Page 1

Overland
Storage
SnapSAN™ VSS
User Guide
August 2012
10400401-001
Page 2

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. All rights reserved.
Overland®, Overland Data®, Overland Storage®, ARCvault®, DynamicRAID®, LibraryPro®, LoaderXpress®, Multi-SitePAC®, NEO®, NEO
®
Series
, PowerLoader®, Protection OS®, REO®, REO 4000®, REO Series®, Snap Appliance®, Snap Care® (EU only), SnapServer®, StorAssure®,
®
Ultamus
GuardianOS™, RAINcloud™, SnapDisk™, SnapEDR™, Snap Enterprise Data Replicator™, SnapExpansion™, SnapSAN™, SnapScale™,
SnapServer DX Series™, SnapServer Manager™, SnapWrite™, and SnapServer Manager™ are trademarks of Overland Storage, Inc.
All other brand names or trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The names of companies and individuals used in examples are fictitious and intended to illustrate the use of the software. Any resemblance to
actual companies or individuals, whether past or present, is coincidental.
PROPRIETARY NOTICE
All information contained in or disclosed by this document is considered proprietary by Overland Storage. By accepting this material the recipient
agrees that this material and the information contained therein are held in confidence and in trust and will not be used, reproduced in whole or
in part, nor its contents revealed to others, except to meet the purpose for which it was delivered. It is understood that no right is conveyed to
reproduce or have reproduced any item herein disclosed without express permission from Overland Storage.
Overland Storage provides this manual as is, without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Overland Storage may make improvements or changes in the product(s) or
programs described in this manual at any time. These changes will be incorporated in new editions of this publication.
Overland Storage assumes no responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, sufficiency, or usefulness of this manual, nor for any problem that
might arise from the use of the information in this manual.
, VR2®, and XchangeNOW® are registered trademarks of Overland Storage, Inc.
Overland Storage, Inc.
9112 Spectrum Center Blvd.
San Diego, CA 92123
U.S.A.
Tel: 1.877.654.3429 (toll-free U.S.)
Tel: +1.858.571.5555 Option 5 (International)
Fax: +1.858.571.0982 (general)
Fax: +1.858.571.3664 (sales)
www.overlandstorage.com
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. ii
Page 3
Preface
This user guide explains how to install, setup, and use the SnapSAN VSS Provider software.
VSS Provider is software that facilitates business backup operations by linking the Volume Shadow Copy
Service (VSS) of Microsoft® Windows Server® 2003 or Microsoft® Windows Server® 2008 with data
replication (VSS Storage Volume Cloning or VSS Provider Replication and Mirroring) and a snapshot
function (VSS Provider Snapshots).
This guide assumes that you are familiar with computer hardware, data storage, and network
administration terminology and tasks. It also assumes you have basic knowledge of Internet SCSI (iSCSI),
Serial-attached SCSI (SAS), Serial ATA (SATA), Storage Area Network (SAN), and Redundant Array of
Independent Disks (RAID) technology.
This guide is intended for those who have basic knowledge of backup and recovery using Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 or Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and the VSS Provider snapshot function or data replication
function.
This manual explains functions implemented by the following program products:
• VSS Provider Manager and VSS Provider base product
• VSS Provider Control Command
This manual is applicable to the program products of the following versions:
• VSS Provider Manager Ver4.2 or later
• VSS Provider Base Product Ver4.2 or later
• VSS Provider Control Command Ver4.2 or later
The VSS Provider series disk array subsystems is referred to as a disk array in this manual unless clearly
specified.
Product Documentation and Firmware Updates
Overland Storage SnapSAN product documentation and additional literature are available online, along
with the latest release of the SnapSAN VSS software.
Point your browser to:
http://docs.overlandstorage.com/snapsan
Follow the appropriate link to download the latest software file or document. For additional assistance,
search at http://support.overlandstorage.com
.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. i
Page 4

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Overland Technical Support
For help configuring and using your SnapSAN VSS, search for help at:
http://support.overlandstorage.com/kb
You can email our technical support staff at techsupport@overlandstorage.com or get additional
technical support information on the Contact Us
web page:
http://www.overlandstorage.com/company/contact-us/
For a complete list of support times depending on the type of coverage, visit our web site at:
http://support.overlandstorage.com/support/overland_care.html
Conventions
This document exercises several alerts and typographical conventions.
Alerts
Convention Description & Usage
IMPORTANT An Important note is a type of note that provides information essential to
the completion of a task or that can impact the product and its function.
CAUTION A Caution contains information that the user needs to know to avoid
damaging or permanently deleting data or causing physical damage to
the hardware or system.
WARNING A Warning contains information concerning personal safety. Failure to
follow directions in the warning could result in bodily harm or death.
Typographical Conventions
Convention Description & Usage
Button_name
Ctrl-Alt-r This type of format details the keys you press simultaneously. In this
NOTE A Note indicates neutral or positive information that emphasizes or
Menu Flow
Indicator (>)
Courier Italic A variable for which you must substitute a value
Courier Bold
Words in this special boldface font indicate command buttons found in
the Web Management Interface.
example, hold down the Ctrl and Alt keys and press the r key.
supplements important points of the main text. A note supplies
information that may apply only in special cases, for example, memory
limitations or details that apply to specific program versions.
Words with a greater than sign between them indicate the flow of actions
to accomplish a task. For example, Setup > Passwords > User indicates
that you should press the
finally the
Commands you enter in a command-line interface (CLI)
User button to accomplish a task.
Setup button, then the Passwords button, and
Information contained in this guide has been reviewed for accuracy, but not for product warranty
because of the various environments, operating systems, or settings involved. Information and
specifications may change without notice.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. ii
Page 5

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Electrostatic Discharge Information
A discharge of static electricity can damage static-sensitive devices. Proper packaging and grounding
techniques are necessary precautions to prevent damage. To prevent electrostatic damage, observe
the following precautions:
• Transport products in static-safe containers such as conductive tubes, bags, or boxes.
• Cover the appliance with approved static-dissipating material.
• Use a wrist strap connected to the work surface and properly-grounded tools and equipment.
• Keep the work area free of non-conductive materials such as foam packing materials.
• Make sure you are always properly grounded when touching a static-sensitive component or
assembly.
• Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. iii
Page 6

