Panasoic SC TM72DV I Service Manual
Service Manual
1
MODELO
SA-TM72DV
SC-TM72DV
AMPLIFICADOR
POTENCIA DE SALIDA:
CONSUMO DE POTENCIA:
ALIMENTACION:
SENSIBILIDAD AUX:
RANGO DE SINTONIA AM:
RANGO DE SINTONIA FM:
DIMENSIONES (BXHXL):
PESO:
SB-VK81
SB-PS81
SB-PC81
SB-WVK81
UNIDAD
Estéreo
Bafles
Surround
Central
Subwoofer
SC-TM72DV
4800 W (P.M.P.O.)
215 W
127 V ca 10% 60 Hz
250 mV
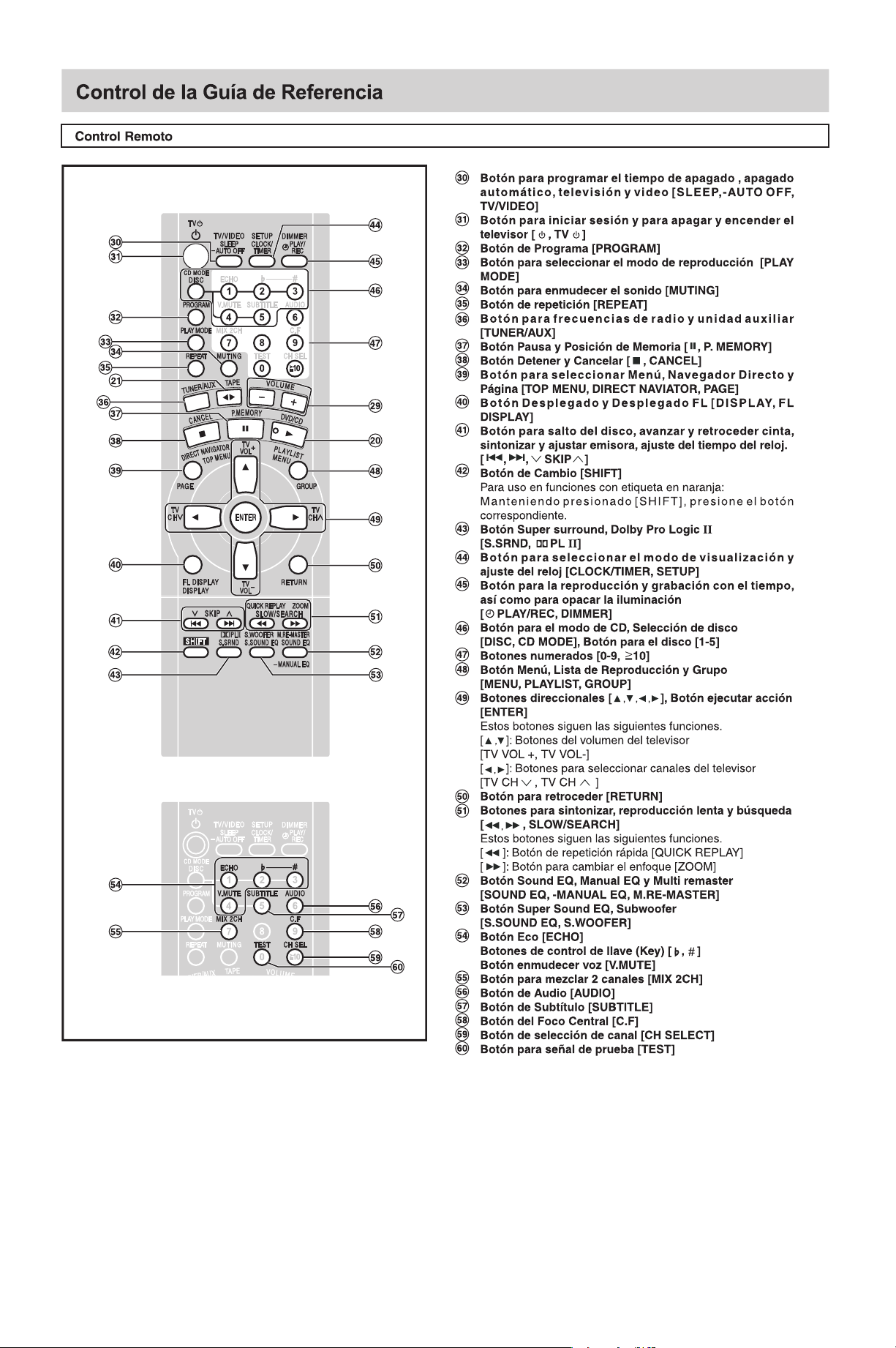
520 - 1710 kHz (paso de 10 kHz)
87,5 - 108,0 MHz (paso de 0,1 MHz)
87,9 - 107,9 MHz (paso de 0,2 MHz)
250 mm x 330 mm x 372 mm
9.6 kg aprox.
SC-TM72DV
Modelo:
FRONTAL
SURROUND
CENTRAL
SUBWOOFER
SC-TM72DV
POTENCIA DE SALIDA (AMPLIFICADOR)
90 W RCM por canal (6 ), 1 kHz, 10% DAT
45 W RCM por canal (6 ), 1 kHz, 10% DAT
90 W RCM por canal (6 ), 1 kHz, 10% DAT
90 W RCM por canal (6 ), 100 Hz, 10% DAT
Notas:
• Las especificaciones están sujetas a cambios sin previo aviso.
• Los pesos y las dimensiones son aproximados.

Table Of Contents
COVER
1 Before Use
2 Before Repair and Adjustment
3 Protection Circuitry
4 Safety Precautions
4.1 General Guidelines
4.1.1 Leakage Current Cold Check
4.1.2 Leakage Current Hot Check (See Figure 1)
5 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
6 Handling the Lead-free Solder
6.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
7 Cautions to be taken when handling Optical Pickup
7.1 Handling Optical Pickup
7.2 Replacing Precautions for Optical Pickup Unit
7.3 Grounding for Preventing Electrostatic Destruction
8 Precaution of Laser Diode
9 Accessories
10 Operation Procedures
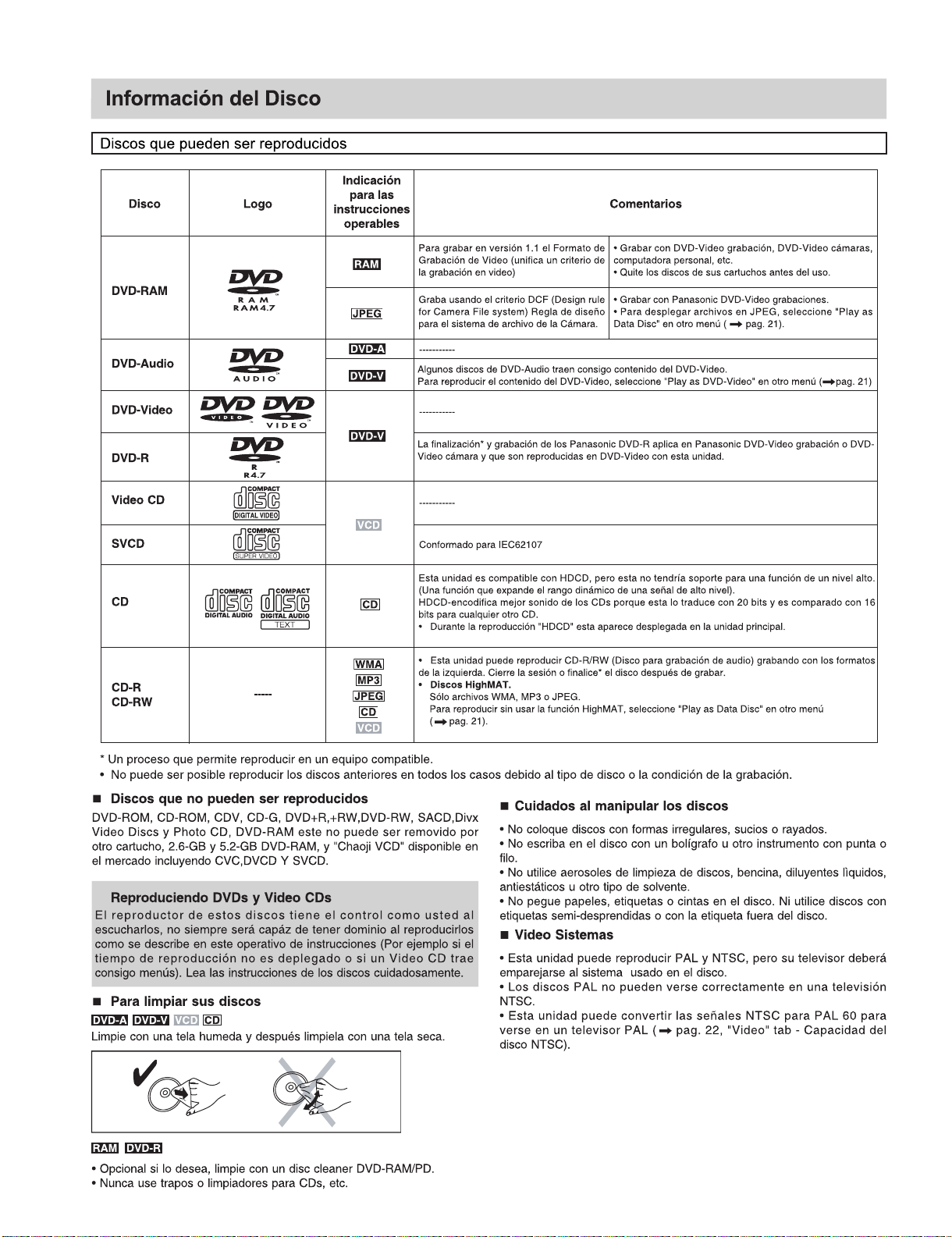
11 Disc information
12 About HighMAT
12.1 What is HighMAT?
12.2 Why use HighMAT?
12.3 The advantages of using HighMAT
12.4 Outline of the HighMAT standard
13 Procedure for repairing the set
13.1 Distinguish the problem
13.1.1 Troubleshooting Guide Part 1
13.1.2 Troubleshooting Guide Part 2
13.1.3 Checking of VIDEO COMPONENT OUTPUT
13.2 Diagnosis of Optical Pick-up Unit
14 Optical Pickup Self-Diagnosis and Replacement Procedure
14.1 Self-diagnosis
14.2 Cautions to Be Taken During Replacement of Optical Pickup and Spindle Motor
14.2.1 Cautions to be taken during replacement of optical pickup
15 Self-Diagnosis Function
15.1 Automatic Displayed Error Codes
15.1.1 Automatic Display Function
15.1.2 Re-Display
15.1.3 Description of Error Code
15.2 Memorized Error Codes
15.2.1 Activating Self-Diagnosis Function and Displaying Method
15.2.2 Re-Display
15.3 Mode Table 1
15.4 DVD / CD Self-Diagnosis Error Code Description
15.5 Error Codes Stored During No Play
15.6 Mode Table 2
15.7 Tray Lock Function
15.7.1 Setting
15.8 Things to Do After Repair
16 Cautions To Be Taken During Servicing

16.1 Recovery after the dvd player is repaired}
16.2 DVD Player Firmware Version Upgrade Process
16.3 Firmware Version Upgrade Process by Using Disc and Recovery Process
16.3.1 Self-Diagnosis Function
16.4 Using Recovery Disc
16.4.1 Recovery Process
16.4.2 Version Upgrade Process
16.5 Total Usage Time Display
16.6 After replacement of DVD Module
17 Disassembly and Assembly of Main Component
17.1 Disassembly flow chart
17.2 Disassembly of Top Cabinet
17.3 Disassembly for DVD changer unit
17.3.1 Disassembly of the DVD Module P.C.B.
17.4 Disassembly for Panel P.C.B., MIC P.C.B. & Tact Switch P.C.B.
17.4.1 Disassembly of Lid
17.5 Disassembly of Main P.C.B., Power P.C.B., , Power Amp P.C.B., Power Supply P.C.B., Transformer P.C.B. & Voltage
Selector P.C.B.
