
Issue 8.0.13, 1 July 2009
2009
EN 55022 - Class B
EN 55024
EN 60950
Paradise Dataco m Ltd. Paradise Dataco m LLC
1 Wheaton Road 328 Innovation Blvd.
Witham, Essex, CM8 3UJ, England. State College, PA 16803, U.S.A.
Tel: +44(0)1376 515636 Tel: +1 814 238 3450
Fax: +44(0)1376 533764 Fax: +1 814 238 3829
http://www .paradisedata.com
Copyrig ht © 2008-2009 Para dise Datacom Ltd. All rights reserved.
Installation and Operating Handbook for
Vision Series Satellite Modems

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
ii
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Welcome.....................................................................................................1-1
Chapter 2 About This Handbook...............................................................................2-1
2.1 Conventions ............................................................................................................2-1
2.2 Trademarks .............................................................................................................2-1
2.3 Disclaimer................................................................................................................2-1
2.4 GNU General Public Licence..................................................................................2-1
Chapter 3 Safety Information ....................................................................................3-1
3.1 Safety ......................................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Environmental .........................................................................................................3-1
3.3 Installation ...............................................................................................................3-1
Chapter 4 Electromagnetic Compatibility................................................................4-1
Chapter 5 Installation.................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Unpacking ...............................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Visual Inspection .....................................................................................................5-1
5.3 Getting Started ........................................................................................................5-1
5.4 Pow er Up.................................................................................................................5-1
Chapter 6 Introduction...............................................................................................6-1
6.1 Overview .................................................................................................................6-1
6.2 Hardw are Options ...................................................................................................6-2
6.2.1
Quad ASI Opt ion Card ....................................................................................6-2
6.2.2
IP Traffic Option Card .....................................................................................6-2
6.2.3
Optional L-band BUC Pow er Supplies ...........................................................6-3
6.2.4
L-band FSK/DC Opt ion Card ..........................................................................6-5
6.3 Softw are Options.....................................................................................................6-5
6.4 Front Panel..............................................................................................................6-7
6.4.1
LEDs ................................................................................................................6-7
6.4.2
LCD Display ....................................................................................................6-7
6.5 Rear Pan el ..............................................................................................................6-9
Chapter 7 User Interfaces ..........................................................................................7-1
7.1 User Na mes, Passw ords and Modem Contro l .......................................................7-1
7.1.1
Local Mode......................................................................................................7-1
7.1.2
Giveaw ay Mode ..............................................................................................7-1
7.1.3
Takeaw ay Mode..............................................................................................7-2
7.2 Front Panel Interface ..............................................................................................7-3
7.2.1
Keypad Operation ...........................................................................................7-3
7.2.2
LCD Screen Layout.........................................................................................7-5
7.3 Front Panel Menu Structure....................................................................................7-6

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
iii
7.3.1
Ma in Menu.......................................................................................................7-6
7.3.2
Status Menu....................................................................................................7-7
7.3.3
Edit Menu ......................................................................................................7-12
7.3.4
View Menu.....................................................................................................7-74
7.3.5
Test Menu .....................................................................................................7-75
7.4 Web User Interface ...............................................................................................7-80
7.4.1
Logging In and Out .......................................................................................7-80
7.4.2
Graphing Features ........................................................................................7-83
7.4.3
Configuration Me mories ................................................................................7-87
7.4.4
Interface Configurations ................................................................................7-89
7.4.5
System Log ...................................................................................................7-90
7.4.6
System Alarms ..............................................................................................7-91
7.4.7
On-line Installat ion and Operation Handbook ..............................................7-92
7.4.8
SAF Screen...................................................................................................7-92
7.4.9
SNMP Configuration .....................................................................................7-93
7.4.10 Remot e Softw are Upgrade ...........................................................................7-94
7.4.11 BER Tester....................................................................................................7-96
7.4.12 Mod em Email Function .................................................................................7-98
7.4.13 IP Static Routes ..........................................................................................7-101
7.4.14 Header Compression ..................................................................................7-102
Chapter 8 Modem Concepts......................................................................................8-1
8.1 Clocking...................................................................................................................8-1
8.1.1
Transmit Clocking ...........................................................................................8-1
8.1.2
Receive Clocking ............................................................................................8-1
8.2 1-for-1 Operation.....................................................................................................8-3
8.2.1
Basic Theory ...................................................................................................8-3
8.2.2
Sw itching Philosophy......................................................................................8-4
8.2.3
Detected Failures ............................................................................................8-4
8.2.4
Man ual Sw itchover..........................................................................................8-4
8.2.5
1-for-1 Setup Procedure .................................................................................8-4
8.3 Softw are Activated Features...................................................................................8-5
8.4 Softw are Upgrading ................................................................................................8-5
8.5 Tutorial On Carrier/No ise and Eb/No Measurements ............................................8-6
8.6 Et hernet Bridge .....................................................................................................8-11
8.7 Paired Carrier ........................................................................................................8-12
Chapter 9 Remote Control Protocol.........................................................................9-1
Chapter 10 Data Interfaces ........................................................................................10-1
Chapter 11 Connector Pinouts ..................................................................................11-1
Chapter 12 Fault Messages.......................................................................................12-1
12.1 Transmit Faults .....................................................................................................12-2
12.2 Transmit Warnings................................................................................................12-2
12.3 Receive Faults ......................................................................................................12-4
12.4 Receive Warnings.................................................................................................12-4
12.5 Unit Fa ults .............................................................................................................12-5
12.6 Unit Warnings........................................................................................................12-6

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
iv
12.7 Start up problems ..................................................................................................12-6
Chapter 13 Specification Summary..........................................................................13-1
13.1 Common Main Specifications ...............................................................................13-1
13.2 Tx Modulator Specifications..................................................................................13-2
13.3 Rx De modulator Specifications.............................................................................13-3
13.4 Clocking and Buffering Specifications ..................................................................13-3
13.5 BERT Option Specifications .................................................................................13-4
13.6 Data Rat e Specifications.......................................................................................13-4
13.7 Traf f ic Log Specifications......................................................................................13-6
13.8 Common Specifications ........................................................................................13-6
13.9 Internet Traffic.......................................................................................................13-8
13.10 BUC / LNB facilities...........................................................................................13-9
Chapter 14 Gloss ary...................................................................................................14-1
Chapter 15 Customer Technical Support.................................................................15-1

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
1-1
Chapter 1 Welcome
Parad ise Dataco m is proud to present its next-generation, state-of-the-art Vision Series of
satellite DVB modems. Its innovative design incorporates a novel architecture that uses
upgradeable programmable logic for all major modem functions, creating a flexible
mod em platform easily adapted t o future demands. It provides a rich feature set and
flexibility of configuration, allow ing you to purchase only what you need initia lly and then
enable further features in the f ield at a later date. It sets new levels of usability by
adopting mu ltiple language support on all user interfaces as standard (including English,
French, Ger man and Spanish - contact Customer Technical Support for up to date details
of other languages that are supported).
The Vision mod em provides a DVB-S2 capability and a bandw idth halving technique
called Paired Carrier.
DVB-S2 is a highly efficient and robust coding and modulation standard for satellite
transmission that can significantly reduce satellite bandw idth requirements compared w ith
legacy standards.
Paired Carrier allows space segment reuse. It incorporates ViaSat’s patented PCMA
technology to overlay transmit and receive carriers in the same space segment reducing
satellite bandw idth requirements by up to 50%. It is used in addition to, not instead of,
other bandw idth saving techniques.
This handbook w ill guide you through the process of installing and using your Vision
Series Satellite Modem. It covers all models including IF and L-band variants. The Vision
Redundancy Sw itch is documented separately – see Installation and Operating
Handbook for Quantum, Evolution and Vision Series Redundancy Switches.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
2-1
Chapter 2 About This Handbook
2.1 Conventions
This symbol i s intended to alert the user to the presence of voltage
levels that constitute a dangerous risk of electric shock a nd
serious injury.
This symbol is i ntended to alert the user to the presence of
importa nt operating i nstructions critical to correct system
function.
2.2 Trademarks
All trademarks used in this handbook are acknow ledged to be the property of their
respective ow ners.
2.3 Disclaimer
Although every effort is made to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the
information in this handbook, this cannot be guaranteed and the information contained
herein does not constitute a product w arranty. A product warranty statement is provided
separately to this handbook. Paradise Datacom maintains a programme of continuous
product improvement and reserves the right to change specif ications w ithout prior notice.
2.4 GNU General Public Licence
This product contains softw are source code distributed under the GNU General Public
Licence (GPL). Paradise Datacom fully acknow ledges the terms of this licence. If you
would like a copy of the GPL source code in this product on a CD, then please send
(USD) $15.00 (along w ith a request for the ‘Vision Series Satellite Mod em GPL Source
Code CD’) to Paradise Datacom to cover the cost of preparing and mailing the CD to you.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
3-1
Chapter 3 Safety Information
PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION BEFORE
INSTALLATION AND USE.
3.1 Safety
To ensure operator safety this Satellite Modem has been designed to comply w ith the
follow ing safety standard:
EN 60950-1 - ‘Safety of Information Technology Equipment’.
Prior to installation and operation, please ensure that the follow ing points are observed.
3.2 Environmental
The equipment is designed to operate in a static 19-inch rack system conforming to IEC
297-2. Operation of the equipment in transportable installations and vehicles equipped
with the means of providing a stable environment is permissible. Operation of the
equipment on vehicles, ships or aircraft w ithout means of environmen tal conditioning may
invalidate the safety compliancy. Please contact Customer Technical Support for further
advice. Operation of the equipment in an environment other than that stated in the
specifications will also invalidate the safety compliancy.
The equipment must not be operated in an environment in w hich the unit is exposed to:
• Unpressurised altitudes greater than 2000 metres
• Extremes of temperature outside the stated operating range
• Excessive dust
• Moisture or humid atmospheres above 95% relative humidity
• Excessive vibration
• Flammable gases
• Corrosive or explosive atmospheres
3.3 Installation
The equipment is classified in EN 60950-1 as a pluggable equipment Class A for
connection to the mains supply (note that a 48V DC version is also available). As such it
is provided w ith a mains inlet cord suitable for use in the country of operation. In normal
circumstances this will be of an adequate length f or installation in a rack. If the mains
cable proves to be too short then any replacement must have a similar type fuse (if fitted)
and be manufactured to a similar specification. ( For example, look for HAR, BASEC or
HOXXX-X ratings on the cable and the connector ends marked w ith BS1636A (UK free

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
3-2
plug 13 amp); BSI, V DE, NF-US E, UL, CSA, OVE, CEBEC, NEMKO, DEMKO, SETI,
IMQ, SEV and KEMA-KEUR f or the IEC 6 amp free socket. Schuko and North American
free plugs must have similar markings.)
The installation of the equipment and the connection to the ma ins supply must be made
in compliance w ith local and national w iring regulations f or a Category II ‘impulse overvoltage’ installation. The positioning of the equipment must be such that the mains supply
socket outlet for the equipment should be near the e quipment and easily accessible or
there should be another suitable means of disconnection from the mains supply.
The equipment is designed to operate f rom a TN-type pow er supply system as specif ied
in EN 60950-1 (i.e. a system that has separate earth, line and neutral conductors). The
equipment is not designed to operate w ith an IT pow er system that has no direct
connection to earth.
This unit has double pole/neutral fusing. To ensure operator
sa fety, fuses should always be replaced wi th identical type a nd
rating – contact Customer Technical Support for details.
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
4-1
Chapter 4 Electromagnetic Compatibility
This Satellite Modem has been show n to comply w ith the follow ing standards:
1. Emissions: EN 55022 Class B - ‘Limits and methods of measurement of radio
interf erence characteristics of Information Technology Equipment’.
2. Immunity: EN 50024 – ‘Information technology equipment immunity
characteristics’.
Extensive testing has been perf ormed to ensure that the unit meets these specifications
when configured w ith any or all of its available hardw are options.
To ensure that the modem maintains compliance with
electr omagnetic compatibility standards please observe the
following points:
The equipment must be operated w ith its cover on at all times. If it is necessary to remove
the cover for any reason, then you must ensure that the cover is correctly refitted before
normal operation.
For the baseband data interfaces, all 'D' type connectors must have grounding fingers on
the plug shell to guarantee continuous shielding. The back-shells must comply w ith the
requirements of VDE 0871 and FCC 20708, providing at least 40dB of attenuation f rom
30 MHz to 1 GHz. A good quality cable w ith a continuous outer shield, correctly
grounded, must be used.
Connections to transmit and receive IF interfaces must be made w ith double-screened
coaxial cable (for example, RG223/U).

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
5-1
Chapter 5 Installation
5.1 Unpacking
Prior to unpacking, inspect the exterior of the shipping container f or any sign of damage
during transit. If damage is evident, contact the carrier immed iately and submit a da mage
report.
Carefully unpack all items, taking care not to discard packing materials, particularly the
mo lded f oam inserts. Should the unit need to be returned to Paradise Dataco m then you
should use the original packing carton as it is designed to provide the necessary level of
protection during shipme nt.
5.2 Visual Inspection
Once unpacked, visually inspect the contents to ensure all parts are present and that
there are no signs of damage.
5.3 Getting Started
If the unit is to be rack mounted then adequate ventilation and cooling should be provided.
This must include leaving adequate clearance around the ventilation holes on the sides and
the fan on the back panel.
Connect the appropriate cables to the Transmit IF and Receive IF connectors at the rear of
the unit. Output pow er level can be controlled using the front-panel menus.
5.4 Power Up
Pow er the unit and wait f or it to complete its initialisat ion w hen it w ill display summary
status information.
For local use, from the f ront-panel menu, select Main, Edit, All to define a ll para meters
prior to operation.
It is also possible to set up the unit from a w eb brow ser (this is described in Section 7.4).
When setting up a number of units, it may be preferable to save the configuration settings
of one unit and then transfer them to each of the others – this procedure is explained in
Section 7.4.3.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-1
Chapter 6 Introduction
6.1 Overview
The Vision Series satellite modems are designed for operation in a variety of
environments (such as ground stations and mobile and fly aw ay terminals) providing a
data link betw een geographically distant sites via satellite.
Features include:
• DVB-S (EN 300 421), DVB-DSNG (EN 301 210) and DVB-S2 (EN 302 307)
operation ( DVB-S/DSNG to 80Mbps/40Msps; DVB-S2 to 80Mbps/37.5Msps).
• Built- in support for DVB-S2 Constant Coding and Modulation (CCM).
• Multistreaming support for ASI (up to 4 ASI ports) and IP. Ability to f ilter o n PID
number and MAC address. PID mon itor that displays statistics for the different
PIDs being transmitted or received.
• Variable Coding and Modulation (VCM) ready! Requires just a software upgrade!
Contact Custo mer Technical Support for more details.
• IF f requency range of 50 to 90MHz and 100 to 180MHz.
• L-band frequency range of 950MHz to 1950MHz (option to 2050MHz).
• Support for QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM and 16APSK modulation schemes.
• Forw ard Error Correction (FEC) options of Viterbi, Trellis Coded Modulation (TCM)
and Low Density Parity Check (L DPC) as part of DVB-S/DSNG/S2.
• Outer FEC options of concatenated Reed-Solomon ( RS) and Bose- ChaudhuriHocquenghem (BCH).
• Terrestrial interface options of ASI and Gigabit Ethernet.
• Front panel display and keypad for local control.
• Remote control through both serial and IP interfaces. IP remote control can be
through a variety of methods includin g: built-in w eb pages served from the
mod em’s embedded w eb server to any supported web browser; the Simple
Netw ork Management Protocol (SNMP); a standard Telnet protocol session w here
the user communicates using a Telnet client ter mina l-emulation program.
• Compact 1U chassis, 405mm deep.
• Rich set of IP features including TCP acceleration, HTTP acceleration, header
compression, Ethernet bridge, DHCP, IEEE 802.1p QOS support, IEEE 802.1q
VLAN support, FTP, telnet, SMTP, SNMP, diagnostic graphs, PID filtering, etc. IP
encapsulation over DVB supports the use of both the Multi-Protocol Encapsulation
(MPE) and Ultra Leightw eight Encapsulation (UL E) standards. It also includes the
ability to transcode betw een (MPEG2 TS over) ASI and (MPEG2 TS over) IP.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-2
6.2 Hardware Options
A single interf ace position is available that supports the follow ing options.
6.2.1 Quad ASI Option Card
The Quad ASI option card (part number P3710) provides four ports (BNC connectors)
that are independently configurable as inputs or outputs. Note that in DVB-S2 CCM
mod e, only a single input and output can be used unless the optional multistreaming SAF
feature has been purschased – the mulstistreaming feature can be used in all DVB
mod es i.e. DVB-S, DVB-DS NG and DVB-S2.
6.2.2 IP Traffic Option Car d
The base modem supports Ethernet M&C interface only. In order to pass traffic over
Et hernet, it is necessary to fit the IP Traffic option card (part number P3714).
This provides tw o 10/100/1000 (GigE) BaseT Ethernet connectors and supports a
number of f eatures including:
1. Packet handling capability of up to 50000 packets per second.
2. Support for Mu lti-Protocol Encapsulation ( MPE) and Ultra Leightw eight
Encapsulation (ULE) of Ethernet frames over DVB.
3. TCP acceleration up to 80Mbps w ith support for up to 10000 concurrent TCP
connections. Typical satellite bandw idth utilization w ith acceleration sw itched on is
around 90%.
4. HTTP acceleration, w hich dow nloads typical w eb pages up to 30% faster on
average.
5. Header compression (Ethernet/IP/UDP) compliant to RFC3095 (ROHC - Robust
Header Compression) is supported at throug hput rates up to 29000 packets per
second one-way, 22000 packets per second tw o-way. Ethernet headers are
typically reduced from 14 bytes to one byte and IP/ UDP headers are typically
reduced from 28 bytes to betw een one and three.
6. Support for Ethernet point-to-point and point-to-multipoint bridging. All netw ork
topologies (including star, mesh and partial mesh) are supported. Transmission
can be unicast, mu lticast or bidirectional.
7. Quality of Service support (IEEE 802.1p) allow ing packet prioritisation.
8. VLAN tagging (IEEE 802.1q) supporting the filtering of traffic streams according to
their VLAN identifier. This can be used in point-to-multipoint operation to filter just
the required packets at any particular re mote modem.
9. Web page real-time d iagnostic graphs that display Tx/Rx throughput (pps and
bps), dropped packets, errored packets, etc. f or both terrestrial and satellite
interf aces.
10. PID filtering to allow particular MPEG2 TS streams to be pulled off at the
demodulator.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-3
11. Transcoding betw een ASI and IP interfaces (allow ing MPEG2 TS packets to be
transmitted on one interf ace and received on the other, interchangeably).
New IP f eatures available as softw are upgrades are constantly in development – please
contact Customer Technical Support for up-to-date details.
6.2.3 Optional L-band BUC Power Supplies
The follow ing PSU options are available for pow ering BUCs:
Part Number BUC PSU
Type
P3531 100W 48V output
A.C. in/D.C. out
P3535 180W 48V output
A.C. in/D.C. out
P3532 100W 24V output
A.C. in/D.C. out
P3536 180W 24V output
A.C. in/D.C. out
P3537 +/-48V input, 180W 48V output
D.C. in/D.C. out
P3538 +/-48V input, 180W 24V output
D.C. in/D.C. out
P3539 +48V input, 180W 48V output
D.C. in/D.C. out
Optional BUC Power Supplies

