Page 1
CM1293A-04SO
4-Channel
Low Capacitance
ESD Protection Array
Product Description
CM1293A−04SO has been designed to provide ESD protection for
electronic components or subsystems requiring minimal capacitive
loading. This device is ideal for protecting systems with high data and
clock rates or for circuits requiring low capacitive loading. Each ESD
channel consists of a pair of diodes in series that steer the positive or
negative ESD current pulse to either the positive (V
supply rail. A Zener diode is embedded between V
helps protect the V
rail against ESD strikes. This device protects
CC
) or negative (VN)
P
and V
P
N
which
against ESD pulses up to 8 kV contact discharge) per the
IEC 61000−4−2 Level 4 standard.
This device is particularly well−suited for protecting systems using
high−speed ports such as USB2.0, IEEE1394 (FireWire
, i.LINKt),
Serial ATA, DVI, HDMI, and corresponding ports in removable
storage, digital camcorders, DVD−RW drives and other applications
where extremely low loading capacitance with ESD protection are
required in a small package footprint.
Features
Four Channels of ESD Protection
Provides ESD Protection to IEC61000−4−2
8 kV Contact Discharge
Low Loading Capacitance of 2.0 pF Max
Low Clamping Voltage
Channel I/O to I/O Capacitance 1.5 pF Typical
Zener Diode Protects Supply Rail and Eliminates the Need for
External By−Pass Capacitors
Each I/O Pin Can Withstand over 1000 ESD Strikes*
This Device is Pb−Free and is RoHS Compliant**
http://onsemi.com
SC−74
SO SUFFIX
CASE 318F
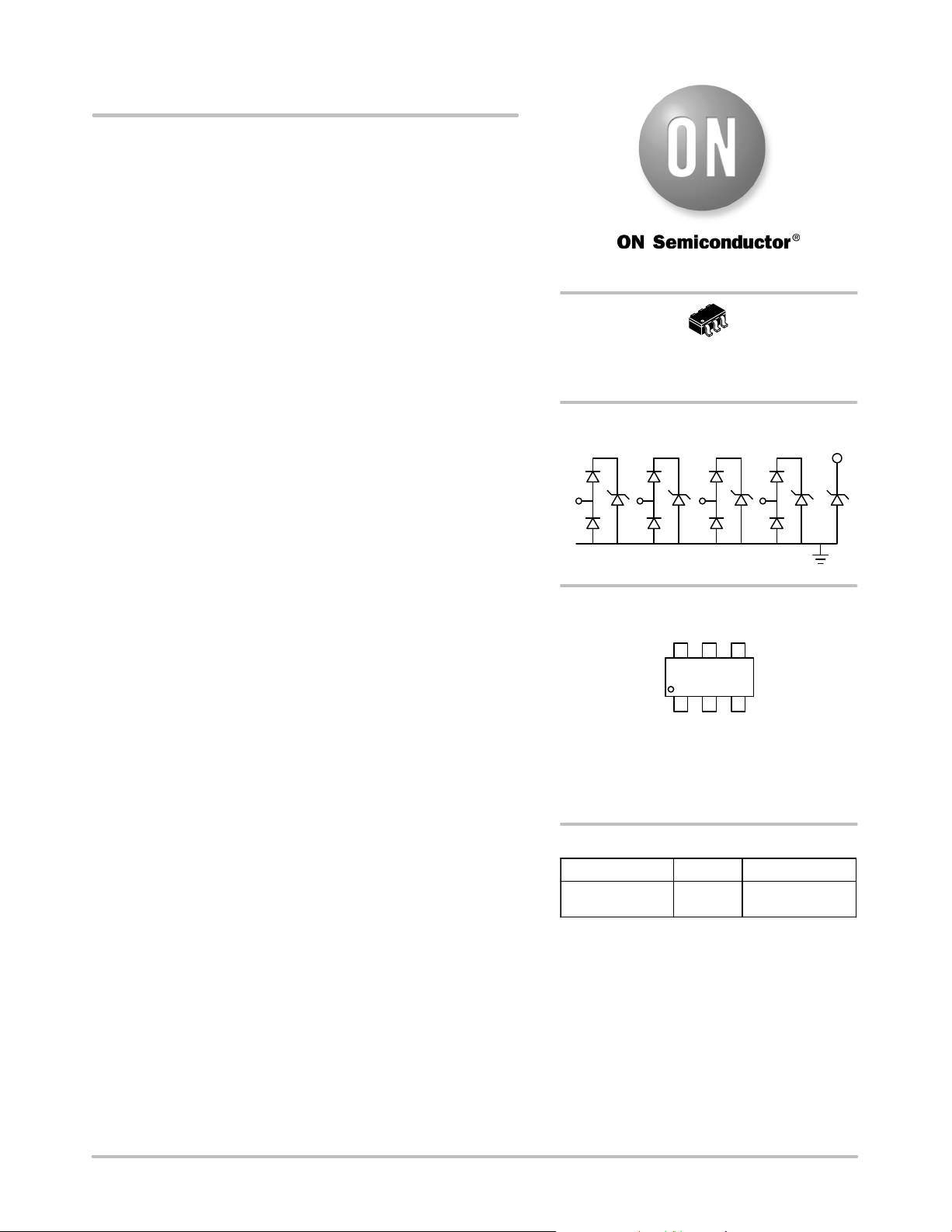
BLOCK DIAGRAM
CH2CH1 CH3 CH4
CM1293A−04SO
MARKING DIAGRAM
XXXMG
G
1
XXX = Specific Device Code
M = Date Code
G = Pb−Free Package
(Note: Microdot may be in either location)
VP
VN
Applications
DVI Ports, HDMI Ports in Notebooks, Set Top Boxes, Digital TVs,
LCD Displays
Serial ATA Ports in Desktop PCs and Hard Disk Drives
PCI Express Ports
General Purpose High−Speed Data Line ESD Protection
**Standard test condition is IEC61000−4−2 level 4 test circuit with each pin
subjected to 8 kV contact discharge for 1000 pulses. Discharges are timed at
1 second intervals and all 1000 strikes are completed in one continuous test run.
