OpenCell 0012TC19001 Users Manual

TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY
TransCell 1900CB System
Installation Manual for Use with
Fiber and Coaxial Cable Networks
Document No. 1000070
Revision A
November 14, 2000
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF TRANSCEPT, INC, AND IS NOT TO BE
USED FOR ANY PURPOSE, EXCEPT IN ACCORDANCE WITH CONTRACTUAL NONDISCLOSURE
TERMS. THIS DOCUMENT IS NOT TO BE DUPLICATED IN WHOLE OR IN PART WITHOUT PRIOR
WRITTEN PERMISSION FROM A DULY AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE OF TRANSCEPT, INC.
THE REVISION STATUS OF ALL PAGES IN THIS DOCUMENT IS THE SAME AS THAT STATED ON THIS
COVER.
Copyright 1999, 2000 Transcept, Inc
All rights reserved.
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY

TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY
TransCell 1900CB System
Installation Manual for Use with
Fiber and Coaxial Cable Networks
REVIEW AND CONCURRENCE
STEVE DALE, APPLICATION ENGINEERING DATE
MATTHEW HUBBARD, APPLICATION ENGINEERING
CHRISTOPHER COLE, DIRECTOR, PRODUCT
MANAGEMENT
ERIK DEVINNEY, CONTINUATION ENGINEERING
MANAGER
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF TRANSCEPT, INC, AND IS NOT TO BE
USED FOR ANY PURPOSE, EXCEPT IN ACCORDANCE WITH CONTRACTUAL NONDISCLOSURE
TERMS. THIS DOCUMENT IS NOT TO BE DUPLICATED IN WHOLE OR IN PART WITHOUT PRIOR
WRITTEN PERMISSION FROM A DULY AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE OF TRANSCEPT, INC.
DATE
DATE
Document No. 1000070
Revision A:
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY
DRAWING NO. 1000070
DOCUMENT CHANGE HISTORY
DATE REV DESCRIPTION APPD
11/14/00 A Released to ECO control per RN001114 km/ED
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Paragraph Page
1 INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................1-1
1.1 SCOPE...........................................................................................................................1-1
1.2 TERMINOLOGY, ACRONYMS, AND ABBREVIATIONS.............................................................1-2
1.2.1 TransCell 1900CB Terminology .............................................................................1-2
1.2.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations..................................................................................1-2
1.2.3 Notation Conventions in this Manual......................................................................1-3
1.3 REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION.........................................................................................1-3
1.4 SYSTEM OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................1-4
1.4.1 Hub Equipment (HE) Enclosure Configurations .....................................................1-5
1.4.1.1 Hub Control Unit (HCU) ..................................................................................1-5
1.4.1.2 RF Interface Assembly (RFIA)........................................................................1-6
1.4.1.3 Hub Interface Converter (HIC)........................................................................1-6
1.4.1.4 Hub Fiber Interface (HFI)................................................................................1-6
1.4.1.5 Cable Assemblies...........................................................................................1-6
1.4.1.6 Equipment enclosure......................................................................................1-7
1.4.1.7 +24 VDC Power Supply Assembly (Optional)..................................................1-7
1.4.2 Remote Fiber Interface (RFI) .................................................................................1-7
1.4.3 Cable Microcell Integrator (CMI) ............................................................................ 1-7
1.4.3.1 Power Extractor ..............................................................................................1-8
1.4.3.2 Internal Fiber Transceiver...............................................................................1-8
1.4.3.3 Transceiver.....................................................................................................1-9
1.4.3.4 Power Supply................................................................................................1-10
1.4.3.5 Power Amplifier.............................................................................................1-10
1.4.4 CMI Antennas ......................................................................................................1-10
1.4.5 Outdoor Enclosure Unit).......................................................................................1-10
2 HUB PRIMARY/EXPANSION RACK INSTALLATION......................................................2-1
2.1 INSTALLATION TASKS ......................................................................................................2-1
2.2 TOOLS, TEST EQUIPMENT, AND SUPPLIES........................................................................2-1
2.3 INSTALLATION PARTS LIST...............................................................................................2-2
2.4 POWER REQUIREMENTS..................................................................................................2-3
2.4.1 Typical Prime Power Requirements .......................................................................2-3
2.4.2 Protective Earth Grounding....................................................................................2-3
2.5 HUB EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION AND SPACE REQUIREMENTS..........................................2-3
2.5.1 Suggested Floor Space Requirements...................................................................2-3
2.5.2 Floor Loading Requirements..................................................................................2-3
2.5.3 Typical Enclosure Configuration.............................................................................2-3
2.6 INSTALLATION OF ASSEMBLIES IN EQUIPMENT ENCLOSURE............................................2-5
2.6.1 Hub Enclosure Installation......................................................................................2-5
2.6.1.1 Hub +24 VDC Power Supply Installation.........................................................2-5
2.6.1.2 Hub Control Unit (HCU) Installation ................................................................2-6
2.6.1.3 +24 VDC Prime Power Installation..................................................................2-8
2.6.1.4 Initial Prime Power Test..................................................................................2-8
2.6.1.5 Initial HCU Test...............................................................................................2-8
2.6.1.6 RF Interface Assembly (RFIA) Installation ......................................................2-9
2.6.1.7 Hub Fiber Interface (HFI) (Option)..................................................................2-9
2.6.1.8 Hub Interface Converter (HIC) Installation....................................................2-10
2.6.1.9 Digital Communications Wiring Installation...................................................2-11
i
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.7 HUB EQUIPMENT CABLE INSTALLATION...........................................................................2-11
2.7.1 10/15 MHz Reference cable Installation between RFIA and HIC..........................2-12
2.7.2 Remote User Interface.........................................................................................2-13
2.7.3 HCU Modem ........................................................................................................2-13
2.8 INSTALLATION CHECKOUT - INITIAL TURN-ON..................................................................2-14
2.8.1 Reverse Link Input from Network Infrastructure...................................................2-14
2.8.2 HIC Initial Turn-on and Communication Test........................................................2-15
2.8.3 HCU Setup for HIC Checkout...............................................................................2-15
2.8.4 HIC Activation ......................................................................................................2-17
2.8.5 HIC Reference and Control Tone Output .............................................................2-19
3 CMI INSTALLATION.........................................................................................................3-1
3.1 CMI INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS .................................................................................3-1
3.1.1 Tools, Test Equipment and Supplies......................................................................3-1
3.1.2 CMI Configurations ................................................................................................3-2
3.1.3 Transcept-Furnished Items for CMI Installation......................................................3-2
3.1.4 Customer-Furnished Items for CMI Installation ......................................................3-2
3.1.5 CMI External Connector Identification....................................................................3-4
3.2 SITE PREPARATION.........................................................................................................3-5
3.3 CMI HARDWARE INSTALLATION GUIDE.............................................................................3-6
3.3.1 CMI Access............................................................................................................3-6
3.3.1.1 Opening the Assembly....................................................................................3-6
3.3.1.2 Closing the Assembly......................................................................................3-6
3.3.2 CMI Port and Power Extractor Configuration Options ............................................3-7
3.3.2.1 CMI CATV Port Configurations.......................................................................3-7
3.3.2.2 Power Extractor Options.................................................................................3-9
3.3.3 Coaxial or Fiber Network Interface to the CMI .....................................................3-11
3.3.4 Power Extractor Reverse Link/Forward Link RF Attenuation (Coaxial Installation)3-11
3.3.5 Installing the CMI .................................................................................................3-11
3.3.5.1 Attaching CMI to Messenger Strand .............................................................3-11
3.3.5.2 Attaching Antennas to Messenger Strand.....................................................3-13
3.3.5.3 Installing and Routing Cables .......................................................................3-14
3.3.5.4 Protective Earth Grounding...........................................................................3-14
3.3.5.5 Antenna Cables ............................................................................................3-15
3.3.6 Power and CDMA SIGNAL Cables ...................................................................... 3-16
3.3.7 CMI Power Check................................................................................................3-16
3.4 MEASUREMENT TEST POINTS ........................................................................................3-16
3.5 FORWARD LINK CMI INSTALLATION MEASUREMENTS AND ADJUSTMENTS .............................3-17
3.5.1 CMI Forward Link Reference and Control Tone Input Level Check......................3-18
3.6 REVERSE LINK CMI INSTALLATION MEASUREMENTS AND ADJUSTMENTS..........................3-19
3.6.1 Activate CMI.........................................................................................................3-19
3.6.2 Reverse Link Gain Adjustment.............................................................................3-22
3.6.2.1 Setting CMI Reverse Link Signal Level Setpoint at HIC................................3-22
3.6.2.2 Measure CMI Reverse Link Control Tone at HIC..........................................3-23
3.6.3 Adjusting Reverse Gain at the HIC ......................................................................3-24
4 BTS INTERFACE AND NETWORK OPTIMIZATION........................................................4-1
4.1 INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................................................4-1
4.2 MEASUREMENT/CALCULATION OF CMI DELAYS ................................................................4-1
4.2.1 Sector Dedicated to TransCell 1900CB - Timing Equal..........................................4-1
4.2.1.1 Description......................................................................................................4-1
ii
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
4.2.1.2 Basic BTS Settings for Dedicated Sector with Equal Timing...........................4-2
4.2.2 Sector Dedicated to TransCell 1900CB - Timing Unequal......................................4-4
4.2.2.1 Description......................................................................................................4-4
