Page 1

A
A
A
DVD-S42EE
DVD-S42GC
DVD-S42GCA
DVD-S42GCS
DVD-S42GCU
DVD-S42PL
DVD-S42PLA
ORDER NO.CHM0603009CE
DVD Player
Specifications
Power supply:
Power consumption: 11 W
Power consumption in standby mode:
Dimensions: 430 (W) × 251 (D) × 43 (H) mm
Mass: 2.2 kg (approx.)
Signal system: PAL 625/50, PAL 525/60, NTSC
Operating temperature range: +5to+35°C
Operating humidity range: 5 to 90 % RH (no condensation)
Discs played [8 cm (3") or 12 cm (5")]:
(1) DVD (DVD-Video, DivX,)
(2) DVD-RAM (DVD-VR, JPEG,, MPEG4,, DivX,, MP3,)
C230 V, 50 Hz
(DVD-S42EE)
C110-240 V, 50/60 Hz
(DVDS42GC/GCA/GCU/GCS/PL)
C120 V, 60 Hz
(DVD-S42PLA)
1 W (approx.)
(DVDS42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU)
NTSC
(DVD-S42PLA/PL)
*6
7
7 7 7 7
*4
*5
*6
*2
DL4.1 Mechanism Series
Color
(S).......................Silver Type
7
*2
7
(3) DVD-R (DVD-Video, DVD-VR, JPEG,, MP3,, DivX,,
(4) DVD-R DL (DVD-Video, DVD-VR)
(5) DVD-RW (DVD-Video, DVD-VR, JPEG,, MP3,, DivX,,
(6) +R/+RW (Video)
(7) +R DL (Video)
(8) CD, CD-R / CD-RW (CD-DA, Video CD, SVCD , MP3,,
*1 Conforming to IEC62107
*2 MPEG-1 Layer 3, MPEG-2 Layer 3
*3 Windows Media Audio Ver.9.0 L3
*4 Exif Ver2.1 JPEG Baseline files
*5 MPEG4 data recorded with the Panasonic SD multi cameras
*6 Plays all versions of DivX®video (including DivX®6) with
*5,7
MPEG4
MPEG4
WMA,, JPEG,, MPEG4,, DivX,,
HighMAT Level 2 (Audio and Image))
Not compatible with Multiple Bit Rate (MBR)
Picture resolution: between 160 × 120 and 6144 × 4096
pixels (Sub sampling is 4:0:0, 4:2:2, 4:2:0, 4:4:4)
Extremely long and slender pictures may not be displayed.
or DVD video recorders conforming to SD VIDEO
specifications (ASF standard) /MPEG4 (Simple Profile) video
system/G.726 audio system
)
*5,7
)
*3
7 7 7 7
*4
*5
*4
*2
7
*4
*6
7 7
*1
7
*6
*6
*2
7
© 2006 Matsushita Electric Industrial CO., Ltd. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
Page 2

V
A
AVV
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
standard playback of DivX®media files. Certified to the
®
DivX
Home Theater Profile.
GMC (Global Motion Compensation) not supported.
*7 The total combined maximum number of recognizable audio,
picture and video contents and groups: 4000 audio, picture
and video contents and 400 groups.
ideo output:
Output level: 1 Vp-p (75 Ω )
Output terminal: Pin jack (1 system)/AV
(DVD-S42EE)
Pin jack (1 system)
(DVDS42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PLA/PL)
S video output:
Y output level: 1 Vp-p (75 Ω )
C output level: NTSC: 0.286 Vp-p (75 Ω )
PAL: 0.300 Vp-p (75 Ω )
(DVDS42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU)
NTSC: 0.286 Vp-p (75 Ω )
(DVD-S42PL/PLA)
Output terminal:
V
(DVD-S42EE)
S terminal (1 system)
(DVDS42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PLA/PL)
Component video output:
[NTSC: (480)p/(480)i,
PAL: (576)p/(576)i]
(DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU)
[NTSC: (480)p/(480)i]
(DVD-S42PL/PLA)
Y output level: 1 Vp-p (75 Ω )
PBoutput level: 0.7 Vp-p (75 Ω )
PRoutput level: 0.7 Vp-p (75 Ω )
Output terminal: Pin jack (Y: green, PB: blue,
P
: red)
R
Number of terminals: 1 system
RGB video output: (DVD-S42EE)
R output level: 0.7 Vp-p (75 Ω )
G output level: 0.7 Vp-p (75 Ω )
B output level: 0.7 Vp-p (75 Ω )
Output terminal:
ideo performance:
Horizontal resolution: More than 500 lines
Video S/N ratio: More than 65dB
Audio output:
Output level: 2 Vrms (1 kHz, 0 dB)
Output terminal: Pin jack/AV
(DVD-S42EE)
Pin jack
(DVDS42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
Number of terminals:
2 channel: 1 system
Audio performance:
(1) Frequency response:
l DVD (linear audio):
4 Hz-22 kHz (48 kHz sampling)
4 Hz-44 kHz (96 kHz sampling)
l CD audio:
4 Hz-20 kHz
(2) S / N ratio:
l CD audio:
115 dB
(3) Dynamic range:
l DVD (linear audio):
l CD audio:
102 dB
98 dB
(4) Total harmonic distortion:
l CD audio:
0.003 %
Digital audio output:
Coaxial digital output: Pin jack
Pickup
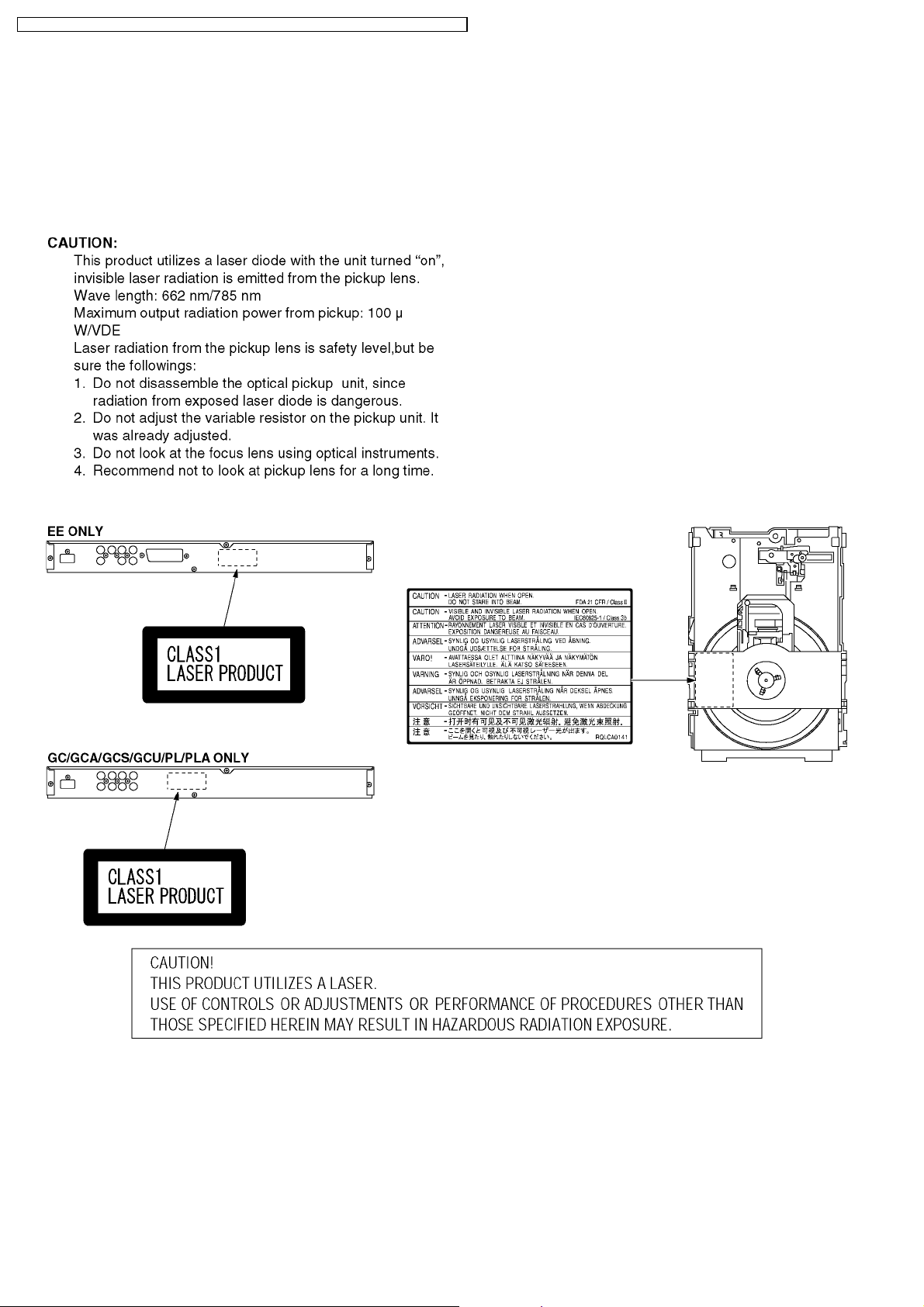
Wave length: 662 nm / 785 nm
Laser power: CLASS 2 / CLASS 3A
Note:
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Mass and dimensions are approximate.
Solder:
This model uses lead free solder (PbF).
2
Page 3

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
CONTENTS
Page Page
1 IMPORTANT SERVICE INFORMATION 5
1.1. Notes
1.2. About DivX
1.3. Manual for Customer
2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
2.1. GENERAL GUIDELINES
3 PREVENTION OF ELECTRO STATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) TO
ELECTROSTATICALLY SENSITIVE (ES) DEVICES
4 PRECAUTION OF LASER DIODE
5 SERVICE CAUTION BASED ON LEGAL RESTRICTIONS
5.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
6 PREVENTION OF STATIC ELECTRICITY DISCHARGE
6.1. Grounding for electrostatic breakdown prevention
6.2. Handling Precautions for Traverse Unit (Optical Pickup)
7 DISASSEMBLING THE CASING AND CHECKING P.C.B.S
7.1. Disassembly Procedure
7.2. Casing Parts and P.C.B. Positions
7.3. Top Panel
7.4. Front Panel
7.5. Operation P.C.B. and Power SW P.C.B.
7.6. Module P.C.B.
7.7. Mechanism Unit
7.8. Rear panel
7.9. Mother P.C.B.
7.10. Service Position
8 ASSEMBLING AND DISASSEMBLING THE MECHANISM UNIT
8.1. Disassembly Procedure
8.2. Traverse Unit
8.3. Tray
8.4. Loading section
8.5. Loading motor P.C.B.
8.6. Optical Pickup Unit
8.7. Traverse Motor
9 SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION AND SERVICE MODES
9.1. Optical Pickup Breakdown Diagnosis
9.2. Service Mode Table 1
9.3. DVD Self Diagnostic Function-Error Code
9.4. Last Error Code saved during NO PLAY
9.5. Service mode table 2
9.6. Sales demonstration lock function
9.7. Handling After Completing Repairs
10 SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
10.1. Recovery after the dvd player is repaired
10.2. Firmware version-up of the DVD player
11 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
10
10
10
11
11
11
12
12
12
12
12
13
13
14
15
15
15
16
17
18
19
21
23
23
24
24
25
26
29
29
30
30
30
31
5
5
6
7
7
7
8
9
9
11.1. Service Tools and Equipment 31
11.2. Important points in adjustment
11.3. Storing and Handling Test Discs
11.4. Optical adjustment
12 ABBREVIATIONS
13 VOLTAGE CHART
13.1. MOTHER P.C.B.
13.2. MODULE P.C.B.
14 BLOCK DIAGRAM
14.1. OVERALL BLOCK DIAGRAM
14.2. POWER SUPPLY BLOCK DIAGRAM
14.3. SERVO BLOCK DIAGRAM
14.4. VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM (DVD-
S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
14.5. VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM (DVD-S42EE)
14.6. AUDIO BLOCK DIAGRAM
15 INTERCONNECTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM & SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM NOTES
15.1. INTERCONNECTION SCHEMAT IC DIAGRAM
15.2. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM NOTES
16 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
16.1. POWER SUPPLY SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (1 / 2))
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-
S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL)
16.2. POWER SUPPLY SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (1 / 2))
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42PLA)
16.3. FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (2 / 2))
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42EE)
16.4. FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (2 / 2))
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-
S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
16.5. MODULE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
17 PRINT CIRCUIT BOARD
17.1. MOTHER P.C.B. (DVD-S42EE)
17.2. MOTHER P.C.B. (DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
17.3. MOTHER P.C.B. ADDRESS INFORMATION
17.4. MODULE P.C.B. (1/2)
17.5. MODULE P.C.B. (2/2)
17.6. MODULE P.C.B. ADDRESS INFORMATION
18 EXPLODED VIEWS
18.1. CASING PARTS & MECHANISM SECTION EXPLODED
VIEW
18.2. MECHANISM SECTION EXPLODED VIEW
18.3. PACKING & ACCESSORIES SECTION EXPLODED
VIEW
31
31
32
34
36
36
37
39
40
41
42
43
44
46
47
47
48
49
49
50
51
53
55
59
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
65
66
67
3
Page 4

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
19 REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST 68
4
Page 5

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
1 IMPORTANT SERVICE INFORMATION
1.1. Notes
When you replace EEPROM or exchange MODULE P.C.B., you have to take "Manu al for customer" to the customer with unit.
(also in the case of unit exchange)
Please take and use "Manu al for customer" from below.
1. Come with MODULE P.C.B. or EEPROM (Service part).
2. Make a photocopy section 1.3. "Manu al for customer" on this service manual.
“Manual for customer” has important information for "DivX Video-on-Demand Service" user.
Please don´t forget take it to the customer with unit!
1.2. About DivX
1.2.1. DivX
A video compression format developed by DivXNetworks, Inc. that compresses video files without any considerable loss of video
quality.
1.2.2. About DivX Video-on-Demand Content
5
Page 6

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
1.3. Manual for Customer
Warning for Customers Who Use the DivX Video-on-Demand content.
1. The registration code has been changed for the repair of the product or the product
exchange.
2. Obtain and register a new registration code, otherwise you will no longer be able to
play DivX Video-on-Demand content.
3. Follow the procedure on the DivX Video-on-Demand web site to register at
http://vod.divx.com/.
* If you do not use the DivX Video-on-Demand content, please ignore this warning.
6
Page 7

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
2.1. GENERAL GUIDELINES
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
2.1.1. LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD
CHECK
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two
prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between
the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabine t
part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors,
control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a
return path to thechassis, the reading should be between
1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to
the chassis, the reading must be
Figure 1
.
2.1.2. LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK
(See Figure 1 .)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an
isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF
capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set
and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in
Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more
sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the
voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the
above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts
RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or
equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage
current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a
measurement is outside of the limits specified, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer.
3 PREVENTION OF ELECTRO STATIC DISCHARGE (ESD)
TO ELECTROSTATICALLY SENSITIVE (ES) DEVICES
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistorsand
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as alminum
foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static (ESD protected)" can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, alminum foil or
comparableconductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
7
Page 8
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise hamless motion such as the brushing
together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficie nt
todamage an ES device).
4 PRECAUTION OF LASER DIODE
8
Page 9

