ORiNG RGS-7244GP, RGS-7244GP-E, Thunder Rack RGS-7168GCP, Thunder Rack RGS-7168GCP-E, Thunder User Manual
...Page 1

RRGGSS--77224444GGPP // RRGGSS--77224444GGPP--EE
IInndduussttrriiaall MMaannaaggeedd GGiiggaabbiitt EEtthheerrnneett SSwwiittcchh
UUsseerr’’ss M
Maannuuaall
VVeerrssiioonn 11..33
DDeecceemmbbeerr,, 22001100
wwwwww..oorriinngg--nneettwwoorrkkiinngg..ccoomm
Page 2

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 1
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Copyright © 2010 ORing Industrial Networking Corp.
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the prior written consent of
ORing Industrial Networking Corp.
TRADEMARKS
is a registered trademark of ORing Industrial Networking Corp.
All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE STATEMENT
Product(s) associated with this publication complies/comply with all applicable regulations.
Please refer to the Technical Specifications section for more details.
WARRANTY
ORing warrants that all ORing products are free from defects in material and workmanship for
a specified warranty period from the invoice date (5 years for most products). ORing will repair
or replace products found by ORing to be defective within this warranty period, with shipment
expenses apportioned by ORing and the distributor. This warranty does not cover product
modifications or repairs done by persons other than ORing-approved personnel, and this
warranty does not apply to ORing products that are misused, abused, improperly inst alled, or
damaged by accidents.
Please refer to the Technical Specifications section for the actual warranty period(s) of the
product(s) associated with this publication.
DISCLAIMER
Information in this publication is intended to be accurate. ORing shall not be responsible for its
use or infringements on third-parties as a result of its use. There may occasionally be
unintentional errors on this publication. ORing reserves the right to revise the contents of this
publication without notice.
CONTACT INFORMATION
ORing Industrial Networking Corp.
4F., No. 3, Lane 235, Baoqiao Rd., Xindian District, New Taipei City 23145, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Tel: + 886 2 2918 3036 // Fax: + 886 2 2918 3084
Website: www.oring-networking.com
T echnical Support
E-mail: support@oring-networking.com
Sales Contact
E-mail: sales@oring-networking.com
(Headquarters)
sales@oring-networking.com.cn
(China)
Page 3

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 2
Table of Content
Getting to Know Your Switch........................................................................5
1.1 About the RGS-7244GP(-E) Industrial Switch................................................................5
1.2 Software Features..............................................................................................................6
1.3 Hardware Features.............................................................................................................6
Hardware Overview........................................................................................7
2.1 Front Panel..........................................................................................................................7
2.2 Rear Panel...........................................................................................................................9
2.3 Rack mount kit assembly...................................................................................................9
2.4 Front Panel LEDs .............................................................................................................10
Cables...........................................................................................................11
3.1 Ethernet Cables................................................................................................................11
3.1.1 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T Pin Assignments................................................................... 11
3.2 SFP.....................................................................................................................................13
3.3 Console Cable...................................................................................................................13
WEB Management........................................................................................14
4.1 Configuration by Web Browser.......................................................................................14
4.1.1 About W eb-based Management......................................................................................14
4.1.2 Basic Setting...................................................................................................................16
4.1.2.1 System Information......................................................................................... 16
4.1.2.2 Admin & Password ......................................................................................... 17
4.1.2.3 IP Setting........................................................................................................ 17
4.1.2.4 HTTPS............................................................................................................ 19
4.1.2.5 SSH ................................................................................................................ 19
4.1.2.6 LLDP............................................................................................................... 20
4.1.2.7 Backup/Restore Configuration ....................................................................... 23
4.1.2.8 Firmware Update............................................................................................ 23
4.1.3 DHCP Server..................................................................................................................24
4.1.3.1 Setting....................................................................................................... 24
4.1.3.2 DHCP Dynamic Client List........................................................................ 24
4.1.3.3 DHCP Client List ....................................................................................... 24
4.1.4 Port Setting.....................................................................................................................25
Page 4

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 3
4.1.4.1 Port Control............................................................................................... 25
4.1.4.2 Rate Limit.................................................................................................. 26
4.1.4.3 Port Trunk.................................................................................................. 27
4.1.4.4 Loop Guard ............................................................................................... 32
Loop Guard is a looping detection/avoid strategy, it helps network administrator to
avoid looping issue.....................................................................................................32
4.1.5 Redundancy....................................................................................................................32
4.1.5.1 O-Ring....................................................................................................... 32
4.1.5.2 MSTP ........................................................................................................ 33
4.1.6 VLAN.............................................................................................................................43
4.1.6.1 VLAN Membership Configuration.............................................................. 43
4.1.6.2 Private VLAN............................................................................................. 51
4.1.7 SNMP.............................................................................................................................53
4.1.7.1 SNMP-System........................................................................................... 53
4.1.7.2 SNMP-Communities.................................................................................. 55
4.1.7.3 SNMP-Users ............................................................................................. 56
4.1.7.4 SNMP-Groups........................................................................................... 57
4.1.7.5 SNMP-Views............................................................................................. 58
4.1.7.6 SNMP-Accesses ....................................................................................... 59
4.1.8 Traffic Prioritization.......................................................................................................60
4.1.8.1 Port Configuration ..................................................................................... 60
4.1.8.2 QoS Control List........................................................................................ 62
4.1.8.3 Storm Control............................................................................................63
4.1.8.4 Wizard....................................................................................................... 64
4.1.9 IGMP Snooping..............................................................................................................65
4.1.9.1 IGMP Snooping......................................................................................... 65
4.1.9.2 IGMP Snooping S tatus.............................................................................. 66
4.1.10 Security ......................................................................................................................67
4.1.10.1 ACL ........................................................................................................... 67
4.1.10.2 802.1x........................................................................................................ 68
4.1.11 Warning (only for RGS-7244GC-E model)...............................................................71
4.1.11.1 Fault Alarm................................................................................................ 71
4.1.11.2 System Warning........................................................................................ 71
4.1.12 Monitor and Diag.......................................................................................................72
4.1.12.1 MAC Table................................................................................................. 72
4.1.12.2 Mirroring.................................................................................................... 74
4.1.12.3 System Log Information............................................................................ 75
Page 5

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 4
4.1.12.4 Detailed Log.............................................................................................. 76
4.1.12.5 Traffic Overview.........................................................................................77
4.1.12.6 Detailed Statistics......................................................................................78
4.1.12.7 Ping........................................................................................................... 79
4.1.12.8 VeriPHY..................................................................................................... 80
4.1.13 System Reboot ...........................................................................................................81
4.1.14 Factory Defaults.........................................................................................................82
Command Line Interface Management ......................................................83
5.1 About CLI Management........................................................................................................83
Technical Specifications .............................................................................95
Page 6

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 5
Getting to Know Your Switch
1.1 About the RGS-7244GP(-E) Industrial Switch
RGS-7244GP series are the managed redundant ring Ethernet switches with
24x10/100/1000Base-(TX) ports and 4x1000Base-X SFP ports. With complete support of
Ethernet Redundancy protocol, O-Ring (Gigabit model recovery time < 20ms over 250 units of
connection) and MSTP/RSTP/STP (IEEE 802.1s/w/D) can protect your mission-critical
applications from network interruptions or temporary malfunctions with its fast recovery
technology.
ORing’s Thunder Series Ethernet switches provide advanced IP-based bandwidth
management which can limit the maximum bandwidth for each IP device. User can configure
IP camera and NVR with more bandwidth and limit other device bandwidth.
ORing’s Thunder Series Ethernet switches also support application-based QoS.
Application-based QoS can set highest priority for data stream according to TCP/UDP port
number. ORing’s special IP police function can permit only allowed IP address with MAC
address to access the networking. Hacker cannot access the IP surveillance network without
permission. It can avoid hacker from stealing video privacy data and attacking IP camera,
NVR and controllers.
Moreover, ORing’s Thunder Series Ethernet switches provide advanced DoS/DDoS auto
prevention. If there is any IP flow become big in short time, ORing’s thunder switch will lock
the source IP address for certain time to prevent the attack. It is hardware-based prevention
so it can prevent DDOS attack immediately and completely. And all functions of
RGS-7244GP can also be managed centralized and convenient by Open-Vision v3.0, except
the Web-based interface, Telnet and console (CLI) configuration. Therefore, the switch is one
of the most reliable choice for highly-managed and Gigabit Fiber Ethernet application.
Page 7

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 6
1.2 Software Features
Industry’s fastest Redundant Ethernet Ring (Gigabit model recovery time < 20ms over
250 units connection)
Suppo rt Ring Coupling, Dual Homing over Ring and standard STP/RSTP
Suppo rt SNMPv1/v2c/v3 & RMON & Port base/802.1Q VLAN Network Management
Event notification by Email and SNMP trap
Wind ows Utility, Web-based ,Telnet and Console(CLI) configuration
Enable/disable ports, MAC based port security
Port based n etwork access control (802.1x)
VLAN (80 2.1q ) to segregate and secure network traffic
RADIUS centralized password management
SNMPv3 encrypted authe ntication and access security
Quality of Service (80 2.1p) for real-time traffic
VLAN (80 2.1q) with double tagging and GVRP supported
IGMP Snoopi ng for multicast filtering
Port config uration, status, statistics, mirroring, security
Remote Monitoring (RMON)
1.3 Hardware Features
One 10 0~240VAC power input and RGS-7244GP-E added dual 36~72VDC power
inputs.
Operating Te mperature : -40 to 70
o
C
Storage Temperature : -40 to 85
o
C
Operating Hu midity : 5% to 95%, non-conden sing
Casing: IP-20
Provided 2 4 x 10/100/1000Base –T(X) RJ-45 ports
Provided 4 x 1000 Ba se-X SFP ports
Con sole Port (DB9 Female connector)
Dimensions :
RGS-7244GP : 443.7 (W) x 200 (D) x 44 (H) mm
RGS-7244GP-E : 431 (W) x 342 (D) x 44 (H) mm
Page 8

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 7
Hardware Overview
2.1 Front Panel
The following table describes the labels that stick on the RGS-7244GP(-E)
Port Description
Gigabit SFP ports
4 x 1000Base-X on SFP port
Gigabit Ethernet
Port
24 x 10/100/1000Base–T(X)
Console
Use RS-232 with DB9 connecter to manage switch.
RGS-7244GP
1. Console port (DB9 Female connector)
2. 10/100/1000Base-T(X) gigabits Ethernet port
3. 1000Base-X Fiber port on SFP port
4. Reset button. Push the button 3 seconds for reset; 5 seconds for factory default.
5. LED for Ethernet ports Link/Act status : Left Green for 1000Mbps indicator, Amber for
10/100Mbps indicator
6. LED for Ethernet ports Duplex status.
7. LED for SFP ports Link/Act status.
8. Front panel LED Status:
.LED for ST A. Green : Indicate that the system is ready . The LED is blinking when the
system is upgrading firmware
.LED for PWR. The LED lights on when the power module is activated.
.LED for R.M (Ring master). When the LED light on, it means that the switch is the ring
master of Ring.
.LED for Ring. When the led light on, it means the O-Ring is activated.
.LED for DEF: System resets to default configuration.
Page 9