17.5.1 Disassembly of Power Amp P.C.B.
17.5.2 Disassembly of Power P.C.B.
17.5.3 Disassembly of Power Supply P.C.B.
17.5.4 Disassembly of Transformer P.C.B. & Voltage Selector P.C.B.
17.6 Replacement for traverse deck
17.7 Replacement for optical pickup unit (DVD mechanism)
17.8 Procedure for removing CD loading mechanism
17.9 CR16 mechanism disassembly procedure
17.9.1 Gear for servicing information
17.9.2 Replacement for the disc tray
17.9.3 Replacement for the traverse deck
17.9.4 Disassembly for CD loading unit
17.10 CR16 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
17.11 Disassembly for Traverse Unit
17.12 Disassembly of Deck Mechanism Unit
17.12.1 Replacement for the CD motor ass ’ y, capstan belt A, capstan belt B and winding belt
17.13 Replacement for the cassette lid ass ’ y
17.14 Counter-measure for tape trouble
18 Service Position
18.1 Checking Procedure
18.2 Checking the Main P.C.B., Power P.C.B., Power Supply P.C.B., Power Amp P.C.B., Transformer P.C.B., Voltage
Selector P.C.B. and AC Inlet P.C.B.
18.3 Checking the Panel P.C.B., Tact Switch P.C.B., Mic P.C.B., Deck P.C.B. & Deck Mechanism P.C.B.
19 Measurements and Adjustments
19.1 Cassette Deck Section
19.1.1 Head Azimuth Adjustment (Deck 1 / 2)
19.1.2 Tape Speed Adjustment (Deck 1 / 2)
19.1.3 Bias and Erase Voltage Check
19.1.4 Bias Frequency Adjustment (Deck 1 / 2)
19.2 Tuner Section
19.2.1 AM-IF Alignment
19.2.2 AM RF Adjustment
19.3 Alignment Points

19.3.1 Cassette Deck Section
19.3.2 Adjustment Point
20 Block Diagram
21 Schematic Diagram
21.1 Optical Pickup Unit Circuit
21.2 (A) DVD Module Circuit
21.3 (B) Main Circuit
21.4 (C) Panel Circuit , (D) Mic Circuit & (E) Tact Switch Circuit
21.5 (F) Deck Circuit & (G) Deck Mechanism Circuit
21.6 (H) Power Supply Circuit
21.7 (I) Power Amp Circuit
21.8 (J) Power Circuit
21.9 (K) Transformer Circuit, (L) AC Inlet Circuit, (M) Voltage Selector Circuit & (N) CD Loading Circuit
22 Printed Circuit Board
22.1 (A) DVD Module P.C.B. (Side: A & B )
22.2 (B) Main P.C.B.
22.3 (C) Panel P.C.B.
22.4 (D) Mic P.C.B. & (E) Tact P.C.B.
22.5 (H) Power Supply P.C.B.
22.6 (I) Power Amp P.C.B. & (N) CD Loading P.C.B.
22.7 (J) Power P.C.B.
22.8 (F) Deck P.C.B. & (G) Deck Mechanism
22.9 (K) Voltage Selector P.C.B.
22.10 (M) Voltage Selector P.C.B. & (L) AC Inlet P.C.B.
23 Wiring Connection Diagram
24 Illustration of ICs, Transistors and Diodes
25 Terminal Function of IC
25.1 IC6800 (C2CBJG000460) System Microprocessor
26 Parts Location and Replacement Parts List
26.1 Deck Mechanism (RAA3412-S)
26.1.1 Deck Mechanism Parts Location
26.1.2 Deck Mechanism Parts List
26.2 DVD Loading Mechanism
26.2.1 DVD Loading Mechanism Parts Location
26.2.2 DVD Loading Mechanism Parts List
26.3 Cabinet
26.3.1 Cabinet Parts Location
26.3.2 Cabinet Parts List
26.4 Electrical Parts List
26.5 Packing Materials & Accessories Parts List
26.6 Packaging
1 Before Use
Be sure to disconnect the mains cord before adjusting the voltage selector.
Use a minus(-) screwdriver to set the voltage selector (on the rear panel) to the voltage setting for the area in which the unit will
be used. (If the power supply in your area is 117V or 120V, set to the “127V” position.)
Note that this unit will be seriously damaged if this setting is not made correctly. (There is no voltage selector for some
countries, the correct voltage is already set.)
2 Before Repair and Adjustment
Disconnect AC power, discharge Power Supply Capacitors C5815~C5818, C5829~C5830, C5835~C5836 and C5841
through a 10? , 5W resistor to ground.
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid state devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
Current consumption at AC 110/127/220~230V, 50/60 Hz in NO SIGNAL at (vol. min, in CD mode) should be as below:
AC 50/60Hz
110 V ~ 1200 mA
127 V ~ 1100 mA
220-230 V ~ 700 mA
240 V ~ 650 mA
2.1 Rework Process for Main Board
Versión RJBX0405A-1
For Main PCB version 1 only (RJBX0405A-1), is necessary add two Axial resistors covered with a plastic tube in order
to countermeasure a Pop Noise during Tuner - Recording.
Be sure that during the usage of this PCB these components are included.
Material Required:
1.) 2 Axial Resistor , (ERDS2TJ123T)
2) 5 Cm Of Spaghetti , (W1VT)
3) 1g of Diabond , (DN83K)
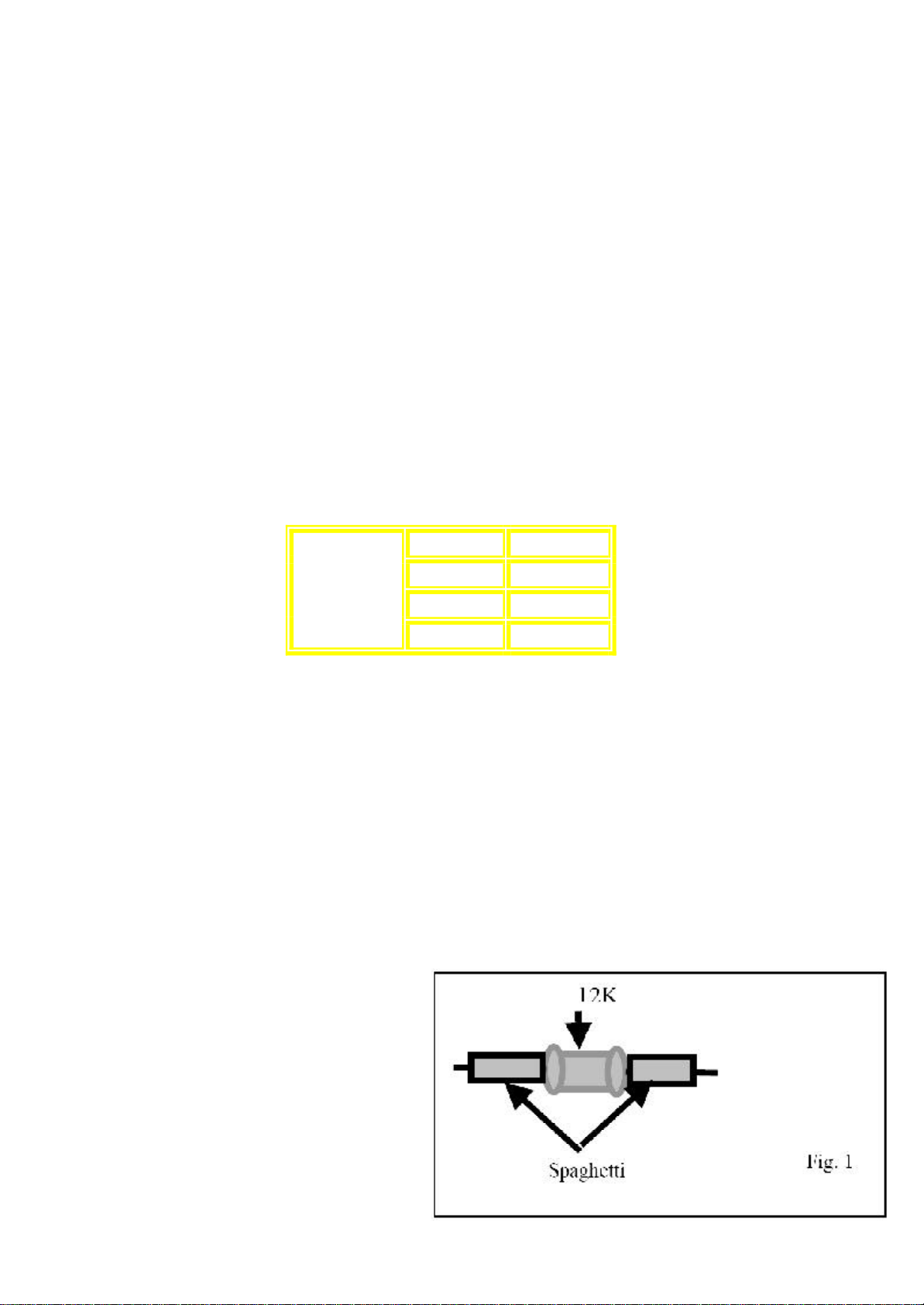
Step1.
