1SMB2EZ11 THRU 1SMB2EZ200
FEATURE
S
MECHANICAL DATA
MAXIMUM RATINGS AND ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC
S
D
FSM
STG
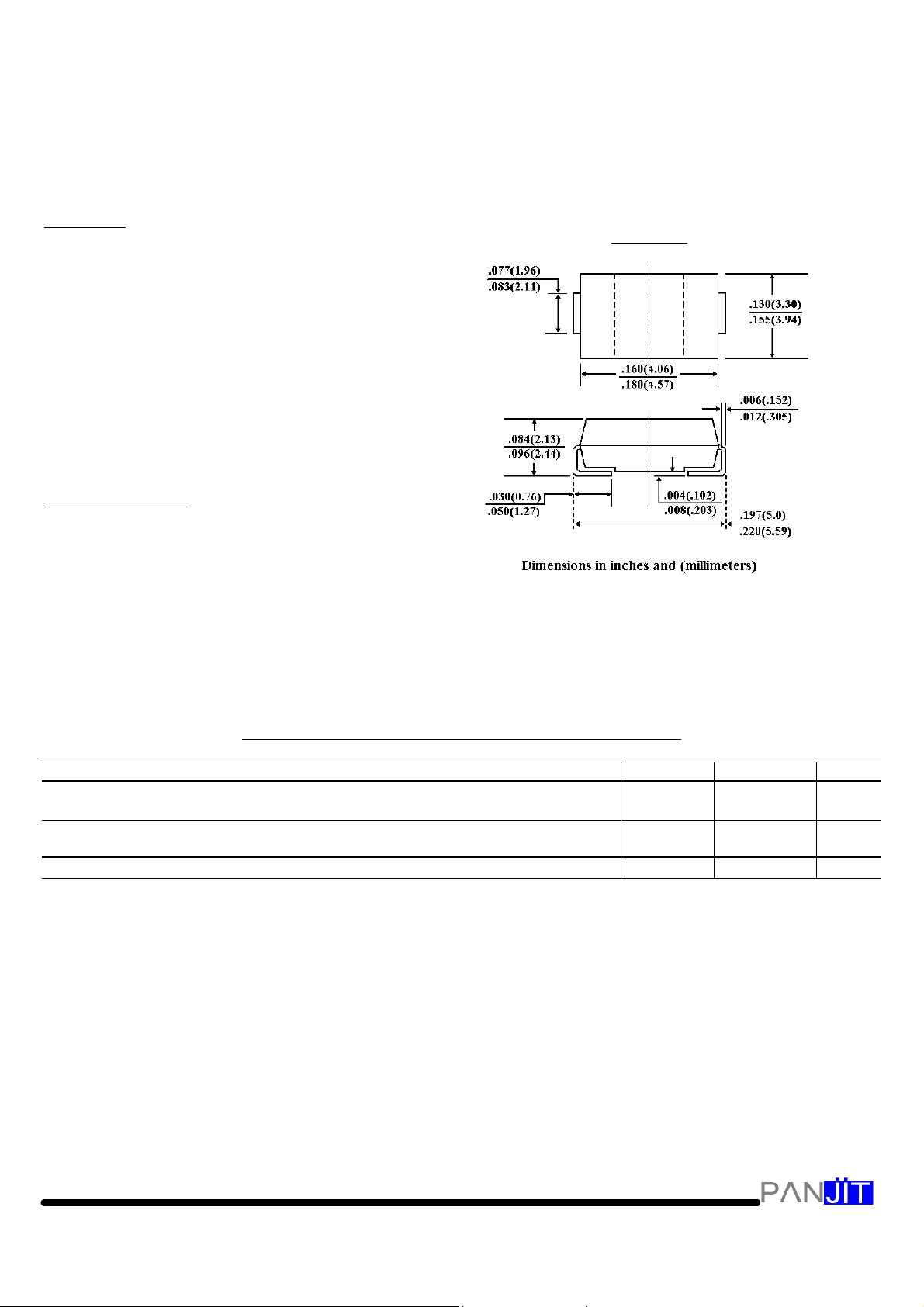
DO-214A
A
SURFACE MOUNT SILICON ZENER DIODE
VOLTAGE - 11 TO 200 Volts Power - 2.0 Watts
l
Low profile package
l
Built-in strain relief
l
Glass passivated junction
l
Low inductance
l
Excellent clamping capability
l
Typical ID less than 1£gA above 11V
l
High temperature soldering :
260¢J/10 seconds at terminals
l
Plastic package has Underwriters Laboratory
Flammability Classification 94V-O
Case: JEDEC DO-214AA, Molded plastic over
passivated junction
Terminals: Solder plated, solderable per
MIL-STD-750, method 2026
Polarity: Color band denotes positive end (cathode)
except Brdirectional
Standard Packaging: 12mm tape (EIA-481)
Weight: 0.003 ounce, 0.093 gram
Ratings at 25¢Jambient temperature unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL VALUE UNITS
