Page 1

GSM/3G User Manual
1 | 82
GSM/3G Gateway User Manual
Address: 10/F, Building 6-A, Baoneng Science and Technology Industrial Park, Longhua
New District, Shenzhen, Guangdong,China 518109
Tel: +86-755-66630978, 82535461, 82535362
Business Contact: sales@openvox.cn
Technical Support: support@openvox.cn
Business Hours: 09:00-18:00(GMT+8) from Monday to Friday
URL: www.openvox.cn
Page 2

GSM/3G User Manual
2 | 82
Version1.0 (2016-05-12)
Full text
The overall layout adjustment
Page 3

GSM/3G User Manual
3 | 82
Confidentiality
Information contained herein is of a highly sensitive nature and is confidential and
proprietary to OpenVox Inc. No part may be distributed, reproduced or disclosed orally or in
written form to any party other than the direct recipients without the express written
consent of OpenVox Inc.
Disclaimer
OpenVox Inc. reserves the right to modify the design, characteristics, and products at any
time without notification or obligation and shall not be held liable for any error or damage of
any kind resulting from the use of this document.
OpenVox has made every effort to ensure that the information contained in this document
is accurate and complete; however, the contents of this document are subject to revision
without notice. Please contact OpenVox to ensure you have the latest version of this
document.
Trademarks
All other trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
owners.
Page 4

GSM/3G User Manual
4 | 82
Contents
1. Overview .................................................................................................................... 6
What is GSM/3G Gateway? .................................................................................... 6
Sample Application ................................................................................................ 7
Main Features ...................................................................................................... 9
Physical Information............................................................................................. 10
Software ............................................................................................................... 10
How to do Cluster?............................................................................................... 10
2. System ...................................................................................................................... 13
Status.................................................................................................................... 13
Time ..................................................................................................................... 15
Login Settings ....................................................................................................... 16
General ................................................................................................................. 17
Language Settings ........................................................................................ 17
Scheduled Reboot ........................................................................................ 18
Cluster .................................................................................................................. 18
Tools and Information .......................................................................................... 18
Reboot Tools ................................................................................................. 18
Update Firmware ......................................................................................... 19
Upload and Backup Configuration ............................................................... 19
Restore Configuration .................................................................................. 20
Information .................................................................................................. 20
3. MODULE ................................................................................................................... 21
MODULE Settings ................................................................................................. 21
IMEI Modification......................................................................................... 23
Call Duration Limit Settings .......................................................................... 26
Call Forwarding .................................................................................................... 29
Call Waiting .......................................................................................................... 30
DTMF .................................................................................................................... 30
BCCH ..................................................................................................................... 32
Toolkit ................................................................................................................... 32
4. VOIP .......................................................................................................................... 35
VOIP Endpoints .................................................................................................... 35
Add New SIP Endpoint ................................................................................. 35
Main IAX2 Endpoint Settings ....................................................................... 41
Advanced SIP Settings .......................................................................................... 45
Networking ................................................................................................... 45
Paesing and Compatibility ............................................................................ 47
Security ........................................................................................................ 48
Media ........................................................................................................... 49
Advanced IAX2 Settings ....................................................................................... 50
5. Routing ..................................................................................................................... 53
Call Routing Rule .................................................................................................. 53
Page 5

GSM/3G User Manual
5 | 82
Groups .................................................................................................................. 56
MNP Settings ........................................................................................................ 57
6. SMS .......................................................................................................................... 58
General ................................................................................................................. 58
Sender Options ............................................................................................ 58
SMS to Email ................................................................................................ 58
SMS Control.................................................................................................. 60
HTTP to SMS ................................................................................................. 62
SMS to HTTP ................................................................................................. 62
SMS Sender .......................................................................................................... 62
SMS Inbox ............................................................................................................. 63
SMS Outbox .......................................................................................................... 64
SMS Forwarding ................................................................................................... 64
7. Network .................................................................................................................... 66
Network Settings .................................................................................................. 66
DDNS Settings ...................................................................................................... 67
Toolkit ................................................................................................................... 68
Security Settings ................................................................................................... 68
Firewall settings ........................................................................................... 68
White List Settings ....................................................................................... 69
Security Rules ....................................................................................................... 71
8. Advanced .................................................................................................................. 72
Asterisk API .......................................................................................................... 72
Asterisk CLI ........................................................................................................... 74
Asterisk File Editor................................................................................................ 74
9. Logs .......................................................................................................................... 76
Appendix Feature List .................................................................................................. 79
Application Diagrams ................................................................................................... 82
Page 6

GSM/3G User Manual
6 | 82
1. Overview
What is GSM/3G Gateway?
OpenVox GSM/3G Gateway is an open source asterisk-based VoIP Gateway solution for
SMBs and SOHOs. With friendly GUI and unique modular design, users may easily setup
their customized Gateway. Also secondary development can be completed through AMI
(Asterisk Management Interface).
OpenVox GSM/3G Gateways have 4 models: WGW1002G, VS-GW1202, VS-GW1600
and VS-GW2120. VS-GW1002 suports 2 GSM Channels. VS-GW1202 supports 4/8
GSM/3G channels. VS-GW1600 support up to 20 GSM/3G channels. VS-GW2120
supports up to 44 GSM/3G channels. Both GSM and 3G/UMTS gateways are developed
for interconnecting the GSM cellular networks with a wide selection of codecs and
signaling protocol, including G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.722, G.723, G.726 and GSM to
quickly reduce communication expenses and maximize cost-savings. With the unique
design of the VoxStack gateway, it can support hot-swap for both SIM cards and
GSM/3G gateway modules. Users can simply add or remove the modules for hardware
expansion or exchange.
The VoxStack gateway designs with 2 LAN switch boards to provide stack ability on the
hardware upgrade, and each GSM/3G module is independent , so each one has a GUI
configuration web. If you connect to ETH1, you can access Board 1 only and access
other boards with different port numbers which can avoid IP conflict. Otherwise if you
connect to ETH2, you can access different Boards with different IP addresses.
Our products support SMS messages sending, receiving, group sending and SMS to Email. The GSM gateway will be 100% compatible with Asterisk, Elastix, trixbox, 3CX,
FreeSWITCH SIP server and VOS VoIP operating platform.
Page 7

GSM/3G User Manual
7 | 82
Sample Application
Figure 1-1 TopologicalGraph
Product Appearance
Figure 1-2 Product Appearance of GSM
Figure 1-3 Front Panel of GSM
Network Data Switch Board: ETH1, ETH2.
ETH1: Access Board 1 only, provide proxy access to other boards with different port
numbers which can avoid IP conflict.
ETH2: Access different Boards with different IP address.
Figure 1-4 Product Appearance of 3G
Page 8

GSM/3G User Manual
8 | 82
Figure 1-5 Front Panel of 3G
Network Data Switch Board: ETH1, ETH2, ETH3.
ETH1: Access Board 1 only, provide proxy access to other boards with different port
numbers which can avoid IP conflict.
ETH2: Access different Boards with different IP address.
ETH3: Access different Boards with different IP address.
VoxStack provides 2 working modes: Stand-alone and Cluster.
Stand-alone: A single IP address manages one GSM modules (4 ports).
Table 1-1 ETH2 IP Addresses
Slot Num
IP
Username
Password
1
172.16.99.1
admin
admin
2
172.16.99.2
admin
admin
3
172.16.99.3
admin
admin
4
172.16.99.4
admin
admin
5
172.16.99.5
admin
admin
6
172.16.99.6
admin
admin
7
172.16.99.7
admin
admin
8
172.16.99.8
admin
admin
9
172.16.99.9
admin
admin
10
172.16.99.10
admin
admin
11
172.16.99.11
admin
admin
Page 9

GSM/3G User Manual
9 | 82
Cluster: A single IP address manages up to 5 GSM modules (up to 20 ports).
Default IP: 172.16.99.1
Figure 1-6 Front Panel
Figure 1-5 LED Indicator
Main Features
Modular and VoxStack design
Based on Asterisk®
Editable Asterisk®
configurationfile
Wide selection of codecs and signaling protocol
Support SMS sending, receiving, group sending
Support transferring SMS to E-mail
Support SMS automatically resend
Support SMS remotely controlling gateway
Support USSD service
Support IMEI modification
Support PIN identification
Support unlimited routing rules and flexible routing settings
Page 10

