Page 1

HOBO® MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
The HOBO MX2300 series data loggers record and transmit temperature and/or relative
humidity (RH) in outdoor or indoor environments. These Bluetooth® Low Energy-enabled
loggers are designed for wireless communication with a mobile device. Using the HOBOmobile®
app, you can easily configure the logger, read it out, and view data on your phone or tablet, or
export the data for further analysis. The logger can calculate minimum, maximum, average, and
standard deviation statistics and be configured to indicate alarms at thresholds you specify. The
logger also supports burst logging in which data is logged at a faster interval when sensor
readings are above or below certain limits. The Temp and Temp/RH models have internal
sensors while the External Temp/RH, External Temp, and 2x External Temp include built-in
external sensors, offering a wide range of solutions for monitoring temperature and RH in
numerous applications.
Specifications
Temperature Sensor
HOBO MX2300 Series
Data Logger
Models:
• MX2301, temp/RH
• MX2302, ext temp/RH
• MX2303, 2 ext temp
• MX2304, ext temp
• MX2305, temp
Included Items:
• Screws
• Cable ties
Required Items:
• HOBOmobile app
• Device with iOS and
Bluetooth
Accessories:
• Solar radiation shield (RS3
for use with MX2302,
MX2303, and MX2304
models; RS1 or M-RSA for
use with MX2301 and
MX2305 models)
• Mounting bracket for solar
radiation shield (MX2300RS-BRACKET), for use with
MX2301 and MX2305
models
• Replacement battery
(HRB-2/3AA)
Range MX2301 and MX2305 internal sensors: -40 to 70°C (-40 to 158°F)
Accuracy ±0.25°C from -40 to 0°C (±0.45 from -40 to 32°F)
Resolution 0.04°C (0.072°F)
Drift <0.01°C (0.018°F) per year
Relative Humidity Sensor* (MX2301, MX2302 only)
Range 0 to 100% RH, -40° to 70°C (-40° to 158°F); exposure to conditions below
Accuracy ±2.5% from 10% to 90% (typical) to a maximum of ±3.5% including
Resolution 0.05%
Drift <1% per year typical
Response Time (typical, to 90% of change)
Temperature MX2301 and MX2305 internal sensors: 17 minutes in air moving 1 m/sec
RH MX2301: 1 minute in air moving 1 m/sec
Logger
Operating Range -40° to 70°C (-40° to 158°F)
Radio Power 1 mW (0 dBm)
Transmission Range Approximately 30.5 m (100 ft) line-of-sight
Wireless Data Standard Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth Smart)
Logging Rate 1 second to 18 hours
Logging Modes Fixed interval (normal, statistics) or burst
Memory Modes Wrap when full or stop when full
Start Modes Immediate, push button, date & time, or next interval
Stop Modes When memory full, push button, date & time, or after a set logging period
Time Accuracy ±1 minute per month 0° to 50°C (32° to 122°F)
Battery Type 2/3 AA 3.6 Volt lithium, user replaceable
MX2302 external temperature sensor: -40 to 70°C (-40 to 158°F)
MX2303 and MX2304 external sensors: -40 to 100°C (-40 to 212°F), with
tip and cable immersion in fresh water up to 50°C (122°F) for one year
±0.2°C from 0 to 70°C (±0.36 from 32 to 158°F)
±0.25°C from 70 to 100°C (±0.45 from 158 to 212°F), MX2303 and
MX2304 only
-20°C (-4°F) or above 95% RH may temporarily increase the maximum RH
sensor error by an additional 1%
hysteresis at 25°C (77°F); below 10% RH and above 90% RH ±5% typical
MX2302 external sensor: 2 minutes, 30 seconds in air moving 1 m/sec
MX2303 and MX2304 external sensors: 3 minutes in air moving 1 m/sec;
20 seconds in stirred water
MX2302: 4 minutes in air moving 1 m/sec
20923-A
Page 2
HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
Specifications (continued)
Battery Life 2 years, typical with logging interval of 1 minute and Power Saving Mode
Memory 128 KB (84,650 measurements, maximum)
Full Memory Download
Time
Dimensions Logger housing: 10.8 x 5.08 x 2.24 cm (4.25 x 2.0 x 0.88 in.)
Weight Logger: 75.5 g (2.66 oz)
Materials Acetal, silicone gasket, stainless steel screws
Environmental Rating NEMA 6 and IP67
*Per RH sensor manufacturer data sheet
disabled; 5 years, typical with logging interval of 1 minute and Power
Saving Mode enabled. Faster logging intervals and statistics sampling
intervals, burst logging, remaining connected with the app, excessive
downloads, and paging may impact battery life.
Approximately 60 seconds; may take longer the further the device is from
the logger
External temperature sensor diameter: 0.53 cm (0.21 in.)
External temperature/RH sensor diameter: 1.17 cm (0.46 in.)
