initial power-up, the modem is in Command
mode. T o verify that the modem is connected and
functioning properly , enter the following:
TYPE: AT
PRESS: Return (Enter)
The screen displays OK.
If the modem does not return OK, refer to Appendix C,
Troubleshooting.
NOTE
If you have already changed the
factory preset configuration you
may have lost AT command
control. To regain A T command
control, select, via the SDCP, the
Async Dial factory preset
configuration as described earlier
in
Selecting Configurations Using
the SDCP.
2-6 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 25

3821Plus Modem Installation
T o change a factory template using AT commands,
perform the following steps (for more information on
changing factory templates using AT commands, refer to
Chapter 4, AT Commands and S-Registers).
" Procedure
1. Use the AT&F&W command to load the
appropriate factory configuration to the appropriate
storage area. Enter the following:
TYPE: AT&Fy&Wn
Where: y is one of the following Factory
configurations:
0 for Async Dial
1 for Sync Dial
2 for Sync Leased (Answer)
3 for UNIX Dial
4 for Sync Leased (Originate)
5 for Cellular (Mobile)
6 for Cellular (PSTN)
(NOTE: &F1, &F2, and &F4 remove AT command
control. The only way to return to AT command
control is through the SDCP as described earlier in
Selecting Configurations Using the SDCP. &F5
and &F6 are available only if ETC is installed.)
and
The &V (View) command can be used to display the
configuration options in effect. The output of the &V
command can be saved to a file and printed (using your
communications software), providing both a record of
your configuration and a worksheet for configuration
enhancements. Refer to Chapter 4, AT Commands and
S-Registers, for more on AT commands.
NOTE
When configuring your modem,
keep a record of its configuration
options as a future reference in
case the modem must be
replaced.
T o establish a connection with a remote modem, use
the D (Dial) command. Refer to Chapter 4, AT Commands
and S-Registers, for more information.
Where: n is one of the following storage areas:
0 for Active (Saved)
1 for Customer 1
2 for Customer 2
(NOTE: These three configuration areas are
nonvolatile memory locations. Active (Saved)
contains the most recently saved changes to any
configuration options. In the event of power loss,
the modem retrieves these configuration options.
Customer 1 and Customer 2 are user-defined
configuration areas.)
PRESS: Return (Enter)
2. The selected factory configuration is saved.
2-73821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 26

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
This page intentionally left blank.
2-8 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 27

SDCP Menus
Menu Structure 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modem Status Messages 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modem Select Branch 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Call Setup Branch 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dial 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disconnect 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Answer 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Change Directory 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering Telephone Numbers and Dial Command Modifiers into Directory Locations 3-10. . . . . . . . . . .
Status Branch 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
VF 3-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Identity 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Options 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Record 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Branch 3-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abort 3-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Self 3-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local Analog Loop 3-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Digital Loop 3-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local Digital Loop 3-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pattern 3-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configure Branch 3-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Editing and Saving a Configuration Option 3-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Interface 3-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Dialer 3-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Dialer 3-30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dial Line 3-34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Leased Line 3-37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
V.42/MNP/Buffer 3-39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test 3-44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Misc 3-45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security Configuration Options 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Branch 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reset 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Make Busy or Remove Make Busy 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Line or Disconnect Service Line 3-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Download Code 3-48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clone To Remote 3-48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
To Local via DTE 3-48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Automatic Firmware Download 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Download Failure 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Branch 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Security Branch 3-49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
3-13821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 28
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Menu Structure
An elaborate menu of options is available from a
Shared Diagnostic Control Panel (SDCP).
The menu tree is a hierarchical structure used to
display functions that configure and control local and
remote 3821Plus modems. It is accessed via the SDCP
and is shown in its entirety in Appendix A.
The menu tree contains the following branches:
Modem Select Used to select one of the three
modems on the card. The
modem shown in uppercase
characters is the modem
connected to the SDCP.
Quick
Configuration
Display
Call Setup Used to dial, disconnect, and
This hidden menu item
displays information about the
modem’s configuration, such
as line mode and rate.
answer telephone calls as well
as store up to 10 telephone
numbers in directory locations.
Status Used to monitor the current
status of the VF line and DTE
interface as well as view the
identity of the modem.
Test Used to begin and end various
modem tests.
Configure Used to change and save the
modem’s configuration
options.
Control Used to control the modem’s
hardware and software
functions.
Remote Used to access and control a
remote 3800Plus modem. See
Chapter 6, Remote Access.
Security Used to control the modem’s
dial access security. See
Chapter 7, Security.
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Call_Setup Control
Status
Test
Remote
SecurityConfigure
495-14520-01
3-2 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 29

SDCP Menus
Modem Status Messages
Access to all menu tree branches from the SDCP
begins at the T op-Level menu, the head of the menu
hierarchy . The LCD’s top line identifies the modem
status, as listed in Table 3-1, while the bottom line
displays the main menu tree branches and operational
and dial access security messages, as listed in T able 3-2
and Table 3-3.
Top-Level Menu Status
Normal Operation
Status Message
Idle:
MR*
Leased:
OnLine:
MR*
MR* EC**
The modem is configured for dial network operation and is on-hook.
The modem is operating on leased lines at the displayed data rate.
Indicates the modem is online, in Data mode, and operating at the displayed data rate. EC (error
control) displays if error control is operational.
Messages listed in Table 3-2 are common operational
messages that occur during modem operation. These
messages normally appear on the second line of the
LCD.
Messages listed in Table 3-3 are dial access security
messages that can occur when the optional security
feature is installed.
The Top-Level menu’s main branches appear on the
LCD in the order of Modem Select, Call Setup, Status,
T est, Configure, Control, Remote, and Security.
Table 3-1
(1 of 3)
Indicates
Fax Tx:
Fax Rx:
Ring Indicate The local modem is receiving an incoming ring.
Test:
Make Busy Indicates the modem is in a Make Busy condition.
Power On Fail Indicates the modem has failed its Power-On Self-Test.
Self Health Fail Indicates a failure in the modem’s hardware components.
*** The Alarm Status Messages only appear when the Normal Operation Status Messages are displayed; the LCD
MR*
MR*
MR*
Alarm Status
Message***
*MR – Modem Rate indicates the data rate the modem is using, in bits per second. One of the following values appears:
300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 7200, 9600, 12K (12,000), 14.4 (14,400), 16.8 (16,800), 19.2 (19,200), 21.6 (21,600), 24K
(24,000), 26.4 (26,400), 28.8 (28,800), 31.2 (31,200), or 33.6 (33,600).
**EC – Error Control indicates the modem is online and using V.42 or MNP error control. One of the following values
appears after the modem rates listed above: MNP2, MNP3, MNP4, MNP5, V42, V42b, V42t (SDC) or NoEC. (NoEC
indicates the modem is connected in Buffer mode rather than error control. If an EC value does not appear , then the
modem is in Direct mode.)
alternates between the two message sets.
The modem is transmitting a fax on a dial line.
The modem is receiving a fax on a dial line.
The modem is in test mode operating at the displayed data rate.
Indicates
3-33821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 30
COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-1
(2 of 3)
Top-Level Menu Status
Normal Call
Setup Messages
Off Hook The modem is off-hook and waiting to dial a telephone number .
Dialing The remote modem is being dialed.
Training The modem is training or retraining.
EC Negotiating The local and remote modems are negotiating the highest possible level of error control
compatible between both modems. Once a level is selected, this LCD message disappears.
Call Failure
Messages
Busy Signal The answering modem is busy .
Delayed Number As a result of failed call attempts, this number may not be called at this time. Try again later.
(Only appears in countries where the number of repeated call attempts is limited.)
Dial Line in Use The modem is already operating on dial networks when another call attempt has been issued.
Forbidden Number As a result of failed call attempts, this number may not be called again. (Only appears in
countries where the number of repeated call attempts is limited.)
Invalid Number The modem has attempted to dial from a directory location that has no phone number.
No Answer Tone No answer tone has been received within the time limit specified by the No Answer Timeout
configuration option. The network tones (if any) could not be interpreted by the modem.
Indicates
Indicates
No Dial – DTR The modem cannot dial because DTR is Off.
No Dial – Test The modem cannot dial because it is running a Test.
No Dial Tone The modem has aborted the call because it cannot detect a dial tone.
No Quiet Answer The modem has detected No Quiet Answer (@) before the time-out setting of the No Answer
Ringback Timeout The answering modem has not answered within the time limit specified by the No Answer
Wrong Call The call was answered, but not by a modem; there was no answer tone.
Call Disconnect
Messages
ATH Disconnect The modem has disconnected due to an A TH command.
Bad Lines Disc The modem has disconnected because the lines do not support the modulation and/or data rate
No Carrier Disc The modem disconnects due to the loss of carrier signal from the remote modem.
DTR Disconnect The modem has disconnected due to the loss of DTR from the DTE.
EC Disconnect The modem has disconnected due to failure to negotiate Error Control mode.
Disconnect configuration option.
Timeout configuration option; a ringback signal was detected.
Indicates
selected.
3-4 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 31

Table 3-1
(3 of 3)
Top-Level Menu Status
Call Disconnect
Messages,
Indicates
continued
LongSpace Disc The modem has disconnected due to the detection of a long space.
NoData Disc The modem has disconnected due to a lack of transmitted and received data.
Disconnecting The modem has begun the disconnect sequence.
SDCP Menus
Rmt Cmnded Disc The modem has disconnected due to a V.32 or V.34 Cleardown received from the remote
modem.
Firmware
Download Result
Indicates
Messages
DownldOnly Mode Indicates that a local download of firmware or a remote cloning of firmware has failed. The
Frmware Upgrade Indicates that a local download of firmware or a remote cloning of firmware was successful.
RemClone Failed Displays on the local modem’s LCD and indicates that a remote cloning of firmware has failed.
Remote Clone OK Displays on the local modem’s LCD and indicates that a remote cloning of firmware was
AT Command
Reset Message
Reset by ATcommand The modem has performed a reset in response to an ATZ command.
modem is currently in a Download Only mode in which only another download attempt is
possible.
successful.
Indicates
Table 3-2
Common Operational Messages
Common
Operational
Indicates
Messages
Please Wait... Appears when a command to a local device takes more than two seconds to complete.
Command Sent... Appears when a command is sent to a remote modem.
No Rem Response or
Remote Modem Fail
Command Complete Appears when a command, issued to a local or remote modem, is completed.
Invalid Command Appears when the modem cannot complete a command.
Appears when a remote modem does not respond to a command within 5 seconds.
3-53821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 32

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-3
Dial Access Security Messages
Dial Access
Security
Indicates
Messages
Get VF PsWd The answering modem is waiting for the originating caller to transmit a VF password.
Get DTE PsWd The answering modem is waiting to receive a valid DTE password from the remote DTE.
VF PsWd Timeout The modem did not finish answering a call (disconnected) because the allowed time limit was
Unknown DTEpswd The modem did not finish answering a call (disconnected) because the DTE passwords received
No Orig PsWd The modem did not attempt to establish a call as requested because the AT dial command did not
Unknown VF PsWd The modem did not finish answering a call (disconnected) because the modem received an
DTEpswd Timeout The modem did not finish answering a call (disconnected) because the allowed time limit was
Inval Orig PsWd The modem did not attempt to establish the call as requested because the originate password in
DTR Dial Blocked Appears if DTR dialing is used and Answer Access or Originate Access security is enabled. DTR
SecurityBlocked Appears only when the modem is in base mode (a mode that occurs during a firmware download)
exceeded before the modem received a VF password from the originating dialer.
from the remote DTE were invalid.
contain an originate access password.
invalid VF password.
exceeded before the modem received a DTE password from the remote DTE.
the A T dial command was not valid.
dialing is not permitted when security is enabled.
and Answer Access Security is enabled. In this case, the access verification capabilities are not
available and the modem does not pass data to the DTE under any circumstances.
3-6 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 33

SDCP Menus
Modem Select Branch
The Modem Select branch is the top level of the menu
structure. The modem selections are displayed when the
SDCP is first connected to a 3800Plus card (using the
key on the SDCP).
Select
Idle : 33.6 >
MDMA mdmb mdmc
F1
F2
F3
Press F1, F2, or F3 to connect the SDCP to modem A,
B, or C, respectively. The connected modem appears on
the SDCP in all uppercase characters.
Quick Configuration Display
The Quick Configuration display indicates the basic
operational characteristics of the modem.
Leased:33.6
Status Configure
F1
F2
The modem’s Quick Configuration information
appears on the LCD’s bottom line.
T o access the Quick Configuration display from the
T op-Level display, press the
configuration of the modem, one of two screens appears.
If the modem is not operating with V.34 modulation,
the following screen appears.
Leased:19.2 >
abbb cdd ee ffff
F1
F2
F3
key. Based on the
F3
If the modem is operating with V.34 modulation, the
following screen appears.
xxxx yyyyy zz >
abbb cdd ee ffff
F1
F2
F3
The V.34 modulation Quick Configuration
information appears on the LCD’s top line.
NOTE
In Dial mode, where Automode
automatically adapts to the
modulation scheme of the remote
modem, the V.34 Quick
Configuration display may not
necessarily indicate the actual
(V.34) online modulation.
For more information on V.34, refer to the V.34
section in this chapter.
The following provides information about the Quick
Configuration LCD display.
a Displays the network position of the modem.
The letter C indicates this is a control
modem, and T indicates this is a tributary
modem.
bbb Displays the network management address
of the modem. The valid address field range
is from 001 to 256.
c Displays the DTE mode. The letter A
indicates the currently selected port is in
Asynchronous mode, and S indicates the
currently selected port is in Synchronous
mode. If the NMS channel is selected, the
letter in this location (A or S) will indicate
the status of Port 1. (The NMS channel is
always in Asynchronous mode.)
dd Displays the line mode. The letters LA
indicate Leased Answer mode, LO indicate
Leased Originate mode, and D indicates Dial
mode.
ee Displays the DTE port. For the 3821Plus
modem, this is always P1.
3-73821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 34

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
ffff Displays the modem’s modulation scheme as
shown below:
V34 indicates V.34 family modulation.
V32t indicates V.32terbo modulation.
V32b indicates V.32bis modulation.
V32 indicates V.32 modulation.
V22b indicates V.22bis modulation.
V27b indicates V.27bis modulation.
V33 indicates V.33 modulation.
V29 indicates V.29 modulation.
V22 indicates V.22 modulation.
V23 indicates V.23 modulation.
V21 indicates V.21 modulation.
212A indicates Bell 212A modulation.
103J indicates Bell 103J modulation.
xxxx Modem Transmit Rate indicates the rate at
which the modem is transmitting data.
Possible values are 2400, 4800, 7200, 9600,
12.0 (12,000), 14.4 (14,400),
16.8 (16,800), 19.2 (19,200), 21.6 (21,600),
24.0 (24,000), 26.4 (26,400),
28.8 (28,800), 31.2 (31,200), or
33.6 (33,600) bps.
yyyyy Symbol Rate indicates the baud rate used by
V.34 modulation. Refer to ITU
specifications. Possible values are 3429,
3200L, 3200H, 3000L, 3000H, 2800L,
2800H, 2743L, 2743H, 2400L, 2400H.
zz Transmit Level indicates the power level at
which the modem is transmitting when
running V.34 modulation. Possible values are
01–64 dBm.
T o exit the Quick Configuration function and return to
the T op-Level menu, press the
or
key.
, ,
3-8 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 35

SDCP Menus
Call Setup Branch
The Call Setup branch of the T op-Level menu allows
you to dial, disconnect, and answer telephone calls. It
also allows you to create and store up to 10 telephone
numbers to directory locations. Four different functions
can appear under Call Setup:
• Dial
• Disconnect
• Answer
• Change Directory
T o access Call Setup from the Top-Level menu, press
key once. Select Call_Setup.
the
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Status
Call_Setup
Dial
Disconnect
Test
Answer
Change_Directory
Control
Remote
SecurityConfigure
If the connection is successful, the modem is online
and one of the Normal Operation status messages
appears on the LCD. If the connection is not successful,
the LCD displays one of the Call Failure status
messages. See T able 3-3.
If DTE dialing is enabled and any character is
received from the DTE before the modem goes online,
the dial sequence is aborted. This is known as any-key
abort.
Disconnect
Disconnect allows the modem to go on-hook (hang
up). Use this function when you want to disconnect an
established call on a dial line.
T o access Disconnect from the initial screen of Call
Setup branch, press F2 or F3 to select Disconnect.
The modem goes on-hook (hangs up) and the call is
disconnected. This includes any calls being used for dial
backup of leased lines. The Command Complete status
message is displayed.
T o exit this function and remain in the Call Setup
branch, press the
key. To exit and return to the
T op-Level menu, press the key .
Answer
Directory Locations 1 – 10
495-14843
Dial
Dial allows you to dial any telephone number stored
in directory locations 1–10. Any telephone number
dialed using the SDCP must already exist in a directory
location. Refer to Change Directory for information on
storing telephone numbers in directory locations.
T o dial a number from the Call Setup branch, make
the following selections:
1. Select Dial by pressing F1. The first directory
telephone number is displayed.
2. To view other directory locations, select Nxt.
3. Once the directory location you want appears on
the LCD, press the F2 or F3 key to dial the
number.
Answer allows the modem to go off-hook, generate an
answer tone, and begin the handshaking process with the
calling modem. Use the Answer function when the
Auto-Answer Ring Count configuration option is
disabled. (See the Line Dialer group under Configure
Branch.)
T o access Answer from the Call Setup branch, make
the following selections:
1. Press the
key until Answer is displayed.
2. Select Answer.
The modem goes off-hook and attempts to establish a
connection in Answer mode. The Command Complete
status message appears on the LCD.
T o exit this function and remain in the Call Setup
branch, press the
key. To exit and return to the
T op-Level menu, press the key .
3-93821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 36

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Change Directory
Change Directory allows you to enter or modify
telephone numbers. The modem has nonvolatile memory
locations that allow you to store up to 10 telephone
numbers. Each directory location can accept up to
40 characters; this includes the telephone number and
dial command modifiers. Any telephone number dialed
using the SDCP Dial command must appear in a
directory location.
T o access Change Directory from the Call Setup
branch, make the following selections:
1. Press the
key until Change Directory is
displayed.
2. Press any function key to select Change Directory.
The phone number listed in directory location 1 is
displayed.
3. Select Nxt to display other directory locations.
Entering Telephone Numbers
and Dial Command Modifiers
into Directory Locations
The following example uses an empty directory
location for describing how to enter a telephone number.
If you want to change an existing telephone number in
any of the ten directory locations, follow the same
procedures.
02 :
NxtąąąĄ"#
F1
F2
F3
Select Nxt until a blank directory appears on the
LCD. (The cursor ( ) always appears in the first
character position.)
Select F2 (") or F3 (#) until the desired character is
selected. This can be an alpha or numeric character. (See
the Dn command in T able 4-1 in Chapter 4 for the
meaning of the different dial command modifiers.)
02 : 9
NxtąąąĄ"#
F1
F2
F3
Press the key to move the cursor to the next
character position.
Continue this key sequence until the dial command
modifiers and telephone number are entered.
01 : 9W5556789 z
NxtąąąĄ"#
T o add a telephone number to a directory location,
make the following selections:
F1
F2
F3
T o save the number just entered, scroll to the next
directory location by selecting Nxt. The number is now
stored in nonvolatile memory.
3-10 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 37

