Optris OPTXI40LTF20CFKT090, OPTXI40LTF20CFT090, OPTXI80LTF05T090, OPTXI41LTF08T090, OPTXI80LTF02T090 User manual
...Page 1

Operator’s Manual
optris
®
Xi
80/ 400/ 410
Spot finder IR camera
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 2

Table of contents 3-
Table of contents
Table of contents .............................................................................................................................................. 3
1 General Notes ........................................................................................................................................... 8
1.1 Intended use ....................................................................................................................................... 8
1.2 Warranty ............................................................................................................................................. 9
1.3 Scope of delivery .............................................................................................................................. 10
1.4 Maintenance ..................................................................................................................................... 10
1.4.1 Cleaning .................................................................................................................................... 10
1.5 Model overview ................................................................................................................................. 11
2 Technical Data ........................................................................................................................................ 12
2.1 General specifications ...................................................................................................................... 12
2.2 Electrical specifications ..................................................................................................................... 16
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 3

-4 -
2.3 Measurement specifications ............................................................................................................. 17
2.4 Optical specifications ........................................................................................................................ 19
3 Mechanical Installation .......................................................................................................................... 26
3.1 Dimensions ....................................................................................................................................... 26
3.2 Accessories....................................................................................................................................... 31
3.2.1 Air purge laminar ...................................................................................................................... 31
3.2.2 Water cooling ............................................................................................................................ 35
3.2.3 Shutter ...................................................................................................................................... 38
3.2.4 Combination of air purge, water cooling and shutter ................................................................ 42
3.2.5 Outdoor protective housing ....................................................................................................... 47
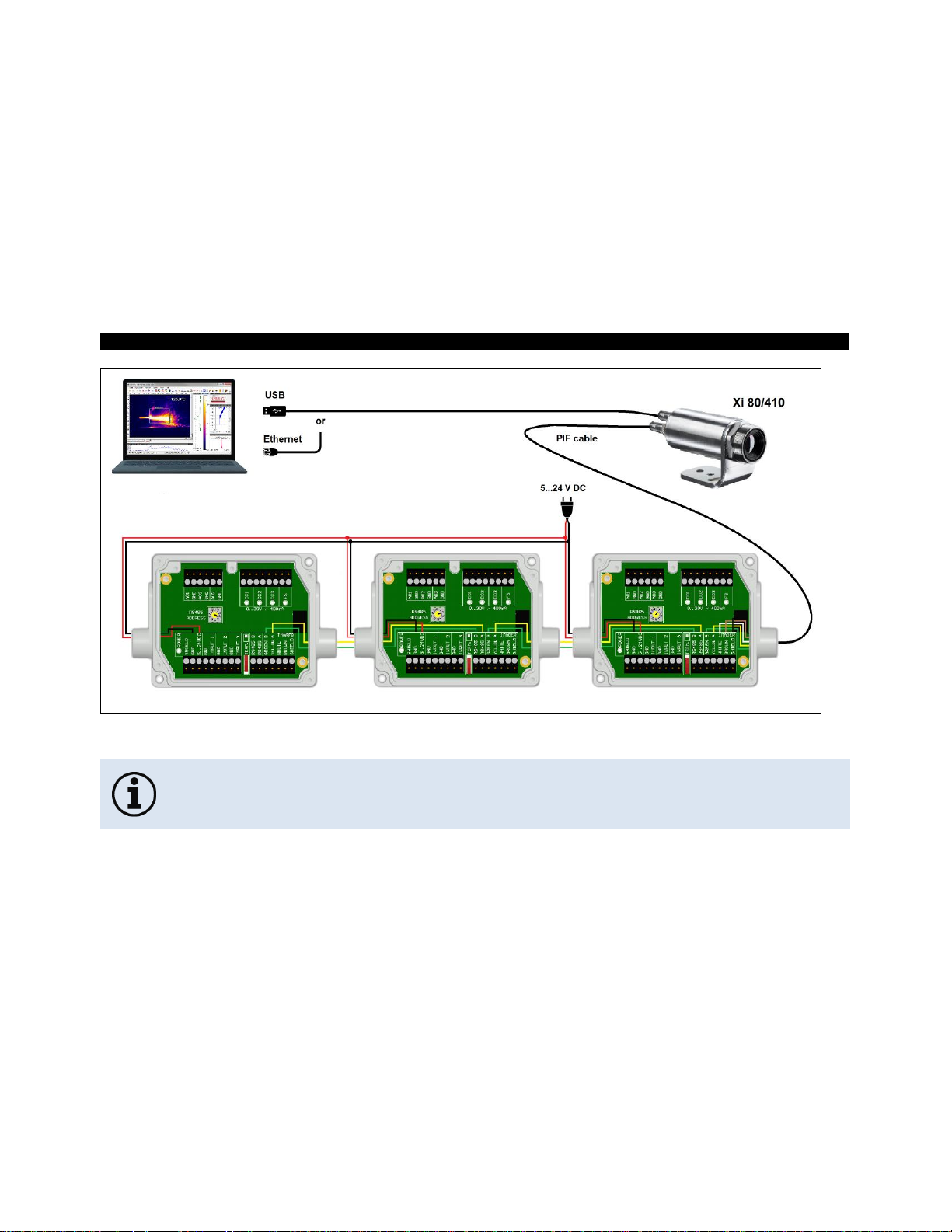
4 Electrical Installation .............................................................................................................................. 48
4.1 Process interface .............................................................................................................................. 49
4.1.1 Process interface Xi 80/410 ...................................................................................................... 49
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 4

Table of contents 5-
4.1.2 Process interface Xi 400 ........................................................................................................... 52
4.1.3 PIN allocation Xi 80/410 ........................................................................................................... 55
4.1.4 PIN allocation Xi 400 ................................................................................................................ 56
4.1.5 Industrial Process Interface for Xi 80/410 (optional)................................................................. 58
4.1.6 Industrial Process Interface for Xi 400 (optional) ...................................................................... 63
4.2 Example for a Fail-Safe monitoring of the Xi with a PLC ................................................................. 67
4.3 USB cable extension for Xi 400 ........................................................................................................ 69
5 Functions ................................................................................................................................................. 70
5.1 Ethernet Xi 80/410 ............................................................................................................................ 70
5.1.1 Ethernet setup (Point-to-Point-Connection) .............................................................................. 72
5.2 Autonomous operation Xi 80/410 ..................................................................................................... 78
5.2.1 Hot- / Coldspot function in autonomous operation ................................................................... 83
5.3 Use of Shutter ................................................................................................................................... 84
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 5

-6 -
5.3.1 Settings in PIX Connect Software............................................................................................. 86
6 IRmobile App ........................................................................................................................................... 87
7 Software PIX Connect ............................................................................................................................ 89
7.1 Installation and initial start-up ........................................................................................................... 90
7.2 Software window ............................................................................................................................... 92
7.3 Basis features of the software PIX Connect ..................................................................................... 94
8 Basics of Infrared Thermometry ........................................................................................................... 97
9 Emissivity .............................................................................................................................................. 102
9.1 Definition ......................................................................................................................................... 102
9.2 Determination of unknown emissivity ............................................................................................. 104
9.3 Characteristic emissivity ................................................................................................................. 106
Appendix A – Table of emissivity for metals ............................................................................................. 107
Appendix B – Table of emissivity for non-metals ..................................................................................... 109
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 6

