Page 1

Orion 3000
Wireless LAN Cable Modem
User’s Guide
Rev. 1.2a
Firmware revision: 5.8.2004
April 14
th
, 2003
Page 2

Contents
1. BEFORE YOU BEGIN ...........................................................................................................5
Understand the Wireless Cable Modem’s Features .......................................................................................... 5
Contact Your Local Cable Operator................................................................................................................... 6
Prepare Your Area for Wireless Cable Modem Installation ............................................................................ 6
Gather Supplied and Required Items................................................................................................................. 6
2. INSTALLING THE MODEM USING WIRELESS.............................................................8
Installing the Hardware ....................................................................................................................................... 8
Troubleshooting the Wireless Installation.......................................................................................................... 8
3. INSTALLING THE WIRELESS CABLE MODEM USING THE USB PORT...............9
Installing the Hardware ..................................................................................................................................... 12
Installing the Software Drivers.......................................................................................................................... 12
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows 98 SE Operating System......................................................... 12
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows Me Operating System............................................................. 17
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows 2000 Operating System........................................................... 20
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows XP Operating System.............................................................. 23
Troubleshooting the USB Installation............................................................................................................... 25
Uninstalling the USB Driver .............................................................................................................................. 27
4. INSTALLING THE MODEM USING THE ETHERNET PORT...................................27
Installing the Hardware ..................................................................................................................................... 28
Troubleshooting the Ethernet Installation ....................................................................................................... 28
5. WIRELESS CABLE MODEM LEDS AND CONNECTORS .........................................29
LEDs on the Front of the Modem ..................................................................................................................... 29
Connectors on the Back of the Modem............................................................................................................. 30
6. PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS..........................................................................................31
2
User’s Guide
Page 3

7. TELNET COMMANDS.......................................................................................................33
Debug.................................................................................................................................................................... 35
Image .................................................................................................................................................................... 35
Ping ....................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Password .............................................................................................................................................................. 36
User-Level ............................................................................................................................................................ 37
Show...................................................................................................................................................................... 37
NVRAM................................................................................................................................................................ 44
TFTP..................................................................................................................................................................... 44
DHCP.................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Interfaces.............................................................................................................................................................. 46
NAT ....................................................................................................................................................................... 48
One to one mapping ..................................................................................................................................49
Port forwarding setting ............................................................................................................................ 49
NAT static ip ..............................................................................................................................................50
NAT static gateway ................................................................................................................................... 51
Management ........................................................................................................................................................ 51
8. WEB USER INTERFACE ..................................................................................................54
Accessing the Web User Interface ..................................................................................................................... 54
Web User Interface Home Page......................................................................................................................... 54
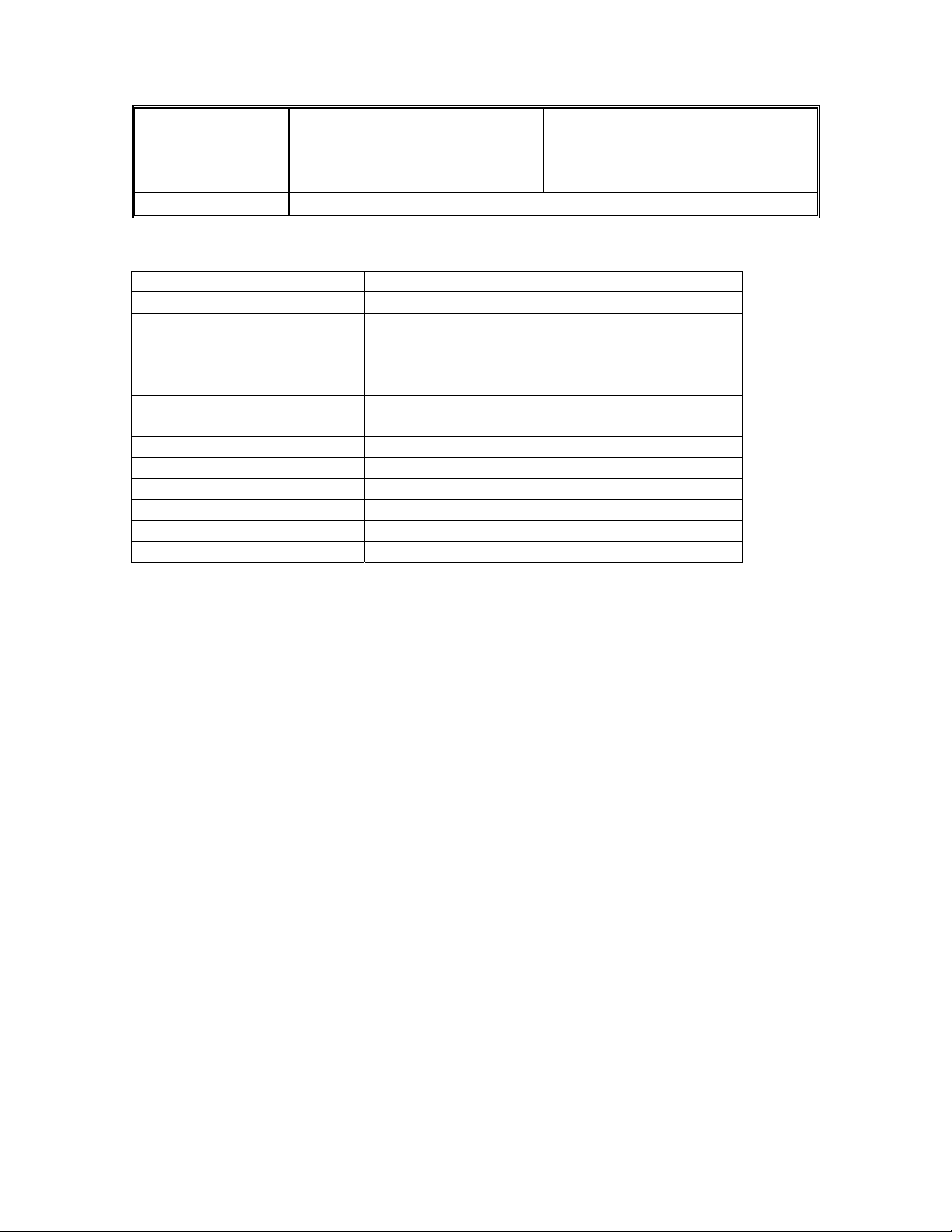
Cable Modem Information ................................................................................................................................ 54
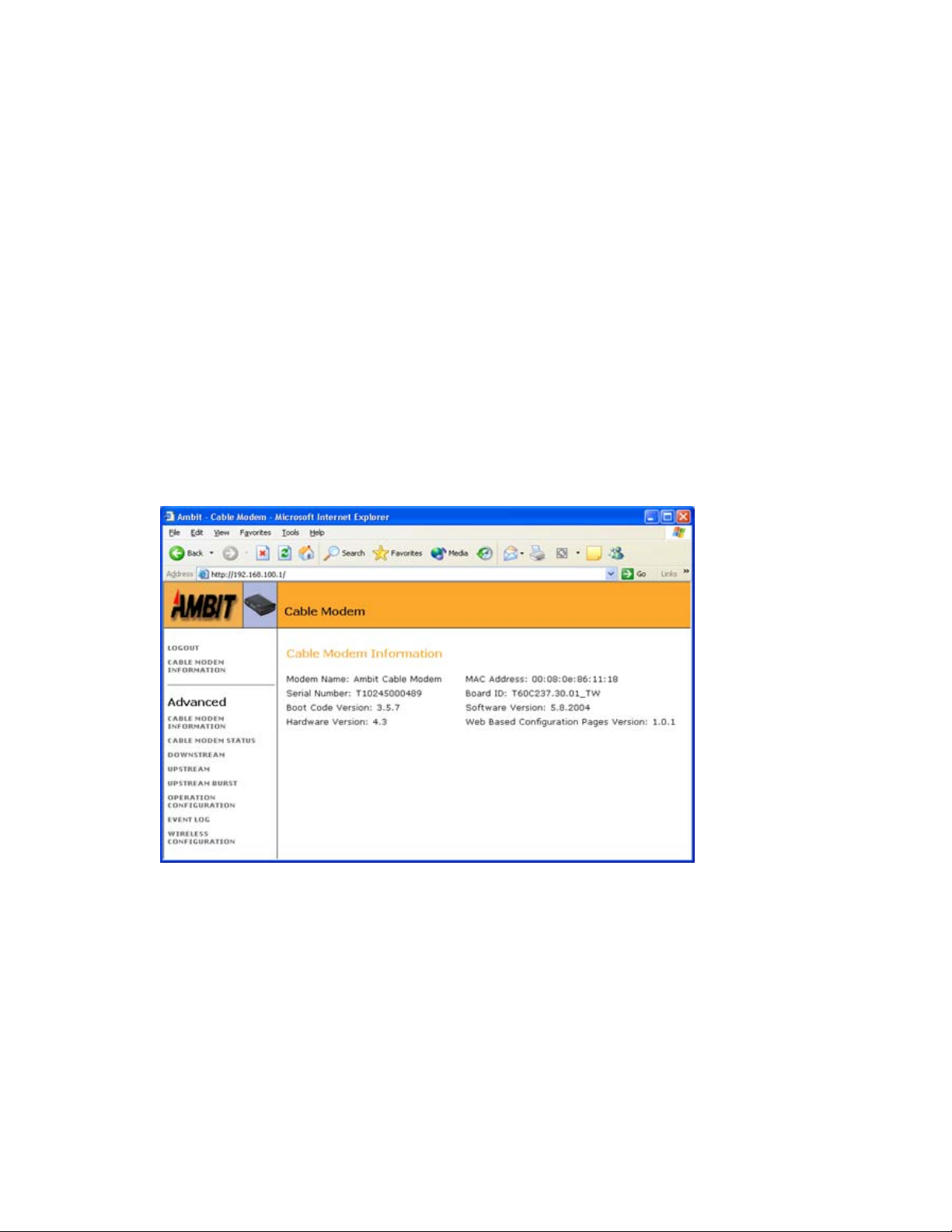
Cable Modem Status........................................................................................................................................... 55
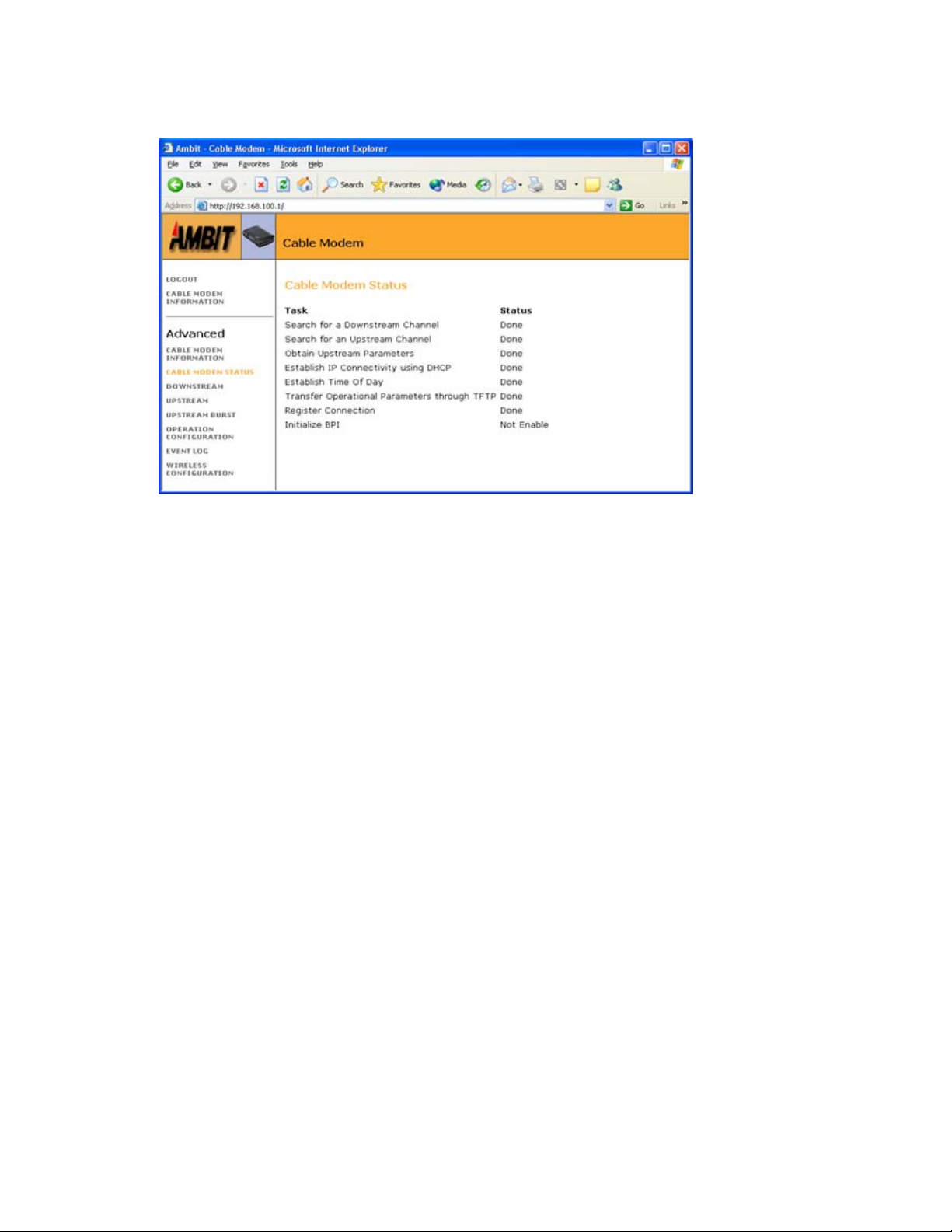
Downstream ......................................................................................................................................................... 56
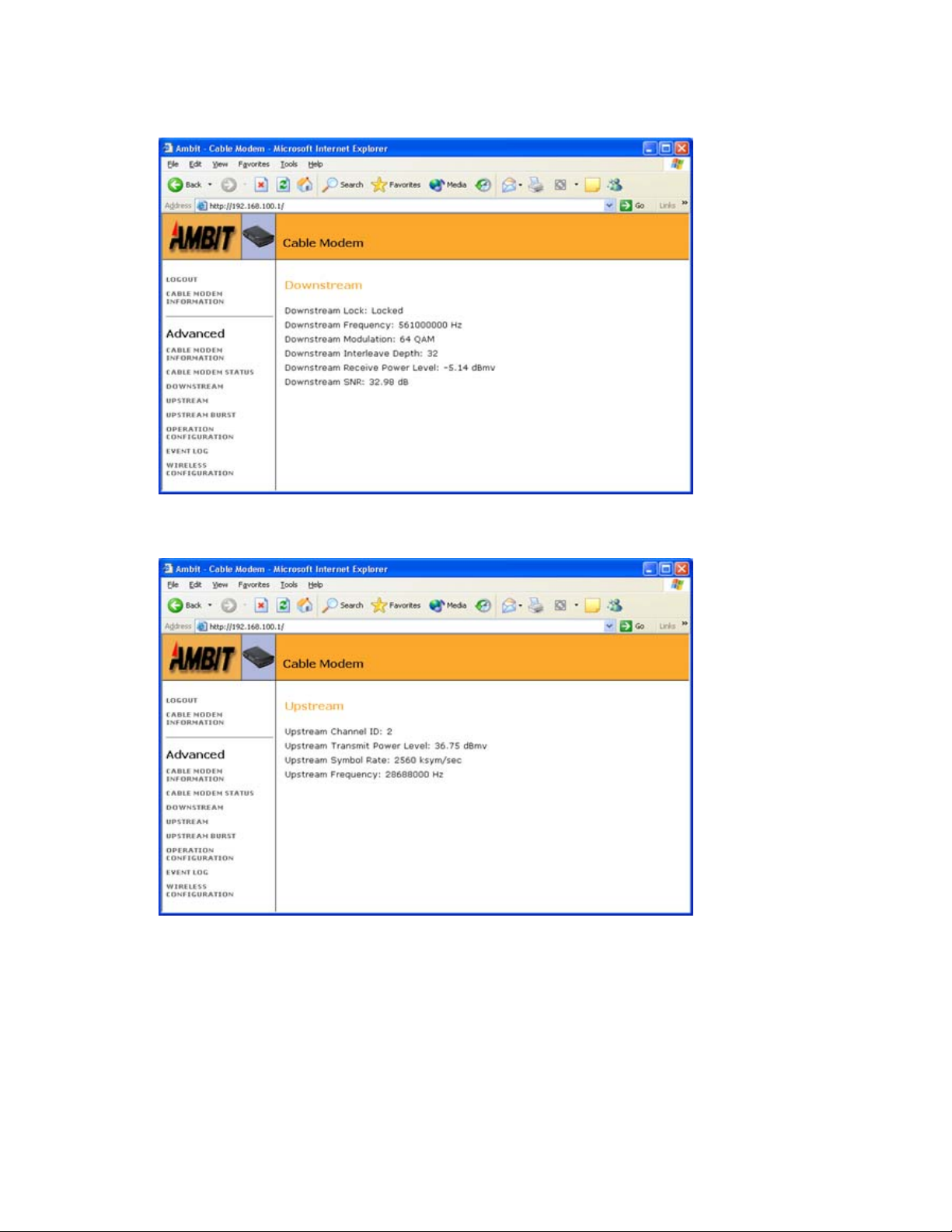
Upstream .............................................................................................................................................................. 56
Upstream Burst ................................................................................................................................................... 57
Operation Parameters ........................................................................................................................................ 57
Event Log ............................................................................................................................................................. 58
Wireless Configuration....................................................................................................................................... 59
SSID ............................................................................................................................................................ 59
Host.............................................................................................................................................................59
Channel ......................................................................................................................................................59
User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Security WEP ............................................................................................................................................ 59
WEP Key .................................................................................................................................................... 60
Access Permission ..................................................................................................................................... 60
Submit ........................................................................................................................................................60
4
User’s Guide
Page 5