4.2.2.2 Basic BTS Settings for Dedicated Sector with Unequal Timing.......................4-5
4.2.3 Simulcasting with a Tower - Timing Equal Within TransCell 1900CB.....................4-6
4.2.3.1 Description......................................................................................................4-6
4.2.3.2 Basic BTS Settings for Shared Sector with Equal Timing ...............................4-6
4.2.4 Split Sector - Timing Unequal Within TransCell 1900CB........................................4-7
4.2.4.1 Description......................................................................................................4-7
4.2.4.2 Basic BTS Settings for Shared Sector with Unequal Timing ...........................4-8
4.3 ASSESSMENT OF BTS SECTORS......................................................................................4-9
4.4 PHYSICAL INTERFACES WITH BTS...................................................................................4-9
4.4.1 Measurement of HIC Reverse Link Output...........................................................4-12
4.4.1.1 HIC CDMA Reverse Link Output to BTS.......................................................4-13
4.4.2 CDMA Forward Link Input from BTS....................................................................4-14
4.4.3 CDMA Forward Link Output to Coaxial Network ..................................................4-15
4.4.3.1 HIC Forward Link CDMA Pilot Level .............................................................4-16
4.5 INITIAL SETTING OF BTS PARAMETERS ..........................................................................4-19
4.5.1 Initial Conditions...................................................................................................4-19
4.5.2 Guidelines for Initial Setting of Parameters ..........................................................4-19
4.6 OPTIMIZING BTS PARAMETER SETTINGS .........................................................................4-20
APPENDIX A RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFACE ASSEMBLY (RFIA) CONFIGURATION
PROCEDURE......................................................................................................................... A-1
RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFACE ASSEMBLY (RFIA) CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE.. A-2
APPENDIX B PCS CHANNEL NUMBER-TO-FREQUENCY CROSS-REFERENCE...........B-1
APPENDIX C HIC CHANNEL NUMBER-TO-FREQUENCY CROSS-REFERENCE ............ C-1
ENCLOSURE/HIC DATA SHEET...........................................................................................C-1
CMI DATA SHEET ..................................................................................................................4-1
iii
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure Page
FIGURE 1-1. TRANSCELL 1900CB SYSTEM FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ...................................1-4
FIGURE 2-1. RECOMMENDED HUB EQUIPMENT FLOOR SPACE......................................................2-4
FIGURE 2-2. TYPICAL ENCLOSURE CONFIGURATION....................................................................2-4
FIGURE 2-3. +24 VDC POWER SUPPLY REAR PANEL..................................................................2-5
FIGURE 2-4. TYPICAL INDOOR ENCLOSURE CONFIGURATION........................................................2-7
FIGURE 2-5. HCU COMPUTER REAR VIEW .................................................................................2-7
FIGURE 2-6. HIC REAR PANEL.................................................................................................2-10
FIGURE 2-7. HIC POWER WIRING HARNESS 1000062G1..........................................................2-10
FIGURE 2-8. THREE HIC CONTROL INTERCONNECT DIAGRAM (NOT TO SCALE)............................2-11
FIGURE 2-9. HIC COMMUNICATION WIRING HARNESS P/N 8339969G1.....................................2-11
FIGURE 2-10. BTS/HIC/COAXIAL NETWORK RF CABLING DIAGRAM (15MHZ FROM RFIA SHOWN)2-12
FIGURE 2-11. CONFIGURATION OPTIONS DIALOG..............................................................2-16
FIGURE 2-12. HUB CONTROL PANEL: USER DIALOG...........................................................2-16
FIGURE 2-13. TYPICAL ADD HIC DIALOG.................................................................................2-18
FIGURE 2-14. REFERENCE AND CONTROL TONES DIALOG...............................................2-20
FIGURE 3-1. CMI CHASSIS RIGHT END VIEW ..............................................................................3-4
FIGURE 3-2. CMI CHASSIS LEFT END VIEW ................................................................................3-4
FIGURE 3-3. CMI BOLT TIGHTENING SEQUENCE .........................................................................3-6
FIGURE 3-4. TYPICAL HOUSING-TO-HARDLINE CONNECTOR INTERFACE .......................................3-7
FIGURE 3-5. PROCEDURE FOR CUTTING CATV PORT CENTER CONDUCTOR TO LENGTH...............3-7
FIGURE 3-6. ASSEMBLY OF TYPICAL HOUSING TO HARD-LINE/POWER CONNECTORS ....................3-8
FIGURE 3-7. POWER EXTRACTOR.............................................................................................3-10
FIGURE 3-8. POWER SUPPLY INPUT CONNECTOR......................................................................3-10
FIGURE 3-9. CMI BRACKET INSTALLATION................................................................................3-12
FIGURE 3-10. ANTENNA INSTALLATION (OPTION 1)....................................................................3-13
FIGURE 3-11. ANTENNA INSTALLATION (OPTION 2)....................................................................3-14
FIGURE 3-12. CMI ASSEMBLY REAR VIEW................................................................................3-15
FIGURE 3-13. CMI TEST POINT ACCESS AND SUBASSEMBLY LAYOUT.........................................3-17
FIGURE 3-14. TYPICAL HUB CONTROL PANEL DIALOG .........................................................3-19
FIGURE 3-15. TYPICAL HIC CONTROL PANEL DIALOG...........................................................3-21
FIGURE 3-16. TYPICAL ADD CMI DIALOG.................................................................................3-22
FIGURE 3-17. TYPICAL CMI CONTROL PANEL DIALOG ..........................................................3-25
FIGURE 4-1. SECTOR DEDICATED TO TRANSCELL 1900CB WITH EQUAL TIMING LINKS .................4-2
FIGURE 4-2. SECTOR DEDICATED TO TRANSCELL 1900CB WITH UNEQUAL TIMING LINKS .............4-5
FIGURE 4-3. TOWER SECTOR SPLIT WITH TRANSCELL 1900CB - TIMING EQUAL..........................4-6
FIGURE 4-4. TOWER SECTOR SPLIT WITH TRANSCELL 1900CB - TIMING UNEQUAL.....................4-8
FIGURE 4-5. TYPICAL FORWARD LINK LEVELS; SINGLE CARRIER ...............................................4-10
FIGURE 4-6. TYPICAL FORWARD LINK LEVELS; THREE CARRIER ................................................4-10
FIGURE 4-7. TYPICAL REVERSE LINK LEVELS; SINGLE CARRIER.................................................4-11
FIGURE 4-8. TYPICAL REVERSE LINK LEVELS; THREE CARRIER .................................................4-11
FIGURE 4-9. HIC CONTROL PANEL: DIALOG.........................................................................4-12
FIGURE 4-10. HIC REAR PANEL...............................................................................................4-13
FIGURE 4-11. RFIA REAR PANEL.............................................................................................4-14
FIGURE 4-12. HIC FORWARD POWER DIALOG.....................................................................4-17
FIGURE C-1. RF INTERFACE PLATE ASSEMBLY .......................................................................... C-3
LIST OF TABLES
iv
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
Table Page
TABLE 2-1. ENCLOSURE INSTALLATION TOOLS AND TEST EQUIPMENT ..........................................2-1
TABLE 2-2. HUB EQUIPMENT ENCLOSURE ASSEMBLY INSTALLATION KIT.......................................2-2
TABLE 3-1. CMI INSTALLATION SUPPORT NEEDS ........................................................................3-1
TABLE 3-2. CMI CONFIGURATIONS.............................................................................................3-2
TABLE 3-3. OPTIONAL TRANSCEPT-FURNISHED ITEMS FOR CMI INSTALLATION.............................3-2
TABLE 3-4. CUSTOMER-FURNISHED ITEMS FOR CMI INSTALLATION..............................................3-3
TABLE 3-5. CMI EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS .................................................................................3-5
TABLE 4-1. SEARCH WINDOW SIZES ..........................................................................................4-4
TABLE 4-2. RECOGNIZED ALARM LIST.......................................................................................4-18
v
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
♦ High leakage current: The Hub rack, internal or external (environmental) enclosure
must be connected to Protective Earth ground before any connection is made to +24
VDC prime power.
♦ High Voltages (110/220 VAC and 24 VDC) are present within the Hub rack or
environmental enclosure. Use extreme caution when working inside the
rack/enclosure.
♦ High voltages may exist close to the CMI location; use standard electrical industry
safety practices when working on an installed CMI.
♦ High voltages (110/220 VAC RMS) exist on the AC power input to the CMI. Use
extreme caution when removing the AC power cable to avoid coming in contact with
the center conductor.
♦ Laboratory tests conducted in accordance with ANSI/IEEE C95.1-1992 show that a
transmitting CMI poses no radiation hazard to persons in close proximity to the
transmitting antenna. However, for added safety when working near a CMI,
maintain a minimum distance of 12 inches from the transmitting antenna.
ESD CAUTION
The CMI contains circuit card assemblies that are sensitive to
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) damage. Whenever handling the CMI, use
ESD precautionary procedures to minimize the risk of permanent ESD
damage to circuit card components. Low relative humidity level increases
the potential for damage to ESD-sensitive devices.
FCC License Data
The CMI is licensed by the Federal Communications Commission for operation in the
frequency band as noted on the product label affixed to the CMI Chassis.
National Recognized Test Laboratories (NRTL) Data
Cable Microcell Integrator (CMI), Models 1000000G1-33, 1000501G1-6, 1000601G1-33, and
1000701G1-6: Listed as Communications Service Equipment NRTL 1950
Hub Equipment Racks (Models 1000023P1 and 1000025P1) with the Hub Interface
Converters (Models 1000604G1-3 and 8334760G1-3) and Hub Control Unit Model
(1000015P1): Basic Listing as Information Technology Equipment, Complementary
Listing as Professional Video Equipment
vi
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 SCOPE
This manual contains installation and checkout instructions for the components of the
TransCell 1900CB system. The TransCell 1900CB system provides the means to distribute
wireless Personal Communications Services (PCS) telephony signals encoded with the
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) protocol over fiber or coaxial cable infrastructures.
This manual addresses the TransCell 1900CB installation for both fiber and coaxial
networks, and for both indoor and outdoor Hub equipment, distinguishing the unique
requirements for each case as needed. The manual is organized as follows:
♦ Section 1, Introduction - terminology definitions, brief descriptions of the TransCell
1900CB system and its major components
♦ Section 2, Hub Indoor/ Outdoor Rack Installation - installation and checkout of the
Hub Equipment (HE) rack configurations; installation of the Hub Control Unit
(HCU), and the Hub Interface Converter (HIC)
♦ Section 3, CMI Installation - Cable Microcell Integrator (CMI) installation and
checkout of the outside cable network at selected remote locations in the service
area
♦ Section 4, BTS Interface and Network Optimization - measurement and adjustment
procedures for optimal integration of the TransCell 1900CB system with the Base
Transceiver Stations (BTS), with variations according to BTS manufacturer
♦ Appendix A, Radio Frequency Interface Unit (RFIA) Installation - installation of the
RFIA, to provide a cable transition at the HIC, provide a stable 10 or 15 MHz
reference signal for the HICs in the primary or expansion racks and the duplexing
of signals between the HICs and the BTS
♦ Appendix B, PCS channel-number-to-frequency cross-reference table
♦ Appendix C, HIC Channel Number-to-frequency cross-reference table
1-1
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.2 TERMINOLOGY, ACRONYMS, AND ABBREVIATIONS
1.2.1 TransCell 1900CB Terminology
The following words and phrases are used throughout this manual when referring to signal
flow over the fiber/cable network, between the subscriber’s PCS handset and the wireless
telephony network’s BTS:
♦ Forward Link – direction of the fiber/cable network from the HIC to the CMI,
supporting communications from the BTS to subscriber units.