Peak Pulse Power Dissipation (Note A)
Derate above 75
Peak forward Surge Current 8.3ms single half sine-wave superimposed on rated
load(JEDEC Method) (Note B)
Operating Junction and Storage Temperature Range TJ,T
NOTES:
A. Mounted on 5.0mm2(.013mm thick) land areas.
B. Measured on 8.3ms, single half sine-wave or equivalent square wave, duty cycle = 4 pulses
per minute maximum.
¢J
P
I
2
24
15 Amps
-55 to +150 ¢J
Watts
mW/
¢J
1SMB2EZ11 THRU 1SMB2EZ200
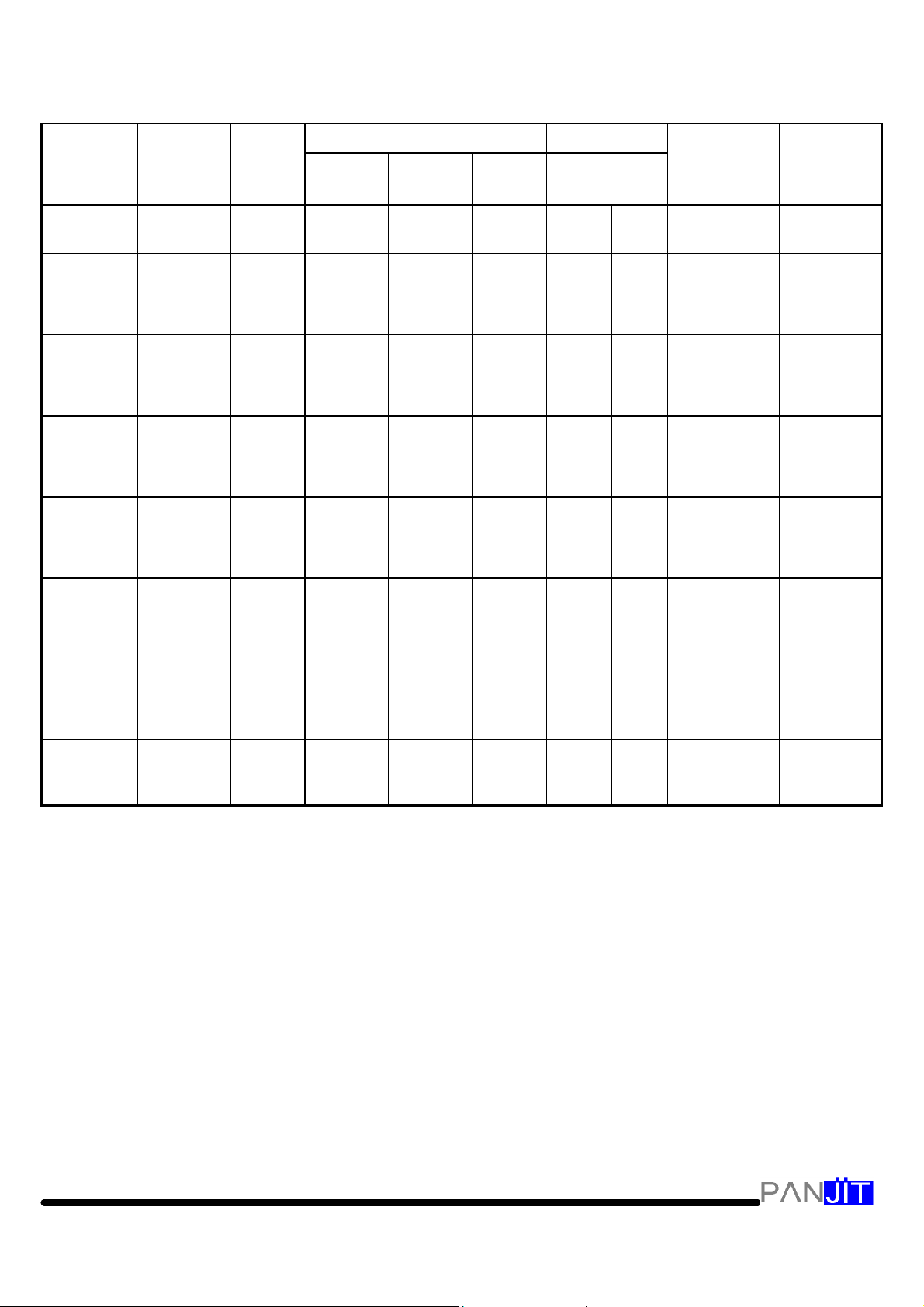
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA=25¢Junless otherwise noted) VF=1.2 V max ,
IF=500 mA for all types
Maximum Zener Impedance (Note 3.)Leakage CurrentType No.(Note 1.)NominalZener
Voltage V
z
@ I
ZT
volts(Note 2.)Testcurrent I
Z
T
m
A
Z
Z
T
@
I
Z
T
OhmsZ
Z
k
@
I
Z
K
OhmsI
Z
K
mAI
R
£g
A Max@VRVolts
Maximum ZenerCurren
t
I
Z
M
mASurge Current
@ TA = 25
¢Jir - mA(Note 4.)
1SMB2EZ11
1SMB2EZ121SMB2EZ1