Prepare the axial resistors as showed in the Fig. 1
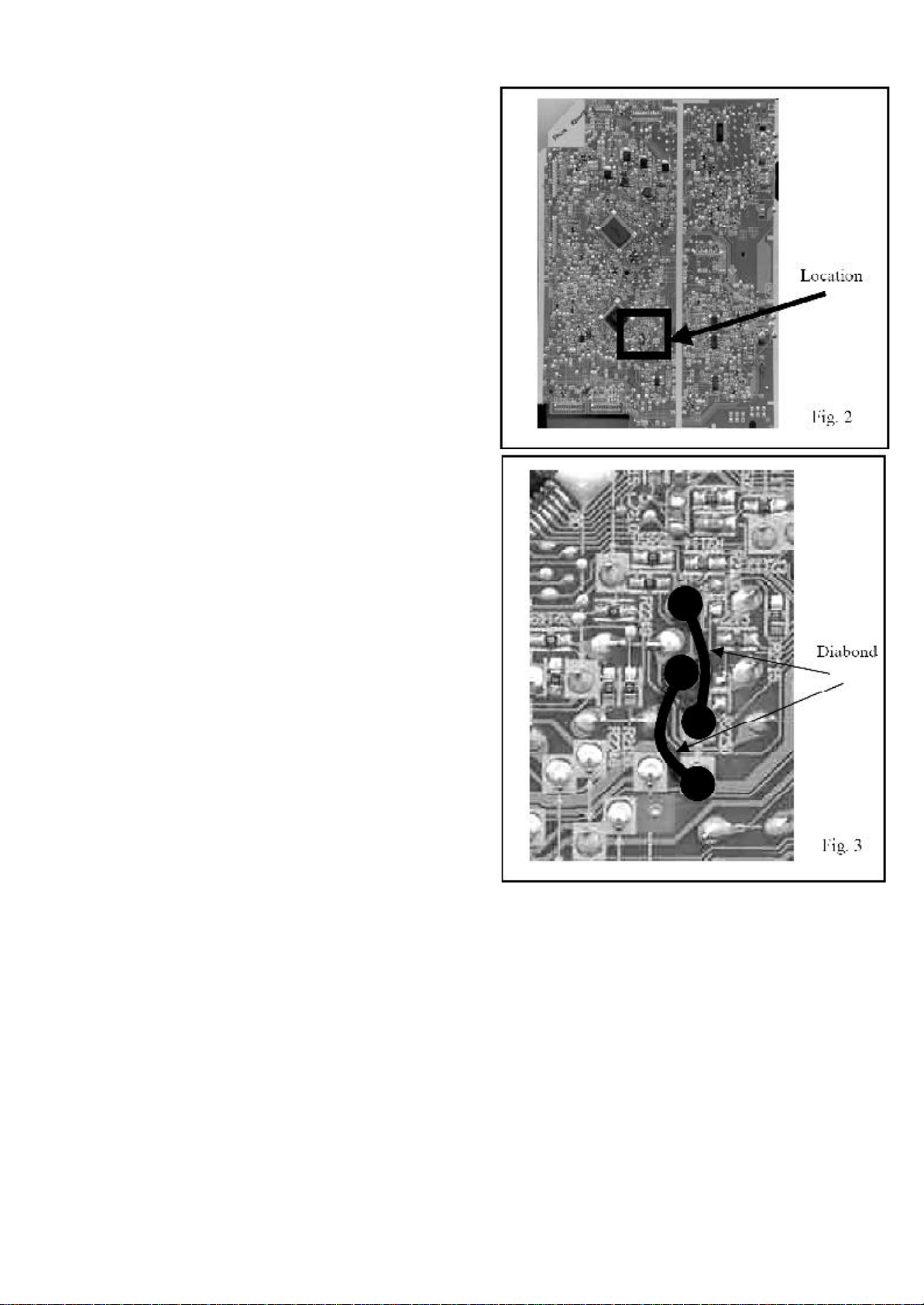
Step2. Locate soldering Points as showed in Fig.2
Step3. Solder the first resistor between W2346 and
(-)C2236 Fig3.
Step4. Solder the second resistor between W2346
and (-)C2139 Fig3.
Step 5. Add Diabond to fix the resistor to the PCB.
Fig.3
3 Protection Circuitry
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
· No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
· Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires
are “shorted”, or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used. If this
occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note :
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
4 Safety Precautions
4.1 General Guidelines
4.1.1 Leakage Current Cold Check
4.1.2 Leakage Current Hot Check (See Figure 1)
4.1 General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
4.1.1 Leakage Current Cold Check
4.1.2 Leakage Current Hot Check (See Figure 1)
4.1.1 Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on
the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis,the reading should be between 1M? and 5.2M?.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be ¥.
Figure 1

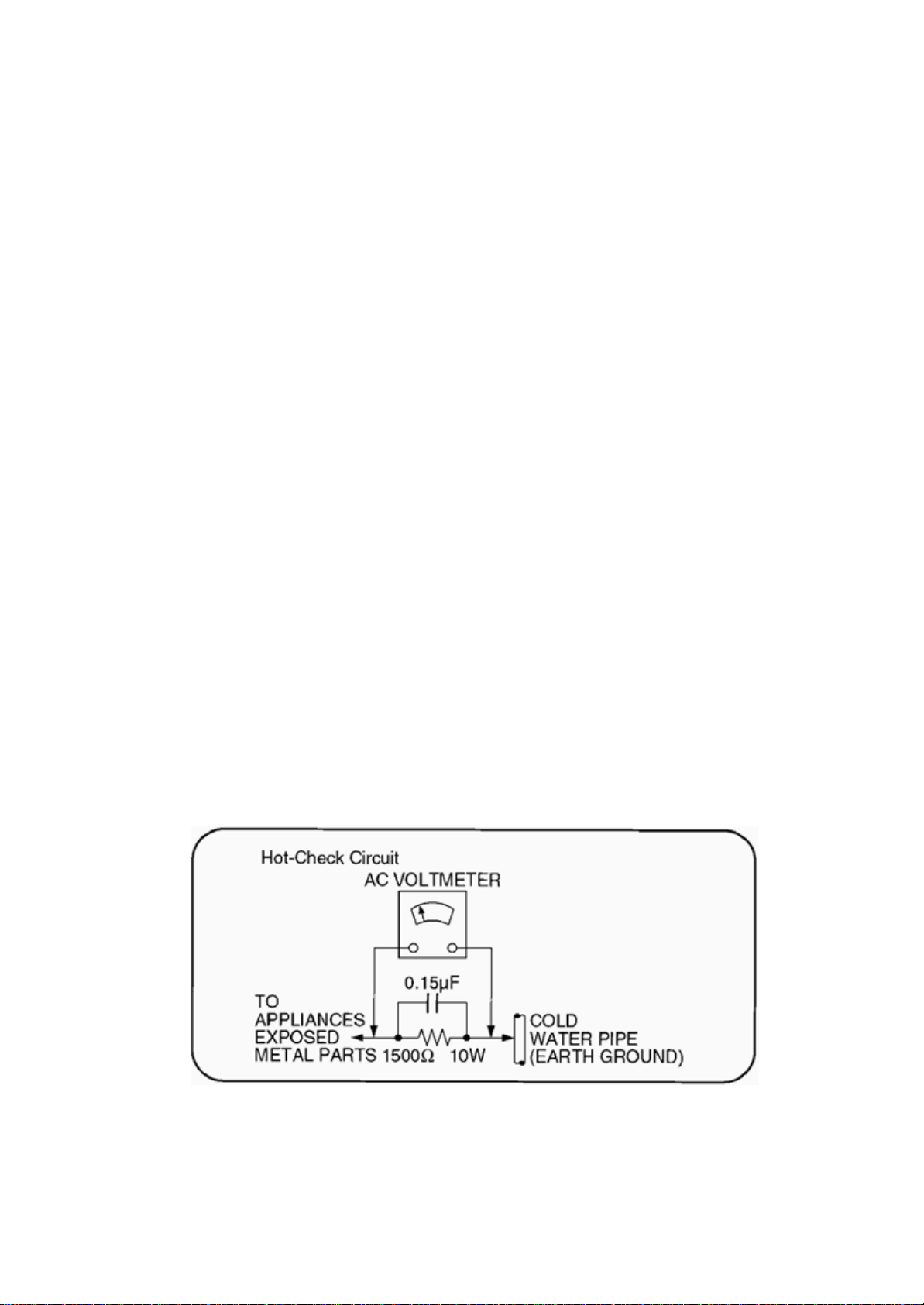
4.1.2 Leakage Current Hot Check
(See Figure 1)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5k? , 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF capacitor, betwee each exposed metallic part on the set and
a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent)
may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a measurement is out ofthe limits
specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaire and rechecked before it is returned to
the customer.
5 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge
(ESD) to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES)
Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistorsand semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of
component damage caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductorequiped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD
wrist strap, whichshould be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equiped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminium foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder remover device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)”
can generate electrical charge to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminium
foil orcomparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective
material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed. Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD)
sufficient todamage an ES device).
6 Handling the Lead-free Solder
6.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
6.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
Distinction of PbF P.C.B.:
P.C.B.s (manufactured) using lead free solder will have a PbF stamp on the P.C.B. Caution:
• Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder; Typically the melting point is 50 - 70°F (30 - 40°C) higher.
Please use a high temperature soldering iron.
In case of soldering iron with temperature control,please set it to 700 ± 20°F (370 ± 10°C).
• Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100°F/600°C).
• When soldering or unsoldering, please completely remove all of the solder on the pins or solder area, and be sure to heat the
soldering points with the Pb free solder until it melts enough.
7 Cautions to be taken when handling
Optical Pickup
The laser diode used inside optical pickup could be destroyed due to static electricity as a potential difference is caused by
electrostatic load discharged from clothes or human body.
Handling the parts carefully to avoid electrostatic destructionduring repair.