SDCP Menus
Status Branch
The Status branch of the T op-Level menu allows you
to view the current status of the dial or leased-line
connection, the DTE interface, and the identity (for
example, serial number and model number) of your
equipment. The selections under Status are:
• VF
• Identity
• DTE
• SDC
• Options
• Record
T o access Status from the Top-Level menu, press the
key until Status appears. Select Status.
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Call_Setup Control
Test
Status
VF Identity
SigQual
RcvLev
Sig/Noise
NearEcho
FarEcho
FarEchDel
EchoFreqOff
Ser#
Mod #
FRev
HPt#
FPt#
Country
DTE
LSD
DTR
DSR
Tst
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
Options Record
VF
VF displays the condition of the dial or leased-line
connection.
T o access VF from the Status branch, press F1 to
select VF.
Remote
Display
Clear
98-14844-01
displayed are approximations that may be affected by the
combination of impairments on the line.
NOTE
SigQual, NearEcho, FarEcho,
FarEchDel, and EchoFreqOff
values appear only for V.34,
V.32
terbo
, V.32bis, and V.32
modulations.
SigQual Signal Quality indicates the
condition of the VF line.
Possible values are Excelent
(Excellent), Good, Fair, Poor,
or No Signal.
RcvLev Receive Signal Level
indicates, in decibels
referenced to one milliwatt
(dBm), the actual strength of
the incoming signal.
Sig/Noise Signal-to-Noise Ratio
indicates, in decibels, the
SecurityConfigure
receive signal strength relative
to noise on the line.
NearEcho Near End Echo displays the
signal level, in decibels
referenced to one milliwatt
(dBm), of that portion of the
transmit signal which has been
echoed back by the local line
termination.
FarEcho Far End Echo displays the
signal level, in decibels
referenced to one milliwatt
(dBm), of that portion of the
transmit signal which has been
echoed back by the remote
line termination.
FarEchDel Far End Echo Delay indicates
the roundtrip delay in
milliseconds of the far end
echo.
EchoFreqOff Echo Frequency Offset
indicates the frequency offset
of the far end echo.
The modem’s signal quality is displayed on the LCD’s
bottom line. Press the
key to scroll and view the
receive signal level, signal-to-noise ratio, near end echo,
far end echo delay, and echo frequency offset. Values
T o exit VF and remain in the Status branch, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level menu, press
the
key.
3-113821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 38

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Identity
Identity displays the modem’s serial number, model
number, firmware revision level, hardware part number
and firmware part number. Retrieval of this information
is useful if you are purchasing additional or replacement
modems and/or making firmware upgrades.
T o access Identity from the initial screen of the Status
branch, press the F2 or F3 key to select Identity.
The modem’s serial number is displayed on the
LCD’s bottom line. Press the
the model number, firmware revision level, hardware
part number, and firmware part number.
Ser # Serial number is an 8-digit number
that identifies the modem.
Mod # Model number is an alphanumeric
number that identifies the modem as a
3821Plus.
FRev Firmware revision level is an
alphanumeric number that identifies
the level of firmware loaded in the
modem.
HPt # Hardware part number is an 11-digit
number that identifies the circuit card
in the modem.
FPt # Firmware part number is an 11-digit
number that identifies to customer
service personnel the firmware release
number.
Country Country is a 7-character field showing
the country or continent the modem is
configured for use in.
T o exit this function and remain in the Status branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
key to scroll and view
DTE
DTE displays the state and/or activity of the
EIA-232-D interface leads. The LSD, DTR, DSR, T st,
TXD, RXD, RTS, and CTS signals are monitored. The
interface leads status is updated every 5 seconds.
T o access DTE from the Status branch, make the
following selections:
2. Select DTE. The activity and state of the modem’s
DTE signal appear on the LCD’s bottom line.
3. Press the
The LCD’s bottom line displays a pair of symbols for
each interface lead. The first symbol indicates the
signal’s activity during the sampling interval. (An *
(asterisk) indicates at least one transition while a blank
space indicates no transitions since the last update.)
The second symbol indicates the state of the interface
lead at the sampling time. (A
or ON condition while an underscore (_) indicates a
Mark or Off condition.)
T o exit this function and remain in the Status branch,
press the
menu, press the
key to scroll other signals into view.
block) indicates a Space
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Options
The Options branch lists special features installed in
the 3821Plus modem.
Record
Record is a troubleshooting tool used by the end user
in conjunction with support personnel. This function
allows the end user to retrieve and report any sequence
faults to support personnel. A sequence fault is an
irregular or unexpected event.
There are two selections under Record: Display and
Clear. Display allows up to eight sequence fault
messages that have been recorded by the modem to be
displayed on the LCD. If no sequence faults have
occurred, then Modem O.K. appears.
Clear is used to remove all sequence fault messages
from nonvolatile memory and the LCD.
T o access Record from the Status branch, press the
key until Record appears. Select Record.
T o display sequence faults, select Display.
The LCD displays the first sequence fault field.
(Sequence fault fields range from 1 to 8 and are
identified by a number in the upper right corner.) Press
key to view the remaining fields. The message
the
Modem O.K. appears if no sequence faults have
occurred.
1. Press the
3-12 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
key until DTE appears.
T o remove sequence fault records from both the LCD
and nonvolatile memory, select Clear. The message
Modem O.K. appears.
Page 39

SDCP Menus
T o exit this function and remain in the Status branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Test Branch
The T est branch of the Top-Level menu allows you to
initiate various modem tests. Use these tests if you are
having data communication problems, such as periodic
character loss, random errors, or constant format errors.
By the process of elimination, you can usually isolate the
fault in your system.
There are six selections under T est:
• Abort
• Self (Self-Test)
• Loc Analog Loop (Local Analog Loopback)
• Rem Digital Loop (Remote Digital Loopback)
• Loc Digital Loop (Local Digital Loopback)
• Pattern
The only tests that can operate concurrently are
Pattern with a Local Analog Loopback and Pattern with
a Remote Digital Loopback. If any test is operating,
besides the two combinations just mentioned, it must be
canceled before starting another test.
The Test branch only initiates and cancels tests. If any
parameters need to be set, refer to T able 3-10.
Abort
Abort ends any test that is in progress and brings the
modem back to the normal mode of operation.
Confirmation is provided by the Command Complete
message.
Select Abort, and the modem stops all tests currently
in progress and displays the Command Complete status
message on the LCD.
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Self
Self performs an internal self-test of the modem,
which takes less than a minute to complete. The modem
must be offline (not connected with another modem),
otherwise Invalid Command appears. This test is not
valid in Remote mode and does not appear on the LCD
of either modem when in Remote mode.
Select Self. (All LCD cells and SDCP status
indicators light.) If the modem passes self-test, Pass
appears on the LCD. If it fails, Failed appears. If the
modem fails, contact your service representative.
If Invalid Command appears on the LCD, then
another test is in progress or the modem is operating on
dial lines. Select Abort to clear the current test, or
disconnect to clear the dial lines, and then choose Self.
If the modem receives a ring signal during this test,
the test is canceled and the RI Abort message appears.
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Call_Setup Control SecurityConfigure
Status
Test
Abort
Loc_Analog_Loop
Self
Rem_Digital_Loop
Remote
Loc_Digital_Loop
Pattern
494-14855
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Local Analog Loop
Loc Analog Loop performs a local analog loopback
(ITU-T V.54 Loop 3) that verifies modem operation as
well as the connection between the DTE and modem.
The modem must be offline and in synchronous or
asynchronous Direct mode to perform this test, otherwise
Invalid Command appears.
T o access Loc Analog Loop from the Test branch,
press the
any function key to start this test.
The message Started appears on the LCD, and the
T est LED lights for the duration of the test.
key until Loc Analog Loop appears. Press
3-133821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 40

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
If the Test Timeout configuration option is enabled,
Test Timeout appears at the conclusion of the test. If it
is disabled, the test operates until aborted. For more
information on the T est Timeout configuration option,
refer to T able 3-10 in this chapter.
A Ring Indicate during this test can cause errors.
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Remote Digital Loop
Rem Digital Loop performs a remote digital loopback
(ITU-T V.54 Loop 2). This test can verify the integrity of
the local modem, the communications link, and the
remote modem. Any data or pattern entered at the local
DTE is sent to and returned from the remote modem. For
this test to operate properly, the modems must be online
and in Synchronous or Asynchronous Direct mode and,
if set for V.34 modulation, must not be in Asymmetric
Rate mode.
T o access Rem Digital Loop from the Test branch,
press the
any function key to start this test.
The message Started appears on the LCD, and the
T est LED lights for the duration of the test.
key until Rem Digital Loop appears. Press
T o access Loc Digital Loop from the Test branch,
press the
key until Loc Digital Loop appears. Press
any function key to start this test.
The message Started appears on the LCD and the
T est LED lights.
If the message Invalid Command appears on the
LCD, then another test is in progress. Select Abort to
clear the current test and then select Loc Digital Loop.
If the Test Timeout configuration option is enabled,
T est Timeout appears at the conclusion of the LCD. If it
is disabled, the test operates until aborted. For more
information on the T est Timeout configuration option,
refer to T able 3-10 in this chapter.
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Pattern
Pattern can transmit and receive a 511 bit error rate
test pattern. It can also be used with a local analog
loopback or a remote digital loopback to simulate data
passing through the modem. For this test to operate
properly, the modems must be online and in Synchronous
or Asynchronous Direct mode. Otherwise, the message
Invalid:Bffr Mde appears when this test is started.
If the Test Timeout configuration option is enabled,
Test Timeout appears at the conclusion of the test. If it
is disabled, the test operates until aborted. For more
information on the T est Timeout configuration option,
refer to T able 3-10 in this chapter.
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Local Digital Loop
Loc Digital Loop is issued by a local modem and
forces it to loopback any data received from the remote
modem. (This test operates the same as a ITU-T V.54
Loop 2 except it is issued at your modem.) This is useful
if a remote modem is incapable of initiating a remote
digital loopback from its location. For this test to operate
properly, the modems must be online and in Synchronous
or Asynchronous Direct mode and, if set for V.34
modulation, must not be in Asymmetric Rate mode.
T o access Pattern from the Test branch, press the
key until Pattern appears. Select Pattern to start this test.
BlksErrd=xxxxxxx displays the number of blocks of
data found in error (block size is 1000 bits per block).
The message NoSync can appear as a value for BlksErrd
while the modem’s receiver is synchronizing. The
message OvrFlw can appear as the value for BlksErrd if
the counter overflows.
Press the
key to display BlksRcvd=xxxxxxx,
number of blocks of data received.
The Pattern test can be exited and reentered without
restarting the test. The BlksErrd and BlksRcvd continue
counting.
If the Test Timeout configuration option is enabled,
Test Timeout appears at the conclusion of the test. If it
is disabled, the test operates until aborted. For more
information on the T est Timeout configuration option,
refer to T able 3-10 in this chapter.
3-14 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 41

SDCP Menus
T o exit this function and remain in the Test branch,
press the
menu, press the
key. To exit and return to the Top-Level
key.
Configure Branch
After installing a 3821Plus modem, you set its
software configuration options using either the SDCP or
the AT command set. This section describes how to
access and use the Configure branch of the T op-Level
menu via the SDCP.
The Configure branch accesses the Edit Area which is
a work space where you view and change any
configuration options (straps). These configuration
options are loaded to the Edit Area from one of five
configuration option areas: Active (Operating), Active
(Saved), Customer 1, Customer 2, or Factory.
• Active (Operating) is a configuration area
containing configuration options currently used by
the modem. When the modem is powered on or
when a save is performed, the contents of Active
(Saved) are loaded into Active (Operating). Any
changes made using AT commands directly affect
this configuration area.
• Active (Saved) is a configuration option area
containing the most recently saved changes made
to any configuration options. In the event of power
loss or reset, the modem retrieves these settings
from nonvolatile memory.
• Customer 1 and Customer 2 are two additional
configuration areas where you can create and store
additional configurations for specific applications.
• Factory is a read-only (unchangeable)
configuration area containing sets of predefined
configuration options for Async Dial, Sync Dial,
Sync Leased (Answer/Originate), UNIX Dial,
and, if ETC is installed, Cellular (Mobile), and
Cellular (PSTN). These sets contain the most
commonly used configuration options for modems
installed in these hardware environments, and give
you a head start in configuring your modem.
NOTE
If you are using AT commands, a
period of time can exist in which
the contents of Active (Operating)
and Active (Saved) differ. Once
you issue an AT&W0 (write)
command, however, the two
storage areas are identical.
The Configure branch of the T op-Level menu
contains all of the modem’s configuration options which
determine how the modem operates. These configuration
options are accessed by scrolling down and across
various levels of the Configure branch.
The Configure branch consists of the following three
levels:
• Ld EditArea frm. Allows the selection of the
Active (Operating), Active (Saved), Customer 1,
Customer 2, and Factory configuration areas.
Choosing Factory results in the further display of
the predefined factory templates.
• Choose Function. Allows you to make changes
(Edit) to existing configuration options or write
(Save) these changes to either the Active (Saved),
Customer 1, or Customer 2 configuration area.
• Edit Strap Group. Contains the software
configuration option groups that determine how
the modem operates.
3-153821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 42

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Status
Call_Setup Control
Test
Configure
Ld EditArea frm:
Activ
(Operating)
Active
(Saved)
Customer2
Customer1
Choose Function
Edit Save
Factory
Async_Dial
Sync_Dial
Sync_Leased
Choose Mode
Answer
UNIX_Dial
Originate
Remote
*
Cellular
(Mobile)
Security
*
Cellular
(PSTN)
Idle : 33.6
Test Configure
F1
F2
F3
Select Configure from the Top-Level menu.
Ld EditArea frm >
Activ (Operating)
F1
F2
F3
Ld EditArea frm <
Factory
F1
F2
F3
Select the Factory configuration area.
Ld Fact Preset : >
Async_Dial
Active (Saved) Customer1 Customer2
DTE_Interface
*
Available if ETC is installed
Line_Dialer
DTE_Dialer
Leased_Line
Dial_Line
Test
V42/MNP/Buffer
Security
Misc
98-14845-01
Editing and Saving a Configuration Option
The following example shows how to change the
Remote Access Password using the SDCP. (If you ever
intend to access another 3800Plus modem via the
Remote branch of the T op-Level menu, the Remote
Access Password must be the same for both modems.)
By following these procedures you learn how to load a
factory preset configuration area (in this case, Async
Dial), how to edit a configuration option (Remote Access
Password), and how to save changes to a configuration
area (Active (Saved)). The shaded key indicates what
key to press.
F1
Select Async_Dial.
Choose Function
Edit Save
F1
Select Edit.
Edit StrapGroup >
DTE_Interface
F1
F2
F2
F2
F3
F3
F3
3-16 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 43

SDCP Menus
Scroll to and select the Misc configuration options
group.
Edit StrapGroup <
Test Misc
F1
F2
F3
StrapsWhenDisc >
Nxt No_Change
F1
F2
F3
Select Nxt until RemAccssPasswrd appears.
RemAccssPasswrd
NxtąĄ°0
F1
0000000
F2
F3
Select the F2 (°) key to increment password values.
T o save the new password to a configuration area,
make the following selections.
RemAccssPasswrd
NxtąĄ°12345678
F1
F2
F3
Press the key to scroll up (twice).
Choose Function
Edit Save
F1
F2
F3
Select Save.
Sav EditArea to >
Active (Saved)
F1
F2
F3
RemAccssPasswrd
NxtąĄ°0
F1
0000000
F2
F3
Press the key to move the cursor to the next
position.
RemAccssPasswrd
NxtąĄ°12345678
F1
F2
F3
Continue this sequence until you have entered the
new password value.
Select a configuration area (Active (Saved),
Customer 1, or Customer 2) by using the
key. Press
F1 or F2 to save the changes.
Select the
select the
key to exit to the T op-Level menu or
key to remain in the Configure branch.
When using the SDCP to edit configuration options,
keep the following in mind:
• Nxt has two functions. First, it indicates that more
configuration options are available within that
group. These are accessed by selecting Nxt
(pressing F1) and scrolling down to the next
configuration option. Second, it indicates that
what is displayed on the LCD is the current
setting. If you scroll left or right, Nxt disappears
and reappears if a new value is selected.
• End appears when you have scrolled down to the
last configuration option available in that group.
Selecting End returns you to the top of the
configuration group. You are free to enter that
group again or scroll left or right to the next
configuration options group.
• The
key takes you one step up in the
Configure branch each time it is pressed.
3-173821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 44

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
• The key causes you to exit the Configure
branch and return to the T op-Level menu. If any
changes are made to configuration options, the
SDCP allows you to save these changes to either
the Active (Saved), Customer 1, or Customer 2
configuration areas.
• The
and keys move selections across the
LCD.
• The function key F2 selects the configuration
option that appears above it on the LCD.
The modem’s configuration options are arranged into
groups based upon functionality: DTE Interface
(Table 3-4), DTE Dialer (Table 3-5), Line Dialer
(Table 3-6), Dial Line (Table 3-7), Leased Line
(Table 3-8), V.42/MNP/Buffer (Table 3-9), Test
(Table 3-10), Misc (Table 3-11), and Security (Table 7-5
in Chapter 7).
Throughout these tables, two selections frequently
appear on the LCD: Enable and Disable. Unless
otherwise stated:
• Enable selects a configuration option and makes it
available for use.
• Disable makes a configuration option unavailable
for use.
Reference to particular country codes in this guide is
not an assurance that the modem has been approved for
use in that country. Consult your sales representative.
NOTE
In some countries, the range of
allowable values of some
configuration options is restricted.
The modem will accept any
selection, but it will set the
configuration option to the closest
allowable value. The actual value
that is accepted by the modem is
displayed when the F2 key is
pressed after a selection.
DTE Interface
The DTE Interface configuration options contain
RS-232D (ITU-T V.24) and asynchronous character
format information essential for maintaining a
connection and for transmitting data between the DTE
and the modem.
T able 3-4 shows each DTE Interface configuration
option as it appears on the LCD, with the Async Dial
factory default setting (the default value if the modem is
just being installed) shown following the colon (:) on the
first line and with all available selections listed on the
second line. Following this is a description of the
configuration option, a description of the available
selections, and any equivalent AT commands.
Not all configuration options are valid in all countries.
The available settings shown in this chapter are
displayed for the North America country code. See
Appendix H.
3-18 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 45

