Page 1

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Flat Solid Polycarbonate Sheet
Page 2

Content
PALSUN® Product Range 3
Standard Dimensions 3
Colors 4
Physical Properties 5
Impact Strength 6
Optical Characteristics 7
Solar Transmission Properties 8
SolarSmart™ Technology 9
Thermal Characteristics 10
Protection from the Harmful Effects of UV Radiation 11
Acoustic Properties 11
Weather Resistance 12
Flammability 12
General Recommendations for Working With PALSUN® 13
Determination of Required Sheet Dimensions 14
Installation 18
Mechanical Fastening 22
General Fabrication Guidelines 23
Sawing & Cutting 23
Routing 27
Drilling 28
Finishing 29
Cleaning 30
Cold Forming 31
Thermoforming 32
Printing 36
Chemical Resistance 37
Adhesives and Sealants 41
Selection of Appropriate PALSUN® Sheet 41
2
Page 3

PALSUN® Technical Guide
PALSUN® Product Range
Some of the products' features below can be combined. Please contact your Palram dealer for further information.
Product Description Features & Applications
PALTUF®
PALSUN®
PALSUN® UV2
PALSUN® FR
PALSUN® Solar Control
PALSUN® Breeze
PALGARD™
Notes:
1. All the above sheets are supplied with a protective polyethylene (PE) film on both sides (one side upon request), with the UV protected side clearly marked. This film
should be removed immediately after installation.
2. For transportation, handling and storage instructions and recommendations, please refer to Handling and Storage Guidelines for Palram Sheets.
3. PALSUN sheets are backed by a 10 years limited warranty, available upon request.
4. Most PALSUN sheets are available in the transparent, translucent or opaque form, in a variety of colors, either standard or custom ordered.
UV stabilized, general purpose, flat solid
polycarbonate sheet.
Flat solid polycarbonate sheet with UV protective
layer on one side.
Flat solid polycarbonate sheet with UV protective
layer on both sides.
Sheet with higher fire resistance rating
(e.g. UL 94 V-0).
Sheet with integrated heat-blocking layer. This
metallic reflective layer that transmits less Infrared
radiation and reduces heat buildup.
This advanced heat-blocking SolarSmart™ tint
offers a clear view due to its high clarity.
Sheet with abrasion resistant layer on one or both
layers.
Recommended for indoor use only.
Suitable for both exterior and indoor applications.
Optional surface textures:
Embossed (E-102)
Prismatic
Hair-cell
Matte - Anti-glare effect
Recommended for applications that involve UV exposure on
both sides (e.g. exterior light boxes)
Recommended for applications in populated areas.
Available with 20, 35, or 50% light transmission.
Can be tailored to achieve different light and heat
transmissions.
Recommended for applications in high traffic areas, harsh
chemical environments or those requiring anti-vandal
properties.
Standard Dimensions*
Thickness (mm)
1
1.5
2
2.5 - 6
8
9 - 12.7
2 - 18
*Other dimensions and specifications are available upon request, subject to a minimum order.
Width x Length
(mm)
1220 x 2440
1250 x 2440
1220 x 2440
1250 x 2440
2050 x 3050
2450 x 3050
Smooth
Both sides
✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔
✔
Embossed
Both sides
Surface Finish
Matte
One side
Hair Cell
One side
Prismatic
One side
3
Page 4

Colors
Color Group Description Colors
Clear
Transparent
Translucent
Transmits up to 90% natural daylight, resulting in high
lighting within the structure.
Low haze colors offering high clarity.
Breeze and Smart are SolarSmart™ colors with that
reduce heat buildup while allowing a clear view
through the sheet (see page 9 for more details on
SolarSmart products).
White Opal: Transmits 11-50% visible light with high
light dispersion, produces mild and even lighting
within the structure.
Diffuser: Transmits 50% visible light with high light
dispersion, produces diffused and consistent lighting
within the structure.
LB (Light Box): Diffuser sheet for illuminated signs and
display applications, offering 44-50% light transmission.
Clear
Solar Gray BlueBronze
Smart
Red
Blue*
White
Yellow
Mint
Green
Opal
Solar Control
(Solar Metallic Grey)
Smart
Green*
White
Diffuser
Solar
Olympic
Green
Bluish
Breeze*
LB
(Light Box Diffuser)
Solar Ice
Red
Opaque* Colors that transmit very little to no light.
Dark Green
Cream
Ral 9001
Red Brick
Light Grey
Ral 7035
Black Dark Blue
Dark Grey
Brown
Off-White
* Subject to minimum quantity. Custom colors and light transmissions are also available in this manner.
** Colors shown above are a reproduction of the actual color. To accurately represent the colors, contact your Palram distributor and request a sample color chip.
SolarSmart™ - Energy Efficiency
SolarSmart™ are energy-efficient colors break the traditional ratio
between light transmission and shading coefficient. SolarSmart™
panels block Infrared energy that causes heat buildup, and transmit
“cool light” that reduces air-conditioning and lighting costs.
More energy-saving, natural
visible light is transmitted.
SolarSmart™ Panel
Blocking Infra-Red
reduces heat buildup.
4
Page 5

Physical Properties
The following table displays physical properties of 3mm (0.12 inch) PALSUN and PALTUF sheets.
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Property Method**
Physical
Density D-792 g/cm (lb/ft) 1.2 (75)
Water Absorption D-570 24 hr. @ 23°C % 0.15
Mechanical
Tensile strength at yield D-638 10 mm/min (0.4 in./min) MPa (psi) 62.5 (9,100)
Tensile strength at break D-638 10 mm/min (0.4 in./min) MPa (psi) 65 (9,500)
Elongation at yield D-638 10 mm/min (0.4 in./min) % 6
Elongation at break D-638 10 mm/min (0.4 in./min) % >80
Tensile Modulus of Elasticity D-638 1 mm/min (0.4 in./min) MPa (psi) 2,300 (290,000)
Flexural Modulus D-790 1.3 mm/min (0.052 in./min) MPa (psi) 2,350 (343,000)
Flexural Strength at Yield D-790 1.3 mm/min (0.052 in./min) MPa (psi) 93 (13,600)
Notched Impact Strength Izod D-256 23°C (73°F) J/m (ft·lbf/in.) 800 (15)
Notched Impact Strength Charpy D-256 23°C (73°F) J/m (ft·lbf/in.) 800 (15)
Impact Falling Weight ISO-6603/1b J (ft·lbf ) 158 (117)
Rockwell Hardness D-785 R scale / M scale 125 / 75
Thermal
Long Term Service Temperature °C (°F) -50 to +100 (-175 to +212)
Short Term Service Temperature °C (°F) -50 to +120 (-175 to +250)
Heat Deflection Temperature D-648 Load: 1.82 MPa (264 psi) °C (°F) 135 (275)
Vicat Softening Temperature D-1525 Load: 1 kg (2.2 lb) °C (°F) 150 (300)
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion D-696 mm/m °C (Mil/in. °F) 0.065 (0.036)
Thermal Conductivity C-177 W/m K (Btuin/hrft°F) 0.21 (1.46)
Specific Heat Capacity C-351 kJ/kg°K (Btu/lb°F) 1.26 (0.31)
Optical
Haze D-1003 Clear Sheet % <0.5
Light Transmission D-1003 Clear Sheet % 89
Refractive Index D-542 Clear Sheet 1.586
Yellowness Index D-1925 Clear Sheet <1
Electrical
Dielectric Constant
Dissipation Factor
Dielectric Strength Short Time D-149 500 V/s kV/mm (V/mil) >30 (>770)
Surface Resistivity D-257 Keithley Ohm 10
Volume Resistance D-257 Keithley Ohm-cm 10
D-150 50 Hz 3.0
D-150 1 MHz 2.9
D-150 1 KHz 0.001
D-150 1 MHz 0.01
Conditions
(U.S. Customary)*
Units - SI
(U.S. Customary)*
Value
(U.S. Customary)*
* Conditions, units and values in U.S. Customary units are presented in the table within parentheses.
** ASTM except where noted otherwise.
5
Page 6
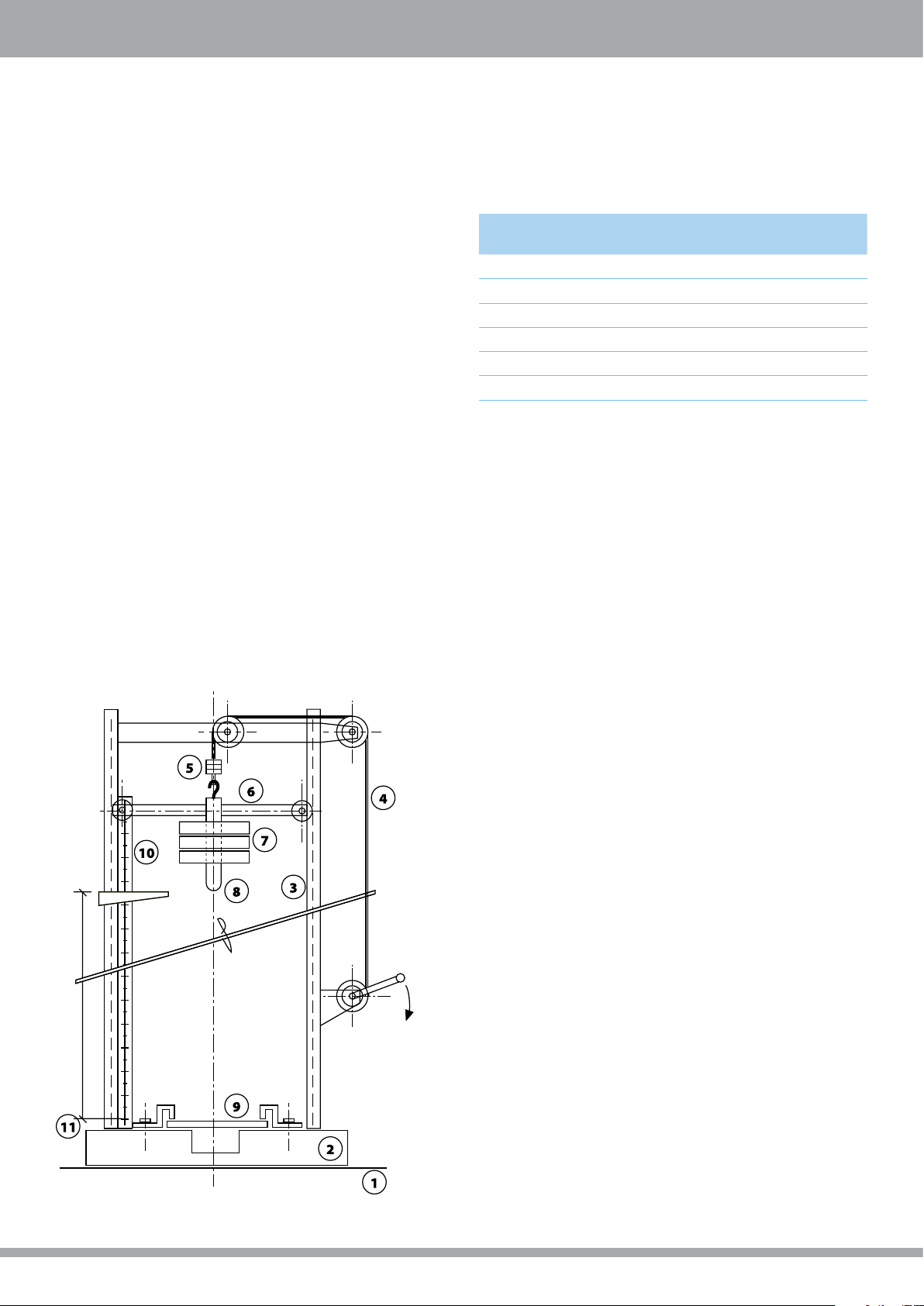
Impact Strength
PALSUN sheets are manufactured from polycarbonate, the
most versatile, toughest transparent thermoplastic. PALSUN
has 200 times the impact strength of glass, offering excellent
protection against riots and public disturbances, breaking &
entering or acts of vandalism.
PALSUN can endure attacks by rocks, clubs, hammers and
thrown objects, and still to retain its original shape, maintain
its integrity with minimal indentations to its surface.
The amount of damage depends on the object mass and
energy, and sheet’s thickness. PALSUN sheets will retain these
energy-absorbing properties over a wide temperature range
(50° to + 100° C).
Falling Dart Method
A uniform energy increment is employed during testing. Energy is decreased or increased by uniform increment after testing
each specimen, depending upon the result (failed / not failed) observed for the former tested sample. A 20 mm diameter dart,
weighing 8 kg, with a rounded tip, is raised to a certain height and released to fall on a suitably sized sample.
Principles: Impact strength is determined by the known weight and height. Adjustment is done by altering height while using a
constant mass.
E50: 50% of Impact Failure Energy. The energy that will cause 50% of the tested samples to fail.
N.B.**: No Break. The energy required to break the sample is greater than what the test instrument can deliver.
Typical impact failure energy of PALSUN® sheets*
Thickness
mm
2 110 100% ductile
3 150 100% ductile
4 190 100% ductile
5 290 100% ductile
6 400 100% ductile
8 - 18 N.B.** N.B.**
* According to ISO 6603/1 1985(E): Determination of multi-axial impact behavior
of rigid plastics.
Energy at Failure
E50 (Jouls)
Type of Failure
Falling Dart Impact Testing Device (Schematic Figure)
Legend
1. Leveled floor
2. Stablized base
3. Supporting guidrails
4. Lifting mechanism
5. Disengagement mechanism
6. Guidance bar
7. Changeable weight
8. 20 mm diameter head falling dart
9. Tested specimen
10. Calibration bar
11. Changeable drop height
6
Page 7
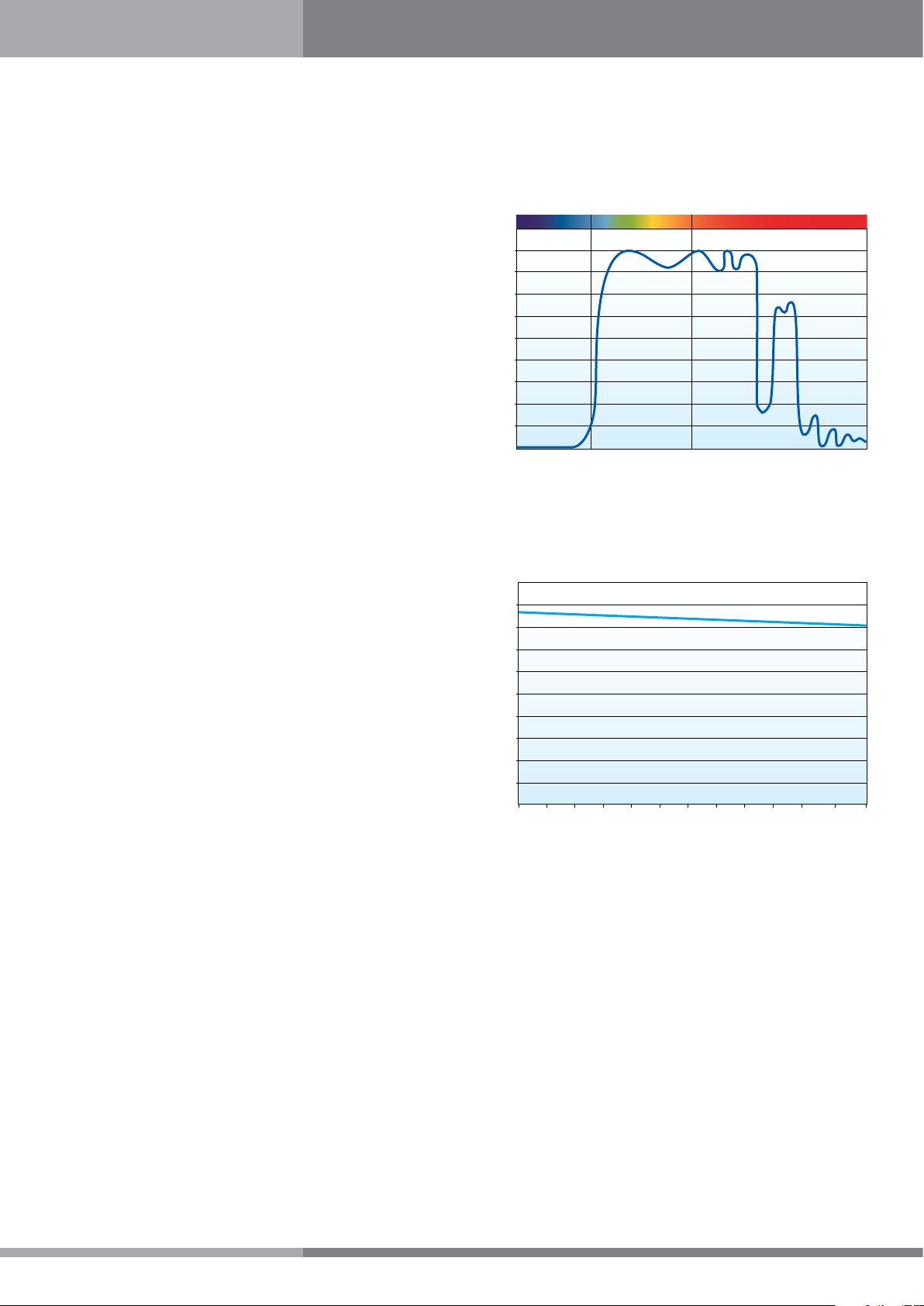
Optical Characteristics
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Blocking - PALSUN sheets completely
block out potentially harmful UV radiation and a significant
portion of Infrared (IR) radiation. Over the visible light range, a
typical 3 mm (0.125 inch) thick clear PALSUN sheet transmits
about 89% (average) of incident light, as seen in the attached
graph.
Light Transmission Versus Thickness
Light transmission decreases slightly with increased thickness
(see attached graph).
Figure 2:
Solar Transmittance of Clear 3mm PALSUN®
UV VISIBLE LIGHT INFRA-RED
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
% Solar Transmittance
20
10
0
250
300
350
400
500
600
700
800
1000
1400
1800
Wavelength (nm)
Figure 3: Light Transmission Versus Thickness
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
% Light Transmission
20
10
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Thickness (mm)
PALSUN® & PALTUF®
2200
2600
3000
7
Page 8

