Panasonic KX-TG6381LB Schematic

ORDER NO. KM40807637CE
Telephone Equipment
Model No. KX-TG6381LBB
KX-TG6381LBS
KX-TG6382LBB
KX-TGA632LBB
KX-TGA632LBS
Expandable Digital Cordless Phone
Black Version
Pearl Silver Version
(for Brazil)
© 2008 Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law.

KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAG E PAG E
1 Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- 4
1.1. For Service Technicians --------------------------------- 4
2 Warning-------------------------------------------------------------- 4
2.1. Battery Caution--------------------------------------------- 4
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)-------------- 4
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board-------------------------------- 5
3 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 6
4 Technical Descriptions ----------------------------------------- 7
4.1. US-DECT Description ------------------------------------ 7
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)---------------------- 9
4.3. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part) -----------------10
4.4. Circuit Operation (Base Unit) --------------------------11
4.5. Block Diagram (Handset)-------------------------------18
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)-------------------19
4.7. Circuit Operation (Handset)----------------------------20
4.8. Circuit Operation (RF Part)-----------------------------24
4.9. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit) ----------------------25
4.10. Signal Route -----------------------------------------------26
5 Location of Controls and Components ------------------27
5.1. Controls -----------------------------------------------------27
5.2. Display ------------------------------------------------------27
6 Installation Instructions ---------------------------------------28
6.1. Connections------------------------------------------------28
6.2. Battery-------------------------------------------------------28
7 Operating Instructions-----------------------------------------30
7.1. Programmable Settings ---------------------------------30
7.2. Dial Lock ----------------------------------------------------32
7.3. Error Messages -------------------------------------------33
7.4. Troubleshooting-------------------------------------------34
8 Test Mode ----------------------------------------------------------37
8.1. Adjustment and Test Mode Flow Chart -------------37
9 Service Mode -----------------------------------------------------44
9.1. How to Clear User Setting------------------------------44
10 Troubleshooting Guide ----------------------------------------45
10.1. Troubleshooting Flowchart -----------------------------45
11 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions ---------------56
11.1. Disassembly Instructions -------------------------------56
11.2. How to Replace the Handset LCD -------------------60
12 Measurements and Adjustments---------------------------61
12.1. Things to Do after Replacing IC or X’tal ------------61
12.2. Base Unit Reference Drawing-------------------------62
12.3. Handset Reference Drawing---------------------------63
12.4. Frequency Table------------------------------------------64
13 Schematic Diagram ---------------------------------------------65
13.1. For Schematic Diagram---------------------------------65
13.2. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main) --------------66
13.3. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part) ----------68
13.4. Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main) ----------------70
13.5. Schematic Diagram (Handset_RF Part) ------------72
13.6. Schematic Diagram (Charger Unit) -----------------73
14 Printed Circuit Board-------------------------------------------75
14.1. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main) -----------------------75
14.2. Circuit Board (Base Unit_RF prat) -------------------77
14.3. Circuit Board (Handset_Main)-------------------------79
14.4. Circuit Board (Handset_RF Part) ---------------------81
14.5. Circuit Board (Charger Unit) ---------------------------82
15 Miscellaneous ----------------------------------------------------83
15.1. CPU Data (Base Unit) -----------------------------------83
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
15.2. CPU Data (Handset) ------------------------------------ 84
15.3. How to Replace the Flat Package IC --------------- 85
15.4. How to Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe
Package) IC ----------------------------------------------- 87
15.5. Explanation of IC Terminals (RF Part) -------------- 90
15.6. Terminal Guide of the ICs, Transistors and
Diodes ------------------------------------------------------ 91
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List ----------- 92
16.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Base Unit) ----------- 92
16.2. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Handset)------------- 93
16.3. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Charger Unit) ------- 94
16.4. Accessories and Packing Materials ----------------- 95
16.5. Replacement Parts List--------------------------------- 98
3
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. For Service Technicians
• Repair service shall be provided in accordance with repair technology information such as service manual so as to prevent fires, injury or electric shock, which can be caused by improper repair work.
1. When repair services are provided, neither the products nor their parts or members shall be remodeled.
2. If a lead wire assembly is supplied as a repair part, the lead wire assembly shall be replaced.
3. FASTON terminals shall be plugged straight in and unplugged straight out.
• ICs and LSIs are vulnerable to static electricity.
When repairing, the following precautions will help prevent recurring malfunctions.
1. Cover plastic parts boxes with aluminum foil.
2. Ground the soldering irons.
3. Use a conductive mat on worktable.
4. Do not grasp IC or LSI pins with bare fingers.
2Warning
2.1. Battery Caution
1. Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
2. Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
3. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's Instructions.
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)
Note:
In the information below, Pb, the symbol for lead in the periodic table of elements, will refer to standard solder or solder that contains lead.
We will use PbF solder when discussing the lead free solder used in our manufacturing process which is made from Tin (Sn),
Silver (Ag), and Copper (Cu).
This model, and others like it, manufactured using lead free solder will have PbF stamped on the PCB. For service and repair
work we suggest using the same type of solder.
Caution
• PbF solder has a melting point that is 50 °F ~ 70 °F (30 °C ~ 40 °C) higher than Pb solder. Please use a soldering iron with temperature control and adjust it to 700 °F ± 20 °F (370 °C ± 10 °C).
• Exercise care while using higher temperature soldering irons.:
Do not heat the PCB for too long time in order to prevent solder splash or damage to the PCB.
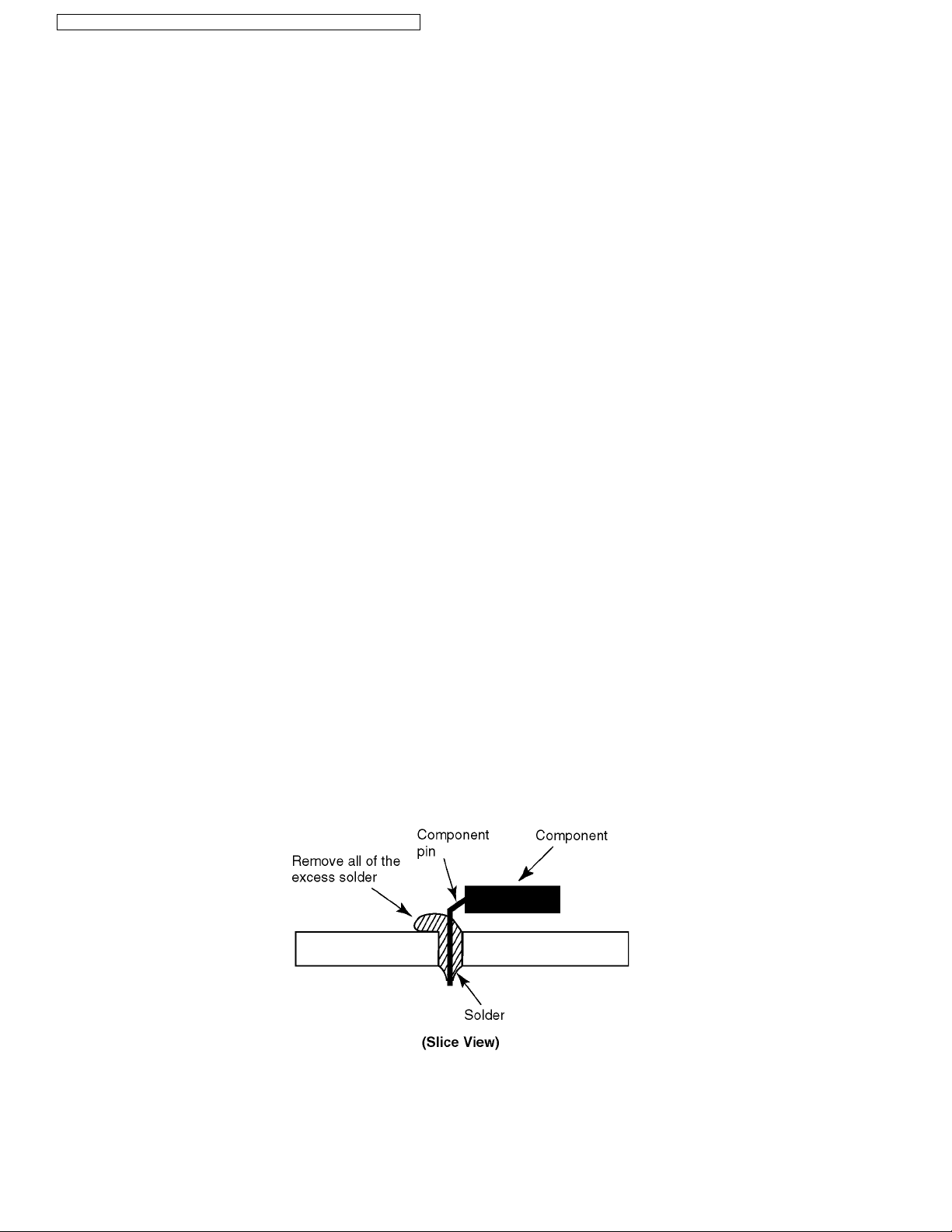
• PbF solder will tend to splash if it is heated much higher than its melting point, approximately 1100 °F (600 °C).
• When applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess which may flow onto the
opposite side (See the figure below).
4
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
2.2.1. Suggested PbF Solder
There are several types of PbF solder available commercially. While this product is manufactured using Tin, Silver, and Copper
(Sn+Ag+Cu), you can also use Tin and Copper (Sn+Cu), or Tin, Zinc, and Bismuth (Sn+Zn+Bi). Please check the manufacturer's specific instructions for the melting points of their products and any precautions for using their product with other materials.
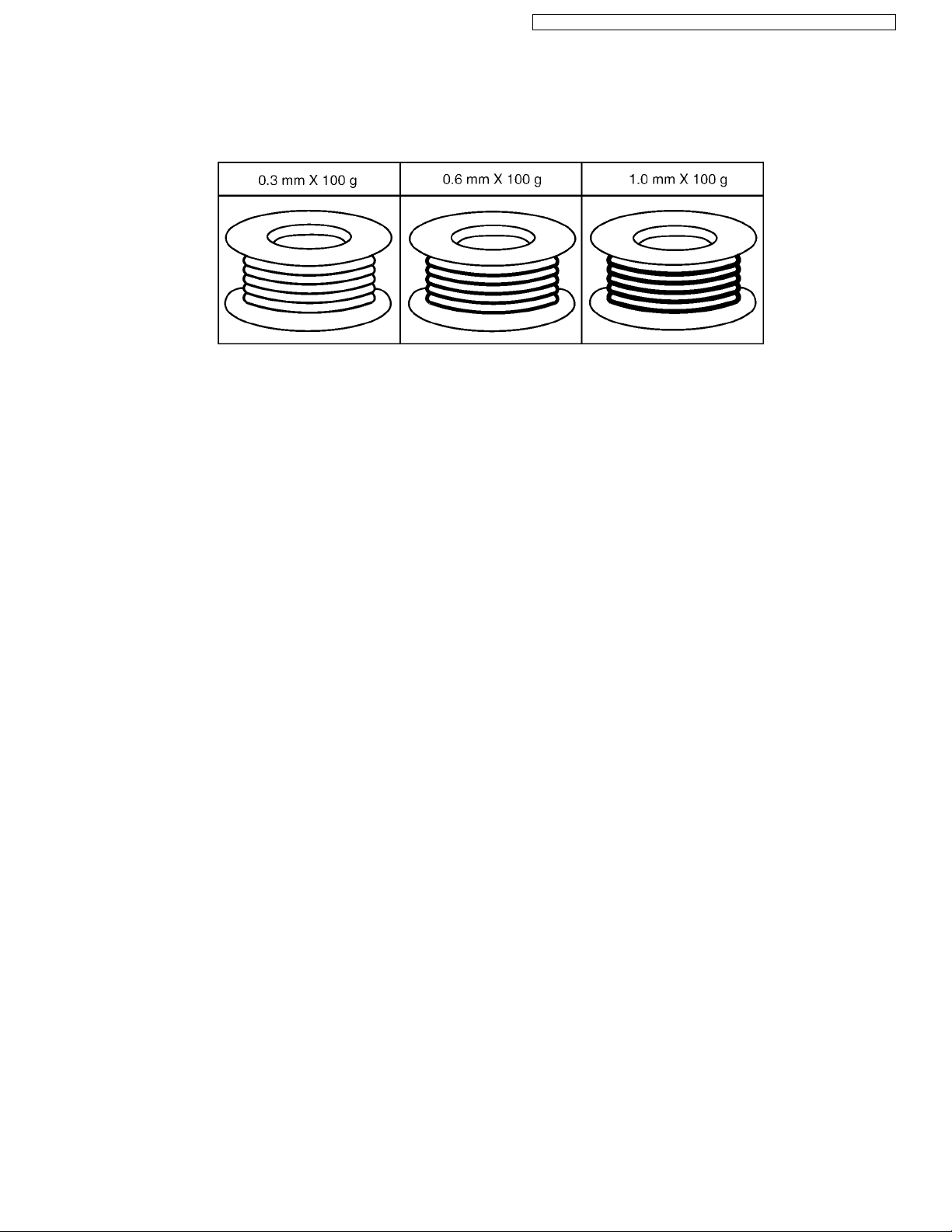
The following lead free (PbF) solder wire sizes are recommended for service of this product: 0.3 mm, 0.6 mm and 1.0 mm.
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board
When discarding P. C. Board, delete all personal information such as telephone directory and caller list or scrap P. C. Board.
