Page 1
Oracle Web
Application Server™
Installation Guide
Release 3.0.1 for Windows NT
Part No. A54857-03
Enabling the Information Age
Page 2

Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Release 3.0.1
Copyright © Oracle Corporation 1996, 1997, 1998
All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
This software was not developed for use in any nuclear, aviation, mass transit, medical,
or other inherently dangerous applications. It is the customer’s responsibility to take all
appropriate measures to ensure the safe use of such applications if the programs are used
for such purposes.
This software/documentation contains proprietary information of Oracle Corporation; it
is provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and
is also protected by copyright law. Reverse engineering of the software is prohibited.
If this software/documentation is delivered to a U.S. Government Agency of the Department of Defense, then it is delivered with Restricted Rights and the following legend is
applicable:
Restricted Rights Legend Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to
restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of DFARS 252.227-7013, Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software (October 1988).
Oracle Corporation, 600 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065.
If this software/documentation is delivered to a U.S. Government Agency not within the
Department of Defense, then it is delivered with “Restricted Rights”, as defined in FAR
52.227-14, Rights in Data - General, including Alternate III (June 1987).
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. If you find any
problems in the documentation, please report them to us in writing. Oracle Corporation
does not warrant that this document is error-free.
REGISTERED TRADEMARKS of Oracle Corporation:
CASE Designer, CASE Dictionary, CASE Exchange, CASE Workshops, CoAuthor, ConText, Cooperative Develop-
ment Environment, Cooperative Server Technology, Datalogix, Easy*SQL, Express, GEMMS, NLS*WorkBench,
Oracle, Oracle Alert, Oracle Application Object Library, Oracle Book, Oracle Card, Oracle ConText, Oracle Financials, Oracle Glue, Oracle Leasing, Oracle Media Objects, Oracle Media Server, Oracle Power Objects, Oracle Press,
Oracle Procedural Gateway, Oracle Secure Network Services, Oracle Transparent Gateway, OracleWare, Pro*Ada,
Pro*COBOL, Pro*FORTRAN, Pro*Pascal, Pro*PL/I, Pro*Rexx, Secure Network Services, SQL*Connect,
SQL*Forms, SQL*Loader, SQL*Menu, SQL*Module, SQL*Net, SQL*Plus, SQL*Report.
NON-REGISTERED TRADEMARKS of Oracle Corporation:
Advanced Networking Option, Advanced Replication Option, AIM Advantage, Alexandria, Alliance Online, Ap-
plication Agent, Architected Best in Class, Athenia, Better Decisions Made Simple, CASE Generator, Charlotte,
CDM Advantage, Content/2000, Corporate Planner Option, Database Server, DDE Manager, Des40, Designer/
2000, Developer/2000, Discoverer, Dynamic Discovery Option, Easy*Query, Enabling the Information Age, End
User Layer, Gist, Global Accounting Engine, Hyper*SQL, Intelligent Data Manager, Internet Video Server, InterOffice, J/SQL, Live HTML, Media Talk, Network Computing Architecture, Object Marketplace, ODP Pulse, ODP
Techwire, Open/2000, Oracle Access, Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Accounts Receivable, Oracle Advanced Benefits, Oracle Agents, Oracle Application Display Manager, Oracle Applications, Oracle Applications Window Manager, Oracle Assets, Oracle Automotive, Oracle BASIC, Oracle Bills of Material, Oracle Bookbatch, Oracle
BookBuilder, Oracle Browser, Oracle Business Analysis, Oracle Business Manager, Oracle Call Interface, Oracle Capacity, Oracle CASE, Oracle CDD/Administrator, Oracle CDD/Repository, Oracle Clinical, Oracle CODASYL
DBMS, Oracle Cooperative Applications, Oracle Cost Management, Oracle Data Browser, Oracle Data Query, Oracle Departmental Server, Oracle DEVCONNECT, Oracle Developer Programme Pulse, Oracle Digital Library Solutions Framework, Oracle Documents, Oracle EDI Ex*tender, Oracle EDI Gateway, Oracle Energy, Oracle
Engineering, Oracle Enterprise Interface Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager Performance Pack, Oracle Expert, Oracle Expert Option, Oracle Express Administrator, Oracle Express Analyzer, Oracle
Express Server, Oracle Financial Analyzer, Oracle Financial Controller, Oracle Forms, Oracle Forms Generator, Oracle Foundation, Oracle GEMMS, Oracle General Ledger, Oracle Government Financials, Oracle Government General Ledger, Oracle Government Human Resources, Oracle Government Payables, Oracle Government Payroll,
Page 3

Oracle Government Purchasing, Oracle Government Receivables, Oracle Government Revenue Accounting, Oracle Graphical Schema Editor, Oracle Graphics, Oracle Human Resource Management Systems, Oracle Human Resources, Oracle Illustrated, Oracle Illustrated Series, Oracle Imaging, Oracle Incident, Oracle Industries, Oracle
Installer, Oracle InstantSQL, Oracle Integrator, Oracle Internet Commerce, Oracle Internet Server, Oracle InterOffice, Oracle InterOffice Client, Oracle InterOffice Manager, Oracle InterOffice Server, Oracle Inventory, Oracle
Magazine, Oracle Magazine Interactive, Oracle Manufacturing, Oracle Master Scheduling, Oracle Master Scheduling/MRP, Oracle Media Data Store, Oracle Media Library, Oracle Mission Control, Oracle Mobile Agents, Oracle
Module Language, Oracle MRP, Oracle MultiProtocol Interchange, Oracle Names, Oracle NetSolutions, Oracle
Network Manager, Oracle Newsroom Manager, Oracle Object Marketplace, Oracle Objects, Oracle Office, Oracle
Office Directory, Oracle Office Mail, Oracle Office Manager, Oracle Office Scheduler, Oracle Online, Oracle Open
Client Adapter, Oracle Open Gateways, Oracle Open World, Oracle Order Entry, Oracle Parallel Server [or Oracle7
Parallel Server], Oracle Payables, Oracle Payroll, Oracle Personal Time and Expense, Oracle Planner Workbench,
Oracle PowerBrowser, Oracle Procedure Builder, Oracle Process Modeller, Oracle Product Configurator, Oracle
Project Accounting, Oracle Project Billing, Oracle Project Costing, Oracle Projects, Oracle Public Sector, Oracle Purchasing, Oracle Quality, Oracle RALLY, Oracle Rdb7, Oracle Receivables, Oracle Release Management, Oracle Replication Manager, Oracle Replication Services, Oracle Reports, Oracle Reports Generator, Oracle Repository
Administrator, Oracle Revenue Accounting, Oracle RMU, Oracle Sales Analysis, Oracle Sales Analyzer, Oracle
Sales and Compensation, Oracle Sales and Marketing, Oracle Sales Brief, Oracle Sales Compensation, Oracle Server
Generator, Oracle Server Manager, Oracle Smart Video, Oracle Store, Oracle System Sizer, Oracle SQL*Tutor, Oracle SQL/Services, Oracle Supplier Scheduling, Oracle Supply Chain Planning, Oracle SupportNotes, Oracle Systems Designer, Oracle Systems Modeller, Oracle Terminal, Oracle Text Server, Oracle TextServer3, Oracle Toolkit,
Oracle TRACE, Oracle TRACE Collector, Oracle TRACE Option, Oracle Training Administration, Oracle Translation Manager, Oracle Universal Database, Oracle Upstream, Oracle Video Client, Oracle Video Server, Oracle Web
Customers, Oracle Web Employees, Oracle Web Suppliers, Oracle Web Application Server, Oracle Work in Process, Oracle Workflow, Oracle Workgroup Server [or Oracle7 Workgroup Server], Oracle*Mail, Oracle7, Oracle7
Enterprise Backup Utility, Oracle7 Server, Oracle7 Spatial Data Option, Oracle8, Oracle 64 Bit Option, Oracle/2000,
PC Express, Personal Express, Personal Oracle [or Personal Oracle7], Personal Oracle Lite, PJM Advantage, PL/
SQL, Profit, ProREXX, Pro*C, Pro*C/C++, Pro*REXX, Programmer/2000, ProRexx, RDB7, Report Card, Security
Without Compromise, Server/2000, Services/2000, Set-top/2000, Smart Application Client, SmartBox, SmartCharts, SmartClient, SmartHints, SmartLayout, SmartSpring, SmartStandards, SmartTab, SmartTriggers,
SQL*TextRetrieval, SQL*VDM, SupportAssistant, SupportNotes, SupportNews, The Oracle Network Builder,
Trusted Oracle, Trusted Oracle7, Tutor, Video Client, Video Server, Web Request Broker, Workgroup/2000,
World/2000.
SERVICE MARKS of Oracle Corporation:
BAP, Business Alliance Programme, CASE*Method, Cooperative Applications Initiative, International Oracle Us-
er's Group, International Oracle User's Week, IOUG, IOUW, Migration Technology Initiative, OOW, Operations
Readiness Assessment, Oracle Alliance Program, Oracle Bronze, Oracle Business Alliance Programme, Oracle Consulting Services, Oracle Education, Oracle Gold, Oracle Master, Oracle Mercury, Oracle Metals, Oracle Platinum,
Oracle Service, Oracle Silver, Oracle Sterling, Oracle SupportFax, Real Time Support Services, Systems Management Tools Initiative, Warehouse Technology Initiative, Web System Initiative.
All other products or company names are used for identification purposes only, and may be trademarks of their
respective owners.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Preface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Chapter 1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Overview of the Product . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Supported Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 — Advanced Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Products Available for Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Chapter 2 Installation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Supported Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Chapter 3 Installation Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Supported Installation Activities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Pre-installation Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
First-time Web Application Server Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Installing over an Existing Web Application Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Uninstalling Oracle Web Application Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Chapter 4 Post-Installation and Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Starting Web Application Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Listeners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Database Access Descriptors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Web-based Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Page 6

Web Application Server Control Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Configuration for Multi-node Install. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Setting Up a Secure Oracle Web Application Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Chapter 5 Configuration of Third-party HTTP Servers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Configuring Netscape Using the Oracle Installer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Microsoft Internet Information Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Chapter 6 Migrating to Oracle Web Listener . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-1
Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Migrating a Netscape Server to Oracle Web Application Server . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Changes Made During Migration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Access Control and Server Side Includes (parse-html). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Chapter 7 Upgrading from Previous Releases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
Upgrade from WebServer 2.x to Web Application Server 3.0.1 . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Appendix A Starting and Stopping the Listener . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
owsctl Utility Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Appendix B Multi-node Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Processes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Cartridge Instances on Each Node. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Distributing the Authentication Server Processes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
Troubleshooting and Tips. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-5
vi Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 7
Audience
Prerequisites
Preface
This Installation Guide is the primary source of introduction, installation, and
configuration information for Oracle Web Application Server for Windows NT.
This Installation Guide is necessary for installing, configuring, or administering
Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 for Windows NT.
This Installation Guide assumes that you are familiar with:
• Windows NT and have installed and tested it for your PC and network
hardware
• Oracle7 or Oracle8 Server and relational database concepts
Oracle Documentation Set
Online documentation is provided in HTML and Adobe Acrobat Portable
Document Format (PDF). To read the HTML documentation, go to the Web
Page 8