Table of contents 7-
Appendix C – Quick start for serial communication ................................................................................. 110
Appendix D – Interprocess Communication (IPC) .................................................................................... 113
Appendix E – PIX Connect Resource Translator ...................................................................................... 114
Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF for Xi 400 ............................................................................................ 115
Appendix G – Declaration of Conformity ................................................................................................... 119
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 7

-8 -
1 General Notes
1.1 Intended use
Thank you for choosing the optris® Xi spot finder infrared camera.
The optris Xi calculates the surface temperature based on the emitted infrared energy of objects
[►8 Basics of Infrared Thermometry]. The two-dimensional detector (FPA - focal plane array) allows a
measurement of an area and will be shown as thermal image using standardized palettes. The radiometric
processing of the picture data enables the user to do a comfortable detailed analysis with the software
PIX Connect.
The Xi is a precise instrument and contains an extremely sensitive infrared detector and a highquality lens.
The alignment of the camera to intensive energy sources (e.g. devices which emit laser
radiation or reflections of such equipment) can cause an irreparable defect of the infrared
detector. This is also valid if the camera is switched off.
Such kinds of damages are excluded from warranty.
Read the manual carefully before the initial start-up. The producer reserves the right to change
the herein described specifications in case of technical advance of the product.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 8

General Notes 9-
• Avoid abrupt changes of the ambient temperature.
• Avoid static electricity, arc welders, and induction heaters. Keep away from very strong EMF
(electromagnetic fields).
• In case of problems or questions which may arise when you use the infrared camera, please
contact our service department.
► All accessories can be ordered according to the referred part numbers in brackets [ ].
1.2 Warranty
Each single product passes through a quality process. Nevertheless, if failures occur contact the customer
service at once. The warranty period covers 24 months starting on the delivery date. After the warranty is
expired the manufacturer guarantees additional 6 months warranty for all repaired or substituted product
components. Warranty does not apply to damages, which result from misuse or neglect. The warranty also
expires if you open the product. The manufacturer is not liable for consequential damage or in case of a nonintended use of the product.
If a failure occurs during the warranty period the product will be replaced, calibrated or repaired without
further charges. The freight costs will be paid by the sender. The manufacturer reserves the right to
exchange components of the product instead of repairing it. If the failure results from misuse or neglect the
user has to pay for the repair. In that case you may ask for a cost estimate beforehand.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 9

-10 -
1.3 Scope of delivery
• Xi 80, Xi 400 or Xi 410
• USB cable:
1 m (standard scope of supply, no IP67 protection class)
1 m, 3 m, 5 m, 10 m, 20 m * (optional, for industrial applications, with IP67)
• Ethernet PoE cable: 1 m (only for Xi 410)
• Mounting nut and mounting bracket (adjustable in one axis, tripod thread)
• Process interface cable incl. terminal block (1 m)
• Software package PIX Connect
• Quick start guide
* 10 m and 20 m version not available for Xi 80 and Xi 410
1.4 Maintenance
Never use cleaning compounds which contain solvents (neither for the lens nor for the housing).
1.4.1 Cleaning
Blow off loose particles using clean compressed air. The lens surface can be cleaned with a soft, humid
tissue (moistened with water) or a lens cleaner (e.g. Purosol or B+W Lens Cleaner).
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 10

General Notes 11-
1.5 Model overview
The cameras of the Xi-series are available in the following basic versions:
Modell
Model code
Temperature range
Spectral range
Frame rate
Typical applications
Xi 80
IR
-20 to 900 °C
8 - 14 µm
USB/Ethernet:
50 Hz
Surface measurements in industrial application,
autonomous operation with automatic spot finder
Xi 400
IR
-20 to 900 °C
200 to 1500 °C (optional)
8 - 14 µm
USB:
80 Hz/ 27 Hz
Real-time thermographic images in high speed;
Detection of smallest temperature differences
Xi 410
IR
-20 to 900 °C
8 - 14 µm
Ethernet: 25 Hz
USB: 4 Hz
Surface measurements in industrial application,
autonomous operation with automatic spot finder
Table 1: Model overview
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 11

-12 -
2 Technical Data
2.1 General specifications
Environmental rating:
IP67 (NEMA-4)
Ambient temperature:
0...50 °C
Storage temperature:
-40...70 °C
Relative humidity:
10...95 %, non-condensing
Material (housing):
Stainless steel
Dimensions:
Xi 80: 36 x 90 mm / M30
Xi 400/410: 36 x 100 mm / M30
Weight (without mounting bracket):
Xi 80: 201-210 g (depending on optics)
Xi 400/410: 216-220 g (depending on optics)
Cable length:
USB: 1 m (standard), 3 m, 5 m, 10 m, 20 m (20 m version not available for Xi 80/410)
Ethernet / RS485 (Xi 80/410): 100 m
Vibration1):
IEC 60068-2-6 (sinus shaped)
IEC 60068-2-64 (broadband noise)
Shock1):
IEC 60068-2-27 (25 G and 50 G)
1)
Used standards for vibration and shock:
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 12

Technical Data 13-
Figure 1: Used standards
Stress program (camera in operation):
Shock, half sinus 25 G – testing Ea 25 G (acc. IEC 60068-2-27)
Acceleration
245 m/s2
(25 G)
Pulse duration
11 ms
Number of directions
6
(3 axes with 2 directions each)
Duration
600 Shocks
(100 Shocks each direction)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 13

-14 -
Shock, half sinus 50 G – testing Ea 50 G (acc. IEC 60068-2-27)
Acceleration
490 m/s2
(50 G)
Pulse duration
11 ms
Number of directions
6
(3 axes with two directions each)
Duration
18 Shocks
(3 Shocks each direction)
Vibration, sinus shaped – testing Fc (acc. IEC60068-2-6)
Frequency range
10 - 500 Hz
Acceleration
29.42 m/s2
(3 G)
Frequency change
1 Octave/ min
Number of axes
3
Duration
1:30 h
(3 x 0.30 h)
Vibration, broadband noise – testing Fh (acc. IEC60068-2-64)
Frequency range
10 - 2000 Hz
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 14

Technical Data 15-
Acceleration
39.3 m/s2
(4.01 G
RMS
))
Frequency spectrum
10 - 106 Hz
0.9610 (m/s2)2/Hz
(0.010 G2/Hz)
106 - 150 Hz
+6 dB/ Octave
150 - 500 Hz
1.9230 (m/s2)2/Hz
(0.020 G2/Hz)
500 - 2000 Hz
-6 dB/ Octave
2000 Hz
0.1245 (m/s2)2/Hz
(0.00126 G2/Hz)
Number of axes
3
Duration
3 h
(3 x 1 h)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 15

-16 -
2.2 Electrical specifications
Power Supply:
Xi 80/410: USB/ PoE/ 5-30 VDC
Xi 400: USB
Current draw:
Max 500 mA
AO: Output Standard/Internal Process
Interface (PIF out)
0 - 10 V (Xi 400), 0/4 – 20 mA (Xi 80/410) (Main measure area, measure area, internal temperature, flag status,
recording status, line scan status, alarm, frame sync, fail-safe, external communication)
[►Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF]
AI: Input Standard/Internal Process
Interface (PIF in)
0 - 10 V (Emissivity, ambient temperature, reference temperature, uncommitted value, flag control, triggered
recording, triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-/valley-hold, switch
temperature range)
[►Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF]
DI: Digital Input Standard Process
Interface (Xi 400)
Flag control, triggered recording, triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak/valley-hold, switch temperature range
[►Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF]
Digital interface:
Xi 80/410: USB 2.0/ Ethernet/ RS485
Xi 400: USB 2.0/ optional USB to GigE (PoE) conversion
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 16