Preface
Chapter 1 - Overview
Overview ...............................................................................................................................................................1-1
Backup ............................................................................................................................................................. 1-1
Providers ........................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Software Required .......................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Volume Types ..................................................................................................................................................1-2
Requestors ....................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Writers ............................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Chapter 2 - VSS Provider Installation
Operating Environment ................................................................................................................................. 2-1
VSS Provider Installation and Operation Procedures ................................................................................. 2-2
Chapter 3 - System Configuration
Hardware Configuration ...................................................................................................................................... 3-1
Software Configuration ....................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Hardware Required ........................................................................................................................................ 3-2
Servers/Software ............................................................................................................................................. 3-2
Snapshot or Data Replication ............................................................................................................................. 3-3
Snapshot Installation ....................................................................................................................................... 3-3
Data Replication Installation ......................................................................................................................... 3-3
Volume Types ..................................................................................................................................................3-3
Initial Setup of Volumes .................................................................................................................................. 3-4
Backup Server Connected to Data Replication Volume (RV) .................................................................. 3-5
Backup and Restore Procedures .................................................................................................................. 3-5
Contents
Chapter 4 - Error Management
Actions When Error Occurs .................................................................................................................................. 4-1
When Backup has Errors ................................................................................................................................. 4-1
When VSS must be Restarted ........................................................................................................................ 4-1
When Returning Volume to Initial State ....................................................................................................... 4-1
Backup Server Connected to Snapshot LV .................................................................................................4-1
Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV ................................................................................... 4-2
Collecting Information of Unclear Failure .................................................................................................... 4-3
Chapter 5 - Troubleshooting
About Snapshot or Data Replication ........................................................................................................... 5-1
Event Log Warning Message ......................................................................................................................... 5-1
Event Log Error Message ................................................................................................................................ 5-2
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. i
Page 7

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Appendix A - Error Failure Messages
Appendix B - Command Lists
Index
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. ii
Page 8
Chapter 1
Overview
Backup
Overview
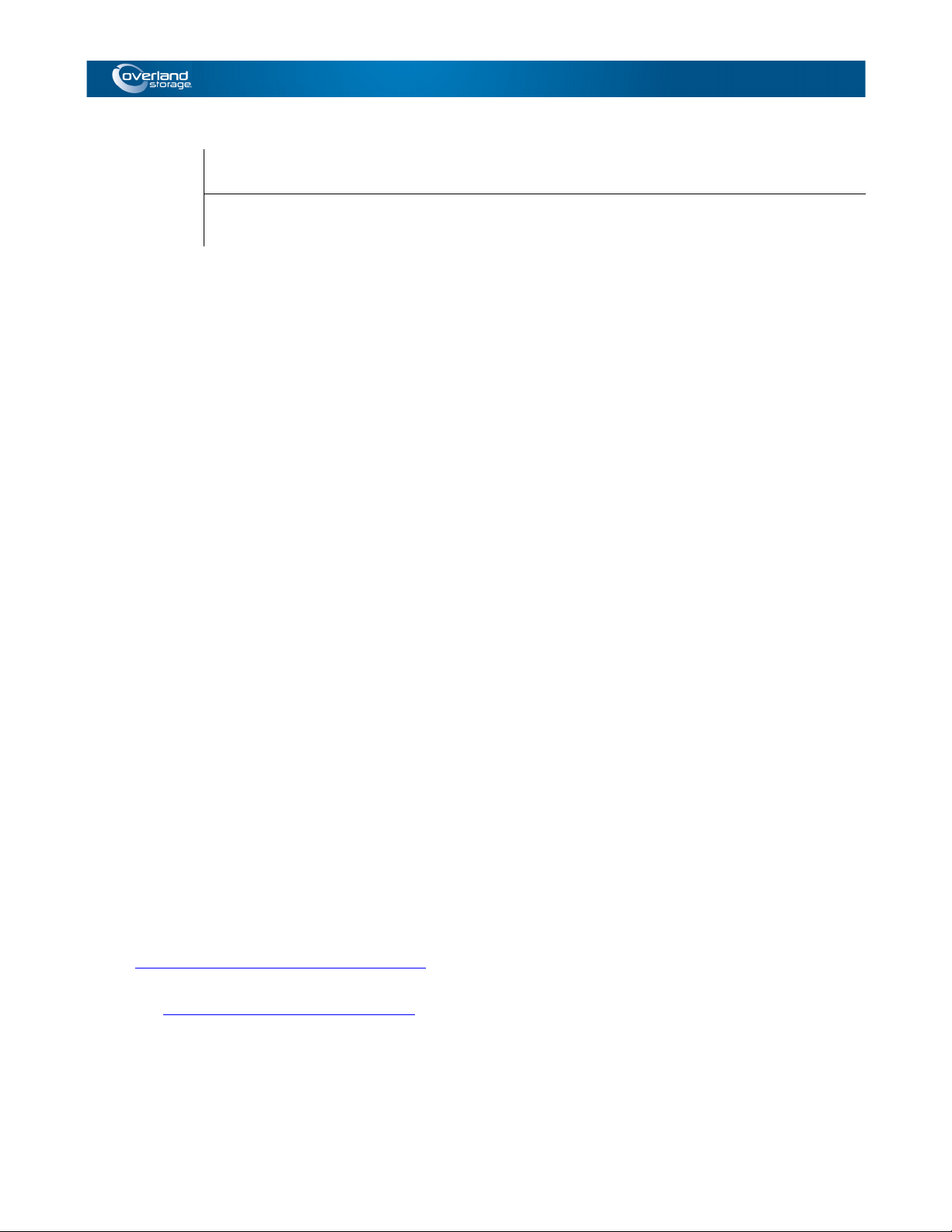
This chapter provides an overview of the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) and explains
system configuration and other fundamentals.VSS was implemented in Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 and Microsoft Windows Server 2008, as a new function for performing storage
management. The graphic shows a basic VSS Configuration made up of backup software
(requestor), business applications (writers), and software that performs disk array shadow
copy (replication) instructions (VSS provider).
Backup using VSS is performed by taking a request from the requestor as a trigger. When
VSS receives a backup request from the requestor, it performs coordinating operations with
the writers and provider, and it instructs the provider to create a replication. This series of
operations is performed entirely under the control of VSS. Accordingly, a user can easily
carry out non-interrupting backup without becoming involved with complicated scripts for
each application, just by executing the requestor.
Figure 1-1: VSS Basic Configuration
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 1-1
Page 9

