Panasonic GP8D Service Manual

K
/
K
/
K
/
ORDER NO. ITD0506035CE
D10 Canada: B07
Progressive Wide Plasma Display
TH-37PWD8BK
TH-37PWD8BS
TH-37PWD8EK
TH-37PWD8ES
TH-37PWD8GK
TH-37PWD8GS
TH-37PWD8UK
TH-42PWD8BK
TH-42PWD8BS
TH-42PWD8EK
TH-42PWD8ES
TH-42PWD8GK
TH-42PWD8GS
TH-42PWD8UK
GP8D Chassis
Specifications
Power Source (UK, GK/S) 120 VAC, 50/60 Hz (GK/GS/UK)
Power Source (EK/S, BK/S) 220-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz (EK/ES/B
Power Consumption (UK, GK/S)
Maximum 225 W (37PWD8GK/GS/UK) 275 W (42PWD8GK/GS/UK)
Stand-bycondition Save OFF 1.0 W, Save ON 0.7 W (GK/GS/UK)
Power off condition 0.05 W (GK/GS/UK)
Power Consumption (EK/S, BK/S)
Normal use 215 W (37PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS) 240 W (42PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS)
Stand-bycondition Save off 1.2 W, Save on 0.9 W (EK/ES/B
Power off condition 0.1 W (EK/ES/B
BS)
BS)
BS)
© 2005 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.

y
A
A
A
Y
A
Y
/
/
A
A
y
y
y
TH-37PWD8BK
Plasma Displaypanel Drive method:AC type 37-inch
16:9 aspect ratio (37 inch)
Drive method:AC type 42-inch
16:9 aspect ratio (42 inch)
Contrast Ratio 4000:1
Screen size 32” 13/64 (818 mm) (W) × 18” 9/64 (461 mm) (H) × 36” 31/32 (939 mm) (diagonal) (37 inch)
36” 7/32 (920 mm) (W) × 20” 25/64 (518 mm) (H) × 41” 37/64 (1,056 mm) (diagonal) (42 inch)
(No. of pixels) 408,960 (852 (W) × 480 (H))
[2,556 × 480 dots]
Operating condition
Temperatuer 32 °F - 104 °F (0 °C - 40 °C)
Humidit
20 % - 80 %
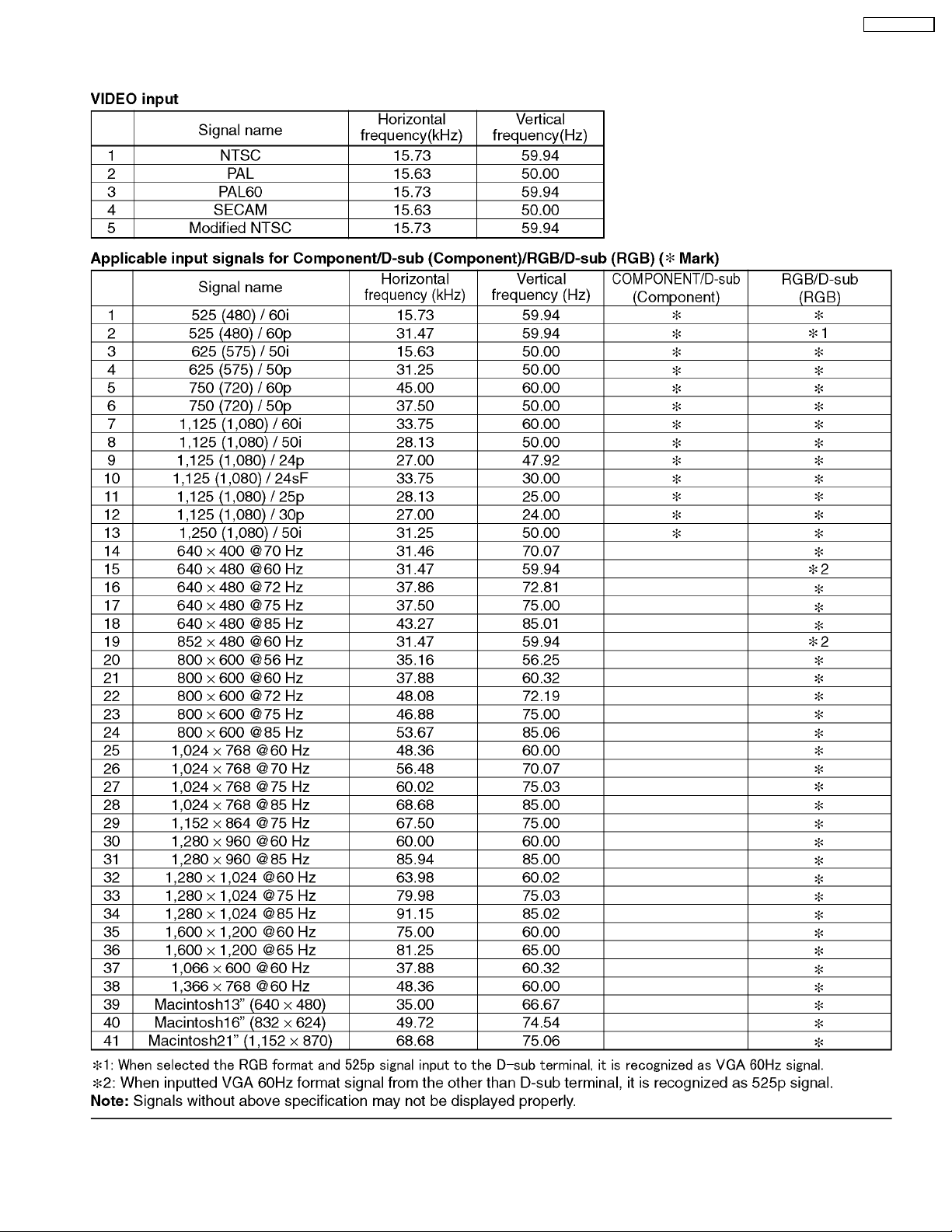
Applicablesignals
Color System NTSC, PAL, PAL60, SECAM, Modified NTSC
Scanning format 525 (480) / 60i 60p, 625 (575)/50i 50p, 750 (720)/60p 50p, 1125 (1080) / 60i 50i 24p 25p
30p 24sF .... SMPTE274M, 1250 (1080) / 50i
PC signals VGAdisplay
VG
SVGA, XGA, SXGA, UXGA..... (compressed)
Horizontal scanning frequency 15 - 110 kHz
Vertical scanning frequency 48 - 120 Hz
Connection terminals
V (EK/S, BK, S, UK) VIDEO IN / OUT (BNC) 1.0 Vp-p (75-ohm or high impedance)
S VIDEO IN (MINI DIN 4PIN) Y: 1 Vp-p (75-ohm), C: 0.286 Vp-p (75-ohm)
UDIO IN (RCA PIN JACK ×2) 0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
COMPONENT / RGB (UK)
/ G (BNC) 1.0 Vp-p/composite (75-ohm)
0.7 Vp-p/non-composite (75-ohm)
PB/ B (BNC), PR/ R (BNC) 0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
UDIO IN (RCA PIN JACK × 2) 0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
PC (GK/GS/UK) (HIGH-DENSITYD-SUB 15PIN) R, G, B/0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
Component
:1.0 Vp-p (75-ohm : include sync)
P
CB:±0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
B
P
CR:±0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
R
HD, VD/1.0 - 5.0 Vp-p (high impedance)
UDIO IN (M3 JACK) 0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
PC (EK/ES/BK/BS) (HIGH-DENSITYD-SUB 15PIN) R, G, B/0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
HD, VD/1.0 - 5.0 Vp-p (high impedance)
UDIO IN (M3 JACK) 0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
SERIAL EXTERNAL CONTROL TERMINAL (D-SUB 9PIN) RS-232C COMPATIBLE
SPEAKERS (6 Ω) 16 W [8 W + 8 W] (10 % THD)
Accessories Supplied
Remote Control Transmitter EUR7636070R
Batteries 2×AASize
Fixing bands (TMME203 or TMME187) × 2
Dimensions (W×H×D) 36.2” (920 mm) × 21.7” (550 mm) × 3.5” (89 mm)
(exclusive of protruding portion) (37 inch)
40.2” (1,020 mm) × 24” (610 mm) × 3.5” (89 mm)
(exclusive of protruding portion) (42 inch)
Mass (Weight) (UK)
main unit onl
approx. 55.1 lbs (37PWD8UK) approx. 65.0 lbs (42PWD8UK)
with speakers approx. 63.9 lbs (37PWD8UK) approx. 73.9 lbs (42PWD8UK)
Mass (Weight) (GK/GS)
main unit onl
approx. 54.0 lbs (37PWD8GK/GS) approx. 63.9 lbs (42PWD8GK/GS)
with speakers approx. 62.8 lbs (37PWD8GK/GS) approx. 72.8 lbs (42PWD8GK/GS)
Mass (Weight) (EK/S, BK/S)
main unit onl
approx. 25.0 kg net (37PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS) approx. 29.5 kg net (42PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS)
with speakers approx. 29.0 kg (37PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS) approx. 33.5 kg (42PWD8EK/ES/BK/BS)
2

TH-37PWD8BK
Notes:
· Design and specifications are subject to change without notice. Mass and dimensions shown are approximate.
· This equipment complies with the EMC standards listed below. EN55022, EN55024, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3.
CONTENTS
Page Page
1 Applicable signals 5
2 Safety Precautions
2.1. General Guidelines
3 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
4 About lead free solder (PbF)
5 PCB Structure sheet of GP8D chassis
6 Service Hint
7 P.C.Board and Plasma panel replacement
7.1. Removal of the back cover
7.2. Removal of the Slot block
7.3. Removal of the J-Board
7.4. Removal of the HX-Board
7.5. Removal of the P-Board
7.6. Removal of the D-Board
7.7. Removal of the AC-Inlet
7.8. Removal of the H3-Board
7.9. Removal of the S1-Board
7.10. Removal of the SU-Board
7.11. Removal of the SD-Board
7.12. Removal of the SC-Board
7.13. Removal of the SS-Board
7.14. Removal of the C1-Board
7.15. Removal of the C2-Board
7.16. Removal of the Front frame (glass)
7.17. Removal of the V1-Board and the V2-Board
7.18. Removal of stand brackets
7.19. Replacement of the plasma panel
8 Location of Lead Wiring
8.1. Wiring for 37 inch model
8.2. Wiring for 42 inch model
9 Adjustment Procedure
9.1. Driver Set-up
9.2. Initialization Pulse Adjust
9.3. P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) exchange
9.4. Adjustment Volume Location
9.5. Test Point Location
10 Service mode
10.1. CAT (computer Aided Test) mode
10.2. IIC mode structure (following items value is sample data.)
11 Alignment
6
6
7
8
9
10
11
11
11
11
11
12
12
12
12
13
13
13
14
14
14
15
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
19
19
20
21
21
21
22
22
24
11.1. PC/RGB panel white balance
11.2. HD/ 525ip /625ip panel white balance
12 Trouble shooting guide
12.1. Self Check
12.2. No Power
12.3. No Picture
12.4. Local screen failure
13 Option Setting
14 Circuit Board Layout
14.1. P-Board
14.2. HA-Board
14.3. HB-Board
14.4. HX-Board (37 inch)
14.5. HX-Board (42 inch)
14.6. J-Board (37 inch)
14.7. J-Board (42 inch)
14.8. D-Board
14.9. C1-Board (37 inch)
14.10. C1-Board (42 inch)
14.11. C2-Board (37 inch)
14.12. C2-Board (42 inch)
14.13. SC-Board
14.14. SU-Board (37 inch)
14.15. SU-Board (42 inch)
14.16. SD-Board (37 inch)
14.17. SD-Board (42 inch)
14.18. SS-Board
14.19. H3, S1, V1 and V2-Board
15 Block and Schematic Diagrams
15.1. Schematic Diagram Notes
15.2. Main Block Diagram
15.3. P-Board Block Diagram
15.4. P-Board (1 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.5. P-Board (2 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.6. P-Board (3 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.7. P-Board (4 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.8. P-Board (5 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.9. P-Board (6 of 6) Schematic Diagram
15.10. HA-Board Block and Schematic Diagram
15.11. HB-Board Block Diagram
25
25
27
29
29
30
30
31
32
35
35
38
39
40
41
42
44
46
48
49
50
51
52
55
56
57
58
59
61
63
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
3

TH-37PWD8BK
15.12. HB-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram 74
15.13. HB-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram
15.14. HX-Board Block Diagram
15.15. HX-Board Schematic Diagram
75
76
77
15.16. S1, V1 and V2-Board Block Diagram and Schematic
Diagram
15.17. J-Board (1 of 2) and H3-Board Block Diagram
15.18. J-Board (2 of 2) Block Diagram
15.19. J-Board (1 of 4) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.20. J-Board (2 of 4) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.21. J-Board (3 of 4) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.22. J-Board (4 of 4) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.23. J-Board (1 of 4) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.24. J-Board (2 of 4) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.25. J-Board (3 of 4) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.26. J-Board (4 of 4) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.27. D-Board Block Diagram
15.28. D-Board (1 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.29. D-Board (2 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.30. D-Board (3 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.31. D-Board (4 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.32. D-Board (5 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.33. D-Board (6 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.34. D-Board (7 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.35. D-Board (8 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.36. D-Board (9 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.37. D-Board (10 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.38. D-Board (11 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.39. D-Board (12 of 12) Schematic Diagram
15.40. C1 and C2-Board Block Diagram
15.41. C1-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
15.42. C1-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.43. C1-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.44. C1-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.45. C2-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.46. C2-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.47. C2-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.48. C2-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.49. SC-Board Block Diagram
15.50. SC-Board (1 of 2) Schematic Diagram
15.51. SC-Board (2 of 2) Schematic Diagram
15.52. SU-Board Block Diagram
15.53. SU-Board Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.54. SU-Board Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.55. SD-Board Block Diagram
15.56. SD-Board Schematic Diagram (37 inch)
15.57. SD-Board Schematic Diagram (42 inch)
15.58. SS-Board Block Diagram
15.59. SS-Board Schematic Diagram
16 Parts Location
16.1. Parts Location (1)
16.2. Parts Location (2)
17 Packing Exploded Views
17.1. Packing Exploded Views (1)
17.2. Packing Exploded Views (2)
17.3. Packing Exploded Views (3)
18 Mechanica l Replacement Parts List
19 Replacement Parts List
19.1. Replacement Parts List Notes
19.2. Electrical Replacement Parts List (37inch)
19.3. Electrical Replacement Parts List (42inch)
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
123
123
124
125
125
126
127
128
131
131
132
153
4
1 Applicable signals
TH-37PWD8BK
5
TH-37PWD8BK
2 Safety Precautions
2.1. General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
2.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two
prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between
the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet
part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors,
control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a
return path to the chassis, the reading should be between
1MW and 5.2MW.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to
the chassis, the reading must be
.