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
5 SERVICE CAUTION BASED ON LEGAL RESTRICTIONS
5.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical components on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainly consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30°C (86°F) more than that of the
normal solder.
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
· The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used. (Definition: The
letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
· To put lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
· Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
· Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt
the lead free solder.
· Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equipped with the temperature control after setting the temperature at 350±30°C
(662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
· RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
· RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
· RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: tin (Sn) 96.5%, silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
9
Page 10
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
6 PREVENTION OF STATIC ELECTRICITY DISCHARGE
The laser diode in the traverse unit (optical pickup) may brake down due to static electricity of clothes or human body. Use due
caution to electrostatic breakdown when servicing and handling the laser diode.
6.1. Grounding for electrostatic breakdown prevention
Some devices such as the DVD player use the optical pickup (laser diode) and the optical pickup will be damaged by static
electricity in the working environment. Proceed servicing works under the working environment where grounding works is
completed.
6.1.1. Worktable grounding
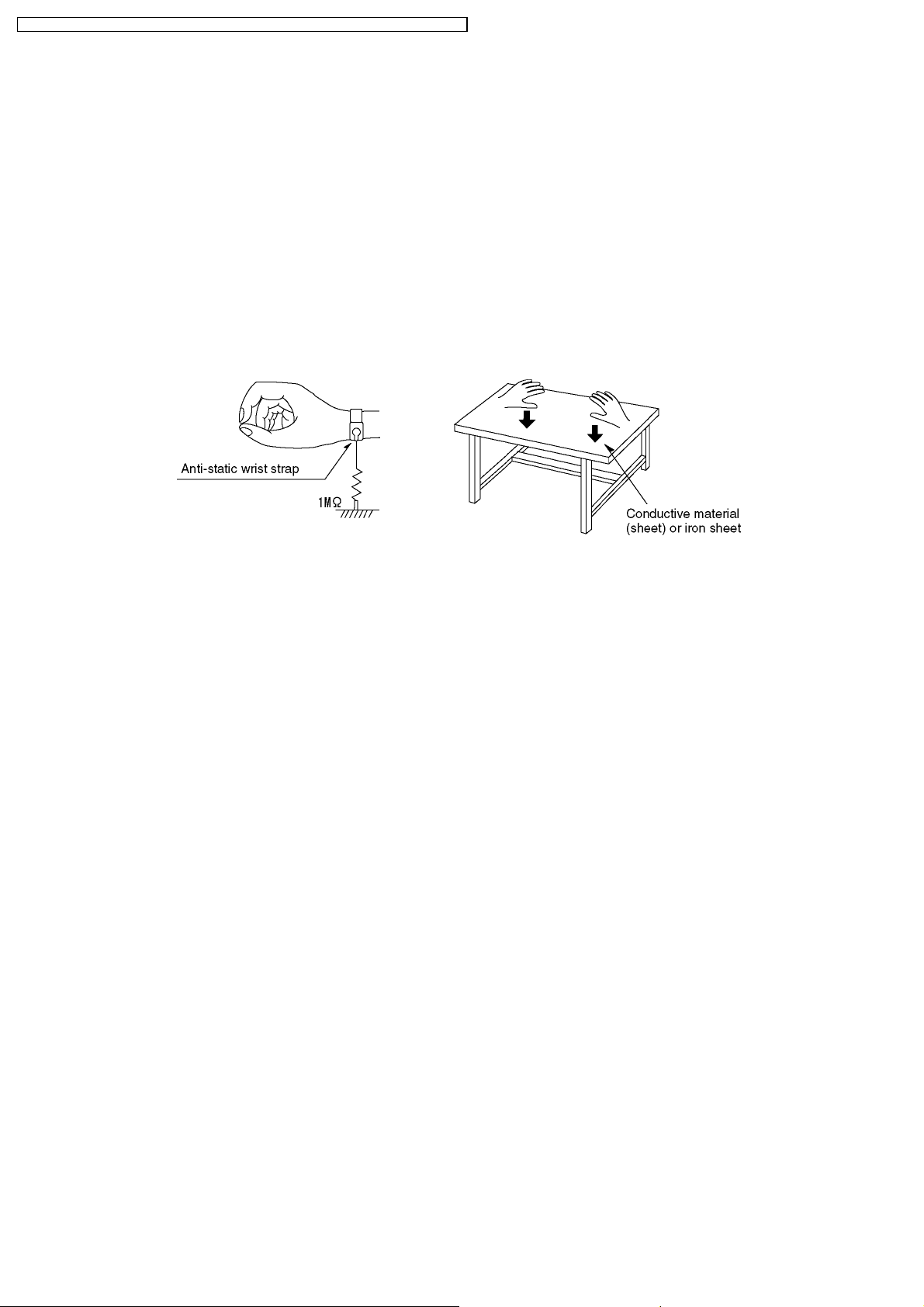
1. Put a conductive material (sheet) or iron sheet on the area where the optical pickup is placed, and ground the sheet.
6.1.2. Human body grounding
1. Use the anti-static wrist strap to discharge the static electricity form your body.
6.1.3. Handling of optical pickup
1. To keep the good quality of the optical pickup maintenance parts during transportation and before installa tion, the both ends of
the laser diode are short-circuited. After replacing the parts with new ones, remove the short circuit according to the correct
procedure. (See this Technical Guide.)
2. Do not use a tester to check the laser diode for the optical pickup. Failure to do so will damage the laser diode due to the power
supply in the tester.
6.2. Handling Precautions for Traverse Unit (Optical Pickup)
1. Do not give a considerable shock to the traverse unit (optical pickup) as it has an extremely high-precise structure.
2. When replacing the optical pickup, install the flexible cable and cut its short land with a nipper. See the optical pickup
replacement procedure in this Technical Guide. Before replacing the traverse unit, remove the short pin for preventing static
electricity and install a new unit. Connect the connector as short times as possible.
3. The flexible cable may be cut off if an excessive force is applied to it. Use caution when handlin g the cable.
4. The half-fixed resistor for laser power adjustment cannot be adjusted. Do not turn the resistor.
10
Page 11
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
7 DISASSEMBLING THE CASING AND CHECKING P.C.B.S
7.1. Disassembly Procedure
7.2. Casing Parts and P.C.B. Positions
11
Page 12
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
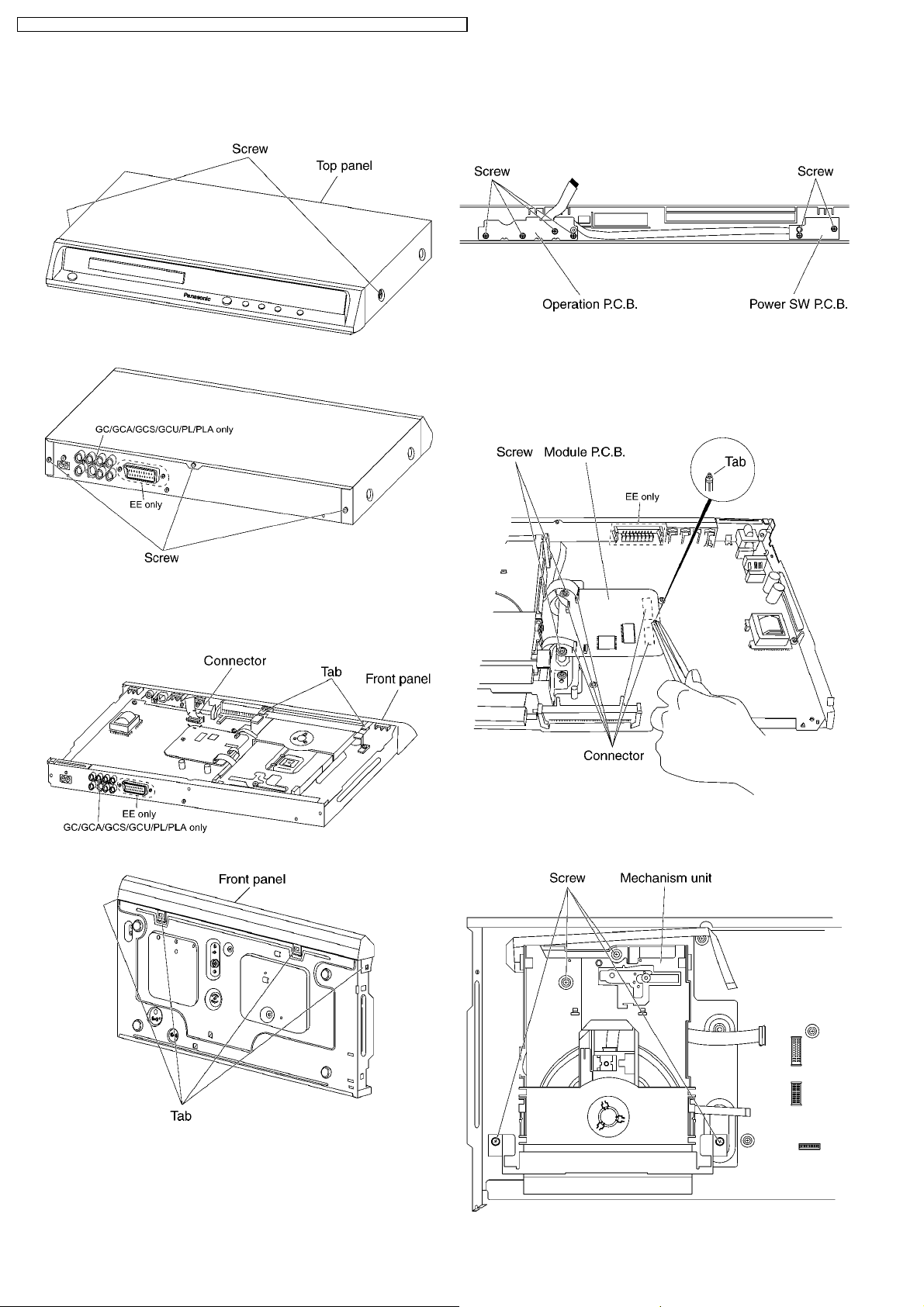
7.3. Top Panel
1. Unscrew the screws.
7.5. Operation P.C.B. and Power
SW P.C.B.
1. Unscrew the screws.
7.6. Module P.C.B.
1. Remove the connectors.
2. Unscrew the screws.
3. Press each tab with the nipper to module PCB vertically.
7.4. Front Panel
1. Release the tabs and connector.
2. Release the tabs.
7.7. Mechanism Unit
1. Unscrew the screws.
12
Page 13
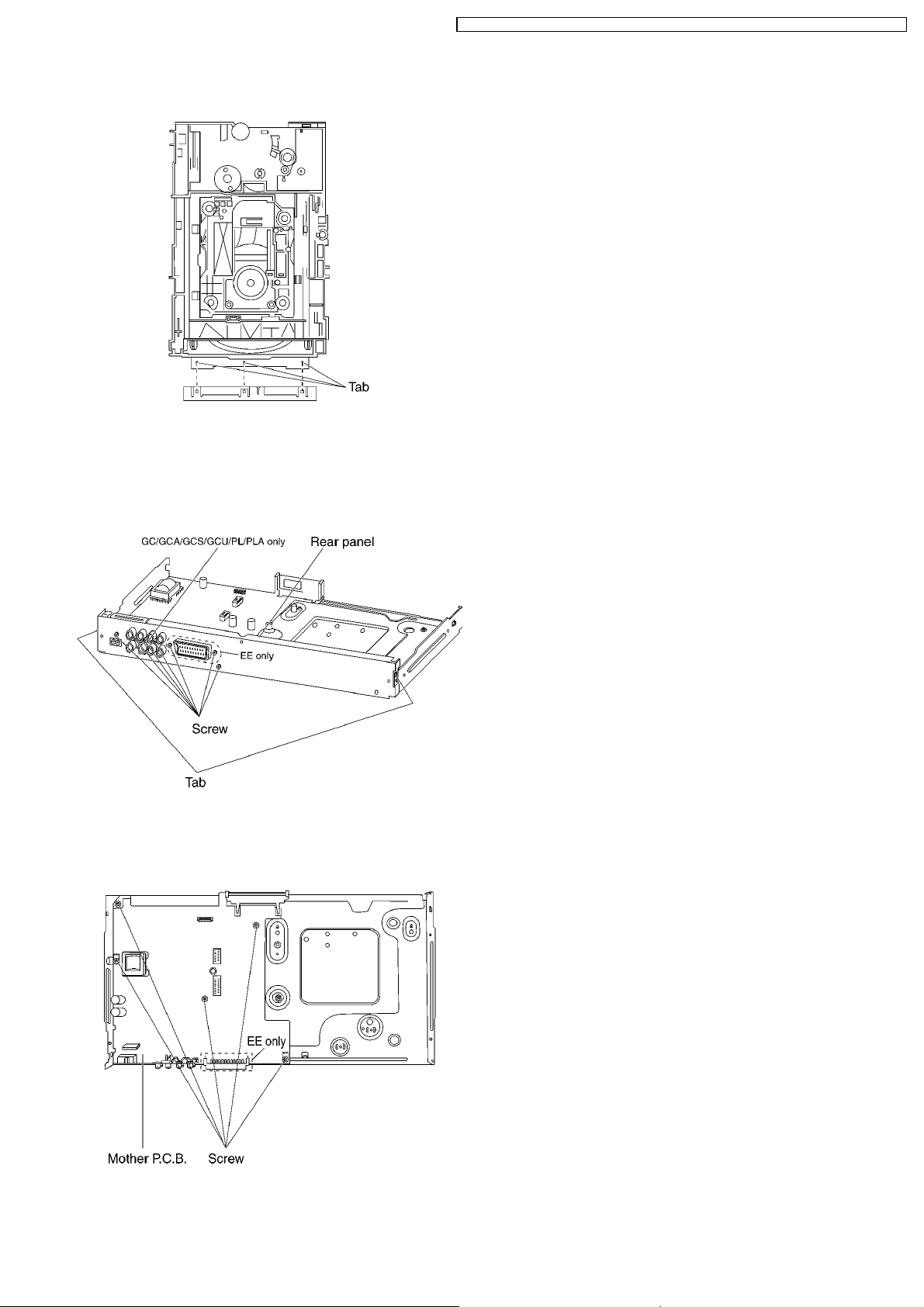
2. Release the tabs.
7.8. Rear panel
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
1. Unscrew the screws.
2. Release the tabs.
7.9. Mother P.C.B.
1. Unscrew the screws.
13
Page 14
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
7.10. Service Position
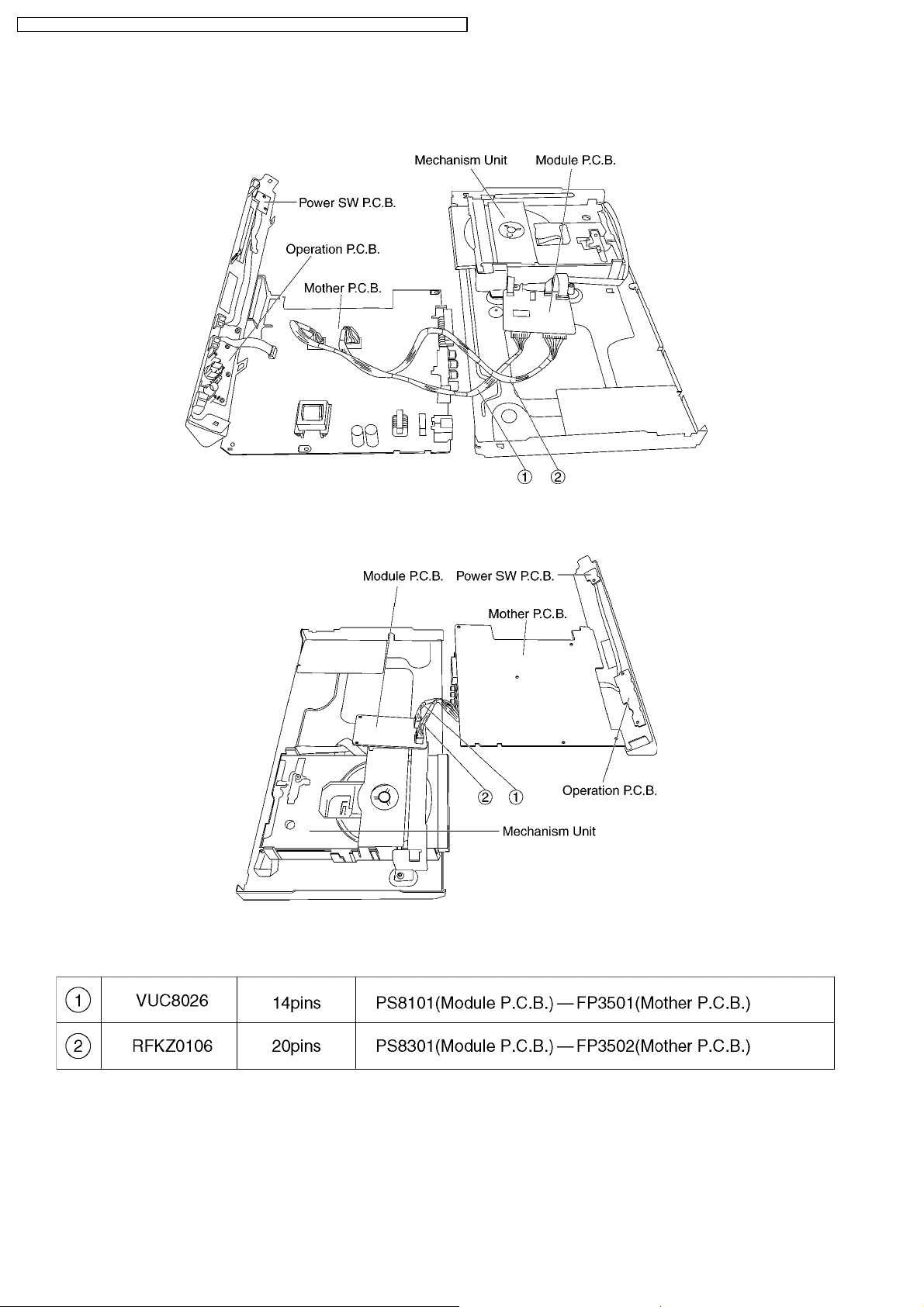
7.10.1. Servicing position of the Module P.C.B.
7.10.2. Servicing position of the Mother P.C.B.
7.10.3. List of the Extension Cables
14
Page 15
8 ASSEMBLING AND
DISASSEMBLING THE
MECHANISM UNIT
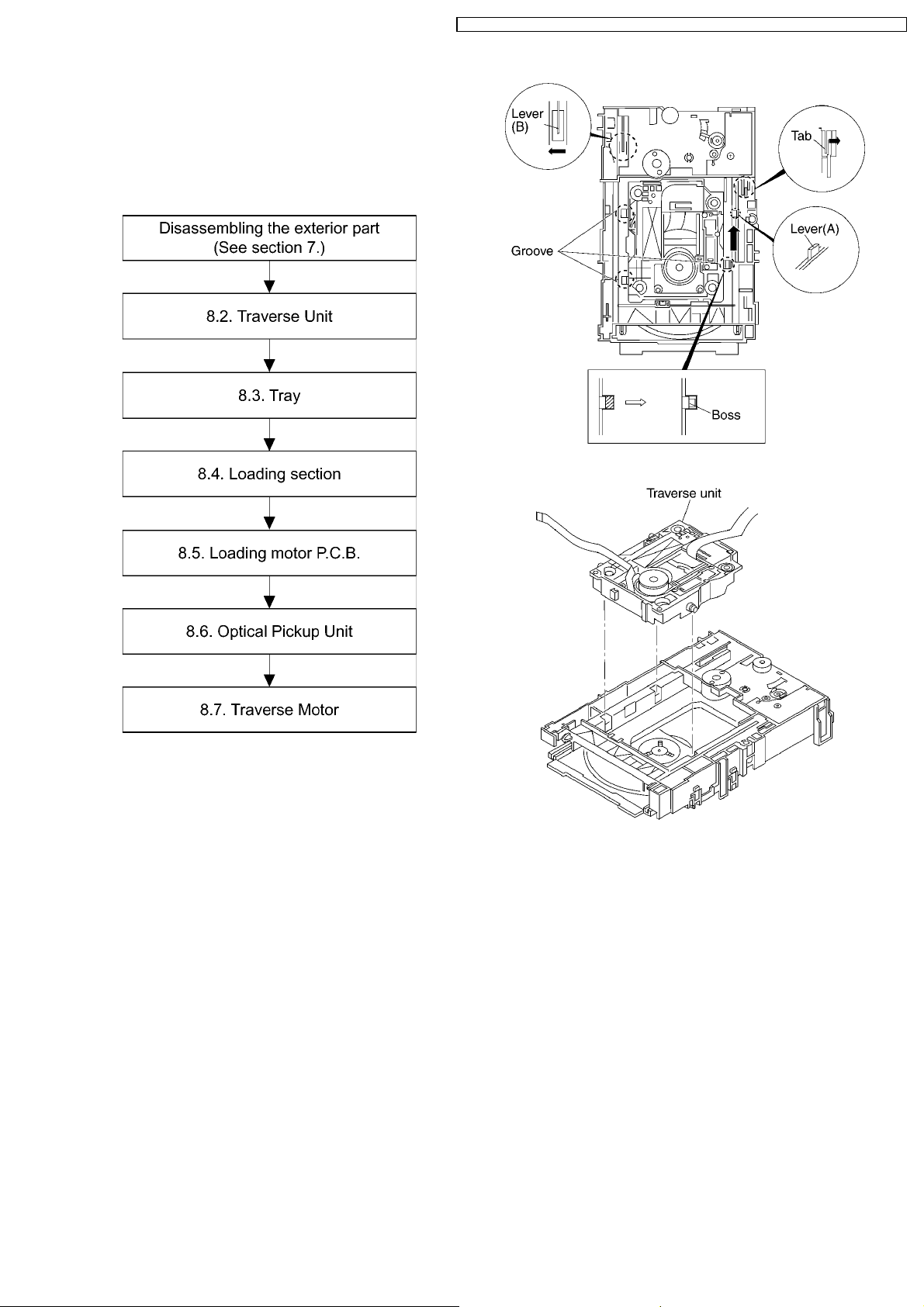
8.1. Disassembly Procedure
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
4. Remove the traverse unit
8.2. Traverse Unit
1. Slide the lever (A) in the arrow direction (to the opposite
side) till it stops.
2. Slide the lever (A) further by bending the tab at the right
side of the lever A in the right direction. (The right groove
opens and the boss becomes seen.)
3. Open the lever (B) to left. (The 2 grooves at the left side
open.)
15
Page 16
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
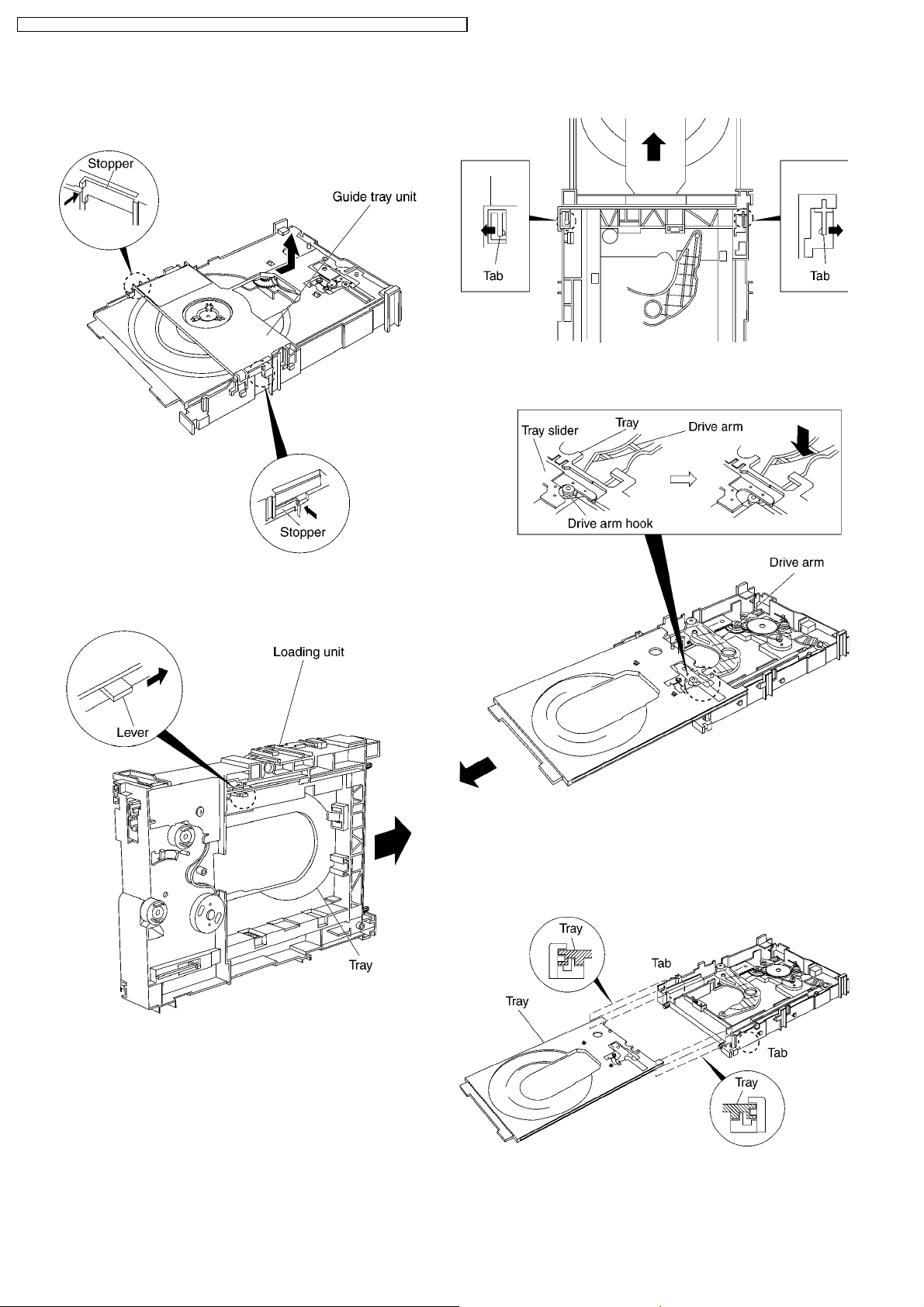
8.3. Tray
1. Slide the guide tray unit while pressing the stopper in the
arrow direction, and remove the guide tray unit.
5. Remove the drive arm concave phase from the tray slider
and tray.
2. Raise the loading unit.
3. Slide the lever in the arrow direction till it stops and pull the
tray out.
<Assembling the tray unit>
1. Insert a part of the tray into the unit sliding over the
groove on the mechanical chassis unit.
2. Insert the tray to the point before the tab of the
mechanical chassis unit.
4. Spread the tabs at the both sides and pull the tray out. (The
tray slides a little forward and stops.)
3. Hook the drive arm concave phase over the tray and the
tray slider.
4. Press in the tray.
16
Page 17
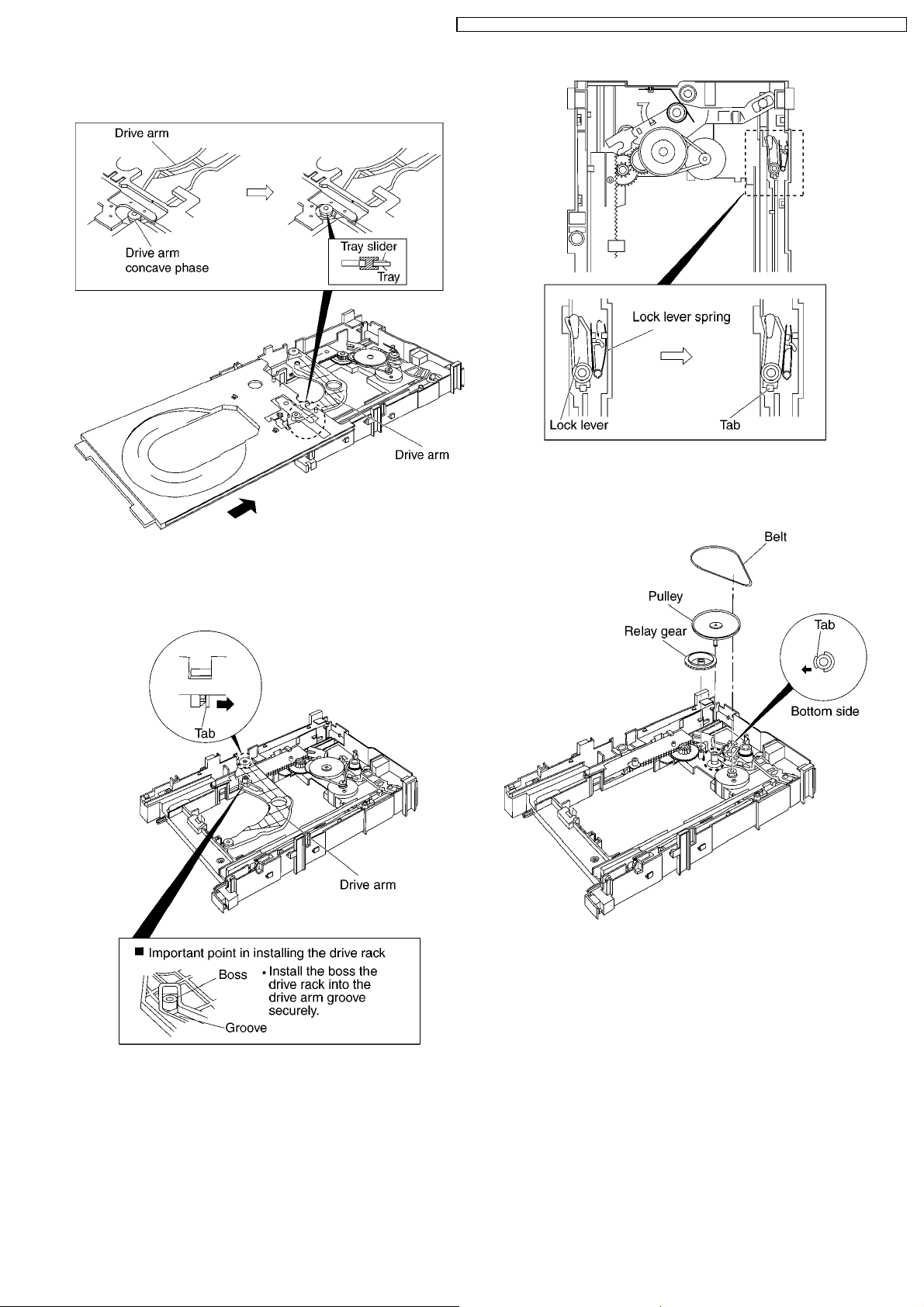
5. Make sure that the tray and the drive arm move
smoothly.
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
4. Remove the belt.
5. Unlock the tab and remove the pulley.
6. Remove the relay gear.
8.4. Loading section
1. Spread the tabs at the both sides and push out the drive
arm shaft.
7. Turn the change lever in the arrow direction till it stops.
8. Hook the change lever spring on the change lever project
part temporarily.
2. Hook the lock lever spring on the lock lever projection part
temporarily.
3. Unlock the tab and remove the lock lever.
17
Page 18
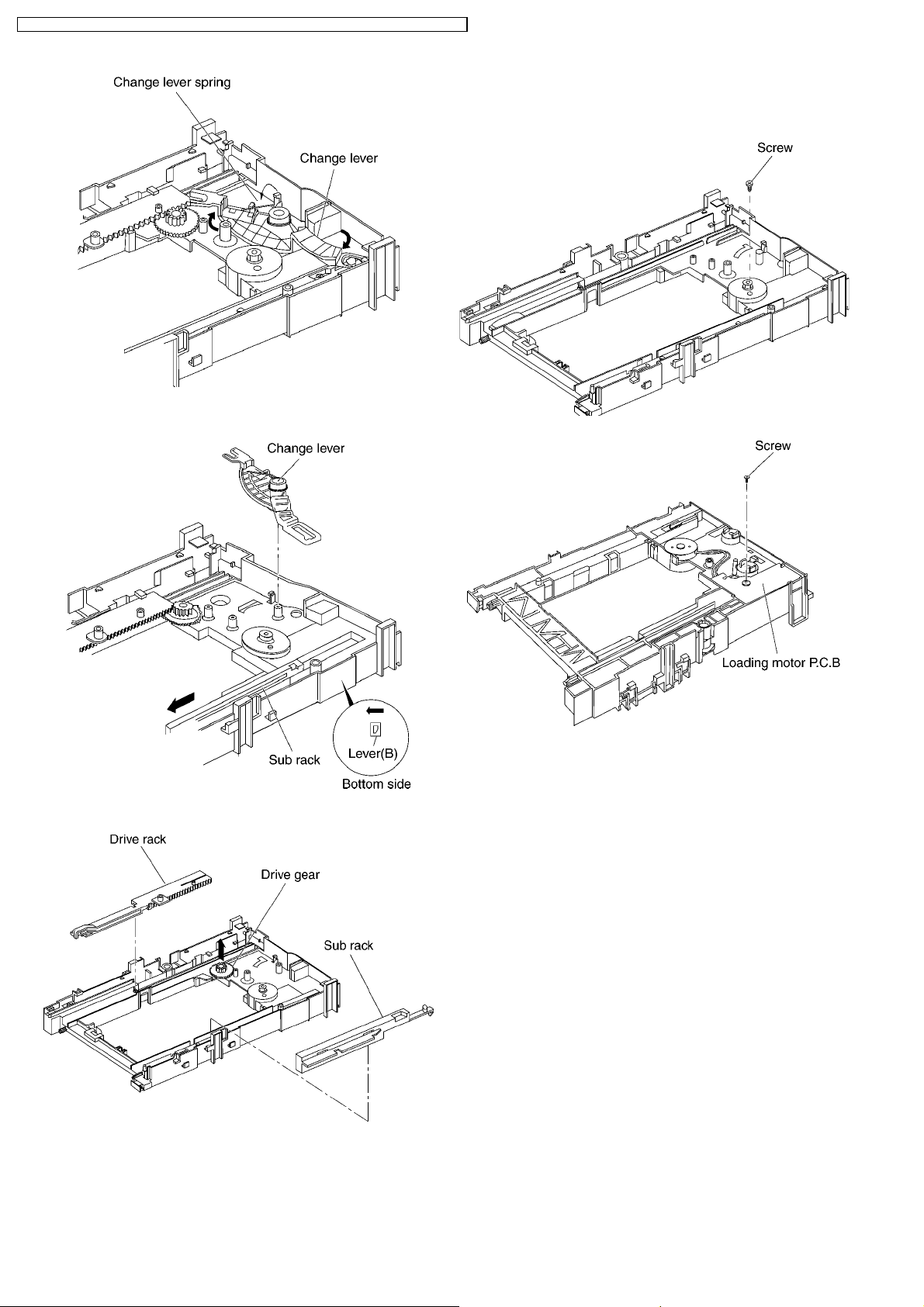
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
9. Pull the lever (B) in the bottom side to your side and remove
the change lever.
8.5. Loading motor P.C.B.
1. Unscrew the screws.
10. Remove the drive rack, the sub rack and the drive gear.
18
Page 19
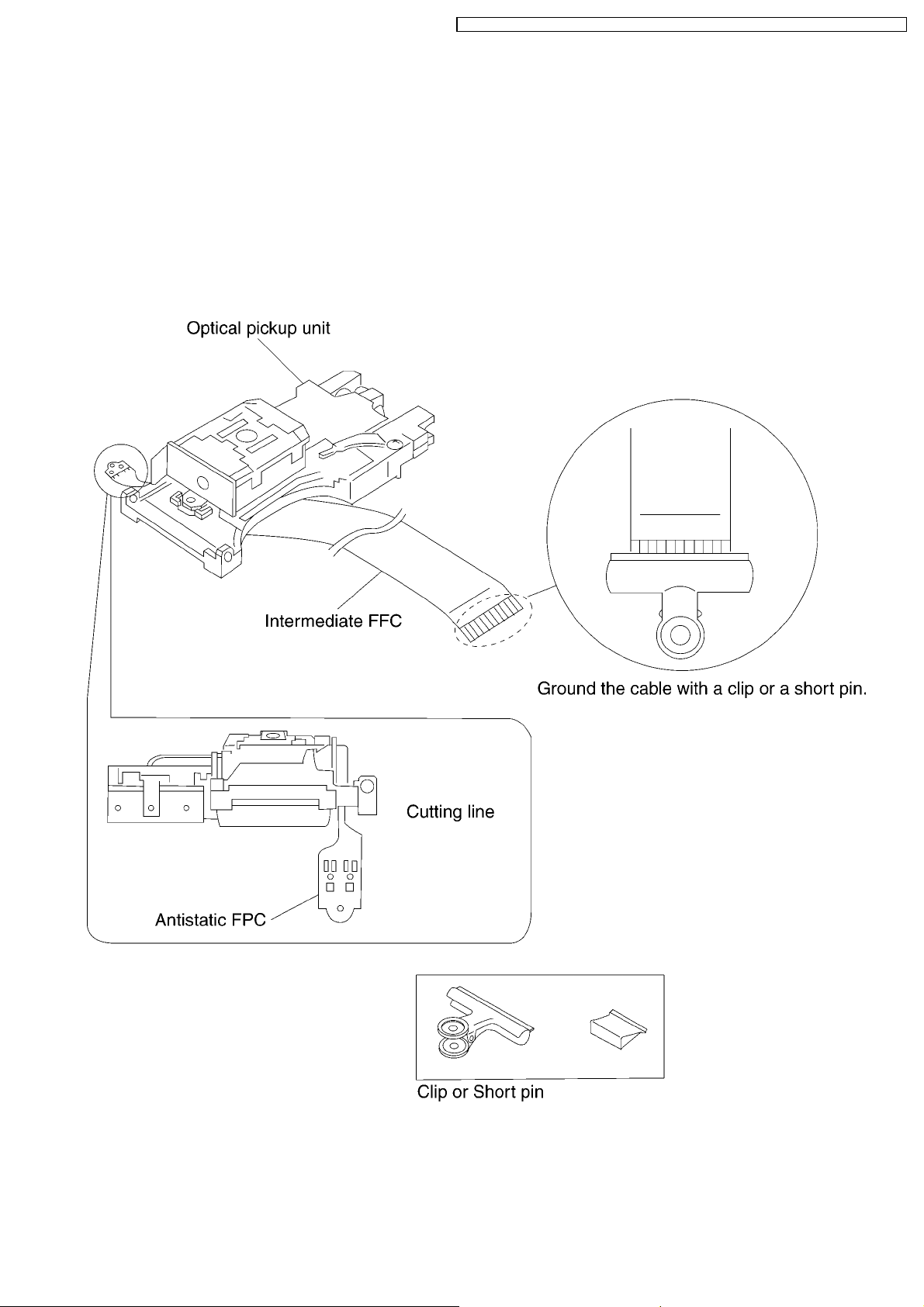
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
8.6. Optical Pickup Unit
8.6.1. Cautions to Be Taken in Handling the Optical Pickup Unit
The laser diode in the optical pickup unit may be damaged due to electrostatic discharge generating from clothes or human body.
Use due caution to electrostatic discharge damage when servicing the laser diode.
1. Do not give a considerable shock to the optical pickup unit as it has an extremely high-precise structure.
2. To prevent the laser diode from the electrostatic discharge damage, the Intermediate FFC of the optical pickup unit removed
from the PCB should be short-circuited with a short pin or a clip.
3. The Intermediate FFC may be cut off if an excessive force is applied to it. Use caution when handling the Intermediate FFC.
4. The antistatic FPC is connected to the new optical pickup unit. After replacing the optical pickup unit and connecting the
fIntermediate FFC, cut off the antistatic FPC.
19
Page 20
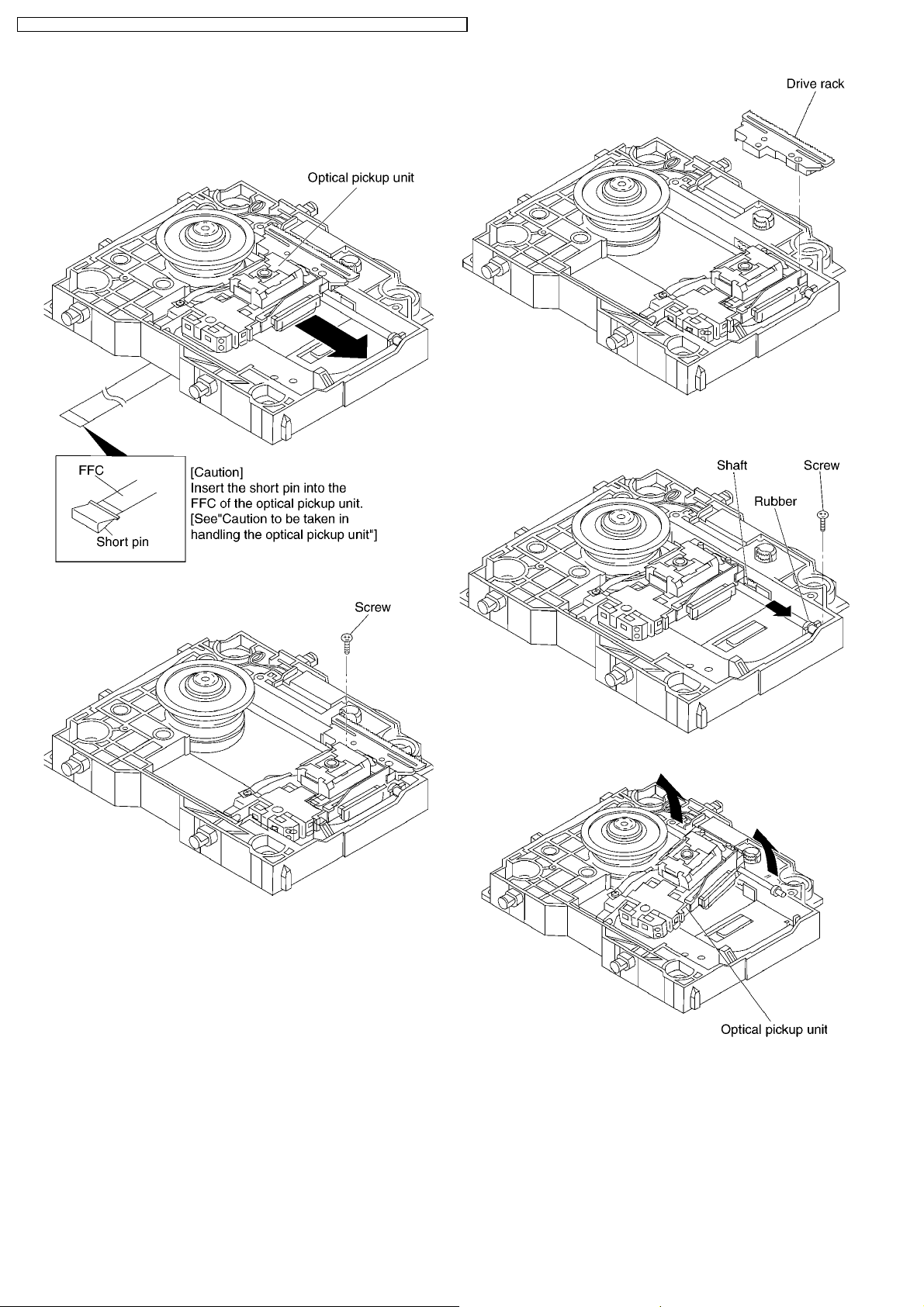
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
8.6.2. Procedure for Disassembling the
Optical Pickup Unit
1. Move the optical pickup unit in the arrow direction till it
stops.
4. Unscrew the screw.
5. Slide the shaft in the arrow direction.
2. Unscrew the screws.
3. Remove the drive rack.
6. Lift the optical pickup unit with the shaft.
7. Remove the optical pickup unit.
20
Page 21
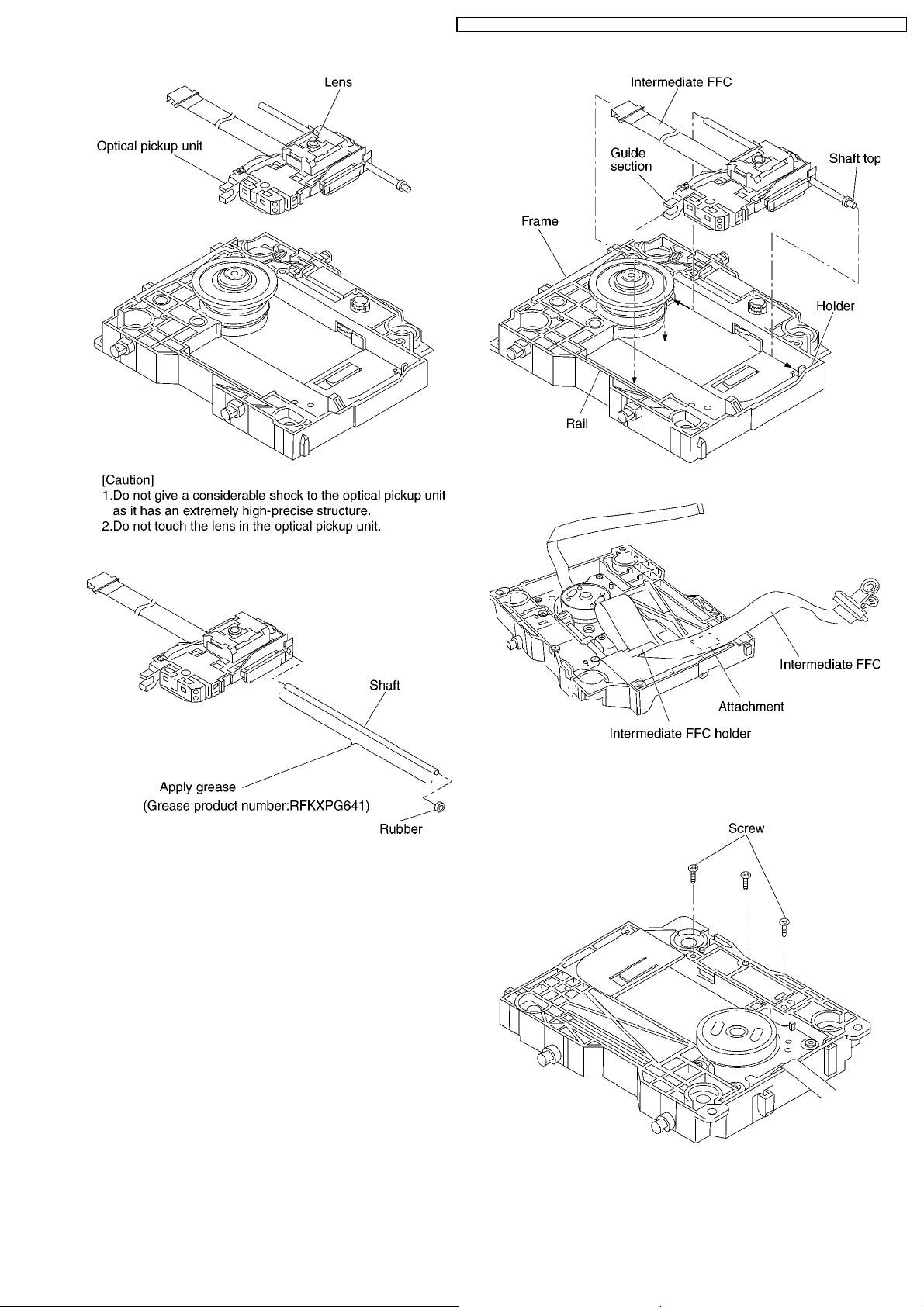
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
8. Pull the shaft and the rubber out.
<Assembling the optical pickup unit>
1. Pass the intermediate FPC through the frame hole.
2. Align the guide section of the optical pickup unit with the
rail.
3. Install the shaft top to the holder.
4. The intermediate FFC is fixed as shown below.
8.7. Traverse Motor
1. Unscrew the screws.
2. Remove the cover while lifting the inner gear.
21
Page 22
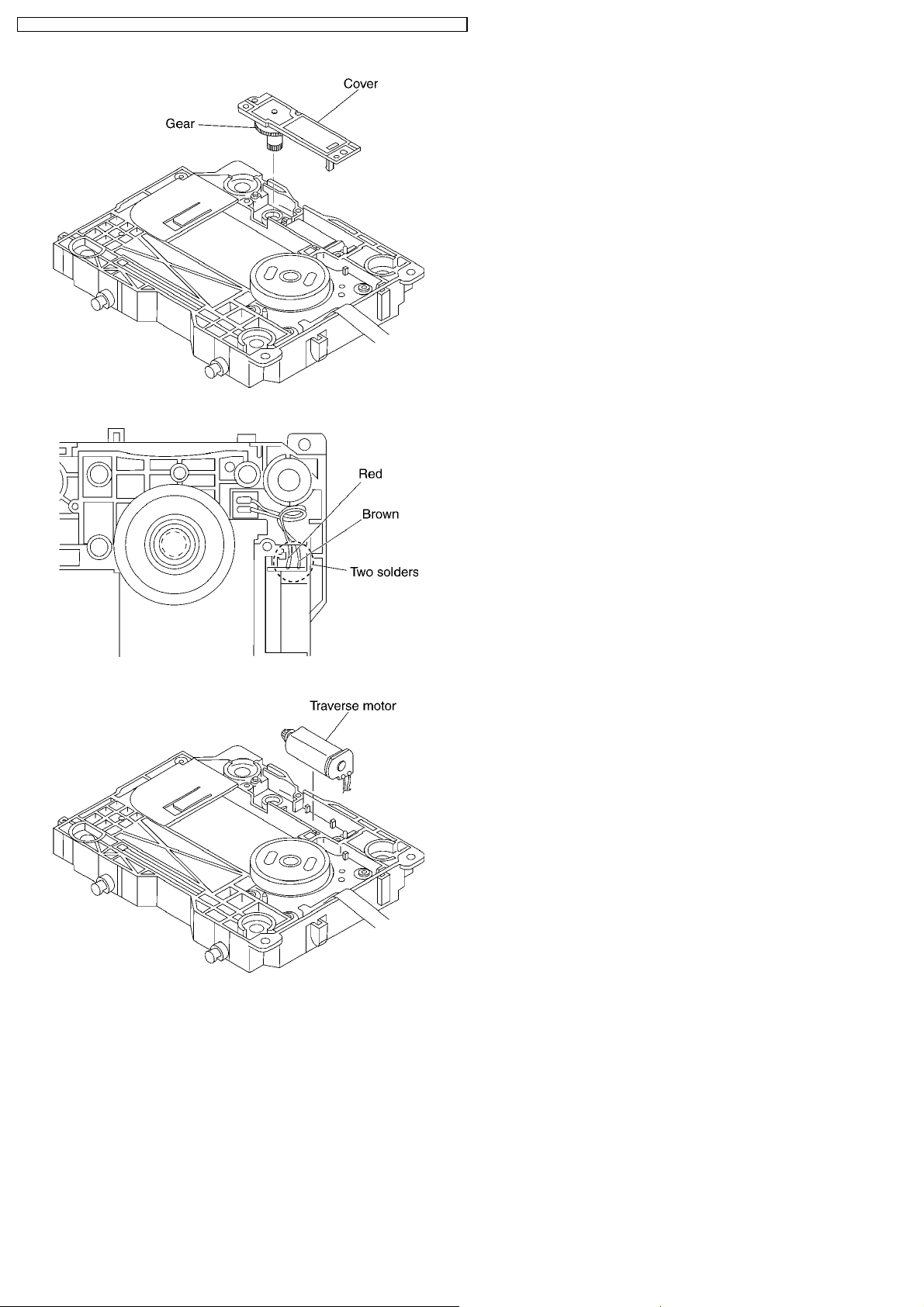
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
3. Remove the solders.
4. Remove the traverse motor.
22
Page 23
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
9 SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION AND SERVICE MODES
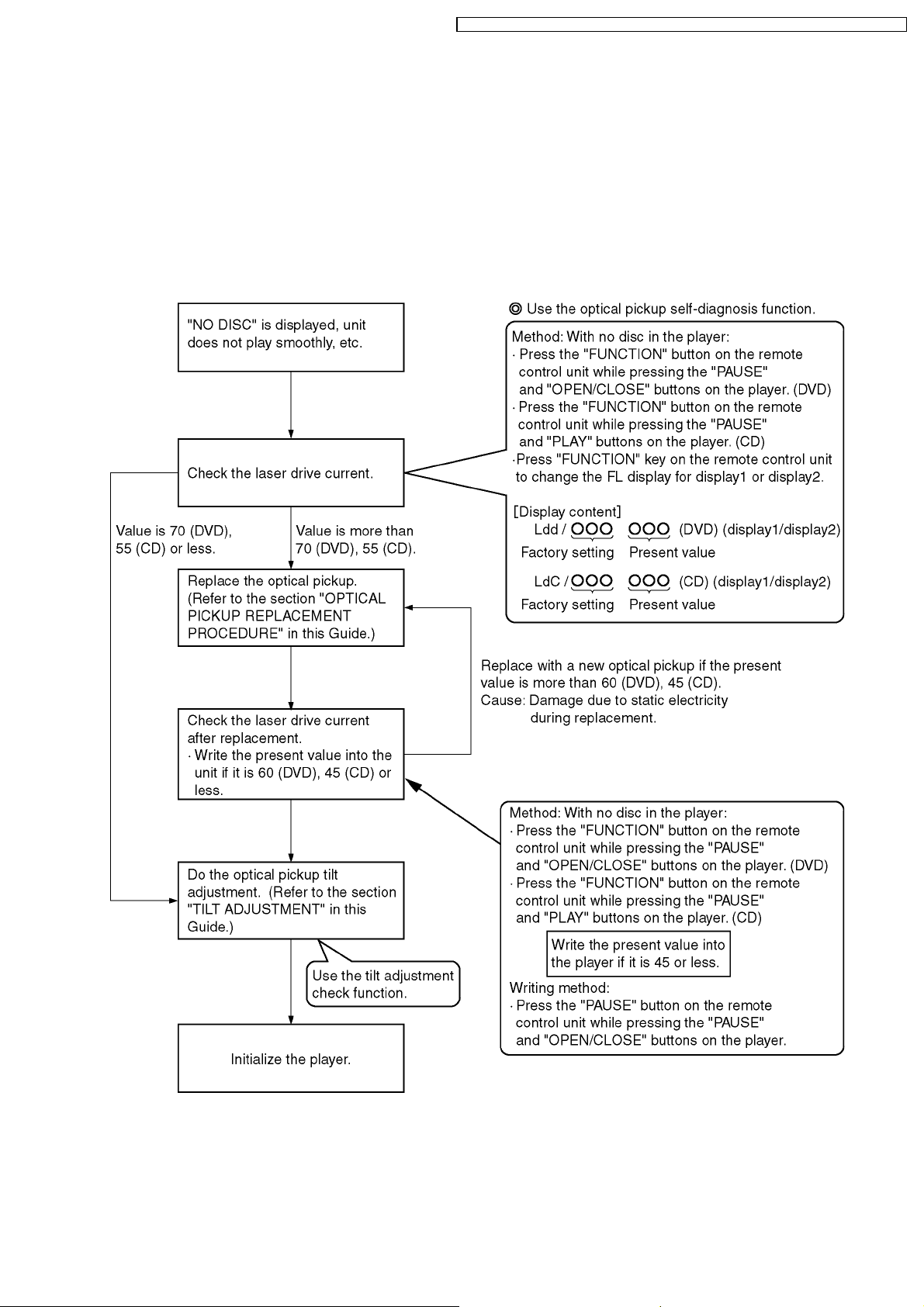
9.1. Optical Pickup Breakdown Diagnosis
The optical pickup self-diagnosis function and tilt adjustment check function have been included in this unit. When repairing, use
the following procedure for effective Self-diagnosis and tilt adjustment.Be sure to use the self-diagnosis function before replacing
the optical pickup when "NO DISC" is displayed. As a guideline, you should replace the optical pickup when the value of the laser
drive current is more than 55.
Note:
Press the power button to turn on the power, and check the value within three minutes before the unit warms up. (Otherwise,
the result will be incorrect.)
23
Page 24