Listener Administrator Home page, and follow the online documentation link
icon. The PDF documentation can be found by clicking the online
documentation icon in the Oracle for Windows NT program group.
Note: To read the PDF online documentation, install the Adobe Acrobat Reader by
double-clicking the file ACROREAD.EXE in the ACROBAT directory on the
product CD.
The Web Application Server 3.0.1 for Windows NT contains the following
documentation:
• Oracle Web Application Server Installation Guide for Windows NT - This
contains installation information for the Oracle Web Application Server
for Windows NT.
• Overview - This provides general information about the Oracle Web
Application Server.
• Using Oracle Web Application Server Cartridges - This describes how to use
the cartridges provided by Oracle for the Web Application Server.
• Developing your own Web Application Server Cartridges - This provides
information for developing your own Web Application Server cartridges.
• Security - This describes how to use the security features of the Web
Application Server. It also describes how to generate certificate requests.
Related Oracle Documentation
Oracle Server Getting Started for Windows NT
Oracle Server Administrator’s Guide
Oracle Server Utilities User’s Guide
Oracle Server Messages and Codes Manual
SQL Language User’s Guide
SQL Language Reference Manual
SQL*Plus User’s Guide
viii Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 9
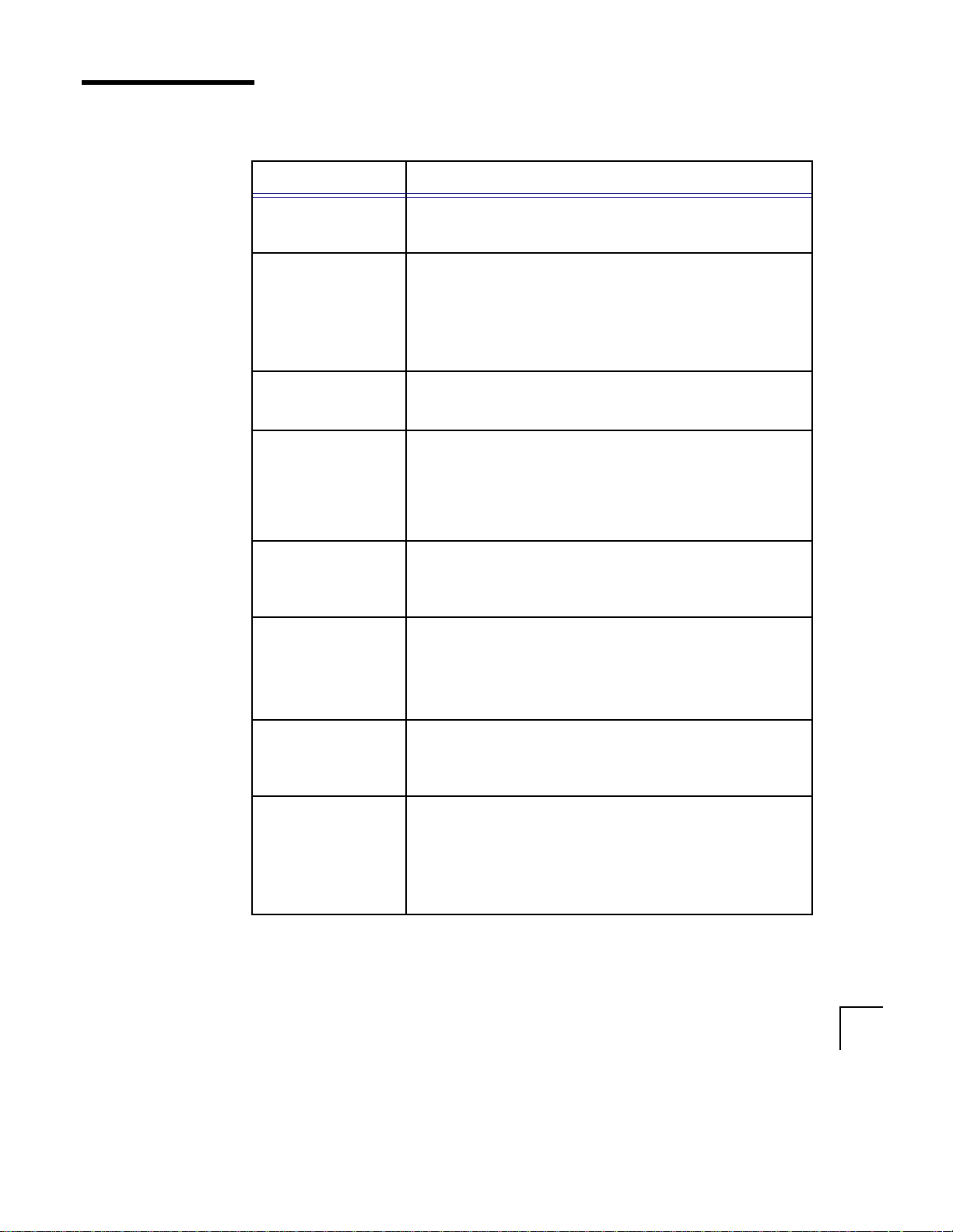
Conventions Used in This Manual
This table lists the typographical conventions used in this manual.
Convention Meaning
Monospace text Indicates text that must be typed exactly as shown.
set echo off
All uppercase
plain
Bold Used for filenames, directories, and utilities such as:
Italics Indicate a value that you must provide. For example, if a
Horizontal
ellipsis...
Vertical bar | Represents an ‘or’ option between several options. You
Indicates command names, SQL reserved words and
keywords as in ALTER DATABASE.
All uppercase plain is also used for directory names and
file names.
ORANT\DATABASE\INITORCL.ORA
owsctl.
command asks you to type filename, you must type the
actual name of the file.
Italics are also used for emphasis in the text and to
indicate the titles of other manuals.
Indicate that parts of the statement or command not
directly related to the example have been omitted.
CHKVAL fieldname value 1 value 2... valueN
must enter only one of the options. Do not enter the
vertical bar. The set of alternative choices is enclosed by
curly braces if one of the items is required, or by square
brackets if the item is an optional alternative.
Curly braces {} Enclose required items. You must choose one of the
alternatives.
..DEFINE { macro1 | macro2 }
Square brackets [ ] Enclose optional items. You can choose one or none of
the alternatives.
cvtcrt termname [outfile]
Square brackets also indicate a function key, for example
[Enter].
Preface ix
Page 10
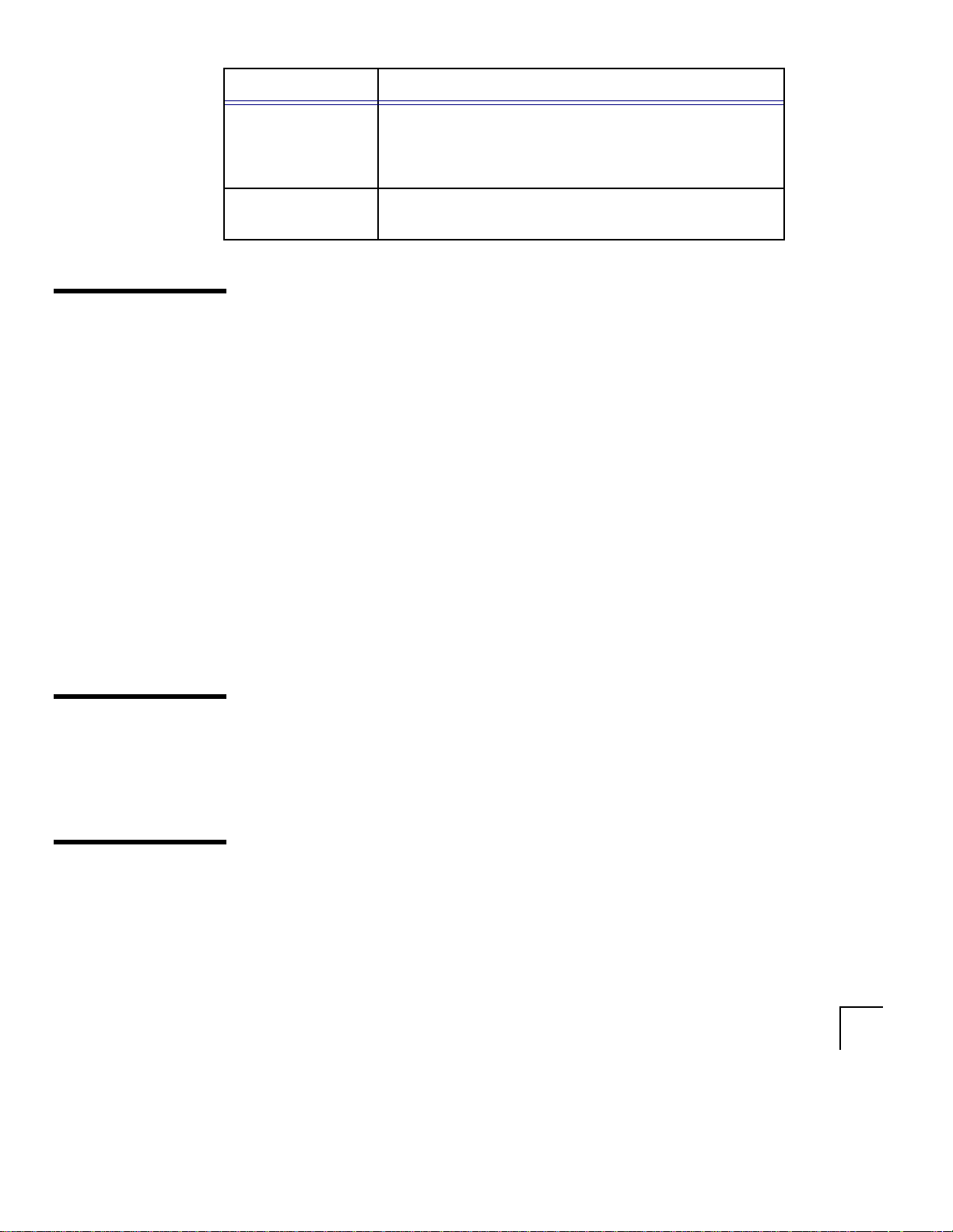
Customer Support
Convention Meaning
C:\> Represents the Windows NT command prompt of the
current hard disk drive. Your prompt may differ and
may, at times, reflect the subdirectory in which you are
working.
Symbols Symbols other than brackets and vertical bars must be
entered in commands exactly as shown.
Oracle Worldwide Technical Support can be reached at the following number
1-650-506-1500 in the United States of America
Be prepared to supply the following information:
• your CSI number (this helps Oracle Corporation track problems recorded
for each customer)
• the release numbers of the Oracle Web Application Server and associated
products
• the operating system name and version number
• details of error numbers and descriptions (write down the exact errors—it
helps Oracle Technical Support track down the problem more quickly)
• a description of the problem
• a description of the changes made to the system
Documentation Sales
To order printed documentation, please call:
1-800-252-0303 in the United States
Your Comments Are Welcome
We value and appreciate your comments as an Oracle user. We encourage you
to send your comments to us at the following address:
x Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 11

Web Application Server Documentation Manager
Oracle Corporation
500 Oracle Parkway
Redwood Shores, CA 94065
Preface xi
Page 12

xii Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 13

C H A P T E R
1 Introduction
Overview of the Product
As the World Wide Web matures, a new generation of Internet and Intranet
business applications is emerging. These new applications will incorporate real
business transactions, data-driven multimedia content, and interactive
information. Database-powered Web applications built on this new platform
will enable corporations to expand their services and customer base as well as
explore lucrative new business endeavors while still leveraging their investment
in existing client-server systems. Such powerful Web applications demand a
new breed of Web platform that combines all the power and reliability of
traditional client-server environments with the flexibility and ease-of-use of the
Internet.
Note: Refer to the online glossary for definitions of terms with which you may not be
Open Architecture
Operating within the framework of Network Computing Architecture, Oracle
Web Application Server 3.0.1 expands dramatically upon the power of standard
Web servers, enabling the development and deployment of full-featured
transaction-based Web sites that are scalable, reliable, and secure.
familiar.
A typical technology infrastructure involves a wide range of operating systems,
languages, networks, applications, Web servers, and databases.
Page 14

Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 operates across a wide range of operating
systems, from PCs to workstations, and through its open cartridge API, supports
a diverse class of languages and applications. Oracle Web Application Server
3.0.1 is the first Web server to support real transactions and it does so using X/
Open DTP standards.
Note: A cartridge is a program, run on the server by the Web Request Broker (WRB),
that interfaces to a Web server (Oracle or otherwise) through the WRB API. A
given cartridge will have a varying number of execution instances called
WRBXs.
Transaction Enable your Netscape or Microsoft Server
The WRB is portable not only across a range of operating systems, but across a
range of Web servers. Oracle bundles its own HTTP listener with Web
Application Server 3.0.1, but this portability means that it can also integrate with
Netscape and Microsoft listeners. This allows application developers to protect
their existing investments as technological infrastructures change.
Scalability
Building a presence on the Web can expand horizons considerably, but only if
your Web site can perform and scale to support the vast Internet audience.
Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 can scale to serve tens of thousands of users.
Through the WRB, Oracle delivers vastly superior performance, dispatching,
and access times, even in the extremely high network traffic environments that
are synonymous with the Internet. Built to a true multi-threaded, multiprocess
architecture, the Web Request Broker offers a superior application environment
over low-level, first generation HTTP APIs.
Reliability
A mission-critical application demands high availability. Oracle Web
Application Server 3.0.1 brings the robustness and reliability of the client-server
world to the Web. Process separation, an object architecture, and independent
cartridge management allow administrators to build, manage, and service their
system on a component basis. Through its independent processing architecture,
the WRB guarantees that third-party server extensions will not affect other parts
of the system security.
1-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 15

Security
With all the potential of real business applications, but no face-to-face contact,
the Web presents new security challenges. Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1
supports full end-to-end security at the client, at every level within the Web
server architecture, and through the firewall to an Oracle database. This
unprecedented degree of granularity supports not only username-password
protection, but also custom security schemes. For even greater protection of vital
data, Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 supports industry standard SSL 3.0.1
encryption, as well as Oracle Advanced Networking Option for secure
communications and transactions.
Supported Features
Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 — Standard Edition
• cartridge-based development platform
• CORBA compliant ORB-based Web Request Broker
• support for fully distributed applications
• listener independence
• language-independent development
• third-party cartridges available through the cartridge solutions network
CORBA-compliant ORB
• Web Request Broker (WRB) services implemented as CORBA-compliant
object services
• supports distributed listener and cartridge architecture
Web Request Broker
• automatic server redirection on maximum connections reached
• safe, scalable architecture
• dynamic load-balancing
• automatic context management
• open API for custom extensions
Introduction 1-3
Page 16

Fully portable WRB API
Java Cartridge
PL/SQL Cartridge
• CORBA-compliant ORB-based Web Request Broker
• unifying API for Netscape, Microsoft, and Oracle HTTP servers
• native Java environment
• auto-generated wrapper classes for PL/SQL
• native access to Oracle
• HTML presentation classes
• National Language Support (NLS)
• support for persistent database connections
• HTML 3.2 support
• 100-percent data encapsulation through stored procedures
• 100-percent portable code
• transparent dispatch to Oracle server
• automatically translates HTML parameters to PL/SQL calls
• HTML 3.2 support
• ICX and transaction support
• enhanced error mapping to relay RDBMS messages to user
• object-oriented design
LiveHTML Cartridge
• enhanced Server Side Include (SSI)
• access to other cartridges through ICX
• HTML files can be target of an HTML form submission
Perl Cartridge
• Perl Version 5 interpreter
• Oracle DBI/DBD extensions
• OraPerl Emulation
1-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 17