3
11.
0
12.013.
0
45.
5
41.538.
5
4.0
4.55.
0
700
70070
0
0.2
5
0.250.2
5
1.0
1.00.
5
8.4
9.19.
9
166
15213
8
1.8
2
1.661.5
4
1SMB2EZ14
1SMB2EZ151SMB2EZ161SMB2EZ17
1SMB2EZ1814.0
15.016.017.
0
18.035.
7
33.431.229.
4
27.85.5
7.08.09.0
10.0700
700700750
7500.25
0.250.250.2
5
0.250.5
0.50.50.5
0.510.6
11.412.213.
0
13.7130
122114107
1001.43
1.331.251.1
8
1.1
1
1SMB2EZ191SMB2EZ2
0
1SMB2EZ22
1SMB2EZ241SMB2EZ2719.020.
0
22.
0
24.027.026.325.
0
22.
8
20.818.511.011.
0
12.
0
13.018.075075
0
750
7507500.250.2
5
0.2
5
0.250.250.50.
5
0.5
0.50.514.415.
2
16.
7
18.220.6959
0
8
2
76681.051.0
0
0.9
1
0.830.7
4
1SMB2EZ30
1SMB2EZ331SMB2EZ361SMB2EZ391SMB2EZ4
3
30.
0
33.036.039.043.
0
16.
6
15.113.912.811.
6
20.
0
23.025.030.035.
0
100
0
100010001000150
0
0.2
5
0.250.250.250.2
5
0.5
0.50.50.50.
5
22.
5
25.127.429.732.
7
6
0
5550474
3
0.6
7
0.610.560.510.451SMB2EZ471SMB2EZ511SMB2EZ56
1SMB2EZ62
1SMB2EZ6847.051.056.0
62.
0
68.010.69.89.
