
GlobeSurfer
®
II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S
Reference Manual
Version 3.16 R1D02

2
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION TO GLOBESURFER ® II 6
2 SETUP 8
2.1 Setting up WAN and LAN connections 8
2.2 PC Network Configuration 9
2.3 GlobeSurfer ® II Quick Setup Wizard 10
2.3.1 Quick Setup Wizard: Language 12
2.3.2 Quick Setup Wizard: Telephony 12
2.3.3 Quick Setup Wizard: UMTS 12
2.3.4 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless 13
2.3.5 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless Encryption 14
2.3.6 Quick Setup Wizard: Firewall Policy 15
2.3.7 Quick Setup Wizard: Finish 16
3 GLOBESURFER ® II MANAGEMENT CONSOLE 18
3.1 Accessing the GlobeSurfer ® II Management Console 18
3.2 Left Sidebar 18
3.3 Connection status 19
3.4 Managing tables 20
3.5 Getting Help 21
4 SMS 22
4.1 SMS Create 22
4.2 Inbox 23
4.3 Sent 24
4.4 Archive 24
4.5 Templates 24
4.6 SIM Card 25
4.7 Drafts 25
4.8 Settings 26
5 CONNECTION SETTINGS 26
5.1 Network Map 26
5.2 Network Connections 27
5.2.1 Connection Wizard 29
5.2.2 LAN Bridge 32
5.2.2.1 Creation with the Connection Wizard 32
5.2.2.2 General 34
5.2.2.3 Internet Protocol 34
5.2.2.4 Bridge Settings 35
5.2.2.5 DNS Server 36
5.2.2.6 IP Address Distribution 36
5.2.2.7 Routing 38
5.2.2.8 Internet Connection Firewall 38
5.2.2.9 Additional IP Addresses 39
5.2.3 LAN Ethernet 39
5.2.3.1 General 40
5.2.3.2 Internet Protocol 41
5.2.3.3 DNS Server 42
5.2.3.4 IP Address Distribution 42
5.2.3.5 Routing 44
5.2.3.6 Internet Connection Firewall 44
5.2.3.7 Additional IP Addresses 45
5.2.4 LAN Wireless 45
5.2.4.1 General 48
5.2.4.2 Wireless Access Point 48
5.2.4.3 Wireless Security 49
5.2.4.4 Internet Protocol 53
5.2.4.5 DNS Server 54
5.2.4.6 IP Address Distribution 54
5.2.4.7 Routing 56
5.2.4.8 Internet Connection Firewall 56
5.2.4.9 Additional IP Addresses 57
5.2.5 WAN Cellular 57
5.2.5.1 General 58
5.2.5.2 Internet Protocol 59
5.2.5.3 DNS Server 59
5.2.5.4 Routing 60
5.2.5.5 Internet Connection Firewall 61
5.2.6 Configuring your Wireless Windows® XP clients 61
5.3 Security 64
5.3.1 General 64
5.3.2 Access control 67
5.3.3 Port forwarding 69
5.3.4 DMZ host 73
5.3.5 Port triggering 74
5.3.6 Website restrictions 78
5.3.7 Advanced filtering 80
5.3.8 Security log 82

3
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6 SYSTEM SETUP 88
6.1 Telephone 88
6.1.1 Missed calls 88
6.1.2 Incoming calls 88
6.1.3 Outgoing calls 89
6.1.4 Telephone settings 89
6.2 SIM setup 89
6.3 Unlock device 91
6.4 System monitoring 91
Connections 91
6.4.1 Log 92
6.4.2 System 93
6.4.3 About GlobeSurfer ® II 93
6.4.4 Configuration file 93
6.4.5 Restart 94
6.4.6 Restore defaults 95
6.4.7 Diagnostics 95
6.4.8 Ping 95
6.4.9 Performing a Traceroute 96
6.5 System settings 96
6.5.1 System 97
6.5.2 GlobeSurfer ® II Management Console Settings 98
6.5.3 Remote administration 98
6.5.4 Management Application Ports 98
6.5.5 System Logging Settings 98
6.5.6 Security Logging Settings 98
6.5.7 Outgoing Mail Server Settings 99
6.5.8 Firmware upgrade 99
6.5.8.1 Upgrading From a Local Computer 99
6.5.9 Date and time 100
6.5.10 Users 101
6.6 Advanced 102
6.6.1 Remote administration 102
6.6.2 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP 104
6.6.3 Universal Plug and Play 105
6.6.4 Scheduler Rules 105
6.6.5 Certificates 107
6.6.5.1 Overview 107
6.6.5.2 Digital Certificates 108
6.6.5.3 X.509 Certificate Format 108
6.6.5.4 GlobeSurfer ® II Certificate Stores 109
6.6.5.4.1 Requesting an X509 Certificate 109
6.6.5.4.2 Creating a Self-Signed Certificate 114
6.6.5.4.3 Loading a PKCS#12 Format Certificate 116
6.6.6 Radius 117
6.6.7 Routing 118
6.6.8 Network objects 119
6.6.9 Dynamic DNS 120
6.6.9.1 Opening a Dynamic DNS Account 121
6.6.9.2 Using Dynamic DNS 121
6.6.10 IP address distribution 122
6.6.10.1 DHCP Server Settings 123
6.6.10.2 DHCP relay settings 124
6.6.10.3 DHCP connections 127
6.6.11 DNS server 128
6.6.11.1 Viewing and Modifying the DNS Table 129
6.6.12 IPSEC Internet Protocol Security 130
6.6.12.1 IPSec Settings 131
6.6.12.1.1 Public Key Management 131
6.6.12.2 IPSec Connection Settings 133
6.6.12.3 IPSec Gateway-to-Host Scenario Connection 138
6.6.12.3.1 Configuring IPSec on GlobeSurfer ® II 139
6.6.12.3.2 Configuring IPSec on the Windows Host 142
6.6.13 L2TP server 156
6.6.13.1 Configuring the L2TP Server 156
6.6.13.2 Advanced L2TP Server Settings 157
6.6.14 PPTP server 158
6.6.14.1 Configuring the PPTP Server 158
6.6.14.2 Advanced PPTP Server Settings 159
6.6.15 Protocols 160
LIST OF ACRONYMS 162
GLOSSARY 164

4
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
1. INTRODUCTION TO GLOBESURFER ® II
Within minutes, you can connect to your mobile network and use a wireless connection to the Internet through the mobile network.
GlobeSurfer ® II is compatible with GSM and 3G mobile networks and supports GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and HSDPA technologies.
Tip: To achieve the best possible reception, check the signal strength on the display of the unit (the more bars the better the reception). You
may find that placing the unit near a window provides the best reception.
Simple set-up
GlobeSurfer ® II provides you with a quick installation and set-up that gets you easily and quickly connected to the Internet. You can use an
Internet browser (e.g. Microsoft ® Internet Explorer 6.0 or Firefox ® 1.5) and most personal computers, including Windows ®, Macintosh ® and
Linux. The ‘Quick Setup Wizard’ introduces you to the basic settings that need to be configured for use with the mobile network. Once you
have configured, you can review and enable customised wireless security settings.
Instant protection
Your GlobeSurfer ® II supports Network Address Translation (NAT). This network service hides the computers in your network so they cannot be
found or directly accessed from outside your network. A firewall is also included which, by default, blocks incoming traffic and allows outgoing
traffic.
Additional security
GlobeSurfer ® II supports both Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2) to protect your network data.
Security logs keep you aware of potential security risks and intrusion attempts. You can view logs online or via email.
Stay in touch
You can use GlobeSurfer ® II to send and receive SMS text messages. The display on the front of the unit lets you know when a new SMS
arrives. You can use GlobeSurfer ® II to make mobile phone calls. When you get a phone call the display shows the caller’s number and
indicates missed calls.
Important note
To protect your network from unauthorised access, and to make it more difficult for hackers to analyse your data, please configure the WLAN
security settings and enable WEP, WPA or WPA2 encryption on your GlobeSurfer ® II.
About This Manual
This manual describes configuration and operation of GlobeSurfer ® II. It is intended as a complement to the GlobeSurfer ® II User Guide to
provide reference information for the advanced user of the GlobeSurfer ® II. It is assumed that the hardware installation of GlobeSurfer ® II has
been done when the Reference Manual is read.
This version of the manual is valid for GlobeSurfer ® II version 3.16 R1D02. Other product versions with customer specific functions not
described in this manual, may be available.
5
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2. SETUP
Connecting your computer or home network to the gateway is a simple procedure, varying slightly depending on your operating system. This
chapter will help you to seamlessly integrate GlobeSurfer ® II with your computer or home network. The Windows default network settings
dictate that in most cases the setup procedure described below will be unnecessary. For example, the default DHCP setting in Windows
2000 is ’client’, requiring no further modification. However, it is advised to follow the setup procedure described below to verify that all
communication parameters are valid and that the physical cable connections are correct. The setup procedure consists of three consecutive
configuration stages:
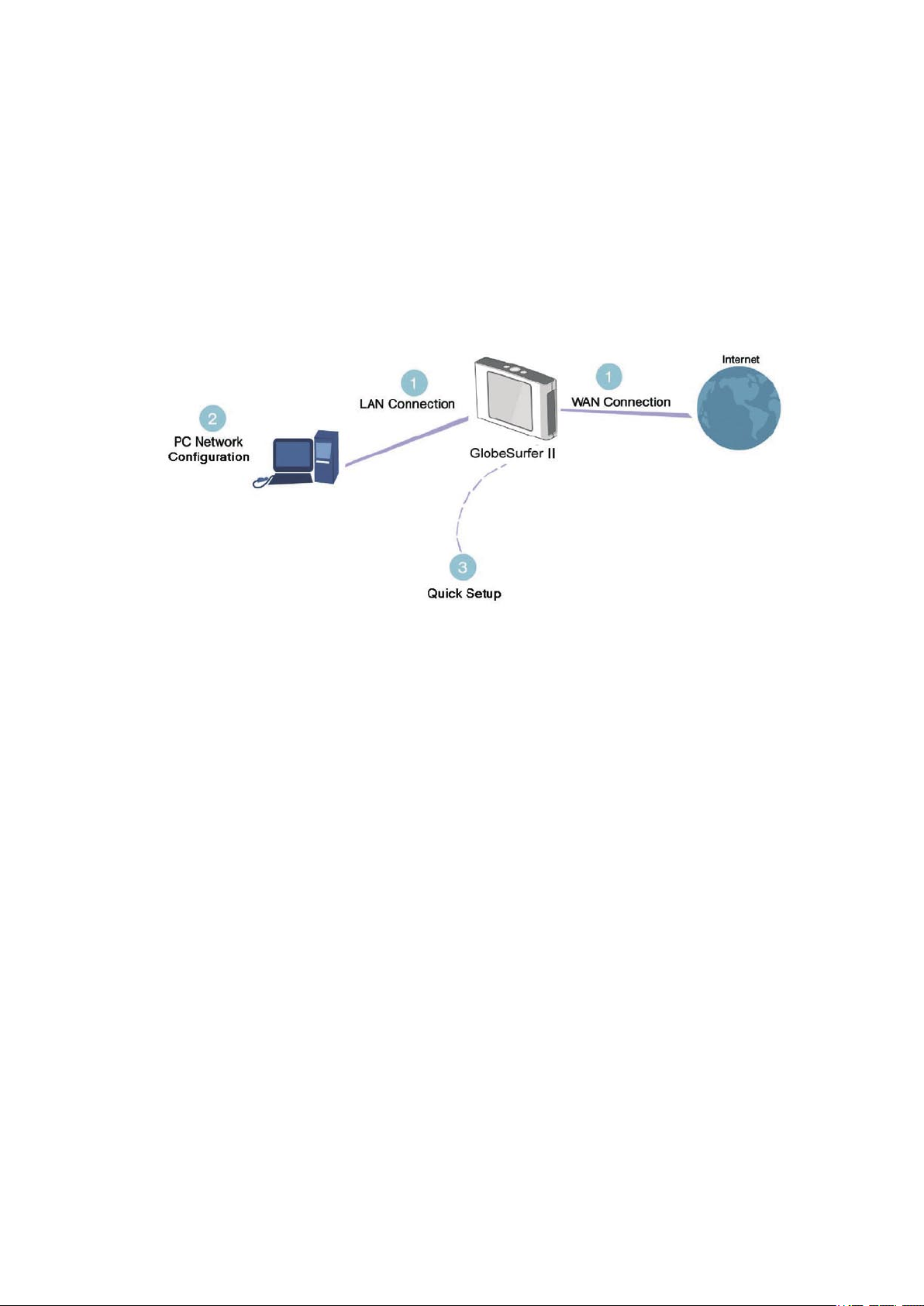
Figure 2.1 Hardware Configuration
1. Setting up WAN and LAN connections [2.1]
2. PC Network Configuration [2.2]
3. GlobeSurfer ® II Quick Setup [2.3]
2.1 Setting up WAN and LAN connections
· WAN Connection: Setting up the WAN connection requires that a SIM card is inserted correctly into the SIM slot of the
GlobeSurfer ® II. See the User Guide for instructions on how to insert the SIM card. With the SIM card in place you configure theWAN
connection through the Quick Setup of GlobeSurfer ® II (see section 2.3). The first time you login to GlobeSurfer ® II you will have to
enter a PIN code. The PIN code is received from your ISP, but normally provided separately from the SIM card for security reasons.
· LAN Connection: Your computer can connect to the gateway in two ways, either through Ethernet or through the use of Wireless.
The most common type of connection is Ethernet, with most platforms featuring four such ports. Use an Ethernet cable to connect
between an Ethernet port on your gateway and your computer’s network card. Please refer to the accompanying Installation Guides
for additional information.
2.2 PC Network Configuration
Each network interface on the PC should either be configured with a statically defined IP address and DNS address, or should be
instructed to automatically obtain an IP address using the Network DHCP server. GlobeSurfer 2 provides a DHCP server on its LAN and
it is recommended to configure your LAN to obtain its IP and DNS server IPs automatically. This configuration principle is identical but
performed differently on each operating system.
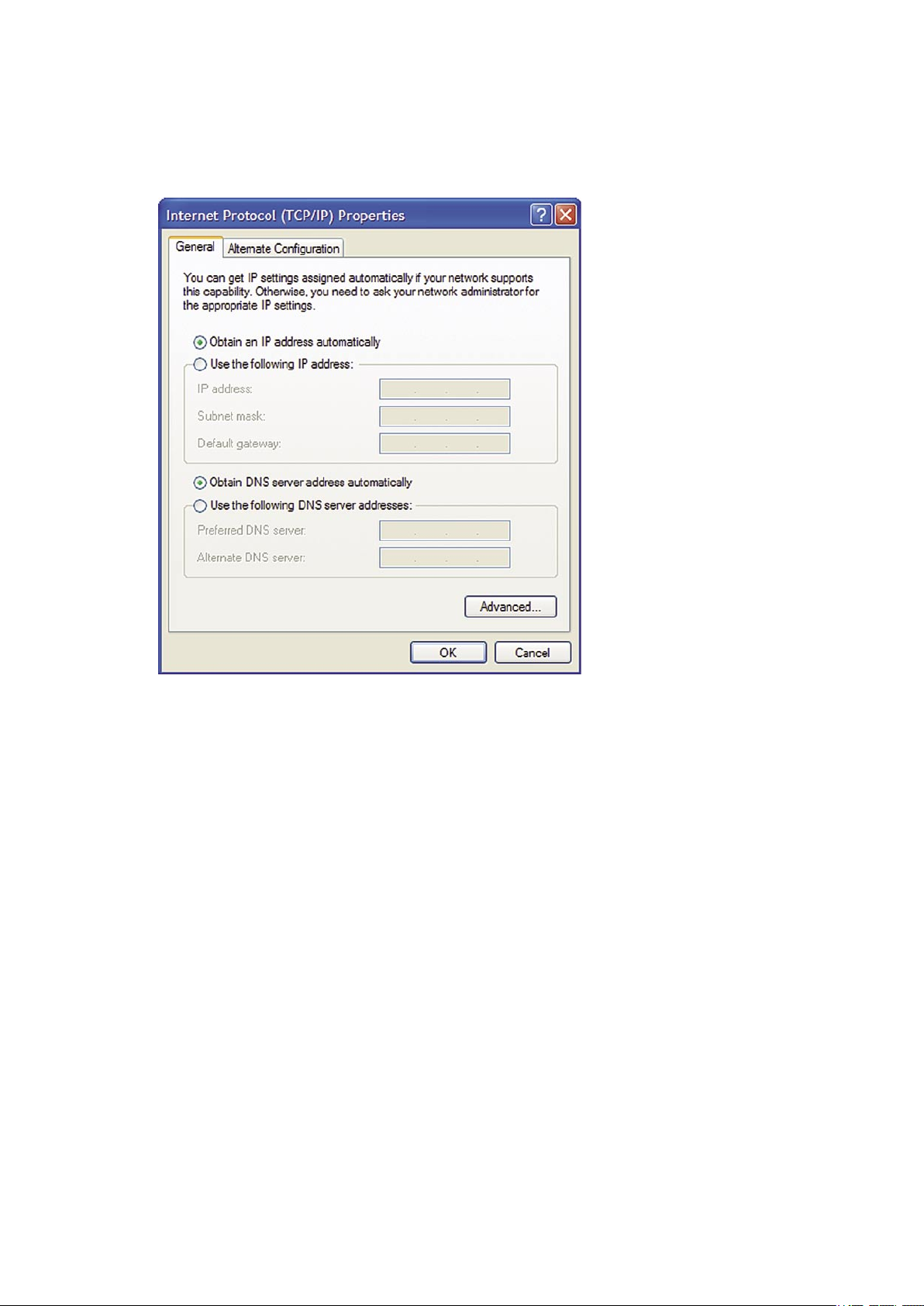
Figure 2.1displays the ’TCP/IP Properties’ dialog box as it appears in Windows XP. Following are TCP/IP configuration instructions for all
supported operating systems.
6
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 2.2 IP and DNS configuration
Windows XP
1. Access ’Network Connections’ from the Control Panel.
2. Right-click the Ethernet connection icon, and select ’Properties’.
3. Under the ’General’ tab, select the ’Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’ component, and press the ’Properties’ button.
4. The ’Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’ properties window will be displayed (see Figure 2.2).
5. Select the ’Obtain an IP address automatically’ radio button.
6. Select the ’Obtain DNS server address automatically’ radio button.
7. Click ’OK’ to save the settings.
Windows 2000/98/Me
1. Access ’Network and Dialing Connections’ from the Control Panel.
2. Right-click the Ethernet connection icon, and select ’Properties’ to display the connection’s properties.
3. Select the ’Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’ component, and press the ’Properties’ button.
4. The ’Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’ properties will be displayed.
5. Select the ’Obtain an IP address automatically’ radio button.
6. Select the ’Obtain DNS server address automatically’ radio button.
7. Click ’OK’ to save the settings.
7
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Windows NT
1. Access ’Network’ from the Control Panel.
2. From the ’Protocol’ tab, select the ’Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’ component, and press the ’Properties’ button.
3. From the ’IP Address’ tab select the ’Obtain an IP address automatically’ radio button.
4. From the ’DNS’ tab, verify that no DNS server is defined in the ’DNS Service Search Order’ box and no suffix is defined in the
’Domain Suffix Search Order’ box.
Linux
1. Login into the system as a super-user, by entering ”su” at the prompt.
2. Type ”ifconfig” to display the network devices and allocated IP addresses.
3. Type ”pump -i <dev>”, where <dev> is the network device name.
4. Type ”ifconfig” again to view the new allocated IP address.
5. Make sure no firewall is active on device <dev>.
2.3 GlobeSurfer ® II Quick Setup Wizard
The GlobeSurfer ® II management console allows you to control various GlobeSurfer ® II system parameters. The interface is accessed
through a web browser:
1. Start a web browser on your PC.
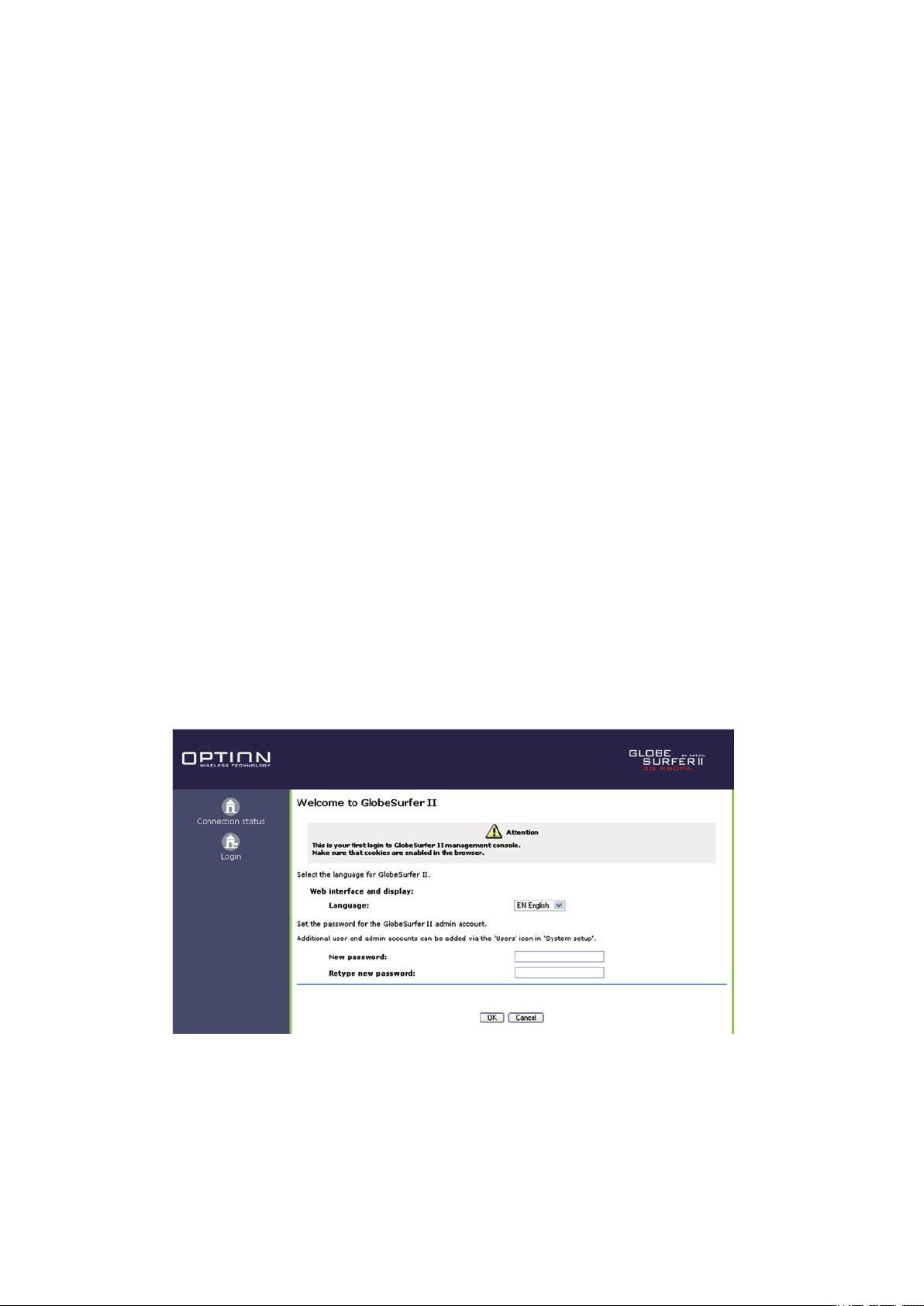
2. Enter the address 192.168.1.1 to display the GlobeSurfer ® II management console. When first logging on to the management
console, the welcome screen will appear (see Figure 2.3). Configure your language settings and enter a password. To verify
correctness retype the password, and click ‘OK’ to login to the management console. For security reasons it is strongly
recommended that you specify a password. However, make sure you remember your new user name and password, since this is the
only way you will be able to login to the GlobeSurfer ® II from now on.
Figure 2.3 Welcome to GlobeSurfer® II
3. After choosing your password and clicking ‘OK’ you will be forwarded to the ‘Quick Setup Wizard’ page (see Figure 2.3). Click ‘OK’ to
continue the ‘Quick Setup Wizard’.