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 8
.LED for Ping: System is processing “PING” request.
.LED for RUN: System is operating continuously.
.LED for RMT: System is accessed remotely.
RGS-7244GP-E
1. Console port (DB9 Female connector)
2. 10/100/1000Base-T(X) gigabits Ethernet port
3. 1000Base-X Fiber port on SFP port
4. Reset button: Push the button 3 seconds for reset; 5 seconds for factory default.
5. LED for Ethernet ports Link/Act status : Left Green for 1000Mbps indicator, Amber for
10/100Mbps indicator
6. LED for Ethernet ports Duplex status.
7. LED for SFP ports Link/Act status
8. Front Panel LED St atus:
.LED for PW1: When the PWR1 links, the green led will be light on.
.LED for PW2: When the PWR2 links, the green led will be light on.
.LED for PW3: When the PWR3 links, the green led will be light on.
.LED for STA: Green : Indicates that the system ready. The LED is blinking when the
system is upgrading firmware
.LED for PWR: This LED lights on when the power module is activated.
.LED for R.M. (Ring master): When the LED lights on, this switch is designated as the
ring master of the Ring topology.
.LED for Ring: When the led light on, the O-Ring is activated.
.LED for DEF: System resets to default configuration.
.LED for Ping: System is processing “PING” request.
.LED for RUN: System is operating continuously.
.LED for RMT: System is accessed remotely.
.LED for Fault: Indicates unexpected event occurred.
Page 10
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 9
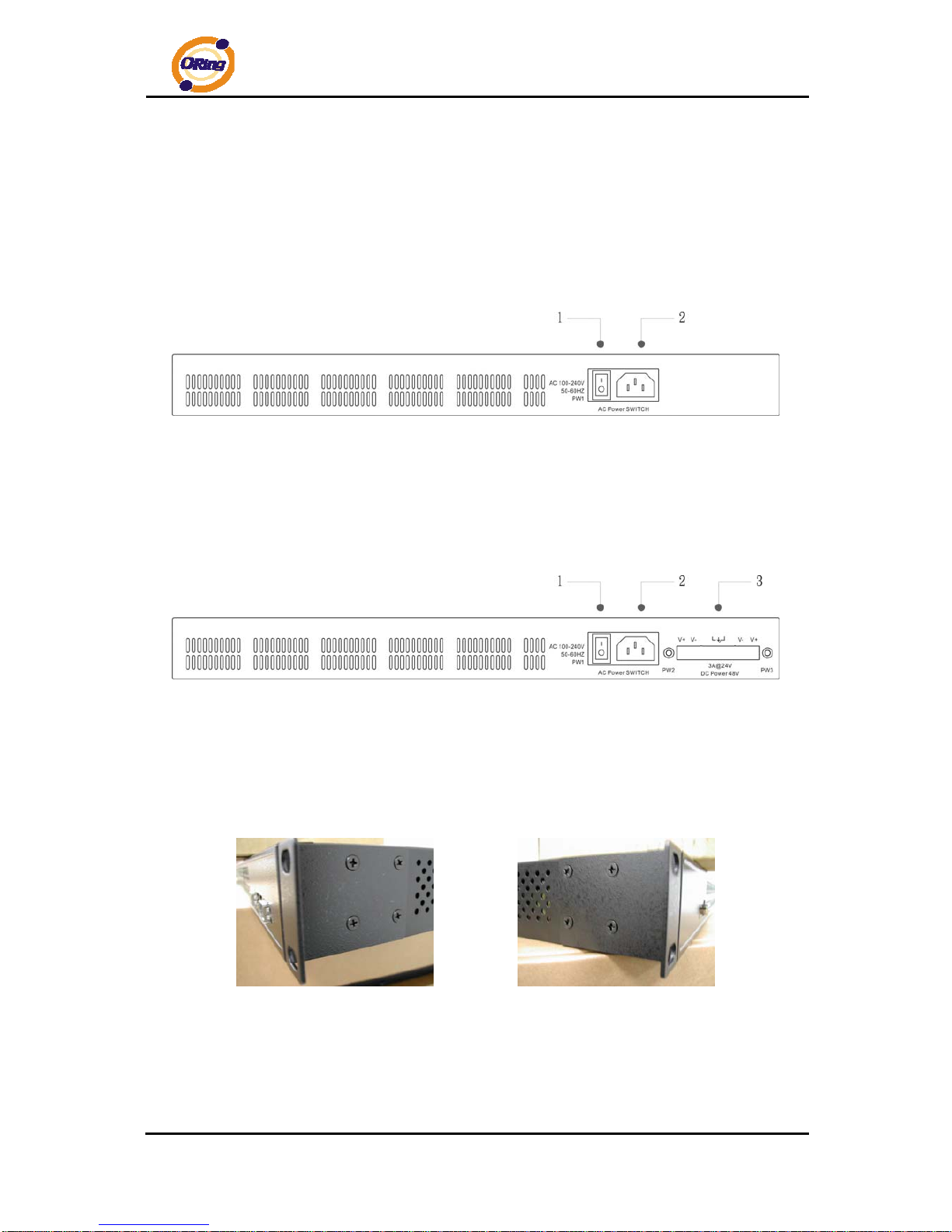
2.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of RGS-7244GP is sho wn as below:
1. Power Switch
2. Power input for AC 100V~240V / 50~60Hz
The rear panel of RGS-7244GP-E is shown as below:
1. Power Switch
2. Power input for AC 100V~240V / 50~60Hz
3. Dual power inputs for DC
2.3 Rack mount kit assembly
You can find the rack mount kit and the screws in the packing box. Please assembly the rack
mount kit on the switch with screws as shown below:
Page 11
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 10
2.4 Front Panel LEDs
LED Color Status Description
PW1
Green On
When the PWR1 links, the
green led will be light on.
PW2
Green On
When the PWR2 links, the
green led will be light on.
PW3
Green On
When the PWR3 links, the
green led will be light on.
On
When the power module is in
PWR UP state, the green LED
lights on.
STA
Green
Blinking
When the system is
upgrading firmware
DEF
Green On
System resets to default
configuration.
RUN
Green Slowly blinking
System is operating
continuously.
PWR
Green On DC power module activated.
Ping
Green Blinking
When the led light on, System
is processing “PING” request
RMT
Green Blinking System is accessed remotely.
On Ring enabled.
Slowly blinking
Ring has only One link. (lacks
one link to build the ring)
Ring
Green
Fast blinking Ring work normally.
R.M
Green On
When the system is operating
in O-Ring Master mode
Fault
Amber On
Indicates unexpected event
occurred.
10/100/1000Base-T(X) Gigabit Ethernet port s
On Port speed 1000M link up
Left Green (two color
LED)
Blinking Data Transmitted on 1000M
On Port speed 10/100M link up
LINK/ACT
Left Amber (two color
LED)
Blinking Data Transmitted on 10/100M
On Full-Duplex
Full-Duplex
Right Amber
Blinking Half-Duplex
SFP
On Port link up.
LINK/ACT
Green
Blinking Data transmitted
Page 12
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 11
Cables
3.1 Ethernet Cables
The RGS-7244GP(-E) switches has standard Ethernet ports. According to the link type,
the switch use CAT 3, 4, 5,5e UTP cables to connect to any other network device (PCs,
servers, switches, routers, or hubs). Please refer to the following table for cable
specifications.
Cable Types and Specifications
Cable Type Max. Length Connector
10BASE-T Cat. 3, 4, 5 100-ohm UTP 100 m (328 ft) RJ-45
100BASE-TX Cat. 5 100-ohm UTP UTP 100 m (328 ft) RJ-45
1000BASE-T
Cat. 5/Cat. 5e 100-ohm
UTP
UTP 100 m (328ft) RJ-45
3.1.1 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T Pin Assignments
With 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T cable, pins 1 and 2 are used for transmitting data, and
pins 3 and 6 are used for receiving data.
10/100 Base-T(X) RJ-45 Pin Assignments
Pin Number Assignment
1 TD+
2 TD3 RD+
4 Not used
5 Not used
6 RD7 Not used
8 Not used
Page 13
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 12
1000 Base-T RJ-45 Pin Assignments
Pin Number Assignment
1 BI_DA+
2 BI_DA3 BI_DB+
4 BI_DC+
5 BI_DC6 BI_DB7 BI_DD+
8 BI_DD-
The RGS-7244GP(-E) switches support auto MDI/MDI-X operation. You can use a
straight-through cable to connect PC to switch. The following table below shows the
10BASE-T/ 100BASE-TX MDI and MDI-X port pin outs.
10/100 Base-T MDI/MDI-X pins assignment
Pin Number MDI port MDI-X port
1 TD+(transmit) RD+(receive)
2 TD-(transmit) RD-(receive)
3 RD+(receive) TD+(transmit)
4 Not used Not used
5 Not used Not used
6 RD-(receive) TD-(transmit)
7 Not used Not used
8 Not used Not used
1000 Base-T MDI/MDI-X pins assignment
Pin Number MDI port MDI-X port
1 BI_DA+ BI_DB+
2 BI_DA- BI_DB3 BI_DB+ BI_DA+
4 BI_DC+ BI_DD+
5 BI_DC- BI_DD6 BI_DB- BI_DA7 BI_DD+ BI_DC+
8 BI_DD- BI_DC-
Note: “+” and “-” signs represent the polarity of the wires that make up each wire pair.
Page 14

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 13
3.2 SFP
The Switch has fiber optical ports with SFP connectors. The fiber optical port s are in
multi-mode (0 to 550M, 850 nm with 50/125 µm, 62.5/125 µm fiber) and single-mode with LC
connector. Please remember that the TX port of Switch A should be connected to the RX port
of Switch B.
Switch A Switch B
3.3 Console Cable
RGS-7244GP(-E) switches can be management by console port. The DB-9 to RJ-45 cable
can be found in the package. You can connect them to PC via a RS-232 cable with DB-9
female connector and the other end (RJ-45 connector) connects to consol e port of switch.
PC pin out (male) assignment RS-232 with DB9 female connector DB9 to RJ 45
Pin #2 RD Pin #2 TD Pin #2
Pin #3 TD Pin #3 RD Pin #3
Pin #5 GD Pin #5 GD Pin #5
Fiber cord
Page 15

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 14
WEB Management
4.1 Configuration by Web Browser
This section introduces the configuration by Web browser.
4.1.1 About Web-based Management
An embedded HTML web site resides in flash memory on the CPU board. It contains
advanced management features and allows you to manage the switch from anywhere on the
network through a standard web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management function supports Internet Explorer 5.0 or later. It is based
on Java Applets with an aim to reduce network bandwidth consumption, enhance access
speed and present an easy viewing screen.
Note: By default, IE5.0 or late r version does not allow Java Applets to open sockets. You need to explicitly modify
the browser setting in order to enable Java Applets to use network ports.
Preparing for Web Management
The default value is as below:
IP Address: 192.168.10.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.10.254
User Name: admin
Password: admin
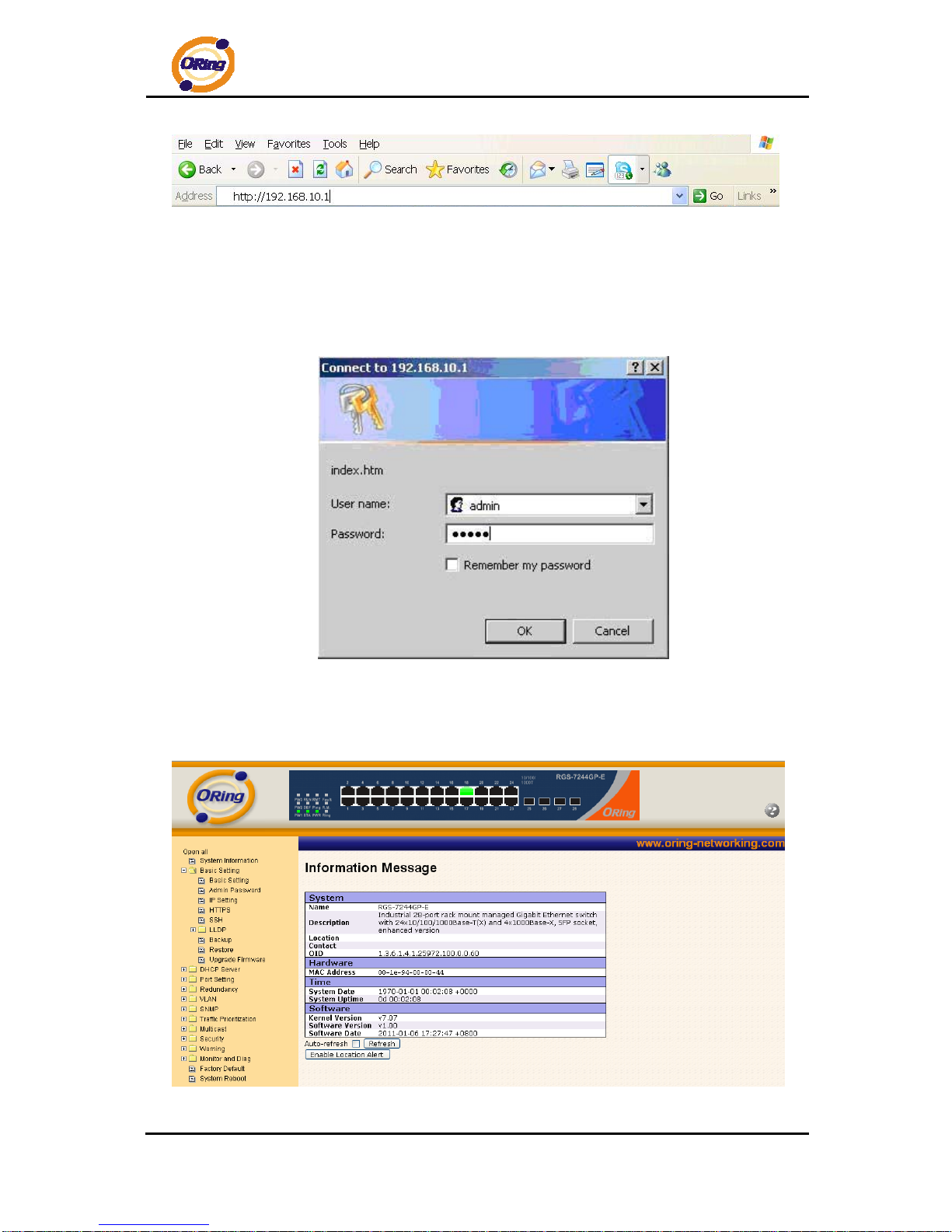
System Login
1. Launch the Internet Explorer.
2. Type http:// and the IP address of the switch. Press “Enter”.
Page 16
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 15
3. The login screen appears.
4. Key in the username and password. The default username and password is
“admin”.
5. Click “Enter” or ”OK” button, then the main interface of the Web-based
management appears.
Login screen
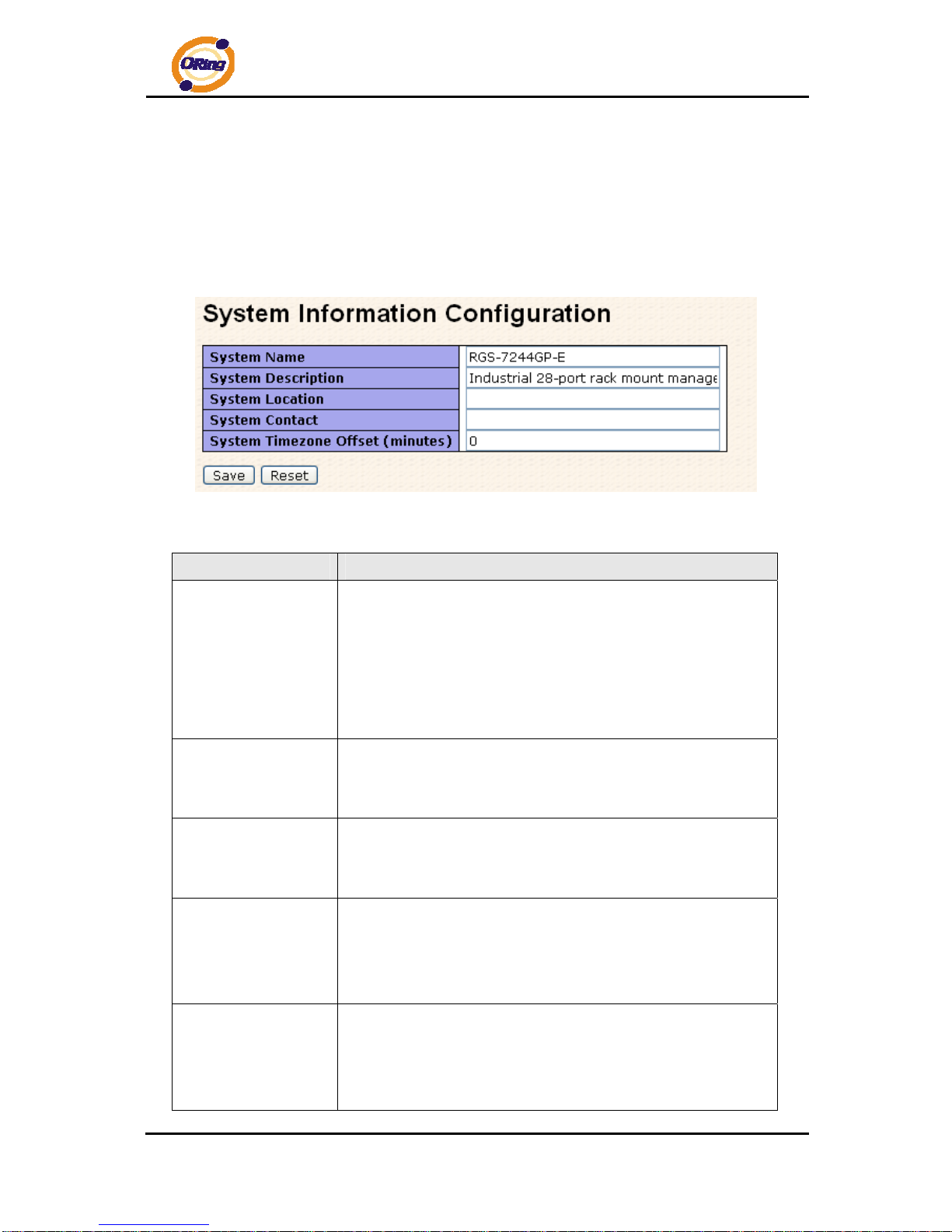
Main Interface
Main interface
Page 17
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 16
4.1.2 Basic Setting
4.1.2.1 System Information
The switch system information is provided here.
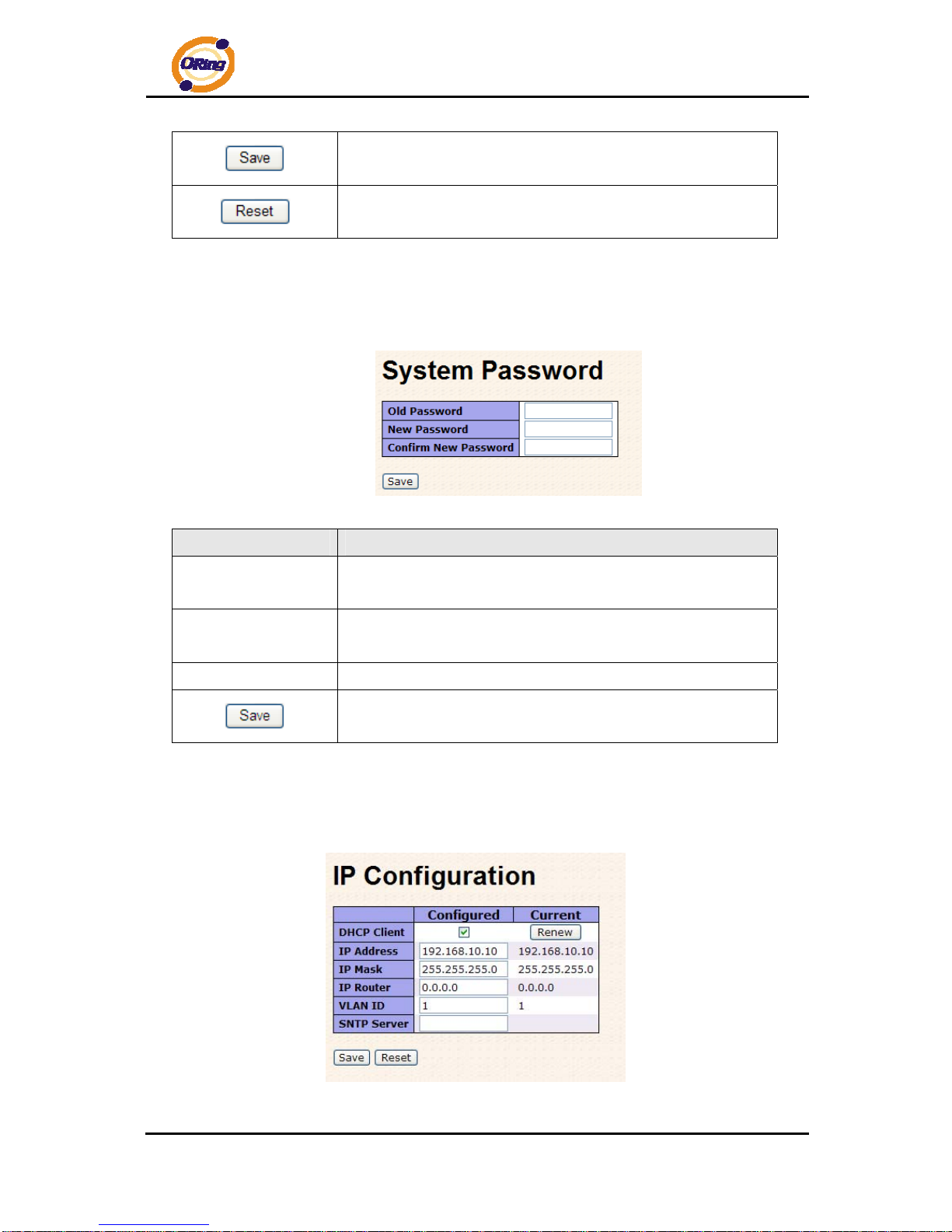
System Information interface
.
Label Description
System Name
An administratively assigned name for this managed node. By
convention, this is the node's fully-qualified domain name – a text
string (0 to 255 characters) drawn from the alphabet (A-Z, a-z),
digits (0-9), and the minus sign (-). No space characters are
permitted as part of a name. The first character must be an
alphabet, and the first or last character must not be a minus sign.
System
Description
The administratively assigned description for this managed
node. The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed
contents are the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
System Location
The physical location of this node (e.g., telephone closet, 3rd
floor). The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
System Contact
The textual identification of the contact person for this managed
node, together with information on how to contact this person.
The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is
the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
Timezone Offset
Enter the name of contact person or organization
Provide the time zone offset relative to UTC/GMT.
The offset is given in minutes east of GMT. The valid range is from
-720 to 720 minutes.
Page 18
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 17
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
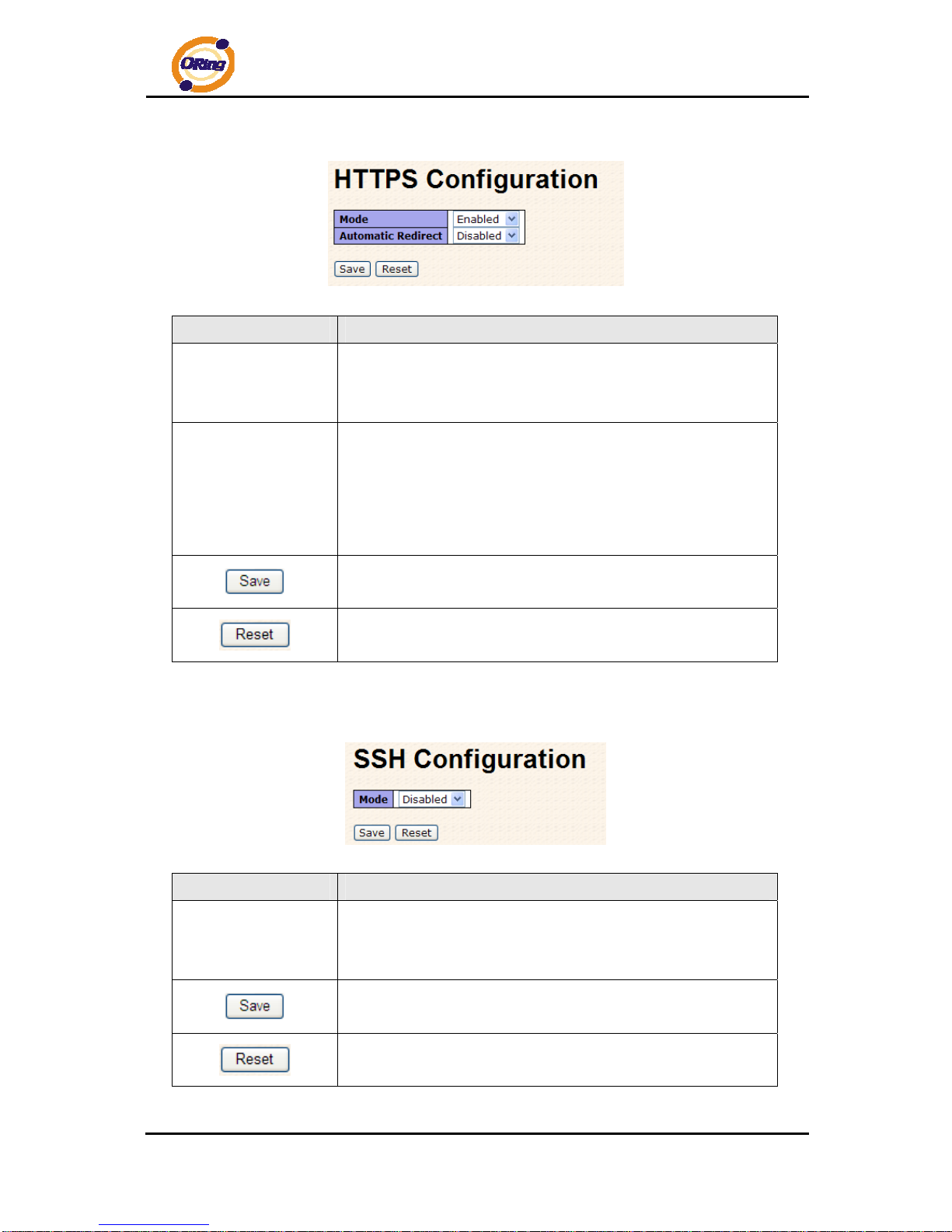
4.1.2.2 Admin & Password
This page allows you to configure the system password required to access the web p ages or
log in from CLI.
Label Description
Old Password
Enter the current system password. If this is incorrect, the new
password will not be set.
New Password
The system password. The allowed string length is 0 to 31, and
the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
Confirm password
Re-type the new password.
Click to save changes.
4.1.2.3 IP Setting
Configure the switch-managed IP information on this pag e.
Page 19