♦ Forward Path - the physical/electrical path for forward link signals
♦ Reverse Link – direction of the fiber/cable network from the CMI to the HIC,
supporting communications from subscriber units to the BTS.
♦ Reverse Path - the physical/electrical path for reverse link signals
1.2.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations
AWG American Wire Gage NOCC Network Operation Control Center
BTS Base Transceiver Station NRTL National Recognized Test Lab
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access OA&M Operation, Administration, and
Maintenance
CMI Cable Microcell Integrator PCS Personal Communications Services
CRT Cathode Ray Tube PEGND Protective Earth Ground
Ctl Control PN Pseudo Noise
EIA Electronic Industries Association POTS Plain Old Telephone Service
ESD Electrostatic Discharge RBW Resolution Bandwidth
FCC Federal Communications Commission RCV Receive
FWD Forward (BTS to Subscriber) Ref Reference
HCU Hub Control Unit REV Reverse (Subscriber to BTS)
HE Hub Equipment RFIA Radio Frequency Interface Assembly
HFC Hybrid Fiber Coax Infrastructure RTN Return
HIC Hub Interface Converter Rx Receive
IF Intermediate Frequency SMIU Sector Management Interface Unit
kbps Kilobits Per Second Tx Transmit
LED Light Emitting Diode UL Underwriters Laboratories
MHz Megahertz XMIT Transmit
1-2
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.2.3 Notation Conventions in this Manual
This manual assumes that the user has a basic knowledge of the Windows NToperating
system. Several typographic conventions and standard Windows NT terms are used in
this manual when discussing the TransCell Network Manager software. They are as
follows:
Mouse Commands - The TransCell Network Manager software uses only the left mouse
button:
♦ “click” - press and release the left mouse button
♦ “double-click” - press and release left mouse button twice in quick succession
Menu Commands - Menu commands are bolded with each command level separated from
the previous one by a slash (/) mark, e.g., “Select Privileges/Modify Privileges.”
Button Names – Command button names in dialogs are underlined, e.g., “To confirm
selection, click OK.”
Key Names - Key names are spelled out and appear in small, bold capital letters, e.g.
ENTER, ESCAPE, AND CONTROL.
Dialogs and Messages - Dialog and message titles appear in all upper case (capital) letters,
and generally the name is referenced exactly as shown on the title bar, e.g., the PCS
FREQUENCY dialog. However, in cases where the dialog title varies according to privilege
level, enclosure, or sector, the title is shortened to exclude this variable information unless
the variable is important. If a dialog title is referenced that includes a specific HIC or CMI
number, the number is represented by the bracketed letter n: e.g., CMI CONTROL
PANEL: ALPHA SECTOR, CMI [n].
Dialog Options - Dialog options (text boxes and radio buttons) are shown in italics, e.g.,
“Type in the desired PCS Frequency.” All instructions to “select” or “choose” an option
imply clicking on that option, although options can be selected via the keyboard as well.
Keyboard Input - Instructions for keyboard entries start with “Type in...”, and anything
that should be typed in verbatim is shown in a contrasting font. For example, “Type in
config01.dtb in the File Name box.”
Displayed Text - Text displayed in a dialog box is shown in another contrasting font, e.g.,
“The CONFIGURATION OPTIONS dialog displays the query “Do you Want To Restore
a Pre-existing Configuration?”.
1.3 REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION
♦ Hub Control Unit (HCU)-associated vendor hardware/software documentation
(Computer, Monitor, Watchdog Timer, etc.) Transcept Document No. 1000015P1
♦ TransCell 1900CB System Acceptance Test Procedure Requirements, Transcept
Document No. 1000095
♦ Mobile Station-Base Station Compatibility Std for Wideband Spread Spectrum
Cellular Systems, TIA/EIA-95-B
1-3
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
• Fiber/
Coaxial Infrastructure
MOBILE
MOBILE
• Fiber/
Coaxial
infrastcr.
1.4 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The TransCell 1900CB system permits the transport of CDMA PCS signals between a Base
Transceiver Station (BTS) and mobile users over fiber/coaxial cable infrastructures. The
cable network (fiber, coax, or hybrid) is used to distribute the PCS signals between the
cable Hub or hub facility and attached remote locations throughout the service area.
The TransCell 1900CB system has four primary components: Cable Microcell Integrator
(CMI), Hub Interface Converter (HIC), RF Interface Assembly (RFIA), and Hub Control
Unit (HCU) and two fiber optic peripherals: Hub Fiber Interface (HFI) and Remote Fiber
Interface (RFI). The HICs and CMIs provide the carrier frequency translation and signal
conditioning needed for the CDMA signal (single carrier or three-carrier) interfaces
between mobile user, BTS, and fiber/coaxial network. The HCU provides the operation,
administration, and maintenance (OA&M) functions for the system. The RFI and HFI
provide the conversion between light and RF energy.
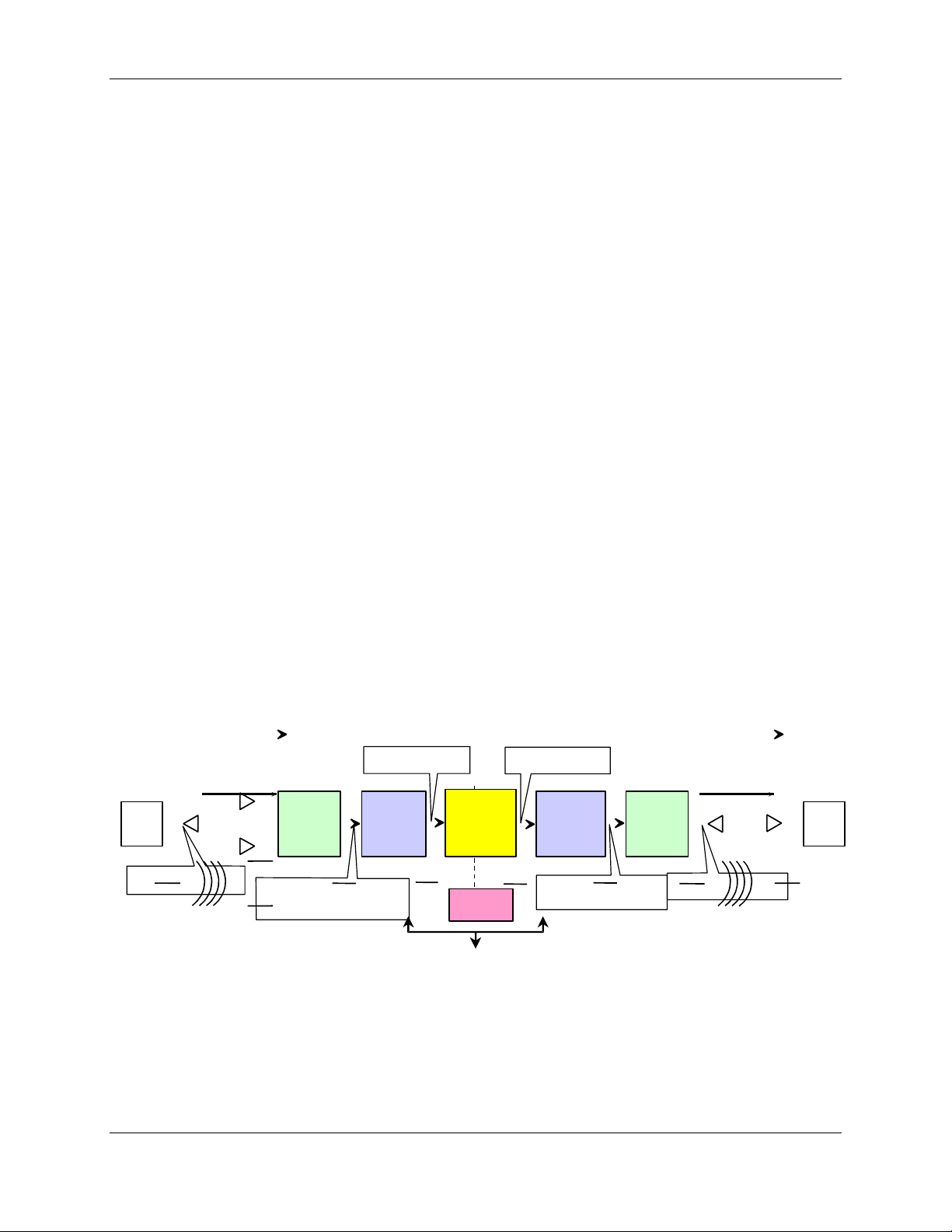
As shown in Figure 1-1, in the reverse path a CMI at a remote location receives a CDMA
signal from a mobile PCS unit via the receive antennas, converts its PCS carrier frequency
to an IF frequency and sends the signal to the associated HIC at the Hub. The HIC
converts the signal carrier back to the PCS frequency and routes the signal to the BTS. The
BTS then switches the signal into the telephone network.
In the forward path, the process is inverted. The HIC receives the CDMA signal from the
BTS, translates the carrier frequency to an IF frequency and sends the signal to the CMI.
The CMI translates the signal carrier back to the PCS frequency, amplifies the signal, and
radiates it via the transmit antenna for capture by the mobile PCS unit. One HIC provides
the BTS interface for up to three CDMA sectors and may control as many as 30 CMIs.
The HICs and CMIs normally handle the transport of PCS traffic over the fiber/coaxial
network without assistance from the HCU. The HCU is used to set up frequency,
attenuation, and fault reporting parameters and to change those parameters as needed. In
normal operation, the HCU allows operators to monitor system operational status and
alarms.
CONNECTION
TO
TELEPHONE
REVERSE FORWARD
• 1850 to 1910 MHz
• CDMA
HIC
REVERSE
LINK
PCS
UNIT
• 1850 to 1910 MHz
• Band Specific Filters
CMI
PCS
RECEIVE
FUNCTION
• Basic - 5 to 52 MHz
NETWORK
BASE
TRANSCEIVER
STATION
(BTS)
HCU
• 1930 to 1990 MHz
• CDMA
HIC
FORWARD
LINK
• 450 to 750 MHz
CMI
PCS
TRANSMIT
FUNCTION
• 1930 to 1990 MHz
• Band Specific Filters
PCS
UNIT
Figure 1-1. TransCell 1900CB System Functional Block Diagram
1-4
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
For installations with existing environmentally controlled indoor Hub or hub facilities, the
typical TransCell 1900CB configuration consists of up to three Hub Equipment (HE)
enclosures stacked, containing a HCU, three Hub Fiber Interface Units (HFIs), three RF
Interface Assemblies (RFIAs), and three HICs. Additional enclosures may be purchased
when more than three HICs are required at a given site. Each HIC is connected to several
CMIs which are installed on the outside fiber/coaxial network.