8
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 2.4 Welcome to the Quick Setup Wizard
4. The ‘Quick Setup Wizard’ helps you to quickly set the most important settings of your GlobeSurfer ® II. If you would like to complete
the ‘Quick Setup’ without using the Wizard just click ‘Cancel’. Alternatively, click the ‘Quick Setup’ icon on the left sidebar, after login
in. The following sections describe the various configuration parameters of ‘Quick Setup’. Once you have filled the ‘Quick Setup’
sections as described below, click the ‘OK’ button to configure your GlobeSurfer ® II.
2.3.1 Quick Setup Wizard: Language
Select the language you would like to use on the GlobeSurfer ® II Management Console and Display (see Figure 2.5).
Figure 2.5 Quick Setup Wizard: Language
2.3.2 Quick Setup Wizard: Telephony
Select the country for your telephone handset. This will adapt the telephone connector of GlobeSurfer ® II to work with your
handset (see Figure 2.6).
Figure 2.6 Quick Setup Wizard: Telephony

9
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2.3.3 Quick Setup Wizard: UMTS
Check or change the following settings on the Quick setup screen to configure the UMTS connection (see Figure 2.7):
Figure 2.7 Quick setup Wizard: UMTS
Access point name:
Enter the access point name as provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), or accept the name already set.
UMTS connect method:
· Connect Manually: connect to the Internet by clicking ‘Connect’ on the ‘Connection Status’ page in the management
console or press the ‘Connect’ button on the GlobeSurfer ® II unit.
· Automatically connect upon traffic: GlobeSurfer ® II will automatically connect when you attempt to send data via the
Internet.
In case of inactivity, disconnect after (minutes): The default is zero (0), meaning UMTS will stay connected until
manually disconnected. The maximum is 1440 minutes (24hrs).
Note: Incoming traffic is treated as inactivity.
2.3.4 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless
SSID:
The Service Set Identifier: enter a name for your local wireless network (WLAN) (maximum 32 characters).
Note: Setting the SSID to something unique will make it much easier to identify your own wireless network, especially if there
are other wieless networks available in the nearby area.
SSID broadcast:
If you set the ‘Enabled’ checkbox to broadcast then other devices can detect and connect to your WLAN. Clear the checkbox
to disable broadcasting and hide the name of your network. This provides minimal security, as other devices have to know the
SSID to connect. You can install the WLAN with this feature enabled and then disable it once you have set up GlobeSurfer ® II
and its associated wireless clients.

10
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 2.8 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless
2.3.5 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless Encryption
In order to prohibit unauthorized access to your GlobeSurfer ® II, make sure to apply sufficient security and encryption on your
wireless network.
If WPA2 is supported by your wireless clients it is recommended to apply WPA2 encryption to your wireless network as it offers
the highest level of security.
Depending on your choice of security method, the Wireless Encryption page will refresh with relevant configuration choices.
Unless ‘No Encryption’ is selected you will be asked to enter an encryption key in either HEX or ASCII format. HEX format
requires a hexadecimal key (‘0’-‘9’, ‘a’-‘f’) of various length depending on your selection. An ASCII key consists of a passphrase of various length that will be translated by the GlobeSurfer ® II into a HEX key. Using an ASCII key could be easier to
remember than a HEX key, but in some cases there are compatability issues between different vendors of wireless equipment.
Hence, if you are experiencing problems when using ASCII key, try to use HEX keys instead.
Available choices are:
· ‘No encryption’ This option is not recommended except during installation of your network.
· ‘WEP’ Wireless Equivalent Privacy is a 64-bit or 128-bit encryption method with user configurable fixed keys.
· ‘WPA’ Wi-Fi Protected Access is a 256-bit encryption method with keys that change automatically over time.
· ‘WPA2’ A more secure version of WPA with implementation of the 802.11i standard.
· ‘Keep current (radius based) scheme’ This option is only available if advanced encryption settings have previously been
configured.
Figure 2.9 Quick Setup Wizard: Wireless Encryption

11
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2.3.6 Quick Setup Wizard: Firewall Policy
The GlobeSurfer ® II has three different predefined Firewall Policies:
· ‘Minimum Security’ Lowest level of firewall security allowing both incoming and outgoing traffic.
· ‘Typical Security’ Offers some firewall security, but is still open for all connections initiated from clients connected to the
GlobeSurfer ® II.
· ‘Maximum Security’ Highest level of firewall security where only most commonly used protocols are allowed also for local
clients trying to connect to the Internet.
To learn more about these predefined security levels, please refer to section 5.3.1. It is also possible to add more advanced
firewall policies than these three predefined levels. To learn more about this, please see chapter 5.3.
Figure 2.10 Quick Setup Wizard: Firewall Policy
2.3.7 Quick Setup Wizard: Finish
The last page of the Quick Setup Wizard shows all the settings made on previous pages. If they all look correct, press the
‘Finish’ button to apply these settings.
If you want to change any settings, use the ‘Back’ button to navigate to the appropriate page and modify that setting.
Press the ‘Cancel’ button if you want to quit the Quick Setup Wizard without applying any new changes.
Figure 2.11 Quick Setup Wizard: Finish

12
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3 GLOBESURFER ® II MANAGEMENT CONSOLE
The GlobeSurfer ® II management console described here allows you to control various GlobeSurfer ® II system parameters, using a userfriendly graphical interface. The management console includes a connection status screen, a quick setup screen, network configuration,
security configuration, authentication with multiple-user support, connection monitoring and more.
3.1 Accessing the GlobeSurfer ® II Management Console
To access the management console:
· Launch a Web-browser on a PC in the LAN or WLAN.
· Type the IP address of the GlobeSurfer ® II or a name as provided by the supplier in the address bar (Internet Explorer) or location bar
(Netscape Navigator). The default IP address is 192.168.1.1, and default name is http://umts-gateway.mydomain.
· Enter your username and password to log on to the web-based management console.
Your session will automatically time-out after a few minutes of inactivity. If you try to operate the management console after the session
has expired the Login screen will appear and you will have to reenter your user name and password before proceeding. This feature
helps to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the management console and changing the GlobeSurfer ® II settings.
3.2 Left Sidebar
The GlobeSurfer ® II management console screens have been grouped into several subject areas and may be accessed by clicking on
the appropriate icon in the left sidebar.
The subject areas are:
· Connection status: Display the status of the Internet connection (see Section 3.3)
· Quick Setup: Quick access to basic configuration settings (see Section 2.3).
· SMS: Manage your SMS messages (see Chapter 4).
· Connection Settings: Create and configure network connections (see Chapter 5).
· System Setup: You can access ‘Telephone’, ‘Date and Time’, ‘SIM’ settings, ‘Firmware upgrade’ and more (see Chapter 6).
· Advanced: This section is intended for more advanced users. Changes to these settings could adversely affect the operation
of your network. Please refer to the ‘Reference Manual’.
· Login / Logout: Login to or Logout from the management console.
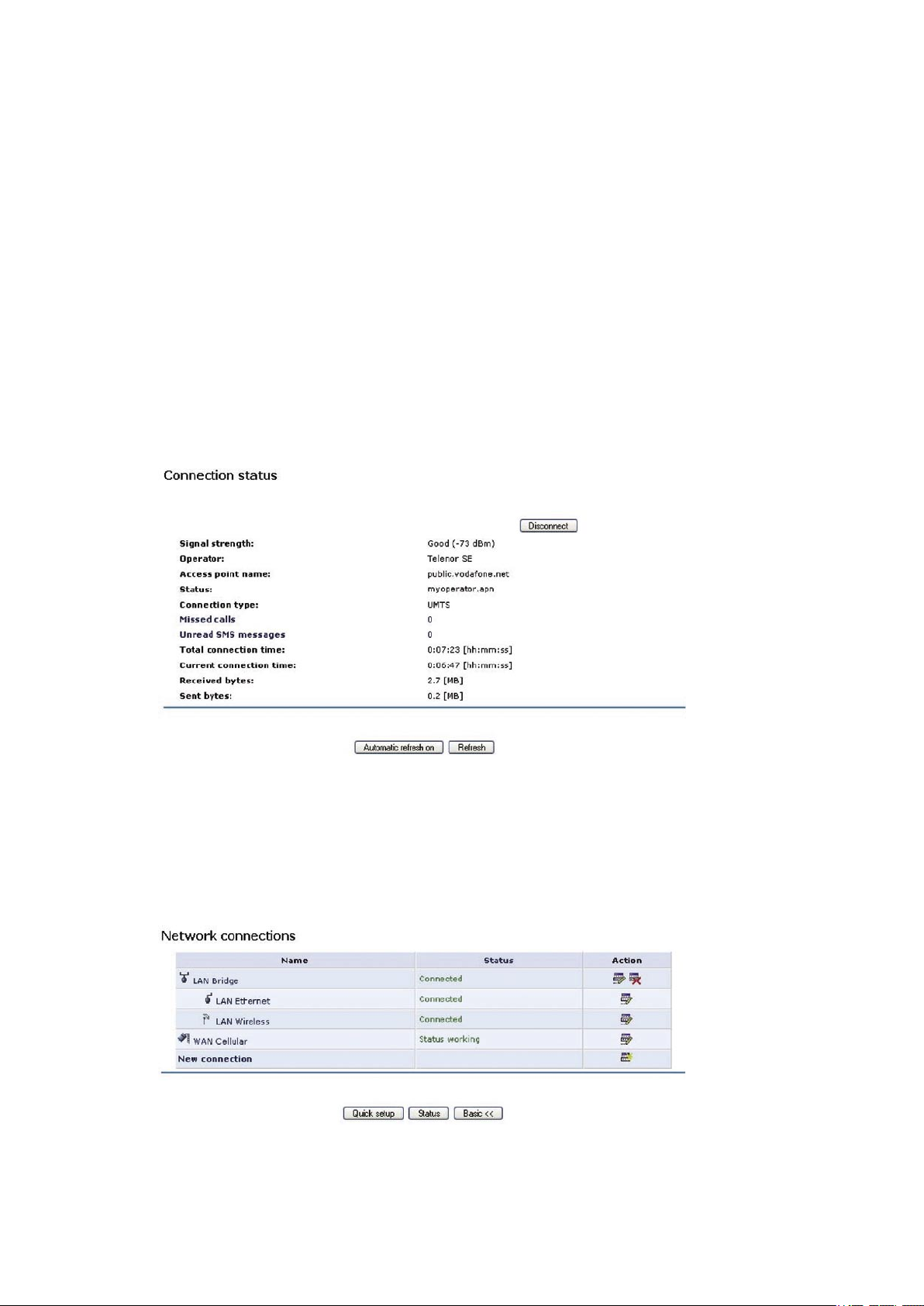
3.3 Connection status
The Connection status screen shows the status of the WAN Cellular connection and provides a button to manually connect and
disconnect. If your GlobeSurfer ® II is configures to automatically connect to the Internet when needed (see section 2.3.3), then the
Connect/Disconnect button on the Connection Status page will force the GlobeSurfer ® II to toggle connection state.
On the Conenction Status page some additional information about the current GlobeSurfer ® II settings could be seen. The following
additional information is provided:
· ‘Signal strength’ Current signal strength on your cellular network.
· ‘Operator’ The name of the cellular network operator that the GlobeSurfer ® II is currently attached to.
· ‘Access Point Name’ The current APN (Access Point Name) setting (see section 2.3.3).
· ‘Status’ Shows the current connection status of the cellular WAN conncetion.
13
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
· ‘Connection Type’ When the GlobeSurfer ® II is connected to a cellular network, the ‘Connection Status’ indicated what kind of
network it is.
· ‘Missed calls’ The amount of missed calls since last checked.
· ‘Unread SMS messages’ The amount of unread SMS messages in the SMS Inbox folder.
· ‘Total connection time’ The total amount of time that this GlobeSurfer ® II unit has been connected to the cellular WAN since last
reset.
· ‘Current connection time’ The amount of time that the GlobeSurfer ® II unit has been connected during this session.
· ‘Received bytes’ The amount of data received from the cellular WAN network, represented in Mb.
· ‘Sent bytes’ The amount of data sent to the cellular WAN network, represented in Mb.
The information in Connection status can be refreshed and updated manually by clicking ‘Refresh’. You can also set Connection status
to update automatically by clicking ‘Automatic refresh on’ once.
Figure 3.1 Connection Status
3.4 Managing tables
Tables are used throughout the GlobeSurfer 3G management console. They handle user-defined entries relating to elements such as
network connections, local servers, restrictions and configurable parameters. The principles outlined in this section apply to all tables in
the management console.
Figure 3.2 Typical Table Structure

14
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 3.2 illustrates a typical table. Each row defines an entry in the table. The following icons located in the Action column enable
adding, editing and deleting table entries:
· Click the Add icon to add an entry of the same type as on that row.
· Click the Edit icon to edit the entry on that row.
· Click the Delete icon to remove the entry on that row.
In many tables the last row includes a link that allows adding a new entry to the table.
3.5 Getting Help
The help icon on the upper right side of the management console may be used to get on-line help about the settings you see on each
particular screen.
View help information about each specific management console screen.

15
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
4 SMS
The GlobeSurfer ® II can send and receive SMS text messages. It supports both incoming and outgoing concatenated messages, and it can
send flash-SMS’s.
When the GlobeSurfer ® II receives a new SMS text message, this is indicated by an envelope symbol shown on the GlobeSurfer ® II display.
4.1 SMS Create
Creating and sending SMS text messages:
1. Select the ‘SMS create’ tab.
2. Type your message text in the ‘SMS message’ field. The Characters left field shows how much space is left.
3. Enter the mobile number of the person you want to contact in the ‘Phone numbers’ field. Use the standard mobile number format:
+4976123456 for international, and 076123456 for national numbers.
Tip: You can enter several numbers separated by commas (no spaces allowed), up to a maximum of ten phone numbers.
4. You can select the ‘Flash SMS’ - ‘Enabled’ checkbox if you want the message text displayed immediately when received (not
supported by all phones).
5. Click ‘Send SMS’ when ready to send. You will be redirected to an intermediate page that gives you information about the send
progress. After the SMS text message has been successfully sent, it will be stored in the ‘Sent’ folder, see section 4.3.
Alternatively you can:
· Click ‘Save as draft’ to save in the Drafts folder for completion later, see section 4.7.
· Click ‘Save as template’ to save the message as a template for future use, see section 4.5.
Figure 4.1 SMS Create
Tip: GlobeSurfer ® II supports concatenated SMS, which works as follows; if you want to send a longer than standard SMS of 160
characters you can type the almost the equivalent of 4 standard messages (up to 609 characters). When you send the message it will
be counted as separate messages.
Note: When you send an SMS, you may incur a charge depending on your subscription with your mobile operator.
4.2 Inbox
Handling SMS text messages in the Inbox:
1. Select the ‘Inbox’ tab to display the messages, with unread message in bold.
2. Click the SMS that you want to read. The message text is shown.

16
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3. When you have read the SMS you can click on:
· ‘Reply’: the message text is displayed in the ‘SMS create’ tab with the phone number of the sender already filled in.
· ‘Delete’: the SMS is permanently removed without confirmation.
· ‘Save to archive’: the SMS is moved to the ‘Archive’ tab, see section 4.4.
· ‘Forward’: the message text is displayed in the ‘SMS create’ tab ready for you to enter a phone number.
To delete an SMS from the list of messages in the ‘Inbox’ tab:
1. Select the ‘Inbox’ tab.
2. Click the ‘Remove’ icon for the message that you want to delete; the SMS is permanently removed without confirmation.
Figure 4.2 SMS Inbox
4.3 Sent
After a SMS text message has been sent from your GlobeSurfer ® II it will be stored in the ‘Sent’ folder. From here it is possible to open
any sent message and choose to delete, forward or save it to the archive (see section 4.4).
Figure 4.3 SMS Sent
4.4 Archive
SMS text messages from ‘Inbox’ or ‘Sent’ folders can be stored in the archive. When selecting the ‘Archive’ tab stored messages are
listed and it is possible to open any message and choose to delete, forward or reply to that message.
Figure 4.4 SMS Archive

17
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
4.5 Templates
From the ‘SMS create’ tab it is possible to chose to save a textmessage as template instead of sending it directly. When a message is
saved as template, it can be loaded from the ‘Templates’ folder. This is convenient when SMS text messages are often sent to the same
recipient or with similar content.
To remove a template, simply click the remove icon for that specific template.
Figure 4.5 SMS Templates
4.6 SIM Card
The ‘SIM Card’ tab shows SMS text messages that are stored on the SIM card inserted in the GlobeSurfer ® II. After opening a SMS
from the ‘Sim Card’ folder you can choose to delete it, reply to it, forward it or save it to the Archive folder.
Figure 4.5 SMS Templates
4.7 Drafts
While creating a new SMS text message from the ‘SMS create’ tab it is possible to choose to save it as draft instead of sending it
directly. This SMS will then be accessable from the ‘Drafts’ folder. When clicking on an SMS in the ‘Drafts’ folder, one will be directed
back to the ‘SMS create’ tab where it can be finalized.
Observe that when a SMS text message in the ‘Drafts’ folder has been opened and then sent, it will be removed from the ‘Drafts’ folder.
Figure 4.7 SMS Drafts