1. Before You Begin
Your new wireless cable modem provides high-speed wireless access to the Internet by using
IEEE 802.11b wireless standard and an active Internet Connection through your cable
service provider. This user guide describes how to set up and use the wireless cable modem.
Before installing the wireless cable modem, you should read this user guide to ensure proper
wireless cable modem operation.
Understand the Wireless Cable Modem’s Features
Your wireless cable modem has the following features to help you access and use the Internet:
• Wireless connectivity means that you can use your PC just about anywhere in your
home.
• 802.11b compliance ensures interoperability with other 802.11b compliant devices
• Your wireless cable modem supports transmission rates of 11, 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps. If
the signal becomes weak, your wireless cable modem will automatically fall back to
the optimal transmission rate.
• Two-way design allows the wireless cable modem to send and receive data over the
cable television network.
• Cable bandwidth allows data rates of up to 38 megabits per second (Mbps)*, which is
faster than analog modems, integrated services digital network (ISDN), or asymmetric
digital subscriber line (ADSL).
• Using your cable line means that the wireless cable modem is always on, always
connected, and doesn’t tie up your phone line.
• Plug-and-play operation through universal serial bus (USB) ensures easy setup and
installation.
• Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) compliance ensures
interoperability with DOCSIS compliant cable operators.
*NOTE: Speeds may vary based on the following factors:
• Computer equipment including available RAM and processor speed
• Software applications utilizing your computer’s resources
• Network traffic depending on the time of day
• Limitations set by your Cable Service Provider
User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Contact Your Local Cable Operator
Before installing you new wireless cable modem, you must contact your local cable service
provider to activate your Internet account. Be sure to have the wireless cable modem’s MAC
address available, which can be found on the underside of the wireless cable modem.
Prepare Your Area for Wireless Cable Modem Installation
Before installing your wireless cable modem, you should first prepare your area. To do this:
1. Locate your cable outlet and ensure that it is located within proper distance of your
wireless cable modem and computer. Be sure not to bend the cable as this may strain
the connector and cause damage.
2. Place wireless cable modem as high as possible. Allow sufficient airflow around the
wireless cable modem to prevent overheating.
3. Place wireless cable modem and wireless clients in open areas or far away from
transformers, heavy-duty motors, microware ovens, refrigerators, fluorescent lights,
and other manufacturing equipment.
4. Ensure that the temperature in the room where the wireless cable modem will be
operating is between 0 and 40°C (32 and 104°F)
5. The wireless signal may be weaker after it has passed through metal, concrete, brick,
walls, or floors. Also, make sure that the wireless cable modem and wireless adapters
are positioned so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling for better
reception. For example, a wall that is 1 foot thick, at a 45-degree angle appears to be
almost 2 feet thick.
Gather Supplied and Required Items
You will use a variety of items to install your wireless cable modem. Some of the items are
supplied with your wireless cable modem.
Supplied
Verify that these items were included in the cable modem’s package:
• Wireless cable modem
• Power adapter
• USB cable (1.5m)
• Ethernet cable (1.8m)
• CD containing:
¾ USB drivers
6
User’s Guide
Page 7