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Providers
A hardware provider is software exclusively for the in-house manufactured disk arrays
(supplied by the storage vendor), makes it possible to create shadow copies using hardwarespecific replication functions. VSS Provider is a hardware provider.
A software provider is software that a software vendor supplies for creating shadow copies.
The system provider that is supplied by Microsoft Corporation is also a software provider.
Software Required
The following software is needed on each server or disk array:
Application Server
• Job management software (Example: JobCenter)
• Requestor (Example: Protection Manager)
• Exchange Server 2003
• VSS Provider
• Control Command
Backup Server
• Job management software (Example: JobCenter)
• Requestor (Example: Protection Manager)
• Backup software (Example: NetBackup)
• VSS Provider
• Control Command
Management
• SnapSAN Manager
Disk Array
• Snapshots, Volume Cloning, or Replication and Mirroring
• Access Control
Volume Types
VSS Provider handles volumes that are subject to snapshot or replication operations by a
disk array’s logical disk.
Requestors
Server
VSS Provider supports Protection Manager and other software as requestors. For
introductions about each requestor, refer to the product-specific manual.
Writers
VSS Provider supports the following as a writer:
• Microsoft Exchange Server 2003
• Microsoft Exchange Server 2007
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 1-2
Page 10

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
• File system (NTFS)
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 1-3
Page 11

Chapter 2
VSS Provider Installation
This chapter provides a description of the basic requirements for installing VSS
Operating Environment
Item Description
Operating Systems Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008.
Required Free Disk Capacity At least 24 MB of free disk capacity is needed to perform
required Memory Capacity At least 6 MB of memory on the application server and at
Cooperation This software cooperates and operates with
Provider.
the installation tasks for this software.
least 30 MB of memory on the backup server are needed
in order to use this software.
ControlCommand
Protection Manager
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 2-1
Page 12
SnapSAN VSS User Guide
VSS Provider Installation and Operation Procedures
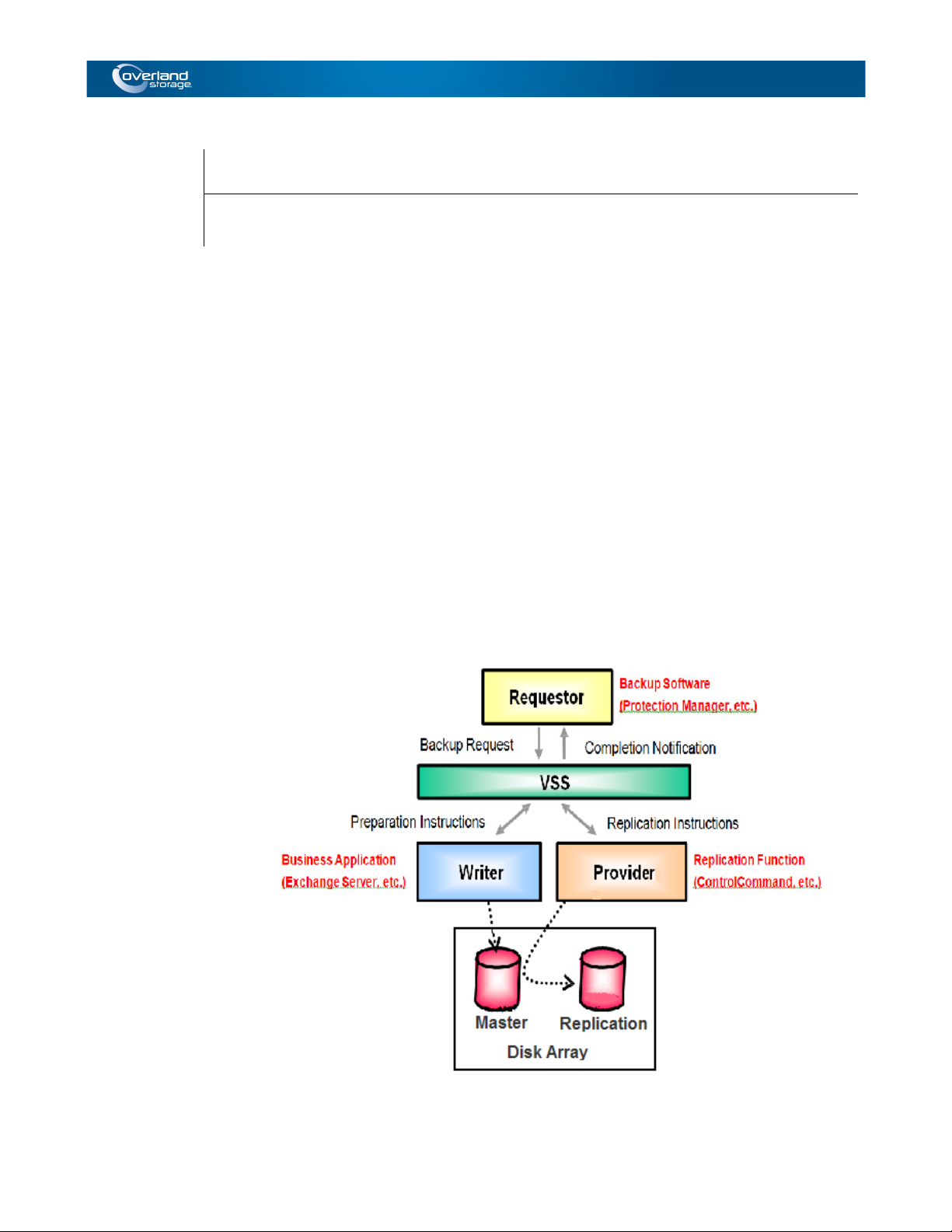
This example shows the system installation procedure by taking a tape backup system in
which the D series is used as an example. For the snapshot environment installation
procedure, refer to
Windows)”. For the data replication environment installation procedure, refer to the “Data
Replication User's Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)”. For hardware
configurations and software configurations, refer to the configurations in this manual. For
requestor installation procedures and operating procedures, refer to the manuals of the
selected requestor. Highlighted portions below are procedures to perform by
other manuals
the “Snapshot
User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
referring to
Figure 2-1: Hardware Configuration Flow
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 2-2
Page 13