SDCP Menus
Table 3-4
(1 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
Async/Sync Mode: Async
Nxt Async Sync
Asynchronous/Synchronous Mode. Determines whether the modem operates in Asynchronous mode or Synchronous
mode. If the A T command set is enabled and this configuration option is set for Sync, then the modem operates in Async
mode when offline.
For Async Dial and UNIX Dial, Async is the factory default. For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, Sync is the factory default.
n
A T command equivalents are &M
Async DTE Rate:19200
Nxt 19200 115200 76800 57600 38400 14400 12000 9600 7200 4800 2400 1200 0–300
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Asynchronous DTE Data Rate. Identifies the asynchronous DTE’s operating rate to the modem. Data rates from
1 15,200 bps to 300 bps are supported.
To originate calls in 76,800 bps Sun Workstation environments, use either SDCP dialing, DTR dialing, or handset dialing.
The modem does not support A T command dialing at this data rate.
To prevent losing data in 115,200 bps applications, DTE cables should be kept as short as possible. For IBM-compatible
PCs, a buffered UART (such as a 16550A) should be used, in conjunction with software that utilizes its 16-byte buffer.
NOTE: This configuration option is ignored in Async Direct mode and synchronous mode since the DTE rate always
equals the VF rate.
The factory default is 19,200 bps.
There is no AT command equivalent; AT prefix determines Async DTE Rate.
and &Qn.
Async #Data Bits: 8
Nxt 8 7 9(DirectMde) 6(DirectMde)
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async or DTE Dialer T ype is
enabled.
Asynchronous Number of Data Bits. Determines if the asynchronous data length is composed of 6, 7, 8, or 9 data bits.
This data length excludes start, parity , and stop bits.
8 – Sets data length to 8 data bits.
7 – Sets data length to 7 data bits.
9(DirectMode) – Sets data length to 9 data bits. Only valid when Error Control configuration option is set to Direct Mode.
6(DirectMode) – Sets data length to 6 data bits. Only valid when Error Control configuration option is set to Direct Mode.
The factory default is 8 data bits.
NOTE: The total character size for Buffer mode must be 10 bits. The total character size for Direct mode must be 11 bits
There is no A T command equivalent; AT prefix determines the async character length.
or less, and Async #Data Bits must be 7 or 8.
3-193821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 46

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-4
(2 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
Asyn Parity Bit: None
Nxt None Even Odd Mark Space
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async or DTE Dialer T ype is
enabled.
Asynchronous Parity Bit. Determines type of asynchronous parity bit. The parity of the DTE must match the parity of the
modem. Parity options include None, Even, Odd, Mark, or Space.
None – No parity bit is used.
Even – Parity bit is set so that total number of 1’s in data bits plus parity bit is even.
Odd – Parity bit is set so that total number of 1’s in data bits plus parity bit is odd.
Mark – Parity bit is always set to 1. Only valid if Async #Data Bits configuration option is set to 7.
Space – Parity bit is always set to 0. Only valid if Async #Data Bits configuration option is set to 7.
The factory default is None.
NOTE: The total character size for Buffer mode must be 10 bits. The total character size for Direct mode must be 11 bits
There is no A T command equivalent; AT prefix determines parity of the async character.
or less, and Async #Data Bits must be 7 or 8.
Asyn #Stop Bits: 1
Nxt 1 2
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async or DTE Dialer T ype is
enabled.
Asynchronous Number of Stop Bits. Selects 1 or 2 bits to signal the end of an asynchronous character.
The factory default is 1.
NOTE: The total character size for Buffer mode must be 10 bits. The total character size for Direct mode must be 11 bits
There is no A T command equivalent; AT prefix determines the number of stop bits via autobauding.
or less, and Async #Data Bits must be 7 or 8.
3-20 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 47

SDCP Menus
Table 3-4
(3 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
DTR Action: Ignore
Nxt Stndrd_RS232 Ignore CntrlsOnHook Off=ReloadStrp Off=CmdMode
Data Terminal Ready Action. DTR is a signal from the DTE to the modem indicating that the DTE is connected and ready
for operation.
Standard RS232 – Allows the DTE to control DTR to the modem as specified in RS-232D and ITU-T V.24 specifications.
If this signal is not present, the modem will not answer or dial.
Ignore – Modem assumes DTR is always ON. This is used when DTE does not provide DTR to the modem.
CntrlsOnHook – Modem does not disconnect from the VF line during an active call until DTR is lowered by the attached
DTE. This setting is required for applications in which the host processor must reset itself for the next session before the
current session is terminated. The setting is ignored if the modem receives a disconnect command from the SDCP or
from the COMSPHERE 6700 Series NMS.
Off=ReloadStrp – Like Standard RS232, except that when DTR is lowered the modem loads the Active (Saved) area
into the Active (Operating) area.
Off=CmdMode – When the modem is online and DTR is Off for longer than the period specified by the S25 register, the
modem enters online Command mode. The A TO command must be issued to return to data mode. This setting has the
same effect as Ignore if AT commands are disabled.
NOTE: If V.25bis mode is used, then this configuration option must be set for Stndrd_RS232. The DTE must provide
DTR to dial or answer a call.
When operating over the dial network, this selection forces DTR Action to behave as CT108/2 (Data Terminal Ready). If
DTE Dialer Type configuration option is set to DTR=Direct 1, then DTR Action behaves as CT108/1 (Connect Data Set to
Line).
For Async Dial, Sync Leased, and UNIX Dial, Ignore is the factory default.
For Sync Dial, Stndrd_RS232 is the factory default.
n
A T command equivalent is &D
.
DSR Control: Forced_On
Nxt Forced_On Stndrd_RS232 WinkWhenDisc Follows_DTR On_Early Delay_ToData DialBkToggle
Data Set Ready Control. DSR is a signal from the modem to the DTE indicating the modem is connected and ready for
operation.
Forced On – Forces DSR output ON constantly . This is usually used for leased-line applications and when the DTE
requires DSR to always be ON.
Standard RS232 – Allows the modem to control DSR to the DTE. The modem raises DSR when it begins the handshake
process. DSR lowers upon disconnect. The modem is not ready to receive data until DSR, CTS, and LSD are active.
An ON state indicates to the DTE that the modem is ready to receive data. An Off state indicates that the modem is not
ready to receive data, and the DTE will not send data to the modem. During a Local Analog Loop and a Remote Digital
Loop, DSR is ON.
Wink When Disconnect – DSR is normally forced ON, but is turned Off for 1 to 2 seconds upon a disconnect.
Follows DTR – When the modem receives DTR from the DTE, it sends DSR to the DTE.
On Early – DSR is low when the modem is in the idle state. DSR goes high immediately upon a command to enter Data
mode. This setting is required for some modem pooling applications.
Delay to Data – Operation is similar to the Standard RS232 setting except that DSR does not turn ON until the modem
enters Data mode. Normally , the modem raises DSR when it begins the handshaking process.
Use this setting when the DTE cannot operate with a long DSR-to-CTS delay (common for V.32bis modulation) or when
dial access security is enabled and requires a DTE-side password entry . Often, the DTE cannot accept the long delay
between DSR and CTS turning ON due to the remote user entering the DTE-side password.
For Async Dial and UNIX Dial, Forced_On is the factory default.
For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, Stndrd_RS232 is the factory default.
n
A T command equivalent is &S
.
3-213821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 48

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-4
(4 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
RTS Action: Ignore
Nxt Ignore Stndrd_RS232 Sim_Cntl_Car
Request-to-Send Action. RTS is a signal from the DTE to the modem indicating the DTE has data to send to the modem.
Ignore – Modem assumes RTS is always ON. Use this selection when the DTE does not provide RTS to the modem.
Standard RS232 – Allows the DTE to control RTS to the modem in normal RS-232D operation. RTS must be ON for the
DTE to transmit to the modem.
Simulated Control Carrier – RTS input controls the remote modem’s LSD signal. This is used for DTEs that require Line
Signal Detect (LSD) to toggle ON and Off to simulate half-duplex operation. Valid only in Synchronous mode and
Asynchronous Direct mode.
NOTE: If RTS Action is set for simulated control carrier, then the remote modem’s LSD Control configuration option must
For Async Dial and UNIX Dial, Ignore is the factory default.
For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, Stndrd_RS232 is the factory default.
A T command equivalent is &R
be set for Simulated Control Carrier. Simulated Control Carrier conforms to V.13 specifications. This setting is
ignored when the modem is configured for Asynchronous mode and RTS/CTS flow control is selected.
n
.
CTS Control: Forced_On
Nxt Forced_On Stndrd_RS232 WinkWhenDisc Follows_DTR
Clear-to-Send Control. CTS is a signal from the modem to the DTE indicating that it can accept data from the DTE.
NOTE: When CTS flow control or CTS/RTS flow control is enabled, CTS will turn ON and Off regardless of the setting of
Forced On – CTS is forced ON at all times. Use this selection for most asynchronous applications.
Standard RS232 – In Synchronous mode, forces the state of CTS to follow the state of RTS in normal RS-232D
operation. The minimum time that elapses between CTS and RTS is determined by the RTS/CTS Delay configuration
option. Use this setting for most synchronous applications.
In A T Command mode, CTS (which is ON in Idle mode) goes Off just prior to DSR going active, and goes ON when the
modem enters Data mode. This operation prevents losing data in applications which begin transmitting as soon as DSR
and CTS are both active.
Wink When Disconnect – CTS is normally forced ON, but is turned Off for 1 to 2 seconds upon a disconnect. Use this
for most UNIX applications.
Follows DTR – The state of CTS follows the state of DTR. When DTR turns ON, CTS turns ON. When DTR turns Off,
CTS turns Off.
For Async Dial, Forced On is the factory default.
For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, Stndrd_RS232 is the factory default.
For UNIX Dial, WinkWhenDisc is the factory default.
A T command equivalent is \D
CTS Control.
n
.
3-22 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 49

SDCP Menus
Table 3-4
(5 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
RTS/CTS Delay: 0 msec
Nxt 0msec 10msec 50msec 150msec 600msec
Request-to-Send/Clear-to-Send Delay. RTS/CTS Delay sets the delay time between the modem receiving RTS from the
DTE and the modem sending CTS to the DTE.
This delay is only valid in Async Direct mode and synchronous applications when it is necessary to have a short delay
between the time the DTE raises RTS and the time the modem presents CTS to allow the DTE to send data.
NOTE: For this configuration option to be valid, both the RTS Action and the CTS Control configuration options must be
The factory default is 0 milliseconds.
A T command equivalent is S-register S26=
LSD Control: Stndrd_RS232
Nxt Stndrd_RS232 Forced_On WinkWhenDisc Follows_DTR Sim_Cntl_Car =DTR/DiscOff BridgeRetrain
Line Signal Detect Control. LSD is a signal indicating that the carrier signal is being received from the remote modem. It
is normally turned Off to the DTE when the power level of the received carrier signal drops below the carrier detect
threshold.
Standard RS232 – LSD is ON when the modem detects the remote modem’s carrier signal. LSD turns Off when the
carrier signal strength drops below carrier detect threshold.
Forced On – Forces LSD to be ON at all times.
Wink When Disconnect – LSD is normally forced ON, but can be turned Off for 1 to 2 seconds upon a disconnect. This
is used for UNIX DTEs.
Follows DTR – The state of LSD follows the state of DTR. When DTR turns ON, LSD turns ON. When DTR turns Off,
LSD turns Off.
Simulated Control Carrier – LSD follows the state of RTS of the remote DTE via the V.13 simulated control carrier
signaling. This is required for hosts that cannot support full-duplex operation. V alid only in Synchronous mode and
Asynchronous Direct mode.
NOTE: If LSD Control is set for simulated control carrier, then the R TS Action configuration option on the remote modem
=DTR/Disconnect Off – The state of LSD follows the state of DTR except when disconnecting once a connection is
established. In this instance, DTR remains ON and LSD turns Off. DTR must then toggle Off and then ON again for LSD
to turn ON. This setting is required for AT&T DATAKIT dial-out applications.
NOTE: If LSD Control is set for =DTR/DiscOff, then the DTR Action configuration option must be set for Stndrd_RS232.
For Async Dial, Sync Dial, and Sync Leased, Stndrd_RS232 is the factory default.
For UNIX Dial, WinkWhenDisc is the factory default.
A T command equivalent is &C
set for Stndrd RS232. If RTS Action is set for Ignore, RTS is always ON and this configuration option has no
effect.
n
.
must be set for Simulated Control Carrier.
n
.
3-233821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 50

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-4
(6 of 6)
DTE Interface Configuration Options
TX Clock Source: Internal
Nxt Internal External RXC_Loop
This configuration option only appears when Async/Sync Mode is configured for Sync.
Transmit Clock Source. Determines the source of timing for synchronous data transmitted from the DTE.
Internal – The transmit data’s clock source is derived from the modem’s internal clock and output on Pin 15 (TXC) of the
RS-232D interface.
External – The transmit data’s clock source is provided by the DTE on Pin 24 (EXT) on the RS-232D interface. This
configuration option automatically disables Autorate, Automode, and Asymmetric Rate mode when running V.34
modulation.
RXC Loop – The modem’s transmit clock is derived from its received signal and is output on Pin 15 (TXC) of the
RS-232D interface.
NOTE: This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Sync.
The factory default is Internal.
n
A T command equivalent is &X
DTE Rate=VF: Disable
End Disable Enable
.
DTE Rate = VF Rate. Forces the data rate of the connection between the DTE (computer) and the modem to be the
same as the VF (telephone line) rate.
Disable – The DTE rate is the value of the Async DTE Rate configuration option.
Enable – The DTE rate is identical with the VF rate.
The factory default is Disable.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S90=
.
3-24 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 51

SDCP Menus
DTE Dialer
T able 3-5 shows each DTE Dialer configuration
option as it appears on the LCD.
The DTE Dialer configuration options establish the
DTE-to-modem protocol for call establishment and
control.
Table 3-5
(1 of 5)
DTE Dialer Configuration Options
DTE Dialer Type: AT
Nxt AT Disable V25bis_Async V25bis_Bsync V25bis_HDLC DTR=Direct1 AT&T_Exclusv
Data Terminal Equipment Dialer Type. Identifies to the modem the type of dialing method and protocol used by the DTE.
AT – Allows AT command protocol to be used as a method for entering commands and dialing when used in an
asynchronous application.
NOTE: The modem will not respond to AT commands if DTE Dialer Type is not set for AT.
Disable – Disables any type of DTE dialing method. Dialing can only be performed using the SDCP’s Dial command or
attached telephone.
V.25bis Async – Selects V.25bis Async as the dialing method and protocol used by the modem. Ths option is available
only when Async/Sync Mode is set to Async. The character length must be 7 data bits with even parity and 1 stop bit.
V.25bis Bisync – Selects V.25bis Bisync as the dialing method and protocol used by the modem. This is also known as
character-oriented protocol. This framing protocol uses two synchronous control characters and a start-of-text control
character before the text block and an end-of-text control character after the text block. This option is available only when
Async/Sync Mode is set to Sync. The character length must be 7 data bits with odd parity and 1 stop bit.
V.25bis HDLC – Selects V.25bis HDLC as the dialing method and protocol used by the modem. This is also known as
bit-oriented protocol. This framing protocol uses flag, address and control characters before the text block and a frame
sequence check and flag after the text block. This option is available only when Async/Sync Mode is set to Sync.
DTR=Direct1 – Allows the modem to automatically dial the number stored in directory location 1 whenever DTR turns
ON.
NOTE: DTR dialing should not be used if dial access security is enabled.
AT&T Exclusive – Enables a subset of the proprietary AT&T command set, which is required for some applications that
use A T&T equipment. Currently, the only application supported is AT&T DA TAKIT. This option is available only when
Async/Sync Mode is set to Async.
For Async Dial and UNIX Dial, AT is the factory default.
For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, Disable is the factory default.
n
A T command equivalents are &M
and &Qn.
*AT Escape Char: 043 ASCI
Nxt 043 ASCI
A T Escape Character. The escape sequence (+++) allows you to move back and forth between Command mode and
Data mode. The ASCII value of the escape character (043 ASCII) can be set to any ASCII value from 0 ASCII to
255 ASCII. However, the escape character is disabled if a value greater than 127 ASCII is entered. When disabled, the
call must be disconnected to return to Command mode.
The factory default is 043 (ASCII AT escape character).
A T command equivalent is S-register S2=
* This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer Type is configured for AT.
n.
3-253821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 52

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-5
(2 of 5)
DTE Dialer Configuration Options
*Escape GuardTim: 1sec
Nxt 1sec 200msec 400msec 600msec 800msec 2sec
Escape Guard Time. Determines the length of the required pause before and after the escape sequence is issued. The
guard time prevents the modem from interpreting data as the escape sequence characters.
The factory default is 1 second.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S12=
*BreakForceEscap: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
Break Forces Escape. Determines whether or not the modem should enter Command mode when it receives a break
character from the DTE.
Disable – A break character is sent to the remote end.
Enable – Modem escapes into AT Command mode, and a break character is not sent to the remote end.
The factory default is Disable.
n
A T command equivalent is \K
.
.
*CommandCharEcho: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Command Character Echo. Controls whether or not characters are echoed back to the DTE when the modem is in
Command mode.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is E
*CarriageRtn Char: 013 ASCI
Nxt ↑ 013 ASCI
Carriage Return Character. Allows you to change the ASCII character used to terminate an AT command to any ASCII
value from 0 to 127.
The factory default is 013 (ASCII carriage return).
A T command equivalent is S-register S3=
*Backspace Char: 008 ASCI
Nxt ↑ 008 ASCI
Backspace Character. Sets the character used to perform a backspace in Command mode.
The factory default is 008 (ASCII backspace character).
A T command equivalent is S-register S5=n.
* This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer Type is configured for AT.
.
n
.
3-26 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 53