5
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
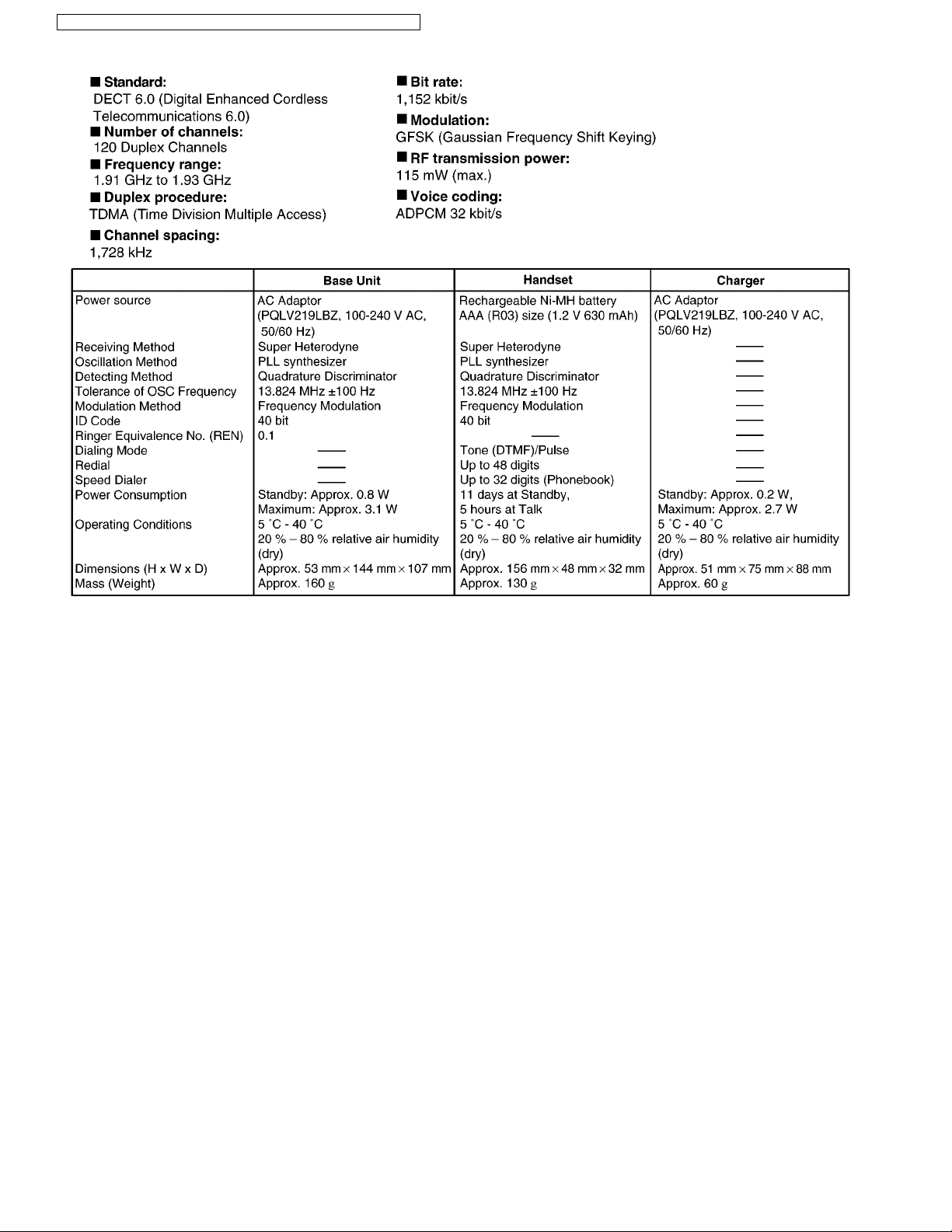
3 Specifications
Note:
• Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
6
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4 Technical Descriptions
4.1. US-DECT Description
The frequency range of 1.92 GHz-1.93 GHz is used. Transmitting and receiving carrier between base unit and handset is same frequency. Refer to Frequency Table (P.64).
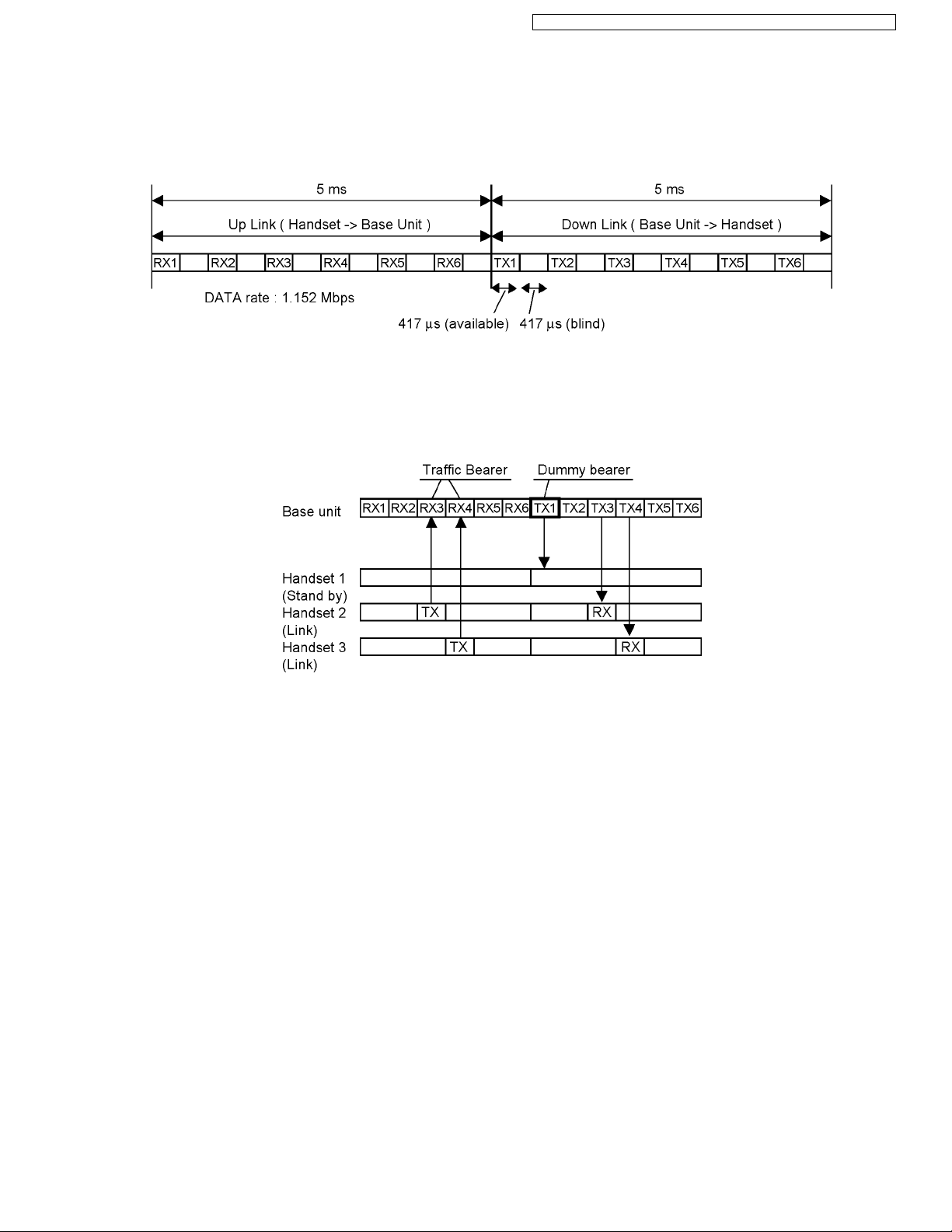
4.1.1. TDD Frame Format
4.1.2. TDMA system
This system is the cycles of 10 ms, and has 6 duplex paths, but maximum duplex communication path is 5 because of dummy
bearer use.
In 1 slot 417 µs, the 10 ms of voice data is transmitted.
• 2 - Handsets Link
Traffic Bearer
A link is established between base unit and handset.
The state where duplex communication is performed.
Handset doesn't make up duplex in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Dummy Bearer
Base unit sends Dummy-data to the all stand-by state handsets.
Handsets receive that data for synchronization and monitoring request from the base unit.
Base unit doesn't send Dummy bearer in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Note:
(*1) It is a feature under FCC 15 regulation and for interference avoidance.
In the case of checking RF parts, it is better in least interference condition.
7

KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.1.3. Signal Flowchart in the Radio Parts
Reception
A voice signal from TEL line is encoded to digital data "TXDATA" by DSP (IC501) in a base unit.
Then TXDATA goes to RF PART, and it's modulated to 1.9 GHz. The RF signal is amplified and fed to a selected antenna.
As for a handset RF, RF signal is received in two antennas.
RFIC (IC701) compares RF signal levels and selects the antenna to be used. Then RFIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal
from RX signal in the selected antenna, and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA".
DSP (IC501) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to speaker.
Transmission
A voice signal from microphone is encoded to digital data "TXDATA" by DSP (IC501) in a handset.
Then TXDATA goes to RF PART, and it's modulated to 1.9 GHz. The RF signal is amplified and fed to a selected antenna.
As for a base unit RF, RF signal is received in two antennas.
RFIC (IC701) compares RF signal levels and selects the antenna to be used. Then RFIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal
from RX signal in the selected antenna, and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA".
DSP (IC501) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to TEL line.
8
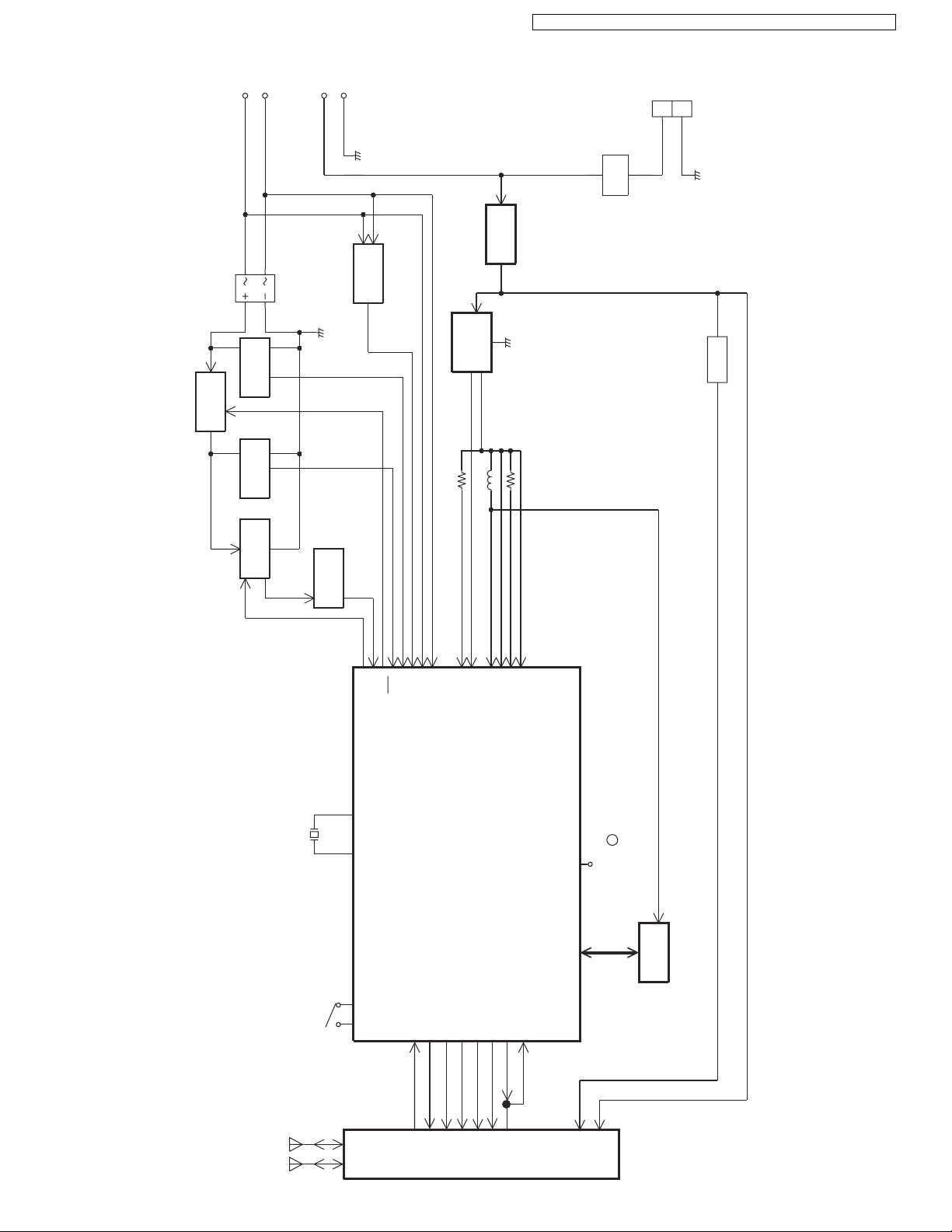
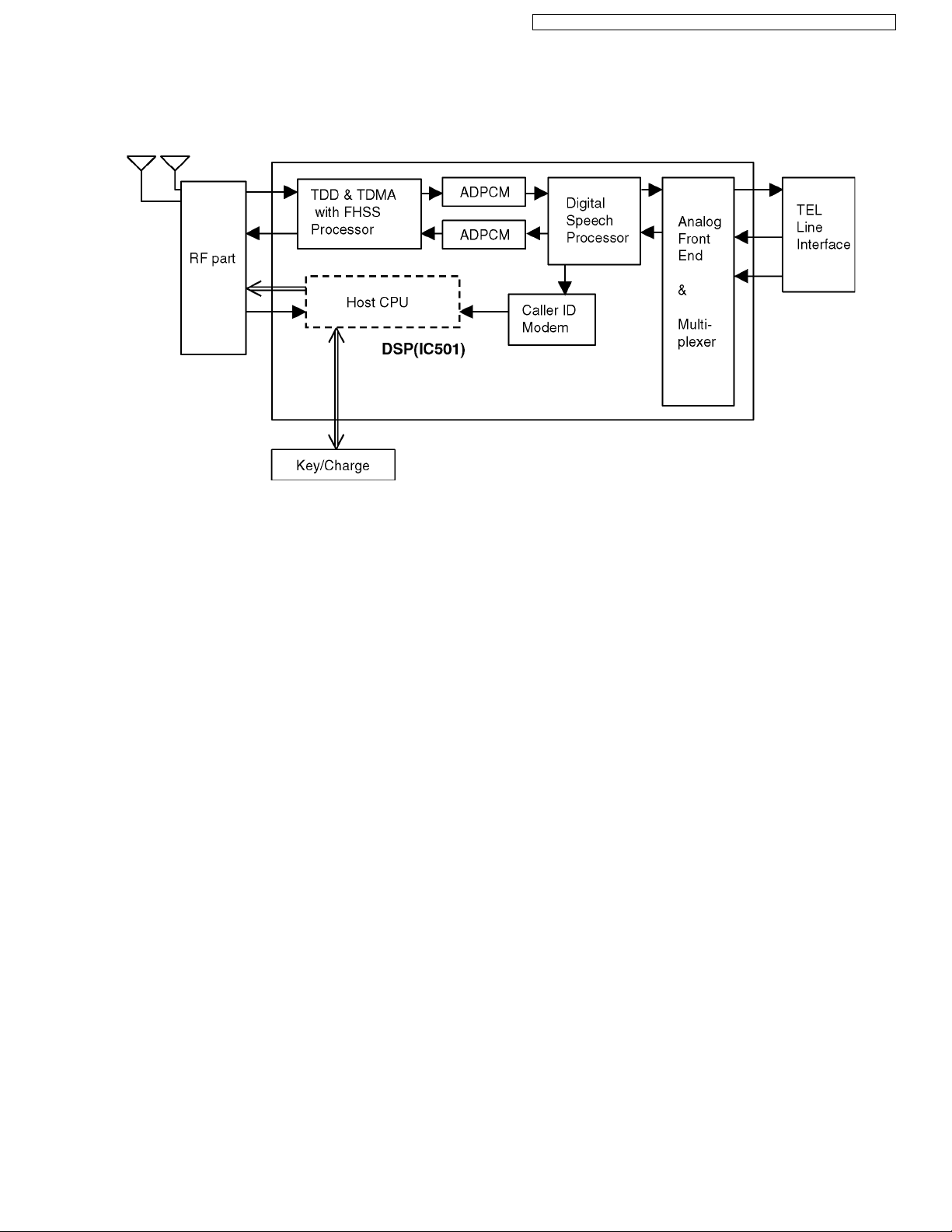
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)
L1T
L1R
DCP
DCM
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
