Panasonic PT-L712NTE User Manual
LCD Projector
Commercial Use
Operating Instructions
(Wireless Function)
Model No.
PT-L712NTE
POWER
INPUT
VIDEO
RGB
AUTO
MENU
SETUP
ENTER
FREEZE
SHUTTER
STD
VOLUME D.ZOOM
INDEX
WINDOW
PROJECTOR
• This LCD projector is equipped with a wireless card function.
These Operating Instructions contain information on how to set up the
wireless function, and on how to capture and transmit images. Please
refer to the separate PT-L712E Operating instructions for details on how
to use the LCD projector.
• Please read the “Read this first” booklet, these Operating Instructions
and the Operating Instructions for the PT-L712E LCD projector before
use. After reading these instructions, keep them in a safe place for later
reference.
• The screen images which appear in this manual were taken from
pre-release versions of the software. Actual screen images may differ
from those shown.
TQBH9002-3
GBR

Contents
Dear Panasonic Customer:.. 3
Safety Precautions............... 3
Notes with regard to the wireless
card and the projector................3
Radio frequencies used by
the wireless card ............... 4
Available channels ............... 5
Check accessories ............... 6
Names of each part .............. 6
Wireless image transfer
system for the projector.... 7
Notes on using the projector9
Explanation of terms.......... 10
Wireless function preparation
.......................................... 14
Installing and removing the
wireless card.................... 18
Inserting the wireless card ..........18
Removing the wireless card........19
On-screen menus ............... 20
List of menu screens...................20
Projector LAN settings....... 21
STATUS ......................................21
LOCK SETUP .............................22
SETUP ........................................22
Setting up the computer
wireless card.................... 27
Installing and removing the
computer’s wireless card .........27
Installing the driver ......................28
Checking the protocol .................31
Installing the Configuration Utility
.................................................35
Using the Wireless Manager
.......................................... 36
Wireless Manager capabilities ....36
Starting and closing the Wireless
Manager...................................36
Computer network settings .........37
Checking communication with the
projector...................................40
Basic image transmission
examples ................................. 41
Before transmitting images......... 42
Capturing and transmitting
computer screen images......... 42
Transmitting existing images...... 47
Other useful Wireless Manager
functions .................................. 50
Using JPEG Convertor....... 52
What JPEG Convertor can do.... 52
Starting JPEG Convertor ............53
Main screen functions ................ 53
Importing presentation files created
using Microsoft PowerPoint .... 54
Importing JPEG, BMP and TIFF
files created using other
applications .............................56
Importing files using drag-and-drop
................................................ 56
Checking, sorting and deleting
images..................................... 57
Conversion settings for saving
images..................................... 58
Saving to other folders ............... 59
DCF standard ............................. 60
Using the SERIAL connector
.......................................... 61
Message List....................... 61
Before asking for service... 61
Specifications..................... 64
Trademark Information....... 67
Dimensions......................... 67
-2-

Dear Panasonic Customer:
These instructions provide all the necessary operating information that you
may require. We hope it will help you get the best performance from your
new product, and that you will be pleased with your Panasonic LCD
projector.
Safety Precautions
Caution
Do not insert any foreign objects into the card slot.
• Inserting foreign objects may damage the projector. If the wireless card is
inserted while some foreign object is inside the slot, it may damage the
wireless card.
Notes with regard to the wireless card and the projector.
Caution
Before touching the wireless card, make sure that you earth
your body to dissipate any static electric charge that might
damage the card.
• Static electricity from the human body can damage the wireless card. To
prevent this, you should touch a nearby metallic object such as an
aluminium sash or a door knob to dissipate the static charge from your
body.
Do not install the accessory wireless card to any device other
than the card slot of the projector.
• If this is not observed, damage to the device may result.
-3-

Radio frequencies used by the wireless card
The accessory wireless card and the optional wireless card (ET-CDWL1
series) operate on electronic frequencies within the 2.4 GHz band. You do
not need a radio licence in order to use a wireless card, but you should
make sure that you understand the following points before using such
cards.
Do not use the cards near other sources of radio
emissions.
The following devices may use the same frequencies that are used by the
wireless card. If the wireless card is used near such devices, radio
interference may prevent successful communication, or it may result in
slower communication speeds being achieved.
• Industrial, scientific, medical equipment, etc
• Electric stoves, etc
• Built-in radio devices used for identifying moving equipment in industrial
production lines
• Certain low-power radio devices
Keep the wireless card as far away as possible
from devices such as mobile telephones, TVs and
radios when using such devices
Devices such as mobile telephones, TVs and radios use different
frequencies from the wireless card, so that there will be no effect on either
wireless card communication or on reception or transmission for such
devices. However, radio emissions from the wireless card may cause video
or audio interference.
Radio emissions from the wireless card will not travel
through steel framework, metal sheets or concrete.
The radio emissions from the wireless card will pass through materials
such as wood and glass (except for glass which is reinforced with metal
fibres), so that communication is possible because the signals can pass
through walls and floors which are made from these materials. However,
the radio emission cannot pass through materials such as steel frames,
metal sheets and concrete, so that communication is not possible because
the signals cannot pass through walls and floors which are made from such
materials.