SDCP Menus
Table 3-5
(3 of 5)
DTE Dialer Configuration Options
*Linefeed Char: 010 ASCI
Nxt ↑ 010 ASCI
Line Feed Character. Sets the character used to perform a line feed in Command mode for responses from the modem.
The factory default is 010 (ASCII line feed character).
A T command equivalent is S-register S4=n.
*Result Codes: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable EnableInOrig
Result Codes. Result codes are informational messages (such as Connect and Ring) sent from the modem and
displayed on the asynchronous DTE terminal. (For a list of result codes, refer to Appendix B
Enable – Modem sends result codes to the DTE.
Disable – Modem does not send result codes to the DTE.
EnableInOrig – For UNIX applications, enable result codes only on the originating modem. This prevents the DTE on the
answer side from interpreting result codes as login attempts.
For Async Dial, Enable is the factory default.
For UNIX Dial, EnableInOrig is the factory default.
A T command equivalent is Qn.
*ExtendResltCode: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable Add/EC Add/V42,MNP Use_DTE_Rate
Extended Result Codes. Informational messages such as VF data rate and Error Control are displayed with the result
codes. (For a list of result codes, refer to Appendix B
Enable – NO DIALTONE, BUSY, NO ANSWER, and CONNECT xxxx (xxxx = VF data rate) are displayed along with
result codes listed in Appendix B.
Disable – Only OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, and ERROR result codes appear.
NOTE: NO DIAL TONE is valid only if Dial Tone Detect configuration option is enabled. BUSY appears if Busy Detect
Add/EC – Places the EC suffix after the result code text if error control is used. For example, CONNECT 9600/EC.
Add/V.42, MNP – Places either the /V.42 or /MNP suffix after the result code text if data compression is used. For
example, CONNECT 9600/V42b.
Use DTE Rate – Allows the DTE rate to be displayed in the Connect message instead of the line rate. This feature is
required in some modem pooling applications.
The factory default is Enable.
A T command equivalent is X
configuration option is enabled.
n
.
.
)
.
)
* This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer Type is configured for AT.
3-273821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 54

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-5
(4 of 5)
DTE Dialer Configuration Options
*ResultCode Form: Words
Nxt Words Numbers (1) Numbers (2)
Result Codes Format. Controls whether or not result codes appear as words or as numeric codes. Some DTEs do not
recognize result codes as words; therefore, numbers are required. The Numbers (2) format is required for some modem
pooling applications. (For a list of result codes, refer to Appendix B.)
The factory default is Words.
n
A T command equivalent is V
*AT Cmnd Mode: Normal
Nxt Normal No_ERROR NoStrapOrERR
A T Command Mode. Determines how the modem responds to valid and invalid AT commands.
NOTE: Since this configuration option affects AT commands, it cannot be changed by the AT&F command. However, it
can be changed by selecting a factory preset configuration via the SDCP.
Normal – Allows normal operation of the AT command set. The modem acts upon all valid AT commands and issues the
ERROR result code for invalid commands. If a string with multiple commands is entered, then an invalid command within
that string will prevent the execution of subsequent valid commands.
No ERROR – Operates similar to Normal mode, however, the modem does not issue an ERROR result code for invalid
commands. When an invalid command equivalent is encountered, the modem ignores it and issues the OK result code. If
a string with multiple commands is entered, then an invalid command within that string will not prevent the execution of
subsequent valid commands.
No Strap or ERROR – Ignores all A T commands (including valid commands) that cause a configuration option to
change. Only nonconfiguring commands (for example A TD, ATA, and ATI) are executed; the ERROR result code is never
returned.
The factory default is Normal.
A T command equivalent is S-register S84=
.
n
V25bis Coding: ASCII
Nxt ASCII EBCDIC
V.25bis Coding. Identifies to the modem whether the DTE is using ASCII code or EBCDIC code for V.25bis commands.
The modem responds to the DTE using the same coding.
NOTE: This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer is configured for V25bis HDLC or V25bis Bisync.
The factory default is ASCII.
A T command equivalent is S-register S62=
* This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer Type is configured for AT.
n.
3-28 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 55

SDCP Menus
Table 3-5
(5 of 5)
DTE Dialer Configuration Options
V25bis IdleFill: Mark
Nxt Mark Flag
V.25bis Idle Fill. Determines whether a mark or flag is used as an idle fill character for the DTE. The modem responds to
the DTE using the same idle fill.
NOTE: This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer is configured for V.25bis HDLC or V25bis Bisync.
The factory default is Mark.
A T command equivalent is S-register S63=
V.25b NewLineChr: CR+LF
Nxt CR+LF CR LF
V.25bis New Line Character. Sets the modem for the command line terminator used by the DTE in V.25bis Async mode.
The modem responds to the DTE using the same line terminator.
NOTE: This configuration option only appears if DTE Dialer is configured for V25bis Async.
The factory default is CR+LF.
A T command equivalent is S-register S64=
n.
n.
DTR Cont Repeat: Disable
End Disable Enable
DTR Continuous Repeat. Determines whether automatic redialing stops after the number in directory location 1 has been
tried unsuccessfully once. If DTR Cont Repeat is enabled, the number is redialed continuously .
A redial attempt is made in response to a bad phone number, a busy signal, no answer, or no quiet answer. However, a
lockout from redialing occurs after the number of successive failing call attempts specified in national regulations. Ten
successive attempts are permitted in North America.
NOTE: DTR Cont Repeat is accessible only if the DTE Dialer Type is DTR=Direct1.
The factory default is Disable.
Disable – Automatic redialing will not be repeated.
Enable – Automatic will be repeated if necessary.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S38=
.
3-293821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 56

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Line Dialer
T able 3-6 shows each Line Dialer configuration
option as it appears on the LCD.
The Line Dialer configuration options establish
parameters used by the modem to answer or originate
calls.
Table 3-6
(1 of 4)
Line Dialer Configuration Options
AutoAnswerRing#: 1
Nxt 1 Disable 246810
Auto-Answer Ring Count. Determines the number of rings necessary before the answering modem answers an incoming
call. For example, if this option is set for 2, then the answering modem answers after the second ring.
NOTE: Although SDCP selections are limited (1, 2, 4, 6, 8, or 10), values set by AT commands can display from 1 to
Disable – If selected, the modem must be answered using either the SDCP’s Answer command or via AT commands.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S0=
Dialer T ype: Tone
Nxt Tone Pulse
Dialer Type. Selects either tone (DTMF) dialing or pulse (rotary) dialing mode.
The factory default is Tone.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalents are the Dial command modifiers T and P.
255 rings.
n
.
DialT one Detect: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Dial Tone Detect. Sets the modem for dial tone detection (enable) or blind dialing (disable).
Enable – Modem disconnects the call if a dial tone is not detected within 10 seconds and displays No Dial Tone on both
the LCD and asynchronous DTE terminal.
Disable – Modem dials a call whether or not it detects a dial tone on the line. This is known as blind dialing. The period of
time the modem waits before dialing is specified in the Blind Dial Pause configuration option.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is X
Blind Dial Paus: 2sec
Nxt 2sec 4sec 6sec 8sec 10sec 20sec
Blind Dial Pause. Determines how long the modem waits before dialing a telephone number when DialTone Detect is
disabled.
NOTE: The Blind Dial Pause configuration option only appears when the Dial Tone Detect configuration option is
disabled.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S6=
.
n
.
3-30 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 57

SDCP Menus
Table 3-6
(2 of 4)
Line Dialer Configuration Options
BusyT one Detect: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Busy Tone Detect. Sets the modem to monitor for Busy Tone (Enable) or ignore Busy Tone (Disable).
This configuration option is normally enabled; however, if the modem receives false busy tones, this configuration option
can be disabled and the modem ignores all busy tones.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is X
‘‘,” Pause Time: 2sec
Nxt 2sec 4sec 6sec 8sec 10sec 20sec
Pause Time. Determines the number of seconds the modem pauses when it encounters a comma (,) in the dial
command string.
NOTE: Although SDCP selections are limited (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, or 20), values set by the AT commands can be displayed as
0 to 255 seconds.
The factory default is 2sec.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S8=
.
n
.
NoAnswer Timout: 45sec
Nxt 45sec 30sec 60sec 120sec
No Answer Abort Time-out. Determines the number of seconds an originating modem waits before abandoning a call
attempt when no answer tone is received.
NOTE: Although SDCP selections are limited (30, 45, 60, or 120), values set by AT commands can display from 1 to
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S7=
Fast Disconnect: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
Fast Disconnect. Allows the modem to disconnect immediately after receiving a disconnect command from a local DTE
or its own diagnostic control panel.
Disable – The modem follows its normal disconnect sequence by issuing a cleardown sequence or long space
disconnect. This is also known as a graceful disconnect since the other modem receives advance notice of a
disconnection.
Enable – Use this setting if the DTE requires that the modem be made available as soon as possible after receiving a
disconnect command.
NOTE: This abrupt method of disconnecting may cause problems with the remote modem, which may interpret the
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S85=
255 seconds.
n
.
disconnection as an error instead of a valid disconnect.
n
.
3-313821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 58

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-6
(3 of 4)
Line Dialer Configuration Options
Long Space Disc: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Long Space Disconnect. Determines the modem’s response to a continuous spacing condition sent from the remote
modem when it goes on-hook. Issuing a long space is one method of disconnecting a call.
NOTE: This configuration option is ignored when the modem operates in Synchronous mode or Dial Backup mode.
Enable – Modem disconnects if it receives a continuous space from the DTE. The modem’s transmitter will transmit
4 seconds of long space upon a disconnect.
Disable – Modem does not disconnect if it receives a continuous space from the DTE. Modem will not transmit a long
space disconnect.
For Async Dial, UNIX Dial, and Sync Leased, Enable is the factory default.
For Sync Dial, Disable is the factory default.
n
A T command equivalent is Y
No Carrier Disc: 2sec
Nxt 2sec 5sec Disable 10sec 20sec
No Carrier Disconnect. If the modem no longer receives carrier from the remote modem, it disconnects the call. This
configuration option determines how long carrier is Off before the modem disconnects. Loss of carrier is one method of
disconnecting a call.
2, 5, 10, 20 sec – Modem disconnects if carrier turns Off for more than 2 seconds, 5 seconds, 10 seconds, or
20 seconds.
Disable – Modem does not disconnect if carrier turns Off.
The factory default is 2sec.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S10=
.
n.
No Data Disc: Disable
Nxt Disable 10min 30min 60min
No Data Disconnect. Forces the modem to disconnect if no data is transmitted or received within a specified amount of
time.
Disable – Modem remains connected despite the lack of data flow.
10, 30, 60 min – Modem disconnects if data is not received or transmitted within 10-minute, 30-minute, or 60-minute
intervals.
The factory default is Disable.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
n
A T command equivalent is \T
.
3-32 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 59

SDCP Menus
Table 3-6
(4 of 4)
Line Dialer Configuration Options
NoDataDiscTrig: TXD and RXD
Nxt TXD and RXD TXD Only RXD Only TXD or RXD
No Data Disconnect Trigger Signal. Works in conjunction with No Data Disconnect (\T), and determines whether Pin 2
(transmit data) or Pin 3 (receive data) of the modem’s RS-232 serial interface is monitored so that the modem can
disconnect the call if there is no activity for a certain period of time.
The No Data Disconnect Trigger Signal configuration option is unavailable and is not displayed on the SDCP when No
Data Disconnect is disabled. The reloading of factory defaults does not affect No Data Disconnect Trigger Signal.
TXD and RXD – Disconnect if no data is transmitted and received for specified period.
TXD Only – Disconnect if no data is transmitted for specified period.
RXD Only – Disconnect if no data is received for specified period.
TXD or RXD – Disconnect if no data is transmitted or received for specified period.
The factory default is TXD and RXD.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S80=
Auto Make Busy: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
.
Automatic Make Busy . Forces the modem to go off-hook under the following conditions: a local analog loopback is
performed, a self-test is performed, or if the modem is switched to the service line.
NOTE: This configuration option should only be used when the modem is located behind a user’s Private Branch
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S40=n.
MakeBusyViaDTR: Disable
End Disable Enable
Make Busy Via DTR. Determines if the modem goes off-hook when DTR is Off. Enable this setting if the DTE normally
keeps DTR ON and turns DTR Off when the DTE cannot accept a call.
NOTE: This configuration option should only be used when the modem is located behind a user’s Private Branch
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S69=
Exchange (PBX). The Make Busy Network Interface Module (NIM) must be installed on the COMSPHERE
3000 Series Carrier. Refer to the
Exchange (PBX).
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Installation Manual
n
.
.
3-333821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 60

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Dial Line
The Dial Line configuration group does not appear if
the modem is configured with the Sync Leased factory
The Dial Line configuration options are used to
configure the modem for operation over dial lines.
preset template, or if the &L1, &L2, &L3, or &L4
command is entered.
T able 3-7 shows each Dial Line configuration option
as it appears on the LCD.
Table 3-7
(1 of 3)
Dial Line Configuration Options
Modulation: V34
Nxt V34 V32bis/terbo V21/V22/BELL
Modulation determines the modem’s primary dial modulation group: V.34; V.32bis and V.32
Bell 212A, and Bell 103J.
The factory default is V34 (V.34 modulations).
Dial LineRate: 33600(V34)
Nxt 33600(V34) 31200(V34) 28800(V34) 26400(V34) 24000(V34) 21600(V34) 19200(V34) 16800(V34)
14400(V34) 12000(V34) 9600(V34) 7200(V34) 4800(V34) 2400(V34)
- OR Nxt 19200(V32t) 16800(V32t) 14400(V32b) 12000(V32b) 9600(V32) 7200(V32b) 4800(V32)
terbo
; or V.21, V.22bis, V.22,
- OR Nxt 2400(V22bis) 1200(V22) 1200(212A) 0–300(V21) 0–300(103J)
Dial Line Rate. This configuration option determines the modem’s data rate and modulation scheme for operation on dial
lines. Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs. Dial Line Rate sets the upper limit rate and modulation;
lower speed connections may still be possible.
What Dial Line Rate configuration options are displayed depends on the setting of Modulation.
33600(V34), 31200(V34), 28800(V34), 26400(V34), 24000(V34), 21600(V34), 19200(V34), 16800(V34), 14400(V34),
12000(V34), 9600(V34), 7200(V34), 4800(V34) – The modem operates using V.34 modulation at the data rate selected.
The change does not take effect until the modem is reset. The modem can be forced by the remote modem to a lower
data rate. Note that if Automode is enabled and Dial Line Rate is set to V.34, the modem can connect in a non-V.34
modulation. However, if Dial Line Rate is not set to V.34, it cannot be Automoded to V.34.
19200(V32t), 16800(V32t), 14400(V32b), 12000(V32b), 9600(V32), 7200(V32b), 4800(V32) – The modem operates
using V.32
to a lower data rate.
2400(V22bis), 1200(V22), 1200(212A) – Modem operates using the modulation and data rate selected.
0–300(V21), 0–300(103J) – Modem operates in full-duplex, Asynchronous mode. These data rates do not support V .42
or MNP error control.
The factory default is 33600(V34).
A T command equivalent is S-register S41=
terbo
, V.32bis, or V.32 modulation at the data rate selected. The modem can be forced by the remote modem
n.
3-34 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 61

SDCP Menus
Table 3-7
(2 of 3)
Dial Line Configuration Options
Automode: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable System 85
Automode. Allows the modem to automatically detect the remote modem’s modulation.
Enable – The modem automatically adapts to the modulation scheme and line rate of the remote modem, and the VF
line condition. However, the maximum data rate the modem uses is determined by the Dial Line Rate configuration
option. Bell 103J protocol is used for data rates of 0–300 bps.
Disable – Connection fails if the remote modem does not support the selected modulation.
System 85 – Modifies parameters used by the connection process. Specify System 85 only if your modem is in a modem
pool attached to a System 85 Private Branch Exchange (PBX).
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S78 =
Autorate: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable StartAt48 StartAt96
Autorate. Controls the modem’s ability to adjust its speed upward and downward to accommodate the conditions of the
VF line.
Enable – Once connected, the modem automatically lowers the line rate if line conditions become impaired. When line
conditions improve, the modem automatically shifts up to the highest data rate the line can support, limited by the value
of the Dial Line Rate configuration option. This autorating only occurs between 4800 bps and 19,200 bps during V.32bis
and V.32
Disable – Line rate does not vary after the initial line rate selection during start-up.
StartAt48, StartAt96 – Useful for lines with known noise problems, these settings cause the modem to connect at
4800 bps (StartAt48) or 9600 bps (StartAt96). If line conditions warrant it, the modem shifts up to the next higher rate until
the value of Dial Line Rate or the highest possible rate for the line is reached.
The factory default is Enable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S76=
terbo
connections and between 2400 bps and 33,600 bps during V.34 connections.
.
n
.
Dial TX Level: Permissv(–9)
Nxt Permissv(–9) –10 dBm –11 dBm –12 dBm –13 dBm –14 dBm –15 dBm –16 dBm –17 dBm
–18 dBm –19 dBm –20 dBm –21 dBm –22 dBm –23 dBm –24 dBm –25 dBm –26 dBm –27 dBm
–28 dBm –29 dBm –30 dBm –31 dBm –32 dBm ETC 1.0_Cell ETC 1.1_Cell
Dial Transmit Level. Sets the power output level of the transmit signal over dial lines.
Permissive (–9 dBm) – The modem transmits data at approximately –9 dBm. This is true whether the modem is
connected to an RJ11-type permissive jack or to an RJ41 or RJ45 programmable jack.
ETC 1.0_Cell – Available only if ETC is installed. Transmit level is automatically adjusted in response to line conditions
according to the proprietary Enhanced Throughput Cellular (ETC) 1.0 specification. Use only with remote modems set to
ETC 1.0_Cell, and limit the data rate to 4800 bps.
ETC 1.1_Cell – Available only if ETC is installed. Transmit level is automatically adjusted in response to line conditions
according to the proprietary Enhanced Throughput Cellular 1.1 specification.
The factory default is Permissv(–9).
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
n
A T command equivalents are &
and &Jn.
3-353821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 62

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-7
(3 of 3)
Dial Line Configuration Options
V22b Guard Tone: Disable
Nxt Disable 550Hz 1800Hz
V.22bis Guard T one. Determines whether the V.22bis guard tone is disabled, set to 550 Hz, or set to 1800 Hz.
Disable – No guard tone.
550 Hz or 1800 Hz – When the modem is in Answer mode, it transmits the guard tone at this frequency .
The factory default is Disable.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is &Gn.
Train T ime: Long
Nxt Long Short
Train T ime. Controls V.34, V.32
are used during the handshaking sequence for both dial and leased line applications.
NOTE: This configuration option only appears when the Dial Line Rate configuration option is set for V.34, V.32
V.32bis, or V.32.
Long – Selects long train. Use this setting whenever far-end frequency offset (phase roll) may be encountered. This is
usually only required when transmitting over satellite links.
Short – Allows the modem to train-up faster.
The factory default is Long.
A T command equivalent is S-register S43=
Asymmetric Rate: Enable
End Enable Disable
Asymmetric Rate. Controls rate symmetry when running V.34 modulation. (This configuration option does not appear
unless V.34 modulation is selected.)
Enable – The modem operates in asymmetric rate mode (the transmit and receive rates can be different) when running
V.34 modulation. Asymmetric Rate must be enabled in both modems.
Disable – The modem operates in symmetric rate mode (the transmit and receive rates are identical) when running
V.34 modulation. Either modem can force symmetric mode by disabling Asymmetric Rate.
The factory default is Enable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S14=
terbo
, V.32bis, and V.32 train. Determines whether minimum or maximum time durations
n
.
n
.
terbo
,
3-36 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 63

