Page 1
LEO
Heliophysics
SORCE
Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment
FACTS AT A GLANCE
Mission Description
The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) consists of a small satellite carrying four
instruments that measure total solar radiation and solar spectral radiation with current state-of-the-art
accuracy. From its orbit at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere, SORCE provides NASA’s Earth Science
Enterprise (ESE) with precise measurements of solar radiation critical to studies of the Sun and its
effect on the Earth. Data obtained by the SORCE instruments is used to model the Sun’s output
and to explain and predict the effect of the Sun’s radiation on the Earth’s atmosphere and climate. In
addition, the SORCE measurements will address policy-relevant questions from the U.S. Global Change
Research Panel including:
• How does the sun’s output vary and what is the impact on terrestrial climate?
• What aspects of solar variability are inuencing the stratospheric ozone layer?
Orbital Sciences Corporation, under contract to the University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric
and Space Physics (LASP), provided the SORCE spacecraft bus, instrument integration, satellite
(instrument and spacecraft bus) environmental test campaign, and launch operations, and provided
ight operations support to LASP mission operators during the spacecraft’s commissioning phase.
The mission has completed its planned
5 years and has been approved for
extended mission operations. The bus
has met or exceeded all requirements
since launch.
SORCE has been so efciently operated
that the University of Colorado at
Boulder (which manages the mission)
presented a $3 million check to NASA
to reect the cost savings associated
with the mission.
Mission:
• NASA Earth Observing System (EOS)
program
• Merger of previous SOLSTICE/SAVE
and TSIM Solar irradiance studies
Customer:
University of Colorado at Boulder, LASP
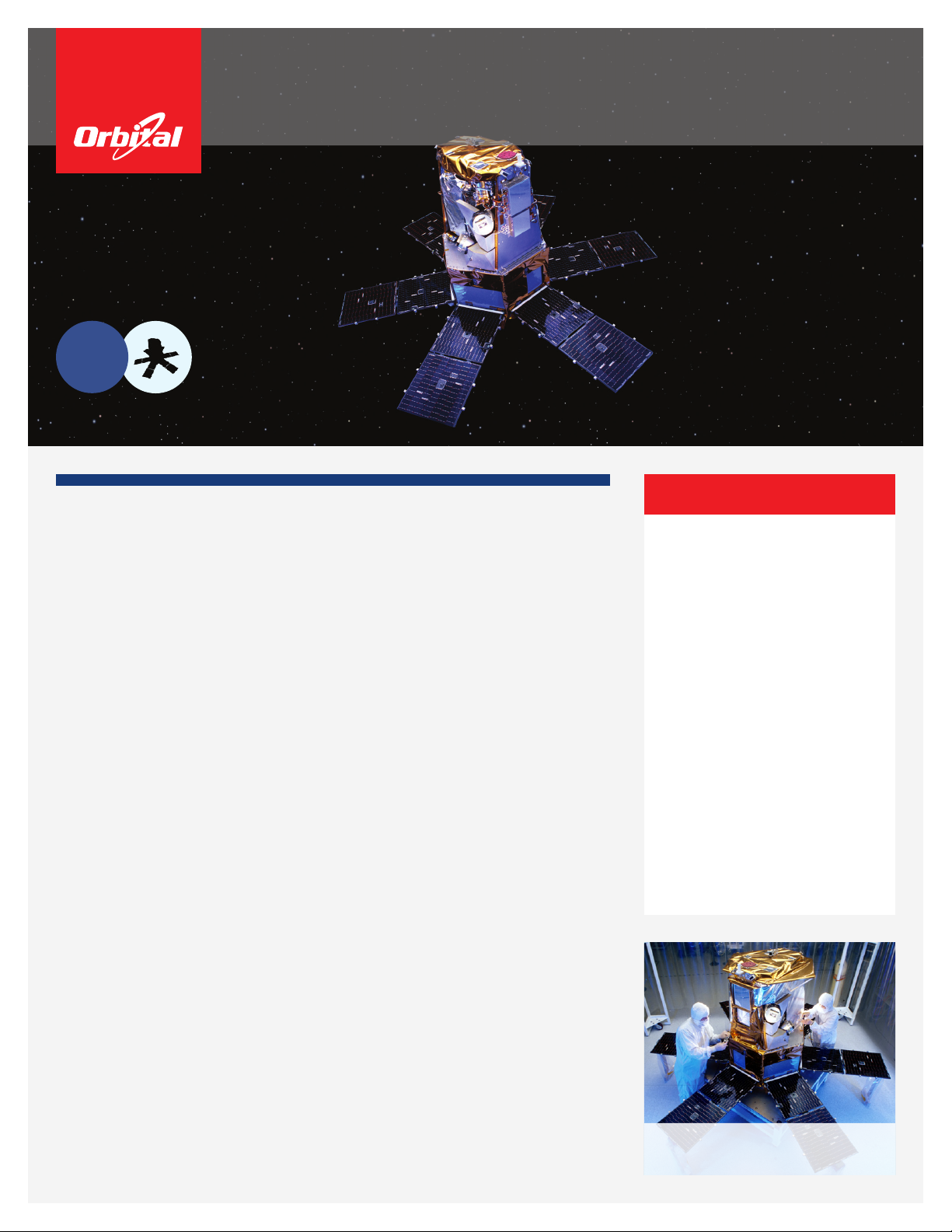
SORCE at Orbital’s Dulles, Virginia satellite
manufacturing facility.