VRML Cartridge
Inter-cartridge Exchange
Security
• VRML 2.0 standard support
• platform for building and deploying business applications in VRML
• VRML Data Repository that manages persistent, scalable, and secure
VRML worlds
• Logic Repository ties together database triggers with the VRML event
model
• easy-to-use mechanism for embedding dynamic content, generated by
custom scripts or SQL statements within a VRML scene
• transport-independent, stateless protocol
• mirrors the HTTP request model
• set of APIs to allow a cartridge to address, send, request, and receive a
response from another cartridge
• IP address restriction
• domain name restriction
• basic authentication
• digest authentication
• SSL 3.0 (International version uses 40-bit key)
• client-side digital ID authentication
Built-in Logging and Analysis Tools
• support for clf/xlf system message formats and client-defined statistics
• support for log file cycling/archiving based on size/date
• support for logging into the database
• graphical log analyzer tool
• report generation on accesses, errors, clients, URLs, etc.
Common Gateway Interface
• CGI 1.1 compliant
Introduction 1-5
Page 18

Miscellaneous
Optional Extensibility
• dedicated process per request
• automatic cleanup
• native imagemap support
• multiple imagemap extensions
• configurable DNS resolution
• Common Log Format
• OCI cartridge (Oracle Call Level Interface)
• Rdb cartridge
• Oracle Security Server
• Oracle Internet Commerce Server (cartridge-based solution for electronic
commerce)
• third-party cartridges available through the Cartridge Solutions Network
Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 — Advanced Edition
In addition to the standard features, the advanced edition offers the following:
ODBC Cartridge
• accepts SQL statements
• returns HTML table with formatted results
• optional use of format strings
• callable through ICX from any other cartridge
Transaction support
• supports X/Open DTP model
• supports open standards — SQL, X/Open’s XA and X/Open’s TX
• defines a set of APIs that is modeled on the XA interface
• APIs to start or join a transaction, retrieve transaction information, commit
and rollback a transaction
1-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 19

• transactional support across multiple cartridges
Persistent Storage Services
• APIs for storing and retrieving content or managing content from a SQL
database
• schema attributes include content-type, author, creation date, etc.
• service supports Oracle DBMS, or file system storage
Products Available for Installation
Components
• Oracle Web Listener
• W eb Application Server Cartridges - The PL/SQL, Java, and Live HTML
cartridges are bundled under the label Web Application Server cartridges
and are automatically installed on the single node and primary multinode install.
• Web Request Broker
Additional Cartridges
You may choose to install the following additional cartridges during installation:
• ODBC
• JDBC
• VRML
Introduction 1-7
Page 20

1-8 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 21
C H A P T E R
2 Installation Requirements
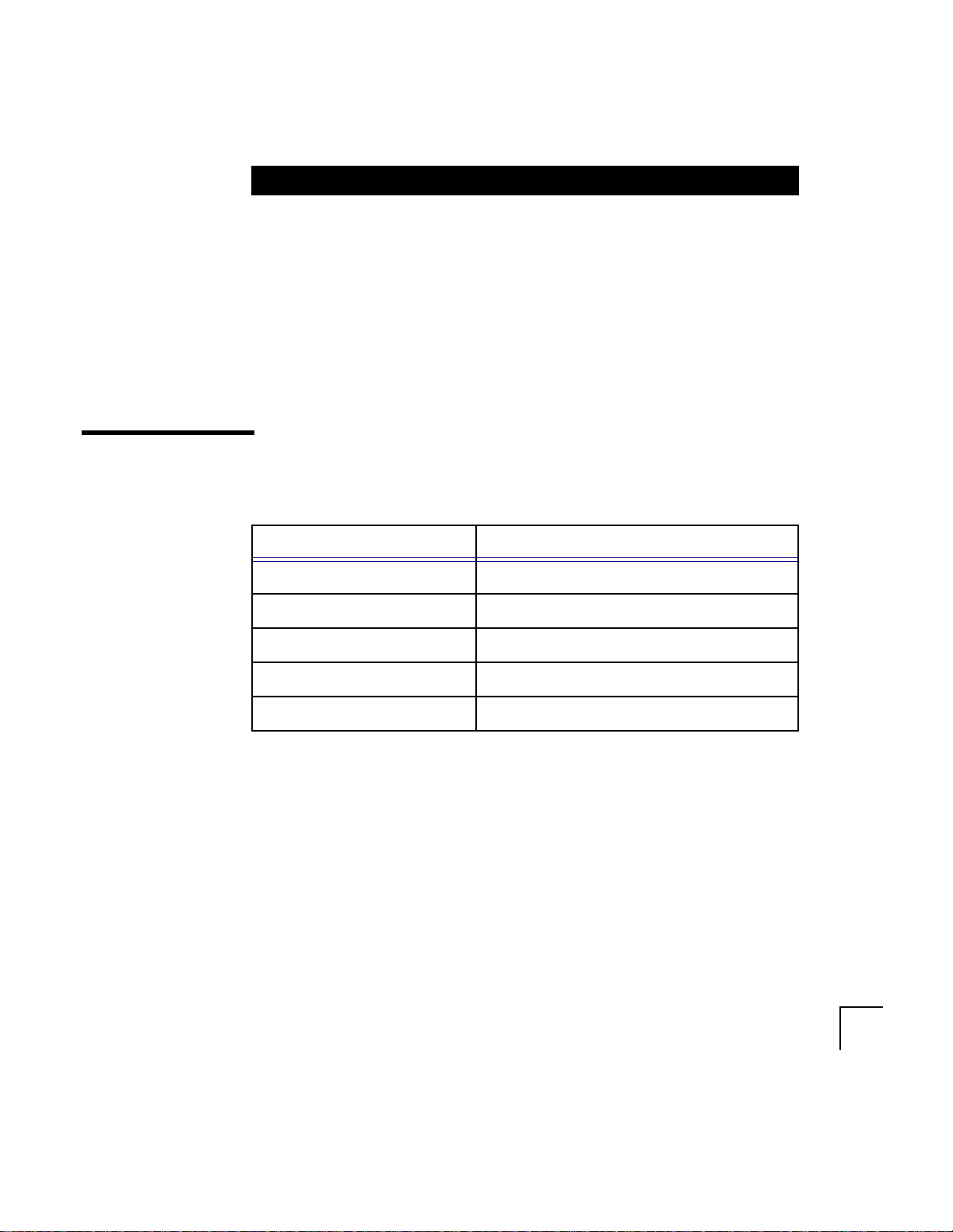
System Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Hardware Item Required
CPU An Intel compatible 486 or higher processor
Memory 64 MB (32 MB for a listener only machine)
Disk Space 150 MB
Swap Space 64 MB
CD-ROM Device RockRidge format
Page 22

Software Requirements
Software Item Version
Operating System Windows NT Server v. 4.0
Web Browser Any browser that supports tables and forms
Listener Oracle 40-bit
Oracle 128-bit
Netscape FastTrack V2.0, V2.0.1
Netscape Enterprise Server V2.0, V2.0.1
Microsoft Internet Information Server V2.0, V3.0
Oracle RDBMS 7.1.6
7.2.2x
7.2.3x
7.3.2.x
7.3.3.x
8.0.3*
8.0.4*
*Note: For cartridges that link with the Oracle client libraries (OCI/PRO*C and
Product Dependencies
JAVA Developer Kit
(JDK)
transactional), the Oracle 7.3 RDBMS client libraries must be used. With these
libraries, the cartridge can connect to supported versions of either Oracle 7.x or
Oracle 8.0.x databases.
If you want to use Oracle Web Application Server with an Oracle database, you
are required to install other products. The following table lists the required
1.0.2
2-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 23

Oracle products and minimum release levels for using the Web Application
Server with an Oracle database.
Products Minimum Release
Oracle Server 7.1.6
PL/SQL 2.1.6
SQL*Net 2.1.6
TCP/IP Protocol Adaptor 2.1.6
Note: The Oracle Server and PL/SQL are not installed automatically with Web
Application Server.
Remote Database Installation
If you wish to access an Oracle database on a remote machine, install the
products listed above on the remote machine.
On your local machine, you must also install SQL*Net and the TCP/IP Protocol
Adapter provided on the Web Application Server CD.
Local Database Installation
If you wish to install Oracle Web Application Server as a stand-alone Internet
server, and you want to access a database on your local machine, you need only
install an Oracle database and PL*SQL.
Note: If you wish to use either Oracle8 or the Multi-Threaded Server option to connect
to a local database, you must install SQL*Net 2.3 and the TCP/IP Protocol
Adaptor. These products are automatically installed with Oracle Web
Application Server 3.0.1.
Supported Configurations
Oracle Web Application Server can be installed as a single-node, where
everything is installed on a single computer; or as a multi-node, which consists
of a primary-node installed on one computer and multiple remote-nodes
installed on different computers.
Oracle Web Application Server is made up of several processes, and you can run
these processes on different machines on the network. You can do this because
Installation Requirements 2-3
Page 24

Single-Node
Multi-Node Primary
the architecture of the Web Application Server is based on CORBA (common
object request broker architecture), which is a standard for distributed objects.
One advantage of distributing the processes on different machines is
performance and scalability. You can handle more requests without using up too
much resources from one machine.
See Appendix C, “Multi-node Configuration” on page 1 for additional
information.
The following are examples of typical Web Application Server installation
configuration choices:
This installation shows components installed on a single-node:
• WRB with Oracle Administrator Listener
• Listener (Oracle, Microsoft, or Netscape)
• Web Application Server cartridges (required)
• Additional cartridges (optional)
This installation shows components installed on the primary-node in a multinode configuration.
• WRB with Oracle Administrator Listener
• Listener (Oracle, Microsoft, or Netscape)
• Web Application Server cartridges (required)
• Additional cartridges (optional)
Multi-Node Remote - Cartridge Only Installation
This installation shows an example of a remote-node in a multi-node
configuration.
• Web Application Server cartridges (required)
• Additional cartridges (optional)
2-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 25

Multi-Node Remote - Listener Only Installation
This installation shows an example of a remote-node in a multi-node
configuration.
• Listener (Oracle, Microsoft, or Netscape)
Multi-Node Remote - Cartridge and Listener Installation
This installation shows an example of a remote-node in a multi-node
configuration.
• Web Application Server cartridges (required)
• Additional cartridges (optional)
• Listener (Oracle, Microsoft, or Netscape)
Installation Requirements 2-5
Page 26

2-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 27

C H A P T E R
3 Installation Procedure
Supported Installation Activities
The following installation activities are described in this chapter:
• Pre-installation Information
• First-time Web Application Server Installation
• Installing over an Existing Web Application Server
• Uninstalling Oracle Web Application Server
You may also use the Installer to configure third-party Web servers for use with
Oracle Web Application Server. See the chapters on configuring third-party
servers and migrating to the Oracle Web Listener for more information on using
third-party servers.
Note to Oracle8 Users: You must follow the pre-installation steps described in the section “Special
Oracle8 User Information” on page 3-2 to be able to successfully install Oracle
Web Application Server Release 3.0.1 with your Oracle8.0.x database.
Installing a Single Node
You may do a fresh, single-node installation of Oracle Web Application Server
Release 3.0.1. Refer to Upgrading from Previous Releases on page 7-1 for
information on upgrading from Version 2.x.
Page 28

Installing a Primary Node in a Multi-node Configuration
The following activities are supported when installing a primary node in a
multi-node setup.
• first time 3.0.1 installation
• 3.0.1 reinstallation (configuration of third-party HTTP products saved
automatically on partial install)
• 3.0.1 reinstallation and configure third-party HTTP products using
complete installation option
• configure if third-party server detected on first time installation
Installing a Remote Node in a Multi-node configuration — Cartridges Only
The following installation activities are supported when installing cartridges
only:
• first time 3.0.1 installation
• partial 3.0.1 reinstallation
• complete 3.0.1 reinstallation
Add Components
You may add components, such as listeners, Oracle Web Application Server
cartridges, or other cartridges to an existing 3.0.1 installation using the Oracle
Installer.
Pre-installation Information
In addition to deciding whether to install a single-node or a multi-node
configuration, you will need the following information. Oracle suggests that you
gather this information before beginning the installation.
Special Oracle8 User Information
An Oracle8 database and Oracle Web Application Server can be installed on the
same machine or different machines. However, doing so requires special
considerations, which are outlined in the following steps:
1. Make sure that the net80 networking component is installed with the
Oracle8 database.
3-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 29

Standard Settings
2. Install Oracle Web Application Server. During installation, make sure that
you check the “Remote Oracle RDBMS Connection (SQL*Net V2.3)”
option in the optional cartridge installation section.
If during installation “Remote Oracle RDBMS Connection” was not
selected, then make sure that SQL*Net V2.3 on the Oracle Web
Application Server CD is installed.
3. Use the SQL*Net Easy Configuration tool to create a database alias for the
database instance.
4. Ensure that TRACE_CLIENT_LEVEL = ON in the sqlnet.ora file.
5. When configuring DADs, you must connect to the Oracle8 database as a
remote database even if the Oracle8 database is on the same machine as
Oracle Web Application Server.
The following settings are common to all installations:
• Language - The default language is English.
• Company Name - A text string identifying the name of your company.
• Oracle Home Directory - The directory for the %ORACLE_HOME%
environment variable. The default is C:\ORANT
• Site Name - The site name for the server. The default is “WEBSITE30”.
• Host Name - This setting is used for the primary node in a multi-node
installation. The default is the local machine name as defined in the
Registry.
• Remote List - This is a list of the remote node names that will form this site
and is needed when installing the primary node in a multi-node
installation.
• UDP Service Port - The UDP service port is used by the ORB and WRB
process. The default is 2649. You can use any number between 1024 and
65535.
• Shared Key (in Hex) - This key is used for encryption in a multi-node
configuration. You will need to enter the same key in all nodes. If you are
setting up a single node, you should still specify a shared key to prevent
unauthorized processes from connecting to your server.
Note: If you plan to add multiple nodes in the future, you should enter a value for the
shared key during installation.
Installation Procedure 3-3
Page 30