-
+
Q141
RLY
D101
INUSE
DETECT 1
R131, R133
INUSE
DETECT 2
R151,R152
SIDE TONE
CIRCUIT
Q161
TEL JACK
Q171
Q111
RECEIVE
AMP
DC JACK
BELL
DETECT
3.3 V
IC331
4.0 V
CONVERTOR
IC300, Q300
REGULATOR
with RESET
CHARGE_CONTACT
R371
R372
Q382
KX-TG6381/6382 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit_Main)
X501
13.824 MHz
SW661
LIN
LOUT
RLY
DCIN 2
KEY_C
KEY 1
BELL
DCIN 1
CID_IN
CID_IN
MSG_LED
ANSWER_LED
SYN_OUT
SYN_EN
VCC
RESET
POWER_DOWN
DSP
IC501
SYN_CLK
SYN_DATA
SLOT_CTROL
VCCA
VCCIN
VCCPA
RADIO_EN
TXDATA
RXDATA
INT_1
CLK,RST
SI,SO,CS,
V_RF
V_RF(VPA)
INT_1 5
VCC
IC611
EEPROM
ANT2ANT1
RF_PART
9
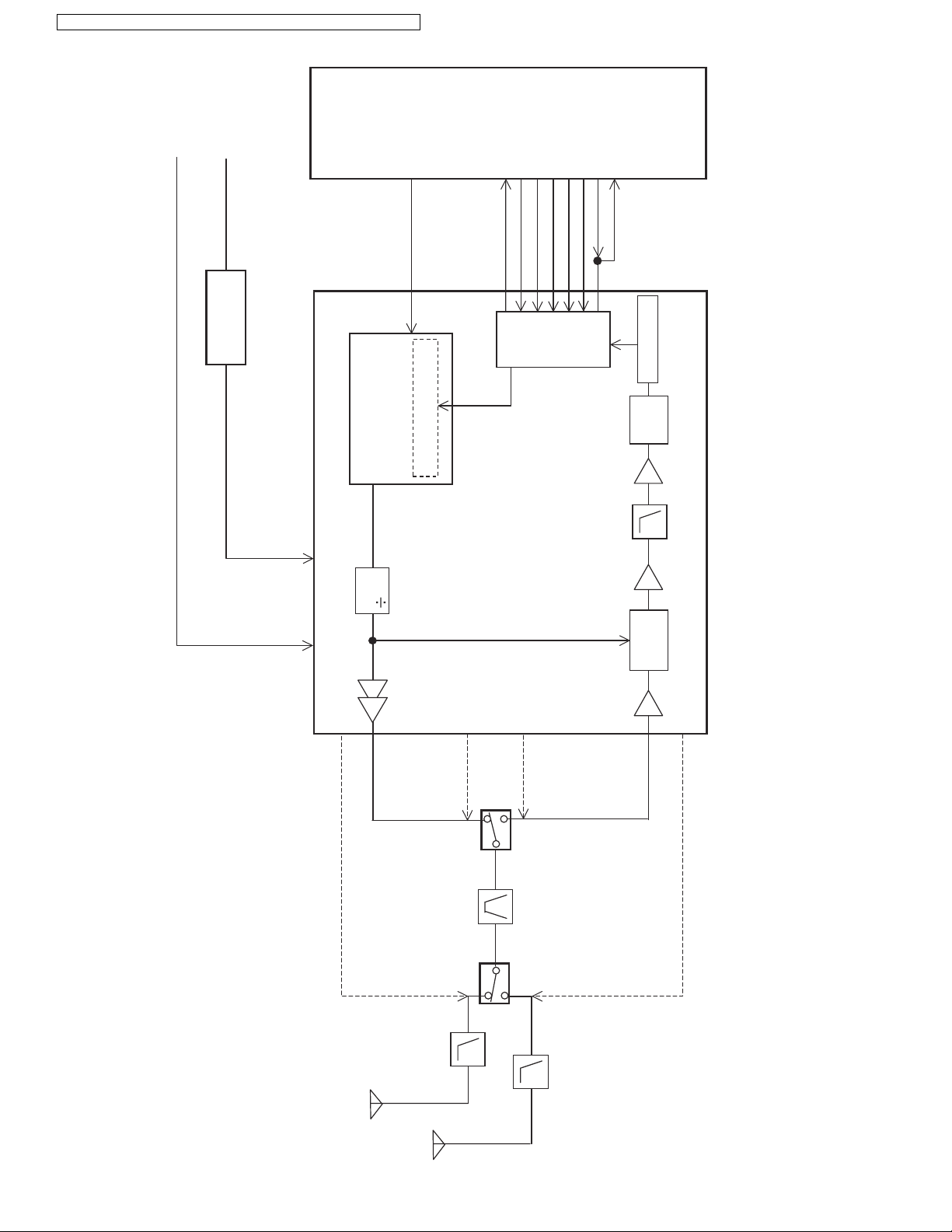
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.3. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part)
DSP
V_PA
V_RF
4.0 V3.0 V
IC501
BCLK
13.824 MHz
SYN_OUT
SYN_EN
SYN_CLK
SYN_DATA
SLOT_CTROL
RADIO_EN
TXDATA
RXDATA
IC741
Regulator
PLL
1.5
Divider
delta-sigma Modulator
IC701
Logic
Control
Demodulator
A/D
KX-TG6381/6382 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit_RF Part)
Mixer
D781 D771
ANT1 (*1)
Note:
ANT2 (*1)
10
(*1) Antenna Type: wired dipole antenna
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.4. Circuit Operation (Base Unit)
General Description:
(DSP, EEPROM) is a digital speech/signal processing system that implements all the functions of speech compression and
memory management required in a digital telephone.
The DSP system is fully controlled by a host processor DSP. The host processor provides activation and control of all that functions as follows.
4.4.1. DSP (Digital Speech/Signal Processing: IC501)
• DTMF Generator
The DTMF detection is implemented by the DSP system in software.
The DTMF detection is performed during Line Monitoring modes of operation.
When the DTMF data from the handset is received, the DTMF signal is output.
• Caller ID demodulation
The DSP implements monitor and demodulate the FSK/DTMF signals that provide CID information from the Central Office.
• Digital Switching
The voice signal from telephone line is transmitted to the handset or the voice signal from the handset is transmitted to the Telephone line, etc. They are determined by the signal path route operation of voice signal.
• Block Interface Circuit
RF part, LED, Key scan, Telephone line.
4.4.2. EEPROM (IC611)
Following information data is stored.
• Settings
ex: ID code, Flash Time, Tone/Pulse
11
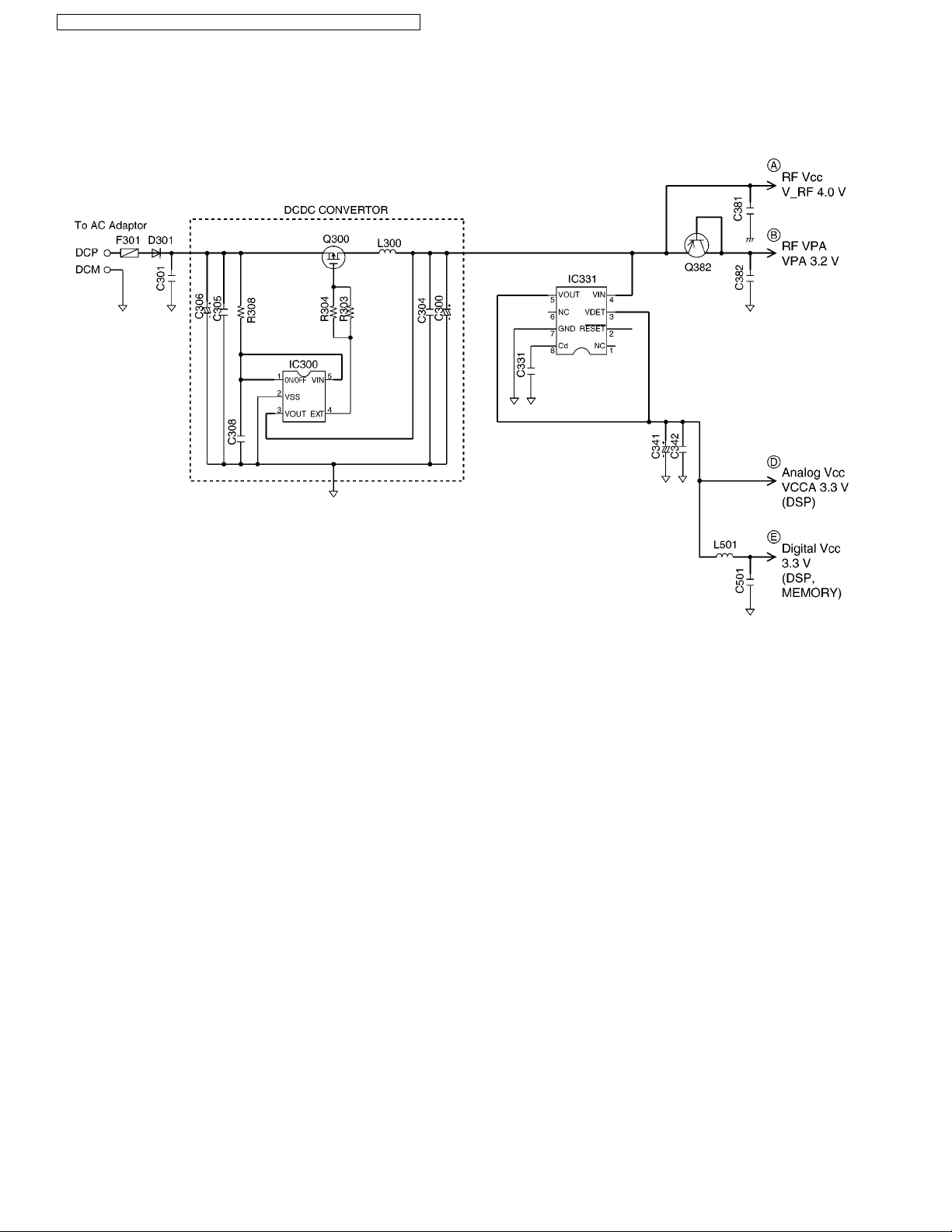
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.4.3. Power Supply Circuit
Function:
The power supply voltage from AC adaptor is converted to the desired voltage of each block.
Circuit Operation:
• Q300 and IC300: 4.0 V DCDC Converter
• IC331: 3.3 V Regulator
12
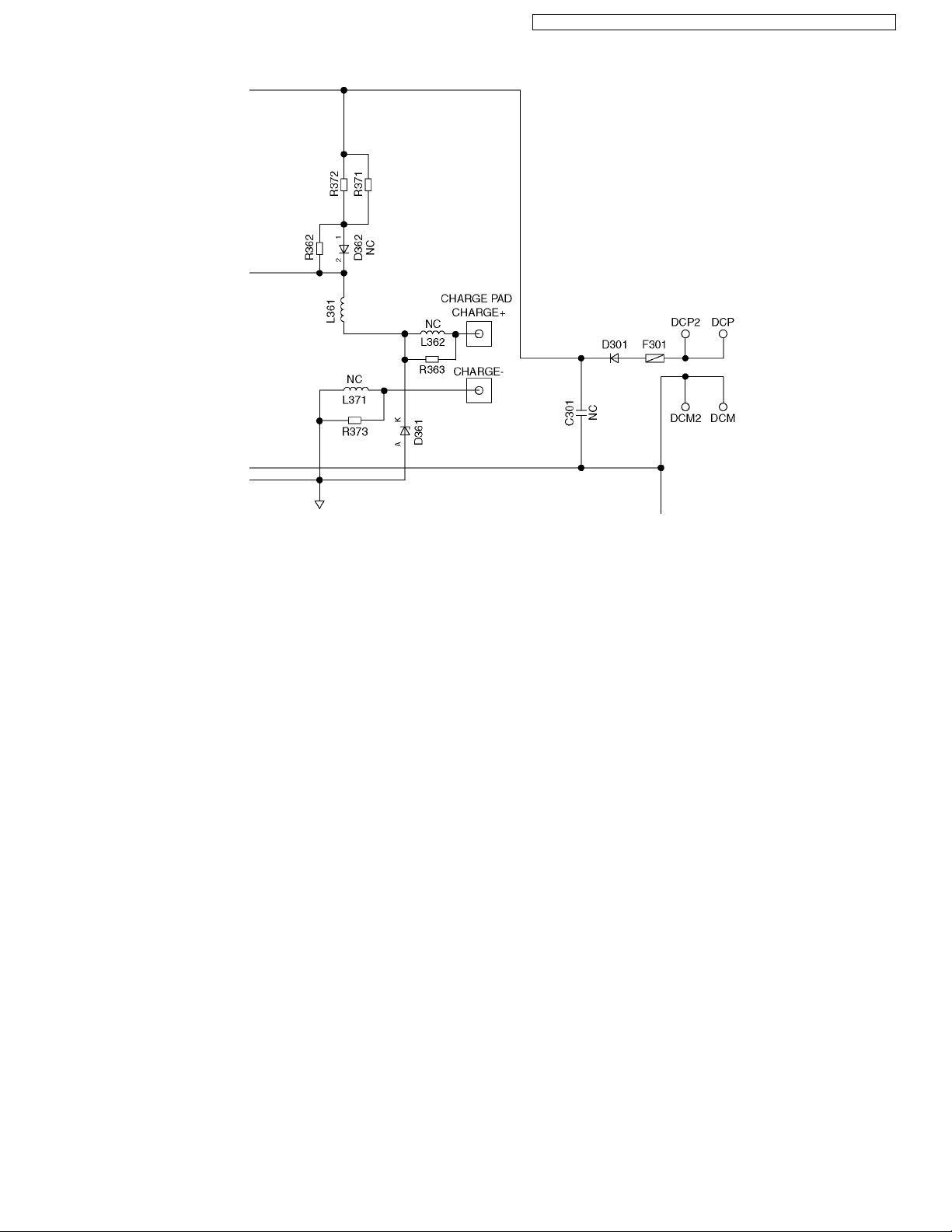
4.4.3.1. Charge Circuit
The voltage from the AC adaptor is supplied to the charge circuits.