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-4
The follow ing table show s w hat BUC PSUs are suitable f or a range of available BUC
types.
PSU Required Paradise ODU PSU
Manufacturer & BUC Type
Voltage Wattage Current 24V 48V
24V 72 3A
P3532 -
Terrasat 5W C-band IBUC
48V 72 1.5A
- P3531
24V 108 4.5A
P3536 -
Terrasat 10W C-band IBUC
48V 96 2A
- P3535
24V 72 3A
P3532 -
Terrasat 4W Ku-band IBUC
48V 72 1.5A
- P3531
24V 120 5A
P3536 -
Terrasat 8W Ku-band IBUC
48V 120 2.5A
- P3535
NJR 1W C-band 5665 & 5666
24V 30W -
P3532 -
NJR 2W C-band 5667 & 5668 24V 37.5W -
P3532 -
NJR 5W C-band 5669 & 5670 24V 55W -
P3532 -
24V 130W -
P3536 -
NJR 10W C-band 5662 & 5663
48V 130W -
- P3535
NJR 1W Ku-band 5015 24V 25W -
P3532 -
NJR 1W Ku-band 5075 24V 18W -
P3532 -
NJR 1.5W Ku-band 5035 24V 24W -
P3532 -
NJR 2W Ku-band 5076 & 5016 24V 37.5W -
P3532 -
NJR 3W Ku-band 5037 24V 30W -
P3532 -
NJR 4W Ku-band 5077 & 5017 24V 48W -
P3532 -
24V 170W -
P3536 -
NJR 8W Ku-band 5018
48V 170W -
- P3535
24V 60W -
P3532 -
Codan 5W C-band 6705
48V 60W -
- P3531
Codan 10W C-band 6710 48V 105W -
- P3535
Codan 20W C-band 6720 48V 130W -
- P3535
24V 80W -
P3532 -
Codan 4W Ku-band 6904
48V 80W -
- P3531
Codan 8W Ku-band 6908 48V 115W -
- P3535
24V 120 5A
P3536 -
Paradise 10W C-band VSAT BUC
48V 120 2.5A
- P3535
24V 144 6A
P3536 -
Paradise 20W C-band VSAT BUC
48V 144 3A
- P3535
24V 111 4.6A
P3536 -
Paradise 8W Ku-band VSAT BUC
48V 111 2.3A
- P3535
24V 120 5A
P3536 -
Paradise 10W Ku-band VSAT BUC
48V 120 2.5A
- P3535
Paradise BUC Pow er Supplies

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-5
6.2.4 L-band FSK/ DC Option Card
An FSK/DC option card (part number P3503) is available f or perf orming FSK
communications w ith a BUC. This allows remote monitoring and control of any compatible
BUC via a modulated FSK signal on the IFL cable to the BUC. The card also provides a
DC supply sw itching capability to the BUC. If FSK communications are not required, then
a cheaper option card, namely, the DC Sw itch card (part number P3509) is available.
6.3 Software Options
There are a number of softw are options available as show n in the table below . These can
be ordered at the t ime of the original purchase or can be activated in the field. The
mechanism that provides access to these f eatures is called Softw are Activated Features
(SAF) – the SAF concept (including time-limited free access to all features) is explained in
Section 8.5.
In the table, the SAF Code column lists the acronyms by w hich each feature is referred to
in relation to the modem user interfaces, technical datasheets, etc. Note also that the
feature set is being expanded all the time – please contact Customer Technical Support
for up to date information.
Note that the follow ing are provided in the standard Vision base modem: Tx, Rx, DR0,
DR1, IRS, VIT, WIF, AUPC, HCP and ESC.
Feature SAF Code
Description
Terrestrial data rate 0
to 80Mbps (98Mbps
for ASI)
DR0,
D1L,
D1H,
DR2,
DR3,
DR4,
DR5
Enables data rates in the given range.
DVB-S Tx DVBST Enables DVB-S Txoperation.
DVB-DSNG Tx DSNGT Enables DVB-DSNG Txoperation.
DVB-S2 Tx DVB2T Enables DVB-S2 Tx operation.
DVB-S Rx DVBSR Enables DVB-S Rx operation.
DVB-DSNG Rx DSNGR En ables DVB-DSNG Rx operation.
DVB-S2 Rx DVB2R Enables DVB-S2 Rx operation.
DVB IP DVBIP Enables MPE and ULE DVB over IP
encapsulation (requires P3714 IP Traffic card).
Without this only MPEG2 TS over IP packets can
be processed by the IP Traffic card.
Software Activate d Features

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-6
Feature SAF Code
Description
Viterbi VIT Enables the Viterbi FEC scheme. This is provided
as part of DVB-S.
Intelsat RS IRS Enables the selection of the Intelsat Reed-
Solomon outer FEC. This is provided as part of
DVB-S.
Wideband IF WIF Enables selection of IF frequencies betw een 100
and 180MHz. Th is is provided as standard.
8PSK 8PSK Enables selection of 8PSK modulation. This is
provided as part of DVB-DSNG a nd DVB-S2.
16QAM 16QAM Enables selection of the 16QAM FEC scheme.
This is provided as part of DVB-DSNG.
Constant Coding and
Mod ulation
CCM En ables DVB-S2 CCM mode. This is provided as
part of DVB-S2.
CCM Mu ltistreaming CCMM Extension to DVB-S2 CCM mode that allows two
or more ports of the Quad ASI card to be
mu ltiplexed together on transmit and
demultiplexed on receive. It also allow s ASI and
IP streams to be multiplexed/demultiplexed. In
DVB-S/DSNG, this f eature allow s only the Quad
ASI ports to be multiplexed/demultiplexed.
PRBS PRBS Enables the internal Pseudo Random Bit
Sequence ( PRBS) Bit Error Rat e (BER) tester.
FSK control FSK Enables remote control of a BUC via an FSK
mod ulated signal multiplexed onto the IF cable.
TCP acceleration at
throughput rates up to
80Mbps
TCP,
TCP16,
TCP25,
TCP55
Enables a Perf ormance Enhancing Proxy that
provides acceleration of TCP data over satellite.
Requires P3714 IP Traffic card.
Et hernet brouting BRT Enables Ethernet brouting function (w hich
supports IP traffic point-to-multipoint operat ion
and the use of an indirect return path). Provided
as standard.
TCM TCM Enables the TCM FEC scheme. This is provided
as part of DVB-DSNG.
Header compression HCP Enables Ethernet header compression. Requires
P3714 IP Traff ic card.
Header compression HCP2 Enables IP and UDP packet header compression.
Requires P3714 IP Traffic card.
Web Acceleration WEB En ables accelerated brow sing using HTTP.
Provided free w ith the TCP acceleration feature.
Software Activate d Features (continue d)

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-7
6.4 Front Panel
Modem Front Panel
The front panel co mprises:
• LEDs (light emitting diodes) that provide basic modem status
• A LCD ( liquid crystal display) display that acts as the main user interf ace
• A keypad for alphanumeric entry and menu selection.
6.4.1 LEDs
The five LEDs display w arning and fault information as show n below .
Off Red Amber Green
Unit Status
Not used Unit fault Not used Unit OK
Rx Traffic
Rx fault or Rx
disabled
Not used Not used Rx OK
Tx Traffic
Tx faul t or Tx
disabled
Not used Not used Tx OK
Test Mode
Normal mode Not used Test mode Not used
Tx Carrier
Carrier muted Not used 1-for-1 standby Carrier active
Front Panel LED Status
6.4.2 LCD Display
The backlit LCD is a graphical display f ormatted to give 3 lines of 40 text characters and
is highly legible even in strong ambient light. The right hand side of the display is
reserved for icons that indicate status information pertinent to keypad op eration. These
icons are listed below . The contrast is adjustable and the backlight can be sw itched off or
on.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-8
Local (front panel) control LOC
Remot e control REM
Keyboard locked
Help screen
?
Numeric entry mode 123
Alphabetic entry mode abc
Mod em is on a Tx Edit screen Tx
Mod em is on an Rx Ed it screen Rx
Front Pane l LCD Icons
6.4.2.1 Keypad
The keypad (see the diagram below ) is based on a sealed tactile membrane and allows
full alphanumeric entry and navigation using arrow keys.
Front Panel Keypad

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-9
6.5 Rear Panel
The rear panel, show n below , provides a full set of terrestrial and satellite data interfaces.
Modem Rear Pane l
Full connector pinouts are given in Chapter 11. From lef t to right, the rear panel consists of :
IEC Mains Power Connector/Voltage Selector/Fuse
The modem is designed to operate from a ma ins AC supply of 100-240V (-10%/+6%, i.e.
90V to 254V at the connector), 1 - 0.4A, 47 to 63Hz. The IEC connector incorporates tw o
fuses, independently f using both live and neutral lines. Access to the fuses is provided by a
slide-out tray. Both fuses are standard 20mm type, rated T3.15A, of the slow-blow (timedelay) type. ALWAYS REPLACE THE FUSE WITH ONE OF THE SAME TYPE AND
RATING.
Chassis Ground Stud
This is an M4 stud for connecting a safety earth conductor directly to the chassis of the unit.
Tx IF Output Option
This connector is a BNC female and can be used in either 50Ω or 75Ω-impedance mode.
The output pow er level can be varied from 0dBm to -20dBm.
Tx L-Band Output Option
This connector is a N type female and is of 50 Ω impedance. The output pow er level can
be varied f rom –5dBm to –30dBm.
Alarms and AGC Connector
This is a 15-pin male 'D' type connector that provides access to the four form `C' relay
contacts that indicate alarm conditions. There is also an AGC output.
The alarm relays have the f ollowing default definitions:
Unit Fault: A unit fault exists, i.e. an equipment failure.
Tx Traffic Prompt: Tx traffic fault exists.
Rx Traffic Prompt: Rx traffic f ault exists.
Deferred Alarm: One of the follow ing conditions exists:
• The receive BER is greater than the user defined threshold.
• The receive Eb/No is low er than the user def ined threshold.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-10
Async ESC Connector
This is a 15-pin `D` f emale connector. The I, Q and symbol clock outputs are used to
monitor the receive constellation (allow ing received signal quality to be monitored on an
oscilloscope). This connector also provides the input port for an RS422-compatible Station
Clock. The connector name is historical and no ESC channel is actually available as part of
the satellite service.
On-line LED
This LED mirrors the front panel Tx Carrier LED, so that from the rear of the equip ment the
operator can tell if the carrier is off and which unit of a 1:1 pair is the offline unit.
Terrestrial Interface Connectors
Although there are tw o terrestrial interface connector positions, only one interface card can
be fitted at any one time. Supported interface cards are Quad ASI and IP Traff ic.
Rx IF Input Option
This is a BNC f emale connector and can be used in either 50Ω or 75Ω-impedance mode.
The carrier signal level presented at the input of the modem should be in the range -60dBm
to -30dBm. A level of -45dBm is recommended. The maximum composite pow er level that
should be applied to this port is 30dB above the desired carrier, up to a maximum of 0dBm.
Rx L-Band Input Option
This is a N type fema le connector of 50 Ω impedance. The carrier signal level presented
at the input of the modem should be in the range -20dBm to -70dBm. A level of -45dBm is
recommended. The maximum comp osite pow er level that should be app lied to this port
is +35dBc up to maximum of -10dBm
Fan
There is a fan that runs at all times w hile the unit is pow ered. This draw s air in from the
sides and expels to the rear. The side vents must not be blocked.
1:1 Redundancy Connector
The modem has a built-in 1-for-1 redundancy-controller that connects to the corresponding
port of another modem via a 9-pin male ' D' type connector. A 1:1 redundancy system
requires two modems, a 1:1 control cable betw een the two redundancy connectors, a data
split (`Y`) cable and passive splitters/combiners for the IF ports. An overview of 1-for-1
operation is provided in Section 8.2.
Remote M&C Connector
This is a 9-pin female 'D' type connector. The modem supports the Paradise Universal
Protocol (PUP) as specified in the document ‘Remote M&C Specification for Vision Series
Satellite Modems’. The electrical interf ace can be selected between RS232 (for direct-toPC applications) and RS485 (for multidrop applications).
Etherne t IP and M&C Connectors
There are tw o RJ45 auto-sensing 10/100Mbps Ethernet connections. The base modem IP
Traff ic Ethernet port is unused on the Vision modem ( IP traf fic over satellite requires the
P3714 IP Traff ic option card). The remote M&C Ethernet port supports both half-duplex and
full-duplex operation. M&C control can be via the Simple Netw ork Management Protocol
(SNMP), an embedded w eb server that sends w eb pages to a w eb browser, a Telnet-style

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
6-11
terminal emulation application or via TCP packets that encapsulate Paradise Universal
Protocol (PUP) commands.
An M&C IP address and subnet mask may be set in the modem. Note that the modem is
not conf igured for auto-sense of the cable type and consequently either a straight or
crossover (patch) cable may be required, depending on the equipment being connected
(typically a straight cable is required w hen connecting direct to a PC and a crossover cable
is required w hen connecting to a router or switch).
Station Clock
This connector is a 75Ω BNC female that accepts a 1-10MHz signal, either a square
wave of >1V p/p (e.g. a G.703 para. 10 `synchronising clock`) or a sinusoid at a pow er
level of 0dBm or greater. An alternative Station Clock signal at RS422 interf ace levels can
be applied to the A sync ESC connector. Either signal can be used by the modem as a
reference f or the receive output clock (the Station Clock does not have to be the same
rate as the data as an internal PLL converts between rates). In addition, if the Rx
Clocking is set to use the Station Clock and the Tx Clocking is set to Rx, t hen the Station
Clock also sources the internally generated Tx Clock (Tx and Rx data rates are
independent). If a 10MHz signal is applied, this signal may also be used in place of the
internal reference f or the Tx and Rx IF synthesisers.
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-1
Chapter 7 User Interfaces
The mod em has the follow ing user interf aces:
• A built-in local user interf ace provided via the modem front panel.
• A built-in remote w eb user interf ace that provides w eb pages from the modem (using
a w eb server) to a w eb browser.
There are also serial and Ethernet re mote control interfaces that allow the built-in
interf aces to be replaced or supplemented by an alternative means of modem control.
These use a proprietary command protocol called the Paradise Universal Protocol (PUP).
This can be used either directly over a serial RS232 or RS485 interf ace (e.g. via a
HyperTerminal session) or via Ethernet (e.g. via a Telnet session). The Simple Netw ork
Man agement Protocol (SNMP) v1 and v2c are supported.
7.1 User Names, Passwords and Modem Control
The modem can be controlled by either a local user via the local front panel, or a remote
web user. In addition, a re mote user can either have f ull control over the modem or be
restricted to view ing modem information. Access to the modem is controlled by
passwords. These concepts are explained in the follow ing sections.
7.1.1 Local Mode
On shipping from the factory, the modem defaults to Local mode w hich allow s control of
the modem from the front panel interface only. Web users can, how ever, log in and view
the modem settings w hile the modem is in Local mode.
Note that SNMP is disabled by default and therefore cannot be used as an alternative
method of remote control until it is enabled. When SNMP is enabled, then SNMP
commands are always ob eyed regardless of any user arbitration that is active within the
modem – this point should be taken into account w hen adding new control f acilities to
those already built into the modem.
7.1.2 Giveaw ay M ode
When the modem is sw itched to Giveaw ay mode, a remote w eb user may assume control
of the modem.
For remote w eb brow sing, there are tw o fixed user names, namely, admin and user. The
admin user can view and change the modem configuration, w hile user can only view the
mod em settings. Only ad min can change the tw o passwords associated w ith these tw o
user names.
Only one remote admin user can be logged in to the modem at any time but multiple
users can be logged in as user at the same time. With re mote control users, there is
alw ays an explicit login process, requiring both a valid user name and passw ord to be
entered. Note that remote admin users cannot log in w hile the modem is in Local mode.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-2
A user-settable timeout controls f or how long the admin user is logged in w ithout any user
entry activity – when user entry is detected then the user session is extended by the
length of the timeout p eriod. An admin user can also choose to log ou t of the modem,
which has the effect of closing the brow ser session and allow ing another user to control
the modem.
View -only user login sessions do not use any timeout and are main tained until the
browser session is closed. They are also unaffected by whether the modem is under local
or remote control.
In Giveaw ay mode, control is passed to the first admin user that logs in. If an attempt is
mad e to log in as admin w hen there is already an admin user logged in, then the login w ill
succeed but the user will have view -only permissions, thereby ensuring there can never
be tw o users in control of the modem at the same time.
In order to allow a sw itch back to local control f rom Giveaw ay mode, when there is no
remote admin user logged in, the local front panel interface can gain control at any time
simp ly by issuing a command from the front panel user interf ace. While a remote admin
user is logged in then the local front panel interface is restricted to view ing modem
settings only.
Once a local user has gained control in Giveaw ay mode, they can then change the
mod em back to local control, thereby locking out remote admin users. Note that unless
the sw itch back is done, local front panel interf ace control w ill time out in a similar w ay to
remote admin users and thereby control may be taken aw ay again by a remote admin
user.
During the period betw een an admin user logging out and either another admin login or a
command being issued via the local f ront panel interface to gain control, no user is in
control of the modem.
Although there is no explicit login associated w ith the local front panel interface, there is
an implicit login w hen a key is first pressed. Conceptually, a user at the local front panel
interf ace is logged in as ad min w hen in Giveaw ay mode and th ere is no remote admin
user currently logged in, otherw ise the local f ront panel interface is logged in as a view only user. In Giveaw ay mode, the user at the local front panel interface can explicitly log
out by pressing the Main key.
7.1.3 Takeaway Mode
In Takeaw ay mode, either the user at the local f ront panel interface or a remote admin
user can control the modem at any time. In this mo de there is no restriction on the
number of admin users that can be logged in at one time. When the modem is sw itched
out of Takeaw ay mode to Local mode then a ll remote admin users w ill be automatically
logged out. When it is sw itched from Takeaw ay to Giveaw ay, then all but one instance of
admin users will be automatically logged out. Although technically only one user is in
control at any time, control is relinquished as soon as a command is sent and therefore
different control requests from diff erent users are simply interleaved w ith each other.
Because of this, Takeaw ay mode is best used in circumstances w here there are clear
operational procedures in place to avoid conf licts arising in relation to modem control.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-3
7.2 Front Panel Interface
7.2.1 Keypad Operation
7.2.1.1 Cursor
A cursor (show n in inverse video) is used to highlight the current position on the LCD
display. This is used w hen making menu selections and w hen entering values.
7.2.1.2 Navigation Ke ys
Men us are displayed as a hierarchy of sub-menus. Navigation is performed using either
the arrow and ENTER keys or by entry of the menu identification number that immediately
precedes each menu name.
The Up arrow key navigates between menu options by moving the cursor up one line
except w hen entering a numeric value w hen it increments the digit highlighted by the
cursor. (Note that when entering the values of timeslots to be dropped or inserted the Up
arrow key is used to enter a hyphen.)
The Down arrow key navigates betw een menu options by moving the cursor dow n one
line except w hen entering a numeric value w hen it decrements the digit highlighted by the
cursor. (Note that w hen entering the values of timeslots to be dropped or inserted the
Down arrow key is used to enter a comma.)
The Left arrow key moves the cursor to the left. On a menu this is used to navigate
betw een menu options. When entering an alphanumeric value it moves the cursor to the
preceding digit. The Left arrow key has a special function w hen view ing the system log,
where it is used to move backw ards in the log by 100 entries.
The Right arrow key moves the cursor to the right. On a menu t his is used to navigate
betw een menu options. When entering an alphanumeric value it moves the cursor to the
next digit. The Right arrow key has a special function w hen view ing the system log, w here
it is used to move f orw ards in the log by 100 entries. (Note that w hen entering the values
of timeslots to be dropped or inserted the 0 key pressed together at the same time as the
Right arrow key deletes the character at the cursor.)
The MAIN key returns the user to the MAIN menu from anyw here in the menu hierarchy.
On a menu, the ENTER key is used to navigate to the submenu highlighted by the cursor.
When entering or selecting a new value, the ENTER key is used to accept the new value
and a f urther press of the ENTER key is required to move to the next screen (w ith the
exception of the ‘configure a ll’ function w here one press of the ENTER key provides both
steps). Note that w hen a new value is accepted, it is applied to the modem hardw are
immediately. On some menus, several screens may be chained together in w hich case
pressing the ENTER key w ill move onto the next screen in the chain.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-4
On a menu, the BACK key is used to navigate to the previous screen. When entering or
selecting a new value, the BACK key is used to cancel any change to the current value
and move backw ard to the previous screen.
7.2.1.3 Alphanumeric Ke ys
The alphanumeric keys provide numeric entry. In special cases, w here it is valid to enter
alphabetic characters, repeated pressing of a numeric key w ill cause the key to cycle
through its associated low er case and then upper case alphabetic characters (in a similar
way to a mobile phone).
7.2.1.4 Special Function Ke ys
Help
Help information can be displayed for any M&C control by holding dow n the 0 key and
pressing the Left arrow key together while the screen containing the M&C control is
displayed. This brings up scrollable text that explains the M&C control’s f unction.
Pressing the 0 key and Left arrow key together for a second time removes the Help text
and reverts the display back to its previous contents.
Keyboard Lock
The keypad can be locked against inadvertent use by holding dow n the 0 key and
pressing the MAIN key together at the same time. Pressing the tw o keys again at the
same time unlocks the keypad.
LCD Contras t
The contrast of the LCD display can be adjusted by holding dow n the 0 key and pressing
the Up (or Down) arrow key together at the same time. The Up arrow key increases the
contrast and the Down arrow key decreases the contrast.
LCD Backlight
The LCD backlight can be sw itched off or on by holding dow n the 0 key and pressing the
ENTER key together at the same time.
Log/Alarm Clear
The system log and system alarms can be cleared by pressing the 0 key w hen on the
relevant log or alarm d isplay screen.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-5
7.2.2 LCD Screen Layout
The front panel user interface uses a menu system to present choices to the user. These
in turn allow either the selection of a value from a list of options or require the entering of
a new value. Examples of these types of screen are show n below .
Screen Type 1: Menu Selection from Pre-defined Numeric Lis t
Note that the menu title is show n on the top line and it show s the nested menu hierarchy
(similar to brow sing folders on a PC, w here each level is reflected in the current path
name). Menu options are show n as both a highlit number (w hich can be pressed directly
on the keypad to select the menu option) or, alternatively, the arrow keys can be used to
highlight a particular option, w hich can then be selected using the Enter key. The
numbers are highlit only in order to differentiate them f rom the menu option text.
Screen Type 2: Entr y of Numeric Value
Screen Type 3: Menu Selection from Scr ollable List
Note that on a scrollable menu the Up and Down arrow keys are used to scroll through
the available options.
Note that features that are not available appear on the display in strikethrough (e.g. Rate
7/8). There are several reasons w hy a feature may not be available:
• The feature is a Softw are Activated Feature (SAF) and the appropriate SA F code has
not been enabled. Please contact Parad ise Sales w ho can issue a SAF key to unlock
the feature. Alternatively, all SAF features can be enabled for a limited time as
described in Section 7.3.3.3.6 (Edit-Unit-Advanced-SAF Code screen).