Administrator Listener Settings
This information is required for a single node or primary node (in a multi-node)
installation.
• Port Number - Defaults to 8888.
• User Name - Defaults to “admin”.
• User Password - The password you will use for the node.
Web Listener Settings
The following information is needed for the general usage Web listener. You
may use the Oracle listener or a third-party HTTP listener such as Netscape
FastTrack or Microsoft IIS.
• Web Listener Name - Defaults to “www” for the Oracle listener.
• Port Number - Defaults to 80.
Note: The Microsoft IIS listener does not take a listener name. You only need to set the
port number.
First-time Web Application Server Installation
These instructions assume that your Oracle home directory is \ORANT and that
your CD-ROM drive is mapped to the G: drive.
At any time during the installation, you can select the Help button to receive
additional information about the information requested on the installation form.
If you have already installed Oracle products, shut down all instances and stop
all Oracle services currently running before you attempt to install the new
software.
1. Start the Oracle Installer.
When you insert the Oracle Web Application Server CD-ROM into the
CD-ROM drive, the Windows “auto run” feature automatically starts the
Oracle Installer program.
If your CD-ROM drive does not support the “auto run” feature, you will
need to navigate to the following directory using any of the standard
Windows navigation methods.
G:\NT_X86\INSTALL
3-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 31

Then launch the SETUP.EXE program, which starts the Oracle Installer.
2. Choose the language you want to use during installation.
3. Enter the following Oracle Installation Settings:
Company Name
Enter the name of your company.
Oracle Home
Enter the directory for the ORACLE_HOME environment variable. This
will be the directory under which the Web Application Server directory
tree will be placed. ORACLE_HOME can be any alphanumeric value up
to 256 characters.
The default is C:\ORANT.
Warning: Windows NT does not support multiple Oracle Homes. If you already
have an existing Oracle Home, changing it here will disable your currently
installed Oracle products.
If you decide to change the default, you can use the browser folder button
to browse your computer’s directory tree, or type in a new directory
directly into the Oracle Home field.
4. The Installer displays two README files with useful information about
the installation. Use the scrollbar to page through the files. Click OK to
proceed.
5. Select the Oracle Web Application Server Installation activity you wish to
perform. The options are:
• Install a Single Node
• Install a Multi-Node
Install a Single Node
Select a single-node installation if you want to complete a full Oracle Web
Application Server installation on a single machine. If you choose a single-node
installation, the Web Request Broker (WRB), Web Listener, and cartridges are
installed on the same machine.
Install a Multi-Node
Select a multi-node installation if you want to install different components on
separate machines. For example, if you want WRB, Listener, and cartridges
installed on three separate machines, you should select a multi-node installation.
Installation Procedure 3-5
Page 32

If you install Oracle Application Server in a multi-node configuration, you must
install one primary node and at least one remote node.
• Primary multi-node installation - The primary node is where your WRB
and configuration files are installed.
• Remote multi-node installation - Related remote nodes are nodes that
share the same WRB. Remote node installation allows you to specify
which components of the Oracle Web Application Server you want for a
specific node.
If you select remote multi-node installation, you are prompted to choose
from the following components:
- Oracle Web Listener
- Oracle Web Request Broker
- Oracle Web Application Server Cartridge
Remote node installations may be run as listener only, cartridge only, or
listener and cartridge nodes.
Note: If you are performing a multi-node installation, you will need to repeat the
installation procedure for each node. That is, you can only install one node
with each pass through the Oracle Installer. Each pass must be run on the
individual node.
For example, if you want to install a primary node and three remote nodes,
you will need to make four passes through the installer making the
appropriate selection for each node.
Note: For a single- or primary multi-node installation, the bundled cartridges
are automatically installed. The Product Components screen does not
appear. The bundled cartridges are PL/SQL, JAVA, LiveHTML, Perl, and
VRML.
6. Choose the optional components/cartridges that you want to install.
You may choose to install additional components or cartridges that are
packaged outside of the Web Application Server bundle.
Note: You must install a copy of the cartridge on the node where you will
perform administration (single or primary node) in order for the Web
Application Server Manager to be able to register the cartridge. You will
be able to administer the actual remote node cartridge from the primary
node.
The optional components/cartridges are:
3-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 33

• ODBC Cartridge
• Oracle JDBC Drivers (Beta)
• Remote Oracle RDBMS Connection (SQL*Net V 2.3)
• VRML Cartridge
Note: If you use Oracle8, you must install SQL*Net regardless of whether your
Oracle8 installation is local or remote.
7. Site Installation
Enter the following information about the installation site.
Site Name - Defaults to “WEBSITE30”. Oracle Web Application
Server allows you to have multiple server sites running in a single
installation environment. Servers are differentiated by site names,
so you must enter the current Web server site name.
Host Name - Defaults to the local machine name as defined in the
Registry. If this is a multi-node remote installation, you need to
supply the name of the primary node for this remote installation.
Host List - If this is a multi-node primary installation, you need to
supply the list of the remote nodes that will be used in this
configuration. Enter the fully qualified hostnames of all remote
nodes in this site. For example, lindros.us.oracle.com. Hostnames
should be separated by a comma and a space.
UDP Service Port - Defaults to 2649. The UDP service port is used
by the Object Request Broker (ORB) and Web Request Broker (WRB)
processes. If the default is already being used by another process,
provide a different number. You may choose a number between
1024 and 65535. For a remote multi-node, you need to supply the
UDP Service Port of the primary host.
Shared Key (in Hex) - If you use a multi-node configuration, the
shared key feature allows you to encrypt messages between the
primary node and remote nodes for security purposes. This ensures
that only users with proper authority can see the contents of the
messages. To encrypt these messages, you use a shared key that is
known among the different nodes of the Web Application Server
distributed installation. The shared key is used to drive encryption
of all messages sent or received by an ORB program.
Note: If you are installing a multi-node, you should enter the same key value for
each node here.
Installation Procedure 3-7
Page 34

The shared key can vary from 0 to 255 bytes. The string is made up
of only hexadecimal characters; for example, 0-9 and a-f. Larger
shared keys have higher security. Shared key size has minimal
impact on performance.
This field should be left blank if you do not wish to use encryption.
8. Administration Listener Information
This screen only displays on a single- or primary-node installation when
the Web Request Broker is installed. System administrators will use these
settings when they manage the system using the Oracle Web Application
Server Administration Tool.
Enter the following Administration listener settings:
Port Number - Defaults to 8888. You should not change this value.
User Name - Defaults to “admin”. It is recommended that you not
change this value.
Password - Enter your administration password.
Confirm Password - Confirm the password.
9. Listener Choice
This dialog appears when one of the following products is detected and
the Web Listener component has been selected:
• Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 Listener
• Microsoft Internet Information Server
• Netscape FastTrack
• Netscape Enterprise Server
If you use a third-party server from Microsoft or Netscape, you may chose
to configure it during installation. If you wish to use the Oracle Listener
included with Web Application Server, select the choice “Oracle Web
Application Server 3.0.1 Listener”.
10. Oracle Web Listener Configuration
Note: Only one general usage listener can be configured during installation. To
configure additional listeners, use the Web Application Service Manager.
Enter the following Oracle Web Listener Configuration information.
Web Listener Name - Defaults to “www” for the Oracle listener.
This is the application specific name. You can change it to match
your listener name.
3-8 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 35

Note: The Microsoft Internet Information Server does not use a listener name.
Port Number - Defaults to 80. Do not change this number.
Note: For Microsoft, you need to follow the Post-Install steps in Post-Installation
and Administration on page 4-1.
11. Copy Files
This dialog allows you to confirm your configuration parameters. When
you click OK, the installation is performed.
12. If you chose to install SQL*Net V 2.3 products, you are now asked to
specify which SQL*Net V2.3 products you want to install.
a. Select the SQL*Net products you wish to install. Your choices are:
SQL*Net Client Version 2.3.2.1.6A and SQL*Net Protocol Adapters.
b. If you select the SQL*Net Protocol Adapters, you will be asked
which Protocol Adapters you want to install. Choose the Oracle
TCP/IP Adapter for use with Oracle Web Application Server.
Note: Oracle Named Pipes Adapter, Oracle SPX Adapter, and Oracle DECNet
Adapter are available, but are not supported for use with Oracle Web
Application Server Release 3.0.1.
Note: For first-time installations, you must restart your machine for the PATH settings
to take effect.
13. After you restart your system, start the Web Request Broker (WRB) and
listeners. Refer to Starting Web Application Server in Chapter 4 for
instructions on how to start these components.
Installing over an Existing Web Application Server
You may upgrade from Release 3.0 to Release 3.0.1 of Web Application Server.
If the Installer detects an existing Web Application Server installation, it may ask
questions that are slightly different from those in a new installation. Some of the
questions you encounter are:
Reinstall Web Application Server
If the Installer detects an earlier version of Web Application Server, you
have two choices. You may:
- Upgrade - This option installs Web Application Server Release 3.0.1
and preserves your existing Web Application Server configuration
Installation Procedure 3-9
Page 36

information. An upgrade copies library and message files only
based on component choices and skips configuration questions.
- New Install - This option installs Web Application Server Release
3.0.1 and overwrites your existing Web Application Server
configuration information. A new install backs up old files before
overwriting them.
In a new install, the configuration files for the administration
listener and the default listener (for example SVADMIN.CFG,
WRB.APP, and SVWWW.CFG) will be replaced with the default
versions. Your configuration files will be backed up with .BAK
appended to the filenames. The web page for your default web
listener, INDEX.HTML, will also be backed up.
Existing NT registry values used by the Web Application Server will
be replaced; however, these old registry values will not be backed
up.
Note: You may want to use standard Windows NT techniques to back up your
Windows NT registry prior to re-installing Oracle Web Application Server.
Add Components
This option appears in the Installation Activity dialog if the Installer
detects an existing installation of Web Application Server. It also appears
during a Remote multi-node installation. Choose the components that you
want to install on this node. You may choose any number of the following
components:
- Oracle Installer
- Oracle Web Listener - You will be given the opportunity to re-
configure this Listener to run Microsoft or Netscape HTTP server in
a later dialog in this install.
- Oracle Web Request Broker - Installs the Oracle Web Request
Broker.
- Web Application Server Cartridges - Installs the bundled
cartridges. These include PL/SQL, JAVA, LiveHTML, Perl, and
VRML cartridges.
Most other installation prompts are similar to the new installation prompts
outlined in the preceding section.
3-10 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 37

Uninstalling Oracle Web Application Server
To uninstall the Oracle Web Application Server for Windows NT, follow these
steps:
1. Shutdown all the listeners (including the Administration listener,
Netscape, and Microsoft IIS listeners).
Warning: Do not shut down services using the Control Panel Services window. Use the
following command at the DOS prompt:
owsctl stop <ListenerName>
Where <ListenerName> is the name of the listener you want to shut down.
2. Once all services have been terminated, shutdown the Web Request
Broker (WRB) services.
owsctl stop wrb
3. If you are running Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) configured
with the Oracle WRB, use the regedt32 to delete the following entries from
the NT Registry:
- Under
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Service
s\W3SVC\Parameters, remove ndwfis30.dll reference in the
Filter DLLs entry.
4. If you are running the Netscape servers, restore the old configuration to
the obj.conf file:
- For Netscape Enterprise Server, in the %Netscape Server
Home%\https-wrb-configured server name\config directory, move
the obj.conf file and restore the old configuration from obj.conf.sav.
- For Netscape FastTrack Server, in the %Netscape Server
Home%\https-wrb-configured server name\config directory, move
the obj.conf file and restore the old configuration from obj.conf.sav.
5. Run the Oracle Installer:
a. From the Start menu, select Programs > Oracle for Windows NT >
Oracle Installer.
b. Respond to the initial Installer prompts as described in First-time
Web Application Server Installation. After you specify your Oracle
Installation Procedure 3-11
Page 38

Home, the Software Asset Manager is displayed.
Figure 3-1: Software Asset Manager
The right side of the window displays products installed on your system.
Select the products you wish to remove. Use Shift + click, or click and drag
to select multiple items.
c. Click Remove. The Installer will remove the selected products from
your system.
3-12 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 39

C H A P T E R
4 Post-Installation and
Administration
Starting Web Application Server
Start the Web Request Broker (WRB) and the Administration Listener by using
the owsctl command. At the DOS prompt, type:
owsctl start wrb
This starts the WRB. To start the Administration Listener, type the following at
the DOS prompt:
owsctl start admin
To start your listener, type the following at the DOS prompt:
owsctl start <listener_name>
where <listener_name> is the name of your listener. The default listener name
that you may have set up during installation is "www".
Warning: Do not use the Control Panel Services to start or stop Web Application Server
services.
Note: The owsstat utility is now a Windows-based utility and can be found in
NT_X86\CoolStuff\OWSSTAT.
Page 40

