Page 1

LEO
Astrophysics
Swift
Space-based Gamma-Ray Observatory
FACTS AT A GLANCE
Mission Description
Swift is a NASA Mid-size Explorer (MIDEX) orbiting observatory that detects Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB)
events and “swiftly” slews itself (within tens of seconds) to focus directly on the event with multi-spectral
instruments that provide accurate burst location and other key data for an international science team.
Swift carries three customer-furnished instruments: The Burst Alert Telescope (BAT), the X-Ray
Telescope, (XRT), and the Ultra Violet Optical Telescope (UVOT).
When a GRB is detected and located, the coordinates are downlinked via TDRSS to enable concurrent
observation using ground-based and other space-based assets.
Within the rst 16 months of its 2-year mission Swift precisely located more GRBs than those of all
previous missions combined. At the completion of the scheduled mission in December 2006, the Swift
spacecraft bus had provided a net mission availability of 99.2 percent and the mission was extended.
Swift continues to provide data with a bus net mission availability of nearly 96 percent.
The Swift Mission Operations Center is located at the Penn State University Department of Astronomy
and Astrophysics.
Spacecraft
Orbital designed and manufactured the fully-redundant Swift spacecraft bus for NASA, and served in a
leadership role at the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) during instrument integration, environmental
testing, launch, early orbit check-out, and initial mission operations. Orbital continues to provide
sustaining engineering support to the mission.
• Launched November 20, 2004 on a
Delta 7320-10 from Cape Canaveral
Air Force Station, Florida
• 600 x 600 km @ 20.6° inclination, Low
Earth Orbit mission
• Observatory automatically slews to
point at gamma ray source within
seconds of the onset of the Gamma
Ray Burst (GRB)
• Swift successfully completed its two
year mission in December 2006 and
continues to provide on-orbit GRB data
• Three payload telescopes: Burst Alert,
X-Ray, and UV Optical
• Simple, easily integrated design based
on Orbital's ight-proven LEOStar™-3
modular spacecraft architecture that
reduces assembly and test time
Customers:
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Penn State University
Page 2
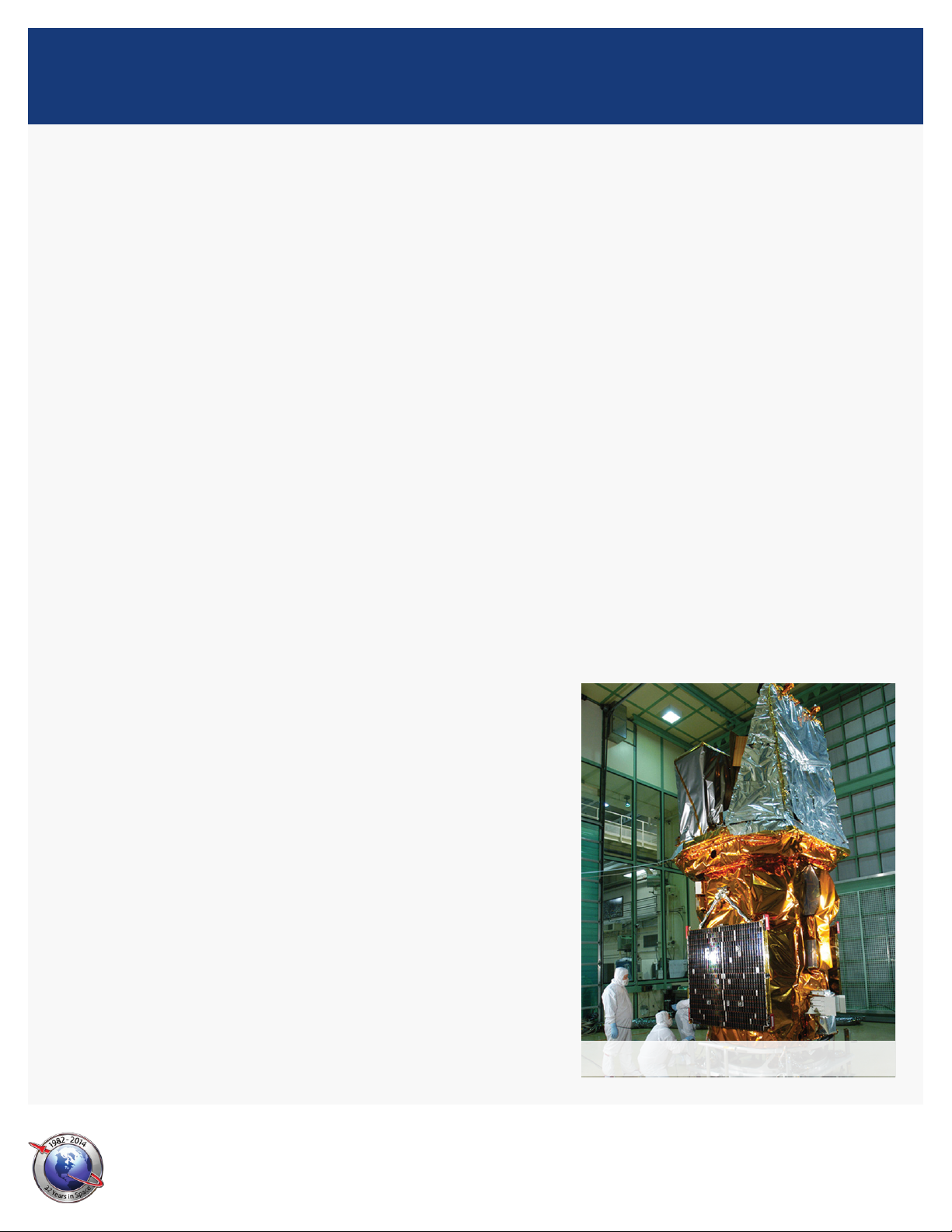
Swift
Specications
Spacecraft
Launch Mass: 1,467 kg (3,234 lb.)
Solar Arrays: Two gimbaled, three panel, triple-junction
GaAs/Ge cells, 2132 W EOL
Orbit: 600 x 600 km @ 20.6
°
inclination
Stabilization: 3-axis, zero momentum bias
Pointing knowledge: 2.2 arcsec P/Y (3s)
Data Storage: 32.0 Gbits
Data Downlink: STDN/TDRSS, to 2.25 Mbps
Propulsion: None