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-6
• The feature is available but its use is precluded by the current operational modem
settings.
7.3 Front Panel Menu Structure
The men u hierarchy for the f ront panel is described in this section.
7.3.1 M ain Menu
The Main menu can be accessed from any display by pressing the MAIN key. It is from this
menu that all functions are selected.
It contains the follow ing sub-menus:
Status Displays modem operational status summary information.
Edit Allow s modification of all modem configurable properties.
View Displays detailed operational status and read-only configurable property
values.
Test Controls the selection of test modes.
A user-settable Modem Identifier is show n on the top line of the screen and is typically used
to specify the physical location of the modem or identify the modem satellite link. This can
be set as described in Section 7.3.3.3.1.
Main: [London-New York]
1Status 2Edit
3View 4Test

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-7
7.3.2 Status Me nu
Note that the 1-for-N and BUC menu options are show n on the screen above for
convenience – in practice it is necessary to scroll dow n to access these options as they
are off-screen. The Status menu contains the current modem status split over several
screens. The 1-f or-N screen is not available unless the modem is the standby modem
built into a 1-for-N redundancy sw itch (the 1-for-N redundancy switch user interf ace is
documented separately in the document Installation and Operating Handbook for
Evolution and Vision Series Redundancy Switch).
Status-Setup Screen
This screen is constantly updated w ith the follow ing information:
• Transmit frequency
• Receive frequency
• Transmit terrestrial data rate
• Receive terrestrial data rate
• Transmit symbol rate
• Receive symbol rate
Status-Traffic Screen
This screen is constantly updated w ith the follow ing information:
Status :
1Setup 2Tr affic 3De m odulator
4Eb/No 5BER 6Power
71-for-N 8BUC
Tx:140.0000MHz Rx:7 0.0000MHz
19500000bps 7437366bps
13109481sps 5000000sps
Tx OK since 10:14:46 on 6/4/08
Rx OK since 10:14:46 on 6/4/08
Carr ier:Norm al

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-8
• When there is no transmit path fault then the message ‘Tx OK since HH:MM:SS on
DD/MM/YY’ is displayed (w here ‘HH’ indicates hours, ‘MM’ indicates minutes, ‘SS’
indicates seconds, ‘DD’ indicates the day of the month, ‘MM’ indicates the month of
the year and ‘YY’ indicates the year). When a transmit path fault exists then a fault
message is displayed instead that indicates the nature of the fault.
• When there is no receive path fault then the message ‘Rx OK since HH:MM:SS on
DD/MM/YY’ is displayed (w here the time and date format is as explained above).
When a receive path fault exists then a fault message is displayed instead that
indicates the nature of the fault.
• The trans mit carrier status, w hich displays one of the follow ing.
o 'Nor mal': the carrier is on.
o 'Mute-Ext': the carrier is muted due to an alar m detected by the modem
hardw are.
o 'Mute-Ter': the carrier is muted due to either the terrestrial Tx RTS pin being
active (this is an input signal that can be used to mute the carrier under
external control as required) or some other proble m being experienced w ith
the terrestrial interface.
o 'Mute-1:1': the carrier is muted due to being the Standby modem in a 1-for-1
Standby system.
o 'Mute-Brk': the carrier is muted due to a pow er outage.
o 'Mute-Flt': the carrier is muted due to an alar m detected by the modem
softw are.
o 'Mute-Cfg': the carrier is muted due to the modem being in the process of
reconfiguring.
o 'Mute-Off ': the carrier has been muted by the user.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-9
Status-Dem odulator Screens
Navigation betw een the three demodulator status screens is via the Up and Down arrow
keys. The screens are constantly updated w ith the follow ing information:
• The receive path Eb/No figure (energy per bit to spectral noise density ratio).
• The receive path Es/ No figure (energy per symbol to spectral noise density ratio).
• The receive path Modulation Error Ratio (MER). This is a measure of how far away
the points in the received constellatio n are f rom their ideal positions due to phase
noise, etc. Due to the sharp ‘w aterfall’ eff ect present in DVB-S2 BER curves, a
mod em can go from error free to losing demodulator lock in a small fraction of a dB;
MER can help determine how close the modem is operating to this edge.
• The receive path final bit error rate (B ER).
• The receive path pow er level.
• The receive signal frequency offset from the carrier centre f requency. This is the
measured error of the received carrier, relative to the expected frequency. It can be
used to determine any frequency shif t due to the satellite and frequency conversion
equipment.
Eb/No:6.3dB BER:<1.0 E-12
Rx power:-33dBm
Freq offset:0.1Hz
Es /No:8.1dB BER:<1.0E-12
Rx power:-33dBm
Freq offset:0.1Hz
MER:9.7dB BER:<1.0 E-12
Rx power:-33dBm
Freq offset:0.1Hz

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-10
Status-Eb/No Screen
This screen shows the receive path Eb/No f igure (energy per bit to spectral noise density
ratio) in large font for easy view ing. It show s the user-settable Modem Identifier on the
bottom line of the screen.
Status-BER Scre en
This screen shows the receive path final bit error rate (BER) in large font for easy view ing.
It shows the user-settable Modem Identifier on the bottom line of the screen.
Status-Power Screen
This screen shows the receive signal pow er level in large font for easy view ing. It shows
the user-settable Modem Identifier on the bottom line of the screen.
Eb/No: >15dB
ID:London-New York
BER: 1.0E-12
ID:London-New York
Rx power: -38dBm
ID:London-New York

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-11
Status-BUC Screen
This screen is available only on L-band modems. It is updated w ith the follow ing
information:
• Output: this is the output pow er in dBm at the w aveguide flange, or Off if the BUC is
not transmitting.
• Mode: in Terminal (closed loop) mode, this presents the Terminal RF output pow er
level (i.e. the modem output pow er to the BUC) and the BUC attenuation level. In
open loop mode, Terminal RF and BUC attenuation data is not show n and instead the
mod e is show n as Independent.
• Status: this show s the temperature in degrees Centigrade reported by the BUC.
• Type: this field shows the BUC pow er class in Watts and the BUC current level in
Amperes.
Output: 40.0dBm
Mode: Te rminal RF: -15.3dBm BUC: -10.0dB
Status : 25ºC Type: 10W 12.8A

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-12
7.3.3 Edit Me nu
This menu contains the following options:
• All. This option leads the user through the most commonly used modem settings,
giving a quick w ay of setting up the modem. The sequence can be terminated at any
time by pressing the MAIN key.
• Tx. This selects the transmit path edit submenu, w hich allow s all of the modem Tx
properties to be changed.
• Rx. This option selects the receive path edit submenu, w hich allows all of the modem
Rx properties to be changed.
• Unit. This selects the unit edit submenu. This allow s all of the modem properties that
are independent of the Tx and Rx paths to be changed.
• Memories. This option selects the configuration memory submenu, w hich allow s the
mod em configuration to be saved or a previous configuration to be recalled.
7.3.3.1 Edit-Tx M enu
This menu contains the following options:
• Interface. This option allows Tx-specif ic terrestrial interf ace options to be set.
• Mode. This option controls the selection of DVB mode and submodes.
• Baseband. This submenu controls DVB-S2 input stream synchronization w hen
mu ltiple data streams are present.
• FEC-Mod. This subme nu controls Forw ard Error Correction (FEC) and modulat ion
options including modulation type, FEC rate, pilot tones and frame size.
• Carrier. This leads to a submenu that a llow s the carrier, frequency, pow er, spectrum
inversion and spectrum roll-off to be controlled.
Edit:
1All 2Tx 3Rx
4Unit 5Memories
Edit/Tx:
1Interface 2Mode 3Baseband
4FEC-Mod 5Carrie r