18
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
4.8 Settings
On the ‘Settings’ tab it is possible to define the SMSC number which is the number to the Short Message Service Center that will be
used for sending SMS messages from your GlobeSurfer ® II unit. This number is usually already filled in by default, but if necessary you
can use the ‘Settings’ tab to change it.
Figure 4.8 SMS Settings
19
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5 CONNECTION SETTINGS
The Connection settings page include three main categories, the Network Map where it is possible to get a static view of currently connected
network components (see section 5.1), the Network connections where all settings are made for UMTS, Ethernet and WLAN interfaces and
where it is also possible to create advanced VPN tunnel connections (see section 5.2) and the Security page where all firewall settings are
made (see section 5.3).
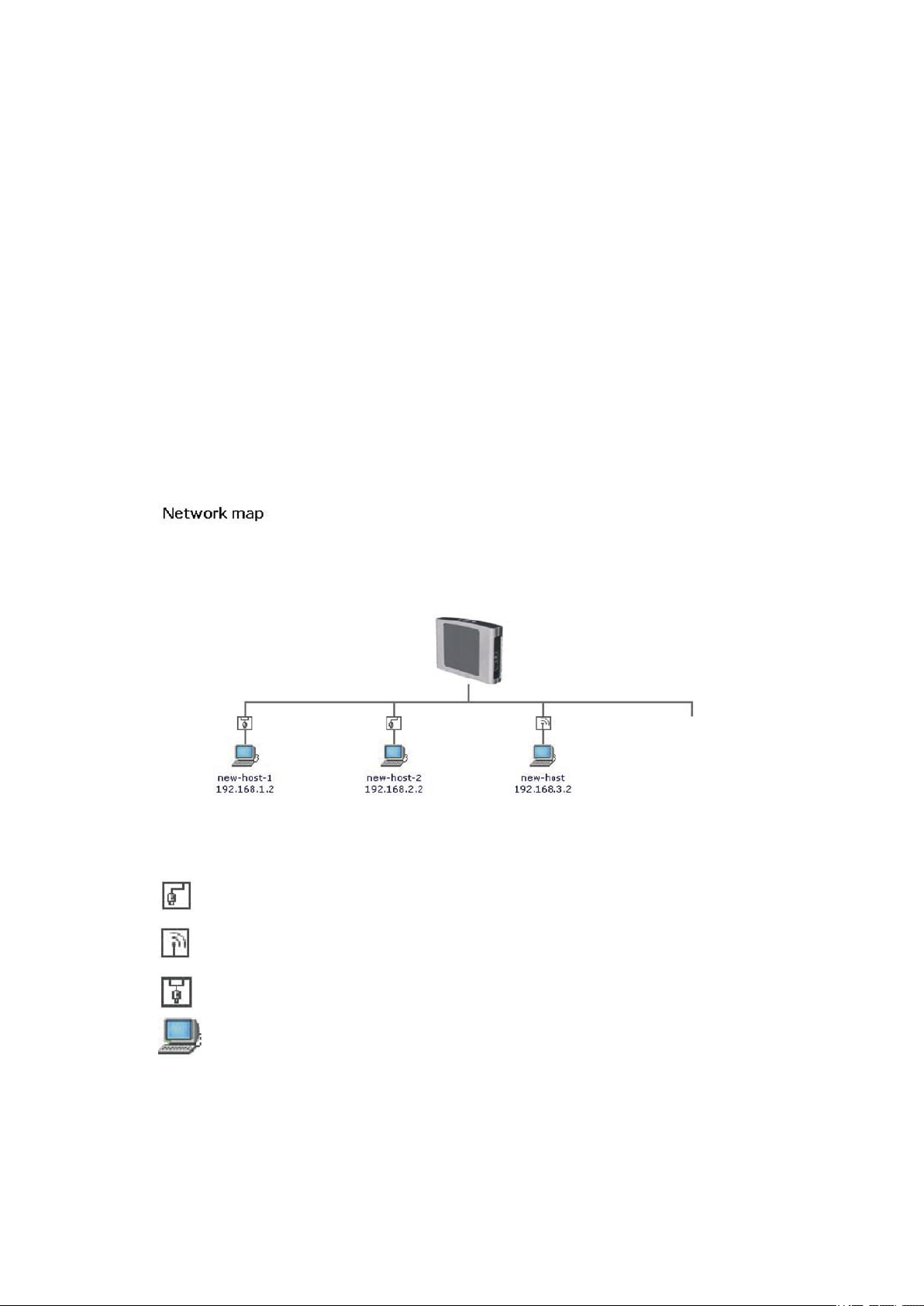
5.1 Network Map
The network map builder provides an up to date accurate graphical representation of the LAN network, displaying the devices
currently connected to the gateway and their parameters. While the standard network map displays devices with a DHCP lease from
GlobeSurfer ® II, with zero configuration technology devices with statically defined IP addresses are also displayed.
The network map builder relies on existing modules, such as the DHCP and the IP auto detection, as well as its own information
collectors to assemble the network information. All information is validated and displayed in the network map.
The network map builder actively sends various messages to discover which network objects are currently active on the network.
Comparing the replies to its list of IP addresses or host names, GlobeSurfer ® II is updated with information on the network view. This
data is then validated and translated to a user friendly, graphic map.
Figure 5.1 Network Map
The network map will display the following icons to indicate the interfaces used for connecting these devices:
· Represents an Ethernet Local Area Network (LAN) connection. Click this icon to configure network parameters for
the Ethernet LAN device (see section 5.2.3).
· Represents a Wireless LAN connection. Click this icon to configure network parameters for the Wireless LAN
device (see section 5.2.4).
· Represents a bridge connected in the home network. Click this icon to view the bridge’s underlying devices.
· Represents a computer (host) connected in the home network. Each computer connected to the network
appears below the network symbol of the network through which it is connected. Click an icon to view network
information for the corresponding computer.
5.2 Network Connections
GlobeSurfer ® II supports various network connections, both physical and logical. The Network Connections screen enables you to
configure the various parameters of your physical connections, the LAN and WAN, and create new connections, using tunneling
protocols over existing connections, such as PPP and VPN.
When clicking the ‘Network Connections’ icon under the ‘Connection Settings’ sidebar menu, the following typical screen will appear:

20
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.2 Network Connections - Basic
Press the ‘Advanced’ button to expand the screen and display all connection entries (see Figure 5.3).
Figure 5.3 Network Connections - Advanced
This chapter describes the different network connections available with GlobeSurfer ® II in their order of appearance in the Network
Connections screen (see Figure 5.3), as well as the connection types that you can create using the Connection Wizard.
GlobeSurfer ® II’s default network connections are:
· LAN - Creating a home/SOHO network
· LAN Bridge (see section 5.2.2).
· LAN Ethernet (see section 5.2.3).
· LAN Wireless (see section 5.2.4).
· WAN - Internet Connection
· WAN Cellular (see section 5.2.5).
The logical network connections available with GlobeSurfer ® II are:
· Virtual Private Network over the Internet
· Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol over Internet Protocol Security.
· Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Server.
· Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol Virtual Private Network.
· Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol Server.
· Internet Protocol Security.

21
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
· Internet Protocol Security Server.
· Advanced Connections
· Network Bridging.
· Internet Protocol over Internet Protocol.
· General Routing Encapsulation.
5.2.1 Connection Wizard
The logical network connections can be easily created using the Connection Wizard. This wizard is consisted of a series of
Web-based management screens, intuitively structured to gather all the information needed to create a logical connention.
In order to create a connection using the Connection Wizard, click the ‘New Connection’ link in the Network Connections
screen. The ‘Connection Wizard’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.4).
Figure 5.4 Connection Wizard
This screen presents you with the main connection types. Each option that you choose will lead you to further options in a
tree-like formation, adding more information with each step and narrowing down the parameters towards the desired network
connection.
· Connect to a Virtual Private Network over the Internet Selecting this option will take you to the ‘Connect to a Virtual Private
Network over the Internet’ screen (see Figure 5.5). This section will help you connect GlobeSurfer ® II to a business network
using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) so you can work from home, your workplace or another location.
Figure 5.5 VPN Wizard Screen
· Advanced Connection Selecting this option will take you to the ‘Advanced Connection’ screen (see Figure 5.6). This section
is a central starting point for all the aforementioned logical network connections. In addition, it provides the sequence for
creating the Network Bridge and VLAN Interface connections.

22
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.6 Advanced Connection Wizard Screen
How to configure a LAN Bridge will be described in section 5.2.2. For more information on how to configure the other
advanced connections that can be seen in Figure 5.3, please contact customer support center (see page 2).
5.2.2 LAN Bridge
The LAN bridge connection is used to combine several LAN devices under one virtual network. For example, creating one
network for LAN Ethernet and LAN wireless devices.
Please note, that when a bridge is removed, its formerly underlying devices inherit the bridge’s DHCP settings. For example,
the removal of a bridge that is configured as DHCP client, automatically configures the LAN devices formerly constituting the
bridge as DHCP clients, with the exact DHCP client configuration.
5.2.2.1 Creation with the Connection Wizard
To configure an existing bridge or create a new one, perform the following steps:
1. Click the New Connection link in the ‘Network Connections’ screen (see Figure 5.2). The ‘Connection Wizard’
screen will appear (see Figure 5.4).
2. Select the Advanced Connection radio button and click Next. The ‘Advanced Connection’ screen will appear (see
Figure 5.6).
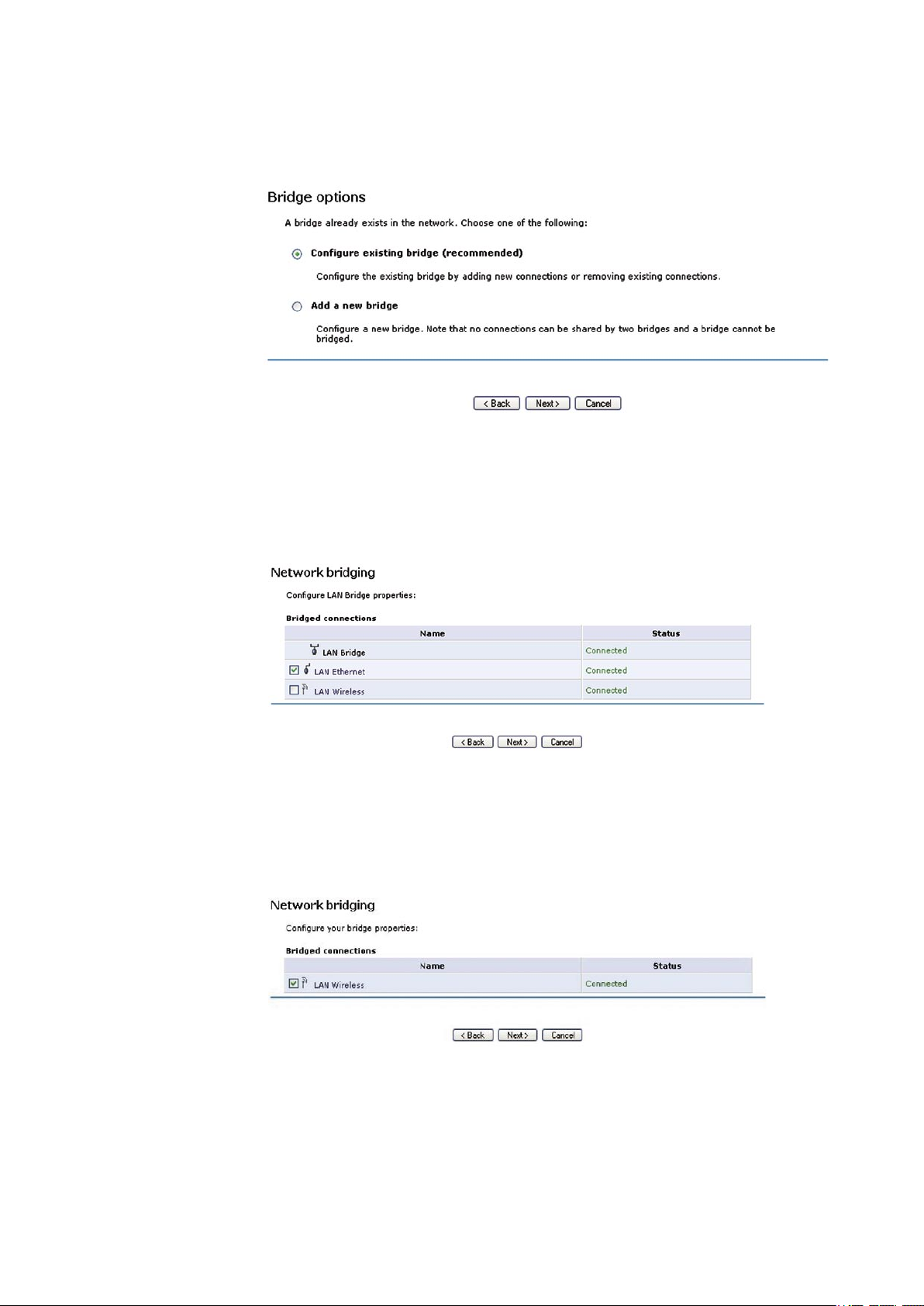
3. Select the Network Bridging radio button and click Next. The ‘Bridge Options’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.7).
23
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.7 Bridge Options
4. Select whether to configure an existing bridge (this option will only appear if a bridge exists) or to add a new one:
a. Configure Existing Bridge Select this option and click Next. The ‘Network Bridging’ screen will appear (see
Quick Setup Wizard: Telephony) allowing you to add new connections or remove existing ones, by checking or
unchecking their respective check boxes.
Figure 5.8 Network Bridging - Configure
For example, checking the ‘LAN Wireless’ check box will add the Wireless LAN interface to the existing bridge.
b. Add a New Bridge Select this option and click Next. A different ‘Network Bridging’ screen will appear (see Figure
5.9) allowing you to add a bridge over the unbridged connections, by checking their respective check boxes.
Figure 5.9 Network Bridging - Add
Important notes:
· The same connections cannot be shared by two bridges.
· A bridge cannot be bridged.
· Bridged connections will lose their IP settings.

24
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5. Click Next. The ‘Connection Summary’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.10), corresponding to your changes.
6. Check the ‘Edit the Newly Created Connection’ check box if you wish to be routed to the new connection’s
configuration screen after clicking Finish.
Figure 5.10 Connection Summary - Configure Existing Bridge
7. Click Finish to save the settings.
The new bridge will be added to the network connections list, and will be configurable like any other bridge.
5.2.2.2 General
The top part of the configuration window displays general communication parameters. It is recommended not to
change the default values in this screen unless you are familiar with the networking concepts they represent. Since
your gateway is configured to operate with the default values, no parameter modification is necessary. You can
configure the following general connection settings:
•
‘Physical Address’
The physical address of the network card used for your network. Some cards allow you to change this address.
•
‘MTU’
MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission.
Manual, allows you to enter the largest packet size that will be transmitted. The recommended size, is 1492. You
should leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. To have the gateway select the best MTU for your Internet
connection, select Automatic (default setting).
Figure 5.11 General Bridge Settings
5.2.2.3 Internet Protocol
Select one of the following Internet Protocol options from the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu:
· No IP Address
· Obtain an IP Address Automatically
· Use the Following IP Address
Please note that according to the selection you make in the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu, the screen will
refresh and display relevant configuration settings.
‘No IP Address’ Select ‘No IP Address’ if you require that this connection will have no IP address. Figure 5.12
Internet Protocol Settings - No IP Address

25
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.12 Internet Protocol Settings - No IP Address
‘Obtain Address Automatically’ Select ‘Obtain Address Automatically’ if you require that this connection will try to
obtain its IP address from a DHCP server.
Figure 5.13 Internet Protocol Settings - DHCP
‘Use the Following IP Address’ The LAN connection is usually configured using a permanent (static) IP address.
Your service provider should provide you with this address, and subnet mask.
Figure 5.14 Internet Protocol Settings - Static IP
5.2.2.4 Bridge Settings
The bridge section allows you to specify the LAN devices that you would like to join under the network bridge.
Select the ‘STP’ check box to enable the Spanning Tree Protocol on the device. You should use this to ensure that
there are no loops in your network configuration, and apply these settings in case your network consists of multiple
switches, or other bridges apart from those created by the gateway.
Figure 5.15 LAN Bridge Settings
5.2.2.5 DNS Server
It is possible to specify IP addresses of primary and secondary DNS servers if for instance local domain names
should be handled by local name servers. Note that for the Cellular WAN interface, DNS servers are configured
separately.
Figure 5.16 DNS Server
5.2.2.6 IP Address Distribution
The ‘IP Address Distribution’ section allows you to configure the gateway’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server parameters. The DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to network PCs. If you enable this
feature, make sure that you also configure your network PCs as DHCP clients. For a comprehensive description of
this feature, please refer to section 6.6.10.
26
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
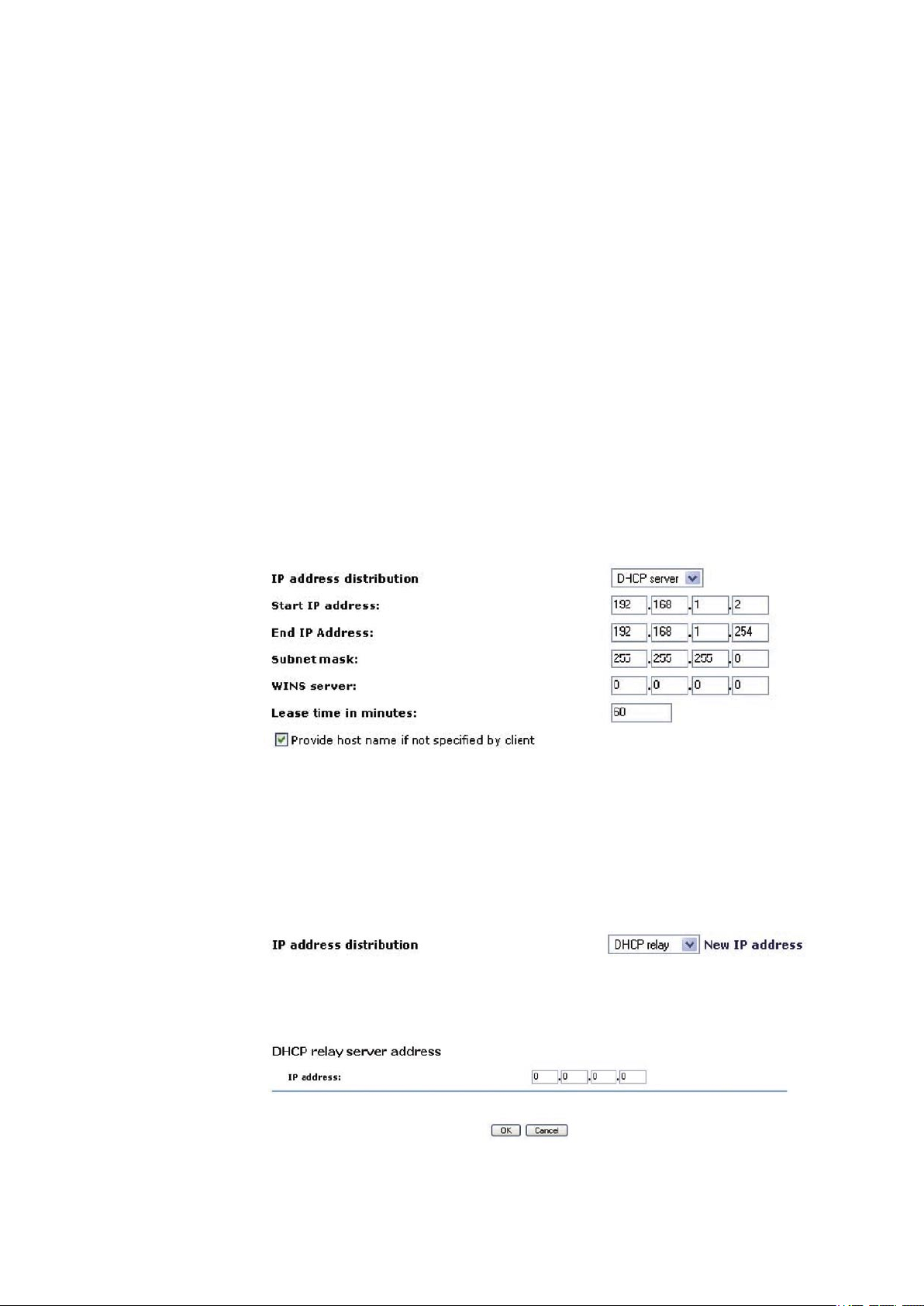
Select one of the following options from the ‘IP Address Distribution’ combo-box:
· DHCP Server
‘Start IP Address’ The first IP address that may be assigned to a LAN host. Since the gateway’s default IP
address is 192.168.1.1, this address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater.
‘End IP Address’ The last IP address in the range that can be used to automatically assign IP addresses to LAN
hosts.
‘Subnet Mask’ A mask used to determine to what subnet an IP address belongs. An example of a subnet mask
value is 255.255.0.0.
‘WINS server’ If you use a Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS), specify the WINS server address in this
field.
‘Lease Time In Minutes’ Each device will be assigned an IP address by the DHCP server for a this amount of
time, when it connects to the network. When the lease expires the server will determine if the computer has
disconnected from the network. If it has, the server may reassign this IP address to a newly-connected computer.
This feature ensures that IP addresses that are not in use will become available for other computers on the
network.
‘Provide Host Name If Not Specified by Client’ If the DHCP client does not have a host name, the gateway will
automatically assign one for him.
Figure 5.17 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Server
· DHCP Relay
Your gateway can act as a DHCP relay in case you would like to dynamically assign IP addresses from a DHCP
server other than your gateway’s DHCP server. Note that when selecting this option you must also change
GlobeSurfer ® II’s WAN to work in routing mode. For more information, see section 6.6.10.2.
1. After selecting ‘DHCP Relay’ from the drop down menu, a ‘New IP Address’ link will appear:
Figure 5.18 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Relay
Click the ‘New IP Address’ link. The ‘DHCP Relay Server Address’ screen will appear:
Figure 5.19 DHCP Relay Server Address
2. Specify the IP address of the DHCP server.
27
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
· Disabled Select ‘Disabled’ from the combo-box if you would like to statically assign IP addresses to your network
computers.
Figure 5.20 IP Address Distribution - Disable DCHP
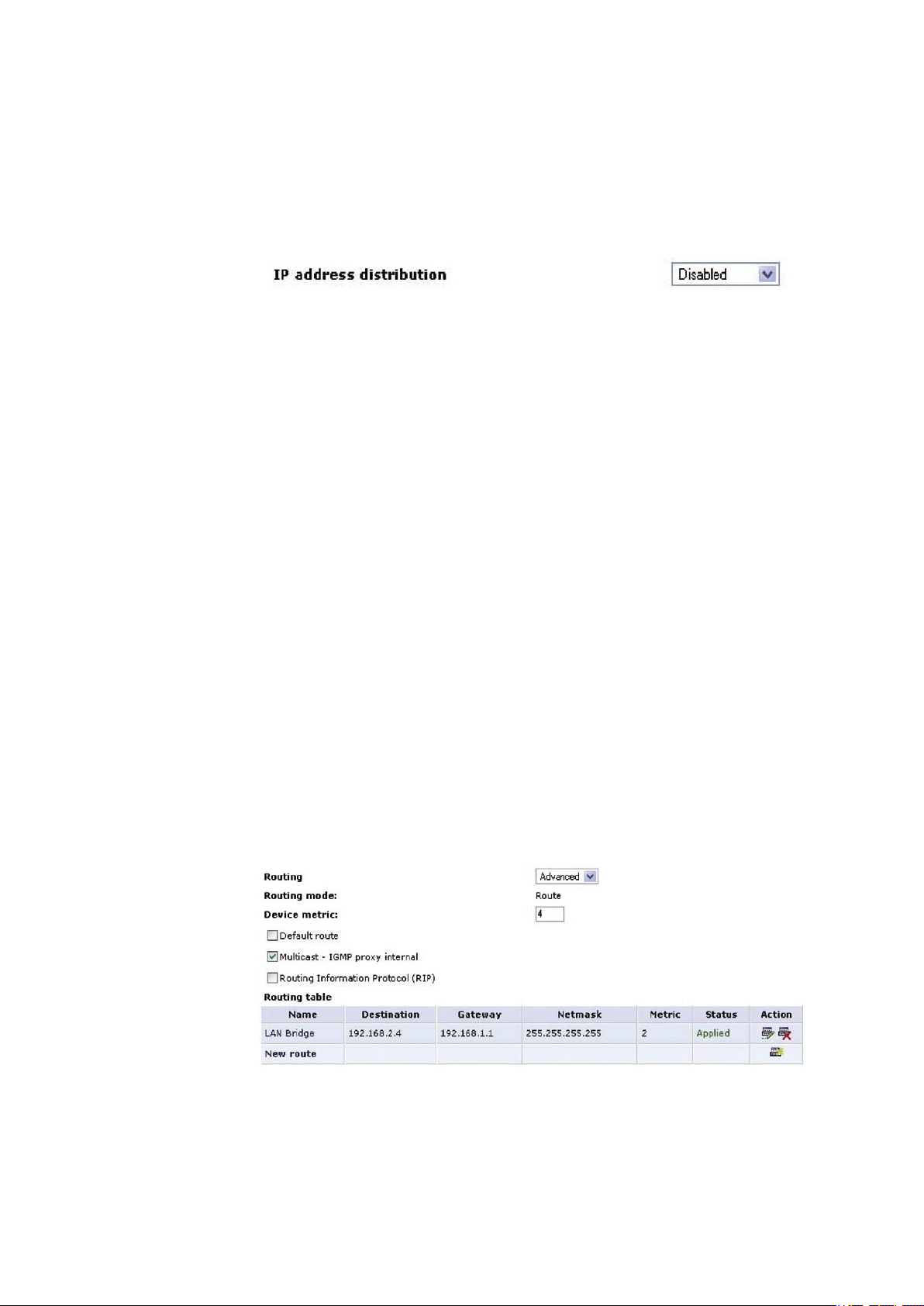
5.2.2.7 Routing
You can choose to setup your gateway to use static or dynamic routing. Dynamic routing automatically adjusts how
packets travel on the network, whereas static routing specifies a fixed routing path to neighboring destinations.
‘Routing’
Select ‘Advanced’ or ‘Basic’ routing.
‘Device Metric’
The device metric is a value used by the gateway to determine whether one route is superior to another,
considering parameters such as bandwidth, delay, and more.
‘Default Route’
Select this check box to define this device as the default route.
‘Multicast - IGMP Proxy Internal’
IGMP proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system discovered
through standard IGMP interfaces. IGMP proxy enables the routing of multicast packets according to the IGMP
requests of LAN devices asking to join multicast groups. Select the ‘Multicast IGMP Proxy Internal’ check-box to
enable this feature.
‘Routing Information Protocol (RIP)’
Select this check box to enable the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP determines a route based on the
smallest hop count between source and destination. When RIP is enabled, select the following:
· Listen to RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2’ or ‘RIPv1/2’.
· Send RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2-broadcast’ or ‘RIPv2-multicast’.
‘Routing Table’
Allows you to add or modify routes when this device is active. Use the ‘New Route’ button to add a route or edit
existing routes.
Figure 5.21 Advanced Routing Properties
To learn more about this feature, please refer to chapter 6.6.7.