¾ Wireless client drivers
¾ Wireless LAN Utility
¾ This user guide
Not Supplied
Verify that these items are available before beginning the installation:
• If using the wireless cable modem’s USB port:
o A PC running Windows 98 Second Edition (SE), Windows Me, Windows 2000,
or Windows XP. The cable modem’s USB setup does not support the Macintosh
operating system, Windows 98 First Edition, and NT.
o Windows 98 SE, Windows Me, Windows 2000, or Windows XP CD or diskettes.
o An active USB port on your PC.
• If using the wireless cable modem’s Ethernet port:
o A PC running Windows 95 (or later) operating system or a Macintosh computer
running system 7.6 (or later) operating system
o An active Ethernet port on your PC or Macintosh
• If using the wireless cable modem’s Wireless feature:
o A PC running Windows 95 (or later) operating system or a Macintosh computer
running system 7.6 (or later) operating system
o An active wireless client on your PC or Macintosh
Be sure to follow the instructions provided for the port that you want to use.
Using the Wireless feature of your wireless cable modem is the simplest and quickest way to
connect your PC or MAC to the Internet. All you need is an 802.11b wireless client that is
connected to your PC or MAC. Depending on your cable service provider, you may be able
to connect multiple wireless clients to your wireless cable modem.
Using the USB port allows you to install the wireless cable modem more quickly and easily
than using the Ethernet port, because you do not have to install and configure a network
interface card (NIC).
USB, however, only enables you to connect one computer to the wireless cable modem.
Using the Ethernet port allows you connect multiple computers to a wireless cable modem
through the use of additional equipment which is not included. Please contact your cable
service provider for more information on using multiple computers.
User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Chapter 2 provides instructions for installing your wireless cable modem using the Wireless
feature.
Chapter 3 provides instructions for installing your wireless cable modem using the USB port.
Chapter 4 provides instructions for installing your wireless cable modem using the Ethernet
port.
2. Installing the Modem Using Wireless
This chapter explains the process for installing your wireless cable modem using the wireless
feature. First you will install the hardware (wireless cable modem, wireless client (not
included), coax cable (not included), and power adapter).
Installing the Hardware
This section explains how to connect the wireless cable modem to the computer, wall cable
outlet, and electrical outlet. To install the hardware:
1. Power off the computer
2. Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the wireless cable modem’s cable connector.
Connect the other end of the coaxial cable to the cable wall outlet. Be sure not to bend
or over tighten the cables as this may strain the connector and cause damage. If you
plan to connect the wireless cable modem and television to the same wall outlet, you
must use a cable line splitter (not included).
3. Plug the wireless cable modem’s power adapter into the wireless cable modem’s
power jack and into an electrical outlet or surge protector.
4. Follow the installation and configuration instructions included with your wireless
client.
5. You are now ready to use your cable modem.
Troubleshooting the Wireless Installation
The WLAN LINK LED is not lit.
• Verify that your Wireless PC Card or Wireless USB client is properly connected to
your computer.
• Try positioning the computer closer to the wireless cable modem. The wireless signal
may be weaker after it has passed through metal, concrete, brick, walls, or floors.
Make sure that the wireless cable modem and wireless adapters are positioned so that
the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling for better reception. For
8
User’s Guide
Page 9

example, a wall that is 1 foot thick, at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 2 feet
thick.
• Make sure PC's wireless client is connecting to right WLCM. Check the SSID of the
WLCM and wireless client.
3. Installing the Wireless Cable Modem Using the USB Port
This chapter explains the process for installing your cable modem using the USB port. First,
you will install the hardware (cable modem, USB cable, coax cable, and power adapter). You
will then install the cable modem drivers and verify that the modem is functioning properly.
NOTE: The cable modem’s USB setup does not support the Macintosh
Windows 95 & NT.
Using the USB port allows you to install the cable modem more quickly and easily than using
the Ethernet port, because you do not have to install and configure a network interface card
(NIC).
USB, however, only enables you to connect one computer to the cable modem. Using the
Ethernet port allows to you connect multiple computers to a cable modem through the use of
additional equipment which is not included. Please contact your cable service provider for
more information on using multiple computers.
operating system,
Installing the Software Drivers Before Hardware Connection
CAUTION: You should run the “Setup.exe” program first before you connect USB
cable to PC.
To install the cable modem software drivers using the Windows operating system:
1. Double click the “Setup.exe” program in the CD.
2. Then the “Choose Setup Language” screen appears. You can choose the language you
need and click “OK”.
User’s Guide
9
Page 10
3. You will see the following Welcome screen.
4. Click “Next>”. You will see the following Start screen.
10
User’s Guide
Page 11
5. Click “Next>”. You will see the following ‘Complete’ screen.
6. Click “Finish”. You will see below screen, and then select ‘Yes.’ Now you can connect the
User’s Guide
11
Page 12