-4-
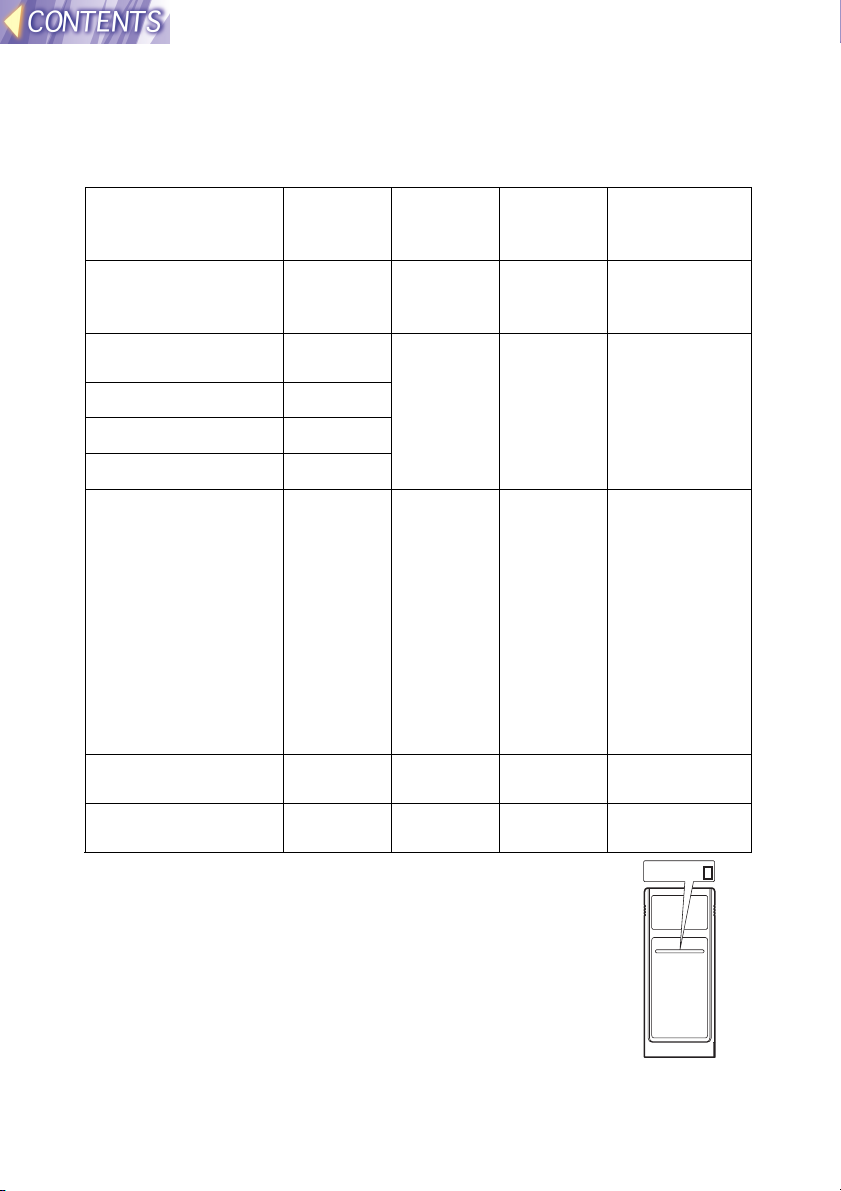
Available channels
The channels (frequency bandwidth) that are available for the wireless
card to use will vary depending on the country or area where the wireless
card is being used. Refer to the following table as a guide.
Country / Area Certificati
on
Japan ARIB
STD33 &
T66
USA FCC part
15
Canada IC
Taiwan DGT
Malaysia SIRIM
Last digit
of card
number *
1 1~14 2412 MHz ~
2 1~11 2412 MHz ~
Operating
channels
Frequency
band (median
frequency)
2484 MHz
2462 MHz
UK, Germany,
France, Italy,
Belgium, Austria,
Sweden, Norway,
Denmark,
Switzerland,
Holland, Finland,
Portugal, Greece,
Thailand, Korea,
Australia, New
Zealand
Spain ETSI
Singapore IDA 5 10~13 2457 MHz ~
* To check the region of intended use for the wireless card
which you have purchased, check the last digit of the
product number which appears on the label on the reverse
side of the card in the position shown in the illustration at
right.
ETSI
300.328
300.328
3 1~13 2412 MHz ~
4 10,11 2457 MHz ~
Note:
• The wireless card cannot be used in countries other
than the country of purchase. If you try to use it in other
countries, you may be infringing the radio transmission
laws and regulations of that country.
-5-
2472 MHz
2462 MHz
2472 MHz
N5HBD0000003
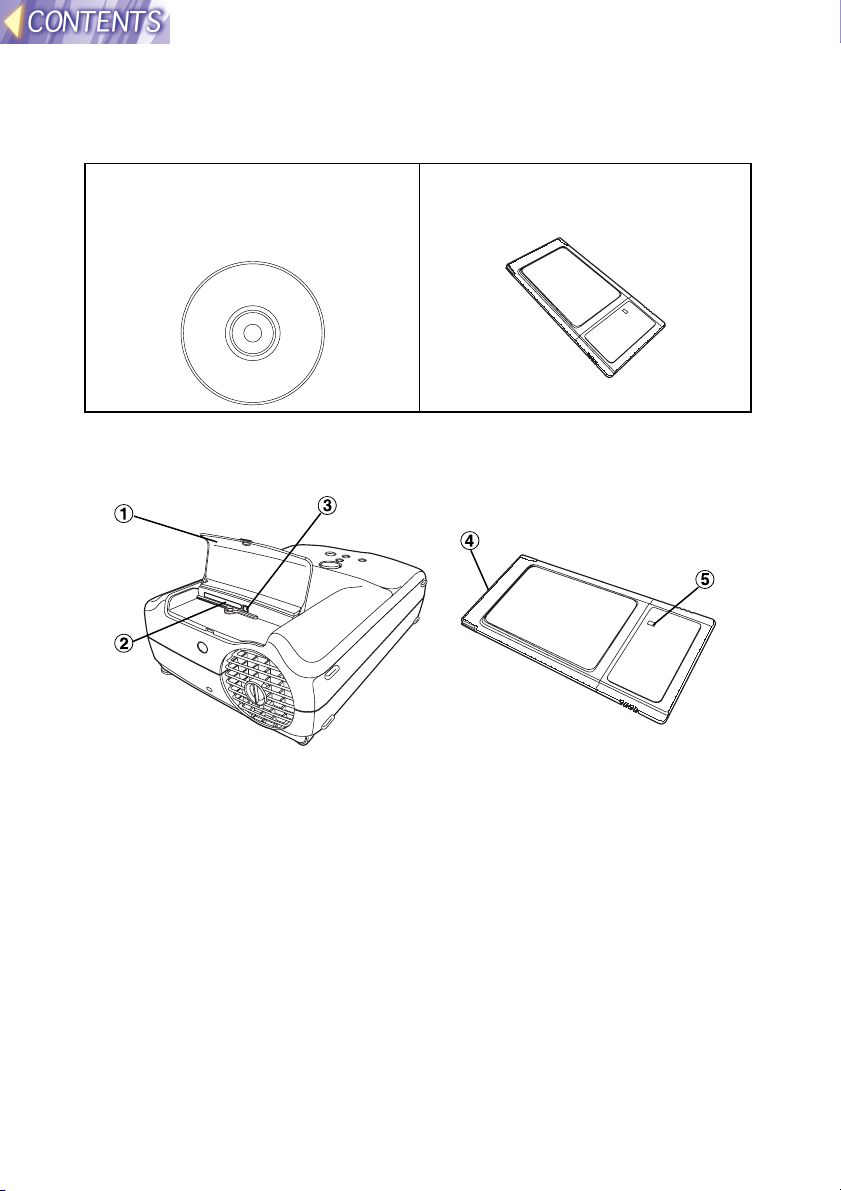
Check accessories
The following accessories are included with the projector, in addition to the
accessories which are listed in the separate Operating Instructions.