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
9.2. Service Mode Table 1
The service modes can be activated by pressing various button combination on the player and remote control unit.
Player buttons Remote control unit buttons Application Note
PAUSE
+
OPEN/CLOSE
PAUSE
QUICK OSD
OPEN/CLOSE
0 Displaying the UHF display F_ _ _ Refer to section 9.3. Self-
5 Jitter check, tilt adjustment
*Display shows J_xxx/yyy_zz
"yyy" and "zz" shown to the right have nothing to do with the jitter
value. "yyy" is the error counter, while "zz" is the focus drive
value.
Refer to section 11.4. for Optical Pickup Tilt Adjustment
Procedure.
6 Checking the region numbers and broadcast system
7 Checking the program version Check the IC8651 FLASH
9 Lighting Confirmation Function of Display Tube
FUNCTION Checking the laser drive current Refer to section 8
PAUSE Writing the laser drive current value after replacing the optical
pickup (do not use for anything other than optical pickup
replacement)
Initializing the DVD player
(restoring factory preset settings)
Diagnosis Function (UHF
Display).
Refer to section 11.4.
Optical Pickup Tilt
Adjustment
ROM program.
Optical Pickup
Replacement Procedure.
Refer to section 9.5.
Initializing the DVD
player.
9.3. DVD Self Diagnostic Function-Error Code
Error Code Error Content Additional error explanation Defect 1 Defect 2 Defect 3 Defect 4
U, H error
U11 Focus error
U15 Unfinalized DVD-R
H01 Tray loading error
H02 Spindle servo error (Spindle servo, DV3.2 (IC8001) SP motor, CLV
H03 Traverse servo error
H04 Tracking servo error
H05 Seek error
H06 Power error Cannot switch off the power because of the panel
H07 Spindle motor drive
error
DSC related
F500 DSC error DV3.2 (IC8001) stops in the occurence of servo
F501 DSC not Ready DSC-system computer communication error
F502 DSC Time out error Similar disposal as F500 Optical
F503 DSC communication
Failure
F505 DSC Attention error Similar disposal as F500 Optical
F506 Invalid media Disc is flipped over, TOC unreadable,
ODC related
F600 Access failure to
management
information caused by
demodulation error
F601 Indeterminate sector ID
requested
F602 Access failure to LEAD-
IN caused by
demodulation error
F603 Access failure to
KEYDET caused by
demodulation error
F610 ODC abnormality No permission for command execution DV3.2
servo error)
and system computer communication error
error (starup, focus error, etc)
(Communication failure caused by idling of DSC)
Communication error (result error occured
although communication command was sent)
incompatible disc
Operation stopped because navigation data is not
accessible caused by the demodulation defect
Operation stopped caused by the request to
access abnormal ID data
LEAD IN data unreadable
Access failure to CSS data of disc
Spindle
motor ass’y
Optical
pickup
DV3.2
(IC8001)
pickup
DV3.2
(IC8001)
pickup
DISC DV3.2
DV3.2
(IC8001)
DV3.2
(IC8001)
(IC8001)
DV3.2
(IC8001)
DV3.2
(IC8001)
EEPROM
(IC8611)
DV3.2
(IC8001)
(IC8001)
servo drive
servo drive
servo drive
24
Page 25

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Error Code Error Content Additional error explanation Defect 1 Defect 2 Defect 3 Defect 4
F611 6626 QCODE don’t
read Error
F612 No CRC OK for a
specific time
F630 No reply to KEY DET
enquiry
F631 CPPM KEY DET is not
available till the FILE
terminal
F632 CPPM KEY DET is not
available
Disc code
F103 Illegal highlight Position Big possibility of disc specification violation during
HIC Error
F4FF Force initialize failure
(time out)
Micro computer error
F700 MBX overflow When replying message to disc manager
F701 Message command
does not end
F702 Message command
changes
F880 Task number is not
appropriate
F890 Sending message when
message is being sent
to AV task
F891 Message couldn’t be
sent to AV task
F893 FROM falsification FROM
F894 EEPROM abnormality EEPROM
F895 Language area
abnormality
F896 No existence model Firm version agreement check for factory preset
F897 Initialize is not
completed
F898 Disagreement of
hardware and software
F8A0 Message command is
not appropriate
Access failure to seek address in CD series DV3.2
Access failure to ID data in DVD series DV3.2
(for internal use only)
(CPPM file system is unreadable caused by
scratches)
Been revoked or falsified DISC EEPROM
highlight display
Next message is sent before replying to disc
manager
Message is changed before it is sent as a reply to
disc manager
Message coming from a non-existing task
Sending message to AV task
Begin sending message to AV task
Firm version agreement check for factory preset
setting failure prevention
setting failure prevention
Initialize completion check for factory preset
setting failure prevention
Unsuitable combination of AV DECORDER,
SDRAM and FLASH ROM (firmware)
Begin sending message to AV task
(IC8001)
(IC8001)
DISC CPPM
(IC8611)
DISC
EEPROM
(IC8611)
(IC8651)
(IC8611)
FROM
(IC8651)
(IC8001)
(IC8001)
communication on lone
(*1)
DV3.2
DV3.2
Serial
CPPM
(*1)
Note:
An error code will be canceled if a power supply is turned OFF.
*1: CPPM is the copy guard function beforehand written in the disk for protection of copyrights.
9.4. Last Error Code saved during NO PLAY
Error code Error Content System computer Setting task System computer internal error code
F0BF 6) Cannot playback because
physical layer is not recoginizable
F0C0 8) DVD: Cannot playback because it
is not DVD Video/Adio/VR
F0C1 9) DVD: Prohibited by the restricted
region code
F0C2 A) DVD: PAL restricted playback PCND_NOPLAY PAL 0x90 DiscManager 0xDOC2
F0C3 B) DVD: Parental lock setting
prohibits the playback of the entire
title
F0C4 C) VCD: Prohibited because it is in
PHOTO CD fromat
F0C5 VCD/CD: Prohibited because it is
CDROM without CD-DA
PCND_NOPLAY PHYSICAL
0x50
PCND_NOPLAY VIDEO 0x70 DiscManager 0xDOC0
PCND_NOPLAY RCD 0x80 DiscManager 0xDOC1
PCND_NOPLAY PTL 0xA0 DiscManager 0xDOC3
PCND_NOPLAY PHOTO CD
0xB0
PCND_NOPLAY CDROM 0xC0 DiscManager 0xDOC5
DriveManager 0xDOBF
DiscManager 0xDOC4
25
Page 26

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
9.5. Service mode table 2
Pressing various button combinations on the player and remote control unit can activate the service modes.
26
Page 27

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
27
Page 28

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
28
Page 29

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
9.6. Sales demonstration lock function
This function prevents discs from being lost when the unit is used for sales demonstrations by disabling the disc eject function.
"LOC" is display ed on the unit, and ordinary operation is disabled.
9.6.1. Setting
The sales demonstration lock is set by simultaneousl y pressing STOP button on the player and POWER button on the remote
control unit for 1 second or longer.
9.6.2. Cancellation
The lock can be cancelled by the same procedure as used in setting. ("UNLOC" is displayed on cancellation. Disconnecting the
power cable from power outlet does not cancel the lock.)
9.7. Handling After Completing Repairs
Use the following procedure after completing repairs.
9.7.1. Method
Confirm that the power is turned on:
1. Press the "OPEN/CLOSE" button to close the tray.
2. Press the "POWER" button to turn off the power.
3. Disconnect the power plug from the outlet.
9.7.2. Precautions
Do not disconnect the power plug from the outlet with the tray still open, then close the tray manually.
29
Page 30

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
10 SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
10.1. Recovery after the dvd player is repaired
· When FROM or module P.C.B. is replaced, carry out the recovery processing to optimize the drive.
Playback the recovery disk to process the recovery automatically .
· Recovery disc [Product number: RFKZD03R005] (RFKZD03R004 can not be recovered as a partial item.
So use the new recovery disc, RFKZD03R005.)
· Performing recovery
1. Load the recovery disc RFKZD03R005 on to the player and run it.
2. Recovery is performed automatically. When it is finished, a message appears on the screen.
3. Remove the recovery disc.
4. Turn off the power.
Note:
This unit requires no initialization process carried out after the traditional DVD players were repaired.
When the recovery measures are taken, the customer setting will return to the factory setting as same as the procedure
described in item of "Initialization" in 9.5. is carried out. Write down the contents of the setting before recovery processing,and
reset the player.
10.2. Firmware version-up of the DVD player
· The firmware of the DVD player may be renewed to improve the quality including operationability and playerbility to the
substandard discs.processing to optimize the drive.
The recovery disc has also firmware version-up.
· After version-up, recovery processing is executed automatically.
· Part number of the recovery disc for version-up will be noticed when it is supplied.
· Updating firmware
1. Load the recovery disc that is supplied to the player and run it.
2. Firmware version of the player is automatically checked. Appropriate message appears whenever necessary.
3. Using remote controller´s cursor key, select whether version updating is to be done or not. (Selection of Yes/No)
4. a. If Yes is selected, version updating is performed.
b. If No is selected, only recovery is performed.
5. a. When updating is finished, remove the disc according to the message appearing on the screen.
b. Remove the disc according to the message appearing on the screen.
6. Turn off the power.
Note:
If the AC power supply is shut out during version-up due to a power failure, the version-up is improperly carried out.
In such a case, replace the FROM and carry out the version-up again.
30
Page 31

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
11 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
11.1. Service Tools and Equipment
Application Name Number
Tilt adjustment DVD test disc DVDT-S15 or DVDT-S01
TORX screw driver (T6) Available on sales route. (T6) or
Inspection Extension cable (module P.C.B. to mother P.C.B.) VUC8026
Extension cable (module P.C.B. to mother P.C.B.) RFKZ0106
Others Hanarl VFK1784
Grease RFKXPG641
Drysurf RFKXGUD24
Confirmation CD test disc PVCD-K06 or any other commercially
VCD test disc PVCD-K06 or any other commercially
Recovery disc RFKZD03R005
11.2. Important points in adjustment
11.2.1. Important points in optical adjustment
· Before starting optical adjustment, be sure to take anti-static measures.
· Optical pickup tilt adjustment is needed after replacement of the following components.
1. Optical pickup unit
2. Spindle motor unit
3. Optical pickup peripheral parts (such as rail)
Notes
Adjustment is generally unnecessary after replacing other parts of the traverse unit. However, make adjustment if there is a
noticeable degradation in picture quality. Optical adjustments cannot be made inside the optical pickup. Adjustment isgenerally
unnecessary after replacing the traverse unit.
RFKZ0185
available disc
available disc
11.2.2. Important points in electrical adjustment
· Follow the adjustment procedures described in this Manua l.
11.3. Storing and Handling Test Discs
· Surface precision is vital for DVD test discs. Be sure to store and handle them carefully.
1. Do not place discs directly onto the workbench, etc., after use.
2. Handle discs carefully in order to maintain their flatness. Place them into their case after use and store them vertically. Store
discs in a cool place where they are not exposed to direct sunlight or air from air conditioners.
3. Accurate adjustment will not be possible if the disc is warped when placed on a surface made of glass, etc. If this happens, use
a new test disc to make optical adjustments.
4. If adjustment is done using a warped disc, the adjustment will be incorrect and some discs will not be playab le.
31
Page 32

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
11.4. Optical adjustment
11.4.1. Optical pickup tilt adjustment
Measurement point Adjustment point Mode Disc
Tangential adjustment screw
Tilt adjustment screw
Measuring equipment Adjustment value
None (Main unit display for servicing is used.) Adjust to the minimum jitter value.
T01 (inner periphery) play
T30 (central periphery) play
T43 (outer periphery) play
DVDR-S15 or DVDT-S01
11.4.1.1. Adjustment procedure
1. While pressing PAUSE and OPEN/CLOSE buttons on the
main unit, press "5" on the remote control unit.
2. Confirm that "J_xxx/yyy_z z" is shown on the front display.
For your information:
"yyy" and "zz" shown to the right have nothing to do with
the jitter value. "yyy" is the error counter, while "zz" is
the focus drive value.
Note:
Jitter value appears on the front display.
3. Play test disc T30 (central periphery).
4. Adjust tangential adjustment screw so that the jitter value is
minimized.
5. Play test disc T30 (central periphery).
6. Adjust tilt adjustment screw 1 so that the jitter value is
minimized.
7. Play test disc T30 (central periphery).
8. Adjust tilt adjustment screw 2 so that the jitter value is
minimized.
9. Repeat adjusting tilt adjustment screws 1 and 2 alternately
until the jitter value is minimized.
10. Finally please reproduce T01 (inner periphery) and T43
(outer periphery) and check the jitter value. (Please
readjust, when the jitter value is extremely different.)
11.4.1.2. Important points
Note:
When FFC has covered the adjustment screw, please insert
a screwdriver, evading FFC(s).
11.4.1.3. Check after adjustment
Play test disc or any other disc to make sure there is no picture
degradation in the inner, middle and outer peripheries, and no
audio skipping. After adjustment is finished, lock each
adjustment screw in position using screw lock.
1. Make tangential adjustment first, and then make tilt
adjustment.
2. Repeat adjusting two or three times to find the optimum
point.
3. Finish the procedure with tilt adjustment.
Jitter value depends on the model:
1. If the jitter value changes like B, the optimum point is easy to
find.
2. If the jitter value changes like A, set the optimum point near the
middle.
32
Page 33

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
11.4.1.4. Procedure for screw lock
Please perform a screw lock in which by the side of the tip or
head of an adjustment screw.
<When a screw lock is performed to the tip part side of an
adjustment screw>
1. After adjustment, remove top panel.
2. After pulling out a tray to the position which does not
become obstructive,remove clamper plate.
3. Fix adjustment screw with screw lock.
4. After fixing, reassemble clamper plate and top panel.
It is also possible to perform screw lock on the head of an
adjustment screw after an adjustment end using an injector etc.
from the hole at the bottom of a product (hole of bottom
chassis), without decomposing.
<When a screw lock is performed to the head side of an
adjustment screw>
1. After adjustment, remove top panel, front panel, rear
panel and mechanism unit in this sequence.
2. Lay the mechanism unit upside down, and fix
adjustment scwer with screw lock.
3. After fixing, reassemble mechanism unit, rear panel,
front panel and top panel.
33
Page 34