Mission Life: 2 year mission; 3 year design; 5 year goal
Current Status: Operational
Launch
Launch Vehicle: Delta II 7320-10
Launch Site: Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida
Date: November 20, 2004
Instruments
Burst Alert Telescope (BAT)
Initially identies coordinates of GRBs to <3 arcmin causing the spacecraft to
change its attitude (slew) to point the XRT and UVOT towards the GRB source.
Covers 10-150 keV; has large coded-aperture; 2 sr FOV; 400 W; 318 kg (optics).
Developed by NASA GSFC.
X-Ray Telescope (XRT)
X-ray CCD imaging spectrometer that measures position, spectrum, and
brightness of GRBs and afterglows from 0.2-10 keV. Has a dynamic range of more
than seven orders of magnitude in ux; 51 cm aperture (tube diameter); 30 cm
mirror aperture; 3.5 m focal length; 23.6 x 23.6 arcmin FOV; 87 W; 198 kg. Jointly
developed by Penn State University, the University of Leicester, and the Brera
Observatory.
Ultra Violet Optical Telescope (UVOT)
Covers wavelengths from 170 to 650 nm with dynamic range from mB = 24 to
mB = 8; 30 cm aperture; 3.8 m focal length; 17 x 17 arcmin FOV; 125 W. Jointly
developed by Penn State University and the Mullard Space Sciences Laboratory.
Mission Partners
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Procuring Agency: provided program and contract
management, Principal Investigators, and development of
the BAT instrument
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Designed and manufactured spacecraft, supported
payload integration and system test, launch support, and
on-orbit engineering
Penn State University
XRT lead and development, UVOT lead, data-processing
unit development, and on-orbit mission operations
University of Leicester, U.K.
Developed the XRT focal plane array and operates the UK
Swift Data Centre
Mullard Space Science Laboratory, U.K.
Developed the UVOT telescope module
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera (OAB), Italy
Provided the optics for the XRT and jointly operates the
Italian Swift Data Centre with ASI
Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI), Italy
Provided software for the XRT, provides the Malindi
(Kenya) Ground station, and jointly operates the Italian
Swift Data Centre with OAB
Data Availability
Swift data is available to the world via the High Energy Astrophysics Science
Archive Research Center (HEASARC) in the U.S., the U.K. Swift Science Data
Center (UKSSDC) in the U.K., and the Italian Swift Archive Center (ISAC) in Italy.
For more information, visit: http://heasarc.nasa.gov/docs/swift/sdc/
Orbital Sciences Corporation
45101 Warp Drive
©2014 Orbital Sciences Corporation FS005_11_2998
•
Dulles, Virginia 20166
•
www.orbital.com
Swift in nal checkout at KSC. (NASA photo)
 Loading...
Loading...