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 18
Label Description
DHCP Client
Enable the DHCP client by checking this box. If DHCP fails and
the configured IP address is zero, DHCP will retry. If DHCP fails
and the configured IP address is non-zero, DHCP will stop and
the configured IP settings will be used. The DHCP client will
announce the configured System Name as hostname to provide
DNS lookup.
IP Address
Assign the IP address that the network is using. If DHCP client
function is enabling, you do not need to assign the IP address.
The network DHCP server will assign the IP address for the
switch and it will be display in this column. The default IP is
192.168.10.1
IP Mask
Assign the subnet mask of the IP address. If DHCP client function
is enabling, you do not need to assign the subnet mask
IP Router
Assign the network gateway for the switch. The default gateway
is 192.168.10.254
VLAN ID
Provide the managed VLAN ID. The allowed range is 1 through
4095.
SNTP Server
SNTP is an acronym for Simple Network T ime Protocol, a netwo rk
protocol for synchronizing the clocks of computer systems. SNTP
uses UDP (datagrams) as transport layer.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Click to renew DHCP. This button is only available if DHCP is
enabled.
Page 20
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 19
4.1.2.4 HTTPS
Label Description
Mode
Indicates the HTTPS mode operation. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable HTTPS mode operation.
Disabled: Disable HTTPS mode operation.
Automatic Redirect
Indicates the HTTPS redirect mode operation. Automatic redirect
web browser to HTTPS during HTTPS mode enabled. Possible
modes are:
Enabled: Enable HTTPS redirect mode operation.
Disabled: Disable HTTPS redirect mode operation.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
4.1.2.5 SSH
Label Description
Mode
Indicates the SSH mode operation. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable SSH mode operation.
Disabled: Disable SSH mode operation.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Page 21
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 20
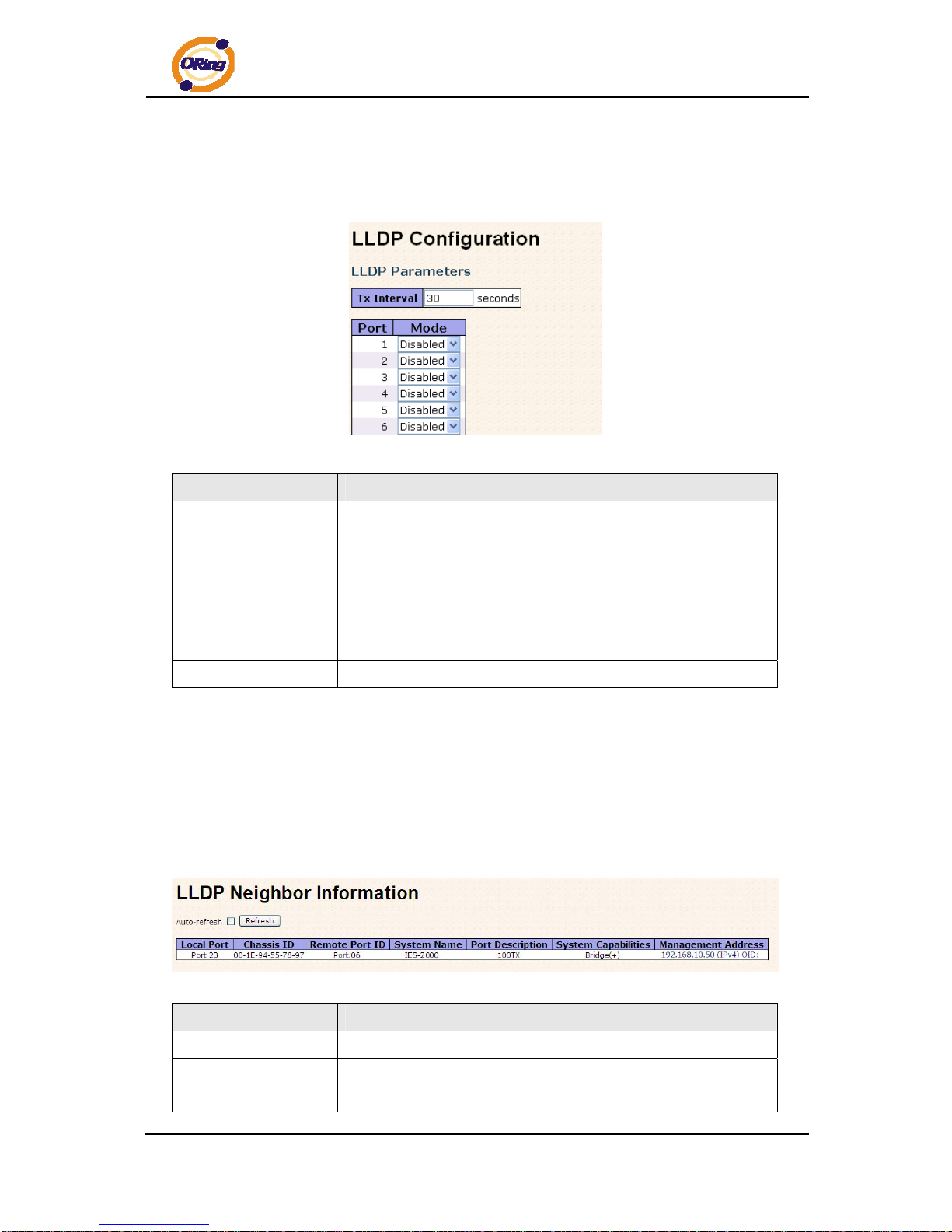
4.1.2.6 LLDP
LLDP Parameters
This page allows the user to inspect and configure the current LLDP port settings.
Label Description
Tx Interval
The switch is periodically transmitting LLDP frames to its
neighbors for having the network discovery information
up-to-date. The interval between each LLDP frame is determined
by the Tx Interval value. Valid values are restricted to 5 - 32768
seconds.
Port
The switch port number of the logical LLDP port.
Mode
Enable or disable LLDP
LLDP Neighbor Information
This page provides a status overview for all LLDP neighbors. The displayed table contains a
row for each port on which an LLDP neighbor is detected. The columns hold the following
information:
Label Description
Local Port
The port on which the LLDP frame was received.
Chassis ID
The Chassis ID is the identification of the neighbor's LLDP
frames.
Page 22