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-13
7.3.3.1.1 Edit-Tx-Interface Screen
Options :
ASI
Selects the Quad ASI card as the source of Tx data.
Only available w hen the P37 10 Quad ASI card is fitted.
IP
Selects the IP card as the source of Tx data.
Only available w hen the P37 14 IP Traffic card is fitted.
Factory default: Depends on hardw are that has been fitted.
Description: This selects the terrestrial data source for the Tx path. The ports on the
Quad ASI card can be individually configured using the
Edit/Unit/Interface/ASI menu option. The IP traffic card settings can be
configured using the Edit/Unit/Interface/IP menu option.
7.3.3.1.2 Edit-Tx- Mode Screen
Options :
DVB-S
Selects DVB-S/DVB-DSNG mode. DVB-S and DVB-
DSNG FEC and
mod ulation options w ill only be available if the respective SAF features
have been enabled.
DVB
-S2
Selects DVB-S2 mode. Af ter selecting this, pressing ENTER for a second
and then a third time w ill allow both the submode of DVB-S2 to be set
(CCM, VCM/ACM) an d the transport mode (Transport, Generic
Edit/Tx/Tx te rrestrial interface :
[ASI]
New :[IP]
Edit/Tx/DVB m ode:
[DV B-S]
New :[DVB-S2]
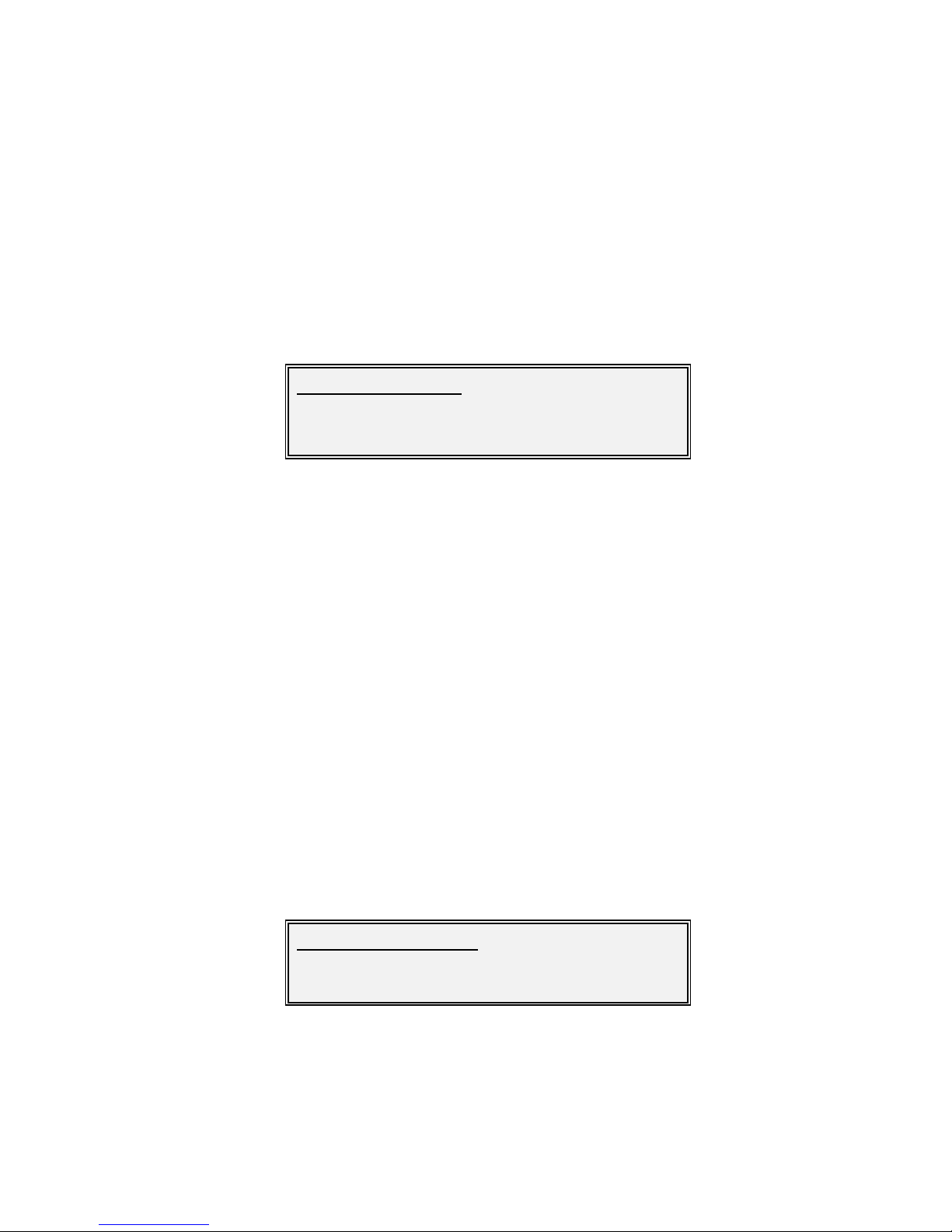
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-14
Continuous, Generic Packetised).
Factory
default:
DVB-S
Description: Controls DVB mode selection.
Edit-Tx-Mode DVB-S2 Mode Screen
Options :
CCM
Selects DVB-
S2 CCM (Constant Coding and Mo dulation) mode. This
applies constant FEC rate and modulation to each DVB-S2 frame.
VCM
Selects DVB-
S2 VCM (Variable Cod ing and Modulation) mode. This
mod e allow s diff erent FEC rates and modulation to be applied to each
data stream.
Factory
default:
CCM
Description: Controls DVB-S2 mode selection. After selecting this, pressing ENTER
for a second w ill allow the DVB-S2 transport mode (Transport, Generic
Continuous, Generic Packetised) to be set.
Edit-Tx-Mode Transport M ode Screen
Edit/Tx/DVB-S2 mode:
[DV B-S]
New :[DVB-S2]
Edit/Tx/Transport m ode:
[Trans port]
New :[Generic Continuous]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-15
Options :
Generic Packetised
This selects the Generic Packetised mode w ithin DVB-
S2. This should be
selected w hen the terrestrial data is IP and the packets are all of the
same fixed length.
Generic Continuous
This selects the Generic Continuous mode w ithin DVB-
S2. Th is should be
selected w hen the terrestrial data is IP
and the size of the packets is
unknow n or variable.
Transport
This selects the MPEG2 Transport Stream ( TS) mode w ithin DVB-
S2.
This should be selected w hen the terrestrial data is MPEG2 TS i.e. w hen
the Quad ASI interface is selected.
Factory
default:
Generic Continuous
Description: This selects the stream type w ithin DVB-S2.
7.3.3.1.3 Edit-Tx-Base band Menu
This menu contains support for DVB-S2 multiple streams. The current version of the
softw are supports single stream CCM mode only. Consequently this menu is reserved for
future use.
7.3.3.1.4 Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod Menu
Note that option 7 is shown above on the same screen for convenvience but the Down
arrow key must be used to scroll down to this in practice.
This menu allows configuration of modulation type, pilot tones, frame size, code rate,
data/symbol rate and scrambler settings.
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod:
1Modulation 2Pilots 3Frame type
4Code rate 5Maintd rate 6Info rate
7Scrambler
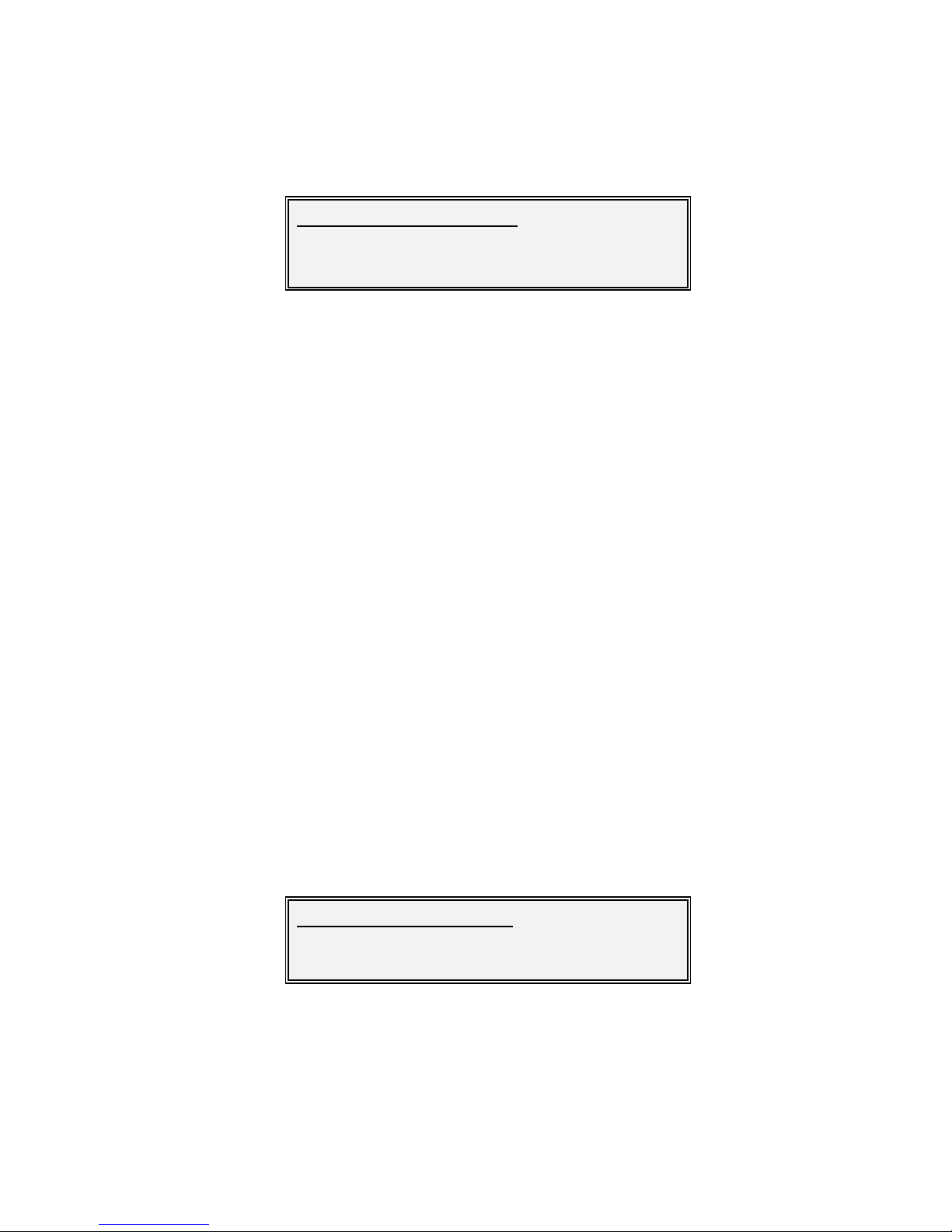
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-16
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Modulation Screen
Options :
QPSK
8PSK
Valid only in DVB-S2 mo de or in DVB-S mode w hen the DVB-
DSNG
SAF is enabled.
16QAM
Valid only in DVB-S mode w hen the DVB-DSNG SAF is enabled.
16APSK
Valid only in DVB-S2 mode.
Factory
default:
QPSK
Description: Selects the modulation type for the Tx path. After selection, if the
ENTER
key is pressed again then the FEC code rate is displayed and can be
changed.
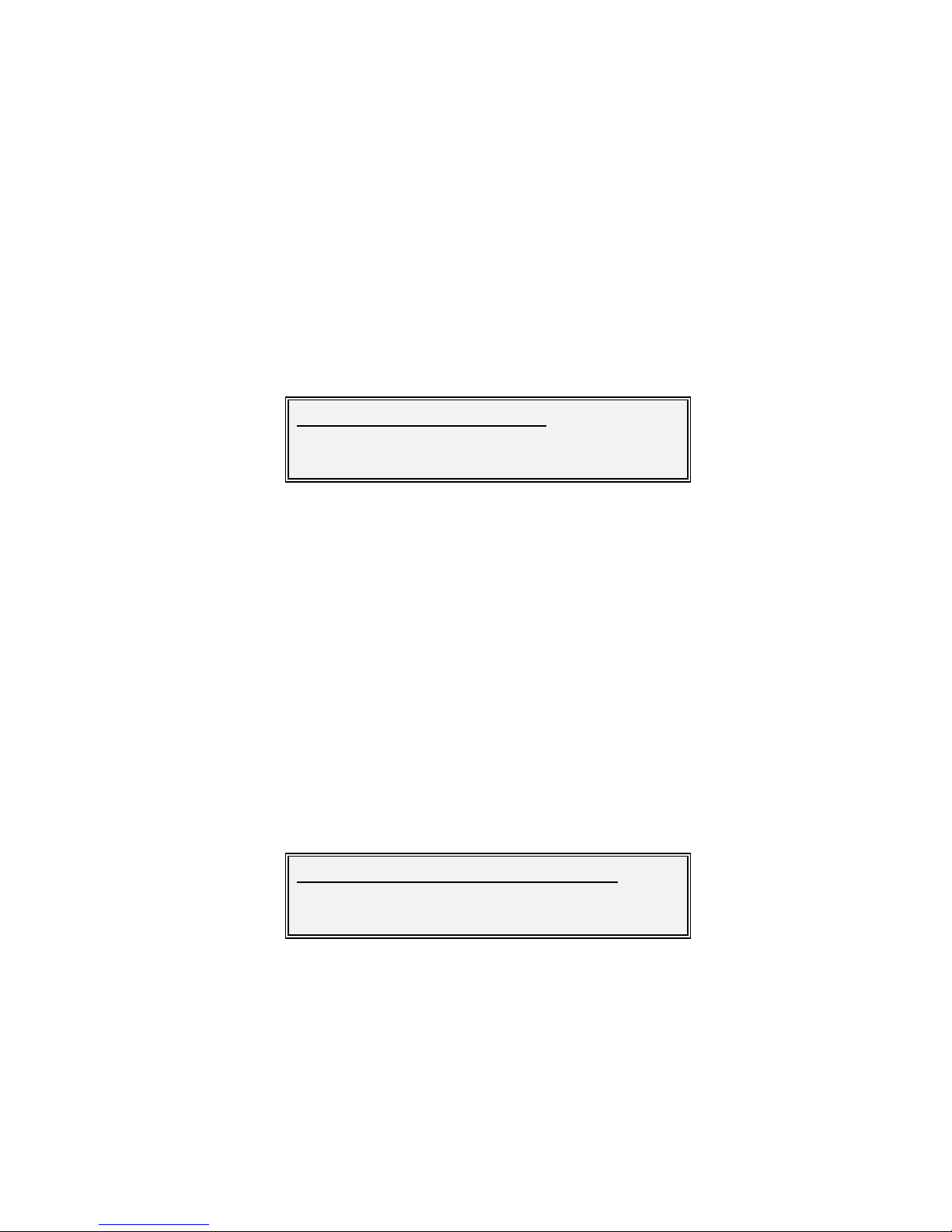
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Pilots Screen
Options :
Off
On
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/M odulation:
[16APSK]
New :[8PSK]
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/Pilot tones:
[Off]
New :[On]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-17
Factory default: Off
Description: Pilot tones are an optional part of DVB-S2. They provide an
unmodulated tone at regular intervals in th e transmitted data that can
help receivers
to lock and stay in lock particularly w hen using higher
order modulation schemes in noisy environments. They add an overhead
of around 2.5% to the transmitt ed data.
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Frame Type Screen
Options :
Short
Selects a DVB-S2 frame size of 16200 bits.
Normal
Selects a DVB-S2 frame size of 64800 bits.
Factory default: Short
Description: Sets the DVB-S2 FEC frame size.
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-
Code Rate
Screen
Options :
1/4
1/3
2/5
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/FEC frame size:
[Norm al]
New :[Short]
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/Code rate/FEC code rate:
[8/9]
New :[5/6]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-18
1/2
3/5
2/3
3/4
4/5
5/6
7/8
8/9
9/10
Factory default: 1/2
Description:
Selects the FEC code rate. The rates that are available depend on the
particular DVB mode and modulation scheme that have been selected.
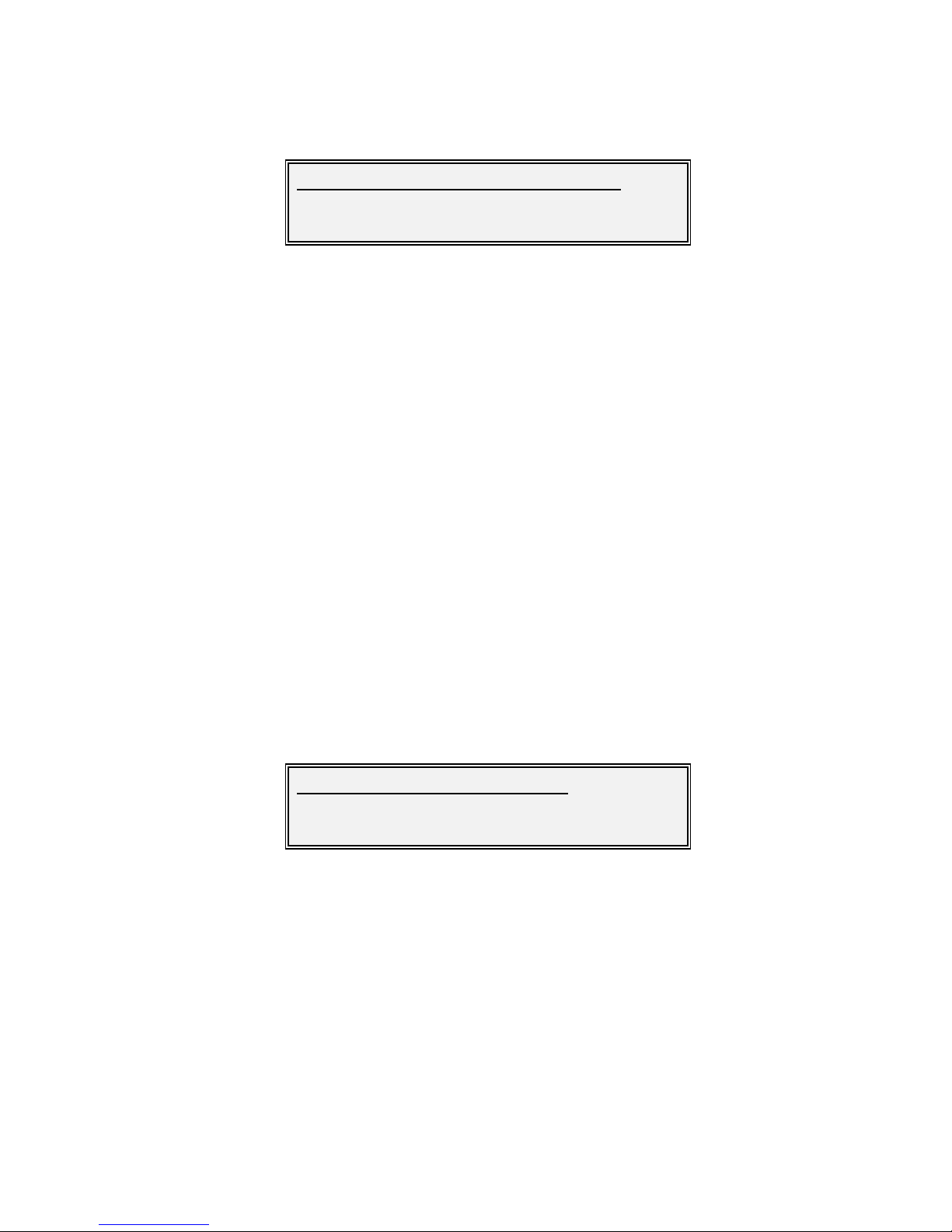
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Maintained Rate Screen
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-19
Options :
Data rate
This option keeps the terrestrial data rate constant at all times.
Symbol rate
This option keeps the modulated symbol rate rate constant at all
times.
Factory
default:
Data rate
Description:
This option allow s either the modulated symbol rate or terrestrial data
rate to be kept consta
nt w hen modifying modulation and coding
parameters.
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Inform ation Rate Screens
One of the tw o follow ing screens will be displayed depending on w hether the Maintained
rate is set to Data rate or Symbol rate.
Factory default: 50000
Description: Sets the terrestrial data rate for the Tx path. It needs to be ensured that
data coming in to the modem from the selected terrestrial interface does
not exceed this rate, otherw ise data w ill be lost.
Note that it is possible to choose whether to maintain data rate and vary
symbol rate or vice versa (see Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Maintained Rate
Screen) w hen changing modulation and coding settings. The Data rate
screen above is only available w hen the Maintained rate is set to Data
rate.
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/M aintd rate/M aintain rate:
[Data rate ]
New :[Sym bol rate]
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/Info r ate/Data rate :
[010000000]
New :[010000000] 50000-98000000bps

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-20
After entering the data rate, if the ENTER key is pressed again then the
symbol rate is displayed (but cannot be altered).
Factory default: 100000
Description: Sets the symbol rate rate for the Tx path.
Note that it is possible to choose whether to maintain data rate and vary
symbol rate or vice versa (see Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Maintain Rate Screen)
when changing modulation and coding settings. The Symbol rate screen
above is only available w hen the Maintained rate is set to Symbol rate.
After entering the symbol rate, if the ENTER
key is pressed again t hen
the data rate is displayed (but cannot be altered).
Edit-Tx-FEC-Mod-Scrambler Screen
Factory default: 0
Description: This sets the DVB-S2 Physical Layer scrambler signature.
This is used
in scrambling the contents of the physical layer f rames (other than the
header) for improved energy dispersal, reducing interference betw een
different signals.
Scrambling sequences are constructed by combining
the output of tw o generator polynomials into a co mplex sequence know n
as a ‘Gold’ code. Setting thi
s to 0 avoids both having to set a value at the
receiver and any unw anted synchronization delay.
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/Info r ate/Symbol rate:
[15167598]
New :[ 15167598] 100000-45000000sps
Edit/Tx/FEC-Mod/Scrambler seed:
[00000]
New :[00000] 0-262141

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-21
7.3.3.1.5 Edit-Tx-Carrier Menu
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• Enable. This controls the carrier (on/off).
• Power. This option controls the output pow er level.
• Frequency. This sets the frequency used to transmit to the satellite.
• Inversion. This controls whether the I and Q channel outputs are swapped, to give
spectrum inversion.
• Roll-off. This controls the gradient on the sloping shoulders of the transmit spectral
mask and therefore can be used to control occupied bandw idth and channel spacing.
• Advanced. This gives access to a BUC control menu on L-band modems.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Enable Screen
Options :
Off
The carrier is off.
On
The carrier is on and w ill remain on even after the equipment is sw itched
off and on again.
On-mute if outage (mute if power break)
Mute on pow er break requires conf irmation of transmission (i.e. selecting
Edit/Unit/Advanced/Operation and selecting Ack Pwr Bre) f ollow ing a
pow er outage.
RTS enabled
When RTS is enabled then the carrier is controlled by the interface RTS
line.
Edit/Tx/Carrier:
1Enable 2Power 3Frequency
4Inversion 5Roll-off 6Advanced
Edit/Tx/Carrier/Carrier mode:
[On]
New :[Off]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-22
Factory
default:
Off
Description:
Tx carrier control.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Power Screen (IF Modem)
Units : dBm
Minimum value : -25.0
Maxim um value: 0
Step size: 0.1
Factory default: -25.0
Description: Tx IF output pow er level.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Power Screen (L-band M odem)
Units : dBm
Minimum value : -30.0
Maxim um value: -5
Step size: 0.1
Factory default: -30.0
Description: Tx L-Band output pow er level.
Edit/Tx/Carrier/IF output power:
[-15.0]
New :[-10.0] -25-0dBm
Edit/Tx/Carrier/RF output power:
[-15.0]
New :[-10.0] -30-(-5)dBm

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-23
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Freque ncy Screen (IF Modem)
Units : MHz
Minimum value : 50.0000
Maxim um value: 180.0000
Step size: 0.0001
Factory default: 70.0000
Description: Tx IF frequency used to transmit to satellite. Note that values betw een
90 and 100MHz cannot be selected.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Freque ncy Screen (L-Band Modem)
Units : MHz
Minimum value : 950.0000
Maxim um value: 1950.0000
Step size: 0.0001
Factory default: 950.0000
Description: Tx L-Band frequency used to transmit to satellite.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Inversion Screen
Edit/Tx/Carrier/IF carrier freq:
[070.0000]
New :[070.0000] 50-90, 100-180MHz
Edit/Tx/Carrier/RF carrier freq:
[950.0000]
New :[950.0000] 950-1950MHz
Edit/Tx/Carrier/Tx spectral inversion:
[On]
New :[Off]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-24
Factory default: Off
Description: Controls w hether the I and Q channel outputs are sw apped. This is
sometimes required f or correct interoperation w ith other manufacturer’s
equipment.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Roll-off Screen
Options :
35%
25%
20%
Factory default: 35%
Description: Controls the gradient on the sloping shoulders of the transmit spectral
mask and therefore can be used to control occupied bandw idth and
channel spacing.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Menu
The follow ing BUC screens are available only on L-band modems.
This menu contains the follow ing options:
Edit/Tx/Carrier/Filter roll-off:
[35%]
New :[25%]
Edit/Tx/Carrier/Advanced/BUC :
1Power offs et 2BUC type 3PSU
4Re ference 5Output 6Attenuation
71-for-1