7.1 Handling Optical Pickup
7.2 Replacing Precautions for Optical Pickup Unit
7.3 Grounding for Preventing Electrostatic Destruction
7.1 Handling Optical Pickup
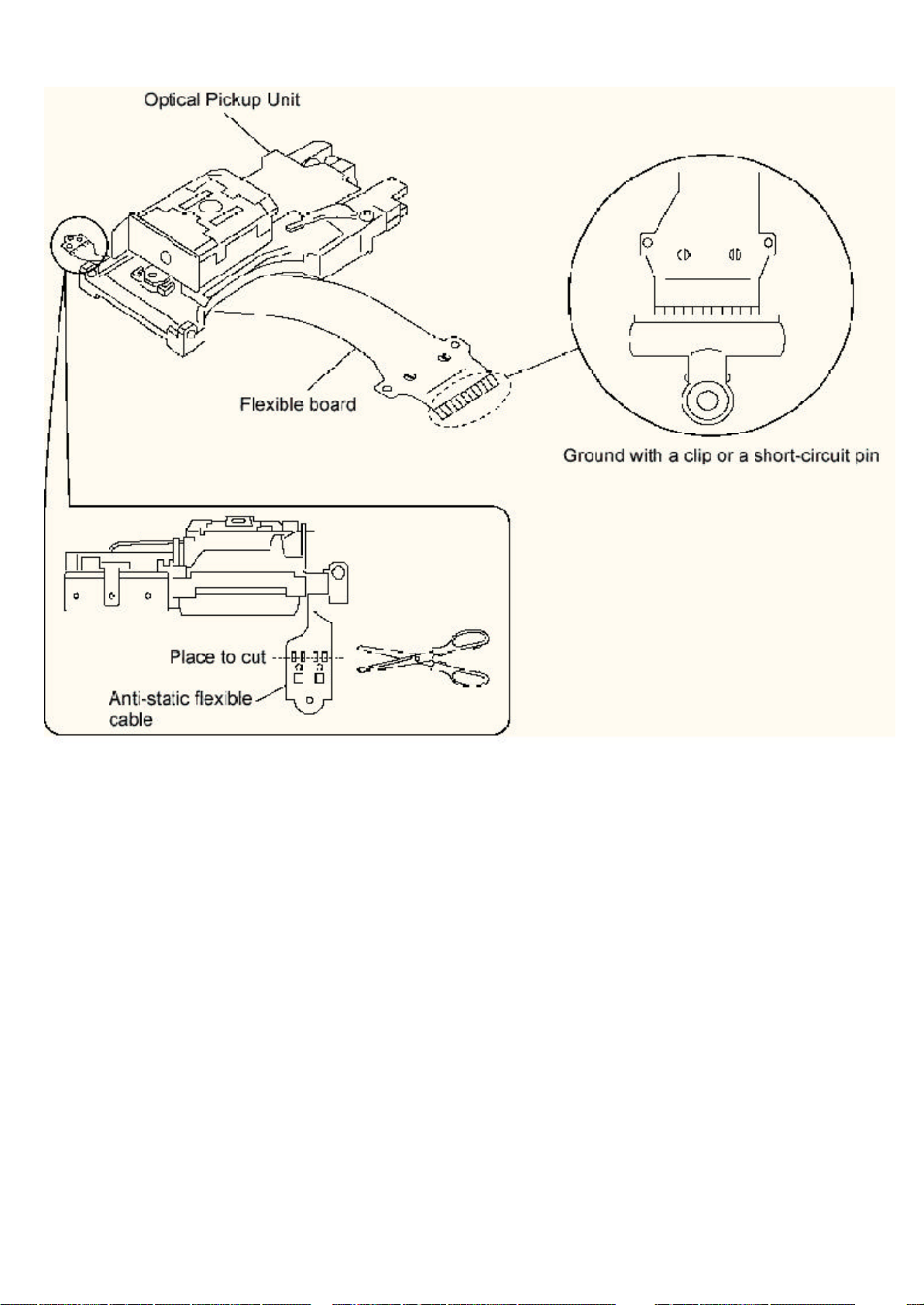
1. Do not impact on optical pickup as the unit structurally uses an extremely precise technology.
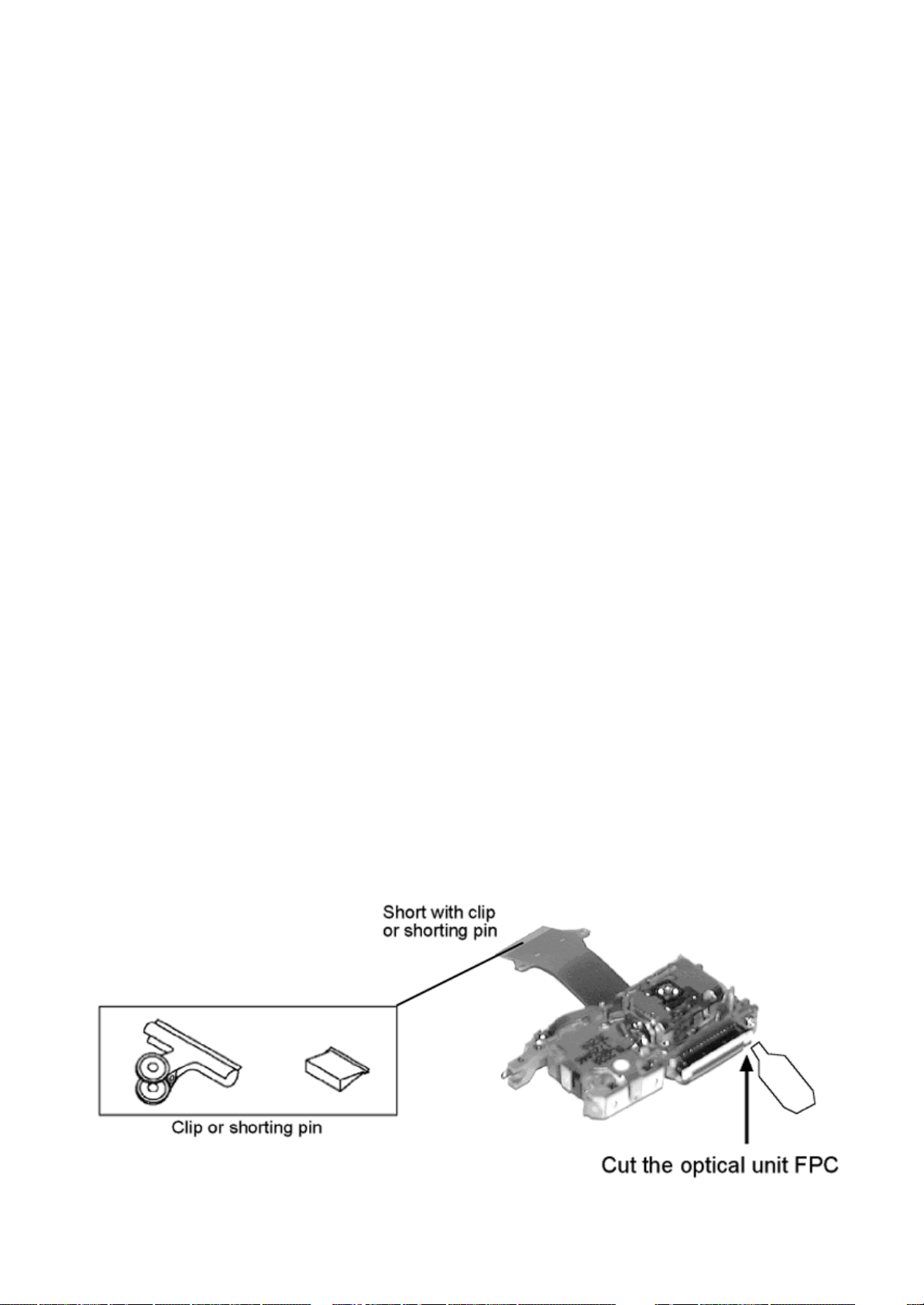
2. Short-circuit the flexible cable of optical pickup remove from the circuit board using a short-circuit pin or clip in order to
prevent laser diode from electrostatic destruction (Refer to Fig. 7.1 and Fig. 7.2)
3. Do not handle flexible cables forcibly as this may cause snapping. Handle the parts carefully (Refer to Fig. 7.1)
4. A new optical pickup is equipped with an anti-static flexible cable. After replacing and connecting to the flexible board, cut
the anti-static flexible cable. (Refer to Fig. 7.1)
Fig. 7.1
7.2 Replacing Precautions for Optical
Pickup Unit
DVD/CD Optical Pickup
The optical pickup by which part supply was carried out attaches the short clip to the flexible board for laser diode electrostatic
discharge damage prevention. Please remove the short clip and be sure to check that the short land is open, beforeconnecting.
(Please remove solder, when the short land short-circuits.)
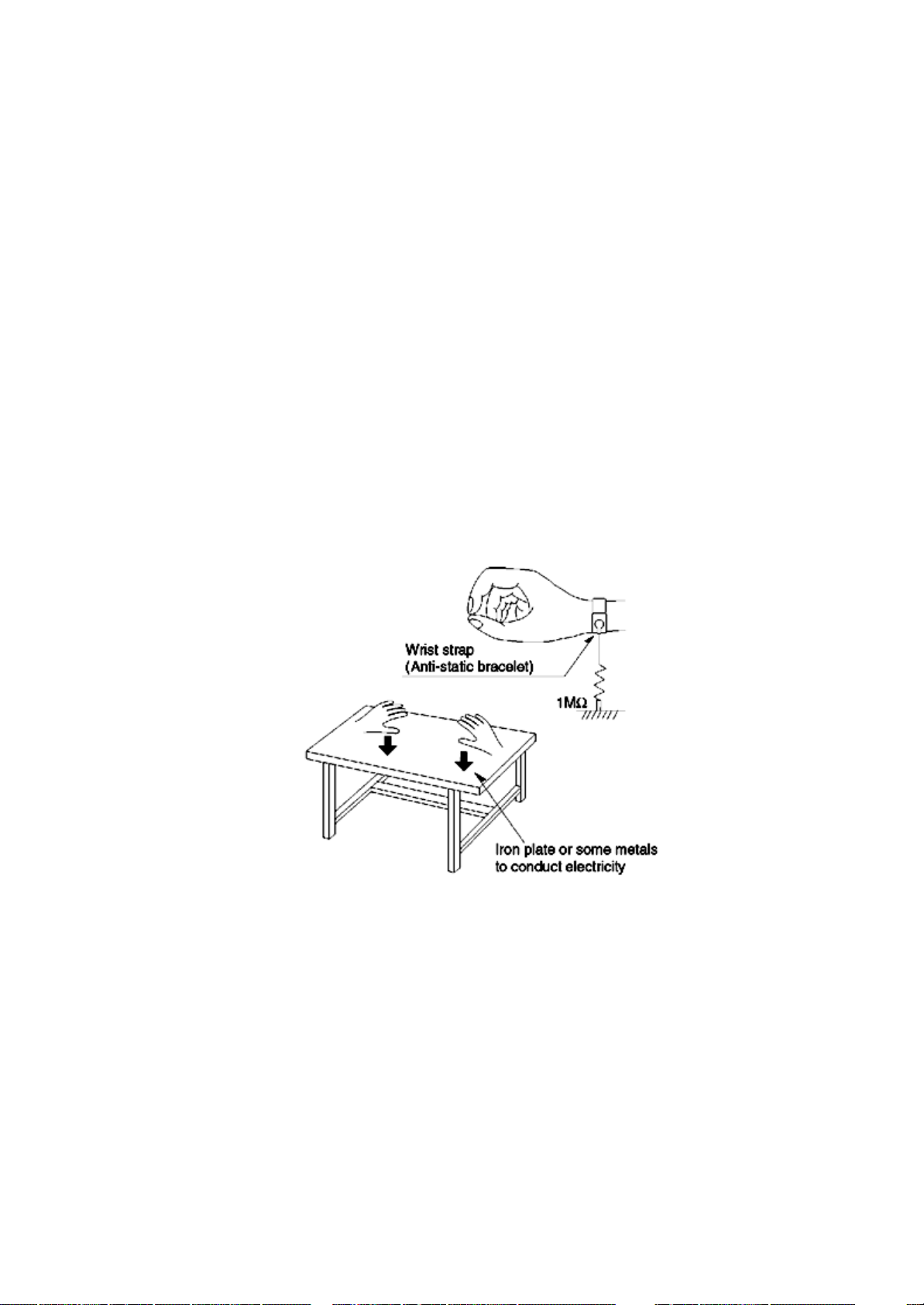
7.3 Grounding for Preventing Electrostatic
Destruction
1. Human body grounding
Use the anti-static wrist strap to discharge the static electricity accumulated in your body. (Refer to Fig. 7.2)
2. Work place grounding
Place a conductive material (conductive sheet) or ironboard where optical pickup is placed. (Refer to Fig. 7.2)
Note :
Keep your clothes away from optical pickup as wrist strap does not release the static electricity charged in clothes.
Fig. 7.2
8 Precaution of Laser Diode
Caution :
This product utilizes a laser diode with the unit turned «ON», invisible laser radiation is emitted from the pick
up lens. Wavelength : 662 nm(CD)/785 nm(DVD) Maximum output radiation power from pick up : 100 µW/
VDE
Laser radiation from pick up unit is safety level, but be sure the followings:
1. Do not disassemble the optical pick up unit, since radiation from exposed laser
diode is dangerous.
