Page 1

FACT SHEET
Glory
Earth Climate and Atmospheric Research Satellite
Ar tist’s rendering of
the Glory satellite
QUICK FACTS:
The Glory spacecraft incorporated
Orbital’s LEOStar™ bus design,
with deployable solar panels, 3-axis
stabilization, and X-band/S-band RF
communications capabilities.
Glory was to be part of the NASA
"A-Train" constellation of six Earth
science satellites ying in close
proximity.
Mission:
Collect data on the proper ties and
distribution of aerosols in the Earth’s
atmosphere, and on solar irradiance
for the long-term Earth climate record
Customer:
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD
Mission Description
Glory was a low-Earth orbit (LEO) scientic research satellite designed to achieve two major
goals:
• Tocollectdataontheproper tiesanddistributionsofaerosolsintheEarth’satmosphere;and,
• Tocollectdataonsolarirradianceforthelong-termEarthclimaterecord.
The data was designed to enable scientists to draw conclusions about the effects of aerosols on
Ear th’s atmosphere and climate system, and to measure the effects of solar irradiance on Earth.
Glory was to accomplish these objectives by utilizing two separate instruments, the Aerosol
Polarimetry Sensor (APS) and the Total Irradiance Monitor (TIM).
Glory was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB), CA aboard Orbital's Taurus® XL
(3110) launch vehicle. The spacecraf t was lost due to a launch vehicle failure.
Spacecraft
The Glory spacecraft employed Orbital’s LEOStar™ bus design, with deployable solar panels,
3-axis stabilization, and X-band/S-band RF communications capabilities. The structure consisted
of an octagonal aluminum space frame and a hydrazine propulsion module containing enough
fuel for at least 36 months of service.
The Glory Aerosol Polarimetr y Sensor (APS) was
designed to take measurements to distinguish
various species of aerosols
Page 2
Glory
Specifications and Salient Features
Spacecraft
Launch Mass: 528 kg (1,164 lb.)
Redundancy: Redundant
Solar Arrays: Bi-axial articulated, one body-
mounted panel
Stability: 3-axis, stabilized, zero momentum
Propulsion: 45 kg, monopropellant blowdown,
4-4N thrusters
Power: 766 W total from arrays and body-
mounted panel
Mission Life: 3 years (goal of 5 years or more)
Orbit: 705 km, sun-synchronous, circular –
low-Earth orbit (LEO)
Instruments
Aerosol Polarimetry Sensor (APS)
The APS was designed to collect global aerosol data
based on measurements of light reected within the
solar reective spectral region of Earth’s atmosphere.
Since clouds can have a signicant impact on the quality
of these measurements, an onboard cloud camera
would be used to distinguish between clear and cloud
lled scenes. A three-year mission life (ve-year or more
goal) was planned to provide a minimum time period to
obser ve seasonal and regional trends and characterize the
evolution of aerosols during different climate events, such
as El Niño, volcanic eruptions, etc.
Key Mission Partners
Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP)
University of Colorado, Boulder, CO – Instrument Development,
TIM Science
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Dulles, VA; Chandler, AZ; Vandenberg AFB, CA – Spacecraft Bus Development,
Satellite Integration and Testing, Launch Vehicle Integration, Mission
Operations and Control, Taurus Launch Vehicle
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC)
Greenbelt, MD – Project Management, Science Data Archives
GSFC Institute for Space Studies (GISS)
Greenbelt, MD – Instrument Development, APS Science
Total Irradiance Monitor (TIM)
Developed and provided by the University of Colorado’s
Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP), the
TIM instrument was designed to collect high accuracy, high
precision measurements of total solar irradiance (TSI), or
the amount of solar radiation in the Earth’s atmosphere
over a period of time. The TIM is a heritage-design
instrument that was originally own on Orbital’s SORCE
satellite, launched in January 2003.