Solar Transmission Properties
Solar energy transmission is an extremely important consideration
with transparent materials. Geographic location and typical thermal/
Figure 4: Solar Radiation Schematic Behavior Through
Light Transmitting Material
optical properties of the specific glazing are the main factors
influencing solar heat gain. Various types of PALSUN - textured,
tinted, opal, diffused, and heat blocking SolarSmart™ sheets - can
be used to deliver the exact quantity and quality of light desired.
Each of these products transmit different amounts of direct light in
varying levels of light diffusion, which may help to spread the light
throughout the structure or enclosure. The sheets also vary in their
selectivity index (SI) values, which determines how efficiently they
keep heat out while letting more “cool light” in (See next page for
more information on SolarSmart™ products). Although colors and
tints reduce the percentage of visible light transmitted through the
sheets, but solar energy is still absorbed by the glazing itself, and in
turn transferred by convection and far IR radiation from the heated
glazing into the building. PALSUN sheets with embossed or matte
surfaces, or diffuser colors, diminish glare and dazzle, preventing
damage by direct irradiance. However solar energy is still transmitted
through and increases the solar heat gain inside the structure.
Color*
Clear 90 <1 0.87 1.00
Bronze
Solar Grey
White Opal 28 100 0.32 0.37
White Diffuser 80 100 0.87 1.00
Solar Ice 20 100 0.37 0.45
Solar Control
Solar Olympic
Smart Green 70 42 0.58 0.67
Smart Blue 70 42 0.57 0.65
Bluish Breeze 70 42 0.55 0.63
*Values in the table above relate to 3mm Sheet. Further information on additional products is available upon request.
Terminology Used in the Table
Solar Radiation: The solar spectrum ranging from 300 nm to 2400 nm. Included are UV, visible and Near-IR radiation.
Visible Light Radiation: The portion of the light spectrum whose wavelength ranges from 400nm to 780nm.
% Light Transmission (ASTM D-1003): Percentage of incident visible light that passes through an object.
% Solar Heat Gain (SHGC): The percent of incident solar radiation transmitted by an object which includes the direct solar transmission plus the part of the solar
absorption reradiated inward.
Shading Coefficient (ASTM E424-71): The ratio of the total solar radiation transmitted by a given material to that transmitted by normal glass, whose light transmission
is 87%. It can be approximately calculated by: %ST + (0.27 x %SA) = %ST
% Light Transmission
ASTM D-1003
20 <1 0.45 0.52
35 <1 0.56 0.64
50 <1 0.65 0.75
20 <1 0.44 0.51
35 <1 0.56 0.64
50 <1 0.65 0.75
20 67 0.33 0.36
35 52 0.45 0.52
50 50 0.54 0.61
20 35 0.41 0.47
35 20 0.52 0.60
50 63 0.63 0.73
%Haze
ASTM D-1003
SC = (1.15 x STt)/100
t
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
ASTM E-424-71
Shading Coefficient
ASTM E-424-71
8
Page 9
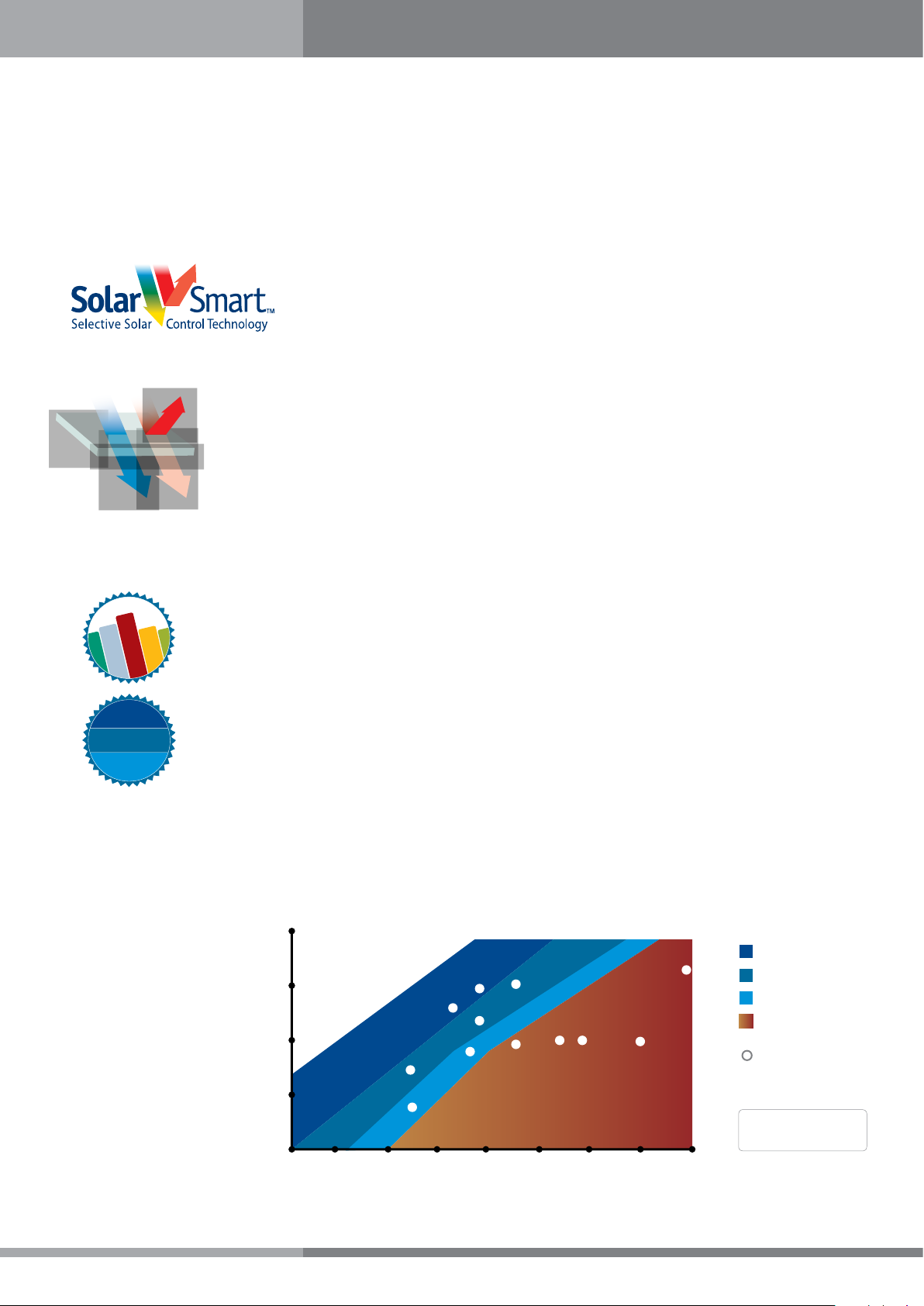
SolarSmart™ Technology - Efficient Daylighting
Enjoy light
without heat.
Promoting Energetic Efficiency and Well Being
SolarSmart technology defies standard transmission of solar energy in transparent sheets and allows more
versatile color and solar transmission specification per project. Unlike regular tints, SolarSmart sheets and
panels admit more natural daylight while reflecting outwards Infrared radiation that creates heat. This
characteristic breaks the traditional link between shading coefficient and light transmission, allowing a
different perspective on the specification of natural light in architectural design.
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Breeze
Smart
Solar Control
SolarSmart tints allow better use of natural lighting without sacrificing the interiors. More natural light results
in a healthier and more productive ambience. Energy saving is also promoted through reduction of both
illumination and air conditioning requirements.
Color Specification
SolarSmart™ tints can be applied to any Palram transparent polycarbonate sheet or panel system, including
PALSUN. The tints can be blended with any color to tailor the desired appearance and solar properties.
Technology Groups
The SolarSmart product range includes 3 technology groups, which have different characteristics and
appearance. For more information please refer to the SolarSmart™ Technology brochure.
Efficiency Comparison
The graph below demonstrates the efficiency of SolarSmart products in comparison with clear and standard
colored sheets. The graph shows how SolarSmart™ tints enable higher light transmission specification while
maintaining or decreasing shading coefficient values.
100%
Breeze
75%
Clear
Smart
Solar Control
Standard
50%
Light Transmission
25%
0%
0.3
Bronze
White Opal
0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
Shading Coefficient
Solar Grey
Sky Blue
3mm
Polycarbonate
Sheet
Tested according
to ASTM E-424
9
Page 10
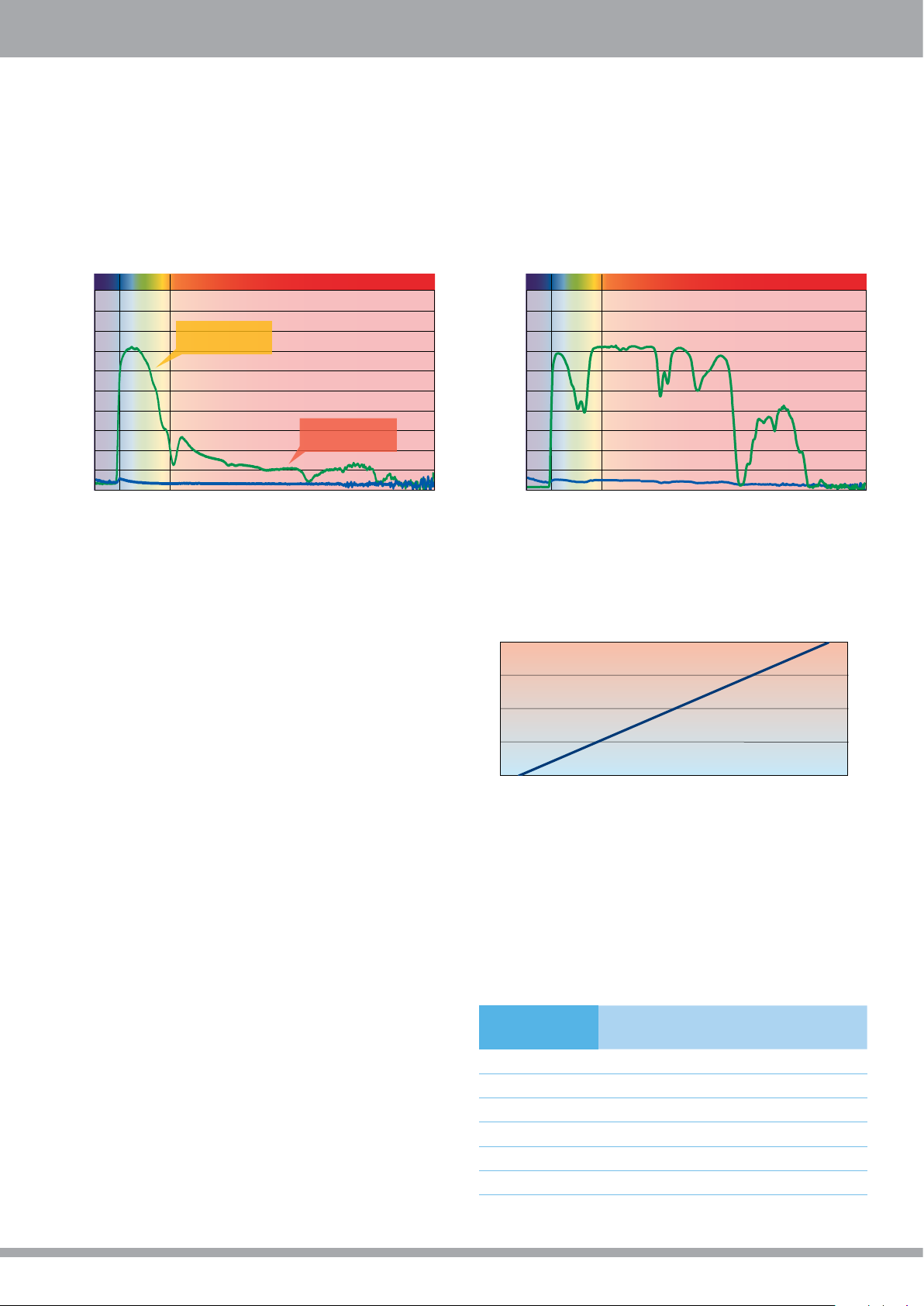
Heat-Blocking with High Clarity by PALSUN® Breeze
PALSUN glazing with Breeze tint transmits plenty of incident daylight (70%), while absorbing/blocking a large portion of the Infrared
radiation, thus significantly reducing heat buildup within the structure. PALSUN Breeze also provides a clear view due to its high
transparency, which is uncommon for heat-blocking products.
PALSUN® 3mm Breeze 70%LT
Solar Performance Graph (250-2,500nm)
UV LIGHT INFRA-RED
100
90
%Solar Trnasmission / Reflection
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
250
500 750 1000 1250 1500 1750 2000 2250 2500
Transmits plenty
of natural daylight
Transmittance
Reflectance
Transmits very little
Infrared heat
Wavelength (nm)
Thermal Characteristics
Thermal Expansion
The thermal expansion of PALSUN sheets is higher than that of
glass. This important factor must be taken into account when
mounting the sheets. The graph on the right shows the degree
of expansion/contraction as a function of temperature.
PALSUN® 3mmTrans. Blue 68%LT
Solar Performance Graph (250-2,500nm)
UV LIGHT INFRA-RED
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
%Solar Trnasmittance / Reflectance
0
250
500 750 1000 1250 1500 1750 2000 2250 2500
Transmittance
Reflectance
Wavelength (nm)
Expansion/Contraction with Temperature
60
40
20
0
Temperature (°C)
-20
-2 -1 0 1 2
Dimensional Change (mm/m)
Service Temperature
The temperature range over which the characteristics of PALSUN are retained extends from -50°C to +120°C (-60°F to +250°F) for
short periods and from -50°C to +100°C (-60°F to +210°F) for long periods. This range of temperatures make PALSUN sheets suitable
for use in most climates.
Thermal Insulation
On very hot days, the surface temperature of the sheet might reach up to 60°C (140°F). The U-value characterizes the degree of
thermal transmittance offered by a given glazing material, so higher U-values are associated with materials that are poor insulators
and result in a greater loss of heat. The following table compares
the U-values of glass and PALSUN sheets of equivalent thicknesses.
Thicker sheets of a given material will offer greater thermal insulation
and be characterized by a lower U-value and reduced heat loss. For
any given thickness, the U-value of PALSUN sheet is lower than that
of glass. This means that heat loss from the building interior, as well
as penetration of heat or cold into a building, will be less if it were
glazed with PALSUN than for one glazed with glass. This can result in
a significant reduction in energy costs both for heating in winter and
air-conditioning during the summer. Note that use of Solar Control
sheets will insulate just as well, but will also reduce air-conditioning
costs because of Near Infra-Red reflection and reduced heat buildup.
mm in
Thermal Insulation of PALSUN® vs. Glass
Thickness
3 (0.12) 5.47 5.81
5 (0.20) 5.19 5.72
6 (0.24) 5.07 5.68
8 (0.31) 4.48 5.60
10 (0.39) 4.63 5.52
12 (0.47) 4.43 5.45
PALSUN U-Value
(W/m·°K)
Glass U-Value
(W/m·°K)
10
Page 11
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Protection from the Harmful Effects of UV Radiation
Exposure to solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation is widely known as a major health concern by now. The adverse affects were once thought
to be associated with solar UV radiation in the 280-315nm (UV-B) range. However, in recent years it has become apparent that exposure
to UV-A (315-400nm) is also detrimental. In addition to skin cancer, premature aging has been associated with exposure to UV-A.
Both UV-A and UV-B portions of the UV spectrum are blocked out by PALSUN sheets. This screening of harmful UV radiation can be
observed in the figure below.
A comparison of the UV protection offered by PALSUN and that offered by sunscreen is indicated in the graph on the right. Note
that no barrier is as effective as PALSUN sheet. Activity below PALSUN will be more protected than that offered by proper application
of sunscreen, though the latter is sufficient in almost all cases. The key word in the previous sentence is proper. Improperly applied
sunscreen or forgetting to apply skin screen will result in undesirable levels of exposure. In addition, note that protection factors
are computed on the basis of UV-B exposure. There is as yet no way to compute protection to UV-A exposure. It should also be
noted that formulations that only block out UV-B are still being marketed. When playing or swimming below PALSUN, protection is
always complete. When swimming, there is no danger that the protection will be washed away. In the last ten years, it has also been
documented that UV exposure can also cause damage to the eyes, specifically to the cornea. Wearing sunglasses manufactured from
polycarbonate protects the eyes. However, most people remove their glasses when entering the pool. This is a factor for both public
and private pools to consider when contemplating a choice of covering.
Irradiance of UV Radiation Trough Various Protective Barriers
(PF=Protective Factor)
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
Irradiance (W/m/min)
0.1
0
300 310 320 330 340 350 360 370 380 390 400
Direct Sunlight
(PF-0)
Window Glass
(PF-10)
Wavelength (nm)
Sun Tan Lotion SPF 15
(5g/m PF-37)
PALSUN®
(PF-81)
Acoustic Properties
Though only about half the weight of an equivalent glass panel, PALSUN glazing offers similar sound insulation properties along with
much higher impact strength. These combined properties make PALSUN glazing the preferred material for see-through sound barriers:
lightweight, easy to maintain or replace if necessary, highly transparent and vandal-proof.
The table on the right portrays the acoustic performance of PALSUN glazing versus glass.
Acoustic Insulation of PALSUN® Sheets According to EN 1793
Thickness
mm
12 31
15 33
Sound Reduction
dB
11
Page 12