Chapter 3
System Configuration
Hardware
Configuration
The configuration example shows: hardware components, performance requirements, and disk capacity.
Figure 3-1: Hardware Configuration Example
To utilize the snapshot or data replication function more efficiently, separate the application
servers, which process tasks from the backup servers. Accordingly, the tape backup
operation gives no additional load to application servers.
Though the application or backup server may also be used as a management server, using a
specific management server is recommended. Use of LAN connection is strongly
recommended for connection with the disk array.
Connect the path of individual servers, to be connected to the disk array, to the port of
different directors of the disk array, limiting the servers to be accessed by AccessControl.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 3-1
Page 14

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Software
Configuration
The example shows a software configuration. Select the software to use from the business
equipment and operations mode. The software configuration varies according to the
requestor selected.
Figure 3-2: Software Configuration Example
Hardware Required
To install and use VSS Provider, the following hardware is needed:
Disk Array – This is a disk array in which the snapshot function (Snapshots) or data
replication function (Volume Cloning or Replication and Mirroring) is loaded.
Application Server – This performs snapshot or data replication operations.
Backup Server – This is arranged to perform backup of data from a replication to tape or
other media.
Magnetic Tape Unit – This is used if tape backup is needed. Use a tape unit that is
supported by the backup software.
Management Server – This performs a disk array management. It can also serve as the
backup server or application server.
Servers/Software
Install the software into the following servers:
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 3-2
Page 15

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Application Serv
• JobCenter
• Protection Manager
• Protection Manager for Exchange
• Exchange Server 2003
• VSS Provider
• ControlCommand
Backup Server
• JobCenter
• Protection Manager
• NetBackup
• VSS Provider
• ControlCommand
Management Server
• SnapSAN Manager
Disk Array
• Snapshots, Volume Cloning, or Replication and Mirroring
• AccessControl
er
Snapshot or Data Replication
Snapsho
Data Replicat
t Installation
Refer to the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” for
system configuration determination and subsequent installation procedures and concerns
when performing operations. Perform through “Installation Procedure” there to prepare for
backup operations in which the snapshot function is used.
ion Installati
Refer to the “Data Replication User's Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)” for system configuration determination and subsequent installation procedures
and concerns when performing operations. Perform through “Installation Procedure” there
to prepare for backup operations in which the data replication function is used.
Requestor Installation
For concerns when installing a requestor, refer to the manuals of the selected requestor.
Volume Types
VSS Provider handles volumes that are subject to snapshot or replication operations by a
disk array’s logical disk. When there are multiple partitions or logical volumes on one logical
disk, depending on the operation, it may not be possible to guarantee data consistency if a
on
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 3-3
Page 16

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
replication operation is executed for a volume made up of multiple partitions or logical
volumes or for a dynamic disk volume. The table below shows the function range for each
disk.
Table 3-1: Available Volume Type
Disk Type Volume Type Availability
Basic disk Primary partition (MBR format)
Dynamic disk
√: Recommended configuration -: Operation inhibited
Initial Setup of Volumes
Backup Se
When performing backup operations in which the snapshot function is used, the initial
setup below is necessary. Execute identical operations for target volumes used in backup
operations. The
“Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows) ended, are
assumed to be “active” for the SV state and “unlink” for the LV link state.
rver Connected to Snapshot Logical Volume (
volume states
√
Primary partition (GPT format)
Logical volume on expanded partition
Simple volume
Spanned volume
Striped volume
Mirror volume
RAID5 volume
LV)
, which are the states in which “Installation Procedure” in the
√
-
-
-
-
-
-
1. Start a command prompt on the backup server.
2. Confirm that volumes used in backup operations have been registered in the volume
list created in (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” and re-create the
volume list.
> iSMvollist -a
3. In order to change the LV access restriction to Not Available (NA), stop the volume
beforehand.
Here, the setting is made for logical disk name lv001.
> iSMvss -devmode disable -vol lv001 -volflg ld
4. Change the LV access restriction to Not Available (NA). Here, settings are made for
logical disk names lv001 and sv001.
> iSMsc_link -lv lv001 -lvflg ld -sv sv001 -svflg ld -lvacc na
> iSMsc_unlink -lv lv001 -lvflg ld
The above is the end of environment setup for operation using the snapshot function.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 3-4
Page 17

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Backup Se
rver Connected to Data Replication Volume (RV)
When performing backup operations in which the data replication function is used, the
initial setup below is necessary. Execute identical operations for target volumes used in
backup operations.
1. Start a command prompt on the backup server.
2. Confirm that volumes used in backup operations have been registered in the volume
list created in “Data Replication Installation”.
a. If they are not registered, refer to the “Data Replication User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” and re-create the volume list.
> iSMvollist -a
b. If the RV is replicate state, execute Separate to separate the Master Volume (MV)
and RV and make the RV available. Here, execute using the settings below. If the
RV is separated, the command below need not be executed.
• Access restriction for RV after separated: rw (Read/Write) (Default value)
• Specify wait for separation to complete
> iSMrc_separate -mv mv001 -mvflg ld – rv rv001 – rvflg ld -wait
3. In order to change the RV access restriction to Not Available (NA), stop the volume
beforehand. Here, the setting is made for logical disk name rv001.
> iSMvss -devmode disable -vol rv001 -volflg ld
4. Change the RV data state to invalid and the RV access restriction to Not Available
(NA). Here, the setting is made for logical disk name rv001.
> iSMrc_rvmode -rv rv001 -rvflg ld -rvdata invalid -rvacc na -force
The above is the end of environment setup for operation using the data replication function.
Backup and Re
For backup and restore operations, refer to the manuals of the selected requestor.
store Procedur
es
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 3-5
Page 18