CD-ROM ... 1 pc. (Wireless
Manager, Driver, Configuration
Utility, JPEG Convertor, Operating
Instructions)
Wireless Card ... 1 pc.
Names of each part
Wireless card slot
#### Slot cover
Covers the card slot.
$$$$ Card slot
Insert the wireless card into here.
%%%% Eject switch
Use to remove the wireless card from the card slot.
Wireless card
&&&& Connector
This connector is for connecting the wireless card to the projector’s
card slot. Be careful not to touch the connector.
(((( Wireless card power monitor
Illuminates when the wireless card is operating.
-6-
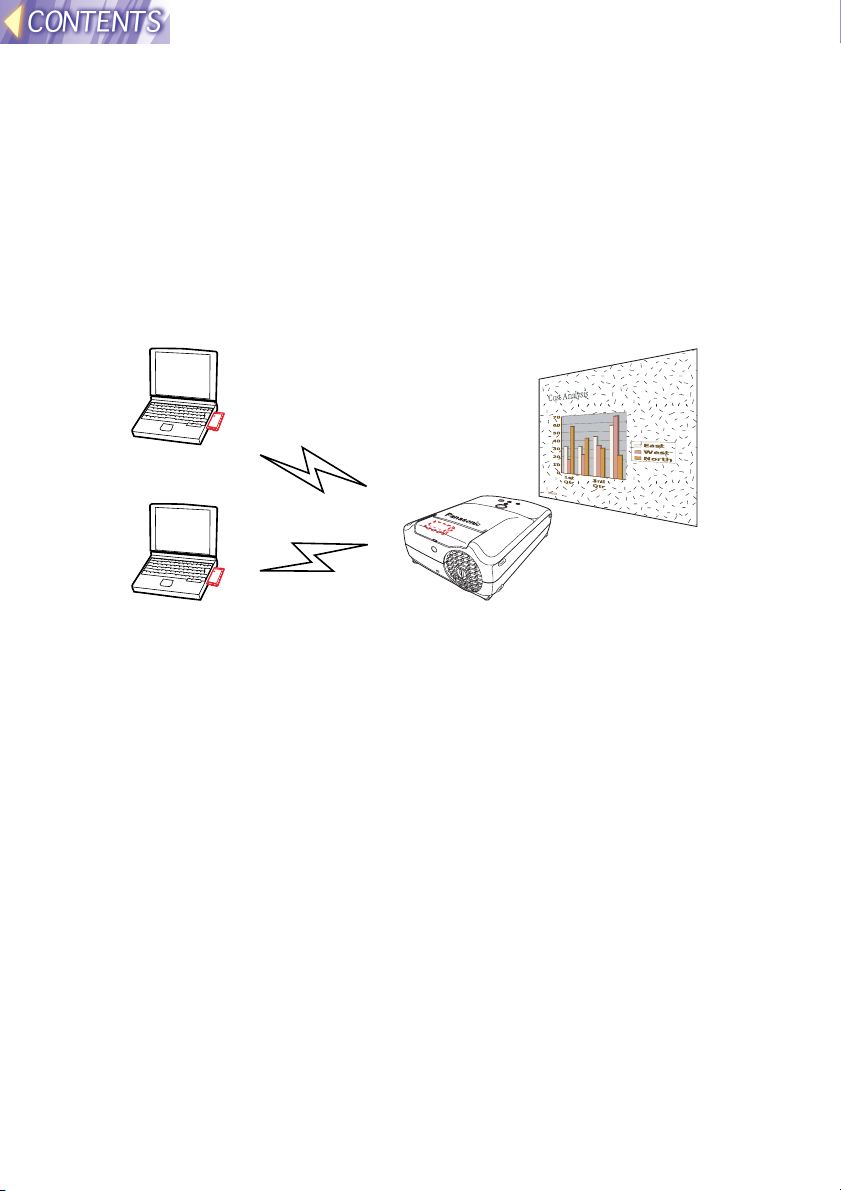
Wireless image transfer system for the projector
This system is designed to let you project images for presentations and
other purposes by transmitting images that appear on a computer screen
to the projector. This is possible by inserting the specified wireless cards
into the projector and into the computers that are to be used. More than
one computer can be connected to the projector in this way.
System diagram
Projected image
Note:
• An optional wireless card (ET-CDWL1 series) must be inserted into the
computer(s).
-7-

Transferable images
# Screen shots of
a whole
computer
screen
$ Screen shots of
the active
window on a
computer
screen
% Screen shots of
specified areas
of a computer
screen
& BMP, JPEG and
PNG images
Computer screens Projection images
-8-
Main functions of the application software
Software Functions
Driver
Configuration Utility
Wireless Manager • Storing multiple network settings
JPEG Convertor • Converting Microsoft PowerPoint files to
• Basic software for carrying out wireless
communication with a optional wireless card
connected to a computer
• Capturing computer screen images and sending
the images to the projector
• Selecting images from a list and transferring
them to the projector
• Automatic playback
DCF-compliant JPEG images
• Converting JPEG, BMP and TIFF images to
DCF-compliant JPEG images
• Sorting images
• Converting images sizes and compression ratios
Notes on using the projector
The following points must always be observed.
• Do not drop the projector or subject it to strong shocks.
• Do not let the projector get wet.
• Do not use unnecessary force to open and close the slot cover.
• Do not use wireless cards which are cracked or bent.
• Do not use the projector in places with high humidity such as bathrooms,
or in places which are very dusty such as warehouses.
Please make sure that you understand the following before
using the wireless card.
• Panasonic shall not be liable for any direct or indirect losses which may
be incurred as a result of using this product or from any malfunction of
this product.
• Panasonic takes no responsibility for any loss or corruption of data
caused by this product.
• Panasonic takes no responsibility for any unauthorized disclosure of data
transmitted by means of this product.
-9-

Explanation of terms
The following terms appear throughout these Operating Instructions, and
are defined here for easy reference.
LAN
Abbreviation for Local Area Network. A network which is small in scale,
such as an intra-company network. Both wired LANs and wireless LANs
can be found. This projector uses a wireless LAN.
TCP/IP
Abbreviation for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The
standard protocol for the Internet.
A protocol is a set of specifications and agreements which allow two
computers to communicate with each other.
IP Address
An Internet Protocol (IP) is a protocol used for the transmission of data,
and the IP address is the address of the destination where the data is
being sent to. Identical IP addresses cannot be used for two different
devices within the one LAN.