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-25
• Power offset. This allows the user to set the system gain or loss af ter the modem,
so the modem can display the transmit carrier level in terms of either the transmit
pow er or EIRP, measured in dBm or dBW.
• BUC type. Allows the type of BUC to be selected from a list of supported BUCs,
with the option of either open loop control (Independent mode) or closed loop
control (Terminal mode). In closed loop mode, the modem attempts to maintain a
constant BUC output pow er by adjusting the modem output pow er and BUC
attenuation level.
• PSU. If the modem is fitted with an internal DC pow er supply option then this screen
allows the user to turn on or off the DC pow er supply to the BUC.
• Reference. This controls whether the modem provides a 10MHz reference signal to
the BUC.
• Output. Turns the BUC RF output on or off .
• Attenuation. This allow s the user to vary the BUC attenuator level.
• 1-for-1. This controls w hether BUC services (i.e. DC supply and 10MHz reference)
stay w ith the on-line modem or sw itch to the standby modem w hen a 1-f or-1
sw itchover occurs in a 1-f or-1 redundant pair of modems. Note that FSK
communications w ill alw ays be switched over.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Pow er Offset Screen
Units : DBm/dBw
Minimum value : -99
Maxim um value: +99
Step size: 0.1dB
Factory default: 0
Description: This screen allows the modem to display and the user to edit the final
SHF pow er instead of the IF carrier level. Use the up/dow n arrow s to
change the sign. Once set, the user is navigated to the Tx pow er units
selection screen.
./Tx/Carr ier/Advanced/BUC/Tx power offset:
[-00.0]
New :[-00.0] -99.9-99.9dB

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-26
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Pow er Units Screen
This allows the user to set the modem to display and edit the Tx carrier level in terms of
either the Tx Pow er or EIRP, measured in dBm or d BW.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Type Screen
Options :
None
There is no BUC a ttached or it is controlled independently.
Other
If you are not using a Paradise BUC, select Other and manually
configure the BUC parameters.
RFT5000 Ku
Uses RS485 comms to RFT5000. LO frequency: 15450 MHz.
User
FSK enabled, but user must set LO frequency of BUC.
C5.85 – 6.725 GHz (CODU)
Uses RS485 comms to CO unit. LO frequency: 4900MHz.
Ku 14 – 14.5 GHz (CODU)
Uses RS485 comms to CO unit. LO frequency: 13050MHz.
./Tx/Carr ier/Advanced/BUC/Tx power units:
[dBm]
New :[dBw ]
./Tx/Carr ier/Advanced/BUC/BUC type:
[None]
New :[C 5.8 – 6.425 GHz]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-27
Ext Ku 13.75 – 14.5 GHz (CODU)
Uses RS485 comms to CO unit. LO frequency: 12800MHz.
RFT5000 C
Uses RS485 comms to RFT5000. LO frequency 4900 MHz.
C 5.8 – 6.425 GHz (VSAT)
Only available if FSK option fitted. LO frequency: 4900MHz.
PALAPA 6.425 – 6.725 GHz (VSAT)
Only available if FSK option fitted. LO frequency: 5475MHz.
INSATC 6.725 – 7.025 GHz (VSAT)
Only available if FSK option fitted. LO frequency: 5775MHz.
Ku 14.0 – 14.5 GHz (VSAT)
Only available if FSK option fitted. LO frequency: 13050MHz.
Offset Ku 13.75 – 14.25 GHz (VSAT)
Only available if FSK option fitted. LO frequency: 12800MHz.
Factory
default:
None
Description
Allow s the user to select from a number of Paradise BUCs or Other if
another manufacturer’s BUC is being used. If an option other than None
is selected, then the user is taken to the following Terminal Mode screen.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Te rm inal Mode Screen
This allows the user to select either open loop control (Independent mode) or closed loop
control (Terminal mode). In closed loop mode, the modem attempts to maintain a constant
BUC output pow er by adjusting the modem output pow er and BUC attenuation level. In
./Carrier/Advanced/BUC/BUC term inal m ode:
[Off]
New :[On]
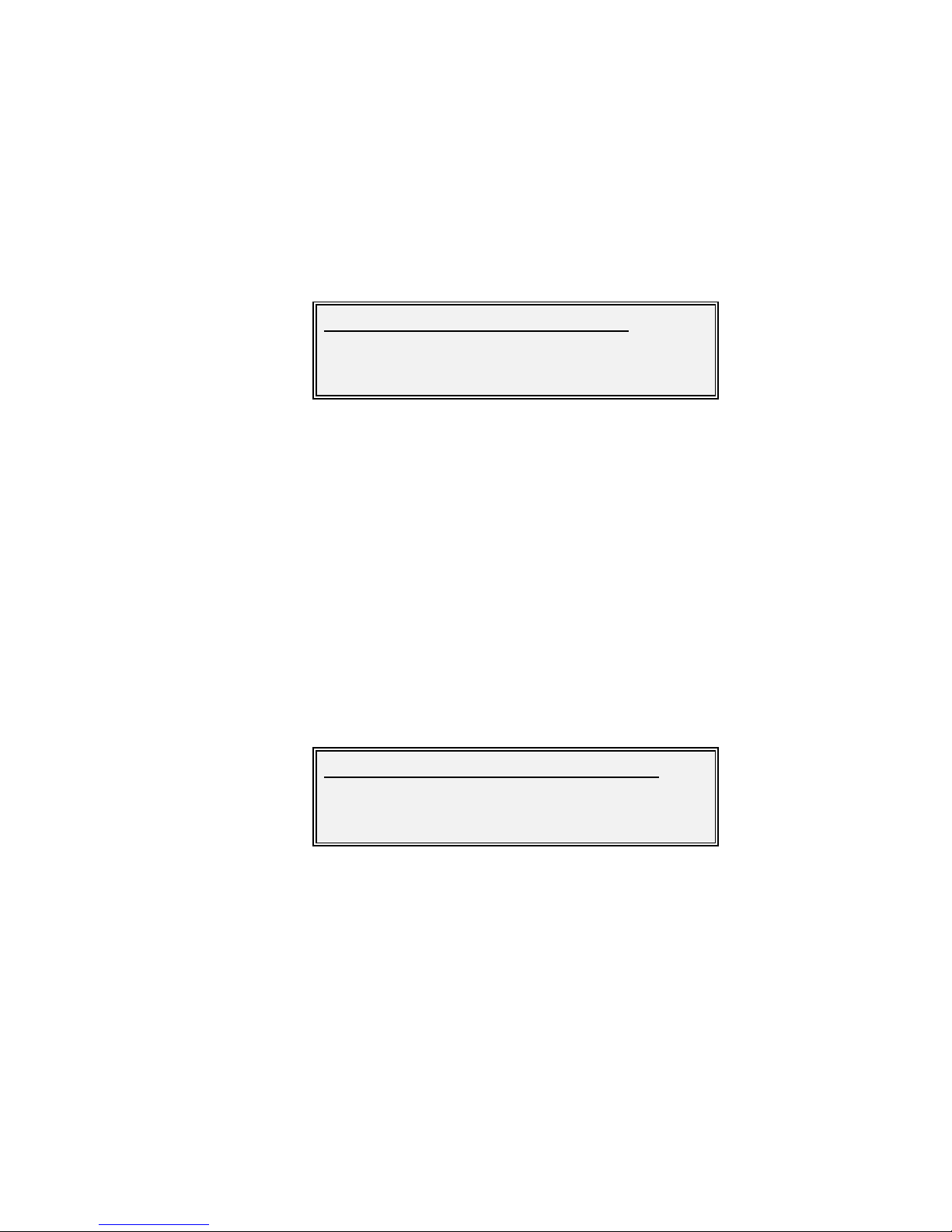
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-28
open loop mode, no feedback f rom the BUC is used. Once a selection has been made and
if the BUC type has been set to Other then the follow ing SHF Frequency Offset screen is
displayed.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Freque ncy Offset Screen
Units : GHz
Minimum value : -99.999
Maxim um value: 99.999
Step size: 0.0000001GHz
Factory default: 0.000
Description:
This screen allow s the modem to be set to display and edit the final SHF
frequencies instead of the IF frequencies. When the BUC type has been
set to a know n Paradise BUC and the modem has the FSK
communications option then this setting is done automatically and the
men u option to manually set the frequency shift is not presented.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Pow er Screen
Units : W
Minimum value : 0
Maxim um value: 999
Step size: 1W
Factory default: 0.000
Description: This screen tells the modem w hat the BUC pow er class is. How ever,
this can be ignored unless a CO has been selected, w ith a pow er output
greater than 170W.
./Carrier/Advanced/BUC/SHF freq offset:
[+12.80000000]
New :[+12.80000000] -99.999-99.999GHz
./Carrier/Advanced/BUC/Powe r if over 170W:
[000]
New :[000] 0-999W

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-29
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC DC Supply Screen
This screen allows the user to control the DC to the BUC. Either +48V DC 3A (200W) or
+24v DC 5.5A (200W) may be sourced via the coax (line pow ered) if the BUC pow er
supply option is fitted.
Severe damage may occur if a DC supply is fed to a BUC not
configured to be `Line powered`.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC 10MHz Reference Screen
By selecting On, the modem’s internal 10MHz reference signal can be sourced from the
mod em up the coaxial site cable to the BUC.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Output Screen
This sw itches the BUC Tx carrier on and off independently of the modem’s Tx carrier
on/off control. This may be useful w here one BUC carries several carriers (passively
combined but w ith one modem providing DC/10MHz Ref/FSK) and you w ish to mute all
the carriers.
./Carrier/Advanced/BUC/DC supply voltage:
[Off]
New :[On]
./Carrier/Advanced/BUC/10MHz reference :
[Off]
New :[On]
./Tx/Carr ier/Advanced/BUC/BUC carrier:
[Off]
New :[On]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-30
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC Attenuation Screen
Units : dB
Minimum value : 0
Maxim um value: -15
Step size: 1dB
Factory default: 0
Description:
This allow s the user to vary the attenuator in t he BUC. Typically this is
used w hen there is a short run from the modem to the BUC made w ith
reasonable quality cable, and w here with a low loss the minimum outp
ut
from the modem could saturate the BUC input unless the attenuator
(early in the BUC gain profile) is set suitably high.
If in doubt alw ays start w ith the minimum modem Tx Carrier level and the
maximum BUC attenuation.
Edit-Tx-Carrier-Advanced-BUC-1-for-1 Screen
This controls w hether BUC services (i.e. DC supply, 10MHz reference and FSK
communications) stay with the on-line modem or sw itch to the standby modem w hen a 1for-1 sw itchover occurs in a 1-f or-1 redundant pair of modems.
7.3.3.2 Edit-Rx Menu
./Advanced/BUC/BUC attenuation:
[-15]
New :[0] -15-0dB
./BUC/Mute services in Standby:
[Off]
New :[On]
Edit/Rx:
1Interface 2Mode 3Baseband
4FEC- Demod 5Carrier 6Rx=Tx

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-31
This menu contains the following options:
• Interface. This option allows Rx-specif ic terrestrial interface options to be set.
• Mode. This option controls the selection of DVB mode and submodes.
• Baseband. This submenu controls DVB-S2 stream synchronization w hen multiple
data streams are present.
• FEC-Mod. This subme nu controls Forw ard Error Correction (FEC) and modulat ion
options including modulation type, FEC rate, pilot tones and frame size.
• Carrier. This leads to a sub menu that allows the receive frequency, spectrum
inversion and spectrum roll-off to be controlled.
• Rx=Tx. This option a llow s the receive path to be automat ically configured to be the
same as the trans mit path, thereby simplifying set up. There are a number of
exceptions including carrier frequency and spectral inversion.
7.3.3.2.1 Edit-Rx-Interface Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
7.3.3.2.2 Edit-Rx-Mode Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
7.3.3.2.3 Edit-Rx-Baseband Menu
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
7.3.3.2.4 Edit-Rx-FEC-De mod Menu
Note that options 7 and 8 are shown above on the same screen for convenvience but the
Down arrow key must be used to scroll dow n to these in practice.
This menu allows configuration of modulation type, pilot tones, f rame size, FEC rate,
data/symbol rate, scramb ler settings and sw eep width.
Edit/Rx/FEC- Dem od:
1Modulation 2Pilots 3Frame type
4FEC rate 5Data rate 6Sym rate
7Scrambler 8Sweep

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-32
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Modulation Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Pilots Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Frame Type Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-FEC Rate Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Data Rate Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Sym bol Rate Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-FEC- Demod-Scramble r Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-Dem odulation-Sweep Screen
Options :
Normal
In this mode the sw eep w idth is controlled automatically by the modem.
The w idth is alw ays set to +/-32kHz by the modem.
Other
Edit/Rx/FEC- Dem od/Sweep mode:
[Norm al]
New :[Other]
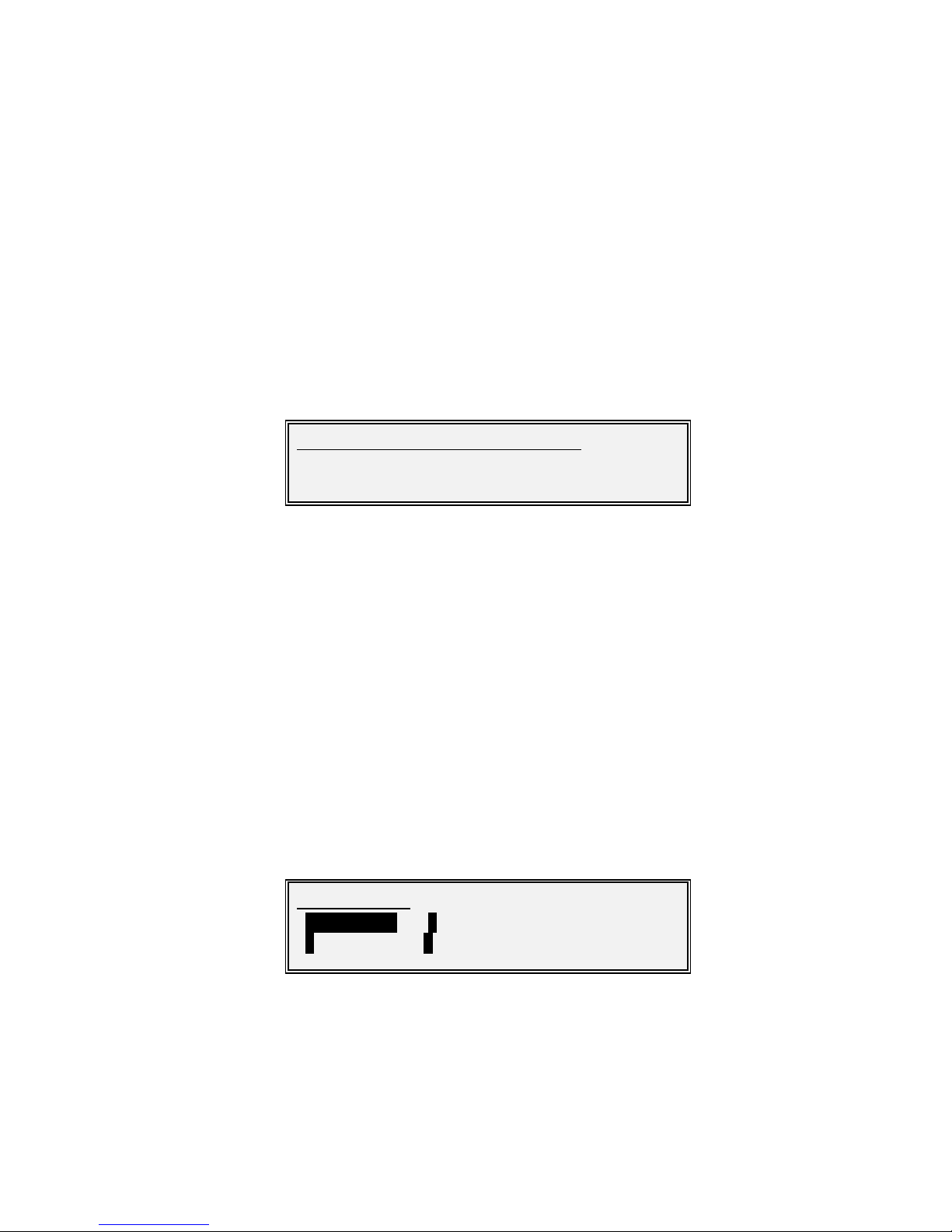
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-33
This mode allow s the user to set the sw eep w idth in order to compensate
for carr
ier frequency uncertainty due to Tx frequency, satellite and Rx
frequency conversions.
Factory
default:
Normal
Description: Controls the Rx signal sw eep conf iguration.
Edit-Rx-Dem odulation-Sweep Width Screen
Units : kHz
Minimum value : 1
Maxim um value: 250
Step size: 1
Factory default: 32
Description: Controls the Rx signal sw eep w idth w hen the Swe ep mode
is set to
Other. This is a +/-
setting, i.e. the total w idth is tw ice the value that is
entered.
7.3.3.2.5 Edit-Rx-Carrier Menu
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• Frequency. This sets the frequency used to receive from the satellite.
• Inversion. This controls whether the I and Q channel outputs are swapped, to give
spectrum inversion.
• Roll-off. This selects the gradient of the sloping shoulders of the spectral mask and
should be set to be the same as that of the transmitted signal.
Edit/Rx/FEC- Dem od/Sweep width(+/-):
[032]
New :[032] 1-250kHz
Edit/Rx/Carrier:
1Frequency 2Inve rsion
3Roll-off 4Advanced