Chapter 4
Actions When Error Occurs
This chapter explains how to address errors that occur during backup when VSS Provider is
used.
When Backup has Errors
When an error has occurred during backup, investigate the cause of the error using the
procedure below and re-execute the backup after eliminating the cause of the error.
1. Verify if the error was output in the application’s event log.
2. If you were able to confirm the error number and error message, check Appendix A
“Error Messages at Time of Failure”.
3.
Refer to the explanation in (Measure) and eliminate the cause of the error.
If there are unformatted partitions, a warning may be output to the (application) event log
when executing VSS backup.
“Event Log Warning Message.
Error Management
This does not affect backup processing. For details, refer to
When VSS must be Restarted
When the VSS must be restarted, follow the instructions:
1. From the Windows (Start) button, select (Administrative Tools) > (Services).
2. Select (VSS Provider) and restart it.
3. Confirm that the service was started.
When Returning Volume to Initial State
Sometimes, an LV or RV for performing VSS backup enters a state in which backup is not
possible because of an error during backup. To initialize the state of the LV or RV to a state
in which re-execution is possible, different operations are needed for operation in which the
snapshot function is used and operation in which the data replication function is used.
Execute the operations for LV or RV for which backup failed.
If Protection Manager is selected as a requester, troubleshoot by referring to the “CLI
Command Reference Guide”.
Backup Se
rver Connected to Snapshot L
This section describes the procedure that returns a volume to its initial state when an error
occurred during operation using the snapshot function. Execute the procedure below for all
volumes subject to backup.
1. Start a command prompt on the backup server.
V
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 4-1
Page 19

SnapSAN YSS User Guide
2. Check the LV state. Here, the state of logical disk name lv001 is checked.
> iSMsc_linkinfo -vol lv001 -volflg ld
Sample output:
Specified Volume
LV:LD Name:
Type : WN
Volume Name: \\?\Volume{91eaf2a9-4e8a-11d9-861c-505054503030}\
Path : State:
Mode : rw
link
Information
lv001
3. If “State” for the LV is “link”, the connection to the SV must be unlinked. Here,
settings are made for logical disk name lv001. If “State” for the LV is “unlink” the
command below is not necessary.
> iSMsc_unlink -lv lv001 -lvflg ld
4. If “Mode” of the LV checked in (2) is other than “NA”, stop the volume beforehand in
order to change the LV access restriction to Not Available (NA). Here, the setting is
made for logical disk name lv001.
> iSMvss -devmode disable -vol lv001 -volflg ld
If the target volume is already stopped, the message below is output. Proceed to
execute the procedure in (5).
iSMvss: Err:iSM20519: Specified disk cannot be disabled.
5. Change the LV access restriction to Not Available (NA). Here, settings are made for
logical disk names lv001 and sv001.
> iSMsc_link -lv lv001 -lvflg ld -sv sv001 -svflg ld -lvacc na
Backup Se
> iSMsc_unlink -lv lv001 -lvflg ld
6. Cancel the “SV guard classification” of the SV. Here, the SV guard classification of
snapshot volume sv001 of logical disk name bv001 is canceled.
> iSMsc_svguard -bv bv001 -bvflg ld -sv sv001 -svflg ld -mode cancel
a. If the target volume is already canceled, the message below is output.
iSMsc_svguard:Info: iSM19127: Request has already completed.
The above is the end of the volume initialization procedure for operation using the snapshot
function.
rver Connected to Data Replication
RV
This section describes the procedure that returns a volume to its initial state when an error
occurred during operation using the data replication function. Execute the procedure below
for all volumes subject to backup.
Start a command prompt on the backup server.
1. Check the RV state. Here, the state of logical disk name rv001 is checked.
> iSMrc_query -rv rv001 -rvflg ld
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 4-2
Page 20

SnapSAN YSS User Guide
Sample output:
MV: Disk No.LD Namemv001
Type WN Volume Name- PathRV: Disk No.2
LD Namerv001
Type WN
Volume Name\\?\Volume{91eaf297-4e8a-11d9-861c-505054503030}\ PathActivity Stateseparate Sync State
Separate Start Time2004/12/24 14:24:53
Separate End Time2004/12/24 14:24:53
Separate Diff32KB Copy Diff
Previous Activesep/exec
2. If “Activity State” of the RV is “replicate”, it is necessary to separate the RV from the
MV. This is executed here using the settings below. If “Activity State” of the RV is
“separate”, the command below need not be executed.
• Access restriction for RV after separated: rw (Read/Write) (Default value)
• Specify wait for separation to complete
> iSMrc_separate -mv mv001 -mvflg ld –rv rv001 –rvflg ld -wait
separated Copy Control State-
0KB RV Accessrw
3. If “RV Access” of the RV checked in (2) is other than “NA”, stop the volume beforehand
in order to change the RV access restriction to Not Available (NA). Here, the setting is
made for logical disk name rv001.
> iSMvss -devmode disable -vol rv001 -volflg ld
If the target volume is already stopped, the message below is output. Proceed to execute
the procedure in (5).
iSMvss: Err:iSM20519: Specified disk cannot be disabled.
4. Change the RV data state to invalid and the RV access restriction to Not Available
(NA). Here, settings are made for logical disk name rv001.
> iSMrc_rvmode -rv rv001 -rvflg ld -rvdata invalid -rvacc na -force
The above is the end of the volume initialization procedure for operation using the data
replication function.
Collecting Information of Unclear Failure
Even when performing the procedures above, if an error occurs during backup, execute the
commands in the procedure below to gather an operation trace and other fault information.
Login as Administrator.
1. Click the Windows [Start] button, and select and execute [All Programs] →
[ControlCommand] →[SnapSAN Manager Volume List] → [Difficulty Information
Gather]. When changing the directory of the storage destination and executing,
specify a directory on the appropriate server and do not specify a directory on a
separate server connected by a network.
2. Confirm that the iSMvolgather directory is created under the installation directory
when the storage destination directory is not changed or under the specified directory
when it is changed, and obtain the files under that directory.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 4-3
Page 21

SnapSAN YSS User Guide
Moreover, since VSS Provider utilizes the snapshot or data replication function, if a failure
occurs, also refer to the measures for errors described in the “Snapshot User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” or the “Data Replication User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)”.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 4-4
Page 22

Chapter 5
About Snapshot or Data Replication
For problems that occur when operating the snapshot or data replication function, refer to
the notes described in the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)” or the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)”.
NOTE: The concerns in snapshot and data consistency described in the “Snapshot User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” and the concerns in data replication and
data consistency described in the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and
operation Guide for Windows)” are resolved by using VSS.
Event Log Warning Message
If there is even one unformatted partition on the server that executes VSS backup
(including volumes not subject to backup), the (sample) warning below may be output to the
(application) event log. This applies to SnapSAN Manager cluster partitions and others.
Troubleshooting
Type: Warning Source:VSS Event ID:12290
Explanation:Volume Shadow Copy Service warning: GetVolumeInformationW
(\\?\Volume{941f0b7b-120c-11d9-b701-505054503030}\,NULL,0,NULL,
NULL,(0x00000000], , 260) == 0x00000057. hr = 0x00000000.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 5-1
Page 23