SDCP Menus
Leased Line
T able 3-8 shows each Leased Line configuration
option as it appears on the LCD.
The Leased Line configuration options are used to
configure the modem for operation over leased lines.
The Leased Line configuration group only appears if
the modem is configured with the Sync Leased factory
preset template, or if the &L1, &L2, &L3, or &L4
command is entered.
Table 3-8
(1 of 2)
Leased Line Configuration Options
Leased Mode: 2WLL-Orig
Nxt 2WLL-Orig 2WLL-Ans
Leased Mode. Sets the modem for either Answer mode (receiving a call) or Originate mode (initiating a call).
NOTE: For proper operation over leased lines, one modem must be set for Originate mode, and the other modem must
The factory default is 2WLL-Orig.
A T command equivalent is &L
Modulation: V34
Nxt V34 V32bis/terbo V22bis
be set for Answer mode.
n
.
Modulation determines the modem’s primary leased line modulation group: V.34, V.32bis and V.32
The factory default is V34 (V.34 modulations).
LeasedLine Rate: 33600(V34)
Nxt 33600(V34) 31200(V34) 28800(V34) 26400(V34) 24000(V34) 21600(V34) 19200(V34) 16800(V34)
14400(V34) 12000(V34) 9600(V34) 7200(V34) 4800(V34) 2400(V34)
- OR Nxt 19200(V32t) 16800(V32t) 14400(V32b) 12000(V32b) 9600(V32b) 7200(V32b) 4800(V32b)
- OR Nxt 2400(V22bis)
Leased-Line Rate. Determines the modem’s data rate and modulation scheme for operation on leased lines. In Async
mode, the DTE rate must equal the leased-line rate. Leased Line Rate sets the upper limit rate and modulation; lower
speed connections may still be possible and the modem can still be commanded to fall back by a remote modem.
What Leased Line Rate configuration options are displayed depends on the setting of Modulation.
33600(V34), 31200(V34), 28800(V34), 26400(V34), 24000(V34), 21600(V34), 19200(V34), 16800(V34), 14400(V34),
12000(V34), 9600(V34), 7200(V34), 4800(V34), 2400(V34) – The modem operates using V.34 modulation at the data
rate selected. The change does not take effect until the modem is reset.
19200(V.32t), 16800(V32t), 14400(V.32bis), 12000(V.32bis), 9600 (V.32bis), 7200(V.32bis), 4800(V.32bis) – The
modem operates using V.32
2400(V.22bis) – The modem operates using V.22bis modulation at 2400 bps.
NOTE: It is recommended that both modems use the same fixed data rate.
The factory default is 33600(V34).
A T command equivalent is S-register S44=
terbo
or V.32bis modulation at the data rate selected.
n.
terbo
, or V.22bis.
3-373821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 64

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-8
(2 of 2)
Leased Line Configuration Options
Autorate: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Autorate. The modems adapt to VF line condition and connect at the optimum rate during initial line establishment. Once
connected, the modem automatically lowers the line rate if line conditions become impaired. When line conditions
improve, the modem automatically shifts up to the highest data rate the line can support. This autorating only occurs
terbo
between 4800 bps and 19,200 bps during V.32bis and V.32
during V.34 connections.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S82=
Leased TX Level: 0
Nxt0–1–2–3–4–5–6–7–8–9–10–11–12–13 –14 –15
Leased Transmit Level. Selects the modem’s transmit power level over leased lines. The transmit output level can be
selected in 1 dBm decrements from 0 dBm to –15 dBm.
For V.34 operation over two-wire connections, do not set Leased TX Level to a value higher than –9 dBm.
The factory default is 0 dBm.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
A T command equivalent is S-register S45=
.
n
.
connections and between 2400 bps and 33,600 bps
CarrierOn Level: –43dbm
Nxt –43dbm –33dbm –26dbm
Carrier On Level. This configuration option controls the carrier detection threshold for leased lines. When the power level
of the receive carrier signal drops 2 dBm below this level (–26 dBm, –33 dBm, or –43 dBm), LSD turns Off. When the
carrier signal is greater than this level, LSD turns ON.
The factory default is –43dbm.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
n
A T command equivalent is S-register S48=
Asymmetric Rate: Enable
End Enable Disable
Asymmetric Rate. Controls rate symmetry when running V.34 modulation. (This configuration option does not appear
unless V.34 modulation is selected.)
Enable – The modem operates in asymmetric rate mode (the transmit and receive rates can be different) when running
V.34 modulation. Asymmetric Rate must be enabled in both modems.
Disable – The modem operates in symmetric rate mode (the transmit and receive rates are identical) when running
V.34 modulation. Either modem can force symmetric mode by disabling Asymmetric Rate.
The factory default is Enable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S14=
.
n
.
3-38 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 65

SDCP Menus
V.42/MNP/Buffer
option is set for synchronous operation (see DTE
Interface configuration options group), then the
V.42/MNP/Buffer configuration options determine the
type of error correction and flow control used by the
modems and attached DTEs.
Some choices within this group may not appear
depending upon how previous configuration options have
V.42/MNP/Buffer group does not appear on the LCD.
Any changes made to configuration options within this
group only take effect after a disconnect.
T able 3-9 shows each V.42/MNP/Buffer configuration
option as it appears on the LCD.
been selected. If the Async/Sync Mode configuration
Table 3-9
(1 of 5)
V.42/MNP/Buffer Configuration Options
Err Contrl Mode: V42/MNPorBfr
Nxt V42/MNPorBfr V42/MNPorDsc MNP_or_Buffr MNP_or_Disc BufferMode DirectMode
LAPM_or_Disc LAPM_or_Buffr
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Determines the type of error control used by the modem. In most cases, V42/MNPorBfr is the best choice. If V.42bis and
MNP are enabled, then the modem uses the following priority for error control negotiation: V.42, MNP 5 and below, and
Buffer Mode. Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
V.42/MNP or Buffer – Modem attempts to connect in V.42 Error Control mode. If this fails, the modem attempts to
connect in MNP mode. If this fails, the modem connects in Buffer mode and continues operation. This is also known as
V42/MNP Autoreliable Mode.
V.42/MNP or Disconnect – Modem attempts to connect in V.42 Error Control mode. If this fails, the modem attempts to
connect in MNP mode. If this fails, the modem disconnects. This is also known as Reliable mode.
MNP or Buffer – Modem attempts to connect in MNP mode. If this fails, the modem connects in Buffer mode. This is also
known as MNP Autoreliable Mode.
MNP or Disconnect – Modem attempts to connect in MNP mode. If this fails, the modem disconnects. This is also
known as Reliable mode.
Buffer Mode – Modem does not use error control and allows the DTE rate to differ from the communications line rate.
This mode should only be used if the DTE provides its own error control or if errors in data can be tolerated. This setting
is also known as Normal mode and is valid even if the remote modem is set for Direct mode.
Direct Mode – Modem connects at a data rate equal to or less than the initial DTE interface rate. (The modem never
connects at a data rate greater than the initial DTE rate.) If the modem connects at a data rate lower than the DTE rate,
the DTE must then adjust its data rate to equal the modem rate. Ultimately , the modem speed and DTE speed must be
the same. Direct mode does not support error control or data buffering.
LAPM or Disconnect – Modem attempts to connect in V.42 Link Access Procedure for Modems (LAPM) error control
mode. If this fails, the modem disconnects. This setting should be used for cellular connections (at both the mobile and
PSTN sides) when it is known that both sides support V.42.
LAPM or Buffer – Modem attempts to connect in V.42 LAPM error control mode. If this fails, the modem connects in
Buffer mode and continues operation.
NOTE: The modem must be reconfigured for Direct mode before changing the leased-line modulation if V.42 error
For Async Dial and UNIX Dial, V42/MNPorBfr is the factory default.
For Sync Dial and Sync Leased, DirectMode is the factory default.
A T command equivalent is \N
control or Buffer mode are enabled with V.32bis on leased lines.
n
.
3-393821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 66

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-9
(2 of 5)
V.42/MNP/Buffer Configuration Options
V42bis Compress: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async and the Error Control Mode
configuration option is set for V42/MNPorBfr or V42/MNPorDsc.
V.42bis Compression. Enables or disables V.42bis data compression.
Enable – Data compression operates in both the transmit and receive directions. This is the recommended setting for all
applications.
Disable – V.42bis data compression is disabled. This is rarely needed because V.42bis data compression does not
cause data expansion for compressed data.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is ″H
MNP5 Compress: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async and the Error Control Mode
configuration option is set for V42/MNPorBfr, V42/MNPorDsc, MNP or Buffr, or MNP or Disc.
.
MNP5 Compression. Determines if the modem uses MNP Class 5 data compression. It can be set independently of
V.42bis data compression. Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
The factory default is Enable.
n
A T command equivalent is %C
EC Negotiat Bfr: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable Disab&Switch
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Error Control Negotiate Buffer . Determines if the answering modem buffers the data that it received from the remote
modem during an interval in which the modem attempts to establish a connection using error control. Online changes do
not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
Disable – Data is not buffered during the link negotiating (handshaking) sequence.
Enable – Data is buffered while the link is being established. Initialization data is not passed on to the DTE during the
handshaking sequence.
Disable and Switch – Data is not buffered during the handshaking sequence. However , when the modem receives an
error control fallback character, it switches to Buf fer mode. (See EC Fallbck Char configuration option.)
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is \C
EC Fallbck Char: 013
Nxt 013 ASCI
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async and EC Negotiate Buffer is
configured for Disab&Switch.
Error Control Fallback Character. This configuration option allows you to enter the ASCII value of the error control
fallback character. This provides the remote modem with the ability to end the error control link negotiating (handshaking)
sequence by sending this character. The modems will connect in Buf fer mode (no error control). Online changes do not
take effect until a disconnect occurs.
When the modem receives this fallback character it switches to Buffer mode and transmits an EC fallback character to
the DTE. When comparing incoming characters for a match against the EC fallback character, the modem ignores parity.
The factory default is 013.
A T command equivalent is %A
.
n
.
n
.
3-40 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 67

SDCP Menus
Table 3-9
(3 of 5)
V.42/MNP/Buffer Configuration Options
Flw Cntl of DTE: CTS_to_DTE
Nxt CTS_to_DTE Disable XON/XOFF
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Flow Control of DTE. Determines how the modem controls the flow of data from the DTE.
CTS to DTE – Method of flow control in which the modem raises and lowers its CTS interface lead to indicate when the
DTE should start and stop sending data.
Disable – The modem cannot control the flow of data from the DTE.
XON/XOFF – Method of flow control in which the modem sends XON and XOFF characters to the DTE to start and stop
the flow of data.
The factory default is CTS to DTE.
n
A T command equivalent is \Q
Flw Cntl of Mdm: Disable
Nxt Disable XON/XOFF RTS_to_Mdm
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
.
Flow Control of Modem. Determines how the DTE controls the flow of data from the modem.
Disable – The DTE cannot control the flow of data from the modem.
XON/XOFF – Method of flow control in which the modem starts and stops data flow based upon XON and XOFF
characters received from the DTE.
RTS to Modem – Method of flow control in which the modem respectively starts and stops data transmission based
upon the ON and Off state of the DTE’s RTS signal.
The factory default is Disable.
n
A T command equivalent is \Q
XON/XOFF Psthru: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async and the Flow Control
configuration option is configured for XON/XOFF.
XON/XOFF Passthrough. Considers an XON/XOFF character as data and passes it on to the remote modem. In this
case, the DTE at one end of the communications link can send flow control characters to the other DTE. This is also
known as DTE to DTE flow control.
Disable – Flow control characters are processed but are not passed on to the remote modem.
Enable – Flow control characters are processed and passed on to the remote modem.
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is \X
.
n
.
3-413821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 68

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-9
(4 of 5)
V.42/MNP/Buffer Configuration Options
Mdm/Mdm FlowCtl: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async and the Flow Control
configuration option is configured for XON/XOFF.
Modem-to-Modem Flow Control. If a modem’s buffers begin to fill due to data it is receiving from the remote modem, but
is not passing on to the DTE, it can issue XON/XOFF flow control characters to the remote modem. This only applies if
Buffer (nonerror control) mode is selected. If Error Control mode is enabled, flow control between the modems will
happen automatically, regardless of the setting of this configuration option.
Disable – Modem does not respond to XON and XOFF characters received over the VF line. Also, the modem will not
transmit an XOFF character to the remote end if its receive buffers are full.
Enable – Modem stops transmitting data to the remote modem if it receives an XOFF character over the VF line. An
XON character will enable data transmission. Also, the modem will transmit an XOFF character to the remote end if its
receive buffers are full. Select this setting if the DTE rate is less than the VF line rate or if the DTE must frequently stop
the flow of data to process it.
The factory default is Disable.
n
A T command equivalent is \G
.
Break Buffr Ctl: Keep_Data
Nxt Keep_Data Discard_Data Discard_Brk
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Break Buffer Control. Determines if data stored in the modem’s buffer is saved or discarded when the DTE issues a
break sequence.
Keep Data (Nondestructive mode) – Saves the data in the buffer in both the local and remote modems.
Discard Data (Destructive mode) – Empties the data buffer . Only buf fers in the same direction of travel as the break are
discarded.
Discard Break – A break received from the DTE is ignored by the modem and not sent across the link.
The factory default is Keep Data.
NOTE: This configuration option is ignored if the Break Forces Escape configuration option (see DTE Dialer
A T command equivalent is \K
Send Break Cntl: Data_First
Nxt Data_First Break_First
This configuration option only appears if Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async.
Send Break Control. Determines what is sent from the modem first, data or break if a break sequence is sent from the
DTE.
Data First (Nonexpedited) – A break is treated as a data character and is sent in the order it was received. This is also
known as Nonexpedited mode.
Break First (Expedited) – A break is sent before the data currently in the buffer . This is also known as Expedited mode.
The factory default is Data_First.
NOTE: This configuration option is ignored if the Break Forces Escape configuration option (see DTE Dialer
A T command equivalent is \K
configuration options group) is enabled.
n
.
configuration options group) is enabled.
n
.
3-42 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 69

SDCP Menus
Table 3-9
(5 of 5)
V.42/MNP/Buffer Configuration Options
TXBuffDiscDelay: 10sec
Nxt 10sec Disable 60sec
This configuration option only appears when Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async, and Error Control
not
Mode is
Transmit Buffer Disconnect Delay. Determines how long the modem continues to transmit data stored in its Transmit
buffer when the modem is commanded to disconnect by a locally attached DTE.
Disable – Modem disconnects immediately without attempting to send data stored in its buffer.
10, 60 sec – Maximum amount of time the modem tries to empty its buffer before disconnecting. In both cases (10 sec
and 60 sec), the modem disconnects much sooner if it can empty its buffer.
The factory default is 10sec.
The A T command for TXBuffDiscDelay is S49=n.
RXBuffDiscDelay: Disable
Nxt Disable 10sec 60sec
This configuration option only appears when Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async, and Error Control Mode
not
is
Receive Buffer Disconnect Delay. Determines how long the modem continues to send to the DTE data stored in its
Receive buffer when the modem is commanded to disconnect by a locally attached DTE, or detects a line disconnect.
Disable – Modem disconnects immediately without attempting to send data stored in its buffer.
10, 60 sec – Maximum amount of time the modem tries to empty its buffer before disconnecting. In both cases (10 sec
and 60 sec), the modem disconnects much sooner if it can empty its buffer.
The factory default is Disable.
The A T command for RXBuffDiscDelay is S39=n.
Max Frame Size: 256
Nxt 256 192 128 64 32 16
This configuration option only appears when Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async, and Error Control Mode
not
is
Maximum Frame Size. Sets the maximum frame size for V.42 and MNP. For MNP operation, 64 is the minimum value.
Any value less than that will automatically default to 64. For cellular applications, at least one of the sides should be set
to a low value. A setting of 32 is recommended. Only one modem needs this setting; both modems will automatically
default to the greatest common value.
The factory default is 256.
The A T Command for Max Frame Size is \An.
CellularEnhance: Disable
End Disable Enable
This configuration option only appears when:
configured for DirectMode.
configured for DirectMode.
configured for BufferMode or DirectMode.
• ETC is installed
• Async/Sync Mode is configured for Async
• Error Control Mode is configured for V42/MNPorBfr, V42MNPorDsc, LAPM_or_Disc, or LAPM_or Bfr
Cellular Enhancement. When enabled, the modem uses non-standard techniques to enhance V.42 operation for cellular
applications. It is still compatible, however, with modems which do not have the cellular enhancement implemented or
enabled.
The factory default is Disable.
The A T command for CellularEnhance is S91=
n
.
3-433821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 70

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Test
T able 3-10 shows each Test configuration option as it
appears on the LCD.
The Test configuration options determine specifics,
such as the duration of a test, for the various diagnostic
tests available to the modem.
Table 3-10
Test Configuration Options
Test Timeout: Disable
Nxt Disable 30sec 60sec 240sec
Test Time-out. Determines how long a test runs before aborting.
Disable – Allows a test to run indefinitely .
30, 60, or 240 seconds – Allows the test to run for 30 seconds, 60 seconds, or 240 seconds.
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is S-register S18=n.
Rcv Remote Loop: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Receive Remote Loopback Response. Determines if the modem responds to a request for a remote loopback issued
from a remote modem.
The factory default is Enable.
A T command equivalents are &T4 (Enable) and &T5 (Disable).
3-44 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 71

SDCP Menus
Misc
T able 3-11 shows each Misc (Miscellaneous)
configuration option as it appears on the LCD.
The Miscellaneous configuration options determine
specifics for various functions, including network
management parameters and remote modem access.
Table 3-11
(1 of 2)
Miscellaneous Configuration Options
StrapsWhenDisc: No_Change
Nxt No_Change Reload RelodNoATChg
Straps When Disconnected. Determines whether or not configuration options in the Active (Saved) configuration area are
reloaded to Active (Operating) when a disconnect occurs. This is useful in modem pooling applications.
No Change – Configuration options do not change upon disconnect.
Reload – The Active (Operating) configuration area, which controls modem operation, is reloaded from the Active
(Saved) configuration area when a disconnect occurs. This is useful in modem pooling applications where it is desirable
to start the modem from a known condition after every call. This allows multiple users to issue A T commands to change
the modem’s operation for their particular call.
Reload, No AT Change – This has the same effect as Reload, except that it becomes impossible to change this
configuration option with an A T command, and the command buffer is cleared so that /A (Repeat Last Command) has no
effect.
NOTE: If Reload or RelodNoATChg is selected, the following AT commands are disabled although the OK result code
Factory default templates do not affect the setting of StrapsWhenDisc.
A T command equivalent is S88=
appears when these commands are issued:
n
. Loads a factory default template into Active(Operating)
A T&F
n
A T&W
A T&Zn=
. Writes Active(Operating) to Active(Saved) or Customer 1 or Customer 2.
x.
Store directory numbers
n
.
Access frm Remt: Enable
Nxt Enable Disable
Access from Remote. Determines if your modem’s SDCP can be accessed by a remote modem via the VF line.
If this configuration option is disabled, the modem cannot be accessed by another modem, and the Clone to Remote
feature is not available.
Enable – Allows access from a remote modem.
Disable – Does not allow access from a remote modem.
The factory default templates do not affect Access from Remote.
Plus
n
.
modem.
n
, S57=n, S58=n, and S59=n.
NOTE: The remote modem must be a 3800
A T command equivalent is S-register S55=
RemAccssPasswrd: 00000000
Nxt 00000000
Remote Access Password. Allows the entry of a password for establishing control of a remote modem from the SDCP of
a local modem. The same password must be used in both the local and remote modem.
NOTE: If the Access from Remote configuration option is set to Disable, the password has no effect.
A T command equivalent is the combination of S-registers S56=
3-453821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 72