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-34
• Advanced. This controls the Paired Carrier (PCMA) carrier overlap feature. On L-band
mod ems it also allow s control of an LNB.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Frequency Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Inversion Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Roll-off Screen
See the description of the transmit path equivalent.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced LNB M enu
The follow ing LNB screens are only available on the L-Band Modem.
This menu has the follow ing options:
• LNB type. This allows selection of the LNB type that is fitted. It also allow s the modem
to display and the user to edit the final SHF f requencies instead of the normal L-band
frequencies.
• PSU. This allows the DC supply to the LNB from the modem to be turned on or off.
• Reference. This controls whether a 10MHz reference signal is supplied to the LNB
from the modem.
• 1-for-1. This controls whether LNB services (i.e. DC supply, 10MHz reference and FSK
communications) stay w ith the on-line modem or sw itch to the standby modem w hen a
1-for-1 switchover occurs in a 1-for-1 redundant pair of modems.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-LNB Type Screen
Edit/Rx/Carrier/Advanced/LNB:
1LNB 2PSU
3Re ference 41:1
./Rx/Carrier/Advanced/LNB/LNB type:
[None]
New :[C 3.635 – 4,2 GHz]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-35
Options :
None
There is no LNB attached.
Other
If you are not using a Paradise LNB, select Other
and manually
configure the BUC parameters.
C 3.635 – 4.200 GHz LO Frequency: 5150MHz.
Ku 10.95 – 11.45 GHz. LO Frequency: 10000MHz.
Ku 11.2 – 11.7 GHz LO Frequency: 10250MHz.
Ku 11.7 – 12.2 GHz LO Frequency: 10750MHz.
Ku 12.25 – 12.75 GHz LO Frequency: 11300MHz.
Factory
default:
None
Description
Allow s the user to select a number of Paradise LNBs or Other if another
manufacturer’s LNB is being used. If Other is selected then the follow ing
LNB Frequency Offset screen is displayed.
Note the `Std C` L NB uses a high side Local Oscillator (LO) and the received SHF
frequency is LO - IF frequency (not LO + IF as w ith most other bands). This is academic
as it is handled automatically by the modem, w hich displays the correct SHF f requency.
Note that w ith the LNB type set to None or Other, there is no w ay to manually enter an
SHF offset that uses a high side LO.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-LNB Freque ncy Offset Screen
./Carrier/Advanced/LNB/SHF freq offset:
[-05.15000000]
New :[-05.15000000] -99.999-99.999GHz
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-36
Units : MHz
Minimum value : 0
Maxim um value: 65535
Step size: 1
Factory default: 0
Description: Once set, all Rx IF frequencies displayed or edited include the frequency
shift of the LNB or dow nconverter chain.
Note this manual entry of SHF Frequency shift always assumes a low
side Local Oscillator (LO) and therefore displays the SHF Frequency =
LO + IF. There is no means to enter
a High Side LO, w here the SHF
frequency received would be LO -
IF Frequency (unlike the situation
where a predef ined Std C band L NB is selected and the modem know s
that a high side LO is being used).
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advance d-LNB PSU Me nu
The Vision L-Band modem can supply either 15V or 24V at 500mA to the LNB up the
coaxial site cable or `line pow ered`. The options available are Off, 15V or 24V.
Severe damage may occur if a DC supply (or the wrong vol tage DC
suppl y) is fed to a LNB not configured to be `Line powered`.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-LNB 10MHz Reference Screen
When sw itched on, the modem’s internal 10MHz reference signal is sourced from the
mod em up the coaxial site cable to the LNB.
./Carrier/Advanced/LNB/DC voltage:
[Off]
New :[15v]
./Carrier/Advanced/LNB/10MHz reference:
[Off]
New :[On]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-37
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-LNB 1:1 Scre en
This controls w hether LNB services (i.e. DC supply and 10MHz reference) stay w ith the
on-line modem or sw itch to the standby modem w hen a 1-for-1 sw itchover occurs in a 1for-1 redundant pair of modems. Note that FSK communications w ill alw ays be switched
over.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced PCMA Menu
This menu has the follow ing options:
• Enable. This is used to sw itch Paired Carrier off and on. Access to this menu option
requires the Paired Carrier f eature to have been previously enabled through the
mod em SAF mechanism.
• Round trip delay. This allow s the option of setting the satellite round trip delay either
by entering positional coordinates for the modem (earth station) and the satellite or
alternatively setting an absolute delay. The delay is required in order for the Paired
Carrier signal processing algorithm to find a best match for its stored copy of the
outgoing trans mitted signal w ith the composite return signal, in order to subtract the
unw anted near signal leaving just the far carrier.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-PCMA Enable Scr een
This is used to switch Paired Carrier off and on. Access to this menu option requires the
Paired Carrier feature to have been previously enabled through the modem SAF
mechanism.
./Advanced/LNB/Mute Services in Standby:
[Off]
New :[On]
PCMA: 1:Enable
2:Round trip delay
PCMA enable : [Off]
1: Off
2: On

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-38
For first-time use please see the Paired Carrier deployment recommendations in
the information box overleaf.
When sw itched on, the modem expects the received signal to consist of two overlapped
carriers utilizing the same space segment. When on, a copy of the modem’s transmitted
signal w ill be stored in memory and the Paired Carrier signal processing algorithm w ill
attempt to match this w ith the composite return signal, in order to subtract the unw anted
near signal leaving just the far carrier.
Prior to enabling Paired Carrier it is necessary to set up the delay to satellite as in the
follow ing menu options.
Note that there are no other control settings that are specific to Paired Carrier operation –
other settings used by the Paired Carrier algorithm such as centre frequency and sweep
width form part of the normal setup of the modem even f or non-overlapped carriers and
work in the same w ay. The cancellation bandw idth itself is automatically deduced by the
mod em from the larger of the transmit and receive symbol rates and roll-off factors (i.e.
occupied bandw idth).

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-39
PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORM ATION FOR FIRST-TIM E
SETUP OF A PAIRED CARRIER LINK.
In relation to Paired Carrier, generally there are no restrictions on how
the overlapped carriers are brought up and the satellite link is
established. How ever, the follow ing guidelines may be usef ul in proving
correct Paired Carrier operation as part of the overall initial link
deploy ment process. Once correct operation is established then Paired
Carrier can be switched on and off or reconfigured just like any other
mod em feature.
1. Ensure Paired Carrier is switched off.
2. Bring up the first carrier (using the selected common trans mission
frequency) and
• Check the receive signal leve l is as expected
• Check the received signal at the second modem is data
transparent.
3. Sw itch the first carrier off.
4. Bring up the second carrier (using the selected common
transmission frequency) and
• Check the receive signal leve l is as expected
• Check the received signal at the second modem is data
transparent.
5. Bring up both overlapping carriers at the same time.
6. Check that the pow er level and frequency overlap are as expected.
7. Sw itch on Paired Carrier in both modems.
8. Check the modems lock to each other’s signal and are data
transparent.
9. If the modems do not lock or are not data transparent then
• Sw itch Paired Carrier off and on again in each modem (to
counter the possibility of a false lock)
• If this does not work then sw itch the carrier itself off and on
again in each modem
• Otherw ise check the general modem settings f or correct
configuration and overlap of the tw o carriers (note that there
are restrictions on the supported level of power asymmetry
and symbol rate asy mmetry).

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-40
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-PCMA Round Trip Delay Screen
Options :
Location
Select this mode if you w ant the modem to automatically calculate th e
satellite round trip dela
y using coordinates that you enter for the mode m
and satellite positions.
Delay
Select this mode to enter f ixed minimu m and maximum satellite round trip
delay times.
Factory
default:
Location
Description: Allow s the selection of the method for dete
rmining the satellite round trip
delay. This can be entered as a time delay or can be automatically
calculated f rom location information. The delay is required in order for
the Paired Carrier signal processing algorithm to find a best match for
its stored
copy of the outgoing trans mitted signal w ith the composite
return signal, in order to subtract the unw anted near signal leaving just
the far carrier.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-PCMA Location Screens
When the Round trip delay method for Paired Carrier is set to Location then the follow ing
screens are displayed in sequence.
Units : Degs
Minimum value : -180.00
Maxim um value: +180.00
Round trip de lay:
1: Location
2: Delay
Earth s tation lon: -180 to +180Degs
[000.00] Ste p 0.01Degs
New : 000.00

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-41
Step size: 0.01
Factory default: 000.00
Description: The longitudinal position of the modem (earth station).
Units : Degs
Minimum value : -90.00
Maxim um value: +90.00
Step size: 0.01
Factory default: 00.00
Description: The latitudinal position of the modem (earth station).
Units : Degs
Minimum value : -180.00
Maxim um value: +180.00
Step size: 0.01
Factory default: 000.00
Description: The longitudinal position of the satellit e.
Edit-Rx-Carrier-Advanced-PCMA Delay Screens
When the Round trip delay method for Paired Carrier is set to Delay then the follow ing
screens are displayed in sequence.
Earth s tation lat: -90 to +90Degs
[00.00] Ste p 0.01Degs
New : 00.00
Satellite lon: -180 to +180Degs
[000.00] Ste p 0.01Degs
New : 000.00

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-42
Units : ms
Minimum value : 000.00
Maxim um value: 300.00
Step size: 0.01
Factory default: 000.00
Description: The minimu m satellite round trip delay.
Units : ms
Minimum value : 000.00
Maxim um value: 300.00
Step size: 0.01
Factory default: 000.00
Description: The maximum satellite round trip delay.
Edit-Rx-Rx=Tx Scre en
Factory default: Off
Description:
Controls w hether specific Rx configuration parameters mirror the
equivalent Tx parameters. Exceptions include carrier frequency, spectral
inversion and parameters that have no Tx equivalent, such as sw eep
control. This feature can be used to simplify the configuration for duplex
links. When sw itched off, the Rx configuration retains its values and does
not return to the values prior to tracking being sw itched on.
Min delay: 0 to 300ms
[000.00] Ste p 0.01ms
New : 000.00
Max de lay: 0 to 300ms
[000.00] Ste p 0.01ms
New : 000.00
Edit/Rx/Rx value s track Tx:
[Off]
New :[On]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-43
7.3.3.3 Edit-Unit Menu
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• Identity. This is a user-assigned field that is typically the unique modem name,
number or location.
• Interface. This submenu allow s the selection and set up of terrestrial and RF interfaces.
• M&C. This submenu controls remote M&C settings including passw ords, interfaces and
timeouts.
• Clocks. This controls the station clock source to be used in place of the internal
10MHz reference.
• Time. This allows the time and date to be set.
• Advanced. This submenu controls alarm thresholds, special modes, 1-for-1 standby
modem sw itching and it also allow s the entry of SAF codes to activate additional
softw are features in the modem.
7.3.3.3.1 Edit-Unit-Modem Identifier Screen
Factory default: Paradise Vision modem
Description: User-
assigned field typically the unique modem na me, number or
location.
7.3.3.3.2 Edit-Unit-Interface Menu
Edit-Unit:
1Identity 2Interface 3M&C
4Clocks 5Time 6Advance d
Edit/Unit/Identity/Modem identifier:
[Paradise Vision m odem]
New :[Paradise Vis ion m odem ]
Edit/Unit/Interface :
1ASI 2IP
3RF

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-44
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• ASI. This allow s each of the ports of the Quad ASI interface card to be set to Tx, Rx or
Off. Any port that is not sw itched off will be routed through to the main traffic channel
of the modem for transmission or reception from satellite, as selected.
• RF. This option is used to set the RF port impedance.
Edit-Unit-Interface-ASI Menu
Each of the options on this menu controls the respective port of the Quad ASI card as
described in the follow ing screen.
Edit-Unit-Interface-ASI-Port Screen
Options :
In (Note this may be show n as Tx in earlier versions of the software)
Sets the respective port of the Quad ASI card to enable it to receive
input
data to be transmitted to the satellite. If the modem is set to allow
mu ltistreaming then the data w ill be interleaved w ith any other port on the
Quad ASI card that is enabled as Tx, as w ell as any other terrestrial
interf ace card that is enabled.
Out (Note this may be show n as Rx in earlier versions of the sof tware)
Sets the respective port of the Quad ASI card to enable it to transmit data
received f rom satellite onto the terrestrial netw ork. If the modem is set to
allow multistreaming then data w ill be deinterleaved
from the multiplexed
receive carrier and passed to the appropri
ate ASI port. Data can either be
passed betw een the same ports at each end of the link (i.e. Tx port 1 to Rx
port 1, Tx port 2 t o Rx port 2, etc.) or data can be filtered based on PID
identifier or ISI identifier.
Edit/Unit/Interface /ASI:
1Port 1 2Por t 2
3Port 3 4Por t 4
Edit/Unit/Interface /ASI/Port 1 mode:
[In]
New :[Out]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-45
Off
Disables the respective port of the Quad ASI card.
Factory
default:
Off
Description: Sets the
trans mit/receive direction of the relevant port of the Quad ASI
card. Note that each port can be set to either transmit or receive but not
both at the sa me time.
After selecting the terrestrial interface as IP from the Edit-Unit-Interface menu, the
following screens w ill be displayed in turn, depending on what features have been
supplied w ith the modem.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-IP Encaps ulation Type Screen
Options :
MPEG over IP
This should be used on ly w hen MPEG2 packets are being encapsulated directly
inside IP packets.
ULE
This selects Ultra Lightw eight Encapsulation (RFC 4326).
MPE
This selects Mu lti Pr otocol Encapsulation (RFC 4259).
PXE
This selects Paradise eXtreme Encapsulation. This is a Paradise proprietary
encapsulation scheme that adds less than 1% overhead. This compares to
typically 10% overhead for MPE and 5 to 7% overhead for ULE.
./Unit/Interface /IP/IP encapsulation type:
[UL E]
New :[MPE]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-46 Factory
default:
ULE
Description: This allows selection of the
IP encapsulation protocol. IP is not natively
supported by existing DVB standards and therefore the data has to be
encapsulated using another protocol in order to be converted into a
format that can be transmitted and received. The easiest w ay to
understand this is to visualize IP packets (potentially of variable size)
being transmitted in fixed-size
satellite f rames (chunks of data similar to
packets) of a different size. This introduces problems of
fragmentation,
padding, etc. Various protocols have evolved to handle th is situation.
MPE is the oldest standard w ith w idespread support but it also has the
higest overhead. UL E is a new er standard w ith low er overhead. Both
encapsulate into MPEG 2 Transport Stream (TS) packets of 188 bytes,
which are natively supported by the various DVB standards.
Paradise
has added its ow n encapsulation scheme (PXE) w ith low er overhead
than either MPE or ULE.
Although the Vision modem supports MPEG2 TS packets wrappered
inside IP packets, it has a general IP capability and can transmit and
receive any IP protocol (TCP, UDP, mu lticast, HTTP, SMTP, FTP, etc.).
When using Vision modems at both ends of a link, PXE should norma lly
be used in order to reduce the overhead to a
minimum. When
interoperating w ith other equipment the Vision modem
can operate either
as a Layer 2 Ethernet Bridge or as a Layer 3 router. The
interoperat ing
equipment must
be set the same as the modem (i.e. to either bridging or
routing mode) in order to be able to communicate, regardless of w hich
encapsulation protocol is used.
MPEG over IP is used w hen MPEG2 packets are provided to the modem
encapsulated inside IP packets. In this case the modem removes the
MPEG2 packets, throws aw ay the IP packet wrapper and sends the
MPEG2 directly over satellite w ith no additional encapsulation. At the
receiving end, it is necessary to rebuild the IP packets, including
destination address and this leads to the follow ing set of screens.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-MPEG Over IP Screen
Options :
UDP/TS
./Unit/Interface /IP/MPEG over IP type :
[UDP/TS]
New :[UDP/RTP/TS]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-47 IP packets w ill consist of UDP packets that contain Transport Stream
packets.
UDP/RTP/TS
IP packets w ill consist of UDP packets that contain R
TP packets that
contain Transport Stream packets.
Factory
default:
UDP/TS
Description: This option is relevant only when MPEG over IP is selected as the
encapsulation type. It
indicates the format of IP packets coming into the
mod em trans mitting to sat
ellite and the format of IP packets to be
generated f rom the modem receiving f rom satellite for forw arding to the
terrestrial netw ork. IP packets w ill either contain UDP or UDP/RTP
packets, in addition to the MPEG2 packets.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Destination Address Screen
Factory default: 000.000.000.000
Description: This option is relevant only when MPEG over IP is selected as the
encapsulation type. It is use
d on the Rx side only and is used to build a
new IP packet f or transmission onto the local terrestrial netw ork. The
MPEG2 packets that are received over satellite are encapsulated into
new IP packets and sent to the se lected destination address.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Destination Port Screen
Factory default: 0
Description:
This option is relevant only when
MPEG over IP
is selected as the
encapsulation type. It is used on the R
x side only and is used to build a
./Unit/Interface /IP/Destination address:
[010.000.070.001]
New :[010.000.070.001]
./Unit/Interface /IP/Destination port:
[05678]
New :[05678] 0-65535

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-48
new IP packet f or transmission onto the local terrestrial netw ork. The
MPEG2 packets that are received over satellite are encapsulated into
new IP packets and sent to the se lected destination UDP port number.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Local M ulticast Address Screen
Factory default: 000.000.000.000
Description: This option is relevant only when MPEG over IP is selected as the
e
ncapsulation type. It is used on the Tx side only and is used to listen
for multicast IP packets being sent to the modem for transmission over
satellite.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Local M ulticast Port Screen
Factory default: 0
Description: This option is relevant only when MPEG over IP is selected as the
encapsulation type. It is used on the Tx side only and is used to listen
for multicast IP packets on a particular UDP port
being sent to the
mod em for transmission over satellite.
Edit-Unit-Interface-Terrestrial-IP Mode Screen
./Unit/Interface /IP/Local multicast address:
[010.000.070.001]
New :[010.000.070.001]
./Unit/Interface /IP/Local multicast port:
[01234]
New :[01234] 0-65535
./Interface/IP/IP m ode:
[Br idge m ode]
New :[Routing m ode]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-49
Options :
Bridge mode
Select this mode for ordinary Ethernet over satellite bridging, i.e. po int-to-
point systems. In this mode, the Ethernet bridge builds up bridging
information b ased on the replies it receives back, allow ing it to ascertain
which netw ork segments devices are located on.
Routing mode
IP packets are f orwarded
based on the contents of the modem’s routing
table. The routing table can be populated by manually entering routes
and/or by turning on one (or more) of the supported dynamic routing
protocols. The dyna mic routing protocols enable the modem to
automatically populate the routing table based on information forw arded by
other routers in the netw ork. The modem operates as a tw o port router in
this mode. See t he TCP/IP w hite paper at
http://www .paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php for more details.
Factory
default:
Bridge mode
Description: The routing option is only applicable if an IP Traff ic card is fitted.
See
the TCP/IP w hite paper at
http://www .paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php for further details on
routing mode operation.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-50
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Ethernet Traffic Mode Screen
Options :
Bridge mode
Select this mode for ordinary Ethernet over satellite bridging, i.e. point-to-
point
systems. In this mode, the Ethernet bridge builds up bridging information based
on the replies it receives back, allow ing it to ascertain w hich netw ork segments
devices are located on.
Hub
Sets up a modem to w ork as a point-to-
multipoint bridge hub. All modems at the
hub site should be configured to this mode. Bridging rather than brouting should
be used in point-to-mu ltipoint systems that have a direct return path via satellite.
Remote
Sets up a modem to w ork as a point-to-
mu ltipoint remote site. All modems
connected to a point-to-
multipoint bridge netw ork that are situated at remote sites
(i.e. not on the hub) should be configured to this mode.
./Unit/Interface /IP/Ethernet traffic mode:
[Br idge m ode]
New :[Mesh]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-51
Header Compression
This is a bridging point-to-point mode w here UDP and IP packet headers
are compressed in order to save satellite bandw idth. The bandw idth savings
depend on the particular packet sizes being used. This f eature supports
header compression at terrestrial throughput rates of up to 2Mbps via the
base modem and throughput rates up to 16896kbps w hen the IP Traffic
card is f itted.
Mesh
The mesh mode supports netw orks w here there is one carrier per site and
mu ltiple Rx-only modems for receiving from other sites. It is implemented as
a variation of the point-to-
mu ltipoint br idging mode (hub operation). Partial
mesh netw orks are also supported.
Brouting mode
Select this mode f or all point-to-multipoint or unidirectional IP systems
where there is an indirect return path (i.e. not via satellite). Both the Tx and
Rx modems should have brouting enable d. In this mode, the Ethernet
bridge in the Tx modem d oes not expect to receive replies and simply
transmits all Ethernet frames over satellite other than those d estined for
itself.
TCP acceleration mode
This mode provides br idging of non-TCP packets co mbined w ith
acceleration of TCP packets using a Performance Enhancing Pr oxy (PEP)
that overcomes performance problems associated w ith using standard TCP
over satellite.
TCP acceleration mode + Header Compression
Only applicab le if an IP traffic Interface card is fitted. This mode provides
bridging of non-
TCP packets, acceleration of TCP packets and header
compression.
Factory
default:
Bridge mode
Description:
This allow s selection of the mode of operation of the modem Ethernet
bridge. See Section 8.12 for further details of bridge operation. Note that
Ethernet traffic is supported by the P3714 IP Traffic card only and
not via the base m odem, which can be used for Ethernet M&C only.
The IP Traffic por t on the base modem is reserved for future us e.