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Event Log Error Message
For Windows Server 2008, if there is a volume on the backup server whose state is Not Ready, such as an RV being replicated or LV being unlinked, the (example) error below may be output to an event log of the backup server by performing a VSS backup.
Table 5-1: Output Example
Variable Output
Log name System
Typ e Er ror
Source: Virtual Disk Service
Event ID: 1
Explanation An unexpected error occurred
Error code 13@02000018
Log name: Application
Typ e Er ror
Source: VSS
Event ID 12289
Explanation Volume shadow copy service error: Unexpected error
IOCTL_DISK_GET_DRIVE_LAYOUT_EX
This error does not affect the operation.
Stopping Service
To stop the (VSS Provider) service of during regular operation, follow the procedure
below.
1. Stop the (Volume Shadow Copy) service.
2. Stop the (VSS Provider) service.
Path Manager Warning Message
The Path Manager version to be used must be V3.3 or later.If Path Manager has been
installed, the warning below may be output in the (application) event log.
Type:
Warning
Source:spsdsm
Event ID:530
Description:A path is lost.
To replace this warning message with an information message, follow the procedure below.
1. Start a command prompt on the backup server.
2. Execute the following: command:
> spscmd -seteventmode 1
The above is the end of the setting of Path Manager.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. 5-2
Page 24

Appendix A
Error Failure
The “Message List” provides explanations of the error messages that are output to the event
log in message ID order. An explanation of each message is given in the format below.
iSMxxxxx: AAAAA<aaa>,<bbb...b>
Message ID (iSMxxxxx) and message body (AAAAA<aaa>,<bbb...b>) are
described
Descriptions using angle brackets such as <aaa> and <bbb...b> indicate that parameter
values are not fixed. (The angle brackets “<” and “>” are not displayed in the actual
message.)
For details on parameter values, refer to Explanation
Term Description
Typ e Message classification (ERROR,
WARNING, or INFO) is described.
Explanation This field describes the causes of
the message output, etc.
Parameters in the message are
also described in this field.
Measure This field describes measures to
be taken.
Messages
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-1
Page 25

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13300
iSM13300: VSS HW provider started successfully.
iSM13301: VSS HW provider terminated by force.
Term Description
Type INFO
Explanation Shows that VSS Provider was forcibly terminated
Measure Check the operation status by referring to the event log or other information
iSM13302: VSS HW provider terminated successfully.
Term Description
Term Description
Typ e INFO
Explanation Shows that VSS Provider started
Measure
Unnecessary
Typ e INFO
Explanation Shows that VSS Provider was forcibly terminated normally
Measure Unnecessary
iSM13420: Shadow Copy session is aborted.
Ter m Description
Typ e
Explanation Shows that a shadow copy session with the VSS service aborted. This is output if a
Measure Check the operation status by referring to the event log or other information.
WARNING
session with the VSS service aborted after being established.
iSM13421: Failed to delete a parameter control file. (<aaa...a>)
Ter m Description
Typ e
Explanation Shows that deletion of a parameter control file failed. aaa...a: Parameter control file
Measure Check the operation status by referring to the event log or other information.
WARNING
name
iSM13850: VSS HW Provider is called by a non-administrative privileged process
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-2
Page 26

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13852: Specified volume does not exist in a vollist file.
Ter m Description
Typ e
Explanation
ERROR
Shows that VSS Provider was called by a process that does not have Administrator
SerialNumber=<aaa...a>,
privileges.
Measure
Re-execute following login to the Windows OS by a user who has Administrator
privileges.
ldn=<bbb... b>.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that the specified volume does not exist in the volume list. aaa...a: Unit serial
number
bbb...b: Logical disk number
Measure Re-create the volume list by referring to the “Snapshot User’s
Operation Guide for Windows)” or the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and
Operation Guide for Windows)”.
Manual (Installation
iSM13853: Specified volume <aaa...a> is not paired.
and
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation Shows that the logical disk indicated by aaa...a was not paired or was forcibly unpaired.
aaa...a: Logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a
mistake in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and
Operation Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data
Replication RV”.
iSM13854: No suitable RV was found for MV <aaa...a>.
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation Shows that the logical disk indicated by aaa...a was not paired or was forcibly unpaired.
aaa...a: Logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation
Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV”.
iSM13858: Memory allocation (malloc) error.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Allocation of a memory area failed.
Measure It is possible that the memory area is insufficient. To use this program, secure free
memory area by add-in or other means.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-3
Page 27

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13859: Failed to replicate. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
iSM13860: Parameter error. (Invalid Snapshot Set ID
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Replication failed.
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
<aaa...a>)
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation A parameter error occurred. The Snapshot Set ID is invalid. aaa...a: Snapshot Set ID
Measure After saving the information below, restart the VSS Provider service by referring to
aaa...a: MV logical disk name bbb...b: RV logical disk name
in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation
Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV”.
Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
• ControlCommand operation log (iSMrpl.log)
•Event log
iSM13861: Failed in waiting for the synchronized state. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation A wait for completion of replication failed. aaa...a: MV logical disk name
bbb...b: RV logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a
mistake in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and
Operation Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data
Replication RV”.
iSM13862: Failed to separate. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Separation failed.
aaa...a: MV logical disk name bbb...b: RV logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation
Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV”.
iSM13863: Failed in waiting for the separated state. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-4
Page 28

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation A wait for completion of separation failed. aaa...a: MV logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
bbb...b: RV logical disk name
in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation
Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV”.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-5
Page 29