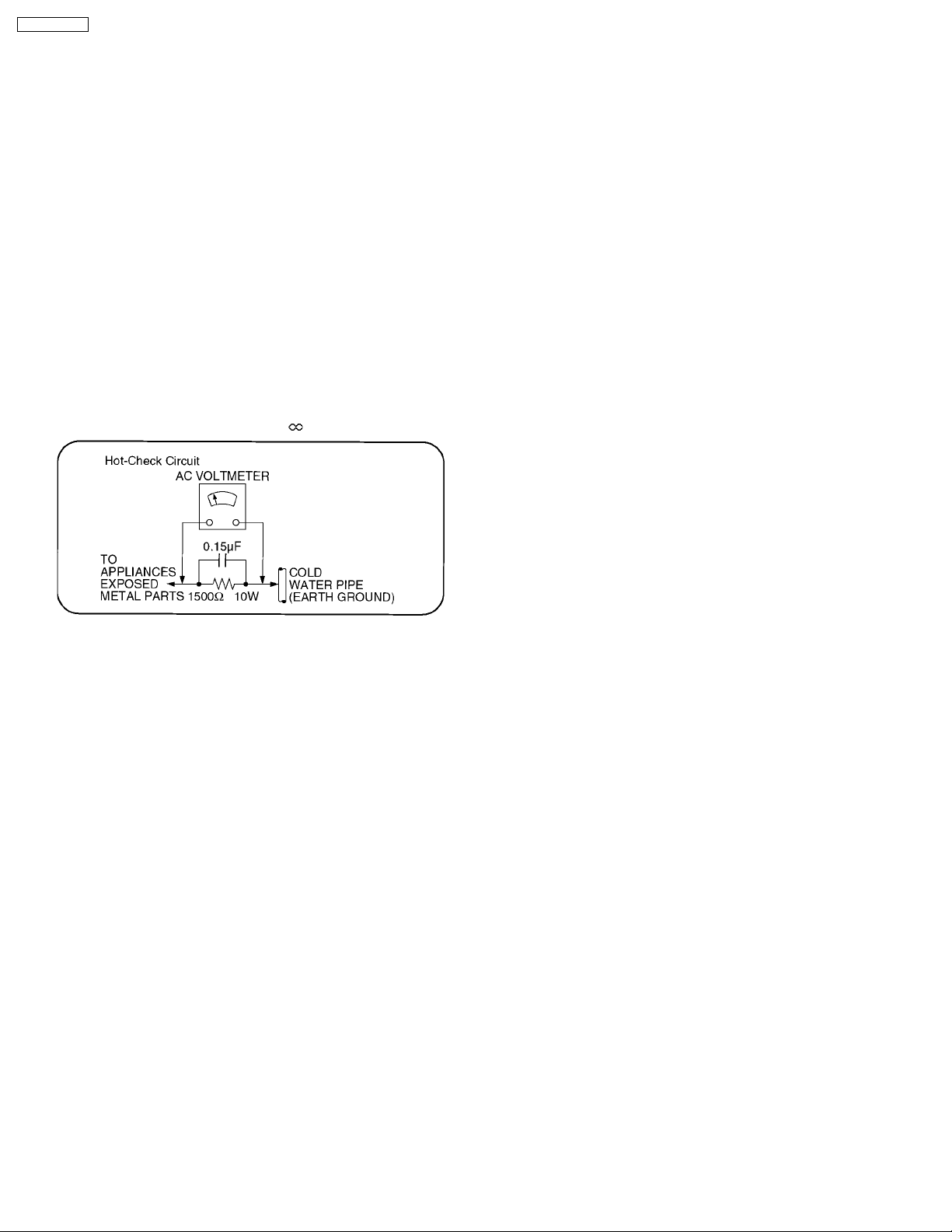
Figure 1
2.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check (See
Figure 1.)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an
isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kW, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF
capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set
and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in
Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more
sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the
voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the
above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts
RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or
equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage
current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a
measurement is outside of the limits specified, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer.
6

TH-37PWD8BK
3 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as alminum
foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static (ESD protected)" can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, alminum foil or comparable
conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise hamless motion such as the brushing
together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient to
damage an ES device).
7
TH-37PWD8BK
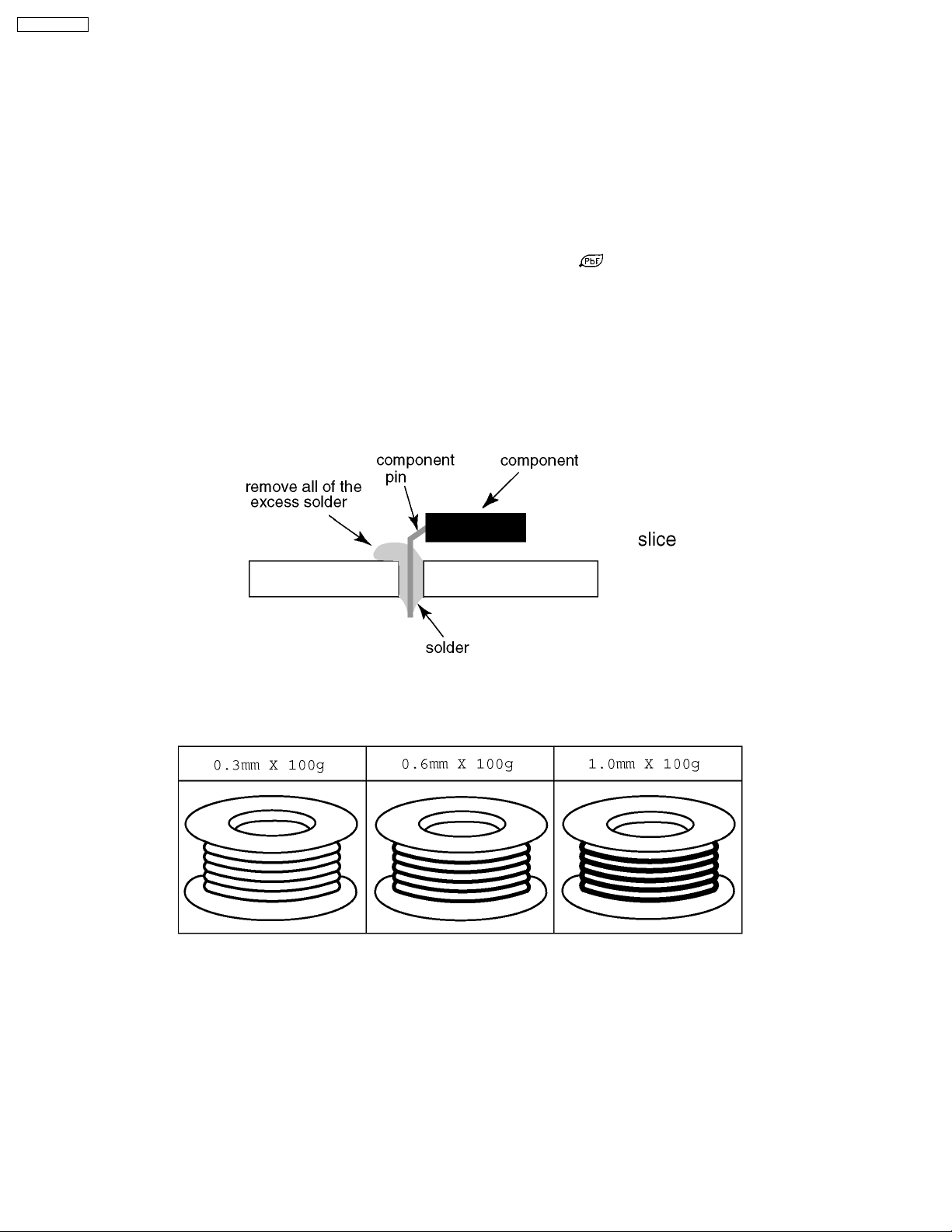
4 About lead free solder (PbF)
Note: Lead is listed as (Pb) in the periodic table of elements.
In the information below, Pb will refer to Lead solder, and PbF will refer to Lead Free Solder.
The Lead Free Solder used in our manufacturing process and discussed below is (Sn+Ag+Cu).
That is Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu) although other types are available.
This model uses Pb Free solder in it’s manufacture due to environmental conservation issues. For service and repair work, we’d
suggest the use of Pb free solder as well, although Pb solder may be used.
PCBs manufactured using lead free solder will have the PbF within a leaf Symbol
Caution
·
· Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder. Typically the melting point is 50 ~ 70 °F (30~40 °C) higher.
· ·
Please use a high temperature soldering iron and set it to 700 ± 20 °F (370 ± 10 °C).
·
· Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100 °F or 600 °C).
· ·
If you must use Pb solder, please completely remove all of the Pb free solder on the pins or solder area before applying Pb
solder. If this is not practical, be sure to heat the Pb free solder until it melts, before applying Pb solder.
·
· After applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess solder which may flow onto
· ·
the opposite side. (see figure below)
Suggested Pb free solder
There are several kinds of Pb free solder available for purchase. This product uses Sn+Ag+Cu (tin, silver, copper) solder.
However, Sn+Cu (tin, copper), Sn+Zn+Bi (tin, zinc, bismuth) solder can also be used.
stamped on the back of PCB.
8
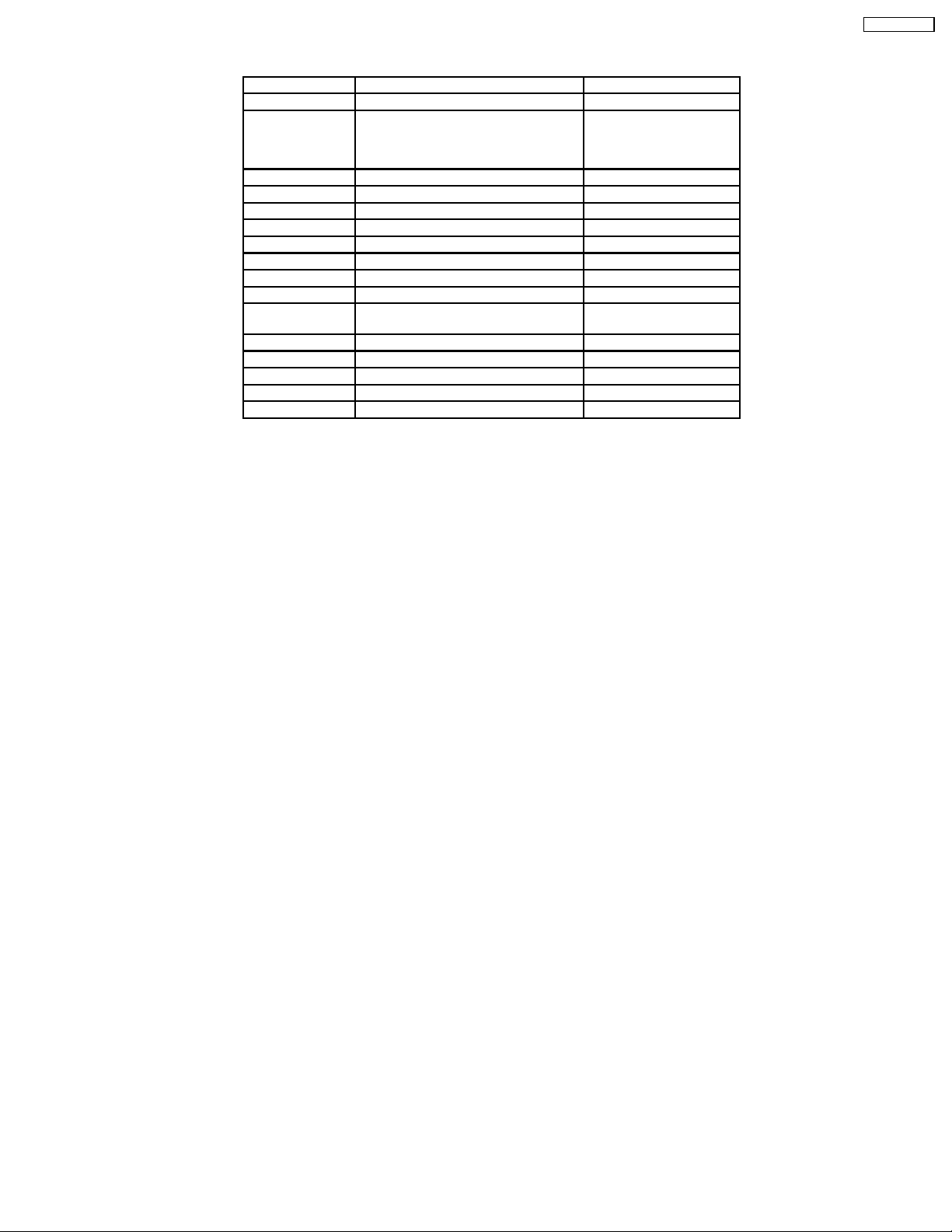
5 PCB Structure sheet of GP8D chassis
Board Name Function Remarks
D Digital Signal Processor 1
J Slot Interface (Audio/Video/Sync input
Switch), SYNC processor, Audio
processor, Speaker out amplifier, DC-
DC converter
SS Sustain Out 1
SC Scan out 1
SU Sustain connection (Upper) 1
SD Sustain connection (Lower) 1
C1 Data Drive (Lower Right)
C2 Data Drive (Lower Left)
H3 Speaker terminal
S1 Power switch
V1 LED (Stand-by/Power on) & Remote
receiver
V2 Key switch 1
P Line filter, Power supply 1
HX PC_type_Input terminal
HB BNC Composite/S Video 2
HA BNC Component Video 3
Remarks
1. Recommend PCB´s for initial service for GP8D chassis.
2. For TH-37/42PWD8UK/BK/BS/EK/ES
3. For TH-37/42PWD8UK
TH-37PWD8BK
1
1
9
TH-37PWD8BK
6 Service Hint
Note:
·
· Extension cable kit for Slot Board is supplied as service fixtures and tools.
· ·
(PartNo.TZSC07040)
·
· J13 Slot is not equiped for 37” model.