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
13
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
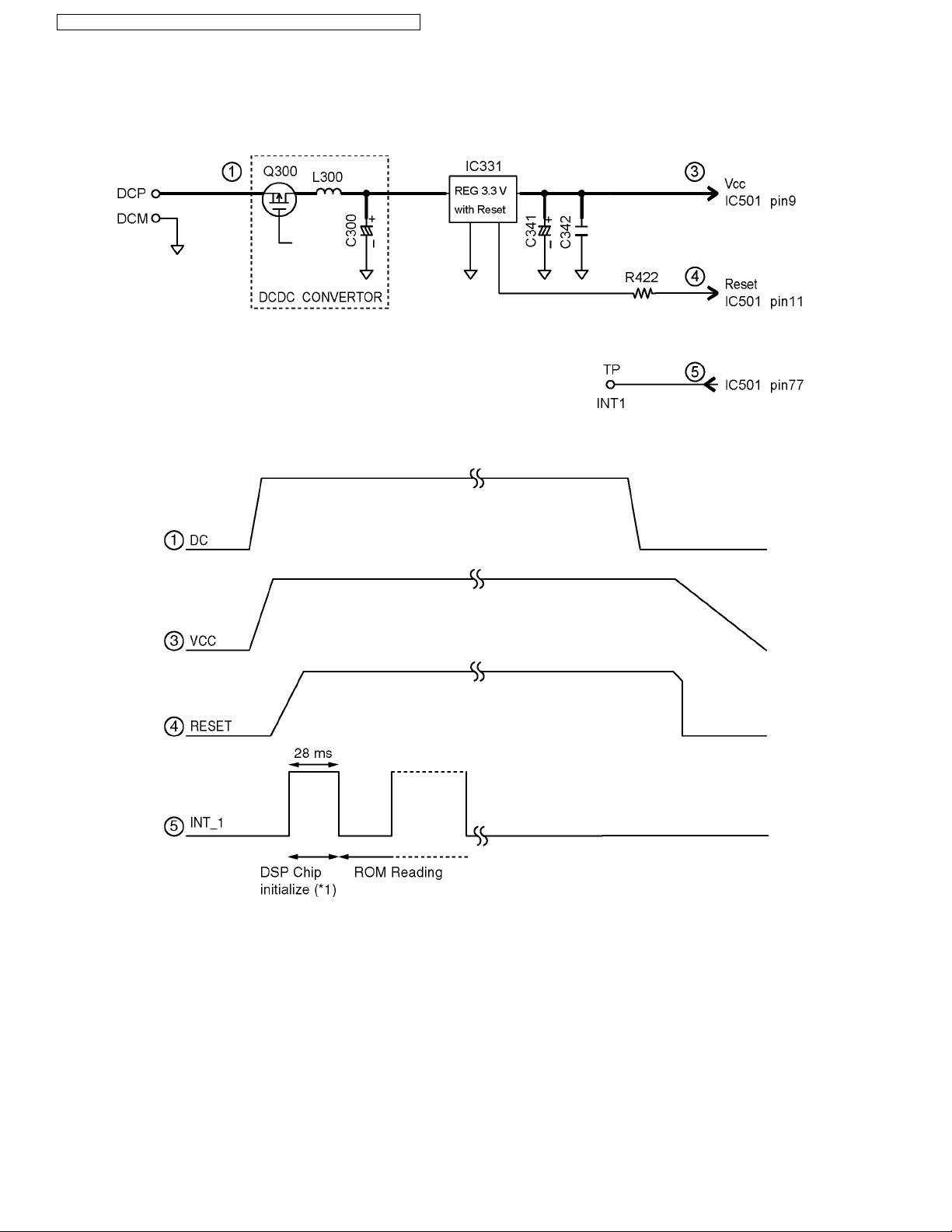
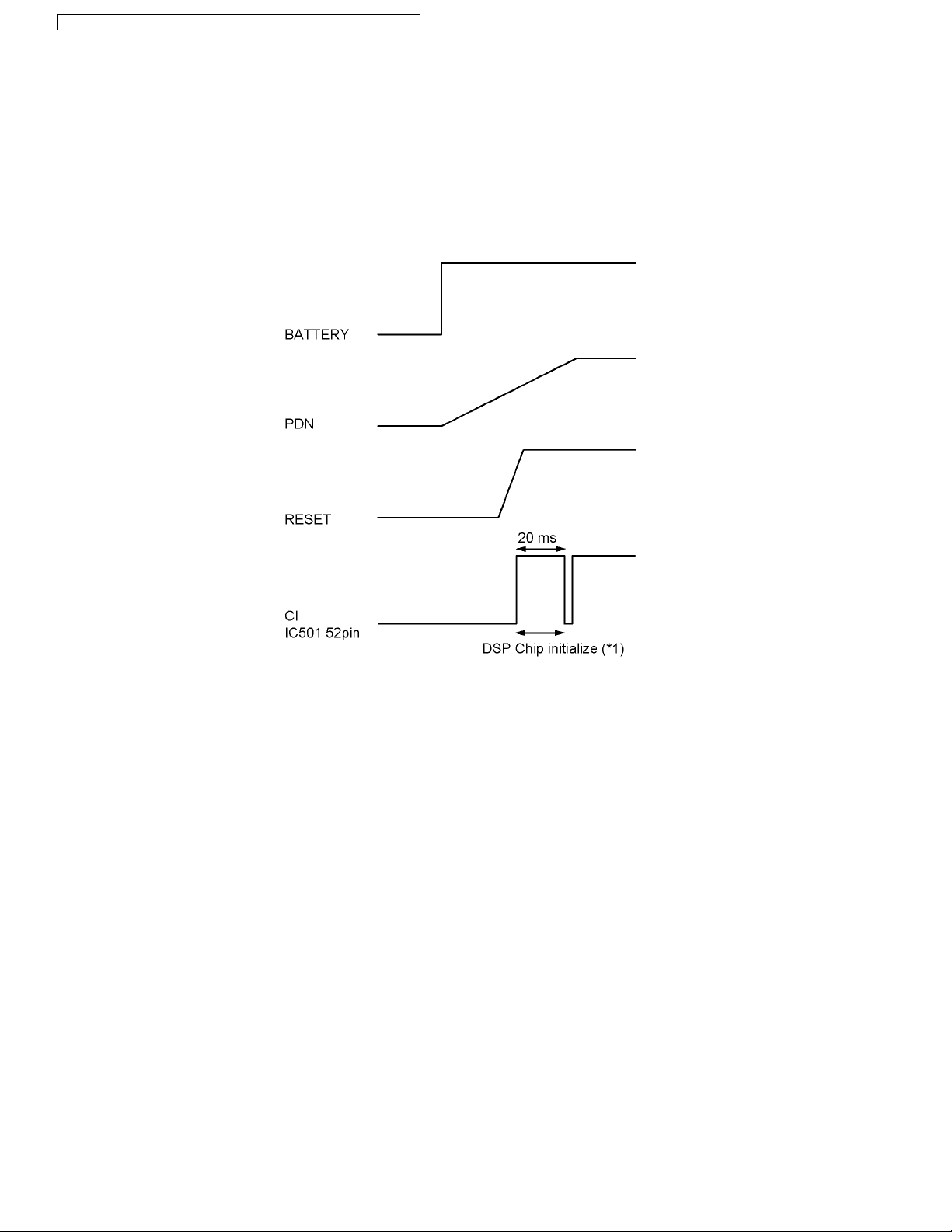
4.4.4. Reset Circuit
Function:
This circuit is used to initialize the microcomputer when it incorporates an AC adaptor.
Circuit Operation:
When the AC Adaptor is inserted into the unit, then the voltage is shifted by IC331 and power is supplied to the DSP.
The set starts to operate when VCC goes up to 3.0 V or more in the circuit voltage diagram.
Note:
(*1) The initializing time of the DSP chip is 28 ms under normal conditions.
14
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
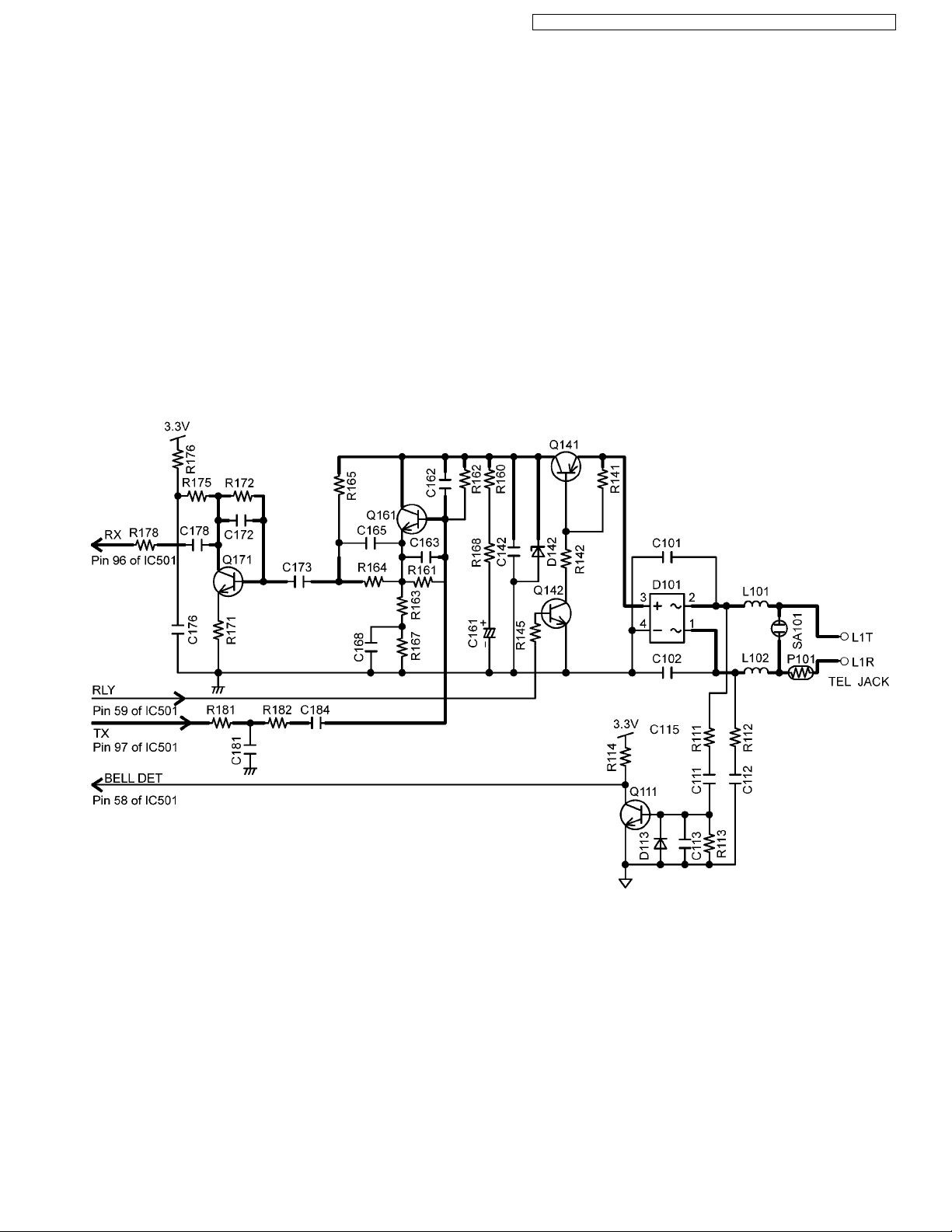
4.4.5. Telephone Line Interface
Telephone Line Interface Circuit:
Function
• Bell signal detection
• ON/OFF hook and pulse dial circuit
• Side tone circuit
Bell signal detection and OFF HOOK circuit:
In the idle mode, Q141 is open to cut the DC loop current and decrease the ring load. When ring voltage appears at the Tip (T)
and Ring (R) leads (When the telephone rings), the AC ring voltage is transferred as follows:
T → L101 → R111 → C111 → Q111 → DSP pin 58 [BELL]
When the CPU (DSP) detects a ring signal, Q141 turns on, thus providing an off-hook condition (active DC current flow through
the circuit). Following signal flow is the DC current flow.
T → L101 → D101 → Q141 → Q161 → R163 → R167 → D101 → L102 → P101 → R
ON HOOK Circuit:
Q141 is open, Q141 is connected as to cut the DC loop current and to cut the voice signal. The unit is consequently in an onhook condition.
Pulse Dial Circuit:
Pin 59 of DSP turns Q141 ON/OFF to make the pulse dialing.
Side Tone Circuit:
Basically this circuit prevents the TX signal from feeding back to RX signal. As for this unit, TX signal feed back from Q161 is
canceled by the canceller circuit of DSP.