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13864: Parameter error. (Invalid LUN information)
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation A parameter error occurred. The LUN information is invalid.
Measure After saving the information below, restart the VSS Provider service by referring to
iSM13865: Failed to change LUN <aaa...a> to data-valid state.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that a snapshot attribute change failed.aaa...a: Logical disk name of operation
Measure If you select Protection Manager as a requester, after checking the state and pairing of
Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
• ControlCommand operation log (iSMrpl.log)
•Event log
target (RV)
the logical disk, set the volume to its initial state by referring to the “Protection Manager
CLI User’s Guide”. If you select a different requester, set the volume to its initial state by
referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
iSM13866: Failed to change LUN <aaa...a> from
NotAvailable state.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that snapshot volume unmasking failed. aaa...a: Logical disk name of
operation target (RV or LV)
Measure If you select Protection Manager as a requester, after checking the state and pairing of
the logical disk, set the volume to its initial state by referring to the “Protection Manager
CLI User’s Guide”. If you select a different requester, set the volume to its initial state by
referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
iSM13872: Failed to change LUN <aaa...a> to data-invalid state.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that a snapshot attribute change failed.
Measure If you select Protection Manager as a requester, after checking the state and pairing of
the logical disk, set the volume to its initial state by referring to the “Protection Manager
CLI User’s Guide”. If you select a different requester, set the volume to its initial state by
referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-6
Page 30

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13874: No suitable SV was found for BV <aaa...a>.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that no SV suitable for VSS backup was found for the logical disk name indicated
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a
iSM13875: Failed to create. BV=<aaa...a>, SV=<bbb...b>.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that snapshot creation failed. aaa...a: BV logical disk name bbb...b: SV logical
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
by aaa...a.
aaa...a: Logical disk name
mistake in setup by referring to the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and
Operation Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.1 “For Backup Server Connected to Snapshot LV”.
disk name
in setup by referring to the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide
for Windows)” or 2.6.1 “For Backup Server Connected to Snapshot LV”.
iSM13876: Failed in waiting for the active state. BV=<aaa...a>, SV=<bbb...b>.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that a wait for snapshot completion failed. aaa...a: BV logical disk name
bbb...b: SV logical disk name
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
in setup by referring to the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide
for Windows)” or 2.6.1 “For Backup Server Connected to Snapshot LV”
iSM13877: Failed to import. LDNAME=<aaa…a>.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Shows that importing of a snapshot failed
aaa...a: Logical disk name of import target (RV or LV)
Measure If you select Protection Manager as a requester, after checking the state and pairing of
the logical disk, set the volume to its initial state by referring to the “Protection Manager
CLI User’s Guide”. If you select a different requester, set the volume to its initial state by
referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
It is also possible that the control volume was not set. Check the control volume setting.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-7
Page 31

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13880: Environment variable 'iSMrpl' not defined.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The environment variable iSMrpl is not defined. [Measure] Confirm that
Measure If ControlCommand is installed, restart the server.
iSM13881: Environment variable 'iSMvol' not defined.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The environment variable iSMvol is not defined. [Measure] Confirm that
Measure If ControlCommand is installed, restart the server.
iSM13882: LD attribute is neither MV nor BV. (ldattr=<a>)
ControlCommand has been installed.
ControlCommand has been installed.
iSM13883: The specified pair is in the restore state. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation [Explanation] The logical disk to be backed up is not the MV or BV. a:Internal number
showing type of logical disk
0: IV
4: RV
8: LV
16: SV
Measure [Measure] If you select Protection Manager as a requester, after checking the state and
pairing of the logical disk, set the volume to its initial state by referring to the “Protection
Manager CLI User’s Guide”. If you select a different requester, set the volume to its
initial state by referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The specified pair is in a restore state. aaa...a: MV logical disk name bbb...b: RV
logical disk name
Measure Check the activity state of the specified pair and change it to separated or replicate
synchronous.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-8
Page 32

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM13884: Failed to change copy control state. MV=<aaa...a>, RV=<bbb...b>.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation A copy control state change failed. aaa...a: MV logical disk name bbb...b: RV logical
Measure After checking messages output by ControlCommand, check whether there is a mistake
iSM13885: The parameter control file analysis error. (<aaa...a>=<bbb...b>)
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation [Explanation] Parameter control file analysis failed. aaa...a: Parameter control file key
Measure [Measure] After saving the information below, restart the VSS Provider service by
disk name
in setup by referring to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation
Guide for Windows)” or 2.6.2 “For Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV”.
name bbb...b: Value corresponding to key name
referring to Chapter 3 “Actions When Error Occurs”.
y ControlCommand operation log (iSMrpl.log)
y Event log
iSM20502: Illegal control option.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The iSMvss command syntax is invalid.
Measure Specify parameters correctly.
iSM20503: Environment variable ‘iSMrpl’ is not defined.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation ControlCommand is not correctly installed.
Measure Install ControlCommand correctly.
iSM20504: Insufficient option. (<aaa…a>)
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation A required iSMvss command option is not specified. aaa…a: Unspecified option
Measure Specify the option correctly.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-9
Page 33

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM20505: Environment variable ‘iSMvol’ is not defined.
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation ControlCommand is not correctly installed.
Measure Install ControlCommand correctly.
iSM20506: Illegal <aaa...a> type. <bbb...b>
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation [Explanation] The type that was specified for the pairvolflg or mode parameter is invalid.
Measure [Measure] Specify pairvolflg or mode correctly.
iSM20507: Illegal volflg type. <aaa...a>
Ter m Description
aaa…a: pairvolflg or mode
bbb…b: The specified
type
Type ERROR
Explanation The type that was specified for the volflg parameter is invalid. aaa…a: The specified type
Measure Specify volflg correctly.
iSM20508: Illegal requester type. <aaa...a>
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation The type that was specified for the requester parameter is invalid. aaa…a: The specified
type
Measure Specify requester correctly.
iSM20509: Illegal rvacc type. <aaa...a>
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The type that was specified for the rvacc parameter is invalid. aaa…a: The specified type
Measure Specify rvacc correctly.
iSM20510: Illegal rvuse type. <aaa...a>
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The type that was specified for the rvuse parameter is invalid. aaa…a: The specified
type
Measure Specify rvuse correctly.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-10
Page 34

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM20511: iSMrc_lsdev: API Error has occurred.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation An error occurred during internal processing.
Measure Make sure that the volume list was correctly created.
iSM20512: Specified volume does not exist in Logical disk list.
iSM20513: Failed to receive volume information.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The target volume was not registered to the volume list.
Measure Check the volume list.
Term Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation An error occurred during internal processing.
Measure Make sure that ControlCommand was correctly installed.
iSM20514: Specified disk type is not supported.
iSM20515: Specified targets are not paired.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The LD type is invalid.
Measure Change the LD type to WN or WG.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The target volumes were not paired.
Measure Set up the target volumes as a pair by using Volume Cloning, Replication and Mirroring,
or Snapshots.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-11
Page 35