Subnet Mask
Limits the range of IP addresses that can be assigned to a computer when
using a TCP/IP connection, in order to allow a network to be divided into
several sub-sections. The parameters which divide the sub-network in this
way are called the subnet mask.
Gateway
A junction point where different types of networks are connected to each
other.
It is used to refer to the hardware and software which is used when
connecting a particular network to another network which has been set up
under different network specifications. It makes adjustments for differences
in the protocols used by the two networks and makes it possible to connect
to other networks.
DHCP
Abbreviation for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A function which
automatically assigns IP addresses to each computer that is connected to
a network. If a device which functions as a DHCP server is located within a
LAN, this device automatically assigns IP addresses to computers which
are connected to the LAN. Not available with this product.
-10-

Ad Hoc Mode
A mode for direct communication between the projector and a computer
with an optional wireless card.
Infrastructure Mode
A mode for communication via an access point which is connected to a
wired LAN.
A computer without an optional wireless card can still be used to send
images to the projector via an access point.
Access Point
A point of connection between a wired LAN and a wireless LAN.
Channel
If several access points which use the same frequency band are located
near each other, radio transmission interference between these access
point can occur when they are being used, and this can in turn result in
drops in transmission speeds. In order to reduce this problem when using
wireless LANs, the frequency band can be divided into 13 channels for
communication purposes. (The number of channels varies depending on
the country.) However, because interference between adjacent channels
can occur, the channels available for use are normally spaced 2 or 3
channels apart from each other.
SSID
Abbreviation for Service Set ID. Wireless LANs that utilise access points
require the setting of SSID identification codes in order to distinguish
between devices which are a part of the LAN and devices which are not.
WEP
Abbreviation for Wired Equivalent Privacy. A method of encrypting
transmitted data. An encryption key is generated and is given only to the
person who will be using the transmitted data, in order to prevent third
parties from decoding the transmitted data. Not available with this product.
-11-

JPEG
Abbreviation for Joint Photographic Experts Group. JPEG is the name of
an international organisation which was jointly established by the ISO and
the ITU-TS (formerly the CCIT), but the term is normally used to refer to the
specifications for the still picture compression algorithm which was
formulated by the JPEG. This algorithm allows still images such as
photographs, single frames of moving images and scanned images to be
compressed to up to 1/100th of their original sizes. However, images which
are compressed in this way cannot be fully restored to their original quality
(some deterioration in quality occurs), so that compression rates of 1/5 to
1/30 are normally used. Because of differences in colour separation, two
format sub-types are used: RGB (red, green and blue) and CMYK (cyan,
magenta, yellow, black).
The projector and the JPEG Convertor software do not support the CMYK
sub-type of JPEG file.
BMP
Abbreviation for BitMaP. This is the standard image format for the
bitmapped files (image files consisting of a collection of dots) which are
handled by Windows.
Colour levels of monochrome, 16 colours, 256 colours and 16.7 million
colours are supported.
PNG
Abbreviation for Portable Network Graphics.
A high compression rate file format that provides restorable compression
for line raster images.
Because it uses restorable compression, it does not result in any loss of
image resolution unlike JPEG.
RLE
Abbreviation for Run Length Encoding. It can be used to achieve high rates
of compression for image files which contain large areas of a single colour.
RLE can be used with monochrome, 16-colour and 256-colour BMP image
files. (JPEG Convertor does not support files compressed using RLE.)
TIFF
Abbreviation for Tagged-Image File Format. This type of file is used to
exchange documents between computers. Colour levels of monochrome,
256 colours and 16.7 million colours are supported. TIFF files in 16.7
million colour format can include transparent colour.
-12-

LZW
Abbreviation for Lempel-Ziv-Welch. LZW is a compression method used
for TIFF files, and is named thus because it was developed by three people
named Lempel, Ziv and Welch. It compresses the files by converting
patterns within the images into short codes. There is no deterioration in
image quality resulting from compression, but high rates of compression
which are comparable to JPEG files cannot be expected to be obtained.
(JPEG Convertor does not support files compressed using LZW.)
DCF
Abbreviation for Design rule for Camera File system. DCF is a standard
which was established by the Japan Electronic Industry Development
Association (JEIDA) with the aim of realising a common image file format,
directory name format and file name format for the images used with digital
still cameras. It is based on recommendations such as Exif Version 2.1.
Exif 2.1
Abbreviation for Exchangeable Image File Format. This is an image file
format which was established by the Japan Electronic Industry
Development Association (JEIDA). It defines the common information
format and range of application for images used with digital still cameras,
centring around TIFF and JPEG-format images. Version 2.1 is the latest
version of the Exif standard.
PowerPoint
Application software for creating presentations which is included as part of
Microsoft Office. 95, 97 and 2000 versions are available, but the JPEG
Convertor software which is bundled with the projector is only compatible
with the 97 and 2000 versions.
-13-

Wireless function preparation
The methods of transferring images using a wireless LAN can be broadly
classified into three types according to the environment you are currently
using.