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-52
Edit-Unit-Interface-Terrestrial-TCP Acce leration
Options :
TCP acceleration mode
This mode provides routing of non-
TCP packets co mbined w ith
acceleration of TCP packets using a Performance Enhancing Proxy (PEP)
that overcomes performance problems associated w ith using standard
TCP over satellite.
No TCP acceleration
TCP acceleration is turned off.
Factory
default:
No TCP acceleration mode
Description: This option is available in routing mode.
./Interface/IP/TCP accelaration:
[No TCP acceleleration]
New :[No TCP accelaration]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-53
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Bridge Filtering Screen
Options :
Off
In this mode, the bridge w ill f orw ard all traf f ic not destined f or the local
subnet to the default gatew ay if one has been specified. If the default
gatew ay is a router, then this allow s the router to be set up to filter data in
whatever way is appropriate. Note that if bridge f iltering is off and point-tomu ltipoint is being used then it is essential that a router is placed betw een
the modem and local netw ork at each remote to stop unw anted traffic
circulating on the netw ork.
On
In this mode, the bridge w ill discard all traf fic other than that destined for
the local subnet. This can be useful in preventing netw ork loops from
occurring. A netw ork loop can be created, f or example, in a point-tomu ltipoint scenario w here there are multiple Rx-only modems w ith a
common indirect return path and a default gatew ay is specified that causes
data not destined for a particular Rx modem to be routed out of the
gatew ay and back to the sender through the return path.
Factory
default:
Off
Description: Controls w hether the Ethernet bridge f ilters out all traffic other than for
the local subnet. This option is accessible only w hen Brouting mode
is
being used.
./Unit/Interface IP//Bridge filter ing:
[On]
New :[Off]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-54
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Bridge M &C Screen
Options :
Off
In this mode, the Re mote M&C Ethernet interf ace w ill not be included in the
Et hernet bridge. When separate, the tw o Ethernet connectors on the base
mod em are no longer interchangeable. Although IP traffic through the base
mod em is not currently supported, having the tw o Ethernet ports
interchangeable has some advantages: it allow s modems to be daisychained w ithout the need for an external hub or sw itch and it allows a cable
to be connected betw een the base modem and IP card for performing a
softw are upgrade to the IP card (which needs the M&C port to be in the
bridge). The advantage of the M&C being out of the bridge is that the
Et hernet is put into non-promiscuous mode, w hich can significantly reduce
the loading on the modem processor as it helps to reduce the number of
Et hernet frames that need to be processed. When out of the bridge, the
base modem Ethernet port marked IP Traffic is currently not used. Note
that care should be taken in selecting this mode for a remot e modem – if
the tw o cables have been mixed up then M&C co mmunications w ith the
mod em w ill be lost.
On
In this mode, the Remote M&C Ethernet interface is included in the
Et hernet bridge, thereby allow ing M&C traf fic to be via either one cable or
via tw o cables w ith them being interchangeable in relation to the tw o
physical Ethernet ports on the base modem. See above for advantages
and disadvantages.
Factory
default:
On
Description:
Controls w hether the Ethernet M&C interface is included in the Ethernet
bridge or w hether the two base modem Ethernet ports are
isolated from
each other.
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/Bridge M&C:
[Off]
New :[On]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-55
Edit-Unit-Interface-Terrestrial-Enable Default OSPF Configuration
Options :
Use OSPF enabled default
Turns on the OSPF dynamic routing protocol by setting a default
configuration that w ill be sufficient in most cases. The configuration can be
further tuned, if required, as specified in
the TCP/IP w hite paper at
http://www .paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php.
Disable OSPF
The OSPF dyna mic routing protocol is turned off. Note: this w ill overw rite
any existing configuration, including any modified as specified above (see
the TCP/IP w hite paper at http://www.paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php
for more details).
Factory
default:
Disable OSPF
Description: This option is available in routing mode.
./Interface/IP/Enable default OSPF configuration:
[Dis able OSPF]
New :[Disable OSPF]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-56
Edit-Unit-Interface-Terrestrial-Enable Default RIP Configuration
Options :
Use RIP enabled default
Turns on the RIP dynamic routing protocol by setting a default configurat
ion
that w ill be suf ficient in most cases. The configuration can be further tuned,
if required, as specified in the TCP/ IP w hite paper at
http://www .paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php.
Disable RIP
The RIP dynamic routing protocol is turned off. Note: this w ill overw rite any
existing configuration, including any modified as specified above (see the
TCP/IP w hite paper at http://w ww .paradisedata.com//w hitepapers.php f or
more details).
Factory
default:
Disable RIP
Description: This option is available in routing mode.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-
Traffic Port IP Address Screen
Factory default: 0.0.0.0
Description: Sets the IP address for the IP Traff ic card. Both of the Ethernet ports on
the IP Traff ic card use this same address and can be used
interchangeably.
Unlike the base modem Remote M&C port, DHCP is
not supported and therefore an address must be manually entered.
The
traffic port IP address is not directly used in straight bridging mode
(although the address must be a valid one for the local network in pointto-
point bridging mode). The IP address is how ever used in modes using
TCP acceleration and header co mpression.
./Interface/IP/Enable default RIP configuration:
[Dis able RIP]
New :[Disable RIP]
./Interface/IP/Tr affic port IP address:
[0.0.0.0]
New :[010.000.070.002]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-57
Edit-Unit-Interface-Terrestrial-IP
-Traffic Port IP Netmask Screen
Factory default: 255.255.255.255
Description: Sets the IP subnet mask for the IP Traff ic card.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-
Traffic Port IP Gateway Screen
Factory default: 0.0.0.0
Description: Sets the IP address of a def ault gatew ay for the IP Traffic card
. The
gatew ay repres
ents the ‘next hop’ destination, w hich is normally the
address of a router, for packets destined for somew here other than the
local netw ork
. This is used w ith TCP acceleration, brouting and header
compression. An address of 0.0.0.0 means that the gatew ay is not set.
In
straight bridging mode it is not normally necessary to set this gatew ay as
the bridge automatically learns the location of each device.
Note that there are two gateways that can be defined in the modem .
The Traffic Port IP Gateway is used exclusive ly in relation to the IP
Traffic card. The Remote Control Port IP Gateway (on the Edi t-Unit-
M&C-IP menu) will be used in relation to the M&C network and the
Remote M&C Ethernet port.
./Interface/IP/Tr affic port IP netm ask:
[255.255.255.255]
New :[255.255.000.000]
./Interface/IP/Tr affic port IP gatew ay:
[0.0.0.0]
New :[010.000.070.003]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-58
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Weighted QoS Screen
Quality of Se rvice is based on IEEE 802.1p priority tagging. It uses a 3-bit field w ithin
a VLAN tag as a means of prioritising packets. The modem responds to the priority level
that is already set in the VLAN tag w hen the packet is received.
The default is to use strict priority que uing, where three queues are established, w ith
the highest priority (level 7) being sent first f ollow ed by the medium priority (levels 6 and
5) and finally packets from the low priority (levels 4 to 0) queue. How ever, if there is a
large amount of high priority traffic this can have the effect of starving bandw idth for low er
priority traffic.
Selecting Weighted QoS enables fair-weighted queuing. This applies a w eighting to the
three traffic queues w here the highest priority data gets most bandw idth, but bandw idth is
reserved for other low er priority data; for every 4 packets sent f rom the high priority
queue, 2 are sent from the medium priority queue and 1 from the low priority queue.
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/Weighted QoS:
[Off]
New :[On]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-59
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-VLAN Filtering Screen
The mod em supports IEEE 802.1q VLAN tagging. If Ethernet frames w ith VLAN tags are
presented to the modem w hen in bridge mode then these packets w ill be transmitted
transparently along w ith the VLAN tags.
VLAN filtering can also be used w ith point-to-multipoint topology to separate traff ic flows
as long as there is a return path. In point-to- multipoint operation, each remote modem
receives all of the data and use of VLAN tags over just the satellite portion of he link is a
useful w ay of being able to filter out unw anted traffic at the remotes. A VLAN id is
assigned by the user to each remote modem. The hub Tx modem automatically learns
what VLAN tags are associated w ith each remote. It also learns the location of every
device connected to each remote. As data is received at the hub, the Tx modem adds a
VLAN tag with the id of the remote for which it is destined. At the remote, unw anted data
is filtered out and discarded. The VLAN tag is also removed from w anted packets that
have been received at the remote before they are forwarded onto the local terrestrial IP
netw ork. Note that the use of point-to-multipoin t VLAN filtering relies on the modem
generating and removing VLAN tags and it cannot theref ore be used in situations w here
VLAN tags are already present in the data at the point at w hich it is passed to the modem
for transmission.
If On is selected, then the follow ing screen is displayed.
The VLAN ID option is used to set the identifier to be used w ith VLAN filtering. 4094
VLAN ids are available (VLAN 0 is usually reserved for priority frames).
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/VLAN filtering:
[Off]
New :[On]
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/VLAN ID:
[0000]
New :[40] 0-4094

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-60
Web Acceleration mode accelerates w eb browsing by pref etching w eb page inline
objects prior to them being requested by the w eb brow ser. It requires a DNS IP address
to be set (see the follow ing screen). Web pages comprise multip le objects w hich are
typically fetched one or tw o at a time by a w eb browser w ithout w eb acceleration and
therefore a full w ebpage can take many t imes the satellite delay to be displayed. The
Parad ise w eb proxy examines w ebpage f rames as they pass through the modem and
pre-f etches all of the content before it is requested. It is therefore typically available in
cache memory at the modem local to the w eb browser prior to the brow ser actually
requesting the remaining content. On average this w ill speed up the display of w eb
pages by around 30%.
When sw itched On, the follow ing screen is displayed:
This represents the IP address of a domain name server that can translate URLs (host
names used in requesting w eb pages e.g. http://www.microsof t.com) into IP addresses.
The DNS server IP a ddress is normally provided by the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or
it is set up in the user’s computer operating system (under TCP/IP properties). Note that
DHCP (allow ing the address to be detected automatically) is not supported in relation to
this address and therefore an actual address has to be provided.
Edit-Unit-Interface-RF-IF Port Impedance Screen
Options :
50 Ohms
75 Ohms
Factory default: 50 Ohms
Description: Sets the IF port impedance.
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/Web acceleration:
[Off]
New :[On]
Edit/Unit/Interface /IP/DNS IP addr:
[0.0.0.0]
New :[10.0.70.4]
Edit/Unit/Interface /RF/IF port impedance:
[50 Ohm s]
New :[75 Ohms]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-61
7.3.3.3.3 Edit-Unit-M&C Menu
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• Control. This controls w hether modem control is via the front panel (Local), via a
remote interface (Giveaway) or w hether all interf aces are allow ed to control the
mod em (Takeaway). It also controls the length of time a user is logged in for w ithout
any input activity before they are automatically logged out.
• Password. This displays a screen that has options to change the tw o system
passwords (Admin and User).
• Interface. This specifies the remote control serial interface type, the remote control
serial interface baud rate and an RS485 address for the modem.
• IP. This allow s the IP address for the remote control interf ace to be set along w ith a
subnet mask and a default IP gatew ay. The gatew ay acts as the next hop w hen
forwarding IP data not destined for the modem or local subnet.
Edit-Unit-M&C-Control Screen
Options :
Local
Giveaway
Takeaway
Factory default: Giveaway
Description:
Controls mo
dem ow nership. In Local mode only the f ront panel can be
used to control the modem. In Giveaw ay mode, the f irst user to issue a
command gains control of the modem until a manual or automatic log out
occurs. Pressing the MA IN key gives aw ay control of the M
odem.
(Allow ing, for example, a Web user or M&C via RS485 / RS232 to have
exclusive control of the Modem.) In Takeaw ay mode, the modem
accepts commands from any interface at any time (relying on clear
Edit/Unit/M &C:
1Control 2Password
3Interface 4IP
Edit/Unit/M &C/Control/Modem control:
[Giveaw ay]
New :[Takeaw ay]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-62
operational procedures to prevent conf licting requests).
Edit-Unit-M&C-Control-Timeout Screen
Units : mins
Minimum value : 1
Maxim um value: 720
Step size: 1
Factory default: 5
Description: This screen is displayed af ter selecting modem control. It specifies the
period of time w ithout any user input activity after w hich a user is logged
out. Th is is true even for the local user interface (t
his has an implicit login
when the operator first presses a key). In Giveaway
mode, logging out
causes ownership of the modem to be lost.
Edit-Unit-M&C-Password Screen
Factory default: paradise
Description: Mod em passw ord for remote admin user login (login n ame is admin
).
The admin user can both view and control the modem. Only one admin
user can be logged in at a time.
Edit/Unit/M &C/Control/Auto-logout period:
[005]
New :[060] 1-720mins
./M&C/Password/Rem ote adm in password:
New :[ ]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-63
Edit-Unit-M&C-Password-View Only Password Screen
Factory
default:
Paradise
Description: This screen is automatically displayed f ollow ing the admin user
password screen. Modem passw ord for remote view -only user login
(login name is user). Multiple view -
only users can be logged in at the
same time.
Edit-Unit-M&C-Interface Screen
Options :
RS232
RS485
Factory
default:
RS232
Description:
Specifies the remote control serial interface mode.
./Password/Remote view-only user password:
New :[ ]
./M&C/Interface/Remote M&C interface:
[RS 232]
New :[RS485]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-64
Edit-Unit-M&C-Baud Rate Screen
Options :
110 baud
150 baud
300 baud
600 baud
1200 baud
2400 baud
4800 baud
9600 baud
19200 baud
38400 baud
57600 baud
76800 baud
115200 baud
Factory default: 9600 baud
Description: Specifies the remote control serial interface baud rate.
Edit-Unit-M&C-RS485 Addr ess Screen
Edit/Unit/M &C/Interface /Baud rate:
[9600 baud]
New :[9600 baud]
./Unit/M &C/Interface/RS485 address:
[1]
New :[1] 0-255

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-65
Units :
Minimum value : 1
Maxim um value: 255
Step size: 1
Factory default: 1
Description: Specifies the modem's RS485 address. This screen is show n follow ing
the selection of the remo te M&C interface if RS485 is selected.
Edit-Unit-Interface-IP-Remote Control Port IP
Address Screen
Factory default: 10.0.70.1
Description: Sets the IP address for the
remote control interf ace. Note that entering
an IP address of 0.0.0.0 causes the modem to dyna mically request an IP
address from a DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Pr otocol) server on the
netw ork, removing the need to allocate static IP addresses to each
mod em. The allocated IP address can be seen on the
View/Unit/Config/Unit screen. Note that the IP address may take a short
period before it appears as the request to the DHCP server is made
every minute until a reply is received.
Edit-Unit-M&C-IP
-Remote Control Port IP
Subne t Mask Screen
Factory default: 255.255.0.0
Description: Sets the remote control port IP subnet mask.
./IP/Remote contr ol port IP address:
[010.000.070.001]
New :[010.000.070.001]
./IP/Remote contr ol port IP netmask:
[255.255.000.000]
New :[255.255.000.000]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-66
Edit-Unit-M&C-IP
-Remote Control Port IP
Gatew ay Screen
Factory default: 0.0.0.0
Description: Sets the IP address of a default ga
tew ay for use with the base modem
Remot e M&C Ethernet port. The gatew ay represents the ‘next hop’
destination, w hich is normally the address of a router, for packets
destined for somew here other than the local netw ork. An address of
0.0.0.0 means that the gatew ay is not set.
7.3.3.3.4 Edit-Unit-Clocks Screen
Options :
None
BNC
RS422
Factory default: None
Description:
Controls the station clock source to be used in place of either the interna l
10MHz reference or to replace only the Rx reference clock. This can be
used for example to run all modems from a co mmon GPS clock signal.
./IP/Remote contr ol port IP gateway:
[0.0.0.0]
New :[010.000.070.002]
Edit/Unit/Clocks/Station clock source:
[None]
New :[RS422]
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-67
Edit-Unit-Clocks-Station Clock Use Screen
Options :
Replace internal 10MHz clock
Replace only Rx ref clock
Factory default: Replace internal 10MHz clock
Description: Controls the function of the station clock i.e. w hether it replaces the
internal 10MHz reference or is used as an Rx-only reference clock.
Edit-Unit-Clocks-Station Clock Frequency Screen
Units : kHz
Minimum value : 1
Maxim um value: 10000
Step size: 1
Factory default: 10000
Description: Indicates to the modem the frequency of the station clock input reference
signal that w ill replace the Rx-only reference clock. If the station clock is
being used to replace the internal 10MHz reference then this screen is
not show n.
Edit/Unit/Clocks/Station clock use:
[Re place internal 10MHz clock ]
New :[Replace internal 10MHz clock ]
Edit/Unit/Clocks/Station clock freq:
[1000]
New : 10000] 1000-10000kHz