GSM/3G User Manual
10 | 82
SIM cards and modules are all hot-swap
Stable performance, flexible dialing, friendly GUI
WCDMA/UMTS: 850/900/1900/2100 MHz
GSM: 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
Physical Information
Weight: 4301g(VS-GW1600-20G) 6144g(VS-GW2120-32w)
Size: 44cm*30cm*4.5cm (VS-GW1600-20G) 44cm*34cm*9cm (VS-GW2120-32w)
Temperature: -20~70°C (Storage) 0~40°C (Operation)
Operation humidity: 10%~90% non-condensing
Max power: 46W(VS-GW1600-20G) 95W(VS-GW2120-32w)
LAN port: 2(VS-GW1600-20G) 3(VS-GW2120-32w)
Software
Default IP: 172.16.99.1
Username: admin
Password: admin
For first time, you can access WGW1002G using default IP 172.16.99.1. Then configure
the module as you want.
For VS-GW2102, VS-GW1600, VS-GW2120 series of GSM/3G gateway, every VSGWM400G/W is independent with each other. There are two RJ45 Network ports: ETH1
and ETH2. They are different.
If you want each module to work stand-alone and access each of them, choose ETH2
please. Default IP of each module is 172.16.99.X (X is slot number).
If you want to use one IP to master all the boards, choose ETH1, access board1 using
default IP 172.16.99.1 and do the cluster. Then you can access to other boards with
different port numbers but the same IP address, this will help to avoid IP conflict. Board1
work as master, and other boards work as slave.
How to do Cluster?
penVox GSM Gateway offers you two ways to cluster your gateway: Automatic Cluster or
Manual Cluster. When you first time log in your gateway, you will only see 4 ports of one
module. Then you can press button, the system will search other
modules in the LAN and communicate.
Page 11

GSM/3G User Manual
11 | 82
Figure 1-7 Automatic Cluster
If you want to choose Manual Cluster, you should switch Detail on first.
There are 3 kinds of cluster mode: stand-alone, Master and Slave.
Stand-alone Mode: Run alone, total 4 ports.
Master Mode: Run as master with two different IP, controlling up to 10 slaves.
(The master can be accessed by the original IP. The target IP is used to
communicate with the slaves.)
Slave Mode: Run as slave with two different IP, controlled by the master. If the
original IP is forbidden, the slave can be accessed by the master with inward IP
only.
Notice: You can choose Remain Original IP address ON or OFF. If set it on, you can log
in your getaway with Original IP and Target IP.
Page 12

GSM/3G User Manual
12 | 82
Notice: Log in
Figure 1-8 LOG Interface
Page 13

GSM/3G User Manual
13 | 82
2. System
Status
On the “Status” page, you will find all GSM, SIP, IAX2, Routing, Network information and
status.
Figure 2-1 System Status
Page 14

GSM/3G User Manual
14 | 82
Table 2-1 Description of System Status
Options
Definition
Port
Number of GSM ports. GSM ports begin with "gsm-", such as gsm-
1.1; 3G ports begin with "umts-", such as umts-2.1.
Signal
Display the signal strength of in each channels of GSM.
BER
Bit Error Rate.
Carrier
Display the network carrier of current SIM card.
Registration
Status
Indicates the registration status of current GSM module.
PDD
Post Dial Delay (PDD) is experienced by the originating customer as
the time from the sending of the final dialed digit to the point at which
they hear ring tone or other in-band information.Where the originating
network is required to play an announcement before completing the
call then this definition of PDD excludes the duration of such
announcements.
ACD
The Average Call Duration (ACD) is calculated by taking the sum of
billable seconds (bill sec) of answered calls and dividing it by the
number of these answered calls.
ASR
Answer Seizure Ratio is a measure of network quality. Its calculated
by taking the number of successfully answered calls and dividing by
the total number of calls attempted. Since busy signals and other
rejections by the called number count as call failures, the ASR value
can vary depending on user behavior. GSM Status Show the status
of port, include blank space and “READY”. Black space means it is
unavailable here and “Ready” means the port is available
Remain
Time
This value is multiplied by to step length is a rest call time.
Page 15

GSM/3G User Manual
15 | 82
Time
Table 2-2 Description of Time Settings:
Options
Definition
System Time
Your gateway system time
Time Zone
The world time zone. Please select the one which is the same
or the closest as your city
POSIX TZ String
Posix time zone strings.
NTP Server 1
Time server domain or hostname. For example,
[time.asia.apple.com].
NTP Server 2
The first reserved NTP server. For example,
[time.windows.com].
NTP Server 3
The second reserved NTP server. For example, [time.nist.gov].
Auto-Sync from
NTP
Whether enable automatically synchronize from NTP server or
not. ON is enable, OFF is disable this function.
Sync from NTP
Sync time from NTP server.
Sync from Client
Sync time from local machine.
For example, you can configure like this:
Page 16

GSM/3G User Manual
16 | 82
Figure 2-2 Time Settings
You can set your gateway time Sync from NTP or Sync from Client by pressing different
buttons.
Login Settings
Your gateway doesn't have administration role. All you can do here is to reset what new
username and password to manage your gateway. And it has all privileges to operate
your gateway. You can modify “Web Login Settings” and “SSH Login Settings”. If you
have changed these settings, you don’t need to log out, just rewriting your new user
name and password will be OK. Also you can specify the web server port number.
Table 2-3 Description of Login Settings
Options
Definition
User Name
Define your username and password to manage your gateway,
without space here.
Allowed characters "-_+. < >&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 1-32 characters.
Password
Allowed characters "-_+. < >&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 4-32 characters.
Confirm
Password
Please input the same password as 'Password' above.
Login Mode
http and https: You can access gateway via link: http://gatewayIP
or https://gatewayIP
https: You can only access gateway via link: https://gatewayIP
Page 17

GSM/3G User Manual
17 | 82
Port
Specify the web server port number.
Figure 2-3 Login Settings
Notice: Whenever you do some changes, do not forget to save your configuration.
General
Language Settings
You can choose different languages for your system. If you want to change language,
you can switch “Advanced” on, then “Download” your current language package. After
that, you can modify the package with the language you need. Then upload your
modified packages, “Choose File” and “Add”.
Figure 2-4 Language Settings
Page 18

GSM/3G User Manual
18 | 82
Scheduled Reboot
If switch it on, you can manage your gateway to reboot automatically as you like. There
are four reboot types for you to choose, “By Day, By Week, By Month and By Running
Time”.
Figure 2-5 Reboot Types
If use your system frequently, you can set this enable, it can helps system work more
efficient.
Cluster
Figure 2-6 cluster
Tools and Information
Reboot Tools
You can choose system reboot and asterisk reboot separately.
Page 19

GSM/3G User Manual
19 | 82
Figure 2-7 Reboot Tools
If you press "OK", your system will reboot and all current calls will be dropped. Asterisk
Reboot is the same.
Update Firmware
We offer 2 kinds of update types for you, you can choose System Update or System
Online Update. For System Update, you can update all the boards together or only
update one of them to make sure all boards have same firmware version.
Figure 2-8 Update Firmware
Notice: In SYSTEM ---> Cluster page, you can find which board has different or
incompatible firmware version.
Figure 2-9 Update Firmware
Upload and Backup Configuration
If you want to update your system and remain your previous configuration, you can first
backup configuration, then you can upload configuration directly. That will be very
convenient for you.
Figure 2-10 Upload and Backup Configuration
Page 20

GSM/3G User Manual
20 | 82
Restore Configuration
Sometimes there is something wrong with your gateway that you don’t know how to solve
it, mostly you will select factory reset. Then you just need to press a button, your gateway
will be reset to the factory status.
Figure 2-11 Restore Configuration
Information
On the “Information” page, there shows some basic information about the GSM/3G
gateway. You can see software and hardware version, storage usage, memory usage
and some help information.
Figure 2-12 Information
Page 21

GSM/3G User Manual
21 | 82
3. MODULE
You can see much information about your SIM cards on this page.
MODULE Settings
Figure 3-1 GSM/UTMS Settings
On this page, you can see your GSM module status and click action button to
configure the port.
Page 22

GSM/3G User Manual
22 | 82
Figure 3-2 Port Configuration
As you see, we have offered “Band” option, you can select different bands easily and
you have many options.
Figure 3-3 Band Binding
If you have set your Pin Code, you can check on like this:
Figure 3-4 PIN Code Application
Then input your password, system will identify numbers of SIM cards. It can help to
prevent SIM card from being stolen and improve security.
If you want to hide your number when you call out, you can just switch CLIR “ON” (Of
course you need your operator’s support).
Figure 3-5 CLIR Application
Page 23

GSM/3G User Manual
23 | 82
OpenVox GSM/3G gateway support optional GSM Voice Codec. See picture below.
Figure 3-6 GSM Voice Codec
IMEI Modification
One more feature, we offer you IMEI automatically modification
Figure 3-7 Automatically IMEI Modify
We have offered you IMEI modification function. If you want to modify your IMEI number,
please do as follows. You can log in your gateway and modify IP address as follows.
Input web site below on your browser. http://172.16.99.1/cgi-bin/php/gsm-autoimei.php.
Page 24