28
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5.2.2.8 Internet Connection Firewall
Your gateway’s firewall helps protect your computer by preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to it
through a network such as the Internet. The firewall can be activated per network connection.
To enable the firewall on this network connection, select the ‘Enabled’ check box. To learn more about your
gateway’s security features, please refer to chapter 5.3.
Figure 5.22 Internet Connection Firewall
5.2.2.9 Additional IP Addresses
You can add alias names (additional IP addresses) to the gateway by clicking the ‘New IP Address’ link. This
enables you to access the gateway using these aliases in addition to the 192.168.1.1.
Figure 5.23 Additional IP Addresses
5.2.3 LAN Ethernet
A LAN Ethernet connection connects computers to GlobeSurfer ® II using Ethernet cables, either directly or via network hubs
and switches.
Figure 5.24 LAN Ethernet Properties
Clicking the “Settings” button at the bottom-right of the connection’s Properties window, will open its Configuration window:

29
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.25 LAN Ethernet Configuration
Note that available configuration options may vary depending on if the LAN Ethernet interface is part of a bridge or not.
5.2.3.1 General
The top part of the configuration window displays general communication parameters. It is recommended not to
change the default values in this screen unless you are familiar with the networking concepts they represent. Since
your gateway is configured to operate with the default values, no parameter modification is necessary. You can
configure the following general connection settings:
‘Physical Address’
The physical address of the network card used for your network. Some cards allow you to change this address.
‘MTU’
MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission.
Manual, allows you to enter the largest packet size that will be transmitted. The recommended size, is 1492. You
should leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. To have the gateway select the best MTU for your Internet
connection, select Automatic (default setting).
Figure 5.26 General LAN Ethernet Settings

30
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5.2.3.2 Internet Protocol
Select one of the following Internet Protocol options from the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu:
· No IP Address
· Obtain an IP Address Automatically
· Use the Following IP Address
Please note that according to the selection you make in the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu, the screen will
refresh and display relevant configuration settings.
‘No IP Address’
Select ‘No IP Address’ if you require that this connection will have no IP address. Figure 5.27 Internet Protocol
Settings - No IP Address
Figure 5.27 Internet Protocol Settings - No IP Address
‘Obtain Address Automatically’
Select ‘Obtain Address Automatically’ if you require that this connection will try to obtain its IP address from a
DHCP server.
Figure 5.28 Internet Protocol Settings - DHCP
‘Use the Following IP Address’
The LAN connection is usually configured using a permanent (static) IP address. Your service provider should
provide you with this address, and subnet mask.
Figure 5.29 Internet Protocol Settings - Static IP
5.2.3.3 DNS Server
It is possible to specify IP addresses of primary and secondary DNS servers if for instance local domain names
should be handled by local name servers. Note that for the Cellular WAN interface, DNS servers are configured
separately.
Figure 5.30 DNS Server
5.2.3.4 IP Address Distribution
The ‘IP Address Distribution’ section allows you to configure the gateway’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server parameters. The DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to network PCs. If you enable this
feature, make sure that you also configure your network PCs as DHCP clients. For a comprehensive description of
this feature, please refer to section 6.6.10.
Select one of the following options from the ‘IP Address Distribution’ combo-box:

31
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
· DHCP Server
‘Start IP Address’
The first IP address that may be assigned to a LAN host. Since the gateway’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1,
this address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater.
‘End IP Address’
The last IP address in the range that can be used to automatically assign IP addresses to LAN hosts.
‘Subnet Mask’
A mask used to determine to what subnet an IP address belongs. An example of a subnet mask value is
255.255.0.0.
‘WINS server’
If you use a Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS), specify the WINS server address in this field.
‘Lease Time In Minutes’
Each device will be assigned an IP address by the DHCP server for a this amount of time, when it connects to the
network. When the lease expires the server will determine if the computer has disconnected from the network.
If it has, the server may reassign this IP address to a newly-connected computer. This feature ensures that IP
addresses that are not in use will become available for other computers on the network.
‘Provide Host Name If Not Specified by Client’
If the DHCP client does not have a host name, the gateway will automatically assign one for him.
Figure 5.31 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Server
· DHCP Relay
Your gateway can act as a DHCP relay in case you would like to dynamically assign IP addresses from a DHCP
server other than your gateway’s DHCP server. Note that when selecting this option you must also change
GlobeSurfer ® II’s WAN to work in routing mode. For more information, see section 6.6.10.2.
4. After selecting ‘DHCP Relay’ from the drop down menu, a ‘New IP Address’ link will appear:
Figure 5.32 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Relay
Click the ‘New IP Address’ link. The ‘DHCP Relay Server Address’ screen will appear:
Figure 5.33 DHCP Relay Server Address
5. Specify the IP address of the DHCP server.

32
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
· Disabled Select ‘Disabled’ from the combo-box if you would like to statically assign IP addresses to your network
computers.
Figure 5.34 IP Address Distribution - Disable DCHP
5.2.3.5 Routing
You can choose to setup your gateway to use static or dynamic routing. Dynamic routing automatically adjusts how
packets travel on the network, whereas static routing specifies a fixed routing path to neighboring destinations.
‘Routing’
Select ‘Advanced’ or ‘Basic’ routing.
‘Device Metric’
The device metric is a value used by the gateway to determine whether one route is superior to another,
considering parameters such as bandwidth, delay, and more.
‘Default Route’
Select this check box to define this device as the default route.
‘Multicast - IGMP Proxy Internal’
IGMP proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system discovered
through standard IGMP interfaces. IGMP proxy enables the routing of multicast packets according to the IGMP
requests of LAN devices asking to join multicast groups. Select the ‘Multicast IGMP Proxy Internal’ check-box to
enable this feature.
‘Routing Information Protocol (RIP)’
Select this check box to enable the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP determines a route based on the
smallest hop count between source and destination. When RIP is enabled, select the following:
· Listen to RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2’ or ‘RIPv1/2’.
· Send RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2-broadcast’ or ‘RIPv2-multicast’.
‘Routing Table’
Allows you to add or modify routes when this device is active. Use the ‘New Route’ button to add a route or edit
existing routes.
Figure 5.35 Advanced Routing Properties
To learn more about this feature, please refer to chapter 6.6.7.
5.2.3.6 Internet Connection Firewall
Your gateway’s firewall helps protect your computer by preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to it
through a network such as the Internet. The firewall can be activated per network connection.
To enable the firewall on this network connection, select the ‘Enabled’ check box. To learn more about your
gateway’s security features, please refer to chapter 5.3.

33
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.36 Internet Connection Firewall
5.2.3.7 Additional IP Addresses
You can add alias names (additional IP addresses) to the gateway by clicking the ‘New IP Address’ link. This
enables you to access the gateway using these aliases in addition to the 192.168.1.1.
Figure 5.37 Additional IP Addresses
5.2.4 LAN Wireless
The LAN Wireless interface in the GlobeSurfer ® II provides wireless connectivity for IEEE 802.11b/g equipped WLAN clients.
GlobeSurfer ® II integrates multiple layers of security. These include the IEEE 802.1x portbased authentication protocol,
RADIUS client, EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-PEAP, Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and industry leading GlobeSurfer ® II
Firewall and VPN applications. In addition, GlobeSurfer ® II’s built-in authentication server enables home/SOHO users to define
authorized wireless users without the need for an external RADIUS server.
To configure the LAN Wireless connection:
1. Click the ‘Network Connections’ icon on the side-bar, the ‘Network Connections’ screen will appear. Press the ‘Advanced’
button to see the devices under the LAN Bridge (see Figure 5.38).
Figure 5.38 Network Connections - Advanced
2. Click the wireless connection link (or its ‘Edit’ action button) to view its properties. The ‘LAN Wireless Properties’ screen will
appear (see Figure 5.39).
Figure 5.39 LAN Wireless Properties

34
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3. Press the ‘Settings’ button to display the various wireless connection settings. The ‘Configure LAN Wireless’ screen will
appear (see Figure 5.40).
Figure 5.40 Configure LAN Wireless
5.2.4.1 General
The top part of the configuration window displays general communication parameters. It is recommended not to
change the default values in this screen unless you are familiar with the networking concepts they represent. Since
your gateway is configured to operate with the default values, no parameter modification is necessary. You can
configure the following general connection settings:
· ‘Physical Address’ The physical address of the network card used for your network. Some cards allow you to
change this address.

35
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
· ‘MTU’ MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size permitted for Internet
transmission. Manual, allows you to enter the largest packet size that will be transmitted. The recommended size,
is 1492. You should leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. To have the gateway select the best MTU for your
Internet connection, select Automatic (default setting).
Figure 5.41 General LAN Wireless Settings
5.2.4.2 Wireless Access Point
The wireless access point settings are:
‘SSID’
The SSID is the network name shared among all points in a wireless network. The SSID must be identical for all
points in the wireless network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 characters (use any of the characters
on the keyboard). Make sure this setting is the same for all points in your wireless network. For added security, you
should change the default SSID to a unique name.
‘SSID Broadcast’
Select this check box to enable the SSID’s broadcast. SSID broadcast is used in order to hide the name of the AP
(SSID) from clients that should not be aware to its existence.
‘802.11 Mode’
Select the Wireless communication standard that is compatible with you PC’s wireless card. You can work in either
802.11g, 802.11b or in mixed mode.
‘Channel’
Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your network settings. All devices in your
wireless network must be broadcast on different channels in order to function correctly.
‘Frame Burst’
Frame Bursting is a method to increase the speed of 802.11g-based wireless networks by unwrapping short
802.11g packets and rebundling them into a larger packet to reduce the impact of mandatory gaps between
packets. If you are experiencing problems with your wireless connection, try to disable Frame Burst.
‘Network Authentication’
The WPA network authentication method is ‘Open System Authentication’, meaning that a network key is not used
for authentication. When using the 802.1X WEP or Non-802.1X WEP security protocols, this field changes to a
combo box, offering the ‘Shared Key Authentication’ method (which uses a network key for authentication), or both
methods combined.
‘Transmission Rate’
The transmission rate is set according to the speed of your wireless connection. Select the transmission rate from the
drop down list, or select ‘Auto’ to have GlobeSurfer ® II automatically use the fastest possible data transmission rate.
‘CTS Protection Mode’
CTS Protection Mode boosts your gateway’s ability to intercept Wireless-G and 802.11b transmissions.
Conversely, CTS Protection Mode decreases performance. Leave this feature disabled unless you encounter severe
communication difficulties between the gateway andWireless-G products.
‘CTS Protection Type’
CTS Protection Type defines if the CTS Protection Mode defined above should use CTS only or both RTS/CTS.
‘Beacon Interval’
A beacon is a packet broadcast by GlobeSurfer ® II to synchronize the wireless network. The Beacon Interval value
indicates how often the beacon is sent.

36
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘DTIM Interval’
The Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) is a countdown value that informs wireless clients of the next
opportunity to receive multicast and broadcast messages. This value ranges between 1 and 16384.
‘Fragmentation Threshold’
Packets that are larger than this threshold are fragmented into multiple packets. Try to increase the fragmentation
threshold if you encounter high packet error rates. Do not set the threshold too low, since this can result in reduced
networking performance.
‘RTS Threshold’
GlobeSurfer ® II sends Request to Send (RTS) packets to the Wireless client in order to negotiate the dispatching of
data. The Wireless client responds with a Clear to Send (CTS) packet, signaling that transmission can commence.
In case packets are smaller than the preset threshold, the RTC/CTS mechanism is not active. If you encounter
inconsistent data flow, try a minor reduction of the RTS threshold size.
‘MAC Filtering Mode’
You can filter wireless users according to their MAC address, either allowing or denying access. Choose the action
to be performed by selecting it from the drop down menu. Then usse the ‘MAC Filtering Settings’ option to add and
remove MAC Addresses to the list of allowed or denied clients.
5.2.4.3 Wireless Security
To configure your wireless security, enable this feature by checking its ‘Enabled’ check-box on the ‘Configure LAN
Wireless Access Point’ screen (see Figure 5.40). The screen will refresh, displaying the wireless security options
(see Figure 5.42). Click ‘Apply’ to if you wish to save this change.
‘Stations Security Type’
Select the type of security protocol for securing your wireless network. Choose between WPA, WPA2, WPA and
WPA2, 802.1x WEP, and Non-802.1x WEP. The screen will refresh, presenting each protocol’s configuration
respectively.
•
‘WPA’ (see Figure 5.42) - a data encryption method for 802.11 wireless LANs.
‘Authentication Method’
Select the authentication method you would like to use. You can choose between Pre-Shared Key and 802.1x.
‘Pre-Shared Key’
This entry appears only if you had selected this authentication method. Enter your encryption key in the ‘PreShared Key’ field.
You can use either an ASCII or a Hex value by selecting the value type in the combo box provided.
‘Encryption Algorithm’
Select whether to use the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) or the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for the
encryption algorithm. ‘Group Key Update Interval’ Defines the time interval in seconds for updating a group key.
Figure 5.42 WPA Wireless Security Parameters
•
‘WPA2’ (see Figure 5.43) – an enhanced version of WPA, and defines the 802.11i protocol.
‘Authentication Method’
Select the authentication method you would like to use. You can choose between Pre-Shared Key and 802.1x.
‘Pre-Shared Key’

37
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
This entry appears only if you had selected this authentication method. Enter your encryption
key in the ‘Pre-Shared Key’ field. You can use either an ASCII or a Hex value by selecting the value type in the
combo box provided.
‘Encryption Algorithm’
The encyption algorithm used for WPA2 is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). ‘Group Key Update Interval’
Defines the time interval in seconds for updating a group key.
Figure 5.43 WPA2 Wireless Security Parameters
•
‘WPA and WPA2’ Mixed Mode (see Figure 5.44)– a mixed data encryption mode.
‘Authentication Method’
Select the authentication method you would like to use. You can choose between Pre-Shared Key and 802.1x.
‘Pre-Shared Key’
This entry appears only if you had selected this authentication method. Enter your encryption key in the ‘PreShared Key’ field. You can use either an ASCII or a Hex value by selecting the value type in the combo box
provided.
‘Encryption Algorithm’
The encyption algorithm used for WPA and WPA2 is a either the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) or the
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). ‘Group Key Update Interval’ Defines the time interval in seconds for
updating a group key.
Figure 5.44 WPA and WPA2 Wireless Security Parameters
•
‘802.1x WEP’ (see Figure 5.45) - a data encryption method utilizing a statically or automatically defined key for
wireless clients that use 802.1x for authentication and WEP for encryption. You may define up to four keys but
use only one at a time.
‘Generate Keys Automatically’
Select this option to generate the encryption keys automatically rather than entering them manually. The screen
will refresh, hiding the table of keys described below.
‘Group Key Update Interval’
Defines the time interval in seconds for updating a group key.
‘Active’
Select the encryption key to be activated.
‘Encryption Key’
Type the encryption key until the entire field is filled. The key cannot be shorter than the field’s length.
‘Format’
Select the character type for the key: Hex or ASCII.
‘Key Length’

38
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Select the key length in bits: 40 or 104 bits.
Figure 5.45 802.1x WEP Wireless Security Parameters
The encryption key must be defined in the wireless Windows client as well. This is done in the Connection
Properties Configuration window (to learn how to reach this window, please refer to section 5.2.6). If you have
manually defined the encryption key, you must also specify it in this window (see Figure 5.46). If you have chosen
the automatic key generation, check the “The key is provided for me automatically” check box instead.
Figure 5.46 Connection Properties Configuration
1. In the ‘Network Authentication’ combo box, select “Shared”.
2. In the ‘Data Encryption’ combo box, select “WEP”.
3. Enter your encryption key in both the ‘Network key’ and the ‘Confirm network key’ fields.

39
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
•
‘Non-802.1x WEP’ - a data encryption method utilizing a statically-defined key for wireless clients that do not
use 802.1x for authentication but WEP for encryption.
This method’s configuration is virtually identical to the 802.1x WEP method described above, excluding the
automatic key generation and the group key update interval specification. Please refer to the 802.1x WEP section
above when configuring this method. Remember that the static key must be defined in the wireless Windows
client as well.
Figure 5.47 Non-802.1x WEP Wireless Security Parameters
5.2.4.4 Internet Protocol
Select one of the following Internet Protocol options from the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu:
•
No IP Address
•
Obtain an IP Address Automatically
•
Use the Following IP Address
Please note that according to the selection you make in the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu, the screen will
refresh and display relevant configuration settings.
‘No IP Address’ Select ‘No IP Address’ if you require that this connection will have no IP address.
Figure 5.48 Internet Protocol Settings - No IP Address
‘Obtain Address Automatically’ Select ‘Obtain Address Automatically’ if you require that this connection will try to
obtain its IP address from a DHCP server.
Figure 5.49 Internet Protocol Settings - DHCP
‘Use the Following IP Address’ The LAN connection is usually configured using a permanent (static) IP address.
Your service provider should provide you with this address, and subnet mask.
Figure 5.50 Internet Protocol Settings - Static IP

40
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5.2.4.5 DNS Server
It is possible to specify IP addresses of primary and secondary DNS servers if for instance local domain names
should be handled by local name servers. Note that for the Cellular WAN interface, DNS servers are configured
separately.
Figure 5.51 DNS Server
5.2.4.6 IP Address Distribution
The ‘IP Address Distribution’ section allows you to configure the gateway’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server parameters. The DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to network PCs. If you enable this
feature, make sure that you also configure your network PCs as DHCP clients. For a comprehensive description of
this feature, please refer to section 6.6.10.
Select one of the following options from the ‘IP Address Distribution’ combo-box:
•
DHCP Server
‘Start IP Address’
The first IP address that may be assigned to a LAN host. Since the gateway’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1,
this address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater.
‘End IP Address’
The last IP address in the range that can be used to automatically assign IP addresses to LAN hosts.
‘Subnet Mask’
A mask used to determine to what subnet an IP address belongs. An example of a subnet mask value is
255.255.0.0.
‘WINS server’
If you use a Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS), specify the WINS server address in this field.
‘Lease Time In Minutes’
Each device will be assigned an IP address by the DHCP server for a this amount of time, when it connects to the
network. When the lease expires the server will determine if the computer has disconnected from the network.
If it has, the server may reassign this IP address to a newly-connected computer. This feature ensures that IP
addresses that are not in use will become available for other computers on the network.
‘Provide Host Name If Not Specified by Client’
If the DHCP client does not have a host name, the gateway will automatically assign one for him.
Figure 5.52 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Server

41
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
•
DHCP Relay
Your gateway can act as a DHCP relay in case you would like to dynamically assign IP addresses from a DHCP
server other than your gateway’s DHCP server. Note that when selecting this option you must also change
GlobeSurfer ® II’s WAN to work in routing mode. For more information, see section 6.6.10.2.
7. After selecting ‘DHCP Relay’ from the drop down menu, a ‘New IP Address’ link will appear:
Figure 5.53 IP Address Distribution - DHCP Relay
Click the ‘New IP Address’ link. The ‘DHCP Relay Server Address’ screen will appear:
Figure 5.54 DHCP Relay Server Address
8. Specify the IP address of the DHCP server.
9. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
•
Disabled
Select ‘Disabled’ from the combo-box if you would like to statically assign IP addresses to your network
computers.
Figure 5.55 IP Address Distribution - Disable DCHP
5.2.4.7 Routing
You can choose to setup your gateway to use static or dynamic routing. Dynamic routing automatically adjusts how
packets travel on the network, whereas static routing specifies a fixed routing path to neighboring destinations.
‘Routing’
Select ‘Advanced’ or ‘Basic’ routing.
‘Device Metric’
The device metric is a value used by the gateway to determine whether one route is superior to another,
considering parameters such as bandwidth, delay, and more.
‘Default Route’
Select this check box to define this device as the default route.
‘Multicast - IGMP Proxy Internal’
IGMP proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system discovered
through standard IGMP interfaces. IGMP proxy enables the routing of multicast packets according to the IGMP
requests of LAN devices asking to join multicast groups. Select the ‘Multicast IGMP Proxy Internal’ check-box to
enable this feature.
‘Routing Information Protocol (RIP)’
Select this check box to enable the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP determines a route based on the
smallest hop count between source and destination. When RIP is enabled, select the following:
•
Listen to RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2’ or ‘RIPv1/2’.
•
Send RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2-broadcast’ or ‘RIPv2-multicast’.