USB cable to the PC by following next section instructions.
Installing the Hardware
This section explains how to connect the cable modem to the computer, wall outlet, and
electrical outlet.
To install the hardware:
1. Power off the computer
2. Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the cable modem’s cable connector. Connect
the other end of the coaxial cable to the cable wall outlet. Be sure not to bend or over
tighten the cables as this may strain the connector and cause damage. If you plan to
connect the cable modem and television to the same wall outlet, you must use a cable
line splitter (not included).
3. Connect one end of the USB cable to the cable modem’s USB port and the other end of
the cable to the USB port on the PC.
4. Plug the cable modem’s power adapter into the cable modem’s power jack and into a
wall outlet or surge protector.
5. You are now ready to install the software drivers.
Installing the Software Drivers
This section explains how to install the software drivers that your PC requires for the cable
modem to operate.
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows 98 SE Operating System
CAUTION: You must install the drivers located on the CD that ships with your cable
modem. If you use the default Windows-supplied software drivers, you will not be able
to properly install the cable modem.
To install the cable modem software drivers using the Windows 98 operating system:
1. Power on your PC. After your computer boots, Windows detects the cable modem.
The Found New Hardware screen appears, followed by the Add New Hardware
Wizard screen.
12
User’s Guide
Page 13
2. Insert the CD into the PC’s CD-ROM and click Next. You will see the following
screen.
3. Select Search for the best driver for your device (Recommended). Then select Next.
You will see the following screen.
User’s Guide
13
Page 14
4. Check the CD-ROM drive check box and verify that the CD is in the CD-ROM drive.
Click Next to have Windows search for the necessary driver files. You will see the
following.
5. Select the updated driver (Recommended) Ambit USB Cable Modem and click next.
You will see the following screen.
CAUTION: You must verify that Ambit USB Cable Modem appears on the screen.
If USB Composite Device appears, you must click Back twice and specify the
14
User’s Guide
Page 15
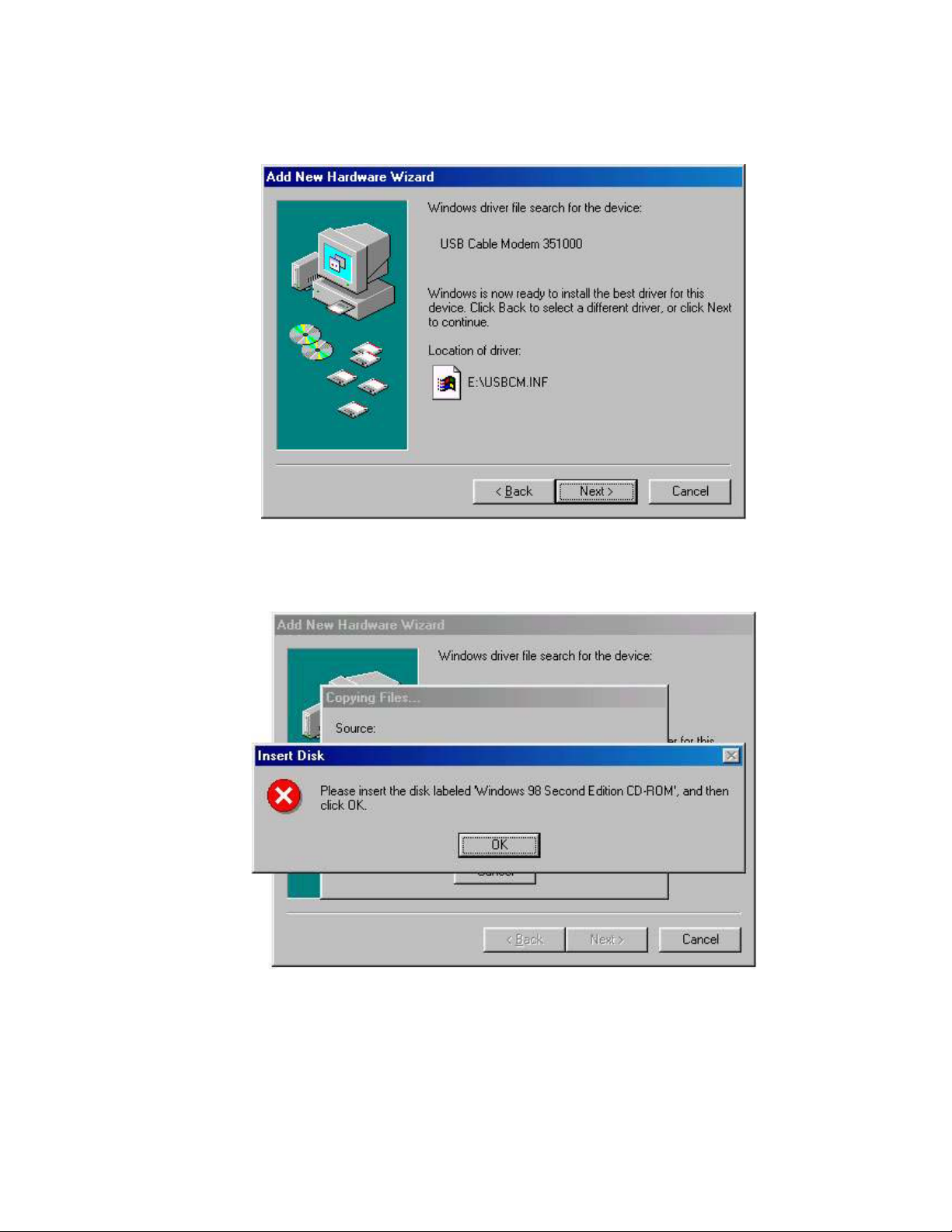
correct location of the driver files. DO NOT proceed if USB Composite Device is
displayed in the above window. Contact your cable provider for further assistance.
6. Click Next. The computer automatically installs the necessary driver files. You may
see the following screen.
7. If the above screen appears, you must insert the Windows 98 CD so that Windows
can copy the remaining files.
User’s Guide
15
Page 16
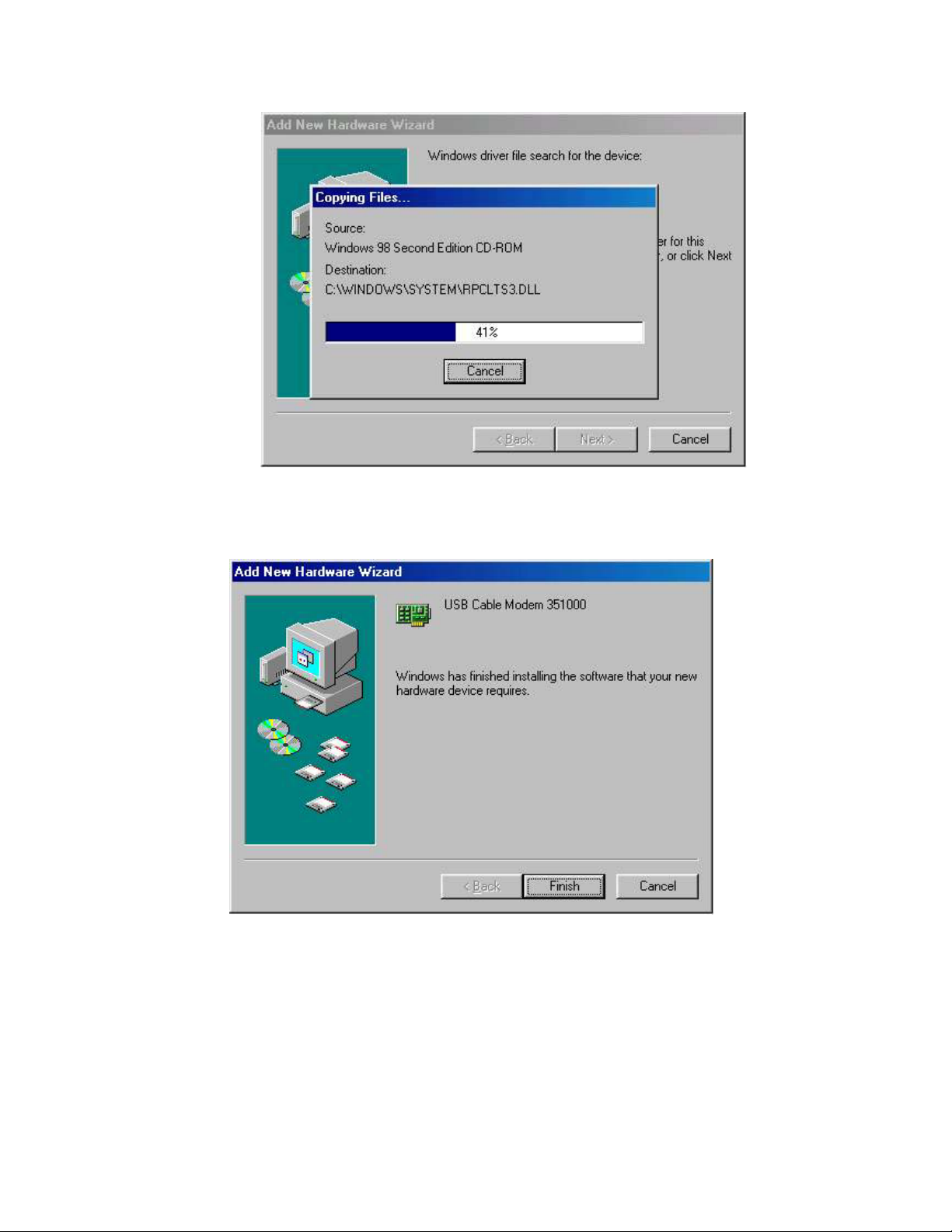
8. After files copying is done, you will see the following screen:
9. Click Finish to complete the installation. You will see the following screen.
16
User’s Guide
Page 17
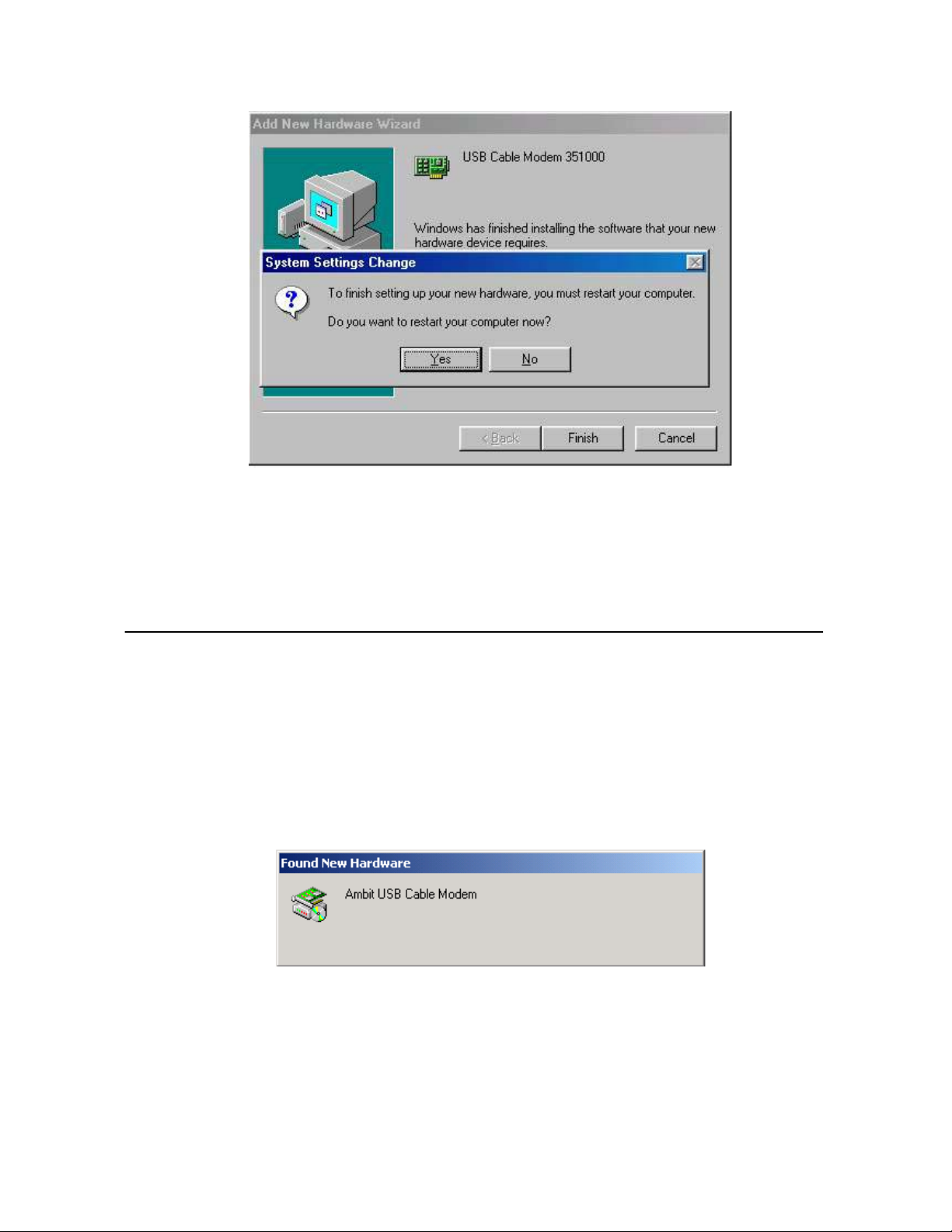
10. Choose Yes to restart your computer.
11. After the computer is rebooted, verify that the USB LED is lit on the front of you
cable modem. If not, refer to the troubleshooting section later in this chapter.
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows Me Operating System
To install the cable modem software drivers using the Windows Me operating system:
1. Power on your PC. After your computer boots, Windows detects the cable modem.
The Found New Hardware screen appears, followed by the Found New Hardware
Wizard screen.
2. Insert the CD into the PC’s CD-ROM and click Next. You will see the following
screen.
User’s Guide
17
Page 18
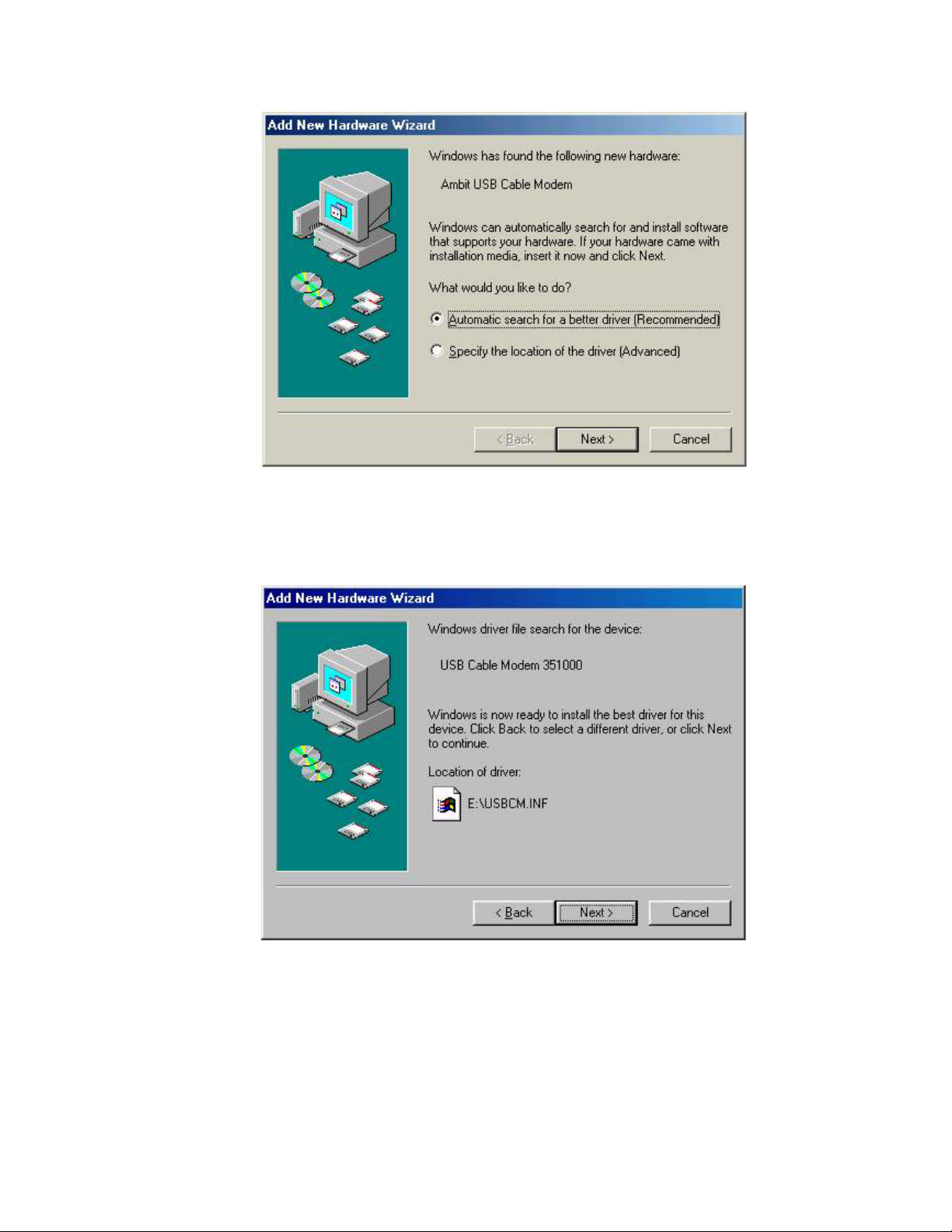
3. Select Automatic search for a better driver (Recommended) and click Next. The
computer automatically copies the necessary driver files from the CD. You will see
the following screen.
4. Click Next. The computer automatically installs the necessary driver files.
18
User’s Guide
Page 19
5. Click Finish after the computer has copied the necessary files. You will see the
following screen.
6. Click Yes to restart the computer
User’s Guide
19
Page 20
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows 2000 Operating System
To install the cable modem software drivers using the Windows 2000 operating system:
1. Power on your PC. After your computer boots, Windows detects the cable modem. The
Found New Hardware screen appears, followed by the Found New Hardware Wizard
screen.
2. Insert the CD into the PC’s CD-ROM Drive and click Next. You will see the following
screen.
3.
20
User’s Guide
Page 21