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 21
Remote Port ID
The Remote Port ID is the identification of the neighbor port.
System Name
System Name is the name advertised by the neighbor unit.
Port Description
Port Description is the port description advertised by the neighbor
unit.
System Capabilites
System Capabilities describes the neighbor unit's capabilities.
The possible capabilities are:
1. Other
2. Repeater
3. Bridge
4. WLAN Access Point
5. Router
6. Telephone
7. DOCSIS cable device
8. Station only
9. Reserved
When a capability is enabled, the capability is followed by (+). If
the capability is disabled, the capability is followed by (-).
Management
Address
Management Address is the neighbor unit's address that is used
for higher layer entities to assist the discovery by the network
management. This could for instance hold the neighbor's IP
address.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
LLDP Statistics
This page provides an overview of all LLDP traffic.
Two types of counters are shown. Global counters are counters that refer to the whole stack,
switch, while local counters refer to counters for the currently selected switch.
Page 23
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 22
Global Counters
Label Description
Neighbor entries
were last changed at
Shows the time for when the last entry was last deleted or added.
It is also shows the time elapsed since last change was detected.
T otal Neighbors
Entries Added
Shows the number of new entries added since switch reboot.
T otal Neighbors
Entries Deleted
Shows the number of new entries deleted since switch reboot.
T otal Neighbors
Entries Dropped
Shows the number of LLDP frames dropped due to that the entry
table was full.
T otal Neighbors
Entries Aged Out
Shows the number of entries deleted due to Time-To-Live
expiring.
Local Counters
Label Description
Local Port
The port on which LLDP frames are received or transm itted.
Tx Frames
The number of LLDP frames transmitted on the port.
Rx Frames
The number of LLDP frames received on the port.
Rx Errors
The number of received LLDP frames containing some kind of
error.
Frames Discarded
If an LLDP frame is received on a port, and the switch's internal
table has run full, the LLDP frame is counted and discarded. This
situation is known as "Too Many Neighbors" in the LLDP
standard. LLDP frames require a new entry in the table when the
Chassis ID or Remote Port ID is not already contained within the
table. Entries are removed from the table when a given port links
down, an LLDP shutdown frame is received, or when the entry
ages out.
TL Vs Discarded
Each LLDP frame can contain multiple pieces of information,
known as TLVs (TLV is short for "Type Length Value"). If a TLV is
malformed, it is counted and discarded.
TL Vs Unrecognized
The number of well-formed TLVs, but with an unknown type
value.
Org. Discarded
The number of organizationally TLVs received.
Page 24
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 23
Age-Outs
Each LLDP frame contains information about how long time the
LLDP information is valid (age-out time). If no new LLDP frame is
received within the age out time, the LLDP information is
removed, and the Age-Out counter is incremented.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Clears the local counters. All counters (including global counters)
are cleared upon reboot.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
4.1.2.7 Backup/Restore Configuration
You can save/view or load the switch configuration. The configuration file is in XML format with
a hierarchy of tags:
4.1.2.8 Firmware Update
This page facilitates an update of the firmware controlling the stack. switch.
Page 25
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 24
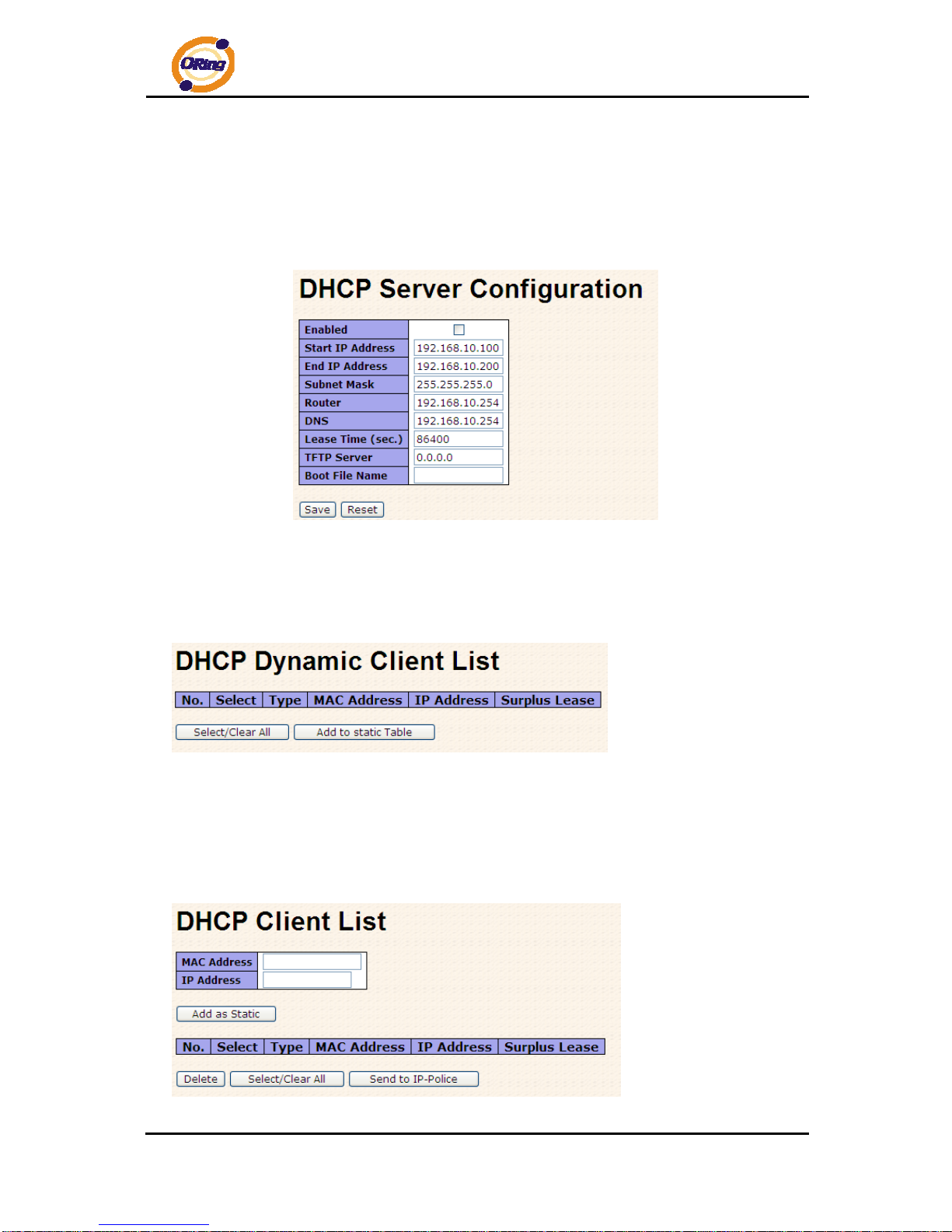
4.1.3 DHCP Server
4.1.3.1 Setting
The system provides with DHCP server function. Enable the DHCP server function, the
switch system will be a DHCP server.
4.1.3.2 DHCP Dynamic Client List
When the DHCP server function is activated, the system will collect the DHCP client
information and display in here.
4.1.3.3 DHCP Client List
You can assign the specific IP address which is in the assigned dynamic IP range to the
specific port. When the device is connecting to the port and asks for dynamic IP assigning,
the system will assign the IP address that has been assigned before in the connected device.
Page 26
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 25
4.1.4 Port Setting
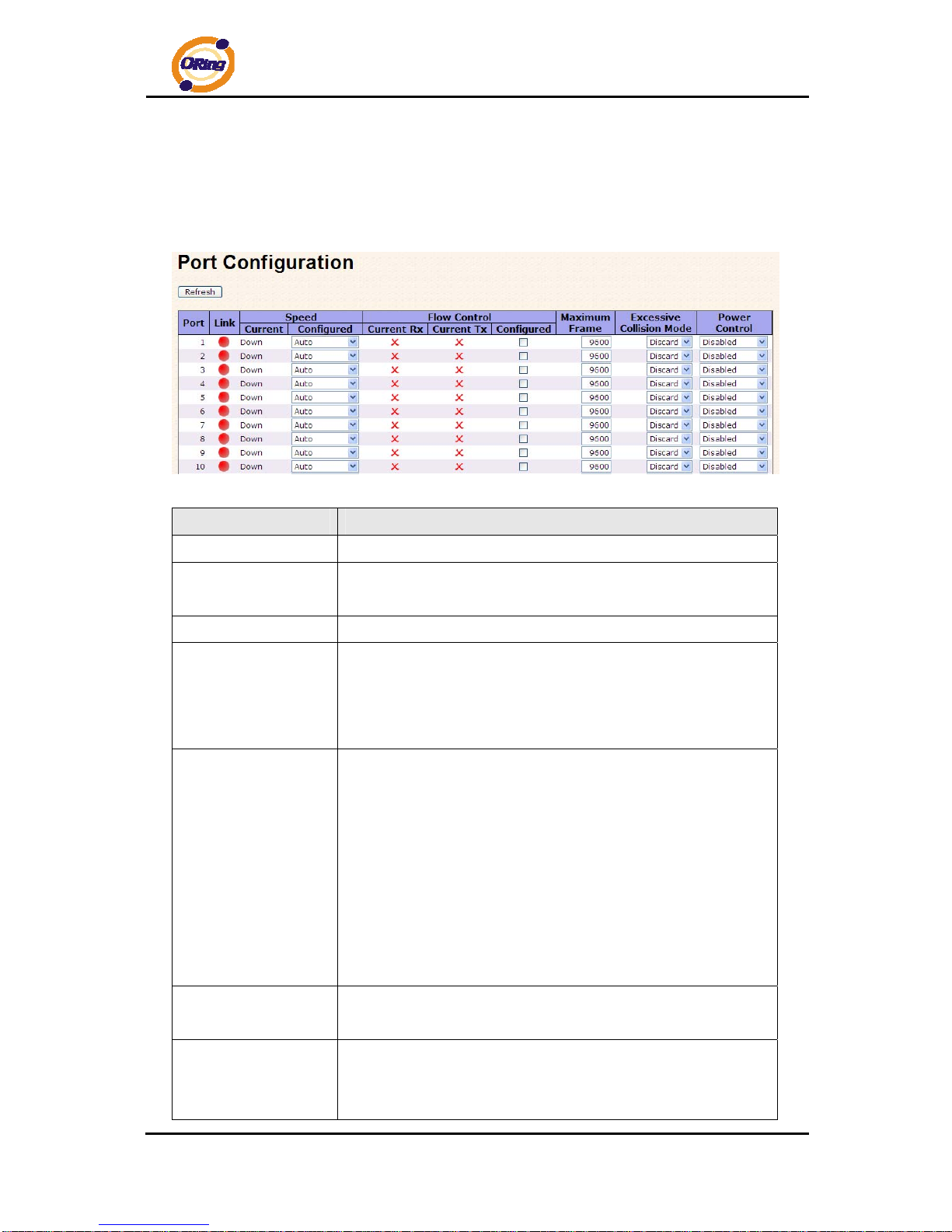
4.1.4.1 Port Control
This page displays current port configurations. Ports can also be configure d here.
Label Description
Port
This is the logical port number for this row.
Link
The current link state is displayed graphically. Green indicates the
link is up and red that it is down.
Current Link Speed
Provides the current link speed of the port.
Configured Link
Speed
Select any available link speed for the given switch port.
Auto Speed selects the highest speed that is compatible with a
link partner.
Disabled disables the switch port operation.
Flow Control
When Auto Speed is selected for a port, this section indicates the
flow control capability that is advertised to the link partner.
When a fixed-speed setting is selected, that is what is used. The
Current Rx column indicates whether pause frames on the port
are obeyed, and the Current Tx column indicates whether pause
frames on the port are transmitted. The Rx and Tx settings are
determined by the result of the last Auto-Negotiation.
Check the configured column to use flow control. This setting is
related to the setting for Configured Link Speed.
Maximum Frame
Enter the maximum frame size allowed for the switch port,
including FCS. The allowed range is 1518 bytes to 9600 bytes.
Excessive Collision
Mode
Configure port transmit collision behavior.
Discard: Discard frame after 16 collisions (default).
Restart: Restart back-off algorithm after 16 collisions.
Page 27
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 26
Power Control
The Usage column shows the current percentage of the power
consumption per port. The Configured column allows for changing
the power savings mode parameters per port.
Disabled: All power savings mechanisms disabled.
ActiPHY: Link down power savings enabled.
PerfectReach: Link up power savings enabled.
Enabled: Both link up and link down power savings enabled.
T otal Power Usage
Total power usage in board, measured in percent.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Click to refresh the page. Any changes made locally will be
undone.
4.1.4.2 Rate Limit
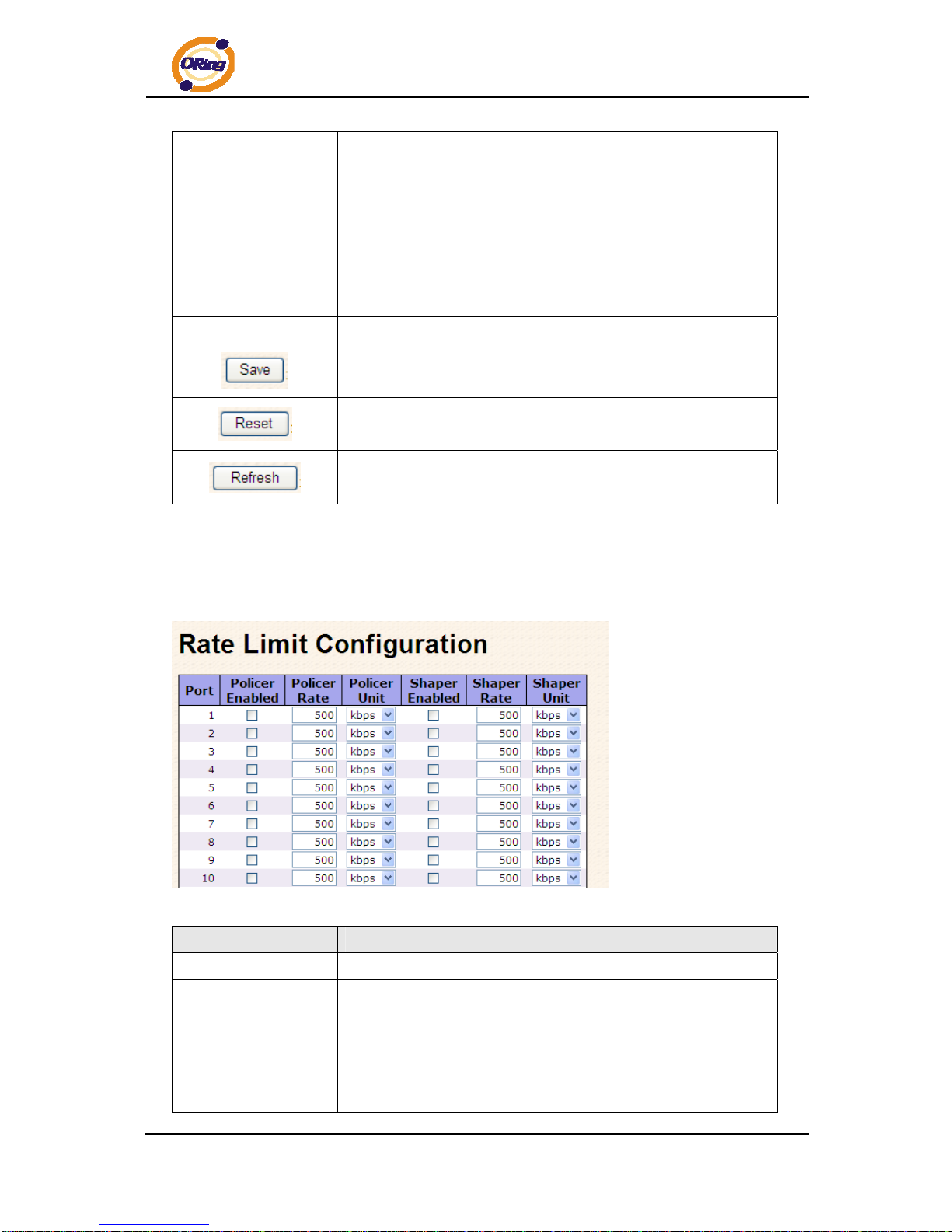
Configure the switch port rate limit for Policers and Shapers on this page.
Label Description
Port
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Policer Enabled
Enable or disable the port policer. The default value is "Disabled".
Policer Rate
Configure the rate for the port policer. The default value is "500".
This value is restricted to 500-1000000 when the "Policer Unit" is
"kbps", and it is restricted to 1-1000 when the "Policer Unit" is
"Mbps"
Page 28