Weather Resistance
Solar UV radiation attacks many polymeric materials. The rate of deterioration and crazing on the exterior surface will vary for
different polymers. Further erosion is accelerated by water, dirt, air pollution, chemicals etc. The extent of attack depends on
environmental factors such as location, altitude, local weather conditions, air pollution etc. The best initial indication is yellowing,
followed by a significant reduction in light transmission and structural strength.
All PALSUN sheets (excluding those designated PALTUF, which are UV stabilized) are manufactured with a co-extruded, UV
protective layer on one or two sides. This protective layer assures a long lifetime of service. PALSUN sheets retain their toughness
and optical quality under intense UV exposure, with minimal reduction in their properties.
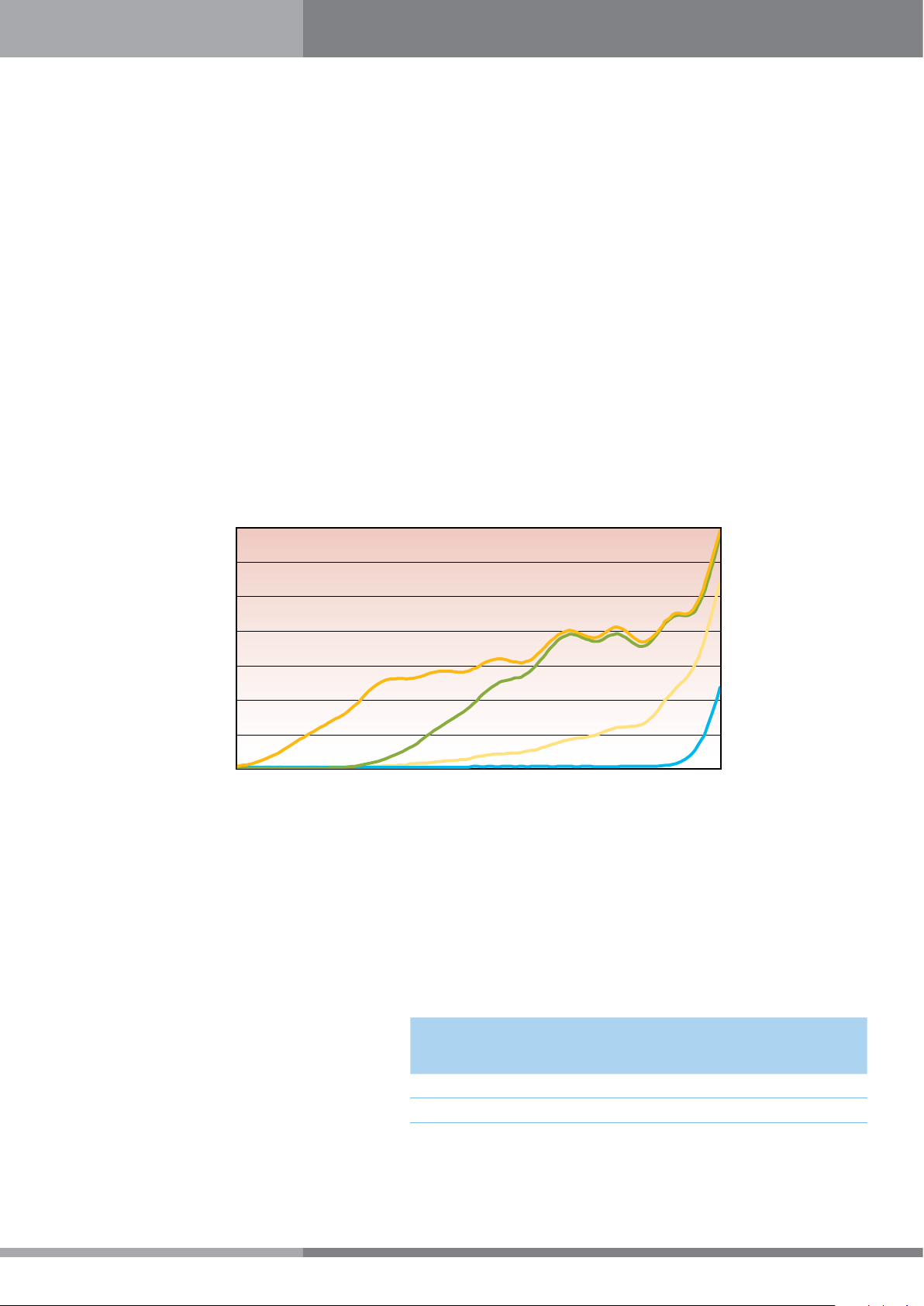
2000 hours of accelerated weathering (UV exposure, QUV - ASTM G154) tests, simulating 20 years of exposure in hot, sunny
climates cause only a minor decrease in light transmission and a slight increase in yellowness Index for PALSUN. The changes
in UV stabilized PALTUF sheet are greater.
The effect of QUV on 3 mm PALSUN & PALTUF sheets appears in the graphs below.
Figure 6a
% Light Transmission Loss of 3mm Sheets
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
%Light Transmission
87
86
85
0 100 250 500 750 1000 1500 2000
Accelerated Weathering (QUV Hours)
PALSUN®
PALTUF®
Flammability
Figure 6b
Yellowness Index Change in 3mm Sheets
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
Change in Yellowness Index
1
0
0 100 250 500 750 1000 1500 2000
PALSUN®
Accelerated Weathering (QUV Hours)
PALTUF®
General
As a thermoplastic, PALSUN eventually melts and burns under the intense heat of a blazing fire. However, PALSUN does not propagate
flame, and is solidified and self-extinguished as soon as the direct flame is taken away. PALSUN doesn’t produce any toxic fumes or
gases when it burns.
PALSUN® FR
PALSUN FR is a fire retardant flat solid polycarbonate sheet with improved flammability ratings. The flame retardant additives make
the it virtually non-combustible. When flame licks the sheet, it will only get scorched and eventually melt, solidifying quickly when the
direct heat source is removed. Drippings do not ignite other combustible materials, as they do not actually burn.
Smoke and heat extraction
In an actual, full-scale combustion, when PALSUN overhead glazing (as in skylights) is exposed to intense heat it will soften at 150°
-160°C and produce apertures in the glazing, enabling heat and smoke to escape. Reduced temperatures inside the structure help
to extinguish the fire.
12
Page 13