To verify that a listener is running, at the DOS prompt, type:
Listeners
The installation process creates two listeners using the values input at install
time, the Administration Listener and the Default Web Listener. If the defaults
are chosen, the values are as listed below. If other values were input, please note
them.
Administration Listener
The Administration Listener is used for Web Application Server configuration
and administration tasks.
owsctl status <listener_name>
• Host Name: hostname.domainname
• Web Listener Name: ADMIN
• Port Number: 8888
• Username: admin
Default Web Listener
One general usage web listener is created by the install. This can be the Oracle
listener or a third-party HTTP listener.
• Web Listener Name: www
• Port Number: 80
Database Access Descriptors
Database Access Descriptors (DADs) are not created automatically by the
installation. DADs are needed only for database access. See the section Web-
based Administration for information on how to set up DADs.
4-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 41

Web-based Administration
Use the Oracle Web-based administration pages to configure and administer
Web Application Server.
1. Use your Web browser to navigate to the Web Application Server
Administrator Welcome Page at:
http://<localhost:port>
where localhost is the hostname of the machine on which Oracle Web
Application Server is installed, and port is the port number you have
assigned to the administration web listener (8888 by default).
A dialog box appears, requesting you to authenticate.
2. Provide your username and password (these settings were determined
during the installation process), and click OK.
Note: The username and password are case sensitive.
The Oracle Web Application Server Administrator Home Page appears.
3. Follow the link to install DADs for database access.
4. Click on Web Application Server Manager icon to begin configuring your
Web Application Server.
Web Application Server Control Utility
The owsctl utility is used to stop, start, and monitor status of the Web Request
Broker, Object Request Broker, and Web listeners. This command is described in
detail in Appendix A.
/
Configuration for Multi-node Install
After installing the files on the primary and remote nodes, you need to configure
the Web Application Server to tell it about the remote nodes.
Tasks to Perform at the Primary Node
On the primary node, you need to:
Post-Installation and Administration 4-3
Page 42

1. Add the remote node names to the wrb.app file on the primary node.
a. In the primary node’s wrb.app file, add the fully qualified name(s)
of any remote hosts. Your entries should be of the form:
<hostname>.<domain>
b. Restart the WRB on the primary node by entering:
owsctl stop wrb
owsctl start wrb
2. Start up the listener processes by typing:
owsctl start <listenerName>
where listenerName specifies the name of the listener.
3. Install the correct components on the remote nodes. During installation,
be sure to specify the same shared key (in Hex) that you specified on the
primary node.
4. Configure the cartridges that you want to run remotely.
Tasks to Perform at the Remote Node
On each of the remote nodes, you need to start up the cartridge factory using this
command:
owsctl start cartridge
The cartridge factory manages the cartridges that run on that machine. It
communicates with the Dispatcher (which runs on the primary node), telling it
about new cartridge instances that are started up and about unoccupied
cartridge instances. The Dispatcher then knows where to direct requests.
Setting Up a Secure Oracle Web Application Server
Refer to the Web Application Server Manager page at:
http://localhost:port/ows-adoc/Intro.html
for instructions on generating a certificate request and obtaining a certificate
from the certifying authority (CA).
4-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 43

C H A P T E R
5 Configuration of Third-
party HTTP Servers
Overview
A feature of Oracle Web Application Server Version 3.0.1 is the HTTP daemon
adapter which enables the Web Request Broker (WRB) to run seamlessly using
third-party HTTP servers (listeners) instead of the Oracle Web Listener shipped
with Oracle Web Application Server. Oracle Web Application Server supports:
• Netscape FastTrack 2.0 and 2.01
• Netscape Enterprise Server 2.0 and 2.01
• Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) 2.0 and 3.0
Configuring Netscape Using the Oracle Installer
Oracle Installer automatically detects Netscape FastTrack and Enterprise HTTP
servers. During installation you can migrate one Netscape HTTP server
automatically. To migrate additional servers, or to perform the migration after
the Oracle Web Application Server installation, use the Oracle migration utility:
http://localhost:port/ows-adoc/migrat.html
Page 44

Oracle Installer automatically creates registry entries under
HKZY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Oracle when you upgrade a Netscape
HTTP server to use the Oracle WRB:
OWS30:<ORANT>\OWS30
OWS_ADdPCFG30:<OWS30>\ADMIN\ADPSPY.CFG
The installation automatically backs up original Netscape FastTrack and
Enterprise HTTP server settings during the migration. The new settings
filename is OBJ.CONF.SAV, and it is saved to the same directory as the original
OBJ.CONF file.
Configuring Using the Oracle Migration Utility
For the Netscape server you want to run with Oracle Web Request Broker:
1. Register the Netscape server with the Oracle Web Application Server
Manager by using the External Listener Registration utility. The Web
Application Server Manager is located at:
http://localhost:port/ows-adoc/Intro.html
2. Using your web browser, navigate to
http://localhost:port/ows-adoc/migrat.html
Authenticate by providing your username and password which were set
during installation.
3. Follow the link to Configure FastTrack/Enterprise Server 2.0 to use Oracle
Web Request Broker 3.0.1.
4. Enter the information for each listener you want to migrate.
• Netscape Server Type
• NS_HOME (Netscape home directory)
• Netscape Server Name
5. Click Configure.
6. Make sure the .APP file mentioned in the \CONFIG\OBJ.CONF file
exists, assuming you are running the Web Request Broker. If it does not
exist, use the sample file SERVAPP.DFL to create the .APP file:
ORANT\OWS30\ADMIN\SVLISTENER.APP.
7. Stop and start your Netscape HTTP server.
After configuration, use the %ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/owsctl to start up the
Netscape server. For example:
5-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 45

owsctl start fnsl
To stop the server:
owsctl stop
To check the status of the server:
owsctl status
Note: If you use owsctl to start the Netscape server, you must register the Netscape
server with the Oracle Web Application Server.
Changes Made During Configuration
The wlmigrat program does the following:
• Configures the Netscape server configuration file obj.conf under:
%NS_HOME%/httpd-server/config (FastTrack Server), or
%NS_HOME%/https-server/config (Enterprise)
• The migration tool links these files with Oracle WRB and saves the original
files into filename.sav.
The init function causes the Netscape server to load the WRB modules and adds
to the obj.conf and magnus.conf files as follows.
Init fn=load-modules shlib=%ORAWEB_HOME%/lib /ndwfns30.dll
funcs=”oracle-adp-init,oracle-adp-auth-trans, \
oracle-adp-service,oracle-adp-addlog,oracle-adp-error, \
oracle-adp-name-trans,oracle-adp-path-check,oracle-adp- \
object-type”
Init fn=oracle-adp-init adapter=%ORAWEB_HOME%/lib/ndwfn30.dll \
cfgfile=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/admin/adpnsapi.cfg” \
serverconf=”%NS-HOME%/httpd-[server]/config/obj.conf” \
servererrfile=”%NS-HOME%/httpd-[server]/logs/errors” \
ORACLE_HOME=”%ORACLE_HOME%” \
ORAWEB_HOME=”%ORAWEB_HOME%” \
userdbdir=”%NS-HOME%/userdb” \
mimetypesfiles=”%NS-HOME%/http-[server]/config/mime.types”
servername
servername
Additional directory mappings for the Netscape server are needed for viewing
Web Application Server release 3.0.1 pages. These are added to the default object
section of the obj.conf file as follows:
NameTrans fn=”oracle-adp-name-trans” \
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/ows-bin \
dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin” name=”cgi”
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/ows-doc \ dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/doc”
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/ows-img \ dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/img”
Configuration of Third-party HTTP Servers 5-3
Page 46

NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/tr-img \
dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/demo/img” \
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/sample/bin \
dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/sample/bin”name=”cgi”
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/sample \
dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/sample” \
NameTrans fn=pfx2dir from=/oracle \ dir=”%ORAWEB_HOME%/doc”
The following functions are added to the obj.conf default object section:
AuthTrans fn=”oracle-adp-auth-trans”
PathCheck fn=”oracle-adp-path-check”
ObjectType fn=”oracle-adp-object-type”
Service fn=”oracle-adp-service”
AddLog fn=”oracle-adp-addlog”
Note: If Netscape FastTrack/Enterprise 2.0 is chosen, ndwfns20.dll and ndwfn20.dll
are used. If FastTrack/Enterprise 2.1 is chosen, ndwfns201.dll and
ndwfn201.dll are used.
The default text/plain type is CMT Commented out (with ##) in the default
object section because it does not interpret the output of Oracle Web Application
Server Java and WRB samples as HTML:
##ObjectType fn=force-type type=text/plain
Microsoft Internet Information Server
For this release you must use the Oracle Installer to migrate Microsoft IIS.
Therefore, Microsoft IIS must be installed before you run the Oracle Web
Application Server installation. Choose to configure Microsoft as the general
usage listener in the Install and proceed with the Post-installation steps listed
below.
Post Installation
To configure the Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) to use the Oracle
Web Request Broker, follow these steps:
1. Install IIS Internet Service Manager (HTML) before performing any web-
based administration for IIS. Install the Internet Service Manager by
running IIS setup.
2. Set authentication to BASIC to allow non-Microsoft Web browsers to
administer IIS. Administration of IIS is protected by the Windows NT
operating system security check. If BASIC authentication is not set, only
5-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 47

browsers that support NTLM (Microsoft Internet Explorer) can configure
the server.
3. Enable anonymous access to IIS.
4. Configure the Web Request Broker for IIS by going to the Web Request
Broker Administration page at
http://localhost:port/ows-doc/Intro.html
where localhost is the name of the host machine and port is the port on
which your administration server is running (default is 8888).
5. Confirm that the following files exist:
• %ORAWEB_HOME%\BIN\NDWFIS30.DLL
• %ORAWEB_HOME%\ADMIN\ADPIIS.CFG
If not, there was a problem with the installation. Try re-installing Oracle
Web Application Server.
6. Restart Microsoft IIS.
Configuration of Third-party HTTP Servers 5-5
Page 48

5-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 49

C H A P T E R
6 Migrating to Oracle Web
Listener
This chapter describes how to migrate from a Netscape server to Oracle Web
Application Server.
Requirements
Before migrating a Netscape FastTrack or Enterprise server to Oracle Web
Application Server, make sure the system meets the following requirements:
• The Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 is installed on the same machine
as the Netscape server. The Oracle Web Application Server
Administration Server must be running.
• Current Netscape server names do not conflict with names in the Oracle
Web Application Server.
• If you want the port number to be re-used by the migrated Oracle Web
Application Server make sure the Netscape server is stopped.
Note: Only the first six characters of the Netscape server name are used as the migrated
Oracle Web Application Server listener name. The migration does not alter any
configuration of the existing Netscape server.
Page 50

Introduction
During Migration of the Netscape server to Oracle Web Application Server, the
Netscape configuration files obj.conf, magnus.conf, and mime.types are read
and parsed, then translated into the Oracle Web Application Server listener and
WRB configuration files such as svserver.cfg and svserver.app. However, some of
the Netscape server features are not converted to the Oracle Web Application
Server listener.
Netscape Server Information
The Netscape FastTrack server has a directory structure similar to the following:
%NS_HOME%/
bin/
docs/
nsapi/
userdb/
httpd-<server1>/
config/
magnus.conf
obj.conf
mime.types
logs/
access
errors
httpd-<server2>/
config/
magnus.conf
obj.conf
mime.types
logs/
access
errors
start-admin*
stop-admin*
For the Netscape Enterprise server, the httpd-server directory is named https-
server. Each Netscape server has three important configuration files associated
with it, which are stored in the /config directory:
• magnus.conf - This file contains information that the listener uses for
initialization. It contains data such as the port the listener should use, the
name of the listener, and the owner of the listener process.
• obj.conf - This file provides the object configuration for the Web
Application Server. When a request is received, the server uses this file to
6-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 51

determine if and how it should service the request. This file contains
information like directory mappings and security restrictions.
• mime.types - This file provides the server with a mapping from file
extensions to the MIME types. Both migration choices (configuring the
Netscape server to use the Oracle WRB, and migrating the Netscape server
to Oracle Web Application Server) use these configuration files
extensively.
Migrating a Netscape Server to Oracle Web Application Server
1. Access the top level of the Migration tool at the following location:
http://hostname.domain:8888/ows-adoc/Migrat.html
2. Select the “MIGRATE the Netscape server to Oracle Web Application
Server 3.0.1” option.
3. Provide the following information:
• Netscape server type (FastTrack, Enterprise)
• Netscape server home directory (full pathname)
• the name of the Netscape server to be migrated
• the port number on which the Netscape server is running
4. Select the “Migrate Netscape server” button. The cgi-bin program
wlmigrat migrates the Netscape server.
The wlmigrat program generates a report showing which Netscape
configurations will not be converted and gives an “ok to migrate” prompt. Select
“ok to migrate” to migrate the Netscape server to the Oracle server.
You must use the Oracle Manager to start up the newly migrated server, after
which you can access your pages as usual. You can access the Oracle Web
Application Server page from:
http://hostname.domain:port/oracle
Notice that port is either the port number of the Netscape server, or the port
number you assigned on the Migration page.
Changes Made During Migration
The migration program does the following:
Migrating to Oracle Web Listener 6-3
Page 52