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
12 ABBREVIATIONS
INITIAL/LOGO ABBREVIATIONS
A A0~UP
ACLK
AD0~UP
ADATA
ALE
AMUTE
AREQ
ARF
ASI
ASO
ASYNC
B BCK
BCKIN
BDO
BLKCK
BOTTOM
BYP
BYTCK
C CAV
CBDO
CD
CDSCK
CDSRDATA
CDRF
CDV
CHNDATA
CKSL
CLV
COFTR
CPA
CPCS
CPDT
CPUADR
CPUADT
CPUIRQ
CPRD
CPWR
CS
CSYNCIN
CSYNCOUT
D DACCK
DEEMP
DEMPH
DIG0~UP
DIN
DMSRCK
DMUTE
DO
DOUT0~UP
DRF
DRPOUT
DREQ
DRESP
DSC
DSLF
DVD
ADDRESS
AUDIO CLOCK
ADDRESS BUS
AUDIO PES PACKET DATA
ADDRESS LATCH ENABLE
AUDIO MUTE
AUDIO PES PACKET REQUEST
AUDIO RF
SERVO AMP INVERTED INPUT
SERVO AMPOUTPUT
AUDIO WORD DISTINCTI ON SYNC
BIT CLOCK (PCM)
BIT CLOCK INPUT
BLACK DROP OUT
SUB CODE BLOCK CLOCK
CAP. FOR BOTTOM HOLD
BYPATH
BYTE CLOCK
CONSTANT ANGULAR VELOCITY
CAP. BLACK DROP OUT
COMPACT DISC
CD SERIAL DATA CLOCK
CD SERIAL DATA
CD RF (EFM) SIGNAL
COMPACT DISC-VIDEO
CHANNEL DATA
SYSTEM CLOCKSELECT
CONSTANT LINEAR VELOCITY
CAP. OFF TRACK
CPU ADDRESS
CPU CHIP SELECT
CPU DATA
CPU ADDRESS LATCH
CPU ADDRESS DATA BUS
CPU INTERRUPT REQUEST
CPU READ ENABLE
CPU WRITE ENABLE
CHIPSELECT
COMPOSITE SYNC IN
COMPOSITE SYNC OUT
D/A CONVERTER CLOCK
DEEMPHASIS BIT ON/OFF
DEEMPHASIS SWITCHING
FL DIGIT OUTPUT
DATA INPUT
DM SERIAL DATA READ CLOCK
DIGITAL MUTE CONTROL
DROP OUT
DATAOUTPUT
DATA SLICE RF (BIAS)
DROP OUT SIGNAL
DATA REQUEST
DATA RESPONSE
DIGITAL SERVO CONTROL LER
DATA SLICE LOOP FILTER
DIGITAL VIDEO DISC
INITIAL/LOGO ABBREVIATIONS
E EC
ECR
ENCSEL
ETMCLK
ETSCLK
F FBAL
FCLK
FE
FFI
FEO
FG
FSC
FSCK
G GND COMMON GROUNDING (EARTH)
H HA0~UP
HD0~UP
HINT
HRXW
I IECOUT
IPFRAG
IREF
ISEL
L LDON
LPC
LRCK
M MA0~UP
MCK
MCKI
MCLK
MDATA
MDQ0~UP
MDQM
MLD
MPEG
O ODC
OFTR
OSCI
OSCO
OSD
P P1~UP
PCD
PCK
PDVD
PEAK
PLLCLK
PLLOK
PWMCTL
PWMDA
PWMOA, B
ERROR TORQUE CONTROL
ERROR TORQUE CONTROL
REFERENCE
ENCODER SELECT
EXTERNAL M CLOCK (81MHz/40.5MHz)
EXTERNAL S CLOCK (54MHz)
FOCUS BALANCE
FRAME CLOCK
FOCUS ERROR
FOCUS ERROR AMP INVERTED INPUT
FOCUS ERROR AMP OUTPUT
FREQUENCY GENERATOR
FREQUENCY SUB CARRIER
FS (384 OVER SAMPLING) CLOCK
HOST ADDRESS
HOST DATA
HOST INTERRUP T
HOST READ/WRITE
IEC958 FORMAT DATA OUTPUT
INTERPOLATION FLAG
I (CURRENT) REFERENCE
INTERFACE MODE SELECT
LASER DIODE CONTROL
LASER POWER CONTROL
L CH/R CH DISTINCTION CLOCK
MEMORY ADDRESS
MEMORY CLOCK
MEMORY CLOCK INPUT
MEMORY SERIAL COMMAND CLOCK
MEMORY SERIAL COMMAND DATA
MEMORY DATA INPUT/OUTPUT
MEMORY DATA I/O MASK
MEMORYSERIAL COMMAND LOAD
MOVING PICTURE EXPERTS GROUP
OPTICAL DISC CONTROLLER
OFF TRACKING
OSCILLATOR INPUT
OSCILLATOR OUTPUT
ON SCREEN DISPLAY
PORT
CD TRACKING PHASE DIFFERENCE
PLL CLOCK
DVD TRACKING PHASE DIFFERENCE
CAP. FOR PEAK HOLD
CHANNEL PLL CLOCK
PLL LOCK
PWM OUTPUT CONTROL
PULSE WAVE MOTOR DRIVEA
PULSE WAVE MOTOR OUT A, B
34
Page 35

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
INITIAL/LOGO ABBREVIATIONS
R RE
RFENV
RFO
RS
RSEL
RST
RSV
S SBI0, 1
SBO0
SBT0, 1
SCK
SCKR
SCL
SCLK
SDA
SEG0~UP
SELCLK
SEN
SIN1, 2
SOUT1, 2
SPDI
SPDO
SPEN
SPRCLK
SPWCLK
SQCK
SQCX
SRDATA
SRMADR
SRMDT0~7
SS
STAT
STCLK
STD0~UP
STENABLE
STSEL
STVALID
SUBC
SBCK
SUBQ
SYSCLK
T TE
TIBAL
TID
TIN
TIP
TIS
TPSN
TPSO
TPSP
TRCRS
TRON
TRSON
READ ENABLE
RF ENVELOPE
RF PHASE DIFFERENCE OUTPUT
(CD-ROM) REGISTER SELECT
RF POLARITY SELECT
RESET
RESERVE
SERIAL DATA INPUT
SERIAL DATA OUTPUT
SERIAL CLOCK
SERIAL DATA CLOCK
AUDIO SERIAL CLOCK RECEIVER
SERIAL CLOCK
SERIAL CLOCK
SERIAL DATA
FL SEGMENT OUTPUT
SELECTCLOCK
SERIAL PORT ENABLE
SERIAL DATA IN
SERIAL DATA OUT
SERIAL PORT DATA INPUT
SERIAL PORT DATA OUTPUT
SERIAL PORT R/W ENABLE
SERIAL PORT READ CLOCK
SERIAL PORT WRITE CLOCK
SUB CODE Q CLOCK
SUBCODE Q DATA READ CLOCK
SERIAL DATA
SRAM ADDRESS BUS
SRAM DATA BUS 0~7
START/STOP
STATUS
STREAM DATA CLOCK
STREAM DATA
STREAM DATA INPUT ENABLE
STREAM DATA POLARITY SELECT
STREAM DATAVALIDITY
SUB CODE SERIAL
SUB CODE CLOCK
SUB CODE Q DATA
SYSTEM CLOCK
TRACKING ERROR
BALANCE CONTROL
BALANCE OUTPUT 1
BALANCE INPUT
BALANCE INPUT
BALANCE OUTPUT 2
OP AMP INPUT
OP AMP OUTPUT
OP AMP INVERTED INPUT
TRACK CROSSSIGNAL
TRACKING ON
TRAVERSE SERVO ON
INITIAL/LOGO ABBREVIATIONS
V VBLANK
VCC
V BLANKING
COLLECTOR POWER SUPPLY
VOLTAGE
VCDCONT
VIDEO CD CONTROL (TRACKING
BALANCE)
VDD
VFB
VREF
VSS
W WAIT
WDCK
WEH
WSR
X X
XALE
XAREQ
XCDROM
XCS
XCSYNC
XDS
XHSYNCO
XHINT
XI
XINT
XMW
XO
XRE
XSRMCE
XSRMOE
XSRMWE
XVCS
XVDS
XVSYNCO
DRAIN POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE
VIDEO FEED BACK
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
SOURCE POWER SUPPLYVOLTAGE
BUS CYCLE WAIT
WORD CLOCK
WRITE ENABLE HIGH
WORD SELECT RECEIVER
X´ TAL
X ADDRESS LATCH ENABLE
X AUDIO DATA REQUEST
X CD ROM CHIP SELECT
X CHIP SELECT
X COMPOSIT E SYNC
X DATA STROBE
X HORIZONTAL SYNC OUTPUT
XH INTERRUPTREQUEST
X´ TAL OSCILLATOR INPUT
X INTERRUPT
X MEMORY WRITE ENABLE
X´ TAL OSCILLATOR OUTPUT
X READ ENABLE
X SRAM CHIP ENABLE
X SRAM OUTPUT ENABLE
X SRAM WRITE ENABLE
X V-DEC CHIPSELE CT
X V-DEC CONTROL BUS STROBE
X VERTICAL SYNC OUTPUT
35
Page 36

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
13 VOLTAGE CHART
Note:
· Circuit voltage and waveform described herein shall be regarded as reference information when probing defect point,
because it may differ from an actual measuring value due to difference of measuring instrument and its measuring condition
and product itself.
13.1. MOTHER P.C.B.
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
12345 679
-0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 0 0 0
-0.1 -0.1 0 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1
IC1101 IC1151 IC1195
123 12345 12345
2.5 0 3.3 0 3.2 8.8 0 0 5.1 0 4.3 3.3 3.3
3.3 0 2.5 12.6 3.2 8.9 0 0 5.1 0 4.3 3.2 3.3
12345678910111213141516
4.8 0 2.4 1.7 2.6 1.7 0 2.3 2.3 0 2.2 2.2 1.6 1.6 1.6 2.2
4.9 2.3 2.4 1.7 2.6 1.7 0 2.3 2.3 0 2.2 2.2 1.6 1.6 1.5 2.2
123456 123456
1.9 0 0 0 1.9 4.9 2.5 0 2.5 0 2.5 4.9
2.2 0 1.8 0 1.9 4.9 2.5 0 2.5 0 0 4.9
1234567891011121314151617181920
4.9 0 0 2.1 2.1 0 1.5 1.3 0 0 0.4 0 0 0 0.5 4.9 0 2.7 0 3.7
4.9 0 0 2.2 4.9 0.4 0 1.5 0 4.9 0.5 0 0 0 0 4.9 2.6 0 0 10
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
3.7 0 3.7 0 0 1.4 1.3 0 1.4 1.4 0 2.3
0 3.5 3.5 0 1.3 1.3 0 1.4 1.4 1.4 0 2.2
12345678
2.5 2.5 2.5 0 0 0 2.6 12.2
2.6 2.5 2.5 -9.8 0 2.5 2.6 13.3
1234567891011121314151617181920
0 0 1.1 3.3 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 1.5 0 0 3.2 0 3.3 1.6 1.6 3.3 3.3 0
0 0 1.1 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.5 0 0 0 0 3.3 1.6 1.6 3.3 3.3 0
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
30.71.700003.303.30-3.8 0 3.2 0 3.2 -6.9 -6.9 -6.8 -6.8
0 1.6 1.6 1.6 0 0 0 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.1 -2.5 32 -3.6 3.3 -3.8 3.2 0 3.2 -6.8
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
-6.5 -6.5 -9.8 -6.5 -6.5 -9.8 -6.4 -9.8 -3.3 -9.9 -6.5 -9.5 -9.9 -9.9 0 -9.9 3.1 2.7 2.7 3
0 0 -3.1 0 -6.4 -6.4 -6.4 -9.7 -9.8 -6.5 -6.5 -6.5 0 0 0 -3.2 0 3.2 2.9 3
IC6001
61 62 63 64
0 0 1.7 3.3
0 0 1.7 3.3
BCE BCE
12.1 0 0 0 0 -5.9
13.2 0 0
Q4423 Q4751 Q6085
BCE BCE BCE BCE BCE
0 0 -5.9 5 1.8 2.5 -6.3 -6.3 -5.6 0 0 3.2 0 0 3.2
0 0 0.7 5 1.8 2.5 -6.3 -6.3 -5.6 0 0 3.2 0 0
QR3502(EE) QR3821(EE) QR3822(EE) QR3823(EE) QR4302
BCE BCE BCE BCE BCE
2.6 0 0 12.1 0 0 0 0 4.9 11.5 11.5 0 -5.9 0 0
2.6 0 0 13.2 0 0 0 0 4.9 12.6 12.6 0 2.5 2.6 0
QR4306
BCE
000
2.6 0 0
IC1021(PLA) IC1021(EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL)
IC3502(EE) IC3802(EE)
IC3811(EE)
IC4301
Q1051 Q1115 Q3801(EE)
123
5.1 4.1 -0.1
5.1 4.1 0
Q3851(EE) Q3852(EE)
0 0 0.7
12345 679
-0.2 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 0 -0.1
-0.1 -0.1 -0.1 -0.1 0 -0.1 -0.1 0
IC3501
IC3811(EE)
IC6001
4
0
0
B
0
0
IC6001
IC6001
123456
5.155550
5.15055
CE
0 -5.9
0 0.7
33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
Q4302 Q4422Q3821(EE)
BCE
4.1 0 0
000
QR1115 QR3501(EE)
0
BCE
12.3 11.5 12.1
13.3 12.6 13.2
BC
00
00
-5.9
0.7
3.2
E
36
Page 37

13.2. MODULE P.C.B.
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
1234567891011121314151617181920
1 0.9 1 1 0 3.3 1.2 1.3 1 1 1.2 1 1 1.2 0 3.3 0 1.3 0 1.2
0.8 0.8 0.9 1.1 0 3.3 1 1.3 0.9 0.9 0.7 0.9 0.7 1.2 0 3.3 1 1.9 0 1.2
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
1.2 0.3 1 2.7 1.5 0.9 2.2 1 1.2 0.8 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 1.9 2.1 1.9 1.4 1.3
0.3 0.6 3 1.7 1.3 2.6 1.3 1.6 0.6 0 3 0 3.3 3.3 2.4 2.4 0.9 0.9 2.4 1.2
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
2 1.2 0 1.2 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 3.3 3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 0
2.2 1.1 0 1.2 3.3 0 0 3.3 0 0 0 3.3 3 3.3 3.3 0 0 3.3 3.3 0
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
3.21.63.3001.81.603.33.30000000000
3.3 1.6 0 0 0 1.7 1.6 0 0 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0
81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
0 0 1.2 0 0.9 2.3 0 1.8 0 0.1 0 3.2 2 2 0 1.8 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.6
0 0 1.2 3.2 0.9 0 0 1.8 0 0.1 1.8 3.2 2.1 2 1.8 1.8 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.6
101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120
1.9 1.4 0.2 0.1 0.2 2.1 3.2 0 2.2 1.6 2.5 0 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 3.2 0 3.2 0
1.9 1.4 0 0.1 0 0.1 3.2 0 2.2 1.6 2.2 2.2 0 2.2 2.2 2.2 3.2 0 3.2 0
121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140
1.8 2.5 1.6 1.7 0 1.6 1.7 3.3 0.8 0.9 0.4 3.3 2.2 0 1.1 2.2 0 0.4 0.9 0
2 1.6 1.6 1.6 0 1.6 1.6 3.3 0.8 0.9 0.4 3.2 2.2 1 1 2.2 0 1.4 0.8 0
141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160
3.3 3.3 0 1.6 0 1.6 3.2 0 0 0 0 1.6 0 3.3 0 1.6 0 1.2 3 3.1
3.3 3.3 0 1.6 0 1.6 3.2 0 0 0 0 1.6 0 3.3 1.6 1.6 0 1.2 3 3.1
161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180
2.8 3.1 2.9 3 0 3.3 3.1 3 3 3.2 3 3 0 3.3 3.1 3 3.1 2.9 2.9 2.8
3.2 2.9 3.1 0 3.3 3.1 3.1 3 3.3 3.1 3 0 3.3 3.2 3 3.1 2.9 2.9 0
2.9
181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200
3.2 0 1.6 3.3 1.6 0 1.2 3.2 0 3.2 3.2 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 1.5
3.2 0 1.6 3.2 1.6 0 1.2 3.2 3.2 3.1 3.2 0 2.4 0 0 3.3 1.6 0 0 1.6
201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216
0 1.8 0 0 3.2 0 0.2 1.4 1.5 0 1.2 1.4 2.6 2.6 1.5 1.4
0.1 0 0.3 0 3.3 1.6 0.3 1.5 0.6 0 1.2 1.6 2.7 2.6 1.2 1.1
221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240
1.2 0 0 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.5 1.8 1.2 0 1.2 3.3 0.3 1.2 0 0 0 3.3 1.5
3.2001.400003.3001.603.31.61.2
241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256
0.9 3.3 0 1.5 0 0 0.3 1 0 0 0.5 3.3 1.2 0 0 0
1.6 0 1.6 0 0 3.3 1.2 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 1.2 0 0
1234567891011121314151617181920
0 2.9 3.3 3 3 0 3 0 3.3 3 2.9 0 2.8 3.3 2.7 3.2 0 0 0 1.9
3.3 3.1 3.3 3.2 3.1 0 3.1 3.3 3.3 3.1 3 0 2.9 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.2 3.2 2.6 1.5
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
1.60000.11.53.301.501.6000000000
0 0 0 0.2 0.1 1.6 3.3 0 1.6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.9 2.9 0 0
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54
0 3 3.3 3.2 3 0 0 2.9 0 2.8 2.8 0 2.9 0
0 3.2 3.3 3.2 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 2.8 0 0 0
12345678 12345
3.3 0 0 1.9 4.7 0 0 5 2.9 5 1.2 1.2 0
3.3 0 0 2 4.7 0 0 0 2.8 2 1.2 1.2 0
1234
3.3 1.6 3.3 3.3 0 1.6 0 8.9 4.2 4.2 4.3 4.2 3.3 5.2 2.5 2.3 1.8 0 1.6 8.9
3.30000008.94.24.24.24.23.83.82.52.52.52.509
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
5 1.6 0 0 1.5 1.8 0 0
4.91.600221.61.6
12345
0 0 2.8 2.2 0 0 0 1.6 0 0 5 0 0 2.4 2.4 4.9
0 2 0 3.3 1.6 0 1.6 1.7 0 0 5 0 0 2.4 2.4 0
IC8601
1234
3.3 1.2 0 0 3.2 1.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0
3.3 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 3.3
1234
0 1.6 1.5 0 0 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 3.3 0 0 0 3.3
02000000003.33.3002.200000
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
003.300000000011.1001.1001.1
0000000011111113.31111
IC8111
5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516
IC8251
5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
IC8051
678
12345
IC8001
IC8420
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8001
IC8051
IC8051
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
IC8151
IC8251
9 10111213141516
12345678
IC8651(EE/GC/GCA/PL/PLA)
IC8651(EE/GC/GCA/PL/PLA)
IC8611IC8606
217 218 219 220
0 1.2 0 3.3
1.6 0 0 0
001.21.4
17 18 19 20
37
Page 38

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
Ref No.
MODE
PLAY
STOP
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48
0000001.21.6
1.2 0.9 1 1.6 0 0 0 0
1234567891011121314151617181920
0.7 0 0 0.7 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 1.5 0 0 3.3 3.3 3.3
0 1.6 0 0.8 0 0 0 1.3 1.4 0 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 1.9 0.6 1.8 2.2 0 0
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
3.33.23.300003.200.90.900.900000.90.90
1.80002.72.500001.200001.33.3000
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 B C E B C E B C E
0000003.30 4.900 04.64.9 3.71.31.9
1.1 1.2 1.6 1.3 0 0 0 1.8 5 0 0 0.5 5 5 5 0 0
BCE 123456 BCE BCE
2.3 4.4 3.7 0 0 0 0 0 4.7 4.1 0 0 3.2 3.3 0
0 5 5 0 0 1.2 0 0 4.7 0 0 3.3 -1.7 3.3 3.3
IC8651(EE/GC/GCA/PL/PLA)
IC8651(GCS/GCU)
Q8562 QR8111
IC8651(GCS/GCU)
IC8651(GCS/GCU)
Q8551 Q8552 Q8561
QR8420 QR8571
38
Page 39

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
14 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Note:
Circuit voltage and waveform described herein shall be regarded as reference information when probing defect point, because it may differ from an actual measuring value due to difference of Measuring instrument and its measu ringcondition and product itself.
39
Page 40

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
14.1. OVERALL BLOCK DIAGRAM
MECHANISM UNIT
OPTICAL
PICK UP
UNIT
SPINDLE
MOTOR
TRAVERSE
MOTOR
LOADING
MOTOR
IC8251
MOTOR
DRIVE
IC6001
MODULE P.C.B.
IC8651
16Mbit
FLASH
ROM
IC8001
DV3.2
FRONT-END PROCESSOR/
OPTICAL DISC CONTROLLER/
DIGITAL SERVO CONTROLLER/
AV DECODER
IC8420
AUDIO
D/A
CONVERTER
MOTHER P.C.B.
MIXL
MIXR
L OUT
R OUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
(COAXIAL)
AV21PIN
(
only for EE)
TRAY
FL
KEY
REMOTE CTL
MOTHER P.C.B.
OPERATION
CPU
IC8611
16Kbit
EEPROM
IC8051
64Mbit
SDRAM
IC3501
VIDEO
DRIVER
IC3811
VIDEO
DRIVER
S-VIDEO OUT
(only for GC/GCA/
GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
VIDEO OUT(LINE)
Y
PB
PR
VIDEO OUT(LINE)
(AV21PIN)
R
G
AV21PIN
B
only for EE
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
OVERALL BLOCK DIAGRAM
40
Page 41

14.2. POWER SUPPLY BLOCK DIAGRAM
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
AC SOCKET
P1001
VA1002
SURGE
KILLER
F1001
L1001
LINE
FILTER
IC1021
D1011,C1011
RECTIFIER
CONSTANT
VOLTAGE
CONTROL
SECONDARY CIRCUITPRIMARY CIRCUIT
T1021
POWER
TRANSFORMER
10
11
12
15
NSW-12V
NSW+12V
Q1115
REG.
QR1115
SWITCH
N.POWER OFF
IC1151
(REG.M+9V)
2
ON/OFF
31 OUTIN
VEE
AUDIO
OP AMPS
VCC
NSW+2.7V
A+5V
D+5V
L
M+9V
IC6001
(OPERATION CPU)
DGT14
34
DGT8
DGT11
SEG0
SEG15
FL
40
37
41
56
Q1051
PHOTO
COUPLER
16
17
SHUNT
REG.
IC1101
IC1195
REG.
STANBY
D6101
NSW+3.3V
FLH-
FLH+
X6001
15
33
32
9
10
RESET
DGT15
DGT16
OSC2
OSC1
REMOTE CTL
AN2
AN1
AN0
21
IR6131
IR
1
RECEIVER
4
5
PAUSE
6
S6171
STOP
S6172
OPEN/CLOSE
S6151
POWER
S6152
PLAY
S6161
QUICK OSD
S6162
41
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
POWER SUPPLY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 42

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
14.3. SERVO BLOCK DIAGRAM
RF SIGNAL MOTOR DRIVE SIGNAL TRACKING ERROR SIGNAL FOCUS ERROR SIGNAL
OPTICAL PICKUP UNIT
PHOTO DETECTOR
B2B1
A2
A1
A3
A4
B3B4
LASER DIODE(DVD)
LASER DIODE(CD)
HEAD
AMP
Q8551, Q8552
LD DRIVE
Q8561, Q8562
LD DRIVE
VIN9
VIN10
VIN5
VIN6
VIN7
VIN8
VIN1
VIN2
VIN3
VIN4
LPC01
LPC1
LPC02
LPC2
RFINN
RFINP
IC8001
(DV3.2)
130
129
131
132
133
134
138
137
135
136
124
123
126
125
113
114
DRV0
PWM1
PWM0
DRV1
AD1
DRV4
DRV3
TRSDRV
91
TRDRV
144
FODRV
145
SPDRV
90
AD1
140
FROM
IC6001-16,17PIN
SP MUTE
87
TRVFT MUTE
88
IC8251
(MOTOR DRIVE)
VIN2
6
VIN4
22
VIN5
23
VIN1
5
OPOUT
27
VIN3
7
CH1
3
MUTE
CH2,4,5
4
MUTE
BIAS1
BIAS2
VO2+
VO2-
OPIN+
VO1+
VO1-
OPIN-
VO3+
VO3-
VO4+
VO4-
VO5+
VO5-
12
11
25
14
13
26
10
9
IC8251-15,16,17,18
4Vp-p(0.5msec./div.)
17
18
15
16
TRAVERS MOTOR
SPINDLE MOTOR
M2601
LOADING MOTOR
OPTICAL PICKUP UNIT
ACTUATOR
TRACKING
ACT T+
ACT T-
ACT F+
ACT F-
COIL
FOCUS
COIL
IC6001
(OPERATION CPU)
-
+
LEVEL
-
+
-
+
+
-
-
+
-
+
-
+
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
42
CH3
MUTE
MUTE3
1
CLOSE SW
S2601
OPEN SW
S2602
TRAY MUTE
TRAY CLOSE
TRAY OPEN
18
20
19
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
SERVO BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 43

14.4. VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM (DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
OPTICAL
PICK-UP
UNIT
IC8651
(16M FLASH ROM)
29
DQ0
31
33
35
38
40
42
44
30
32
34
36
39
41
43
45
DQ15
DATA
XWEXCE
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
XOE
281126
A0
A7
A8
A15
A16
A20
25
18
48
17
16
10
IC8001
(DV3.2)
139
138
131
C
Y
Y/PY/G
113
114
18
RFINN
RFINP
A0
DAC5OUT
DAC4OUT
DAC1OUT
64
63
62
61
DAC2OUT
60
59
A7
58
51
8
50
1
49
A8
ADDRESS
48
47
46
43
A15
42
41
A16
57
56
9
54
A20
65
MEMORY
ADDRESS
12bit
ADDRESS
DAC3OUT
MA0
MA1
MA2
MA3
MA4
MA5
MA6
MA7
MA8
MA9
MA10
MA11
MDQ0
20
55
19
23
25
27
29
31
33
37
39
24
26
28
30
32
36
38
40
NEXOE
NEXWE
NEXCE
EXDT0
EXDT15
DATA
MEMORY
DATA
16bit
MDQ1
MDQ2
MDQ3
MDQ4
MDQ5
MDQ6
MDQ7
MDQ8
MDQ9
MDQ10
MDQ11
MDQ12
MDQ13
MDQ14
MDQ15
NCSM
NRAS
NCAS
NWE
MCK
MCK1
NRST
130
129
241
243
245
247
246
244
242
240
236
232
237
230
199
201
203
207
209
211
213
217
216
212
210
208
206
202
200
198
229
228
227
221
223
225
84
CB/PB/B
CR/PR/R
IC8001-131
0.92Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC8001-138
0.92Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC8001-129
0.49Vp-p(20usec./div.)
FROM IC8601-1PIN
IC8001-130
0.49Vp-p(20usec./div.)
FROM IC8606-1PIN
IC3501
(VIDEO DRIVE)
CIN
2
YIN
4
CYIN
6
CBIN
8
CRIN
9
IC8001-139
0.6Vp-p(20usec./div.)
BIAS
CLAMP
CLAMP
BIAS
BIAS
COUT
75
1.4V
2dB
DRIVER
+
75
8dB
DRIVER
75
2dB
DRIVER
MUTE
MUTE
75
2dB
DRIVER
75
2dB
DRIVER
75
2dB
DRIVER
IC3501-15
2.0Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC3501-11
1.2Vp-p(20usec./div.)
CVBS
OUT
YOUT
CYOUT
CBOUT
CROUT
16
15
14
13
12
11
IC3501-16
1.5Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC3501-12
1.2Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC3501-13,14
2.0Vp-p(20usec./div.)
JK4401
VIDEO OUT
JK4401
Y
PB
PR
IC8051
(64M SDRAM)
A0
23
A1
24
A2
25
A3
26
29
A4
30
A5
31
A6
32
A7
A8
33
A9
34
22
A10
A11
35
DQ0
2
DQ1
4
DQ2
5
DQ3
7
DQ4
8
10
DQ5
11
DQ6
13
DQ7
42
DQ8
44
DQ9
45
DQ10
47
DQ11
48
DQ12
50
DQ13
51
DQ14
53
DQ15
19
CS
18
RAS
17
CAS
16
WE
38
CLK
JK4401
S-VIDEO OUT
MEMORY
ADDRESS
12bit
MEMORY
DATA
16bit
4dB
LPF
6.75MHz
-6dB
4dB
LPF
6.75MHz
BIAS
4dB
LPF
13.5MHz
4dB
LPF
6.75MHz
4dB
LPF
6.75MHz
DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
VIDEO BLOCK DIAGR AM
VIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
43
Page 44