GSM/3G User Manual
24 | 82
Then you will see the following picture. Don’t forget to switch “Enable” to “ON”, or you
can’t change your IMEI numbers.
Figure 3-8 IMEI Modification
Also you can choose to modify one or more certain ports or all ports. You can set
automatic modification interval by filling in the time you
want.
If you choose “Immediately”, then the ports you have chosen will modify IMEI numbers
at once. On the contray, system will keep time from now until the time of next
modification. And If you choose “Force”, System will hang up all your current calls, then
modify IMEI.
You can press to do some settings. We offer you
two ways to modify your IMEI. You can choose Autogeneration or Manual.
Figure 3-9 Advanced Settings
As you can see, you can set any number you wan for every port. “X” means any digits
from 0 to 9.
You just need to fill in “Set to All ”, then press “Set to All”, you can see the interface as
above. Don’t forget to press “Save”. Then “Current IMEI” will change. That means
Autogeneration. If you want to set a certain number as your IMEI, you can press
“Manual”. Then you will be required to input a new IMEI.
Page 25

GSM/3G User Manual
25 | 82
Figure 3-10 Manual
After configuration, you can press “Back Home” to return your gateway interface.
Table 3-1 Definition of GSM Settings
Options
Definition
Name
The alias of the GSM port. Input name without space here.
Allowed characters "-_+.<>&0-9a-zA-Z".Length: 1-32
characters.
Speaker Volume
The speaker volume level, the range is 0-100.
This will adjust the loud speaker volume level by an AT
command.
Microphone
Volume
The microphone volume, range is: 0-15.
This will change the microphone gain level by an AT command.
DAC Gain
The range is: -42 to +20
ADC Gain
The range is: -42 to +20
Dial Prefix
The prefix number of outgoing calls from this GSM channel
PIN Code
Personal identification numbers of SIM card. PIN code can be
modified to prevent SIM card from being stolen.
Page 26

GSM/3G User Manual
26 | 82
Custom AT
commads when
start
User custom AT commands when start system, use “|” to split
AT command.
CLIR
Caller ID restriction, this function is used to hidden caller ID of
SIM card number. The gateway will add ‘#31#’ in front of mobile
number. This function must support by Operator.
SMS Center
Number
Your SMS center number of your local carrier.
GSM Module
IMEI
You can click “Modify” button and automatically modify it.
Call Duration Limit Settings
Now we can offer you two types of call duration limit, you can choose “Single Call
Duration Limit” or “Call Duration Limitation” to control your calling time
Single Call Duration Limit: This will limit the time of each call.
First you need to switch “Enable” on, then you can set “Step” and “Single Call Duration
Limitation” any digits you want. When you make a call by this port, it will limit your calling
time within the product of
Step * Single Call Duration Limitation
And if your calling time overtops the value above, the system will hang up this call.
Figure 3-11 Single Settings
Call Duration Limitation: This will limit your total calling time of this port. If remain time
is 0, it will not send calls through this port.
Page 27

GSM/3G User Manual
27 | 82
Figure 3-12 Call Duration Limitation Settings
The same algorithm with single time limitation, the total calling time of this port can’t
beyond the product of “Step” and “Call Duration Limitation”.
If the duration of a call is less than “Minimum Charging Time”, it will be not included in
“Call Duration”.
You can set a digit for “Alarm Threshold”, when the call minutes less than this value, the
gateway will send alarm info to designated phone.
You can enable your Auto Reset, then choose by day, by week, or by month.
Figure 3-13 Auto Reset Settings
Table3-2 Description of Call Duration Limit Settings
Options
Definition
Step
of single call just said a single call duration time allowed.
Enable Single Call
Duration Limit
Definite maximum call duration for single call. Example: if Time of
single call set to 10, the call will be disconnected after talking
10*step seconds.
Page 28

GSM/3G User Manual
28 | 82
Enable Call
Duration Limitation
The max call duration is between 1 to 65535 minutes.
Call Duration
Limitation
The value of limitation single call, this value range is 1-65535.
Step length multiplied by time of single call just said a single call
duration time allowed.
Minimum Charging
Time
collect fees, unit for seconds.
Alarm Threshold
Define a threshold value of call minutes, while the call minutes
less than this value, the gateway will send alarm information to
designated phone.
Alarm Description
Alarm port information description, which will be sent to user
mobile phone with alarm information.
Alarm Phone
Number
Receiving alarm phone number, user will received alarm
message from gateway.
Remain Time
Enable Auto Reset
Automatic restore remaining talk time, that is, get total call
minutes of GSM channel.
Auto Reset Type
Reset call minutes by date, by week, by month.
Next Reset Time
Defined next reset date, system will count start from that date
and work as Reset Period setting
You can save your configuration to other ports.
Figure 3-14 Save To Other Ports
If you have set like this, you will see many on the Web GUI, you can set whether to
check.
Notice: When you do some changes, you need to Save and Apply, then “Remain Time”
will show as you set.
Your calling status will show on the main interface.
Page 29

GSM/3G User Manual
29 | 82
Figure 3-15 GSM/UMTS Information
Call Forwarding
Sometimes it’s not convenient for you to answer a call, if you don’t want to lose some
important calls, you can choose Call Forwarding. You can choose Call Forwarding
Unconditional, Call Forwarding No Reply, Call Forwarding Busy or Call Forwarding on
Not Reachable. If want to cancel your call forwarding settings, you can choose Cancel
All.
Figure 3-16 Call Forwarding
Notice: Don’t forget to save your settings. Please first press button, then press button..
Page 30

GSM/3G User Manual
30 | 82
Call Waiting
You can turn on/off the call waiting function of the sim cards in the ports on this page.
Table3-3 Description of Call Waiting
Options
Definition
Turn on call
waiting
choose the ports you want to set, select "On", then click
"Settings" button.
Turn off call
waiting
choose the ports you want to set, select "Off", then click
"Settings" button.
Status
Settings
Query
used to query the status of call waiting. To see call waiting
function of the ports you select is on or off.
Figure 3-17 Call Waiting
DTMF
You can do some DTMF Detection Settings if you choose “GSM -> DTMF”.
Page 31

GSM/3G User Manual
31 | 82
Figure 3-18 DTMF Detection Settings
Notice: If you don’t have special need, you don’t have to modify these settings. You can
just choose “Default”.
Table3-4 Description of DTMF Detection Settings
Options
Definition
DTMF Normal
Twist and Reverse
Twist
energies. Normal Twist is where the Column energy is greater
than the Row energy. Reverse Twist is where the Row energy is
greater.
DTMF Relative
Peak Row
some numbers, you can try to put the value down. The
adjustment range is 0.02 at a time.
DTMF Relative
Peak Col
numbers, you can try to put the value down. The adjustment
range is 0.1 at a time.
DTMF Hits Begin
Sampling matching value. You can choose 2 or 3.
DTMF Misses End
The time interval between the two digits you input. Adjust the
speed of input. The smaller value represents the shorter
intervals.
Page 32

GSM/3G User Manual
32 | 82
BCCH
Figure 3-19 BCCH setting
You can click button, and you can change the BCCH Mode as bellow.
Figure 3-20 BCCH Mode
Toolkit
You can get USSD information, send AT command and check number with this module.
When you have a debug of the GSM module, AT command is useful.
Page 33

GSM/3G User Manual
33 | 82
Figure 3-21 Function Options
Table3-5 Description of Definition of Functions
Options
Definition
Check Number
number it is of the SIM card. Click "Execute", then the gateway
will dial to the number you already input. It only rings for one time
and hangs up at once. Not generating telephone charge during
this procedure.
Get USSD
Enter a specific USSD number (For example,*142# to check your
SIM card's balance. This USSD number is might be different from
different carriers) to get the USSD information. The gateway will
try to get by AT commands.
AT Command
To perform some specific AT commands. This is useful when you
have a debug of the GSM modem. e.g. perform [ AT+CSQ ] to
check what signal qualify it is. In AT commands, there is no
difference between “a” and “A”
If you want to send AT command, first you should input your command, then select
certain ports and choose “Copy to Selected”, finally choose “Execute”.
Page 34