· ·
10
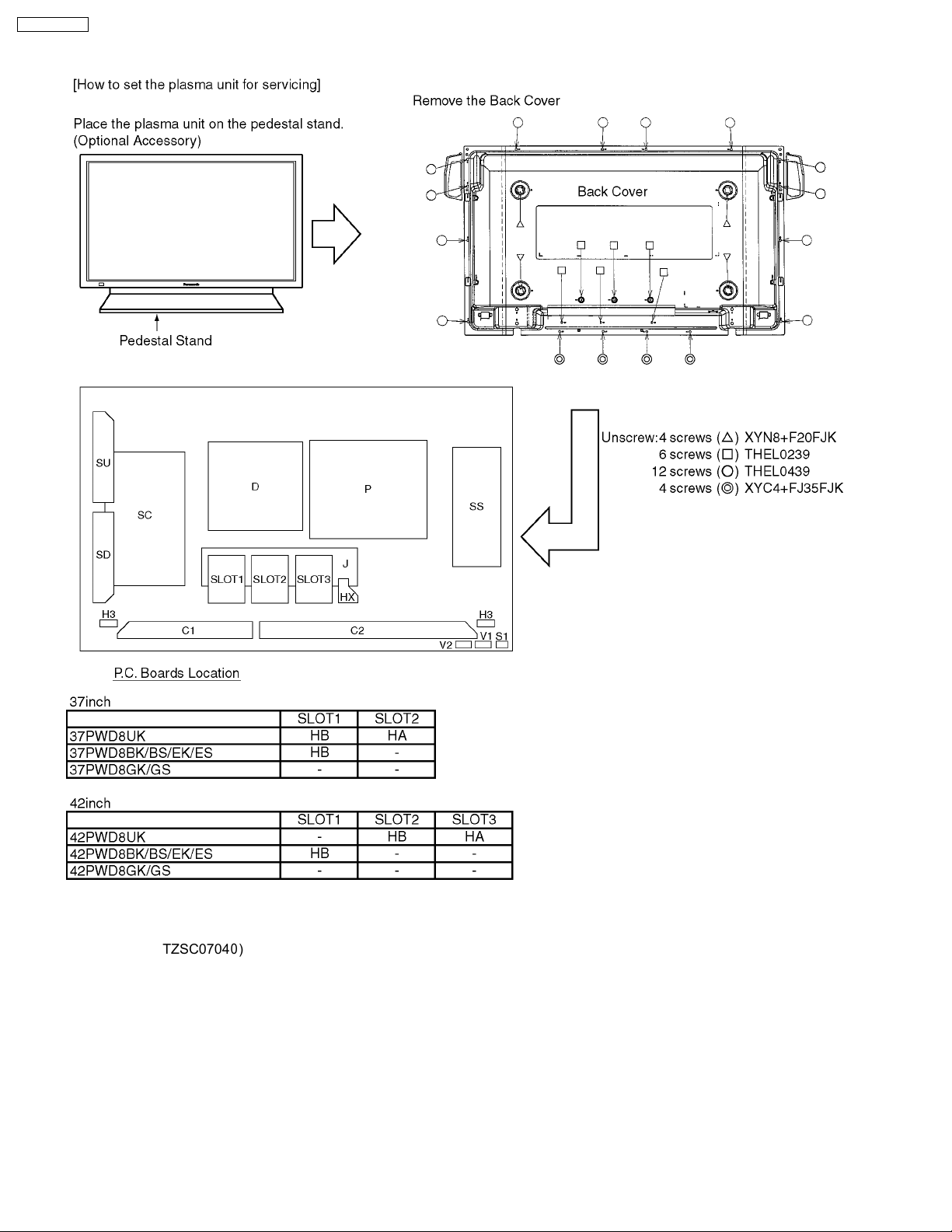
7 P.C.Board and Plasma panel replacement
TH-37PWD8BK
Prior to the replacement of Plasma panel, place the unit on
the pedestal stand and remove the front frame.
7.1. Removal of the back cover
1. Unscrew the screws (×12 ,×6 ,×4 ,×4 ) and
remove the back cover.
7.2. Removal of the Slot block
Caution:
To remove P.C.B., wait 1 minute after power was off for
discharge from electrolysis capacitors.
1. Remove the couplers (J1, J2, J3, J4, J5, J6, J7, J8, J10,
J15).
2. Release the cable from the clampers at left side of the slot
block.
3. Unscrew the screws (×4
) and remove the slot block.
7.3. Removal of the J-Board
1. Unscrew the screws (×8 ), release J14 from the HXBoard and remove the J-Board.
7.4. Removal of the HX-Board
1. Unscrew the screws (×6 ) and remove the slot case.
2. Unscrew the screws (×4 ).
3. Unscrew the screws (×1 ) and remove the HX-Board.
11
TH-37PWD8BK
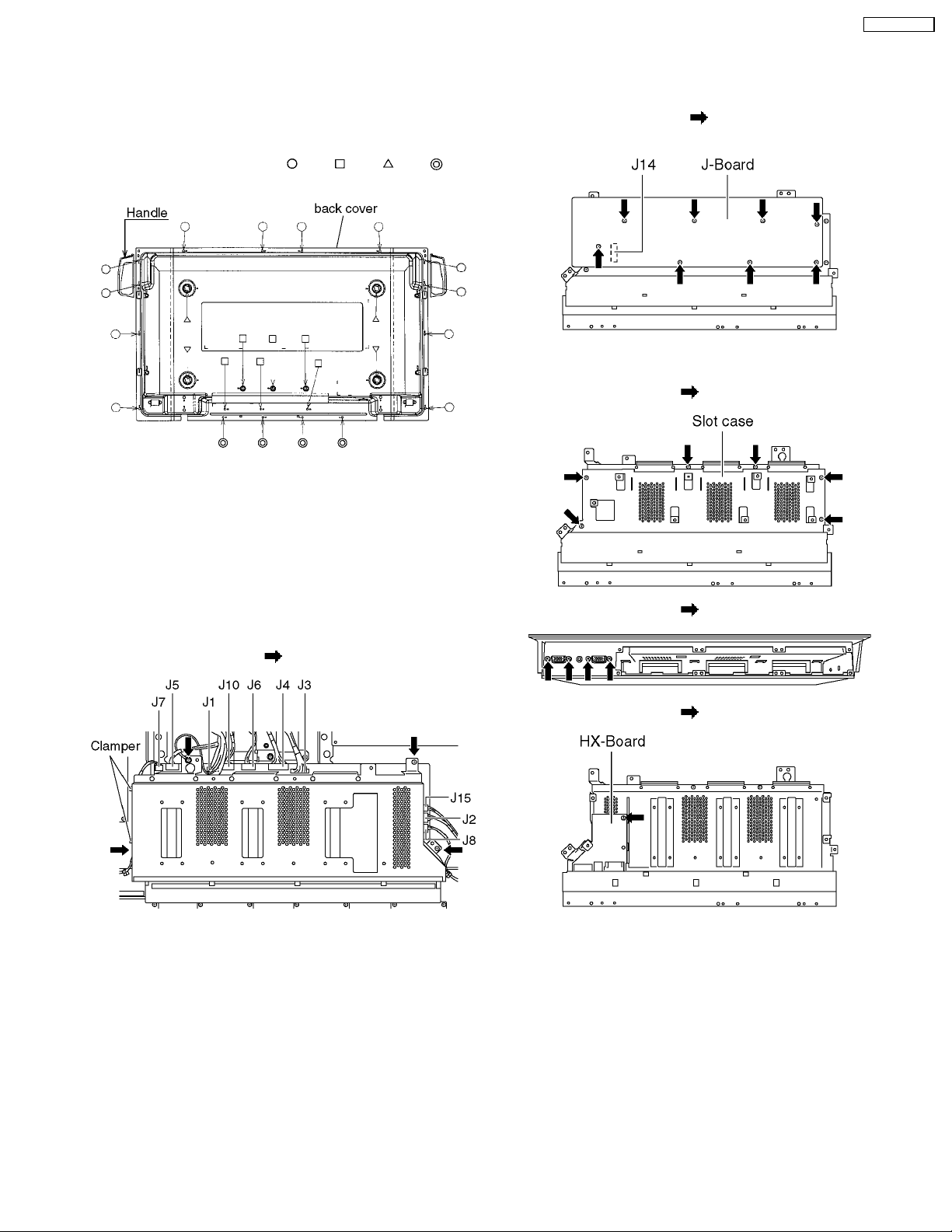
7.5. Removal of the P-Board
7.7. Removal of the AC-Inlet
1. Remove the couplers (P2, P5, P7, P9, P10, P11, P12, P23
and P25).
2. Unscrew the screws (×5
) and remove the P-Board.
7.6. Removal of the D-Board
1. Remove the coupler (P9) on the P-Board and release the
cables from the clamper.
2. Unscrew the screws (×2
) and remove the AC inlet.
7.8. Removal of the H3-Board
1. Unscrew the screws (×2 ), and remove the H3-Board
with the Bracket (right & left).
1. Disconnect the couplers (D1, D3, D5, D20, D25) and the
flexible cables (D31, D32).
2. Unscrew the screws (×5
) and remove the D-Board.
2. Remove the couplers (H37).
3. Unscrew the screws (×6
(right & left).
), and remove the H3-Board
12
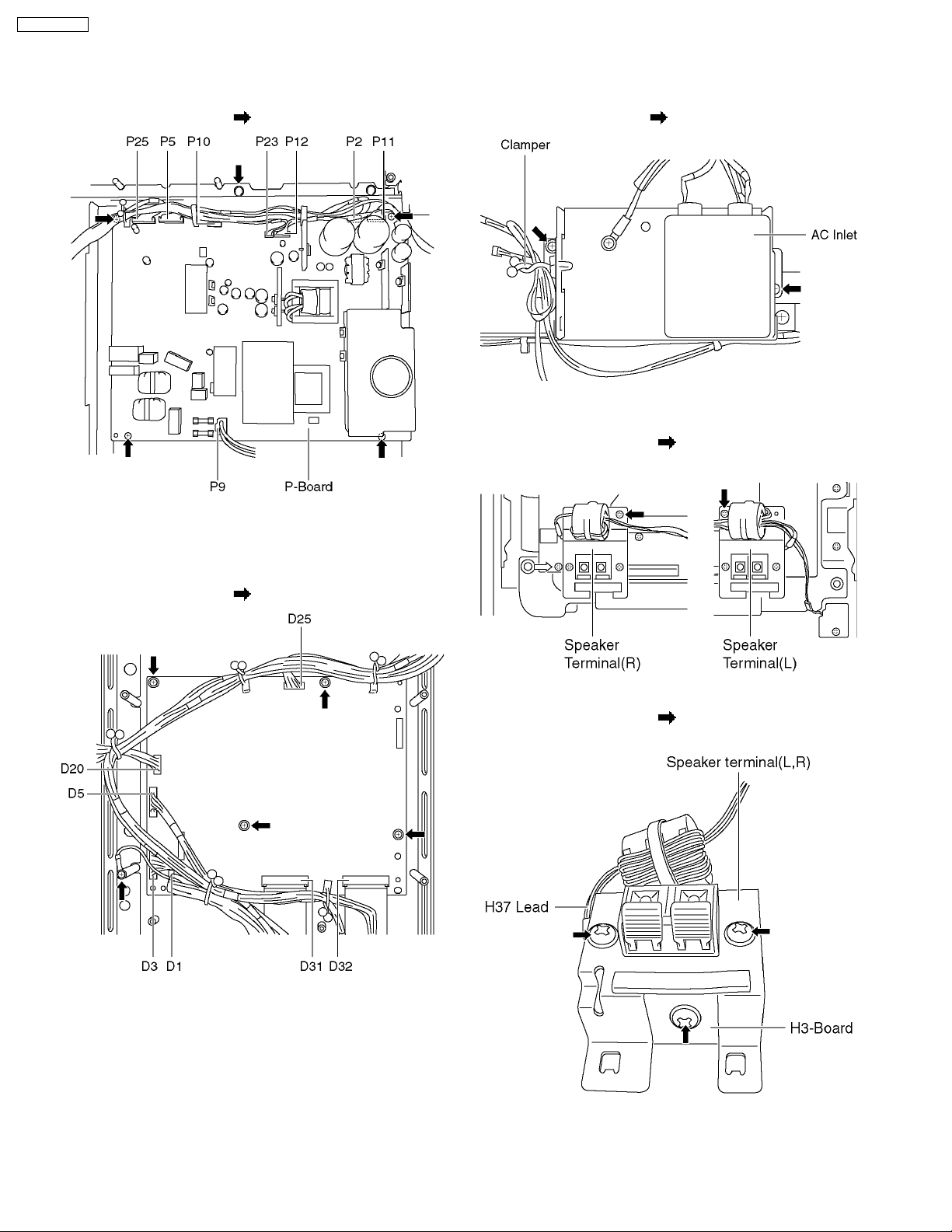
7.9. Removal of the S1-Board
1. Release the cable from the clamper.
2. Unscrew the screws (×2
the bracket.
3. Remove a coupler (S34), unscrew a screw (×1
remove the S1-Board.
) and remove the S1-Board with
) and
7.10. Removal of the SU-Board
1. Unscrew the screws (×2 ).
2. Slide the SU-Board to the left and disconnect from the
couplers (SC41) on the SC-Board.
3. Remove the coupler (SU45).
TH-37PWD8BK
7.11. Removal of the SD-Board
1. Unscrew the screws (×2 ).
2. Slide the SD-Board to the left and disconnect from the
couplers (SC42) on the SC-Board.
3. Remove the coupler (SD46).
4. Remove the flexible cables (SU1, SU2, SU3) connected to
the SU-Board from the plasma panel, and remove the SUBoard.
4. Remove the flexible cables (SD1, SD2, SD3) connected to
the SD-Board from the plasma panel, and remove the SDBoard.