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
14.5. VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM (DVD-S42EE)
IC8001
(DV3.2)
IC8651
(16M FLASH ROM)
29
DQ0
31
33
35
38
40
42
44
30
32
34
36
39
41
43
45
DATA
DQ15
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
XOE
XWEXCE
281126
A0
A7
A8
A15
A16
A20
25
18
48
17
16
10
DAC5OUT
DAC4OUT
OPTICAL
PICK-UP
UNIT
8
1
9
113
114
18
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
51
50
49
48
47
46
43
42
41
57
56
54
65
20
55
19
23
25
27
29
31
33
37
39
24
26
28
30
32
36
38
40
RFINN
RFINP
A0
A7
ADDRESS
A8
A15
A16
ADDRESS
A20
NEXOE
NEXWE
NEXCE
EXDT0
EXDT15
DATA
IC8051
(64M SDRAM)
MEMORY
ADDRESS
12bit
MEMORY
DATA
16bit
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
CLK
23
24
25
26
29
30
31
32
33
34
22
35
10
11
13
42
44
45
47
48
50
51
53
19
18
17
16
38
DAC1OUT
241
MA0
243
MA1
245
MA2
247
MA3
246
MA4
244
MA5
242
MA6
240
MA7
236
MA8
232
MA9
237
MA10
MA11
230
2
4
5
7
8
199
201
203
207
209
211
213
217
216
212
210
208
206
202
200
198
229
228
227
221
223
225
MDQ0
MDQ1
MDQ2
MDQ3
MDQ4
MDQ5
MDQ6
MDQ7
MDQ8
MDQ9
MDQ10
MDQ11
MDQ12
MDQ13
MDQ14
MDQ15
NCSM
NRAS
NCAS
NWE
MCK
MCK1
DAC2OUT
DAC3OUT
MEMORY
ADDRESS
12bit
MEMORY
DATA
16bit
NRST
157
156
149
148
147
84
C
Y
Y/PY/G
CB/PB/B
CR/PR/R
IC8001-147
0.49Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC8001-149
0.92Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC8001-156
0.92Vp-p(20usec./div.)
FROM IC8601-1PIN
FROM IC8606-1PIN
IC8001-148
0.49Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC8001-157
0.6Vp-p(20usec./div.)
1
2
3
4
5
44
DVD-S42EE
VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 45

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
VIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
IC3501-11
IC3501
(VIDEO DRIVE)
BIAS
1
2
3
4
5
CIN
2
CLAMP
YIN
4
CLAMP
CYIN
6
CBIN
8
CNIN
9
IC3811
(VIDEO DRIVE)
CIN
CVIN
YIN
PY/G
IN
PB/B IN
PR/R IN
S1
S2
SEL
BIAS
CLAMP
CLAMP
4
6
8
11
13
15
2
3
7
4dB
LPF
6.75MHz
4dB
6.75MHz
4dB
13.5MHz
BIAS
4dB
6.75MHz
BIAS
4dB
6.75MHz
6dB
6dB
6dB
BIAS
CLAMP
BIAS
BIAS OUT
H
L
LPF
BIAS
LPF
LPF
LPF
SEL
+
-6dB
1.4V
L
H
S-DCOUT
S1/S2
+
6dB
6dB
6dB
2dB
8dB
2dB
2dB
2dB
2dB
6MHz
LPF
6MHz
LPF
6MHz
LPF
12MHz
LPF
12MHz
LPF
12MHz
LPF
75
DRIVER
75
DRIVER
75
DRIVER
MUTE
75
DRIVER
75
DRIVER
75
DRIVER
MUTE
75
75
75
75
75
75
1.2Vp-p(20usec./div.)
COUT
16
CVBS
OUT
15
YOUT
14
CYOUT
13
CBOUT
12
CROUT
11
COUT
32
CVOUT
30
CVOUT
SAG
29
YOUT
27
YOUT
SAG
26
PY/G
OUT
24
PY/G
OUT
SAG
23
PB/B
OUT
21
PB/B
OUT
SAG
20
PR/R
18
PR/R
OUT
SAG
17
S-DCOUT
31
IC3501-12
1.2Vp-p(20usec./div.)
IC3802
4
6
2
1
IC3501-15
2.0Vp-p(20usec./div.)
RED I/O
V-OUT
GREEN I/O
BLUE I/O
IC3501-13
2.0Vp-p(20usec./div.)
JK3871
SCART OUT
JK4401
JK4401
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
VIDEO OUT
Y
PB
PR
21
19
17
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
45
D-WIDE2/YC-H/MIC DET
D-WIDE1/RGB-H/MIC MUTE
DVD-S42EE
VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM
FROM IC6001-27PIN
FROM IC6001-26PIN
Page 46

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
14.6. AUDIO BLOCK DIAGRAM
IC8001
(DV3.2)
IC8420
(AUDIO DAC)
AUDIO MAIN SIGNAL
SRCK
LRCK
ADOUT3
P9
P10
P11
DACCK
168
167
169
76
78
77
166
SRCK IN
LRCK IN
DMIXOUT
STBDAC
SBT3
SBQ3
ADAC-CLK
7
8
6
2
3
4
5
SERIAL
INPUT
I/F
FUNCTION
CONTROL
I/F
SYSTEM CLOCK
MANAGER
SYSTEM
CLOCK
4X / 8X
OVERSAMPLING
DIGITAL FILTER
WITH
FUNCTION
CONTROLLER
ZERO DETECT
ENHANCED
MULTI-LEVEL
DELTA-SIGMA
MODULATOR
DAC
DAC
OUTPUT AMP AND
LOW-PASS FILTER
OUTPUT AMP AND
LOW-PASS FILTER
15
14
VOUTL
VOUTR
IC4301
AMP
2
IC4301
67
AMP
IC8420-14,15 PIN
1.2Vp-p(0.5msec./div.)
JK4401
1
MIX L OUT
MIX R OUT
JK3871
(only for EE)
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Q4422
MUTE
L OUT
R OUT
QR4302,QR4306
MUTE
Q4423
MUTE
Q3852
(only for EE)
MUTE
IECOUT
173
Q3851
(only for EE)
MUTE
Q4302
SWITCHING
Q4751
AMP
JK4401
FROM
IC6001 - 62 PIN
DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
(COAXIAL)
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
AUDIO BLOCK DIAGRAM
46
Page 47

15 INTERCONNECTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM & SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM NOTES
15.1. INTERCONNECTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
F
E
OPTICAL PICKUP UNIT
FP8531
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
T+
F+
FTHFM
TA(DVD)
TB(DVD)
TD(DVD)
TC(DVD)
FE2(DVD/CD)
FE1(DVD/CD)
GND
RF
VREF2(RF-)
PIN(DVD)
LDCD
LDGND
LDDVD
GND(OEIC)
VREF1
VCC
SUB2
SUB1
PIN(CD)
SUBSEL
GND(VRCD)
DGND
D+5V
DGND
A+5V
AGND
D+2.7V D+2.7V
DGND
M+9V
MGND
TRAY-DRV
TRAY-MUT
DOP-CPU-CLK
DOP-CPU-CMD
DOP-CPU-STAT
PS8101 FP3501
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
DGND
D+5V
DGND
A+5V
AGND
DGND
M+9V
MGND
TRAY-DRV
TRAY-MUT
DOP-CPU-CLK
DOP-CPU-CMD
DOP-CPU-STAT
STBYLED
DGND
KEY-SCAN1
KEY-SCAN2
KEY-SCAN3
PJ6101
1
2
3
4
5
JW6101
1
2
3
4
5
STBYLED
DGND
KEY-SCAN1
KEY-SCAN2
KEY-SCAN3
OPERATION P.C.B.
D
STBYLED
KEY-SCAN1
DGND
MODULE P.C.B.
MOTHER P.C.B.
JW6102JW6102
1
2
3
C
TRV-INNER-SW
DGND
TRVM+
TRVMSPM+
SPM- 1
6
5
4
3
2
MECHANISM UNIT
B
LDLDLD+
LD+
CLOSE-SW
GND(SW)
A
OPEN-SW
FP2601
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
FP8251
6
5
4
3
2
1
FP8252
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TRV-INNER-SW
DGND
TRVM+
TRVMSPM+
SPM-
LDLDLD+
LD+
CLOSE-SW
GND(SW)
OPEN-SW
MIX-L
ADGND
MIX-R
ADGND
A-REF
ZFLAG & AMUTE
ADGND
AUDIODIGITAL
ADAC5V
OPEN-SW
CLOSE-SW
CR/PR/R
VGND
CB/PB/B
VGND
Y/PY/G
VGND
Y
VGND
C
PS8301
FP3502
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
MIX-L
1
ADGND
2
MIX-R
3
4
ADGND
5
A-REF
6
ZFLAG & AMUTE
7
ADGND
8
AUDIODIGITAL
ADAC5V
9
OPEN-SW
10
CLOSE-SW
11
CR/PR/R
12
13
VGND
CB/PB/B
14
15
VGND
16
Y/PY/G
VGND
17
18
Y
19
VGND
C
20
231
STBYLED
KEY-SCAN1
DGND
POWER SW P.C.B.
LOADING MOTOR P.C.B.
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
INTERCONNECTION
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
54321
9876
47
Page 48

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
15.2. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM NOTES
This schematic diagram may be modified at any time with the development of new technology.
Important safety notice:
Components identified by
Furthermore, special parts which have purpose of fire-retardant (resistors), high-quality sound (capacitors), low-noise
(resistors), etc. are used. When replacing any of components, be sure to use only manufacture´s specified parts shownin
theparts list.
Important safety notice:
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by
manufacture r’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire, or other hazards. Do not modify the original designwithout permission of
manufacturer.
Caution!
IC and LSI are sensitive to static electricity.
Secondary trouble can be prevented by taking care during repair.
Cover the parts boxes made of plastics with aluminum foil.
Ground the soldering iron.
Put a conductive mat on the work table.
Do not touch the legs of IC or LSI with the fingers directly.
mark have special characteristics important for safety.
in the schematic diagrams. It is essential that these critical parts should be replaced with
48
Page 49

16 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
16.1. POWER SUPPLY SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (1 / 2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL)
A
ZA1111
F
E
D
C
B
A
COLD
HOT
!
P1001
K2AA2B000011
C1021
220P
K4CZ01000027
ZA1112
12 3
RMCC0001-1
K1005
K1006
CL1004
R1072
C1071
0.01
ZA1001
EYF52BCY
!
F1001
K5D162BLA013
125V/250V 1.6A
D1072
MA2C16500E
CL1001
!
C1001
0.1
ZA1002
EYF52BCY
C1092
50V 10
24 9
C0DACZH00033
1357
D1061
MA2C16500E
C1051
0.0015
VA1002
!
CL1005
IC1021
R1051
20K
ERZVA5Z471
6
K1091
!
C1003
*
L1001
!
ELF15N003A
R1002
CL1007
R1001
43
470K
2
1
470K
C1011
450V 10
D1082
MA2C16500E
R1083
27K
R1082
R1062 R1061
18K
D1051
MAZ40910HF
C1081
0.0015
CL1002
!
C1002
0.1
CL1006
C1012
450V 10
R1071
4.3K
R1081
3.3K
C1082
0.0047
R1041 D1041
C1041
50V 100
C1061
100P
4.7
D1011
B0EDKT000009
34
R1031
68K
D1071
MAZ41000MF
MAZ40910HF
R1084
3.3K
B0HAGM000006
1.8K
12
C1031
0.0033
D1031
B0HADV000001
D1081
G4D2A0000265
2
34
56789
B3PBA0000241
4
3
!
!
!
T1021
C1004
1000P
Q1051
K1171
D1152
B0JAMK000023
D1151
B0JAMK000023
D1111
B0JAMG000013
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
10
1
2
C1111 C1112
10V 680 10V 1000
D1141
B0JAMK000023
CAR
IC1101
C0DAEMB00003
G0A100HA0023
B0JAMG000013
R1105
2.2K
R1104
1K
32
1
D1171
B0JAME000037
C1151
25V 330
L1111
D1121
C1102
C1101
0.68
1K
L1151
G0A220GA0026
IP1112
C1121
6.3V 680
K1141
0.1
R1107
10K
R1106
C1171
10V 100
R1115
100K
R1101
180
R1102
4.7K
R1103
4.7K
C1153
25V 330
D1153
B0EAKM000122
C1115
0.1
K1172
L1131
G0C330KA0065
Q1115
B1DHDD000029
43
52
61
QR1115
B1GBCFNN0043
B0EAKM000117
C1141
25V 100
R1116
D1122
K1155K1154
G0C100JA0048
1K
C1116 C1117
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
L1117
C1122
6.3V 2200
C1197
C0DBZHG00047
IN
12345
C1155
0.1
6.3V 100010V 220
K1122
L1141
G0C330KA0065
1
VB
VIN
GND CD
123
C1195
1
IC1151
OUTNCGND
ON/OFF
C1154
16V 220
R1191
100K
45
RST
CL1112
CL1104
CL1106
CL1108
IC1195
C0DBFGC00008
C1196
0.01
CL1116
CL1115
CL1111
CL1107
CL1105
CL1101
CL1113
CL1109
C1110
1000P
FLH+
FLH-
NSW+12V
ADGND
M+9V
NPOFF_L
D+5V
A+5V
VGND
DGND
AGND
MGND
NSW+2.7V
NSW-12V
NSW+3.3V
RESET
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
:PO(POWER SUPPLY SECTION)
A
B
:F/AV(FRONT & AV OUT SECTION)
49
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL
POWER SUPPLY SECTION(MOTHER P.C.B.(1/2))SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
54321
9876
Page 50

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
16.2. POWER SUPPLY SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (1 / 2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42PLA)
A
ZA1111
RMCC0001-1
F
K1171
COLD
HOT
ZA1001
F1001
!
C1001
CL1001
0.1
ZA1002
EYF52BCY
VA1002
!
CL1005
CL1007
ERZVA5Z471
R1002
1000K
R1001
1000K
K1001
!
P1001
K2AB2B00000
E
K1002
K1003
K1004
K1005
K1006
CL1004
EYF52BCY
!
K5D162APA008
125V/250V 1.6A
! C1003
1000P
!
L1001
G0B183D00006
43
2
1
C1011
25V 0.33
!
C1002
CL1002
0.1
CL1006
C1012
450V 10
D1011
B0EDKT000009
34
12
G4D2A0000265
2
34
!
T1021
D1152
B0JAMG000031
B0JAMG000031
D1151
D1171
B0JAME000037
C1151
25V 330
C1171
10V 100
L1151
G0A220GA0026
D1153
B0EAKM000122
C1153
25V 330
K1172
L1131
G0C330KA0065
CL1116
CL1115
CL1111
CL1112
IC1151
C0DBZHG00047
IN
OUTNCGND
ON/OFF
12345
K1155K1154
C1155
0.1
C1154
16V 220
CL1107
C1110
1000P
FLH+
FLH-
NSW+12V
ADGND
M+9V
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
D
C
B
A
C1021
0.001
ZA1112
K4CZ01000027
12 3
C1071
6800P
D1072
MA2C16500E
C1092
50V 10
24 9
IC1021
C0DACZH00032
1357
D1061
MA2C16500E
C1051 R1051
0.0015
20K
6
R1062
10K
D1051
MAZ40910HF
MA2C16500E
R1083 C1081
470P
D1082
R1071
2.2K
C1082
0.004727K
C1041
50V 100
C1061
470P
R1081
3.9K
R1041
27K
D1071
MAZ41000MF
MAZ40910HF
R1084
D1041
B0HAGM000006
R1061
3.3K
D1081
56789
C1004
!
2200P
!
Q1051
B3PBA0000241
1
4
2
3
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
10
D1111
B0JAME000033
C1111 C1112
10V 680 10V 1000
D1141
B0JAMG000031
R
A
C
IC1101
C0DAEMB00003
2
3
1
L1111
G0A100HA0023
D1121
B0JAME000033
R1105
2.2K
R1104
1K
C1101
0.33
K1141
C1121
IP1112
R1106
1K
R1115
100K
R1101
180
R1102
4.7K
R1103
4.7K
C1115
0.1
Q1115
B1DHDD000029
43
52
61
R1116
QR1115
B1GBCFNN0043
D1122
B0EAKM000117
C1141
25V 100
AV
NPOFF_L
AV
L1117
G0C100JA0048
1K
C1116 C1117
C1122
6.3V 22006.3V 680
6.3V 100010V 220
C1197
1
C1195
K1122
L1141
G0C330KA0065
VB
RST
VIN
GND CD
123
1
R1191
100K
45
IC1195
C0DBFGC00008
C1196
0.01
CL1105
CL1104
CL1106
CL1108
CL1101
CL1113
CL1109
D+5V
A+5V
VGND
DGND
AGND
MGND
NSW+2.7V
NSW-12V
NSW+3.3V
RESET
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
:PO(POWER SUPPLY SECTION)
A
B
:F/AV(FRONT & AV OUT SECTION)
50
DVD-S42PLA
POWER SUPPLY SECTION(MOTHER P.C.B.(1/2))SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
54321
9876
Page 51

16.3. FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (2 / 2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42EE)
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
RF SIGNALAUDIO MAIN SIGNALVIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
B
F
FLH+
PO
FLH--
PO
E
NSW-12V
PO
NPOFF_L
PO
D
RESET
PO
NSW+3.3V
PO
DGND
PO
C
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
VGND
ADGND
MGND
AGND
NSW+12V
A+5V
D+5V
B
NSW+2.7V
PO
M+9V
PO
PO
W
E
R_S
W
EVQ11G05R
S6152
R6101 150
D6101
LNJ201LPQJA
A
POWER-SW P.C.B.
R6081
D6081
MAZ40910LF
G0C101JA0019
R6061
100K
JW6102
KEY-SCAN1 KEY-SCAN1
DGND
STBTLED STBTLED
(2mm FLAT CABLE) (2mm FLAT CABLE)
L6001
CL6007
1
2
3
180
B1ABGC000011
R6086
100K
K6009
K6001
0
C6006
50V 10
0.01
K5H252Z00003
OPERATION P.C.B.
JW6102
1
2
DGND
3
Q6085
R6085
8.2K
A5
C6005
A6
A7
R6021*
12
IP4751
R6151 1.2K
E
EVQ11G05R
S
Y
LO
LA
P
S6161
OPEN/C
S6151
EVQ11G05R
F-
24
1
CL6081
FLHEATER
R6161
EVQ11G05R
SE
AU
P
S6171
SD
O
K
QUIC
S6162
EVQ11G05R
F-
R6023*
R6024* R6026*R6022*
1.2K
P
TO
S
CL6082
P9
P10
P11
P12
P13
P14
P15
P16
4G
4G
P16
P15
567 89
CL6083
CL6084
4G
P16
P15
R6204
100K
R6202
100
R6025*
JW6101
REZ1708REZ1709REZ1709
R6171
1.2K
EVQ11G05R
S6172
5
4
3
2
1
STBTLED
DGND
KEY-SCAN1
KEY-SCAN2
KEY-SCAN3
DP6081
A2BA00000229
4G
P14
CL6085
P14
CL6086
3G
P13
P12
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 31 32
CL6087
CL6088
CL6089
3G
P13
P12
R6040
R6050 R6060
10K 10K 10K
C6040 C6050
0.01 0.01 0.01
TO OPERATION P.C.B.
PJ6101
K1MP05A00004
5
STBTLED
4
DGND
KEY-SCAN1
3
2
KEY-SCAN2
KEY-SCAN3
1
P11
P10P9P8
CL6090
CL6091
P11
P10
P9
P8P7P6P5P4P3P2
48
495051525354555657585960
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
VPP
TXD,SBO0
RXD/SBIO
SBT0
SBO2/SDA
61626364
SB12/AN7
SBT2/SCL
AN4
AN5
123456789
C6060
CL6026
CL6027
CL6028
CL6029
CL6030
3G
2G
CL6092
CL6093
CL6094
2G
P8
SEG1/DGT6
SEG2/DGT5
SEG3/DGT4
SEG4/DGT3
SEG5/DGT2
[48]SEG7/DGT0
[47]SEG6/DGT1
IC6001
MN101C87AAG
[64]BUZZER/AN6
VREF+
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
0.1C6002
2G
P7P6P5
CL6095
CL6096
CL6097
P7P6P5
P1
2G1G3G
4G
FLHEATER
DGT9
DGT8
DGT12
DGT11
DGT10
[34]DGT14
SEG0/DGT7
[33]DGT15
[17]TM1IO
[16]RMOUT/TM0IO
XOXIVSS
OSC1
OSC2
VDD
10111213141516
CL6001
2
C6001
6.3V 100
X6001
H2D800400009
A5
A6
K6008
0
FP3501
TO PS8101
K1KA14A00135
MODULE P.C.B.
DOP_CPU-STAT
1G
P4
P3
CL6098
CL6099
1G
P4
P3
333435363738394041424344454647
DGT16
DGT17
DGT13
VDD3
VDD2
LED2
LED1
LED0
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ1/ACZ
IRQ0
TM71O
TM31O
TM21O
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
XRST
MMOD
10K
R6004
10K
R6006
C6003
0.01
13
A7
11
121314
10
TRAY_DRV
TRAY_MUT
DOP_CPU-CLK
DOP_CPU-CMD
1G
R4302
10K
M+9V
MGND
P2
CL6100
DGND
P1
CL6102
P2
P1
CL6005
K6007
CL4303
A+5V
AGND
NSW+2.7V
1G
DGND
F+
CL6103
R6011
10K
R6009
L6131
C6132
0.1
B3RAD0000115
B1ABDF000033
123456789
D+5V
DGND
F+
R6066
10K
IR6131
100K
GND
C6081
0.01
123
VCC
Q4302
R6072
47K
R6071
30K
ROUT
K3502
K3601
K3503
K3504
A1
A2
A3
A4
A3
A4
FP3502
TO PS8301
K1KA20A00215
MODULE P.C.B.
1
2
3
4
5
6
CL4903
R4309
C4313
0.1
IP3802
F
22K
D4301
MAZ40560HF
2
C4323
35V 220
C4314
0.1
IC4301
9.1K
CL4904
C0ABBB000230
R4355
9.1K
R4331
9.1K
C4324
35V 220
C4315
0.1
R4301
270
CL4301
K4904
CL4902
R4332
:PO(POWER SUPPLY SECTION)
A
B
:F/AV(FRONT & AV OUT SECTION)
K4903
CL4901
K4901
2.2K
MIX-R
ADGND
123456789
MIX-L
R4320
2.2K
QR4302
UNR211H00L
K5H501Z00005
1
R4304
QR4306
B1GBCFJA0017
A2
A1
C4291
10V 1000
L4291
G0C220KA0065
11
121314151617181920
VGND
CB/PB/B
10
CR/PR/R
OPEN_SW
CLOSE_SW
ADAC5V
AUDIODIGTAL
ADGND
ZFLAG&AMUTE
A-REF
ADGND
Y
C
VGND
VGND
VGND
Y/PY/G
C4337
82P
R4356 15K
7
82P
C4336
56
VEE
8
VCC
1234
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
DVD-S42EE
FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B.(2/2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
51
54321
9876
Page 52

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
F
E
D
C
B
A
L3502
G0C220JA0019
B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
:PO(POWER SUPPLY SECTION)
A
B
:F/AV(FRONT & AV OUT SECTION)
K3505
0
K3811
K3810
L3501
G0C220JA0019
C3510
C351111
0
0
R3501
22K
QR3502
B1GBCFLL0043
C4591
0.1
6.3V 47
C4781
C3811
C3812
C3813
C3814
C3815
C3816
C3817
C3818
C3819
C3518
C3505
C3506
C3507
C3508
C3509
R4751
1K
K4CZ01000027
6.3V 47
0.1
0.01
1
1
6.3V 22
1
1
1
6.3V 47
0.1
0.01
6.3V 22
1
1
ZA4751
12
K3813
0
3
C4751
25V 47
C9ZB00000461
VCC1
1
2
S1
S2
3
4
CIN
5
MUTE1
6
CVIN
7
SEL
8
YIN
9
BIAS
10
SEL
(BLASACLAMP)
11
PY/YI
12
GND
13
PB/BI
14
MUTE2
15
PRIN
16
VCC2
IC3501
C9ZB00000498
VCC
1
2
CIN
BIAS
3
4
YIN
MUTE
5
6
CYIN
7
GNDT
8
CBIN
C4703
IC3811
COUT
VOUT
YOUT
CYOUT
CBOUT
CROUT
GND2
0.1
CNIN
R4752
R4753
S-DCOUT
CVOUT
CVOUT SAG
YOUT SAG
PYGOUT
PUGOTSAG
PBOUT
PBOUT SAG
PROUT
P/ROUTSAG
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
1K
1K
COUT
GND
YOUT
GND
GND
GND
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
Q4751
B1ABDF000033
R4754
220
R4755
75
C3503
C3504
C4502
K3815
C3804
0.01
K3816
K3817
C3805
C3806
6.3V 47
0.01
IC3802
C1AB00001731
4
IN2
5
GND
6
IN1
VCC
OUT
SW
3
2
1
VIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
D3821
MA3X152A0L
2
820
1
Q3851
R3828
470
C3851
1000P
Q3852
B1ABDF000033
C3852
1000P
K3873
K3874
R3535
75
R3536
75
R3534
C4431
0.1
75
LB3536
J0JBC0000015
LB3534
J0JCC0000186
R3533
75
R4756
10K
R3875
220
R3876
220
R3871
75
R3872
75
R3874
75
R3873
75
J0JBC0000015
J0JBC0000015
C6020
0.1
J0JBC0000015
J0JBC0000015
3
R3826
18K
Q3801
R3827
B1ABDF000033
22K
R3521
22K
QR3501
B1GBCFLL0043
C3516
6.3V 1000
C3502
0.01
IC3502
C1AB00001935
1
4
IN2
5
GND
6
IN1
1
0.1
C4752
25V 47
VCC
OUT
SW
3
2
1
C4414 25V 47
C4415
R4756
10K
25V 47
R3821
22K
C3512
C3514
6.3V 1000
C3513
6.3V 1000
R4423
47K
6.3V 1000
R4428
680
R4422
47K
R3823
R3824
QR3821
B1GBCFLL0043
123
R4452
B1ABDF000033
820
R4451
820
B1ABDF000033
R4429
680
4.7K
B1GDCFJJ0041
22K
456
R3822
22K
Q4422
Q4423
QR3823
Q3821
XN0460100L
QR3822
B1GBCFLL0043
R4459
C4427
1000P
R4460
C4423
1000P
R3852
220
220
R3851
680
B1ABDF000033
R3853
820
R3854
680
LB3871
J0JBC0000015
LB3872
J0JBC0000015
LB3874
LB3873
C4501
1000P
K3872
0
LB3535
C4432
0.1
LB3533
AUDIO MAIN SIGNAL
JK3871
K1FB121B0016
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
ZA4754
RMCC0027
JK4401
K2YZ07000005
17
16
15
14
13
12
4
11
10
7
5
9
6
8
3
2
1
C3871
100P
C3872
100P
R3877
75
R3878
75
PB
PR
VGND
Y
V
VGND
METAL_GND
CK
CK_GND
Y{S}
C{S}
MIX-L
MIX_R
A_GND
R3825
4.7K
DVD-S42EE
FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B.(2/2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
52
131211109
17161514
Page 53