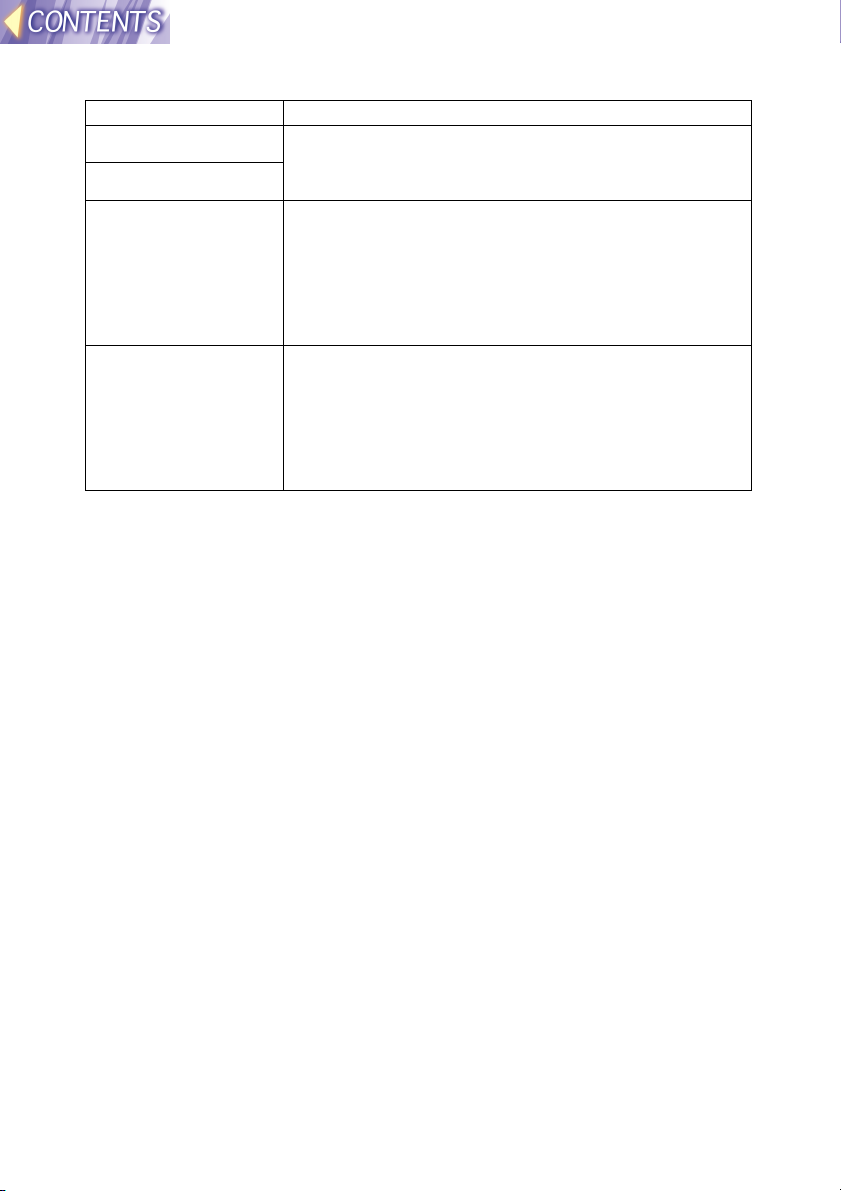
(1) Firstly, when using the wireless function
Insert an optional ET-CDWL1 series wireless card into a computer, and
use Ad Hoc mode so that the computer can carry out direct wireless
communication with the projector.
Computer Projector
Setting procedure
Set the computer and the projector according to the following procedure.
Preparation & settings Check
communication
<Projector> <Computer> <Computer> <Computer>
Inserting the
wireless
card (page
18)
LAN
settings
(page 21)
Inserting the
wireless card
(page 27)
Network
settings using
Wireless
Manager
(page 37)
Use Wireless
Manager to
check
communicatio
n with the
projector
(page 40)
Transmit
images
Use Wireless
Manager to
transmit the
images (page
41)
Setting example
Setting item Projector LAN
settings
IP ADDRESS 192.168.10.10 (default)
If using two or more
projectors, use different
addresses for each.
SUBNET MASK 255.255.255.0 (default) 255.255.255.0
MODE AD HOC Ad Hoc
CHANNEL 11 (default)
Use the same setting
for the computer.
Network settings using
Wireless Manager at
computer
Set the address to
something like
192.168.10.11 or
192.168.10.12. Do not
use the same address as
used for the projector.
11
Use the same setting for
the projector.
-14-
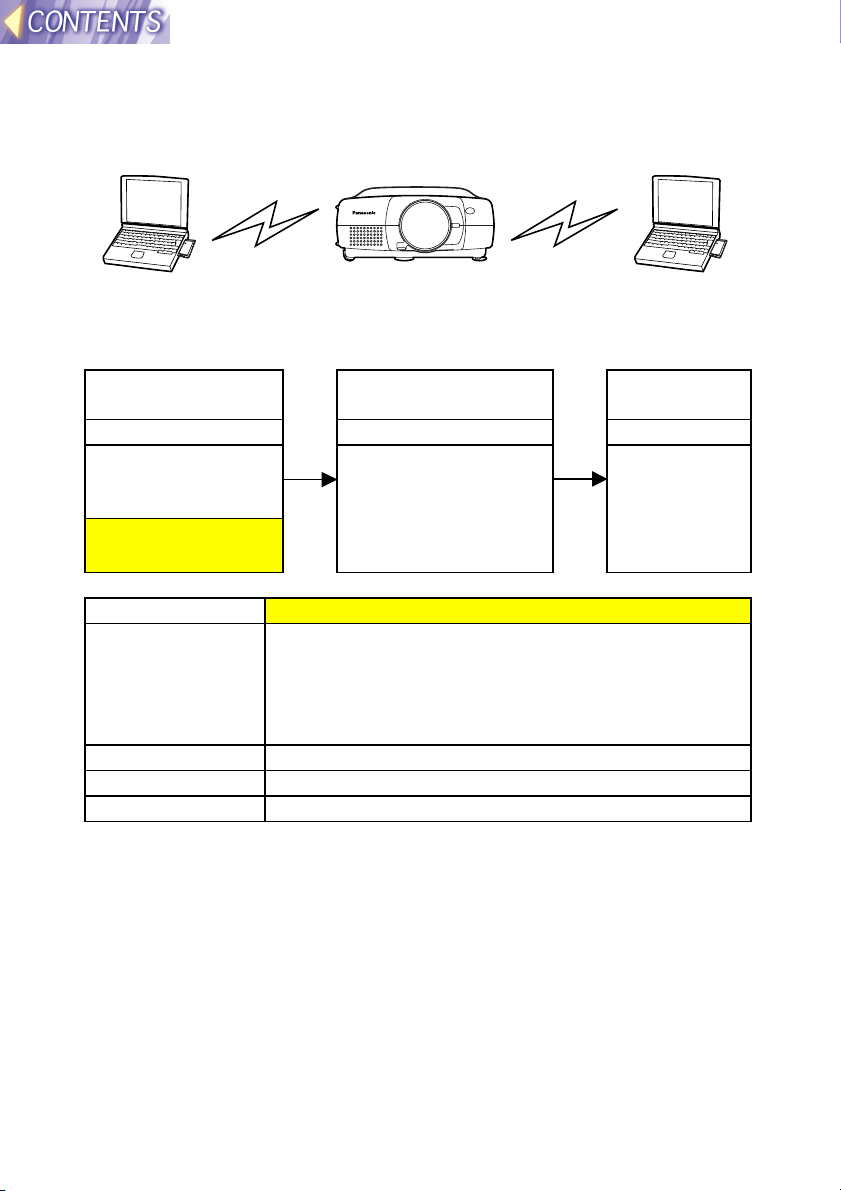
(2) If already using computers for wireless
transmission (Ad Hoc mode)
Use the existing wireless cards for the computers to carry out direct
wireless communication with the projector in Ad Hoc mode.