2. Do not adjust the variable resistor on the pick up unit. It was already adjusted.
3. Do not look at the focus lens using optical instruments.
4. Recommend not to look at pick up lens for a long time.
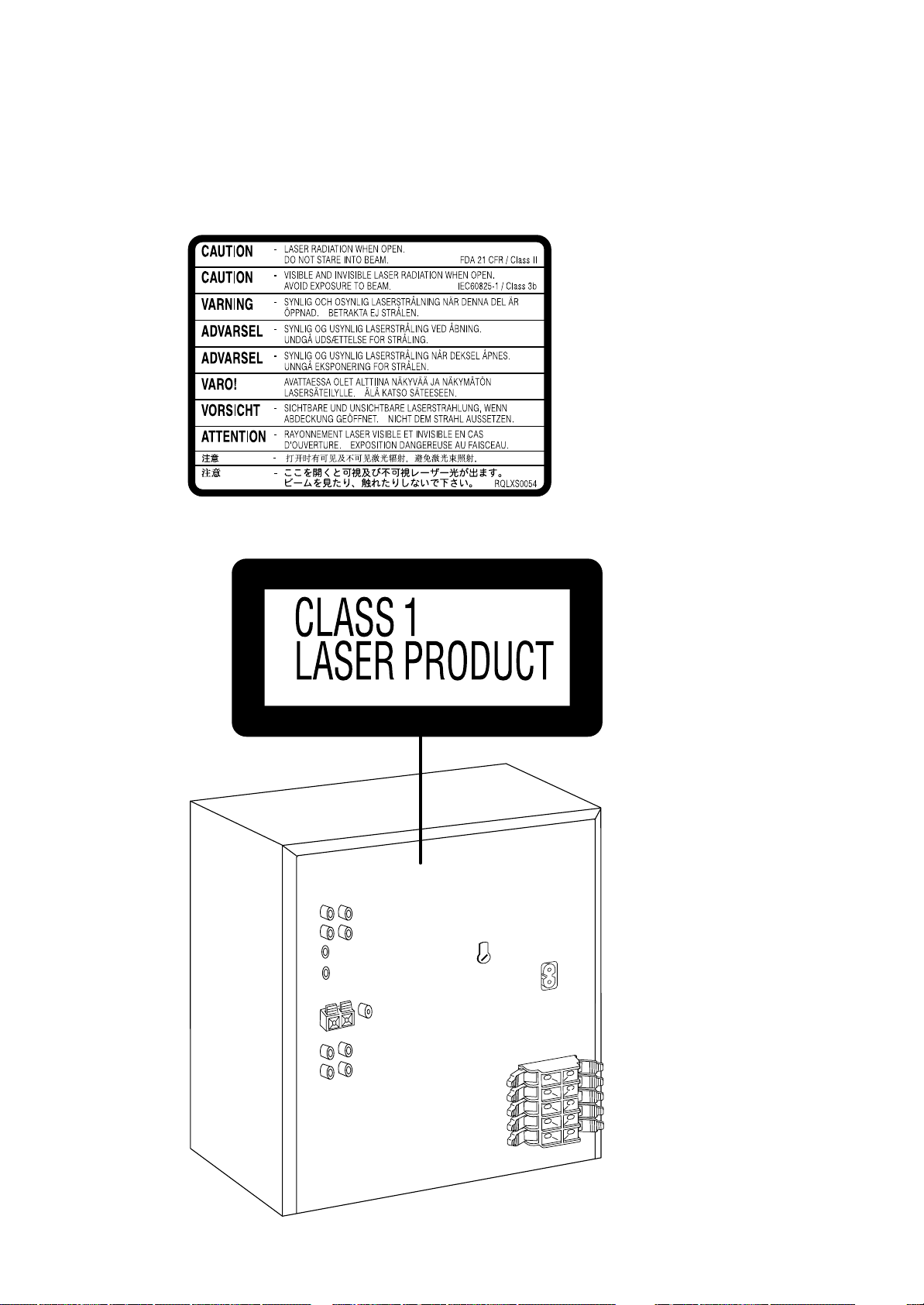
CAUTION!
THIS PRODUCT UTILIZES A LASER.
USE OF CONTROLS OR ADJUSTMENTS OR PERFORMANCE OF PROCEDURES OTHER THAN THOSE SPECIFIED HEREIN MAY RESULT IN HAZARDOUS
RADIATION EXPOSURE.
_ Use of Caution Labels
(Inside of product)

9 Accessories
Remote Control
N2QAJB000110
FM Indoor Antenna
RSA0007-L
AM Indoor Antenna
N1DAAA00001
Video Cable
RJL1P016B15A
10 Operation Procedures
11 Disc information
12 About HighMAT
12.1 What is HighMAT?
12.2 Why use HighMAT?
12.3 The advantages of using HighMAT
12.4 Outline of the HighMAT standard
12.1 What is HighMAT?
This word combines the abbreviations of Matsushita Electric Industrial Co. Ltd. and High Performance Media Access Technology,
and is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation. The products with the HighMAT logo shown below are made according to the
HighMATstandard.
HighMAT is a format that allows users to save digital contents such as photographs, audio, and images on a CD. This gives
consistency in the way of reading data when general consumer products (such as DVD players) and PCs are used, and thus,
itis easy to operate for the user.
12.2 Why use HighMAT?
Up to now, there was no harmonized standard from playing digital content stored in CD-ROM formats (including CD-R) on
consumer products like DVD players.Therefore, we used to have problems such as follow:
• There was no common play list or attached information on contents, which is called metadata.
• The data compression method differed according to the equipment.
• As the number of CD-ROMs recorded increased retrieved the contents became more difficult.
• Because display and operation methods were different depending on the equipment, the play order of the content on
the same disc could change.
12.3 The advantages of using HighMAT
Applying the HighMAT standard will solve the following problems and will improve usability.
• It will create a common user interface for both PC and consumer products.
Regardless of the types of consumer products, such as DVD players, portable CD players, car stereos, and micro computers,
a consistent way to pay for digital content will be created and it will make it easier to retrieve data.
You can also play digital content on the disc, which was created in accordance with the HighMAT format with a conventional
CD-ROM player.
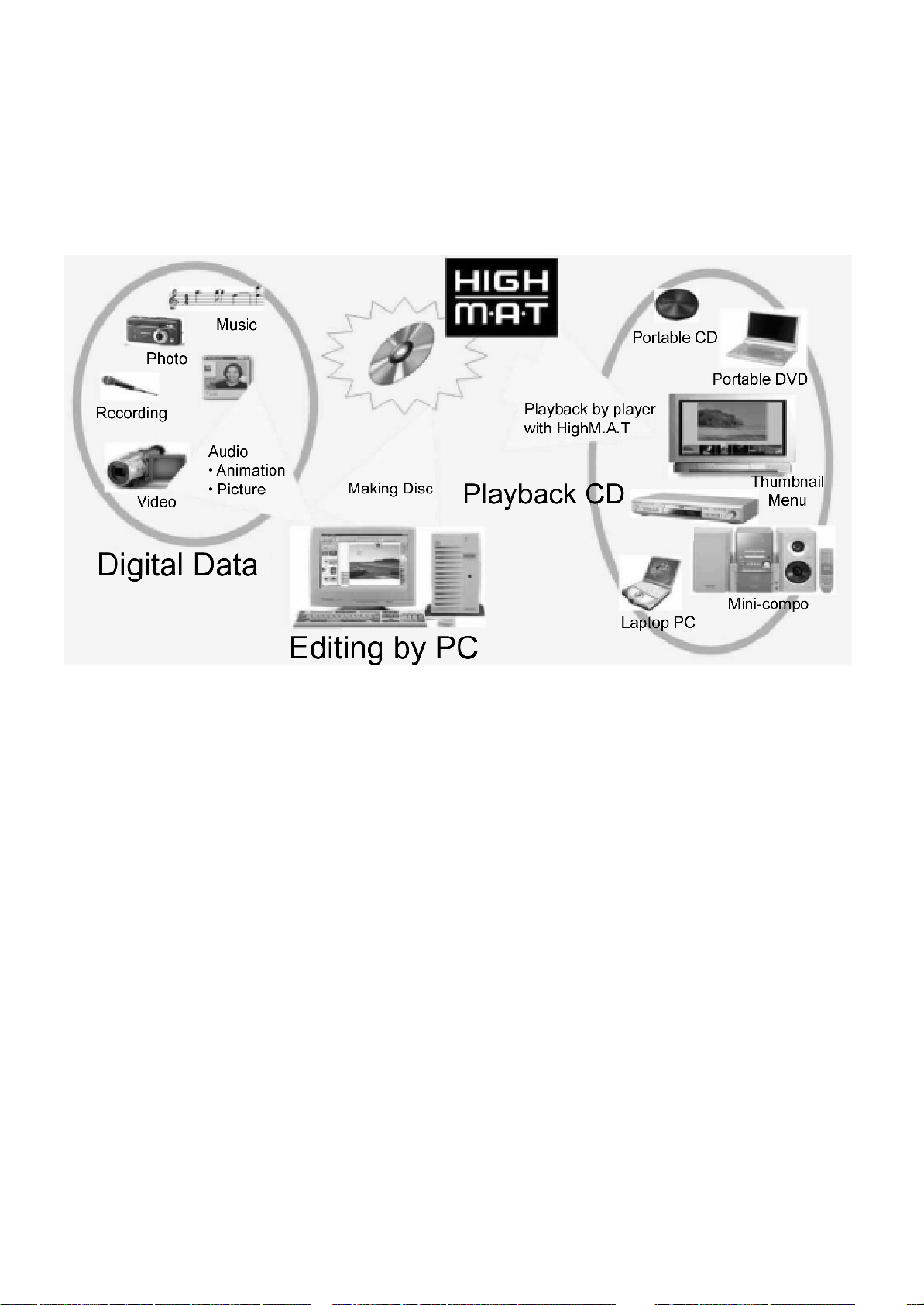
12.4 Outline of the HighMAT standard
Recording medium
• CD-R/CD-RW
• Supports ISO 9660 Level Expanded Joliet
• For multiple session
Support data format
• Level 1 player: WMA, MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3)
• Level 2 player: WMA, MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3), JPEG
• Level 3 player: WMA, MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3), JPEG, WMV, MPEG4 (optional)
Limitation of data format
• WMA, MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) 64 kbps - 160.999 kbps, 44.1 KHz, stereo, fixed bit rate/ variable bit rate.
• WMA, V2 and above, excluding Lossless/Voice/Pro
• JPEG: Max 6M pixel, Maximum file size: 3 MB
Limitations regarding the number of files on the media, etc.
• Total number of audio files: Maximum 450
• Total number of still picture files: Maximum 999
• Total number of animation files: Maximum 200
• Total number of directories: Maximum 400
• Length of a file name: Maximum 108 characters (Unicode)
• Total number of play lists: Maximum 200
• Number of contents in the playlist: Maximum 900
Composition of HighMAT disc
• Menu: Classified for the navigation of the HighMAT digital contents. When menu selected, its submenu or the play list
will be displayed.
• Play list: A list in which one or more digital contents are arranged in order
• Group: Sub-divided group of a play list.
• Digital Contents: Audio, still picture, and animation data.