Technical Data 17-
2.3 Measurement specifications
Xi 80
Xi 400
Xi 410
Temperature ranges
-20...100 °C; 0...250 °C;
(20) 150...900 °C 1)
20...100 °C; 0...250 °C;
(20) 150...900 °C 1)
Option: 200…1500 °C
20...100 °C; 0...250 °C;
(20) 150...900 °C 1)
Spectral range
8 - 14 µm
Detector
UFPA,
80 x 80 pixel @ 50 Hz
UFPA,
382 x 288 pixel @ 80 Hz/ 27 Hz
UFPA,
Ethernet: 384 x 240 Pixel @ 25 Hz
USB: 384 x 240 Pixel @ 4 Hz
Lenses (FOV)
12° x 12° (F=1,0); 30° x 30° (F=0,9);
55° x 55° (F=0,9); 80° x 80° (F=0,9)
18° x 14° (F=1,1); 29° x 22° (F=0,9);
53° x 38° (F=0,9); 80° x 54° (F=0,9)
18°x12° (F=1,1), 29°x18° (F=0,9),
53°x31° (F=0,9), 80°x44° (F=0,9)
Microscope lens (FOV)
-
18° x 14° (F=1,1, minimum spot size:
81 µm @ 90 mm, working distance:
90-110 mm)
-
Optical resolution
190:1 (12° optic)
390:1 (18° optic)
System accuracy2)
±2 °C or ±2 %
Thermal sensitivity (NETD):
100 mK
80 mK
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 17

-18 -
Warm-up time
10 min
Emissivity
0.100...1.100
Software / App
PIX Connect / IRmobile
1)
Accuracy statement effective from 150 °C
2)
At ambient temperature 235 °C; whichever is greater
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 18

Technical Data 19-
2.4 Optical specifications
Make sure that the focus of thermal channel is adjusted correctly. The cameras have a
motorized focus, which can be adjusted in the PIX Connect software (Menu View/ Windows/
Distance or over the icon ). An adjustment to the left leads to the focus setting "near" and an
adjustment to the right to the focus setting "infinite".
Figure 2: Motorized focus settings in PIX Connect
The variety of different lenses offers the possibility to precisely measure objects in different distances. We
offer lenses for close, standard distances and large distances. Please note that the Xi has a fixed optic. A
change of optics is not possible. Different parameters are important if using infrared cameras. They display
the connection between the distance of the measured object and the size of the pixel (Table 2).
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 19

-20 -
■
HFOV: Horizontal enlargement of the total measuring at object level
■
VFOV: Vertical enlargement of the total measuring at object level
■
IFOV: Size at the single pixel at object level
■
DFOV: Diagonal dimension of the total measuring field at object level
■
MFOV: Recommended, smallest measured object size of 3 x 3 pixel
(Xi 400/410) and 2 x 2 pixel (Xi 80)
Geometric resolution for ideal temperature measurement
When designing optics for measuring IR cameras, special attention must be paid to the quality of detail
contrast with which an object can be represented in the image. This is described by the modulation transfer
function (MTF). Since in contrast to visual cameras, with IR cameras the thermal contrast is of more interest,
this is used together with the slit response function (SRF). The result is determined by the number of pixels
an object needs to fill to allow its temperature to be measured exactly. In high-performance infrared optical
systems as used by Optris, this is 3×3 pixels or 2x2 pixels, with lower quality optical systems, in some
circumstances as many as 10×10 pixels may be required, to receive 90 % of the energy. A high-performance
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 20

Technical Data 21-
camera lens also allows a larger measuring distance with the same number of pixels of the detector, or the
precise temperature measurement of smaller structures and objects. The 3×3 pixel (2x2 pixels) geometry is
described as MFOV (measurement field of view) - one single pixel on the object surface is described as
IFOV (instantaneous field of view). The MFOV is comparable with the measuring spot definition with
infrared thermometers.
The following tables with examples showing what spot sizes and
pixel sizes will be reached in which distance. For individual
configuration there are different lenses available. Wide angle
lenses have a radial distortion due to their large opening angle;
the software PIX Connect has an algorithm which corrects this
distortion. As an alternative to the tables below, the optics
calculator can also be used on the optris website or via the
optris calculator app. The app can be downloaded for free from
the Google Play Store (see QR code).
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 21

-22 -
Table 2:
* Note: The accuracy of measurement can be outside of the specifications for distances below the defined minimum distance.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 22

Technical Data 23-
* Note: The accuracy of measurement can be outside of the specifications for distances below the defined minimum distance.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 23

-24 -
* Note: The accuracy of measurement can be outside of the specifications for distances below the defined minimum distance.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 24

Technical Data 25-
* Note: The accuracy of measurement can be outside of the specifications for distances below the defined minimum distance.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 25

-26 -
3 Mechanical Installation
3.1 Dimensions
The Xi is equipped with a metric M30x1 thread and can be installed either directly via the sensor thread or
with help of the supplied mounting nut (standard) and adjustable mounting bracket (standard) to a mounting
device available.
Figure 3: Xi with mounting bracket
Figure 4: Mounting bracket, adjustable in one axis, with tripod thread
[Order No. - ACXIFB] – standard scope of supply
For correct orientation, the USB port must be on the left side and the PIF port on the right side,
see Figure 5 or Figure 6.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 26

Mechanical Installation 27-
Figure 5: Xi 80, dimensions [mm]
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 27

-28 -
Figure 6 : Xi 400, dimensions [mm]
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 28

Mechanical Installation 29-
Figure 7 : Xi 410, dimensions [mm]
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 29

-30 -
Figure 8: Industrial/stackable PIF (Process Interface) – electronic box, control box shutter, dimensions [mm]
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 30

Mechanical Installation 31-
3.2 Accessories
3.2.1 Air purge laminar
The lens must be kept clean at all times from dust, smoke, fumes and other contaminants in order to avoid
reading errors. These effects can be reduced by using an air purge. (Part-No.: ACXIAPL)
• Make sure to use oil-free, technically clean air, only.
• The needed amount of air (approx. 2...10 l/min.) depends on the application and the
installation conditions on-site.
• The laminar air purge has a Si-protective window. Typical transmission value: 0.82
(deviations possible), replacement window available under the Part-No.: ACXIAPLPWSI
• The corresponding mounting bracket (Part-No.: ACXIAPLAB) is mandatory.
• Material: Anodized aluminum, weight: 218 g / 494 g with mounting bracket
• Ambient temperature: 0...80 °C (T
Amb
camera: 0...50 °C); with water cooled housing up to
250 °C
Air flow
The air purge can be mounted in
four different positions.
The direction of the airflow must
always be clear.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 31

-32 -
Figure 9: Laminar air purge with Si protective window, dimensions [mm]
How-to Video
Replacement of Siprotective window
https://www.optris.global/
replacement-of-the-siprotective-window-of-thelaminar-air-purgeattachment
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 32