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-68
7.3.3.3.5 Edit-Unit-Time Screen
This option allows the current time and date of the modem to be set in t he format
HH:MM:SS DD/MM/YYYY. The time is maintained even w hile the modem is sw itched off .
7.3.3.3.6 Edit-Unit-Advanced Menu
This menu allows configuration of alarm settings, 1-f or-1 and 1-f or-N redundancy settings,
SAF (Softw are Activated Feature) settings and adjustment to the internal 10 MHz
reference clock.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms Me nu
This menu allows configuration of alarm threshold and action settings.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Thresholds Menu
This menu allows configuration of alarm threshold settings.
Edit/Unit/Date & time:
[14:41:45 06/04/2008]
New :[14:41:45 06/04/2008]
Edit/Unit/Advanced:
1Alarms 2Operation 31-for-N
4SAF 5Adj ref 61-for-1
Edit/Unit/Advanced/Alarms :
1Thresholds
2Actions
Edit/Unit/Advanced/Alarms /Thresholds:
1BER max 2Eb/ No
3BUC PSU

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-69
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Thresholds-BER Thr eshold Screen
Minimum value : 9.9E-15
Maxim um value: 1.0E-2
Step size: 0.1E1
Factory default: 1E-4
Description: Sets the error-rate threshold above which a deferred alarm w ill
be
generated. This alarm can be sw itched off or on using the BER threshold
alarm option of the Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Actions menu.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Thresholds-Eb/No Threshold Screen
Units : dB
Minimum value : 0.0
Maxim um value: 99.0
Step size: 0.1
Factory default: 3.0
Description:
Sets the Eb/No threshold below w hich a def erred alarm w ill be
generated.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Thresholds-BUC PSU Screen
./Alarms/Thresholds/BER threshold:
[1.0E-4]
New :[1.0E-4] 9.9E-15-1.0 E-2
./Alarms/Thresholds/Eb/No threshold:
[03.0]
New :[03.0] 0-99dB
./Alarms/Thresholds/DC current min:
[0.10]
New :[0.10] 0.1-6A

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-70
Units : A
Minimum value : 0.1
Maxim um value: 6
Step size: 0.01A
Factory default: 0.1
Description: On L-
band modems, sets the trip threshold at w hich a fault is declared
when the current drawn by the Tx ODU is outside the limit.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Alarms-Actions Screens
A number of screens are available that control the follow ing:
• BER. Controls w hether the BER threshold alar m is enabled.
• BUC PSU. Controls w hether the combined over/under-current, over-temperature
alarm for the Tx DC sw itch is considered a fault or not.
• Clr 1:1 alm. Allow s the user to temporarily clear a modem alarm that is preventing a
1:1 changeover.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Operation Me nu
This m enu allows configuration of redundancy settings, power supply break
acknowledgement and allows a SAF demonstration test shot to be ended,
returning the SAF settings to their s tate prior to the demonstration mode starting.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Operation-1 For 1 Screen
Options :
Standby
Edit/Unit/Advanced/Ope ration:
11-for-1 21-for-n
3Ack Pw r Bre 4End demo
Edit/Unit/Advanced/Ope ration/1-for-1:
1Standby 2Maintenance
3In-service

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-71
This option forces a mode m that is on-
traffic to standby. This is done by
mo mentarily creating a fault condition that forces a sw itchover to occur.
Maintenance
Allow s the modem to be removed f rom the redundancy group, therefore
preventing the unit being sw itched on line.
In-service
Allow s the modem to enter a redundancy group and be available to come
on line.
Factory default: None
Description: Forces a swi
tch to the standby unit and allow s a modem to be removed
or added to a redundancy group.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Operation-1 For N Screen
This menu is only available if the modem is an integral part of a 1-f or-N redundancy
sw itch. Please see separate redundancy sw itch operating ma nual.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Operation-Ack Pwr Bre Screen
This allow s the transmit carrier to be restored follow ing a ma ins pow er f ailure, if the
transmit carrier control has been set to On-mute if outage. Please see Edit-Tx-Carrier
men us.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Operation-End Demo Screen
This allows the modem demonstration ‘test shot’ features to be turned off, therefore
effectively losing the remaining balance of demonstration time left and returning the
mod em to a state w hereby it is using only permanent SAF features that have been set.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-1-for-N Screen
Options : Address range 1 to 16
Minimum value : 1
Maxim um value: 16
./Advanced/1-for-N/1:N address:
[01]
New :[01] 1-16

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-72
Step size: 1
Factory default: None
Description: Sets the 1:N address for the modem to commu nicate w ith a Vision
redundancy sw itch. Not e: the modem’s position w ithin the redundancy
sw itch system dictates the 1:N address. Please see
separate
redundancy switch operating man ual.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-SAF Code Screen
Factory default: None
Description: Encrypted code for enabling Softw are Activated Features. Enter 0 to
enable a free 10-day test shot of all features. Three test shots are
available and may be activated singly or together (one after another) to
give up to a 30-day test period.
Edit-Unit-Advanced-Adjust Reference Screen
This is only applicable on L-Band modems and allows compensation for ageing affects. It
allow s the frequency of the internal 10MHz reference to be adjusted by using the up and
dow n arrow s. This can be adjusted off line by setting the modem to CW. Use a
calibrated spectrum analyser set to count mode, or frequency counter and adjust the
mod em output for exactly 10MHz.
./Advanced/SAF/Ente r new SAF code:
New :[ ]
./Advanced/Adj ref/Adjust 10MHz reference:
[080]
New :[080]

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-73
Edit-Unit-Advanced-1-for1 Screen
This allows a modem to ignore loss of demod lock, which would otherwise result
in a 1:N changeover to a backup modem.
7.3.3.4 Edit-Memor ies Menu
This menu contains the follow ing options:
• Store. This allow s the current M&C configuration to be stored to a named
configuration me mory for later use. Up to 20 configuration me mories can be created
(more may be stored if memory allow s). The memories are non-volatile and w ill
persist betw een successive pow er-ups of the modem. Configuration memories can be
assigned any desired name using the alphanumeric keypad.
• Recall. This allow s a previously stored configuration to be selected and used in place of
the current conf iguration.
• Erase. This option allow s configuration memories to be deleted.
Note that one configuration me mory, namely LOAD_DEFAULTS alw ays exists. When this
is recalled then it has the effect of setting the modem back to the factory defaults.
(Although the LOAD_DEFAULTS memory also appears under Store and Erase, these
operations have no effect on this particular configuration me mory.)
Note that there are restrictions on w hat characters can be included in the configuration
me mory names. Only the letters of the alphabet and numerals should be used.
./Advanced/1-for-1/Receive fail switchover:
[Off]
New :[On]
Edit/Memories :
1Store 2Re call
3Erase

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-74
7.3.4 View Menu
In general, the View menu provides access to a summary of the information entered via
the Edit menus. Consequently, these menus are not described in detail here.
The menu contains the follow ing options:
• Unit. This submenu contains manufacturing information such as model number, serial
number, software version, firmw are version and details of the modem hardw are
configuration.
• SAF. This displays details of which software activated features are currently active,
which are disabled, the number of SAF test shots remaining and the remaining SAF test
shot period before the temporary SAF features time out.
• Monitor. This provides access to transmit, receive and unit information that is
continually updated, including the data rates at diff erent points in the transmit and
receive processing chain, pow er supply levels, modem interna l temperature and
mod em loopback status.
• Alarms. This provides access to transmit, receive and unit current alar m informat ion.
Note that entering 0 clears any existing latched alarm.
• Log. This provides access to the system log. This includes a list of all notable events
that have occurred including alarms. Entries are timestamped. Note that entering 0
clears the log.
• Config. This provides access to summaries of the transmit, receive and unit settings.
View : 1:Unit 2:SAF
3:Monitor 4:Alarm s
5:Log 6:Config
View :
1Unit 2SAF 3Monitor
4Alarms 5Log 6Config
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-75
7.3.5 Test Me nu
The menu contains the follow ing options:
• Loopback. This allows selection of internal loopback betw een the transmit and receive
paths, at different points in the processing chain. This provides a convenient way of
checking modem operation in isolation from other equipment. Local loopback refers to
returning local signals traveling w ithin the modem in the direction of the satellite, back
tow ards the terrestrial interface. Remote loopback ref ers to returning remote signals
traveling in the direction of the terrestrial interface, back towards the satellite interface.
• BER test. This feature provides the ability to inject a test pattern into the modem and to
monitor the results, using the modem’s internal Pseudo- Random-Bit-Sequence (PRBS)
Bit Error Rate (BER) Tester. MPEG2 Transport Stream 188-byte packets (excluding the
sync byte in the header) are generated and filled w ith PRBS data. The receiving end
attempts to synchronize w ith the data stream and check each packet for errors.
• RF. This provides two types of signal – a CW (pure carrier) signal and an alternate 1,0
signal – that can be used to test modem operation.
Test-Loopback Screen
Test:
1Loopback 2BER test
3RF
Loopback:
[Off ]
New : Off

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-76
Options :
Off
Interface (local)
Interface (local and remote)
Framer/deframer (local)
RS (local)
FEC (local)
IF (local)
Factory default: Off
Description: Allow s a number of Loopbacks to be selected to aid fault diagnosis
and
resolution of system level problems.
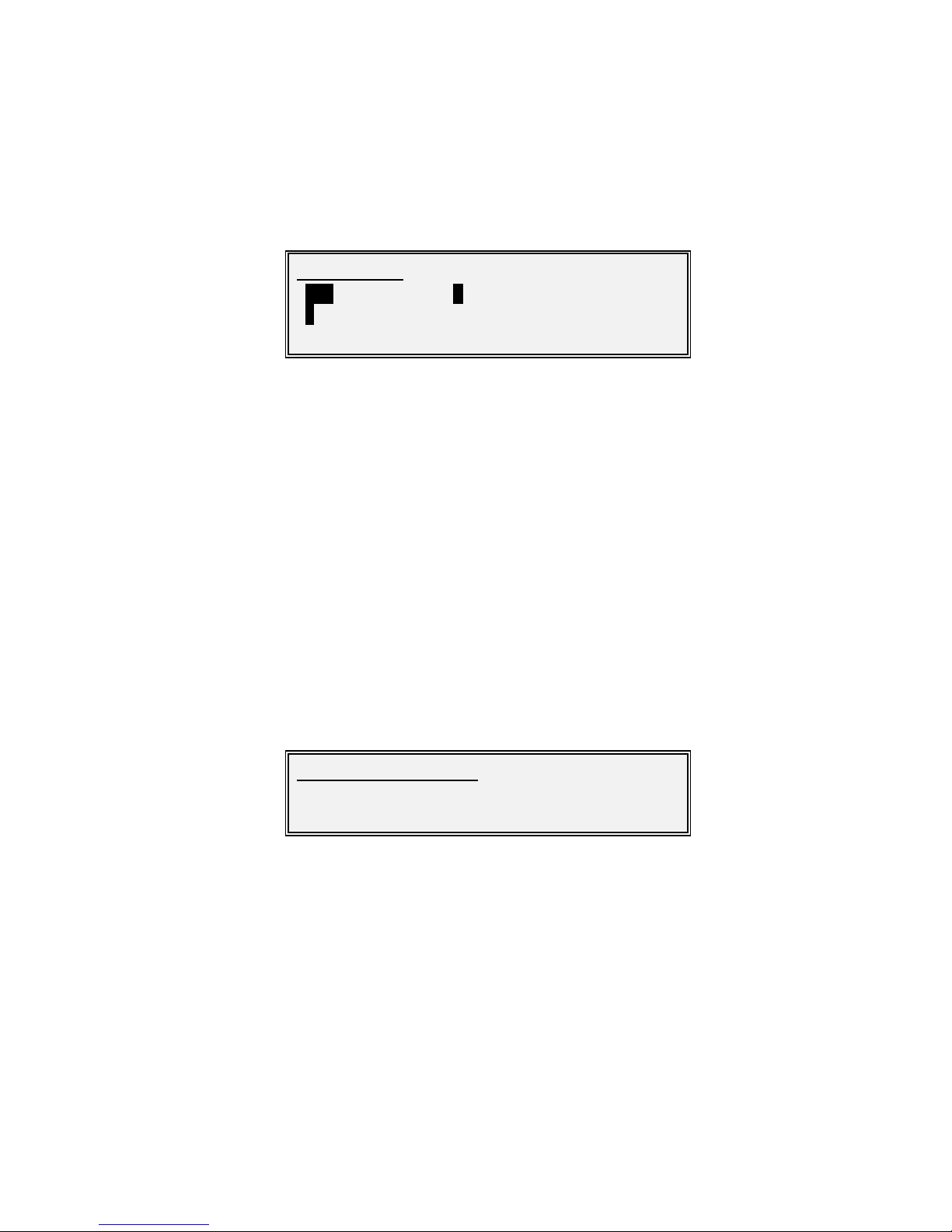
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-77
7.3.5.1 Test-BER Te st Menu
This menu contains the following options:
• Tx. This allows the setup of the internal Pseudo-Random-Bit-Sequence (PRBS)
Bit Error Rate (BER) Tester for the Tx path.
• Rx. This allow s the setup of the internal PRBS BER Tester (BERT) for the Rx
path.
• Results. This screen displays the BER test results and allows single errors to be
injected or the test to be restarted.
The internal BER tester is available as a SAF option. It provides the ability to monitor the
BER of the Rx satellite path. It allows a test pattern to be sent and received.
Note that the follow ing BER test screens apply to Tx and Rx but only the Tx screens are
show n.
Test-BER-Tx-Mode Screen
Options :
Off
Sw itches the BER tester off.
On
Sw itches the BER tester on.
Factory default: Off
Description: Controls the BER test mode.
Test/BER te st:
1Tx 2 Rx
3Re s ults
Test/BER/Tx/BER m ode:
[Off]
New :[On]
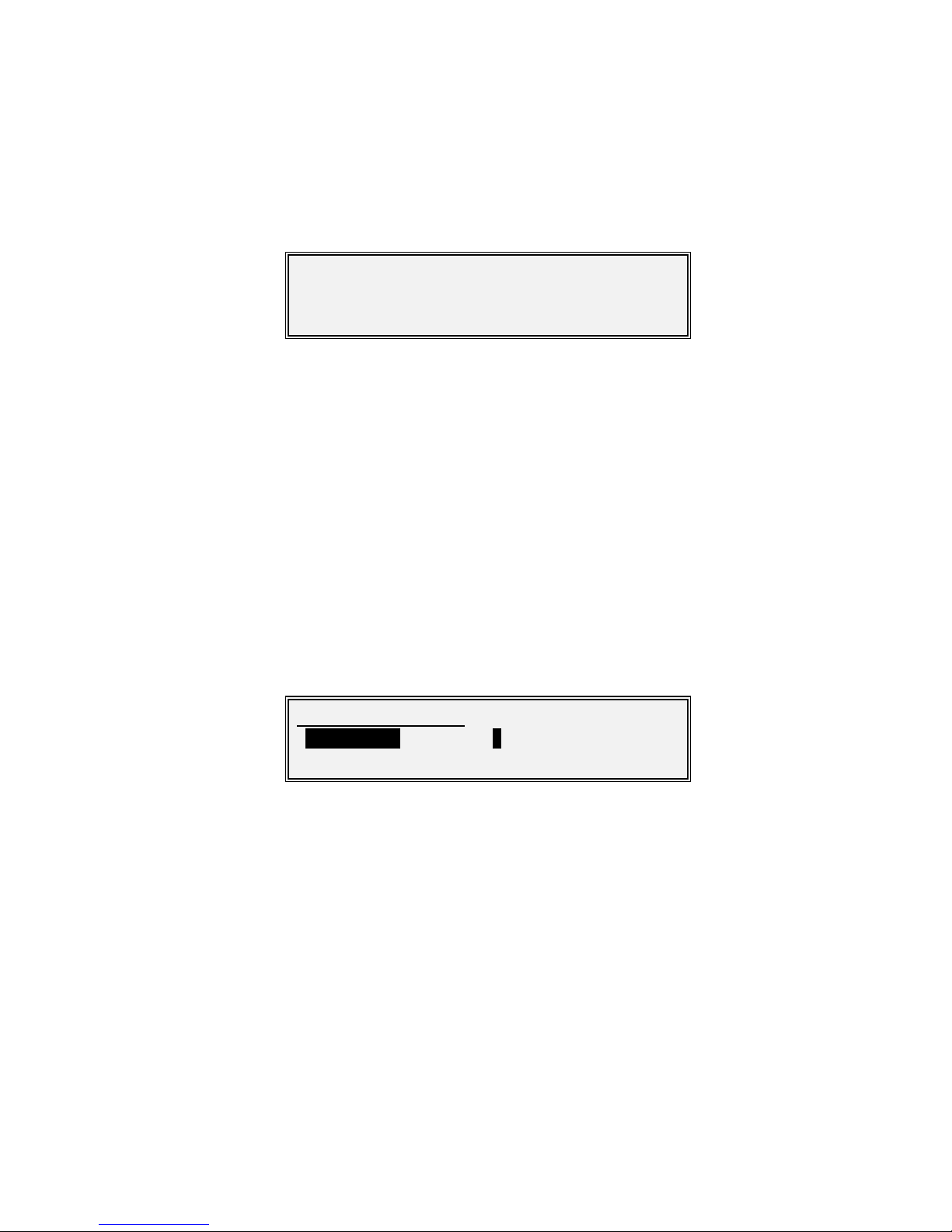
Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-78
Test-BER-Tx-Results Screen
The BERT show s the instantaneous test pattern synchronisation status. When the Rx
path is synchronised to the incoming Tx test pattern then this w ill display ‘Sync OK’ and
when synchronisation is lost it w ill display ‘NO SYNC’.
The Time field ind icates the elapsed time since the test w as started or restarted.
The Loss# f ield is a count of the number of times that pattern synchronisation has been
lost since the test started.
The Errors field indicates the total number of bits received in error since the test started.
The BER field indicates Bit Error Rate, computed from the number of bit errors divided by
the number of bits received.
Pressing the Down arrow key at any point displays the follow ing screen.
The Inject error option can be used to inject a single error into the bit pattern, w hich has
the eff ect of incrementing the number of bit errors by one.
The Restart test option is used to restart the BER test including clear ing all of the error
counts. Pressing the Back key returns the display to the previous results screen.
BERT :Sync OK Time:40.0mins
Loss #:1 Errors:3
BER:1.0E-6
Test/BER te st/Results:
1Inject error 2Restart test

Vision Series Installat ion and Operating Handbook
7-79
Test-RF-Modulator CW Screen
Factory default: Off
Description:
Selecting Tx CW causes a pure carrier to be transmitted rather than the
normal modulated carrier. This is useful for evaluating phase noise and
spurious, but should no
t be used over a live satellite link w ithout the
operator’s permission.
Test-M odulator-RF-Alternate 1,0 Screen
Factory default: Off
Description: Selecting Tx alt 1,0 causes an alternating 1,0,1,0 ……pattern
to be fed to
the modulator at the symbol rate. This causes two discrete frequencies
to be generated, spaced at the symbol rate about the (suppressed)
carrier. This is useful for evaluating the carrier suppression of the
mod ulator but should not be used over a live satellite link.
Test/RF/Modulator CW:
[Off]
New :[On]
Test/RF/Modulator alternate 1,0:
[Off]
New :[On]:
 Loading...
Loading...