0
8.1
7.440.048.055.0
60.
0
75.015001500200
0
200
0
20000.250.250.2
5
0.2
5
0.250.50.50.5
0.5
0.535.838.842.6
47.
1
51.739363
2
2
9
270.420.390.3
6
0.3
2
0.291SMB2EZ75
1SMB2EZ82
1SMB2EZ911SMB2EZ1001SMB2EZ11075.0
82.
0
91.0100.0110.06.7
6.1
5.55.04.590.0
100.0
125.0175.0250.02000
300
0
3000300040000.2
5
0.2
5
0.250.250.250.5
0.5
0.50.50.556.0
62.
2
69.276.083.62
4
2
2
2018170.2
7
0.2
4
0.220.200.181SMB2EZ1201SMB2EZ1301SMB2EZ14
0
1SMB2EZ15
0
1SMB2EZ160120.0130.0140.0
150.0
160.04.23.83.
6
3.3
3.1325.0400.0500.
0
575.0
650.0450050005500
600
0
65000.250.250.2
5
0.2
5
0.250.50.50.5
0.5
0.591.298.8106.
4
114.0
121.6151413
1
2
110.160.150.1
4
0.1
3
0.121SMB2EZ17
0
1SMB2EZ18
0
1SMB2EZ1901SMB2EZ200170.0
180.0
190.0200.02.9
2.8
2.62.5675.0
725.0
825.0900.0700
0
700
0
800080000.2
5
0.2
5
0.250.250.5
0.5
0.50.5130.4
136.8
144.8152.01
1
1
0
1090.12
0.1
1
0.100.1
0
NOTES:
1. TOLERANCES - Suffix indicates 5% tolerance any other tolerance will be considered as a special device.
2. ZENER VOLTAGE (Vz) MEASUREMENT - guarantees the zener voltage when measured at 40 ms¡Ó 10ms
from the diode body , and an ambient temperature of 25 ¢J (¡Ï 8 ¢J, -2 ¢J).
3.ZENER IMPEDANCE (Zz) DERIVATION - The zener impedance is derived from the 60 cycle ac voltage,
which results when an ac current having an rms falue equal to 10% of the dc zener current (IZT or IZK) is
superimposed on IZT or IZK.
4. SURGE CURRENT (Ir) NON-REPETITIVE - The rating listed in the electrical characteristics table is
maximum peak, non-repetitive, reverse surge current of 1/2 square wave or equivalent sine wave pulse
of 1/120 second duration superimposed on the test current, IZT, per JEDEC standards, however, actual
device capability is as described in Figure 3.

RATING AND CHARACTERISTICS CURVES
3
P.W. PULSE WIDTH (ms)
NOMINAL VZ (VOLTS
)
8
-4
VZ, ZENER VOLTAGE @IZT (VOLTS
)
VZ, ZENER VOLTAGE @IZT (VOLTS
)
PP
C
C
1SMB2EZ11 THRU 1SMB2EZ200
30
D = 0.5
20
10
0.2
7
5
0.1
3
0.05
2
0.02
RESISTANCE
£c JL (t,D) TRANSIENT THERMAL
1
0.7
0.5
JUNCTION-TO-LEAD(¢J/W)
0.01
0.3
0.0001 0.0002 0.0005 0.001 0.002 0.005 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10
D = 0
Fig. 2-TYPICAL THERMAL RESPONSE L,
500
250
150
100
50
30
20
10
K, PEAK SURGE POWER(WATTS)
.1 .2 .3
RECTANGULAR NONREPETITIVE
WAVEFORM TJ = 25¢J PRIOR TO
INITIAL PULSE
5 1
2
5 10 20
50 100
NOTE BELOW 0.1 SECOND,
THERMAL RESPONSE
CURVE IS APPLICABLE TO
ANY LEAD LENGTH (L)
IR, REVERSE LEADAGE(uAdc)
SINGLE PULSE£GTJL =£KJL(t)PPK
REPETITIVE PULSES£GTJL =£KJL(t,D)PPK
0.1
0.05
0.03
0.02
0.01
0.005
0.003
0.002
CHAR. TABLE
0.001
0.0005
0.0003
0.0002
@VR AS SPECIFIED IN ELEC.