4. Select Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended. Then select Next. You
will see the following screen
User’s Guide
21
Page 22
5. Check the CD-ROM drive check box and verify that the CD is in the CD-ROM drive.
Click Next to have Windows locate the necessary driver files. You will see the following
screen.
6. Click Next to install the driver files for the cable modem. You will see the following
screen.
22
User’s Guide
Page 23

7. Click Finish to complete the installation.
8. After the installation is completed, verify that the USB LED is lit on the front of you
cable modem. If not, refer to the troubleshooting section later in this chapter.
Installing the Software Drivers in Windows XP Operating System
1. Power on your PC. After your computer boots, Windows detects the cable modem. The
Found New Hardware screen appears, followed by the Found New Hardware Wizard
screen.
User’s Guide
23
Page 24
2. Choose the software automatically (Recommended). Click Next to continue. You will
see the following screen.
24
User’s Guide
Page 25

3. Click Finish to complete the installation.
Troubleshooting the USB Installation
None of the LEDs are on when I power on the Wireless LAN Cable Modem.
Check the connection between the power adapter and the cable modem. Power off the
Wireless LAN Cable Modem and wait for 5 Seconds and power on the modem again. If the
problem still exists, you may have a hardware problem.
When attempting to install the USB driver in Windows 98 SE, I receive the following
error message: Device not installed at this time. Driver not found.
This usually occurs when the wrong driver has been installed. To remove the wrong driver
and install the correct driver:
1. Right-click on the My Computer icon on your desktop and choose Properties.
2. Click the Device Manager tab
3. Click the plus sign next to Universal Serial Bus controllers to view the list of
installed USB device drivers
User’s Guide
25
Page 26

4. Select USB Composite Device and click Remove
5. Click Refresh
The Add New Hardware Wizard window appears, displaying the device name USB
Composite Device. Refer to the proper operating system instructions in this chapter for
information on reinstalling the driver properly.
All of the LEDs on the front of my modem look correct, but I cannot access the
Internet.
• If the POWER, USB, SYNC, and READY are solidly lit, the cable modem is
working properly. Use the following procedures to verify connectivity between
the PC and the cable modem:
o Launch Your PC’s Internet Browser (e.g., Netscape, IE)
o Enter http://192.168.100.1
into your browser. This URL connects you directly
to the web server within your cable modem. A successful connection indicates
that the PC is able to communicate with the cable modem. The next step is to
enter a public URL to ensure connectivity between the cable modem and your
cable service provider. If this fails, please contact your cable service provider
for further assistance.
• Try restarting the computer so that it could re-establish a connection with the cable
26
User’s Guide
Page 27

modem.
• Power cycle the cable modem by removing the power adapter from the electrical
outlet and plugging it back in. Wait several minutes for the cable modem to
re-establish communications with your cable service provider.
• Remove any other USB devices from your computer and connect the cable modem’s
USB cable directly to the USB port on your computer.
• If you are using a cable splitter, try removing the splitter and connect the cable
modem directly to the cable wall outlet. Wait several minutes for the cable modem to
re-establish communications with your cable service provider.
• Your USB or coaxial cable may be damaged. Try using another cable.
• If none of these suggestions work, contact your cable service provider for further
assistance.
Uninstalling the USB Driver
1. Insert the supplied CD into your CD-ROM drive
2. Click on the My Computer icon on your desktop. Then click on the icon that belongs
to your CD-ROM Drive.
3. Locate the file called “Uninstall” and click on the file. This program will remove all
the necessary files from you computer.
4. Installing the Modem Using the Ethernet Port
This chapter explains the process for installing your wireless cable modem using the
Ethernet port. Using the Ethernet port allows to you connect multiple computers to a
wireless cable modem through the use of additional equipment which is not included. Please
contact your cable service provider for more information on using multiple computers.
See Chapter 2 “Installing the Wireless Cable Modem Using the USB Port” for instructions
on installing the wireless cable modem using the USB port.
You can use the wireless cable modem’s Ethernet port if you have:
• A PC running Windows 95 (or later) operating system or a Macintosh computer
running system 7.6 (or later) operating system
• An active Ethernet port on your PC
Before you begin, verify that your Network Interface Card (NIC) has been installed and
configured for use with your wireless cable modem. The wireless cable modem requires
TCP/IP to be installed. Contact your cable service provider for assistance with installing and
User’s Guide
27
Page 28

configuring TCP/IP. After installed the hardware, your computer can connect the wireless
cable modem directly by using Network Interface Card. Unlike USB installation, there is no
needed for software installation for the Ethernet connection.
Installing the Hardware
This section explains how to connect the wireless cable modem to the computer, wall cable
outlet, and electrical outlet.
To install the hardware:
1. Power off the computer
2. Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the wireless cable modem’s cable connector.
Connect the other end of the coaxial cable to the cable wall outlet. Be sure not to bend
or over tighten the cables as this may strain the connector and cause damage. If you
plan to connect the wireless cable modem and television to the same wall outlet, you
must use a cable line splitter (not included).
3. Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the wireless cable modem’s Ethernet port and
the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on the PC or network interface card
(NIC).
4. Plug the wireless cable modem’s power adapter into the wireless cable modem’s
power jack and into a wall outlet or surge protector.
5. If the POWER, ENET, SYNC, and READY LEDs are solidly lit, the wireless cable
modem is working properly.
Troubleshooting the Ethernet Installation
None of the LEDs are on when I power on the Wireless LAN Cable Modem.
Check the connection between the power adapter and the cable modem. Power off the
Wireless LAN Cable Modem and wait for 5 seconds and power on the modem again. If the
problem still exists, you may have a hardware problem.
The ENET LED on my wireless cable modem is not lit.
• Try restarting the computer so that is could re-establish a connection with the
wireless cable modem.
• Check for a resource conflict (Windows users only). To do this:
1) Right-click on the My Computer icon on your desktop and choose Properties.
2) Click the Device Manager tab and look for a yellow exclamation point or red
28
User’s Guide
Page 29

X over the NIC in the Network Adapters field. If you see either one, you may
have an IRQ conflict. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or you
cable service provider for further assistance.
• Verify that TCP/IP is the default protocol for your network interface card (NIC)
• Power cycle the wireless cable modem by removing the power adapter from the
electrical outlet and plugging it back in. Wait several minutes for the wireless cable
modem to re-establish communications with your cable service provider.
• Your Ethernet cable may be damaged. Try another cable.
All of the LEDs on the front of my modem look correct, but I cannot access the Internet.
• If the POWER, ENET, SYNC, and READY LEDs are solidly lit, the wireless cable
modem is working properly. Try restarting the computer so that is could re-establish
a connection with the wireless cable modem.
• Power cycle the wireless cable modem by removing the power adapter from the
electrical outlet and plugging it back in. Wait several minutes for the wireless cable
modem to re-establish communications with your cable service provider.
• If your PC is connected to a hub or gateway, try connecting the PC directly into the
wireless cable modem.
• If you are using a cable splitter, try removing the splitter and connect the wireless
cable modem directly to the cable wall outlet. Wait several minutes for the wireless
cable modem to re-establish communications with your cable service provider.
• Your Ethernet or coaxial cable may be damaged. Try using another cable.
• If none of these suggestions work, contact your cable service provider for further
assistance.
5. Wireless Cable Modem LEDs and Connectors
This chapter describes the functions of the wireless cable modem’s LEDs and connectors.
When the PWR, SYNC, and RDY LEDs are lit, the wireless cable modem is working
properly. The USB or ENET LED should also be lit depending on what port is being used.
The following provides an overview of the LED indicator lights on the front of the wireless
cable modem and what the LEDs mean.
LEDs on the Front of the Modem
User’s Guide
29
Page 30

• PWR: Indicates that the wireless cable modem has successfully completed
internal power-on tests.
• USB: Indicates connectivity between the USB port on the wireless cable modem
and the PC’s USB port.
• ENET: Indicates connectivity between the Ethernet port on the wireless cable
modem and the Ethernet port on the PC or Mac. This LED blinks when the
wireless cable modem is transferring or receiving data over the Ethernet cable.
• SEND: Indicates that data is being transmitted from the wireless cable modem to
the cable network.
• RECV: Indicates that data is being received from the cable network.
• SYNC: Indicates the connection status between the wireless cable modem and
the cable network. The LED is lit when the wireless cable modem has
established a downstream channel with the cable service provider’s Cable
Modem Termination System (CMTS).
• READY: Indicates that the wireless cable modem has completed the
ranging/registration process and is ready to send/receive data.
• WLAN LNK: Indicates that a wireless client(s) is linked to the wireless cable
modem.
• WLAN ACT: This LED blinks when the wireless cable modem is transferring or
receiving data with the wireless clients.
Installation problems with the wireless cable modem are commonly due to the cable network and
its topography. LEDs on the front panel of the wireless cable modem reveal operational status
and help you determine problem areas.
Connectors on the Back of the Modem
This list of connectors describes where to connect the cables and power adapter when installing
the wireless cable modem.
30
User’s Guide
Page 31