External sensor cable length: 2 m (6.56 ft)
Solar radiation shield bracket: 10.8 x 8.3 cm (4.25 X 3.25 in.)
Solar radiation shield bracket: 20.4 g (0.72 oz)
The CE Marking identifies this product as complying with all relevant
directives in the European Union (EU).
See last page
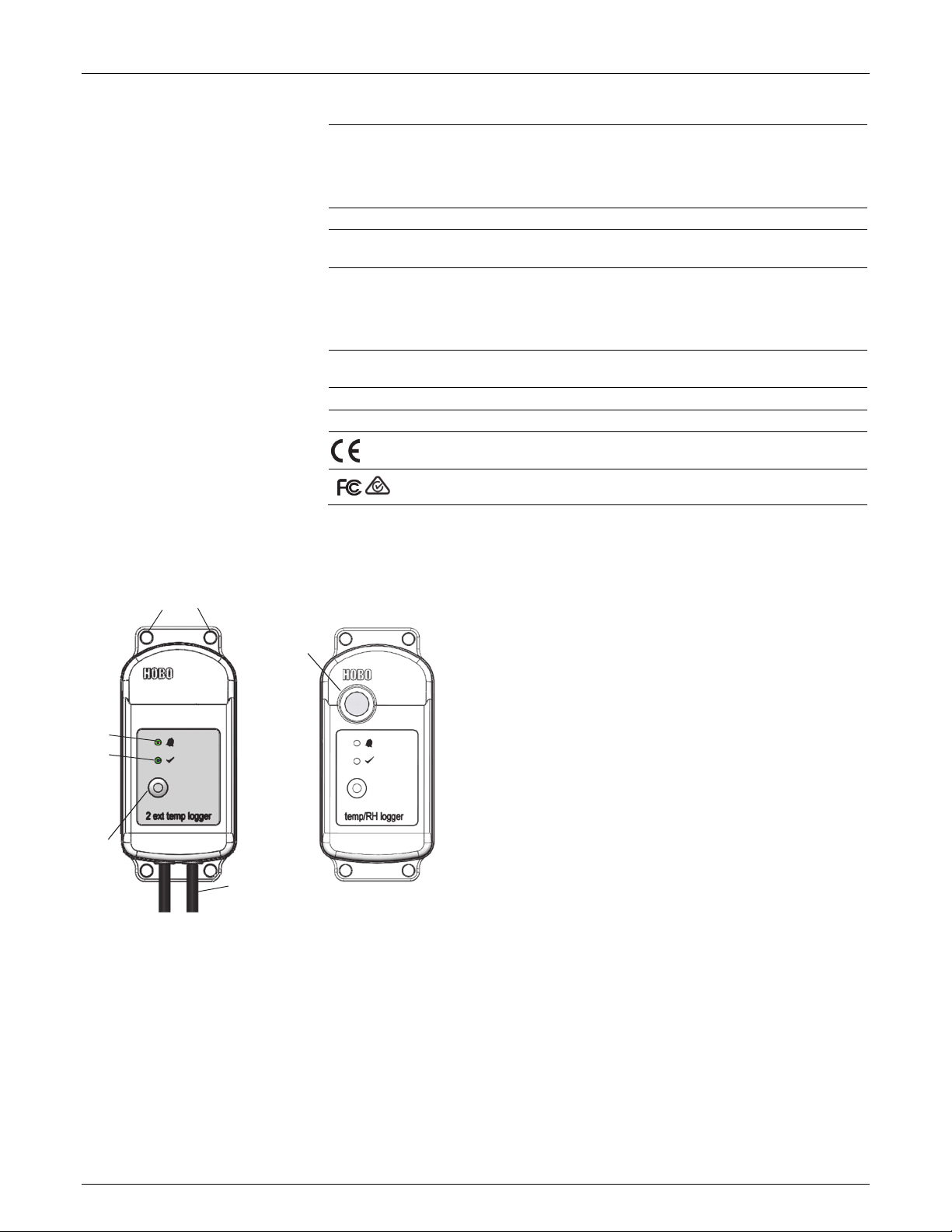
Logger Components and Operation
Mounting
Holes
Vent
Alarm LED
Status LED
Start Button
External Sensor
MX2303 model shown
Mounting Holes: Use the holes at the top and bottom of the
logger to mount it (see Deploying and Mounting the Logger).
Alarm LED: This LED blinks red every 4 seconds when an alarm
is tripped (unless Show LED is disabled as described in
Configuring the Logger). If the logger is logging faster than 4
seconds, the LED blinks at the logging rate when an alarm is
tripped.
Status LED: This LED blinks blue every 4 seconds when the
logger is logging (unless Show LED is disabled as described in
Configuring the Logger). If the logger is logging faster than 4
seconds, the LED blinks at the logging rate. If the logger is
MX2301 model shown
waiting to start logging because it was configured to start “On
Button Push” or with a delayed start, it will blink every 8
seconds.