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 27
Policer Unit
Configure the unit of measure for the port policer rate as kbps or
Mbps. The default value is "kbps".
Shaper Enabled
Enable or disable the port shaper. The default value is "Disabled".
Shaper Rate
Configure the rate for the port shaper. The default value is "500".
This value is restricted to 500-1000000 when the "Policer Unit" is
"kbps", and it is restricted to 1-1000 when the "Policer Unit" is
"Mbps"
Shaper Unit
Configure the unit of measure for the port shaper rate as kbps or
Mbps. The default value is "kbps".
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
4.1.4.3 Port Trunk
4.1.4.3.1 Trunk Configuration
This page is used to configure the Aggregation hash mode and the aggregation group.
Label Description
Source MAC Address
The Source MAC address can be used to calculate the
destination port for the frame. Check to enable the use of the
Source MAC address, or uncheck to disable. By default, Source
MAC Address is enabled.
Destination MAC
Address
The Destination MAC Address can be used to calculate the
destination port for the frame. Check to enable the use of the
Destination MAC Address, or uncheck to disable. By default,
Destination MAC Address is disabled.
IP Address
The IP address can be used to calculate the destination port for
the frame. Check to enable the use of the IP Address, or uncheck
to disable. By default, IP Address is enabled.
TCP/UDP Port
The TCP/UDP port number can be used to calculate the
Page 29
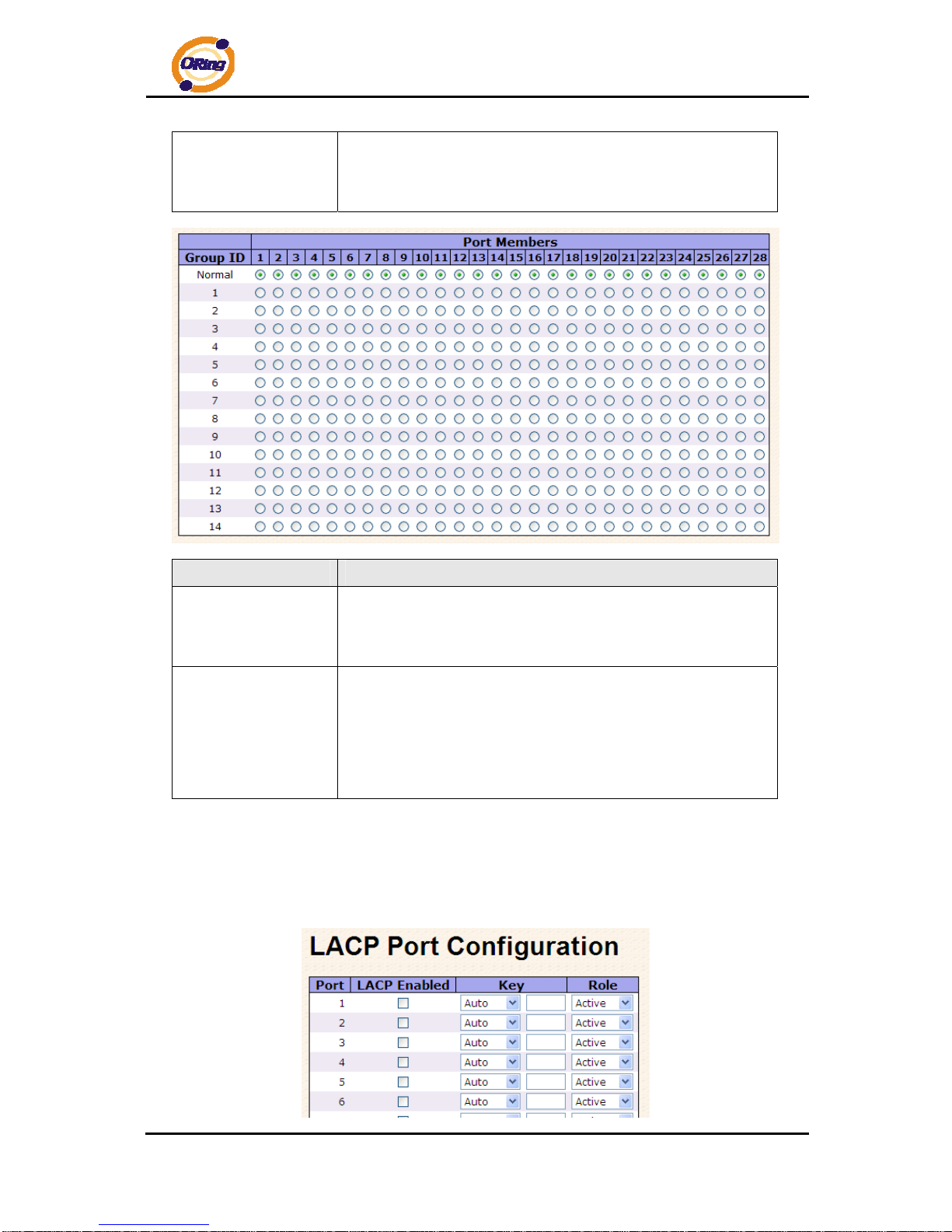
RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 28
Number
destination port for the frame. Check to enable the use of the
TCP/UDP Port Number, or uncheck to disable. By default,
TCP/UDP Port Number is enabled.
Label Description
Group ID
Indicates the group ID for the settings contained in the same row.
Group ID "Normal" indicates there is no aggregation. Only one
group ID is valid per port.
Port Members
Each switch port is listed for each group ID. Select a radio button
to include a port in an aggregation, or clear the radio button to
remove the port from the aggregation. By default, no ports belong
to any aggregation group. Only full duplex ports can join an
aggregation and ports must be in the same speed in each group.
4.1.4.3.2 LACP Port Configuration
This page allows the user to inspect the current LACP port configurations, and possibly
change them as well.
Page 30

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 29
Label Description
Port
Indicates the group ID for the settings contained in the same row.
Group ID "Normal" indicates there is no aggregation. Only one
group ID is valid per port.
LACP Enabled
Each switch port is listed for each group ID. Select a radio button
to include a port in an aggregation, or clear the radio button to
remove the port from the aggregation. By default, no ports belong
to any aggregation group. Only full duplex ports can join an
aggregation and ports must be in the same speed in each group.
Key
The Key value incurred by the port, range 1-65535 . The Auto
setting will set the key as appropriate by the physical link speed,
10Mb = 1, 100Mb = 2, 1Gb = 3. Using the Specific setting, a
user-defined value can be entered. Ports with the same Key value
can participate in the same aggregation group, while ports with
different keys cannot.
Role
The Role shows the LACP activity status. The Active will transmit
LACP packets each second, while Passive will wait for a LACP
packet from a partner (speak if spoken to).
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
4.1.4.3.3 LACP System Status
This page provides a status overview for all LACP instances.
Label Description
Aggr ID
The Aggregation ID associated with this aggregation insta nce. For
LLAG the id is shown as 'isid:aggr-id' and for GLAGs as 'aggr-id'
Partner System ID
The system ID (MAC address) of the aggregation partner.
Page 31

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 30
Partner Key
The Key that the partner has assigned to this aggregation ID.
Last Changed
The time since this aggregation changed.
Last Channged
Shows which ports are a part of this aggregation for this
switch/stack. The format is: "Switch ID:Port".
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
4.1.4.3.4 LACP Status
This page provides a status overview for LACP status for all ports.
Label Description
Port
The switch port number.
LACP
'Yes' means that LACP is enabled and the port link is up. 'No'
means that LACP is not enabled or that the port link is down.
'Backup' means that the port could not join the aggregation group
Page 32

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 31
but will join if other port leaves. Meanwhile it's LACP status is
disabled.
Key
The key assigned to this port. Only ports with the same key can
aggregate together.
Aggr ID
The Aggregation ID assign ed to this aggregation group.
Partner System ID
The partners System ID (MAC address).
Partner Port
The partners port number connected to this port.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
4.1.4.3.5 LACP Statistics
This page provides an overview for LACP st atistics for all ports.
Label Description
Port
The switch port number
LACP Transmitted
Shows how many LACP frames have been sent from each port
LACP Received
Shows how many LACP frames have been received at each port.
Page 33

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 32
Discarded
Shows how many unknown or illegal LACP frames have been
discarded at each port.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
Clears the counters for all ports
4.1.4.4 Loop Guard
Loop Guard is a looping detection/avoid strategy, it helps network administrator to avoid
looping issue.
Label Description
Active
Enable Loop Guard function
Port State
Guarding:This port is protected against looping.
Locked:This port has been locked to avoid looping.
4.1.5 Redundancy
4.1.5.1 O-Ring
Ring is the most powerful Ring in the world. The recovery time of Ring is less than 10 ms.
It can reduce unexpected damage caused by network topology change. Ring Supports 3
Ring topology: Ring, Coupling Ring and Dual Homing.
Ring interface
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Page 34

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 33
Label Description
O-Ring
Mark to enable O-Ring.
Ring Master
There should be one and only one Ring Master in a ring.
However if there are two or more switches which set Ring
Master to enable, the switch with the lowest MAC address will
be the actual Ring Master and others will be Backup Masters.
1st Ring Port
The primary port, when this switch is enable O-Ring
2nd Ring Port
The backup port, when this switch is enable O-Ring
Coupling Ring
Mark to enable Coupling Ring. Coupling Ring can be used to
divide a big ring into two smaller rings to avoid effecting all
switches when network topology change. It is a good
application for connecting two Rings.
Coupling Port
Link to Coupling Port of the switch in another ring
. Coupling
Ring need four switch to build an active and a backup link.
Set a port as coupling port. The coupled four ports of four
switches will be run at active/backup mode.
Dual Homing
Mark to enable Dual Homing. By selecting Dual Homing
mode, Ring will be connected to normal switches through
two RSTP links (ex: backbone Switch). The two links work as
active/backup mode, and connect each Ring to the normal
switches in RSTP mode.
Apply
Click “Apply” to set the configurations.
Note: We don’t suggest you to set one switch as a Ring Master and a Coupling Ring at the
same time due to heavy load.
4.1.5.2 MSTP
Bridge Settings
This page allows you to configure RSTP system settings. The settings are used by all RSTP
Bridge instances in the Switch Stack.
Label Description
Page 35

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 34
Protocol Version
The STP protocol version setting. Valid values are STP, RSTP
and MSTP.
Forward Delay
The delay used by STP Bridges to transition Root and Designated
Ports to Forwarding (used in STP compatible mode). Valid values
are in the range 4 to 30 seconds.
Max Age
The maximum age of the information transmitted by the Bridge
when it is the Root Bridge. Valid values are in the range 6 to 40
seconds, and MaxAge must be <= (FwdDelay-1)*2.
Maximum Hop Count
This defines the initial value of remainingHops for MSTI
information generated at the boundary of an MSTI region. It
defines how many bridges a root bridge can distribute its BPDU
information. Valid values are in the range 4 to 30 seconds, and
MaxAge must be <= (FwdDelay-1)*2.
Transmit Hold Count
The number of BPDU's a bridge port can send per second. When
exceeded, transmission of the next BPDU will be delayed. Valid
values are in the range 1 to 10 BPDU's per second.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
MSTI Mapping
This page allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI bridge instance priority
configurations, and possibly change them as well.
Page 36

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 35
Label Description
Configuration Name
The name identifiying the VLAN to MSTI mapping. Bridges must
share the name and revision (see below), as well as the
VLAN-to-MSTI mapping configuration in order to share spanning
trees for MSTI's. (Intra-region). The name is at most 32
characters.
Configuration
Revision
The revision of the MSTI configuration named above. This must
be an integer between 0 and 65535.
MSTI
The bridge instance. The CIST is not available for explicit
mapping, as it will receive the VLANs not explicitly mapped.
VLANS Mapped
The list of VLAN's mapped to the MSTI. The VLANs must be
separated with comma and/or space. A VLAN can only be
mapped to one MSTI. A unused MSTI should just be left empty.
(I.e. not having any VLANs mapped to it.)
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Page 37

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 36
MSTI Priorities
This page allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI bridge instance priority
configurations, and possibly change them as well.
Label Description
MSTI
The bridge instance. The CIST is the default instance, which is
always active.
Priority
Controls the bridge priority. Lower numerical values have better
priority. The bridge priority plus the MSTI instance number,
concatenated with the 6-byte MAC address of the switch forms a
Bridge Identifier.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
CIST Ports
This page allows the user to inspect the current STP CIST port configurations, and possibly
change them as well.This page contains settings for physical and aggregated ports. The
aggregation settings are stack global.
Page 38

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 37
Label Description
Port
The switch port number of the logical STP port.
STP Enabled
Controls whether STP is enabled on this switch port.
Path Cost
Controls the path cost incurred by the port. The Auto setting will
set the path cost as appropriate by the physical link speed, using
the 802.1D recommended values. Using the Specific setting, a
user-defined value can be entered. The path cost is used when
establishing the active topology of the network. Lower path cost
ports are chosen as forwarding ports in favor of higher path cost
ports. Valid values are in the range 1 to 200000000.
Priority
Controls the port priority. This can be used to control priority of
ports having identical port cost. (See above).
OpenEdge(setate
flag)
Operational flag describing whether the port is connecting directly
to edge devices. (No Bridges attached). Transitioning to the
forwarding state is faster for edge ports (having operEdge true)
than for other ports.
AdminEdge
Controls whether the operEdge flag should start as beeing set or
cleared. (The initial operEdge state when a port is initialized).
AutoEdge
Controls whether the bridge should enable automatic edge
detection on the bridge port. This allows operEdge to be derived
from whether BPDU's are received on the port or not.
Restricted Role
If enabled, causes the port not to be selected as Root Port for the
CIST or any MSTI, even if it has the best spanning tree priority
vector. Such a port will be selected as an Alternate Port after the
Page 39

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 38
Root Port has been selected. If set, it can cause lack of spanning
tree connectivity. It can be set by a network administrator to
prevent bridges external to a core region of the network
influencing the spanning tree active topology, possibly because
those bridges are not under the full control of the administrator.
This feature is also know as Root Guard.
Restricted TCN
If enabled, causes the port not to propagate received topology
change notifications and topology changes to other ports. If set it
can cause temporary loss of connectivity after changes in a
spanning trees active topology as a result of persistent incorrectly
learned station location information. It is set by a network
administrator to prevent bridges external to a core region of the
network, causing address flushing in that region, possibly
because those bridges are not under the full control of the
administrator or is the physical link state for the attached LANs
transitions frequently.
Point2Point
Controls whether the port connects to a point-to-point LAN rather
than a shared medium. This can be automatically determined, or
forced either true or false. Transition to the forwarding state is
faster for point-to-point LANs than for shared media.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
MSTI Ports
This page allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI port configurations, and possibly
change them as well. A MSTI port is a virtual port, which is instantiated seperately for each
active CIST (physical) port for each MSTI instance configured and applicable fo r the port. The
MSTI instance must be selected before displaying actual MSTI port configuration options.
This page contains MSTI port settings for physical and aggregated ports. The aggregation
settings are stack global.
Page 40

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 39
Label Description
Port
The switch port number of the corresponding STP CIST (and
MSTI) port.
Path Cost
Controls the path cost incurred by the port. The Auto setting will
set the path cost as appropriate by the physical link speed, using
the 802.1D recommended values. Using the Specific setting, a
user-defined value can be entered. The path cost is used when
establishing the active topology of the network. Lower path cost
ports are chosen as forwarding ports in favor of higher path cost
ports. Valid values are in the range 1 to 200000000.
Priority
Controls the port priority. This can be used to control priority of
ports having identical port cost. (See above).
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Page 41

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 40
STP Bridges
This page provides a status overview for all STP bridge instances.
The displayed table contains a row for each STP bridge instance, where the
column displays the following information:
Label Description
MSTI
The Bridge Instance. This is also a link to the STP Detailed Bridg e
Status.
Bridge ID
The Bridge ID of this Bridge instance.
Root ID
The Bridge ID of the currently elected root bridge.
Root Port
The switch port currently assigned the root port role.
Root Cost
Root Path Cost. For the Root Bridge this is zero. For all other
Bridges, it is the sum of the Port Path Costs on the least cost p ath
to the Root Bridge.
T opology Flag
The current state of the Topology Change Flag for this Bridge
instance.
T opology Change
Last
The time since last Topology Change occurred.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
STP Port Status
This page displays the STP CIST port status for port physical ports in the currently selected
switch.
Page 42