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Flammability Classifications
PALSUN and PALSUN FR are classified as appears in the following table, based on tests executed by certified independent testing
laboratories.
PALSUN® PALSUN® FR
Standard Classification* Standard Classification*
EN 13501 B, s1, d0 UL-94 V-0
NSP 92501, 4 M1(1 mm) ASTM D-2863-87 L.O.I. = 30
NSP 92501, 4 M2 (1.5 to 12mm)
BS 476/7 Class 1y Spread of Flame Index = 8
DIN 4102 B1, B2 Heat Evolved Index =10
CSE RF 2/75/A, CSE RF 3/77 Class 1 Smoke Developed Index = 8
UL-94 V2 (File e221255)
ASTM D-635 CC1
* Depends on thickness. For additional information please contact your PALSUN distributor.
AU 1530.3-1982
Ignitability Index = 9
General Recommendations for Working With PALSUN®
Handling & Storage
1. PALSUN sheets should be transported and stored horizontally, on a flat, sturdy pallet whose dimensions are equal or larger
than the largest of the sheets.
The sheets should be secured to the pallet during transportation and on-site handling. It is possible to stack the sheets with
the longer sheets at the bottom and the shorter on top, leaving no unsupported overhang.
2. When moving a pallet with a forklift, always use forks as long as the sheets’ width. Shorter forks used on a wider pallet may
cause damage to the sheets.
3. PALSUN sheets leave the factory in packages, wrapped in white, watertight polyethylene. The wrapping should be removed
as close to the actual time of installation (or use) as possible.
Storage of the sheets should be in a covered, dry, ventilated place, away from direct sunlight and rain.
4. Avoid extended exposure to direct sunlight, which may cause excessive heat buildup. Long term heating may lead to softening
of the protective polyethylene masking, fusing it to the sheet’s face and making removal difficult or even impossible.
5. Avoid leaving the sheets stored unwrapped. Dirt may accumulate on the sheets and/or their edges, attracted by electrostatic
charges in the sheets, necessitating extra time and labor for cleaning before installation.
6. Whenever necessary to store the pallet in the open, cover it with white opaque polyethylene sheet, cardboard or any other
insulating material, taking care to cover the stack completely.
Figure 7: Storing PALSUN® Sheets
13
Page 14

Determination of Required Sheet Dimensions
The information below is presented to assist in ordering the required dimensions.
Determination of Sheet Size
Due to thermal expansion, PALSUN & PALTUF sheets have to be cut
accurately at predetermined lengths smaller than the dimensions
of the frame. At the end of the frame, clearance must be left for
expansion. The following tables and diagram help calculate the
required sheet dimensions. In addition, there is a table showing
the expansion clearance necessary for various sizes of PALSUN &
PALTUF sheets.
Determination of Thickness
In order to determine the required thickness, the following table
lists the sheet thickness required for a given wind load and width
(at the narrow side of the sheet).
A-A
A
a - width
BB
b - length
A
B-B
PALSUN® Recommended Panel width
Wind/Snow Load Chart for Flat 4 Sides Clamped, Single Panel, Single Span
Length / Width Ratio (b/a)
Thickness
4mm
5mm
6mm
Load
(kg/m)
50 985 875 820 795 785
75 860 765 715 695 685
100 780 695 650 630 620
125 725 645 605 585 575
150 685 605 570 550 540
175 650 575 540 525 515
200 620 550 515 500 490
50 1235 1090 1025 995 980
75 1075 955 895 870 855
100 980 865 815 790 775
125 910 805 755 730 720
150 855 755 710 690 680
175 810 720 675 655 645
200 775 685 645 625 615
50 1450 1300 1225 1200 1175
75 1300 1150 1075 1050 1025
100 1175 1025 975 950 925
125 1090 965 910 885 865
150 1025 910 850 830 815
175 975 865 810 790 775
200 925 825 775 755 740
Ratio 1:1 Ratio 1.25:1 Ratio 1.5:1 Ratio 1.75:1 Ratio 2:1
14
Page 15

PALSUN® Recommended Panel width - 4 sides clamped (Continued)
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Length / Width Ratio (b/a)
Thickness
Load
kg/m
Ratio 1:1 Ratio 1.25:1 Ratio 1.5:1 Ratio 1.75:1 Ratio 2:1
50 1975 1750 1625 1590 1575
75 1725 1525 1425 1390 1375
100 1565 1390 1300 1270 1250
8mm
125 1455 1290 1210 1180 1160
150 1375 1210 1140 1110 1090
175 1300 1150 1080 1050 1035
200 1250 1100 1035 1005 990
50 2050 2050 2050 1990 1960
75 2050 1910 1795 1740 1715
100 1960 1735 1630 1580 1555
10mm
125 1820 1610 1515 1465 1445
150 1710 1515 1425 1380 1360
175 1625 1440 1355 1310 1290
200 1555 1375 1295 1255 1235
50 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
75 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
100 2050 2050 1955 1895 1870
12mm
125 2050 1935 1815 1760 1735
150 2050 1820 1710 1655 1630
175 1950 1730 1625 1575 1550
200 1865 1655 1555 1505 1480
50 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
75 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
100 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
14mm
125 2050 2050 2050 2050 2025
150 2050 2050 2000 1930 1900
175 2050 2000 1890 1835 1810
200 2050 1925 1810 1755 1730
50 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
75 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
100 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
15mm
125 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
150 2050 2050 2050 2050 2025
175 2050 2050 2025 1950 1925
200 2050 2050 1925 1875 1850
50 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
75 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
100 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
18mm
125 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
150 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
175 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
200 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050
* For wind load data in N/m units, multiply value by 10 (e.g. 40 kg/m = 400 N/m).
Notes:
1. For 2 sides clamped installation please refer to the ratio 2:1 column.
2. The table is referring to various ratios of Length (b) and width (a) and valid for both Snow and wind load.
3. The table is referring to 4 sides clamped, flat installed Palsun panels.
4. Bedding depth shall be minimum 20mm.
5. The values are calculated according to deflection criterion of L/20 of the short span.
6. The table is not referring to self-weight deflections which might cause aesthetic issues.
7. The table is not referring to the sheet flexibility when vertically installed.
8. The data in the table refer to the short dimension, a.
15
Page 16

PALSUN® Recommended Panel Width for Curved Installation - Metric
Maximum Recommended on Center Distance between Supporting Arches
Maximum Recommended on Center Distance between Supporting Arches
According to Wind/Snow Loads Below (mm)
Uniform Wind/Snow Loads
Thickness
Sheet Curvature
Radius
50 80 100 120 150 200 250 300
700 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750 1600
900 2050 2050 1850 1650 1500 1350 1200 1000
1100 2050 1900 1750 1600 1450 1250 1050 900
1300 1950 1800 1650 1480 1320 1180 1000 820
1500 1800 1650 1500 1380 1200 1050 900 750
4mm
5mm
6mm
8mm
10mm
12mm
* See notes on next page
1800 1650 1580 1420 1320 1120 950 820 700
2000 1580 1480 1350 1250 1050 880 750 650
2200 1500 1400 1300 1180 980 800 680 600
2800 1350 1250 1180 1100 900 720 600 NA
4000 1200 1050 950 850 780 650 450 NA
6000 850 780 720 650 600 450 NA NA
900 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750
1100 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750 1600
1300 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1750 1600 1450
1500 2050 2050 2050 1950 1850 1700 1550 1400
1800 2050 2050 1950 1850 1750 1550 1350 1150
2000 2050 1950 1850 1750 1550 1350 1150 1050
2200 1950 1850 1750 1650 1500 1300 1100 1000
2800 1600 1500 1400 1300 1200 1050 900 750
4000 1400 1300 1200 1100 1000 850 750 600
6000 1200 1050 950 850 750 600 450 NA
1100 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 2000 1900 1750
1300 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750 1600
1500 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750 1600 1450
1800 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1650 1500 1350
2000 2050 2050 1950 1850 1700 1550 1400 1250
2200 2050 1950 1850 1750 1650 1500 1350 1200
2800 1700 1600 1500 1400 1300 1150 1000 850
4000 1600 1500 1400 1300 1150 1000 850 720
6000 1480 1380 1300 1200 1080 920 780 620
1500 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1900 1750 1600
1800 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1650 1500
2000 2050 2050 2050 2000 1900 1750 1600 1450
2200 2050 2050 2050 1950 1850 1700 1550 1400
2500 2050 2050 1920 1850 1720 1580 1420 1280
2800 2050 1950 1820 1720 1600 1450 1300 1150
4000 1950 1820 1720 1620 1500 1350 1200 1000
6000 1820 1680 1520 1380 1250 1100 950 780
1800 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1650
2200 2050 2050 2050 2050 2000 1850 1700 1550
2800 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1750 1600 1450
4000 2050 2050 2000 1900 1780 1620
6000 2050 1920 1820 1720 1550 1400 1250 1100
2200 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800
2800 2050 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1650
4000 2050 2050 2050 2050 1950 1800 1650 1480
6000 2050 2050 2050 1950 1720 1580 1420 1280
(kg/m)
1480 1320
16
Page 17

PALSUN® Recommended Panel Width for Curved Installation - US Customary
Maximum Recommended on Center Distance between Supporting Arches
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Max. Recommended on Center Distance between Supporting Arches
According to Wind/Snow Loads Below (in.)
Uniform Wind/Snow Loads
(psf)
Thickness
Sheet Curvature
Radius
(mm)
In. mm In. Ft. 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 60
28 2’ – 4” 81 81 81 81 81 75 69 63
36 3’ 81 81 73 65 59 53 48 40
44 3’-8” 81 75 69 63 57 50 42 36
52 4’-4” 77 71 65 58 52 47 40 36
5
/32”
13
/
64
1
/4”
5
/16”
13
/32”
1
/2”
Notes for Tables “PALSUN® Recommended Panel Width for Curved Installation”:
1. PALSUN glazing sheets should be installed with their curved edges sustained on the supporting arches, with 15 to 25mm (5/8” to 1”) edge engagement, depending
on the span, in addition to a thermal expansion gap of 2-3mm (/”- /”).
2.
Thin sheets up to 6mm (¼”) can be bent as relatively short glazing panels, 2m to 3m at 1000 to1220mm width (6’7” to10’ length, at 40” to 48” width). Thick 8mm
sheets (/”) and above can be cold curved only as special long panels 4m to 7m (13’ 2” to 23’), particularly when full width of 2050mm (6’ 9”) or similar is installed.
3. Supporting arches and clamps should withstand total maximum permitted loads without difficulty.
4. Spans under 500mm (20”) are generally impractical for an installation method of this type.
5. The lowest radius value indicated is the minimal permitted radius for that specific PALSUN sheet.
6. Indicated spans are suitable for most common stationary structures, under pressure or uplift loads. Special structures, like mobile pool covers, may use wider spans,
subject to preceding approval.
4mm
5mm
”
6mm
8mm
10mm
12mm
59 4’-11” 71 65 59 54 48 42 36 36
71 5’-11” 65 62 56 52 45 38 33 28
79 6’-7” 62 58 53 50 42 35 30 26
87 7’-3” 59 55 51 47 39 32 27 24
110 9’-2” 53 50 47 44 36 29 24 NA
158 13’-2” 48 42 38 34 31 26 18 NA
236 19’-8” 34 31 29 26 24 18 NA NA
36 3’ 81 81 81 81 81 81 75 69
44 3’-8” 81 81 81 81 81 75 69 63
52 4’-4” 81 81 81 81 77 69 63 57
59 4’-11” 81 81 81 77 73 67 61 55
71 5’-11” 81 81 77 73 69 61 53 46
79 6’-7” 81 77 73 69 61 53 46 42
87 7’-3” 77 73 69 65 59 51 44 40
110 9’-2” 63 59 55 51 48 42 36 30
158 13’-2” 55 51 48 44 40 34 30 20
236 19’-8” 48 42 38 34 30 20 450 NA
44 3’-8” 81 81 81 81 81 79 75 69
52 4’-4” 81 81 81 81 81 75 69 63
59 4’-11” 81 81 81 81 75 69 63 57
71 5’-11” 81 81 81 77 71 65 59 53
79 6’-7” 81 81 77 73 67 61 55 50
87 7’-3” 81 77 73 69 65 59 53 48
110 9’-2” 67 63 59 55 51 46 40 34
158 13’-2” 63 59 55 51 46 40 34 29
236 19’-8” 58 54 51 48 43 37 31 21
59 4’-11” 81 81 81 81 81 75 69 63
71 5’-11” 81 81 81 81 77 71 65 59
79 6’-7” 81 81 81 79 75 69 63 57
87 7’-3” 81 81 81 77 73 67 61 55
98 8’-2” 81 81 76 73 68 62 56 50
110 9’-2” 81 77 72 68
158 13’-2” 77 72 68 64 59 53 48 40
236 19’-8” 72 66 60 54 50 44 38 31
71 5’-11” 81 81 81 81 81 77 71 65
87 7’-3” 81 81 81 81 79 73 67 61
110 9’-2” 81 81 81 77 71 69 63 57
158 13’-2” 81 81 79 75 70 64 58 52
236 19’-8” 81 76 72 68 61 55 50 44
87 7’-3” 81 81 81 81 81 81 77 71
110 9’-2” 81 81 81 81 81 77 71 65
158 13’-2” 81 81 81 81 77 71 65 58
236 19’-8” 81 81 81 77 68 62 56 51
63 57 51 46
17
Page 18