GSM/3G User Manual
34 | 82
Figure 3-22 AT Command Example
Page 35

GSM/3G User Manual
35 | 82
4. VOIP
VOIP Endpoints
This page shows everything about your SIP&IAX2, you can see status of each
SIP&IAX2.
Figure 4-1 SIP&IAX2 Endpoints
Add New SIP Endpoint
Main SIP Endpoint Settings
You can click button to add a new SIP endpoint, and if you want to
modify existed endpoints, you can click button.
There are 3 kinds of registration types for choose. None, Server or Client.
You can configure as follows:
If you set up a SIP endpoint by registration “None” to a server, then you can’t register
other SIP endpoints to this server. (If you add other SIP endpoints, this will cause Outband Routes and Trunks confused.)
Page 36

GSM/3G User Manual
36 | 82
Figure 4-2 None Registration
For convenience, we have designed a method that you can register your SIP endpoint to
your gateway, thus your gateway just work as a server.
Figure 4-3 Sever
Also you can choose registration by “This gateway registers with the endpoint”, it’s the
same with “None”, except name and password.
Page 37

GSM/3G User Manual
37 | 82
Figure 4-4 Client
table 4-1 Definition of SIP Options
Options
Definition
Name
Display name
Username
Register name in your SIP server
Password
Authenticating with the gateway and characters are allowed.
Registration
None --- Not registering;
Endpoint registers with this gateway --- When register as this
type, it means the GSM gateway acts as a SIP server, and SIP
endpoints register to the gateway;
This gateway registers with the endpoint --- When register as this
type, it means the GSM gateway acts as a client, and the endpoint
should be register to a SIP server;
Hostname or
IP Address
IP address or hostname of the endpoint or 'dynamic' if the endpoint
has a dynamic IP address. This will require registration.
Transport
This sets the possible transport types for outgoing. Order of usage,
when the respective transport protocols are enabled, is UDP, TCP,
Page 38

GSM/3G User Manual
38 | 82
TLS. The first enabled transport type is only used for outbound
messages until a Registration takes place. During the peer
Registration, the transport type may change to another supported
type if the peer requests so.
NAT
Traversal
No --- Use Rport if the remote side says to use it.
Force Rport on --- Force Rport to always be on.
Yes --- Force Rport to always be on and perform comedia
RTP handling.
Rport if requested and comedia --- Use Rport if the remote
side says to use it and perform comedia RTP handling.
Advanced -- Registration Options
Table 4-2 Definition of Registration Options
Options
Definition
Authentication User
A username to use only for registration.
Register Extension
When Gateway registers as a SIP user agent to a SIP proxy
(provider), calls from this provider connect to this local
extension.
From User
A username to identify the gateway to this endpoint.
From Domain
A domain to identify the gateway to this endpoint.
Remote Secret
A password which is only used if the gateway registers to the
remote side.
Port
The port number the gateway will connect to at this endpoint.
Qualify
Whether or not to check the endpoint's connection status
Qualify Frequency
How often, in seconds, to check the endpoint's connection
status.
Outbound Proxy
A proxy to which the gateway will send all outbound signalling
instead of sending signalling dirrectly to endpoints.
Call Settings
Table 4-3 Definition of Call Options
Options
Definition
Page 39

GSM/3G User Manual
39 | 82
DTMF Mode
Set default DTMF Mode for sending DTMF. Default:
rfc2833. Other options: 'info', SIP INFO message
(application/dtmf-relay); 'Inband', Inband audio (require 64kbit
codec -alaw, ulaw).
Trust Remote-
Party-ID
Whether or not the Remote-Party-ID header should be trusted.
Send Remote-
Party-ID
Whether or not to send the Remote-Party-ID header.
Remote Party
ID Format
or from P-Asserted-Identity.
Caller
ID Presentation
Whether or not to display Caller ID.
Call Limit
Usually used when this sip work as a trunk. To limit number of
maximum channels supported by the sip trunk.
Advanced -- Signalling Settings
Table 4-4 Definition of Signaling Options
Options
Definition
Progress Inband
Set default DTMF Mode for sending DTMF. Default: rfc2833.
Other options: 'info', SIP INFO message (application/dtmf-relay);
'inband', Inband audio (require 64kbit codec -alaw, ulaw).
Allow Overlap
Dialing
Append
user=phone to
URI
Whether or not to send the Remote-Party-ID header.
Add Q.850
Reason Headers
or from P-Asserted-Identity.
Honor SDP
Version
Whether or not to display Caller ID.
Allow Transfers
Whether or not to globally enable transfers. Choosing 'no' will
disable all transfers (unless enabled in peers or users). Default is
enabled.
Page 40

GSM/3G User Manual
40 | 82
Allow
Promiscuous
Redirects
Whether or not to allow 302 or REDIR to non-local SIP address.
Note that promiscredir when redirects are made to the local
system will cause loops since this gateway is incapable of
performing a "hairpin" call.
Max Forwards
Send TRYING on REGISTER Send a 100 Trying when the
endpoint registers.
Outbound Proxy
A proxy to which the gateway will send all outbound signaling
instead of sending signaling directly to endpoints.
Advanced -- Timer Settings
Table 4-5 Definition of Timer Options
Options
Definition
Default T1 Timer
for Timer T1 is 500ms or the measured run-trip time between the
gateway and the device if you have qualify=yes for the device.
Call Setup Timer
the call will auto-congest. Defaults to 64 times the default T1
timer.
Session Timers
originate, Request and run session-timers always; accept, run
session-timers only when requested by other UA; refuse, do not
run session timers in any case.
Minimum Session
Maximum
Session Refresh
Interval
Maximum session refresh interval in seconds. Defaults to
1800secs.
Session Refresher
The session refresher, uac or uas. Defaults to uas.
Page 41

GSM/3G User Manual
41 | 82
Main IAX2 Endpoint Settings
You can click button to add a new IAX2 endpoint, and if you
want to modify existed endpoints, you can click button.
There are 3 kinds of registration types for choose. You can choose None, Endpoint
registers with this gateway(work as a Server) or This gateway registers with the
endpoint(work as a Client).
You can configure as follows:
If you set up a IAx2 endpoint by registration “None” to a server, then you can’t register
other IAX2 endpoints to this server, just authenticate the username and password.
Figure 4-5 None Registration
For convenience, we have designed a method that you can register your IAX2 endpoint
to your gateway, thus your gateway just work as a server.
Page 42

GSM/3G User Manual
42 | 82
Figure 4-6 Endpoint Register With this Gateway
Also you can choose registration by “This gateway registers with the endpoint”, it will
work as a Client.
Figure 4-7 This Gateway Register With the Endpoint
Page 43

GSM/3G User Manual
43 | 82
Table 4-6 Definition of IAX2 Options
Options
Definition
Name
Display name
Username
Authenication name in your IAX2 server
Password
Authenticating with the gateway and characters are allowed.
Registration
None --- Not registering;
Endpoint registers with this gateway --- When register as this type,
it means the GSM/3G gateway acts as a IAX2 server, and IAX2
endpoints register to the gateway;
This gateway registers with the endpoint --- When register as this
type, it means the GSM/3G gateway acts as a IAX2 client, and the
endpoint should be register to a IAX2 server;
Hostname
or
IP Address
IP address or hostname of the endpoint or 'dynamic' if the endpoint
has a dynamic IP address. This will require registration.
Auth
There are three authentication methods that are supported: md5,
plaintext and rsa. The least secure is "plaintext", which sends
passwords cleartext across the net. "md5" uses a challenge/response
md5 sum arrangement, but still requires both ends have plain text
access to the secret. "rsa" allows unidirectional secret knowledge
through public/private keys.If "rsa" authentication is used, "inkeys" is a
list of acceptable public keys on the local system that can be used to
authenticate the remote peer, separated by the ":" character. "outkey"
is a single, private key to use to authenticate to the other side.
Transfer
This application allows you to transfer calls.
Trunk
"trunk=yes" Purpose: To obtain a better chart of actual bandwidth
usage per codec as seen "on-the-wire" when using IAX2 trunking
between two Asterisk telephony servers.
Page 44

GSM/3G User Manual
44 | 82
Advanced:Registration Options
Table 4-7 Definition of Registration Options
Options
Definition
Qualify, Qualify
Freq Ok, Qualify
Freq Not Ok
The qualify, qualifyfreqok and qualifyfreqnotok settings are used
to determine the status availability of an IAX peer. If a peer is
consdered to be in a reachable (OK or LAGGED) state, it is
queried for availability every "qualifyfreqok" milliseconds. If it is
considered to be in an UNREACHABLE state, it is queried for
availability every "qualifyfreqnotok" milliseconds.The qualify=
setting turns the qualify system on (if the "yes" or xxx options
are used) or off (if qualify=no, which is by default). The
millisecond value of the qualify= setting specifies the maximum
response time of the availability acknowledgement before the
peer is considered to be in a "LAGGED" state.
Qualify Smothing
Use an average of the last two PONG result to reduce falsely
detected LAGGED host. The default is ‘no’.
Port
The port number the gateway will connect to at this endpoint.
IAX2 Encryption
Table 4-8 Definition of Encryption Options
Options
Definition
Encryption
Enable IAX2 encryption. The default is no.
Force Encryption
both sides support encryption. By turning this option on,
encryption is automatically; turned on as well. The default is no
IAX2 Trunk Settings
Table 4-9 Definition of Trunk Options
Options
Definition
Page 45