Start Button: Press this button to wake up the logger; both the
alarm and status LEDs will blink. Once the logger is awake,
press this button to move it to the top of the loggers list in
HOBOmobile. Press this button for 3 seconds to start or stop
the logger when it is configured to start or stop “On button
push” (see Configuring the Logger). Both LEDs will blink four
times when you press the button to start or stop logging. Press
this button for 10 seconds to reset a password (see Setting a
Password).
External Sensor: This is the external probe attached to the
bottom of the logger that measures temperature or
temperature/RH. The MX2302 logger has one external sensor
that measures both temperature and RH and the MX2304
logger has one sensor that measures temperature only. The
MX2303 logger (shown at left) has two external temperature
sensors; the left sensor is channel 1 and the first temperature
shown in HOBOmbile, and the right sensor is channel 2 and the
second in HOBOmobile.
Vent: The RH sensor is located behind the vent (MX2301 model
only).
Downloading HOBOmobile and
Connecting to a Logger
Install the HOBOmobile app to connect to and work with the
logger.
1. Download the HOBOmobile app from the App Store.
1-800-LOGGERS 2 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 3
HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
2. Open the app and enable Bluetooth in the device settings if
prompted.
3. Press the button on the logger to wake it up.
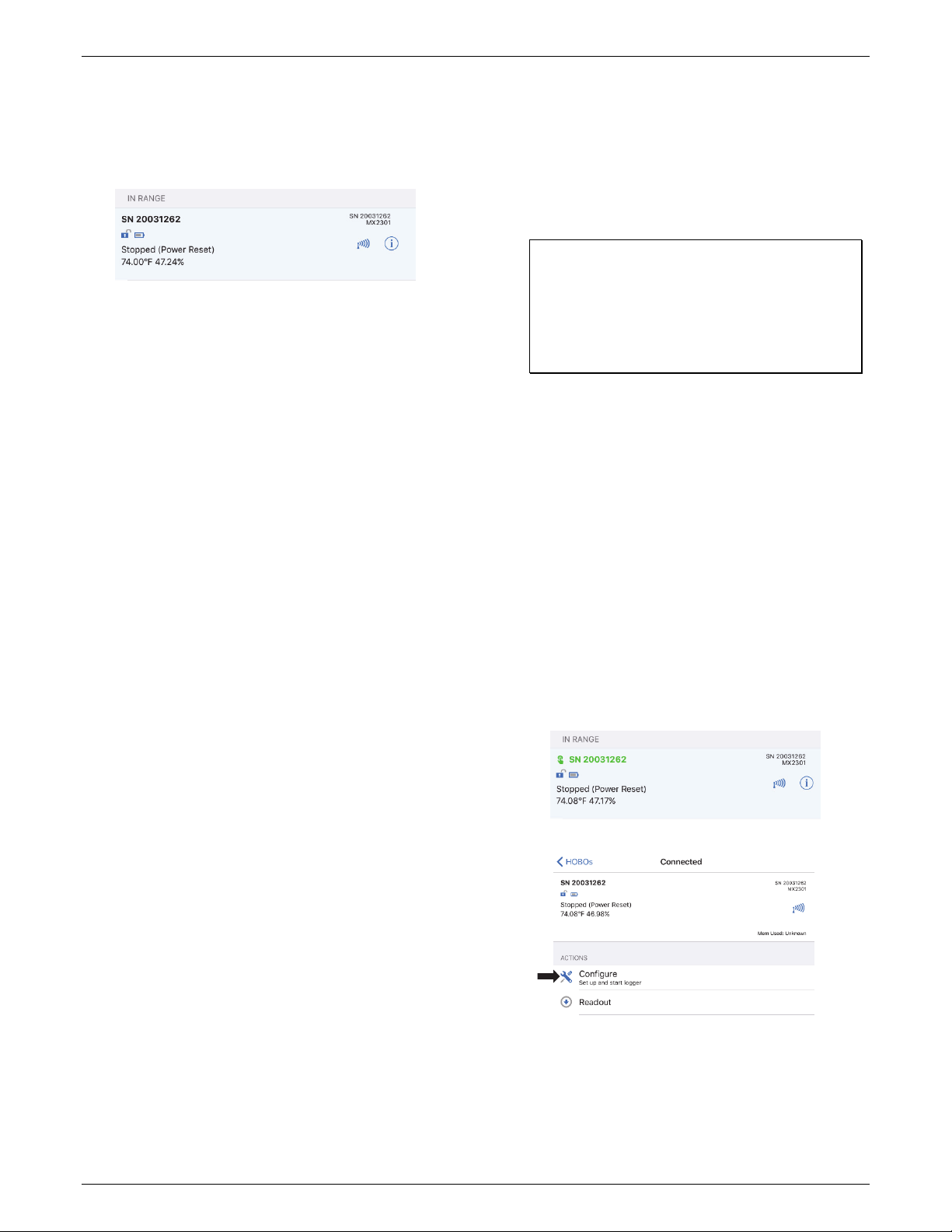
4. Tap the HOBOs icon at the bottom of the screen. Tap the
logger in the list to connect to it.