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 3-11
(2 of 2)
Miscellaneous Configuration Options
NetMngmtAddress: 256
Nxt 256
Network Management Address. Determines the address used when accessing a locally attached modem from the
6700 Series NMS. This configuration option is ignored by remote modems.
Address values range from 001 to 256.
The factory default templates do not affect Network Management Address.
A T command equivalent is S-register S75=n.
NMS_Call_Msgs: CallCnct&Prg
Nxt CallCnct&Prg Disable CallCnctOnly CallProgOnly
NMS Call Messages. Determines if modem status and/or call summary information is sent to the 6700 Series NMS. The
modem can itemize status, such as CallProgress messages, or it can report a summary of activity, such as Call Connect
messages, to the NMS.
Call Connect & Progress – Enables both Call Connect and Call Progress information to be reported to the NMS.
Disable – Modem status and call summary information is not sent to the NMS.
Call Connect Only – The modem accumulates call statistics over a period of time and then reports these statistics to the
NMS. The NMS uses this data to produce utilization reports.
Call Progress Only – The modem reports detailed modem status information to the NMS. These messages include any
events that can display on the LCD.
The factory default templates do not affect NMS Call Messages.
n
A T command equivalent is S66=
.
NMS DTR Alarm: Disable
Nxt Disable Enable
NMS DTR Alarm. Determines whether an NMS DTE alarm report is generated when DTR is Off.
Disable – The state of DTR does not cause an alarm condition to be reported.
Enable – A DTE alarm condition is reported to the NMS controller in the Device Health & Status message if DTR is Off
for more than 10 seconds. The alarm condition is reported as inactive after DTR is ON for 3 seconds.
The factory default templates do not affect NMS DTR Alarm.
n
A T command equivalent is S77=
NetworkPosition: Tributary
Nxt Tributary Control
Network Position Identification. Each modem must be identified either as a control modem or a tributary modem.
NOTE: This configuration option is only applicable for leased-line network management applications.
The factory default is Tributary.
A T command equivalent is S74=n.
CellulrRJ11Adpt: Disable
End Disable Enable
This configuration option appears only if ETC is installed.
Cellular RJ1 1 Adapt. Allows the modem to support an RJ11 connection to a 3-watt phone. It also causes the modem to
transmit the ETC 1.1 Calling Tone during call origination.
Disable – No RJ11 support or ETC 1.1 Calling Tone.
Enable – For use when the Cellular(Mobile) factory template is loaded, enables RJ1 1 support and ETC 1.1 Calling Tone.
The factory default is Disable.
A T command equivalent is S93=
.
n
.
3-46 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 73

SDCP Menus
Security Configuration Options
The Security configuration options group is described
in Chapter 7, Security.
Control Branch
The Control branch of the T op-Level menu allows
you to manage hardware and software functions, such as
speaker volume, reset, busy out, and firmware download.
The 3821Plus modem has the additional hardware
function, Service Line.
T o access Control from the Top-Level menu, press the
key until Control appears. Select Control.
(Modem Status)
MDMA mdmb mdmc
Status
Call_Setup
Test
Control
Reset
Make_Busy
or
RemoveMakeBusy
Service_Line
DiscServLine
Reset
Reset causes the modem to stop operation and
perform a complete program restart. The modem begins
the power-up test sequence that ends with the Top-Level
menu displayed on the LCD. Configuration options
stored in an Active (Saved) configuration area are copied
to the Active (Operating) configuration area.
or
Remote
Download
SecurityConfigure
Code
495-14846
Make Busy or Remove Make Busy
The Make Busy function is available only on 3821-B1
models.
The Make Busy function forces the modem off-hook
so it cannot answer a call. This is often used with PBX
systems to permit the busy out of a PBX port for rotary
or hunt groups.
WARNING
To not violate FCC and DOC
regulations, this function must
only be used behind a user’s
PBX.
Service Line or Disconnect Service Line
The Service Line function is available only on
3821-B1 models.
The Service Line function allows you to switch a
specific 3821Plus modem installed in a COMSPHERE
3000 Series Carrier from normal dial operation to
service-line operation. This switch only places the
modem on the service line. For a connection to be
established, you must still use the normal dialing
methods as described earlier in this chapter under Call
Setup Branch (page 3-9).
A service line is an extra dial line connected to a
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier. This line is normally
shared by up to eight 3821Plus cards (24 modems)
installed in either Slots 1–8 or Slots 9–16. However, by
daisy chaining the service-line connector of one Network
Interface Module (NIM) to the service line of another
NIM installed in the same carrier, you can permit all
16 cards (48 modems) to share one service line. The
service line can also be extended to other carriers in a
cabinet. Only one modem may be switched to the service
line at a time. For more information regarding daisy
chaining of modems to the service line, refer to the
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier, Installation Manual.
3-473821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 74

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Download Code
The Download Code function allows firmware to be
loaded into a modem from another modem or from a
DTE.
There are two selections under Download Code:
Clone to Remote and T o Local via DTE. Clone to
Remote is used to transfer an exact copy of the firmware
currently stored in a 3821Plus modem to another
3821Plus modem. For this to occur, the modem must be
connected to the remote modem via a leased-line
network or an established dial-line network. If these
prerequisites do not exist, then this selection does not
appear on the LCD.
The second selection appearing on the LCD is T o
Local via DTE. This function permits firmware upgrades
to be transferred to a 3821Plus modem. This type of
download requires a locally attached PC-controller to be
connected to the modem’s DTE port as well as special
download software. Any downloads using this selection
are intended to be performed by service personnel
only.
Clone To Remote
This function allows you to transfer an exact copy of
the local modem’s firmware to a remote modem. Before
using Clone to Remote, perform the following:
• Make sure the modems have an established dial
network connection using V.34, V.32 terbo ,
V.32bis, or V .32 modulation or a leased-line
connection using either V.34, V.32 terbo , V.32bis,
or V.32 modulation.
However, to continue with the transfer, press the
key to display the Reprogram Remote selection.
WARNING
Pressing any function key now
begins the transfer to the
remote modem. This process
takes the communications link
out of service for
several minutes depending
upon the data rate of the link
(28,800 bps = 5 minutes). If the
Clone to Remote process is
interrupted, the remote modem
is left in a partially programmed
state in which its functional
capabilities are limited to those
required to initiate and
complete another download
attempt. If you cannot complete
a download, call your service
representative.
Press any function key (F1, F2, or F3) to begin the
transfer.
The local modem’s LCD displays Establish Remote,
indicating the modem is attempting to establish a
Remote Cloning Download session with the remote
modem.
If unsuccessful, the modem remains in the Download
Transfer mode. The LCD’s top line displays RemClone
Failed.
• Make sure the remote modem’s Access From
Remote configuration option is enabled.
• Make sure the password (Remote Access Password
configuration option) is the same in both the local
and remote modems. (For an example of how to
change the password, refer to Editing and Saving a
Configuration Option, page 3-16.)
T o access Download Code from the Control branch,
make the following selections:
Press the
key until Download Code appears. Press
any function key to select Download Code.
Press any function key to select Clone to Remote.
Correct the problem and attempt another download
from the local modem. If this fails, contact your service
representative.
As data banks are transferred, the local and remote
LCD’s bottom line displays the status of the download
process, and the number of records sent versus the total
number of records for that bank.
If the download is successful, the local modem
displays Remote Clone OK and the remote modem
displays Frmware Upgrade. If the download took place
over the dial network, the modems disconnect when the
download is complete.
To Local via DTE
At this point, if you do not want to continue this
process, abort the transfer by selecting any function key.
This returns the modem to the T op-Level menu.
3-48 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
This function is for use only by service personnel to
transfer new firmware to 3821Plus modems.
Page 75

SDCP Menus
Automatic Firmware
Download
New releases may be available for the 3821Plus
modem. The latest 3821Plus firmware is avaiable at no
charge from the Automatic Firmware Download Center.
Refer to page A in the front of this document for contact
information.
T o download the firmware, your modem must be
configured for dialing. Save your modem’s current
configuration to the Customer 1 or Customer 2 memory
area, and load the Async Dial factory template. (See
Configure Branch, page 3-15, for information about
saving and changing configuration options.)
Using your 3821Plus modem, dial the Automatic
Firmware Download Center at 1-727-530-7026. You may
use any dialing technique (SDCP Dial, AT command, or
V.25bis Call Request).
If you have a DTE (a terminal or PC) attached to your
modem, informational messages are displayed on it
when the modem is connected. These show the amount
of time the download will take.
However, a DTE is not required. The download
begins without any operator action. When the download
begins, the SDCP displays download status messages
with the data bank number, current block being loaded,
and the total number of blocks. There are two data
banks.
Download Failure
If the download is interrupted, the modem is left in a
state in which it can only be used to make or receive a
call for a download.
If an interruption occurs and your modem is left in
this state, repeat the download process by directing the
modem to dial the Automatic Firmware Download
Center. (See Call Setup Branch, for information about
dialing a number using the SDCP.) If you are unable to
complete the download, your service representative for
assistance.
Remote Branch
The Remote branch is described in Chapter 6,
Remote Access.
Security Branch
The Security branch is described in Chapter 7,
Security.
If the modem connects at 14,400 bps, the download
takes about 10 minutes. When the download is complete,
the modem resets itself and displays a normal status
message (such as Idle:33.6).
Reload your configuration options from the
Customer 1 or Customer 2 memory area that you saved
them to.
3-493821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 76

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
This page intentionally left
blank.
3-50 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 77

AT Commands and S-Registers
Overview 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Modes 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switching Between Data Mode and Online Command Mode 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Escape Sequence and Escape Guard Time 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Command Guidelines 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AT Command List 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
S-Register List 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Recovering AT Commands 4-26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Initialization Strings 4-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
V.25bis Applications 4-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Synchronous Leased-Line Applications 4-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AT&T Exclusive Dialing for DATAKIT Applications 4-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
Overview
This chapter discusses guidelines necessary to operate
AT commands as well as listing all AT commands
supported by the 3821Plus modem. AT commands are
issued from asynchronous DTEs.
Operating Modes
The 3821Plus modem has two operating modes:
Command mode and Data mode. Before a modem goes
online (establishes a successful connection with a remote
modem), it is considered to be in Command mode, an idle
state where you can modify its operating parameters or
issue modem commands. (Any command issued is
acknowledged with a response in either words or digits
known as result codes. Refer to T able B-1 in Appendix B
for a listing of result codes.)
Once the modems are online, either by answering or
originating a call, they automatically switch to Data mode.
Data mode is a state where any entries made from the
DTE are considered data and are transmitted and received
between modems. The modems remain in Data mode until
the connection is broken or until they are forced into
online Command mode using the escape sequence (+ + +).
Switching Between Data Mode
and Online Command Mode
Sometimes it is necessary to change operating
parameters while the modems are online. The Escape
Sequence allows you to toggle the modem between Data
mode and online Command mode while maintaining a
connection with the remote modem. This is accomplished
using the escape sequence (+ + +) to exit Data mode and
the O command to return to Data mode.
Escape Sequence and Escape Guard Time
The escape sequence is only issued when the modem is
online and in Data mode. The 3821Plus modem uses three
consecutive plus (+) characters as the escape sequence.
(To change this value, refer to S-register S2 discussed
later in T able 4-2 in S-Register List.)
T o prevent the modem from interpreting an embedded
+ + + in data as an escape sequence, the Escape Guard
Time value determines the idle time required before and
after the escape sequence is issued. The 3821Plus uses a
1-second pause as the Escape Guard Time. (To change
this value, refer to S-register S12 discussed later in
T able 4-2 in S-Register List.)
4-13821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 78

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
T o enter online Command mode while in Data mode,
enter the following sequence:
TYPE: +++
Use the O command to return to Data mode from
online Command mode. Enter the following command:
TYPE: ATO
PRESS: Enter
Command Guidelines
Review the following guidelines before using any
AT Commands.
• The escape sequence (+ + +) is used to enter online
Command mode from Data mode.
• The asynchronous character format for the
AT command set must be one of the following:
— 8 data bits + no parity + 1 stop bit.
— 7 data bits + no parity + 2 stop bits.
— 7 data bits + parity + 1 stop bit (parity can be
odd, even, mark, or space).
• All commands except A/ (repeat last command) and
the escape sequence (+ + +) must begin with the
characters AT and end by pressing the Enter key.
The AT (or at) prefix clears the command buffer
and matches the modem speed and parity to that of
the DTE. Commands can be upper- or lowercase,
but the modem will not recognize mixed case
prefixes (At or aT).
• Commands can be entered one at a time or in
strings. Strings can have up to 40 characters after
the AT prefix. You can use spaces, hyphens (-), and
parentheses ( ) as fillers to make the commands
easier to read; the modem ignores these fillers and
they are not counted among the characters which
make up the command string. Commands must be
entered on one line and end with the carriage return
character (Enter key).
• Commands shown with the suffix n have several
options associated with them. For example, in the
Ln command, L1 sets the speaker volume to Low
and L3 sets the speaker volume to High. Omitting
the suffix has the same effect as using a zero suffix;
for example, ATX is equivalent to ATX0.
• The A/ command (without pressing the Enter key)
causes the modem to repeat the last command
entered.
• Valid commands are acknowledged with numeric or
word result codes (unless the result codes have
been disabled using the Q1 command).
Appendix B lists all available result codes with
numeric and word equivalents.
AT Command List
AT commands are issued from an asynchronous DTE,
such as a PC, and control the modem’s operation and
software configuration. AT commands are only applicable
when the DTE Dialer T ype configuration option is set for
AT . (See &Mn and &Qn commands.)
AT commands are entered while the modem is in
Command mode and use the following format:
TYPE: ATXn
Where: X is the AT command and n is the specific
value for that command.
PRESS: Enter
T able 4-1 lists all AT commands supported by the
3821Plus modem. The Async Dial factory default is listed
in bold.
Reference to particular country codes in this guide is
not an assurance that the modem has been approved for
use in that country. Consult your sales representative.
Not all commands are valid in all countries. See
Appendix H.
4-2 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 79

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(1 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
*** – AT Command Recovery Mode
Allows the modem to remain in Asynchronous data mode so that A T commands can be used to change the modem’s
current configuration. Use this command when A T commands are disabled or the modem is operating in Synchronous
data mode.
This command can only be executed after the completion of a power-up self-test. Refer to
later in this chapter for procedures and guidelines on this command.
A/ – Repeat Last Command
Reexecutes the last command string. (Not to be preceded with A T or followed by pressing the Enter key.)
A – Answer Mode
Allows the modem to go off-hook and attempts to establish a connection without waiting for a ring.
B – ITU-T/Bell Mode
Determines the protocol used if the dial-line rate is set to 300 or 1200 bps. It has no effect if the rate is set to another
value. (See %B.)
B, B0 V.21 or V.22 (300 or 1200 bps)
B1 Bell 103 or Bell 212A (300 or 1200 bps)
Dn – Dial
Begins the dialing sequence. The dial string n (modifiers and telephone number) is entered after the D command.
Any digit 0–9, * , # , A, B, C, D, may be dialed as a DTMF tone. Only the digits 0–9 can be dialed in Pulse Dial mode.
The following example shows how to dial through a PBX. The dial string consists of the command string and the
telephone number:
Recovering AT Commands
ATDT9,5551234
Command Telephone
String Number
Dial String
Modifiers include the following parameters:
T – Tone (DTMF) dial. Any digit 0–9, * , # , A, B, C, or D can be dialed as tone.
P – Pulse dial. Only the digits 0–9 can be dialed in Pulse Dial mode.
NOTE: Once a dialing method (tone or pulse) has been specified, it will remain active only until the end of that dial string.
The factory setting is Tone dial.
, – Pause. Causes the modem to pause before processing the next character in the dial string. The length of this pause is
determined by the value held in S-register S8, the Pause Time configuration option.
W – Wait for dial tone. Modem waits for a second dial tone before processing the dial string. This can be the initial dial
tone or a second tone received when dialing through a tandem PBX (for example, 9W555-6789), or when invoking
special features (for example, 70#W555-6789, where 70# is the local telephone company command that disables Call
Waiting).
4-33821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 80

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(2 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
Dn, continued
R – Reverse Dial mode. Causes the originating modem to send out an answertone once it no longer detects ringback.
(Ringback is the ring you hear at the originating site when making a call.) The R parameter must be the last character in
the dial string. For correct operation, at least one ringback must be detected; therefore, the remote modem should be
configured to answer on the second ring or subsequent rings.
@ – Quiet answer. Wait for five seconds of silence after dialing the number. If the silence is not detected, the modem
sends a NO ANSWER result to the DTE.
! – Hook flash. This causes the modem to go on-hook for 0.5 seconds, then return to off-hook.
; – Return to Command mode. Modem returns to Command mode after dialing a number without disconnecting the call.
This is useful when the number exceeds 40 characters, or when the wait time between parts of a dial string is unknown.
Space, – , and ( ). These characters are ignored by the dial string and can be included in the dial string to enhance
readability.
DS=n – Dial Stored Number
Dials the number stored in Location n (1–10). (To store a telephone number, refer to the
&Zn=x
command.)
En – Command Character Echo
Controls whether or not characters are echoed back to the DTE when the modem is in Command mode.
E, E0 Disables echo to the DTE.
E1 Enables echo to the DTE.
Hn – Hook Switch Control
Allows the modem to go off-hook or on-hook.
H, H0 Modem goes on-hook.
H1 Modem goes off-hook.
In – Identity
Provides useful information when upgrading or servicing the product.
I, I0 Displays product code (default is 144).
I1 Displays 3-digit firmware revision number.
I2 Performs an EPROM check.
I3 Displays serial number.
I4 Displays model number.
I5 Displays hardware part number.
I6 Displays software part number.
I7 Displays the country code.
I9 Displays 3-digit firmware revision number (same as I1).
I10 Allows you to change the value displayed by I0:
I10=0 causes I0 to display 144 (default).
I10=1 causes I0 to display 240.
I10=2 causes I0 to display 480.
I10=3 causes I0 to display 960.
I10=4 causes I0 to display 120.
I11 Displays the program memory checksum.
I17 Displays the last eight critical errors; the first is the most recent. (Service personnel use only.)
I19 Displays the entire firmware revision number.
O – Return to Online or Data Mode
Returns modem to Data mode from Online Command mode.
4-4 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 81