Mechanical Installation 33-
Figure 10: Laminar air purge with Si protective window (ACXIAPL) and mounting
bracket (ACXIAPLAB), dimensions [mm]
How-to video Xi 80
https://www.optris.global/mountingthe-air-purge-unit-on-xi-80
How-to video Xi 400
https://www.optris.global/mountingthe-air-purge-unit-on-xi-400
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 33

-34 -
Figure 11: Mounting bracket (ACXIAPLAB), dimensions [mm], weight: 276 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 34

Mechanical Installation 35-
3.2.2 Water cooling
The IR camera is for application at ambient temperatures up to 50 °C. For applications at higher ambient
temperatures we recommend the usage of the optional water cooled housing (operating temperature up to
250 °C) and the optional high temperature cable (operating temperature up to 250 °C).
• When using water cooling, a corresponding mounting kit (Part-No.: ACXIxxxWAKx) is
required (WAK1: Usage without air purge, WAK2: Usage with air purge).
• Water flow rate: approx. 1-5 l/ min (Cooling water temperature should not exceed 30 °C)
• When using the water cooling the air purge (Part-No.: ACXIAPL) is recommended in order
to avoid condensation
• Material: Stainless steel
• Weight: 1480 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 35

-36 -
Figure 12: Water cooling (ACXIW) and mounting kit (ACXIxxxWAK1), dimensions [mm], weight: 1710 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 36

Mechanical Installation 37-
Figure 13: Shutter for water cooling (ACXISW), dimensions [mm], weight: 600 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 37

-38 -
3.2.3 Shutter
To protect the optics of the camera, an optional shutter (closing mechanism) can be purchased. It is
equipped with a servomotor that can open and close a mechanical lock as needed. The special feature of
the shutter is not only the opening and closing, but also the complete seal in the closed state. This ensures
that the shutter is completely closed and no dirt can get on the optics.
• The shutter has a 100 ms fast-closing mode.
• Complete seal when closed.
• Includes a control box for connections.
• Shutter can be used in combination with Process Interface (PIF).
• The corresponding mounting bracket (Part-No.: ACXIAPLAB) is mandatory.
• Material: Stainless steel
• Weight: 550 g / 826 g Shutter with mounting bracket
• When using more than one shutter and the opening / closing of the shutter should be
simultaneously, the switch S4 on one control box must be set to mA and the others to mV
(see Figure 16).
• Ambient temperature: 0...60 °C (T
Amb
camera: 0...50 °C); with water cooled housing up to
250 °C
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 38

Mechanical Installation 39-
Figure 14: Shutter (ACXIS) with mounting bracket (ACXIAPLAB), dimensions [mm], weight: 826 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 39

-40 -
Figure 15: Shutter (ACXIS), dimensions [mm], weight: 550 g
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 40

Mechanical Installation 41-
Figure 16: Control box of shutter, dimensions (see Figure 8)
Power supply: 12-24 V
Upper terminal screw Connection
for Process Interface (PIF)
Switch for different operation
modes:
S1: Switching between switch
operation and pulse operation
S2: Activation/deactivation of fastclosing mode
S3: Only for factory calibration
(Switch must be at Normal)
S4: Switching between mV or mA
input
Lower screw terminal: Connection for power supply,
Inputs (Start/Stop signal) and Motor
Inputs (Start/Stop signal, max. 24 V, input is
active LOW (open input = HIGH)):
IN 1: Trigger input for normal operation (S1)
IN 2: Currently no usage
IN 3: Trigger input for fast-closing mode (S2)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 41

-42 -
3.2.4 Combination of air purge, water cooling and shutter
It is possible to combine all three components (air purge, water cooling and shutter) with each other. It
should be noted that there are differences between the Xi 80 and Xi 400/410. Various mounting kits
(ACXIxxxWAKx) are available in combination with water cooling. The mounting bracket (ACXIAPLAB) is
always required for air purge and shutter. For water cooling (ACXIW), the mounting bracket is included and
does not have to be ordered separately.
Part-No.:
Combinations
ACXIAPL
ACXIAPLAB ACXIS
ACXISW
ACXIW
ACXI80WAK1 ACXI80WAK2 ACXI400WAK1 ACXI400WAK2
Air purge
✓
✓
Water cooling Xi 80
✓
✓
Water cooling Xi 400/410
✓
✓
Shutter
✓
✓
Air purge and water cooling Xi 80
✓
✓ ✓ Air purge and water cooling Xi 400/410
✓
✓ ✓ Air purge and shutter
✓ ✓ ✓
Water cooling and shutter Xi 80
✓ ✓ ✓
Water cooling and shutter Xi 400/410
✓
✓
✓
Air purge, water cooling and shutter Xi 80
✓
✓
✓ ✓
Air purge, water cooling and shutter Xi 400/410
✓
✓
✓
✓
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 42

Mechanical Installation 43-
Figure 17: Air purge (ACXIAPL), water cooling (ACXIW), shutter (ACXISW) and appropriate
mounting kit (ACXIxxxWAKx), dimensions [mm]
Components:
• Air purge
• Water cooling
• Shutter
• Mounting kit
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 43

-44 -
Figure 18: Air Purge (ACXIAPL), water Cooling (ACXIW) and appropriate mounting kit
(ACXIxxxWAKx), dimensions [mm]
Components:
• Air purge
• Water cooling
• Mounting kit
How-to video
https://www.optris.global
/assembly-of-xi-400-intothe-water-coolinghousing-with-the-use-ofthe-laminar-air-purge
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 44

Mechanical Installation 45-
Figure 19: Water Cooling (ACXIW), Shutter (ACXISW) and appropriate mounting kit
(ACXIxxxWAKx), dimensions [mm]
Components:
• Water cooling
• Shutter
• Mounting kit
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 45

-46 -
Figure 20: Air purge (ACXIAPL) with mounting bracket (ACXIAPLAB) and shutter (ACXIS),
dimensions [mm]
Components:
• Air purge
• Mounting
bracket
• Shutter
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 46

Mechanical Installation 47-
3.2.5 Outdoor protective housing
• The infrared camera Xi can also be used for outdoor applications by using the outdoor
protective housing (Part-No.: ACXIOPH24).
• In addition, the industrial or stackable PIF (Part-No.: ACCJAPIPIFMA (Xi 400) or
ACOPHXIPIF (Xi 80/410)) can be installed as an accessory without housing and a USB
Server (Part-No.: ACPIUSBSGB).
• For detailed information see installation manual.
Figure 21: Outdoor protective housing for Xi camera
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 47

-48 -
4 Electrical Installation
At the back side of the Xi there are the two connector plugs (see Figure 22 and Figure 23).
Figure 22: Backside of the Xi 80/410 with connectors
Figure 23: Backside of the Xi 400 with connectors
1
Plug for USB / Ethernet1) / PoE cable
2
Plug for in- and outputs or RS485
1
Plug for USB cable
2
Plug for PIF cable
1)
When using the Ethernet connector, a 5...30 V DC power supply must be ensured via the terminal block
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 48

Electrical Installation 49-
4.1 Process interface
4.1.1 Process interface Xi 80/410
The Xi 80/410 is equipped with an integrated process interface
(cable with terminal block included in scope of supply), which
can be programmed via the software as a direct analog input
(AI), as a direct analog output (AO) in order to control the
process or as an RS485 interface1). The signal level is 0-10 V
for AI and 0/4-20 mA for AO.
The process interface can be activated via the software choosing the following options:
Analog Input (AI):
Emissivity, ambient temperature, reference temperature, uncommitted value, flag control, triggered recording,
triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-/valley-hold, switch temperature
range
Analog Output (AO):
Main measure area, measure area, internal temperature, flag status, recording status, line scan status, alarm,
frame sync, fail-safe, external communication
1)
Direct out- and inputs are not available while using the RS485 interface
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 49