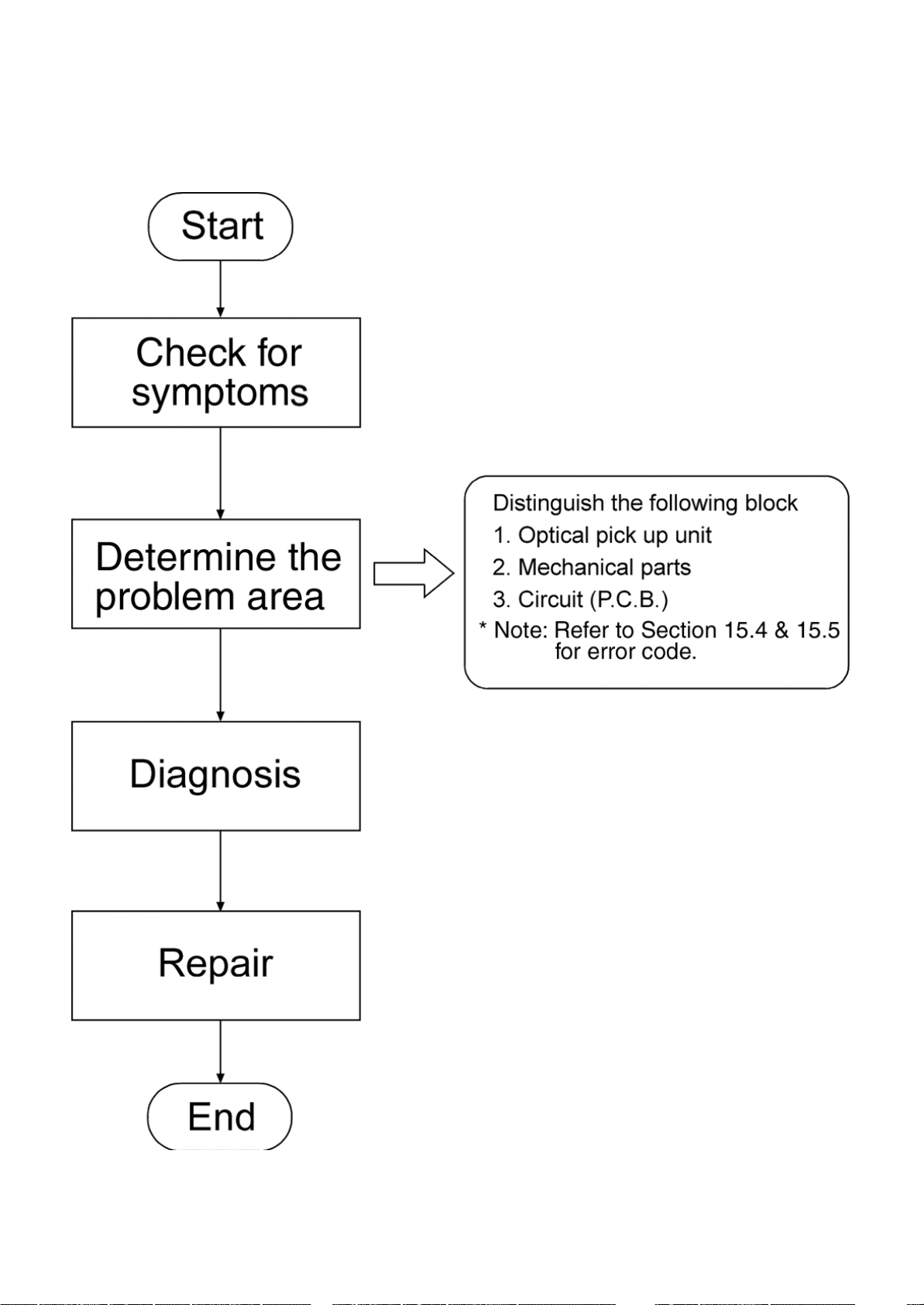
13 Procedure for repairing the set
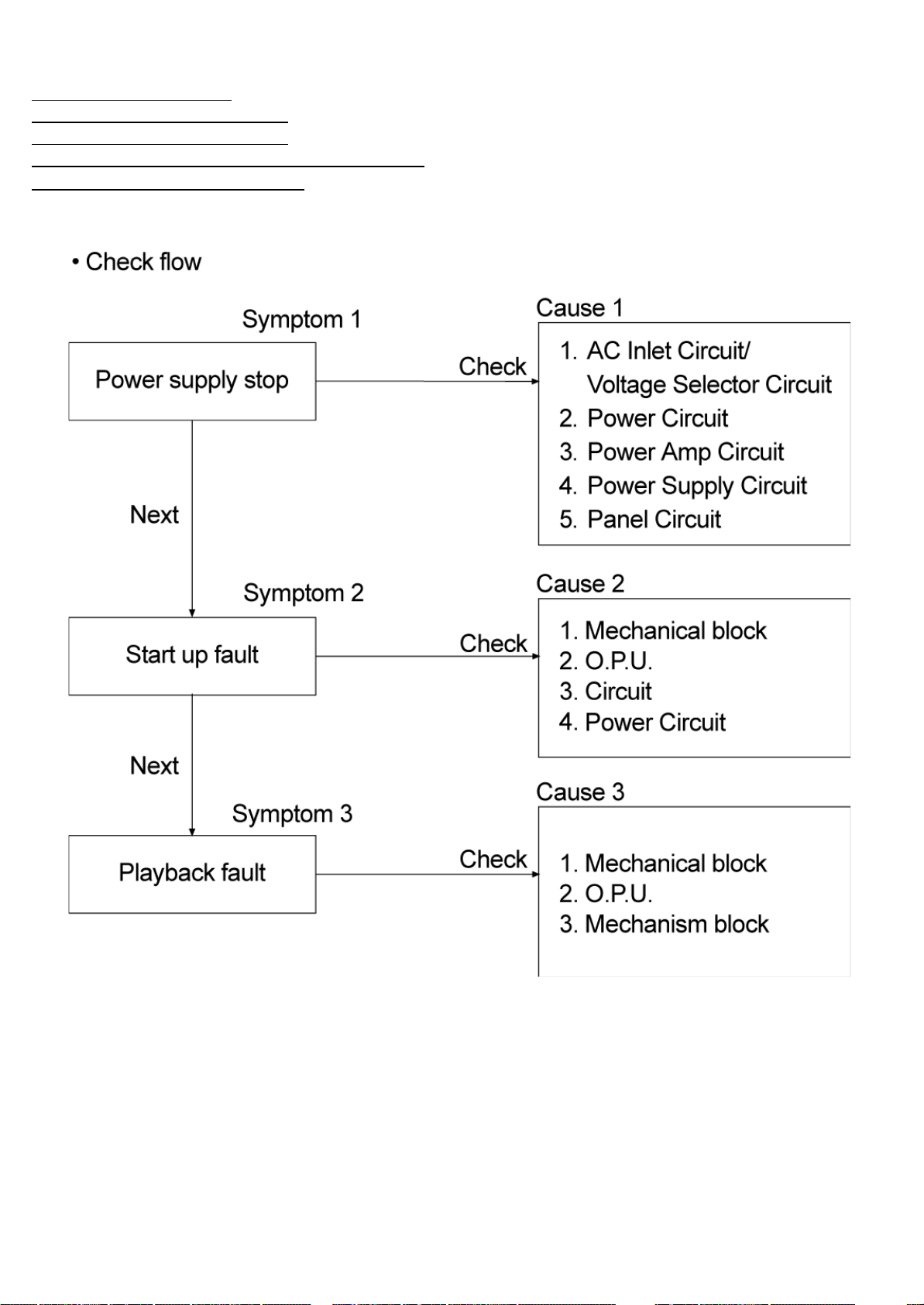
13.1 Distinguish the problem
13.1.1 Troubleshooting Guide Part 1
13.1.2 Troubleshooting Guide Part 2
13.1.3 Checking of VIDEO COMPONENT OUTPUT
13.2 Diagnosis of Optical Pick-up Unit
13.1 Distinguish the problem
How to distinguish the trouble
View mechanical part if visual damage occurred.
Confirm the movement of mechanical parts assembly (tray ass’y, loading mechanism ass’y, etc.).
Diagnose if Optical Pickup Unit is faulty (refer to diagnosis of Optical Pickup Unit).
If mechanism and OPU are OK, it is P.C.B.
13.1.1 Troubleshooting Guide Part 1
13.1.2 Troubleshooting Guide Part 2
13.1.3 Checking of VIDEO COMPONENT OUTPUT
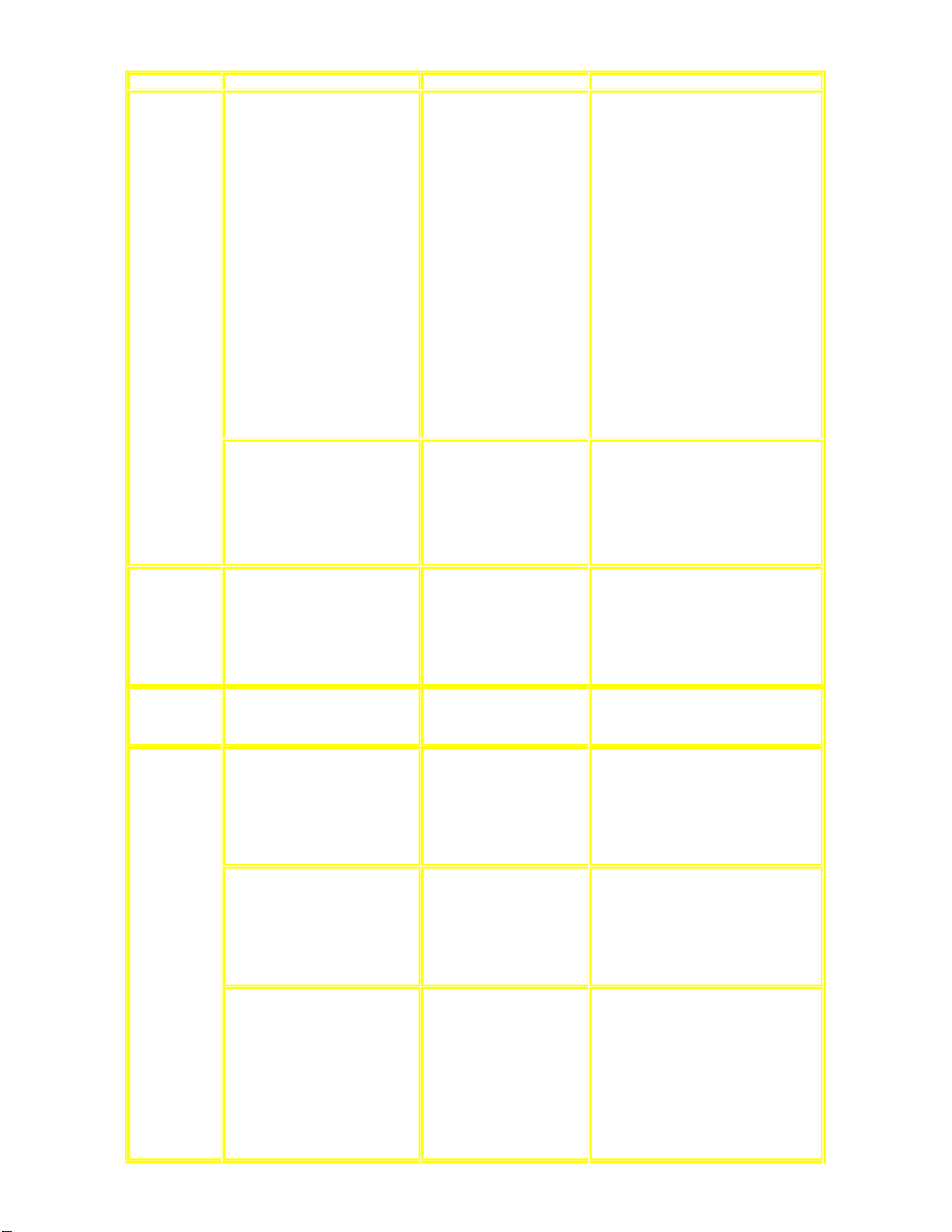
13.1.1 Troubleshooting Guide Part 1
•
•
Checking Points Possible Faults Possible Reasons Countermeasure
AC Inlet
Circuit/Voltage
Selector Circuit
1. Failure to power-up the main unit.
2. Power On switch
Intermittent Power supply to main
3.
unit.