13
TH-37PWD8BK
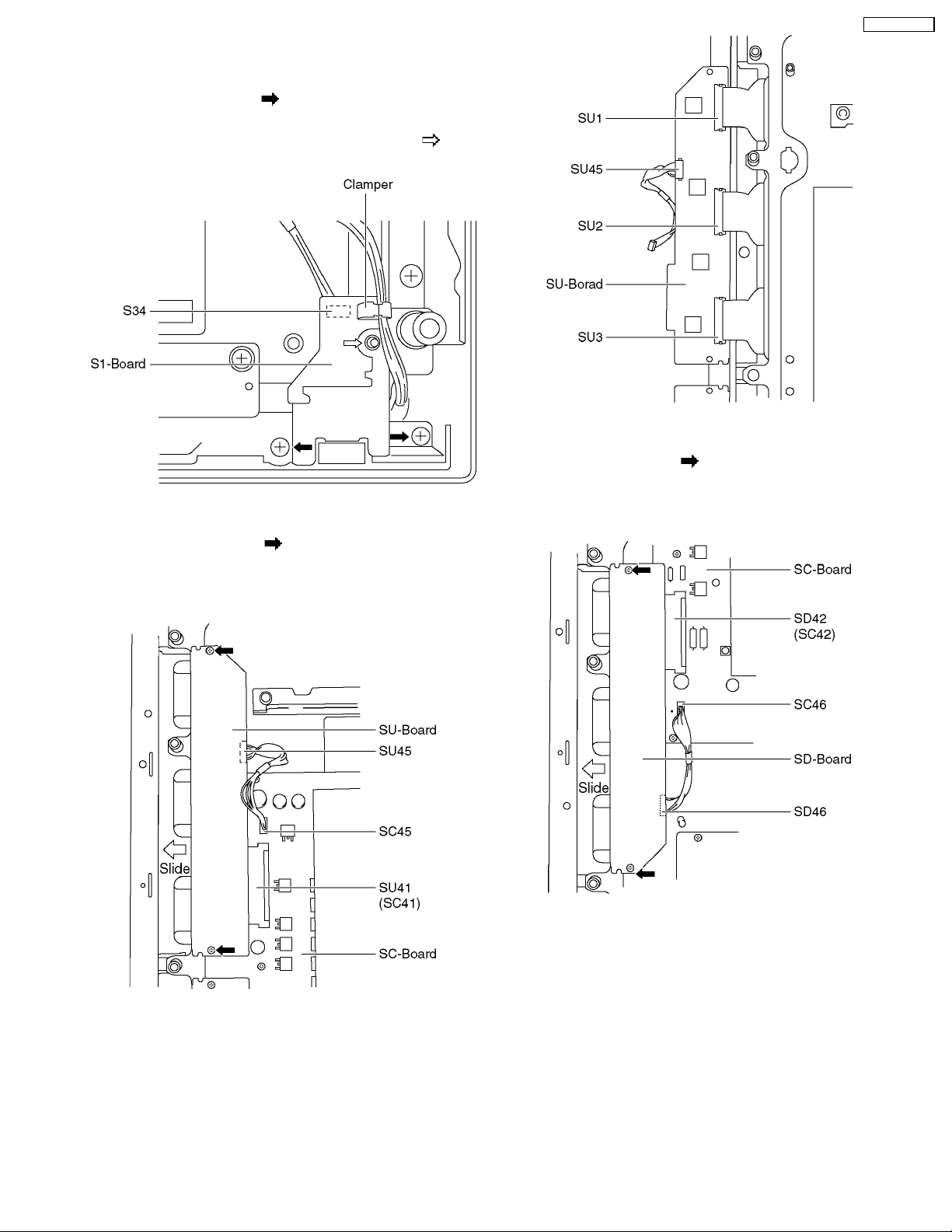
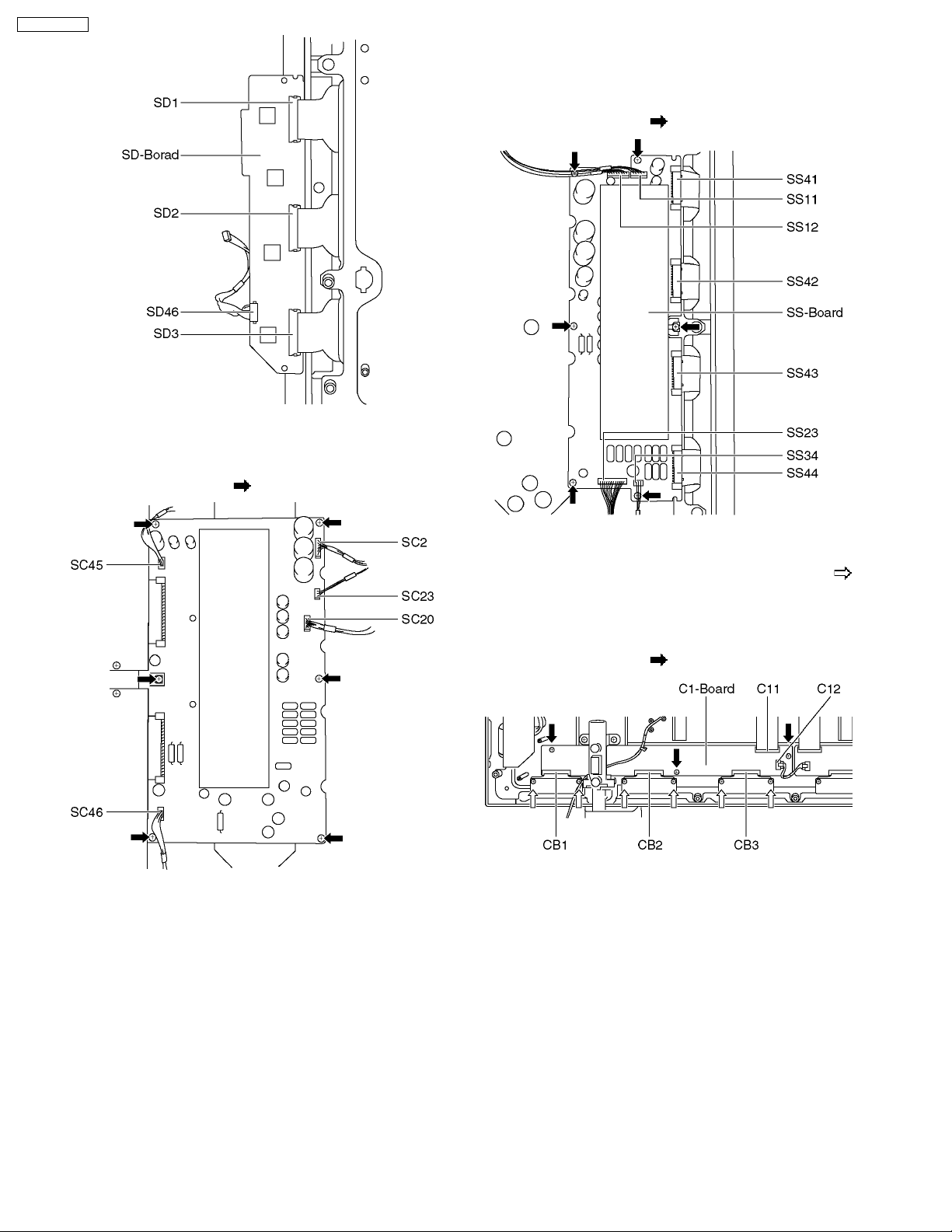
7.12. Removal of the SC-Board
1. Remove the couplers (SC2, SC20, SC23, SC45, SC46).
2. Unscrew the screws (×6
) and remove the SC-Board.
7.13. Removal of the SS-Board
1. Remove the couplers (SS11, SS12, SS23, SS34).
2. Remove the flexible cables (SS41, SS42, SS43, SS44).
3. Unscrew the screws (×6
), and remove the SS-Board.
7.14. Removal of the C1-Board
1. Unscrew the flexible cable holder fastening screws (×6 ).
2. Remove the flexible cables (CB1, CB2, CB3).
3. Remove a flexible cable (C11), a coupler (C12) and release
the speaker cables from a clamper (×1) on the C1-Board.
4. Unscrew the screws (×3
), and remove the C1-Board.
14
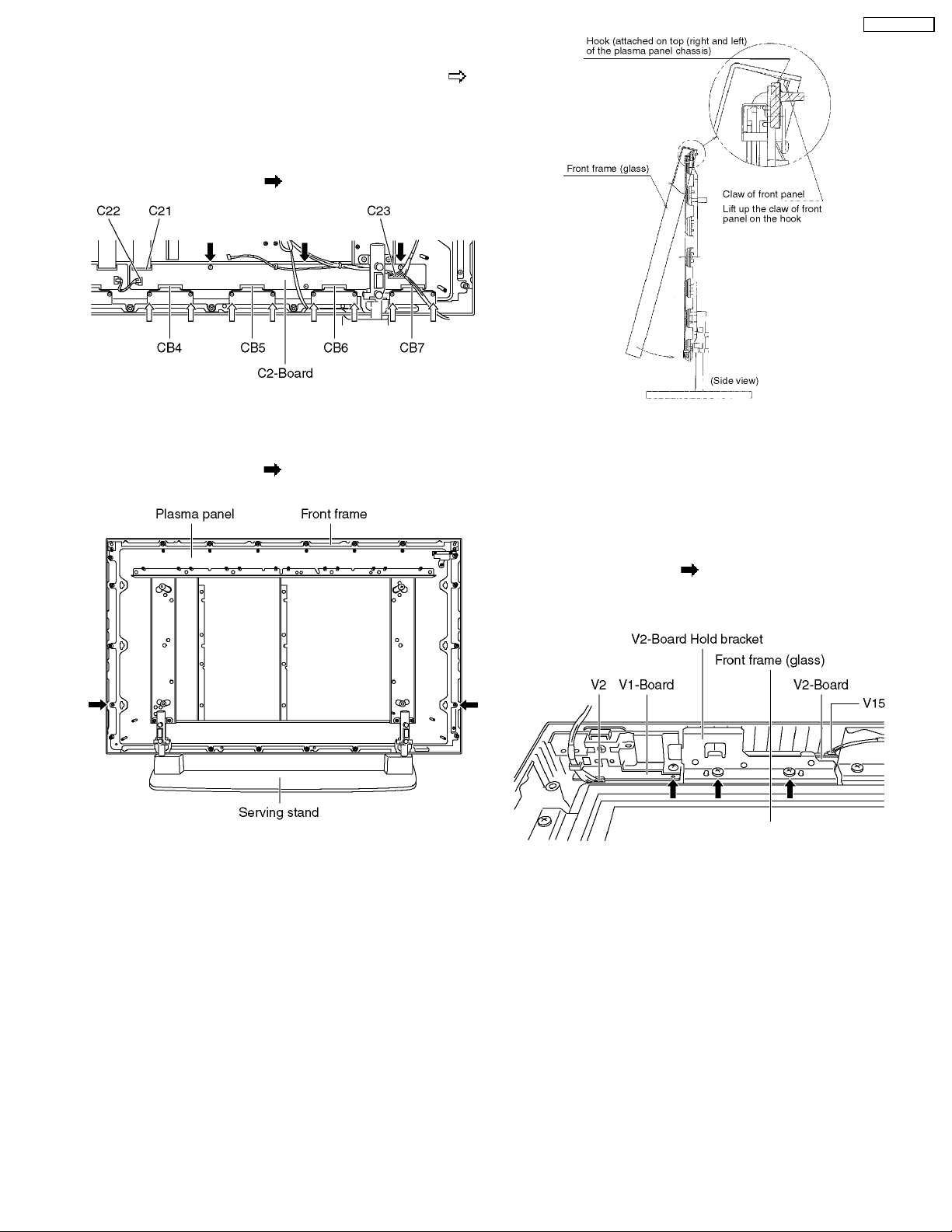
7.15. Removal of the C2-Board
1. Unscrew the flexible cable holder fastening screws (×8 ).
2. Remove the flexible cables (CB4, CB5, CB6, CB7).
3. Remove the couplers (C22, C23), a flexible cable (C21) and
release the speaker cables from the clamper on the C2Board.
4. Unscrew the screws (×3
), and remove the C2-Board.
7.16. Removal of the Front frame
(glass)
1. Remove the screws (×2 ) fixing the front frame and the
plasma panel.
TH-37PWD8BK
7.17. Removal of the V1-Board and
the V2-Board
1. Lay down the front frame on the flat surface of the table
(covered by a soft cloth not to damage the surface.)
2. Remove the couplers (V2 on the V1-Board and V15 on the
V2-Board).
3. Unscrew the screws (×3
4. Remove the V1-Board, the V2-Board hold bracket and the
V2-Board.
).
2. Confirm the S1-Board has been removed and the cable to
the V1-Board and V2-Board released.
3. For leaving the front frame from the plasma panel, pull the
bottom of the front frame to forward, lift up, and remove.
15
TH-37PWD8BK
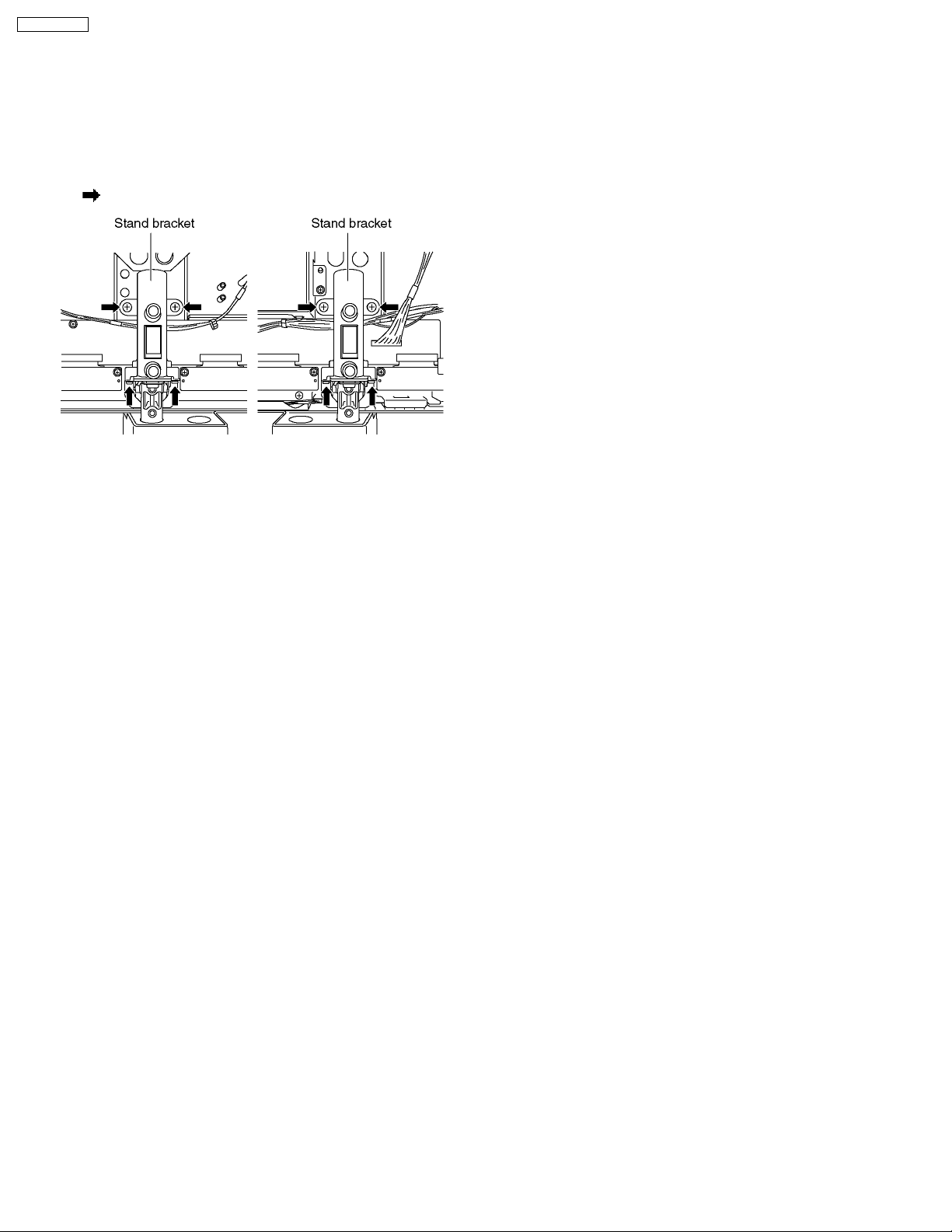
7.18. Removal of stand brackets
1. Remove the plasma panel section from the servicing stand
and lay on a table (covered), with the plasma panel surface
facing downward.