• reads and parses the Netscape obj.conf, magnus.conf, and mime.types
files and translates the migratable items into the Oracle Web Application
Server configuration
• writes the translated configuration and the default Oracle Web
Application Server configuration to the Oracle Web Listener svserver.cfg
file
• registers the newly migrated Oracle Web Application Server with the
owl.cfg file
Migrating the magnus.conf File
The ServerName directive defines the server host name. For example:
ServerName wchan-sun.us.oracle.com
It is mapped into the Web Application Server svserver.cfg MULTIPORT section.
The Port directive defines the TCP port the server listens to. For example:
Port 7000
It is mapped into the Web Application Server svserver.cfg MULTIPORT section.
The Security directive tells the server whether encryption is enabled. For
example:
Security off
It is mapped into the Web Application Server svserver.cfg MULTIPORT section.
The Security column of the MULTIPORT section will be SSL if encryption is
enabled.
If security is activated, the user must generate a new SSL Key certificate for the
newly migrated Oracle Web Application Server. Refer to the Oracle Web
Administration Server for setting up SSL for Oracle Web Application Server.
The DNS directive specifies whether DNS lookup is performed on the clients
that access the server. For example:
DNS off
It is mapped into the Web Application Serversvserver.cfg [NetInfo] section. DNS
Resolution is always, if activated, otherwise DNS Resolution is never.
6-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 53

Migrating the obj.conf and mime.types Files
Theobj.conffile defines how the server should handle the incoming requests for
documents and programs. An object contains a name or a pattern match which
defines the resources it applies to. For example:
<Object ppath=...>
Directives.
</Object>
Object also contains a series of directives. For example:
Directive fn=function [parameters]
The following directives can be converted:
• Init fn=load-types mime-types=xxx
The value for mime-types= is the file name that contains the MIME type
and ENCODING extension mapping, formatted as follows:
type=application/octet-stream exts=bin,exe
euc=x-gzip exts=gz,gzip,gzzipp
These MIME type and ENCODING extensions are translated into the
svserver.cfg [MIMETypes] and [Encoding] sections as:
[MIMETypes]
application/octet-stream bin exe
[Encoding]
x-gzip gz gzip
Note: Oracle Web Application Server only allows extensions with less than five
characters. Any extensions with more than four characters are not migrated and
are reported after the migration is complete.
• NameTrans fn=”pfx2dir” from=/img dir=/Netscape/img
The value for from= is the virtual path; the value for dir= is the physical
path. This directive is mapped into the svserver.cfg [DirMaps] section as:
[DirMaps]
/Netscape/img/ NR /img/
• NameTrans fn=”pfx2dir” from=”/cgibin” dir=/Netscape \
/cgibin name=cgi
The value for from= is the virtual path and the value for dir= is the
physical path. The name=cgi means this is a cgi-bin directory. This
directive is mapped into the svserver.cfg [DirMaps] section as
Migrating to Oracle Web Listener 6-5
Page 54

[DirMaps]
/Netscape/cgibin/ CR /cgibin/
• NameTrans fn=document-root root=/Netscape/docs
The value of root= is the document root. This directive is mapped into the
svserver.cfg [DirMaps] section as:
[DirMaps]
/Netscape/docs/ NR /
• NameTrans fn=unix-home from=/~subdir=”public_html,home.html”
The value of subdir= is the user directory if the URL specifies ~user. It is
mapped into the svserver.cfg [Server] section as:
[Server]
UserDir = public_html
Note: Oracle Web Application Server allows only one directory to be specified in the
Userdir parameter, while Netscape allows multiple directories to be specified in
a comma-separated list. Only the first directory specified in the list is used by
Oracle Web Application Server.
• ObjectType fn=force-type type=text/html
The value of type= is the default MIME type for the server. It is mapped
into the svserver.cfg [Server] section as:
[Server]
DefaultMIMEType=text/html
• Service fn=imagemap method=(GET|HEAD) type=magnus-internal/
imagemap
The value of type= represents the MIME types used for imagemap. It is
required to look for its corresponding MIME extension from the file listed
in (1) and mapped into svserver.cfg [Server] section as:
[Server]
ImageMap = map
Note: Oracle Web Application Server only allows one extension to be specified in the
imageMap parameter, while Netscape allows multiple extensions for the
imagemap. Only the first extension specified in the list is used by Oracle Web
Application Server.
• Service fn=index-simple method=(GET|HEAD)
type=magnus-internal/directory
The value of fn= can be index-simple or index-common. If either appears,
it is mapped into the svserver.cfg [Server] section as:
6-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 55

[Server]
UseDirIndexing = true
• PathCheck index-names=index.html,home.html fn=find-index
The value of index-names= is the initial file to be searched if a URL does
not specify the file name. It is mapped into the svserver.cfg [Server] section
as:
[Server]
InitialFile = index.html
Note: Oracle Web Application Server only allows one file to be specified in the
InitialFile parameter, while Netscape allows multiple files to be specified in a
comma-separated list. Only the first file specified in the list is used by Oracle
Web Application Server.
Access Control and Server Side Includes (parse-html)
The Netscape server schema for the access control and Server Side Includes (SSI)
is quite different from that of Oracle Web Application Server. Therefore
wlmigrat does not migrate any Netscape access control information or SSI
(parse-html) information to Oracle Web Application Server.
Access Control
Netscape keeps all the user and group information in binary format under
%NS_HOME%/authdb/<dbname>/*
Oracle Web Application Server keeps all user, group and realm information in
the svserver.cfg file in ASCII format.
The Netscape administration tool generates the ACL command, saves it under
%NS_HOME%/httpacl, and uses the ACL in obj.conf to apply the access
control on any files on the server machine. The ACL can be a combination of
user, group, IP address, and hostname.
Oracle Web Application Server applies access control on files that exist in its
virtual directory map. Its access control can be the combination of realms and/
or IP address, or realms and/or hostname.
The user can use Oracle Web Application Server Administration Manager to
group all Netscape user and group information into Oracle Application Server’s
user, group and realms, and apply the access control on the file, based on the
virtual path (but not the physical path).
Migrating to Oracle Web Listener 6-7
Page 56

Server Side Includes (parse-html)
On Netscape, the parse-html option means it will parse the HTML files with any
SSI before sending them to the client. The parse-html option is associated with
the optional opts=no-exec (which prevents the client from executing anything
on the server machine), and can be applied to any files and directories on the
server machines, whether the files and directories appear on its directory
mapping or not. For example:
#
# dirmap
#
...
NameTrans from=”/ows/3.0” fn=”pfx2dir” dir=”/d1/ows/3.0”
...
#
# file with parse-html enabled
#
...
<Object ppath=”/d1/ows/3.0/docs/sstest.html”>
Service fn=”parse-html” method=”(GET|HEAD)” type=”magnusinternal/parsed-html”
</Object>
<Object ppath=”/d1/noway/sstest.html”>
Service fn=”parse-html” opts=no-exec method=”(GET|HEAD)”
type=”magnus-internal/parsed-html”
</Object>
Both /d1/noway/sstest.html and /d1/ows/3.0/docs/sstest.html are parsed before
being sent to the client, although /d1/noway/sstest.html does not appear on the
directory mapping. In addition, accessing /d1/noway/sstest.html does not allow
any exec on the server machine, but accessing /d1/ows21/docs/sstest.html does
allow exec on the server machine.
Oracle Web Application Server only allows the SSI processing of the files under
the directory specified in wrb.app [AppDirs] section with use of SSI. For
example, in wrb.app:
[AppDirs]
/ssi SSI /oracle/ows/3.0/sample/ssi
All files under /oracle/ows/3.0/sample/ssi are processed with the SSI cartridge
before being sent to the client. In addition, the global SSI flag ParseHTMLExtn
must stay TRUE to parse the file with any extension, or you can set the
ExtensionList = html shtml to include the extension of files that must be parsed.
Similarly, the global SSI flag EnableExecTag is global to the whole server and
cannot be associated with any particular files. Therefore, the user can move all
6-8 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 57

parsed-html or SSI files into the Oracle Application Server’s virtual directory to
be processed with SSI. The SSI parameters ParseHTMLExtn, EnableExecTag,
and ExtensionList can be configured as the user requires.
The wlmigrat tool lists all files and directories with the parse-html option set to
on at the end of migration. The user is encouraged to move them into a directory
where they can be processed by the Oracle Web Application Server SSI.
Migrating to Oracle Web Listener 6-9
Page 58

6-10 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 59

C H A P T E R
7 Upgrading from Previous
Releases
Upgrade from WebServer 2.x to Web Application Server 3.0.1
To upgrade from WebServer 2.x to Web Application Server 3.0.1:
1. Install Oracle Web Application Server 3.0.1 on the same machine as Oracle
WebServer 2.x. Make sure you do not use the same listener name and DCD
name as used in WebServer 2.x.
Warning: Windows NT does not support multiple Oracle Homes. If you already have an
Upgrade Tool
existing Oracle Home, changing it during installation of Release 3.0.1 will
disable the Oracle products currently installed on your machine.
2. Reboot your machine.
3. Start the Web Request Broker and the Administration Listener.
4. Launch your Web browser, and navigate to the upgrade page. Detailed
instructions on how to access and use the Upgrade Tool follow.
When you upgrade, use the following files:
• %ORAWEB_HOME%/admdoc/Migrat.html
Page 60

Access the Upgrade Page
Make sure that the Oracle Administration Server 3.0.1 is running.
• %ORAWEB_HOME%/admdoc/OWS2xto30.html
• %ORAWEB_HOME%/admbin/wlupgrade
1. Access the upgrade page from the Web Application Server 3.0.1
Administration Server by entering the following location in your Web
browser:
http://hostname.domain:port/ows-adoc/Migrat.html
You may also access this page by clicking on the following links:
a. Click on the Web Application Server Manager icon, and enter your
username and password as specified during installation.This brings
you to the Web Application Server Administration Home Page.
b. Click on the Oracle Web Application Server icon.
2. Click on the Migration icon.
3. Select the ”Upgrade the Oracle WebServer 2.x to Oracle Web Application
Server 3.0.1” option. The page prompts you to:
• upgrade from 2.0 or 2.1
• enter your ORACLE_HOME
The cgi-bin program, wlupgrade, upgrades the server and does the following:
• Lists the available Oracle WebServer 2.x from the ORACLE_HOME. You
may then choose to upgrade.
Note: The upgrade utility does not list the Oracle WebServer 1.0 available for
upgrade. If you want to upgrade from WebServer 1.0, create a new Oracle
Web Listener 3.0.1.
• Upgrades the Oracle Web PL/SQL Agent DCD in WebServer 1.0 and 2.x,
and registers them in Web Application Server 3.0.1.
Warning: If you are still using Oracle Web PL/SQL Agent 1.0, you will not be able
to access it after you upgrade. Refer to “Upgrade Oracle PL/SQL Agent
1.0” on page 8 to make the application available after upgrade.
• Detects the cartridge, application directory mapping, cartridge section,
and the application protection that might conflict with that defined in the
current Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app file.
7-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 61

• If conflicts are found, it lists the conflicts and prompts you to ‘keep 2.x
parameters’ or ‘use 3.0.1 parameters’. If there is no conflict, you are
prompted with ‘ok to upgrade’.
• Merges the Oracle WebServer 2.xsvserver_name.app information into Web
Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app file.
• Merges the Oracle WebServer 2.x svserver_name.cfg security information
such as user, group, and realms into the wrb.app file.
• Updates the svserver_name.cfg for Web Application Server 3.0.1.
• Upgrades the Oracle Web Application Server svserver.cfg file from Oracle
1.2 format to Oracle 2.1 format.
• Continues to upgrade the next chosen Oracle Web Application Server 2.x
to be upgraded.
Determine a List of Registered WebServer 2.x Listeners
The following sections describe the upgrade tool in detail. The upgrade tool
examines the %ORACLE_HOME%/ows2/admin/owl.cfg file or
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows21/admin/owl.cfg to determine which registered
Oracle WebServer is available for upgrade.
Upgrade Oracle Web PL/SQL Agent DCDs
The upgrade tool upgrades DCDs and merges them into the Web Application
Server 3.0.1 wrb.app file. It shows a list of DCDs that have been successfully
upgraded and a list of DCDs that cannot be upgraded because the names have
already been used by the Web Application Server 3.0.1.
Oracle WebServer 1.0 and 2.x stores the DCD information in the
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows2/admin/owl.cfg, and each entry has the following
information:
Entry Description
owa_service DCD name
owa_user database login
owa_password database user password
oracle_home database ORACLE_HOME
oracle_sid sid if using local database
Upgrading from Previous Releases 7-3
Page 62