42
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Routing Table’
Allows you to add or modify routes when this device is active. Use the ‘New Route’ button to add a route or edit
existing routes.
Figure 5.56 Advanced Routing Properties
To learn more about this feature, please refer to chapter 6.6.7.
5.2.4.8 Internet Connection Firewall
Your gateway’s firewall helps protect your computer by preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to it
through a network such as the Internet. The firewall can be activated per network connection.
To enable the firewall on this network connection, select the ‘Enabled’ check box. To learn more about your
gateway’s security features, please refer to chapter 5.3.
Figure 5.57 Internet Connection Firewall
5.2.4.9 Additional IP Addresses
You can add alias names (additional IP addresses) to the gateway by clicking the ‘New IP Address’ link. This
enables you to access the gateway using these aliases in addition to the 192.168.1.1.
Figure 5.58 Additional IP Addresses
5.2.5 WAN Cellular
The WAN Cellular connection connects the GlobeSurfer ® II to the Internet and other networks through the GSM and UMTS
mobile telecommunications standards. The ‘WAN Cellular Properties’ screen displays a summary of the connection properties
(see Figure 5.59).
Figure 5.59 WAN Cellular Properties

43
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Clicking on the ‘Settings’ button at the bottom-right of the connection’s Properties window, will open its Configuration window
(see Figure 5.60).
Figure 5.60 WAN Cellular Configuration
5.2.5.1 General
The top part of the configuration window displays general communication parameters. It is recommended not to
change the default values in this screen unless you are familiar with the networking concepts they represent. Since
your gateway is configured to operate with the default values, no parameter modification is necessary. You can
configure the following general connection settings:
‘MTU’
MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission.
Manual, allows you to enter the largest packet size that will be transmitted. The recommended size, is 1492. You
should leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. To have the gateway select the best MTU for your Internet
connection, select Automatic (default setting).
5.2.5.2 Internet Protocol
Select one of the following Internet Protocol options from the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu:
· No IP Address
· Obtain an IP Address Automatically
· Use the Following IP Address

44
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Please note that according to the selection you make in the ‘Internet Protocol’ drop down menu, the screen will
refresh and display relevant configuration settings.
‘No IP Address’
Select ‘No IP Address’ if you require that this connection will have no IP address.
Figure 5.61 Internet Protocol Settings - No IP Address
‘Obtain Address Automatically’
Select ‘Obtain Address Automatically’ if you require that this connection will try to obtain its IP address from a
DHCP server.
Figure 5.62 Internet Protocol Settings - DHCP
‘Use the Following IP Address’
The LAN connection is usually configured using a permanent (static) IP address. Your service provider should
provide you with this address, and subnet mask.
Figure 5.63 Internet Protocol Settings - Static IP
5.2.5.3 DNS Server
It is possible to specify IP addresses of primary and secondary DNS servers if for instance local domain names
should be handled by local name servers. Note that for the Cellular WAN interface, DNS servers are configured
separately.
If the ‘Internet Protocol’ setting mentioned above is set to ‘Obtain an IP address automatically’, then there is also
an option to configure the ‘DNS Server’ setting to obtain DNS Server settings automatically.
Figure 5.64 DNS Server
5.2.5.4 Routing
You can choose to setup your gateway to use static or dynamic routing. Dynamic routing automatically adjusts how
packets travel on the network, whereas static routing specifies a fixed routing path to neighboring destinations.
‘Routing’
Select ‘Advanced’ or ‘Basic’ routing.
‘Routing Mode’
When Advanced routing is selected, select one of the following Routing modes:
•
‘Route’ Use route mode if you want your GlobeSurfer 3G to function as a router between two networks.
•
‘NAPT’ Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) refers to network address translation involving the mapping
of port numbers, allowing multiple machines to share a single IP address. Use NAPT if your LAN encompasses

45
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
multiple devices, a topology that necessitates port translation in addition to address translation.
‘Device Metric’
The device metric is a value used by the gateway to determine whether one route is superior to another,
considering parameters such as bandwidth, delay, and more.
‘Default Route’
Select this check box to define this device as the default route.
‘Multicast - IGMP Proxy Internal’
IGMP proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system discovered
through standard IGMP interfaces. IGMP proxy enables the routing of multicast packets according to the IGMP
requests of LAN devices asking to join multicast groups. Select the ‘Multicast IGMP Proxy Internal’ check-box to
enable this feature.
‘Routing Information Protocol (RIP)’
Select this check box to enable the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP determines a route based on the
smallest hop count between source and destination. When RIP is enabled, select the following:
•
Listen to RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2’ or ‘RIPv1/2’.
•
Send RIP messages - select ‘None’, ‘RIPv1’, ‘RIPv2-broadcast’ or ‘RIPv2-multicast’.
‘Routing Table’
Allows you to add or modify routes when this device is active. Use the ‘New Route’ button to add a route or edit
existing routes.
To learn more about this feature, please refer to chapter 6.6.7.
5.2.5.5 Internet Connection Firewall
Your gateway’s firewall helps protect your computer by preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to it
through a network such as the Internet. The firewall can be activated per network connection.
To enable the firewall on this network connection, select the ‘Enabled’ check box. To learn more about your
gateway’s security features, please refer to chapter 5.3.
Figure 5.66 Internet Connection Firewall
5.2.6 Configuring your Wireless Windows® XP clients
If your PC has wireless capabilities, Microsoft® Windows® XP will automatically recognize this and create a wireless connection
for you. You can view this connection under Window’s Network Connections.
Note: The following description and images are in accordance with Microsoft® Windows® XP, Version 2002, running Service Pack 2.

46
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
1. Open your Network Connections window from Window®’s Control Panel (see Figure 5.67).
Figure 5.67 Network Connections
2. Double-click the wireless connection icon. The ‘Wireless Network Connection’ screen will appear, displaying all available
wireless networks in your vicinity. If your gateway is connected and active, you will see GlobeSurfer ® II’s wireless connection
(see Figure 5.68). Note that the connection’s status is ‘Not connected’ and defined as “Unsecured wireless network”.
Figure 5.68 Available Wireless Networks
3. Click the connection once to mark it and then press the ‘Connect’ button at the bottom of the screen. After the connection is
established, its status will change to ‘Connected’:
Figure 5.69 Connected Wireless Network
An icon will appear in the notification area, announcing the successful initiation of the wireless connection (see Figure 5.70).
Figure 5.70 Wireless Network Information

47
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
You can now use GlobeSurfer ® II’s wireless network from the configured PC. However, so can any other user with a wireless
PC, which happens to be in your network’s radio range. Such a user has access to any disk shares available in your network.
To prevent this scenario, the next logical step is to secure your wireless network, allowing only specific users to connect. To
learn more about securing your Wireless Network, see section 5.2.4.3.
5.3 Security
The GlobeSurfer ® II includes comprehensive and robust security services: Stateful Packet Inspection Firewall, user authentication
protocols and password protection mechanisms. These features together allow users to connect their computers to the Internet and
simultaneously be protected from the security threats of the Internet.
The firewall, the cornerstone of the GlobeSurfer ® II security services, has been exclusively tailored to the needs of the residential/office
user and has been pre-configured to provide optimum security.
The GlobeSurfer ® II firewall provides both the security and flexibility that home and office users seek. It provides a managed,
professional level of network security while enabling the safe use of interactive applications, such as Internet gaming and
videoconferencing.
The GlobeSurfer ® II firewall supports advanced filtering, designed to allow comprehensive control over the firewall’s behavior. You can
define specific input and output rules, control the order of logically similar sets of rules and make a distinction between rules that apply
to WAN and LAN network devices.
•
The General tab allows you to choose the security level for the firewall (see section 5.3.1)
•
The Access control tab can be used to restrict access from the local network to the Internet (see section 0).
•
The Port forwarding tab can be used to enable access from the Internet to specified services provided by computers in the local
network and special Internet applications (see section 5.3.3).
•
The DMZ host tab allows you to configure a LAN host to receive all traffic arriving at your GlobeSurfer ® II, which does not belong
to a known session (see section 0).
•
The Port triggering tab allows you to define port triggering entries, to dynamically open the firewall for some protocols or ports.
(see section 0).
•
The Website Restrictions tab allows you to block LAN access to a certain host or Web site on the Internet (see section 5.3.6).
•
Advanced filtering tab allows you to implicitly control the firewall setting and rules (see section 5.3.7).
•
Security log tab allows you to view and configure the firewall Log (see section 5.3.8)
5.3.1 General
Use the ‘General’ screen to configure the gateway’s basic security settings.
Figure 5.71 General overview

48
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
The firewall regulates the flow of data between the home network and the Internet. Both incoming and outgoing data are
inspected and then either accepted (allowed to pass through GlobeSurfer ® II) or rejected (barred from passing through
GlobeSurfer ® II) according to a flexible and configurable set of rules. These rules are designed to prevent unwanted intrusions
from the outside, while allowing home users access to the Internet services that they require.
The firewall rules specify what types of services available on the Internet may be accessed from the home network and what
types of services available in the home network may be accessed from the Internet. Each request for a service that the firewall
receives, whether originating in the Internet or from a computer in the home network, is checked against the set of firewall
rules to determine whether the request should be allowed to pass through the firewall. If the request is permitted to pass, then
all subsequent data associated with this request (a “session”) will also be allowed to pass, regardless of its direction.
For example, when you point your Web browser to a Web page on the Internet, a request is sent out to the Internet for this
page. When the request reaches GlobeSurfer ® II the firewall will identify the request type and origin, HTTP and a specific PC in
your home network, in this case. Unless you have configured access control to block requests of this type from this computer,
the firewall will allow this request to pass out onto the Internet (see section 5.3.2 for more on setting access controls). When
the Web page is returned from the Web server the firewall will associate it with this session and allow it to pass, regardless of
whether HTTP access from the Internet to the home network is blocked or permitted.
The important thing to note here is that it is the origin of the request, not subsequent responses to this request, that
determines whether a session can be established or not.
You may choose from among three pre-defined security levels for GlobeSurfer ® II: Minimum, Typical and Maximum. The table
below summarizes the behavior of GlobeSurfer ® II for each of the three security levels.
SECURITY LEVEL
REQUESTS ORIGINATING IN THE
WAN (INCOMING TRAFFIC)
REQUESTS ORIGINATING IN THE LAN
(OUTGOING TRAFFIC)
Maximum Securityww
Blocked: No access to home network
from Internet, except as configured in
the Port Forwarding, DMZ host and
Remote Access screens
Limited: By default, Only commonlyused services, such as Webbrowsing
and e-mail, are permitted *
Typical Security
Blocked: No access to home network
from Internet, except as configured in
the Port Forwarding, DMZ host and
Remote Access screens
Blocked: No access to home network
from Internet, except as configured in
the Port Forwarding, DMZ host and
Remote Access screens
Minumum Security
Unrestricted: Permits full access
from Internet to home network; all
connection attempts permitted
Blocked: No access to home network
from Internet, except as configured in
the Port Forwarding, DMZ host and
Remote Access screens
* These services include Telnet, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, IMAP, POP3 and SMTP. The list of allowed services at ‘Maximum
Security’ mode can be edited in the Access Control page.
Attention: Some applications (such as some Internet messengers and Peer-To-Peer client applications) tend to use these
ports, if they cannot connect with their own default ports. When applying this behavior, these applications will not be blocked
outbound, even at Maximum Security Level.
To configure GlobeSurfer ® II’s security settings:
1. Choose from among the three predefined security levels described in the table above.
Using the Minimum Security setting may expose the home network to significant security risks, and thus should only be
used, when necessary, for short periods of time.
2. Check the ‘Block IP Fragments’ box in order to protect your home network from a common type of hacker attack that could
make use of fragmented data packets to sabotage your home network.
Note that VPN over IPSec and some UDP-based services make legitimate use of IP fragments. You will need to allow IP
fragments to pass into the home network in order to make use of these select services.
3. Click the ‘OK’ button to save your changes.

49
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5.3.2 Access control
You may want to block specific computers within the home network (or even the whole network) from accessing certain
services on the Internet. For example, you may want to prohibit one computer from surfing the Web, another computer from
transferring files using FTP, and the whole network from receiving incoming e-mail.
Access Control defines restrictions on the types of requests that may pass from the home network out to the Internet, and
thus may block traffic flowing in both directions. It can also be used for allowing specific services when maximum security
is configured. In the e-mail example given above, you may prevent computers in the home network from receiving e-mail by
blocking their outgoing requests to POP3 servers on the Internet.
There are numerous services you should consider blocking, such as popular game and file sharing servers. For example, if you
want to make sure that your employees do not put your business at risk from illegally traded copyright files, you may want to
block several popular P2P and file sharing applications.
To allow or restrict services:
1. Select the ‘Access Control’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen. The ‘Access Control’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.72).
Figure 5.72 Access Control
2. Click the ‘New Entry’ link. The ‘Add Access Control Rule’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.73).
Figure 5.73 Access Control Add Rule
3. The Address combo box provides you the ability to specify the computer or group of computers for which you would like
to apply the access control rule. You can select between any or a specific computer address in your LAN. If you choose
the ‘User defined’ option, the screen will refresh, and you will be directed to the ‘Edit Network Object’ page where you can
specify a network object. To learn more about network objects, see chapter 6.6.8.
4. The Protocol combo box lets you select or specify the type of protocol that will be used. In addition to the list of popular
protocols it provides, you may also choose any or a specific protocol. If you choose the ‘User defined’ option, the screen
will refresh, and you will be redirected to the ‘Edit Service’ page where you can specify a protocol. To learn more about
defining protocols, see chapter 6.6.15.
5. The Schedule combo box allows you to define the time period during which this rule will take effect. You can select
between ‘Always’ or a specific schedule. If you choose the ‘Specify Schedule’ option, the screen will refresh, and you will
be directed to the ‘Edit Scheduler rule’ page where you can define your own rule. To learn more about defining scheduler
rules, see section 6.6.4.

50
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6. Click the ‘OK’ button to save your changes. The ‘Access Control’ screen will display a summary of the rule that you just
added (see Figure 5.74).
Figure 5.74 Access control Rule Summary
5.3.3 Port forwarding
In its default state, GlobeSurfer ® II blocks all external users from connecting to or communicating with your network. Therefore
the system is safe from hackers who may try to intrude on the network and damage it. However, you may want to expose
your network to the Internet in certain limited and controlled ways in order to enable some applications to work from the LAN
(game, voice and chat applications, for example) and to enable Internet-access to servers in the home network. The Port
Forwarding feature supports both of these functionalities. If you are familiar with networking terminology and concepts, you
may have encountered this topic referred to as “Local Servers”.
The ‘Port Forwarding’ tab lets you define the applications that require special handling by GlobeSurfer ® II. All you have to do is
select the application’s protocol and the local IP address of the computer that will be using or providing the service. If required,
you may add new protocols in addition to the most common ones provided by GlobeSurfer ® II.
For example, if you wanted to use a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) application on one of your PCs, you would simply select
‘FTP’ from the list and enter the local IP address or host name of the designated computer. All FTP-related data arriving at
GlobeSurfer ® II from the Internet will henceforth be forwarded to the specified computer.
Similarly, if you want to grant Internet users access to servers inside your home network, you must identify each service that
you want to provide and the PC that will provide it. For example, if you want to host a Web server inside the home network you
must select ‘HTTP’ from the list of protocols and enter the local IP address or host name of the computer that will host the
Web server. When an Internet user points her browser to the external IP address of GlobeSurfer ® II, the gateway will forward
the incoming HTTP request to the computer that is hosting the Web server.
Additionally, port forwarding enables you to redirect traffic to a different port instead of the one to which it was designated.
Lets say, that you have a Web server running on your PC on port 8080 and you want to grant access to this server to anyone
who accesses GlobeSurfer ® II via HTTP. To accomplish this, do the following:
•
Define a port forwarding rule for the HTTP service, with the PC’s IP or host name.
•
Specify 8080 in the ‘Forward to Port’ field.
All incoming HTTP traffic will now be forwarded to the PC running theWeb server on port 8080. When setting a port forwarding
service, you must ensure that the port is not already in
use by another application, which may stop functioning. A common example is when using SIP signaling in Voice over IP - the
port used by the gateway’s VoIP application (5060) is the same port on which port forwarding is set for LAN SIP agents.
Note: Some applications, such as FTP, TFTP, PPTP and H323, require the support of special specific Application Level Gateway
(ALG) modules in order to work inside the home network. Data packets associated with these applications contain information
that allows them to be routed correctly. An ALG is needed to handle these packets and ensure that they reach their intended
destinations. GlobeSurfer ® II is equipped with a robust list of ALG modules in order to enable maximum functionality in the
home network.
Note: The ALG is automatically assigned based on the destination port.

51
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
To add a new port forwarding service:
1. Select the ‘Port Forwarding’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen. The ‘Port Forwarding’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.75).
Figure 5.75 Port Forwarding
2. Click the ‘New Entry’ link. The ‘Add Port Forwarding Rule’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.76).
Figure 5.76 Add port Forwarding Rule
3. Enter the IP address or the host name of the computer that will provide the service (the “server”). Note that only one LAN
computer can be assigned to provide a specific service or application.
4. The Protocol combo box lets you select or specify the type of protocol that will be used. In addition to the list of popular
protocols it provides, you may also choose any or a specific protocol. If you choose the ‘User defined’ option, the screen
will refresh, and you will be redirected to the ‘Edit Service’ page where you can specify a protocol. To learn more about
defining protocols, see chapter 6.6.15.
5. By default, GlobeSurfer ® II will forward traffic to the same port as the incoming port. If you wish to redirect traffic to a
different port, select the ‘Specify’ option. The screen will refresh, and an additional field will appear enabling you to enter
the port number:
Figure 5.77 Forward to a specific port
6. The Schedule combo box allows you to define the time period during which this rule will take effect. You can select
between ‘Always’ or a specific schedule. If you choose the ‘User Defined’ option, the screen will refresh, and you will be
directed to the ‘Edit Scheduler rule’ page where you can define your own rule. To learn more about defining scheduler
rules, see section 6.6.4.
7. Click the ‘OK’ button to save your changes. The ‘Port Forwarding’ screen will display a summary of the rule that you just
added (see Figure 5.78).

52
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.78 Port Forwarding Summary
You may edit the port forwarding rule by modifying its entry under the ‘Local Host’ column in the ‘Port Forwarding’ screen.
To modify an entry:
1. Click the Edit action icon for the rule. The ‘Edit Port Forwarding Rule’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.79). This screen
allows you to edit all the parameters that you configured when creating the port forwarding rule.
Figure 5.79 Port Forwardin Edit Rule
2. Click the ‘OK’ button to save your changes and return to the ‘Port Forwarding’ screen.
You can disable a port forwarding rule in order to make a service unavailable without having to remove the rule from the ‘Port
Forwarding’ screen. This may be useful if you wish to make the service unavailable only temporarily and expect that you will
want to reinstate it in the future.
•
To temporarily disable a rule, clear the check box next to the service name.
•
To reinstate it at a later time, simply reselect the check box.
•
To remove a rule, click the Remove action icon for the service. The service will be permanently removed.
5.3.4 DMZ host
The DMZ (Demilitarized) Host feature allows one local computer to be exposed to the Internet. Designate a DMZ host when:
•
You wish to use a special-purpose Internet service, such as an on-line game or video-conferencing program, that is not
present in the Port Forwarding list and for which no port range information is available.
•
You are not concerned with security and wish to expose one computer to all services without restriction.

53
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Warning: A DMZ host is not protected by the firewall and may be vulnerable to attack.
Designating a DMZ host may also put other computers in the home network at risk.
When designating a DMZ host, you must consider the security implications and protect it if necessary.
An incoming request for access to a service in the home network, such as a Web-server, is fielded by GlobeSurfer ® II.
GlobeSurfer ® II will forward this request to the DMZ host (if one is designated) unless the service is being provided by another
PC in the home network (assigned in Port Forwarding), in which case that PC will receive the request instead.
To designate a local computer as a DMZ Host:
1. Select the ‘DMZ Host’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen. The ‘DMZ Host’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.80).
Figure 5.80 DMZ Host
2. Enter the local IP address of the computer that you would like to designate as a DMZ host, and select the check-box. Note
that only one LAN computer may be a DMZ host at any time.
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
You can disable the DMZ host so that it will not be fully exposed to the Internet, but keep its IP address recorded on the ‘DMZ
Host’ screen. This may be useful if you wish to disable the DMZ host but expect that you will want to enable it again in the future.
To disable the DMZ host so that it will not be fully exposed to the Internet, clear the check-box next to the DMZ IP designation,
and click ‘OK’.
To reinstate it at a later time, simply reselect the check box.
5.3.5 Port triggering
Port triggering can be used for dynamic port forwarding configuration. By setting port triggering rules, you can allow inbound
traffic to arrive at a specific LAN host, using ports different than those used for the outbound traffic. This is called port
triggering since the outbound traffic triggers to which ports inbound traffic is directed.
For example, consider a gaming server that is accessed using UDP protocol on port 2222. The gaming server responds by
connecting the user using UDP on port 3333 when starting gaming sessions. In such a case you must use port triggering,
since this scenario conflicts with the following default firewall settings:
The firewall blocks inbound traffic by default.
The server replies to GlobeSurfer ® II’s IP, and the connection is not sent back to your host, since it is not part of a session.
In order to solve this you need to define a Port Triggering entry, which allows inbound traffic on UDP port 3333, only after
a LAN host generated traffic to UDP port 2222. This will result in accepting the inbound traffic from the gaming server, and
sending it back to the LAN Host which originated the outgoing traffic to UDP port 2222.
Select the ‘Port Triggering’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen. The ‘Port Triggering’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.81).
This screen will list all of the port triggering entries.