Page 2

SORCE
Specications
Spacecraft
Satellite Mass: 290 kg (639 lb.)
Redundancy: Near fully redundant
Solar Arrays: Fixed GaAs
Power: 348 W
Stabilization: 3-axis, zero momentum; Capability: Slew rate >1
°
/sec;
Knowledge: <36 arcsec; Control: <60 arcsec
Communications: Redundant S-band transceivers
Mission Life: 5 years; 6-year goal
Orbit: 645 km, 40° inclination
Status: Baseline mission complete, currently in extended mission operations
Launch
Launch Vehicle: Pegasus
®
XL
Site: KSC, Cape Canaveral, Florida
Date: January 25, 2003
Instruments
Total Irradiance Monitor (TIM)
Measures the total solar irradiance (TSI) at 100 parts per million accuracy for the duration of the
SORCE mission by monitoring changes in incident sunlight to the Earth’s atmosphere via an ambient
temperature active cavity radiometer.
Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SIM)
Measures the solar spectral irradiance in the 200 to 2,000 nanometer range and contains two
completely independent and identical (mirror-image) spectrometers, which are fully interchangeable.
Solar Stellar Comparison Experiment (SOLSTICE)
Provides precise daily measurements of solar spectral irradiance at ultraviolet wavelengths.
Measurements provide coverage from 115 nanometer to 300 nanometer with a spectral resolution
between 0.1-0.2 nanometer, an absolute accuracy better than 5 percent, and a relative accuracy of
0.5 percent.
Extreme Ultraviolet Photometer System (XPS)
Measures the solar irradiance and consists of a package of twelve silicon XUV photodiodes for
measuring the XUV and EUV irradiance from 1 to 35 nanometers.
Key Mission Partners
University of Colorado at Boulder,
Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Space Physics
Principal Investigator: Dr. Gary J.
Rottman, Associate Director LASP/
CU; Space and ground segment
management, instrument development,
ground data system, mission operations
and science team management
NASA Goddard
Space Flight Center
Project management and science data
archives
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Spacecraft bus development, satellite
integration and test, launch vehicle
integration, ight operations support and
Pegasus launch vehicle
Science Team
Co-Investigators
• Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space
Physics (LASP) University of Colorado
• Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences
(APS) University of Colorado
• Naval Research Laboratory (NRL)
• High Altitude Observatory/National
Center for Atmospheric Research
(HAO/NCAR)
• NASA Ames Research Center
Space Segment
The SORCE space segment consists of the LASP-supplied Instrument
Module and the Orbital-supplied spacecraft bus combined to form the
SORCE satellite. The spacecraft bus provides all the on-orbit support
required for the instrument suite to obtain the mission science data and
transmit it to the ground for distribution and processing. SORCE measures
the Sun’s output with the use of state-of-the-art radiometers, spectrometers,
photodiodes, detectors, and bolometers engineered into the suite of
instruments.
Orbital Sciences Corporation
45101 Warp Drive
©2014 Orbital Sciences Corporation FS004_02_2998
•
Dulles, Virginia 20166
•
www.orbital.com
Ground Segment
The ground segment is comprised of the Mission Operations Center (MOC),
the Science Operations Center (SOC), and the ground antenna site. The
MOC, located at LASP’s facility in Boulder, Colorado, is responsible for
command and control of the satellite and mission science planning. NASA’s
Space/Ground Network, through antenna sites at Wallops Island, Virginia,
provides the communication link to the satellite. LASP provides the SOC
for science data processing and distribution to the NASA-GSFC Distributed
Active Archive Center (DAAC).
 Loading...
Loading...