Computer Projector Computer
Setting procedure
Set the computer and the projector according to the following procedure.
Preparation &
settings
<Projector> <Computer> <Computer>
Inserting the
wireless card (page
18)
LAN settings (page
21)
Check communication Transmit
images
Use Wireless
Manager to check
communication with
the projector (page
40)
Use Wireless
Manager to
transmit the
images (page
41)
Setting example
Setting item Projector LAN settings
IP ADDRESS Set the computer IP address to an address with the
last number different.
e.g. If the computer IP address is 192.168.10.11, set
the projector’s address to something like
192.168.10.12.
SUBNET MASK Use the same setting for the computer.
MODE AD HOC
CHANNEL Use the same setting for the computer.
Note:
• The computer settings can be used without further changes. However, if
using the WEP function, communication with the projector will not be
possible. You will first need to turn off the WEP function for all computers
which are to communicate with the projector.
Furthermore, when the WEP function is turned off, the data encryption
function will also be turned off, so it is recommended that you use a
feature such as the Sharing Settings for folders to set password
protection for your data. Ask your network administrator for further
details.
• If you any wireless cards other than the optional ET-CDWL1 series,
correct operation cannot be guaranteed.
-15-
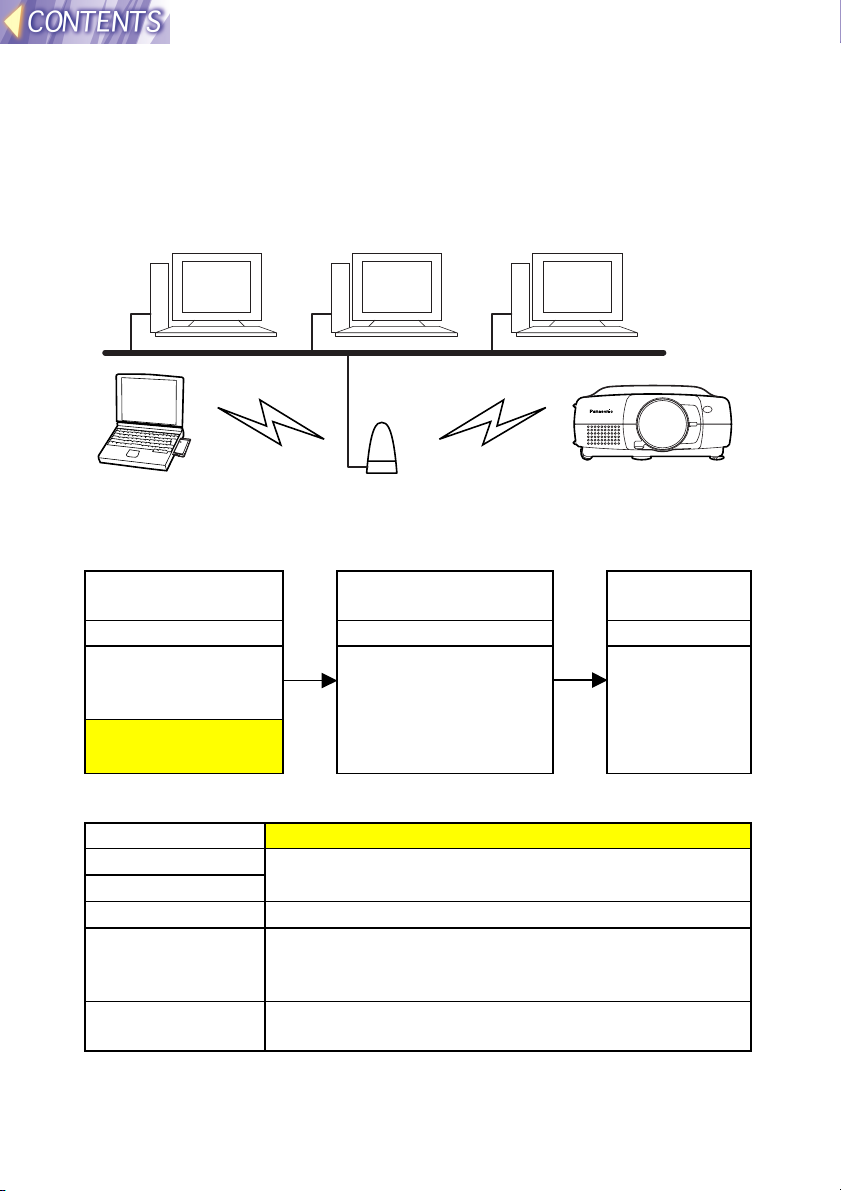
(3) When using an existing access point for
wireless communication
Use the access point to carry out wireless communication between the
computer and the projector in Infrastructure mode. Some access points
may not let you make connections.
Computer Computer Computer
LAN
Computer Access point Projector
Setting procedure
Set the computer and the projector according to the following procedure.
Preparation &
settings
<Projector> <Computer> <Computer>
Inserting the
wireless card (page
18)
LAN settings (page
21)
Check communication Transmit
images
Use Wireless
Manager to check
communication with
the projector (page
40)
Use Wireless
Manager to
transmit the
images (page
41)
Setting example
Setting item Projector LAN settings
IP ADDRESS
SUBNET MASK
MODE INFRASTRUCURE
CHANNEL Set to the same CHANNEL as the CHANNEL for the
SSID Set to the same SSID as the SSID for the access
Ask your network administrator for details on
settings.
access point. (Ask your network administrator for
details.)
point. (Ask your network administrator for details.)
Note:
• If either the projector or computer is out of the range of the access point,
use Ad Hoc mode as described in page 14.
-16-

• The projector’s SSID can be up to 16 characters in length, and must
consist of capital letters (A-Z) and numerals (0-9). Accordingly, if the
SSID that has been set for the access point is invalid as an SSID for the
projector, ask your network administrator to change the access point’s
SSID to one that can be used by the projector.
• The projector is not compatible with DHCP. For LANs that use DHCP
servers, a fixed IP address needs to be assigned to the projector for it to
be used. Ask your network administrator for further details.
• If using the WEP function, communication with the projector will not be
possible. You will first need to turn off the WEP function for all computers
which are to communicate with the projector.
Furthermore, when the WEP function is turned off, the data encryption
function will also be turned off, so it is recommended that you use a
feature such as the Sharing Settings for folders to set password
protection for your data. Ask your network administrator for further
details.