For ruggedized outdoor installations, the HCU and HICs are housed in an outdoor
environmental controlled enclosure.
Either the indoor or outdoor system installation may also include a network interface unit
to remote the HCU for centralized monitoring and control of PCS network operation.
1.4.1 Hub Equipment (HE) Enclosure Configurations
The HE enclosure contains these major components:
♦ Hub Control Unit (HCU)
♦ RF Interface Assembly (RFIA)
♦ Hub Interface Converters (HICs)
♦ Hub Fiber Interface Unit (HFI) (Optional)
♦ +24 VDC Power Supply (Optional)
There are three stackable enclosure configurations available. One enclosure houses the
HCU (PC, Monitor, and Keyboard). The second enclosure houses an RFIA, HIC, HFI
(optional), Power Supply (Optional), and a network interface box (remote configuration
only). The third enclosure houses two RFIAs, two HICs, and two HFIs (Optional). Section
2 of this manual contains a detailed assembly list for each enclosure configuration. The
following paragraphs describe the major assemblies that are normally installed in the
configurations along with some optional assemblies.
1.4.1.1 Hub Control Unit (HCU)
The HCU is installed in one Hub equipment enclosure. A single HCU supports up to 26
HICs. The HCU may also be installed in a central location (NOCC) and remoted to an
outside enclosure. This configuration is used for those installations in uncontrolled
environments. The major HCU hardware components are:
♦ Computer chassis
♦ Color CRT Monitor
♦ Keyboard/Touchpad/Mouse
The HCU is the monitoring and control device for the attached HIC units and their
assigned CMIs. It monitors various system parameters to verify that these units are
operational and that signal power is being maintained at the proper levels. The HCU
communicates with the HICs over an RS-485 interface via a LonWorks® card located in the
computer, and through the HICs it communicates with the CMIs. The HCU interprets all
faults reported by the HICs and CMIs into alarms, which are logged and displayed. The
computer also contains one or more modems for remote monitoring and control of the HCU
located at a central control point.
1-5
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
The major HCU software components are:
♦ Microsoft® Windows NT
♦ pcANYWHERE Version 8.0 or later (optional)
♦ TransCell Network Manager software
♦ Software drivers for custom HCU functions
1.4.1.2 RF Interface Assembly (RFIA)
The RFIA provides a transition from the larger and more rigid cables from the BTS and
cable plant to smaller and more flexible cables for connecting the HICs. It also provides a
stable 10 or 15-MHz reference signal for the HICs.
Depending on the site requirements these RFIA configurations provide duplexing of the RF
signals between the HIC and the BTS and the cabling between the HIC and HFI or
Fiber/Coaxial Network. One RFIA is required for each HIC installed in the enclosure(s).
Each RFIA requires +24 VDC for operation. For more detailed description and installation
instructions, see Appendix A.
1.4.1.3 Hub Interface Converter (HIC)
The HIC is the direct interface between the RFIA and Fiber/Coaxial network. It processes
up to three forward link sector of CDMA PCS signals (single carrier or three carriers) and
up to three pairs of diversity reverse link CDMA PCS signals (single carrier or three
carriers). The HIC converts the PCS frequencies from the BTS to an intermediate
frequency (IF) suitable for transmission over fiber/coaxial cable to its associated CMIs, and
it converts the IF signals from the CMIs to PCS frequencies for the BTS. The HIC uses
rear panel connectors to interface with the RFIA and HFI or coaxial cable network. Each
HIC supports up to 10 CMIs on each of three CDMA sectors (up to 30 CMIs total per HIC).
The HIC assigns each CMI its frequency and gain levels.
Each HIC consists of two-circuit card assemblies that contains the components for the
three sector interfaces and the digital circuitry. A DC-operated fan cools the HIC by pulling
air into the front and exhausting the air via the rear side panels.
1.4.1.4 Hub Fiber Interface (HFI)
The HFI is an interface unit that converts IF CDMA signals to/from light and interfaces
the HIC with the fiber network. The HFI contains three independent fiber optic
transceivers that may be configured to support multiple fiber optic networks. Typical
configurations are one HFI per HIC since one sector is typically designated to a
geographical area and each HIC supports three sectors. The HFI power source
requirements is +24VDC. Each fiber optic transceiver unit contains a separate laser on/off
lockable switch located on the front panel of the unit.
1.4.1.5 Cable Assemblies
Cable assemblies provided with each enclosure interconnect the installed assemblies
within the enclosure. Cable assemblies are not provided for external interconnection
between the enclosure and BTS or fiber/cable network. Refer to Section 2 for a list of cable
assemblies provided with each enclosure configuration.
1-6
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.4.1.6 Equipment enclosure
The indoor and outdoor equipment enclosure is a standard EIA design that holds and
secures standard 19-inch-wide enclosure-mounted assemblies. The equipment enclosure
dimensions are:
Indoor Enclosure Outdoor Enclosure
♦ Height 24 inches 39 inches (minus lift brackets)
♦ Depth 25 inches 26 inches
♦ Width 20 inches 24 inches
1.4.1.7 +24 VDC Power Supply Assembly (Optional)
For installation sites where an external +24 VDC prime power source is unavailable, an
optional +24 VDC Power Supply is available for enclosure installation. The +24 VDC Power
Supply operates on either 110 or 220 VAC. The +24 VDC Power Supply will be used to
power all three of the HICs installed in an enclosure.
1.4.2 Remote Fiber Interface (RFI)
The RFI is a fiber node. The unit contains a fiber optic transceiver and an AC
(110/220VAC) to DC power supply. The RFI resides at the demarcation point, between the
Hub HFI and a network of Coaxial CMIs, where the fiber no longer is available and coaxial
cable must be extended to the CMIs.
1.4.3 Cable Microcell Integrator (CMI)
The CMI is the communications link between the PCS handset and the fiber/cable network.
It processes a single forward link and single pair of diversity reverse link CDMA PCS
carriers (single carriers or three-carriers). Each CMI is controlled by its assigned HIC. The
CMI is comprised of the following major hardware assemblies:
♦ Power Extractor - routes the tapped coaxial IF CDMA signals to/from the RF
Transceiver in a coaxial CMI.
♦ Internal Fiber Interface – converts light to/from the IF frequencies to/from the RF
transceiver in a fiber CMI.
♦ Transceiver - responds to control messages from the assigned HIC and converts the
CDMA signals to the appropriate transmission frequencies.
♦ Power Amplifier - enabled/disabled by the assigned HIC; boosts the CDMA signal
sent to the PCS handset via an antenna.
♦ Power Supply - converts the 110/220VAC power to the DC voltages required by the
Transceiver, Internal Fiber Interface, and Power Amplifier.
♦ CMI Housing Assembly - environmentally sealed fireproof enclosure for all of the
four CMI assemblies.
♦ Antennas – one transmit and two receive, typically omnidirectional. Antennas are
optionally available from Transcept, depending on customer preference.
1-7
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.4.3.1 Power Extractor
The CMI Power Extractor is available in two configurations:
♦ Single (or Combined) Mode, Sub-Split: Basic frequency range - 5 to 42 MHz
♦ Single (or Combined) Mode, Mid-Split: Extended frequency range - 5 to 52 MHz
The Power Extractor routes the following signals:
♦ Reverse link signals from the Transceiver module, 5 to 42 MHz (basic) or 5 to 52
MHz (extended)
♦ Forward link signals to the Transceiver module, 450 to 750 MHz
NOTE
References to reverse link frequency range in this manual imply a range of 5
to 52 MHz. However, if a single mode sub-split (basic) Power Extractor
module is installed in a CMI, the range for that CMI will be 5 to 42 MHz.
The relationship between the Power Extractor configuration and the way in which the CMI
is electrically connected to the coaxial cable is as follows:
♦ The Single Mode is configured to operate with both the forward and reverse link
signals on a single interface port (FWD/REV). The CMI is configured in this mode
by installing the Single Mode, Sub-Split (basic frequency range) or the Single Mode,
Mid-Split (extended frequency range) Power Extractor module.
The Power Extractor accommodates field-replaceable, plug-in attenuator pads for both the
forward and reverse paths, and a field-replaceable, plug-in equalizer (should be zero for
typical installations) in the forward path. These component locations are accessible when
the CMI housing cover is open, without the need to remove the Power Extractor. The CMI
is shipped with no pads or equalizer installed. It will accept Scientific Atlanta model
numbers PP-0 to PP-10 attenuator pads, or equivalent, and Scientific Atlanta model
number EQ750 equalizers, or equivalent.
1.4.3.2 Internal Fiber Transceiver
The Internal Fiber Transceiver converts 1310nm-laser light to IF energy that feeds the RF
Transceiver in the forward direction. In the reverse direction, the unit converts IF energy
from the RF Transceiver to 1550nm light (2mW max). The power interface to the Internal
Fiber Interface is DC power coming from the power supply. The fiber optic cable is
connected to the fiber network via a coupler and passes through a housing interface and
connected directly to the Internal Fiber Transceiver.
1-8
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.4.3.3 Transceiver
The Transceiver contains a dual receiver and a transmitter, and incorporates both analog
and digital signal processing and control. Reverse link RF signals, originating in the PCS
wireless domain, are received by both the primary and diversity receivers, processed and
sent, via the coaxial/fiber network, to a Hub location. Forward link signals, originating at
the Hub, travel via the coaxial/fiber network to the CMI where they are processed by the
transmitter and sent to the Power Amplifier.
The Transceiver has four LED indicators on its outer surface, clearly visible when the CMI
cover is open. One LED is normally lit to indicate presence of +5 VDC power, while the
other three are normally unlit. These three LEDs light only to indicate particular
Transceiver fault conditions. The Transceiver is available in three different PCS frequency
band sets (A/D, B/E, C/F) (see Table 3-2); the desired band set is selected at the time of
order.
1-9
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
1.4.3.4 Power Supply
The Power Supply requires a 110/220VAC, 50/60-Hz voltage input. It produces four DC
voltages, +25V, +15V, +5V, and -15V, for use by the Transceiver and Power Amplifier. For
overcurrent protection, the Power Supply AC input is fused. The fuse is accessible with the
power supply cover removed.