GSM/3G User Manual
45 | 82
Trunk Max Size
ulaw at 20ms a frame.
Trunk MTU
bad voice quality when allowing the Linux system to handle
fragmentation of UDP packets. Depending on the side of each
payload, allowing the OS to handle fragmentation may not be
very efficient. This setting sets the maximum transmission unit
for AIX2 UDP trunking. The default is 1240 bytes which means
if a trunk’s payload is over 1240 bytes for every 20ms it will be
broken into multiple 1240 bytes messages. Zero disables this
functionality and let’s the OS handle fragmentation.
Trunk Frequency
How frequently to send trunk msgs (in ms). This is 20ms by
default.
Trunk Time Stamps
within trunk frames? There is a small bandwith use for these
(less than 1kbps/call), but they ensure that frame timestamps
get sent end-to-end properly. If both ends of all your trunks go
directly to TDM, _and_your trunkfreq equals the frame length
for your codecs, you can probably suppress these. The
receiver must also need to have it enabled.
Min. RegExpire
Minimum amounts of time that IAX2 peers can request as a
registration interval (in seconds).
Max. RegExpire
registration expiration interval(in seconds).
Advanced SIP Settings
Networking
Table 4-10 Definition of Networking General Options
Options
Definition
UDP Bind Port
UDP Bind Port
Enable TCP
Enable server for incoming TCP connection (default is no).
TCP Bind Port
Page 46

GSM/3G User Manual
46 | 82
TCP
Authentication Timeout
The maximum number of seconds a client has to
authenticate. If the client does not authenticate before this
timeout expires, the client will be disconnected.(default value
is: 30 seconds).
TCP
Authentication Limit
be allowed to connect at any given time (default is: 50).
Enable
Hostname Lookup
gateway only uses the first host in SRV records Disabling
DNS SRV lookups disables the ability to place SIP calls
based on domain names to some other SIP users on
the Internet specifying a port in a SIP peer definition or when
dialing outbound calls with suppress SRV lookups for that
peer or call.
Enable Internal
SIP Call
the registration option "Endpoint registers with this gateway".
Internal SIP Call Prefix
Table 4-11 Definition of NAT Settings Options
Options
Definition
Local Network
address or IP ranges which are located inside a NATed
network. This gateway will replace the internal IP address in SIP
and SDP messages with the external IP address when a NAT
exists between the gateway and other endpoints.
Local Network List
Subscribe
Network Change
Event
has the ability to detect when the perceived external network
address has changed. When the stun_monitor is installed and
configured, chan_sip will renew all outbound registrations when
the monitor detects any sort of network change has occurred.
By default this option is enabled, but only takes effect once
res_stun_monitor is configured. If res_stun_monitor is enabled
and you wish to not generate all outbound registrations on
a network change, use the option below to disable this feature.
Page 47

GSM/3G User Manual
47 | 82
Match
External Address
Locally
Only substitute the externaddr or externhost setting if it
matches.
Dynamic
Exclude Static
address used for statically defined hosts. This helps avoid the
configuration error of allowing your users to register at the same
address as a SIP provider.
Externally Mapped
TCP Port
static NAT or PAT.
External Hostname
The external hostname (and optional TCP port) of the NAT.
Hostname
Refresh Interval
How often to perform a hostname lookup. This can be useful
when your NAT device lets you choose the port mapping, but
the IP address is dynamic. Beware, you might suffer from
service disruption when the name server resolution fails.
Table 4-12 Definition of RTP Settings Options
Options
Definition
Start of RTP Port Range
Start of range of port numbers to be used for RTP
End of RTP port Range
End of port numbers to be used for RTP
Paesing and Compatibility
Table 4-13 Instruction of Parsing and Compatibility
Options
Definition
Strict RFC Interpretation
multiline headers for strict SIP compatibility(default is yes)
Send Compact Headers
Send compact SIP headers
SDP Owner
Allows you to change the username filed in the SDP
owner string. This filed MUST NOT contain spaces.
Disallowed SIP Methods
The external hostname (and optional TCP port) of the
NAT.
Shrink Caller ID
'.', and '-' not in square brackets. For example, the caller
Page 48

GSM/3G User Manual
48 | 82
id value 555.5555 becomes 5555555 when this option is
enabled. Disabling this option results in no modification of
the caller id value, which is necessary when the caller
id represents something that must be preserved. By
default this option is on.
Maximum Registration
Expiry
Maximum allowed time of incoming registrations and
subscriptions (seconds).
Minimum Registration
Expiry
Default Registration
Expiry
Registration Timeout
How often, in seconds, to retry registration calls. Default
20 seconds.
Number of Registration
Attempts Enter '0' for unlimited Number of registration
attempts before we give up. 0 = continue
forever, hammering the other server until it accepts the
registration. Default is 0 tries, continue forever.
Security
Table 4-14 Instruction of Security
Options
Definition
Match Auth Username
from the authentication line instead of the 'from' field.
Realm
unique according to RFC 3261. Set this to your host name
or domain name.
Use Domain as Realm
Use the domain from the SIP Domains setting as the
realm. In this case, the realm will be based on the request
'to' or 'from' header and should match one of the domain.
Otherwise, the configured 'realm' value will be used.
Always Auth Reject
for any reason, always reject with an identical response
equivalent to valid username and invalid password/hash
Page 49

GSM/3G User Manual
49 | 82
instead of letting the requester know whether there was a
matching user or peer for their request. This reduces
the ability of an attacker to scan for valid SIP usernames.
This option is set to 'yes' by default.
Authenticate Options
Requests
just like INVITE requests are. By default this option is
disabled.
Allow Guest Calling
gateway is connected to the Internet and you allow guest
calls, you want to check which services you offer everyone
out there, by enabling them in the default context.
Media
Table 4-15 Instruction of Media
Options
Definition
Premature Media
Some ISDN links send empty media frames before the call
is in ringing or progress state. The SIP channel will then
send 183 indicating early media which will be empty - thus
users get no ring signal. Setting this to "yes" will stop any
media before we have call progress (meaning the SIP
channel will not send 183 Session Progress for early
media). Default is 'yes'. Also make sure that the SIP peer is
configured with progressinband=never. In order for
'noanswer' applications to work, you need to run the
progress() application in the priority before the app.
TOS for SIP Packets
TOS for RTP Packets
Page 50

GSM/3G User Manual
50 | 82
Codec Settings
Select codecs from the list below.
Figure 4-8 Codec Settings
Advanced IAX2 Settings
Table 4-16 Instruction of General
Options
Definition
Bind Port
Bind port and bindaddr may be specified
Enable IAXCompat
More than once to bind to multiple addresses, but the first will be the
default.
Enable
Nochecksums
Set iaxcompat to yes if you plan to use layered switches or some
other scenario which may cause some delay when doing a lookup in
the dialplan. It incurs a small performance hit to enable it. This option
cause Asterisk to spawn a separate thread when it receives an IAX
DPREQ (Dialplan Request) instead of blocking while it waits for a
response.
Enable Delay
Reject
Disable UDP checksums (if no checksums is set, then no checksums
will be calculated/checked on system supporting the feature)
ADSI
ADSI (Analog Display Services Interface) can be enable if you have
(or may have) ADSI compatible CPE equipment.
SRV Loopup
Whether or not to perform an SRV lookup on outbound calls
AMA Flags
You may specify a global default AMA flag for iaxtel calls. These flags
are used in the generation of call detail records.
autokill
If we don’t get ACK to our NEW within 2000ms,and autokill is set to
Page 51