Spread a soft cloth for protection, to prevent panel surface
from scratching.
2. Remove the stand bracket (left, right) fastening screws (×4
each) and remove the stand brackets (left, right).
7.19. Replacement of the plasma
panel
1. Place the new plasma panel (finished) on the flat surface of
the table (covered by a soft cloth), with the plasma panel
surface facing downward.
2. Fit the stand brackets (left, right.) fasten 4 screws each on
the new plasma panel.
3. Place the plasma panel section on the servicing stand.
4. Attach the front frame, each P.C.Board and so on, to the
new plasma panel.
* When fitting the front frame, be careful not to allow any
debris, dust or handling residues to remain between the
front glass and plasma panel.
16
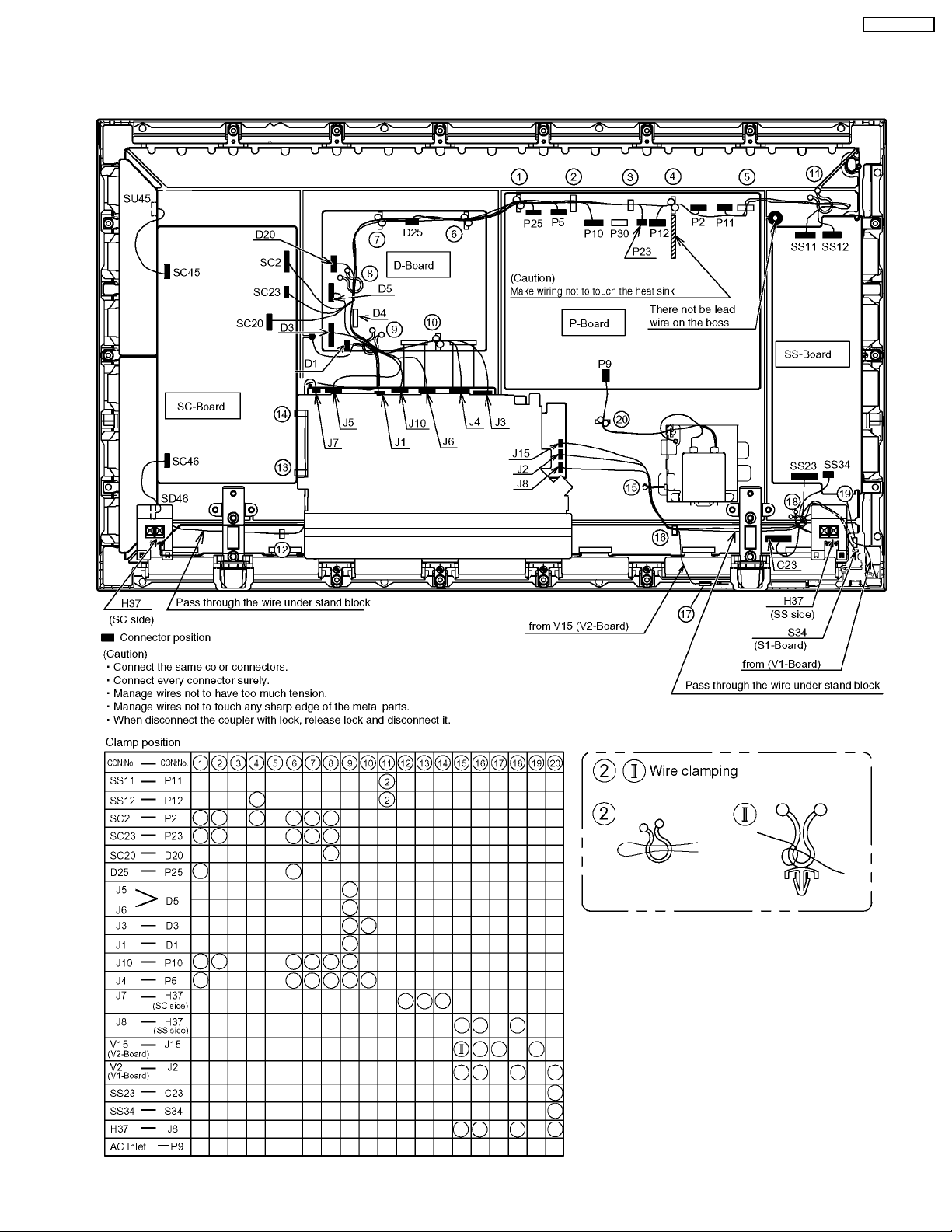
8 Location of Lead Wiring
8.1. Wiring for 37 inch model
TH-37PWD8BK
17
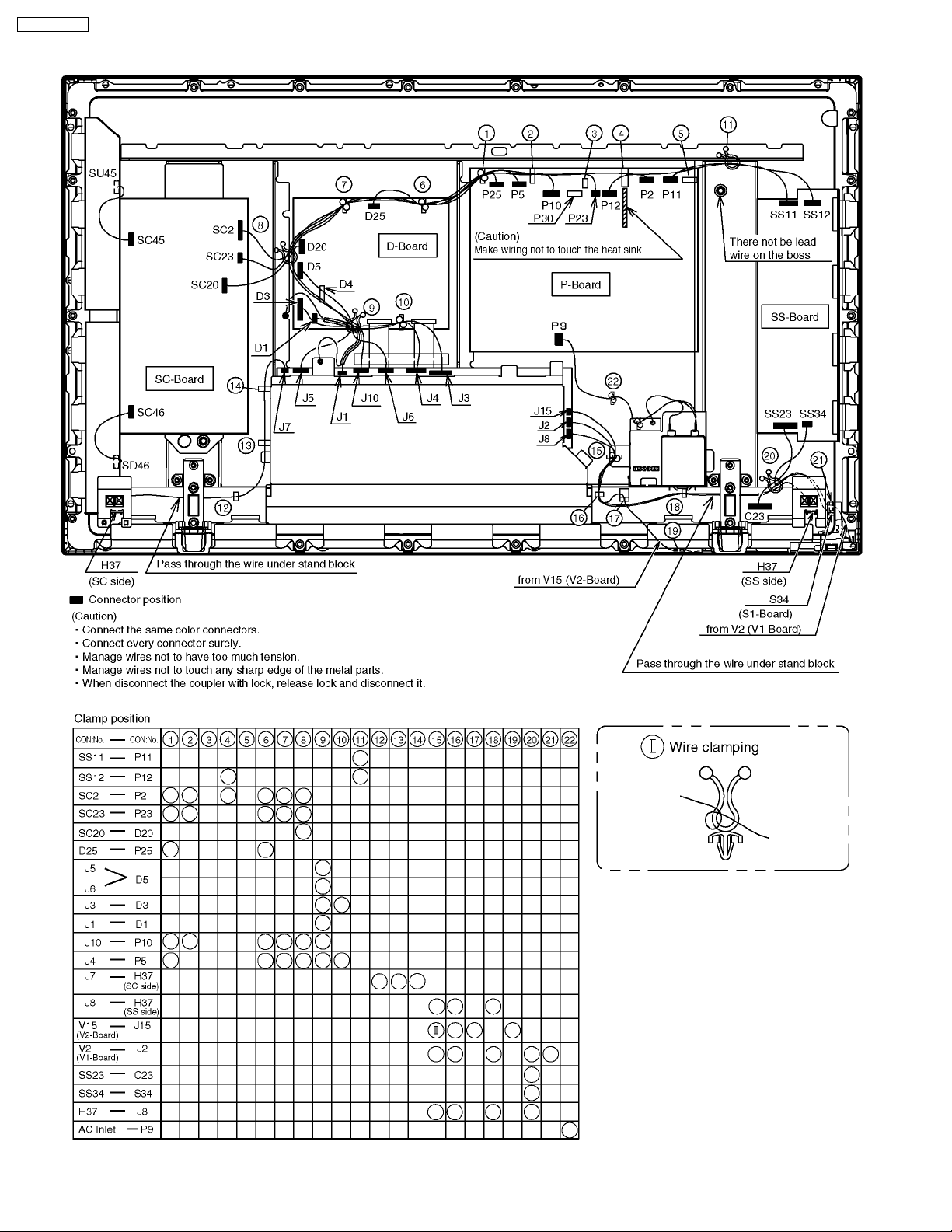
TH-37PWD8BK
8.2. Wiring for 42 inch model
18

9 Adjustment Procedure
TH-37PWD8BK
9.1. Driver Set-up
9.1.1. Item / Preparation
1. Input a white signal of the RGB signal generator.
2. Set the picture controls: -
Picture menu: Standard
Color temperature: Middle
Picture: 25
Aspect: Full
Caution
1. First perform Vsus adjustment.
2. Confirmation of Vscn voltage should be performed after
confirmation of Vad adjustment.
When Vad=-90V, Voltage of Vscn is 30V ±3V.
9.1.2. Adjustments
Adjust driver section voltages referring the panel data on the
panel data label.
Name Test Point Voltage Volume Remarks
Vsus TPVSUS
(SS)
Ve TPVE (SS) Ve ± 2V VR6074 (SS) *
Vset TPVSET
(SC)
Vad TPVAD (SC) -90V ± 1V VR6477
Vscn TPVSCN
(SC)
Vda TPVDA (SS) 67V ± 1V R665 (P)
PFC C446 (+)(-) 395V ± 0.5V R443 (P)
Vlow C555 (+)(-) 73V ± 0.1V R661 (P) load
Csus TPVSUS
(SS)
*See the Panel label.
Vsus ± 1V R628 (P) *
232V ± 7V Fixed
(SC)
Vad+120V ±3VFixed
current :
0.4A
164V ± 0.5V R671 (P) load
current :
1.45A
19
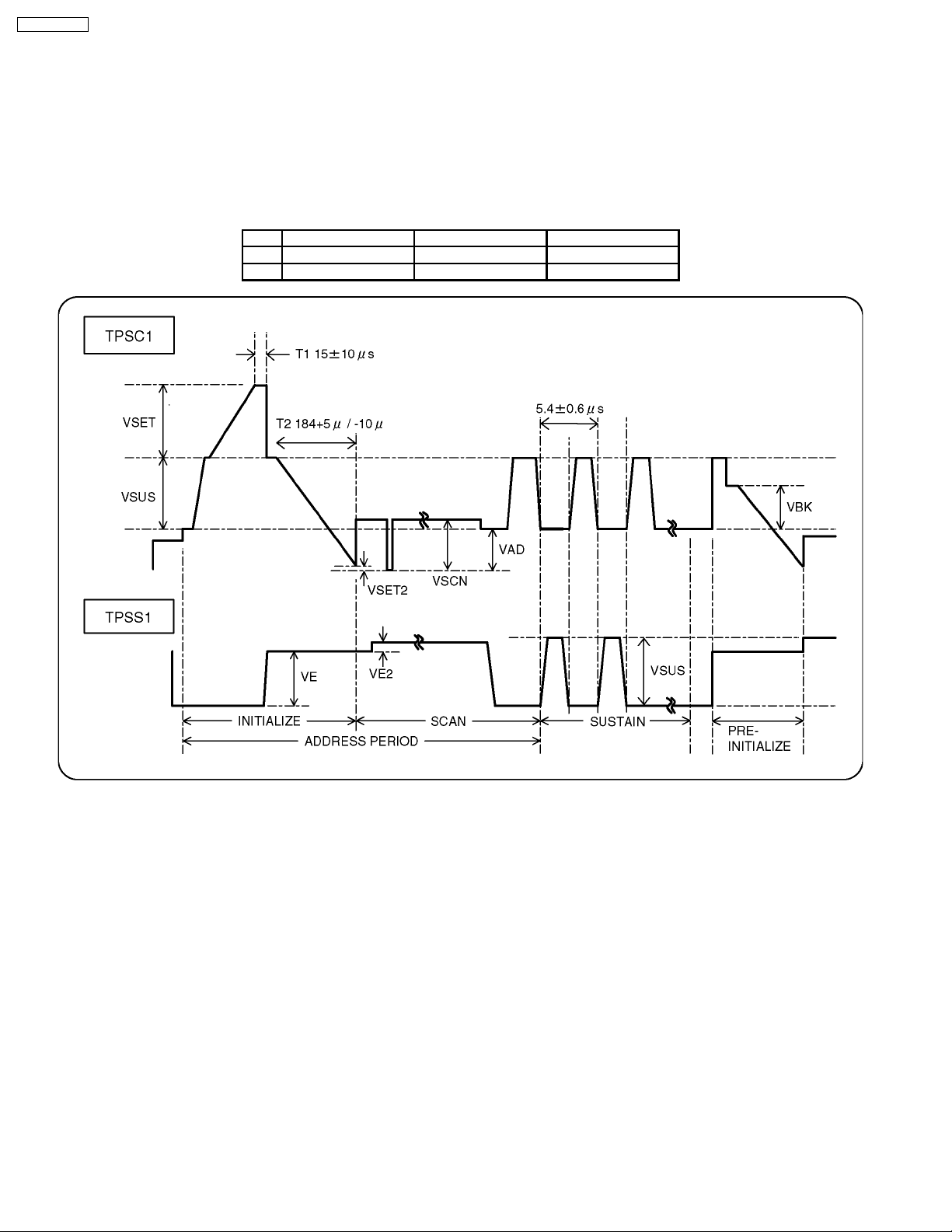
TH-37PWD8BK
9.2. Initialization Pulse Adjust
1. Input the White signal to plasma video input.
2. Set the picture controls as follows.
·
· Picture menu: Standard
· ·
·
· Color temperature : Middle
· ·
·
· Picture : 25
· ·
3. Connect Oscilloscope to TPSC1 (T1) and check for 15±10µ Sec.
4. Connect Oscilloscope to TPSC1 (T2) and adjust R6557 for 184+5µ /-10µ Sec.
Test point Volume Level
T1 TPSC1 (SC) --- 15 ± 10µ Sec
T2 TPSC1 (SC) R6557 (SC) 184 + 5µ / - 10µ Sec
20
9.3. P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) exchange
9.3.1. Caution
1. To remove P.C.B. , wait 1 minute after power was off for discharge from electrolysis capacitors.
9.3.2. Quick adjustment after P.C.B. exchange
P.C.B. Name Test Point Voltage Volume Remarks
P Board Vsus TPVSUS (SS) Vsus ± 2V R628 (P) *
Vda TPVDA (SS) 67V ± 1V R665 (P)
PFC C446 (+) (-) (P) 395V ± 0.5V R443 (P)
Vlow C557 (+) (-) (P) 73V ± 0.1V R661 (P) load current : 0.4A
Csus TPVSUS (SS) 178V ± 0.5V R671 (P) load current : 1.45A
SC Board Vad TPVAD (SC) -90V ± 1V VR6477 (SC)
SS Board Ve TPVE (SS) Ve ± 2V VR6074 (SS) *
D, DG Board White blance, Pedestal and Sub brightness for NTSC, PAL, HD, PC and 625i signals
*See the Panel label.