If the logger does not appear in the list or if it is having trouble
connecting, follow these tips:
• Make sure the logger is “awake” by pressing the start
button. The alarm and status LEDs will blink once when
the logger wakes up. You can also press the button a
second time to bring it to the top of the list if you are
working with multiple loggers.
• Make sure the logger is within range of your mobile
device. The range for successful wireless communication
is approximately 30.5 m (100 ft) with full line-of-sight.
• If there are several loggers in the area, move the logger
to a location with fewer loggers. Interference can
sometimes occur when numerous loggers are in one
location.
• If your device can connect to the logger intermittently or
loses its connection, move closer to the logger, within
sight if possible.
• If the logger appears in the list, but you cannot connect
to it, close HOBOmobile and power cycle the mobile
device. This forces the previous Bluetooth connection to
close.
Once connected to the logger you can select one of the
following actions:
Update Firmware. When new logger firmware is
available, this action appears in the list. Select it and
follow the instructions on the screen. If the connection
is lost between the logger and the mobile device
during the firmware update, a Firmware Update
Pending Status displays for the logger in the HOBOs
list. Connect to the logger and select Restore Logger
(or Update Firmware if that option is available) to
continue updating the firmware.
Important: Before updating the firmware on the
logger, always read out the logger first. Check the
remaining battery level by selecting Full Status Details
and make sure it is no less than 30%. Make sure you
have the time to complete the entire update process,
which requires that the logger remains connected to
the device during the upgrade.
• Force Offload. This may appear if an error was
encountered when loading configuration settings. Select
this to offload all the data on the logger before
reconfiguring it.
Configuring the Logger
Use HOBOmobile to set up the logger, including selecting the
logging options, configuring alarms, and enabling Power Saving
Mode. These steps provide an overview of setting up the
logger. For complete details, see the HOBOmobile User’s Guide.
1. Press the button on the logger to wake it up.
2. Find the logger in the list and tap it to connect to it. If you
are working with multiple loggers, you can press the button
on the logger a second time to bring it to the top of the list.
The logger name (or serial number if no name has been
assigned) turns green when the logger moves to the top of
the list. Note that the current readings are displayed even
when the logger is not logging.
• Configure. Select logger settings and load them onto the
logger to start logging. See Configuring the Logger.
• Readout. Download logger data. See Reading Out the
Logger.
• Full Status Details. Check the battery level and view the
configuration settings currently selected for the logger.
• Start Logging. Select this option to begin logging (if the
logger is configured to start “On Button Push” as
described in Configuring the Logger).
• Stop Logging. Stop the logger from recording data. This
overrides any Stop Logging settings described in
Configuring the Logger.
• Page Logger LED. Press and hold this option to illuminate
the alarm and status LEDs for 4 seconds.
• Logger Password. Select this to create a password for the
logger that will be required if another mobile device
attempts to connect to it. To reset a password, connect
to the logger, tap Set Logger Passkey, and select Reset to
Factory Default. You can also press the button on the
logger for 10 seconds to reset a password.
1-800-LOGGERS 3 www.onsetcomp.com
3. Once connected, tap Configure.
4. Tap Name and type a name for the logger up to 20
characters (optional). Tap Done. If no name is selected, the
logger serial number is used as the name.
5. Tap Group to add the logger to the Favorites group, an
existing custom group, or create a new group name with up
to 20 characters (optional). Tap Done.
Page 4

HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
6. Tap Logging Interval and choose how frequently the logger
will record data unless operating in burst logging mode (see
Burst Logging). Note: If you configure an alarm, the logger
will use the logging interval you selected as the rate to
check for alarm conditions (alarms are not available if burst
logging is configured). See Setting up Alarms for more
details.
7. Tap Start Logging and select when logging will begin:
• Now. Logging will begin immediately after tapping Start
in the Configure screen.
• On Next Logging Interval. Logging will begin at the next
even interval as determined by the selected logging
interval.
• On Button Push. Logging will begin once you press the
button on the logger for 3 seconds.
• On Date/Time. Logging will begin on a date and time you
specify. Select the Date and time and tap Done.
Tap Done in the Start Logging screen.
8. Tap Stop Logging and select the options for when logging
will end.
a. Choose one of two memory options:
• When Memory Fills. The logger will continue recording
data until the memory is full.
the second is channel 2 (and “-1” and “-2” is used in the
column headings in the data file to differentiate the two
sensors).
10. Tap Logging Mode. Select either fixed interval logging or
burst logging. With fixed interval logging, the logger records
data for all enabled sensors and/or selected statistics at the
logging interval selected (see Statistics Logging for details
on choosing statistics options). In burst mode, logging
occurs at a different interval when a specified condition is
met. See Burst Logging for more information. Tap Done.