GSM/3G User Manual
51 | 82
yes, then we cancel the whole thing(that’s enough time for one
retransmission only ).This is used to keep things from stalling for a
long time for a host that is not available for bad connections.
Language
You may specify a global default language for users. This can be
specified also on a per-user basis. If omitted, will fallback to
English(en)
Account Code
You may specify a default account for Call Detail Records (CDRs) in
addition specifying on a per-user basis.
Table 4-17 Instruction of Music on Hold
Options
Definition
Mohsuggest
The ‘Mohsuggest’ option specifies which music on hold class to
suggest to the peer channel when this channel place the peer on
hold. It may be specified globally or on a per-user or per-peer basis.
Mohinterpret
You may specify a global default language for users. This can be
specified also on a per-user basis. If omitted, will fall back to
English(en)
Table 4-18 Instruction of Codec Settings
Options
Definition
Band Width
Specify bandwith of low, medium, or high to control which codes are
used in general
Disallow
Fine tune codes here using “allow” and “disallow” clause with specific
codes
Allow
Fine tune codes here using “allow” and “disallow” clause with specific
codes
Codec Priority
Codec priority controls the codec negotiation of an inbound IAX2 call.
This option is inherited to all user entity separately which will override
the setting in general.
Table 4-19 Instruction of Jitter Buffer
Options
Definition
Jitter Buffer
Global default as to whether you want the jitter buffer at all
Force Jitter Buffer
In the ideal world, when we bridge VoIP channels we don’t want to
jitter buffering on the switch, since the endpoints can each handle
this. However, some endpoints may have poor jitter buffers
themselves, so this option will force to always jitter buffer, even in
this case.
Max Jitter Buffers
A maximum size for the jitter buffer
Resyncthreshold
When the jitter buffer notice a significant change in delay that
Page 52

GSM/3G User Manual
52 | 82
continue over a few frames, it will resync, assuming that the change
in delay was caused by a timestamping mix-up. The threshold for
noticing a change in delay is measured as twice the measured jitter
plus this resync threshold.
Max Jitter Interps
The maximum number of interpolation frames the jitter buffer should
return in a row. Since some clients do not send CNG/DTX frames to
indicate silence, the jitter buffer will assume silence has begun after
returning this many interpolations. This prevents interpolating
throughout a long silence.
Jitter Target Extra
Number of milliseconds by which the new jitter buffer will pad its
size. The default is 40, so without modification, the new jitter buffer
will set its size to the jitter value may help if your network normally
has low jitter, but occasionally has spikes.
Table 4-20 Instruction of Misc Settings
Options
Definition
IAX Thread Count
Establishes the number of iax helper thread to handle
I/O
IAX Max Thread Count
Establishes the number of extra dynamic threads that
may by spawned to handle I/O
Max Call Number
The ‘maxcallnumbers’ option limits the amount of call
numbers allowed for each individual remote IP address.
Once an IP address reaches its call number limit, no
more new connections are allowed until the previous
ones close. This option can be used in a peer definition
as well, but only takes effect for the IP of a dynamic peer
after it completes registration.
MaxCallNumbers_Nonvalidated
The ‘maxcallnumbers-nonvalidated’ is used to set the
combined number of call numbers that can be allocated
for connections where call token validation has been
disabled. Unlike the ‘maxcallnumbers’ option, this limit is
not separate for each individual IP address. Any
connection resulting in a non-call token validated call
number being allocated contributes to this limit. For use
cases, see the call should be sufficient in most cases.
Table 4-21 Instruction of Quality of Service
Options
Definition
Tos
Type of service
Cos
Class of service
Page 53

GSM/3G User Manual
53 | 82
5. Routing
Figure 5-1 Routing Rules
You are allowed to set up new routing rule by , and after setting
routing rules, move rules’ order by pulling up and down, click button to edit
the routing and to delete it. Finally click the button to save what
you set. shows current routing rules. Otherwise you can set up unlimited routing
rules.
Call Routing Rule
You can click button to set up your routings.
Page 54

GSM/3G User Manual
54 | 82
Figure 5-2 Example of Set up Routing Rule
The figure above realizes that calls from “1001” SIP endpoint switch you have registered
will be transferred to Port-1. When “Call Comes in From” is T1/E1 Port, “prepend”,
“prefix” and “match pattern” in “Advanced Routing Rule” are ineffective, and just
“CallerID” option is available.
Page 55

GSM/3G User Manual
55 | 82
Table5-1 Definition of Routing Options
Options
Definition
Routing Name
types of calls this route matches (for example, 'SIP2GSM' or
'GSM2SIP').
Call Comes in From
Send Call Through
The destination to receive the incoming calls.
Table5-2 Description of Advanced Routing Rule
Options
Definition
Dial Patterns that will
use this Route
route and send the call to the designated trunks. If a dialed
pattern matches this route, no subsequent routes will be tried.
If Time Groups are enabled, subsequent routes will be
checked for matches outside of the designated time(s).
Rules:
X matches any digit from 0-9
Z matches any digit from 1-9
N matches any digit from 2-9
[1237-9] matches any digit in the brackets (example:
1,2,3,7,8,9)
. wildcard: matches one or more dialed digits.
prepend: Digits to prepend to a successful match
If the dialed number matches the patterns specified by the
subsequent columns, then this will be prepended before
sending to the trunks
prefix: Prefix to remove on a successful match
The dialed number is compared to this and the subsequent
columns for a match. Upon a match, this prefix is removed
from the dialed number before sending it to the trunks.
match pattern: The dialed number will be compared against
the prefix + this match pattern. Upon a match, the match
pattern portion of the dialed number will be sent to the trunks
CallerID: If CallerID is supplied, the dialed number will only
match the prefix + match pattern if the CallerID has been
transmitted matches this.
When extensions make outbound calls, the CallerID will be
their extension number and NOT their Outbound CID.
Page 56

GSM/3G User Manual
56 | 82
The above special matching sequences can be used for
CallerID matching similar to other number matches.
Set the Caller
ID Name to
call to the endpoint.
Set the Caller
ID Number to
call to the endpoint.
Forward Number
when you have a transfer call.
Failover Call Through
Number
the order you specify. You can create various time routes and
use these time conditions to limit some specific calls.
Figure 5-3 Time Patterns that will use this Route
If you configure like this, then from January to March, from the first day to the last day of
these months, from Monday to Thursday, from 00:00 to 02:00, during this time (meet all
above time conditions), all calls will follow this route. And the time will synchronize with
your Sever time.
Figure 5-4 Failover Call Through Number
You can add one or more “Failover Call Through Numbers”.
Groups
Sometimes you want to make a call through one port, but you don’t know if it is available,
so you have to check which port is free. That would be troublesome. But with our
Page 57

GSM/3G User Manual
57 | 82
product, you don’t need to worry about it. You can combine many GSM or SIP to groups.
Then if you want to make a call, it will find available port automatically.
Figure 5-5 Routing Group
MNP Settings
Mobile Number Portability allows switching between mobile phone operators without
changing the mobile number. Sounds simple, but there are loads of tasks performed
behind the scene at the operator end.
The URL is shown in the password string way. So please type the url in other place such
a txt file, check it, then copy it to the gateway. The outgoing number in the url should be
replaced by the variables ${num}.
Here is an example of the MNP url:
https://s1.bichara.com.br:8181/chkporta.php?user=832700&pwd=sdsfdg&tn=838816690
2
The 8388166902 is the outgoing phone number, when config the MNP url, should replce
it with ${num}. Then it turns to
https://s1.bichara.com.br:8181/chkporta.php?user=832700&pwd=sdsfdg&tn=${num}.
Figure 5-6 MNP Settings
Page 58

GSM/3G User Manual
58 | 82
6. SMS
General
You can choose enable SMS Received, SMS Local Strored and SMS Status Report or
not.
Figure 6-1 SMS Settings
Sender Options
You can change sender options here, include resend, times of resend.
Figure 6-2 Sender Options
Table 6-1 Description of Sender Options
Options
Definition
Resend Failed Message
message.
Repeat Same Message
SMS to Email
This is a tool that makes it available for you to email account to transmit the SMS to other
email boxes. The following settings realize that received SMS through
openvpnvoip@gmail.com transmit to openvpnvoip@yahoo.com.cn,
openvpnvoip@hotmail.com and support@openvox.cn
Page 59

GSM/3G User Manual
59 | 82
Figure 6-3 SMS to Email
Table6-2 Types of E-mail Box
E-mail Box
Type
SMTP Server
SMTP
Port
SMTP Security
Connectivity
Gmail
smtp.gmail.com
587 √ HotMail
smtp.live.com
587
√
Yahoo!
smtp.mail.yahoo.co.in
587 × e-mail
smtp.163.com
25
×
Table6-3 Definition of SMS to E-mail
Options
Definition
Enable
When you choose on, the following options are available,
otherwise, unavailable.
Page 60