Launch
Launch Vehicle: Taurus XL
Site: Vandenberg Air Force Base, CA
Date: March 4, 2011
Orbital Sciences Corporation
|
21839 Atlantic Boulevard
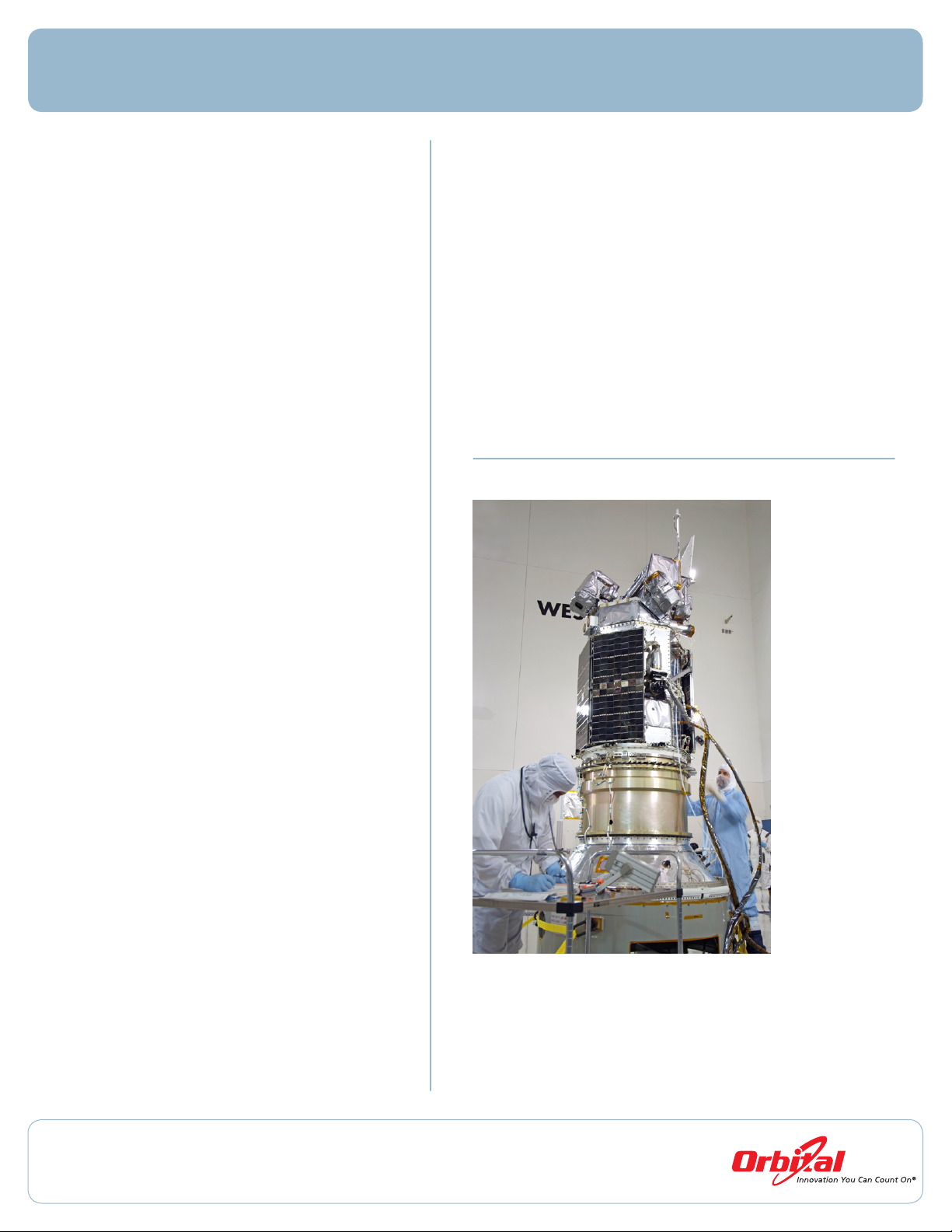
Technicians make nal preparations to the Glory spacecraft at
Vandenberg Air Force Base prior to launch
|
Dulles, Virginia 20166
|
www.orbital.com
©2011 Orbital Sciences Corporation. FS003_05f
 Loading...
Loading...