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
iSM20516: Paramter control file write error.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Writing to a control file failed.
Measure Check the system operation state by referring to the event log or other information.
iSM20517: Illegal devmode type. <aaa...a>
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation The type that was specified for the devmode parameter is invalid. aaa…a: The specified
Measure Specify devmode correctly.
iSM20518: Specified disk cannot be enabled.
Ter m Description
Typ e ERROR
Explanation Enabling a device failed.
Measure Check the system operation state by referring to the event log or other information.
type
iSM20519: Specified disk cannot be disabled.
Ter m Description
Type ERROR
Explanation Disabling a device failed.
Measure Check the system operation state by referring to the event log or other information.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-12
Page 36

Appendix B
Command Lists
The table contains a list of commands.
Table B-1: Commands
No. Command Name Operation Explanation
1 iSMvss Change state of recognition by OS
for LV or RV.
2 iSMvss_clear Initialize the device entry
information.
Remarks (1) iSMvss and iSMvss_clear can be used by installing VSS Provider.
(2) iSMvss and iSMvss_clear can be executed only by users belonging to the Administrators group.
Command Reference
isMvss
[NAME]
iSMvss - Changes state of recognition by OS for LV or RV.
[SYNOPSIS]
iSMvss -devmode dev_mode -vol volume -volflg vol_flg
[DESCRIPTION]
The iSMvss command changes the state of recognition by the OS for a LV or RV.
Changes the state of recognition by the
OS for a LV or RV.
Allows all operating systems to
recognize devices.Unnecessary device
entry information is deleted from the
registry.
z
OPTIONS
The iSMvss command recognizes the following options:
-devmode dev_modeSpecifies the state of recognition by the OS.
Either of the following can be specified in dev_mode.
dPuts the volume in a stop state.
enableEnable recognition by OS.
Puts a volume for which disable had been specified in a start state.
-vol volumeSpecifies the LV or RV volume.
A logical disk name can be specified in volume.
-volflg vol_flgSpecifies the type of the volume specified in -vol.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. B-1
Page 37

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
This parameter must be specified together with -vol. The vol_flg that can be specified here is
limited to ld.
[USAGE]
(1) Change the state of OS recognition for a LV to stop state (disable).
A message is not output if the command succeeds.
C:\> iSMvss-devmode disable-vollv001-volflgld
C:\>
(2) If the state of OS recognition for a LV could not be changed to stop state (disable)
C:\> iSMvss-devmode disable-vollv001-volflgld iSMvss: Err:iSM20519: Specified disk
cannot be disabled. C:\>
[NOTES]
•
iSMvss cannot be executed if the access restriction of the LV or RV subject to the
operation is
“na”.
•
iSMvss cannot be executed if the state of OS recognition for the LV or RV subject to the
operation is the same as the specified state.
•
iSMvss cannot be executed if the disk array in which the LV or RV subject to the
operation is stored is in a frozen state.
[RETURN VALUE]
0: Change of state of OS recognition of LV or RV terminated normally.
1: Change of state of OS recognition of LV or RV terminated abnormally. iSMvss
terminates abnormally in the following cases.
- A parameter is invalid.
- A condition for operation is not satisfied.
- An attempt to operate a disk array fails.
iSMvss_clear
[NAME]
iSMvss - Initializes device entry information.
[SYNOPSIS]
iSMvss_clear iSMvss_clear delete
[DESCRIPTION]
The iSMvss_clear command changes all the volumes that were set to the disable state
(which prevents volumes from being recognized by the OS) by the iSMvss command to the
enable state (which allows volumes to be recognized by the OS).
This command also deletes unnecessary device entry information from the registry.
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. B-2
Page 38

SnapSAN VSS User Guide
z
OPTIONS
The iSMvss_clear command recognizes the following options:
NoneChanges all the volumes to the enable state (which allows volumes to be recognized by
the OS).
deleteDeletes unnecessary device entry information from the registry.
[USAGE]
(1) Change all the volumes that were set to the disable state (which prevents volumes from
being recognized by the OS) by the iSMvss command to the enable state (which allows
volumes to be recognized by the OS).
Use this command by registering it to the task scheduler so that it is executed at computer
startup.
C:\> iSMvss_clear
C:\>
(2) Delete unnecessary device entry information from the
regi
stry.
Execute this command after performing a backup using VSS.
C:\> iSMvss_clear delete
C:\>
•
If a computer is restarted when a device is in the disable state (which prevents the device
from being recognized by the OS), a backup using VSS after computer startup may fail.
Register the iSMvss_clear command (with no option) to the task scheduler so that it is
executed at computer startup.
•
Unnecessary device entry information accumulates when a backup using VSS is
repeated.
If the amount of such information increases, the OS may fail to recognize Plug and Play
devices. Execute the iSMvss_clear delete command after performing a backup using VSS.
[RETURN VALUE]
0: Normal termination
1: Abnormal termination
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. B-3
Page 39

Index
A
Application server 3-2
B
Backup has Errors 4-1
Backup server 3-2
Backup Server Connected to Data Replication RV 4-2
Backup Server Connected to Snapshot LV 3-4
Backup using VSS 1-2
Basic 3-4
Basic disk 3-4
, 3-3
, 4-1
C
Collecting Information of Unclear Failure 4-3
customer support 1-ii
D
Data Replication Installation 3-3
Disk array 3-2
Dynamic disk 3-4
, 3-3
M
Magnetic tape unit 3-2
Management server 3-2, 3-3
Message Output Format A-2
O
Operating Environment 2-1
Overland Technical Support 1-ii
P
Path Manager Warning Message 5-2
R
Returning Volume to Initial State 4-1
S
Snapshot Installation 3-3
Software Configuration 3-2
Stopping Service 5-2
E
Error 4-1
Event Log Error Message 5-2
Event Log Warning Message 5-1
T
technical support 1-ii
V
Volume Shadow Copy Service 1-1
H
Hardware Configuration Flow 2-2
VSS Provider Installation and Operation Procedures 2-
2
VSS Provider Service Restarted 4-1
I
Initial Setup of Volumes 3-4
10400401-001 08/2012 ©2012 Overland Storage, Inc. A-1
 Loading...
Loading...