1. ENET Port: This is where you plug the included Ethernet cable. The other end
connects to the Ethernet Jack on the PC or NIC. This is not needed when using the
USB port or wireless feature.
2. USB Port: This is where you plug the included USB cable. The other end connects to
the USB port on your PC. This is not needed when using the Ethernet port or
wireless feature.
3. CABLE Connector: This is where you connect the coaxial cable (not included) that
leads to the cable splitter (not included) or the cable wall outlet.
4. PWR: This is where you plug the include power adapter. Remember to use only the
power adapter that came with the wireless cable modem.
6. Product Specifications
This chapter describes the cable modem’s operating and hardware specifications.
Item Downstream (Receiver) Upstream (Transmitter)
Frequency Range 88MHz ~ 860MHz 5MHz ~ 42MHz
Channel Bandwidth DOCSIS: 6MHz 200K, 400K, 800K, 1.6M, 3.2MHz
Modulation 64QAM/256QAM QPSK/16QAM
Symbol Rate 5.057/5.361 Msymbols/sec 160, 320, 640, 1280, 2560 Ksymbols/sec
Data Rate 30Mbits/sec (64QAM)
43Mbits/sec (256QAM)
Input Output Power -15dBmV ~ +15dBmV +8dBmV ~ +58dBmV (QPSK)
Carrier To Noise
Ratio @BER<10
RF Cable Interface 75Ω F-type female connector
PC Host Interface Ethernet, USB cable, 802.11b wireless
Power Dissipation < 6 Watts
MAC, LLC/SNAP,
IP and CPE Filter
ARP, ICMP, IP,
TCP/UDP, IGMPv2
DHCP, TFTP, ToD
client
SNMP v2c RFC1905 SNMP Protocol
-8
RFC826, RFC792, RFC791,
RFC768/793 RFC2236
RFC2131/2132, RFC1350,
RFC867
64QAM: 23.5dB, 256QAM: 30dB
0.32 ~ 5.12Mbs (QPSK)
0.64 ~ 10.24Mbs (16QAM)
+8dBmV ~ +55dBmV (16QAM)
DOCSIS-RFI
Internet Protocol Stack
Applications for Provisioning usage
User’s Guide
31
Page 32
MIBs Support RFC1213, RFC2011, RFC2012,
RFC2013,RFC2669, RFC2670,
RFC2233, RFC1907, RFC1493,
draft-ietf-ipcdn-mcns-bpi-mib-01
Syslog client Send event to syslog server
MIB-2, Interface and Cable,
Security MIB support
Description Specification
Dimensions (H x W x D) ) 2.0 x 13.0 x 19.5cm
Linear: AC 100 ~ 120 Volt (50 ~ 60 Hz)
AC Power (Input)
Power Consumption 8 to 10W
Temp eratu re
Humidity 5 to 90% non-condensing
Cable Interface Type F coaxial connector
LAN Interface Ethernet 10/100BaseT (RJ-45)
USB Interface USB Series B Connector
Wireless LAN Interface 802.11b
Regulatory Compliance FCC part 15, UL/CSA C22.2, CB, VCCI
or AC 220 ~ 240 Volt (50 ~ 60 Hz)
Switching: AC 100 ~ 240 Volt (Optional)
Operating: 32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
Non-operating: 14°F to 158°F (-10°C to 70°C)
32
User’s Guide
Page 33

7. Telnet commands
The Cable Router telnet Login and Password:
Login:
Password:
** Note: Default Wireless LAN Cable Modem Router Telnet IP address is 192.168.100.1
Getting Help
Entering a question mark (?) at the system prompt displays a list of commands for each command
mode. To list keywords or arguments, enter a question mark (?) in place of a keyword or argument.
Include a space before the ?. This form of help is called command syntax help, because it reminds
you which keywords or arguments are applicable based on the command, keywords, and arguments
you already have entered.
CM>?
debug Debugging functions
undebug Disable debugging functions
image Image commands
ping Ping specified IP address
pwd Change password
user-level Change User's access right
show Show commands
nvram NVRAM command
tftp Display/Set TFTP information
dhcp NAT DHCP commands
nat NAT commands
interface Interface commands
ip IP commands
web-access Web access control command
access-list Access list command
copy Copy command
write Write configuration to nvram
reset Reboot Cable Modem
quit Disconnect
User’s Guide
33
Page 34

To list keywords or arguments, enter a question mark (?) in place of a keyword or argument.
Include a space before the ?. This form of help is called command syntax help, because it reminds
you which keywords or arguments are applicable based on the command, keywords, and
arguments you already have entered. This example shows what the show ? command displays on
an Ambit Cable router:
CM>show ?
config-file Display all options in Configuration file
dhcp Display all options in DHCP response
version Display system version information
arp Display ARP table
ip Display IP configuration
interface Display interface information
running-config Display Cable Router configuration
cpe-info Display CPE information
downstream Display current downstream information
upstream Display current upstream information
nat Show NAT commands
user List login user(s)
access-list Display access list information
To complete a partial command, keyword, or argument use the <Ta b> key. This example shows
what how <Tab> key works:
CM>show inter<Tab>
CM>show interface
Redisplaying a command
To redisplay a command you previously entered, press the up-arrow key. You can continue to press
the up-arrow key for more commands.
34
User’s Guide
Page 35

Debug
¾ debug
Display corresponding message, the protocol debug just show packet information send to or
receive from RF interface.
CM>debug ?
console Display console message
ip IP information
dhcp DHCP protocol information
arp ARP information
l2 Layer 2 information
nat NAT translation information
CM>debug ip ?
tcp TCP information
udp UDP information
icmp ICMP information
rip RIP protocol information
Example:
CM>debug ip tcp
TCP: rcvd src:10.0.0.3(1150) dst:172.17.100.134(23) chksum:F368
TCP: Seq#:1711689473 Ack#:1591494822 dataOffset:20 Flags:10(h)
TCP: rcvd src:172.17.100.134(23) dst:10.0.0.3(1150) chksum:7587
TCP: Seq#:1591494822 Ack#:1711689473 dataOffset:20 Flags:18(h)
TCP: rcvd src:10.0.0.3(1150) dst:172.17.100.134(23) chksum:F368
TCP: Seq#:1711689473 Ack#:1591494977 dataOffset:20 Flags:10(h)
TCP: rcvd src:172.17.100.134(23) dst:10.0.0.3(1150) chksum:DC13
¾ undebug
Disable debug function
CM>undebug ?
console Disable console message
ip IP information
dhcp DHCP protocol information
arp ARP information
l2 Layer 2 information
nat NAT translation information
all Disable all debugging functions
Image
¾ image upgrade {1|2}
User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Download the specified firmware image name from TFTP server and store in as “image 1” or
“image 2”. If {1|2} is not specified, cable modem will upgrade the other image. (If cable modem
boot with image 2, it will upgrade image 1)
Example:
CM>image upgrade 1
Downloading ram.compress from 172.146.1.177
..................
Download file size=596407
Board ID is U10C005.00.01_JP01
Compatible list is U10C005.00.01_US01
Match compatible list
Update image 1...
Reboot Cable Modem...
¾ image use {1|2}
Activate and boot with the firmware stored in “image 1” or “image 2”.
Ping
¾ ping {IP address} [-t]
Ping specified IP address. When [–t] parameter is specified, continually ping until Ctrl-C or Ctrl-Z
is pressed. The Ctrl-C key ceases ping and display summery results of ping test. The Ctrl-Z key
pauses ping test and display summery results collect from the beginning of ping test.
Example:
CM>ping 92.146.1.254 -t
Pinging 92.146.1.254 with 64 bytes of data:
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=10ms TTL=255 seq=0
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=10ms TTL=255 seq=1
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=10ms TTL=255 seq=2
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=10ms TTL=255 seq=3
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=20ms TTL=255 seq=4
Reply from 92.146.1.254: bytes=64 time=10ms TTL=255 seq=5
Control-C Pressed...
Ping statistics:
Packets sent: 6; received: 6; Lost: 0 (0% loss)
Round trip time in milli-seconds:
Minimum time: 0ms; Maximum time: 20ms; Average time: 11ms
Password
¾ pwd {user name}
36
User’s Guide
Page 37

Change the password of accessing Telnet command.
Example:
CM>pwd admin
Old password:
New password:
Reconfirm:
Change password successfully.
User-Level
¾ user-level [user name] {1-90}
Change the password of accessing Telnet command.
Example:
CM>user-level admin 90
password:
Change user admin access level to 90.
Change user access level successfully.
Show
¾ show config-file
Display all options declared in DOCSIS that apply to modem got configuration file.
Example:
CM>show config-file
Network Access: ON
DOCSIS 1.0 Class of Service:
Class ID: 1
Maximum Upstream Channel Transmit Burst : 25000
CM MIC: F1 70 FC 50 47 29 B1 63 E1 93 C4 D1 81 16 2E EC
CMTS MIC: 74 EC 20 12 3F F1 27 89 B7 C6 EE A8 0D B2 6E 68
¾ show dhcp
Display all options provided in DHCP response.
Example:
CM>show dhcp
TFTP Server IP address: 92.146.1.250
Cable Modem IP address: 10.146.1.31
Configuration file: chard.cfg
Lease time: 18000 (secs)
UTC time offset: 28800 (secs)
System Log Server IP address: 92.146.1.254
Router IP address: 10.146.1.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
User’s Guide
37
Page 38

¾ show version
Display hardware and software reversion and board ID.
Example:
CM>show version
Hardware revision: 4.3
Board ID: T60C237.30.01_TW
Serial number: T10245000489
Bootcode revision: 3.5.7
Software revision: 5.8.2003
Web Page revision: 1.0.1
Software build time: Nov 26 2002 17:57:19
¾ show ip route
Display routing table
Example:
CM>show ip route
Route Table:
Index Destination Net Mask Gateway Metric Static
1 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.17.100.254 3 RIP
2 172.17.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.17.100.134 1 connected
3 92.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.17.100.254 1 RIP
4 30.0.0.8 255.255.255.248 30.0.0.9 1 connected
5 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 30.0.0.9 1 connected
¾ show interface
Display interface information
Example:
CM>show interface ?
ethernet Display ETHERNET interface information
cable Display CABLE interface information
usb Display USB interface information
wireless Display WIRELESS interface information
¾ show interface ethernet
Display ethernet interface configuration
Example:
CM>show interface ethernet
Interface Ethernet
MAC address: 00D0.5904.5E16
38
User’s Guide
Page 39

IP address 30.0.0.9 subnet-mask 255.255.255.248
Link status: link
Mode: 10Mbps, half-duplex
RIP status: Enable
RIP send version: 2
¾ show interface cable
Display cable interface information
Example:
CM>show interface cable
Interface Cable
MAC address: 0008.0E86.1118
IP address 10.71.135.99 subnet-mask 255.255.240.0
Downstream information
FEC Lock : Locked
Downstream Frequency : 561000000 Hz
Downstream Modulation : 64 QAM
Downstream Interleave Depth : 32
Downstream Receive Power Level : -1.18 dBmv
Downstream SNR : 33.28 dB
Upstream information
Upstream Channel ID : 2
Upstream Transmit Power Level : 36.00 dBmv
Upstream Symbol Rate : 2560 ksym/sec
Upstream Frequency : 28688000 Hz
Upstream Mini-Slot Size : 8
Upstream Burst Descriptor :
Initial Periodic
request(1) Ranging(3) Ranging(4) shortData(5) longData(6)
Modulation Type QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK
Differential off off off off off
Preamble Length 64 128 128 72 80
Preamble Value 952 896 896 944 936
FEC Error no FEC 5 5 5 8
FEC Codeword 16 34 34 75 220
Scrambler Seed 338 338 338 338 338
Maximum Burst Size 0 0 0 6 0
Guard Time Size 8 48 48 8 8
Last Codeword fixed fixed fixed fixed fixed
Scrambler on/off on on on on on
¾ show interface usb
Display ethernet interface configuration
Example:
CM>show interface usb
User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Interface USB
USB-Host MAC address: 0002.8A0E.ECCA
Speed: 12Mbps
Link status: disconnect
¾ show interface wireless
Display ethernet interface configuration
Example:
CM>show interface wireless
Interface Wireless
Speed: 11Mbps
SSID: WLCM
HOST: WLCM
Channel: 11
WEP mode: Disable
¾ show running-configuration
Display system running information
Example:
CM>show running-configuation
Interface USB
Hardware revision: 4.3
Board ID: T60C237.30.01_TW
Bootcode revision: 3.5.7
Software revision: 5.8.2004
System up time is 0 days 00:32:46
System time is 2002-11-26 03:41:55
Interface Cable
MAC address: 0008.0E86.1118
IP address 10.71.135.99 subnet-mask 255.255.240.0
Downstream information
FEC Lock : Locked
Downstream Frequency : 561000000 Hz
Downstream Modulation : 64 QAM
Downstream Interleave Depth : 32
Downstream Receive Power Level : -1.34 dBmv
Downstream SNR : 33.48 dB
Upstream information
Upstream Channel ID : 2
Upstream Transmit Power Level : 36.00 dBmv
40
User’s Guide
Page 41