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
16.4. FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B. (2 / 2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
RF SIGNALAUDIO MAIN SIGNALVIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
D
C
F
E
B
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
FLH+
FLH--
NSW-12V
NPOFF_L
RESET
NSW+3.3V
DGND
VGND
ADGND
D6081
MAZ40910LF
R6081
L6001
G0C101JA0019
CL6007
180
K6009
K6001
C6006
0.01
R6086
100K
0
C6005
50V 10
R6061
100K
1
CL6081
Q6085
B1ABGC000011
R6085
8.2K
FLHEATER
A5
A6
A7
R6021*
R6022*
F-
F-
24
R6023*
R6024*
4G
P16
P15
567 89
CL6082
CL6083
CL6084
4G
P16
P15
P9
P10
P11
P12
P13
P14
P15
P16
R6204
100K
R6202
100
R6025* R6040
R6026*
DP6081
A2BA00000229
4G
CL6085
4G
P14
CL6086
P14
3G
P13
P12
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 31 32
CL6087
CL6088
CL6089
3G
P13
P12
R6050
10K
10K
C6050
C6040
0.01
0.01
3G
P11
P10
P9
CL6090
CL6091
P11
P10P9P8
P8P7P6P5P4P3P2
49
SEG8
50
SEG9
51
SEG10
52
SEG11
SEG5/DGT2
SEG12
53
[48]SEG7/DGT0
54
SEG13
[47]SEG6/DGT1
SEG14
55
56
SEG15
VPP
57
TXD,SBO0
58
59
RXD/SBIO
[64]BUZZER/AN6
SBT0
60
61
SBO2/SDA
62
SB12/AN7
SBT2/SCL
63
64
AN3
AN4
AN5
123456789
R6060
10K
C6060
0.01
2G
P8
CL6092
CL6093
2G
SEG2/DGT5
SEG3/DGT4
SEG4/DGT3
IC6001
MN101C87AAG
AN0
AN1
AN2
2G
P7P6P5
CL6094
CL6095
CL6096
P7P6P5
P1
2G1G3G
4G
FLHEATER
DGT9
DGT8
DGT11
DGT10
[34]DGT14
SEG0/DGT7
SEG1/DGT6
[33]DGT15
[17]TM1IO
[16]RMOUT/TM0IO
OSC1
OSC2
VDD
VREF+
10 11 12 13 14 15 16
C6002 0.1
C6001
6.3V 100
X6001
H2D800400009
1G
CL6097
DGT16
DGT17
DGT13
DGT12
IRQ1/ACZ
TM71O
TM31O
TM21O
MMOD
XOXIVSS
CL6001
R6006 10K
2
P4
CL6098
1G
33343536373839404142434445464748
VDD3
VDD2
LED2
LED1
LED0
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ0
XRST
C6003
0.01
13
P3
CL6099
P4
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
R6004
1G
P3
10K
P2
P1
CL6100
CL6102
P2
CL6005
B3RAD0000115
P1
K6007
R4302
10K
1G
F+
CL6103
R6011
10K
IR6131
C6132
0.1
F+
C6081
0.01
R6012
10K
R6066
100K
R6009
10K
L6131
123
GND
VCC
Q4302
B1ABDF000033
ROUT
R6072
47K
R6071
30K
CL4903
C4337
82P
A1
A2
A3
A4
R4304
2.2K
CL4901
R4320
22K
QR4302
B1GDCFEJ0008
QR4306
B1GBCFJA0017
K4903
K4901
CL4301
R4309
22K
C4313
0.1
R4301
270
D4301
MAZ40560HF
C4323
35V 220
C4324
35V 220
C4314
C4315
K4904
0.1
IC4301
C0ABBB000230
0.1
C4336
R4355
15K
CL4909
9.1K
R4331
9.1K
R4332
R4356 15K
8
7
VCC
1234
82P
56
VEE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MGND
PO
AGND
PO
NSW+12V
PO
A+5V
PO
D+5V
PO
B
NSW+2.7V
PO
M+9V
PO
P
OW
ER
_S
W
EVQ11G05R
S6152
R6101
(2mm FLAT CABLE) (2mm FLAT CABLE)
150
D6101
LNJ201LPQJA
A
POWER-SW P.C.B.
OPERATION P.C.B.
JW6102
JW6102
REZ1709REZ1709
1
KEY-SCAN1 KEY-SCAN1
DGND
STBTLED STBTLED
1
2
2
DGND
3
3
12
IP4751
K5H252Z00003
R6151 1.2K
E
S
Y
LO
LA
P
S6151
OPEN/C
EVQ11G05R
S6161 EVQ11G05R
SE
EVQ11G05R
AU
P
EVQ11G05R
S6171
SD
K O
S6162
QUIC
STBTLED
DGND
KEY-SCAN1
KEY-SCAN2
KEY-SCAN3
R6171
1.2K
1.2K
R6161
P
S6172
EVQ11G05R
STO
JW6101
REZ1708
TO OPERATION P.C.B.
PJ6101
K1MP05A00004
5
5
STBYLED
4
4
DGND
3
KEY-SCAN1
3
2
2
KEY-SCAN2
1
KEY-SCAN3
1
CL6026
CL6027
CL6028
CL6029
CL6030
A6
K6008
0
FP3501
TO PS8101
K1KA14A00135
MODULE P.C.B.
DOP_CPU-STAT
A7
A5
11
121314
10
MGND
TRAY_DRV
TRAY_MUT
DOP_CPU-CLK
DOP_CPU-CMD
M+9V
DGND
NSW+2.7V
AGND
A+5V
D+5V
DGND
123456789
DGND
9
10
11
K3601
K3502
K3503
K3504
A2
A3
A4
A1
FP3502
TO PS8301
K1KA20A00215
MODULE P.C.B.
IP3802
K5H501Z00005
1
C4291
10V 1000
L4291
G0C220KA0065
VGND
VGND
CB/PB/B
11
12131415161718
CR/PR/R
CLOSE_SW
10
ADAC5V
OPEN_SW
AUDIODIGTAL
ADGND
20
19
Y
C
VGND
VGND
Y/PY/G
A-REF
ADGND
ZFLAG&AMUTE
MIX-R
123456789
MIX-L
ADGND
CL4902
2
F
:PO(POWER SUPPLY SECTION)
A
B
:F/AV(FRONT & AV OUT SECTION)
DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B.(2/2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
54321
9876
53
Page 54

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
B
L3501
1
F
2
3
4
5
E
6
G0C220JA0019
C3510
1
C3511
1
R3501
22K
C3518 6.3V 47
0.1
C3505
0.01
C3506
C3507
6.3V 22
1
C3508
1
C3509
IC3501
C9ZB00000498
VCC
1
CIN
2
3
BIAS
YIN
4
MUTE
5
CYIN
6
GNDT
7
CBIN
8
COUT
VOUT
YOUT
CYOUT
CBOUT
CROUT
GND2
CNIN
C3517
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
K3501
0
0.1
C3516
6.3V 1000
C3515
6.3V 1000
6.3V 1000
C3514
C3513
6.3V 1000
C3512 6.3V 1000
K3874
K3873
VIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
AUDIO MAIN SIGNAL
K3872
0
C4501
1000P
D
C
B
R3535
75
R3536
75
R3534
C4414
7
8
9
10
25V 47
C4415
25V 47
C4781
6.3V 47
C4591
0.1
C4703
0.1
R4752
1K
R4422
47K
R4423
47K
R4428
680
R4452
820
R4451
680
R4429
680
Q4422
B1ABDF000033
Q4423
B1ABDF000033
C4427
1000P
C4423
1000P
R4459
220
R4460
220
C4431
0.1
75
R3533
75
R3532
75
R3522
10K
R3531
75
LB3536
J0JBC0000015
LB3534
J0JCC0000186
LB3535
J0JBC0000015
C4432
0.1
LB3533
J0JBC0000015
LB3532
J0JBC0000015
LB3531
J0JBC0000015
JK4401
K2YZ19000001
17
16
15
14
13
12
4
11
10
7
5
9
6
8
3
2
1
ZA4754
RMCC0027
PB
PR
VGND
Y
V
VGND
METAL_GND
CK
CK_GND
Y{S}
C{S}
MIX-L
MIX_R
A_GND
A
C4751
R4751
25V 47
11
ZA4751
K4CZ01000027
123
1K
R4753
1K
Q4751
B1ABDF000033
R4754
220
R4755
75
C4502
0.1
C4752
25V 47
R4756
10K
C6020
0.1
DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
FRONT & AV OUT SECTION (MOTHER P.C.B.(2/2)) SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
131211109
17161514
54
Page 55

16.5. MODULE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
E
D
C
B
A
F
TO FP3501
MOTHER P.C.B.
(F/AV SECTION)
PS8101
K1KB14A00074
DGND
D+5V
DGND
A+5V
AGND
D+2.7V
DGND
M+9V
MGND
TRAY_DRV
TRAY_MUT
DOP_CPU-CLK
DOP_CPU-CMD
DOP_CPU-STAT
TO OPTICAL
PICKUP UNIT
FP8531 K1MN26AA0041
T+
F+
FTHFM
TA(DVD)
TB(DVD)
TD(DVD)
TC(DVD)
FE2(DVD/CD)
FE1(DVD/CD)
GND
RF
VREF2(RF-)
PIN(DVD)
LDCD
LDGND
LDDVD
GND(OEIC)
VREF1
VCC
SUB2
SUB1
PIN(CD)
SUBSEL
GND(VRCD)
TO MECHANISM UNIT
FP8251 KIMN06AA0076
SPMSPM+
TRVMTRVM+
DGND
TRV_INNER_SW
S2601
K0L1BA000078
CLOSE SW
1
2
S2602
K0L1BA000078
OPEN SW
1
2
TO FP3502
MOTHER P.C.B.
(F/AV SECTION)
PS8301
K1KB20A00165
MIX-L
ADGND
MIX-R
ADGND
A-REF
ZFLAG & AMUTE
ADGND
AUDIODIGTAL
ADAC5V
OPEN-SW
CLOSE-SW
CR/PR/R
VGND
CB/PB/B
VGND
Y/PY/G
VGND
Y
VGND
C
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0.1C8537
1
2
3
4
5
6
L6AAYYYC0001
3
4
3
4
C8571 10
R8531 1.5K
C8531 100P
C8533 0.1
C8530
0.1
0.1C8536
MT2601
LD-MOTOR
TL2602
LB8261 0
LB8262
LB8691
LB8693
LB8692
C8572 0.1
LB8257 0
LB8259
LB8260
LB8258
LB8571 J0JBC0000042
LB8561 J0JBC0000042
LB8551 J0JBC0000042
LB8531 0
LB8530 J0JHC0000097
TL2601
TO MODULE P.C.B.
FP2601
K1MN07B00009
LOADING MOTOR P.C.B.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
LB8421 0
LB8422
LB8423
LB8424
LB8491
LB8305 J0JBC0000042
LB8304 J0JBC0000042
LB8303 J0JBC0000042
LB8301 J0JBC0000042
LB8302 J0JBC0000042
K8105
0
0
100
100
100
0
0
0
LDLDLD+
LD+
CLOSE-SW
GND(SW)
OPEN-SW
0
0
0
0
B1
B2
B3
B4
C8550
6.3V 33
TO LOADING MOTOR P.C.B.
FP8252
K1MN07AA0076
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
LDLDLD+
LD+
CLOSE-SW
GND(SW)
OPEN-SW
LB8256
0
LB8255
0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
RX8532
56x4
1
3
5
7
RX8534
56x2
RX8531
56x2
RX8533
56x2
R8532 2.2K
R8533 0
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
QR8420
B1GBCFJJ0040
(MUTE)
2
4
6
8
3124
3124
3124
CL8435
E00
C8532
220P
K8421
VIN1
VIN2
VIN4
VIN3
VIN8
VIN7
VIN6
VIN5
B6
B7
B10
RF SIGNALAUDIO MAIN SIGNALVIDEO MAIN SIGNAL
A6
C8251
6.3V 220
C8252
0.1
PVCC12
PVCC45
VO3 -
PVCC3
987654321
VCOM
VOUTR
MD
MC
B17
PGND
VO3 +
AGND
SCK
R8421 0
B18
B19
A7A10
VO4 -
VO2 -
VCC
DATA
B20
A4
10111213141516
VO4 +
VO2 +
NC
BCK
B21
9
87654321
VO5 -
VO1 -
NC
LRCK
A5
151617181920213022232425262728
C8253
VO5 +
VO1 +
0.1
C8111 0.1
IC8111
C0CBCBD00018
(REG.D+3.3V)
C8258
0.1
TL8111
K8251
0
C8424
0.1
C8428
0.1
CODBEYY00016
NC
VINVO
NC
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
NC
GND
IC8151
5678
CONT
CN
4321
C8113
470P
C8112
1
C8152
VCC
CTL
OUT
ADJ
GND
5214
3
R8151
1K
1
54
6
321
K8325
0
K8321
0
K8331
0
K8335
0
K8341
0
C8151
10
RX8111
22Kx2
QR8111
XP0621400L
(SWITCHING)
4213
B29
R8325
68
R8326
0
B28
R8321
68
R8322
0
B27
R8331
68
R8332
0
B26
R8335
68
B25
R8341
68
OPIN+
MUTE2
B13
GND
VIN1
A11
VIN5
VIN2
B14
A12
VIN4
VIN3
29 1413121110
CL8252
CL8251
VOUTL
ZEROR
XMS
ZEROL
B15
B16
K8103
0
K8101
0
K8102
00
L8550
G1C100KA0055
B8
B9
CL8571
B5
QR8571
B39
0
6.3V 100
C8421
R8420
2.2K
K8104
D8571
MA2J72800L
B1GDCFEC0001
C8422
0.1
R8261
82K
R8263
82K
C8255
16V47
C8256
0.1
C8257
0.1
C8423
6.3V 33
R8262
15K
K8261
0
C8261
0.1
C0GBG0000054
(MOTOR DRIVE)
CL8434
R8264
IC8251
CL8262
CL8261
(AUDIO D/A CONVERTER)
15K
BIAS2MUTE3
CL8428
CL8427
CL8426
CL8425
CL8424
CL8423
CL8422
CL8421
OPIN-
OPOUT
MUTE1
BIAS1
B12
B11
IC8420
C0FBBK000049
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
MODULE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
55
54321
9876
Page 56

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
1
2
3
LB8001
F
J0JHC0000097
CL8052
CL8064
CL8051
CL8065
CL8068
CL8066
CL8069
C8017
0.1
E1
E2
8
9
10
E31
C8014
0.1
E32
E33
E35
E37
C8015
0.1
RX8032
22x2
42
C8011
C8001
6.3V 100
RX8031
22x2
31
24
13
4V 330
E20
E22E21
C8003 0.1
R8011 22
E19E18E17
R8012 22
C8004
0.1
E12
E13
E14
E16
R8013 22
C8012 0.1
E11
E7
E5
E3
E6
E4
E9
C8016
0.1
E10
E8
E15
E23
E24
E25
C8013 0.1
E27
E29
E30
E28
E26
E36
E34
11
E
D
C
B
A
LB8011
J0JHC0000097
4
5
6
7
CL8053
C8018
0.1
CL8063
CL8054
CL8062
CL8055
C8019
0.1
CL8061
CL8056
CL8060
CL8057
CL8059
CL8058
C8020
0.1
D37
B32
B31
C8006
0.1
D36
D35
D34
D33
D32
D31
D30
D29
D28
D27
D26
C8021
0.1
D25
D24
D23
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
C8007
0.1
D17
D16
D15
D14
D13
D12
C8022
0.1
D11
B30
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
MDQ18
1
VSS
2
VDD33
3
MDQ28
4
MDQ19
5
MDQ27
6
MDQ20
7
VDD33
8
VSS
9
MDQ26
10
MDQ21
11
MDQ25
12
MDQ22
13
MDQ24
14
MDQ23
15
VSS
16
VDD33
17
EXADT0
18
NEXCE
19
NEXOE
20
VSS
21
VDD12
22
EXDT0
23
EXDT8
24
EXDT1
25
EXDT9
26
EXDT2
27
EXDT10
28
EXDT3
29
EXDT11
30
EXDT4
31
EXDT12
32
EXDT5
33
VSS
34
VDD33
35
EXDT13
36
EXDT6
37
EXDT14
38
EXDT7
39
EXDT15
40
EXADR16
41
EXADT15
42
EXADT14
43
VSS
44
VDD12
45
EXADT13
46
EXADT12
47
EXADT11
48
EXADT10
49
EXADT9
50
EXADT8
51
VSS
52
VDD33
53
EXADR19
54
NEXWE
55
EXADR18
56
EXADR17
57
EXADT7
58
EXADT6
59
EXADT5
60
EXADT4
61
EXADT3
62
EXADT2
63
EXADT1
64
R8002
47K
MDQ17
MDQ29
P1
P0
B33
B34
MDQ30
P2
C8023
0.1
MDQ31
MDQ16
VDD33
VSS
DQM3
P3
2
4
RX8691
10Kx2
1
3
RX8001
10Kx2
DQM2
P4
CL8021
CL8020
1
3
2
4
VDD33
P5
CL8022
VSS
P6
MA3
P7
223224225226227228229230231232 193194195196197198199200201202203204205206207208209210211212213214215216217218219220221222233234235236237238239240241242243244245246247248249250251252253254255256
VDD12
DRV4
B12
VSS
DRV3
B10
MA9
DRV2
BA0
DRV1
MA11
DRV0
NRAS
NCSM
VDD33
VSS
CL8231
CL8232
VSS
MCKI
NCAS
IC8001
MN2DS0009VP
(DV3.2)
MONI5
MONI6
MONI7
CL8017
CL8016
R8231
22K
R8232
7.5K
VDD33
MONI4
CL8015
CL8014
C8231
0.1
C8232
0.1
MCK
MONI3
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877767574737271706968676665
CL8013
VSS
MONI2
CL8012
B14
B13
NWE
MONI1
CL8011
DQM0
DQM1
VDD12
PLFIL1
AVDDD
MONI0
CL8010
C8502 0.1
C8527 0.033
MDQ8
MDQ7
VREFH7
AVSSD
C8523 0.1
VSS
MDQ6
VDD33
AVSSC
CCAPA
VREFL7
C8524 0.1
C8525 5600P
R8230
8.2K
MDQ5
MDQ9
MDQ10
ANAMONI1
AVDDC
CDATA
CL8002
CL8001
CL8512
CL8511
C8512
C8503 0.1
C8526 0.018
MDQ3
MDQ4
MDQ11
RFINP
RFINN
ANAMONI2
1
C8511 1
B8
B9
VSS
VDD33
MDQ12
VIN4RF
VIN2RF
VIN1RF
C8516 0.1
C8514 0.1
C8513 0.1
VIN4
VIN2
VIN1
MDQ1
MDQ2
MDQ13
VREFH5
AVDDB
VIN3RF
C8521 0.1
C8504 0.1
C8515 0.1
VIN3
MDQ0
MDQ15
MDQ14
LPC1
AVSSB
VREFL5
C8522 0.1
B1
B36
VDD33
LPCO1
B6
VSS
LPC2
B37
TRCST
TRCDATA3
VREFH
LPCO2
128127126125124123122121120119118117116115114113112111110109108107106105104103102101100
B39
B4
TRCDATA1
TRCDATA2
TRCDATA0
TRCCLK
EXTRG0
SDATA
SCLOCK
EXTRG1
VSS
VDD33
VDIO0
VDIO1
VDIO2
VDIO3
VDIO4
VDIO5
VDIO6
VDIO7
VDD33
VSS
IECOUT
ADOUT0
ADOUT1
ADOUT2
ADOUT3
SRCK
LRCK
DACCK
VDD12
VSS
OSCO
OSCI
AVSSG
AVDDG
AVSSE
AVDDE
DAC5OUT
DAC4OUT
AVSSF
COMP2
IREF1
VREF
COMP1
AVDDF
DAC1OUT
DAC2OUT
DAC3OUT
AVDDH
PWM0
PWM1
AVSSH
AD4
AD2
AD1
AD0
VIN1
VIN2
VIN4
VIN3
VIN8
VIN7
VIN6
VIN5
VIN9
VIN10
VHALF
TL8201
C8529
1
192
191
190
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
175
174
173
172
171
170
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
158
157
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
C8505
0.1
C8528
1
C8025 0.1
C8026 0.1
C8305 0.1
C8304 0.1
C8312 1
C8202 0.1
VIN1
VIN2
VIN4
VIN3
VIN8
VIN7
VIN6
VIN5
VIN5
VIN6
C8501
6.3V 100
VDD33
VSS
0.1
100K
VDD12
MA8
MA10
FG
NRST
C8024 0.1
DRV5
CL8230
B11
B7B35B5E00B16B17B15
MA7
MA0
MA6
MA1
MA5
MA2
MA4
P14
P13
P12
P11
P10
P9
P8
C8008
R8004
47K
R8601
R8003
47K
C8602
0.015
A1A3A2
BA1
VSS
CL8031
CL8028
CL8027
CL8026
CL8025
CL8024
CL8041
CL8023
CL8030
C8005 0.1
C8313 1
R8041
33
R8313
9.1K
CL8541
C8541
4700P
6.3V 100
G1C100K00019
MA2J11100L
G1C100K00019
C8201
L8501
D8211
L8201
R8401
100
R8314
390
R8541
15K
CL8211
R8621
A8
390
C8622
18P
X8621
H0J270500080
B29
B28
B27
B26
C8311
B25
R8622
1M
B38
18PC8621
0.1
CL8221
CL8213
CL8212
C8302
6.3V 33
R8312
C8225
1200P
C8221
1200P
C8211
1200P
C8306
0.1
C8203
0.1
J0JBC0000042
1K
R8225
8.2K
R8221
8.2K
R8211
10K
RX8403
100x2
1
34
RX8401
100x2
1
34
LB8401
R8311
2.4K
C8303
0.1
CL8226CL8225
C8226
1200P
CL8222
C8222
820P
2
2
B20
B21
B18
C8401
15P
L8302
G1C100K00019
L8301
G1C100K00019
C8301
6.3V 220
A11
A12
A10
B19
12
13
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
MODULE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
56
131211109
17161514
Page 57

F
E
D
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
8
9
10
11
IC8051
C3ABPG000133
(SD RAM)
E18
RX8017
C8057
1
E4
2468
82x4
G1
G31
VSSVDD
1
3
DQ15
DQ0
E1E2E3
G4G3G2
G33
VSSQ
VDDQ
E8
82x4
RX8016
G5
G27
DQ14
DQ1
2468
3157
DQ13
VDDQ
VSSQ
DQ2
E5E6E7
G8G7G6
G29
RX8015
G23
DQ12
DQ3
82x4
E14
G10
G9
DQ11
DQ4
E12
E10
3
G11
VSSQVDDQ
9876543
G12
G25
E9
8642
751157
DQ10
DQ5
RX8020
4353254
DQ9
DQ6
22x2
G13
E13
E11
1243
G14
VDDQ
VSSQ
DQ8
DQ7
22x2
RX8018
C8056
2200P
VSS
VDD
1413121110
E17
G15
G16
40414245 4446474849505152
E16
3421
NC
LDQM
16 17 18 19 20 21 2215
RX8019
/WE UDQM
22x2
G17
E21
CLK
/CAS
E20
G18
3421
CKE
/RAS
RX8014
NC
/CS
E25
E24
2468
82x4
157
G20
G19
G9G18G21G19
G10
A11
BA0
E23
E22
3
G22
G21
G11
A8
A9
A10/AP
BA1
82x4
RX8013
G5
32333437 363839 35
A0
E28
2468
157
3
G26
G24
G25
G23
G7
G1
A6A1A5A7
E26
G3
A2
RX8012
A4
A3
E32
2468
82x4
157
3
G28
G29
G27
28293031
VSS
VDD
2724 25 2623
E30
G30
82x4
RX8011
G31
E34
E36
2468
157
3
G34
G32
G33
IC8606
C0EBE0000455
(RESET)
B33
B34
E35
E37
E31
E33
E27
E29
C0EBA0000029
(RESET)
1
2
C8601
0.1
C8606
0.1
NC CD
IC8601
OUT
VDD
GND
NC
123
OUTVDDVSS
54
4
3
CL8612
CL8611
R8611
100
C8611
RX8611
4.7Kx2
3421
0.1
5678
WP
SCL
VCCA0
SDA
IC8611
RFKSDVDS42A
(EEPROM)
GND
A2
A1
4321
C
B
A
C8551
0.1
R8559
15K
TL8510
B2
B38
B3
E19
G15
G26
C8053
0.1
D27
D26
DQ5A19
DQ13
A8
10 11 12 13 14
D1
D11
CL8652
G20
D28
DQ12
A20
B30
DQ4
XWE
B35
DQ7
A11
D23
D14
D24
DQ14
A10
G30
D13
G24
D25
DQ6
A9
D12
G28
G34G32
IC8651
C8052
0.1
D21
D22
CL8654
47 37
VSS
XBYTE
DQ15/A-1
A12
A13
A14
A15 A16
1482
3456789
D16
D19
D18
D17
D15
C8051
1
C8652
C8651
0.1
0.1
D20
RFKWSSA0B160
(FOR EE/GC/GCA/PC/DLA)
RFKWSSA0C160
(FOR GCS/GCU)
(16M FLASH ROM)
12
13
G22
D29
VDD
DQ11
NC
XRESET
D30
G17
C8054
220P
D31
34353639 3840414243444546
DQ3
DQ10
RDY/XBSY
WP/ACC
D32
D10
D33
D34
DQ9
A18 DQ2
A17
16 17 18 19 20 21 2215
D9
D8
DQ1
A7
E15
D35
G14
B31
D36
VSS
DQ0
DQ8
XOE
A3
A4
A5
A6
D5
D7
D4
D6
B32
G2
G6
C8055
1
CL8651CL8653
26272831 303233 29
A0A1
XCE
A2
242523
D3
D2
D37
B37
B36
G4
G8
G12
G13
G16
CL8561
CL8551
R8561
0
R8551
0
Q8561
B1ABDF000018
R8562
1K
C8564
1
Q8551
B1ABDF000018
(LD DRIVE) (LD DRIVE)
R8552
1K
C8554
1
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
C8562
16V 10
C8552
16V 10
R8564
R8563
1K
R8554
R8553
1K
22
R8565
2.2
C8563
6.3V 47
68
R8555
2.2
C8553
6.3V 47
TL8521
TL8511
Q8562
B1ADGB000008
(LD DRIVE)(LD DRIVE)
R8567
R8566
51
56
Q8552
B1ADGB000008
R8557
R8556
51
56
C8561
0.1
R8568
47K
R8558
47K
MODULE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
57
2120191817
25242322
Page 58