-50 -
Figure 24: Configuration terminal block Xi 80/410
Shield
Black
GND
0 V
Ground
Brown
VCC
5-30 V
Power1)
White
IN A Analog/Digital Input or RS485 (A)
Green
OUT
B
Analog Output or RS485 (B)
Yellow
GND
ISO
Isolated Ground for IN and OUT
Gray
1)
Power supply only necessary when using the Ethernet connection (without PoE) or self-sufficient operation
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 50

Electrical Installation 51-
The Xi 80/410 provides the following direct inputs and outputs:
Name
Description
max range / status
AI
or
DI
Analog input
0-10 V 1)
Digital input
(active-low = 0…0,6 V)
24 V
AO
Analog output
Alarm output
0/4-20 mA
0/4-20 mA
1)
The AI is designed for max. 24 V, the voltage level above 10 V is not interpreted
In addition to the above direct in- and outputs, the Xi 80/410 has an RS485 interface. This interface can be
used to control the external industrial PIF.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 51

-52 -
4.1.2 Process interface Xi 400
The process interface (electronics within cable as well as industrial interface) must be powered
separately (5-24 VDC). Before switching on the power the PIF cable must be connected to the
camera.
The Xi is equipped with a process interface (cable with integrated electronics
and terminal block), which can be programmed via the software as an Analog
Input (AI) and Digital Input (DI) in order to control the camera or as an Analog
Output (AO) in order to control the process. The signal level is always 0-10 V
(DI = 24 V).
The process interface can be activated via the software choosing the following options:
Analog Input (AI):
Emissivity, ambient temperature, reference temperature, uncommitted value, flag control, triggered recording,
triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-/valley-hold, switch temperature
range
Analog Output (AO):
Main measure area, measure area, internal temperature, flag status, recording status, line scan status, alarm,
frame sync, fail-safe, external communication
Digital Input (DI):
Flag control, triggered recording, triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-
/valley-hold, switch temperature range
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 52

Electrical Installation 53-
Figure 25: Configuration Standard Process Interface (PIF) Xi 400
Shield
Black
Gnd
Ground
Brown
DI
Digital Input
Gray
Vcc
Power supply, 5…24 V DC
White
AI
Analog Input
Green
AO
Analog Output
Yellow
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 53

-54 The standard process interface provides the following inputs and outputs:
Name
Description
max range1)/ status
AI
Analog input
0-10 V 2)
DI
Digital input
(active-low = 0…0,6 V)
24 V
AO
Analog output
Alarm output
0-10 V
0/ 10 V
1)
Depending on supply voltage; for 0-10 V on the AO the PIF has to be powered with min. 12 V.
2)
The AI is designed for max. 24 V, the voltage level above 10 V is not interpreted
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 54

Electrical Installation 55-
4.1.3 PIN allocation Xi 80/410
Figure 26: Rear side of Xi 80/410
USB
Ethernet
PIF
1 VCC
1 VCC
2 D +
2 RS485 or AO
3 D -
3 RS485 or AI
4
Tx +
4 GND
5
Tx -
5 GND-ISO
6
Rx +
7
Rx - 8 GND
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 55

-56 -
4.1.4 PIN allocation Xi 400
Figure 27: Rear side of Xi 400
USB
PIF
1 VCC
1 INT
2 GND
2 SDA (I²C)
4 D -
3 SCL (I²C)
5 D +
4 DGND
5 3,3 V (Out)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 56

Electrical Installation 57-
If the process interface of the camera is directly connected to external hardware1) (without using the supplied
PIF cable) an activation of the field „Support proprietary PIF cable” in the menu Tools/
Configuration/ Device (PIF) in the PIX Connect software is necessary.
Figure 28: Support proprietary PIF cable
Consider that the input of the PIF is not protected if there is a direct PIF connection!
A voltage > 3 V on the INT pin will destroy the device!
1)
We recommend using only a switching contact between INT and DGND as external hardware (button, relay).
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 57

-58 -
4.1.5 Industrial Process Interface for Xi 80/410 (optional)
For use in industrial environment the industrial process interface with 500 V ACRMS isolation voltage between
Xi and process is available (connection box with IP65, 5 m, 10 m or 20 m standard or high temperature cable
for camera connection, terminal for process integration). [►Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF]
Pin assignment PIF cable (industrial process interface)
Figure 29: Connections of the industrial Process Interface for
Xi 80/410
GREEN
RS485 B
YELLOW
RS485 A
WHITE
12 V
BROWN
GND
SHIELD
GND
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 58

Electrical Installation 59-
The process interface can be activated via the software choosing the following options:
Analog Input (AI):
Emissivity, ambient temperature, reference temperature, uncommitted value, flag control, triggered recording,
triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-/valley-hold, switch temperature
range
Analog Output (AO):
Main measure area, measure area, internal temperature, flag status, recording status, line scan status, alarm,
frame sync, fail-safe, external communication, autonomous status
Digital Output (DO):
Flag status, recording status, line scan status, alarm, frame sync, fail-safe, external communication, autonomous
status
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 59

-60 The industrial process interface provides the following in- and outputs:
Name
Description
max range1)/ status
INPUT 1 / 2 / 3
Analog or digital input
0-10 V 2)
AO1 / 2 / 3
Analog output 1, 2 and 3
Alarm output 1, 2 and 3
0-10 V
0/4-20 mA
DO1 / 2 / 3
Relay output 1, 2 and 3
open/ closed (red LED on) / 0...30 V, 400 mA
FS
Fail-safe relay
open/ closed (green LED on)/ 0...30 V, 400 mA
1)
depending on supply voltage; for 0-10 V on the AO the PIF has to be powered with min. 12 V.
2)
the AI is designed for max. 24 V, the voltage level above 10 V is not interpreted
The industrial PIF has a maximum of 3 analog outputs. To use more outputs, you can cascade
up to three PIFs, allowing you to use up to 9 analog or alarm outputs in total.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 60
Electrical Installation 61-
Figure 30: Connection of 3 industrial PIFs via RS485
Each stackable industrial PIF must have its own RS485 address. The address must be set
directly on the board. For the PIF which is the furthest away the 120R switch (TERM. –
Termination) has to be set.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 61

-62 -
The RS485 interface is defined for a length of 500 m.
The process interface has an integrated fail-safe mode. This allows to control conditions like interruption of
cables, shut-down of the software etc. and to give out these conditions as an alarm. The time constant of the
fail-safe is 1.5 seconds.
Controlled conditions on camera and software
Standard Process interface
ACXIIOCB1
Industrial Process interface
ACXIPIFCBxx
Interruption USB cable to camera
✓
-
Interruption data cable camera - PIF
✓
✓
Interruption power supply PIF
✓
✓
Shut-down of PIX Connect software
✓
-
Crash of PIX Connect software
-
-
Fail-Safe-Output
0 mA at analog output (AO)
open contact (fail-safe relay)/ green LED off
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 62