11. Enable or disable Show LED. If Show LED is disabled, the
alarm and status LEDs on the logger will not be illuminated
while logging (the alarm LED will not blink if an alarm trips).
You can temporarily turn on LEDs when Show LED is
disabled by pressing the button on the logger for 1 second.
12. Enable or disable Power Saving Mode. If Power Saving
Mode is disabled, the logger will “advertise” or regularly
send out a Bluetooth signal for the phone or tablet to find
via HOBOmobile while it is logging, which uses battery
power. When Power Saving Mode is enabled, the logger will
only advertise during logging when you press the button on
the logger to wake it up, thereby preserving as much
battery power as possible.
13. Tap Start in the upper right corner of the Configure screen
to load the settings onto the logger.
• Never (Wrap When Full). The logger will continue
recording data indefinitely, with newest data
overwriting the oldest. This option is not available if
the Logging Mode is set to Burst (see Burst Logging).
b. Select On Button Push if you want to be able to stop
logging by pushing the button on the logger for 3
seconds. Note that if you also choose On Button Push for
the Start Logging option, then you will not be able to stop
logging until 30 seconds after logging begins.
c. Select one of the following time options for when to stop
logging:
• Never. Select this if you do not want the logger to stop
at any predetermined time frame.
• On Date/Time. Select this if you want the logger to
stop logging on a specific date and time. Select the
date and time and then tap Done.
• After. Select this if you want to control how long the
logger should continue logging once it starts. Choose
the amount of time you want the logger to log data
and then tap Done. For example, select 30 days if you
want the logger to log data for 30 days after logging
begins.
d. Tap Done in the Stop Logging screen.
9. Select the sensor measurement types that will be logged.
Both the temperature and RH sensors are required to
calculate dew point, which is an additional data series
available for plotting after reading out the logger. You can
also set up alarms to trip when a sensor reading rises above
or falls below a specified value. See Setting up Alarms for
details on enabling sensor alarms. Note for MX2303 models
only: The first temperature sensor listed is channel 1 and
Logging will begin based on the settings you selected. See
Deploying and Mounting the Logger for details on mounting
and see Reading Out the Logger for details on downloading.
Setting up Alarms
You can set up alarms for the logger so that if a sensor reading
rises above or falls below a specified value, the logger alarm
LED will blink and an alarm icon will appear in the app. This can
alert you to problems so you can take corrective action.
To set an alarm:
1. Tap the HOBOs icon and tap the logger to connect to it. If
the logger was configured with Power Saving Mode
enabled, press the button on the logger to wake it up.
When working with multiple loggers, you can also press the
button on the logger to bring it to the top of the list.
2. Once connected, tap Configure.
3. In Sensor & Alarm Setup, tap an enabled sensor.
4. Enable the High Alarm if you want an alarm to trip when the
sensor reading rises above the high alarm value. Drag the
slider to the reading that will trip the alarm or tap the value
field and type a specific reading. In the example, an alarm
will trip when the temperature rises above 85°F.
1-800-LOGGERS 4 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 5

5. Enable the Low Alarm if you want an alarm to trip when the
sensor reading falls below the low alarm value. Drag the
slider to the reading that will trip the alarm or tap the value
field and type a specific reading. In the example, an alarm is
configured to trip when the temperature falls below 32°F.
Note: The actual values for the high and low alarm limits are
set to the closest value supported by the logger.
6. Under Raise Alarm After, select the duration before an
alarm is tripped and tap Done in the Alarm Duration screen.
7. Select either Cumulative or Consecutive Samples. If you
select Cumulative Samples, then the alarm will trip when
the time the sensor is out of range over the course of the
deployment is equal to the selected duration. If you select
Consecutive Samples, then the alarm will trip when the
time the sensor is continuously out of range is equal to the
selected duration. For example, the high alarm for
temperature is set to 85°F and the duration is set to 30
minutes. If Cumulative is selected, then an alarm will trip
once a sensor reading has been at or above 85°F for a total
of 30 minutes since the logger was configured; specifically,
this could be 15 minutes above 85°F in the morning and
then 15 minutes above 85°F again in the afternoon. If
Consecutive is selected, then an alarm will trip only if all
sensor readings are 85°F or above for a continuous 30minute period.
8. Tap Done and repeat steps 3–8 for the other sensor if
desired. Note that when both alarms are configured, an
alarm is raised when either sensor is in an alarm condition.
9. Back in the Configure screen, select one of the following
options to determine how the alarm indications are cleared:
• Logger Reconfigured. The alarm indication will display
until the next time the logger is reconfigured.
• Sensor in Limits. The alarm icon indication will display
until the sensor reading returns to the normal range
between any configured high and low alarm limits.
10. Tap Start in the Configure screen to load the alarm settings
onto the logger if you are ready to start.