54
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.81 Port triggering
Let’s add an entry for the gaming example above:
1. Select ‘User Defined’ from the ‘Add...’ drop down list. The ‘Edit Service’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.82).
Figure 5.82 Add Port Triggering Rule
2. Enter a name for the service (e.g. “game_server”), and click the ‘New Trigger Ports’ link. The ‘Edit Service Server Ports’
screen will appear (see Figure 5.83).
Figure 5.83 Edit Service Server Ports
3. In the Protocol combo-box, select UDP. The screen will refresh, providing source and destination port options (see Figure 5.84).

55
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
4. Leave the Source Ports combo-box at its default “Any”. In the Destination Ports combo-box, select “Single”. The screen will
refresh again, providing an additional field in which you should enter “2222” as the destination port.
Figure 5.84 Edit Server Ports
5. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
6. Back in the ‘Edit Service’ screen, click the ‘New Opened Ports’ link. The ‘Edit Service Opened Ports’ screen will appear (see
Figure 5.85).
Figure 5.85 Edit Service Opened Ports
7. Similar to the trigger ports screen, select UDP as the protocol, leave the source port at “Any”, and enter a 3333 as the
single destination port (see Figure 5.86).
Figure 5.86 Edit Service Opened Ports
8. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings. The ‘Edit Service’ screen will present your entered information. Click ‘OK’ again to save the
port triggering rule. The ‘Port Triggering’ screen will now include the new port triggering entry (see Figure 5.87).

56
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.87 New Port Triggering Rule
You can disable a port triggering rule without having to remove it from the ‘Port Triggering’ screen.
•
To temporarily disable a rule, clear the check box next to the service name.
•
To reinstate it at a later time, simply reselect the check box.
•
To remove a rule, click the Remove action icon for the service. The service will be permanently removed. There may be a
few default port triggering rules listed when you first access the port triggering screen. Please note that disabling these
rules may result in impaired gateway functionality.
5.3.6 Website restrictions
You may configure GlobeSurfer ® II to block specific Internet websites so that they cannot be accessed from computers in the
home network. Moreover, restrictions can be applied to a comprehensive and automaticallyupdated table of sites to which
access is not recommended.
To block access to a website:
1. Click the ‘Website Restrictions’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen (see Figure 5.88).
Figure 5.88 Website restrictions
2. Click the ‘New Entry’ link. The ‘Restricted Website’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.89).

57
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.89 restricted Website
3. Enter the website address (IP address or URL) that you would like to make inaccessible from your home network (all Web
pages within the site will also be blocked). If the website address has multiple IP addresses, GlobeSurfer ® II will resolve all
additional addresses and automatically add them to the restrictions table.
4. The Local Host combo box provides you the ability to specify the computer or group of computers for which you would like
to apply the website restriction.
You can select between any or a specific computer address in your LAN. If you choose the User Defined’ option, the screen
will refresh, and you will be redirected to the ‘Edit network object’ page. To learn more about network objects, see chapter
6.6.8.
5. The Schedule combo-box allows you to define the time period during which this rule will take effect. By default, the rule
will always be active. However, you can configure scheduler rules by selecting ‘User Defined’. To learn how to configure
scheduler rules please refer to section 6.6.4.
6. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.You will be returned to the previous screen while GlobeSurfer ® II attempts to find the site.
‘Resolving. . . ‘ will appear in the Status column while the site is being located (the URL is ‘resolved’ into one or more IP
addresses).
7. Click the ‘Refresh’ button to update the status if necessary. If the site is successfully located then ‘Resolved’ will appear
in the status bar, otherwise ‘Hostname Resolution Failed’ will appear. In case GlobeSurfer ® II fails to locate the website, do
the following:
a. Use a Web browser to verify that the website is available. If it is, then you probably entered the website address
incorrectly.
b. If the website is not available, return to the ‘Website Restrictions’ screen at a later time and click the ‘Resolve Now’
button to verify that the website can be found and blocked by GlobeSurfer ® II.
You may edit the website restriction by modifying its entry under the ‘Local Host’ column in the ‘Website Restrictions’ screen.
To modify an entry:
1. Click the Edit action icon for the restriction. The ‘Restricted Website’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.89). Modify the
website address, group or schedule as necessary.
2. Click the ‘OK’ button to save your changes and return to the ‘Website Restrictions’ screen.
To ensure that all current IP addresses corresponding to the restricted websites are blocked:
1. Click the ‘Resolve Now’ button. GlobeSurfer ® II will check each of the restricted website addresses and ensure that all IP
addresses at which this website can be found are included in the IP addresses column.
You can disable a restriction in order to make a website available again without having to remove it from the ‘Website
Restrictions’ screen. This may be useful if you wish to make the website available only temporarily and expect that you will
want to block it again in the future.
•
To temporarily disable a rule, clear the check box next to the service name.

58
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
•
To reinstate it at a later time, simply reselect the check box.
•
To remove a rule, click the Remove action icon for the service. The service will be permanently removed.
5.3.7 Advanced filtering
Advanced filtering is designed to allow comprehensive control over the firewall’s behavior. You can define specific input and
output rules, control the order of logically similar sets of rules and make a distinction between rules that apply to WAN and
LAN devices.
To view GlobeSurfer ® II’s advanced filtering options, click the ‘Advanced Filtering’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen.
The ‘Advanced Filtering’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.90).
Figure 5.90 Advanced Filtering
This screen is divided into two identical sections, one for ‘Input Rule Sets’ and the other for ‘Output Rule Sets’, which are for
configuring inbound and outbound traffic, respectively. Each section is comprised of subsets, which can be grouped into three
main subjects:
•
Initial rules - rules defined here will be applied first, on all gateway devices.
•
Network devices rules - rules can be defined per each gateway device.
•
Final rules - rules defined here will be applied last, on all gateway devices.
Note: The order of the firewall rules’ appearance in the ‘Advanced Filtering’ screen represents the sequence by which they will
be applied.
There are numerous rules automatically inserted by the firewall in order to provide improved security and block harmful
attacks.
To configure an advanced filtering rule:
1. After choosing the traffic direction and the device on which to set the rule, click the appropriate New Entry link. The ‘Add
Advanced Filter’ screen will appear (see Figure 5.91).

59
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 5.91 Add Advanced Filtering
Matching To apply a rule, a matching must be made between IP addresses, and a traffic protocol must be defined:
•
‘Source Address’ The source address of the packets sent to or received from the network object (computer A in the
above example). To add an address:
a. Select the ‘User Defined’ option in the combo box. The screen will refresh and you will be directed to the ‘Edit
Network Object’ page.
b. Use the ‘Edit Network Object’ page to define your address. Please refer to section 6.6.8 in order to learn how to do so.
•
‘Destination Address’ The destination address of the packets sent to or received from the network object. This address
can be configured in the same manner as the source address.
•
‘Protocol’ You may choose a specific traffic protocol from the combo box, or add a new one. To add a new traffic protocol:
a. Select the ‘User Defined’ option in the combo box. The screen will refresh and you will be directed to the ‘Edit
Service’ page.
b. Use the ‘Edit Service’ page to define your protocol. Please refer to section 6.6.15 in order to learn how to do so.
‘Operation’ Define what action the rule will take, by selecting one of the following radio buttons:
•
‘DROP’ Deny access to packets that match the source and destination IP addresses and service ports defined in
‘Matching’.
•
‘REJECT’ Deny access to packets that match the source and destination IP addresses and service ports defined in
‘Matching’ and sends and sends an ICMP error or a TCP reset to the origination peer.
•
‘ACCEPT’ Allow access to packets that match the source and destination IP addresses and service ports defined in
‘Matching’. The data transfer session will be handled using Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI).
•
‘ACCEPT PACKET’ Allow access to packets that match the source and destination IP addresses and service ports defined
in ‘Matching’. The data transfer session will not be handled using Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI), meaning that other
packets that match this rule will not be automatically allowed access. For example, this can useful when creating rules that
allow broadcasting.

60
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Logging’ Monitor the rule:
•
‘Log Packets Matched by This Rule’ Check this check box to log the first packet from a connection that was matched by
this rule.
‘Schedule’ By default, the rule will always be active. However, you can configure scheduler rules in order to define time
segments during which the rule may be active. To learn how to configure scheduler rules please refer to section 6.6.4.
2. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
5.3.8 Security log
The Security Log displays a list of firewall-related events, including attempts to establish inbound and outbound connections,
attempts to authenticate through an administrative interface (Web-based management or Telnet terminal), firewall
configuration and system start-up.
To view the security log, click the ‘Security Log’ tab in the ‘Security’ management screen. The ‘Security Log’ screen will appear
(see Figure 5.92).
Figure 5.92 Security Log
‘Time’
The time the event occurred.
‘Event’
There are five kinds of events:
•
Inbound Traffic: The event is a result of an incoming packet.
•
Outbound Traffic: The event is a result of outgoing packet.
•
Firewall Setup: Configuration message.
•
WBM Login: Indicates that a user has logged in to WBM.
•
CLI Login: Indicates that a user has logged in to CLI (via Telnet).

61
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Event-Type’
A textual description of the event:
Blocked: The packet was blocked. The message is colored red.
Accepted: The packet was accepted. The message is colored green.
‘Details’
More details about the packet or the event, such as protocol, IP addresses, ports, etc.
To view or change the security log settings:
1. Click the ‘Settings’ button that appears at the top of the ‘Firewall Log’ screen. The ‘Security Log Settings’ screen will
appear (see Figure 5.93).
Figure 5.93 Security Log Settings
2. Select the types of activities for which you would like to have a log message generated:
•
‘Accepted Events’
‘Accepted Incoming Connections’ Write a log message for each successful attempt to establish an inbound connection
to the home network.
‘Accepted Outgoing Connections’ Write a log message for each successful attempt to establish an outgoing connection
to the public network.
•
‘Blocked Events’
‘All Blocked Connection Attempts’ Write a log message for each blocked attempt to establish an inbound connection to
the home network or vice versa. You can enable logging of blocked packets of specific types by disabling this option,
and enabling some of the more specific options below it.
‘Specific Events’ Specify the blocked events that should be monitored. Use this to monitor specific event such as
SynFlood. A log message will be generated if either the corresponding check-box is checked, or the “All Blocked
Connection Attempts” check-box is checked.
•
‘Other Events’
‘Remote Administration Attempts’ Write a log message for each remote-administration connection attempt, whether
successful or not.
‘Connection States’ Provide extra information about every change in a connection opened by the firewall. Use this
option to track connection handling by the firewall and Application Level Gateways (ALGs).
•
‘Log Buffer’
‘Prevent Log Overrun’ Select this check box in order to stop logging firewall activities when the memory allocated for
the log fills up.
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.

62
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
The following are the available event types that can be recorded in the firewall log:
1. Firewall internal - an accompanying explanation from the firewall internal mechanism will be added in case this event-type
is recorded.
2. Firewall status changed - the firewall changed status from up to down or the other way around, as specified in the event
type description.
3. STP packet - an STP packet has been accepted/rejected.
4. Illegal packet options - the options field in the packet’s header is either illegal or forbidden.
5. Fragmented packet - a fragment has been rejected.
6. WinNuke protection - a WinNuke attack has been blocked.
7. ICMP replay - an ICMP replay message has been blocked.
8. ICMP redirect protection - an ICMP redirected message has been blocked.
9. Packet invalid in connection - a packet has been blocked, being on an invalid connection.
10. ICMP protection - a broadcast ICMP message has been blocked.
11. Broadcast/Multicast protection - a packet with a broadcast/multicast source IP has been blocked.
12. Spoofing protection - a packet from the WAN with a source IP of the LAN has been blocked.
13. DMZ network packet - a packet from a demilitarized zone network has been blocked.
14. Trusted device - a packet from a trusted device has been accepted.
15. Default policy - a packet has been accepted/blocked according to the default policy.
16. Remote administration - a packet designated for GlobeSurfer ® II management has been accepted/blocked.
17. Access control - a packet has been accepted/blocked according to an access control rule.
18. Parental control - a packet has been blocked according to a parental control rule.
19. NAT out failed - NAT failed for this packet.
20. DHCP request - GlobeSurfer ® II sent a DHCP request (depends on the distribution).
21. DHCP response - GlobeSurfer ® II received a DHCP response (depends on the distribution).
22. DHCP relay agent - a DHCP relay packet has been received (depends on the distribution).
23. IGMP packet - an IGMP packet has been accepted.
24. Multicast IGMP connection - a multicast packet has been accepted.
25. RIP packet - a RIP packet has been accepted.
26. PPTP connection - a packet inquiring whether GlobeSurfer ® II is ready to receive a PPTP connection has been accepted.
27. Kerberos key management 1293 - security related, for future use.
28. Kerberos 88 - for future use.
29. AUTH:113 request - an outbound packet for AUTHprotocol has been accepted (for maximum security level).
30. Packet-Cable - for future use.
31. IPV6 over IPV4 - an IPv6 over IPv4 packet has been accepted.
32. ARP - an ARP packet has been accepted.
33. PPP Discover - a PPP discover packet has been accepted.
34. PPP Session - a PPP session packet has been accepted.
35. 802.1Q - a 802.1Q (VLAN) packet has been accepted.
36. Outbound Auth1X - an outbound Auth1X packet has been accepted.
37. IP Version 6 - an IPv6 packet has been accepted.
38. GlobeSurfer ® II initiated traffic - all traffic that GlobeSurfer ® II initiates is recorded.
39. Maximum security enabled service - a packet has been accepted because it belongs to a permitted service in the
maximum security level.
40. SynCookies Protection - a SynCookies packet has been blocked.
41. ICMP Flood Protection - a packet has been blocked, stopping an ICMP flood.
42. UDP Flood Protection - a packet has been blocked, stopping a UDP flood.

63
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
43. Service - a packet has been accepted because of a certain service, as specified in the event type.
44. Advanced Filter Rule - a packet has been accepted/blocked because of an advanced filter rule.
45. Fragmented packet, header too small - a packet has been blocked because after the defragmentation, the header was too
small.
46. Fragmented packet, header too big - a packet has been blocked because after the defragmentation, the header was too
big.
47. Fragmented packet, drop all - not used.
48. Fragmented packet, bad align - a packet has been blocked because after the defragmentation, the packet was badly
aligned.
49. Fragmented packet, packet too big - a packet has been blocked because after the defragmentation, the packet was too
big.
50. Fragmented packet, packet exceeds - a packet has been blocked because defragmentation found more fragments than
allowed.
51. Fragmented packet, no memory - a fragmented packet has been blocked because there was no memory for fragments.
52. Fragmented packet, overlapped - a packet has been blocked because after the defragmentation, there were overlapping
fragments.
53. Defragmentation failed - the fragment has been stored in memory and blocked until all fragments arrived and
defragmentation could be performed.
54. Connection opened - usually a debug message regarding a connection.
55. Wildcard connection opened - usually a debug message regarding a connection.
56. Wildcard connection hooked - usually debug message regarding connection.
57. Connection closed - usually a debug message regarding a connection.
58. Echo/Chargen/Quote/Snork protection -a packet has been blocked, protecting from Echo/Chargen/Quote/Snork.
59. First packet in connection is not a SYN packet - a packet has been blocked because of a TCP connection that had started
without a SYN packet.
60. Error: No memory - a message notifying that a new connection has not been established because of lack of memory.
61. NAT Error : Connection pool is full - a message notifying that a connection has not been created because the connection
pool is full.
62. NAT Error: No free NAT IP - a message notifying that there is no free NAT IP, therefore NAT has failed.
63. NAT Error: Conflict Mapping already exists - a message notifying that there is a conflict since the NAT mapping already
exists, therefore NAT has failed.
64. Malformed packet: Failed parsing - a packet has been blocked because it is malformed.
65. Passive attack on ftp-server: Client attempted to open Server ports - a packet has been blocked because of an
unauthorized attempt to open a server port.
66. FTP port request to 3rd party is forbidden (Possible bounce attack) - a packet has been blocked because of an
unauthorized FTP port request.
67. Firewall Rules were changed - the firewall rule set has been modified.
68. User authentication - a message during login time, including both successful and failed authentication.
69. First packet is Invalid - First packet in connection failed to pass firewall or NAT

64
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6 SYSTEM SETUP
The System Setup include settings and functions rrelated to the general behaviour of your GlobeSurfer ® II.
6.1 Telephone
GlobeSurfer ® II is equipped with a telephony connector and can replace a regular fixed line service (POTS). In order to setup fixed
line telephony to make phone calls through GlobeSurfer ® II, connect GlobeSurfer ® II to the first telephony plug. Note that you should
configure your country in the GlobeSurfer ® II Quick setup wizard, see section 2.3.2.
6.1.1 Missed calls
The ‘Missed calls’ tab shows a list of calls, with Caller ID if received, that was received but not answered including a time
stamp of the event (see Figure 6.1). By clicking ‘Clear log’ you will erase the history of missed calls.
Figure 6.1 Missed Calls
6.1.2 Incoming calls
The ‘Incoming calls’ tab shows calls, with Caller ID if received, that was received and answered including a time stamp and
duration of the event (see Figure 6.2). By clicking ‘Clear log’ you will erase the history of incoming calls.
Figure 6.2 Incoming Calls
6.1.3 Outgoing calls
The ‘Outgoing calls’ tab shows calls, with Caller ID, that has been initiated from your telephones using GlobeSurfer ® II
including a time stamp and duration of the event (see Figure 6.3). By clicking ‘Clear log’ you will erase the history of outgoing
calls.

65
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.3 Outgoing Calls
6.1.4 Telephone settings
The ‘Telephone settings’ tab controls the behaviour of the fixed line telephony sopprt of GlobeSurfer ® II.
Use the ‘Telephone settings’ tab to make the following settings:
6.2 SIM setup
The SIM card in the GlobeSurfer ® II requires a PIN code to be entered before it can be used. The PIN code you receive from your ISP
can be changed to a PIN code of your own. By default the PIN code is required but it can be stored in the GlobeSurfer ® II after the first
use so that you don’t have to enter it more than once. These settings can be changed but note that you should disconnect before doing
any changes to the SIM setup.
Figure 6.4 SIM Setup
To change the PIN of your SIM card or save PIN on GlobeSurfer ® II, perform the following:
1. Click ‘SIM Setup’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. The SIM Setup screen will appear (see Figure 6.4).
2. Enter the PIN code in the first field to be able to change any settings.
3. a. To be forced to enter the PIN code each time the GlobeSurfer ® II is started, de-select the Enabled checkbox at Save PIN.
b. If you want to change the PIN code, enter a new PIN code in the ‘New PIN code’ and ‘Verify new PIN code’ fields.
4. Click OK to save your changes.

66
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.5 SIM PIN enable
To disable PIN on the SIM, perform the following:
1. Click ‘SIM setup’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. Click the ‘SIM PIN enable’ tab (see Figure 6.5).
2. By default the PIN is enabled on your SIM card. To disable the PIN, de-select the first Enabled checkbox.
3. Click OK to save your changes.
6.3 Unlock device
In case the GlobeSurfer ® II is locked to a specific ISP it can be unlocked with a code that you should be able to get from your ISP.
Normally there are certain conditions that must be fulfilled to be able to unlock the device.
To unlock the GlobeSurfer ® II:
1. Click ‘Unlock device’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. If the GlobeSurfer ® II really is locked, the ‘Unlock
device’ screen will appear.
2. Enter the unlock code.
3. Click OK.
6.4 System monitoring
Connections
The Monitoring screen displays a table summarizing the monitored connection data (see Figure 6.6). GlobeSurfer ® II constantly
monitors traffic within the local network and between the local network and the Internet. You can view statistical information about data
received from and transmitted to the Internet (WAN) and to computers in the local network (LAN).
Figure 6.6 System monitoring
Click the ’Refresh’ button to update the display, or press the ’Automatic Refresh On’ button to constantly update the displayed
parameters.

67
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6.4.1 Log
The Log screen (see Figure 6.7)
Figure 6.7 System log
6.4.2 System
The systems tab shows current uptime for the system (see Figure 6.8).
Figure 6.8 System
6.4.3 About GlobeSurfer ® II
To view technical information regarding GlobeSurfer ® II, click ‘About GlobeSurfer ® II’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the
management console. Technical information such as ‘Version’, ‘IMSI’ and ‘IMEI’ will appear (see Figure 6.9).