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
58
Page 59

17 PRINT CIRCUIT BOARD
17.1. MOTHER P.C.B. (DVD-S42EE)
MOTHER P.C.B.
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
CL6083
CL6084
CL6085
CL6086
CL6088
CL6087
CL6089
CL6082
CL6081
F
K6009
K6001
C6005
D6081
R6081
E
D
C
B
C4591
W220
W221
132
A
CL3507
ZA4751
CL3504
CL3501
CL3503
CL3502
CL3506
CL3505
CL6090
CL6091
W223
C6006
W32
CL6095 CL6099 CL6100
CL6093
DP6081
CL6094
CL6092
W53
W33
W34
W36
W38
W40
W41
W23
W222
R6061
W16
W9
C4501
CL6103
CL6102
49
64 33
IC6001
132
CL6001
16
W35
R6006
C6003
R6071
C6002
W44
W43
W48
CL6201
W258
R6202
W226
R6204
W25
C6050
R6050
C6040
R6040
C6060
R6060
W227
W28
W10
W13
W12
W225
R3851
R3852
Q3851
C3851
R3875
C3872
C3871
W39
W47
R6023
R6021
R6025
CL6096
W37
W21
W52
C4431
CL6097
W54
W57
W49
W22
W24
W14
W228
W19
W20
K3873
R6066
K3874
R6024
R6022
R6026
W27
CL6098
C6001
X6001
W255
W42
W50
W11
R6072
C6081
IR6131
Q6085
W112
W51
R6086
R6085
W230
W55
W56
R6012
R6011
CL6007
48
17
W103
R6009
R6004
W106
W45
W110
W46
W229
CL6202
W26
W29
W30
W31
W17
W18
R3826
Q3801
R3827
QR3823
QR3501
W8
W58
W224
W63
W15
R3854
R3853
K3815
Q3852
C3852
R3876
R3871
W114
W116
W117
K6008
W118
W119
CL6005
K6007
W108
W109
W111
W89
W94
W238
W98
W75
W77
W78
W79
W81
QR3821
QR3822
R3521
D3821
W64
W65
W70
K3816
R3872
LB3871 LB3872
R3828
L6131
W76
W80
L3502
C3811
JK3871
C6132
W72
W120
K3601
FP3501
10
11
12
13
14
FP3502
1011
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
W88
C3819
W231
C3812
W59
K3817
R3874
W115
CL6026
W122
W121
W123
W124
W105
6789
5
4
3
2
1
W90
9
8
7
R4331
6
5
W239
4
W99
W97
3
2
R4332
1
W84
W83
W82
K3810
C3815
W234
K3813
C3818
C3817
C3814
W232
16
IC3811
17 32
W60
W62
W66
W67
C3806
IC3802
64
13
R3873
LB3874
LB3873
R3877
R3878
W113
CL6028
CL6027
W100
W101
W107
4
58
R4356
W85
W235
W236
C3813
K3811
1
W68
W74
C3805
C3804
PJ6101
W91
R4355
C4336
C4337
K3502
K3503
CL6029
15
CL6030
R4304
C4314
W144
R3821
R3822
W93
R3825
C4291
W95
W129
R4320
W155
W156
QR4306
R4309
R4302
CL4303
D4301
R4301
C4324
L4291
W92
W153
W140
W126
K3505
QR3502
W136
Q3821
64
13
R3823
R3824
K3872
W143
C3511
K4904
Q4302
W159
W160
W162
W164
W145
W146
W242
W243
W150
W152
W246
W247
W137
W138
C3510
C3509
C3508
C3506
R3501
W241
891
W125
IC3501
16
W127
W128
W130
W135
C3512
C3513
R3535
R3536
LB3535
W102
W104
W237
C4315
1
W96
IC4301
W87
C3816
W233
W61
W69
W71
W73
W163
LB3536
C3505
K3504
L3501
C3518
QR4302
W154
R3534
CL1109
IP4751
W167
W168
K4901
CL4902
L6001
IP3802
CL1113
CL4901
C3507
W157
C4313
W166
W151
W139
W240
LB3534
W256
CL4301
W158
W257
W262
CL4903
W161
C4323
K4903
W165
W253
W147
W148
W244
W149
W245
W142
W132
W131
C3504
C3503
IC3502
C3502
W134
C3516
C3514
R3533
LB3533
10
7
5
JK4401
41215
K1122
CL1101
W193
CL1104
W183
C1196
IC1195
13
C1195
R1191
CL1111
C1197
L1141
W178
R1101
W261
C1102
R1102
R1103
W180
W177
W173
W141
W174
W176
W175
C4415
C4414
W170
W133
11
7
R4422
R4452
R4428
Q4422
C4427
R4459
8
C4432
6
1
ZA4754
W182
CL1106
W185
W184
L1131
C1141
K1141
R1107
R1106
C1101
IC1101
R1104
W179
W181
C1004
W1
R1061
D1081
W248
R4751
W249
R4752
Q4751
C4752
W169
W171
W172
R4423
R4451
R4429
Q4423
C4423
C4460
2313141617
C1117
CL1112
CL1105
C1122
D1122
C1121
D1121
D1141
R1105
1
Q1051
4
92
W2
R1041
D1041
R1062
C1082
C1061
D1071
K1062
D1061
R1071
R1081
R1084
C4751
R4753
C4703
R4754
R4756
R4755
W250
F1001
ZA1002
ZA1001
C4781
C4502
K1091
L1111
D1111
C1041
W5
W3
CL1004
C6020
CL1108
L1117
W254
IP1112
W191
C1112
C1111
T1021
9
7
6
5
IC1021
4
3
2
1
W4
D1082
C10511
D1051
R1051
R1072
CL1006
R1001
CL1005
K1006 K1005
ZA1111
C1081
D1011
C1002
VA1002
C1001
C1116
CL1007
C1151
W189
C1021
L1001
Q1115
L1151
D1151
C1092
R1083
R1082
D1072
C1071
W187
R1002
P1001
C1115
D1031
R1115
D1152
1810
CL1001
W192
CL1002
R1116
CL1107
C1155
C1153
R1031
C1154
K1171
K1172
W186
QR1115
W188
IC1151
15
CL1115
C1110
C1031
W6
C1012
C1011
C1003
CL1003
CL1116
K1155
K1154
D1153
D1171
ZA1112
C1171
OPERATION P.C.B.
Q_OSD
R6161
S6161S6162 S6171
PLAY PAUSE
W263
W264
STOP
S6172
S6151
R6171
OPEN
W265
R6151
15
JW6101
JW6102
31
POWER SW P.C.B.
POWER_SW
D6101
S6152
R6101
1
3
JW6102
DVD-S42EE
MOTHER P.C.B.(VEP76126C)
OPERATION P.C.B.(VEP70131A)
POWER SW P.C.B.(VEP70132A)
59
54321
9876
Page 60

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
17.2. MOTHER P.C.B. (DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA)
MOTHER P.C.B.
CL6083
CL6084
CL6085
CL6086
CL6088
CL6087
CL6089
CL6082
CL6081
F
K6009
K6001
C6005
D6081
R6081
E
D
C
B
C4591
W220
CL3507
W221
132
A
ZA4751
CL3504
CL3503
CL3501
CL3506
CL3502
CL6090
CL6091
W223
C6006
W32
CL3505
CL6095 CL6099 CL6100
CL6093
DP6081
CL6094
CL6092
W53
W33
W34
W38
W40
W41
W23
W222
R6061
W16
W9
C4501
W36
CL6103
CL6102
C6001
49
64 33
IC6001
132
CL6001
16
W35
R6006
C6003
R6071
C6002
W44
W43
W48
CL6201
W258
R6202
W226
R6204
W25
C6050
R6050
C6040
R6040
C6060
R6060
W227
W28
W10
W13
W12
W225
CL6096
W39
W47
R6023
R6021
R6025
CL6097
CL6098
W52
W54
W57
X6001
W255
W228
W37
R6066
W42
W49
W50
W19
W20
W21
W22
W24
R6024
R6022
R6026
W27
C4431
W11
W14
K3874
K3873
R6072
C6081
W56
48
17
W46
W30
W17
W15
R6086
R6085
W26
CL6202
W29
W18
W224
IR6131
Q6085
W112
W51
W230
W55
R6012
R6011
CL6007
W103
R6009
R6004
W106
W108
W45
W110
W229
W31
W8
W58
W63
W116
W89
CL6005
K6007
W64
W65
C6132
W115
W114
L6131
W117
K6008
W121
W120
W118
W119
K3601
FP3501
W109
W111
W81
W70
6789
5
10
4
11
3
12
2
13
1
14
FP3502
W94
W238
1011
9
12
8
13
7
14
6
15
W98
5
16
4
17
3
18
2
19
1
20
W75
W76
W77
W78
W79
W80
W88
W231
W59
W72
W113
PJ6101
CL6028
CL6026
CL6027
W122
W123
W124
W100
W101
W105
W107
W91
W90
R4355
C4336
R4331
4
W239
W99
W97
58
R4332
C4337
R4356
W85
W84
W83
W82
W235
W236
W234
W232
W60
W62
W66
W67
W68
W74
W96
IC4301
W73
K3502
K3503
CL6029
15
CL6030
R4304
C4314
R4320
W155
W156
QR4306
R4309
R4302
CL4303
D4301
R4301
C4324
L4291
C4291
W92
W93
W95
W153
W137
W140
W143
W144
W126
W129
C3511
W136
K3872
K4904
Q4302
W159
W160
W162
W164
W145
W146
W242
W243
W150
W152
W246
W247
W138
W241
C3510
C3509
C3508
C3506
R3501
891
W125
IC3501
16
C3517
W127
W128
W130
W135
C3512
C3513
R3535
R3536
LB3535
W102
W104
W237
C4315
1
W87
W233
W61
W69
W71
W163
LB3536
C3505
K3504
QR4302
L3501
C3518
CL1109
IP4751
W167
W168
K4901
CL4902
L6001
IP3802
CL1113
CL4901
W157
C4313
W166
W151
W154
W139
C3507
R3534
LB3534
W256
CL4301
W158
W257
(EXCEPT PLA)
W262
CL4903
W161
W240
C4323
K4903
W165
W253
W147
W148
W244
W149
W245
W142
W132
W131
W134
C3516
C3514
LB3532R3532
R3533
LB3533
10
7
5
JK4401
41215
K1122
CL1101
W193
CL1104
W183
C1196
IC1195
13
C1195
R1191
CL1111
C1197
L1141
W178
R1101
W261
C1102
R1102
R1103
W180
W177
W173
W141
W174
W176
W175
C4415
C4414
R3522
W169
W170
W133
C3515
11
7
R4422
R4452
R4428
Q4422
LB3531R3531
C4427
R4459
8
C4432
6
1
ZA4754
L1131
W179
W171
W172
R1107
IC1101
W1
W185
R1106
W249
R4752
R4423
R4429
Q4423
C4423
W182
CL1106
C1117
CL1112
W184
CL1105
C1122
D1122
C1121
C1141
K1141
(EXCEPT PLA)
C1004
R1061
D1081
W248
Q4751
C4752
R4451
C4460
2313141617
D1121
D1141
C1101
R1104
W181
R1105
1
Q1051
4
92
W2
R1041
D1041
R1062
(EXCEPT PLA)
D1071
R4751
R4753
C4703
R4754
R4756
R4755
W250
D1061
C4781
C4751
R1081
C1061
R1084
K1091
C1082
K1062
R1071
F1001
ZA1002
ZA1001
C4502
L1111
D1111
C1041
W5
W3
CL1004
C6020
ZA1111
CL1108
L1117
W254
IP1112
W191
C1112
C1111
T1021
9
7
6
5
IC1021
4
3
2
1
W4
D1082
C1081
C10511
D1051
R1051
R1072
D1011
C1002
CL1006
R1001
CL1005
VA1002
C1001
K1006 K1005
C1116
CL1007
K1003
W189
C1151
C1021
L1001
W187
C1115
R1115
Q1115
L1151
D1152
D1151
D1031
C1092
R1083
R1082
D1072
C1071
R1002
CL1001
K1004
(ONLY FOR PLA)
P1001
R1116
W192
CL1107
C1155
1810
CL1002
W186
QR1115
C1154
15
C1153
CL1115
K1171
C1110
R1031
(EXCEPT PLA)
C1031
W6
C1012
C1011
CL1003
K1001
K1172
IC1151
C1003
K1002
CL1116
W188
K1155
K1154
D1153
D1171
(EXCEPT PLA)
C1171
ZA1112
(EXCEPT PLA)
OPERATION P.C.B.
Q_OSD
R6161
S6161S6162 S6171
PLAY PAUSE
W263
W264
STOP
S6172
R6171
S6151
OPEN
R6151
15
W265
JW6101
JW6102
31
POWER SW P.C.B.
POWER_SW
D6101
S6152
R6101
1
3
JW6102
DVD-S42GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
MOTHER P.C.B.(VEP76126B:GC/GCA)
(VEP76126K:GCS/GCU)
(VEP76126L:PL)
(VEP76127A:PLA)
OPERATION P.C.B.(VEP70131A)
POWER SW P.C.B.(VEP70132A)
60
54321
9876
Page 61

17.3. MOTHER P.C.B. ADDRESS INFORMATION
Transistor
Q1051
Q1115
Q3801 (EE)
Q3821
Q3851
Q3852
(EE)
(EE)
(EE)
Q4302
Q4422
Q4423
D-5
E-6
B-3
A-4
A-2
A-2
E-4
A-5
A-5
Q4751 B-5
Q6085 F-3
Transistor-resistor
QR1115 F-6
QR3501
QR3502
QR3821
QR3822
QR3823 B-3
QR4302
(EE)
(EE)
(EE)
(EE)
(EE)
B-3
B-4
B-3
B-3
E-4
QR4306 E-4
Inntegrated Circuit
C-6IC1021
IC1101 D-5
IC1151 E-6
IC1195 E-5
IC3501 B-4
IC3502
IC3802 A-3
IC3811 B-3
IC4301
(EE)
(EE)
(EE)
B-4
C-3
IC6001 E-2
Test Point
CL1001
CL1002
CL1003
CL1004
CL1005
CL1006
CL1007
CL1101
B-6
B-6
B-6
A-6
B-6
B-6
B-6
F-5
CL1104 E-5
CL1105 E-5
CL1106 F-5
CL1107 E-6
CL1108 F-6
CL1109 F-4
CL1111 E-5
CL1112 F-5
CL1113 E-4
CL1115 E-6
CL1116 E-6
CL3501 A-1
CL3502 A-1
CL3503 A-1
CL3504 A-1
CL3505 A-1
CL3506 A-1
CL3507 A-1
CL4301 E-4
CL4303 E-4
CL4901 E-4
CL4902 E-4
CL4903 E-4
CL6001 E-2
CL6005 E-3
CL6007 E-3
CL6026 F-3
CL6027 F-3
CL6028 F-3
CL6029 F-3
CL6030 E-4
CL6081 F-1
CL6082 F-1
CL6083
CL6084 F-1
CL6085 F-1
CL6086 F-1
CL6087 F-1
CL6088 F-1
CL6093
CL6095 F-2
CL6097 F-2
ADDRESS INFORMATION
MOTHER P.C.B.
F-1
F-2
CL6089
CL6090
CL6091
CL6092
CL6094
CL6096
CL6098
CL6099
CL6100
CL6102
CL6103
CL6201
F-1
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
F-2
D-2
CL6202 D-2
Connector
FP3501 D-3
FP3502 C-3
P1001 A-6
PJ6101 E-6
JK3871 A-3
(EE)
JK4401 A-4
Transformer
T1021 D-6
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
61
Page 62

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
17.4. MODULE P.C.B. (1/2)
MODULE P.C.B.(1/2)
E
D
C
B
A
FP8531
CKE5
CL8252
C8251
CKE22
226
CKE4
C8530
CKE12
CL8251
CKE6
LB8530
R8531
C8531
CL8261
2
6
CKE24
CKE18
CKE21
CKE16
RX8534
CKF6
C8572
CL8262
R8261
CKE11
C8261
CKE20
CKE17
R8263
C8601
C8611
8
1
R8559
CKE19
R8264
CKE9
114 29
28
C8232
C8258
LB8561 LB8551
R8568
R8558
RX8532
CL8211
C8231
4
5
IC8601
CL8612
IC8611
C8571
TL8521
TL8511
C8528
IC8606
D8211
R8211
C8529
C8511
C8512
R8262
K8261
R8230
R8231
R8232
Q8562
Q8552
CL8551
3
1
R8601
5
4
R8567
R8557
L8201
C8211
LB8571
TL8201
C8606
R8611
R8566
R8556
L8501
CL8512
CL8231
CL8232
CL8611
R8563 R8564 R8565 R8553 R8554 R8555 R8551
C8541
C8201
CL8511
C8526
C8505
R8002
RX8611
TL8510
R8541
CL8541
C8525
CL8652
C8563
C8553
R8552
CL8213
C8521
C8501
C8527
1
24
C8222
R8221
CL8222
C8522
C8523
CL8230
D8571
Q8551
CL8012
CL8017
C8221
C8524
CL8221
C8515
C8516
C8514
C8513
CL8002
CL8001
CL8011CL8013
CL8016
C8562
C8552
L8301
C8301
CL8022
C8554
CL8010
CL8015
QR8571
CL8226
CL8225
R8311
C8311
R8312
CL8014
CL8021
CL8212
C8312
C8564
Q8561
C8551
C8226
R8225
C8225
C8203
R8313 R8314
CL8020
IC8651
CL8571
R8562
CL8561
C8561
R8561
C8313
R8004
L8302
C8302
C8621 C8622R8621 R8622
CL8024CL8030
CL8023
C8550
K8341
R8341
CL8026
CL8027
CL8028CL8025
C8401
X8621
L8550
K8335
R8335
LB8401
CL8654
RX8401
RX8019
48
25
CL8651
K8321
R8322 R8321
K8331
R8332
R8331
RX8403
R8401
CL8041
C8052
C8053
C8054
R8012
R8013
RX8020
C8652
C8651
CL8653
C8428
3
CKG11
CKG10
CKG9
1
85
K8421
CKH5
K8105
TL8111
LB8421
LB8423
C8111
CKC10
CKC2
K8103
LB8422
CKC1
CKC6
CKC9
CKC8
CKG2
CKC3
CKC5
LB8424 LB8491
K8102
CKG6
CKG4
K8101
CKG7
CKG5
LOADING MOTOR P.C.B.
17
FP2601
26
TL2601
TL2602
CLOSE-SW
S2601
OPEN -SW
S2602
CKD10
CL8435
QR8420
K8325
R8326
1
27
C8055
R8325
RX8001
CL8031
C8051
RX8691
IC8051
CL8434
R8421
CL8421
CL8422
CKB6
R8420
CL8427
CL8423
CKB8
CL8425
CL8424
RX8032
RX8031
CKA5
IC8151
CKD6
CKD8
CKD9
CKD4
C8422
16 9
IC8420
18
CL8428
CL8426
CKB9
CKB1
CKB3
CKB2
CKA7
CKA3
CKA1
54
C8057
C8056
28
CKB4
LB8011
C8011
C8001
5
C8151
R8151
C8152
1
CKD2
CL8431
LB8302
LB8301
CKA2
CKA6
CKA4
CKD1
CL8432
LB8303
CKG14
LB8692
LB8693
CL8433
CKC20
CKC18
LB8304
LB8305
CKG13
CKG12
CKC16
CKC14
CKC12
C8113
4
LB8691
LB8262
LB8261
C8423
IC8111
CKG8
K8104
C8421
CKC13
CKC11
C8112
RX8111
64
QR8111
1
LB8001
F
25 1
CKE14
CKE13
CKE7
CKE25
LB8259
CKH6
C8253
CKE23
CKE26
LB8260
LB8257
LB8258
CKH7
CKE3
7
FP8252
CKH3
15 30
C8255
CKE2
1
CKH1
LB8256LB8255
C8257
C8256 C8252
CKF4
CKF3
R8532 C8532
C8533
LB8531
IC8251
CKF2
CKF1
1
CKF5
5
CKE1
RX8533
R8533
RX8531
K8251
FP8251
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
MODULE P.C.B.(1/2)(VEP76129A:EE/GC/GCA/PL/PLA)
(VEP76129E:GCS/GCU)
(COMPONENT SIDE)
LOADING MOTOR P.C.B.(VEP70114A-1)
62
54321
9876
Page 63

17.5. MODULE P.C.B. (2/2)
MODULE P.C.B. (2/2)
F
DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
C8537
E
D
C
B
R8011
CL8065
C8014C8015
C8012C8003C8013
RX8018
C8004
C8016
C8017
CL8064
CL8055 CL8053
CL8062
CL8054
C8424
R8041
MK1
193
256
CL8063
C8025
CL8061 CL8060 CL8059
CL8058
CL8057
CL8056
C8026
C8536
C8304C8306
C8305C8005
IC8001
C8303
C8202
129192
128
C8504
C8503
C8502
C8024
C8602
C8008
R8003
C8023
65
MK2
641
C8022
C8007C8021C8006C8020C8019C8018
201
PS8301
PS8101
11
RX8011
RX8012
RX8013
RX8014
141
RX8015
RX8016
RX8017
8
CL8069
CL8068
CL8066
CL8051 CL8052
10
7
A
(FOIL SIDE)
63
DVD-S42EE/GC/GCA/GCS/GCU/PL/PLA
MODULE P.C.B.(2/2)(VEP76129A:EE/GC/GCA/PL/PLA)
(VEP76129E:GCS/GCU)
54321
9876
Page 64

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
17.6. MODULE P.C.B. ADDRESS INFORMATION
Transistor
Q8551 E-3
Q8552 E-3
Q8561 E-4
Q8562 F-3
Transistor-resistor
QR8111 C-6
QR8420 F-5
QR8571 F-3
Inntegrated Circuit
IC8001 C-4
IC8051 B-5
IC8111 C-6
IC8151 A-5
IC8251 C-2
IC8420
IC8601
E-5
B-2
IC8611 A-2
IC8651 B-4
Test Point
CKA1 C-5
CKA2 D-6
CKA3 D-5
CKA4 C-6
CKA5
CKA6
CKA7
CKB1
CKB2
CKB3
CKB4
CKB6
D-5
D-6
D-5
D-5
D-5
D-5
D-6
D-5
CKB8 D-5
MODULE P.C.B.
CKB9 D-5
C
C
C
C
CKC1 F-7
CKC2 F-7
CKC3 F-7
CKC5 E-7
CKC6 E-7
C
C
C
CKC8 D-7
CKC9 D-7
CKC10 D-7
CKC11 D-6
F
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
CKC12 D-6
CKC13 D-6
CKC14 D-6
CKC16 D-6
CKC18 E-6
CKC20 E-6
CKD1 F-6
CKD2 F-6
CKD4 F-6
CKD6 F-5
CKD8 F-5
CKD9 F-6
CKD10 F-5
CKE1 E-2
CKE2 E-2
CKE3
E-2
CKE4 E-2
CKE5 E-2
CKE6 E-2
CKE7 E-2
CKE9 E-2
CKE11
F-2
CKE12
C
CKE13
C
CKE14
C
CKE16
C
CKE17
C
CKE18
C
CKE19
C
CKE20
C
CKE21
C
CKE22
C
CKE23
C
CKE24
C
CKE25
C
CKE26
C
CKF1
C
CKF2
C
CKF3
C
CKF4
C
CKF5
C
CKF6
C
CKG2
C
CKG4
C
CKG5 B-7
C
CKG6 B-7
C
CKG7 B-7
C
CKG8 A-6
C
CKG9 B-6
C
CKG10 B-6
C
CKG11 B-6
C
CKG12 B-6
C
CKG13 B-6
C
CKG14 B-6
C
E-2
F-2
E-2
E-2
F-2
E-2
E-2
E-2
F-2
F-2
E-1
F-2
E-1
E-1
B-2
B-2
B-1
B-1
A-2
A-2
C-7
B-7
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
Test Point
CKH1
CKH3
D-1
D-1
CKH5 D-6
CKH6
CKH7
D-1
E-1
CL8001 C-3
CL8002 C-3
CL8010 C-3
CL8011 C-3
CL8012 C-3
CL8013 C-3
CL8014 C-3
CL8015 C-3
CL8016 C-3
CL8017
CL8020
C-3
B-4
CL8021 B-3
CL8022 B-3
CL8023 C-4
CL8024 C-4
CL8025 C-4
CL8026 C-4
CL8027 C-4
CL8028
CL8030
CL8031
CL8041
CL8211
CL8212
CL8213
CL8221
C-4
C-4
D-5
D-4
D-2
D-3
D-3
D-3
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
MODULE P.C.B.
CL8222
CL8225
CL8226
CL8230
CL8231
CL8232
CL8251
CL8252
CL8261
CL8262
CL8421
CL8422
CL8423
CL8424
CL8425
CL8426
CL8427
CL8428
CL8431
CL8432
CL8433
CL8434
D-3
D-4
D-3
C-3
C-3
C-3
D-2
D-2
D-2
D-2
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-5
E-6
E-6
E-6
E-5
CL8435 F-5
CL8511
CL8512
CL8541
C-3
C-3
D-3
CL8551 E-3
CL8561
E-3
CL8571 F-4
CL8611
CL8612
B-3
B-2
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
CL8651
CL8652
CL8653
CL8654
TL8111
TL8201
A-4
B-3
B-4
B-4
D-6
D-3
TL8510 E-3
TL8511 E-2
TL8521
F-2
Connector
FP8251
FP8252
FP8531
PS8101
PS8301
A-2
E-1
F-2
B-1
E-1
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
F
F
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
ADDRESS INFORMATION
C......COMPONENT SIDE
F......FOIL SIDE
64
Page 65

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
18 EXPLODED VIEWS
18.1. CASING PARTS & MECHANISM SECTION EXPLODED VIEW
65
Page 66

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
18.2. MECHANISM SECTION EXPLODED VIEW
66
Page 67

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
18.3. PACKING & ACCESSORIES SECTION EXPLODED VIEW
67
Page 68

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
19 REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST
Notes:
*Important safety notice:
Components identified by
mark have special
characteristics important for safety.
Furthermore, special parts which have purposes of fireretardant (resistors), high-quality sound (capacitors), lownoise (resistors), etc. are used.
When replacing any of components, be sure to use only
manufacture’s specified parts shown in the parts list.
*Warning: This product uses a laser diode. Refer to caution
statements.
*Capacity values are in microfarads (µF) unless specified
otherwise, P=Pico-farads (pF), F=Farads (F).
*Resistance values are in ohms, unless specified otherw ise,
1K=1,000 (OHM), 1M=1,000k (OHM).
*The marking (RTL) indicates the retention time is limited
for this item. After the discontinuation of this assembly in
production, it will no longer be available.
*” (IA)-(IF)”, marks in Remarks indicate languages of
instruction manuals. [(IA): Arabic, (IB): English, (IC):
Traditional Chinese, (ID): Russian/Ukrainian, (IE):
Portuguese, (IF): Spanish]
*All parts except parts mentioned [SPC] in the Remarks
column are supplie d by PAVCS G.
*Parts mentioned [SPC] are supplied by PAVC-CSG.
Ref.
No.
1 VEP76129AT MODULE P.C.B. 1 (RTL)
1 VEP76129ET MODULE P.C.B. 1 (RTL) GCS/GCU
2 VEP76126B MOTHER P.C.B. 1 (RTL) GC/GCA
2 VEP76126C MOTHER P.C.B. 1 (RTL) EE
2 VEP76126K MOTHER P.C.B. 1 (RTL) GCS/GCU
2 VEP76126L MOTHER P.C.B. 1 (RTL) PL
2 VEP76127A MOTHER P.C.B. 1 (RTL) PLA
3 REZ1710 FFC(7P) 1
5 RGKC0068-B TRAY TOP 1
6 RGQC0037 INSULATION SHEET 1
7 RGQC0037 INSULATION SHEET 1
8 RGRC0022A-N REAR PANEL 1 GC
8 RGRC0022A-M REAR PANEL 1 GCA
8 RGRC0022A-K REAR PANEL 1 GCS
8 RGRC0022A-Q REAR PANEL 1 GCU
8 RGRC0022A-P REAR PANEL 1 PLA
8 RGRC0022A-U REAR PANEL 1 PL
8 RGRC0022B-B REAR PANEL 1 EE
9 RHD30101-1J SCREW 1
10 RHD30101-1J SCREW 1
11 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
12 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
13 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
14 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
15 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
16 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
17 RHD30111-3J SCREW 1
18 RHDC0023-J SCREW 1
19 RHDC0023-J SCREW 1
20 RGQC0038 FRONT ANGLE 1
21 RMNC0016 PCB SUPPORT(A) 1
22 RMNC0017 PCB SUPPORT(B) 1
23 RMNC0019 PCB SUPPORT 1
25 RKA0130-K FOOT RUBBER 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
EE/GC/GCA/PL/
PLA
Ref.
No.
26 RKA0130-K FOOT RUBBER 1
27 RKA0130-K FOOT RUBBER 1
28 RKA0130-K FOOT RUBBER 1
29 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
31 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
32 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
33 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
34 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1 EE
35 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1 EE
36 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
39 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
40 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
41 VHD0690-1 SCREW 1
44 RKMC0012-S TOP PANEL 1
45 RFKGDVDS42AS FRONT PANEL ASS’Y 1
46 RGQC0054 DUSTPROOF SHEET 1
47 RHD26046 SCREW 1
48 RHD26046 SCREW 1
49 RHD26046 SCREW 1
50 RHD26046 SCREW 1
51 RHD26046 SCREW 1
52 RHD26046 SCREW 1
55 VEP70131A FRONT P.C.B. 1 (RTL)
55-1 REZ1709 CABLE (3P) 1
55-2 REZ1708 CABLE (5P) 1
56 VEP70132A SW P.C.B. 1 (RTL)
59 RHD30007-1SJ SCREW 1
60 RHD30007-1SJ SCREW 1
101 RXQ1327 SPINDLE MOTOR
102 RDG0557 PINION SHAFT 1
103 RDG0558 BEVEL GEAR 1
105 RMB0713-1 THRUST SPRING 1
107 RMG0617-H CUSHION RUBBER(A) 1
108 RMQ1112 MOTOR COVER 1
110 RMS0788 GUIDE SHAFT 1
111 RMS0798 GEAR SHAFT 1
112 RMX0233 THRUST WASHER 1
113 RMX0247 WASHER 1
114 RWJ6702042 MOTOR CABLE 1
115 RXQ0946 TRAVERSE MOTOR
116 RAF3114A-CG OPTICAL PICK-UP 1
117 REZ1686-1 FFC 1
118 RHD14112-J SCREW 1
119 RHD17046-1 SCREW 1
121 RMM0261 OPU DRIVE RACK 1
122 VHD1224-1 SCREW 1
123 VHD1224-1 SCREW 1
124 VHD1224-1 SCREW 1
125 VHD1224-1 SCREW 1
127 RDG0597 PULLEY GEAR 1
128 RDG0548 RELAY GEAR 1
129 RDG0549 DRIVE GEAR 1
130 RDV0070 BELT 1
131 REM0132 LOADING MOTOR
132 VEP70114A-1 MOTOR P.C.B. 1 (RTL)
133 RMC0387 SUPPORT SPRING 1
134 RME0351 LOCK LEVER SPRING 1
135 RMEC0350 CHANGE LEVER
136 RMK0616-1 MECHA CHASSIS
137 RML0680-1 DRIVE ARM 1
138 RML0628 CHANGE LEVER 1
139 RML0629 LOCK LEVER 1
140 RMM0283 DRIVE RACK 1
141 RMM0284 SUB RACK 1
144 RQLCA0141 LASER CAUTION
Part No. Part Name &
Description
ASS’Y
ASS’Y
ASS’Y
SPRING
ASS’Y
LABEL
Pcs Remarks
1
1
1
1
1
1
68
Page 69