Caution:
Absolutely do not reduce Vsus below Ve not to damage the P.C.B.
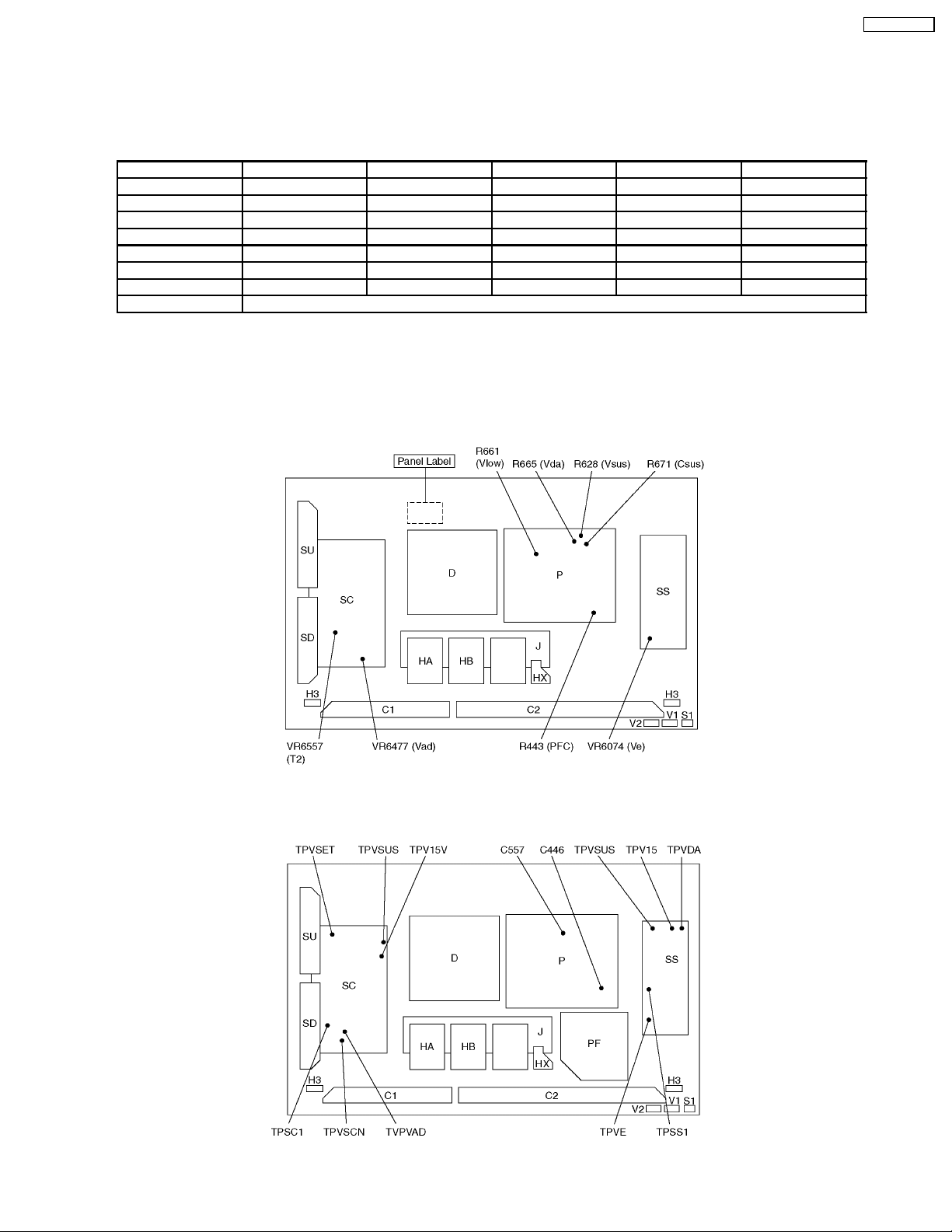
9.4. Adjustment Volume Location
TH-37PWD8BK
9.5. Test Point Location
21
TH-37PWD8BK
10 Service mode
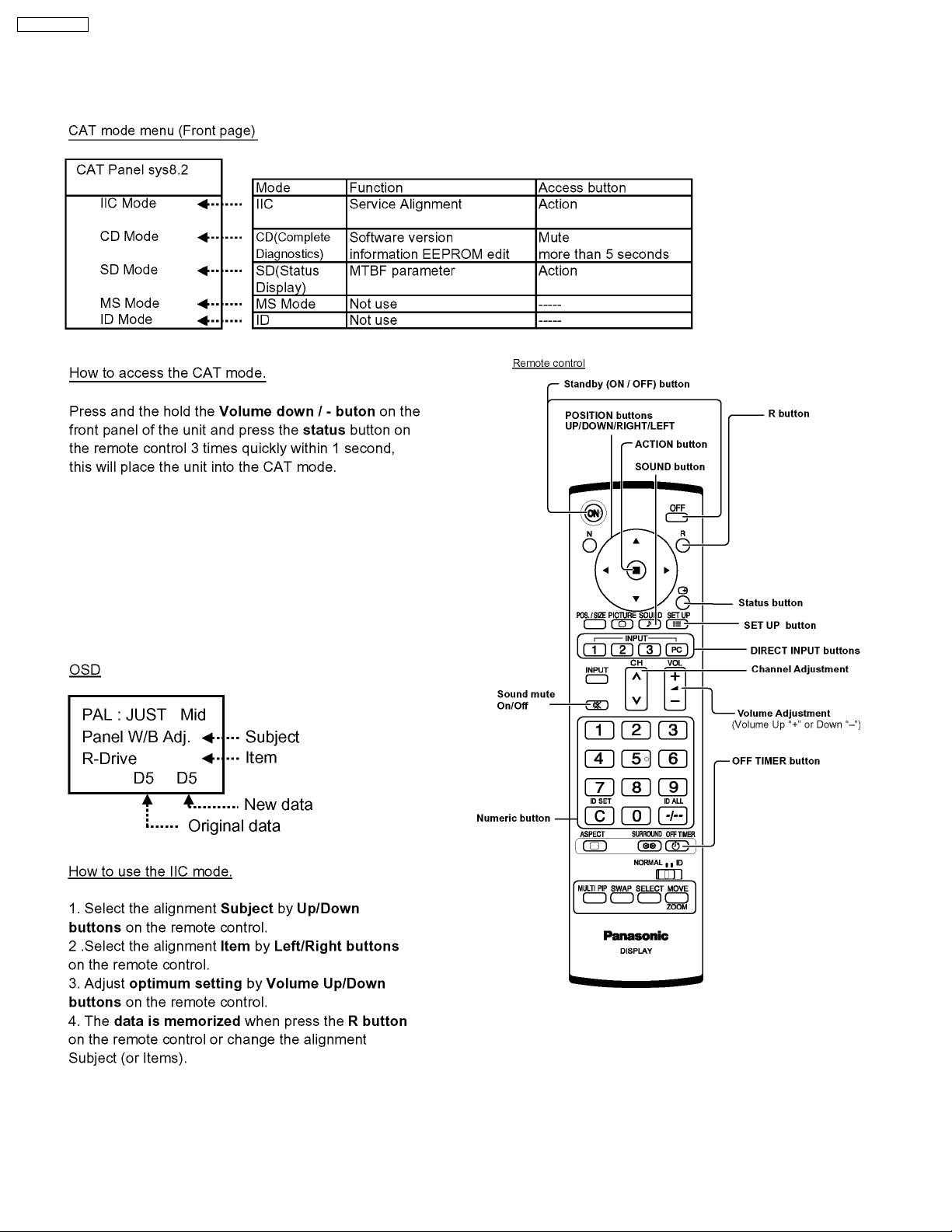
10.1. CAT (computer Aided Test) mode
To exit the CAT mode, access the ID mode and switch off
the main power.
10.1.1. IIC mode
Select the IIC mode by Up/Down button on the remote control
at the front page of CAT mode then press the Action button on
the remote control.
Subject and item are mentioned on page 24.
To exit the IIC mode, press the R button on the remote control.
22
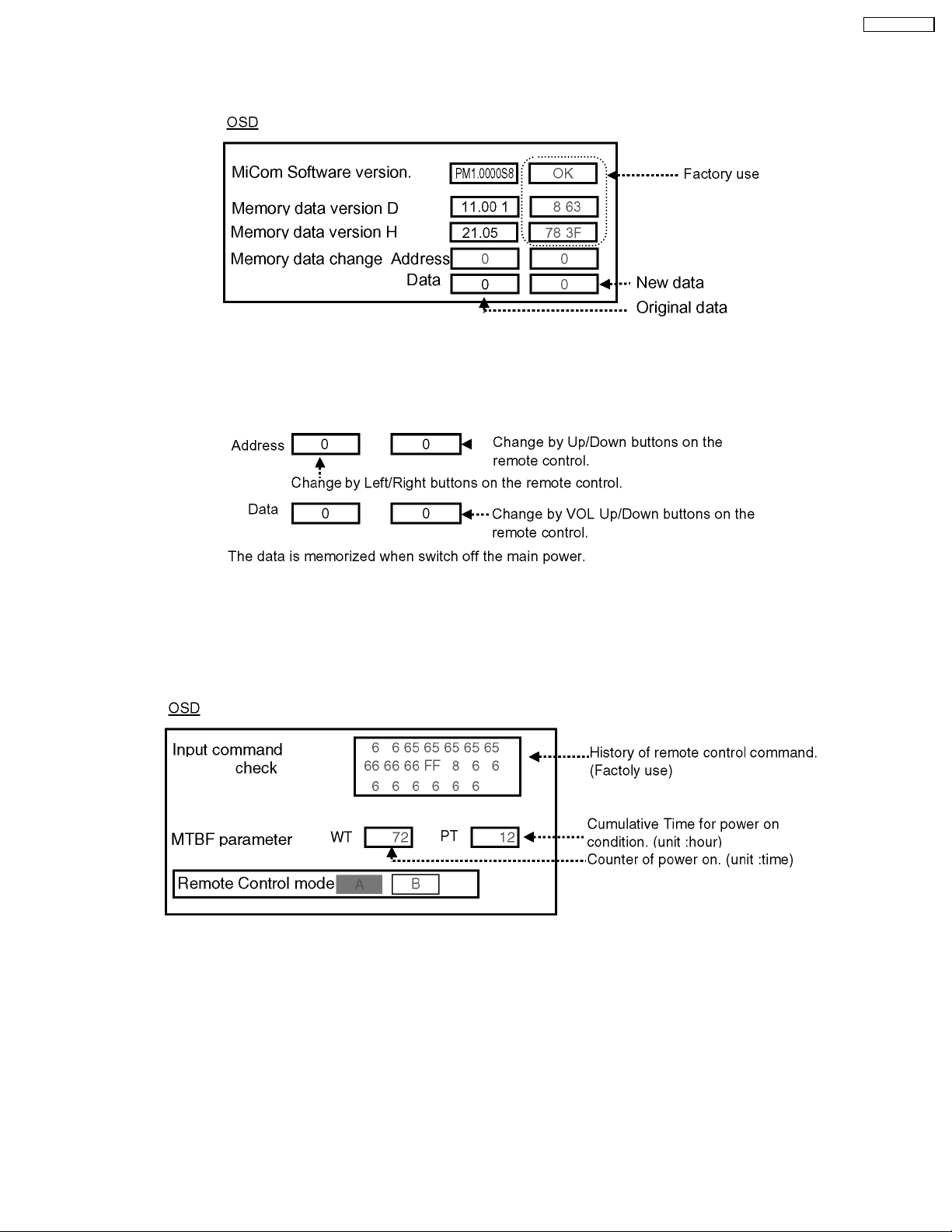
TH-37PWD8BK
10.1.2. CD mode
Select the CD mode by Up/Down button on the remote control at the front page of CAT mode then press the Mute button on the
remote control more than 5 sec.
Micom software version (IC9703), this version can be upgrade by
1. replace of new version IC
2. Loading the new version software from loader tool, TZSC07036.
Memory data change
To exit the CD mode, press the R button on the remote control.
10.1.3. SD mode
Select the SD mode by Up/Down button on the remote control at the front page of CAT mode then press the Action button on the
remote control.
To exit the SD mode, press the R button on the remote control.