-17-
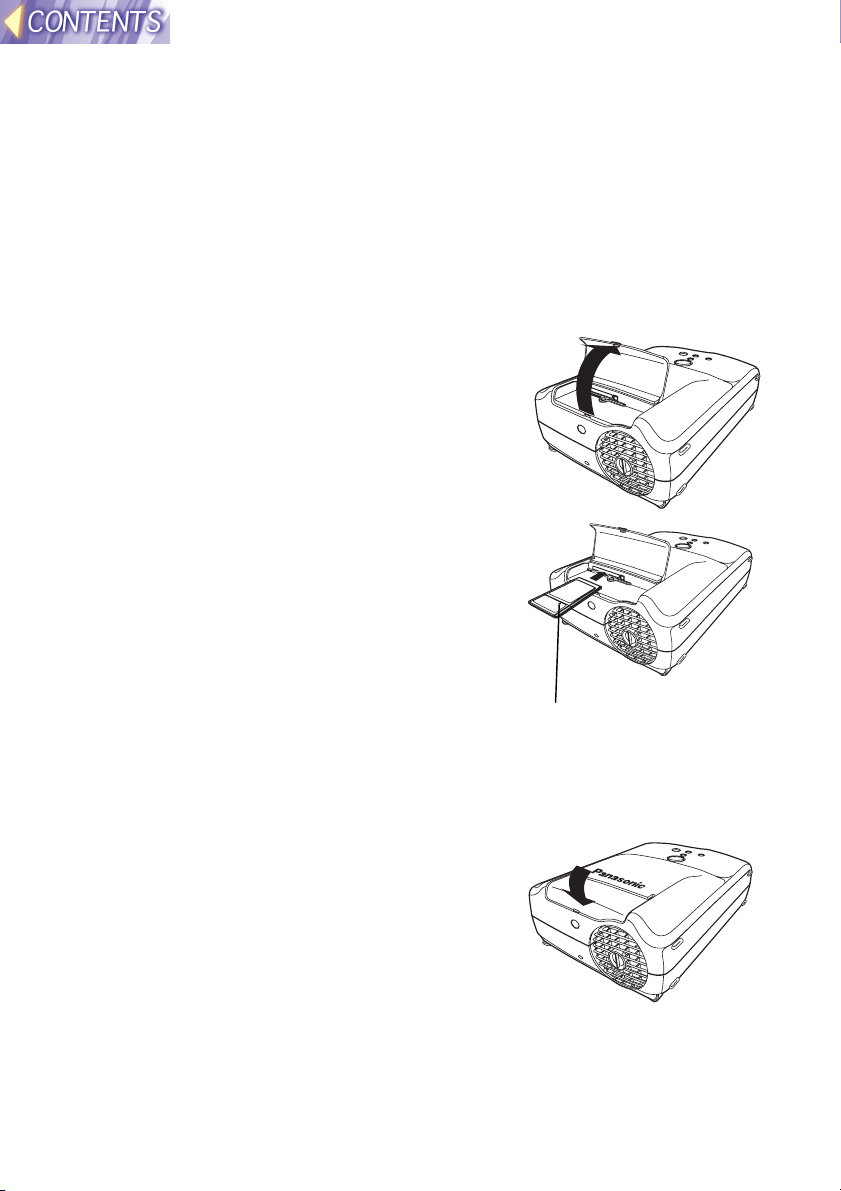
Installing and removing the wireless card
Inserting the wireless card
#### Turn off the power supply for the projector.
Turn of the power supply for the projector while referring to “Turning off
the power” on page 23 of the PT-L712E Operating Instructions.
$$$$ Open the slot cover.
%%%% Insert the wireless card as shown in
the illustration at right.
Hold the wireless card so that the power
monitor is facing upward when inserting it,
and push it all the way in until it locks.
Wireless card power monitor
Note:
• Make sure the wireless card is facing the correct way when inserting it. If
you try to force the wireless card the wrong way into the slot, it will
damage the wireless card and the projector.
&&&& Close the slot cover.
-18-
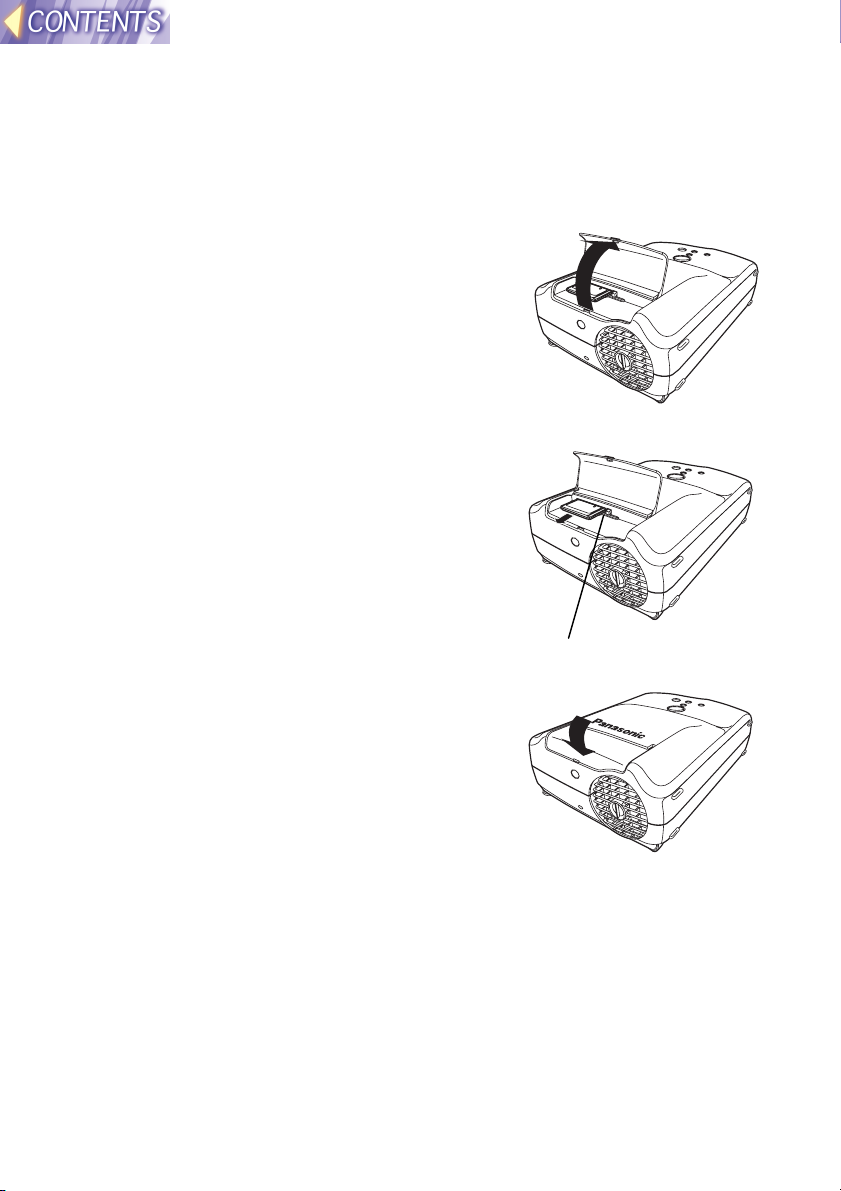
Removing the wireless card
#### Turn off the power supply for the projector.
Turn of the power supply for the projector while referring to “Turning off
the power” on page 23 of the PT-L712E Operating Instructions.
$$$$ Open the slot cover.