When an alarm trips, the logger alarm LED blinks every 4
seconds (unless Show LED is disabled), an alarm icon appears in
the app, and an Alarm Tripped event is logged. The alarm state
will clear when the readings return to normal if you selected
HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
Sensor in Limits in step 9. Otherwise, the alarm state will
remain in place until the logger is reconfigured.
Notes:
• Alarm limits are checked at every logging interval. For
example, if the logging interval is set to 5 minutes, then
the logger will check the sensor readings against your
configured high and low alarm setting every 5 minutes.
• The actual values for the high and low alarm limits are set
to the closest value supported by the logger. For
example, the closest value to 85°F that the logger can
record is 84.990°F and the closest value to 32°F is
32.043°F. In addition, alarms can trip or clear when the
sensor reading is within the logger specifications of
0.072°F resolution. This means the value that triggers the
alarm may differ slightly than the value entered. For
example, if the High Alarm is set to 75.999°F, the alarm
can trip when the sensor reading is 75.994°F (which is
within the 0.072°F resolution).
• When you read out the logger, alarm events can be
displayed on the plot or in the data file. See Logger
Events.
Burst Logging
Burst logging is a logging mode that allows you to set up more
frequent logging when a specified condition is met. For
example, a logger is recording data at a 5-minute logging
interval and burst logging is configured to log every 30 seconds
when the temperature rises above 85°F (the high limit) or falls
below 32°F (the low limit). This means the logger will record
data every 5 minutes as long as the temperature remains
between 85°F and 32°F. Once the temperature rises above
85°F, the logger will switch to the faster logging rate and record
data every 30 seconds until the temperature falls back to 85°F.
At that time, logging then resumes every 5 minutes at the
normal logging interval. Similarly, if the temperature falls below
32°F, then the logger would switch to burst logging mode again
and record data every 30 seconds. Once the temperature rises
back to 32°F, the logger will then return to normal mode,
logging every 5 minutes. Note: Sensor alarms, statistics, and the
Stop Logging option “Wrap When Full” are not available in
burst logging mode.
To set up burst logging:
1. Tap the HOBOs icon and tap the logger to connect to it. If
the logger was configured with Power Saving Mode
enabled, press the button on the logger to wake it up.
When working with multiple loggers, you can also press the
button on the logger to bring it to the top of the list.
2. Once connected, tap Configure.
3. Tap Logging Mode and then tap Burst Logging.
4. Tap a sensor under Burst Sensor Limits.
5. Enable High Limit if you want burst logging to occur when
the sensor reading rises above a specific reading. Drag the
slider to the reading that will trigger burst logging or tap the
value field and type a specific reading. In this example, the
logger will switch to burst logging when the temperature
rises above 85°F.
1-800-LOGGERS 5 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 6

6. Enable Low Limit if you want burst logging to occur when
the sensor reading falls below a specific reading. Drag the
slider to the reading that will trigger burst logging or tap the
value field and type a specific reading. In the example, the
logger will switch to burst logging when the temperature
falls below 32°F.
7. Tap Done and repeat steps 4–7 for the other sensor if
desired.
8. Tap Burst Logging Interval and select an interval faster than
the logging interval. Keep in mind that the faster the burst
logging rate, the greater the impact on battery life and the
shorter the logging duration. Because measurements are
being taken at the burst logging interval throughout the
deployment, the battery usage is similar to what it would be
if you had selected this rate for the normal logging interval.
Tap Done.
9. Tap Done to exit the Logging Mode screen.
10. Tap Start in the Configure screen to load the burst settings
onto the logger if you are ready to start.
Notes:
• The high and low burst limits are checked at the burst
logging interval rate whether the logger is in normal or
burst condition. For example, if the logging interval is set
to 1 hour and the burst logging interval is set to 10
minutes, the logger will always check for burst limits
every 10 minutes.
• If high and/or low limits have been configured for more
than one sensor, then burst logging will begin when any
high or low condition goes out of range. Burst logging will
not end until all conditions on all sensors are back within
normal range.
• The actual values for the burst logging limits are set to
the closest value supported by the logger. For example,
the closest value to 85°F that the logger can record is
84.990°F and the closest value to 32°F is 32.043°F.
• Burst logging can begin or end when the sensor reading is
within the logger specifications of 0.072°F resolution.
This means the value that triggers burst logging may
differ slightly than the value entered. For example, if the
high limit for a temperature alarm is set to 75.999°F,
burst logging can start when the sensor reading is
75.994°F (which is within the 0.072°F resolution).
• Once the high or low condition clears, the logging
interval time will be calculated using the last recorded
data point in burst logging mode, not the last data point
recorded at the normal logging rate. For example, the
logger has a 10-minute logging interval and logged a data
point at 9:05. Then, the high limit was surpassed and
HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
burst logging began at 9:06. Burst logging then continued
until 9:12 when the sensor reading fell back below the
high limit. Now back in normal mode, the next logging
interval will be 10 minutes from the last burst logging
point, or 9:22 in this case. If burst logging had not
occurred, the next data point would have been at 9:15.