• Wrong selection of
AC power to main
it.
un
• Replace of fuse if found faulty.
• Replace of voltage selector if found
faulty.
• Voltage selector is
faulty.
• Replace of AC Inlet if found faulty
damaged.
or
• AC inlet JK500 is
faulty.
AC Line filter L500 is
faulty.
• Replace AC Line filter is found
faulty or damaged.
• Replace Power On button switch if
necessary.
• Power On switch
br
oken.
• If conditions as mentioned above is
in good condition. Check for wire
connection.
(W1/
W2/W3/W4/W6/W7). If
connection is good, please proceed
to check for Transformer Circuit.
• Check for connection. • If condition 1 to 4 as mentioned
above is in good condition. Check
for wire connection.
(W1/
W2/W3/W4/W6/W7). If
connection is good, please proceed
to
checkfor Transformer Circuit
Transformer
Circuit
Power Circuit
1. No power supply voltage to the Power
Circuit from AC In.
1. No supply voltage to Power Supply
Circuit from Transformer Circuit.
(+VccL/+VccH/-VccL/-VccH)
1. No supply voltage to Main & Power
pply Circuit from Transformer
Su
Circuit. (+VccL/+VccH/-VccL/-VccH)
1.
No supply voltage to Panel Circuit.
Transformer no output
vo
ltage.
• Power Line filter
relay RL502.
• D950 open circuit.
• Fuse F3/F4 blown.
• Rectifier Circuit
oblem.
pr
• Rectifier Circuit
oblem.
pr
• F5801/FP5802 open
circuit.
• Q5815/D5835 faulty.
VP voltage not
(sufficient to power FL
di
splay at - 30V)
• Q5816/D5839 faulty.
ys 6V not sufficient
(S
to
power micro-
ssor IC at 6V.
proce
• Replace of Transformer T501 if
fo
und faulty.
• Replace of Power Relay if found
faulty.
• Replace fuse F3/F4 if found faulty.
• Replace
D5832/D5831/D5846/D5847 if any
is found to be faulty or damage.
• Replace D5844 if found faulty.
• Replace FP5801/FP5802 of the
same type as indicated in the part-
if found faulty.
list
• Replace Q5815/D5835 if found
faulty.
• Replace Q5816/D5839 if found
faulty.
13.1.2 Troubleshooting Guide Part 2
Checking
Po
ints
Deck Circuit
Panel
Circuit
ssible Faults Possible Reasons Countermeasure
Po
1. No PLAYBACK
B)/Rec signal.
(P
• IC1001 problem. (Check pin 23/24 for PB
put, pin 5/20 for PB output).
in
• Replace IC1001 if necessary.
• Replace Q1013/Q1012 if necessary.
• Q1013/Q1012 shorted to ground with no
muting OFF.
• Replace Q1020/Q1021 if necessary.
• Q1020/Q1021 shorted to ground with no
muting OFF.
2. Bias frequency.
3. No supply voltage
(+B/M0+B)
1. FL No Display
Error codes
2.
• L1002 /IC1004/ Q1004/Q1005 problem.
Check level of bias frequency and
cillation.
os
• See section on Panel Circuit.
• -Vp too low to power FL display.
• FL Display Driver IC problem. (IC6803)
• Replace these components if
necessary when level is below
specification.
• See section on Power Circuit.
• Replace IC6803 is faulty.
• See section on error codes (Micro-processor
IC6800)
Main Circuit
1. Audio Signal (I/P &
O/P) problem.
2. Video Signal
pr
oblem.
• Check for IC2815. • Replace IC2815 if faulty.
• Refer to below section.
13.1.3 Checking of VIDEO COMPONENT OUTPUT
VIDEO SIGNAL Y C CR/PR/R CB/PB/B PY/Y/G
Input Pin 5 (IC2809) Pin 3 (IC2809) Pin 14 (IC2809) Pin 12 (IC2809) Pin 8 (IC2809)
VIDEO SIGNAL Y C CR CB/PB/B PY
Output Pin 24/25 (IC2809) Pin 32 (IC2809) Pin 17 (IC2809) Pin 19 (IC2809) Pin 21/22 (IC2809)
Terminal Defination (IC2809 - C9ZB00000377)
Pin No Pin Name Pin Description
21/22 PYOUT1/PYOUT2 Signal Output Terminal for luminance signal (progressive type)
17/19 CrOUT/CbOUT Signal Output Terminal for color-difference signal
32 COUT Signal Output Terminal for chroma signal
29/30 MIXOUT1/MIXOUT2 Signal Ouptut Terminal for Y/C Mix Signal
24/25 YOUT1/YOUT2 Signal Output Terminal for luminance signal (interlaced type)
3/12/14 CIN/CBIN/CRIN Input signal terminal for chroma signal and color difference
5/8 YIN/PYIN Input signal terminal for luminance signal
13.2
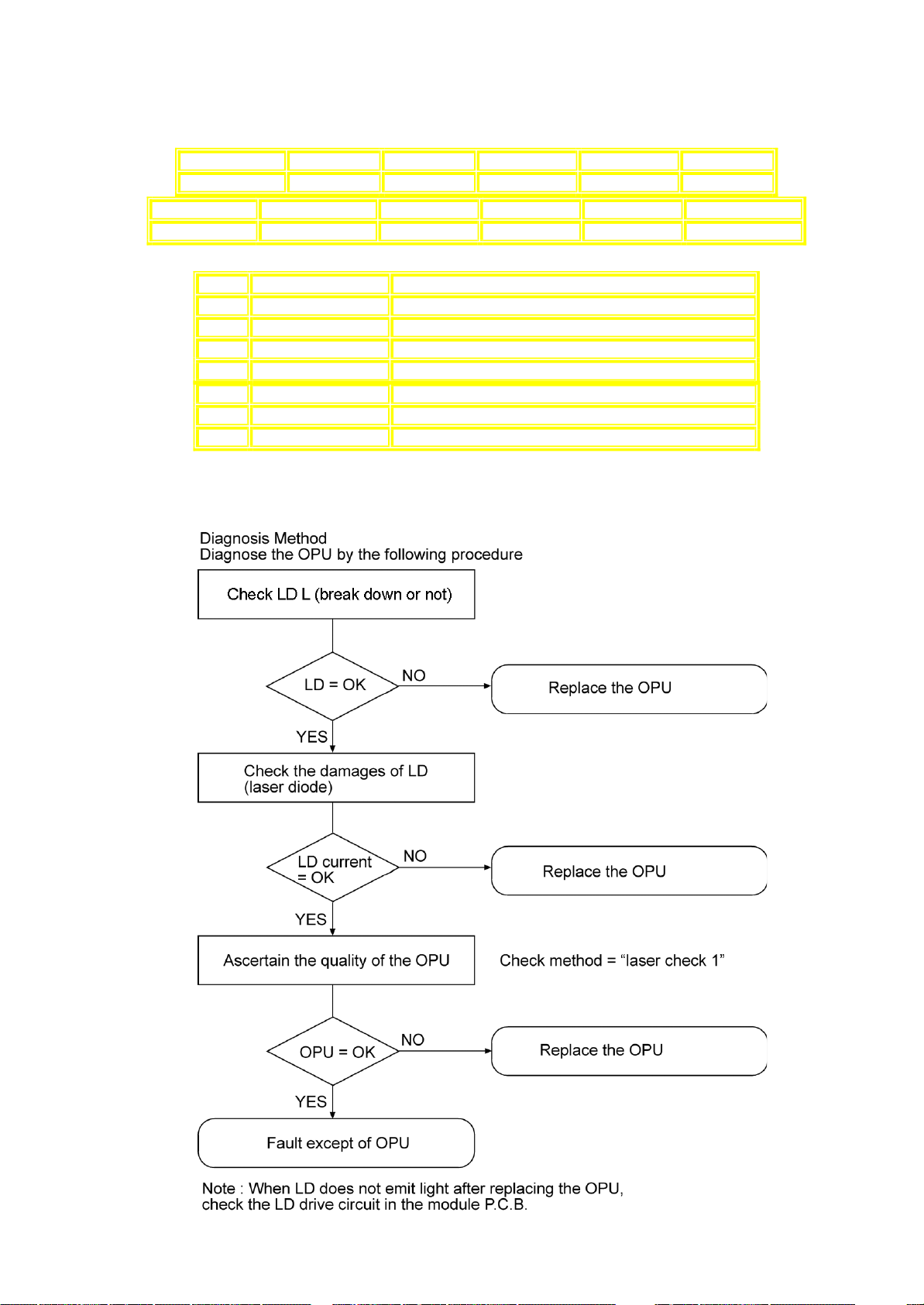
Diagnosis of Optical Pick-up Unit

How to distinguish Laser destruction/damage
Confirmation 1
Remove cover of mechanism block so that you will see the lens of optical pickup.
Confirm emission of laser at the moment when power switch is turned on.
If there is no laser emission, laser diode is faulty.
Confirmation 2
While press and hold “STOP” on main unit , press “Display” button on the remote controller. Unit display laser current on FL.
From the reading of display, you can judge if laser diode is damaged or not.
Reading on the right side should be less than 70. If reading is more than 70, laser is damaged.
How to confirm if Optical Pickup is OK
Confirmation 1
1. Confirmation of jitter value with test disc. (Refer below for how to check jitter)
2. Lens cleaning.
3. Reconfirm jitter value.
4. Perform tile adjustment. (Refer to tilt adjustment)
5. Reconfirm jitter value. (To confirm jitter value, while pressing “STOP” on main unit and “5” on remote controller.)
Unit display jitter value on FL.
Confirmation 2
If servo is very unstable due to optical error and you cannot confirm jitter value, clean the lens and check appearance of pick
up unit (cutting coil of actuator, etc), then check circuitry.