%%%% Press the eject switch.
When you press the eject switch, it pops
out.
&&&& Push in the eject switch and then
remove the wireless card.
Eject switch
(((( Close the slot cover.
-19-
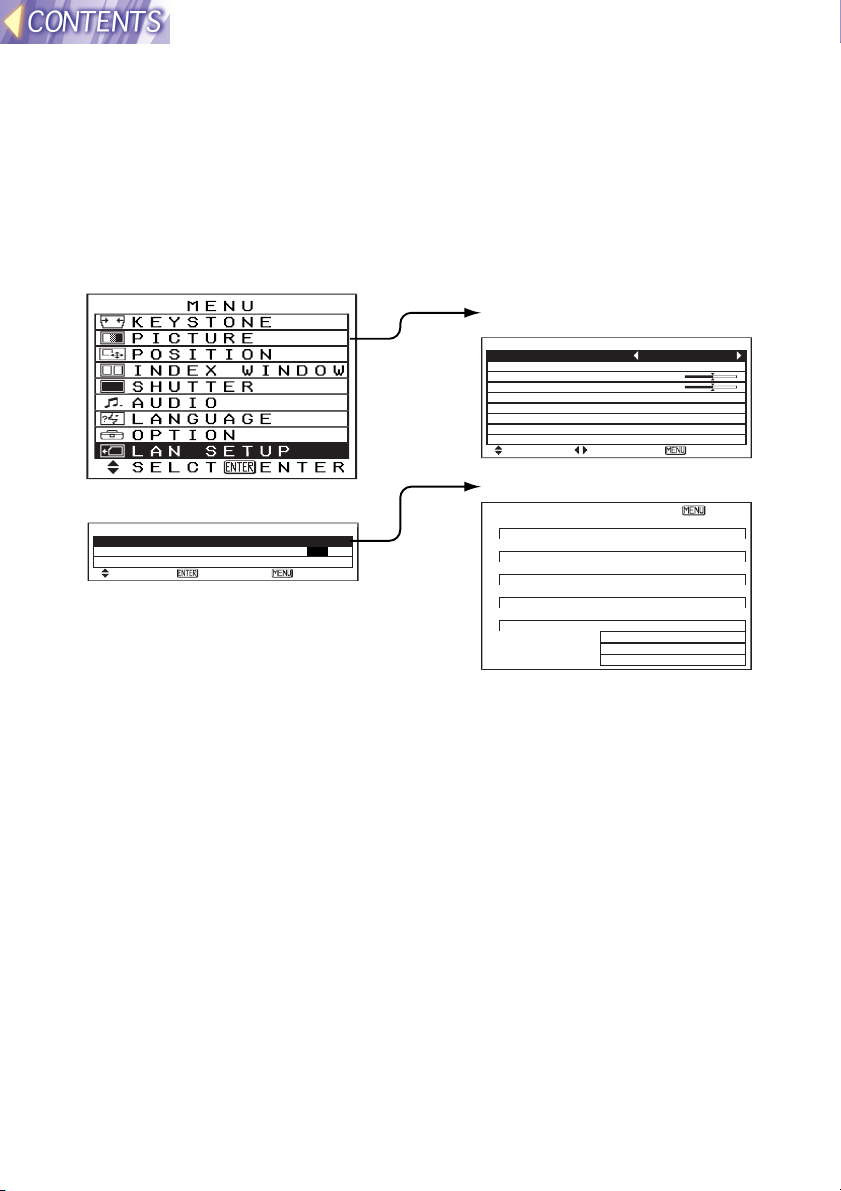
On-screen menus
List of menu screens
Adjustments and setting changes for this projector are carried out using
on-screen menu operations. The configuration for the projector’s LAN
SETUP menu is shown in the illustration below.
MAIN MENU
PICTURE
PICTURE
PICTURE MODE NATURAL
BRIGHT 32
CONTRAST 32
SELCT ADJ ESC
LAN SETUP(page21)
LAN SETUP
STATUS LAN 1
LOCK SETUP OFF ON
SETUP
SELCT ENTER ESC
[LAN 1] ESC
IP ADDRESS
192.168. 10. 10
SUBNET MASK
255.255.255. 0
HOSTNAME
PANASONIC PRJ-01
MODE
AD HOC
SSID
SSID
CH 11
ENCRYPT OFF
KEY 0- 0
Note:
Please refer to the separate PT-L712E Operating instructions for details on
main menu items other than LAN SETUP.
STATUS(page21)
-20-

Projector LAN settings
After inserting the wireless card into the projector, you need to make the
necessary LAN settings.
Displaying the LAN Setup screen
#### Press the MENU button. The MAIN
MENU screen will be displayed.
$$$$ Press the FFFF or GGGG button to select
“LAN SETUP”.
%%%% Press the ENTER button. The LAN
SETUP screen will be displayed.
STATUS
LAN SETUP
STATUS LAN 1
LOCK SETUP OFF ON
SETUP
SELCT ENTER ESC
The projector can store up to five different types
of LAN settings. The STATUS command can
be used to view the settings which are currently
selected.
Press the F or G button on the projector’s
control panel or the remote control to select
[LAN 1] ESC
IP ADDRESS
192.168. 10. 10
SUBNET MASK
255.255.255. 0
HOSTNAME
PANASONIC PRJ-01
MODE
AD HOC
SSID
SSID
CH 11
ENCRYPT OFF
KEY 0- 0
“STATUS”, and then press the [ENTER] button.
The STATUS screen will be displayed.
Note:
• Refer to SETUP on page 22 for details on making the various LAN
settings.
• If the CH display appears in red, it means that the selected channel
cannot be used. Use the SETUP menu to change the CHANNEL setting.
-21-
 Loading...
Loading...