Upstream Symbol Rate : 2560 ksym/sec
Upstream Frequency : 28688000 Hz
Upstream Mini-Slot Size : 8
Upstream Burst Descriptor :
Initial Periodic
request(1) Ranging(3) Ranging(4) shortData(5) longData(6)
Modulation Type QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK
Differential off off off off off
Preamble Length 64 128 128 72 80
Preamble Value 952 896 896 944 936
FEC Error no FEC 5 5 5 8
FEC Codeword 16 34 34 75 220
Scrambler Seed 338 338 338 338 338
Maximum Burst Size 0 0 0 6 0
Guard Time Size 8 48 48 8 8
Last Codeword fixed fixed fixed fixed fixed
Scrambler on/off on on on on on
Interface Ethernet
MAC address: 0002.8A0E.ECC8
IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
Link status: disconnect
Interface USB
USB-Host MAC address: 0002.8A0E.ECCA
Speed: 12Mbps
Link status: disconnect
Interface Wireless
Speed: 11Mbps
SSID: Ambit
HOST: WLCM
Channel: 11
WEP mode: Disable
Router Configuration
IP Route: Disable
NAT : Enable
NAT public IP configuration : Automatically
NAT public IP address : 68.5.203.15 Subnet Mask : 255.255.254.0
NAT public Gateway IP address : 68.5.202.1
DHCP server enable
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 20 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.21
DHCP server lease time : 1800
Provision assigned DNS 68.4.16.30
Provision assigned DNS 68.6.16.30
User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Web access control
CPE interface web access enable.
Cable interface web access enable.
Access List is empty
¾ show cpe-info
Display CPE information
Example:
CM>show cpe-info
MAC IP Port
0003.4793.064B 30.0.0.10 Ethernet
¾ show downstream
Display downstream information
Example:
CM>show downstream
FEC Lock : Locked
Downstream Frequency : 561000000 Hz
Downstream Modulation : 64 QAM
Downstream Interleave Depth : 32
Downstream Receive Power Level : -1.48 dBmv
Downstream SNR : 33.28 dB
¾ show upstream
Display current upstream information
Example:
CM>show upstream
Upstream Channel ID : 2
Upstream Transmit Power Level : 36.00 dBmv
Upstream Symbol Rate : 2560 ksym/sec
Upstream Frequency : 28688000 Hz
Upstream Mini-Slot Size : 8
Upstream Burst Descriptor :
Initial Periodic
request(1) Ranging(3) Ranging(4) shortData(5) longData(6)
Modulation Type QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK QPSK
Differential off off off off off
Preamble Length 64 128 128 72 80
Preamble Value 952 896 896 944 936
FEC Error no FEC 5 5 5 8
42
User’s Guide
Page 43

FEC Codeword 16 34 34 75 220
Scrambler Seed 338 338 338 338 338
Maximum Burst Size 0 0 0 6 0
Guard Time Size 8 48 48 8 8
Last Codeword fixed fixed fixed fixed fixed
Scrambler on/off on on on on on
¾ show nat config
Display all settable NAT/PAT information
Example:
CM>show nat config
NAT : Enable
WAN S E T UP :
NAT public IP configuration : Automatically
NAT public IP address : 68.5.203.15 Subnet Mask : 255.255.254.0
NAT public Gateway IP address : 68.5.202.1
LAN SETUP :
Ethernet interface IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 20 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.21
Provision assigned DNS 68.4.16.30
Provision assigned DNS 68.6.16.30
DHCP server lease time : 1800
¾ show nat timer
Display all settable NAT/PAT information
Example:
CM>show nat timer
Aging Timer (second)
ICMP protocol : 5 (secs)
UDP protocol : 1800 (secs)
TCP protocol : 3600 (secs)
GRE protocol : 3600 (secs)
Default Time OUT : 5 (secs)
¾ show user
Display all telnet user information
Example:
User’s Guide
43
Page 44

CM>show user
Index User Name From Alive(sec) Idle(sec)
1 admin 192.168.100.2 221 1
¾ show access-list
Display access list information
Example:
CM>show access-list
Access List
ID Control Address
41 Permit 00D0.5900.0000, hardware address mask FFFF.FF00.0000
42 Permit 0008.0E00.0000, hardware address mask FFFF.FF00.0000
1 Permit 192.168.100.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.16
21 Permit 64.168.39.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.8
NVRAM
¾ nvram factory-default
Restore cable modem to factory default.
TFTP
¾ tftp filename {file name}
Set the file name of the firmware image to download.
Example:
CM>tftp filename ram.cpr
Set TFTP filename to "ram.cpr"
¾ tftp server {Server IP address}
Establishes the IP address of the TFTP server for firmware download
Example:
CM>tftp server 92.146.1.250
Set TFTP Server to 92.146.1.250
DHCP
¾ dhcp {enable/disable}
44
User’s Guide
Page 45

Enable/disable dhcp server
¾ dhcp lease-time { 30-2147483647 seconds}
Set dhcp server ip lease time
¾ dhcp dns add {1~4} {ip address}
Set dhcp server dns ip address, it allows maximum 4 dns setting.
¾ dhcp dns delete {1~4/all}
Remove dhcp server dns ip address setting.
Note: if NAT is enabling, the following DHCP command can bet set
¾ dhcp ip-pool add {start IP} {end ip}
Set dhcp server ip pool range
Example:
CM> dhcp ip-pool add 192.168.100.2 192.168.100.4
CM>show dhcp
TFTP Server IP address : 172.19.89.19
Cable Modem IP address : 10.71.135.99
Configuration file : DEF001.cfg
Lease time : 86400 (secs)
UTC time offset : -28800 (secs)
SystemLog Server IP address : 172.19.89.19
Router IP address : 10.71.128.1
SubnetMask : 255.255.240.0
DHCP server enable
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 3 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.2 192.168.100.4
Provision assigned DNS 68.4.16.30
Provision assigned DNS 68.6.16.30
DHCP server lease time : 1800
¾ dhcp ip-pool delete {1-20/all}
Delete dhcp server ip pool range
¾ dhcp reserve-mac add {ip address} {mac address}
Reserve the specific ip address for specific mac address
User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Example:
CM>dhcp reserve-mac add 192.168.100.4 0002.8A25.251D
CM>show dhcp
TFTP Server IP address : 172.19.89.19
Cable Modem IP address : 10.71.135.99
Configuration file : DEF001.cfg
Lease time : 86400 (secs)
UTC time offset : -28800 (secs)
SystemLog Server IP address : 172.19.89.19
Router IP address : 10.71.128.1
SubnetMask : 255.255.240.0
DHCP server enable
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 3 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.2 192.168.100.4
NAT DHCP Server MAC reserved Table :
NAT DHCP Server support 16 reserved MAC address:
Index Begin IP MAC address
1 192.168.100.4 0002.8A25.251D
Provision assigned DNS 68.4.16.30
Provision assigned DNS 68.6.16.30
DHCP server lease time : 1800
¾ dhcp reserve-mac delete {1-16|all}
Delete one reserved mac address or all
Interfaces
¾ interface ethernet address {ip address} mask {subnet netmask}
Set ethernet interface IP address
Example:
CM>interface ethernet address 192.168.100.1 mask 255.255.255.224
CM>show interface ethernet
Interface Ethernet
MAC address: 0002.8A0E.ECC8
IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
Link status: disconnect
¾ interface ethernet dhcp-relay {ip address|enable|disable}
Ethernet interface dhcp-relay
46
User’s Guide
Page 47

¾ interface ethernet mac-address {mac address}
Assign mac-address for ethernet interface
CM>interface ethernet mac-address 0008.0E86.1118
CM>show interface ethernet
Interface Ethernet
MAC address: 0008.0E86.1118
IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
Link status: disconnect
¾ interface ethernet shutdown
Ethernet interface shutdown
¾ interface ethernet startup
Ethernet interface startup
¾ interface cable upstream channel {id}
Change upstream channel ID
¾ interface cable downstream preset {frequency}
Add frequency to downstream frequency preset table
¾ interface cable shutdown
Cable interface shutdown
¾ interface cable startup
Cable interface startup
¾ interface wireless shutdown
Wireless interface shutdown
¾ interface wireless startup
Wireless interface startup
¾ interface wireless ssid {ssid name}
Set Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point SSID name
User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Example:
CM>interface wireless ssid Ambit
Set SSID to Ambit
¾ interface wireless host {host name}
Set Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point host name
Example:
CM>interface wireless host Conference-Room
Set host to Conference-Room
¾ interface wireless channel {1~11}
Set Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point channel
Example:
CM>interface wireless channel 11
Set Channel to 11
¾ interface wireless wep {64bits|128bits} key (xxxxxxxxxx|xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)
Set Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point wep key
Example:
CM>interface wireless wep 64bits key 1122334455
Set Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point 64bits wep key to 1122334455
¾ interface wireless wep disable
Disable Wireless LAN Cable Router Access Point wep key
NAT
Network Address Translation/Port Address Translation (NAT/PAT) gateway is designed for IP
address simplification and conservation, as it enables private IP network that uses no registered IP
addresses to connect to the Internet. NAT/PAT operates on a wireless LAN cable modem,
connecting to Internet, and translates the private (not globally unique) addresses in the internal
network into legal addresses before packets are forwarded onto the Internet. As part of this
functionality, NAT can be configured to advertise only one address for the entire network to the
outside world. This provides additional security, effectively hiding the entire internal network
from the world behind that address. NAT has the dual functionality of security and address
conservation, and is typically implemented in remote access environments.
48
User’s Guide
Page 49