68
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.9 About GlobeSurfer® II
6.4.4 Configuration file
Click ‘Configuration file’ on the ‘System setup’ screen to view the contents of GlobeSurfer ® II«s configuration file.
Figire 6.10 Configuration file
•
Click ‘Save configuration file’ to save a copy of the configuration file.
•
Click Load configuration file to load a configuration file and restart GlobeSurfer ® II.
6.4.5 Restart
To restart the GlobeSurfer ® II:
1. Click ‘Restart’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. The ‘Restart’ screen will be displayed (see
Figure 6.11).
2. Click OK to restart GlobeSurfer ® II. This may take up to one minute. To reenter the management console after restarting
GlobeSurfer ® II, click the browser’s Refresh button.
Figure 6.11 Restart
6.4.6 Restore defaults
You may sometimes wish to restore GlobeSurfer ® II’s factory default settings This may happen, for example, when you wish to
build a new network from the beginning, or when you cannot recall changes made to the network and wish to go back to the

69
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
default configuration.
Figure 6.12 Restore Defaults
To restore default settings:
1. Click ‘Restore defaults’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. The Restore defaults screen will be
displayed (see Figure 6.12).
2. Click OK to restore GlobeSurfer ® II’s factory default settings.
Note: All web-based management settings and parameters, not only those in the ‘Advanced’ section, will be restored to their
default values. This includes the administrator password; a user-specified password will no longer be valid.
6.4.7 Diagnostics
The ‘Diagnostics’ screen can assist you in testing network connectivity and viewing statistics, such as the number of packets
transmitted and received, round-trip time and success status
6.4.8 Ping
To diagnose network connectivity, perform the following steps:
1. Click the ’Diagnostics’ icon from the ’System setup’ screen. The ’Diagnostics’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.13).
2. Under the Ping section, enter the IP address or URL to be tested in the ’Destination’ field.
3. Enter the number of pings you would like to perform.
4. Press the ’Go’ button.
In a few seconds, diagnostic statistics will be displayed. If no new information is displayed, press the ’Refresh’ button.
Figure 6.13 Diagnostics
6.4.9 Performing a Traceroute
To perform a traceroute, follow these steps:
1. Click the ’Diagnostics’ icon from the ’System setup’ screen in the Web-based Management. The ’Diagnostics’ screen will

70
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
appear (see Figure 6.13).
2. Under the Traceroute section, enter the IP address or URL to be tested in the ’Destination’ field.
3. Press the ’Go’ button.
A traceroute will commence, constantly refreshing the screen. To stop the trace and view the results, press ’Cancel’.
6.5 System settings
The ‘System settings’ screen allows you to configure various system and management parameters.
Figure 6.14 System settings
6.5.1 System
Use this section to configure the following:
1. Specify the ‘GlobeSurfer ® II host name’. The host name is the URL address of the GlobeSurfer ® II.
2. Specify your network’s ‘Local domain’.
6.5.2 GlobeSurfer ® II Management Console Settings
Use this section to configure the following:
1. ‘Automatic refresh of system monitoring web pages’: Select this checkbox to enable the automatic refresh of system
monitoring web pages.
2. ‘Warn user before network configuration changes’: Select this checkbox to activate user warnings before network
configuration changes take effect.

71
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3. ‘Session lifetime’: Controls the session lifetime (minutes) for logins to the management console. When the time has
expired the login screen will appear again.
‘Language’: Controls the language for GlobeSurfer ® II’s management console and display.
6.5.3 Remote administration
‘Remote administration is a hyperlink to ‘Remote administration’ under the ‘Advanced’ menu (see Error! Reference source not found.).
6.5.4 Management Application Ports
This section allows you to configure the following management application ports:
1. ‘Primary/secondary HTTP ports’
2. ‘Primary/secondary HTTPS ports’
3. ‘Primary/secondary Telnet ports’
4. ‘Secure Telnet over SSL ports’
6.5.5 System Logging Settings
Use this section to configure the following:
1. ‘System log buffer size’
2. ‘Remote system notify level’
•
‘None’
•
‘Error’
•
‘Warning’
•
‘Information’
6.5.6 Security Logging Settings
Use this section to configure the following:
1. ‘System log buffer size’
2. ‘Remote system notify level’
•
‘None’
•
‘Error’
•
‘Warning’
•
‘Information’
6.5.7 Outgoing Mail Server Settings
Use this section to configure the following:
1. Enter the hostname of your outgoing (SMTP) server in the ‘Server’ field.
2. Each email requires a from address and some outgoing servers refuse to forward email without a valid from address for
anti-spam considerations. Enter a from email address in the ‘From email address’ field.
3. The ‘Port’ field can be used to alter the server port, if your mail server does not use the standard port 25.
4. If your outgoing email server requires authentication check the ‘Server requires authentication’ checkbox and enter your
username and password in the ‘Username’ and ‘Password’ fields respectively.
6.5.8 Firmware upgrade
GlobeSurfer ® II offers a built-in mechanism for upgrading its software, without losing any of your custom configurations and
settings. The software is upgraded by loading a software image file that you have previously downloaded from the Internet or
received on CD.
6.5.8.1 Upgrading From a Local Computer
To upgrade GlobeSurfer ® II using a locally stored file:
1. Click the ‘Firmware upgrade’ icon from the ‘System setup’ screen. The GlobeSurfer ® II Firmware upgrade screen
will appear (see Figure 6.15).

72
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.15 Firmware upgrade
2. Enter the path of the software image file, or click the ‘Browse’ button to browse for the file on your PC. Click ‘OK’
when ready.
Note: You can only use files with an rmt extension when performing the firmware upgrade procedure. The file will
start loading into your GlobeSurfer ® II. When loading is completed, a confirmation screen will appear, asking you if
you want to upgrade to the new version (see Figure 6.16):
Figure 6.16 GlobeSurfer® II firmware upgrade
4. Click ‘OK’ to confirm. The upgrade process will begin and should take no longer than one minute to complete (see
Figure 6.17).
Figure 6.17 Upgrade in process
When the upgrading is ready the GlobeSurfer ® II will automatically reboot. The new software version will run,
maintaining your custom configurations and settings.
6.5.9 Date and time
To configure date and time settings perform the following:

73
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
1. Click ‘Date and time’ on the ‘System setup’ screen of the management console. The ‘Date and time’ settings screen will be
displayed (see Figure 6.18).
Figure 6.18 Date and time
2. Select the local time zone from the pull-down menu.
3. If you want the GlobeSurfer ® II to perform an automatic time update, perform the following:
•
Select the Enabled checkbox under the ‘Automatic time update’ section.
•
Select the protocol to be used to perform the time update by selecting either the ‘Time of Day (TOD)’ or ‘Network Time
Protocol (NTP)’ radio button.
•
Specify how often to perform the update in the ‘Update every’ field.
•
You can change the default timeserver address by clicking the ‘New entry’ link in the bottom of the ‘Automatic time
update’ section.
6.5.10 Users
To access the list of defined remote users, click the Users icon from the ‘System setup’ screen. The Users table will be
displayed (see Figure 6.19).
Figure 6.19 Users
You can add, edit and delete users allowed to access the GlobeSurfer ® II and your local network by managing the user table
as described in Section 2.5. To add a new user click ‘New user’ in the table and specify the following parameters:

74
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Full name’: The remote user’s full name.
‘Username’: The name the remote user will use to access your local network.
‘New password’: Type a new password for the remote user. If you do not want to
assign a password to the remote user leave this field empty.
‘Retype new password’: If a new password was assigned, type it again to verify
correctness.
‘Permissions’: Select the remote user’s privileges on your local network.
•
Administrator privileges: Grants remote system setting modification via the web-based management console or telnet.
•
Remote access by PPTP: Grants access with no system modification privileges.
6.6 Advanced
6.6.1 Remote administration
It is possible to access and control GlobeSurfer ® II not only from within the home network, but also from the Internet. This
allows you to view or change settings while travelling. It also enables you to allow your ISP to change settings or help you
troubleshoot functionality or communication issues from a remote location.
Remote access to GlobeSurfer ® II is blocked by default to ensure the security of your home network. However, remote access
is supported by the following services, and you may use the ‘Remote Administration’ screen to selectively enable these
services if they are needed.
To view GlobeSurfer ® II’s remote administration options, click the ‘Remote Administration’ icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen of the
Web-based management. The ‘Remote Administration’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.20).
Figure 6.20 Remote administration
‘Allow Incoming Access to the Web-Management’: Used to obtain access to the Web-based Management and gain access
to all system settings and parameters (using a browser). Both secure (HTTPS) and non-secure (HTTP) access is available.
‘Allow Incoming Access to the Telnet Server’: Used to create a command-line session and gain access to all system settings
and parameters (using a text-based terminal). Allow Incoming Access to the SSH Server Similar to Telnet, this protocol is used
to create a secured commandline session and gain access to all system settings and parameters.

75
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Note: Web-Management, Telnet and SSH may be used to modify settings of the frewall or disable it. The user may also
change local IP addresses and other settings, making it diffcult or impossible to access the gateway from the home network.
Therefore, remote access to Telnet or HTTP services should be blocked and should only be permitted when absolutely
necessary.
‘Allow SNMP Control and Diagnostic Requests’: Used to allow Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) requests
to remotely con gure and monitor GlobeSurfer ® II. For more information, please refer to section Error! Reference source not
found.
‘Diagnostic Tools’: Used for troubleshooting and remote system management by you or your Internet Service Provider. The
utilities that can be used are Ping and Traceroute (over UDP).
6.6.2 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
SNMP enables network management systems to remotely configure and monitor GlobeSurfer ® II. Your Internet service
provider (ISP) may use SNMP in order to identify and resolve technical problems. Your ISP should provide technical information
regarding the properties of GlobeSurfer ® II’s SNMP agent.
Figure 6.21 SNMP
To configure GlobeSurfer ® II’s SNMP agent perform the following:
1. Click ‘Simple Network Management Protocol’ on the ‘Advanced’ screen of the Management Console. The SNMP screen
will appear (see Figure 6.21).
2. Check the ‘enable SNMP agent’ checkbox and specify the SNMP parameters, as provided by your Internet service provider:
‘Read-Only/Read-Write Community Names’
SNMP community strings are passwords used in SNMP messages between the management system and
GlobeSurfer ® II. A read-only community allows the manager to monitor GlobeSurfer ® II. A read-write community
allows the manager to both monitor and configure GlobeSurfer ® II.
‘Trusted peer’
The IP address, or subnets of addresses, that identify which remote management stations are allowed to perform
SNMP operations on GlobeSurfer ® II.
‘SNMP traps’
Messages sent by GlobeSurfer ® II to a remote management station, in order to notify the manager about the
occurence of important events or serious conditions. GlobeSurfer ® II supports both SNMP version 1 and SNMP
version 2c traps.
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.

76
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6.6.3 Universal Plug and Play
To access the UPnP settings perform the following:
1. Click ‘Universal Plug and Play’ on the ‘Advanced’ screen of the management console. The Universal Plug and Play
settings screen will be displayed (see Figure 6.22).
2. Check the Allow other network users to control GlobeSurfer ® II’s setwork features checkbox, to enable the UPnP feature.
This will enable you to define UPnP services on any of the LAN hosts.
Check the Enable automatic cleanup of old unused UPnP services checkbox, to enable automatic cleanup of invalid rules.
When enabled, this feature checks validity of all the UPnP services and rules every 5 minutes. Any UPnP defined service
that is found to be old and not in use, is removed, unless any user defined rule (see Security screen) depends on it. This
feature is disabled by default.
Since there is a limitation on the maximum number of UPnP defined services to 256, you should want to enable the
cleanup feature if you might exceed this limit.
In which case might the limit be exceeded UPnP services are not deleted when disconnecting a computer without proper
shutdown of the UpnP application
(e.g. messenger). Thus, if you are running a boingo, services may often not be deleted, and will eventually lead to
exhaustion of rules and services, and no new services could be defined. In this scenario the cleanup feature will find the
services that are no longer valid and will remove them, preventing services exhaustion.
Figure 6.22 UPnP
6.6.4 Scheduler Rules
Scheduler rules are used for limiting the activation of settings, such as firewall rules, to specific time periods, specified in days
of the week, and hours.
Figure 6.23 Scheduler rules
To define a Rule:
1. Click ‘Scheduler rules’ on the ‘Advanced’ screen of the management console. The Scheduler rules screen will appear
(see Figure 6.23).
2. Click the ‘New scheduler entry’ link. The Scheduler rule edit screen will appear (see Figure 6.24).

77
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.24 Edit scheduler rule
3. Specify a name for the rule in the ‘Name’ field.
4. Specify if the rule will be active/inactive during the designated time period, by selecting the appropriate ‘Rule activity
settings’ check box.
5. Click the ‘New time segment’ entry link to define the time segment to which the rule will apply — the Time segment edit
screen will appear (see Figure 6.25).
Figure 6.25 Edit time segment
6. Select active/inactive days of the week.
7. Click the ‘New hours segment entry’ link to define an active/inactive hourly range.
8. Click OK.
Figure 6.26 Edit hour range

78
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6.6.5 Certificates
6.6.5.1 Overview
Public-key cryptography uses a pair of keys: a public key and a corresponding private key. These keys can play
opposite roles, either encrypting or decrypting data. Your public key is made known to the world, while your private
key is kept secret.
The public and private keys are mathematically associated; however it is computationally infeasible to deduce the
private key from the public key. Anyone who has the public key can encrypt information that can only be decrypted
with the matching private key. Similarly, the person with the private key can encrypt information that can only be
decrypted with the matching public key.
Technically, both public and private keys are large numbers that work with cryptographic algorithms to produce
encrypted material. The primary benefit of public-key cryptography is that it allows people who have no preexisting
security arrangement to authenticate each other and exchange messages securely.
GlobeSurfer ® II makes use of public-key cryptography to encrypt and authenticate keys for the encryption of
Wireless and VPN data communication, the Web Based Management (WBM) utility, and secured telnet.
6.6.5.2 Digital Certificates
When working with public-key cryptography, you should be careful and make sure that you are using the correct
person’s public key. Man-in-the-middle attacks pose a potential threat, where an ill-intending 3rd party posts a
phony key with the name and user ID of an intended recipient. Data transfer that is intercepted by the owner of the
counterfeit key can fall in the wrong hands. Digital certificates provide a means for establishing whether a public
key truly belongs to the supposed owner. It is a digital form of credential. It has information on it that identifies you,
and an authorized statement to the effect that someone else has confirmed your identity.
Digital certificates are used to foil attempts by an ill-intending party to use an unauthorized public key. A digital
certificate consists of the following:
A PUBLIC KEY
Certificate information
The “identity” of the user, such as name, user ID and so on.
Digital signatures
A statement stating that the information enclosed in the certificate has been vouched for by a Certificate Authority (CA).
Binding this information together, a certificate is a public key with identification forms attached, coupled with a
stamp of approval by a trusted party.
6.6.5.3 X.509 Certificate Format
GlobeSurfer ® II supports X.509 certificates that comply with the ITU-T X.509 international standard. An X.509
certificate is a collection of a standard set of fields containing information about a user or device and their
corresponding public key. The X.509 standard defines what information goes into the certificate, and describes
how to encode it (the data format). All X.509 certificates have the following data:
The certificate holder’s public key
The public key of the certificate holder, together with an algorithm identifier that specifies which cryptosystem the
key belongs to and any associated key parameters.
The serial number of the certificate
The entity (application or person) that created the certificate is responsible for assigning it a unique serial number
to distinguish it from other certificates it issues. This information is used in numerous ways; for example when a
certificate is revoked, its serial number is placed on a Certificate Revocation List (CRL).
The certificate holder’s unique identifier
This name is intended to be unique across the Internet. A DN consists of multiple subsections and may look
something like this: CN=Option Wireless Sweden AB, EMAIL=info@option.com, OU=Development Department,
O=Option Wireless Sweden AB, C=SE (These refer to the subject’s Common Name, Organizational Unit,

79
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Organization, and Country.)
The certificate’s validity period
The certificate’s start date/time and expiration date/time; indicates when the certificate will expire.
The unique name of the certificate issuer
The unique name of the entity that signed the certificate. This is normally a CA. Using the certificate implies
trusting the entity that signed this certificate. (Note that in some cases, such as root or top-level CA certificates,
the issuer signs its own certificate.) The digital signature of the issuer the signature using the private key of the
entity that issued the certificate.
The signature algorithm identifier
Identifies the algorithm used by the CA to sign the certificate.
6.6.5.4 GlobeSurfer ® II Certificate Stores
GlobeSurfer ® II maintains two certificate stores:
1. GlobeSurfer ® II Local Store This store contains a list of approved certificates that are used to identify
GlobeSurfer ® II to its clients. The list also includes certificate requests that are pending a CA’s endorsement.
You can obtain certificates for GlobeSurfer ® II using the following methods:
•
Requesting an X509 Certificate
This method creates both a private and a matching public key. The public key is then sent to the CA to be
certified.
•
Creating a Self-Signed Certificate
This method is the same as requesting a certificate, only the authentication of the public key does not
require a CA. This is mainly intended for use within small organizations.
•
Loading a PKCS#12
Format Certificate This method loads a certificate using an already available and certified set of private
and public keys.
2. Certificate Authority (CA) Store This store contains a list of the trusted certificate authorities, which is used
to check certificates presented by GlobeSurfer ® II clients.
6.6.5.4.1 Requesting an X509 Certificate
To obtain an X509 certificate, you must ask a CA to issue you one. You provide your public key, proof
that you possess the corresponding private key, and some specific information about yourself. You
then digitally sign the information and send the whole package – the certificate request – to the CA.
The CA then performs some due diligence in verifying that the information you provided is correct
and, if so, generates the certificate and returns it.
You might think of an X509 certificate as looking like a standard paper certificate with a public key
taped to it. It has your name and some information about you on it, plus the signature of the person
who issued it to you.
1. Click the ’Certificates’ icon in the ’Advanced’ screen of the Web-base Management. The
’Certificates’ screen will appear (see figure Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.
Figure 6.27 Certificates

80
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2. Click the ’GlobeSurfer ® II’s local’ certificates tab.
3. Click the ’Create Certificate Request’ button. The ’Create X509 Request’ screen will appear (see
Figure 6.28).
4. Enter the following certification request parameters:
1. Certificate Name
2. Subject
3. Organizatin
4. State
5. Country
5. Click the ’Generate’ button. A screen will appear stating that the certification request is being
generated (see Figure 6.29).
Figure 6.28 Create X509 request
Figure 6.29 New X509 request
6. After a short while, press the ’Refresh’ button, until the ’Save Certificate Request’ screen appears
(see Figure 6.30).
Click the ’Save Certificate Request’ button and save the request to a file.
7. Click the ’Close’ button. The main certificate management screen will reappear, listing your
certificate as “Unsigned” (see Figure 6.31). In this state, the request file may be opened at any time
by pressing the ’save’ icon under the ’Action’ column and then ’Open’ in the dialogue box (Windows
only).
9. After receiving a reply from the CA in form of a ’.pem’ file, click the ’Load Certificate’ link. The
’Load GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local Certificate’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.32).
Figure 6.30 Save certificate request

81
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.31 Certificate unsigned
Figure 6.32 Load local certificate
10. Use the ‘Browse’ button to browse to the signed certificate ’.pem’ file. Leave the password entry
empty and press ”Load” to load the signed certificate. The certificate management screen will
appear, displaying the certificate name and issuer (see Figure 6.32).
11. You can click the ’save’ icon under the ’Action’ column, and then ’Open’ in the dialogue box to view
the ’Certificate’ window (Windows only) box to save the certificate to a file (see Figure 6.34).
Figure 6.33 Open certificates

82
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.34 Windows certificate information
12. You can also click the ’edit’ icon under the ’Action’ column to view the ’Certificate Detail’ screen
(see Figure 6.35).
Figure 6.35 Certificate details
6.6.5.4.2 Creating a Self-Signed Certificate
A default self-signed certifcate is included in GlobeSurfer ® II (see Figure 6.36), in order to enable
certifcate demanding services such as HTTPS. Note that if deleted, this certificate is restored when
GlobeSurfer ® II’s Restore Defaults operation is run (see section 6.4.6).
To create a self-signed certificate:
1. Click the ’Certificates’ icon in the ’Advanced’ screen of the Web-based Management. The
Certificates screen will appear (see Figure 6.36).

83
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.36 Certificate default
2. Click the ’ GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local’ certificates tab.
3. Click the ’Create Self Signed Certificate’ button. The ’Create Self Signed X509 Certificate’ screen will
appear (see Figure 6.37).
4. Enter the following certification request parameters:
•
Certificate Name
•
Subject
•
Organization
•
State
•
Country
Figure 6.37 Create self signed certificate
5. Click the ’Generate’ button. A screen will appear stating that the certificate is being generated (see
Figure 6.38).
Figure 6.38 Generating self signed certificate
6. After a short while, press the ’Refresh’ button, until the ’Certificate Detail’ screen appears (see
Figure 6.39).

84
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.39 Self signed certificate details
7. Click the ’Close’ button. The main certificate management screen will reappear, displaying the
certificate name and issuer (see Figure 6.40)
Figure 6.40 Certificate main screen
6.6.5.4.3 Loading a PKCS#12 Format Certificate
You can also load certificates in PKCS#12 format (usually stored in .p12 files) to GlobeSurfer ® II’s
certificate store. You must first obtain the ’.p12’ file, containing the private and public keys and
optional CA certificates.
1. Click the ’Certificates’ icon in the ’Advanced’ screen of the Web-based Management. The
Certificates screen will appear (see Figure 6.40)
2. Click the ’GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local’ certificates tab.
3. Click the ’Load Certificate’ link. The ’Load GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local Certificate’ screen will appear
(see Figure 6.41).
Figure 6.41 Load local certificate
4. Click the ’Load Certificate’ link. The ’Load GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local Certificate’ screen will appear
(see Figure 6.41).