1.4.3.5 Power Amplifier
The Power Amplifier operates in one of three 20-MHz pass bands corresponding to the
selected Transceiver frequency band for a single carrier CMI. For a multi-carrier (three)
unit, the power amplifier covers the entire 60MHz pass band. Power Amplifier parameters
include:
• Gain Approximately 60 dB
• Power Output +35.0 dBm/+39.0dBm max
• Power Output Dynamic Range 15 dB minimum
1.4.4 CMI Antennas
The CMI requires three antennas for operation: two receive and one transmit. For typical
aerial operation, 6-dBi gain antennas, approximately 8 inches in length, are used. The
receive antennas are installed on brackets and extend below a messenger strand. The
transmit antenna is installed on a bracket and extends above a messenger strand. A
separation of six feet between the diversity receive antennas is recommended to achieve
reasonable spatial diversity. The use of the 6-dBi gain antennas with a minimum transmitto-receive antenna distance of 36 inches will achieve the required transmit-to-receive
antenna isolation in excess of 40 dB. See the paragraph 3.3.5.2 for installation procedures.
1.4.5 Outdoor Enclosure Unit)
The outdoor enclosure configuration is a ruggedized equivalent of an indoor enclosure
without the HCU, used for installation in uncontrolled environments. The enclosure
accommodates a network interface unit, HIC, an RFIA (timing reference source), a
+24VDC power supply (optional), and a heating/cooling unit. All modules in the enclosure
are either rack mountable or mounted on 19-inch trays. The maximum footprint of the
pedestal is 24 x 26 inches. The maximum height of the cabinet is 45 inches (including lift
brackets). The enclosure conforms to NEMA 3R requirements.
1-10
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
SECTION 2
HUB ENCLOSURE INSTALLATION
2 HUB PRIMARY/EXPANSION RACK INSTALLATION
This section describes the installation of the Hub equipment and their constituent
components. Most of the component installation procedures are identical between the
indoor and outdoor configurations; differences are stated in the installation procedures.
2.1 INSTALLATION TASKS
Installing the Hub equipment involves the following major tasks:
♦ Preparing space for the individual enclosure
♦ Installing equipment in the enclosure
♦ Installing interconnecting cables in the rack
♦ Installing interconnecting cables between equipment and fiber/coaxial network
♦ Installing interconnecting cables between equipment and BTS
♦ Installing interconnecting cables between HIC and HFI
♦ Installation checkout
2.2 TOOLS, TEST EQUIPMENT, AND SUPPLIES
Table 2-1 lists the tools and test equipment needed (but not supplied) to support the
enclosure installation.
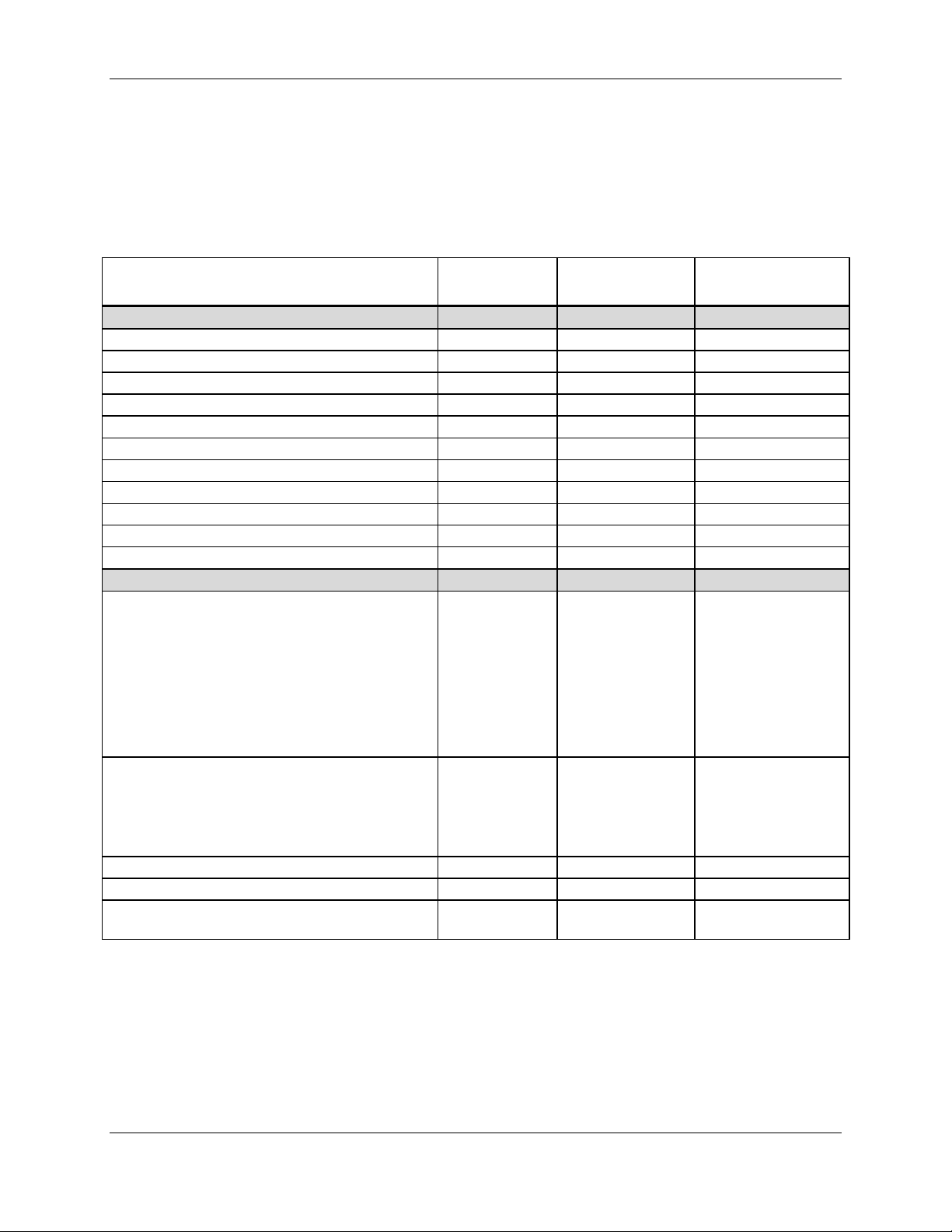
Table 2-1. Enclosure Installation Tools and Test Equipment
Hand Tools Test Equipment
• Philips Screwdriver # 2 head • Hand-held Digital Multimeter with test probes
• Flat Blade Screwdriver # 2 head • Spectrum Analyzer, HP 8593 or equivalent
• Wrench, 5/16 inch
• Wrench, 7/16 inch
• Wrench, 3/8 inch
• Nut Driver ¼ inch
• Tape Measure
• Torque Wrenches
• Cable Tie Installation Tool, Panduit GS2B,
or equivalent
2-1
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.3 INSTALLATION PARTS LIST
Table 2-2 lists the typical parts shipped for each Hub installation. Before proceeding with
the installation, inventory the kit contents to ensure all parts are present for the applicable
installation.
Table 2-2. Hub Equipment Enclosure Assembly Installation Kit
Indoor Enclosure
Assembly Item Part No.
Equipment enclosure
Indoor Hub Enclosure 1000023P1 Up to 3
Outdoor Hub Enclosure 1000025P1 1
Hub Enclosure Stacking Kit 1000059G1 Up to 2
Hub Enclosure Cable Kit 1000064G1 Up to 3 1
Hub Power Supply Assembly (Optional) 1000056G1 1 (Optional) 1 (Optional)
Communications Harness 1000063G1 1 1
Cable ties, 12 inches long PLT3S-C 12 12
Cable ties, 5.25 x 3.32 inches SST1.5I-C 10 2
Cable Tie Mount, Self Adhesive ABMM-AT-C 2 2
Cable Clamp, 3/8”, Nylon NAS1397P6N 5 2
Busbar Assembly P/O Enclosure Up to 3 1
Equipment
Hub Control Unit (HCU) Assembly
Computer, Pentium
Monitor, 14-inch color
PS/2 Keyboard with Touchpad,
Computer Power Cord
Monitor Power Cord
Rack Mounting Brackets
Windows NT, Version 4.0
PcANYWHERE, Version 8.0 (Optional)
Hub Interface Converter (HIC) 1000604G1,G2,
Hub Fiber Interface (HFI) (Optional) 1000014P2 Up to 3 (Optional) 1 (Optional)
Hub Power Supply Assembly (Optional) 1000056G1 1 (Optional) 1 (Optional)
RF Interface Assembly (RFIA) 1000035G1,G2,
1000022G1 1 N/A
or G3
OR
8334760G1,G2,
or G3
G3
1000023P1
Up to 3
OR
Up to 3
Up to 3 1
Outdoor Enclosure
8339254G1
1
2-2
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.4 POWER REQUIREMENTS
Both the indoor and outdoor enclosures require external 110/220 VAC, single phase, 50/60
Hz with use of power supply and HCU, or +24 VDC for prime power.
2.4.1 Typical Prime Power Requirements
When both 110/220 VAC, single phase, 50/60 Hz and +24 VDC are available at the
installation site, an enclosure with 3 HICs/HFIs installed requires approximately 8
amperes of +24 VDC power. The HCU requires approximately 2.0 amperes of 110 VAC,
50/60 Hz (or approximately 1.0 ampere of 220 VAC, 50/60 Hz), single phase power.
2.4.2 Protective Earth Grounding
The Hub Equipment Enclosures must be properly grounded to protect installers and
operators from electrical shock. For this purpose there are two-1/4 in. x 20 ground studs
located on the left and right rear of the enclosure floor panel. These studs are used to
ground the internal components to the enclosure and to connect the enclosure to the site
ground. The site grounding cable should consist of UL-approved wire of no less than 14
gauge. The wire should attach to one of the ground stud by means of a properly sized ring
terminal. The enclosure is supplied with a split washer and a 1/4-in. x 20 nut to secure the
grounding cable ring terminal to the stud.