Installation
Choice of the Frame
PALSUN & PALTUF sheets can be mounted in most existing frames made of wood, rigid PVC, aluminum or other metals. It is recommended
to use neoprene or EPDM packing (never use soft PVC) to secure the sheet in its frame, rather than fixing with screws. Butyl rubber
sealing strip or silicone sealant (PALRAM has tested and recommends Dow Corning Q3-7098 or Q3-3793 and Novasil S 64) are also
permissible. For a list of compatible adhesives and sealants see Palram “Recommended Adhesives and Sealants for Polycarbonate Sheets”.
Adjusting The Sheet to Frame Dimensions
(“c” and “d” refer to the indicated dimension in the diagram shown
below).
If sash dimension “c” or “d” is: Trim sheet by:
Sheet Thickness Required for Given Sheet Width* and Rabbet
Depth. (“a” and “e” refer to the indicated dimensions in the diagram
shown below).
300 mm (11.8 in.) 1 mm (0.04 in.)
300 mm (11.8 in.) - 700 mm (27.6 in.) 2 mm (0.08 in.)
700 mm (27.6 in.) - 1000 mm (39.4 in.) 3 mm (0.12 in.)
1000 mm (39.4 in.) - 1300 mm (51.2 in.) 4 mm (0.16 in.)
1300 mm (51.2 in.) - 1700 mm (66.9 in.) 5 mm (0.20 in.)
1700 mm (66.9 in.) - 2000 mm (78.7 in.) 6 mm (0.24 in.)
2000 mm (78.7 in.) - 2300 mm (90.6 in.) 7 mm (0.28 in.)
2300 mm (90.6 in.) - 2700 mm (106 in.) 8 mm (0.31 in.)
2700 mm (106 in.) - 3000 mm (118 in.) 9 mm (0.35 in.)
Example Frame
Legend
a . . . Sheet width
b . . . Sheet length
c . . . Sash width
d . . . Sash length
e . . . Edge engagement
f . . . Thermal expansion allowance
g . . . Rabbet depth = ½f + e
A-A
Width* (a) Thickness Rabbet Depth (e)
700 mm (28 in.) 3 mm (0.12 in.) 15-20 mm (0.6 - 0.8 in.)
900 mm (35 in.) 4 mm (0.16 in.) 15-20 mm (0.6 - 0.8 in.)
1100 mm (43 in.) 5 mm (0.20 in.) 15-20 mm (0.6 - 0.8 in.)
1300 mm (51 in.) 6 mm (0.24 in.) 20-30 mm (0.8 - 1.2 in.)
1500 mm (59 in.) 8 mm (0.31 in.) 20-30 mm (0.8 - 1.2 in.)
1700 mm (67 in.) 10 mm (0.39 in.) 20-30 mm (0.8 - 1.2 in.)
1900 mm (75 in.) 12 mm (0.47 in.) 20-30 mm (0.8 - 1.2 in.)
*Width refers to the smaller dimension.
A
c
f
e
db
BB
½f ½f
a
e
A
B-B
18
Page 19

PALSUN® Glazing
PALSUN® Technical Guide
GA-2004 Glazing Detail
19
Page 20

Glazing System Detail
Designed by Checked by Approved by
Date
Date
Hybrid Glazing System Detail
20
Page 21

Oriented Glazing System Detail
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Wet Glazing Detail
21
Page 22

Glazing System Detail
Mechanical Fastening
PALSUN & PALTUF sheets can be fastened with nuts and bolts, providing that several points be kept in mind:
Never use rivets, as they apply excessive force and could cause cracks in the sheets.
Always drill a slightly over-sized hole by 2-3mm (/” - /”) to compensate for thermal expansion.
Never use soft PVC washers!
Use neoprene and aluminum washers to distribute the load.
When using mechanical fasteners, they should be evenly spaced to avoid stress accumulation at particular points.
With nuts and bolts, tighten moderately and use only rust-free materials.
Wherever possible, a “floating sheet in frame” is preferable, similar to glass, and without mechanical drilled fasteners.
Treatment of Sheets after Installation
The sheet’s polyethylene masking must be removed after it is installed. The masking covers the sheet to protect it during handling,
storage, and installation, but once the sheet is installed - it must be removed within 24 hours.
A non-standard masking that can be left on the sheets for up to one month and then removed immediately is available upon
special request and is subject to a minimum quantity order.
PALSUN & PALTUF sheets may be cleaned by carefully following the instructions on page 30.
22
Page 23

PALSUN® Technical Guide
General Fabrication Guidelines
Tools
PALSUN sheets can be fabricated with standard power or hand tools for wood or metal, as long as they are well sharpened and
have the clearance required for machining rigid plastics. Only speed regulated tools should be used. The highest possible speed
that will not melt the sheet during processing, due to the heat buildup, will achieve the best results.
High-Speed steel tools are adequate in most cases. Carbide-tipped tools are preferred for continuous production lines.
Tools should be set up so just the cutting edges should come into actual contact with the fabricated material, to reduce frictional
heat buildup.
Cooling
Cooling is not required under standard machining conditions.
When high-speed machining is necessary, clean water or compressed air can be used to cool the material and tool, and remove
the machining chips.
Never use cooling oil or emulsions, as they may damage the PALSUN sheet.
In order to avoid induced internal stresses generated by overheating, care must be taken to keep heat buildup to absolute
minimum.
Size Regulation
Due to the high thermal expansion rate of PALSUN, which is considerably greater than that of metals, glass or concrete, precision
measurement checks should always be done at a fixed reference ambient temperature.
Protective Film (Masking)
The PALSUN polyethylene (PE) protective masking may be left on the sheet during most regular fabrication, to prevent damage
to the surface.
Fabrication Markings
When necessary, mark sheets to be fabricated on the protective masking. If, for some reason, it is necessary to mark directly on
the sheet, use wax pencils or felt tipped marking pens.
Marking the exposed surface by scratch marks with sharp objects may initiate fractures and induce failure under load.
Sawing & Cutting
A variety of power saws, either table mounted or portable can be used to saw PALSUN. Shearing or punching are also possible.
Laser or water-jet cutting are less common but also possible techniques.
Table Mounted or Portable Circular Saws
These types of saw are widely used to saw PALSUN. There are two major workshop types and one portable type:
A Moving Table, Fixed Blade Bench Saw: is preferable for long, straight sawing.
Radial Arm Saw: is generally used for “cross-cut” (width) or diagonal sawing.
Portable Circular Saw: usually restricted for use on site for straight cutting, is slower and not as accurate as table saws. This type of
saw may be attached underneath a special bench to function as an on-site, limited operation fixed table saw.
Circular Saw Blades
Should be fine toothed hollow ground, or preferably carbide tipped, triple chipped or alternate bevels (Alt 1 and Alt 2, see
figures 9a & 9b on next page, respectively), with minimal blade body contact with the cut material. Such blades can offer clean,
good quality cuts.
23
Page 24

Generally Accepted Recommendations for Circular Blade Specifications
Property Units Sign Value
Clearance angle α 10 – 20°
Rake angle γ 5 – 15°
Alternate double-bevel angle (Alt. 1) α° 45°
Alternate bevel angle (Alt. 2) β° 10 – 15°
Cutting speed - m/min. (ft/min) 1,000 - 3,000 (3,300 - 10,000)
Rate of feed mm/sec. (inch/sec.) 30 (/)
Thin gauge: 1.5-2.5 mm tooth pitch (/” - /” ) Teeth per mm ( Teeth per inch) t 2.5 - 6 (10 - 12)
Heavy gauge: 3.2 - 12 mm tooth pitch (/” - /” ) Teeth per mm (Teeth per inch) t 6.5 - 8.5 (3 - 4)
Notes:
1. 2 Possible alternatives (Alt 1 & Alt 2, see figures 9a & 9b below) are supplied by different tools manufacturers as alternate beveled teeth for blades intended for cutting
plastics, and both offer satisfactory cuts (line 3 in the table).
2. For sawing thin gauge sheets of less than 2mm thickness, It is recommended to batch together 10 - 15 such sheets, with a thicker (3-4mm) bottom sheet for support.
3. Shearing is the preferable option for cutting a single thin gauge sheet.
Palram Particular Circular Saw Cutting Recommendations
These recommendations are based on technical know-how, particular tests and vast practical experience accumulated during years
of work. These recommendations are to be accepted only as general guidelines.
Figure 8: Typical Circular Saw Blade (segment)
Figure 9a: ALT1 - Alternate Teeth Configuration Figure 9b: ALT2 - Alternate Teeth Configuration
24
Page 25

Saw Blade Specifications for Cutting PALSUN up to 5mm Thickness
Property Units Value
Clearance angle mm (inch) 300 (12)
No. of teeth in blade 96
Thickness mm (inch) 2.2 - 3.2 (/” - /” )
Teeth angles Rake: 45° Clearance: 15°
Alternating: Left - Right
Tooth appearance
Speed rpm 1800 - 2400
Saw Blade Specifications for Cutting PALSUN 6mm Thickness and Above
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Property Units Value
Clearance angle mm (inch) 350 (14)
No. of teeth in blade 108
Thickness mm (inch) 2.2 - 3.2 (/” - /” )
Teeth angles Rake: 10° Clearance: 15°
Alternating: Left - Right
Tooth appearance
Speed rpm 1800 - 2400
Notes:
1. Teeth shapes sketches are not to scale. They should be considered to serve only as an indication.
2. The PALSUN should be placed on a firm flat base and clamped into position during sawing.
3. When sawing PALSUN, it is recommended to leave the protective masking on.
4. If the cut sheet vibrates during sawing, cardboard sheet padding may be placed beneath it to absorb the vibrations.
5. When sawing thin gauge PALSUN it is recommended not to cut single sheets by themselves, but saw a pack of 5-10 sheets at the time, clamped firmly together to
a steady base.
6. Low to moderate feed rate should be used when the sheets approach the blade, or vice versa. A feed rate that is too high can cause gumming, splitting or breaking
of the sheet edges.
Band Saw
Band saws can be used for cutting PALSUN sheets of most thicknesses with
acceptable results. Band saws are workshop tools. In PALSUN fabrication they are
mostly used to cut formed parts or irregular shapes. It is possible to cut flat sheets
in straight lines too, but in limited length and width, due to the tool’s limitations.
Thin gauge sheets are better sawed when stacked to a thickness of 10 -12
mm (0.4 - 0.5 in.)
The preferred band saw blade should have slightly set teeth, with 10 – 20 mm
(0.4” - 0.8” inch) blade widths.
Figure 10: Typical Band Saw Blade Configuration
25
Page 26