GSM/3G User Manual
60 | 82
Email Address
of Sender
To set the email address of an available email account. For
example, openvpnvoip@gmail.com.
Domain
To set outgoing mail server. e.g. smtp.gmail.com
SMTP Port
To set port number of outgoing mail server. (Default is 25)
SMTP User
Name
The login name of your existing email account. This option might
be different from your email address. Some email client doesn't
need the email postfix
SMTP
Password
The password to login your existing email.
TLS Enable
When you choose Yahoo and 163 free e-mails, this option is not
available.
SMTP Server
To set outgoing mail server. e.g. mail.openvox.cn.
Destination
Email Address1
The first email address to receive the inbox message.
Destination
Email Address2
The second email address to receive the inbox message.
Destination
Email Address3
The third email address to receive the inbox message.
SMS Control
Allowing endpoints to send some specific KEY WORDS and corresponding PASSWORD
to operate the gateway and message is case-sensitive. In default, this function is
disabled.
Page 61

GSM/3G User Manual
61 | 82
Figure 6-4 SMS Control
For example, SMS control password is 123456789 which has nothing to do with the login
password, you can send “get info 123456789” to the GSM module’s phone number to get
your gateway’s IP information.
Table6-4 Definition of SMS Control
Options
Definition
Enable
ON(enable), OFF(disable)
Password
The password to confirm that SMS makes the gateway rebooted,
shut down, restored configuration files and get info on this gateway.
SMS Format
For example, the message formats:
reboot system PASSWORD: To reboot your whole gateway.
The PASSWORD is referring to the PASSWORD you set up from
option “PASSWORD” above.
Reboot asterisk PASSWORD: To restart your gateway core.
Restore configs PASSWORD: To reset the configuration files back
to the default factory settings.
Get info PASSWORD: To get your gateway IP address
SMS inbox
Auto clean
switch on: When the size of the SMS inbox record file reaches the
max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New record will be
retained.
switch off: SMS record will remain, and the file size will increase
gradually. default on, max size = 20 MB
Page 62

GSM/3G User Manual
62 | 82
HTTP to SMS
Figure 6-5 HTTP to SMS
SMS to HTTP
Figure 6-6 SMS to HTTP setting
SMS Sender
You can choose one or more ports to send SMS to the destination number, different
numbers should be separated by symbols: '\r', '\n', space character, semicolon and
comma. Then you can see much feedback information.
Page 63

GSM/3G User Manual
63 | 82
Figure 6-7 SMS Sender
SMS Inbox
On this page, you are allowed to scan, delete, clean up, and export each port’s received
SMS. Also you are allowed to check messages by port, phone number, time order and
message keywords.
Figure 6-8 SMS Inbox
Page 64

GSM/3G User Manual
64 | 82
SMS Outbox
On this page, you are allowed to scan, delete, clean up, and export each port’s received
SMS. Also you are allowed to check messages by port, phone number, time order and
message keywords.
Figure 6-9 SMS Outbox
SMS Forwarding
Using this feature, you can forward incoming sms to your mobile. You can
click button to add new routing.
Such as:
SMS received by gsm-1.1 and gsm-1.2, will be transfered to phone number
13923704563 through port umts-2.1 or gsm-3.1.
Page 65

GSM/3G User Manual
65 | 82
Figure 6-10 Create a routing
For "ascending" Policy, if you choose 2 or more ports members, it will use first available
port to transfer sms. For this case, if umts-2.1 is availble, it will always use umts-2.1 to
trnasfer sms; Otherwise, it will use gsm-3.1 to transfer sms.
Page 66

GSM/3G User Manual
66 | 82
7. Network
On “Network” page, there are three sub-pages: “LAN Settings”, “DDNS Settings”, and
“Toolkit”.
Network Settings
There are three types of WAN/LAN port IP, Factory, Static and DHCP. Factory is the
default type, and it is 172.16.99.1. When you Choose LAN IPv4 type is “Factory”, this
page is not editable.
A reserved IP address to access in case your gateway IP is not available. Remember to
set a similar network segment with the following address of your local PC.
Figure 7-1 LAN Settings
Page 67

GSM/3G User Manual
67 | 82
Table7-1 Definition of LAN Settings
Options
Definition
Interface
The name of network interface.
Type
Number (System information to check slot
number). Static: manually set up your gateway
IP. DHCP: automatically get IP from your local LAN.
MAC
Physical address of your network interface.
Address
The IP address of your gateway.
Netmsk
The subnet mask of your gateway.
Default Gateway
Default getaway IP address.
Basically this info is from your local network service provider, and you can fill in four DNS
servers.
DNS Servers: A list of DNS IP address. Basically this info is from your local network
service provider.
DDNS Settings
You can enable or disable DDNS (dynamic domain name server).
Figure 7-2 DDNS Settings
Page 68

GSM/3G User Manual
68 | 82
Table7-2 Definition of DDNS Settings
Options
Definition
DDNS
Type
Set the type of DDNS server.
Username
Your DDNS account’s login name.
Password
Your DDNS account’s password.
Your domain
The domain to which your web server will belong.
Toolkit
It is used to check network connectivity. Support Ping command on web GUI.
Figure 7-3 Toolkit
Security Settings
Firewall settings
Table7-3 Definition of Firewall settings
Options
Definition
Firewall Enale
must enble this option.
Page 69

GSM/3G User Manual
69 | 82
Ping Enable
not allow to ping.
Figure 7-4 Firewall Setting
White List Settings
White List Enbale: To enable white list or not.
List IP Settings: IPs are separated only by "," character.
Click "Save" button to save configration; Click "submit" button to submit and apply
configuration.
If "List IP Settings" has no problem, you will see popup window like below. Please read
the warning and tips carefully. And Click "Apply" button in 1 minute. If time runs out, this
window will close automatically.
Page 70

GSM/3G User Manual
70 | 82
Figure 7-5 Firewall Rules Apply
If you see windows like below. It means your configuration has been applied
successfully.
Figure 7-6 Firewall Rules Apply
Page 71

GSM/3G User Manual
71 | 82
Security Rules
Figure 7-7 Security Rules
Click "submit" button to submit and apply configuration.
If "List IP Settings" has no problem, you will see popup window like below. Please read
the warning and tips carefully. And Click "Apply" button in 1 minute. If time runs out, this
window will close automatically.
If you see windows like below. It means your configuration has been applied
successfully.
Page 72

GSM/3G User Manual
72 | 82
8. Advanced
Asterisk API
When you make “Enable” switch to “ON”, this page is available.
Figure 8-1 Asterisk API Interface
Table8-1 Definition of Asterisk API
Options
Definition
Page 73

GSM/3G User Manual
73 | 82
Port
Network port number
Manager Name
Manager secret
“-_+.<>&0-9a-zA-Z”. Length:4-32 characters.
Deny
as separator. <br/><br/>Example: 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
or 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0&10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0
Permit
as separator.<br/><br/>Example: 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
or 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0&10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0
System
system management commands, <br/>such as Shutdown,
Restart, and Reload.
Call
a running channel.
Log
Verbose
Command
Agent
Information about queues and agents and ability to add
queue members to a queue.
User
Config
DTMF
Receive DTMF events. Read-only.
Reporting
cdr, manager, if loaded. Read-only.
Dialplan
Receive NewExten and Varset events. Read-only.
Originate
All
Select all or deselect all.
Page 74

GSM/3G User Manual
74 | 82
Once you set like the above figure, the host 172.16.100.110/255.255.0.0 is allowed to
access the gateway API. Please refer to the following figure to access the gateway API
by putty. 172.16.179.1 is the gateway’s IP, and 5038 is its API port.
Figure 8-2 Putty Access Gateway API
Asterisk CLI
In this page, you are allowed to run Asterisk commands.
Figure 8-3 Asterisk CLI
Command: Type your Asterisk CLI commands here to check or debug your gateway.
Notice: If you type “help” or “?” and execute it, the page will show you the executable
commands.
Asterisk File Editor
On this page, you are allowed to edit and create configuration files. Click the file to edit.
Page 75

GSM/3G User Manual
75 | 82
Figure 8-4 Asterisk File Editor
Click “New Configuration File” to create a new configuration file. After editing or creating,
please reload Asterisk.
Page 76