2.5 HUB EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION AND SPACE REQUIREMENTS
2.5.1 Suggested Floor Space Requirements
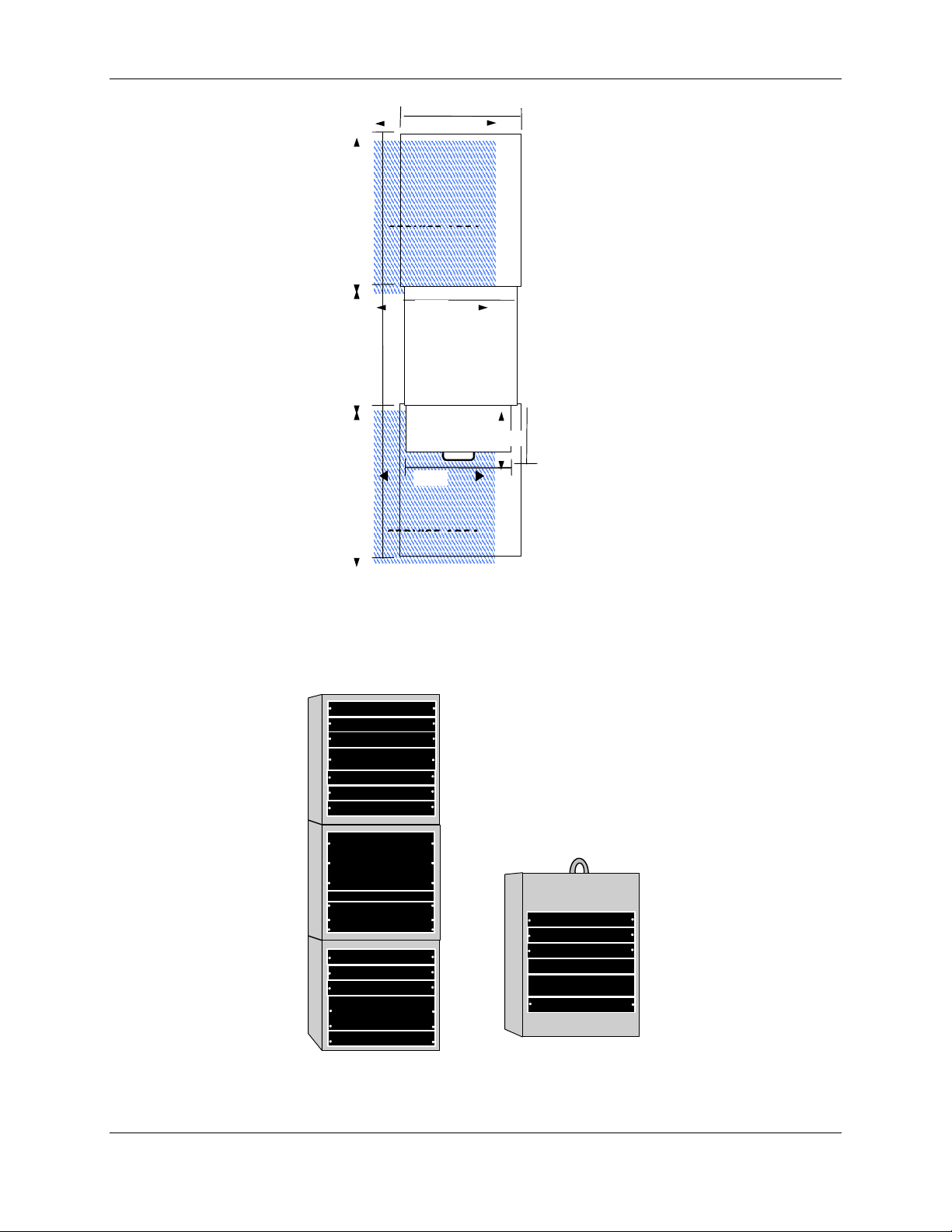
Figure 2-1 shows the suggested floor space to support the Indoor Hub Equipment enclosure
installation, operator workspace, and service area.
2.5.2 Floor Loading Requirements
In order to safely support the weight of a fully loaded enclosure unit, the floor of the
installation site must be rated for a load of 150 pounds per square foot or more .
2.5.3 Typical Enclosure Configuration
Figure 2-2 shows a typical enclosure configuration as it appears before installation of the
rack-mounted assemblies. The indoor enclosure configurations use the same enclosures
and are stackable up to three high. Each individual enclosure is 24 inches high, 25 inches
deep, and 20 inches wide (outside dimensions). A minimum of 36 inches of clear space
behind the enclosure is recommended for servicing and proper ventilation. The HCU
contains an extendable keyboard tray, which adds another 36 inches of clearance
requirement in front of the enclosure for operator workspace. The enclosures are bolted
together via the “Hub Enclosure Stacking Kit; PN 1000059G1” and it is recommended that
the enclosure be bolted to the floor.
2-3
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
SUGGESTED
SUGGESTED
Monitor
Computer
HIC
RFIA
HFI
Blank
HIC
RFIA
HFI
HIC
RFIA
HFI
Blank
HIC
RFIA
HFI
Network I/F Unit
Blank
24 IN.
36 IN.
26 IN.
Hub Enclosure
PULL-OUT KEYBOARD
TRAY WITH TOUCHPAD
36 IN.
NOTES
1. Suggested work area for installation
2. Suggested work area to support
1
20 IN.
12 IN.
17 IN.
2
and maintenance
installation and operation
Figure 2-1. Recommended Hub Equipment Floor Space
Keyboard
Power Supply (Optional)
Power Supply (Optional)
Indoor Unit
Outdoor Unit
Figure 2-2. Typical Enclosure Configuration
2-4
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6 INSTALLATION OF ASSEMBLIES IN EQUIPMENT ENCLOSURE
Paragraph 2.6.1, Indoor and outdoor enclosure installation, provides step-by-step
instructions for installing hardware assemblies, cables, wiring, etc.
2.6.1 Hub Enclosure Installation
For installation sites that do not provide an external +24 VDC power source, an optional
internal +24 VDC Power Supply, part number 1000056G1, must be installed in the
enclosure. If an external +24 VDC power source is available, skip to paragraph 2.6.1.2.
2.6.1.1 Hub +24 VDC Power Supply Installation
If the +24 VDC Power Supply has been procured as an option, install as follows:
a. Connect Power Supply Input Cable (supplied with unit) to an AC outlet/source as
follows:
Black wire to Line AC (L1) terminal
White wire to Neutral AC (L2) terminal
Green wire to ground terminal
b. Verify polarity of wires, then connect ring terminal ends of Power Supply Output
Cable P/N 1000056G1 to V1 (+) and (–) terminals.
NOTE
See 2.6.1.3 for connecting the output of the +24 VDC Power Supply to the
Prime Power Panel.
c. Connect ring terminal of PEGND cable P/N 1000060G1 to ¼-inch ground stud on
back of the +24 VDC Power Supply.
d. Install +24 VDC Power Supply into rack in the bottom of the lower enclosure unit.
e. Secure +24 VDC Power Supply to rack with two 10-32 in. x 0.50 screws and
washers.
f. Connect FASTON connector of PEGND cable to PEGND leg of busbar at a position
adjacent to +24 VDC Power Supply.
g. Ensure that input power switch on the Power Supply is off, before connecting power
to Power Supply.
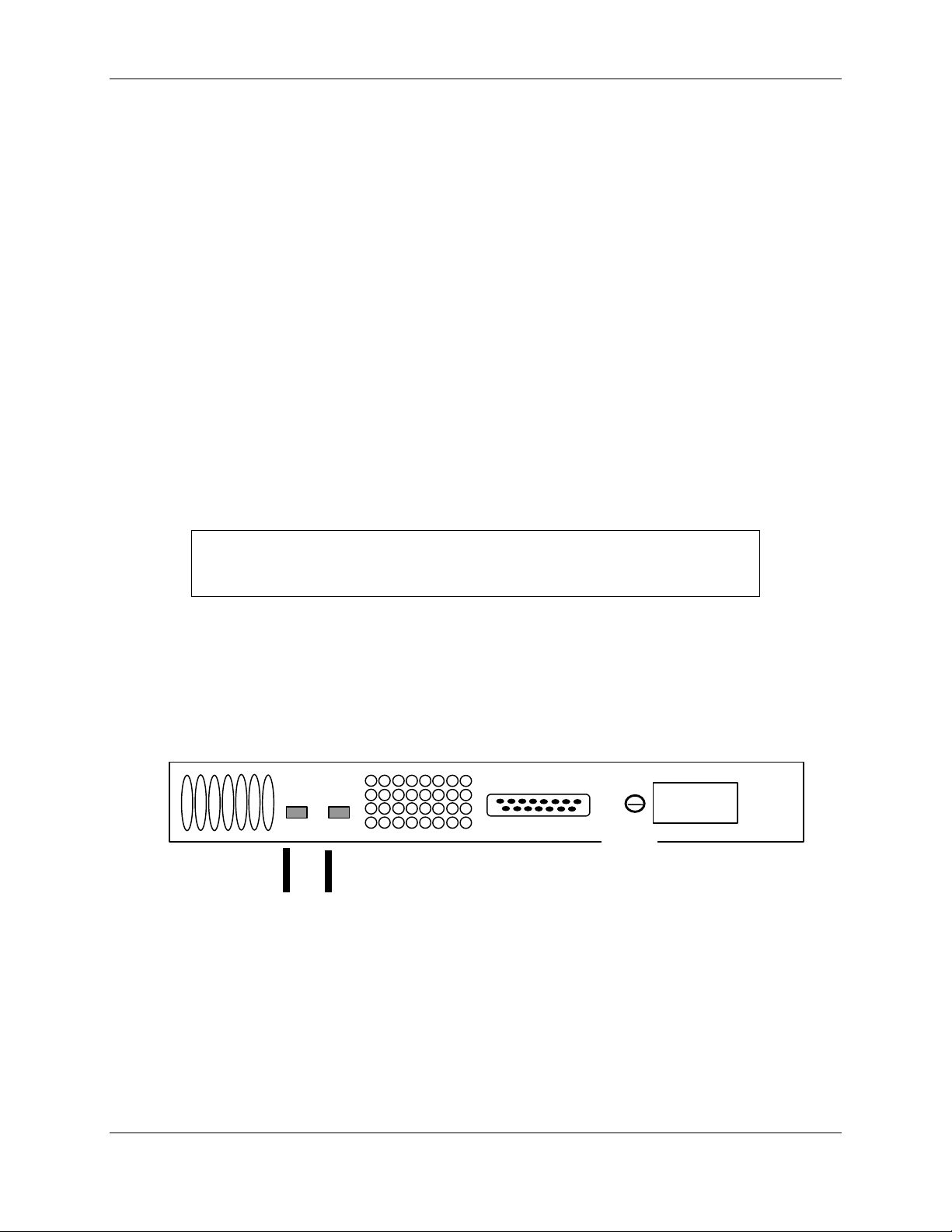
DC Terminals
GND
AC
Terminals
Figure 2-3. +24 VDC Power Supply Rear Panel
2-5
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6.1.2 Hub Control Unit (HCU) Installation
The HCU, Keyboard, and Computer will take up one entire enclosure. For the outside
enclosure, these items are replaced with a network interface unit (PN 1000057G1) and the
HCU is remote from the outside enclosure. The following procedure is for the indoor
enclosure configuration.