Entry Description
owa_connect_string SQL*Net v2 connect string if using remote
database
owa_valid_ports ports allow access to database
owa_log_dir directory that stores database errors
owa_nls_lang database language type
owa_error_page html page that shows errors
There are two built-in DCDs, owa_dba and owa_default_service, in the
owa.cfg. These DCDs are not upgraded because they are created during
installation.
Upgrade and merge the entries into wrb.app. The entries are split into two
entries that are DAD and PL/SQL descriptors.
In Oracle WebServer 2.x owa.cfg, you will find an entry. For example:
#
(
owa_service=DOHC_WEB
(
owa_user=www_dba
)
(
owa_password=manager
)
(
oracle_home=/private/home/wchan/work/ows-home
(
)
owa_connect_string=DOHC
)
(
owa_valid_ports=8818 3368
)
(
owa_log_dir=/private/home/wchan/work/ows-home/ows21/log
(
)
owa_nls_lang=AMERICAN_AMERICA.US7ASCII
The above entry is updated into wrb.app as:
[DAD_DOHC_WEB]
7-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 63

username=www_dba
password=manager
oracle_home=private/home/wchan/work/ows-home
connect_string=DOHC
nls_lang=AMERICAN_AMERICA.US7ASCII
[PLSQL_DOHC_WEB]
owa_valid_ports=8818 3368
owa_log_dir=/private/home/wchan/work/ows-home/log/
owa_dad_name=DOHC_WEB
You can refer to the DCD by using DOHC_WEB.
The following table shows the parameter mappings between WebServer 2.x
DCD, Web Application Server 3.0.1 DAD, and Web Application Server 3.0.1 PL/
SQL.
OWS2.x DCD OWS3.0.1 DAD_xx OWS3.0.1 PL/SQL_xx
owa_service suffix of [DAD_xx] suffix of [PL/SQL_xx]
section name
owa_user username
owa_password password
oracle_home oracle_home
owa_connect_string connect_string
owa_oracle_sid oracle_sid
owa_nls_lang nls_lang
owa_valid_ports owa_valid_ports
owa_log_dir owa_log_dir
owa_error_page owa_error_page
In order to direct the PL/SQL to use the appropriate DAD, the
owa_dad_name=xx parameter is added to the PL/SQL_xx section of the Web
Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app file.
Upgrade the Oracle WebServer 2.x svserver_name.cfg
The upgrade tool updates the svserver_name.cfg file in two steps.
Upgrading from Previous Releases 7-5
Page 64

1. The upgrade tool updates the [DynApps] section to Web Application
Server 3.0.1.
In WebServer 2.0, the section is:
[DynApps]
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows2/lib/libndwll.so ndwlld_DynamicInit
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows2/lib/ndwrd.so sndwrdini_init
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows2/lib/ndwp.so ndwp_dinit
In WebServer 2.1, the section is:
[DynApps]
%ORACLE_HOME%/ows21/lib/ndwfss.so oracle_adp_init
The upgrade tool will update the entry to:
[DynApps]
%ORAWEB_HOME%/lib/libwrl.so oracle_adp_init
2. The upgrade tool updates the svserver_name.cfg from Oracle 1.2 format to
2.1 format.
Merge WebServer 2.x svserver_name.app into Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app
In Web Application Server 3.0.1 there is only one wrb.app file that stores the
cartridge application related information, as opposed to one svserver.app per
listener in Oracle WebServer 2.x.
The upgrade tool does not alter default cartridges such as JAVA, Live HTML,
PL/SQL and HELLO in the Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app file, which
allows you to use the Web Application Server 3.0.1 default cartridges after the
upgrade.
The upgrade tool updates JAVA settings such as CLASSPATH and
LD_LIBRARY_PATH. The JAVA settings CLASSPATH and
LD_LIBRARY_PATH are found in WebServer 2.x svserver.app and are
appended into Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app’s JAVA setting. After this,
the upgrade tool detects conflicts in:
• user-defined cartridges in the [Apps] section of svserver.app
• application directory mapping in the [AppDirs] section of the svserver.app
• cartridge section parameters and application protection in the
[AppsProtection] section of the svserver.app
It also indicates conflicts between the WebServer 2.x svserver.app and Web
Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app by showing the conflicts in table format before
it merges svserver.app into wrb.app.
7-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 65

Conflicts occur when cartridges, application directory mapping, section
parameters, and application protection defined in Web Application Server 3.0.1
wrb.app are already defined in WebServer 2.x svserver.app with different
values. For example:
In WebServer 2.x svserver.app:
[Apps]
..
MYAPP1 /private/oracle/ows21/myapp1/libmyapp1.so myapp1entry
0 100
[AppDirs]
/usr/myapp1 MYAPP1 /private/oracle/ows21/myapp1
[MYAPP1]
MyApp1Param1 = True
MyApp1Param2 = False
In Web Application Server 3.0.1, wrb.app:
[Apps]
...
MYAPP1 /usr/hr/myapp1/Myapp1.so Myentry 0 100
...
[AppDirs]
...
/usr/myapp1 MYAPP1 /private/oracle/ows/3.0/myapp1
[MYAPP1]
MyApp1Param1 = False
Param2 = False
In this case, the MYAPP1 cartridge is defined in WebServer 2.x svserver.app and
Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app; however, they are different cartridges.
The application directory mapping /usr/myapp1 has a conflict in WebServer 2.x
svserver.app and Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app because they have
different physical paths. The cartridge section parameter MyApp1Param1 has a
conflict because it has a different value.
When conflicts occur, the upgrade tool prompts you with two choices:
• keep 2.x parameters
• use 3.0.1 parameters
If you choose to keep the WebServer 2.x parameters, the svserver.app is used to
replace the parameters in Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app.
If you choose to use Web Application Server 3.0.1 parameters, conflicting
parameters are not merged into Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app. In the
Upgrading from Previous Releases 7-7
Page 66

example shown above, the cartridge MYAPP1 is in conflict, thus the definition
for MYAPP1 in WebServer 2.x svserver.app is not merged into Web Application
Server 3.0.1 wrb.app. Its related parameters such as application directory
mapping /usr/myapp1, and the cartridge section [MYAPP1] are not merged into
Web Application Server 3.0.1 wrb.app either. Parameters without conflict are
upgraded with the tool and merged into the Web Application Server 3.0.1
wrb.app file.
In addition, the upgrade tool migrates all the security information from the
chosen Web Listener into the wrb/app file.
Register WebServer 2.x with Web Application Server 3.0.1
After updating the svserver_name.cfg and merging it into Web Application
Server 3.0.1 wrb.app, the upgrade tool registers the WebServer 2.x, which has
been upgraded with Web Application Server 3.0.1. Now you can connect to the
Web Application Server 3.0.1 Administration server and start the listener.
Upgrade Oracle PL/SQL Agent 1.0
If you use the Oracle PL/SQL Agent 1.0, the agent application is accessed
through the cgi-bin program owa under %ORACLE_HOME%/ows/bin. The
DCD information is derived from the virtual path defined in svlsnrcfg file.
For example, the svlsnrcfg file directory mapping is in /private/oracle/ows/bin
CR /ows1.When the URI /ows1/owa/hr.tree is requested, the Web Listener looks
for DCD ows1 information and executes the cgi-bin based PL/SQL agent owa.
Then, owa executes the PL/SQL package hr.tree.
To abandon the use of Oracle PL/SQL Agent 1.0, so you can use the new PL/
SQL cartridge, do the following:
• Comment out the virtual path entry in sv.lsnr.cfg. For example, in the
sv.lsnr.cfg file, comment out the directory mapping entry that uses the cgibased PL/SQL Agent; such as:
/private/oracle/ows/bin CR /ows1
• Add the application virtual path entry to the wrb.app file. Use the WRB
administration page to add the application path into the application
directories section. For example:
/ows1/owa PLSQL /private/oracle/ows/bin
After completing the above steps, the next time the URI /ows1/owa /... is
requested, the cartridge version of PL/SQL agent is used.
7-8 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 67

APPENDIX
A Starting and Stopping the
Listener
owsctl Utility Commands
Theowsctl utility starts, stops, reloads, and displays the status of the Oracle Web
Listener, Oracle Web Status Monitor, WRB, ORB and Cartridge processes. You
can also use it to display the version number of the cartridge.
Syntax
Options
The syntax has the following options:
owsctl [ start | stop | reload | status ] [
owsctl [ start | stop | status ] [-e]
-p process_name
owsctl [ start | stop| status ] -stat [
[-poll<
-action<
start
Starts the process specified by the next argument as follows:
polling period
trigger script
| ncx }
> | -uri <uri> | -timeout <
wrb|cartridge
> ]
listener_name
listener_name
]
|
]
timeout>
|
Page 68

•Iflistener_name is supplied, it starts the named Oracle Web Listener.
• If the Netscape server is registered with Oracle Web Application Server,
owsctl starts up the Netscape server based on the registration information.
• The ORB processes are mnaddrsrv, mnrpcnmsrv, and mnorbsrv. Use
NCX or ncx to run these processes. Make sure you run the NCX processes
before exclusively starting the WRB process.
• If WRB or wrb is supplied, it starts the mnaddrsrv, mnrpcnmsrv,
mnorbsrv, wrbcfg, wrblog, wrbasrv, wrbahsrv, wrbroker, wrbvpm, and
wrbfac processes. Always start the WRB process before starting an Oracle
Web Listener or Netscape server on any machine.
• If CARTRIDGE or cartridge is supplied, the Cartridge process such as
wrbfac is started.
stop
Stops the process specified by the next argument as follows:
•Iflistener_name is supplied, it stops the named Oracle Web Listener.
• If the Netscape server is registered with Oracle Web Application Server,
owsctl stops the Netscape server based on the registration information.
• Uses NCX or ncx to stop the NCX (ORB) processes, such as mnaddrsrv,
mnrpcnmsrv, and mnorbsrv.
• If WRB or wrb is supplied, it stops the WRB processes, such as mnaddrsrv,
mnrpcnmsrv, mnorbsrv, wrbcfg, wrblog, wrbasrv, wrbahsrv, wrbroker,
wrbvpm, and wrbfac and child processes forked by wrbfac, such as wrbc.
• If CARTRIDGE or cartridge is supplied, it stops the Cartridge process,
such as wrbfac, and child processes such as wrbc.
reload
Reloads the Oracle Web Listener configuration. This option is ONLY valid for
Oracle Web Listener, not for WRB or cartridge processes or Netscape server.
status
Displays the status of the process specified by the next argument as follows:
•Iflistener_name is supplied, it shows the current status of the named Oracle
Web Listener.
• If NCX or ncx is given, it shows the current status of the ORB process.
• If WRB or wrb is supplied, it shows the current status of WRB processes.
A-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 69

• If CARTRIDGE or cartridge is supplied, it shows the current status of
cartridge processes, such as wrbfac.
-e
This option exclusively starts/stops the WRB processes. When you use this
option to start/stop the WRB, the NCX (ORB) processes are not started/stopped.
Environment
To use owsctl, you must have the following environment variables set:
• ORAWEB_HOME - Absolute path where Oracle Web Application Server
is installed.
• ORAWEB_SITE - This is the site name for the Oracle Web Application
Server.
• ORACLE_HOME - ORACLE_HOME is the absolute path where you
install Oracle products.
WRB, ORB and Cartridge Processes
The Web Request Broker (WRB), Object Request Broker (ORB), and cartridge
processes coordinate the distributed interprocess communications for Oracle
Web Application Server 3.0.1.
The ORB processes are: mnaddrsrv, mnrpcnmsrv, and mnorbsrv. Run the ORB
processes with NCX or ncx. You should run these processes before you start the
WRB processes. To start the ORB processes, use:
owsctl start ncx
If you want to exclusively start the WRB processes without the ORB processes,
use:
owsctl start -e wrb
The WRB Oracle Web Logger process, wrblog, can be started individually and
executed with multiple instances.
When a cartridge execution request is entered, wrbfac starts one or more child
processes, wrbc, to execute the cartridge. Start the cartridge process after all
WRB processes are started and running on a primary machine.
The cartridges can run on the same primary machine as the WRB processes, or
they can run on a remote machine. Multiple cartridge processes can be run on
the same machine.
Starting and Stopping the Listener A-3
Page 70

The following examples show how to run the processes:
Example 1: Starting the WRB Process
Start the WRB processes on the primary machine by entering:
owsctl start wrb
Example 2: Displaying the WRB Status
Show the status of WRB processes on the primary node by entering:
owsctl status wrb
Example 3: Starting the Listener (Optional)
Start the Oracle Web Listener Admin by entering:
owsctl start admin
Example 4: Displaying the Listener Status (Optional)
Show the status of the Oracle Web Listener Admin by entering:
owsctl status admin
Example 5: Starting the Cartridge on a Remote Machine (Optional)
Start the cartridge process on the remote machine by entering:
owsctl start cartridge
Example 6: Starting the Oracle Web Logger Process (Optional)
Start the Oracle Web Logger process on the primary machine by entering:
owsctl start -p wrblog
Example 7: Checking the Oracle Web Logger Status (Optional)
Check the status of the Oracle Web Logger by entering:
owsctl status -p wrblog
Example 8: Starting the Oracle Web Status Monitor for the Listener ’admin’
Start the Oracle Web Status Monitor for the Listener ’admin’ by entering:
owsctl start -stat admin
Example 9: Starting the ORB Processes
Start the ORB processes on the primary machine by entering:
A-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 71