Electrical Installation 63-
4.1.6 Industrial Process Interface for Xi 400 (optional)
For use in industrial environment the industrial process interface with 500 V ACRMS isolation voltage between
Xi and process is available (connection box with IP65, 5 m, 10 m or 20 m standard or high temperature cable
for camera connection, terminal for process integration). [►Appendix F – Wiring diagrams PIF]
Pin assignment PIF cable (industrial process interface)
Figure 31: Connections of the industrial Process Interface for Xi 400
GREY
Interrupt
GREEN
SCL (I²C)
YELLOW
SDA (I²C)
WHITE
3.3 V
BROWN
GND
SHIELD
GND
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 63

-64 The process interface can be activated via the software choosing the following options:
Analog Input (AI):
Emissivity, ambient temperature, reference temperature, uncommitted value, flag control, triggered recording,
triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak-/valley-hold, switch temperature
range
Analog Output (AO):
Main measure area, measure area, internal temperature, flag status, recording status, line scan status, alarm,
frame sync, fail-safe, external communication
Digital Input (DI):
Flag control, triggered recording, triggered snapshots, triggered line-scanner, triggered event grabber, reset peak/valley-hold, switch temperature range
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 64

Electrical Installation 65-
The industrial process interface provides the following inputs and outputs:
Name
Description
max range1)/ status
A IN 1 / 2
Analog input 1 and 2
0-10 V 2)
D IN 1
Digital input
(active-low = 0…0,6 V)
24 V
AO1 / 2 / 3
Analog output 1, 2 and 3
Alarm output 1, 2 and 3
0/4-20 mA
DO1 / 2/ 3
Relay output 1, 2 and 3 3)
open/ closed (red LED on) / 0...30 V, 400 mA
FS
Fail-safe relay
open/ closed (green LED on)/ 0...30 V, 400 mA
1)
depending on supply voltage; for 0-20 mA on the AO the PIF has to be powered with min. 5V < (1.5 + working resistance * 0.021) <
24 V; Example: R
Load
= 500 ohm → U
min
= 1.5 + 500 * 0.021 = 12 V, R
Load
= 100 ohm → U
min
= 1.5 + 100 * 0.021 = 3.6 V → min. 5 V
2)
the AI is designed for max. 24 V, the voltage level above 10 V is not interpreted
3)
active if AO1, 2 or 3 is/ are programmed as alarm output
The alarm output can be configured as a threshold between 0-4 mA for no alarm and between
10-20 mA as alarm. For values outside the respective range, the relay does not switch on the
DO.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 65

-66 The process interface has an integrated fail-safe mode. This allows to control conditions like interruption of
cables, shut-down of the software etc. and to give out these conditions as an alarm. The time constant of the
fail-safe is 1.5 seconds.
Controlled conditions on camera and software
Standard Process interface
ACPIPIF
Industrial Process interface
ACPIPIFMACBxx
Interruption USB cable to camera
✓
✓
Interruption data cable camera - PIF
✓
✓
Interruption power supply PIF
✓
✓
Shut-down of PIX Connect software
✓
✓
Crash of PIX Connect software
-
✓
Fail-Safe-Output
0 V at analog output (AO)
open contact (fail-safe relay)/ green LED off
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 66

Electrical Installation 67-
4.2 Example for a Fail-Safe monitoring of the Xi with a PLC
Figure 32: Fail-Safe monitoring states
Fail-Safe monitoring states
[1]
Breakdown of PIF power supply
[4]
Malfunction of Xi
[2]
Cable break of fail-safe cable
[5]
Breakdown of Xi power supply/ Interruption of USB cable
[3]
Interruption of cable Xi-PIF
[6]
Malfunction of PIX Connect software
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 67

-68 -
Figure 33: Fail-Safe monitoring states
Fail-Safe monitoring states
[1]
Breakdown of PIF power supply
[5]
Malfunction of Xi
[2]
Cable break of fail-safe cable
[6]
Breakdown of Xi power supply/ Interruption of USB cable
[3]
Short circuit of fail-safe cable
[7]
Malfunction of PIX Connect software
[4]
Interruption of cable Xi-PIF
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 68

Electrical Installation 69-
4.3 USB cable extension for Xi 400
The maximum USB cable length is 20 m. For greater distances between Xi 400 and computer or for standalone solutions the optional USB Server Gigabit (Part No.: ACPIUSBSGB) is provided:
Figure 34: USB Server Gigabit
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 69

-70 -
5 Functions
5.1 Ethernet Xi 80/410
The Xi 80/410 has a direct Ethernet interface. The advantage is cable lengths of up to 100 m. For example, a
switch can be used to extend the distances. The associated Ethernet cable (Order No.: ACXIETCBx) must
be ordered separately. Ethernet is supported from software version Rel. 3.2.3020.0 and firmware 3008.
Using the Ethernet connection, the device must be supplied with power. This can be done either via:
• the internal PIF cable via the terminal block (5-30 V)
• the stackable PIF (5-24 V, Order No.: ACXIPIFCBx)
• PoE (Power over Ethernet)
For the PoE variant, a PoE adapter (Order No.: ACXIETPOECB1) and a PoE injector (Order No.:
ACPIPOE) or PoE switch (e.g. Netgear GS510TLP) are also required.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 70

Functions 71-
Figure 35: Possibilities of power supply for Xi 80/410 via Ethernet connection
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 71

-72 -
5.1.1 Ethernet setup (Point-to-Point-Connection)
After connecting the Ethernet cable to the camera and the PC, the first thing you need to do is to make the
network settings on the PC.
The devices are delivered with the following factory settings:
• IP address camera: 192.168.0.101
• IP address PC: 192.168.0.100
• Port number: 50101
To do this, go to Control Panel and open the Network and Sharing Center. Go on LAN connection.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 72

Functions 73-
Click on Properties.
Mark Internet protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and go
to Properties again
In the register card General enable the
checkbox Use the following IP
address. Now enter a user defined IP
address for your PC (192.168.0.100).
This must be identical to the address
set in the PIX Connect software.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 73

-74 Then close all windows with OK. The network settings on the PC are complete.
Now start the PIX Connect software and activate the Ethernet
function. To do this, go to the menu Devices and Enable Ethernet.
When a Windows Firewall window appears make sure to select allow all three network parts
(domain, private, public) in order to allow the communication with the device.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 74

Functions 75-
The approval of programs can also be activated afterwards in the Windows Firewall settings of
the PC (under Windows Firewall and Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall).
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 75

-76 -
The device is now ready for the Ethernet connection
and is listed in the menu under Devices. The
camera is identified by a network icon and the
network address and port number. Select the
device. A connection to the device is established
and the temperature measurement can begin.
To change the address settings, go to Devices and
Ethernet settings (TCP/IP). The address for the device is
assigned under Device address. This must have a
different address (last block) to the other participant (e.g.,
PC) (Send to address (local computer)). It is important
that the network part (first three blocks) must be identical
for both addresses. The address range of the individual
blocks can be between 0 and 255.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 76

Functions 77-
Additionally, a separate port number must be configured. The selected number can be between 1 and
65535.
If several cameras with different port numbers are connected and a specific camera is to be communicated
with, the corresponding camera can be determined via Listen on port number.
The port range used should be between 49152 ... 65535. When using other ports, it could be
that they are already reserved or assigned.
When using multiple Xi 80/410 cameras in a network, the data rate must be considered:
➢ Switch with 100 Mbps: approx. 17 devices (Xi 80), approx. 2 devices (Xi 410 with 25 Hz)
➢ Switch with 1000 Mbps: approx. 170 devices (Xi 80), approx. 26 devices (Xi 410 with
25 Hz)
In addition to the data rate also make sure the power performance of the PC is high enough.
Each device used requires its own instance.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 77