NOTE
Both fixed and sliding sections of the keyboard slides are installed in the rack
at the factory. As part of the HCU installation, the sliding (keyboard tray)
section of each slide is removed from the rack and installed on the keyboard
tray.
a. Using a short cable tie, secure both touchpad cable and keyboard cable to cable tie
mount at rear of left slide.
b. Using six short cable ties, secure both touchpad cord and keyboard cable along
length of cable retractor. Do not over-stretch keyboard cable coils.
c. Locate two HCU rack-mounting brackets packed with HCU software media.
d. Remove hardware from bracket mounting holes on left and right sides toward front
of computer.
e. Using hardware removed, attach two brackets to chassis and tighten.
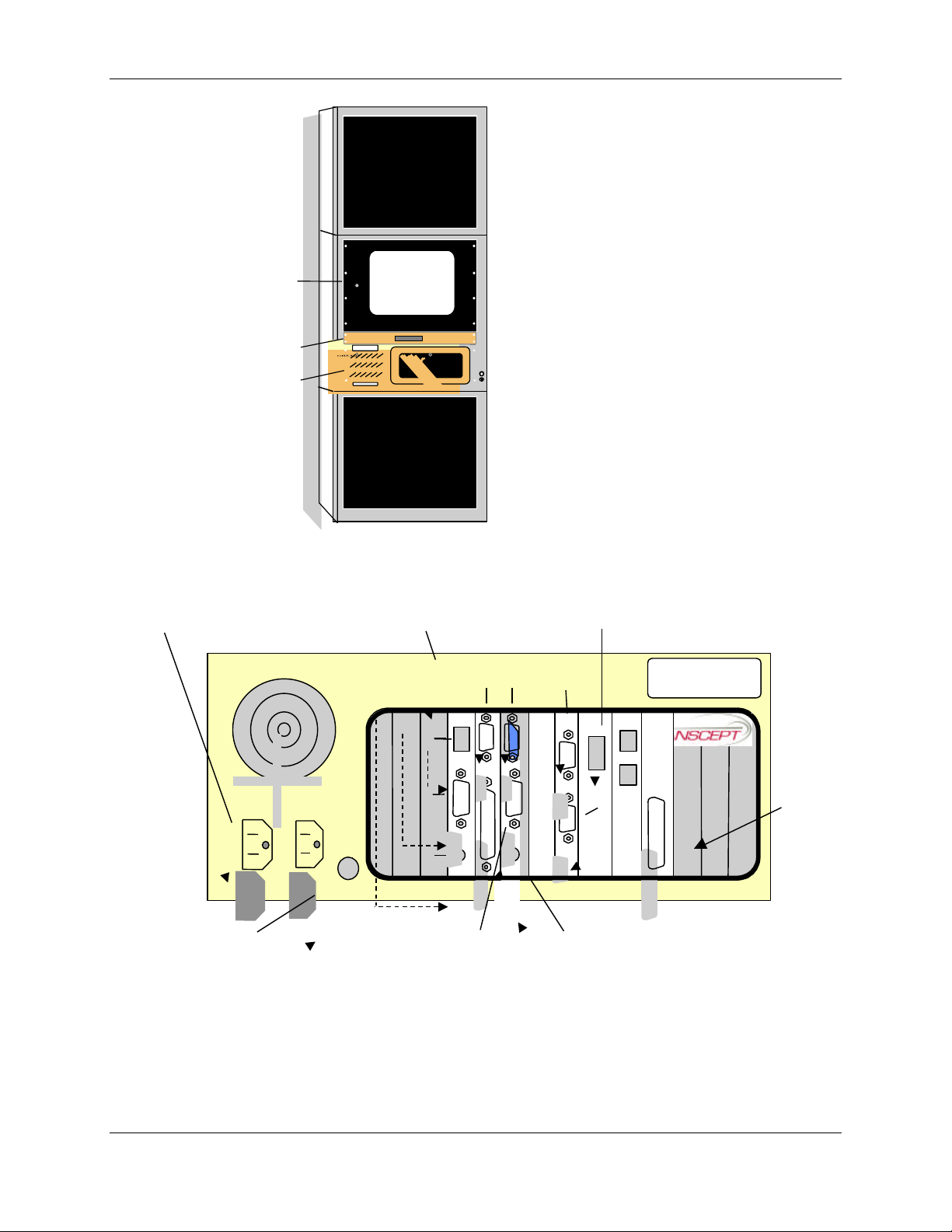
f. Insert computer into enclosure at location shown in Figure 2-4.
g. Slide computer onto angle rails and secure to rack using four 10-32 in. x .50
mounting screws and washers.
h. Connect keyboard cable to KEYBOARD connector at rear of HCU computer chassis
(Figure 2-5).
i. Connect touchpad cable to MOUSE connector at rear of HCU computer chassis
(Figure 2-5).
j. While supporting front and back of HCU monitor, carefully insert monitor into front
of rack at location shown in Figure 2-4.
k. Secure HCU monitor to rack using eight mounting screws and washers supplied
with monitor.
l. Connect HCU monitor video cable to video connector at rear of HCU computer
chassis (Figure 2-5).
2-6
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
LP
CO
M
PH
LI
BT
HCU
Monitor
HCU
Keyboard
Tray
HCU
Computer
Power
Reset
HDD
KB-LK
KB-LK
I
0
Connect Power Cable
to AC input connector
Connect Keyboard Cable
to Keyboard connector
Figure 2-4. Typical Indoor Enclosure Configuration
Network Interface
Card (Ethernet)
10base2
10base 5
10baseT
KEYBOARD
Connect Monitor Cable
to Video connector
Connect the HIC Communication
Cable P1 to the RS-485 connector
COM 2COM 1
T 1
MOUSE
COM 3
M1
COM 4
O
DE
M
C
A
O
NE
NE
S
AL
AR
M
Connect Touchpad Cable
to Mouse connector
Figure 2-5. HCU Computer Rear View
2-7
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6.1.3 +24 VDC Prime Power Installation
The +24 VDC interface for the Indoor Enclosures are terminal blocks located on the inside
of each enclosure on the upper rear panels. The terminal block accepts two wires (+24VDC
and RTN) and distributes the power through busbars. Wire sizes accepted by the terminal
block range from AWG #14 to AWG # 4.
a. Before connecting power to enclosure, ensure that internal or external +24 VDC
power is OFF.
b. Secure +24 VDC input wires from the Power Supply or external power source to
Input Terminal Block with compression screws. Using a flat blade screwdriver, back
off the two screws on input section of Input Terminal Block.
NOTE
For enclosures using the optional +24 VDC Power Supply, use power supply
output cable P/N 1000056G1 in place of the on-site external +24 VDC power
cabling.
2.6.1.4 Initial Prime Power Test
This test requires a multimeter capable of measuring +24 VDC, and associated test probes.
The external or internal +24 VDC supply should be energized at this time. Perform the
following procedure to verify the voltage:
Using a multimeter, measure and record busbar voltage. (The Enclosure/HIC data
sheet at the end of this manual may be reproduced and used for recording.) Verify that
voltage is between +20 and +28 VDC and that polarity matches labels on busbar
mounting brackets.
2.6.1.5 Initial HCU Test
a. At the HCU front panel, set monitor power switch to ON and observe that power
indicator lights. (The monitor power may be from the computer.)
b. Set computer power switch to ON and observe that power indicator lights. If
monitor is powered from computer, monitor power indicator will also light.
c. Observe that computer boots up within 45 seconds and monitor displays Windows
NT desktop screen.
d. Pull out keyboard tray and operate touchpad to verify cursor control.
e. Place cursor on Start button on Windows NT desktop and click left mouse button. A
pop up menu appears.
f. Place cursor on Shut Down … selection and click left mouse button. A
SHUTDOWN WINDOW dialog appears.
g. Click on Shut down the computer? Then click on Yes button. The computer begins
an orderly shutdown process. Wait until a screen message appears indicating that it
is safe to remove power from computer.
2-8
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE

TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6.1.6 RF Interface Assembly (RFIA) Installation
NOTE
It is highly recommended that the RFIAs be installed in the enclosure in the
following order so that the enclosure does not become top-heavy and unstable
if the enclosure is not bolted to the floor:
• The first RFIA should be installed in the top slot of the lower enclosure
below the keyboard.
• RFIAs 2 and 3 should be installed starting in the slot just above the bottom
slot of the top enclosure followed by one in the top slot of the top enclosure.
a. Install RFIAs in enclosure by sliding them onto angle brackets and securing them
with screws and washers.
b. Repeat step a for remaining RFIAs.