85
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
5. Use the Browse button to browse to the ‘.p12’ file. If the private key is encrypted using a
password, type it in the password entry (otherwise leave the entry empty) and press ‘Load’ to load
the certificate. The certificate management screen will appear, displaying the certificate name and
issuer (see Figure 6.40). If the ‘.p12’ file contained any CA certificates, they will be displayed in
the CA store (click the ‘CA’s’ tab to view the CA certficates).
6.6.6 Radius
For authentication to work, the client’s transmission must go through GlobeSurfer ® II, and reach the back-end server that
performs the actual authentication. The wireless client contacts the access point, which in turn communicates with the Remote
Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) server. The RADIUS server verifies the client’s credentials to determine whether
the device is authorized to connect to the LAN. If the RADIUS server accepts the client, the server responds by exchanging
data with GlobeSurfer ® II, including security keys for subsequent encrypted sessions.
Figure 6.42 Radius system setup
To configure the RADIUS authentication mechanism, perform the following steps:
1. Click the ‘RADIUS’ icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen of the Web-based Management. The RADIUS screen will appear (see
Figure 6.43).
2. Specify the following parameters:
‘Enabled’ Select this check-box to enable RADIUS client authentication.
‘Server IP’ Type in the RADIUS server’s IP address.
‘Server Port’ Type in the RADIUS server’s port.
‘Shared Secret’ Type in your shared secret.
Figure 6.43 Radius configuration

86
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6.6.7 Routing
Access GlobeSurfer ® II’s routing settings by clicking the ‘Routing’ icon from the ‘Advanced’ screen.
Figure 6.44 Routing
You can add, edit and delete routing rules from the routing table (see Figure 6.44) in the manner described in Section 3.4.
When adding a routing rule, you need to specify (see Figure 6.45):
‘Name’ Select the type of network device (LAN Bridge or WAN Cellular)
‘Destination’ The destination is the destination host, subnet address, network address, or default route. The destination for
a default route is 0.0.0.0.
‘Netmask’ The network mask is used in conjunction with the destination to determine when a route is used.
‘Gateway’ Enter the IP address of the GlobeSurfer ® II.
‘Metric’ A measurement of the preference of a route. Typically, the lowest metric is the most preferred route. If multiple
routes exist to a given destination network, the route with the lowest metric is used.
Figure 6.45 Route setttings
‘Routing Information Protocol (RIP)’
Select this check-box in order to enable connections previously defined to use RIP. If this check-box is not selected, RIP will be
disabled for all connections, including those defined to use RIP.
‘Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)’
GlobeSurfer ® II provides support for IGMP multicasting, which allows hosts connected to a network to be updated whenever an
important change occurs in the network. A multicast is simply a message that is sent simultaneously to a pre-defined group
of recipients. When you join a multicast group you will receive all messages addressed to the group, much like what happens
when an e-mail message is sent to a mailing list. IGMP multicasting may be useful when connected to the Internet through
a router. When an application running on a LAN computer sends out a request to join a multicast group, GlobeSurfer ® II will
listen and intercept this group’s messages, sending them to the subscribed application.

87
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Domain Routing’
When GlobeSurfer ® II’s DNS server receives a reply from an external DNS server, it will add a routing entry for the IP address
of the reply through the device from which it arrived. This means that future packets from this IP address will be routed
through the device from which the reply arrived.
6.6.8 Network objects
Network Objects is a method used to abstractly define a set of LAN hosts, according to one or more MAC address, IP address,
and host name. Defining such a group can assist when configuring system rules. For example, network objects can be used
when configuring GlobeSurfer ® II’s security filtering settings such as IP address filtering, host name filtering or MAC address
filtering.
You can use network objects in order to apply security rules based on host names instead of IP addresses. This may be useful,
since IP addresses change from time to time. Moreover, it is possible to define network objects according to MAC addresses,
making rule application more persistent against network configuration settings.
To define a network object:
1. Click the ‘Network Objects’ icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen of the Web-based Management. The ‘Network Objects’ screen will
appear (see Figure 6.46).
Figure 6.46 Network objects
2. Click the ‘New Entry’ link, the ‘Edit Network Object’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.47).
Figure 6.47 Edit network object
3. Name the network object in the Description field, and click ‘New Entry’ to actually create it. The ‘Edit tem’ screen will appear
(see Figure 6.48). The source address can be entered in one of the following methods:
• IP Address
• IP Subnet
• IP Range
• MAC Address
• Host Name
When selecting a method from the combo box, the screen will refresh, presenting the respective fields by which to enter the
relevant information.

88
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.48 Edit item
4. Select a method and enter the source address accordingly.
5. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
6.6.9 Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service enables you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname, allowing your computer
to be more easily accessible from various locations on the Internet. Typically, when you connect to the Internet, your service
provider assigns an unused IP address from a pool of IP addresses, and this address is used only for the duration of a specific
connection. Dynamically assigning addresses extends the usable pool of available IP addresses, whilst maintaining a constant
domain name.
When using the DDNS service, each time the IP address provided by your ISP changes, the DNS database will change
accordingly to reflect the change. In this way, even though your IP address will change often, your domain name will remain
constant and accessible.
6.6.9.1 Opening a Dynamic DNS Account
In order to use the DDNS feature, you must first obtain a DDNS account. For example, you can open a free account
at http://www.dyndns.org/account/create.html. When applying for an account, you will need to specify a user name
and password. Please have them readily available when customizing GlobeSurfer ® II’s DDNS support.
6.6.9.2 Using Dynamic DNS
Use the DDNS feature to define different a static host name for your WAN connection.
1. Access the Dynamic DNS settings by clicking the ‘Dynamic DNS’ icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen. The ‘Dynamic
DNS’ connections screen will appear (see Figure 6.49).
Figure 6.49 Dynamic DNS

89
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2. Click the ‘Add connection’ link to add a new DDNS entry. The ‘Dynamic DNS’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.50).
Figure 6.50 Dynamic DNS new connection
3. Specify the DDNS parameters:
‘User Name’
Enter your DDNS user name
‘Password’
Enter your DDNS password
‘Host Name’
Enter your full DDNS domain name
‘Click Here to Initiate and Manage your Subscription’
Clicking this link will open the selected provider’s account creation Web page. For example, when dyndns.org is
selected, the following page will open: http://www.dyndns.com/account/
‘Wildcard’
Select this check-box to enable use of special links such as www.<your host>.<DDNS domain>
‘Mail Exchanger’
Enter your mail exchange server address, to redirect all e-mails arriving at your DDNS address to your mail server
‘Backup MX’
Select this check-box to designate the mail exchange server to be a backup server
‘Offline’
If you wish to temporarily take your site of ine (prevent trafc from reaching your DDNS domain name), check this
box to enable redirection of DNS requests to an alternative URL, predefined in your DDNS account. The availability
of this feature depends on your account’s level and type of service.
4. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
6.6.10 IP address distribution
GlobeSurfer ® II’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server makes it possible to easily add computers that are
configured as DHCP clients to the home network. It provides a mechanism for allocating IP addresses and delivering network
configuration parameters to such hosts. GlobeSurfer ® II’s default DHCP server resides on the LAN bridge.
A client (host) sends out a broadcast message on the LAN requesting an IP address for itself. The DHCP server then checks its
list of available addresses and leases a local IP address to the host for a specific period of time and simultaneously designates
this IP address as `taken’. At this point the host is configured with an IP address for the duration of the lease. The host can
choose to renew an expiring lease or let it expire. If it chooses to renew a lease then it will also receive current information
about network services, as it did with the original lease, allowing it to update its network configurations to reflect any changes
that may have occurred since it first connected to the network. If the host wishes to terminate a lease before its expiration it
can send a release message to the DHCP server, which will then make the IP address available for use by others.

90
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
GlobeSurfer ® II’s DHCP server:
• Displays a list of all DHCP host devices connected to GlobeSurfer ® II
• Defines the range of IP addresses that can be allocated in the LAN
• Defines the length of time for which dynamic IP addresses are allocated
• Provides the above configurations for each LAN device and can be configured and enabled/disabled separately for each
LAN device
• Can assign a static lease to a LAN PC so that it receives the same IP address each time it connects to the network, even
if this IP address is within the range of addresses that the DHCP server may assign to other computers
• Provides the DNS server with the host name and IP address of each PC that is connected to the LAN
Additionally, GlobeSurfer ® II can act as a DHCP relay, escalating DHCP responsibilities to a WAN DHCP server. In this case,
GlobeSurfer ® II will act merely as a router, while its LAN hosts will receive their IP addresses from a DHCP server on the WAN.
6.6.10.1 DHCP Server Settings
To view a summary of the services currently being provided by the DHCP server click the ‘IP Address Distribution’
icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen. The ‘IP Address Distribution’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.51).
Figure 6.51 IP address distribution
To edit the DHCP server settings for a device:
1. Click the device’s Edit action icon. The DHCP settings for this device will appear (see Figure 6.52).
Figure 6.52 DHCP settings
2. Select the DHCP service:
‘Disabled’ Disable the DHCP server for this device.
‘DHCP Server’ Enable the DHCP server for this device.
‘DHCP Relay’ Set this device to act as a DHCP relay (see section 6.6.10.2).

91
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Assuming you have chosen DHCP Server, complete the following fields:
‘Start IP Address’
The first IP address that may be assigned to a LAN host. Since the gateway’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1,
this address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater.
‘End IP Address’
The last IP address in the range that can be used to automatically assign IP addresses to LAN hosts.
‘Subnet Mask’
A mask used to determine to what subnet an IP address belongs. An example of a subnet mask value is
255.255.0.0.
‘Lease Time In Minutes’
Each device will be assigned an IP address by the DHCP server for this amount of time, when it connects to the
network. When the lease expires the server will determine if the computer has disconnected from the network.
If it has, the server may reassign this IP address to a newly connected computer. This feature ensures that IP
addresses that are not in use will become available for other computers on the network.
‘Provide Host Name If Not Specified by Client’
If the DHCP client does not have a host name, the gateway will automatically assign one for him.
4. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
6.6.10.2 DHCP relay settings
To configure a device as a DHCP relay, perform the following steps:
1. Select the ‘DHCP Relay’ option in the ‘IP Address Distribution’ combo-box under the Service section (see Figure
6.53). The screen will refresh (see Figure 6.54).
Figure 6.53 DHCP relay choice
Figure 6.54 DHCP relay settings

92
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2. Click the ‘New IP Address’ link. The ‘DHCP Relay Server Address’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.55).
Figure 6.55 DHCP relay server
3. Specify the IP address of the DHCP server.
4. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
5. Click ‘OK’ once more in the ‘DHCP Settings’ screen.
6. Click the ‘Network Connections’ tab in the ‘Connection settings’ screen. The ‘Network Connections’ screen will
appear (see Figure 6.56).
Figure 6.56 Network connections
7. Click the ‘WAN Cellular’ link. The ‘WAN Cellular Properties’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.57). Click the
‘Settings’ button to see the ‘Configure WAN Cellular’ page.
Figure 6.57 WAN Cellular properties

93
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
8. In the ‘Routing’ section, select ‘Advanced’ from the combo-box. The screen will refresh (see Figure 6.58).
Figure 6.58 WAN cellular advanced
9. In the ‘Routing Mode’ combo-box, select ”Route”. This will change GlobeSurfer ® II’s WAN to work in routing
mode, which is necessary in order for DHCP relaying to function properly.
10. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
6.6.10.3 DHCP connections
To view a list of computers currently recognized by the DHCP server, press the ‘Connection List’ button that
appears at the bottom of the ‘IP Address Distribution’ screen (see Figure 6.51). The ‘DHCP Connections’ screen
will appear (see 7.334).
Figure 6.59 DHCP connections list
To define a new connection with a fixed IP address:
1. Click the ‘New Static Connection’ link. The ‘DHCP Connection Settings’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.60).
Figure 6.60 DHCP connection settings
2. Enter a host name for this connection.
3. Enter thefixed IP address that you would like to have assigned to the computer.
4. Enter the MAC address of the computer’s network card.

94
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Note: A device’s fixed IP address is actually assigned to the specific network card’s (NIC) MAC address installed
on the LAN computer. If you replace this network card then you must update the device’s entry in the DHCP
Connections list with the new network card’s MAC address.
5. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
The ‘DHCP Connections’ screen will reappear (see Figure 6.61), displaying the defined static connection. This
connection can be edited or deleted using the standard action icons.
Figure 6.61 DCHP connections list static
6.6.11 DNS server
Domain Name System (DNS) provides a service that translates domain names into IP addresses and vice versa. GlobeSurfer ®
II’s DNS server is an auto-learning DNS, which means that when a new computer is connected to the network the DNS server
learns its name and automatically adds it to the DNS table. Other network users may immediately communicate with this
computer using either its name or its IP address. In addition GlobeSurfer ® II’s DNS server:
•
Shares a common database of domain names and IP addresses with the DHCP server.
•
Supports multiple subnets within the LAN simultaneously.
•
Automatically appends a domain name to unqualified names.
•
Allows new domain names to be added to the database using GlobeSurfer ® II’s WBM.
•
Permits a computer to have multiple host names.
•
Permits a host name to have multiple IPs (needed if a host has multiple network cards).
The DNS server does not require configuration. However, you may wish to view the list of computers known by the DNS, edit
the host name or IP address of a computer on the list, or manually add a new computer to the list.
6.6.11.1 Viewing and Modifying the DNS Table
Figure 6.62 DNS server
To view the list of computers stored in the DNS table. Access the DNS Server settings by clicking the ‘DNS Server’
icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen. The DNS table will be displayed (see Figure 6.62).
To add a new entry to the list:
1. Click the ‘New DNS Entry’ button. The ‘DNS Entry’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.63).
2. Enter the computer’s host name and IP address.

95
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
Figure 6.63 New DNS entry
To edit the host name or IP address of an entry:
1. Click the ‘Edit’ button that appears in the Action column. The ‘DNS Entry’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.63)
2. If the host was manually added to the DNS Table then you may modify its host name and/or IP address,
otherwise you may only modify its host name.
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
To remove a host from the DNS table:
1. Click the ‘Delete’ button that appears in the Action column. The entry will be removed from the table.
6.6.12 IPSEC Internet Protocol Security
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a series of guidelines for the protection of Internet Protocol (IP) communications. It
specifies procedures for securing private information transmitted over public networks. The IPSec protocols include:
•
AH (Authentication Header) provides packet-level authentication.
•
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) provides encryption and authentication.
•
IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiates connection parameters, including keys, for the other two services.
Services supported by the IPSec protocols (AH, ESP) include confidentiality (encryption), authenticity (proof of sender), integrity
(detection of data tampering), and replay protection (defense against unauthorized resending of data).
IPSec also specifies methodologies for key management. Internet Key Exchange (IKE), the IPSec key management protocol,
defines a series of steps to establish keys for encrypting and decrypting information; it defines a common language on
which communications between two parties is based. Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), IPSec and IKE
together standardize the way data protection is performed, thus making it possible for security systems developed by different
vendors to interoperate.
Technical specifications
•
Security architecture for the Internet Protocol
•
IP Security Document Roadmap
•
Connection type: Tunnel, Transport
•
Use of Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) in main and aggressive modes
•
Key management: Manual, Automatic (Internet Key Exchange)
•
NAT Traversal Negotiation for resolution of NATed tunnel endpoint scenarios
•
Dead Peer Detection for tunnel disconnection in case the remote endpoint ceases to operate
•
Gateway authentication: X.509, RSA signatures and pre-shared secret key
•
IP protocols: ESP, AH
•
Encryption: AES, 3DES, DES, NULL, HW encryption integration (platform dependent)
•
Authentication: MD5, SHA-1
•
IP Payload compression
•
Interoperability: VPNC Certified IPSec, Windows 2000, Windows NT, FreeS/WAN, FreeBSD, Checkpoint
•
Firewall-1, Safenet SoftRemote, NetScreen, SSH Sentinel

96
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
6.6.12.1 IPSec Settings
By clicking the ‘IPSec’ icon in the ‘Advanced’ screen. The ‘Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)’ screen will appear
(see Figure 6.102).
Figure 6.64 Internet protocol security (IPSec)
This screen enables you to configure:
‘Block Unauthorized IP’ Select the Enabled check-box to block unauthorized IP packets to GlobeSurfer ® II.
Specify the following parameters:
‘Maximum Number of Authentication Failures’
The maximum number of packets to authenticatebefore blocking the origin’s IP address.
‘Block Period (in seconds)’
The timeframe in which packets from an unauthorized IP address will be dropped.
‘Enable Anti-Replay Protection’
Select this option to enable dropping of packets that are recognized (by their sequence number) as already
been received.
‘Connections’
This section will display the list of IPSec connections. To learn how to create an IPSec connection, please refer
to section 6.6.12.3.1.
6.6.12.1.1 Public Key Management
The Settings button in the IPSec screen enables you to manage GlobeSurfer ® II’s public keys.
1. Press the ‘Settings’ button view GlobeSurfer ® II’s public key (see Figure 6.65). If necessary, you
can copy the public key from this screen.
Figure 6.65 Internet protocol security (IPSex) settings

97
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
2. Press the ‘Recreate Key’ button to recreate the pubic key, or the ‘Refresh’ button to refresh the key
displayed in this screen.
7.8.1.2.2 Log Settings
The IPSec Log can be used to identify and analyze the history of the IPSec package commands,
attempts to create connections, etc. IPSec activity, as well as that of other GlobeSurfer ® II modules, is
displayed together in this view.
1. Press the ‘Log Settings’ button. The ‘IPSec Log Settings’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.66).
2. Select the check-boxes relevant to the information you would like the IPSec log to record.
3. Click ‘OK’ to save the settings.
Figure 6.66 IPSec Log Settings
6.6.12.2 IPSec Connection Settings
The IPSec connections are displayed under the ‘Connections’ section of the ‘Internet Protocol Security
(IPSec)’ screen (see Figure 6.64), in addition to the general ‘Network Connections’ screen (see
section Error! Reference source not found.).
To configure an IPSec connection settings, perform the following:
1. Press the connection’s Edit action icon. The ‘VPN IPSec Properties’ screen will appear (see
Figure 6.67).

98
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
Figure 6.67 VPN IPSec Properties
2. Press the ‘Settings’ button. The ‘Configure VPN IPSec’ screen will appear (see Figure 6.68),
enabling you to configure the following IPSec connection settings.
Figure 6.68 Configure VPN IPSec
‘Host Name or IP Address of Destination Gateway’
The IP address of your IPSec peer. If your connection is an IPSec Server, this field will display
”Any Remote Gateway”.
‘Encapsulation Type’
Select between ‘Tunneling’ and ‘Transport’ encapsulation. ‘Transport’ encapsulation is
performed between two gateways (no subnets), and therefore needs no explicit configuration.
‘Tunneling’
requires that you configure the following parameters:
•
Local Subnet Define your local endpoint, by selecting one of the following options:
•
IP Subnet (default) – enter GlobeSurfer ® II’s Local Subnet IP Address and Local Subnet Mask.
•
IP Range – enter the ‘From’ and ‘To’ IP addresses, forming the endpoints range of the local
subnet(s).
•
IP Address – enter the Local IP Address to define the endpoint as a single host.
•
None – select this option if you do not want to define a local endpoint. The endpoint will be set
to the gateway.
‘Remote Subnet’
This section is identical to the ‘Local Subnet’ section above, but is for defining the remote
endpoint.

99
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Compress (Support IPComp protocol)’
Select this check-box to compress packets during encapsulation with the IP Payload
Compression protocol. Please note that this reduces performance (and is therefore unchecked
by default).
‘Protect Protocol’
Select the protocols to protect with IPSec: All, TCP, UDP, ICMP or GRE. When selecting TCP or
UDP, additional source port and destination port combo-boxes will appear, enabling you to select
‘All’ or to specify ‘Single’ ports in order to define the protection of specific packets. For example,
in order to protect L2TP packets, select UDP and specify 1701 as both single source and single
destination ports.
‘Route NetBIOS Broadcasts’
Select this option to allow NetBIOS packets through the IPSec tunnel, which otherwise would not
meet the routing conditions specified.
‘Key Exchange Method’
The IPSec key exchange method can be ‘Automatic’ (the default) or ‘Manual’. Selecting one of
these options will alter the rest of the screen.
a. Automatic key exchange settings:
Figure 6.69IPSec automatic key exchange

100
GlobeSurfer ® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S REFERENCE MANUAL
‘Auto Reconnect’
The IPSec connection will reconnect automatically if disconnected for any reason.
‘IPSEC AUTOMATIC PHASE 1 – PEER AUTHENTICATION’
‘Mode’
Select the IPSec mode – either ‘Main Mode’ or ‘Aggressive Mode’. Main mode is a
secured but slower mode, which presents negotiable propositions according to the
authentication algorithms that you select in the check-boxes. Aggressive Mode is faster
but less secured. When selecting this mode, the algorithm check-boxes are replaced by
radio buttons, presenting strict propositions according to your selections.
‘Negotiation attempts’
Select the number of negotiation attempts to be performed in the automatic key exchange
method. If all attempts fail, GlobeSurfer ® II will wait for a negotiation request.
‘Life Time in Seconds’
The timeframe in which the peer authentication will be valid.
‘Rekey Margin’
Specifies how long before connection expiry should attempts to negotiate a replacement
begin. It is similar to that of the key lifetime and is given as an integer denoting seconds.
‘Rekey Fuzz Percent’
Specifies the maximum percentage by which Rekey Margin should be randomly increased
to randomize re-keying intervals.
‘Peer Authentication’
Select the method by which GlobeSurfer ® II will authenticate your IPSec peer:
•
IPSec Shared secret – enter the IPSec shared secret.
•
RSA Signature – enter the peer’s RSA signature (equivalent to GlobeSurfer ® II’s
public key – see section 6.6.12.1).
•
Certificate – if a certificate exists on GlobeSurfer ® II, it will appear when you
select this option. Enter the certificate’s local ID and peer ID. To learn how to add
certificates to GlobeSurfer ® II, please refer to section 6.6.5.
‘Encryption Algorithm’
Select the encryption algorithms that GlobeSurfer ® II will attempt to use when negotiating
with the IPSec peer.
‘Hash Algorithm’
Select the hash algorithms that GlobeSurfer ® II will attempt to use when negotiating with
the IPSec peer.
‘Group Description Attribute’
Select the Diffie-Hellman (DH) group description(s). Diffie-Hellman is a public-key
cryptography scheme that allows two parties to establish a shared secret over an insecure
communications channel.
‘IPSEC AUTOMATIC PHASE 2 – KEY DEFINITION’
‘Life Time in Seconds’
The length of time before a security association automatically performs renegotiation.
‘Use Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)’
Select whether Perfect Forward Secrecy of keys is required on the connection’s keying
channel (with PFS, penetration of the key-exchange protocol does not compromise keys
negotiated earlier). Deselecting this option will hide the next parameter.
‘Group Description Attribute’
Select whether to use the same group chosen in phase 1, or reselect specific groups.
‘Encryption Algorithm’
Select the encryption algorithms that GlobeSurfer ® II will attempt to use when negotiating
with the IPSec peer.
 Loading...
Loading...