23
TH-37PWD8BK
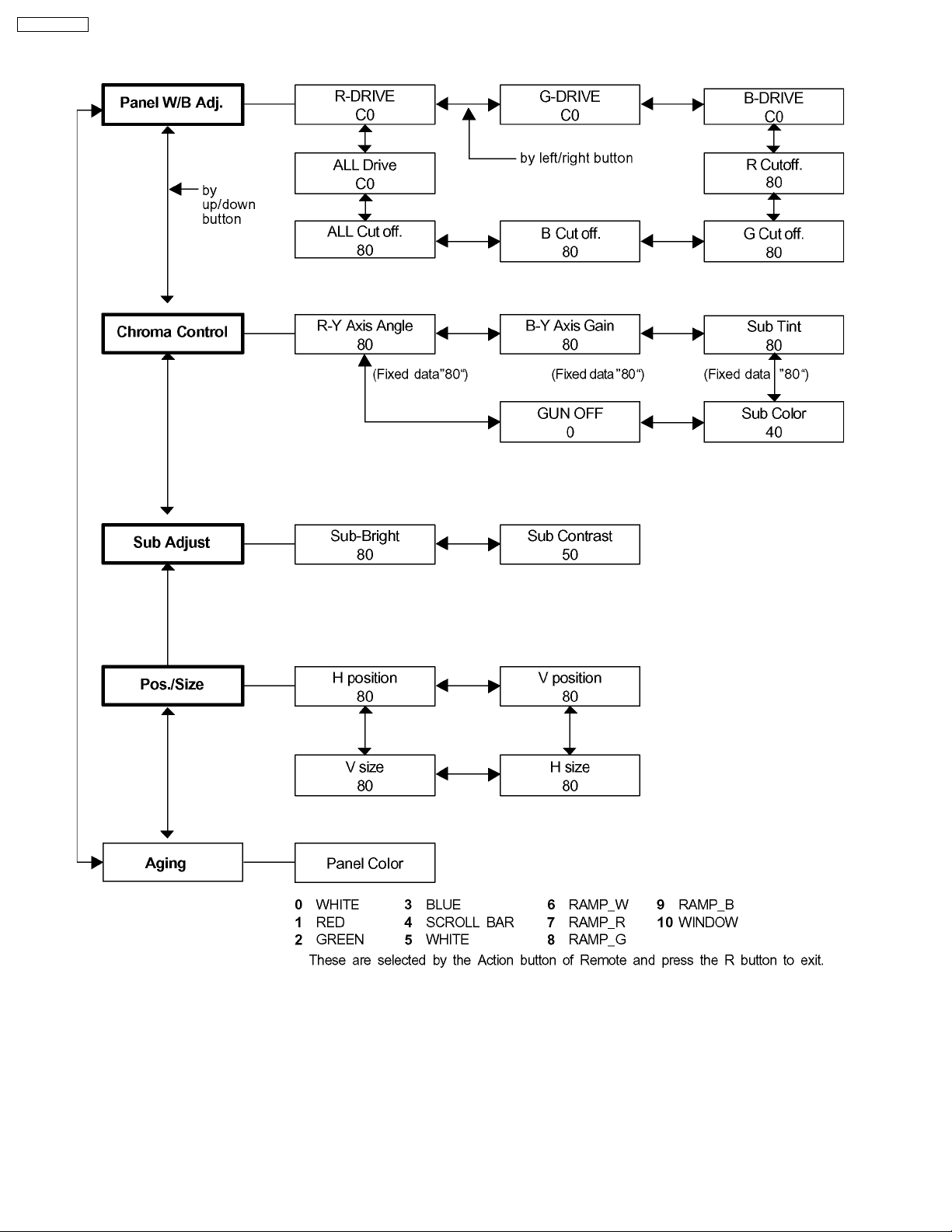
10.2. IIC mode structure (following items value is sample data.)
24
11 Alignment
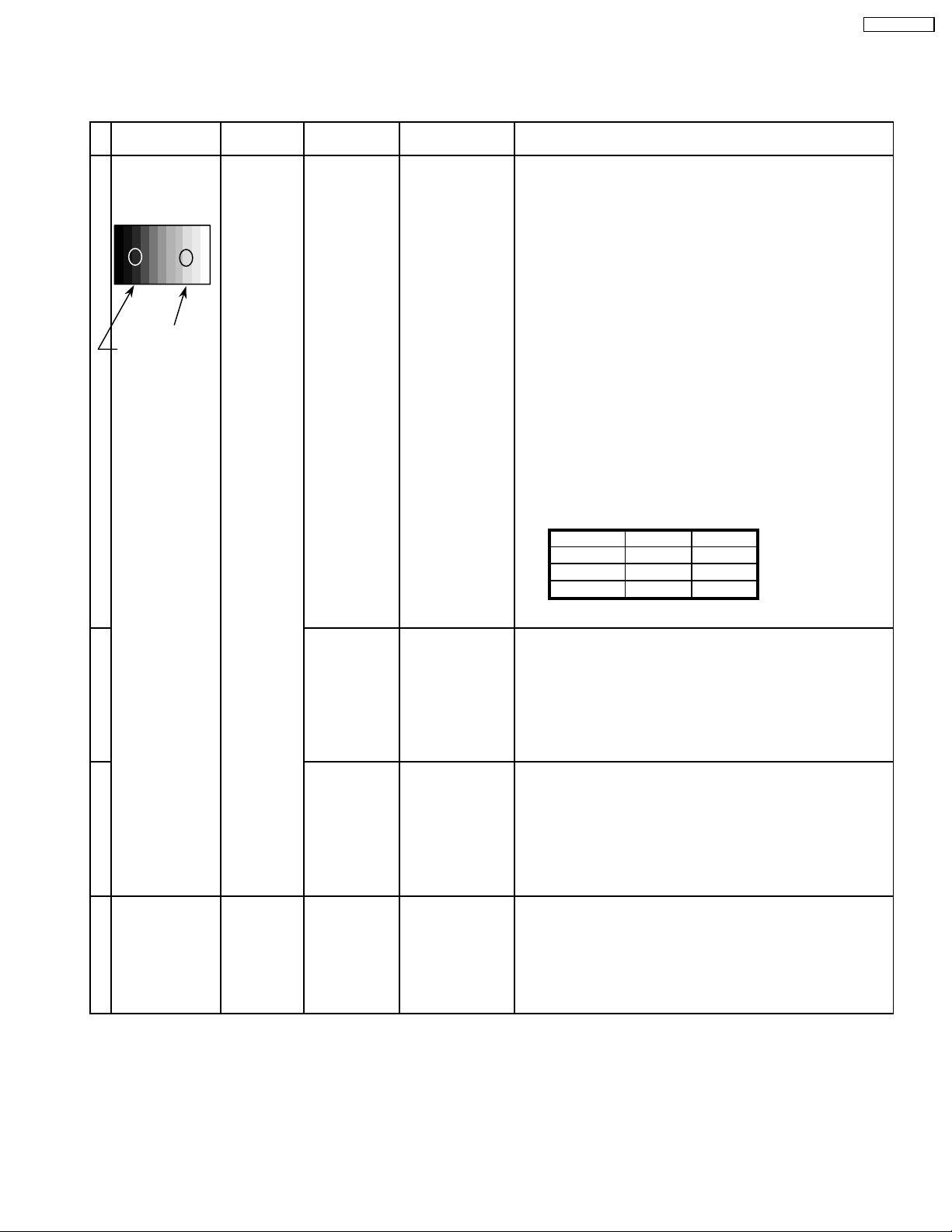
11.1. PC/RGB panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
TH-37PWD8BK
1 PC (VGA) Color Picture menu:
Gray Scale Analyzer Standard
Pattern
High light 75%
Low light 15%
Picture:
White balance:
Cool
Aspect:
Component/
RGB-IN Select:
RGB
IIC mode:
Panel W/B Adj
Color
temprature:
High
25
Full
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
Note: · Before adjustment, color signal has not been displayed
on panel.
· The pedestal adjustment has been done.
· The signal root must be A side.
1) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
2)Find 75% (amplitude) of white area by color sensor.
G Drive 3) Set G Drive to " E0 ".
B Drive 4) Adjust B and R Drive to set the High color temperature
R Drive as shown Table 1.
R,G,B Drive 5) Increase equaly R, G and B Drive to get the
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
R,G,B cut off
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.276 0.276
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Table 1 W/B adjustment value
2 Picture menu: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Standard PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) In Mid color temperature, repeat the procedures 1) to 5) of
Normal PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
Full
3 Picture menu: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Standard PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) In Low color temperature, repeat the procedures 1) to 5) of
Warm PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
Full
· NTSC
4 1) Copy the R drive, G drive and B drive data obtained in above
· PAL
· DVI
Cool mode.
Cool mode.
steps into NTSC, PAL and DVI area.
25
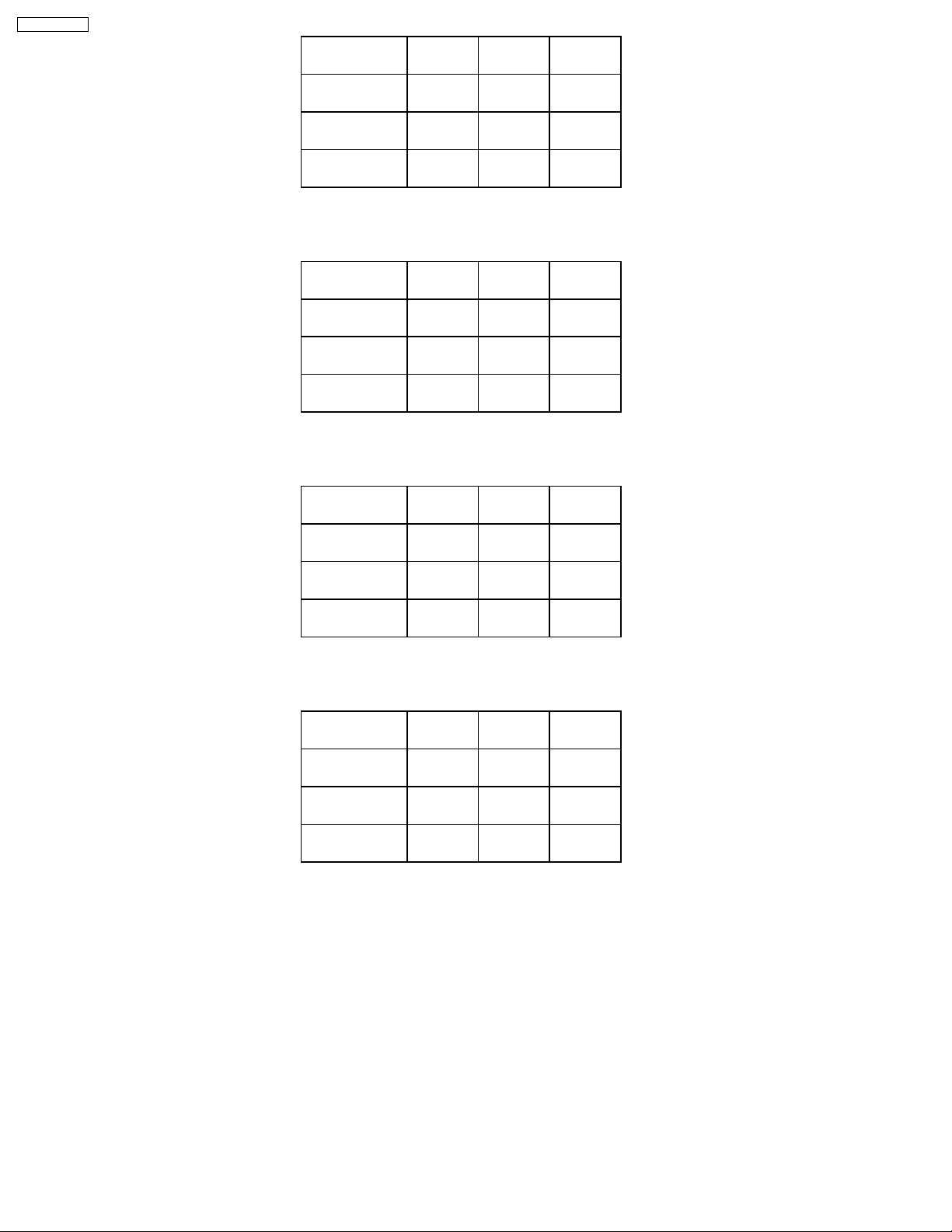
TH-37PWD8BK
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-11AD
A0-11B0
A0-11B3
G
A0-11AE
A0-11B1
A0-11B4
Table 2 Drive data addresses (PC/RGB)
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-1180
A0-1183
A0-1186
G
A0-1181
A0-1184
A0-1187
Table 3 Drive data addresses (NTSC)
Color temperature
R
G
B
A0-11AF
A0-11B2
A0-11B5
B
A0-1182
A0-1185
A0-1188
B
High
Medium
Low
A0-1189
A0-118C
A0-118F
A0-118A
A0-118D
A0-1190
Table 4 Drive data addresses (PAL)
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-11B6
A0-11B9
A0-11BC
A0-11B7
A0-11BA
A0-11BD
Table 5 Drive data addresses (DVI)
A0-118B
A0-118E
A0-1191
G
B
A0-11B8
A0-11BB
A0-11BE
26
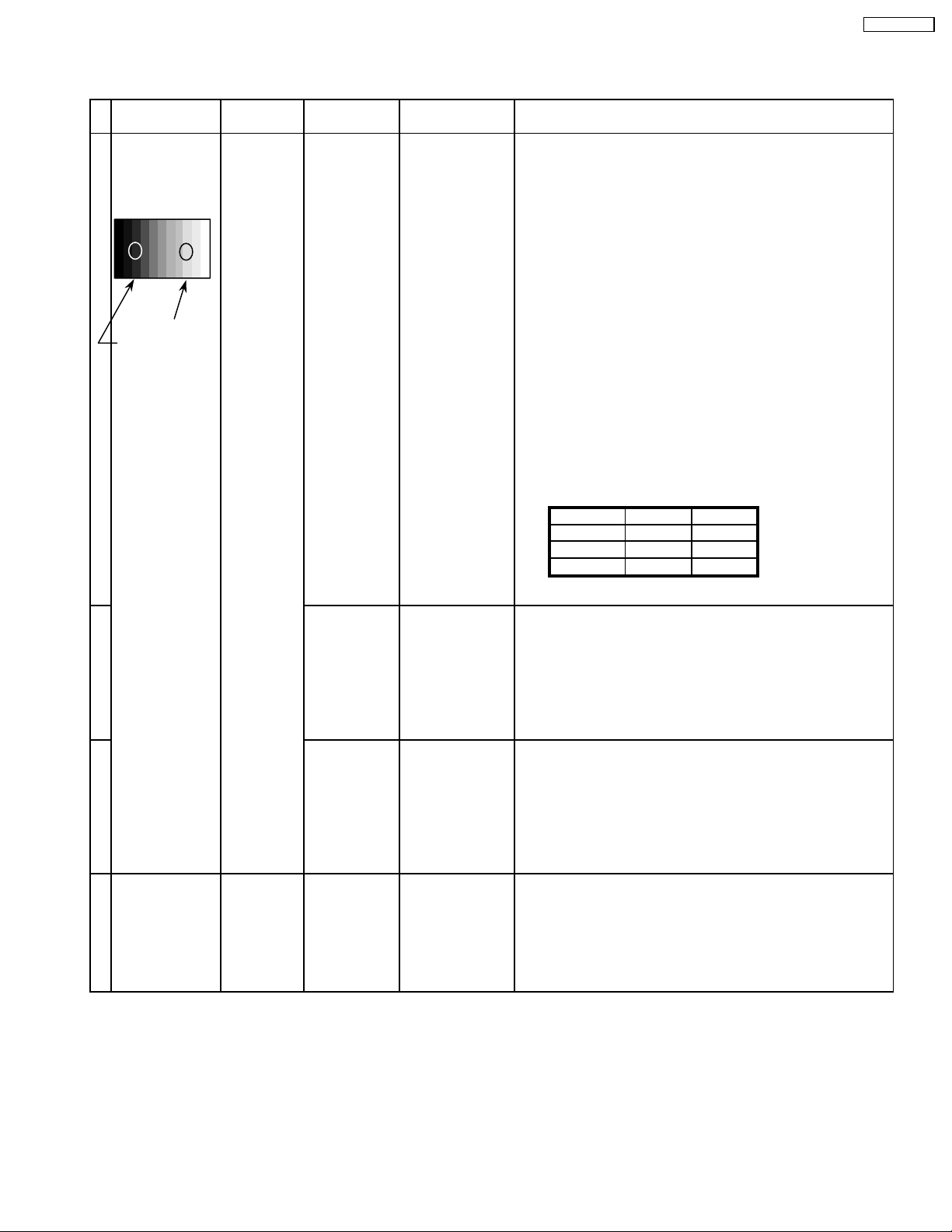
11.2. HD/ 525ip /625ip panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
TH-37PWD8BK
1 Color Picture menu:
HD
(YUV2_HD)
Gray Scale
Pattern
High light 75%
Low light 15%
Analyzer Standard
Picture:
White balance:
Cool
Aspect:
Component/
RGB-IN Select:
RGB
IIC mode:
Panel W/B Adj
Color
temprature:
High
25
Full
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
Note: · Before adjustment, color signal has not been displayed
on panel.