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
145 JSMC0048 MAGNET 1
146 RMR1685-X CLAMPER 1
147 RMA1890 MAGNET HOLDER 1
148 RMR1686-K CLAMP PLATE 1
150 RGQ0417-K TRAY 1
151 RME0353-1 TRAY SLIDER SPRING 1
152 RML0631 TRAY SLIDER 1
153 XQN17+C25FJ SCREW 1
154 XTB26+6GFJ SCREW 1
155 XTN2+6GFJ SCREW 1
156 RMQ1280 FFC HOLDER PIECE 1
A1 EUR7631190R REMOTE CONTROL
A1 EUR7631200R REMOTE CONTROL
A1-1 UR76EC3103A BATTRY COVER 1
A2 K2CQ2CA00006 AC CORD 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
A2 K2CA2DA00013 AC CORD 1 PL
A2 K2CB2CB00020 AC CORD 1 PLA
A3 K2KA6BA00004 AV CORD 1
A4 RPFC0042 POLYETHYLENE
A5 RQT8505-A OPERATING
A5 RQT8509-B OPERATING
A5 RQT8686-K OPERATING
A5 RQT8506-R OPERATING
A5 RQT8504-U OPERATING
A5 RQT8511-1M OPERATING
A6 K2DR42E00001 POWER PLUG ADAPTOR 1 PL
A7 K2CT3CA00004 AC CORD 1 GC
C1001 F0CAF104A024 0.1U 1
C1002 F0CAF104A024 0.1U 1
C1003 ECKMNA102MEV 1000P 1 PLA
C1003 ECKMNA471MBV 470P 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1004 ECKMNA222MEV 2200P 1 PLA
C1004 ECKMNA102MEV 1000P 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1011 ECA2VHG220E 350V 22U 1 PLA
C1011 ECA2WHG100E 450V 10U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1012 ECA2VHG220E 350V 22U 1 PLA
C1012 ECA2WHG100E 450V 10U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1021 F1B3A102A009 1000V 0.001U 1 PLA
C1021 F1A3D221A010 2000V 220P 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1031 F1B3A332A008 1000V 0.0033U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1041 F2A1H1010044 50V 100U 1
C1051 ECQB1H821JF4 50V 820 1 PLA
C1051 ECQB1H152JF4 50V 0.0015U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1061 ECQB1H471KF4 50V 470P 1 PLA
C1061 ECQB1H101KF4 50V 100P 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1071 ECQB1H682JF4 50V 6800P 1 PLA
C1071 ECQB1H103JF4 50V 0.01U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1081 ECQB1H471JF4 50V 470P 1 PLA
C1081 ECQB1H152JF4 50V 0.0015U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1082 ECQB1H472JF4 50V 0.0047U 1
C1092 F2A1H100A003 50V 10U 1
C1101 ECQV1H334JL2 25V 0.33U 1 PLA
C1101 ECQV1H684JL2 50V 0.68U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
Part No. Part Name &
Description
ASS’Y
ASS’Y
BAG(F.B.)
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
Pcs Remarks
1 PL/PLA
1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
/GCU
/GCU
1
1 GC/GCA (IA)
1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
U (IB)
1 GCS/GCU (IC)
1 EE (ID)
1 PL/PLA (IE)
1 PL/PLA (IF)
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
Ref.
No.
C1102 ECQB1H104JF4 50V 0.1U 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
C1110 F1H1H102A798 50V 1000P 1
C1111 F2A1A681A539 10V 680U 1
C1112 F2A1A102A206 10V 1000U 1
C1115 ECJ1VF1C104Z 16V 0.1U 1
C1116 F2A1A221A206 10V 220U 1
C1117 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1
C1121 F2A0J681A550 6.3V 680U 1
C1122 F2A0J222A247 6.3V 2200U 1
C1141 F2A1E1010067 25V 100U 1
C1151 F2A1E3310051 25V 330U 1
C1153 F2A1E331A205 25V 330U 1
C1154 F2A1C221A236 16V 220U 1
C1155 ECJ1VB1E104K 25V 0.1U 1
C1171 F2A1A1010072 10V 100U 1
C1195 ECJ1VB1A105K 10V 1U 1
C1196 ECJ1VB1H103K 50V 0.01U 1
C1197 ECJ1VB1A105K 10V 1U 1
C3502 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1 EE
C3503 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3504 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3505 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C3506 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1
C3507 F2A0J220A245 6.3V 22U 1
C3508 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C3509 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C3510 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C3511 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C3512 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1
C3513 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1
C3514 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1
C3515 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
C3516 F2A0J102A247 6.3V 1000U 1
C3517 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C3518 F2A0J470A245 6.3V 47U 1
C3804 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1 EE
C3805 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1 EE
C3806 F2A0J470A245 6.3V 47U 1 EE
C3811 F2A0J470A245 6.3V 47U 1 EE
C3812 ECJ1VB1C104K 16V 0.1U 1 EE
C3813 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1 EE
C3814 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3815 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3816 F2A0J220A245 6.3V 22U 1 EE
C3817 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3818 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3819 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1 EE
C3851 ECJ1VC1H102J 50V 1000P 1 EE
C3852 ECJ1VC1H102J 50V 1000P 1 EE
C3871 F1H1H101A799 50V 100P 1 EE
C3872 F1H1H101A799 50V 100P 1 EE
C4291 F2A1A102A206 10V 1000U 1
C4313 F1H1C104A090 16V 0.1U 1
C4314 F1H1C104A090 16V 0.1U 1
C4315 F1H1C104A090 16V 0.1U 1
C4323 F2A1V221A082 35V 220U 1
C4324 F2A1V221A082 35V 220U 1
C4336 F1H1H820A799 50V 82P 1
C4337 F1H1H820A799 50V 82P 1
C4414 F2A1E470A205 25V 47U 1
C4415 F2A1E470A205 25V 47U 1
C4423 ECJ1VC1H102J 50V 1000P 1
C4427 ECJ1VC1H102J 50V 1000P 1
C4431 F1H1C104A090 16V 0.1U 1
C4432 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C4501 F1H1H102A798 50V 1000P 1
C4502 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C4591 F1H1C104A090 16V 0.1U 1
C4703 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C4751 F2A1E470A205 25V 47U 1
C4752 F2A1E470A205 25V 47U 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
U/PL/PLA
69
Page 70

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
C4781 F2A0J470A599 6.3V 47U 1
C6001 F2A0J101A245 6.3V 100U 1
C6002 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C6003 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1
C6005 F2A1H100A236 50V 10U 1
C6006 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1
C6020 ECJ1VB1E104K 25V 0.1U 1
C6040 ECJ1VF1H103Z 50V 0.01U 1
C6050 ECJ1VF1H103Z 50V 0.01U 1
C6060 ECJ1VF1H103Z 50V 0.01U 1
C6081 F1H1H103A798 50V 0.01U 1
C6132 F1H1C104A065 16V 0.1U 1
C8001 F2G0G331A012 4V 330U 1
C8003 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8004 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8005 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8006 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8007 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8008 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8011 F2G0J101A066 6.3V 100U 1
C8012 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8013 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8014 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8015 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8016 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8017 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8018 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8019 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8020 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8021 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8022 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8023 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8024 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8025 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8026 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8051 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8052 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8053 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8054 ECJ0EC1H221J 50V 220P 1
C8055 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8056 ECJ0EB1E222K 25V 2200P 1
C8057 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8111 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8112 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8113 ECJ0EB1E471K 25V 470P 1
C8151 ECJ2FB0J106K 6.3V 10U 1
C8152 ECJ1VB1C105K 16V 1U 1
C8201 F2G0J101A066 6.3V 100U 1
C8202 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8203 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8211 ECJ0EB1E122K 25V 1200P 1
C8221 ECJ0EB1E102K 25V 1200P 1
C8222 F1G1E821A056 25V 820P 1
C8225 ECJ0EB1E102K 25V 1200P 1
C8226 ECJ0EB1E102K 25V 1200P 1
C8231 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8232 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8251 F2G0J221A065 6.3V 220U 1
C8252 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8253 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8255 F2G1C470A076 16V 47U 1
C8256 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8257 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8258 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8261 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8301 F2G0J221A031 6.3V 220U 1
C8302 F2G0J330A031 6.3V 33U 1
C8303 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8304 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8305 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8306 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8311 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8312 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
Ref.
No.
C8313 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8401 F1G1H150A542 50V 15P 1
C8421 F2G0J101A083 6.3V 100U 1
C8422 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8423 F2G0J330A083 6.3V 33U 1
C8424 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8428 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8501 F2G0J101A031 6.3V 100U 1
C8502 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8503 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8504 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8505 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8511 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8512 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8513 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8514 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8515 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8516 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8521 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8522 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8523 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8524 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8525 F1G1C562A040 16V 5600P 1
C8526 F1G1C183A004 16V 0.018U 1
C8527 F1G1C333A004 16V 0.033U 1
C8528 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8529 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8530 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8531 F1G1H1010005 50V 100P 1
C8532 ECJ0EC1H221J 50V 220P 1
C8533 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8536 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8537 F1G1A104A014 10V 0.1U 1
C8541 ECJ0EB1E472K 25V 4700P 1
C8550 F2G0J330A031 6.3V 33U 1
C8551 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8552 F2G1C100A072 16V 10U 1
C8553 F2G0J470A031 6.3V 47U 1
C8554 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8561 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8562 F2G1C100A072 16V 10U 1
C8563 F2G0J470A031 6.3V 47U 1
C8564 ECJ1VB0J105K 6.3V 1U 1
C8571 F1K1A1060017 10V 10U 1
C8572 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8601 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8602 ECJ0EB1C153K 16V 0.015U 1
C8606 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8611 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8621 ECJ0EC1H180J 50V 18P 1
C8622 F1G1H180A542 50V 18P 1
C8651 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
C8652 F1G1C104A042 16V 0.1U 1
D1011 B0EDKT000009 DIODE 1
D1031 B0HADV000001 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
D1041 B0HAGM000006 DIODE 1
D1051 MAZ40910HF DIODE 1
D1061 MA2C16500E DIODE 1
D1071 MAZ41000MF DIODE 1
D1072 MA2C16500E DIODE 1
D1081 MAZ40910HF DIODE 1
D1082 MA2C16500E DIODE 1
D1111 B0JAME000033 DIODE 1 PLA
D1111 B0JAMG000013 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
D1121 B0JAME000033 DIODE 1 PLA
D1121 B0JAMG000013 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
D1122 B0EAKM000117 DIODE 1
D1141 B0JAMG000031 DIODE 1 PLA
D1141 B0JAMK000023 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
70
Page 71

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
D1151 B0JAMG000031 DIODE 1 PLA
D1151 B0JAMK000023 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
D1152 B0JAMG000031 DIODE 1 PLA
D1152 B0JAMK000023 DIODE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
D1153 B0EAKM000122 DIODE 1
D1171 B0JAME000037 DIODE 1
D3821 MA3X152A0L DIODE 1 EE
D4301 MAZ40560HF DIODE 1
D6081 MAZ40910LF ZENER DIODE 1
D6101 LNJ201LPQJA LED 1
D8211 MA2J11100L DIODE 1
D8571 MA2J72800L DIODE 1
DP6081 A2BA00000229 FL DISPLAY SCREEN 1
F1001 K5D162APA008 FUSE 1 PLA
F1001 K5D162BLA013 FUSE 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
FP2601 K1MN07B00009 7PIN JACK 1
FP3501 K1KA14A00135 CONNECTOR(MALE)
FP3502 K1KA20A00215 CONNECTOR(MALE)
FP8251 K1MN06AA0076 JACK 1
FP8252 K1MN07AA0076 JACK 1
FP8531 K1MN26AA0041 JACK 1
IC1021 C0DACZH00032 IC 1 PLA
IC1021 C0DACZH00033 IC 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
IC1101 C0DAEMB00003 IC 1
IC1151 C0DBZHG00047 IC 1
IC1195 C0DBFGC00008 IC 1
IC3501 C9ZB00000498 IC 1
IC3502 C1AB00001935 IC 1 EE
IC3802 C1AB00001731 IC 1 EE
IC3811 C9ZB00000461 IC 1 EE
IC4301 C0ABBB000230 IC 1
IC6001 MN101C87AAG IC 1
IC8001 MN2DS0009VP IC 1
IC8051 C3ABPG000133 IC 1
IC8111 C0CBCBD00018 IC 1
IC8151 C0DBEYY00016 IC 1
IC8251 C0GBG0000054 IC 1
IC8420 C0FBBK000049 IC 1
IC8601 C0EBA0000029 IC 1
IC8606 C0EBE0000455 IC 1
IC8611 RFKWDVDS42A IC(EEPROM) 1
IC8651 RFKWSSA0B160 IC 1 EE/GC/GCA/PL/
IC8651 RFKWSSA0C160 IC 1 GCS/GCU [SPC]
IP3802 K5H501Z00005 IC PROTECTOR 1
IP4751 K5H252Z00003 IC PROTECTOR 1
IR6131 B3RAD0000115 REMOTE RECEIVING
JK3871 K1FB121B0016 JACK AV 1 EE
JK4401 K2YZ07000005 JACK AUDIO VIDEO
JK4401 K2YZ19000001 JACK AUDIO VIDEO
K3501 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
K3505 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 EE
K3810 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 EE
K3811 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 EE
K3813 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 EE
K3872 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K6001 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K6008 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
14P
20P
SENSOR
OUT
OUT
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
1
1
/GCU/PL
PLA [SPC]
1
1 EE
1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
U/PL/PLA
U/PL/PLA
Ref.
No.
K8101 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8102 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8103 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8104 ERJ6GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8105 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8251 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
K8261 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8321 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8325 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8331 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8335 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8341 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
K8421 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
L1001 G0B183D00006 NOISE FILTER 1 PLA
L1001 ELF15N003A NOISE FILTER 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
L1111 G0A100HA0023 10UH 1
L1117 G0C100JA0048 10UH 1
L1131 G0C330KA0065 10UH 1
L1141 G0C330KA0065 10UH 1
L1151 G0A220GA0026 10UH 1
L3501 G0C220JA0019 22UH 1
L3502 G0C220JA0019 22UH 1 EE
L4291 G0C220KA0065 22UH 1
L6001 G0C101JA0019 100UH 1
L8201 G1C100K00019 10UH 1
L8301 G1C100K00019 10UH 1
L8302 G1C100K00019 10UH 1
L8501 G1C100K00019 10UH 1
L8550 G1C100KA0055 10UH 1
LB3531 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
LB3532 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
LB3533 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1
LB3534 J0JCC0000186 COIL 1
LB3535 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1
LB3536 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1
LB3871 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 EE
LB3872 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 EE
LB3873 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 EE
LB3874 J0JBC0000015 COIL 1 EE
LB8001 J0JHC0000097 COIL 1
LB8011 J0JHC0000097 COIL 1
LB8255 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8256 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8257 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8258 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8259 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8260 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
LB8261 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8262 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8301 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8302 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8303 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8304 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8305 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8401 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8421 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8422 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8423 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8424 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8491 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8530 J0JHC0000097 COIL 1
LB8531 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
LB8551 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8561 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8571 J0JBC0000042 COIL 1
LB8691 ERJ2GEJ101X 1/16W 100 1
LB8692 ERJ2GEJ101X 1/16W 100 1
LB8693 ERJ2GEJ101X 1/16W 100 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
U/PL/PLA
U/PL/PLA
71
Page 72

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
P1001 K2AB2B000008 AC JACK 1 PLA
P1001 K2AA2B000011 AC JACK 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
PC1 RPGC0405 PACKING CASE 1 PLA
PC1 RPGC0406 PACKING CASE 1 GCA
PC1 RPGC0407 PACKING CASE 1 GC
PC1 RPGC0408 PACKING CASE 1 EE
PC1 RPGC0450 PACKING CASE 1 GCU
PC1 RPGC0451 PACKING CASE 1 GCS
PC1 RPGC0477 PACKING CASE 1 PL
PC2 RPNC0110A-1 CUSHION(A) 1
PC3 RPNC0110B-1 CUSHION(B) 1
PC4 RPFC0071-B POLYETHYLENE BAG 1
PJ6101 K1MP05A00004 JACK 1
PS8101 K1KB14A00074 CONNECTOR(14P) 1
PS8301 K1KB20A00165 CONNECTOR(20P) 1
Q1051 B3PBA0000241 TRANSISTOR 1
Q1115 B1DHDD000029 TRANSISTOR 1
Q3801 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
Q3821 XN0460100L TRANSISTOR 1 EE
Q3851 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
Q3852 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
Q4302 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1
Q4422 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1
Q4423 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1
Q4751 B1ABDF000033 TRANSISTOR 1
Q6085 B1ABGC000011 TRANSISTOR 1
Q8551 B1ABDF000018 TRANSISTOR 1
Q8552 B1ADGB000008 TRANSISTOR 1
Q8561 B1ABDF000018 TRANSISTOR 1
Q8562 B1ADGB000008 TRANSISTOR 1
QR1115 B1GBCFNN0043 TRANSISTOR 1
QR3501 B1GBCFLL0043 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
QR3502 B1GBCFLL0043 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
QR3821 B1GBCFLL0043 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
QR3822 B1GBCFLL0043 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
QR3823 B1GDCFJJ0041 TRANSISTOR 1 EE
QR4302 B1GDCFEJ0008 TRANSISTOR 1
QR4306 B1GBCFJA0017 TRANSISTOR 1
QR8111 XP0621400L TRANSISTOR 1
QR8420 B1GBCFJJ0040 TRANSISTOR 1
QR8571 B1GDCFEC0001 TRANSISTOR 1
R1001 ERDS2FJ105T 1/4W 1000K 1 PLA
R1001 ERDS2FJ474T 1/4W 470K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1002 ERDS2FJ105T 1/4W 1000K 1 PLA
R1002 ERDS2FJ474T 1/4W 470K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1031 ERG2SJ683P 2W 68K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1041 ERG12SJ270E 1/2W 27K 1 PLA
R1041 ERX12SJ4R7E 1/2W 4.7 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1051 D1AA2002A005 1/4W 20K 1
R1061 ERDS2TJ332T 1/4W 3.3K 1 PLA
R1061 D1AA1801A006 1/4W 1.8K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1062 ERDS2TJ103T 1/4W 10K 1 PLA
R1062 ERDS2TJ183T 1/4W 18K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1071 EROS2THF2201 1/4W 2.2K 1 PLA
R1071 EROS2THF4301 1/4W 4.3K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1081 EROS2THF3901 1/4W 3.9K 1 PLA
R1081 D1AA3301A006 1/4W 3.3K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1083 D1AA2702A005 1/4W 27K 1
R1084 D1AA3301A006 1/4W 3.3K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
/GCU/PL
Ref.
No.
R1101 ERDS2TJ181T 1/4W 180 1
R1102 D1AA4701A006 1/4W 4.7K 1
R1103 D1AA4701A006 1/4W 4.7K 1
R1104 ERJ6GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R1105 ERJ3GEYJ222V 1/10W 2.2K 1
R1106 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R1107 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1 EE/GC/GCA/GCS
R1115 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R1116 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R1191 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R3501 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1
R3521 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1 EE
R3522 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
R3531 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
R3532 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1 GC/GCA/GCS/GC
R3533 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1
R3534 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1
R3535 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1
R3536 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1
R3821 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1 EE
R3822 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1 EE
R3823 ERJ3GEYJ472V 1/10W 4.7K 1 EE
R3824 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1 EE
R3825 ERJ3GEYJ472V 1/10W 4.7K 1 EE
R3826 ERJ3GEYJ183V 1/10W 18K 1 EE
R3827 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1 EE
R3828 ERJ3GEYJ471V 1/10W 470 1 EE
R3851 ERJ3GEYJ681V 1/10W 680 1 EE
R3852 ERJ3GEYJ821V 1/10W 820 1 EE
R3853 ERJ3GEYJ821V 1/10W 820 1 EE
R3854 ERJ3GEYJ681V 1/10W 680 1 EE
R3871 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R3872 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R3873 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R3874 ERJ3GEYF750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R3875 ERJ3GEYJ221V 1/10W 220 1 EE
R3876 ERJ3GEYJ221V 1/10W 220 1 EE
R3877 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R3878 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1 EE
R4301 ERJ3GEYJ271V 1/10W 270 1
R4302 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R4304 ERJ3GEYJ222V 1/10W 2.2K 1
R4309 ERJ3GEYJ223V 1/10W 22K 1
R4320 ERJ3GEYJ222V 1/10W 22K 1
R4331 D0HB912ZA002 1/10W 9.1K 1
R4332 D0HB912ZA002 1/10W 9.1K 1
R4355 D0HB153ZA002 1/10W 15K 1
R4356 D0HB153ZA002 1/10W 15K 1
R4422 ERJ3GEYJ473V 1/10W 47K 1
R4423 ERJ3GEYJ473V 1/10W 47K 1
R4428 ERJ3GEYJ681V 1/10W 680 1
R4429 ERJ3GEYJ681V 1/10W 680 1
R4451 ERJ3GEYJ821V 1/10W 820 1
R4452 ERJ3GEYJ821V 1/10W 820 1
R4459 ERJ3GEYJ221V 1/10W 220 1
R4460 ERJ3GEYJ221V 1/10W 220 1
R4751 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R4752 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R4753 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1/10W 1K 1
R4754 ERJ3GEYJ221V 1/10W 220 1
R4755 ERJ3GEYJ750V 1/10W 75 1
R4756 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6004 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6006 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6009 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6011 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6012 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6021 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6022 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
R6023 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
/GCU/PL
U/PL/PLA
U/PL/PLA
U/PL/PLA
72
Page 73

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
R6024 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1/10W 1.2K 1 GCS/GCU
R6024 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1 EE/GC/GCA/PL/
R6025 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6026 ERJ3GEYJ472V 1/10W 4.7K 1 EE
R6026 ERJ3GEYJ472V 1/10W 2.7K 1 GCA/GC/GCS/GC
R6026 ERJ3GEYJ472V 1/10W 1.2K 1 PLA/PL
R6040 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6050 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6060 ERJ3GEYJ103V 1/10W 10K 1
R6061 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R6066 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R6071 ERJ3GEYJ303V 1/10W 30K 1
R6072 ERJ3GEYJ473V 1/10W 47K 1
R6081 ERQ14AJW181E 1/4W 180 1
R6085 ERJ3GEYJ822V 1/10W 8.2K 1
R6086 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R6101 ERJ3GEYJ151V 1/10W 150 1
R6151 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1/10W 1.2K 1
R6161 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1/10W 1.2K 1
R6171 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1/10W 1.2K 1
R6202 ERJ3GEYJ101V 1/10W 100 1
R6204 ERJ3GEYJ104V 1/10W 100K 1
R8002 ERJ2GEJ473X 1/16W 47K 1
R8003 ERJ2GEJ473X 1/16W 47K 1
R8004 ERJ2GEJ473X 1/16W 47K 1
R8011 ERJ2GEJ220X 1/16W 22 1
R8012 ERJ2GEJ220X 1/16W 22 1
R8013 ERJ2GEJ220X 1/16W 22 1
R8041 ERJ2GEJ330X 1/16W 33 1
R8151 ERJ2GEJ102X 1/16W 1K 1
R8211 ERJ2GEJ103X 1/16W 10K 1
R8221 ERJ2GEJ822X 1/16W 8.2K 1
R8225 ERJ2GEJ822X 1/16W 8.2K 1
R8230 ERJ2GEJ222X 1/16W 8.2K 1
R8231 ERJ2GEJ223X 1/16W 22K 1
R8232 ERJ2GEJ752X 1/16W 7.5K 1
R8261 ERJ2GEJ823X 1/16W 82K 1
R8262 ERJ2GEJ153X 1/16W 15K 1
R8263 ERJ2GEJ823X 1/16W 82K 1
R8264 ERJ2GEJ153X 1/16W 15K 1
R8311 ERJ2RHD242X 1/16W 2.4K 1
R8312 ERJ2RHD102X 1/16W 1K 1
R8313 ERJ2RHD912X 1/16W 9.1K 1
R8314 ERJ2GEJ391X 1/16W 390 1
R8321 ERJ3RED680V 1/20W 68 1
R8322 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
R8325 ERJ3RED680V 1/20W 68 1
R8326 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
R8331 ERJ3RED680V 1/20W 68 1
R8332 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
R8335 ERJ3RED680V 1/20W 68 1
R8341 ERJ3RED680V 1/20W 68 1
R8401 ERJ2GEJ101X 1/16W 100 1
R8420 ERJ2GEJ222X 1/16W 2.2K 1
R8421 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
R8531 ERJ2GEJ152X 1/16W 1.5K 1
R8532 ERJ2GEJ222X 1/16W 2.2K 1
R8533 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
R8541 ERJ2GEJ153X 1/16W 15K 1
R8551 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
R8552 ERJ2GEJ102X 1/16W 1K 1
R8553 ERJ2GEJ102X 1/16W 1K 1
R8554 ERJ2GEJ680X 1/16W 68 1
R8555 ERJ2GEJ2R2X 1/16W 2.2 1
R8556 ERJ3GEYJ560V 1/10W 56 1
R8557 ERJ3GEYJ510V 1/10W 51 1
R8558 ERJ2GEJ473X 1/16W 47K 1
R8559 ERJ2GEJ153X 1/16W 15K 1
R8561 ERJ2GE0R00X 1/16W 0 1
R8562 ERJ2GEJ102X 1/16W 1K 1
R8563 ERJ2GEJ102X 1/16W 1K 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
PLA
U
Ref.
No.
R8564 ERJ2GEJ220X 1/16W 22 1
R8565 ERJ2GEJ2R2X 1/16W 2.2 1
R8566 ERJ3GEYJ560V 1/10W 56 1
R8567 ERJ3GEYJ510V 1/10W 51 1
R8568 ERJ2GEJ473X 1/16W 47K 1
R8601 ERJ2GEJ104X 1/16W 100K 1
R8611 ERJ2GEJ101X 1/16W 100 1
R8621 ERJ2GEJ105X 1/16W 1M 1
R8622 ERJ2RHD391X 1/16W 390 1
RX8001 D1H410320002 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8011 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8012 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8013 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8014 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8015 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8016 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8017 D1H88204A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8018 D1H422020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8019 D1H422020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8020 D1H422020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8031 D1H447220001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8032 D1H447220001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8111 D1H422320002 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8401 D1H410120001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8403 D1H410120001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8531 D1H456020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8532 D1H85604A024 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8533 D1H456020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8534 D1H456020001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8611 D1H447220001 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
RX8691 D1H410320002 RESISTOR-RESISTOR 1
S2601 K0L1BA000078 SWITCH 1
S2602 K0L1BA000078 SWITCH 1
S6151 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
S6152 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
S6161 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
S6162 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
S6171 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
S6172 EVQ11G05R SWITCH 1
T1021 G4D2A0000265 TRANSFORMER 1
VA1002 ERZVA5Z471 TRANSIENT/SURGE
W220 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W221 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W222 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W223 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W224 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W225 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W226 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W227 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W228 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W229 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W230 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W231 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W232 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W233 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W234 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W235 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W236 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W237 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W238 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W239 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W240 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W241 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W242 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W243 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W244 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W245 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
ABSORBER
Pcs Remarks
1
73
Page 74

DVD-S42EE / DVD-S42GC / DVD-S42GCA / DVD-S42GC S / DVD-S42GCU / DVD-S 42PL / DVD-S42PLA
Ref.
No.
W246 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W247 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W248 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W249 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W250 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W253 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W256 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W257 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W258 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W263 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
W264 ERJ3GEY0R00V 1/10W 0 1
X6001 H2D800400009 CERAMIC OSCILLATOR 1
X8621 H0J270500080 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 1
ZA1001 EYF52BCY FUSE HOLDER 1
ZA1002 EYF52BCY FUSE HOLDER 1
ZA1111 RMCC0001-1 EARTH SPRING 1
ZA1112 K4CZ01000027 TERMINAL 1
ZA4751 K4CZ01000027 TERMINAL 1
ZA4754 RMCC0027 TERMINAL 1
Part No. Part Name &
Description
Pcs Remarks
74
FLE060300006JA
 Loading...
Loading...