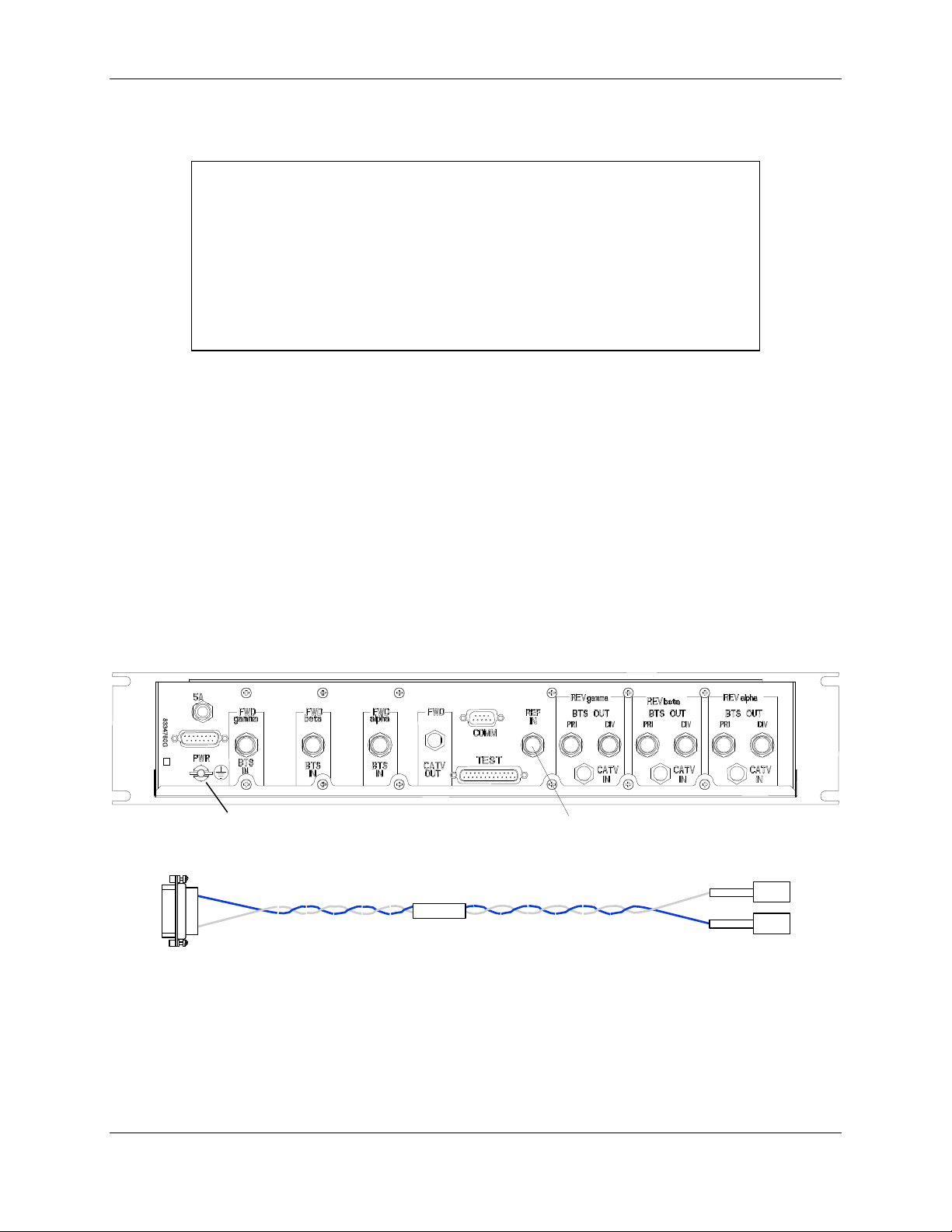
c. Locate +24VDC Power Wiring Harness P/N 1000062G1 (Figure 2-7) for each RFIA.
d. At a location parallel to RFIA PWR connector, connect +24VDC connector of wiring
harness to +24VDC busbar and +24VRTN connector to +24VRTN busbar.
e. Plug mating connector of power cable into RFIA PWR connector and tighten
connector retaining screws.
f. Repeat steps d and e for remaining RFIAs.
2.6.1.7 Hub Fiber Interface (HFI) (Option)
a. Install HFIs in enclosure by sliding them onto angle brackets and securing them
with screws and washers.
b. Repeat step a for remaining HFIs.
c. Locate +24VDC Power Wiring Harness P/N 1000074G1 for each HFI.
d. At a location parallel to HFI PWR connector, connect +24VDC connector of wiring
harness to +24VDC busbar and +24VRTN connector to +24VRTN busbar.
e. Plug mating connector of power cable into HFI PWR connector and tighten
connector retaining screws.
f. Repeat steps d and e for remaining HFIs.
2-9
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6.1.8 Hub Interface Converter (HIC) Installation
NOTE
It is highly recommended that the HICs be installed in the enclosure in the
following order so that the enclosure does not become top-heavy and unstable
if the enclosure is not bolted to the floor:
• The first HIC should be installed in the slot below the RFIA of the lower
enclosure below the keyboard.
• HICs 2 and 3 should be installed starting in the lower slot of the top
enclosure followed by one in the upper part of the top enclosure below the
RFIA.
a. Install HICs in enclosure by sliding them onto angle brackets and securing them
with screws and washers.
b. Connect one end of GND Cable Assembly P/N 1000060G1 to ground studs on the
enclosures located on the bottom panel of the enclosure and the other end on to the
wing nut screw on the back of the HIC.
c. Repeat steps a and b for remaining HICs.
d. Locate +24VDC Power Wiring Harness P/N 1000062G1 (Figure 2-7) for each HIC.
e. At a location parallel to HIC PWR connector, connect +24VDC connector of wiring
harness to +24VDC busbar and +24VRTN connector to +24VRTN busbar.
f. Plug mating connector of power cable into HIC PWR connector and tighten
connector retaining screws.
g. Repeat steps d and f for remaining HICs.
Ground Stud
10 or 15 MHz
Figure 2-6. HIC Rear Panel
P3
8337944
P2
+24RTN
+24VDC
P1
Figure 2-7. HIC Power Wiring Harness 1000062G1
2-10
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
TransCell 1900CB Installation Manual Document No. 1000070A
2.6.1.9 Digital Communications Wiring Installation
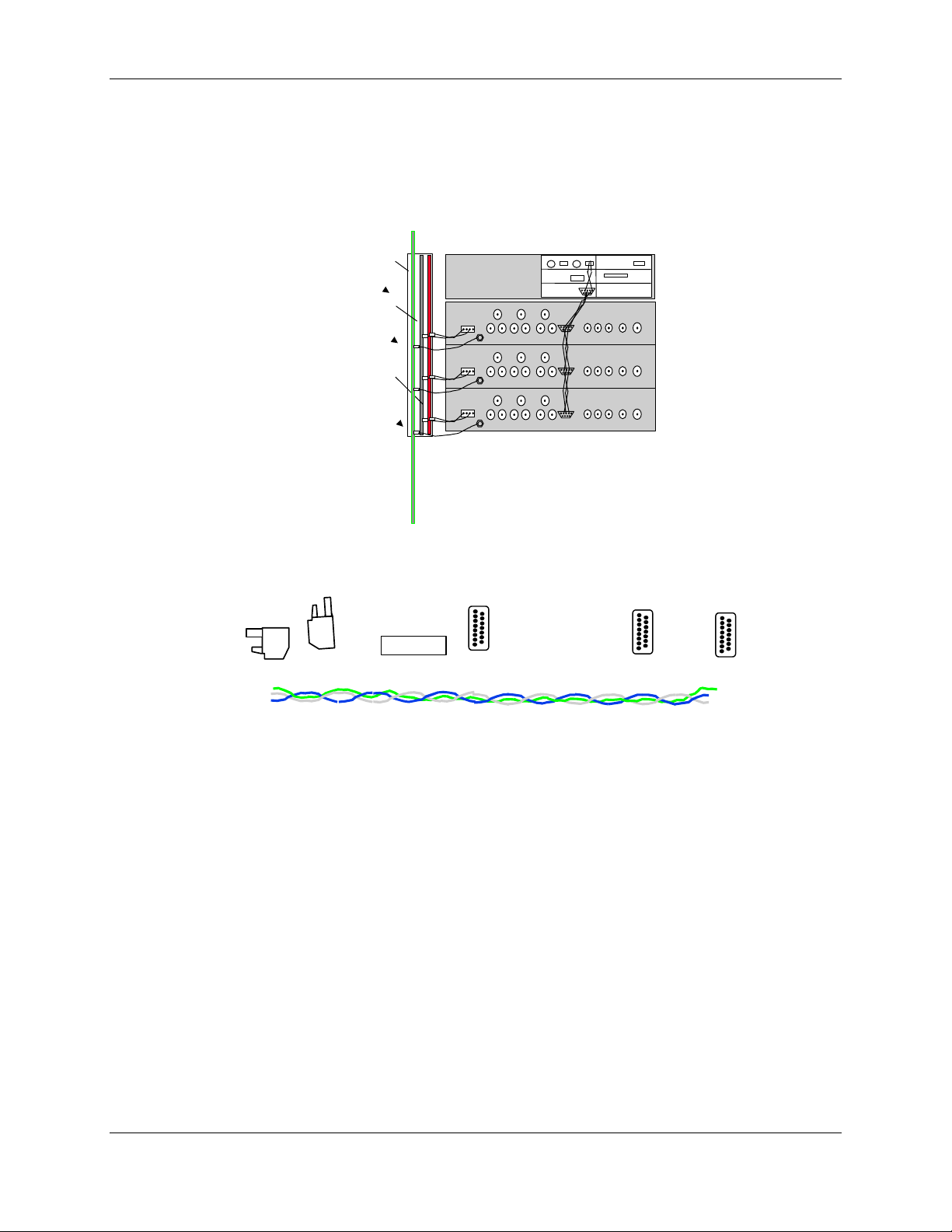
The HIC communicates with the computer via an RS-485 interface using a LonWorks®
protocol. The RS-485 interface uses twisted 3-wire 22-gauge wire, beginning at the
computer and connecting to the upper and lower HIC modules a RS-485 cable assembly PN
1000063G1. Figure 2-8.
GND
BUSBAR
+24VDC
RTN
BUSBAR
+24VDC
BUSBAR
CONTROL COMPUTER
LONWORKS
Figure 2-8. Three HIC Control Interconnect Diagram (not to scale)
a. Mate connector P1 of HIC Communication Wiring Harness P/N 1000063G1 (Figure
2-9) to RS-485 port on computer rear panel (Figure 2-5).
1000063
Figure 2-9. HIC Communication Wiring Harness P/N 8339969G1
b. Connect the other connector to the additional HICs.
2.7 HUB EQUIPMENT CABLE INSTALLATION
With the exception of the indoor and outdoor interface cables between the RFIA and HIC
and between the HIC and HFI, external RFIA interface cables are not provided with the
enclosures or HICs. The cables are provided locally by the user at the installation site. For
the Hub Equipment enclosures, the user must provide up to 14 cables for each RFIA/HIC
installed:
One cable to interface the 15 MHz Reference to the HIC (if using external reference), four
cables interface the HIC with the coaxial network (if applicable), three fiber cables
interface the HFI with the fiber network (if applicable), and nine cables interface the RFIA
with the BTS. Figure 2-10 shows the RF cable interconnections between a single installed
HIC, an RFIA, coaxial network, and BTS. If the HFI is required, configure the cables
between the HIC and HFI to meet the fiber network architecture.
2-11
TRANSCEPT PROPRIETARY - DATA ON THIS PAGE SUBJECT TO RESTRICTIONS CITED ON COVER AND TITLE PAGE
 Loading...
Loading...