Recommended Band Saw blade Properties
Property Sign Units Value
Clearance angle α 10 – 20°
Rake angle γ 5 – 15°
Cutting speed m/min (ft/min) 1,000 - 6,000 (1,950 - 3,300)
Rate of feed mm/sec (inch/sec) 20 (/)
Thin gauge: 1.5-2.5 mm tooth pitch (/” - /” ) t Teeth per mm (Teeth per in.) 1.5 - 2.0 (12 - 18)
Heavy gauge: 3.2 - 12 mm tooth pitch (/” - /” ) t Teeth per mm (Teeth per in.) 2.5 - 3.5 (7 - 10)
Notes:
1. A band saw is suitable for cutting curved lines and 3-dimensional, formed parts.
2. For cutting a few formed objects of the same shape, they must be firmly clamped together.
3. A band saw cutting usually yields rougher finished edge, which must be smoothed by sanding and polishing.
An endless belt sander is a preferred tool for such an operation.
4. Palram recommends using a circular saw for better-finished edges, whenever possible.
Portables: Jigsaw or Saber Saw
Portable saws of these types use short movement, reciprocating blades, instead of one-direction orientation, continuous
movement blades like those of circular or band saws, and are much slower in operation.
Chipping: Various sized chips are broken off on both edges of the sawing line, leaving the cut edges rough and uneven.
Gumming: Chips and splinters from the advancing saw blade overheat during the sawing process, melt and create a mass of
cooled down material in front of the blade and on both sides of the cut. The swarf sticks to the edges, leaving an unsightly, rough
edge finish, which would be difficult to clean.
Jigsaw or saber saw cutting usually results in an inferior finish of the cut edges, worse than the results achieved by a circular
saw. Palram recommends sanding and polishing of the cut edges as standard practice. An endless belt sander is the preferred
tool for such an operation.
Gummed material may also stick to the blade itself and cause seizure.
The same uncontrolled heat that creates gumming may also induce undue internal stresses along the edges of the cut,
necessitating cooling of the sheet.
Recommended Remedies:
Choose the correct tooth size and pitch.
Select a more appropriate saw speed.
Lower the feed rate.
Examine the sharpness of the blade.
Examine the blade alignment.
Cool the blade with compressed air when long cuts are required.
Take frequent pauses during long production runs, to let the saw blade cool down.
Begin sawing with the blade already running at the full recommended speed.
26
Page 27

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Routing
A versatile technique, enabling diversity of edge fabrications and trimming of PALSUN sheets, notably for parts too large or of irregular
shape for a band saw. With sharp two-flute straight cutters, this technique can produce very smooth edges.
The feed rate should be slow, to avoid excessive heat buildup and shattering.
As a safety measure, when routing, always guide the sheet with a suitable jig.
A jet of compressed air can be used to cool the bit and the sheet at the spot of cutting and assist in chip removal.
Static bench routers: Fast, strong and stable, for complex and accurate straight-line fabrications.
Portable routers: Less powerful, for smaller or on site jobs. Also used for trimming and edge fabrications of irregular shapes.
Can perform certain small milling jobs like butt shaping on rectangular or round apertures or tongue and groove butt finish
on thicker sheets.
Applications - Primary Edge Finishing
Quick and accurate trimming or finishing of straight-edged or curved cut PALSUN sheets.
Easily produced straightedge corners or curved butts.
Preparation of varied lap and butt joint fabrications.
Applications - Tooling
Routers: Universal, commercially available equipment.
Routing cutters: new metalworking cutters, kept at utmost sharpness.
Recommended Band Saw blade Properties
Property Units Value
Clearance angle 5 - 10°
Rake angle 0 - 10°
Router speed - w/o load rpm 15,000 - 22,000
Cutting speed m/min. (ft./min.) 100 - 500 (330 - 1640)
Feed rate mm/rev. (inch/rev.) 0.1 - 0.5 (0.004 - 0.07)
Routing and milling tips For clean, smooth routing work ensure cutter’s sharpness and faultless alignment before starting work.
Compressed air jet cooling following the cutting head improves the culter’s speed, cut quality and blows the swarf away. Let
the tool reach its maximum (unloaded) operating speed before commencing work.
Milling & Joining
A portable router, with suitable cutters, can be used for small milling jobs.
A standard woodworking jointer-planer, preferably with carbide or high-speed blades/cutters, can be used for trimming, resulting
in a good quality edge finish.
Avoid excessive stock removal, which may result in shattering or rough edges. A cut of 0.4 mm (0.016 in.) or less per pass is
recommended.
Finishing Recommendations for Well Done Sawing and Cutting
Unintended saw marks, rough or jagged corners, or uneven, drawn edges created by imperfect shearing may result in crazing
and cracking, that can develop further to failure under load.
Palram recommends finishing the edges of cut PALSUN sheets by finishing the edges to a smooth appearance.
This will ensure that no cracks will develop from the irregularities at the edges.
Smoothing techniques are discussed in
“Finishing” Section on page 29.
27
Page 28

Drilling
General Indications
Drill bits: Regular, new high-speed steel twist drills, or new carbide-tipped drills are suitable for drilling holes in PALSUN sheets of
various thicknesses, as long as they are sharpened well. They are used mainly for bores up to 12 mm(1/2 “) diameter.
Figure 14a: Regular Drill Bit Figure 14b: Flat Chisel Edged Drill Blade
Larger holes may be drilled by flat, chisel edged drill blades with a triangular cutting tip, similar to those used in woodworking, kept
always very sharp. Rake angle should be about 5° to avoid side friction. They are used mainly for bores from 12 to 20mm (/ “ to / “).
Commercially available cutting cups or circle cutters of several types can be used for performing large round apertures.
Speed: Decrease the drill’s speed as hole diameter and / or sheet thickness gets larger. Drilling speed may vary due to actual conditions.
Feed rate: May vary due to actual conditions.
Drilling Speed and Feed Rate Change in Accordance with Bore Diameter
Hole Diameter Drill Speed Feed Rate
mm Inch 1 Inch 2 rpm mm/rev inch/rev
3 / 0.12 1500 - 1800 0.03 - 0.07 0.012 - 0.028
6 / 0.24 800 - 1500 0.03 - 0.07 0.012 - 0.028
10 / 0.4 500 - 1000 0.01 - 0.07 0.004 - 0.028
15 / 0.6 350 - 700 0.07 0.028
20 / 0.8 250 - 350 0.07 0.028
Recommended Drill Bit Configurations
Property Sign Units Value
Clearance angle 10 – 20°
Rake angle γ° 0 – 10°
Drill tip angle β° 110 – 150°
Helix angle α° 30°
Cutting velocity m/min. (ft./min.) 15 - 30 (49 - 98)
Notes: For small gauge sheets (1 - 2 mm or 0.04 - 0.08 in.) we recommend using flatter tip drill bits (β = 140 - 150°) for achieving a cleaner bore with less risk of chipping.
28
Page 29

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Drilling tips and recommendations
Location: Locate holes no closer to the edges than 2 – 2.5 times the diameter of the pertinent hole, with a 10mm (0.4 inch)
minimum.
Precision: It is imperative to keep the sheet (or stack of sheets) firmly clamped to a stable workbench (or a similar base) to avoid
fluttering during drilling.
Cooling: Usually cooling is not required with regular drills.
However, in cases of deep drilling, like putting perpendicular holes through the sheet’s edge, or when drilling through a stack of
sheets, cooling both the drill bit and the vicinity of the hole with a jet of compressed air is a good practice.
It is also recommended, when drilling deep holes, to stop frequently, pull the drill out and clear the hole from swarf and debris
with compressed air.
Preventing internal stresses: Producing a clean, smooth bore, keeping heat buildup to the minimum, by the procedure
described above, prevents excessive heat buildup, meltdown and gumming of the drilling dust and debris, and possible seizure
of the bit. It also prevents undue internal stresses at the vicinity of the hole.
Honing and polishing the edge of the hole by mechanical or chemical means contributes to keeping the sheet stress-free,
preventing cracking.
Maintaining the edge: Carbide tipped twist drill bits are preferable for long or continuous production runs. They are more
durable and improve the edge quality.
Finishing
General Comments
Reasons, Means and Targets
The final step in fabrication, finishing improves both the practical and aesthetic properties of PALSUN sheet prior to assembly.
Grinding & Polishing
This is mostly done as a part of edge preparation.
Practical objective: Rough, uneven, untended edges may be starting points for crazing and cracks after the PALSUN sheet is
installed and subjected to day by day exposure to wind loads, UV radiation and thermal expansion & contraction, not to mention
man-made impacts.
Aesthetic objective: Nicely finished, smooth edges are a must for a quality appearance of the finished product, often installed
with exposed edges.
Decorating: A type of finishing intended mostly for aesthetic appearance or for display purposes. Executed by painting, printing,
films or hot stamping.
Grinding / Sanding
General
A primary stage in edge finishing, rough or jagged edges and cutting tool marks created by a saw, shearing machine or a router,
can be removed by grinding.
Grinding / Sanding Recommendations
A belt sander, equipped with a 400-500 grit belt, running at 20 - 30 m/sec (65 - 100 ft./sec), is the preferred option, applying low
contact pressure during operation. Wet sanding and waterproof belts are preferable, as they prevents heat buildup, sanding
dust accumulation, and prolong sanding belt life.
A reciprocating or orbital sander can also be used, but it can be applied only by the dry sanding method.
Manual Sanding can also be used, wet or dry, working with successive grit size abrasive paper (Starting with 100, then 280-grit
silicon-carbide, and finally 400-600 grit sandpaper).
29
Page 30

Cleaning
General Polycarbonate Cleaning Guidelines
Never use abrasive or high alkaline cleaners on PALSUN sheets.
Do not use cleaners on PALSUN sheets for an extended period of time. Rinse immediately with clean, cold water.
Do not apply cleaners in direct sunlight.
Never use sharp objects, wipers (squeegees) or razors on PALSUN sheets.
Do not clean with gasoline.
Always practice safety first and never step directly on PALSUN sheets.
Always test cleaners in a small inconspicuous area prior to cleaning entire panel to prevent adverse results.
When using a pressure washer, do not allow the spray tip to come too close to the panel, as it could have enough pressure to
penetrate or tear the panel.
Avoid dry cleaning, as sand and dust particles clinging to the exterior of the panels may scratch the surface.
General Cleaning Instructions for Products
The Palram polycarbonate products can be easily cleaned utilizing a soft sponge or cloth made from 100% cotton, lukewarm
water and a mild dish washing detergent. All surfaces should then be rinsed with cold water and dried with a soft cotton cloth
to reduce water spotting. In some instances this procedure may be inadequate and require the use of additional cleaning agents.
The agents listed below have all been approved for use at room temperature.
30
Page 31

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Cold Forming
Cold Curving
1.
PALSUN sheets can be cold bent or curved, within their minimal permitted bending radius, without damaging their mechanical
performance. The minimal permitted bending radius for a PALSUN sheet is a factor of their thickness and should be calculated in the
following manner: 200 x sheet thickness (e.g. for a 5mm PALSUN sheet, 5 x 200 = 1000mm minimum cold bending radius). Moreover,
based on our experience and observations, the internal stresses induced by curving give them extra strength and rigidity in both
directions, as in pre-stressed concrete elements.
2. Rigidity and support spans increase progressively as the curve radius is reduced (down to the minimal permitted radius). A shallow
curve should be considered virtually the same as a flat panel, while a deep curve may add significantly to the bridging ability.
Brake Forming
General Notes
1. PALSUN sheets can be cold-bent in a straight line (line bending). Standard metalworking tools, like a brake press, may be used for
bending. The bending process results in permanent plastic deformation. The degree and quality of this change depend on the
thickness of the PALSUN sheet, the final bending angle required, and the actual tools used.
When brake forming of PALSUN is conducted, the internal elastic stresses induced along the bent line reduce the mechanical
2.
properties, UV resistance, and chemical resistance of the sheet along the bending line. Palram recommends using this process for less
demanding applications, and protecting the cold bent areas of the sheet from contact with aggressive chemicals or excessive forces.
3. Annealing can reduce the residual stress level induced by the cold bending process, improving the sheet’s mechanical properties.
The maximum angles that can be obtained using this process depend on the PALSUN sheet thickness, and the extent of the internal
4.
elastic strain. Palram recommends a 24-48 hour delay for sheet to relax after bending. In order to achieve the desired angle, the
sheet has to be bent 20-40 degrees in excess of that angle, depending on the angle and sheet thickness. During the stress relaxation
period immediately after bending, the bent sheet will expand and regain the required shape.
5. Certain types of sheets are not suitable for either cold or thermal forming, such as PALGARD abrasion resistant sheet. This type is
supplied with a tough, scratch-proof finish, which can not be bent and must be installed “as is”.
Practical Recommendations & Work Instructions
1. Preparations of the PALSUN Sheets and Tooling for Bending:
a. Cut the sheet to its required pre-bending size. Palram recommends leaving the protective film on both sides during the cutting,
edge preparation and cold bending operations.
b. Sand and polish the sheet’s edges to a very smooth finish. Rough edges or the tiniest fissure may initiate cracks and fractures at the
vicinity of the bending lines, due to internal stresses induced by the bending process.
Palram recommends conducting preliminary bending tests on small samples of the same (or varied) thickness of the intended sheet,
c.
and try a few different values of excess bending. After arriving at a satisfactory result you can start production.
It is advised to use special tooling, like blades and anvils, designed for plastic sheet bending. Standard metalworking blades and anvils are not
d.
necessarily suitable for bending plastic sheets. For plastics, we recommend using a special bending blade with a straight, rounded business
edge. The edge radius should be about 4-6 mm (0.16 to 0.24 in.). The thicker the sheet, the larger edge radius required. The anvil channel outer
“banks” (corners) should be rounded. Both blade and anvil are to be smooth and polished, with no projections, irregularities or rough edges.
Please note that an anvil channel for plastics bending is different than the one suitable for metalworking. It has a wider, flat bottom
and much steeper “banks”.
2. Cold Bending Fabrication:
a. Bending a sheet with an UV protected side (the printed protective film side) on the exterior of the bend gets best results. Therefore,
unless otherwise requested, lay the sheet to be bent with the printed side face down.
b. For optimal results, perform the brake forming quickly, with an additional 20-40 degrees as explained above, then leave the sheet
to relax for 24-48 days.
31
Page 32