0.0001
1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200 500 1K
Fig. 3-MAXIMUM SURGE POWER Fig. 4-TYPICAL REVERSE LEAKAGE
200
6
4
2
0
-2
£c VZ, TEMPERATURE
OEFFICIENT(mV/¢J) @ IZT
3 4 6 8 10 12
RANGE
100
) @ IZT
¢J
50
40
30
VZ, TEMPERATURE
20
£c
OEFFICIENT(mV/
10
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
RANGE
Fig. 5-UNITS TO 12 VOLTS Fig. 6-UNITS 10 TO 200 VOLTS

RATING AND CHARACTERISTICS CURVES
VZ, ZENER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
VZ, ZENER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
VZ, ZENER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
L, LEAD LENGTH TO HEAT SINK (INCH
)
1SMB2EZ11 THRU 1SMB2EZ200
100
50
30
20
10
5
3
2
1
0.5
0.3
IZ, ZENER CURRENT (mA)
0.2
0.1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
IZ, ZENER CURRENT (mA)
100
0
50
30
20
10
5
3
2
1
0.5
0.3
0.2
0.1
10
30
40
50
20
60 70
80
Fig. 7-VZ = 3.9 THRU 10 VOLTS Fig. 8-VZ = 12 THRU 82 VOLTS
100
50
30
20
10
5
3
2
1
0.5
0.3
IZ, ZENER CURRENT (mA)
0.2
0.1
100 120 140 160 180 200
/W)
¢J
80
70
60
50
40
RESISTANCE (
30
20
£c JL, JUNCTION-LEAD THERMAL
10
0
PRIMARY PATH OF
CONDUCTION IS THROUGH
THE CATHODE LEAD
0 1/8 1/4 3/8 1/2 5/8 3/4 7/8 1
90 100
Fig. 9-VZ = 100 THRU 200 VOLTS Fig. 10-TYPICAL THERMAL RESISTANCE

APPLICATION NOTE:
Since the actual voltage available from a given zener
diode is temperature dependent, it is necessary to
determine junction temperature under any set of
operating conditions in order to calculate its value. The
following procedure is recommended:
Lead Temperature, TL, should be determined from:
TL = £cLAPD + T
A
£cLA is the lead-to-ambient thermal resistance (¢J/W)
and PD is the power dissipation. The value for £cLA will
vary and depends on the device mounting method.
£cLA is generally 30-40 ¢J/W for the various chips and
tie points in common use and for printed circuit board
wiring.
The temperature of the lead can also be measured using
a thermocouple placed on the lead as close as possible to
the tie point. The thermal mass connected to the tie point
is normally large enough so that it will not significantly
respond to heat surges generated in the diode as a result
of pulsed operation once steady-state conditions are
achieved. Using the measured value of TL, the junction
temperature may be determined by:
TJ = TL + £GT
JL
£GTJL is the increase in junction temperature above the
lead temperature and may be found from Figure 2 for a
train of power pulses or from Figure 10 for dc power.
£GTJL = £cLAP
D
For worst-case design, using expected limits of Iz, limits
of PD and the extremes of TJ (£GTJL ) may be estimated.
Changes in voltage, Vz, can then be found from:
£GV = £c
VZ
£GT
J
£cVZ , the zener voltage temperature coefficient, is
found from Figures 5 and 6.
Under high power-pulse operation, the zener voltage
will vary with time and may also be affected significantly
be the zener resistance. For best regulation, keep current
excursions as low as possible.
Data of Figure 2 should not be used to compute surge
capability . Surge limitations are given in Figure 3. They
are lower than would be expected by considering only
junction temperature, as current crowding effects cause
temperatures to be extremely high in small spots resulting
in device degradation should the limits of Figure 3 be
exceeded.
 Loading...
Loading...