15
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
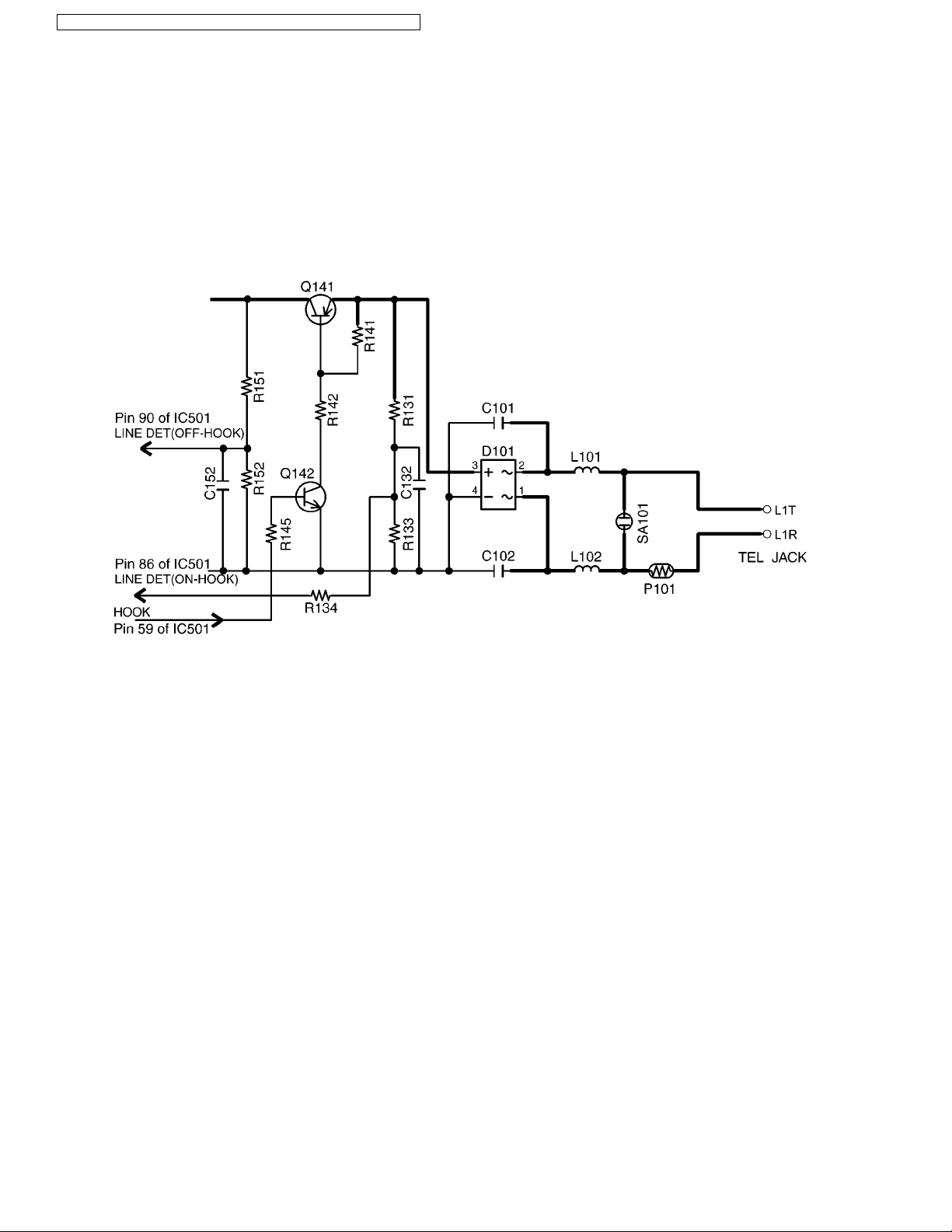
4.4.6. Parallel Connection Detect Circuit
Function:
In order to disable call waiting and stutter tone functions when using telephones connected in parallel, it is necessary to have a
circuit that judges whether a telephone connected in parallel is in use or not. This circuit determines whether the telephone connected in parallel is on hook or off hook by detecting changes in the T/R voltage.
Circuit Operation:
Parallel connection detection when on hook:
When on hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 86 of IC501. There is no parallel connection if the voltage is
1.65 V or higher, while a parallel connection is deemed to exist if the voltage is lower.
Parallel connection detection when off hook:
When off hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 90 of IC501; the presence/absence of a parallel connection is determined when
the voltage changes by 0.2 V or more.
16
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
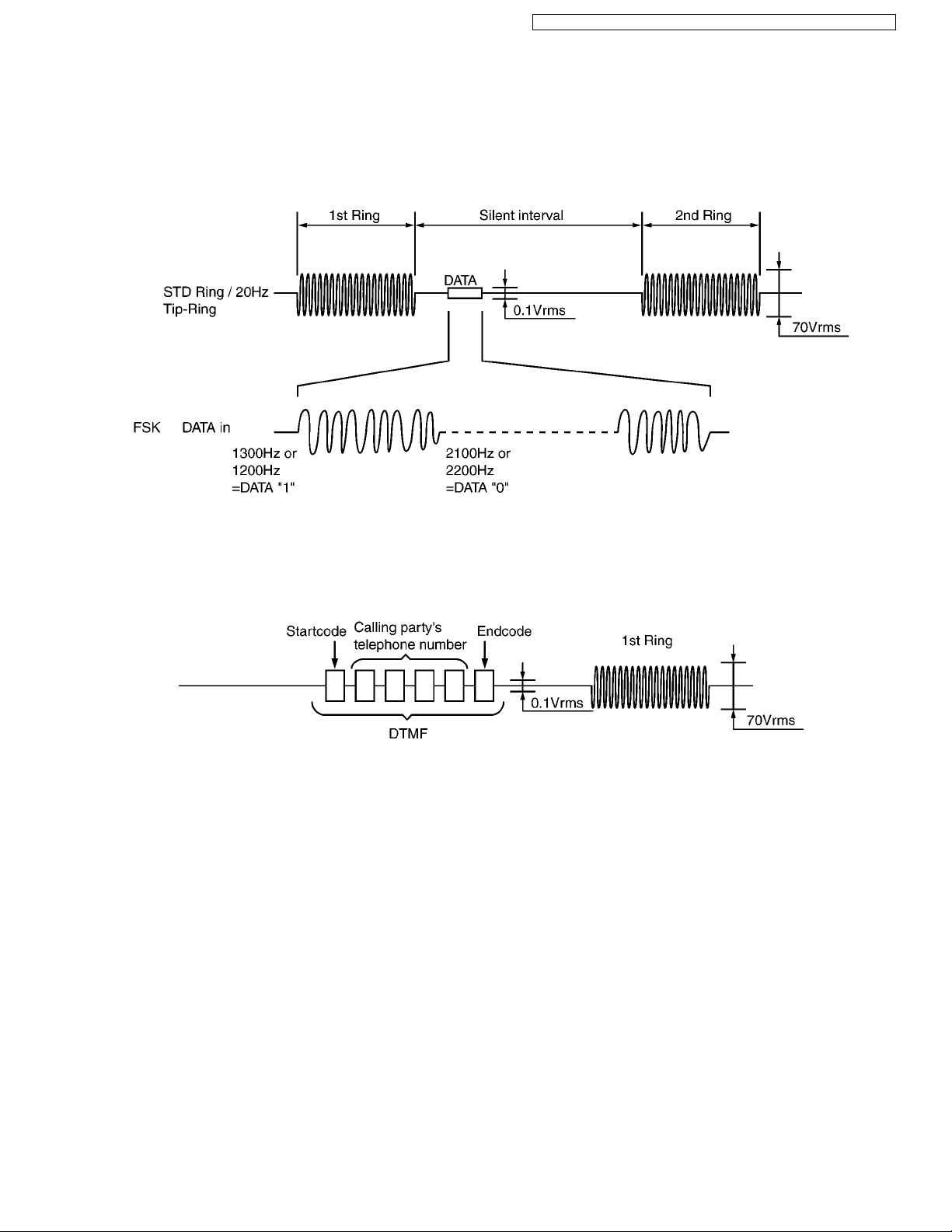
4.4.7. Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)
Function:
The caller ID is a chargeable ID which the user of a telephone circuit obtains by entering a contract with the telephone company
to utilize a caller ID service. For this reason, the operation of this circuit assumes that a caller ID service contract has been
entered for the circuit being used.
The Caller-ID data from exchange is supplied to the telephone using either method of FSK or DTMF. The method is chosen
according to the exchange of telephone office. This unit is available to receive the data with both methods and displays the
received data on LCD.
• FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) format
• DTMF format
It is the method to send the telephone number of calling party with DTMF to the telephone. DTMF is sent before the first bell signal.
The data is sent in turn; first the start code, secondly the telephone number of calling party, lastly end code.
The DTMF is chosen from A (1633 Hz and 697 Hz), B (1633 Hz and 770 Hz), C (1633 Hz and 852 Hz) and D (1633 Hz and 941
Hz) as the start code and end code according to the exchange.
17
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
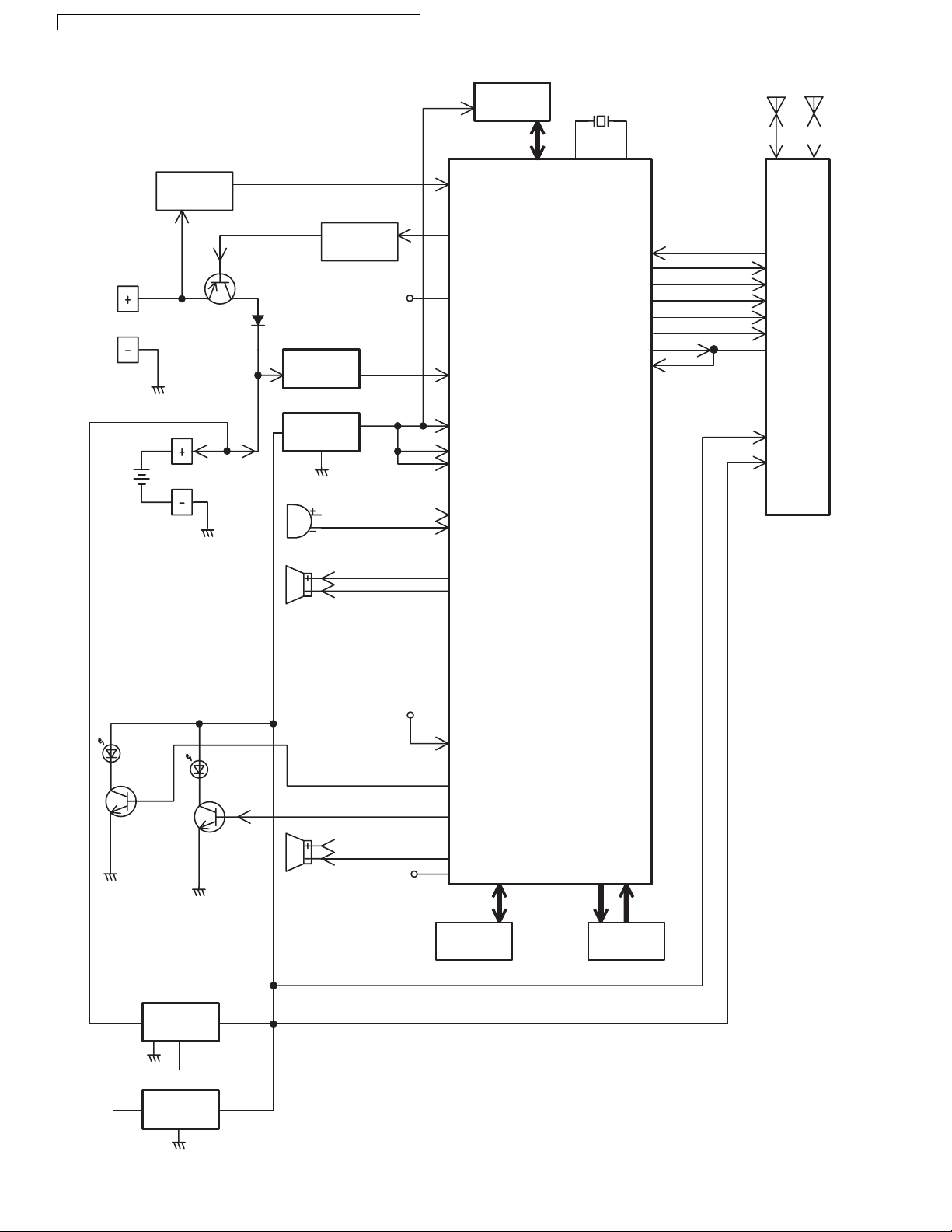
4.5. Block Diagram (Handset)
CHARGE
Q531
CHARGE
DETECT
BATTERY
Q361
D361
IC374
IC371
2.7 V
REGULATOR
MIC
Q362, Q364
CHARGE
CONTROL
RST
RST
IC541
EEPROM
CHG_DET
CHG_CTL
RESET
PDN
VCC
VCCA
VCCPA
MIP
MIN
TA
A
, D
LK
, C
P
W
IC501
DSP
X501
13.824 MHz
SYN_OUT
SYN_EN
SYN_CLK
SYN_DATA
SLOT_CTROL
RADIO_EN
TXDATA
RXDATA
V_PA
V_RF
ANT1
RF part
ANT2
LED555-557
(KEY)
Q563
IC372
DC/DC
CONVERTER
LED561
(ANT)
Q561
SP
Monitor SP
VCC
CI
SPP1
SPN
HEADSET_DET
BL_LED
ANT_LIGHT
SPP2
SPPN
CI
LCD
E
~
_A
E
B
O
R
O
T
S
Y
E
K
KEYS
~5
_1
IN
Y
E
K
IC373
DC/DC
CONVERTER
KX-TGA632 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset)
18
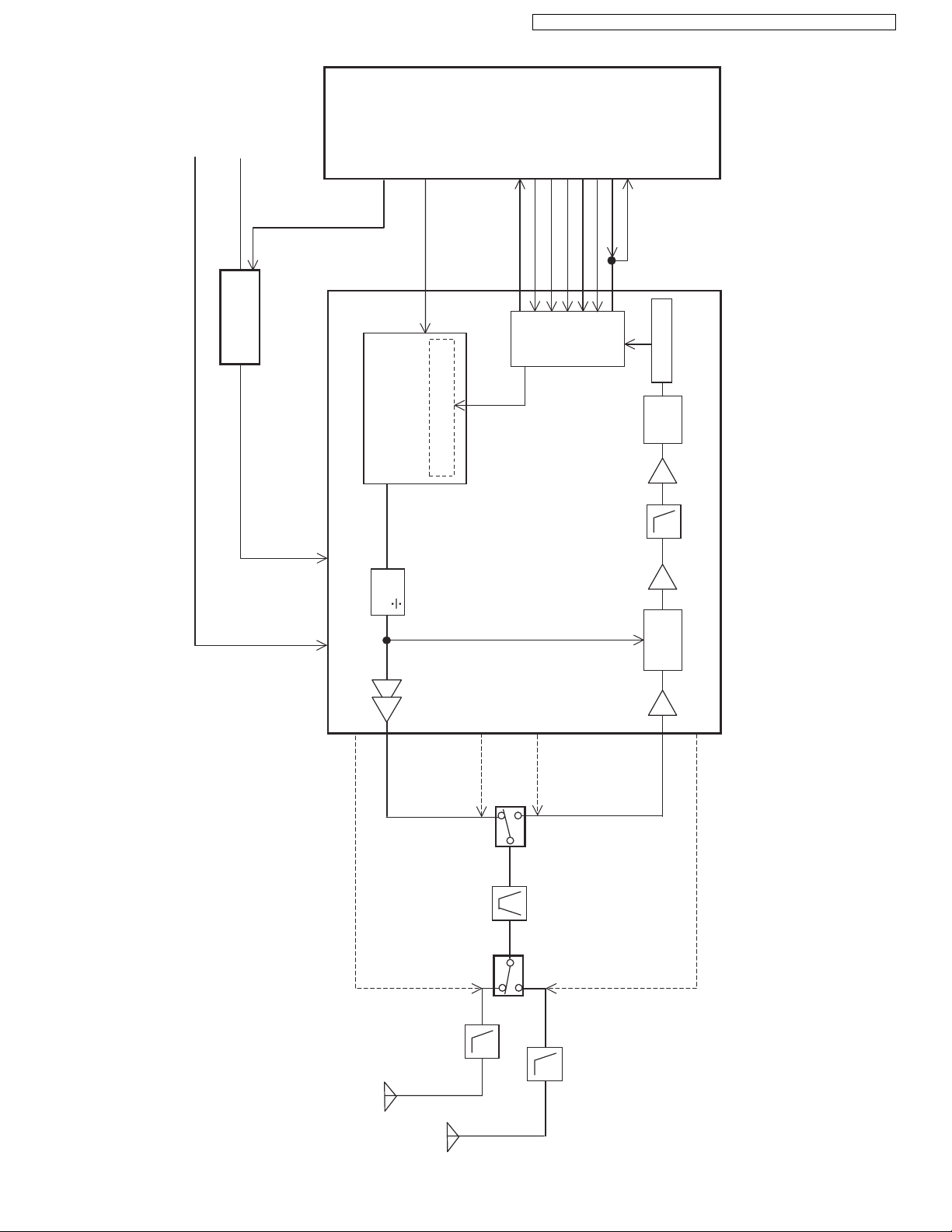
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)
DSP
V_PA
V_RF
3.1 V2.7 V
IC501
RF_POWER
BCLK
13.824 MHz
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
SYN_OUT
SYN_EN
SYN_CLK
TXDATA
SYN_DATA
SLOT_CTROL
RADIO_EN
RXDATA
IC741
Regulator
PLL
1.5
Divider
delta-sigma Modulator
IC701
Logic
Control
Demodulator
A/D
KX-TGA632 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset_RF Part)
Mixer
D781 D771
ANT2: patterned antenna
ANT1: wired dipole antenna
ANT1 (*1)
(*1) Antenna Type ( difference between base unit and handset in Radio parts)
ANT2 (*1)
19
Note:
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.7. Circuit Operation (Handset)
4.7.1. Construction
The circuit mainly consists of DSP and RF part as shown in the block diagram.