3. Installation
a. Cold bent polycarbonate is more sensitive to mechanical or chemical abuse in the vicinity of the bend. Therefore, Palram
recommends a design that offers better protection for bent areas from any detrimental influence.
b. Avoid putting additional strain on bent parts, like forcing a bent angle in or out to fit into an existing framework.
Thermoforming
Pre-Drying
General Guidelines
Nearly all types of PALSUN sheets are suitable for various thermoforming (TF) procedures. However, due to a native small moisture
content absorbed after manufacture, they demand a thorough pre-drying process prior to most thermoforming techniques.
During this process, the sheet’s temperature will be raised to over 160°C (320°F). Avoiding this preliminary treatment may result in
moisture blisters, marring the appearance of the finished product, and/or reduce its properties.
Higher thicknesses require longer periods in the drying oven.
Typical Pre-Drying Time in Oven for Various Thicknesses*
Sheet Thickness Drying Time at 125°C (260°F)
mm Inch Hours
1 0.04 1.5
2 0.08 4
3 0.12 7
4 0.15 12
5 0.2 18
6 0.24 26
8 0.32 45
Notes: Time for thicker sheets can be calculated through interpolation.
The sheets are put into an oven, with the protective film removed from both sides, and arranged 20-30mm (3/4”-1”) apart, to
enable free air circulation. They can be stacked horizontally (on stays or suspended) or vertically- just so they will not be distorted
or twisted.
The pre-drying process should be performed as close as possible to the actual forming. Fully dried sheets taken out of the oven
and cooled down to room temperature may be workable within 1 to 10 hours (depending on relative humidity and temperature
in the workshop).
Longer delay may necessitate repeated pre-drying session. A recommended practice, if possible, is leaving the pre-dried sheets
in the switched-off oven until the actual thermoforming process. This method saves energy and time on the thermoforming
apparatus.
32
Page 33

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Guidelines to the Heating Process
Good quality thermoformed products can only be achieved through a careful and controlled heating process. All parts of the
treated sheet should reach even, uniform temperature, achieved by a slow, controlled heating rate, avoiding sudden changes in air
circulation and temperature. Such events may result in hot spots and possible distortions. Sheet edges must maintain the same
forming temperature as the whole sheet.
Pre-heating of the clamping frame from 120°C to 130°C is recommended.
Temperature Regulation: Continuous regulation of the sheet’s temperature must be maintained inside the thermoforming device itself.
PALSUN sheet (of any type) tends to cool quite quickly, and may need a regulating system for adding or dispersing of excess heat on the spot.
The sheet’s temperature at the thermoforming zone (or the whole sheet) should be kept between 180°C and 210°C during the forming process.
Forcing the sheet to form at a lower temperature may induce detrimental internal stresses, reducing the sheet’s impact
resistance and increasing its chemical sensitivity. Internal stresses are invisible and can be detected only by polarized light.
Annealing may reduce the stresses, although it is a complicated process and could be inefficient or impossible to perform in most cases.
Protective Polyethylene (PE) masking in Thermoforming: Special masking is available for sheets intended for thermoforming and
should be specified in these cases. This type of masking may be kept on the sheet when practicing most thermoforming methods
and peeled off right before performing the procedure. When using sheets with standard masking, it should be removed prior to the
thermal treatment, otherwise it is likely to fuse into the sheet’s face.
Hot-Line Bending
General Guidelines
1.
Description: A simple bending technique, used for forming local, straight line, one axis bent parts (such as corners, boxes, and
machine guards). This type of bending is usually preferable (if possible) to cold line-bending.
2. The process: A bending device with localized heaters on one or two sides of the sheet to be bent is used. The “sandwiched“ twosided heating method is preferable, since it retains the same temperature on both sides at the time. a one-side heater method
requires turning the sheet over a few times during the heating period, in order to maintain optimal temperature on both sides.
Steps & Indications
One-sided heating method may suffice for sheets up to 3 mm (0.12 in.). Thicker sheets or more demanding cases require using two-
sided heating. Keeping control of the sheet’s temperature limits of 155-167°C (31-332°F) is of the utmost importance.
Forcing the bend at lower temperatures will render the sheet fragile at the bend. This simple bending process enables working with
regular sheets, without pre-drying. Experimenting with small samples before final execution is highly recommended.
Figure 15: Heat bending device
33
Page 34

PE Masking: When preparing for bending of regularly cladded sheets- peel off the masking on both sides of the sheet along the
bend line for about 100 mm (4 in) on each side in TF prepared sheets. It is possible to process the sheet with the masking on, up
to 5 mm (0.2 in) thickness. For sheets of 6 mm thickness or more the PE masking should be removed along the bending line, as
described above. Always test a few samples before proceeding to production.
Heaters: Linear IR (Infrared) or resistance wires strip heating elements are used, preferably with heat reflectors. The width of the
heated zone depends on the number of elements used, the spacing between them depends on their specific thermal output and
the distance from the target sheet.
Bending process: When the sheet has reached the required temperature the heaters are to be switched off. The sheet, held in
pivoted clamps, preferably equipped with a caliper, is then bent to the required angle and secured there until it cools down and sets.
Note: It is recommended to perform the bend a few degrees tighter than the required angle, as the angle may increase as the sheet
cools. The desired angle may be reached after a few trials.
Cooling is to be done in ambient air, taking care to avoid sudden drafts. These can cause distortion of the final product.
The minimal Hot-Line Bending Radius is 3 times the thickness of the bent sheet. Larger radii can be achieved by widening the
heated zone.
Forming - Notes for Consideration
Local hot line bending (or any other localized heating) induces internal stresses in the finished part, reducing the chemical resistance
of the element at the bending line zone. Such treatment is therefore recommended for use in less demanding environments.
Localized heating and cooling expansion/contraction characteristics are unpredictable in many cases. Short elements (up to
1.00m or 3.0’) usually remain flat. Longer elements may distort to a concave shape (the outer edges are longer than the line-
bent side due to uneven contraction).
This phenomenon can be corrected or reduced by simple jigs or frames, which hold the part in the right position during the
cooling period.
It is always advised to fabricate experimental test samples to check feasibility of the bending operation.
PALSUN® Thermoforming Tips
Consistent part-to-part uniformity is better ensured if the sheet blanks prepared for the thermoforming process are cut from the
basic sheet always at the same direction.
Best results in thermoforming are achieved when parts are heated to temperatures just above the HDT (150 °C- 300 °F).
Thermoforming parts below the HDT temperature induces internal stresses.
Secure the cooling area for thermoformed parts against undue drafts. Uneven cooling may result in warping and/or curling of parts.
Assure precise and systematic control over oven temperature and heating time.
PALGARD (abrasion resistant) and PALSUN FR (fire retardant) are not recommended for use in thermoforming. The bending and
stretching involved during the process will permanently damage the sheets.
34
Page 35

Fault and Remedies in Thermoforming Practice
# Recognized Fault Probable Cause Proposed Treatment
PALSUN® Technical Guide
Hot Line
Bending
Drape
Forming
Vacuum
Forming
Blown
Free
1
Bubbles in sheet
2 Working temp. too high Decrease working temp. + + +
3
4 Mold under-heated Increase mold temp. +
5 Late extraction of part Diminish cooling cycle +
Hair fissures, fragile parts
6 Vacum speed too high Reduce vacum rate +
7 Mold corners too sharp Round sharp corners +
8 Basic sheet size too small Increase sheet size +
9
10 Mold lead inadequate Check spacing-min. depth x 2 +
Webbing
11 Vacum speed too high Reduce vacume rate +
12 Basic sheet size too large Clamp/mold spacing <50mm +
13
Blurred or partial detailing
14 Sheet rigid, under-heated Extend heating period or temp. +
15
Product sticks to mold
16 Product release delayed Shorten release period +
17 Draft angle too steep Enlarge draft angle up to 4-6° +
18
Marked zones on product
19 Suction holes misplaced Install new, better placed holes +
20 Sheet overheated Decrease heating period/ temp. + +
21
Exterior flaws / roughness
22 Suction holes misplaced Install new, better placed holes +
23
Inconsistent shape of part
24 Irregular heating/ cooling Prevent drafts, fix faulty heater + + + +
25 Product release delayed Shorten release period +
Moisture content too high Pre-drying + + + +
Part overheated Decrease heating period + +
Erratic heating Prevent hot or cold spots +
Vacum too weak Seal leaks/add vacum holes +
Mold overheated Decrease mold temperature +
Irregular finish of mold Treat mold to consistent finush +
Dirt/ grime on sheet / mold Wipe/Vacum-clean mold/sheet + +
Mold/ brace under-heated Extend pre-heat of mold/brace +
35
Page 36

Printing
PALSUN is suitable for all printing methods which are applicable to rigid sheets. It has been tested and approved by leading digital
printer manufacturers, achieving excellent results in all parameters. Clear PALSUN sheets match the high clarity of other thermoplastic
sheets, yet offer far better adhesion properties and ease of printing with no requirement for any further surface treatment.
Direct Digital Printing
Wide format (Roll-to-roll) and flatbed printers use various ink and ink curing technologies to allow high quality printing at relatively
high speeds. High quality digital printing depends on various factors:
Printer capabilities
Ink technology and quality
Type of printing substrate and quality
Machine operator
PALSUN is suitable for use with UV curing and solvent-based digital inks, and for IR drying when water-based inks are used. PALSUN
will retain its clarity or tint, even after intense UV curing.
Protective Film Masking
The protective polyethylene film mask helps prevent surface abrasion and stains. However, removing the protective film may cause
an increase of static electric charge, which can affect ink coverage. Therefore, after peeling the film away from the sheet, the static
electricity that has built up in the sheet should be discharged using an ionized gun or a suitable device provided by the printer
manufacturer.
Cleaning PALSUN® and Preparing for Printing
The surface should be clean before printing. Carefully inspect each panel to ensure there is no: dust, fingerprints, residue or other
problematic substances that may affect ink coverage or adhesion. If needed, the PALSUN should be cleaned with a damp rag, or
with isopropyl alcohol.
Ink Adhesion
PALSUN is suitable for all types of inks: aqueous, solvent based, and UV curable. This suitability is affirmed by major printer OEM’s,
including HP, AGFA, Océ, Gandy Digital, Mutoh, and more. For compatibility information and recommendations, please consult the
printer manual or contact the printer manufacturer.
Ink Drying
There are two main technologies used for ink drying in digital printing:
IR (Infrared) – PALSUN’s short and long term service temperatures are 120°C and 100°C respectively, which make it highly suitable
for printers with IR drying tunnels.
UV (Ultraviolet) – PALSUN is immune to long term UV exposure and is suitable for UV curing.
Print Head Adjustment
The distance between the print head and the substrate can have a significant affect on print quality. Manufacturer specifications,
combined with operator experience, should determine print head distance from the substrate.
The suggested starting distance should not be more than 2 mm from the print head to the substrate.
36
Page 37

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Chemical Resistance
PALSUN sheets are compatible with many materials and chemicals, show limited resistance to others, and are incompatible with a third
group, with which contact may be devastating. The mechanism of chemical attack on polycarbonate sheets differs significantly from
the mechanism of corrosion of metals. Corrosion of metals results in a gradual loss of surface material as a result of electrolytic action
by the relevant chemicals. In the cases where chemical attack on polycarbonate sheet occurs, all or a portion of a range of effects can
be observed. Ethylene choride, chloroform, tetrachloroethane, m-cresol, pyridene and other chemicals can cause partial dissolution
of polycarbonate. Swelling agents include benze, chlorobenzene, tetralin, acetone, ethyl acetate, acetonitrile and carbontetrachloride.
Additional effects include color change and/or whitening. These effects may not always lead to product failure, especially for nonloaded sheets. Nevertheless, the level of measured mechanical properties will be reduced. The most critical effect of chemical attack is
stress cracking or crazing, which may range in size from being visible to the naked eye to being only observable under a microscope.
Stress cracks will always result in sheet failure which will eminate from areas of greatest stress (screws, fixings, bends, etc.).
Polycarbonate sheets are generally not recommended for use with acetone, ketones, ethers, and aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons
in addition to aqueous or alcoholic alkaline solutions, ammonia gas and its solutions and amines.
Polycarbonate is resistant to mineral acids, many organic acids, oxidizing and reducing agents, neutral and acid salt solutions, many
greases, waxes and oils, saturated, aliphatic and cycloaliphatic hydrocarbons and alcohols, with the exception of methol alcohol. The
resistance of polycarbonate to water may be described as good up to approximately 60 °C. At higher temperatures, degradation
occurs, the extent of which depends on time and temperature. Polycarbonate should therefore not be exposed for long periods of
time to hot water. However, brief contact with hot water has no effect. For example, polycarbonate tableware can be washed over
1000 times in a dish washing machine with no adverse effects being observed.
The table that appears on the following pages lists the resistance of polycarbonate sheet to a number of commonly encountered
chemicals and other corrosive media at room temperature. (Information on chemical resistance at higher temperatures will be supplied
upon request). Where the chemical resistance varies with concentration, the results of tests at different concentrations is presented.
The information on chemical resistance is based on our research and experience. (Note that information on compatible adhesives
and sealants can be found in a separate leaflet which will be supplied upon request) It serves as a basis for recommendation. PALRAM
Industries does not guarantee chemical resistance unless specific separate documentation is supplied.
For chemicals and corrosive media not indicated in the list, please contact your PALRAM representative. He will place you in contact
with the PALRAM R&D & Technology Department.
The table on the following pages uses the following key:
R - Resistant
LR - Limited Resistance (gradual attack over time may occur)
N - Not Resistant (rapid attack or attack over short time period will occur)
Chemical Resistance of PALSUN® Sheets at Room Temperature
The chemical resistance of PALSUN & PALTUF sheets, specified in the following pages, has been demonstrated in actual installations
and/or laboratory tests. The information in the table is based on our research and experience. It should be considered solely as a basis
for recommendation, but not as a guarantee, unless specifically stated in separate documentation supplied by PALRAM Industries.
37
Page 38