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(3 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
P – Pulse Dial
Sets the modem for Pulse Dial mode. See D command.
Qn – Result Codes
Result codes are informational messages (such as Connect and Ring) sent from the modem and displayed on the
asynchronous DTE terminal. Refer to Table B-1 for a list of result codes.
Q, Q0 Enables modem to send result codes to the DTE.
Q1 Disables modem from sending result codes to the DTE.
Q2 Enables in Originate mode only for modem to send result codes to the DTE. Required for most
Sn=r – Change S-Register
Changes the contents of an S-register, where n is the S-register, and r is the new value.
Sn? – Display S-Register
Displays the value of an S-register, where n is the S-register number.
T – T one Dial
Sets the modem for Tone (DTMF) dial mode. See D command.
UNIX applications.
Vn – Result Codes Format
Controls whether or not result codes appear as words or as numeric codes. Some DTEs do not recognize result codes as
words; therefore, numbers are required. The Numbers (2) format is required for some modem pooling applications. Refer
to Table B-1 for a list of result codes.
V, V0 Displays result codes in Number (1) format (digits).
V1 Displays result codes as text.
V2 Displays result codes in Number (2) format (digits).
4-53821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 82

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(4 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
Xn– Extended Result Codes,Dial Tone Detect,and Busy Tone Detect
n
command sets three configuration options simultaneously:
The X
Extended Dial Tone Busy Tone
Result Codes Detect Detect
X0 Disable Disable Disable
X1 Enable Disable Disable
X2 Enable Enable Disable
X3 Enable Disable Enable
X4 Enable Enable Enable
X5 Add/EC Enable Enable
X6 Add/V42,MNP Enable Enable
X7 Use DTE Rate Enable Enable
EXTENDED RESULT CODES
Informational messages such as VF (line) connect rate and Error Control are displayed with the result codes.
Disable. Displays basic result codes: OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, and ERROR.
Enable. Displays basic result codes in addition to the CONNECT rate message (for example, CONNECT 14400).
Add/EC. If error control is negotiated, attaches the /EC suffix to the CONNECT rate message.
Add/V42,MNP. Attaches the V42b, V42, MNP5, MNP4, MNP3, MNP2, or NoEC suffixes to the CONNECT rate message.
Use DTE Rate. Displays DTE data rate instead of line CONNECT rate message.
DIAL TONE DETECT
Sets the modem for dial tone detection (enable) or blind dialing (disable).
Disable. Sets the modem for blind dialing.
Enable. Sets the modem for dial tone detect.
BUSY TONE DETECT
Sets the modem to monitor for Busy Tone (Enable) or ignore Busy Tone (Disable).
Disable. Modem ignores busy tone.
Enable. Modem monitors for busy tone.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
Yn – Long Space Disconnect
Determines the modem’s response to a continuous spacing condition sent from the remote modem when it goes on-hook.
Issuing a long space is one method of disconnecting a call.
Y, Y0 Disable. Ignores long space.
Y1 Enable. Disconnects if long space is detected. Enables transmission of a long space.
Zn – Reset and Load Active
Z, Z0 Loads configuration options from Active (Saved) to Active (Operating).
Z1 Loads configuration options from Customer 1 to Active (Operating).
Z2 Loads configuration from Customer 2 to Active (Operating).
Z3 Loads configuration options from Active (Saved) to Active (Operating) and performs a reset.
Z9 Performs a full modem reset as if the modem were powered Off and ON.
4-6 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 83

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(5 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
″F – Clear Error Buffer
Clears the buffer where information about the last critical error is stored. For service personnel use only.
″F Clear error buffer.
″Hn – V.42bis Compression
Enables or disables V.42bis data compression.
″H, ″H0 Disable.
″H1 Transmit only.
″H2 Receive only.
″H3 Enable for transmit and receive.
&&P1 – Clone Remote
Copies the firmware from the modem that receives the command to another 3821
Online Command mode. (Online Command mode is established with the +++ escape sequence.) The initial response to
the command is the message Cloning Remote, or one of several error messages, such as:
NO CIRCUIT
INCOMPATIBLE MODULATION
REMOTE ACCESS DISABLED
INVALID REMOTE PASSWORD
Plus
modem. The modem must be in
If the cloning is successful, the messages Clone Completed and OK are sent to the DTE. If the cloning fails, the ERROR
result code is preceded by an explanatory message:
Clone Aborted
Clone Failed: COMM
Clone Failed: SEQ
Clone Failed: Incompat. Config.
In the event of an error, the remote modem is placed in download-only mode, signaled by the slow flash of its MR/Pwr
LED. Contact your service representative if you are unable to complete the cloning.
&Cn – LSD Control
Line Signal Detect (LSD) is a signal indicating that the carrier signal is being received from the remote modem. It is
normally turned Off to the DTE when the power level of the received carrier signal drops below the carrier detect
threshold.
&C0 Forced On. LSD ON at all times.
&C1 Standard RS232. LSD is ON when the remote modem’s carrier signal is detected. LSD is Off when
carrier signal is not detected.
&C2 Wink When Disconnect. LSD normally forced ON, turns Off for approximately one second upon
disconnecting.
&C3 Follows DTR. State of LSD follows state of DTR.
&C4 Simulated Control Carrier. State of LSD follows state of remote modem’s RTS via V.13 simulated
control carrier signaling. Note that the remote modem’s RTS Action configuration option must be
set to Simulated Control Carrier.
&C5 DTR/Disconnect Off. State of LSD follows state of DTR except upon a disconnect where LSD
always turns Off. DTR must then toggle Off and ON to turn LSD ON. Use this setting for AT&T
DATAKIT applications. Note that to use this configuration option, the DTR Action configuration
option must be set to Stndrd_RS232 (&D1 or &D2).
4-73821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 84

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(6 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
&Dn – DTR Action
Data Terminal Ready (DTR) is a signal from the DTE to the modem indicating that the DTE is connected and ready for
operation.
&D0 Ignore. Modem ignores the true status of DTR and treats it as always ON.
&D1 Off=Command Mode. Modem enters online Command Mode if connected when DTR switches off.
&D2 Standard RS232. DTR Signal is controlled by the DTE.
&D3 Off=Reload Strap. Follows Standard RS232 operation, except that when DTR switches Off, the
modem loads the Active (Saved) area into the Active (Operating) area.
&D4 Controls On-Hook. Follows Standard RS232 operation, except that modem does not disconnect
until DTR is lowered by the DTE.
&D6 Off=Restrap to Async Dial. The factory default template Async Dial is loaded when DTR switches off.
&Fn – Select Factory Default Configuration Options
Loads factory configuration options into the Active (Operating) area. &F5 and &F6 are valid only for the North America
country code, and only if ETC is installed.
&F0 Async Dial
&F1 Sync Dial
&F2 Sync Leased (Answer Mode)
&F3 UNIX Dial
&F4 Sync Leased (Originate Mode)
&F5 Cellular (Mobile)
&F6 Cellular (PSTN)
&Gn – V.22bis Guard Tone
Determines whether the V.22bis guard tone is disabled, set to 550 Hz, or set to 1800 Hz.
&G0 Disable
&G1 550 Hz
&G2 1800 Hz
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
4-8 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 85

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(7 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
&In – Dial Transmit Level for Cellular Auto
When Dial Transmit Level Type is set to Permissive, &In sets Dial Transmit Level to a value between –10 and –32 dBm.
&I99 and &I100 cause the level to be varied automatically according to conditions for ETC operation. &J0 overrides this
command, and is the default for North America.
&I0 –0 dBm
D D
D D
&I7 –7 dBm
&I8 –8 dBm
&I9 –9 dBm
&I10 –10 dBm
&I1 1 –11 dBm
&I12 –12 dBm
&I13 –13 dBm
&I14 –14 dBm
&I15 –15 dBm
&I16 –16 dBm (Set by &F5)
D D
D D
&I32 –32 dBm
&I99 Valid only if ETC is installed. Automatically adjusted according to the ETC1.0 specification. Set by &F6. Use
only with remote modems set to &I99, and limit the data rate to 4800 bps (S41 = 5).
&I100 Valid only if ETC is installed. Automatically adjusted according to the ETC1.1 specification.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
&Jn – Dial Transmit Type
Sets the power output level of the transmit signal over dial lines. The &In command overrides the &Jn command.
&J0 Permissive (–9 dBm). Valid only for North America.
&Ln – Leased Mode
Sets the modem for 2-wire leased-line operation in Answer mode or in Originate mode.
&L0 Disables leased-line operation.
&L1 2-wire originate leased-line operation.
&L3 2-wire answer leased-line operation.
The &L command will cause the modem to reset before entering or exiting Leased-Line mode. Therefore, it must be
entered as the last command in an initialization string.
WARNING: Do not configure the modem for leased line operation if the modem is connected to the PSTN.
4-93821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 86

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(8 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
&Mn or &Qn – Async/Sync Mode and DTE Dialer Type
Sets the modem for either asynchronous or synchronous operation and selects the type of dialing method the modem
uses.
&M, &M0, &Q, &Q0
Modem operates in Asynchronous mode and uses A T Command protocol.
&M1, &M3, &Q1, &Q3
Modem operates in Synchronous mode and uses A T Command protocol.
&M2, &Q2
Modem operates in Synchronous mode and dials the telephone number stored in directory location 1
when the DTR signal turns Off and then ON.
&M231, &Q231
Modem operates in Asynchronous mode and disables any type of A T command dialing protocol.
&M232, &Q232
Modem operates in Asynchronous mode and uses V.25bis asynchronous dialing.
&M233, &Q233
Modem operates in Synchronous mode and uses V.25bis bisynchronous dialing.
&M234, &Q234
Modem operates in Synchronous mode and uses V.25bis HDLC dialing.
&M235, &Q235 Modem operates in Asynchronous mode and enables a subset of the A T&T command set. This is
required for A T&T DAT AKIT dial-out applications.
The &M2, &M231 through &M235, &Q2, and Q231 through Q235 commands disable the use of A T commands and force
the modem into Dumb mode. The only way to regain control of the modem is to recover A T Commands as described in
Recovering AT Commands
&Rn – RTS Action
Request-to-Send (RTS) is a signal from the DTE to the modem indicating the DTE has data to send to the modem.
&R, &R0 Standard RS232. DTE controls R TS to the modem in normal EIA-232-D operation. RTS must be
ON for the DTE to transmit to the modem.
&R1 Ignores RTS. Modem assumes RTS is always ON. Use this selection when the DTE does not
provide RTS to the modem.
&R2 Simulated Control Carrier. RTS input controls the remote modem’s LSD signal. This is used for
DTEs that require Line Signal Detect (LSD) to toggle ON and Off to simulate half-duplex operation.
section in this chapter.
4-10 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 87

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(9 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
&Sn – DSR Control
Data Set Ready (DSR) is a signal from the modem to the DTE indicating the modem is connected and ready for
operation.
&S, &S0 Forced On. Forces DSR output ON constantly. This is usually used for leased-line applications and
when the DTE requires DSR to always be ON.
&S1 Standard RS232. Modem controls DSR to the DTE. The modem raises DSR when it begins the
handshake process. DSR lowers upon disconnect. The modem is not ready to receive data until
DSR, CTS, and LSD are active.
&S2 Wink When Disconnect. DSR is normally forced ON, but is turned Off for 1 to 2 seconds upon a
disconnect.
&S3 Follows DTR. When the modem receives DTR from the DTE, it sends DSR to the DTE.
&S4 On Early. DSR is low when the modem is in the idle state. DSR goes high immediately upon a
command to enter Data mode. This setting is required for some modem pooling applications.
&S5 Delay to Data. Operation is similar to the Standard RS232 setting except that DSR does not turn
ON until the modem enters Data mode. Normally , the modem raises DSR when it begins the
handshaking process.
&Tn – Tests
&T, &T0 Abort. Stops any test in progress.
&T1 Local Analog Loopback. The modem must be in Direct mode.
&T2 Pattern. Transmits and receives a 511 Bit Error Rate Test (BERT). The modem must be online and in
&T3 Local Digital Loopback test. The modem must be online and in Direct mode.
&T4 Enables Receive Remote Loopback Response configuration option.
&T5 Disables Receive Remote Loopback Response configuration option.
&T6 Remote Digital Loopback test. The modem must be online and in Direct mode.
&T7 Remote Digital Loopback with Pattern. The modem must be online and in Direct mode.
&T8 Local Loopback with Pattern. The modem must be in Direct mode.
&T9 Self-Test.
To start a test, set the S18 register to a desired test duration in seconds (for example, 30 seconds), and then issue the
&Tn command. Test results are displayed as the number of errors sent or received over the number of blocks sent or
received.
&Vn – View Configuration Options
Displays each configuration group within the Active (Operating), Active (Saved), Customer 1, and Customer 2
configuration areas as well as the telephone numbers stores in directory locations 1–10.
&V, &V0 Active (Operating) configuration options.
&V1 Active (Saved) configuration options.
&V2 Customer 1 configuration options.
&V3 Customer 2 configuration options.
&V4 Directory locations 1–10.
&V5 Status of VF line characteristics.
&Wn – Write (Save to Memory)
Saves the current configuration options in Active (Operating) to one of three configuration areas:
Direct mode.
&W, &W0 Saved to Active (Saved).
&W1 Saved to Customer 1.
&W2 Saved to Customer 2.
4-113821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 88

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(10 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
&Xn – Transmit Clock Source
Determines the source of timing for synchronous data transmitted from the DTE.
&X, &X0 Internal. Modem provides transmit clock source for synchronous data (Pin 15).
&X1 External. Modem derives external transmit clock source provided on Pin 24 for synchronous data.
&X2 Receive Clock Loop. Modem derives transmit clock source from receive signal for synchronous data (Pin 17).
&Z
n=x
– Store Telephone Numbers
x
Modem saves the telephone number and dial command modifiers (if any) entered for
Directory Location
For example, the command A T&Z1=5551234 stores the telephone number 555-1234 into directory location 1.
To clear a telephone number from a memory location, issue the &Zn command without entering a telephone number.
%An – Error Control Fallback Character
This configuration option allows you to enter the ASCII value of the error control fallback character. This provides the
remote modem with the ability to end the error control link negotiating (handshaking) sequence by sending this character.
The modems will connect in Buffer mode (no error control). Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
n
(1–10). The DS command dials numbers stored this way .
(up to 40 characters in length) in
%An Where n is an ASCII value from 0 to 127. Factory default is 013 (ASCII carriage return).
%Bn, %BLn – Modulation/Data Rate
Sets the modulation and maximum dial VF rate. The same function can be performed with S-register S41; the %B and
%BL commands are provided for compatibility with environments where those commands are used.
The %B300 and %B1200 commands work in conjunction with the B (ITU-T/ Bell Mode) command to determine
modulation.
The %B2400 through %B33600 commands set the modem for V.34 operation, and the %BL2400 through %BL19200
commands set the modem for V.22bis, V.32, V.32bis, or V.32
%B300 V.21 or Bell 103 — max. rate 300 bps
%B1200 V .22 or Bell 212A — max. rate 1200 bps
%B2400 V .34 — max. rate 2400 bps
%B4800 V .34 — max. rate 4800 bps
%B7200 V .34 — max. rate 7200 bps
%B9600 V .34 — max. rate 9600 bps
%B12000 V.34 — max. rate 12,000 bps
%B14400 V.34 — max. rate 14,400 bps
%B16800 V.34 — max. rate 16,800 bps
%B19200 V.34 — max. rate 19,200 bps
%B21600 V.34 — max. rate 21,600 bps
%B24000 V.34 — max. rate 24,000bps
%B26400 V.34 — max. rate 26,400 bps
%B28800 V.34 — max. rate 28,800 bps
%B31200 V.34 — max. rate 31,200 bps
%B33600 V.34 — max. rate 33,600 bps
%BL2400 V.22bis — max. rate 2400 bps
%BL4800 V.32bis/V.32 — max. rate 4800 bps
%BL7200 V.32bis — max. rate 7200 bps
%BL9600 V.32bis/V.32 — max. rate 9600 bps
%BL12000 V.32bis — max. rate 12,000 bps
%BL14400 V.32bis — max. rate 14,400 bps
%BL16800 V.32
%BL19200 V.32
terbo
— max. rate 16,800 bps
terbo
— max. rate 19,200 bps
terbo
operation.
4-12 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 89

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-1
(11 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
%Cn – MNP5 Data Compression
Determines if the modem uses MNP Class 5 data compression. It can be set independently of V.42bis data compression.
Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
%C, %C0 Disable.
%C1 Enable.
+FCLASS=
Normally set by fax software, Service Class Selection determines the fax protocol. The command is sent to the modem in
the format +FCLASS=
0 = Data
1 = Class 1 Fax (EIA 578)
2 = Class 2 Fax (EIA/TIA SP-2388 dated 20 August 1990)
In the format +FCLASS?, the +FCLASS command returns the current Service Class: 0, 1, or 2. In the format
+FCLASS=?, the +FCLASS command returns the Service Classes available: 0,1, 2.
NOTE: Other fax commands supported by the 3821
\An – Maximum Frame Size
Sets the maximum frame size for V.42 and MNP. For MNP, the minimum value is 64; if a smaller value is specified, it will
default to 64.
\A, \A0 64
\A1 128
\A2 192
\A3 256
\A4 32
\A5 16
\Cn – Error Control Negotiate Buffer
Determines if the answering modem buffers the data that it received from the remote modem during an interval in which
the modem attempts to establish a connection using error control. Online changes to this configuration option do not take
effect until a disconnect occurs.
\C, \C0 Disable.
\C1 Enable.
\C2 Disable and Switch. Modem automatically switches to Buffer mode if it receives an error control fallback
character (an ASCII carriage return see %A command) during error control negotiation.
n
– Service Class Selection
n
, where n can be set to one of three values:
Plus
modem are not documented in this manual because they are
not normally issued by the user. They follow the EIA 578 and EIA/TIA SP-2388 specifications.
\Dn – CTS Control
Clear-to-Send (CTS) is a signal from the modem to the DTE indicating that it can accept data from the DTE.
\D, \D0 Forced On. Forces CTS to always ON.
\D1 Standard RS232.
\D2 Wink When Disconnect. CTS is turned Off for 1 to 2 seconds upon a disconnect.
\D3 Follows DTR. The state of CTS follows the state of DTR.
\Gn – Modem to Modem Flow Control
If a modem’s buffers begin to fill due to data it is receiving from the remote modem, but is not passing the data on to the
DTE, it can issue flow control messages to the remote modem. This only applies during Buffer mode connections where
the remote modem also has modem-to-modem flow control enabled. If Error Control mode is enabled, flow control
between the modems will happen automatically , regardless of the setting of this configuration option.
\G, \G0 Disable.
\G1 Enable.
4-133821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 90