4.7.1.1. DSP: IC501
Function
• Battery Low, Power down detect circuit
• Ringer Generation
• Interface circuit
RF part, Speaker, Mic, LED, Key scan, LCD
Initial waves
Note:
(*1) The initializing time of the DSP chip is 20 ms under normal conditions.
4.7.1.2. RF part
Mainly voice signal is modulated to RF, or it goes the other way.
4.7.1.3. EEPROM: IC541
Setting data is stored.
ex: ID code, user setting
20
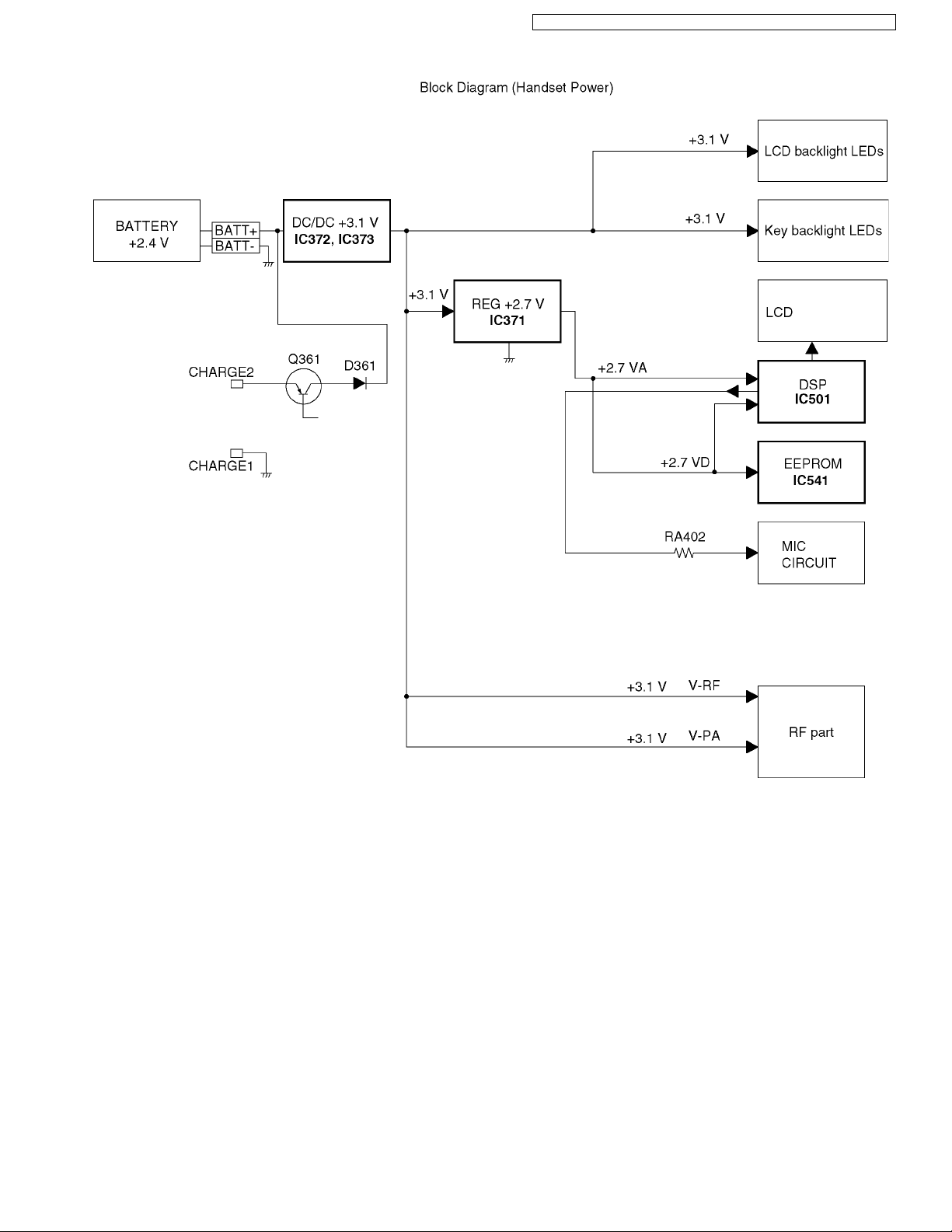
4.7.2. Power Supply Circuit
Voltage is supplied separately to each block.
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
21
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
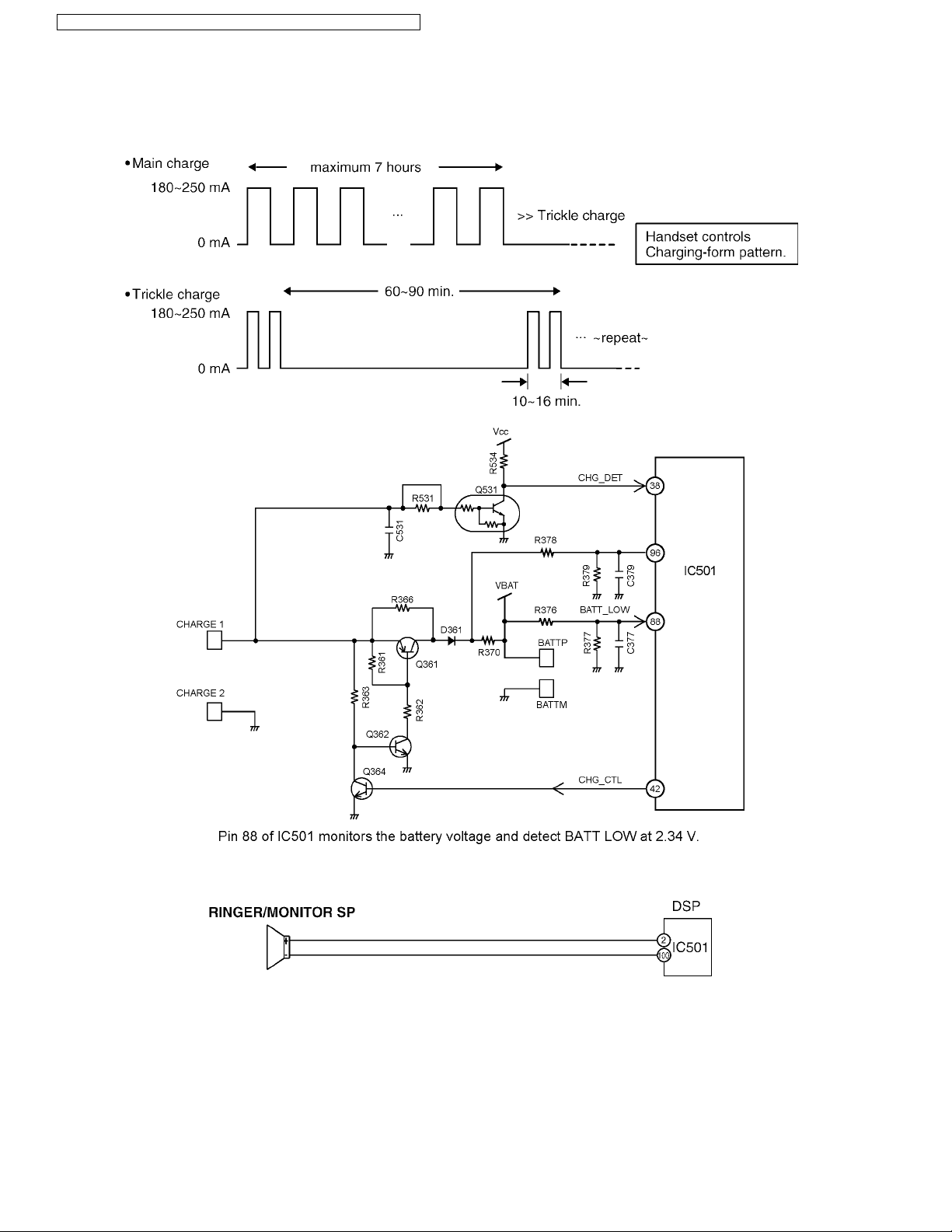
4.7.3. Charge Circuit
When the handset is put on the cradle of the base unit, the power is supplied from CHARGE+ and CHARGE- terminals to
charge the battery via R366 or Q361. The voltage between CHARGE+ and CHARGE- flows Q531 → pin 38 of IC501, where the
charge is detected. Then IC501 calculates the battery consumption amount from the previous charge, and it controls Q361/
Q362/Q364 by pin 42 of IC501 until charging is complete. When charging is complete, the control pattern is switched to Trickle
charging form from Operational charging form.
4.7.4. Ringer and Handset SP-Phone
22
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
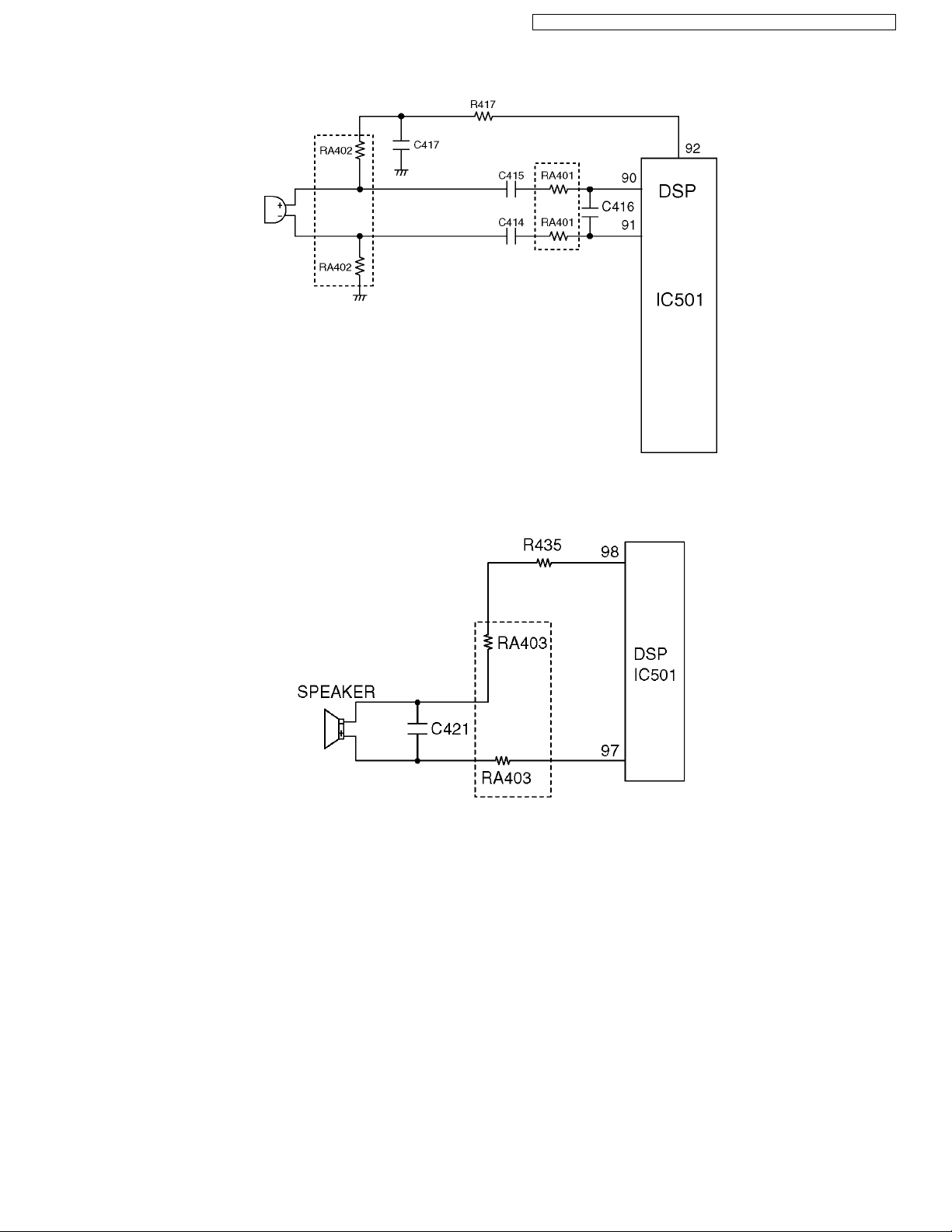
4.7.5. Sending Signal
The voice signal from the microphone is input to DSP (90, 91). Also the power for the microphone is supplied from DSP (92) and
the power is turned OFF on standby.