Files
owsctl start ncx
Example 10: Starting the WRB Processes without the ORB processes:
To exclusively start the WRB processes use:
owsctl start -e wrb
WRB/Cartridge pid:
%ORAWEB_ADMIN%/ows/%ORAWEB_SITE%/wrb/config/
.ows_machine_name.pid
WRB/Cartridge address:
%ORAWEB_ADMIN%/ows/%ORAWEB_SITE%/wrb/config/.omnaddr
Web Listener registration file:
%ORAWEB_ADMIN%/ows/%ORAWEB_SITE%/httpd_machine_name/
owl.cfg
WRB process files:
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/mnaddrsrv.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/mnrpcnmsrv.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/mnorbsrv.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbcfg.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrblog.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbasrv.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbahsrv.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbroker.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbfac.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/wrbvpm.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/oraweb.exe
%ORAWEB_HOME%/bin/owstat.exe
Notes: • Always useowsctl to start the WRB processes on the primary machine and
then start the Oracle Web Listener.
• If you want to distribute the cartridge over remote machines, use owsctl
with the start CARTRIDGE option.
• If you want to start the individual WRB or cartridge process, you must
first invoke owsctl start wrb on a primary machine.
Starting and Stopping the Listener A-5
Page 72

A-6 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 73
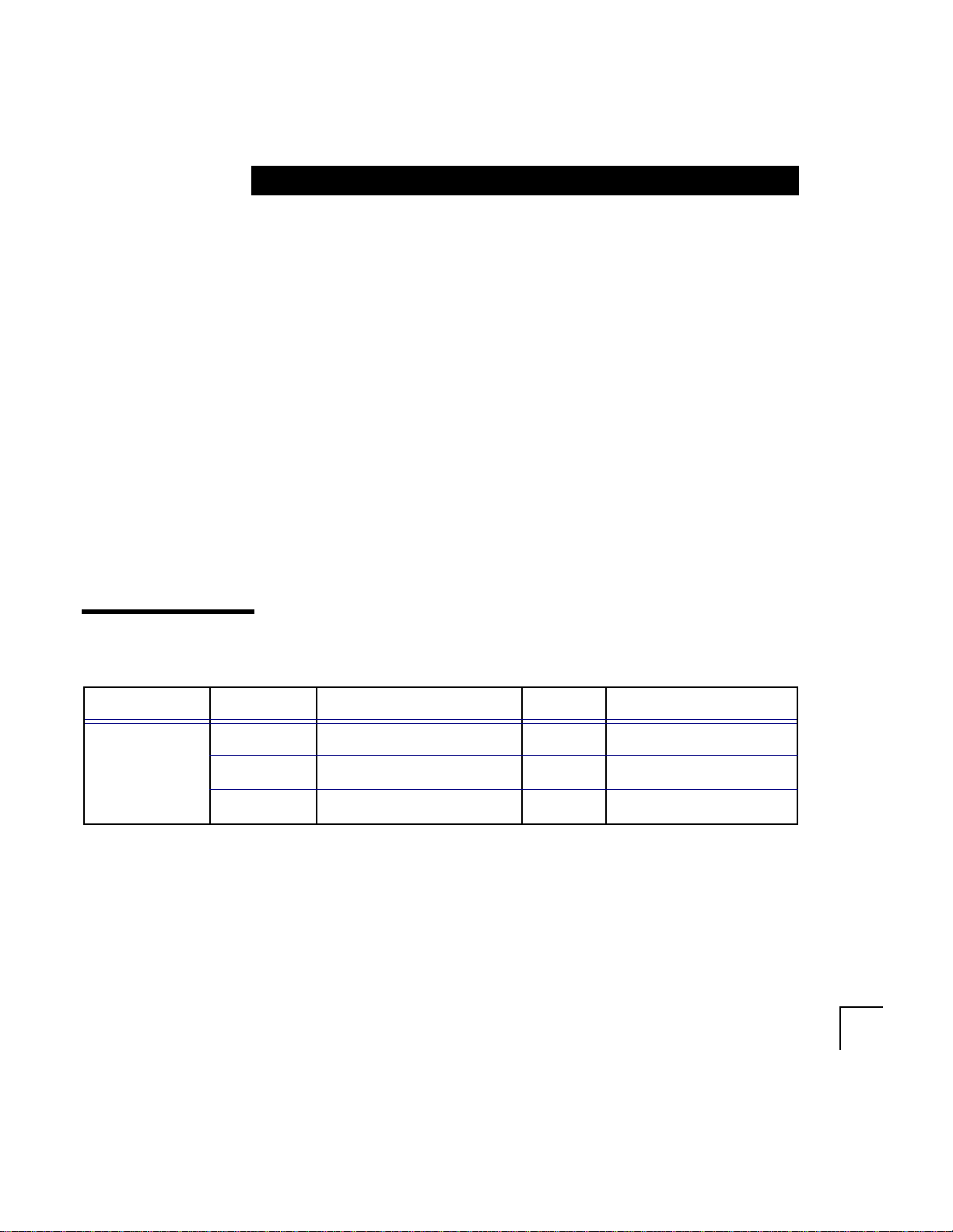
APPENDIX
B Multi-node Configuration
The Oracle Web Application Server is made up of several processes — most of
which are defined as services on Windows NT. You can run these processes on
different machines on the network. You can do this because the architecture of
the Web Application Server is based on CORBA (common object request broker
architecture), which is a standard for distributed objects. Two advantages of
distributing the processes on different machines are performance and
scalability.
Processes
The Web Application Server consists of the following processes and services:
Type Process Services Runs on Description
ORB Processes
mnorbsrv OraMediaNet_mnorbsrv
mnaddsrv OraMediaNet_mnaddsrv
mnrpcmnsrv OraMediaNet_mnrpcmnsrv
Primary The ORB service
Primary The ORB address server
Primary The RPC name server
Page 74

Type Process Services Runs on Description
WRB Processes
Listener
Process
wrbcfg OraWeb_wrbcfg
wrblog OraWeb_wrblog
wrbasrv
wrbahsrv
wrbroker OraWeb_wrbroker
wrbvpm OraWeb_wrbvpm
wrbfac OraWeb_wrbfac
wrbc
oraweb OracleWWWListen-
OraWeb_wrbsrv
OraWeb_wrbahsrv
er30%NAME%
Primary The WRB configuration
provider
Primary The WRB logger
Primary
and
The WRB authentication
servers
Remote
Primary The Web Request Broker
Primary The WRB virtual path
manager
Primary
The cartridge factory
and
Remote
Primary
Cartridge processes
and
Remote
Primary The web listener
process.
Cartridge Instances on Each Node
This section describes when cartridge instances are started up and how the
Dispatcher directs requests to them. The step numbers correspond to the
numbers in the figure below.
1. A client sends a request for a cartridge to the Listener.
2. The Listener sees that the request is for a cartridge, and sends it to the
Dispatcher.
3. If the Dispatcher knows of no free cartridge instances for that cartridge, it
sends the request to the Web Request Broker.
4. The WRB then directs one or more cartridge factories to allocate cartridge
instances. The WRB tries to ensure that each cartridge factory allocates
approximately the same number of cartridge instances for a particular
cartridge type for each node.
5. Each cartridge factory spawns the appropriate number of cartridge
B-2 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 75

instances for its node.
6. The cartridge instances are then registered with the Dispatcher, so that the
Dispatcher can direct requests to them.
When subsequent requests for the cartridge come in, the Dispatcher sends the
requests to unoccupied cartridge instances.
Client
1
Listener Dispatcher WRB
2
Primary Node
The MIN and MAX configuration parameters for the cartridge type determine
the minimum and maximum number of cartridge instances. Note the following
points about the meaning of these parameters if you are running in a distributed
environment:
• The MIN and MAX values include cartridge instances running on all
nodes. For example, if you set a MIN for the PL/SQL Cartridge at 10, then
10 instances can be running on one node or spread over several nodes.
3
4
Cartridge
Factory
Instance 1 of Cartridge A
5
Instance 2 of Cartridge A
Instance 3 of Cartridge A
Instance 4 of Cartridge A
6
Instance 5 of Cartridge A
4
Cartridge
Factory
Instance 6 of Cartridge A
5
Instance 7 of Cartridge A
Instance 8 of Cartridge A
6
Instance 9 of Cartridge A
Instance 10 of Cartridge A
Remote Node
• If you set the MIN value to 0, the cartridge factory spawns one cartridge
instance to handle a request, but it does not spawn any extra cartridge
instances. In this case, the Dispatcher does not have a list of cartridge
instances, and it sends all requests for the cartridge to the WRB. The WRB
then directs a cartridge factory to start up a cartridge instance to handle
the request.
Multi-node Configuration B-3
Page 76

Distributing the Authentication Server Processes
You can run the Authentication Server on machines other than the primary
node, and you can run multiple copies of the Authentication Server. The main
reasons for doing this are performance and reliability.
• If the primary node is running many processes and resources on the node
are scarce, you might get better performance if you move the
Authentication Server to a less busy machine.
• If you are using the Oracle database server to authenticate clients, you can
improve performance if you move the Authentication Server to the same
machine as the database.
• If you have only one Authentication Server and several clients are
requesting authentication, then the requests are queued up. You can
improve this bottleneck situation by running multiple copies of the
Authentication Server.
• If you run running multiple copies of the Authentication Server on
different machines and one machine fails, clients can still access the
Authentication Servers that are running on other machines.
The services for the Authentication Server are ORAWEB_wrbasrv and
ORAWEB_wrbahsrv. ORAWEB_wrbasrv is the Authentication Broker service,
and ORAWEB_wrbahsrv is the Authentication Provider service.
Installing the Authentication Server on Remote Nodes
To run the Authentication Server on a remote node, you run orainst on the
remote node. In orainst, select the multi-node option, then select “remote”, and
then select “WRB” when prompted on what to install on the remote node.
During installation of the WRB on the remote node, you need to provide the
name of the primary node. The name of this node appears in the registry entry
HKZY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Oracle\OMN_ADDR.
Unlike running cartridges on remote nodes, you do not need to list the names of
the remote nodes in the Web Application Server Manager.
Running the Authentication Server
To start up the processes for the Authentication Server:
owsctl start -p wrbasrv
owsctl start -p wrbahsrv
B-4 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
Page 77

To stop the processes for the Authentication Server:
owsctl stop -p wrbasrv
owsctl stop -p wrbahsrv
Troubleshooting and Tips
If requests are not being sent to the remote nodes, consider the following:
• You have to use the same UDP port number on all nodes. This number is
saved in the registry entry
HKZY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Oracle\Medianet\OMNADD
R.
• If you are using remote nodes to run the Java or the LiveHTML cartridges,
you have to use the same definition of the ORACLE_HOME environment
variable for all nodes. This is not required for the PL/SQL cartridge.
• If you are running a custom cartridge that uses the physical path
parameter, you need to set the same value for all nodes. If your physical
path parameter uses environment variables, you need to check that the
environment variables refer to the same physical path.
• Check that you have entered the name of the primary node correctly
during installation. The name is not verified until the Web Application
Server needs to use it.
• You need to start up the WRB before starting up the Listener or the
cartridge processes. To stop these processes, you stop them in the reverse
order.
Multi-node Configuration B-5
Page 78

Index
A
Administration Listener, default settings, 4-2
Adobe Acrobat Reader, installation, viii
C
cartridges
remote installation, 3-6
running on remote nodes, B-1
certificate, requesting, 4-4
common gateway interface, 1-5
configuration files
Netscape Server, 6-2
configuring Microsoft IIS to use WRB, 5-4
CORBA-compliant ORB, 1-3
customer support, x
D
database connection descriptors (DCD), 4-2
database installation
local, 2-3
remote, 2-3
Default Web Listener, default settings, 4-2
distributing cartridges, B-1
E
External Listener Registration utility, 5-2
H
hardware requirements, 2-1
Home Page, 4-3
I
installation procedure, 3-4
Installer
multi-node, 3-6
remote node, 3-6
requirements
hardware, 2-1
software, 2-2
inter-cartridge exchange, 1-5
J
Java Cartridge, 1-4
Page 79

L
Listener
remote installation, 3-6
LiveHTML Cartridge, 1-4
local database installation, 2-3
localhost, definition, 4-3
logging, 1-5
M
Microsoft IIS, configuring to use WRB, 5-4
migrating
changes made during, 5-3, 6-3
from Netscape Server, 6-2
tools, 6-2
migration utility, using with Netscape servers, 5-2
multi-node configuration, 2-4
N
Netscape Server
configuration information, 6-2
migrating from, 6-2
O
ODBC cartridge, 1-6
open architecture, 1-1
Oracle WebServer 2.1 Home Page, 4-3
owsctl utility
cartridges, A-3
environment variables, A-3
files, A-5
syntax, A-1
primary node
installation, 3-6
product dependencies, 2-2
R
reliability, 1-2
remote database installation, 2-3
remote installation
cartridges, 3-6
listener, 3-6
remote node
installation, 3-6
required products, 2-2
S
scalability, 1-2
security, 1-3, 1-5
server side includes, 6-7
shared key, 3-3, 4-4
single node configuration, 2-4
software requirements, 2-2
starting the listener, A-1
stopping the listener, A-1
support
customer, x
T
third-party HTTP servers, 5-1
tools
migrating, 6-2
transaction support, 1-6
P
U
Perl Cartridge, 1-4
persistent storage, 1-7
PL/SQL Cartridge, 1-4
port, default for administration listener, 4-3
Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide Index-2
uninstallation procedure, 3-11
upgrading
Oracle PL/SQL Agent, 7-8
Page 80

V
VRML Cartridge, 1-5
W
Web Application Server
starting, 4-1
Web Request Broker, 1-3
administration page location, 5-5
Web Request Broker (WRB), 3-6
remote installation, 3-6
WebServer 2.1 Home Page, 4-3
WebServer Manager, home page location, 5-2
Index-3 Oracle Web Application Server™ Installation Guide
 Loading...
Loading...