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-1
(12 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
\Kn – Buffer Control, Send Break Control, Break Forces Escape
n
The \K
command sets three configuration options simultaneously:
Break Send Break
Buffer Break Forces
Control Control Escape
\K0 Discard Data Break First Enable
\K1 Discard Data Break First Disable
\K2 Keep Data Break First Enable
\K3 Keep Data Break First Disable
\K4 Keep Data Data First Enable
\K5 Keep Data Data First Disable
\K6 Discard Break Not Applicable Disable
BREAK BUFFER CONTROL
Determines if data stored in the modem’s buffer is saved or discarded when the DTE issues a break sequence.
SEND BREAK CONTROL
Determines what is sent from the modem first, data or break if a break sequence is sent from the DTE.
BREAK FORCES ESCAPE
Determines whether or not the modem should enter Command mode when it receives a break character from the DTE.
\Nn – Error Control Mode
Determines the type of error control used by the modem. In most cases, V42/MNPorBfr is the best choice. If V.42bis and
MNP are enabled, then the modem uses the following priority for error control negotiation: V.42bis, V.42, MNP 5 and
below. Online changes do not take effect until a disconnect occurs.
\N0 Buffer Mode.
\N1 Direct Mode.
\N2 MNP or Disconnect.
\N3 MNP or Buffer.
\N4 V.42/MNP or Disconnect.
\N5 V.42/MNP or Buffer.
\N6 LAPM or Disconnect.
\N7 LAPM or Buffer .
If ETC is installed, &F5 and &F6 (Cellular) set this to \N6.
4-14 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 91

Table 4-1
(13 of 13)
3821
Plus
AT Commands
\ –
n
The \Q
FLOW CONTROL OF DTE
Determines how the modem controls the flow of data from the DTE.
FLOW CONTROL OF MODEM
Determines how the DTE controls the flow of data from the modem.
command controls two configuration options simultaneously:
Flow Control Flow Control
of DTE of Modem
\Q0 Disable Disable
\Q1 XON/XOFF XON/XOFF
\Q2 CTS to DTE Disable
\Q3 CTS to DTE RTS to Modem
\Q4 XON/XOFF Disable
\Q5 Disable XON/XOFF
\Q6 Disable RTS to Modem
AT Commands and S-Registers
\Tn – No Data Disconnect Timer
Forces the modem to disconnect if no data is transmitted or received within a specified amount of time.
\T, \T0 Disable. \T2 is the default for Denmark, and \T3 is the default for France and Germany . See Appendix H.
\T
n
Where n is a value from 1 to 255 in 1-minute increments.
\Xn – XON/XOFF Passthrough
The way this configuration option functions depends on how the modem is configured for flow control.
When the modem is configured for XON/XOFF flow control (see \Qn, Flow Control of DTE), this configuration option
determines if flow control characters received from the local DTE will be passed on to the remote modem.
If configured for modem-to-modem flow control (see \G – Modem to Modem Flow Control), this configuration option
determines if flow control characters received from the line will be passed on to the DTE.
\X, \ X0 Disable.
\ X1 Enable.
4-153821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 92

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
S-Register List
S-registers affect the operating parameters of the
3821Plus modem. These registers are applicable only
when the DTE Dialer T ype configuration option is set for
AT . (See &Mn and &Qn commands.)
S-registers can be displayed and/or modified when the
modem is in Command mode. T o display the value of an
S-register, issue the following command:
TYPE: ATSn?
Where: n is the register number.
PRESS: Enter
T o modify the value of an S-register, issue the
following command:
TYPE: ATSn=r
Where: n is the register number, and r is the new
value.
PRESS: Enter
T able 4-2 lists S-registers supported by the 3821Plus .
Not all S-register values are valid in all countries. See
Appendix H.
NOTE
In some countries, the range of
allowable values of some
S-registers is restricted. If the DTE
attempts to enter a restricted
value, the modem answers OK,
but it sets the register to the
nearest allowable value. The DTE
can check the actual value of the
register with the S
n
? command.
Table 4-2
(1 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S0 – Auto-Answer Ring Number
Determines the number of rings the modem will count before automatically answering a call.
Enter zero (0) if you do not want the modem to automatically answer any calls. Otherwise, enter a value from 1–255 for
the number of rings to count before answering. Note that if disabled, the modem can only answer with an A TA command.
The factory setting is 1.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S2 – AT Escape Character
Determines ASCII value used for escape sequence (+++) to enter Command mode from Data mode.
Enter a value from 0 to 127 for the escape character. Any value greater than 127 causes the modem to disable the
escape sequence. When the escape sequence is disabled, the modem cannot return to Command mode until the call is
disconnected.
Factory setting is 43 (ASCII + key).
S3 – Carriage Return Character
Determines ASCII value used as the carriage return (Enter key). This character is used to end command lines and result
codes.
Enter a value from 0 to 127 for the command end character.
Factory setting is 13 (ASCII carriage return).
NOTE: The &W command used to save this change must be on a separate line. This ensures both that the change is
intentional, and that the DTE can enter the new character.
4-16 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 93

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-2
(2 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S4 – Line Feed Character
Determines ASCII value used as the line feed character.
Enter a value from 0–127 for the line feed character.
Factory setting is 10 (ASCII line feed).
S5 – Backspace Character
Determines ASCII value used as the backspace (Backspace key). This character moves the cursor to the left and erases
the previous character.
Enter a value from 0–127.
Factory setting is 08 (ASCII backspace).
S6 – Blind Dial Pause
Determines how long (in seconds) the modem waits after going off-hook before dialing a telephone number if using result
code X0, X1, or X3.
Enter a value from 2–255 seconds.
The factory setting is 2 seconds.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S7 – No Answer Timeout
Determines how long (in seconds) an originating modem waits before abandoning a call when no answer tone is
received.
Enter a value from 1–255 seconds.
The factory setting is 45 seconds.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S8 – ‘‘,” Pause Time for the Dial Modifier
Determines how long (in seconds) the modem pauses when it encounters a comma (,) in the Dial command string.
Enter a value from 0–255 seconds.
The factory setting is 2 seconds.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S10 – No Carrier Disconnect
Determines how long (in tenths of seconds) the modem allows the carrier signal to be Off before disconnecting the call.
Enter a value from 0–254 in 0.1 second increments. A value of 255 disables this register.
Factory setting is 20 (2 seconds).
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S12 – Escape Guard Time
Sets the value (in 20-millisecond increments) for the required pause before and after the escape sequence is issued. The
guard time prevents the modem from interpreting data as the escape sequence characters.
Enter a value from 0–255 in 20-millisecond increments. For example, the factory setting of 50 equals 1000 milliseconds or
one second. Factory setting is 50 (1 second).
4-173821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 94

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-2
(3 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S14 – Asymmetric Rate Mode
Register determines whether VF rates for transmitting and receiving are identical when using V.34 modulation. Enabling
the function permits the two rates to be different.
Register has the following values:
0 = Enable
1 = Disable
Factory setting is Enable.
S18 – Test Timeout
Sets the duration (in seconds) for the modem tests. This automatically cancels any test in progress after the time of this
register expires. Any test can be manually canceled by issuing the escape sequence (+++) followed by the &T0
command.
Enter a value from 0–255 seconds. (A value of 0 disables this register.)
Factory setting is Disable.
S26 – RTS-to-CTS Delay
Sets the length of time (in 10-millisecond increments) the modem waits after receiving RTS before issuing CTS to the
DTE.
Enter a value from 0–255.
Factory setting is 0 milliseconds.
S38 – DTR Continuous Repeat
Determines whether automatic dialing of dial backup directory location 1 will be repeated continuously if unsuccessful, or
halted after the first try .
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Factory setting is Disable.
S39 – Receive Buffer Disconnect Delay
Determines the maximum amount of time the modem can continue to send data in its Receive Buffer to the DTE after the
modem is commanded by the DTE to disconnect, or after the modem detects a line disconnect.
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable (Immediate disconnect)
1 = 1 second
2 = 2 seconds
D D
D D
255 = 255 seconds
Factory setting is Disable.
4-18 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 95

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-2
(4 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S40 – Auto Make Busy
Register determines whether the modem automatically goes into a Make Busy state in the following conditions: during a
Local Analog Loop Test; during a Self Test not invoked by powering on the modem, and after a failed Self T est; during a
DTE or NMS download, and after a failed download; and upon a switch to the Service Line.
WARNING: Auto Make Busy should be enabled only for modems connected to a PBX, or to a local phone system that
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Factory setting is Disable.
S41 – Dial-Line Rate
Determines the modem’s highest data rate and modulation scheme for operation on dial lines. S41 can also be set using
the %B and %BL commands.
Register has the following values (shown in bps):
1 = 14,400 (V.32bis)
2 = 12,000 (V.32bis)
3 = 9600 (V.32bis/V32)
4 = 7200 (V.32bis)
5 = 4800 (V.32bis/V.32)
6 = 2400 (V.22bis)
7 = 1200 (V.22)
8 = 1200 (212A; invalid for UK)
10 = 0–300 (V21)
1 1 = 0–300 (103J; invalid for UK)
20 = 19,200 (V.32
21 = 16,800 (V.32
27 = 33,600 (V.34)
28 = 31,200 (V.34)
29 = 28,800 (V.34)
30 = 26,400 (V.34)
31 = 24,000 (V.34)
32 = 21,600 (V.34)
33 = 19,200 (V.34)
34 = 16,800 (V.34)
35 = 14,400 (V.34)
36 = 12,000 (V.34)
37 = 9600 (V.34)
38 = 7200 (V.34)
39 = 4800 (V.34)
40 = 2400 (V.34)
allows it.
terbo
terbo
)
)
Factory setting is 33,600 (V.34).
S43 – Train Time
Register controls the modem’s train time for V.34, V .32
Register has the following values:
0 = Long (A long train is required for satellite links which have long roundtrip delays.)
1 = Short
Factory setting is Long.
terbo
, V.32bis, and V.32 mode.
4-193821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 96

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-2
(5 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S44 – Leased Line Rate
Determines the modem’s highest data rate and modulation scheme for operation on 2-wire leased lines in either Answer
or Originate mode.
Register has the following values (shown in bps):
1 = 14,400 (V.32bis)
2 = 12,000 (V.32bis)
3 = 9600 (V.32)
4 = 7200 (V.32bis)
5 = 4800 (V.32)
6 = 2400 (V.22bis)
18 = 19,200 (V.32
19 = 16,800 (V.32
25 = 33,600 (V.34)
26 = 31,200 (V.34)
27 = 28,800 (V.34)
28 = 26,400 (V.34)
29 = 24,000 (V.34)
30 = 21,600 (V.34)
31 = 19,200 (V.34)
32 = 16,800 (V.34)
33 = 14,400 (V.34)
34 = 12,000 (V.34)
35 = 9600 (V.34)
36 = 7200 (V.34)
37 = 4800 (V.34)
38 = 2400 (V.34)
NOTE: Turn your modem off and on after setting S44 for the setting to take effect.
terbo
terbo
)
)
Factory setting is 33,600 (V.34).
S45 – Leased Line Transmit Level
Level determines the modem’s transmit power output level over leased lines.
Enter a value from 0–15 dBm.
The factory setting is 0 dBm.
NOTE: The default and permitted settings of this option are country-dependent. See Appendix H.
S48 – Leased Line Carrier On Level
Determines if the modem disconnects if the carrier signal on leased lines falls below –26 dBm or –43 dBm.
Register has the following values:
0 = –43 dBm
1 = –26 dBm
2 = –33 dBm
The factory setting is –43 dBm for all countries except France, for which it is fixed at –33 dBm. See Appendix H.
4-20 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 97

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-2
(6 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S49 – Transmit Buffer Disconnect Delay
Determines the maximum amount of time the modem can continue to send data in its Transmit Buffer to the remote
modem after it is commanded by the DTE to disconnect.
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable (Immediate disconnect)
1 = 1 second
2 = 2 seconds
D D
D D
255 = 255 seconds
Factory default is 10 seconds.
S55 – Access from Remote
Determines whether the 3821
dial-line or leased-line connection.
Register has the following values:
Plus
modem’s configuration options can be accessed by a remote 3800
Plus
modem via a
0 = Enable
1 = Disable
The value of S55 is not affected by factory default templates.
S56 – Remote Access Password (Part 1)
Register allows entry of the first pair (leftmost) of digits of a remote access password. Any value from 00 to 99 is valid.
For example, if the remote access password is 12345678, then S56=12.
The value of S56 is not affected by factory default templates.
S57 – Remote Access Password (Part 2)
Register allows entry of the second pair of digits of a remote access password. Any value from 00 to 99 is valid.
The value of S57 is not affected by factory default templates.
S58 – Remote Access Password (Part 3)
Register allows entry of the third pair of digits of a remote access password. Any value from 00 to 99 is valid.
The value of S58 is not affected by factory default templates.
S59 – Remote Access Password (Part 4)
Register allows entry of the fourth pair (rightmost) of digits of a remote access password. Any value from 00 to 99 is valid.
The value of S59 is not affected by factory default templates.
S62 – V.25bis Coding
Identifies to the modem the type of coding used by the DTE while in V.25bis HDLC or V.25bis Bisync mode.
Register has the following values:
0 = ASCII
1 = EBCDIC
Factory setting is ASCII.
4-213821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 98

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-2
(7 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S63 – V.25bis Idle Character
Identifies to the modem the type of idle fill used by the DTE while in V.25bis HDLC or V.25bis Bisync mode.
Register has the following values:
0 = Mark
1 = Flag
Factory setting is Mark.
S64 – V.25bis New Line Character
Identifies to the modem the type of line terminator used by the DTE while in V.25bis Async mode.
Register has the following values:
0 = Carriage Return and Line Feed
1 = Carriage Return
2 = Line Feed
Factory setting is carriage return and line feed (CR + LF).
S66 – NMS Call Messages
Register determines if the modem sends information regarding status (Call Progress) and/or sends summarized call
statistics (Call Connect) to the COMSPHERE 6700 Series NMS.
Register has the following values:
0 = Call Connect & Progress
1 = Disable
2 = Call Connect Only
3 = Call Progress Only
The value of S66 is not affected by factory default templates.
S69 – Make Busy Via DTR
Determines if the modem goes off-hook (busy) when DTR is Off. In the UK, the default value cannot be modified.
WARNING: The Make Busy function must be used only when the modem is connected to a PBX, or to a local phone
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Factory setting is Disable.
S74 – Network Position Identification
Register identifies each modem as either a control or tributary modem.
Register has the following values:
0 = Tributary
1 = Control
Factory setting is Tributary.
S75 – Network Management Address
Register determines the modem’s network address. This address is used when accessing the modem from the NMS.
Enter a value from 0 (network address 001) to 255 (network address 256).
The value of S75 is 255 when the modem is shipped. The value of S75 is not affected by factory default templates.
system that allows it.
4-22 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
Page 99

AT Commands and S-Registers
Table 4-2
(8 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S76 – Autorate (Dial Line)
Determines if the Autorate function is used on dial lines when connected in V.32bis, V.34
allows the modem to adjust line speed due to varying VF line quality .
Register has the following values:
0 = Enable
1 = Disable
2 = Start at 4800 bps (V.32bis only)
3 = Start at 9600 bps (V.32bis only)
Factory setting is enable.
S77 – DTR Alarm Reporting
Register determines whether an alarm is sent to the 6800 Series NMS controller when the DTR signal has been Off for
more than 10 seconds.
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
The value of S77 is Disable when the modem is shipped. The value of S77 is not affected by factory default templates.
terbo
, or V.34 mode. Autorate
S78 – Automode (Dial Line)
If enabled, automode permits the modem to automatically connect to a remote modem using any supported modulation
scheme.
If disabled, the modem only supports the modulation scheme selected by the S41 register (Dial-Line Rate).
If the modem is in a modem pool attached to a System 85 PBX, S78 should be set to 2. This modifies parameters used
during connection to the PBX.
Register has the following values:
0 = Enable
1 = Disable
2 = System 85
Factory setting is Enable.
S80 – No Data Disconnect Trigger Signal
Register determines whether Pin 2 (transmit data) or Pin 3 (receive data) of the modem’s RS-232 serial interface is
monitored so that the modem can disconnect the call if there is no activity for a certain period. (See the \T command.)
Register has the following values:
0 = Transmit or Receive
1 = Transmit only
2 = Receive only
3 = Transmit and Receive
Factory setting is 3.
S82 – Autorate (Leased Line)
terbo
Determines if the Autorate function is used on leased lines when connected in V.32bis, V.32
allows the modem to adjust line speed due to varying VF line quality .
, or V.34 mode. Autorate
Register has the following values:
0 = Enable
1 = Disable
Factory setting is Enable.
4-233821-A2-GB20-40 January 1999
Page 100

COMSPHERE 3821Plus Modem
Table 4-2
(9 of 10)
3821
Plus
S-Registers
S84 – AT Command Mode
Determines how the modem responds to valid and invalid A T commands. The selections No ERROR and No Strap or
ERROR permit installation into applications that are customized for a different modem.
Register has the following values:
0 = Normal.
1 = No ERROR. The modem executes all valid commands, ignores invalid commands, and never issues an ERROR
message.
2 = No Strap or ERROR. The modem ignores all configuration commands, but always issues an OK response message.
The value of S84 is Normal when the modem is shipped. The value of S84 is not affected by factory default templates.
S85 – Fast Disconnect
Allows the modem to disconnect immediately after receiving a disconnect command.
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Factory setting is Disable.
S88 – Straps When Disconnected
Determines if configuration options in the Active (Saved) configuration area are loaded to Active (Operating) when the
modem disconnects.
Register has the following values:
0 or 231 = No Change
1 or 232 = Reload
The value of S88 is No Change when the modem is shipped. The value of S88 is not affected by factory default
templates.
S89 – V.42 ARQ Window Size Increase
Register allows the V.42 Automatic Request for Transmission (ARQ) window size to be set to a value from 6 to 15 frames
to accommodate satellite delays.
Register has the following values:
0 = Automatic Adjust (6–15 frames)
1 = 7 frames
2 = 8 frames
3 = 9 frames
D D
D D
9 = 15 frames
This command applies only to connections made using V.42bis data compression or V.42 error control.
Factory setting is Automatic Adjust.
S90 – DTE Rate = VF Rate
Register forces the DTE (computer) data rate to be equal to the VF (telephone line) data rate.
Register has the following values:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Factory setting is Disable.
4-24 January 1999 3821-A2-GB20-40
 Loading...
Loading...