4.7.6. Reception Signal
The voice signal from the base unit is output to DSP (98). This signal is led to R435 and drives the speaker, and the other signal
output from DSP (97) drives the speaker.
23
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.8. Circuit Operation (RF Part)
General Description:
RF part includes Transmitter and Receiver functions. Digital signals (Mainly voice data) that come from DSP, are modulated and
are transmitted. On the other hand, received signals are demodulated and go out to DSP.
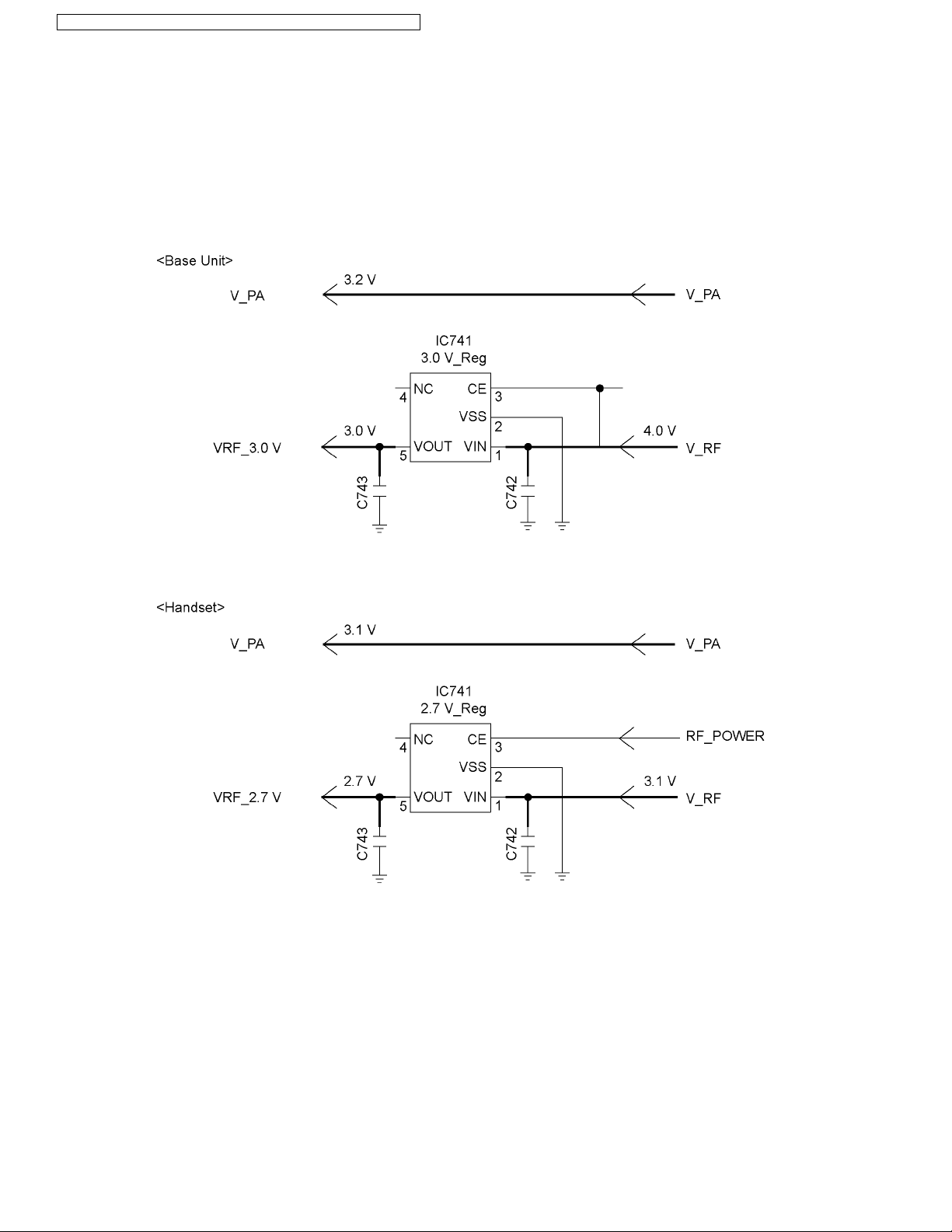
4.8.1. Power Supply Circuit
As indicated below, the various voltages are supplied to each block.
V_PA, about 3.2 V at base unit or 3.1 V at handset, is supplied to the Power amplifier.
IC741 is 3.0 V at base unit or 2.7 V at handset Regulator and outputs VRF (3.0 V at base unit or 2.7 V at handset) by order of
RADIO_EN signal.
V_RF is approximately 4.0 V (Base Unit) or 3.1 V (Handset).
24
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
4.9. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit)
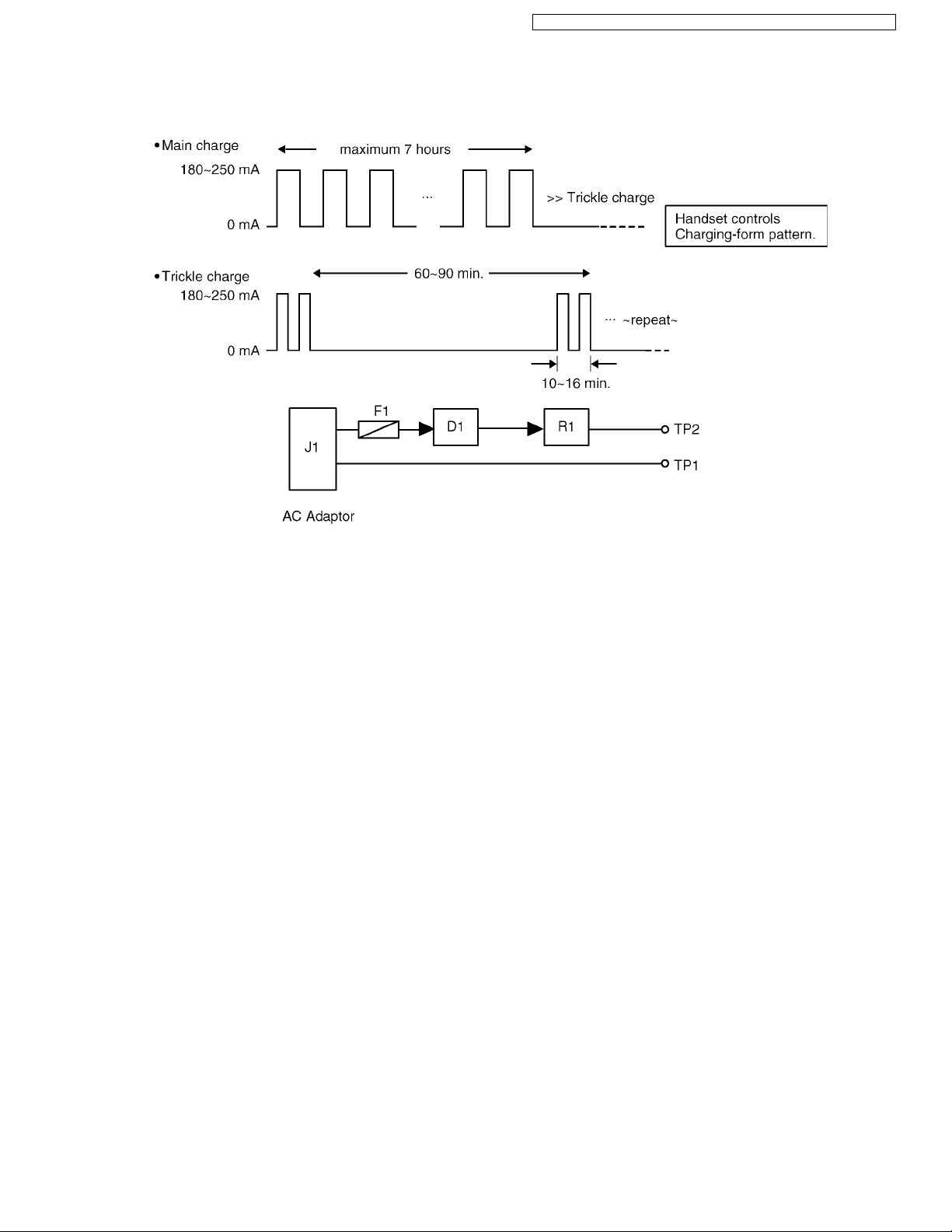
The voltage from the AC adaptor is supplied to the charge circuits. Main charge (180~250 mA at the Battery) of maximum 7hours is started soon after the handset is placed on the charger unit. Then it changes to Trickle charge to prevent from overcharging.
Charging form