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 41
Label Description
Port
The switch port number of the logical STP port.
CIST Role
The current STP port role of the CIST port. The port role can be
one of the following values: AlternatePort BackupPort RootPort
DesignatedPort.
State
The current STP port state of the CIST port. The port state can be
one of the following values: Blocking Learning Forwarding.
Uptime
The time since the bridge port was last initialized.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
STP Statistics
This page displays the RSTP port statistics counters for bridge ports in the currently selected
switch.
Page 43

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 42
Label Description
Port
The switch port number of the logical RSTP port.
RSTP
The number of RSTP Configuration BPDU's received/transmitted
on the port.
STP
The number of legacy STP Configuration BPDU's
received/transmitted on the port.
TCN
The number of (legacy) Topology Change Notification BPDU's
received/transmitted on the port.
Discarded Unknown
The number of unknown Spanning Tree BPDU's received (and
discarded) on the port.
Discarded Illegal
The number of illegal Spanning Tree BPDU's received (and
discarded) on the port.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at
regular intervals.
Page 44

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 43
4.1.6 VLAN
4.1.6.1 VLAN Membership Configuration
The VLAN membership configuration for the selected stack switch unit switch can be
monitored and modified here. Up to 64 VLANs are supported. This page allows for adding and
deleting VLANs as well as adding and deleting port members of each VLAN.
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
VLAN ID
The VLAN ID for the entry.
MAC Address
The MAC address for the entry.
Port Members
Checkmarks indicate which ports are members of the entry.
Check or uncheck as needed to modify the entry.
Adding a New Static
Entry
Click
to add a new VLAN ID. An empty
row is added to the table, and the VLAN can be configured as
needed. Legal values for a VLAN ID are 1 through 4095.
The VLAN is enabled on the selected stack switch unit when you
click on "Save". The VLAN is thereafter present on the other stack
switch units, but with no port members.
A VLAN without any port members on any stack unit will be
deleted when you click "Save".
The button can be used to undo the addition of new
VLANs.
Page 45

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 44
Example:
Port-based VLAN Setting
(For ingress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port 1 & VID=50
2. VLAN Port 1 Configuration Î Disable VLAN Aware
3. VLAN Port 1 Configuration Î Mode=specific,ID=50
Page 46

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 45
(For egress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port 2 & VID=50
2. VLAN Port 2 Configuration Î don't care VLAN Aware
3. VLAN Port 2 Configuration Î Mode=specific,ID=50
(any packet can enter egress port )
802.1Q Access port Setting
(For ingress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port & VID=50
Page 47

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 46
2. VLAN Port Configuration Î Enable VLAN Aware
1. VLAN Port Configuration Î Mode=specific,ID=50
(For egress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port & VID=50
2. VLAN Port Configuration Î Disable VLAN Aware
3. VLAN Port Configuration Î Mode=specific,ID=50
Page 48

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 47
(untagged & tag=50 packet can enter egress port )
802.1Q Trunk port setting (multi-tag)
(For ingress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port & VID=11,22,33
2. VLAN Port Configuration Î Enable VLAN Aware
Page 49

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 48
3. VLAN Port Configuration Î Mode=specific,ID=11
(when entering packet is untagged frame, added tag = 11;
when entering the tagged frame, only VID = 11,22,33 three kinds of packets can
pass)
(For egress port)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port, VID=11,22,33
2. VLAN Port Configuration Î Enable VLAN Aware
Page 50

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 49
3. VLAN Port Configuration Î Mode=none
(egress port can receive tag=11,22,33 packet
In addition ,ony tag=11packet can enter egress port )
QinQ VLAN Setting
ingress Port 1------------------->egress Port 2
Page 51

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 50
(For ingress port-----Port 1)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port 1、2、3 & VID=50
2. VLAN Port Configuration-->Disable Port 1 VLAN Aware
3. VLAN Port Configuration-->Port 1 Mode=specific,ID=50
(For egress port ----Port 2)
1. VLAN Membership Configuration setting port & VID=50
Page 52

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 51
2. VLAN Port Configuration-->Enable Port 2、3 VLAN Aware.
3. VLAN Port Configuration-->Mode=none
(only tag=50 packet can enter egress port )
4.1.6.2 Private VLAN
The Private VLAN membership configurations for the switch can be monitored and modified
here. Private VLANs can be added or deleted here. Port members of each Private VLAN can
be added or removed here. Private VLANs are based on the source port mask, and there are
no connections to VLANs. This means that VLAN IDs and Private VLAN IDs can be identical.
A port must be a member of both a VLAN and a Private VLAN to be able to forward packets.
By default, all ports are VLAN unaware and members of VLAN 1 and Private VLAN 1.
A VLAN unaware port can only be a member of one VLAN, but it can be a member of multiple
Private VLANs.
Page 53

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 52
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Private VLAN ID
Indicates the ID of this particular private VLAN.
MAC Address
The MAC address for the entry.
Port Members
A row of check boxes for each port is displayed for each private
VLAN ID. To include a port in a Private VLAN, check the box. To
remove or exclude the port from the Private VLAN, make sure the
box is unchecked. By default, no ports are members, and all
boxes are unchecked.
Adding a New Static
Entry
Click
to add a new private
VLAN ID. An empty row is added to the table, and the private
VLAN can be configured as needed. The allowed range for a
private VLAN ID is the same as the switch port number range.
Any values outside this range are not accepted, and a warning
message appears. Click "OK" to discard the incorrect entry, or
click "Cancel" to return to the editing and make a correction.
The Private VLAN is enabled when you click "Save".
The
button can be used to undo the addition of new
Private VLANs.
Label Description
Port Members
A check box is provid ed for each port of a private VLAN.
When checked, port isolation is enabled for that port.
When unchecked, port isolation is disabled for that port.
By default, port isolation is disabled for all ports.
Page 54

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 53
4.1.7 SNMP
4.1.7.1 SNMP-System
Label Description
Mode
Indicates the SNMP mode operation. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP mode operation.
Disabled: Disable SNMP mode operation.
Version
Indicates the SNMP supported version. Possible versions are:
SNMP v1: Set SNMP supported version 1.
SNMP v2c: Set SNMP supported version 2c.
SNMP v3: Set SNMP supported version 3.
Read Community
Indicates the community read access string to permit access to
SNMP agent. The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
The field only suits to SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. SNMPv3 is using
USM for authentication and privacy and the community string will
associated with SNMPv3 communities table
Write Community
Indicates the community write access string to permit access to
SNMP agent. The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
The field only suits to SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. SNMPv3 is using
USM for authentication and privacy and the community string will
associated with SNMPv3 communities table.
Engine ID
Indicates the SNMPv3 engine ID. The string must contain an even
number between 10 and 64 hexadecimal digits, but all-zeros and
all-'F's are not allowed. Change of the Engine ID will clear all original
local users.
Page 55

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 54
Label Description
Trap Mode
Indicates the SNMP trap mode operation. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP trap mode operation.
Disabled: Disable SNMP trap mode operation.
Trap Version
Indicates the SNMP trap supported version. Possible versions are:
SNMP v1: Set SNMP trap supported version 1.
SNMP v2c: Set SNMP trap supported version 2c.
SNMP v3: Set SNMP trap supported version 3.
Trap Community
Indicates the community access string when send SNMP trap packet.
The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Trap Destination
Address
Indicates the SNMP trap destination address.
Trap Destination IPv6 Address
Trap Destination
IPv6 Address
Provide the trap destination IPv6 address of this switch. IPv6 address
is in 128-bit records represented as eight fields of up to four
hexadecimal digits with a colon separates each field (:). For exampl e,
'fe80:215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7'. The symbol '::' is a special syntax that can
be used as a shorthand way of representing multiple 16-bit groups of
contiguous zeros; but it can only appear once. It also used a
following legally IPv4 address. For example, '::192.1.2.34'.
Trap
Authentication
Failure
Indicates the SNMP entity is permitted to generate authentication
failure traps. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP trap authentication failure.
Disabled: Disable SNMP trap authentication failure.
Trap Link-up and
Link-down
Indicates the SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation.
Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation.
Page 56

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 55
Disabled: Disable SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation.
Trap Inform Mode
Indicates the SNMP trap inform mode operation. Possible modes
are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP trap inform mode operation.
Disabled: Disable SNMP trap inform mode operation.
Trap Inform
Timeout(seconds)
Indicates the SNMP trap inform timeout. The allowed range is 0 to
2147.
Trap Inform Retry
Times
Indicates the SNMP trap inform retry times. The allowed range is 0 to
255.
Trap Probe
Security Engine ID
Indicates the SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of operatio n.
Possible values are:
Enabled: Enable SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of
operation.
Disabled: Disable SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of
operation.
Trap Security
Engine ID
Indicates the SNMP trap security engine ID. SNMPv3 sends traps
and informs using USM for authentication and privacy. A unique
engine ID for these traps and informs is needed. When "Trap Probe
Security Engine ID" is enabled, the ID will be probed automatically.
Otherwise, the ID specified in this field is used. The string must
contain an even number between 10 and 64 hexadecimal digits, but
all-zeros and all-'F's are not allowed.
Trap Security
Name
Indicates the SNMP trap security name. SNMPv3 traps and informs
using USM for authentication and privacy. A unique security name is
needed when traps and informs are enabled.
4.1.7.2 SNMP-Communities
Configure SNMPv3 communities table on this page. The entry index key is Community.
Page 57

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 56
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Community
Indicates the community access string to permit access to SNMPv3
agent. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is
the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Source IP
Indicates the SNMP access source address.
Source Mask
Indicates the SNMP access source address mask.
4.1.7.3 SNMP-Users
Configure SNMPv3 users table on this page. The entry index keys are Engine ID and User
Name.
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Engine ID
An octet string identifying the engine ID that this entry should belong
to. The string must contain an even number between 10 and 64
hexadecimal digits, but all-zeros and all-'F's are not allowed. The
SNMPv3 architecture uses the User-based Security Model (USM) for
message security and the View-based A ccess Control Model (VACM)
for access control. For the USM entry, the usmUserEngineID and
usmUserName are the entry's keys. In a simple agent,
usmUserEngineID is always that agent's own snmpEngineID value.
The value can also take the value of the snmpEngineID of a remote
SNMP engine with which this user can communicate. In othe words,
if user engine ID equal system engine ID then it is local user;
otherwize it's remote user.
User Name
A string identifying the user name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Page 58

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 57
Security Level
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possi ble
security models are:
NoAuth, NoPriv: None authentication and none privacy.
Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and none privacy.
Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exists.
That means must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
Authentication
Protocol
Indicates the authentication protocol that this entry should belong to.
Possible authentication protocols are:
None: None authentication protocol.
MD5: An optional flag to indicate that this user using MD5
authentication protocol.
SHA: An optional flag to indicate that this user using SHA
authentication protocol.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exists.
That means must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
Authentication
Password
A string identifying the authentication pass phrase. For MD5
authentication protocol, the allowed string length is 8 to 32. For SHA
authentication protocol, the allowed string length is 8 to 40. The
allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Privacy Protocol
Indicates the privacy protocol that this entry should belong to.
Possible privacy protocols are:
None: None privacy protocol.
DES: An optional flag to indicate that this user using DES
authentication protocol.
Privacy Password
A string identif ying the privacy p ass phrase. The allo wed string length
is 8 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33 to
126.
4.1.7.4 SNMP-Groups
Configure SNMPv3 groups table on this pag e. The entry index keys are Security Model and
Security Name.
Page 59

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 58
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Security Model
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possi ble
security models are:
v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
Security Name
A string identifying the security name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Group Name
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
4.1.7.5 SNMP-Views
Configure SNMPv3 views table on this page. The entry index keys are View Name and OID
Subtree.
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
View Name
A string identifying the view name that this entry should belong to.
Page 60

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 59
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
View Type
Indicates the view type that this entry should belong to. Possible view
types are:
included: An optional flag to indicate that this view subtree should be
included.
excluded: An optional flag to indicate that this view subtree should be
excluded.
General, if a view entry's view type is 'excluded', it should be exist
another view entry which view type is 'included' and it's OID subtree
overstep the 'excluded' view entry.
OID Subtree
The OID defining the root of the subtree to add to the named view.
The allowed OID length is 1 to 128. The allowed string content is
digital number or asterisk(*).
4.1.7.6 SNMP-Accesses
Configure SNMPv3 accesses table on this page. The entry index keys are Group Name,
Security Model and Security Level.
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Group Name
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the
ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Security Model
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possi ble
security models are:
any: Accepted any security model (v1 / v2c / usm).
v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
Page 61

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 60
Security Level
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possi ble
security models are:
NoAuth, NoPriv: None authentication and none privacy.
Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and none privacy.
Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
Read View Name
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this
request may request the current values. The allowed string length is
1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33 to
126.
Write View Name
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this
request may potentially SET new values. The allowed string length is
1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33 to
126.
4.1.8 Traffic Prioritization
4.1.8.1 Port Configuration
This page allows you to configure QoS settings for each port.
Frames can be classified by 4 different QoS classes: Low, Normal, Medium, and High.
The classification is controlled by a QCL that is assigned to each p ort.
A QCL consists of an ordered list of up to 12 QCEs.
Each QCE can be used to classify certain frames to a specific QoS class.
This classification can be based on parameters such as VLAN ID, UDP/TCP port, IPv4/IPv6
DSCP or Tag Priority.
Frames not matching any of the QCEs are classified to the default QoS class for the port.
Page 62

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 61
Label Description
Port
A check box is provid ed for each port of a private VLAN.
When checked, port isolation is enabled for that port.
When unchecked, port isolation is disabled for that port.
By default, port isolation is disabled for all ports.
Default Class
Configure the default QoS class for the port, that is, the QoS class
for frames not matching any of the QCEs in the QCL.
QCL#
Select which QCL to use for the port.
Tag Priority
Select the default tag priority for this port when adding a Tag to
the untagged frames.
Queuing Mode
Select which Queuing mode for this port.
Queue Weighted
Setting Queue weighted (Low=Normal, Medium=High) if the
"Queuing Mode" is "Weighted".
Page 63

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 62
4.1.8.2 QoS Control List
This page lists the QCEs for a given QCL.
Frames can be classified by 4 different QoS classes: Low, Normal, Medium, and High.
The classification is controlled by a QoS assigned to each port.
A QCL consists of an ordered list of up to 12 QCEs.
Each QCE can be used to classify certain frames to a specific QoS class.
This classification can be based on parameters such as VLAN ID, UDP/TCP port, IPv4/IPv6
DSCP or Tag Priority. Frames not matching any of the QCEs are classified to the default QoS
Class for the port.
Label Description
QCL#
Select a QCL to display a table that lists all the QCEs for that
particular QCL.
QCE Tyep
Specifies which frame field the QCE processes to determine the
QoS class of the frame.
The following QCE types are supported:
Ethernet Type: The Ethernet Type field. If frame is tagged, this is
the Ethernet Type that follows the tag header.
VLAN ID: VLAN ID. Only applicable if the frame is VLAN tagged.
TCP/UDP Port: IPv4 TCP/UDP source/destination port.
DSCP: IPv4 and IPv6 DSCP.
ToS: The 3 precedence bit in the ToS byte of the IPv4/IPv6 header
(also known as DS field).
Tag Priority: User Priority. Only applicable if the frame is VLAN
tagged or priority tagged.
Page 64