14 Optical Pickup Self-Diagnosis and Replacement
Procedure
14.1 Self-diagnosis
14.2 Cautions to Be Taken During Replacement of Optical Pickup and Spindle Motor
14.2.1 Cautions to be taken during replacement of optical pickup
14.1 Self-diagnosis
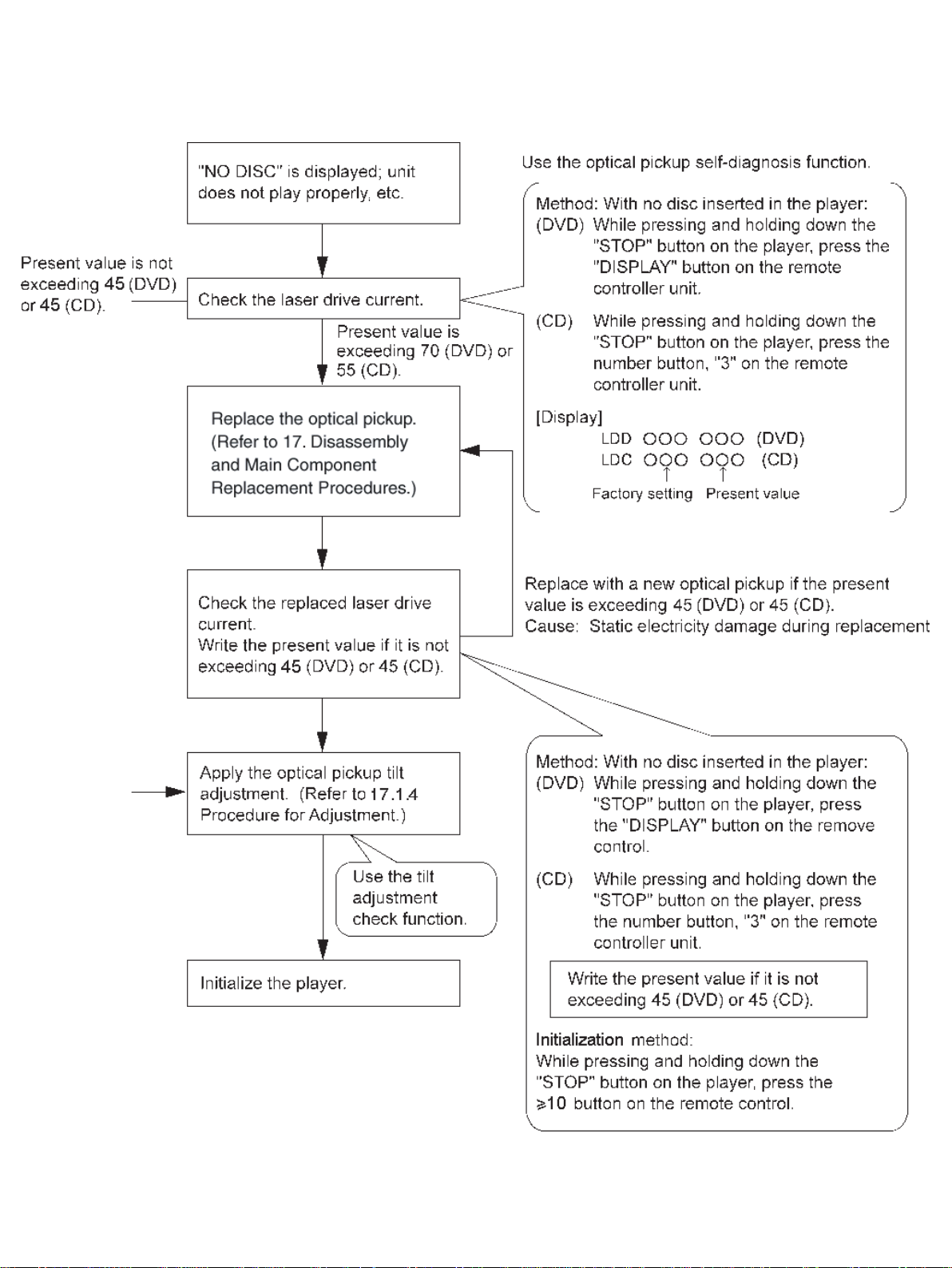
This unit is equipped with the optical pickup self-diagnosis function and the tilt adjustment check function. Follow the procedure
described below during repair in order to perform self-diagnosis and tilt adjustment effectively. Especially when “NODISC” is
displayed, be sure to apply the self-diagnosis function before replacing with an optical pickup.
Replacement of optical pickup generally requires when the present value of laser drive exceeds 45 (DVD) or 45 (CD).
Note:
Start diagnosis within three minutes after turning on the power (as diagnosis fails when the unit becomes warm).
14.2 Cautions to Be Taken During Replacement of
Optical Pickup and Spindle Motor
Before replacing the optical pickup and spindle motor, check a total usage time respectively. Follow the checking method
described below.
Item Status and Key Function Display
Checking DVD, CD laser
usage time
With
the unit stopped and no disc inserted, press
e.
th
button on the player and the
buttonon the remote controller unit.
T1_xxxx_yyyy
xxxx(DVD), yyyy(CD): total time is displayed with a four-digit
nu
mber by the ten hours.
Checking spindle motor
usage time
Resetting DVD, CD laser
usage time
Resetting spindle motor
usage time
With
the unit stopped and no disc inserted, press
e
th
button on the player and the
buttonon the remote controller unit.
While the DVD and CD laser usage times are
splayed, press the
di
button on the player and the
button on the remote controller unit.
While the spindle motor usage time is displayed,
press the
button on the player and the
buttonon the remote controller unit.
T2_xxxxx
xxxxx: total time is displayed with a four-digit number by the ten
hours.
T1_0000_0000
T2_0000
14.2.1 Cautions to be taken during replacement of
optical pickup
Optical pickup could be damaged due to the static electricity discharged from human body.
Wear proper protection gear against static electricity during optical pickup and its peripheral repair. (Refer to “Cautions to Be
Taken When HandlingOptical Pickup”.)
• Do not touch laser diode, actuator and their peripherals.
• Do not check laser diode with a tester and such. (The tester will be destroyed.)
• For short-circuiting or removing laser diode, the use of an anti-static soldering iron is recommended. (Recommended model:
HAKKO ESD product)
• Solder the land of the flexible cable in the optical pickup.
Note:
If an anti-static soldering iron is not available, short-circuit the terminal surface of the flexible cable and then the land using a clip
or equivalent device.
15 Self-Diagnosis Function
This unit is equipped with the self-diagnosis function, which displays an error when it occurs, for use during servicing.
15.1 Automatic Displayed Error Codes
15.1.1 Automatic Display Function
15.1.2 Re-Display
15.1.3 Description of Error Code
15.2 Memorized Error Codes
15.2.1 Activating Self-Diagnosis Function and Displaying Method
15.2.2 Re-Display
15.3 Mode Table 1
15.4 DVD / CD Self-Diagnosis Error Code Description
15.5 Error Codes Stored During No Play
15.6 Mode Table 2
15.7 Tray Lock Function
15.7.1 Setting
15.8 Things to Do After Repair

15.1 Automatic Displayed Error Codes
15.1.1 Automatic Display Function
15.1.2 Re-Display
15.1.3 Description of Error Code
15.1.1 Automatic Display Function
For a power unit error, the code is automatically displayed.
• F61:
Automatically displayed on the LCD of the player.
15.1.2 Re-Display
• For F61 Display
o When the code, F61 is displayed, the power is automatically turned off.
o The code, F61 is displayed for three seconds, and then the current time appears.
o To retrieve the code, turn on the power button so that the code F61 appears, however, is switched to time display after three
seconds, and the power is automatically turned off.
• For F76
o The abnormalities is an output or the abnormalities in a power supply of POWER AMP.
15.1.3 Description of Error Code
15.1.3.1 F61
• State, Condition
When the power is turned on, the unit is automatically turned off. The power does not turn on.
• Cause, Troubleshooting
Power circuit system failure and/or direct current flown to speaker terminal Identify the cause and replace with new parts.
15.2 Memorized Error Codes
15.2.1 Activating Self-Diagnosis Function and Displaying Method
15.2.2 Re-Display

15.2.1 Activating Self-Diagnosis Function and
Displaying Method
1. Turn on the power.
2. Select DVD/CD function. With no DVD/CD inserted in the player, press and hold down the button for at least two
seconds, and press the “0” buttonon the remote control for at least two seconds in order to display “DVD_F_ _ _ ”.
3. Press the button. If a memorized error is detected, the result of self diagnosis is displayed.
(Ex.: T H15)
If several errors are detected, press the button to display each.
15.2.2 Re-Display
• Press the power button to turn off the power, and then turn on the power
• The details of self diagnosis are stored in the unit memory.
To retrieve them, follow the procedure described the above, “Activating Self- Diagnosis Function and Displaying Method”.
15.3 Mode Table 1
Following modes are available with combinations of the pressed buttons on the player and on the remote controller unit.
Player Remote Controller Unit Usage
0 Error code display (Refer to the Item 15.4. DVD Error Code Description)
button
5 Tilt adjustment (Jitter)
6 Region number and broadcasting system check
8 Bulit-in program version check (Micro-P)
DISPLAY DVD laser drive current check
3 CD laser drive current check
PAUSE Writing of laser drive current value after replacement of optical pickup
(Do use this function only when optical pickup is replaced.)
Initialization of the player (factory setting is restored.)
Used after replacement of micro-computer and its peripherals and printed circuit board.
15.4 DVD/CD Self-Diagnosis Error Code Description
Error Code State, Conditon Cause, Troubleshooting
H15 The disc tray cannot be opened: it closes spontaneously.
H16 The disc tray cannot be closed: it opens spontaneously.
Error Code Meaning Details
U. H. Error
U11 Focus servo failure
H01 Tray loading failure
H02 Spindle servo failure (Spindle servo, DSC, SP motor, CLV servo failure)
H03 Traverse motor failure
H04 Tracking servo error
H05 Seek timeout failure
H06 Power supply error
DSC system
F500 DSC failure DSC stops due to servo failure.
F501 DSC not Ready failure Communication failure between DSC and system computer
F502 DSC Time out failure See F500.
F503 DSC communication failure Communication failure (Result failure occurs after communication command is
F505 DSC Attention Error See F500.
F506 Invalid media Disc is placed upside down; TOC is unreadable or invalid disc is inserted.
Disc Code
F103 Ilegal highlight position Disc standard is possibly illegal when highlight is displayed.
IIC Error
F4FF Forced initialization failure (Time out)
F880 Unsuitable task number When a message arrives from not existing task
F890 A message is sent during AV task
F891 Unable to transmit a message to AV task When transmission of a message to AV task starts
F893 DVD Module problem Check for firmware version
F894 EEPROM failure
F895 Firmware compatibility problem Check for firm version for Main & DVD Module P.C.B.
F897 Initialization is not done properly Follow proper steps for initialization & reset
F8A0 Unsuitable message command When transmission of a message to AV task starts
ansmission
tr
(Startup, focus failure, etc.)
(No communication because DSC does not move)
tr
ansmitted.)
During transmission of a message to AV task
Disc tray open/close detection switch (S1001) failure.
(Check and replace)
15.5 Error Codes Stored During No Play
Error
Code
F0BF 6) Unable to replay due to physical layer
F0C0 8) DVD: Unable to replay due to no DVD
F0C1 9) DVD: Prohibited due to illegal regional code PCND_NOPLAY_RCD 0x80 DiscManager 0xD0C1
F0C2 A) DVD: No replay due to PAL system PCND_NOPLAY_PAL 0x90 DiscManager 0xD0C2
F0C3 B) DVD: All title replay prohibited in parental
F0C4 C) VCD: Prohibited due to PHOTO CD format PCND_NOPLAY_PHOTOCD
F0C5 D) VCD/CD: Prohibited due to CD-ROM without
identification failure
Video/Audio/VR
setting
CD
-DA
Meaning System Computer Item Setting Task Internal error in system
PCND_NOPLAY_PHYSICAL
0x50
PCND_NOPLAY_VIDEO 0x70 DiscManager 0xD0C0
PCND_NOPLAY_PTL 0xA0 DiscManager 0xD0C3
B0
0x
PCND_NOPLAY_CDROM 0xC0 DiscManager 0xD0C5
DriveManager 0xD0BF
DiscManager 0xD0C4
computer
 Loading...
Loading...