GSM/3G User Manual
76 | 82
9. Logs
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding
logs page. For example, set “System Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to
“System” page for system logs, otherwise, system logs is unavailable. And the same with
other log pages.
Figure 9-1 Log Settings
Figure 9-2 System Logs
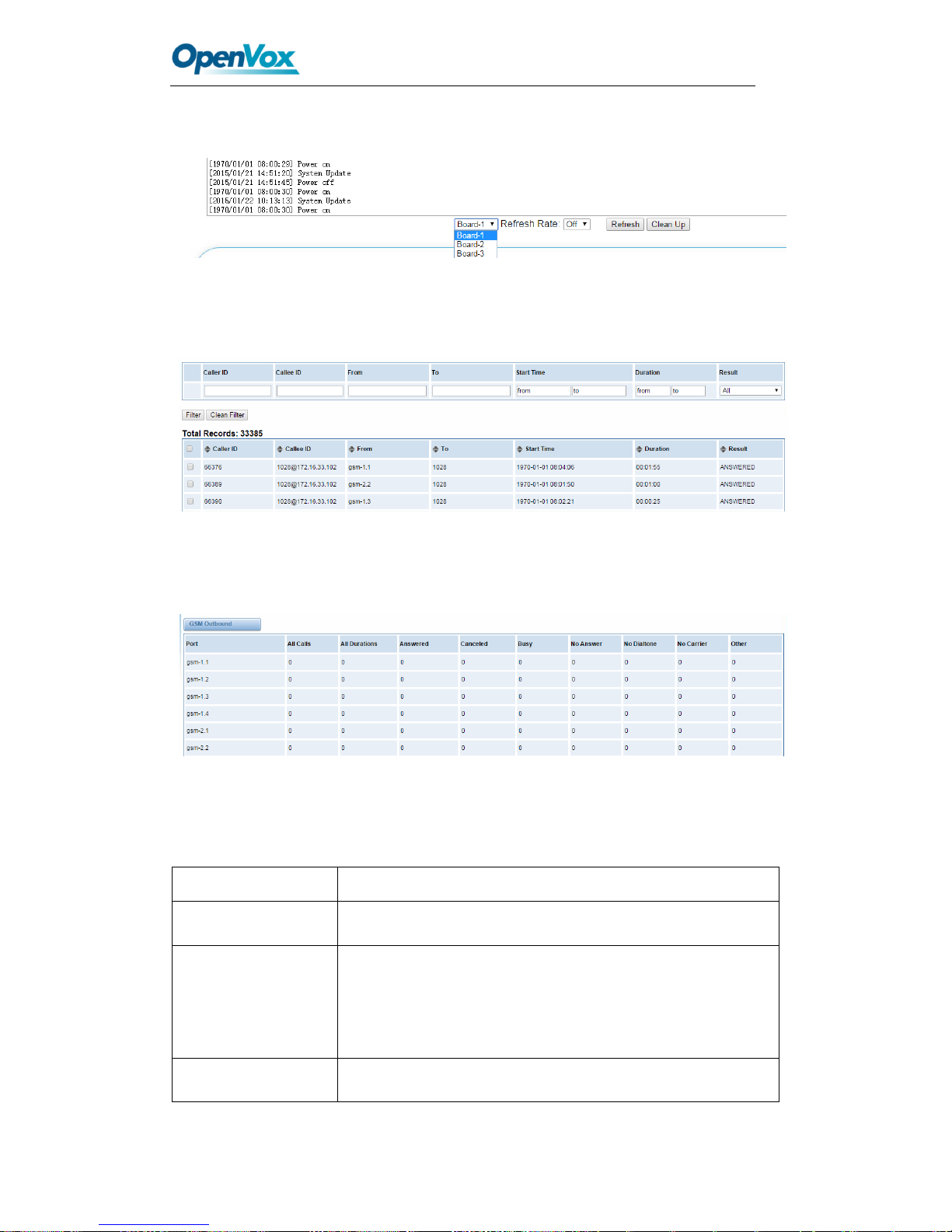
Page 77
GSM/3G User Manual
77 | 82
You can choose one specific board to see it related logs.
Figure 9-3 Choose One Board
You can scan your CDR easily on web GUI, and also you can delete, clean up or export
your CDR information.
Figure 9-4 CDR Output
Recently we have made our LOGS display richer, you can see your GSM Outbound of
every port clearly.
Figure 9-5 Time Patterns that will use this Route
Table9-1 definition of Logs
Options
Definition
System Logs
Auto clean (System
Logs)
system will cut a half of the file. New logs will
be retained; switch off : logs will remain, and the file size
will increase gradually. default on, maxsize=1M.
Verbose
Page 78
GSM/3G User Manual
78 | 82
Notice
Warning
Debug
Error
Asterisk console error message switch.
DTMF
Asterisk console DTMF info switch.
Auto clean (asterisk
logs)
system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be
retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file size will
increase gradually. default on, maxsize=100KB.
SIP Logs
Auto clean (SIP logs)
switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max
size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be
retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file
size will increase gradually. default on, maxsize=100KB.
IAX Logs
Whether enable or disable IAX log.
Auto clean( IAX logs)
system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be
retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file
size will increase gradually. default on, maxsize=100KB.
Debug AT Command
Logs
Auto clean (AT logs)
system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be
retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file size
will increase gradually. default on, maxsize=100KB.
Call Detail Record
Auto clean (CDR
logs)
the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be
retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file size
will increase gradually. default on, max size=20MB.
Page 79

GSM/3G User Manual
79 | 82
Appendix Feature List
General Info
Size: VS -GW21(GSM) 48.3cm*33.1cm*8.8cm
VS-GW1600(GSM) 44cm*4.5cm*30cm
VS-GW1202(GSM) 15cm*19cm*4.5cm
WGW1002G 16cm*10.1cm*3.1cm
VS-GW2120(3G) 44cm*34cm*9cm
VS-GW1600(3G) 44cm*4.5cm*30cm
VS-GW1202(3G) 15cm*19cm*4.5cm
VS-GW1002: 2 GSM channels
VS-GW1202: 4/8 GSM/UMTS channels
VS-GW1600: up to 20 GSM/UMTS channels
VS-GW2120: up to 44 GSM/UMTS channels
Power: VS-GW2120 88W
VS-GW1600 46W
VS-GW1202 18W
WGW1002G 6W
Weight: VS-GW2120(GSM) 8624g
VS-GW1600(GSM) 4301g
VS-GW1202(GSM) 1300g
WGW1002G 237g
VS-GW2120(3G) 6144g
VS-GW1600(3G) 3682g
VS-GW1202(3G) 502g
LAN Port: 2
SIM Cards: Hot-Swap
GWM400G/GWM400W Module: Hot-Swap
Operation Humidity Range:10%~90% non-condensing
Storage Temperature Range: -20~70°C
Operation Temperature Range: 0~40°C
GSM/WCDMA Features
CLID Display & Hide (Need operators’ support )
WCDMA/UMTS: 850/900/1900/2100 MHz
GSM: 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
Real Open API Protocol (based on Asterisk)
Call Duration Limitation
SMSC/SMS/USSD
Gain Adjustment
Page 80

GSM/3G User Manual
80 | 82
PIN Identification
IMEI Number Automatically Modify
Band Binding
Bind Carrier
Optional GSM/UMTS Voice Codec
Call Waiting
Call Forwarding (unconditional, no reply, busy, not reachable)
GSM/UMTS Ports Group Management
SMS Bulk Transceiver, Sent to Email and Automatically Resend
SMS Coding/Detecting Automatically Identification
SMS Remotely Controlling Gateway
SMS Forwarding and Quick Reply
USSD transceiver
VOIP Characters
Support SIP, IAX2 Protocol
Add, Modify & Delete SIP/IAX2 Trunk
SIP/IAX2 Registration with Domain
Combine Different SIP/IAX2 Trunk into Group
DTMF Mode: RFC2833/Inband/SIPInfo
SIP V2.0 RFC3261 Compliance
Multiple SIP/IAX2 Registrations modes: None (No registration, just IP and
Password authenication)Endpoint registers with this gateway (work as a SIP
Sever)This gateway registers with the endpoint (work as a SIP/IAX2 client)
Network
IPv4, UDP/TCP, DHCP, TFTP, TELNET, HTTP/HTTPS, SMTP, POP3
HTTP/SSH (Optical Telnet)
Ping & Traceroute Command on the Web
Two Types of IP Access
Simple Security Strategy: white list, black list, security rules
Page 81

GSM/3G User Manual
81 | 82
System Features
Abundant Codecs:G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.722, G.723, G.726, GSM
Simple and convenient configuration via Web GUI
Firmware Update by HTTP
Automatically Reboot
Extensible Automatic Callback and Speed Dial
TTL Serial Port and Virtual Serial via TCP/IP Protocol
Support DISA
Customizable IVR
Multiple Detailed LOG Output
Call Status Display
PDD/ACD/ASR/BER Display
Mobile number portability (MNP)
CDR (More than 200,000 Lines CDRs Storage Locally)
Support configuration files backup and upload
Support for custom scripts, dialplans
Least Cost Routing(LCR),according to Time, Port, Calling Number
Independent System for Each Module
Restore Factory Settings
High Equipment Materials Specifications, Suitable for Long Distance
Transportation
Page 82

GSM/3G User Manual
82 | 82
Application Diagrams
 Loading...
Loading...