· The pedestal adjustment has been done.
· The signal root must be A side.
1) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
2)Find 75% (amplitude) of white area by color sensor.
G Drive 3) Set G Drive to " E0 ".
B Drive 4) Adjust B and R Drive to set the High color temperature
R Drive as shown Table 1.
R,G,B Drive 5) Increase equaly R, G and B Drive to get the
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
R,G,B cut off
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.276 0.276
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Table 1 W/B adjustment value
2 Picture menu: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Standard PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) In Mid color temperature, repeat the procedures 1) to 5) of
Normal PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
Full
3 Picture menu: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Standard PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) In Low color temperature, repeat the procedures 1) to 5) of
Warm PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
Full
· YUV1_525ip
4 1) Copy the R drive, G drive and B drive data obtained in above
· YUV3_625ip
Cool mode.
Cool mode.
steps into YUV1_525ip, YUV3_625ip area.
27
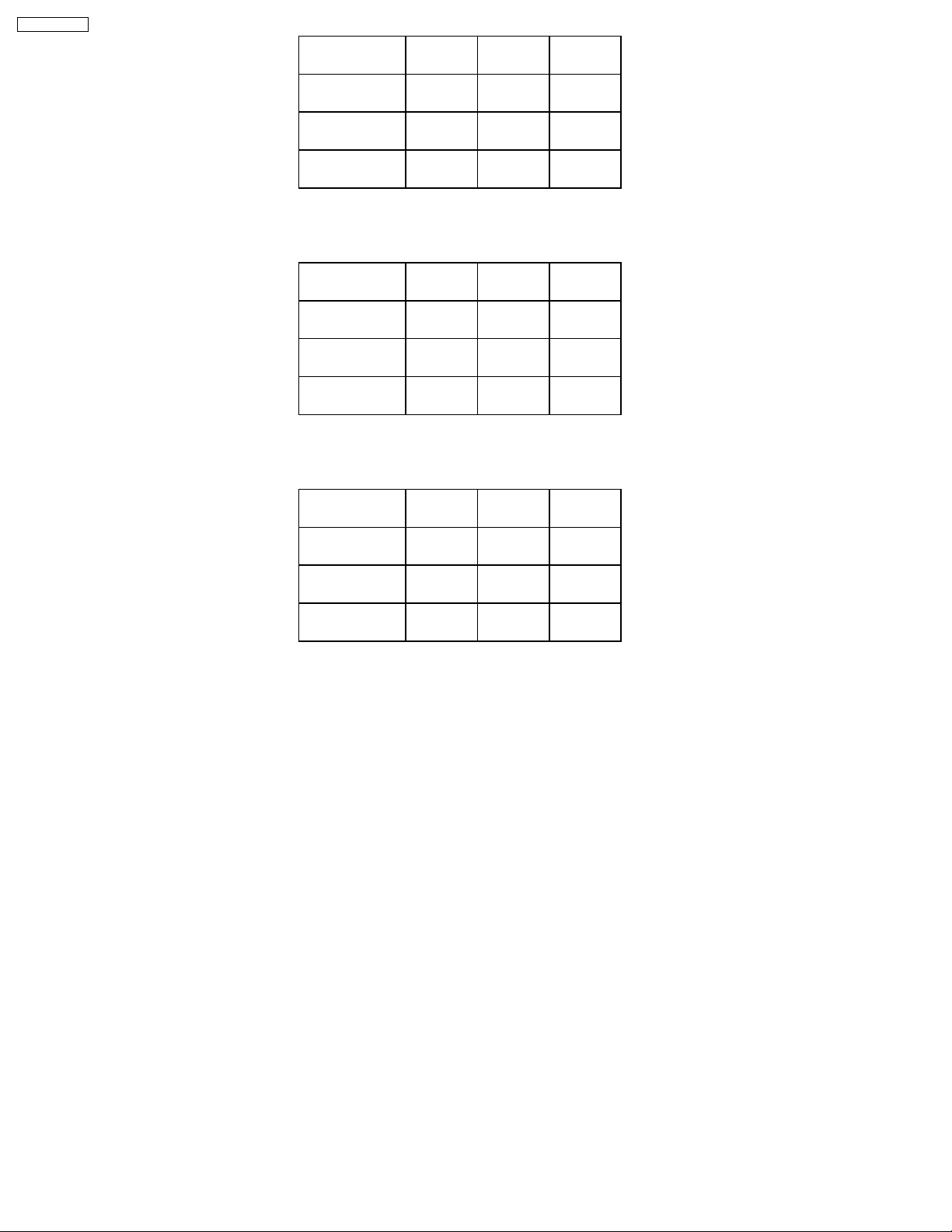
TH-37PWD8BK
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-119B
A0-119E
A0-11A1
G
A0-119C
A0-119F
A0-11A2
Table 2 Drive data addresses (YUV2_HD)
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-1192
A0-1195
A0-1198
G
A0-1193
A0-1196
A0-1199
Table 3 Drive data addresses (YUV1_525ip)
B
A0-119D
A0-11A0
A0-11A3
B
A0-1194
A0-1197
A0-119A
Color temperature
High
Medium
Low
R
A0-11A4
A0-11A7
A0-11AA
G
A0-11A5
A0-11A8
A0-11AB
Table 4 Drive data addresses (YUV3_625ip)
B
A0-11A6
A0-11A9
A0-11AC
28
12 Trouble shooting guide
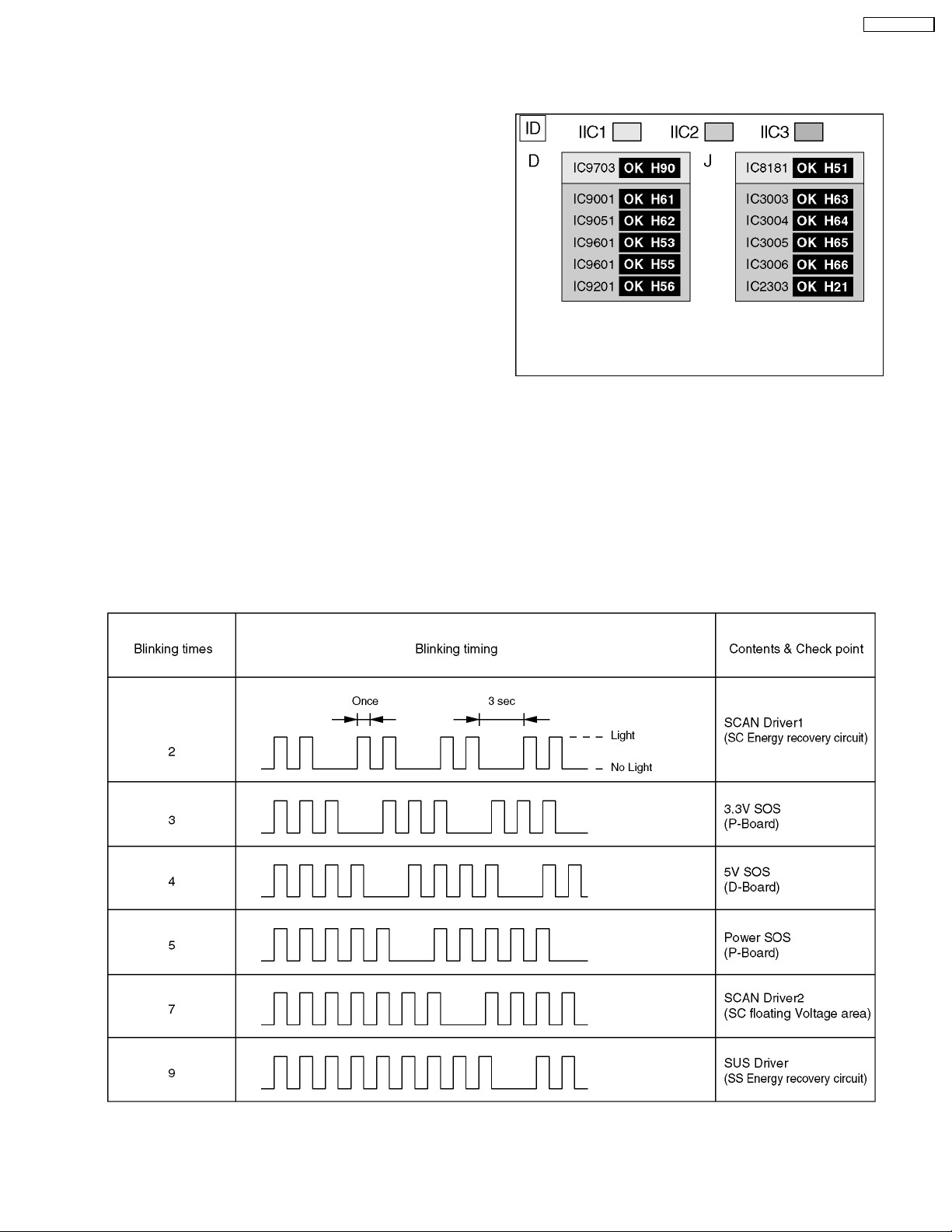
12.1. Self Check
12.1.1. Display Indication
1. Self-check is used to automatically check the bus line
controlled circuit of the Plasma display.
2. To get into the Self-check mode, press the volume down
button on the customer controls at the front of the set, at the
same time pressing the OFF-TIMER button on the remote
control, and the screen will show :-
If the CCU ports have been checked and found to be incorrect
Or not located then " - - " will appear in place of " OK "
12.1.2. Power LED Blinking timing chart
1. Subject
Information of LED Flashing timing chart.
2. Contents
When an abnormality has occurred the unit, the protection circuit operates and reset to the stand by mode. At this time, the
defective block can be identified by the number of blinkes of the Power LED on the front panel of the unit.
TH-37PWD8BK
29
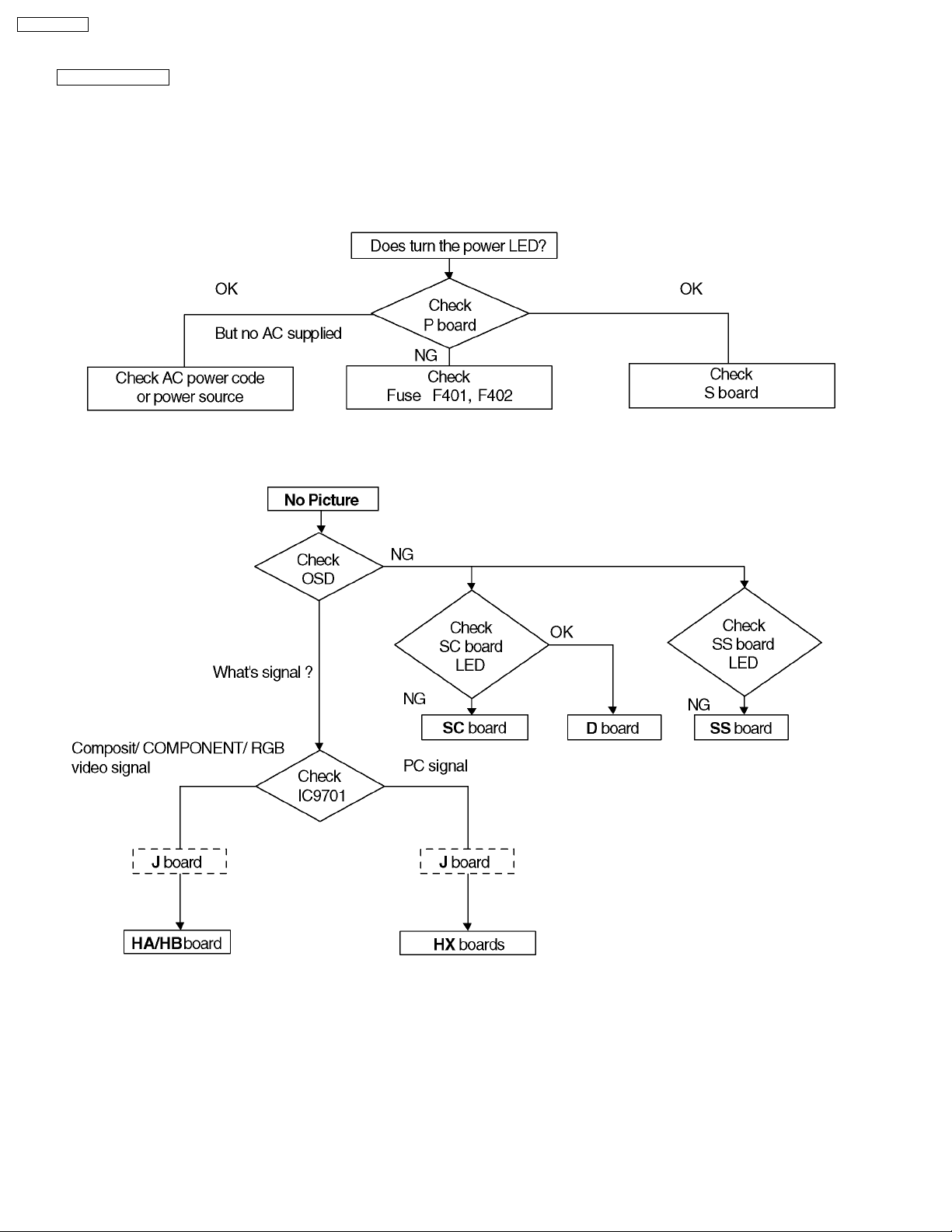
TH-37PWD8BK
12.2. No Power
First check point
There are following 3 states of No Power indication by power LED.
1. No lit
2. Green is lit then turns red blinking a few seconds later.
3. Only red is lit.
1. No lit
12.3. No Picture
30
 Loading...
Loading...