Chemical
Acetaldehyde N Butane R
Acetic Acid 10 R Butter R
Acetic Acid 25 (concentrated) LR (N) Butyl Acetate N
Acetone N Butyl Alcohol (Butanol) R
Acetylene R Butylene Glycol R
Acrylonitrile N Butyric Acid N
Ajax Detergent R Calcium Chloride Saturated R
Allspice N Calcium Hypochlorite R
Allyl Alcohol LR Calcium Nitrate R
Alum (Aluminum Ammonsium Sulfate) R Calcium Soap Fat R
Aluminum Chloride Saturated R Camphor Oil N
Aluminum Oxalate R Carbolic Acid N
Aluminum Sulfate Saturated R Carbon Bisulfite N
Ammonia (Gas) N Carbon Dioxide Gas (Moist) R
Ammonia (Aqueous) N Carbon Disulfide N
Ammonium Carbonate LR Carbon Monoxide R
Ammonium Chloride R Carbon Tetrachloride N
Ammonium Fluoride N Castor Oil R
Ammonium Hydroxide N Catsup (Ketchup) R
Ammonium Nitrate R Caustic Potash (Potassium Hydroxide) N
Ammonium Sulfate Saturated R Caustic Soda (Sodium Hydroxide) N
Ammonium Sulfide N Chlorine Gas (Dry) LR
Amyl Acetate N Chlorine Gas ( Wet) N
Amyl Alcohol LR Chlorobenzene N
Aniline N Chloroform N
Antimony Trichloride Saturated R Chocolate R
Aqua Regia (3 parts HCl:1 part HNO3) LR Chrome Alum Saturated R
Arsenic Acid 20 R Chromic Acid 20 R
Automatic Switch Grease R Cinnamon R
Automotive Waxes LR Citric Acid 10 R
Baby Lotion R Cloves N
Bacon Fat R Coal Gas R
Barium Chloride R Coca Cola LR
Battery Acid R Cocoa LR
Beer R Cod Liver Oil R
Beet Syrup R Coffee LR
Benzaldehyde N Cooking Oil R
Benzene N Copper Sulfate Saturated R
Benzoic Acid N Cresol N
Benzyl Alcohol N Cupric Chloride Saturated R
Betadine R Cuprous Chloride Saturated R
Bleach (Clorox) R Cyclohexane R
Blood and Blood Plasma R Cyclohexanol LR
Borax R Cyclohexanone N
Boric Acid R DDT R
Brake Fluid N Dekalin R
Bromine N Detergent (most) LR or R
Bromobenzene N Developing Solutions N or LR
Entries indicate the following: R - resistant, LR - limited resistance, N - not resistant
*Concentration of aquesous solution except where noted
Concentration
%*
Resistance Chemical
Concentration
%*
Resistance
38
Page 39

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Chemical
Diamyl Phthalate N Kerosene R
Diesel Fuel R Lactic Acid 20 R
Diethyl Ether (Ethyl Ether) N Lacquers and Thinners R
Dimethyl Formaldehyde (DMF) N Laundry Detergents (Most) R
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) N Ligroin (Hydrocarbon Mixture) R
Dinonyl Phthalate (plasticizer) LR Lime Solution (2%) or paste R
Doctyl Phthalate (plasticizer) LR Liquors or Liqueurs R
Dioxane N Linseed Oil R
Diphyl 5,3 LR Loctite R
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol) and Water 96 R Lubricating Oils (Most) R
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol) Pure LR Machine Oils (Most) R
Ethyl Amine N Magnesium Chloride Saturated R
Ethyl Acetate N Magnesium Sulfate Saturated R
Ethyl Bromide N Manganese Sulfate Saturated R
Ethylene Chloride N Margarine R
Ethylene Chlorohydrin N Mayonnaise R
Ethylene Dichloride N Meat R
Ethylene Glycol (Antifreeze) LR Mercuric Chloride Saturated N
Ferric Chloride Saturated R Mercury N
Ferrous Sulfate R Methane R
Fish and Fish Oils R Methanol (Methyl Alcohol) Pure LR
Floor Polish R Methylamine R
Formalin 10% R Methylcellusolve N
Formic Acid 10% (30%) R (LR) Methylene Chloride N
Freon TF R Methyl Ethyl Keton (MEK) N
Freon (all others) N Methylmethacrylate N
Fruit Juices and Pulp R Milk N
Gasoline N Mineral Oil R
Gear Oil R Motor Oils (Most) R
Glazers Putty R Mustard R
Glucose R Naphtha (Stanisol) R
Glycerine R Nickel Sulfate N
Glycerol R Nitric Acid 20 R
Glycols R Nitrobenzene R
Glutaraldehyde 50% R Nitropropane R
Grease, Automotive (Most) R Nitrous Oxide R
Heptane R Nutmeg N
Hexane R Oleic Acid N
Hydrazine N Onions R
Hydrochloric Acid 20 (Concentrated) R (N) Oxalic Acid 10 R
Hydrofluoric Acid 20 R Oxygen R
Hydrogen Peroxide 30 R Ozone R
Hydrogen Sulfide R Paprika R
Iodine (aqueous solution) 5 R Paraffin R
Iodine N Pentane LR
Inks (Most) R Pepper LR
Isoamyl Alcohol LR Perchloric Acid 10 (concentrated) N
Isopropyl Alcohol R Perchloroethylene R
Entries indicate the following: R - resistant, LR - limited resistance, N - not resistant
*Concentration of aquesous solution except where noted
Concentration
%*
Resistance Chemical
Concentration
%*
Resistance
39
Page 40

Chemical
Petroleum LR Sodium Sulfide N
Petroleum Ether LR Sodium Thiosulfate R
Petroleum Oil (Refined) R Spindle Oil R
Phenol N Stannous Chloride R
Phosphoric Acid 10 R Starch R
Phosphorous Oxychloride R Styrene N
Phosphorous Pentoxide 25 LR Sugar Saturated R
Phosphorous Trichloride N Sulfur Dioxide (Gas) R
Polyethylene R Sulfuric Acid <50 (50<70) R (LR)
Polyethylene Glycol R Sulfurous Acid 10 N
Potassium Acetate LR Sulfuryl Chloride N
Potassium Aluminum Alum (Sulfate) Saturated R Tapping Oil R
Potassium Bichromate R Tartaric Acid 30 R
Potassium Bromate R Tear Gas (Chloracetophenone) LR
Potassium Bromide R Terpineol N
Potassium Chloride Saturated R Tetrahydrofuran N
Potassium Cyanide N Tetralin N
Potassium Dichromate Saturated R Thiophene N
Potassium Hydroxide N Thyme R
Potassium Metabisulfite 4 R Titanium Tetrachloride R
Potassium Nitrate Saturated R Tobacco R
Potassium Perchlorate 10 R Toluene N
Potassium Permanganate 10 R Transformer Oils R
Potassium Persulfate 10 R Transmisssion Fluid R
Potassium Rhodanide Saturated R Trichloroacetic Acid 20 LR
Potassium Sulfate Saturated R Tricholorethylamine N
Propane R Trichloroethylene N
Propargyl Alcohol R Trichloroethylphosphate LR
Propionic Acid 20 R Tricresylphosphite N
Propionic Acid Concentrated N Trisodium Phosphate R
Propyl Alcohol (1-Propanol) R Turpentine LR
Pyridine N Urea R
Salad Oil R Vacuum Pump Oil R
Salt R Vanilla R
Silicofluoric Acid 30 R Vanillin R
Silicone Grease R Varnish N
Silicone Oil R Vaseline R
Silver Nitrate R Vegetable Juices R
Soap (Ivory) R Vegetable Oils R
Sodium Bicarbonate Saturated R Vinegar R
Sodium Bisulfate Saturated R Water (Demineralized or Sea) R
Sodium Bisulfite Saturated R White Spirit N
Sodium Carbonate Saturated R Wine, Whiskey, Vodka, Rum, Cognac R
Sodium Chlorate R Witch Hazel R
Sodium Chloride Saturated R Worcester Sauce R
Sodium Chromate R Xylene N
Sodium Hydroxide N Zinc Chloride R
Sodium Hypochlorite 5% Chlorine R Zinc Oxide R
Sodium Nitrate N Zinc Stearate R
Sodium Sulfate Saturated R Zinc Sulfate R
Entries indicate the following: R - resistant,. LR - limited resistance, N- not resistant. * Concentration of aqueous solution except where noted
The chemical resistance information in this table is based on our research and experience and may be considered solely as a basis for recommendation, but not as a
guarantee, unless specifically furnished as such by Palram.
Concentration
%*
Resistance Chemical
Concentration
%*
Resistance
40
Page 41

PALSUN® Technical Guide
Adhesives and Sealants
Adhesives and sealants are a special class of substances often required during installation or fabrication of PALSUN. The guidelines for
their use, appearing below, must be followed.
1. Use only sealants, adhesives, rubber packing, sealing strips & gaskets that are compatible with PALSUN and approved by Palram
or its distributors. An updated list of compatible adhesives and sealants can be found in the Recommended Adhesives and
Sealants for Palram Polycarbonate Products brochure (Also available from www.palram.com).
EPDM rubber sealing strips and gaskets are the preferred choice, (though the use of neoprene is permitted) due to a longer life
expectancy and durability.
2. Use of sealants, adhesives and other sealing products not included in the recommended list “Recommended Adhesives &
Sealants for Palram Polycarbonate Products” must receive the Manufacturer’s explicit approval, which can be obtained through
your local distributor.
Important: Soft PVC gaskets and/or sealing strips are absolutely forbidden for use, as they are detrimental and may cause sheet
failure.
3. Use of materials that are not on the list, and/or which have not received the Manufacturer’s explicit approval, may harm the
sheets and void all warranties and any responsibility of the Manufacturer for the performance of PALSUN.
4. Your local distributor can provide additional information, and forward materials for testing and evaluation of their compatibility
with the PALSUN sheets.
5. See Milling & Joining section on page 27 for additional specific details.
Selection of the Appropriate PALSUN® Sheet
PALSUN sheets are manufactured in thicknesses of 1.0 to 12 mm.
PALTUF® Sheets
Intended mainly for indoor use (transparent partitions, interior design applications, industrial shields, and thermoformed items). They
are also used in pavilions (exhibitions), or other temporary structures. Use of PALTUF sheets outdoors, for permanent applications, even
in areas with mild UV radiation (Northern Europe, USA, Canada and similar) is not recommended.
Thin PALSUN® Sheets
Frequently used in temporary structures, (exhibitions, pavilions etc.). These products may also be used in conservatories or other
horticultural / agricultural structures, where economy and lower cost are imperative. They are repeatedly used in Thermoforming
applications, the forms generated render them rigid and suitable for special requirements, in signs and other advertising elements.
PALSUN® Sheets for Permanent Glazing Applications
The recommended permanent installation method is inside a suitable supporting frame, made of metal (steel or aluminum), wood
or rigid PVC profiles. Glazing thickness is determined according to the sash width of said frame, the wind/snow loads dictated by the
environmental conditions and the building codes in place at the project location.
41
Page 42

All marketing materials and any content therewith provided by Palram® are provided solely for the purpose of supporting and enhancing the marketing of Palram® products.
These materials are protected by Palram’s intellectual property rights and may not be used for any other purpose or in connection with the sale of products of any other manufacturer.
These materials may not be transferred to or used by any third party without prior permission of Palram.
PALRAM H.Q.
Tel: +972 4 8459900
Fax: +972 4 8444012
palram@palram.com
www.palram.com
In as much as Palram Industries has no control over the use to which others may put the material, it does not guarantee that the same
results as those described herein will be obtained. Each user of the material should make his own tests to determine the material’s
suitability for his own particular use. Statements concerning possible or suggested uses of the materials described herein are not to
be construed as constituting a license under any Palram Industries patent covering such use or as recommendations for use of such
materials in the infringement of any patent. Palram Industries or its distributors cannot be held responsible for any losses incurred
through incorrect installation of the material. In accordance with our company policy of continual product development you are
advised to check with your local Palram Industries supplier to ensure that you have obtained the most up to date information.
©1997 Palram Industries Ltd | PALSUN is a registered trademark of Palram Industries Ltd
PALRAM EUROPE LTD.
Tel: +44 1302 380777
Fax: +44 1302 380778
sales.europe@palram.com
www.palram.com
PALRAM AMERICAS
Tel: 610 2859918
Fax: 610 2859928
palramamericas@palram.com
www.palramamericas.com
11.2014
 Loading...
Loading...