• A New Interval event is created each time the logger
enters or exits burst logging mode. See Logger Events for
details on plotting and viewing the event. In addition, if
the logger is stopped with a button push while in burst
logging mode, then a New Interval event is automatically
logged and the burst condition is cleared, even if the
actual high or low condition has not cleared.
Statistics Logging
During fixed interval logging, the logger records data for
enabled sensors and/or selected statistics at the logging
interval selected. Statistics are calculated at a sampling rate you
specify with the results for the sampling period recorded at
each logging interval. The following statistics can be logged for
each sensor:
• The maximum, or highest, sampled value,
• The minimum, or lowest, sampled value,
• An average of all sampled values, and
• The standard deviation from the average for all sampled
values.
For example, a logger is configured with both the temperature
and RH sensors enabled, and the logging interval set to 5
minutes. The logging mode is set to fixed interval logging with
Normal and all four statistics enabled and with a statistics
sampling interval of 30 seconds. Once logging begins, the logger
will measure and record the actual temperature and RH sensor
values every 5 minutes. In addition, the logger will take a
temperature and RH sample every 30 seconds and temporarily
store them in memory. The logger will then calculate the
maximum, minimum, average, and standard deviation using the
samples gathered over the previous 5-minute period and log
the resulting values. When reading out the logger, this would
result in 10 data series (not including any derived series, such
as dew point): two sensor series (with temperature and RH
data logged every 5 minutes) plus eight maximum, minimum,
average, and standard deviation series (four for temperature
and four for RH with values calculated and logged every 5
minutes based on the 30-second sampling).
To log statistics:
1. Tap the HOBOs icon and tap the logger to connect to it. If
the logger was configured with Power Saving Mode
enabled, press the button on the logger to wake it up.
When working with multiple loggers, you can also press the
button on the logger to bring it to the top of the list.
2. Once connected, tap Configure.
3. Tap Logging Mode and then select Fixed Interval Logging.
4. Select Normal to record the current reading for each
enabled sensor at the logging interval shown at the top of
the screen. Do not select this if you only want to log
statistics.
1-800-LOGGERS 6 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 7

HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
5. Select the statistics you want the logger to record at each
logging interval: Maximum, Minimum, Average, and
Standard Deviation (average is automatically enabled when
selecting Standard Deviation). Statistics will be logged for all
enabled sensors. In addition, the more statistics you record,
the shorter the logger duration and the more memory is
required.
6. Tap Statistics Sampling Interval and select the rate to use
for calculating statistics. The rate must be less than, and a
factor of, the logging interval. For example, if the logging
interval is 1 minute and you select 5 seconds for the
sampling rate, then the logger will take 12 sample readings
between each logging interval (one sample every 5 seconds
for a minute) and use the 12 samples to record the resulting
statistics at each 1-minute logging interval. Note that the
faster the sampling rate, the greater the impact on battery
life. Because measurements are being taken at the statistics
sampling interval throughout the deployment, the battery
usage is similar to what it would be if you had selected this
rate for the normal logging interval.
7. Tap Done.
8. Tap Done again to exit the Logging Mode screen.
9. Tap Start in the Configure screen to load the statistics
settings onto the logger if you are ready to start.
Setting a Password
You can create an encrypted password for the logger that will
be required if another phone or tablet attempts to connect to
it. This is recommended to ensure that a deployed logger is not
mistakenly stopped or purposely altered by others. This
password uses a proprietary encryption algorithm that changes
with every connection.
To set a password:
1. Tap the HOBOs icon and connect to the logger.
2. Tap Logger Password.
3. Type a password up to 10 characters.
4. Tap Save.
Only the phone or tablet used to set the password can then
connect to the logger without entering a password; all other
mobile devices will be required to enter the password. For
example, if you set the password for the logger with your tablet
and then try to connect to the device later with your phone,
you will be required to enter the password on the phone but
not with your tablet. Similarly, if others attempt to connect to
the logger with different devices, then they would also be
required to enter the password. To reset a password, connect
to the logger, tap Set Logger Passkey, and select Reset to
Factory Default or press the button on the logger for 10
seconds.
Reading Out the Logger
To offload data from the logger:
1. Tap the HOBOs icon and tap the logger to connect to it. If
the logger was configured with Power Saving Mode
enabled, press the button on the logger to wake up
communications. When working with multiple loggers, you
can also press the button on the logger to bring it to the top
of the list.
2. Once connected, tap Readout.
3. Tap the Data Files icon to view a mini-graph of the
downloaded data.
4. Tap the mini-graph to view a larger version of the graph or
to share the file. See the HOBOmobile User’s Guide for
details on viewing graphs and sharing data.
Data can also be uploaded automatically to HOBOlink, Onset’s
web-based software. Tap the Settings icon to enable the
HOBOlink Upload Data option (this requires a HOBOlink
account at www.hobolink.com). See the HOBOmobile User’s
Guide for more details on this setting and see the HOBOlink
help for details on working with data in HOBOlink.