¾ ip nat {enable/disable}
Enable/disable NAT/PAT gateway function
¾ nat timer {tcp/udp/gre/icmp} {1~86400 sec}
Set aging time for different protocol session
One to one mapping
¾ nat static ipmapping add { private ipaddress} { global ipaddress}
Set NAT one to one mapping table
Example:
CM>nat static ipmapping add 68.5.203.16 192.168.100.22
Set global IP 68.5.203.16 to private IP 192.168.100.22
CM>show nat config
NAT : Enable
WAN SETUP :
NAT public IP configuration : Automatically
NAT public IP address : 68.5.203.15 Subnet Mask : 255.255.254.0
NAT public Gateway IP address : 68.5.202.1
LAN SETUP :
Ethernet interface IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 20 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.21
Provision assigned DNS 68.4.16.30
Provision assigned DNS 68.6.16.30
DHCP server lease time : 1800
IP Mapping Table:
Index Global IP Local IP
1 68.5.203.16 192.168.100.22
¾ nat static ipmapping delete {index/all}
Remove NAT one to one mapping entry
index: The index number in one to one mapping table (see “show nat config” command )
Port forwarding setting
¾ nat static portmapping add {index }{ private ipaddress} {port}{protocol}
User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Set NAT/PAT Port forwarding table
CM>nat static portmapping add 21 192.168.100.23 ftp
CM>show nat config
NAT : Enable
WAN SETUP :
NAT public IP configuration : Manually
Static NAT public IP address : 68.5.203.15 Subnet Mask : 255.255.254.0
Static NAT public Gateway IP address : 68.5.202.1
LAN SETUP :
Ethernet interface IP address 192.168.100.1 subnet-mask 255.255.255.224
NAT DHCP Server Pool Table :
NAT DHCP server support 20 IP pools
NAT DHCP server support 512 IP, Created 20 IP
Pool Index Begin IP End IP
1 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.21
DNS server(1) 68.6.16.30
DHCP server lease time : 1800
IP Mapping Table:
Index Global IP Local IP
1 68.5.203.16 192.168.100.22
Port Mapping Table:
Index Port Local IP Protocol
1 21 192.168.100.23 ftp
¾ nat static portmapping delete {index/all}
Remove the entry from the portmapping table
Example:
CM>nat static portmapping delete 1
Delete static portmapping index 1
NAT static ip
¾ nat static ip {enable|disable|ipaddress}
Enable/disable NAT/PAT gateway function or assign global ip
Example:
CM>nat static ip disable
Static IP will be disabled after "reset" command.
50
User’s Guide
Page 51

Example:
CM>nat static ip enable
Static IP will be enabled after "reset" command.
¾ nat static ip {ipaddress} mask (mask)
Set static IP and network mask for NAT/PAT
Example:
CM>nat static ip 68.5.203.15 mask 255.255.254.0
Set NAT public IP to 68.5.203.15, subnet mask to: 255.255.254.0
NAT static gateway
¾ nat static gateway {ipaddress}
Set static router address
Example:
CM>nat static gateway 68.5.202.1
Set NAT public Gateway IP to 68.5.202.1
CM>show nat config
NAT : Enable
WAN SETUP :
NAT public IP configuration : Manually
Static NAT public IP address : 68.5.203.15 Subnet Mask : 255.255.254.0
Static NAT public Gateway IP address : 68.5.202.1
Management
¾ web-access cpe {enable|disable}
Enable|disable the CM web access via CPE interface
¾ web-access cable {enable|disable}
Enable|disable the CM web access via Cable interface
¾ access-list {1~20|21~40|41~60|61~75} {deny|permit} {any|source IP|mac address}
[wildcard bit]
The standard access list performs packet filtering based on source IP address from the CPE host(s).
The management access list performs packet filtering based on destination IP address matching the
User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Wireless LAN Cable Router IP address. The standard MAC access list performs frame filtering
based on source MAC address from the CPE host(s). Basically, the access list works as a source
address packet filter, if the access list is empty, the cable router will forward any packet, if access
list is not empty, packet filtering will be enforced according to the access list(s). The wireless MAC
access list performs filtering based on source MAC address from the wireless card, configure this
list will make only the wireless card’s MAC address match this list will be associate to wireless AP.
1~20, access list ID, for standard IP access list
21~40, access list ID, for management access list
41~60, access list ID, for standard MAC access list
61~75, access list ID, for Wireless MAC access list
Example:
1) Set the access list to permit source IP 192.168.100.xxx to access network.
CM>access-list 1 permit 192.168.100.1 0.0.0.255
Note: 0.0.0.255 means 192.168.100.1~192.168.100.255
2) Set the access list to permit source IP 192.168.100.10 to access cable router (telnet, web-page,
snmp)
CM>access-list 21 permit 192.168.100.10 0.0.0.0
Note: No network packet will be filtered
3) Set the access list to permit source MAC 00D0.5921.3354 to access network
CM>access-list 41 permit 00d0.5921.3354 ffff.ffff.ffff
Note: The cable router only forward packet with this source MAC, all other packet will be
discarded.
4) Set the access list to permit source MAC 00D0.5911.22.33 to associated the wireless Cable
Router
CM>access-list 61 permit 00d0.5911.2233
¾ access-list delete {list ID|all}
Delete a specific access-list or delete all access-list
¾ pppoe-forwarding {enable|disable} (Optional)
To enable|disable PPPoE packet pass-through the NAT gateway
¾ copy tftp:config {tftp server ip address} {configuration filename}
52
User’s Guide
Page 53

Download the Wireless Cable Router configuration from remote tftp server. The configuration file
must be text file.
¾ write
Write configuration to NVRAM
¾ reset
Reboot cable modem
¾ quit
Disconnect telnet.
User’s Guide
53
Page 54
8. Web User Interface
Accessing the Web User Interface
1. The PC connected to the wireless cable modem must support TCP/IP connection and
dynamic DHCP IP address acquisition, and must have a web browser installed.
2. Open the web browser and set the URL location as: http://192.168.100.1
Web User Interface Home Page
A main menu is shown at the top of the pages and the user can select different options to view
wireless cable modem information. The main menu contains 8 categories of wireless cable
modem information. They include:
Cable Modem Information
54
User’s Guide
Page 55
Cable Modem Status
User’s Guide
55
Page 56
Downstream
Upstream
56
User’s Guide
Page 57

Upstream Burst
Operation Parameters
User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Event Log
58
User’s Guide
Page 59
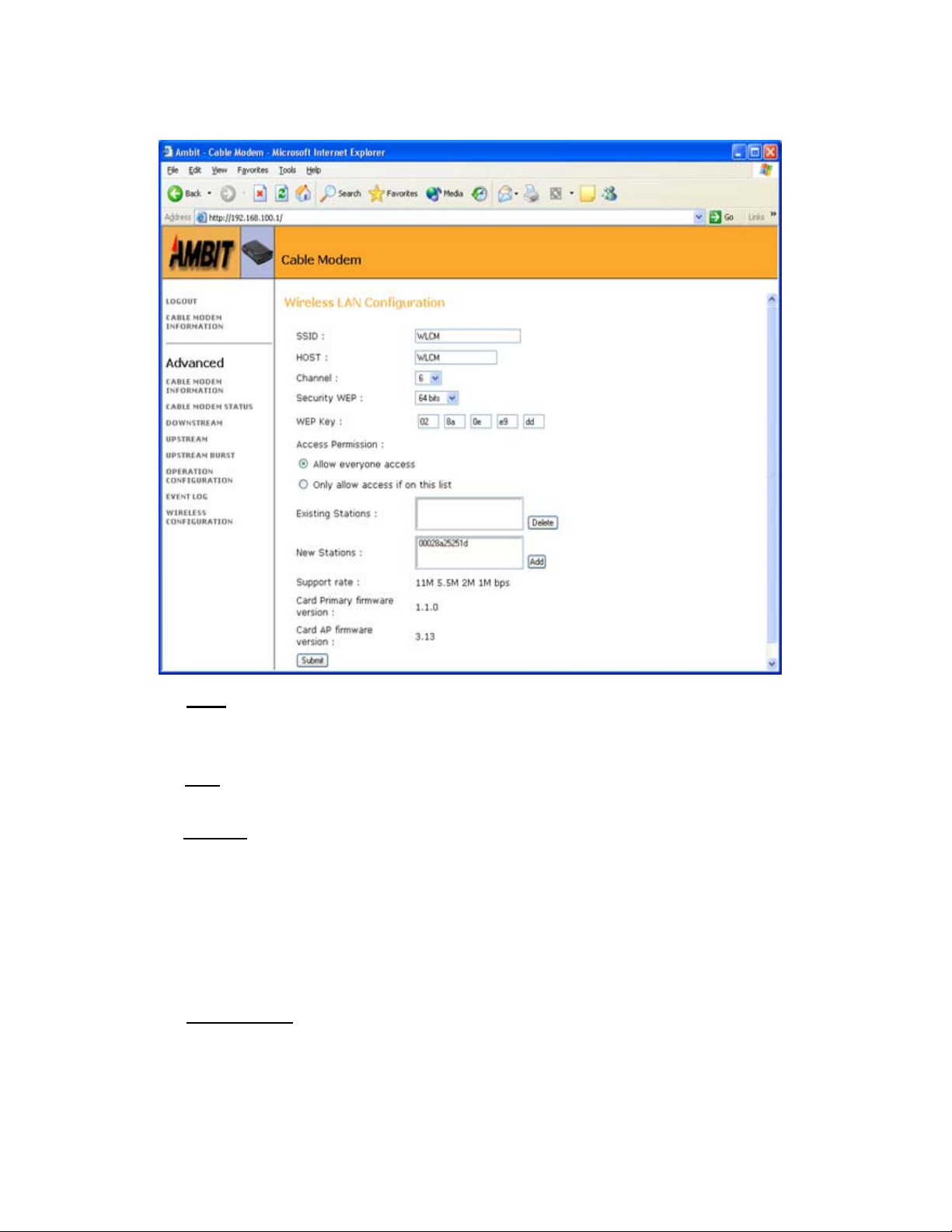
Wireless Configuration
SSID
• You can input SSID to group your wireless network. The wireless clients that have the
same SSID can communicate with others.
Host
• In Host item, you can define the wireless cable modem name.
Channel
• There are 11 channels available for US. You also can specific wireless
communication channel in Channel section. If there are multiple wireless cable
modems or access points in the same area, wireless channels should be well organized
to avoid interference. We recommended the adjacent wireless cable modems or
access points should be 5 channels apart. For example, WLCM1 is channel 1, then the
next cell, WLCM2 should use channel 6.
Security WEP
• Security WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) offers wireless data security. The default
WEP setting is “off”. You can enable this function by choosing two types of WEP
keys, 64 or 128 bits.
User’s Guide
59
Page 60

WEP Key
• 64 bits WEP requires a 10 Hexadecimal digits key, and 128 bits WEP key needs a 26
Hexadecimal digits key.
Access Permission
• Access permission is set for “Allow everyone access” by default.
• If Access Permission is set for “only allow access if on this list”, only CPE with
matching MAC address from the list is allowed to access.
Submit
• Any configuration changes must be “submit” before changes will occur.
60
User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...