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 63
Type Value
Indicates the value according to its QCE type.
Ethernet T y pe: The field shows the Ethernet Typ e value.
VLAN ID: The field shows the VLAN ID.
TCP/UDP Port: The field shows the TCP/UDP port range.
DSCP: The field shows the IPv4/IPv6 DSCP value.
Traffic Class
The QoS class associated with the QCE.
Modification Buttons
You can modify each QCE in the table using the following buttons:
: Inserts a new QCE before the current row .
: Edits the QCE.
: Moves the QCE up the list.
: Moves the QCE down the list.
: Deletes the QCE.
: The lowest plus sign adds a new entry at the bottom of the
list of QCL.
4.1.8.3 Storm Control
Storm control for the switch is configured on this page.
There is a unicast storm rate control, multicast storm rate control, and a broadcast storm rate
control. These only affect flooded frames, i.e. frames with a (VLAN ID, DMAC) pair not present
on the MAC Address table.
The rate is 2^n, where n is equal to or less than 15, or "No Limit". The unit of the rate can be
either pps (packets per second) or kpps (kilopackets per second). The configuration indicates
the permitted packet rate for unicast, multicast, or broadcast traffic across the switch.
(Note: Frames, which are sent to the CPU of the switch are always limited to aproximately 4
kpps. For example, broadcasts in the management V LAN are limited to this rate. The
management VLAN is configured on the IP setup page.)
Label Description
Frame Type
The settings in a particular row apply to the frame type listed here:
unicast, multicast, or broadcast.
Page 65

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 64
Status
Enable or disable the storm control status for the given frame type.
Rate
The rate unit is packet per second (pps), configure the rate as 1, 2, 4,
8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1K, 2K, 4K, 8K, 16K, 32K, 64K, 128K,
256K, 512K, or 1024K.
The 1 kpps is actually 1002.1 pps.
4.1.8.4 Wizard
This handy wizard helps you set up a QCL quickly.
Label Description
Set up
Port Policies
Group ports into several types according to different QCL policies.
Set up Typical
Network
Application Rules
Set up the specific QCL for different typical network application
quality control.
Set up T oS
Precedence
Mapping
Set up the traffic class mapping to the precedence part of ToS (3 bits)
when receiving IPv4/IPv6 packets.
Set up VLAN T ag
Priority Mapping
Set up the traffic class mapping to the User Priority value (3 bits)
when receiving VLAN tagged packets.
Page 66

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 65
4.1.9 IGMP Snooping
4.1.9.1 IGMP Snooping
This page provides IGMP Snooping related configuration.
Label Description
Snooping Enabled Enable the Global IGMP Snooping.
Unregistered
IPMC Flooding
enabled
Enable unregistered IPMC traffic flooding.
VLAN ID
The VLAN ID of the entry.
IGMP Snooping
Enabled
Enable the per-VLAN IGMP Snooping.
IGMP Querier
Enable the IGMP Querier in the VLAN. The Querier will send out if no
Querier received in 255 seconds after IGMP Querier Enabled. Each
Querier's interval is 125 second, and it will stop act as an IGMP
Querier if received any Querier from other devices.
Router Port
Specify which ports act as router ports. A router port is a port on the
Ethernet switch that leads towards the Layer 3 multicast device or
IGMP querier.
If an aggregation member port is selected as a router port, the whole
aggregation will act as a router port.
Fast Leave
Enable the fast leave on the port.
Page 67

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 66
4.1.9.2 IGMP Snooping Status
Label Description
VLAN ID
The VLAN ID of the entry.
Groups
The present IGMP groups. Max. are 128 groups for each VLAN.
Port Members
The ports that are members of the entry.
Querier Status
Show the Querier status is "ACTIVE" or "IDLE".
Querier Receive
The number of Tran smitted Querier.
V1 Reports
Receive
The number of Received V1 Reports.
V2 Reports
Receive
The number of Received V2 Reports.
V3 Reports
Receive
The number of Received V3 Reports.
V2 Leave Receive
The number of Received V2 Leave.
Click to refresh the page immediately.
Clears all Statistics counters.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at regular
intervals.
Page 68

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 67
4.1.10 Security
4.1.10.1 ACL
Configure the ACL parameters (ACE) of each switch port. These parameters will affect frames
received on a port unless the frame matches a specific ACE.
Label Description
Port
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Policy ID
Select the policy to apply to this port. The allowed values are 1
through 8. The default value is 1.
Action
Select whether forwarding is permitted ("Permit") or denied ("Deny").
The default value is "Permit".
Rate Limiter ID
Select which rate limiter to apply to this port. The allowed values are
Disabled or the values 1 through 15. The default value is "Disabled".
Port Copy
Select which port frames are copied to. The allowed values are
Disabled or a specific port number . The default value is "Disabled".
Logging
Specify the logging operation of this port. The allowed values are:
Enabled: Frames received on the port are stored in the System Log.
Disabled: Frames received on the port are not logged.
The default value is "Disabled". Please note that the System Log
memory size and logging rate is limited.
Page 69

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 68
Shutdown
Specify the port shut down operation of this port. The allowed values
are:
Enabled: If a frame is received on the port, the port will be disabled.
Disabled: Port shut down is disabled.
The default value is "Disabled".
Counter
Counts the number of frames that match this ACE.
4.1.10.2 802.1x
This page allows you to configure how an administrator is authenticated when h e logs into the
switchstack via TELNET, SSH or the web pages.
Page 70

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 69
Client Configuration
The table has one row for each Client and a number of columns, which are:
Label Description
Client
The Client for which the configuration below applies.
Authentication
Method
Authentication Method can be set to one of the following values:
none : authentication is disabled and login is not possible.
local : use the local user database on the switch stack for
authentication.
radius : use a remote RADIUS server for authentication.
Fallback
Enable fallback to local authentication by checking this box.
If none of the configured authentication servers are alive, the local
user database is used for authentication.
This is only possible if the Authentication Method is set to
something else than 'none or 'local'.
Click to save changes.
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Common Server Configuration
These setting are common for all of the Authentication Servers.
Label Description
Timeout
The Timeout, which can be set to a number between 3 and 3600
seconds, is the maximum time to wait for a reply from a server.
If the server does not reply within this timeframe, we will consider
it to be dead and continue with the next enabled server (if any).
RADIUS servers are using the UDP protocol, which is unreliable
by design. In order to cope with lost frames, the timeout interval is
divided into 3 subintervals of equal length. If a reply is not
received within the subinterval, the request is transmitted again.
This algorithm causes the RADIUS server to be queried up to 3
times before it is considered to be dead.
Dead Time
The Dead Time, which can be set to a number between 0 and
Page 71

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 70
3600 seconds, is the period during which the switch will not send
new requests to a server that has failed to respond to a previous
request. This will stop the switch from continually trying to contact
a server that it has already determined as dead.
Setting the Dead Time to a value greater than 0 (zero) will enable
this feature, but only if more than one server has been configured.
RADIUS Authentication Server Configuration
The table has one row for each RADIUS Authentication Server and a number of columns,
which are:
Label Description
#
The RADIUS Authentication Server number for which the
configuration below applies.
Enable
Enable the RADIUS Authentication Server by checking this box.
IP Address
Enable fallback to local authentication by checking this box.
If none of the configured authentication servers are alive, the local
user database is used for authentication.
This is only possible if the Authentication Method is set to
something else than 'none or 'local'.
Port The UDP port to use on the RADIUS Authentication Server. If the
port is set to 0 (zero), the default port (1812) is used on the
RADIUS Authentication Server.
Secret
The secret - up to 29 characters long - shared between the
RADIUS Accounting Server and the switchstack.
Page 72

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 71
4.1.11 Warning (only for RGS-7244GC-E model)
4.1.11.1 Fault Alarm
When any selected fault event is happened, the Fault LED in switch panel will light up and the
electric relay will signal at the same time.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Power Failure
Mark the blank of PWR 1 or PWR 2 to monitor.
Port Link Down/Broken
Mark the blank of port 1 to port 8 to monitor.
Apply
Click “Apply” to set the configurations.
Help
Show help file.
4.1.11.2 System Warning
The SYSLOG is a protocol to transmit event notification messages across networks. Please
refer to RFC 3164 - The BSD SYSLOG Protocol
Page 73

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 72
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
IP Address
The remote SYSLOG Server IP address.
Apply
Click “Apply” to set the configurations.
Help
Show help file.
4.1.12 Monitor and Diag
4.1.12.1 MAC Table
The MAC Address Table is configured on this page. Set timeouts for entries in the dynamic
MAC Table and configure the stati c MAC table here.
Aging Configuration
By default, dynamic entries are removed from the MAC after 300 seconds. This removal is also
called aging.
Configure aging time by entering a value here in seconds; for example, Age
time
seconds.
The allowed range is 10 to 1000000 seconds.
Disable the automatic aging of dynamic entries by checking
Disable automatic aging.
Page 74

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 73
MAC Table Learning
If the learning mode for a given port is grayed out, another module is in control of the mode, so
that it cannot be changed by the user. An example of such a module is the MAC-Based
Authentication under 802.1X.
Each port can do learning based upon the following settings:
Label Description
Auto
Learning is done automatically as soon as a frame with unknown
SMAC is received.
Disable
No learning is done.
Secure
Only static MAC entries are learned, all other frames are drop ped.
Note: Make sure that the link used for managing the switch is
added to the Static Mac Table before changing to secure learning
mode, otherwise the management link is lost and can only be
restored by using another non-secure port or by connecting to the
switch via the serial interface.
Static MAC Table Configuration
The static entries in the MAC table are shown in this table. The st atic MAC table can cont ain 64
entries.
The maximum of 64 entries is for the whole stack, and not per switch.
The MAC table is sorted first by VLAN ID and then by MAC address.
Label Description
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
VLAN ID
The VLAN ID for the entry.
MAC Address
The MAC address for the entry.
Port Members
Checkmarks indicate which ports are members of the entry.
Check or uncheck as needed to modify the entry.
Adding a New Static
Entry
Click
to add a new entry to the
static MAC table. Specify the VLAN ID, MAC address, and port
members for the new entry. Click "Save".
Page 75

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 74
4.1.12.2 Mirroring
Configure port Mirroring on this page.
To debug network problems, selected traffic can be copied, or mi rrored, to a mirror port where
a frame analyzer can be attached to analyze the frame flow.
The traffic to be copied to the mirror port is selected as follows:
All frames received on a given port (also known as ingress or source mirroring).
All frames transmitted on a given port (also known as egress or destination mirroring).
Port to mirror also knwon as the mirror port. Frames from ports that have either source (rx) or
destination (tx) mirroring enabled are mirrored to this port. Disabled disables mirroring.
Label Description
Port
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Mode
Select mirror mode.
Rx only : Frames received at this port are mirrored to the mirror port.
Frames transmitted are not mirrored.
Tx only :Frames transmitted from this port are mirrored to the mirror
port. Frames received are not mirrored.
Disabled : Neither frames transmitted nor frames received are
mirrored.
Enabled : Frames received and frames transmitted are mirrored to
the mirror port.
Note: For a given port, a frame is only transmitted once. It is
therefore not possible to mirror Tx frames for the mirror port.
Because of this, mode for the selected mirror port is limited to
Disabled or Rx only.
Page 76

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 75
4.1.12.3 System Log Information
The switch system log information is provided here.
Label Description
ID
The ID (>= 1) of the system log entry.
Level
The level of the system log entry. The following level types are
supported:
Info: Information level of the system log.
Warning: Warning level of the system log.
Error: Error level of the system log.
All: All levels.
Time
The time of the system log entry.
Message
The MAC Address of thi s switch.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at regular
intervals.
Updates the system log entries, st arting from the cu rrent entry ID.
Flushes all system log entries.
Updates the system log entries, starting from the first available entry
ID.
Updates the system log entries, ending at the last entry currently
displayed.
Updates the system log entries, starting from the last entry currently
displayed.
Updates the system log entries, ending at the last available entry ID.
Page 77

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 76
4.1.12.4 Detailed Log
The switch system detailed log information is provided here.
Label Description
ID
The ID (>= 1) of the system log entry.
Message
The detailed messages of the system log entry.
Updates the system log entries, st arting from the cu rrent entry ID.
Flushes all system log entries.
Updates the system log entries, starting from the first available entry
ID.
Updates the system log entries, ending at the last entry currently
displayed.
Updates the system log entries, starting from the last entry currently
displayed.
Updates the system log entries, ending at the last available entry ID.
Page 78

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 77
4.1.12.5 T raffic Overview
This page provides an overview of general traffic statistics for all switch ports.
Label Description
Port
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Packets
The number of received and transmitted packets per port.
Bytes
The number of received and transmitted bytes per port.
Errors
The number of frames received in error and the number of
incomplete transmissions per port.
Drops
The number of frames discarded due to ingress or egress
congestion.
Filtered
The number of received frames filtered by the forwarding process.
Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at regular
intervals.
Updates the counters entries, starting from the current entry ID.
Flushes all counters entries.
Page 79

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 78
4.1.12.6 Detailed Statistics
This page provides detailed traf fic st atistics for a sp ecific switch port. Use the p ort select box to
select which switch port details to display.
The displayed counters are the totals for receive and transmit, the size counters for receive
and transmit, and the error counters for receive and transmit.
Detailed Statistics-Receive & Transmit Total
Label Description
Rx and Tx Packets
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) packets.
Rx and Tx Octets
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) bytes.
Includes FCS, but excludes framing bits.
Rx and Tx Unicast
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) unicast
packets.
Rx and Tx
Multicast
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) multicast
packets.
Rx and Tx
Broadcast
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) broadcast
packets.
Rx and Tx Pause
A count of the MAC Cont rol frames received or transmitted on this
port that have an opcode indicating a PAUSE operation.
Rx Drops
The number of frames dropped due to lack of receive buffers or
egress congestion.
Rx
CRC/Alignment
The number of frames received with CRC or alignment errors.
Page 80

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 79
Rx Undersize
The number of short 1 frames received with valid CRC.
Rx Oversize
The number of long 2 frames received with valid CRC.
Rx Fragments
The number of short 1 frames received with invalid CRC.
Rx Jabber
The number of long 2 frames received with invalid CRC.
Rx Filtered
The number of received frames filtered by the forwarding process.
Tx Drops
The number of frames dropped due to output buffer congestion.
Tx Late / Exc.Coll.
The number of frames dropped due to excessive or late collisions.
Short frames are frames that are smaller than 64 bytes.
Long frames are frames that are longer than the configured maximum frame length for this
port.
4.1.12.7 Ping
This page allows you to issue ICMP PING packet s to troubleshoot IP connectivity issues.
After you press
, 5 ICMP packets are transmitted, and the sequence number and
roundtrip time are displayed upon reception of a reply. The page refreshes automatically until
responses to all packets are received, or until a timeout occurs.
PING6 server ::10.10.132.20
64 bytes from ::10.10.132.20: icmp_seq=0, time=0ms
64 bytes from ::10.10.132.20: icmp_seq=1, time=0ms
64 bytes from ::10.10.132.20: icmp_seq=2, time=0ms
64 bytes from ::10.10.132.20: icmp_seq=3, time=0ms
64 bytes from ::10.10.132.20: icmp_seq=4, time=0ms
Sent 5 packets, received 5 OK, 0 bad
You can configure the following properties of the issued ICMP packets:
Page 81

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 80
Label Description
IP Address
The destination IP Address.
Ping Size
The payload size of the ICMP packet. Values range from 8 bytes
to 1400 bytes.
4.1.12.8 V eriPHY
This page is used for running the VeriPHY Cable Diagnostics.
Press to run the diagnostics. This will take approximately 5 seconds. If all ports are
selected, this can take approximately 15 seconds. When completed, the page refreshes
automatically, and you can view the cable diagnostics results in the cable status table. Note
that VeriPHY is only accurate for cables of length 7 - 140 meters.
10 and 100 Mbps ports will be linked down while runni ng VeriPHY. Therefore, running VeriPHY
on a 10 or 100 Mbps management port will cause the switch to stop responding until VeriPHY
is complete.
Page 82