-78 -
5.2 Autonomous operation Xi 80/410
A special feature of the Xi 80/410 is the autonomous operation. There is no need for a permanent connection
to the PIX Connect software. Only a few settings must be set in advance in the software.
To do this, connect the PIF and Ethernet or USB cables
to the device. Then connect the Xi to your PC and start
the PIX Connect software (see 7 Software PIX
Connect).
Position and focus (see 2.4 Optical specifications) the
camera so that your object to be measured is perfectly
visible in the image. First define the desired
measurement area with the corresponding mode you
want to output.
Figure 36: Connection Xi 80/410 to PC via
Ethernet/USB
Now go to the configuration menu on Device (PIF). There you first select the PIF type (in this case: Internal
PIF). Then select under Analog Outputs (AO) the function that is to be output autonomously. Then press
Setup, make your settings, and make sure that the checkbox is set to using autonomously by device. By
pressing the OK button an @ sign can be found in the configuration menu Devices (PIF), which indicates the
autonomous operation.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 78

Functions 79-
Figure 37: Configurations menu Device (PIF)
Figure 38: Setup
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 79

-80 -
Only for Xi 410
When using the Xi 410 camera, an important additional
setting must be made for autonomous operation. When
all the configurations have been made, it is important to
write them to the device. This is done in the menu under
Devices and Set configuration to device.
If the device is reconnected to a PC after autonomous
operation and the settings are to be transferred from the
device to the software, this is done in the menu under
Devices and Get configuration from device.
Figure 39: Set configuration to device
An arrow marked in red means that the configuration is different between the camera and the
software. As soon as the configuration is loaded into the device, the arrow appears blue .
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 80

Functions 81-
In general, these are all the settings that must be set in the PIX Connect software in order to operate the
device autonomously. You can now close the software and then disconnect the Ethernet or USB cable. To
start the device autonomously, a 5-30 V power supply must be connected to the terminal block. Now the
used input/output must be connected. The resulting value can be displayed for example on a multimeter (see
Figure 40).
Figure 40: Electrical installation for autonomous operation Xi 80/410
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 81

-82 -
• Autonomous operation also works via the industrial/stackable PIF of the Xi 80. The device is
powered by the power supply of the PIF.
• Up to 9 measure areas (for Xi 80 with firmware 3013 or higher) and up to 3 measure areas
(Xi 410) can be output autonomously. The use of three stackable PIFs is required. Three
analog outputs are possible per stackable PIF. The response time is 20 ms for Xi 80 and
640 ms for Xi 410.
Note: Several measuring areas can be combined into one measuring area via a so-called
super area.
• Autonomous mode cannot be set using the Main measure area function (configuration menu-
Device (PIF)). To output a measure area autonomously, the function Measure area must be
used.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 82

Functions 83-
5.2.1 Hot- / Coldspot function in autonomous operation
The setting for a hot- or coldspot in autonomous mode differs from the general procedure. Marking a
measure area as hot- or coldspot does not work. Instead, a user defined rectangle must be selected under
the tab measure areas of the configuration dialog. In addition, under Mode, you must set whether the
maximum (for hotspot) or minimum (for coldspot) should be output.
Figure 41: Setting a hotspot for autonomous operation
For a hot- or coldspot output in the full field of view of the
camera, the user defined rectangle must also fill out this size.
Note: Predefined Layout in the software available under
Tools and Layouts: Xi 80 Hot spot autonomous or Xi 410
Hot spot autonomous.
Figure 42: Measure area over entire field of view
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 83

-84 -
5.3 Use of Shutter
The shutter system is supplied with a control box
(for pin assignment, see also Figure 16). The
servo motor of the shutter is connected to this
control box. There are several ways to operate
the control box. For all listed options, an input
signal (IN 1) must be connected. This input signal
can, for example, come from a PLC, a light
barrier or a sensor. This signal opens and closes
the shutter. A second input signal (IN 3) can be
used to realize a fast-closing mode. The closing
time in this mode is only 100 ms.
Figure 43: Control box Shutter
By using the process interface (PIF), the input signal to the software can be passed on and used as a trigger
signal in the software. For example, an automatic recording can take place when the shutter is opened.
The process interface cable supplied with the cameras can be connected directly to the control box (upper
terminal block: CAMERA INTERFACE / PIF). Alternatively, the separately obtained industrial or stackable
PIF can also be connected to the control box (if several outputs and inputs are used). In this case, the
outputs and inputs used (e.g. AO from control box with AO from PIF) must be connected with each other.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 84

Functions 85-
When using more than one shutter and the opening / closing of the shutter should be
simultaneously, the switch S4 on one control box must be set to mA and the others to mV (see
Figure 43).
Figure 44: Connection of control box, shutter and industrial PIF
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 85

-86 -
5.3.1 Settings in PIX Connect Software
After the hardware installation (connection control box shutter and PIF) the following settings can be made in
the software:
• Automatic Recording: By opening the shutter through input signal IN 1, an automatic recording can
be started. For this, the AI must be configured to Triggered Recording in the software in the
configuration menu Device (PIF).
• Close shutter after recording/line scan: When the recording is finished, the shutter can be closed
by an analog signal. To do this, in the software in the configuration menu Device (PIF) of the AO
must be configured for Recording Status. If the shutter is to be closed after a line scan, Line scan
status must be selected.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 86

IRmobile App 87-
6 IRmobile App
The imagers have a direct connection to an Android smartphone or tablet. All you must do
is download the IRmobile app for free in the Google Play Store. This can also be done via
the QR code. An IRmobile app connector is recommended for connection to the device
(Xi 80/410: Part-No.: ACXI80IACM (micro-USB) or ACXI80IACC (USB-C), Xi 400: Part-
No.: ACPIIACM (micro-USB) or ACPIIACC (USB-C).
With IRmobile you can monitor and analyze your infrared temperature measurement directly on a connected
smartphone or tablet. All you need is an Optris infrared camera. This app runs on most Android (5 or higher)
devices with a micro-USB port or USB-C port that supports USB OTG (On The Go). The app is easy to use:
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 87

-88 After you have connected your camera to the micro-USB port or USB-C port of your smartphone or tablet,
the app launches automatically. The calibration files are automatically downloaded from the internet. The
device is powered by your smartphone. A hotspot indicates the hottest pixel in the image and a coldspot the
coldest pixel in the image.
IRmobile app features:
➢ Live infrared image with automatic hot-/ and coldspot search
➢ Changing the color palette, scaling and temperature range
➢ Change of temperature unit: Celsius or Fahrenheit
➢ Setting of temperature range scaling (Manual, Min/Max, 3 sigma)
➢ Creating a snapshot
➢ Integrated simulator
IRmobile supported for:
➢ Optris IR cameras: Xi and PI series
➢ Optris pyrometers: Compact series, high performance series and video
thermometers
➢ For Android 5 (or higher) devices with a micro-USB port or USB C port
that supports USB OTG (On The Go)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 88