The route for this is as follows: DC+pin of J1(+) → F1 → D1 → R1 → CHARGE+pad → Handset → CHARGE-pad → DC-pin of
J1(-).
25
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
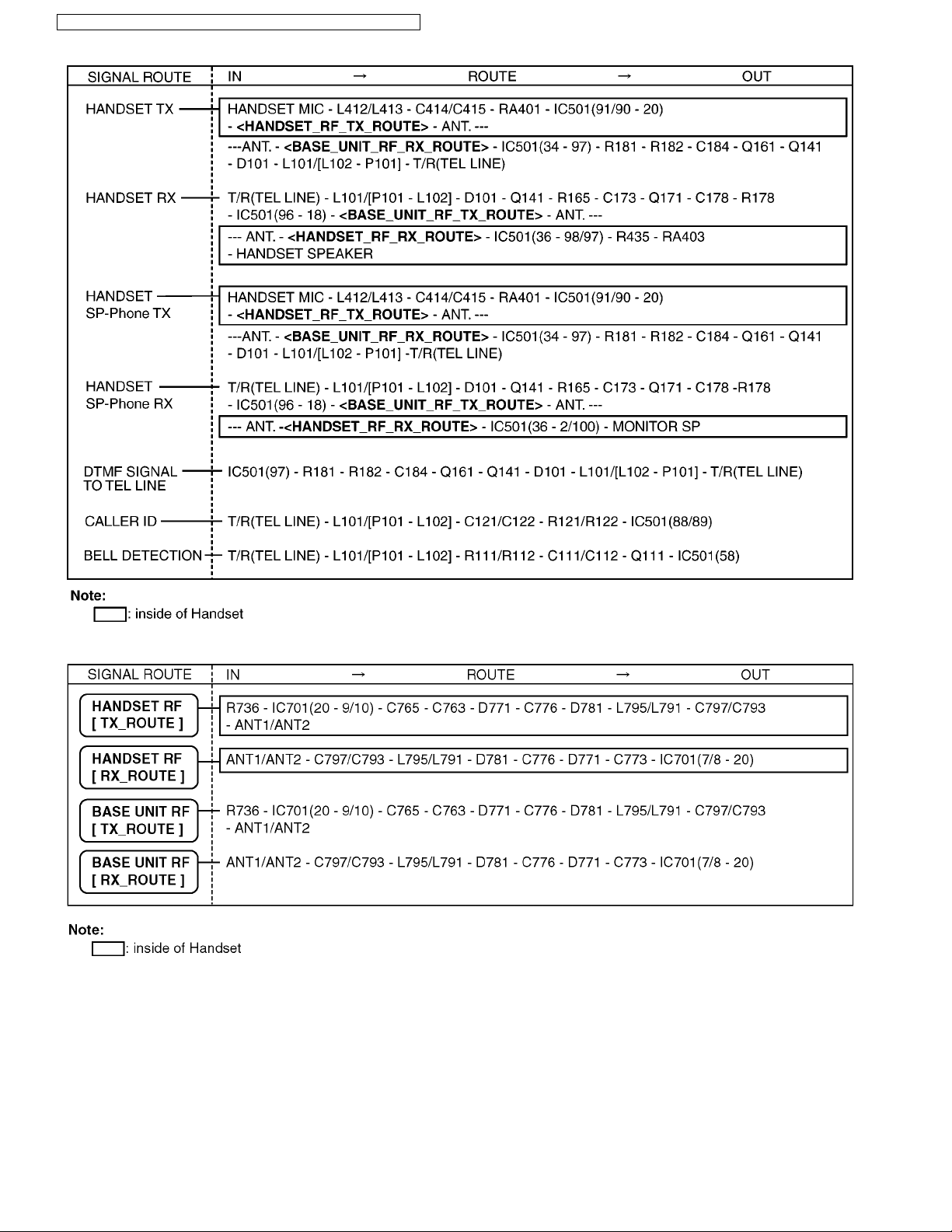
4.10. Signal Route
RF part signal route
26
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
5 Location of Controls and Components
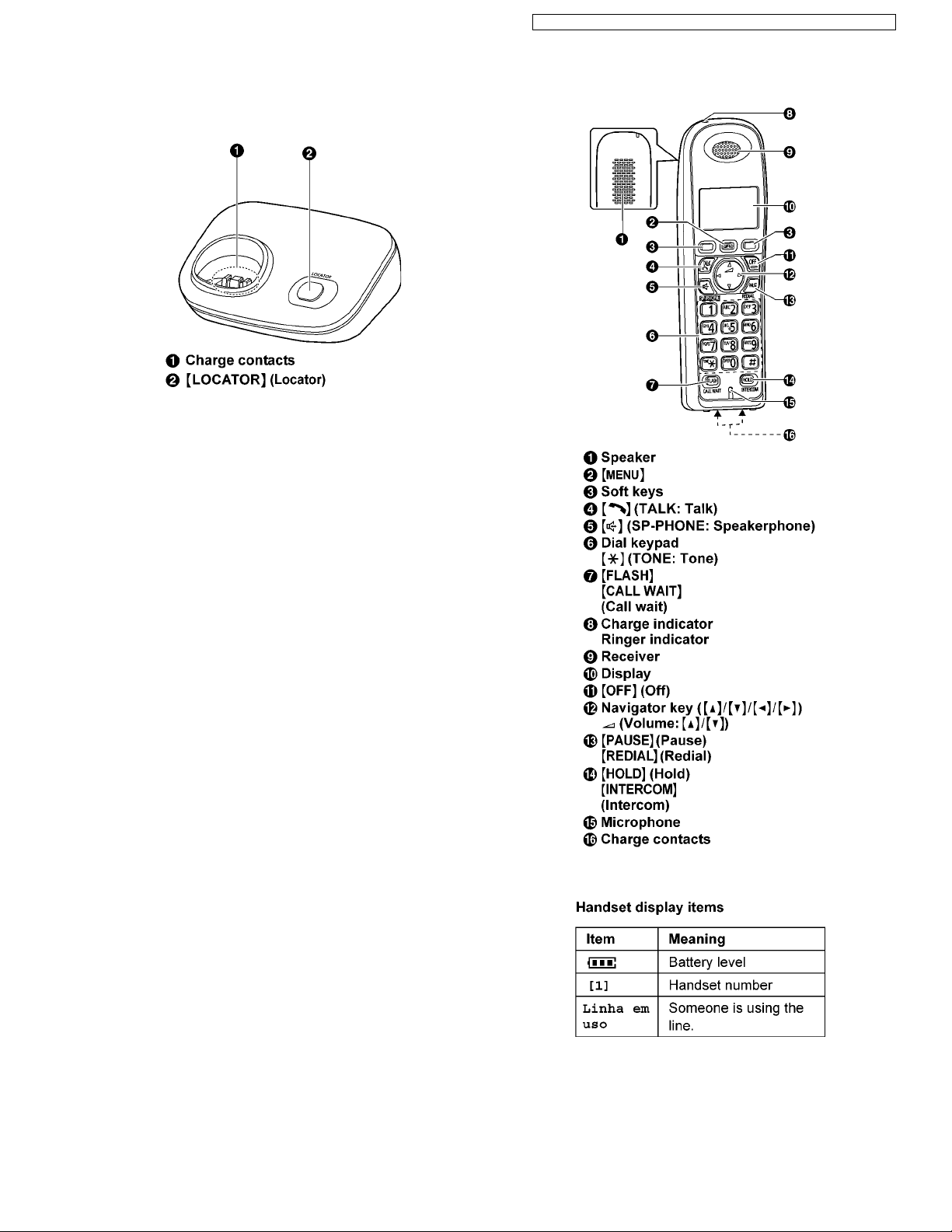
5.1. Controls
5.1.1. Base Unit
5.1.2. Handset
5.2. Display
27
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
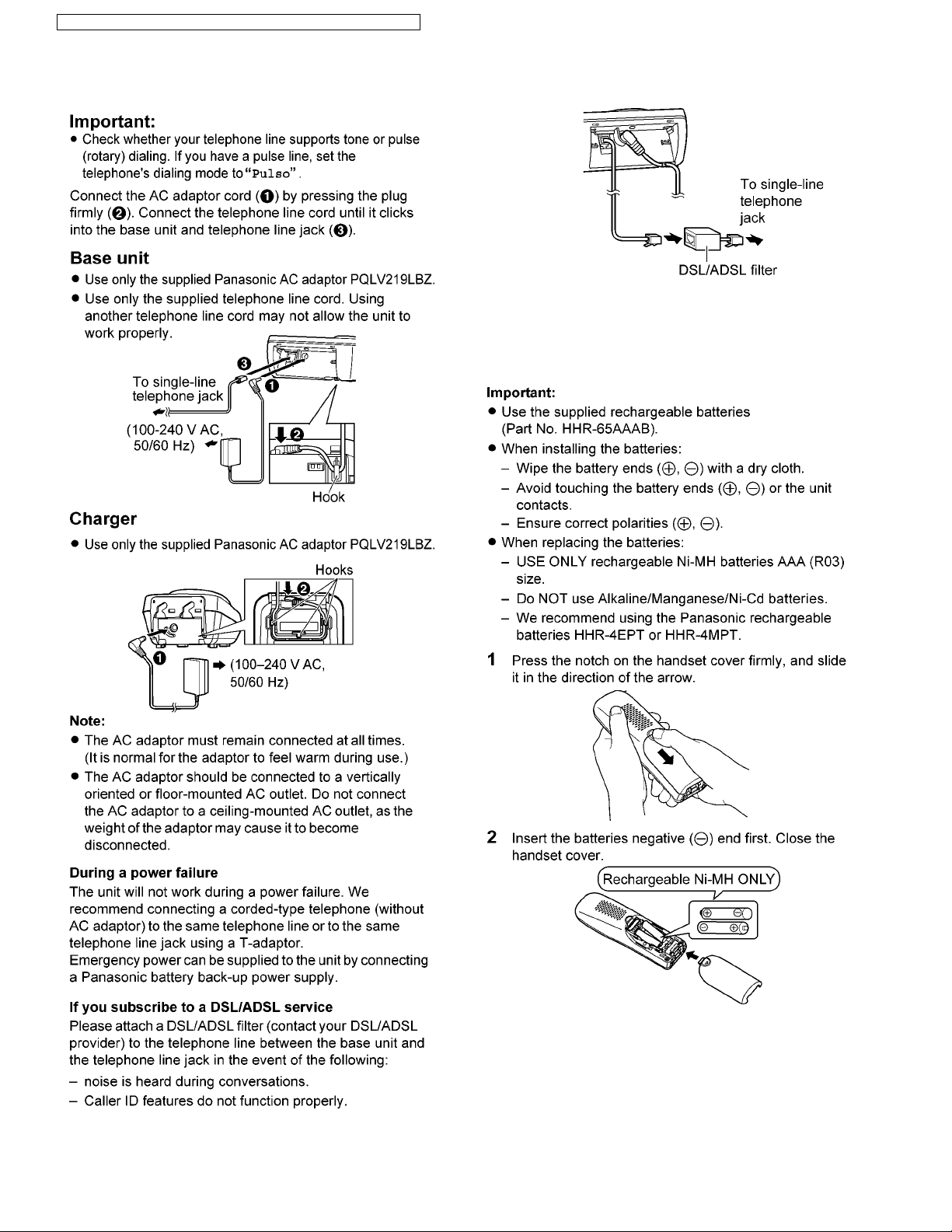
6 Installation Instructions
6.1. Connections
6.2. Battery
6.2.1. Battery Installation and
Replacement
28
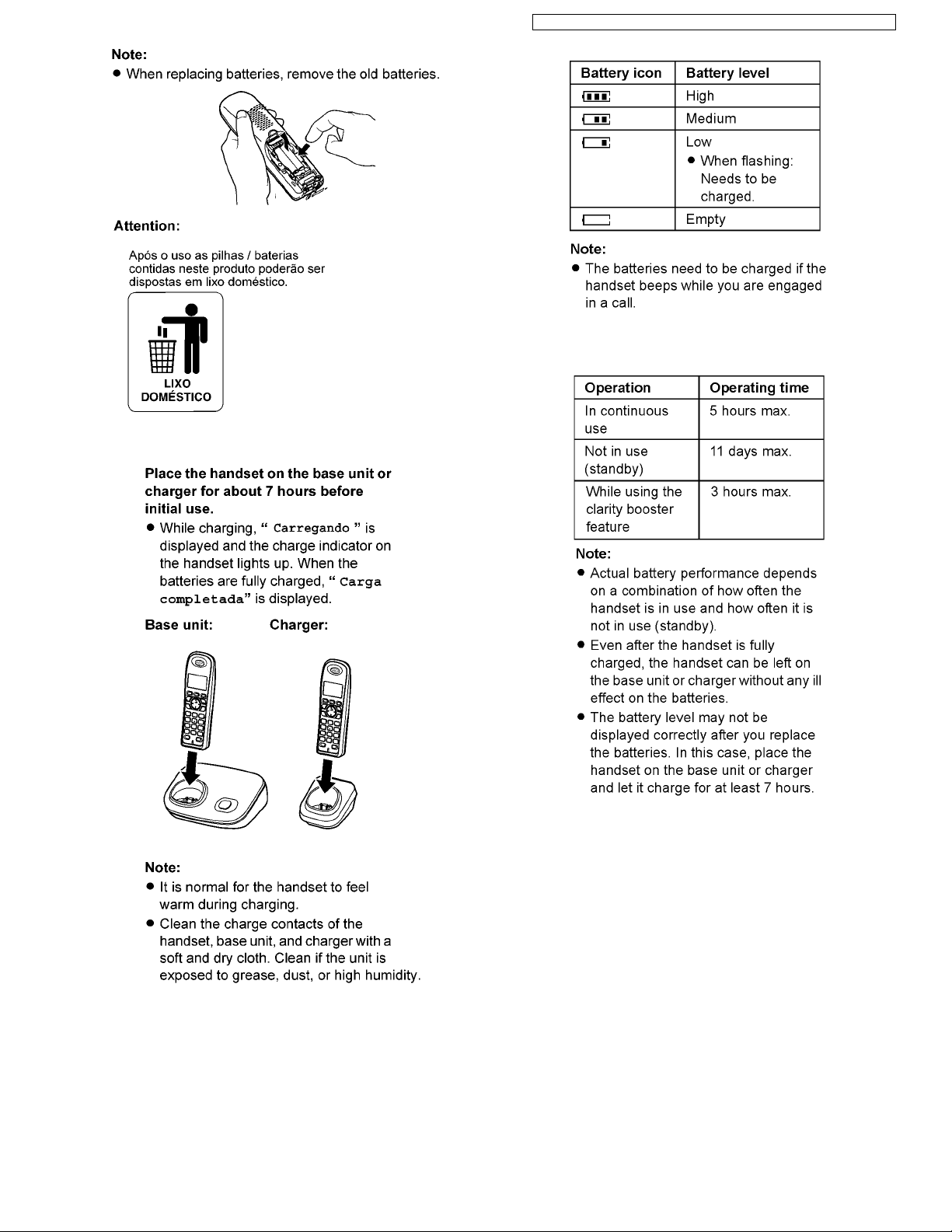
6.2.2. Battery Charge
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
6.2.3. Battery Level
6.2.4. Panasonic Ni-MH Battery
Performance (supplied batteries)
Note for service:
The battery strength may not be indicated correctly if the
battery is disconnected and connected again, even after it is
fully charged. In that case, by recharging the battery as
mentioned above, you will get a correct indication of the
battery strength.
29
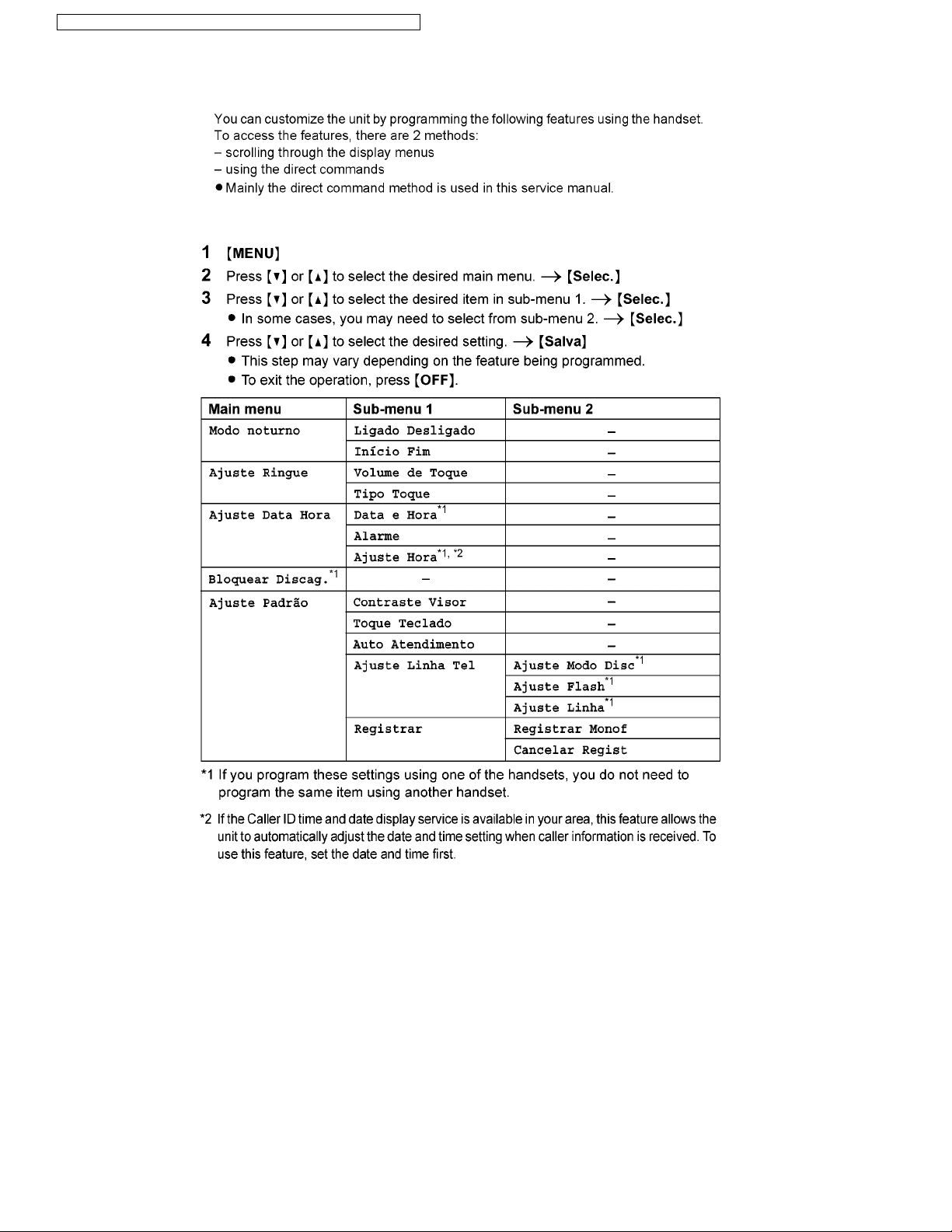
KX-TG6381LBB/KX-TG6381LBS/KX-TG6382LBB/KX-TGA632LBB/KX-TGA632LBS
7 Operating Instructions
7.1. Programmable Settings
7.1.1. Programming by Scrolling through the Display Menus
30
 Loading...
Loading...