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 81
Label Description
Port
The port where you are requesting VeriPHY Cable Diagnostics.
Cable Status
Port: Port number.
Pair: The status of the cable pair.
Length: The length (in meters) of the cable pair.
4.1.13 System Reboot
You can reset the stack switch on this page. After reset, the system will boot normally as if you
had powered-on the devices.
Label Description
Click to reboot device.
Click to return to the Port State page without rebooting.
Page 83

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 82
4.1.14 Factory Defaults
You can reset the configuration of the stack switch on this page. Only the IP configuration is
retained.
Label Description
Click to reset the configuration to Factory Defaults.
Click to return to the Port State page without resetting the
configuration
Page 84

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 83
Command Line Interface Management
5.1 About CLI Management
Besides WEB-base management, RGS-7244GP(-E) also support CLI management. You
can use console or telnet to management switch by CLI.
CLI Management by RS-232 Serial Console (115200, 8, none, 1, none)
Before Configuring by RS-232 serial console, use an DB9-M to DB9-F cable to connect the
Switches’ RS-232 Console port to your PC’s COM port.
Follow the steps below to access the console via RS-232 serial cable.
Step 1
From the Windows desktop, click on Start -> Programs -> Accessories ->
Communications -> Hyper Terminal
Page 85

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 84
Step 2 Input a name for new connection
Step 3
Select to use COM port number
Page 86

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 85
Step 4 The COM port properties setting, 115200 for Bits per second, 8 for Data bits, None
for Parity, 1 for Stop bits and none for Flow control.
Step 5
The Console login screen will appear. Use the keyboard to enter the Username
and Password (The same with the password for Web Browser), then press “Enter”.
Page 87

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 86
CLI Management by Telnet
Users can use “TELNET” to configure the switches.
The default values are as below:
IP Address: 192.168.10.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.10.254
User Name: root
Password: root
Follow the steps below to access the console via Telnet.
Step 1
Telnet to the IP address of the switch from the Windows “Run“ command (or from
the MS-DOS prompt) as below.
Step 2
The Login screen will appear. Use the keyboard to enter the Username and
Password (The same with the password for Web Browser ), and then press “Enter”
Page 88

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 87
Commander Groups
System
Configuration [all] [<port_list>]
Reboot
Restore Default [keep_ip]
Contact [<contact>]
Name [<name>]
Location [<location>]
Description [<description>]
Password <password>
Username [<username>]
Timezone [<offset>]
System>
Log [<log_id>] [all | info | warning | error] [clear]
Syslog
Syslog> ServerConfiguration [<ip_addr>]
IP
IP> Configuration
Page 89

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 88
DHCP [enable | disable]
Setup [<ip_addr>] [<ip_mask>] [<ip_router>] [<vid>]
Ping <ip_addr_string> [<ping_length>]
SNTP [<ip_addr_string>]
Auth
Configuration
Timeout [<timeout>]
Deadtime [<dead_time>]
RADIUS [<server_index>] [enable | disable] [<ip_addr_string>] [<secret>]
[<server_port>]
ACCT_RADIUS [<server_index>] [enable | disable] [<ip_addr_string>]
[<secret>] [<server_port>]
Client [console | telnet | ssh | web] [none | local | radius] [enable | disable]
Auth>
Statistics [<server_index>]
Port
Configuration [<port_list>]
State [<port_li st>] [enable | disable]
Mode [<port_list>] [10hdx | 10fdx | 100hdx | 100fdx | 1000fdx | auto]
Flow Control [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
MaxFrame [<port_list>] [<max_frame>]
Power [<port_list>] [enable | disable | actiphy | dynamic]
Excessive [<port_list>] [discard | restart]
Statistics [<port_list>] [<command>]
Port>
VeriPHY [<port_list>]
Aggr
Configuration
Add <port_list> [<aggr_id>]
Delete <aggr_id>
Lookup [<aggr_id>]
Aggr>
Mode [smac | dmac | ip | port] [enable | disable]
Page 90

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 89
LACP
Configuration [<port_list>]
Mode [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Key [<port_list>] [<key>]
Role [<port_list>] [active | passive]
Status [<port_list>]
LACP>
Statistics [<port_list>] [clear]
STP
Configuration
Version [<stp_version>]
Non-certified release, v
Txhold [<holdcount>]lt 15:15:15, Dec 6 2007
MaxAge [<max_age>]
FwdDelay [<delay>]
bpduFilter [enable | disable]
bpduGuard [enable | disable]
recovery [<timeout>]
CName [<config-name>] [<integer>]
Status [<msti>] [<port_list>]
Msti Priority [<msti>] [<priority>]
Msti Map [<msti>] [clear]
Msti Add <m sti> <vid>
Port Configuration [<port_list>]
Port Mode [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port Edge [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port AutoEdge [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port P2P [<port_list>] [enable | disable | auto]
Port RestrictedRole [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port RestrictedTcn [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port bpduGuard [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Port Statistics [<port_list>]
Port Mcheck [<port_list>]
Msti Port Configuration [<msti>] [<port_list>]
STP>
Msti Port Cost [<msti>] [<port_list>] [<path_cost>]
Page 91

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 90
Msti Port Priority [<msti>] [<port_list>] [<priority>]
Dot1x
Configuration [<port_list>]
Mode [enable | disable]
State [<port_list>] [macbased | auto | authorized | unauthorized]
Authenticate [<port_list>] [now]
Reauthentication [enable | disable]
Period [<reauth_period>]
Timeout [<eapol_timeout>]
Statistics [<port_list>] [clear | eapol | radius]
Clients [<port_list>] [all | <client_cnt>]
Agetime [<age_time>]
Dot1x>
Holdtime [<hold_time>]
IGMP
Configuration [<port_list>]
Mode [enable | disable]
State [<vid>] [enabl e | disable]
Querier [<vid>] [enable | disable]
Fastleave [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Router [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Flooding [enable | disable]
Groups [<vid>]
IGMP>
Status [<vid>]
LLDP
Configuration [<port_list>]
Mode [<port_list>] [enable | disable | rx | tx]
Optional_TLV [<port_list>][port_descr | sys_name | sys_descr | sys_capa |
mgmt_addr] [enable | disable]
Interval [<interval>]
Hold [<hold>]
LLDP>
Delay [<delay>]
Page 92

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 91
Reinit [<reinit>]
Info [<port_list>]
Statistics [<port_list>] [clear]
MAC
Configuration [<port_list>]
Add <mac_addr> <port_list> [<vid>]
Delete <mac_addr> [<vid>]
Lookup <mac_addr> [<vid>]
Agetime [<age_time>]
Learning [<port_list>] [auto | disable | secure]
Dump [<mac_max>] [<mac_addr>] [<vid>]
Statistics [<port_list>]
MAC>
Flush
Page 93

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 92
VLAN
Configuration [<port_list>]
Aware [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
PVID [<port_list>] [<vid> | none]
FrameType [<port_list>] [all | tagged]
Add <vid> [<port_list>]
Delete <vid>
VLAN>
Lookup [<vid>]
PVLAN
Configuration [<port_list>]
Add <pvlan_id> [<port_list>]
Delete <pvlan_id>
Lookup [<pvlan_id>]
PVLAN>
Isolate [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
QOS
Configuration [<port_list>]
Classes [<class>]
Default [<port_list>] [<class>]
Tagprio [<port_list>] [<tag_prio>]
QCL Port [<port_list>] [<qcl_id>]
QCL Add [<qcl_id>] [<qce_id>] [<qce_id_next>]
(etype <etype>) |
(vid <vid>) |
(port <udp_tcp_port>) |
(dscp <dscp>) |
(tos <tos_list>) |
(tag_prio <tag_prio_list>)
<class>
QCL Delete <qcl_id> <qce_id>
QCL Lookup [<qcl_id>] [<qce_id>]
Mode [<port_list>] [strict | weighted]
Weight [<port_list>] [<class>] [<weight>]
Rate Limiter [<port_list>] [enable | disable] [<bit_rate>]
QoS>
Shaper [<port_list>] [enable | disable] [<bit_rate>]
Page 94

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 93
Storm Unicast [enable | disable] [<packet_rate>]
Storm Multicast [enable | disable] [<packet_rate>]
Storm Broadcast [enable | disable] [<packet_rate>]
ACL
Configuration [<port_list>]
Action [<port_list>] [permit | deny] [<rate_limiter>] [<port_copy>]
[<logging>] [<shutdown>]
Policy [<port_list>] [<policy>]
Rate [<rate_limiter_list>] [<packet_rate>]
Add [<ace_id>] [<ace_id_next>] [switch | (port <port>) | (policy <policy>)]
[<vid>] [<tag_prio>] [<dmac_type>]
[(etype [<etype>] [<smac>] [<dmac>]) |
(arp [<sip>] [<dip>] [<smac>] [<arp_opcode>] [<arp_flags>]) |
(ip [<sip>] [<dip>] [<protocol>] [<ip_flags>]) |
(icmp [<sip>] [<dip>] [<icmp_type>] [<icmp_code>] [<ip_flags>]) |
(udp [<sip>] [<dip>] [<sport>] [<dport>] [<ip_flags>]) |
(tcp [<sip>] [<dip>] [<sport>] [<dport>] [<ip_flags>] [<tcp_flags>])]
[permit | deny] [<rate_limiter>] [<port_copy>] [<logging>] [<shutdown>]
Delete <ace_id>
Lookup [<ace_id>]
ACL>
Clear
Mirror
Configuration [<port_list>]
Port [<port> | disable]
Mirror>
Mode [<port_list>] [enable | disable | rx | tx]
Config
Save <ip_server> <file_name>
Config>
Load <ip_server> <file_name> [check]
Page 95

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 94
SNMP
Trap Inform Retry Times [<retries>]
Trap Probe Security Engine ID [enable | disable]
Trap Security Engine ID [<engineid>]
Trap Security Name [<security_name>]
Engine ID [<engineid>]
Community Add <community> [<ip_addr>] [<ip_mask>]
Community Delete <index>
Community Lookup [<index>]
User Add <engineid> <user_name> [MD5 | SHA] [<auth_p assword>] [DES]
[<priv_password>]
User Delete <index>
User Changekey <engineid> <user_name> <auth_p assword>
[<priv_password>]
User Lookup [<index>]
Group Add <security_m odel> <security_name> <group_name>
Group Delete <index>
Group Lookup [<index>]
View Add <view_name> [included | excluded] <oid_subtree>
View Delete <index>
View Lookup [<index>]
Access Add <group_name> <security_model> <security_level>
[<read_view_name>] [<write_view_name>]
Access Delete <index>
SNMP>
Access Lookup [<index>]
Firmware
Firmware> Load <ip_addr_string> <file_name>
fault
Alarm PortLinkDown [<port_list>] [enable | disable]
Fault>
Alarm PowerFailure [pwr1 | pwr2 | pwr3] [enable | disable]
Page 96

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 95
Technical Specifications
ORing Switch Model RGS-7244GP RGS-7244GP-E
Physical Ports
10/100/1000 Base-T(X) Ports in RJ45
Auto MDI/MDIX
24
1000Base-X SFP Port 4
Technology
Ethernet Standards
IEEE 802.3 for 10Base-T
IEEE 802.3u for 100Base-TX
IEEE 802.3ab for 1000Base-T
IEEE 802.z for 1000Base-X
IEEE 802.3x for Flow control
IEEE 802.3ad for LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol )
IEEE 802.1p for COS (Class of Service)
IEEE 802.1Q for VLAN Tagging
IEEE 802.1D for STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
IEEE 802.1w for RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
IEEE 802.1s for MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol)
IEEE 802.1x for Authentication
IEEE 802.1AB for LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
MAC Table 8K
Priority Queues 4
Processing Store-and-Forward
Switch Properties
Switching latency: 7 us
Switching bandwidth: 56Gbps
Max. Number of Available VLANs: 256
IGMP multicast groups: 128 for each VLAN
Port rate limiting: User Define
Jumbo frame Up to 9K Bytes
Security Features
IP Police security feature
Enable/disable ports, MAC based port security
Port based network access control (802.1x)
VLAN (802.1Q ) to segregate and secure network traffic
Radius centralized password management
SNMPv3 encrypted authentication and access security
Software Features
STP/RSTP/MSTP (IEEE 802.1D/w/s )
Redundant Ring (O-Ring) with recovery time less than 20ms over 250 units
TOS/Diffserv supported
Quality of Service (802.1p) for real-time traffic
VLAN (802.1Q) with VLAN tagging and GVRP supported
IGMP Snooping
IP-based bandwidth management
Application-based QoS management
DOS/DDOS auto prevention
Port configuration, status, statistics, monitoring, security
DHCP Client/Server
Network Redundancy
O-Ring
STP
RSTP
MSTP
RS-232 Serial Console Port RS-232 in DB9 connector with console cabl e. 115200bps, 8, N, 1
LED Indicators
Power Indicator (PWR) Green : Power indicator For AC Green : Power indicator For AC and DC
Power-1 Indicator (PW1) N/A Green : Indicate Power-1 input
Power-2 Indicator (PW2) N/A Green : Indicate Power-2 input
Power-3 Indicator (PW3) N/A Green : Indicate Power-3 input
Page 97

RGS-7244GP(-E) User’s Manual
ORing Industrial Networking Corp 96
System Ready Indicator ( STA) Green : Indicate that the system is ready. The LED is blinking when the system is upgrading firmware
Ring Master Indicator (R.M.) Green : Indicate that the system is operating in O-Ring Master mode
O-Ring Indicator (Ring) Green : Indicate system operated in O-Ring mode Blinking to indicate Ring is broken.
Fault Indicator (Fault) N/A Amber : Indicate unexpected event occurred
Sysem Runnig Indicator (RUN) Green : System operated continuously
Supervisor Login Indicator (RMT) Green : System is accessed remotely
Reset To Default Running Indicator
(DEF)
Green : System reset to default configuration
Ping Command To The Switch
Indicator (Ping)
Green : System is processing “PING” request
10/100/1000Base-T(X) RJ45 Port
Indicator
Left Green for 1000Mbps Link/Act indicator. Amber for 10/100Mbps Link/Act indicator
Right Amber for full-duplex indicator
100/1000Base-X SFP Port Indicator Green for port Link/Act.
Fault contact
Relay N/A Relay output to carry capacity of 1A at 24VDC
Power
Input Power 100 ~ 240VAC with power cord
100~240VAC with power cord, d ual 36 ~ 72VDC power
inputs at 6-pin terminal block
Power Consumption (Typ.) 36 Watts 36 Watts
Overload Current Protection Present
Physical Characteristic
Enclosure 19 inches rack mountable
Dimension (W x D x H) 443.7 (W) x 200 (D) x 44 (H) mm 431 (W) x 342 (D) x 44 (H) mm
Weight (g) 2700g 4250g
Environmental
Storage Temperature -40 to 85oC (-40 to 185oF)
Operating Temperature -40 to 70oC (-40 to 158oF )
Operating Humidity 5% to 95% Non-condensing
Regulatory approvals
EMI FCC Part 15, CISPR (EN55022) class A
EMS
EN61000-4-2 (ESD)
EN61000-4-3 (RS),
EN61000-4-4 (EFT),
EN61000-4-5 (Surge),
EN61000-4-6 (CS),
EN61000-4-8,
EN61000-4-11
Shock IEC60068-2-27
Free Fall IEC60068-2-32
Vibration IEC60068-2-6
Warranty 5 years
 Loading...
Loading...