Software PIX Connect 89-
7 Software PIX Connect
Minimum system requirements:
• Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10
• USB interface
• Hard disc with at least 30 MByte of free space
• At least 128 MByte RAM
A detailed description is provided in the software manual on the USB stick. See also Help menu
in the PIX Connect software (Help → Documentation).
Alternatively, the software can also be downloaded via the Optris website under the following
link: https://www.optris.global/pix
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 89

-90 -
7.1 Installation and initial start-up
• All drivers are booted via Windows OS automatically. A driver installation is not necessary.
• By default, the program starts automatically in the installed language.
1. Insert the included USB stick into the according port on your computer.
2. Please start Setup.exe. Follow the instructions of the wizard until the installation is finished.
The installation wizard places a launch icon on the desktop and in the start menu:
Start\Programs\Optris GmbH\PIX Connect
3. To connect the camera to the PC, plug the USB cable to the camera first. Afterwards connect it with
the PC (to disconnect the camera and the computer remove the USB cable from the computer first
and then disconnect it from the camera).
4. Start the software.
At the initial start the software asks for the calibrations files which are available via internet or on the
USB stick (only for Xi 400). With the Xi 80/410, the calibration files are already included in the
device.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 90

Software PIX Connect 91-
5. Install the calibration files at first start of the software (only necessary for Xi 400).
After the calibration files have been installed the live image from the camera is shown inside a
window on your PC screen.
6. Choose the desired language in the menu Tools → Language.
7. Adjust the focus of the image by using the distance function in the software (Menu View/ Windows/
Distance or over the icon ):
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 91

-92 -
7.2 Software window
Figure 45: Software window
1
2 3 2
5 6 7 9 4
10
11 128
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 92

Software PIX Connect 93-
1
IR image from the camera
2
Temperature profile: Shows the temperatures along max. 2 lines at any size and position in the image.
3
Control displays: Displays all temperature values in the defined measure areas like Cold Spots, Hot Spots, temperature at
cursor, internal temperature and chip temperature.
Alarm settings: Bar showing the defined temperature thresholds for low alarm value (blue arrow) and high alarm value (red
arrow). The color of numbers within control displays changes to red (when temp. above the high alarm value) and to blue
(when temp. below the low alarm value).
4
Temperature of measure area: Analyses the temperature according to the selected shape, e.g. average temperature of the
rectangle. The value is shown inside the IR image and the control displays.
5
Reference bar: Shows the scaling of temperature within the color palette.
6
Temperature time diagram: Shows the temperature curves over time for selectable region of interest (ROI)
7
Histogram: Shows the statistic distribution of single temperature values.
8
Automatic / manual scaling of the palette (displayed temperature range): Man., </> (min, max), 1σ : 1 Sigma, 3σ : 3 Sigma,
OPT: Palette optimization
9
Distance function: Adjustment of the motor focus to focus the IR picture
10
Menu and Toolbar (Icons)
11
Icon enabling switching between color palettes
12
Status bar: Serial number, optic, temperature range, cursor position, device framerate/ display framerate, emissivity, ambient
temperature, flag status
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 93

-94 -
7.3 Basis features of the software PIX Connect
Extensive infrared camera software
• No restrictions in licensing
• Modern software with intuitive user interface
• Remote control of camera via software
• Display of multiple camera images in different windows
• Compatible with Windows 7, 8 and 10
High level of individualization for customer specific display
• Various language option including a translation tool
• Temperature display in °C or °F
• Different layout options for an individual setup (arrangement of
windows, toolbar)
• Range of individual measurement parameter fitting for each application
• Adaption of thermal image (mirror, rotate)
• Individual start options (full screen, hidden, etc.)
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 94

Software PIX Connect 95-
Video recording and snapshot function (IR)
• Recording of video sequences and detailed frames for further analysis
or documentation
• Adjustment of recording frequency to reduce data volume
• Display of snapshot history for immediate analysis
Extensive online and offline data analysis
• Analysis supported by measurement fields, hot and cold spot
searching, image subtraction
• Real time temperature information within main window as digital or
graphic display (line profile, temperature time diagram)
• Slow motion repeat of radiometric files and analysis without camera
being connected
• Editing of sequences such as cutting and saving of individual images
• Various color palettes to highlight thermal contrasts
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 95

-96 -
Automatic process control
• Individual setup of alarm levels depending on the process
• Definition of visual or acoustic alarms and analog data output
• Analog and digital signal input (process parameter)
• External communication of software via COM-Ports and DLL
• Adjustment of thermal image via reference values
Temperature data analysis and documentation
• Triggered data collection
• Radiometric video sequences (*.ravi) radiometric snapshots (*.tiff)
• Text files including temp. information for analysis in Excel (*.csv, *.dat)
• Data with color information for standard programs such as Photoshop
or Windows Media Player (*.avi, *.tiff)
• Data transfer in real time to other software programs DLL or COM-Port
interfaces
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 96

Basics of Infrared Thermometry 97-
8 Basics of Infrared Thermometry
Depending on the temperature each object emits a certain amount of infrared radiation. A change in the
temperature of the object is accompanied by a change in the intensity of the radiation.
Searching for new optical material William Herschel by chance found the infrared radiation in 1800.
Figure 46: William Herschel (1738-1822)
He blackened the peak of a sensitive mercury thermometer. This thermometer, a glass prism that led sun
rays onto a table made his measuring arrangement. With this, he tested the heating of different colors of the
spectrum. Slowly moving the peak of the blackened thermometer through the colors of the spectrum, he
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 97

-98 noticed the increasing temperature from violet to red. The temperature rose even more in the area behind
the red end of the spectrum. Finally he found the maximum temperature far behind the red area.
Nowadays this area is called “infrared wavelength area”.
Figure 47: The electromagnetic spectrum and the area used for temperature measurement
For the measurement of “thermal radiation” infrared thermometry uses a wave-length ranging between 1 µm
and 20 µm. The intensity of the emitted radiation depends on the material. This material contingent constant
is described with the help of the emissivity which is a known value for most materials (►9 Emissivity).
Infrared thermometers are optoelectronic sensors. They calculate the surface temperature based on the
emitted infrared radiation from an object. The most important feature of infrared thermometers is that they
enable the user to measure objects contactless. Consequently, these products help to measure the
temperature of inaccessible or moving objects without difficulties.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 98

Basics of Infrared Thermometry 99-
Figure 48: Main principle of non-contact thermometry
Infrared thermometers basically consist of the following components:
• Lens
• Spectral filter
• Detector
• Electronics (amplifier/ linearization/ signal processing)
The specifications of the lens decisively determine the optical path of the infrared thermometer, which is
characterized by the ratio Distance to Spot size. The spectral filter selects the wavelength range, which is
relevant for the temperature measurement. The detector in cooperation with the processing electronics
transforms the emitted infrared radiation into electrical signals.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 99

-100 The advantages of non-contact thermometry are clear - it supports:
• temperature measurements of moving or overheated objects and of objects in hazardous
surroundings
• very fast response and exposure times
• measurement without inter-reaction, no influence on the
• measuring object
• non-destructive measurement
• long lasting measurement, no mechanical wear
Figure 49: Non-contact thermometry
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 100

Basics of Infrared Thermometry 101-
Application field:
Monitoring of electronic
cabinets
R&D of electronics
R&D of electronic parts
Process control extruding
plastic parts
Process control
manufacturing solar
modules
Process control at
calendering
R&D of mechanical parts
Monitoring of cables
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
 Loading...
Loading...