Logger Events
The logger records the following internal events to track logger
operation and status. To plot events in HOBOmobile, tap a
mini-graph and then tap . Select the events you wish to plot
and then tap again. You can also view events in shared or
exported data files.
Internal Event Name Definition
Host Connected The logger was connected to the mobile
Started The logger started logging.
Stopped The logger stopped logging.
Alarm
Tripped/Cleared
New Interval The logger has switched to logging at the
Safe Shutdown The battery level dropped below a safe
device.
An alarm has occurred because the reading
was outside the alarm limits or back within
range. Note: Although the reading may have
returned to a normal range during logging,
an alarm cleared event will not be logged if
the logger was set up to maintain alarms
until reconfigured.
burst logging rate or back to the normal rate.
operating voltage and the logger performed
a safe shutdown.
Deploying and Mounting the Logger
Follow these guidelines when deploying the logger:
• A solar radiation shield is required if the MX2301 or
MX2305 logger or the external sensors from an MX2302,
MX2303, or MX2304 logger will be in sunlight at any
time.
• When using a solar radiation shield with an MX2301 or
MX2305 model, the logger must be mounted using the
solar radiation shield bracket (MX2300-RS-BRACKET) to
the underside of the mounting plate as shown on the
next page.
1-800-LOGGERS 7 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 8

HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
• For more details on the solar radiation shield, refer to the
Solar Radiation Shield Installation Guide at
www.onsetcomp.com/manuals/rs1.
• When deploying an MX2302 logger, it is recommended
that the sensor must be mounted vertically. If it must be
mounted horizontally, then make sure the vent on the
side of the sensor is vertical or facing down. If the sensor
is being deployed in a solar radiation shield, mount it
vertically as shown below.
• When deploying a logger with external sensors (MX2302,
MX2303, and MX2304), mount the logger so the sensor
cable is not being pulled. Leave about 5 cm (2 in.) of drip
loop in the cable where it comes out of the logger to
prevent water from entering the logger housing.
Protecting the Logger
Note: Static electricity may cause the logger to stop logging.
The logger has been tested to 8 KV, but avoid electrostatic
discharge by grounding yourself to protect the logger. For more
information, search for “static discharge” on onsetcomp.com.
Battery Information
The logger requires one user-replaceable 2/3 AA 3.6 V lithium
battery (HRB-2/3AA). Battery life is 2 year, typical with a logging
interval of 1 minute, but may be extended to 5 years when the
logger is configured with Power Saving Mode enabled.
Expected battery life varies based on the ambient temperature
where the logger is deployed, the logging or sampling interval,
frequency of offloading and connecting to the mobile device,
number of channels that are active, and use of burst mode or
statistics logging. Deployments in extremely cold or hot
temperatures or logging interval faster than 1 minute can
impact battery life. Estimates are not guaranteed due to
uncertainties in initial battery conditions and operating
environment.
To install or replace the battery:
1. Use a Phillips-head screwdriver to unscrew the four screws
from the back of the logger.
Unscrew these four
screws to replace
the battery
Drip Loop
• For MX2301 and MX2305 loggers that are not being
deployed with a solar radiation shield or for loggers with
external sensors (MX2302, MX2303, and MX2304), you
can either use the included large screws or cable ties to
mount the logger via the mounting holes. Use the screws
to attach the logger to a wall or flat surface. Use the
cable ties to affix the logger to a PVC pipe or mast. The
MX2301 logger must also be mounted vertically or with
the sensor vent facing down when not using the solar
radiation shield.
2. Carefully separate the top and bottom of the logger
enclosure.
3. Remove the old battery and insert the new battery
observing polarity.
4. Make sure the rubber seal is clean and free of any debris
and then carefully reassemble the logger enclosure and
screw in the four screws.
WARNING: Do not cut open, incinerate, heat above 85°C
(185°F), or recharge the lithium battery. The battery may
explode if the logger is exposed to extreme heat or conditions
that could damage or destroy the battery case. Do not dispose
of the logger or battery in fire. Do not expose the contents of
the battery to water. Dispose of the battery according to local
regulations for lithium batteries.
1-800-LOGGERS 8 www.onsetcomp.com
Page 9

HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user
is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Industry Canada Statements
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Avis de conformité pour l’Industrie Canada
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1)
l'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
To comply with FCC and Industry Canada RF radiation exposure limits for general population, the logger must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20cm from
all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
© 2016 Onset Computer Corporation. All rights reserved. Onset, HOBO, HOBOmobile, and HOBOlink are
registered trademarks of Onset Computer Corporation. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc. Bluetooth and
1-800-LOGGERS (564-4377) • 508-759-9500
www.onsetcomp.com/support/contact
Bluetooth Smart is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their
respective companies.
Patent #: 8,860,569 20923-A
 Loading...
Loading...