The part is then subjected to standard production test to verify that all of the
tested parameters are within spec after the 1000 strikes.
**For additional information on our Pb−Free strategy and soldering details,
please download the ON Semiconductor Soldering and Mounting Techniques
Reference Manual, SOLDERRM/D.
Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2012
January, 2012 − Rev. 0
1 Publication Order Number:
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device Package Shipping
CM1293A−04SO
†For information on tape and reel specifications,
including part orientation and tape sizes, please
refer to our Tape and Reel Packaging Specification
Brochure, BRD8011/D.
SC−74
(Pb−Free)
Tape & Reel
CM1293A−04SO/D
†
3,000 /
Page 2
CM1293A−04SO
Table 1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name Type Description
1 CH1 I/O ESD Channel
2 V
N
3 CH2 I/O ESD Channel
4 CH3 I/O ESD Channel
5 V
P
GND Negative Voltage Supply Rail
PWR Positive Voltage Supply Rail
PACKAGE/PINOUT DIAGRAM
Top View
CH1 CH4
V
CH2
635
N
4−Channel SC−74
V
P
CH3
6 CH4 I/O ESD Channel
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter Rating Units
Operating Supply Voltage (VP − VN) 6.0 V
Operating Temperature Range –40 to +85 C
Storage Temperature Range –65 to +150 C
DC Voltage at any Channel Input (VN − 0.5) to (VP + 0.5) V
Stresses exceeding Maximum Ratings may damage the device. Maximum Ratings are stress ratings only. Functional operation above the
Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Extended exposure to stresses above the Recommended Operating Conditions may affect
device reliability.
Table 3. STANDARD OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter Rating Units
Operating Temperature Range –40 to +85 C
Package Power Rating 225 mW
Table 4. ELECTRICAL OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS (Note 1)
Symbol
V
I
V
I
LEAK
C
DC
V
ESD
Operating Supply Voltage (VP−VN) 3.3 5.5 V
P
Operating Supply Current (VP−VN) = 3.3 V 8.0
P
Diode Forward Voltage I
F
Channel Leakage Current T
Channel Input Capacitance At 1 MHz, V
IN
Channel I/O to I/O Capacitance 1.5 pF
IO
ESD Protection
Peak Discharge Voltage at any
Channel Input, in System
Contact Discharge per
IEC 61000−4−2 Standard
V
Channel Clamp Voltage
CL
Positive Transients
Negative Transients
R
DYN
Dynamic Resistance
Positive Transients
Negative Transients
1. All parameters specified at T
2. Standard IEC 61000−4−2 with C
3. These measurements performed with no external capacitor on V
Parameter Conditions Min Ty p Max Units
= 8 mA, T
F
= 25C, V
A
T
= 25C (Notes 2 and 3) 8
A
T
= 25C, I
A
(Note 3)
= 25C 0.90 V
A
= 5 V, V
P
= 3.3 V, V
P
= 1A, tP = 8/20 mS
PP
= 0 V 0.1 1.0
N
= 0 V, V
N
= 1.65 V 2.0 pF
IN
+9.9
–1.6
T
= 25C, I
A
(Note 3)
= 1A, tP = 8/20 mS
PP
0.96
0.5
= –40C to +85C unless otherwise noted.
A
Discharge
= 150 pF, R
= 330 W, VP = 3.3 V, VN grounded.
Discharge
.
P
mA
mA
kV
V
W
http://onsemi.com
2
Page 3
CM1293A−04SO
PERFORMANCE INFORMATION
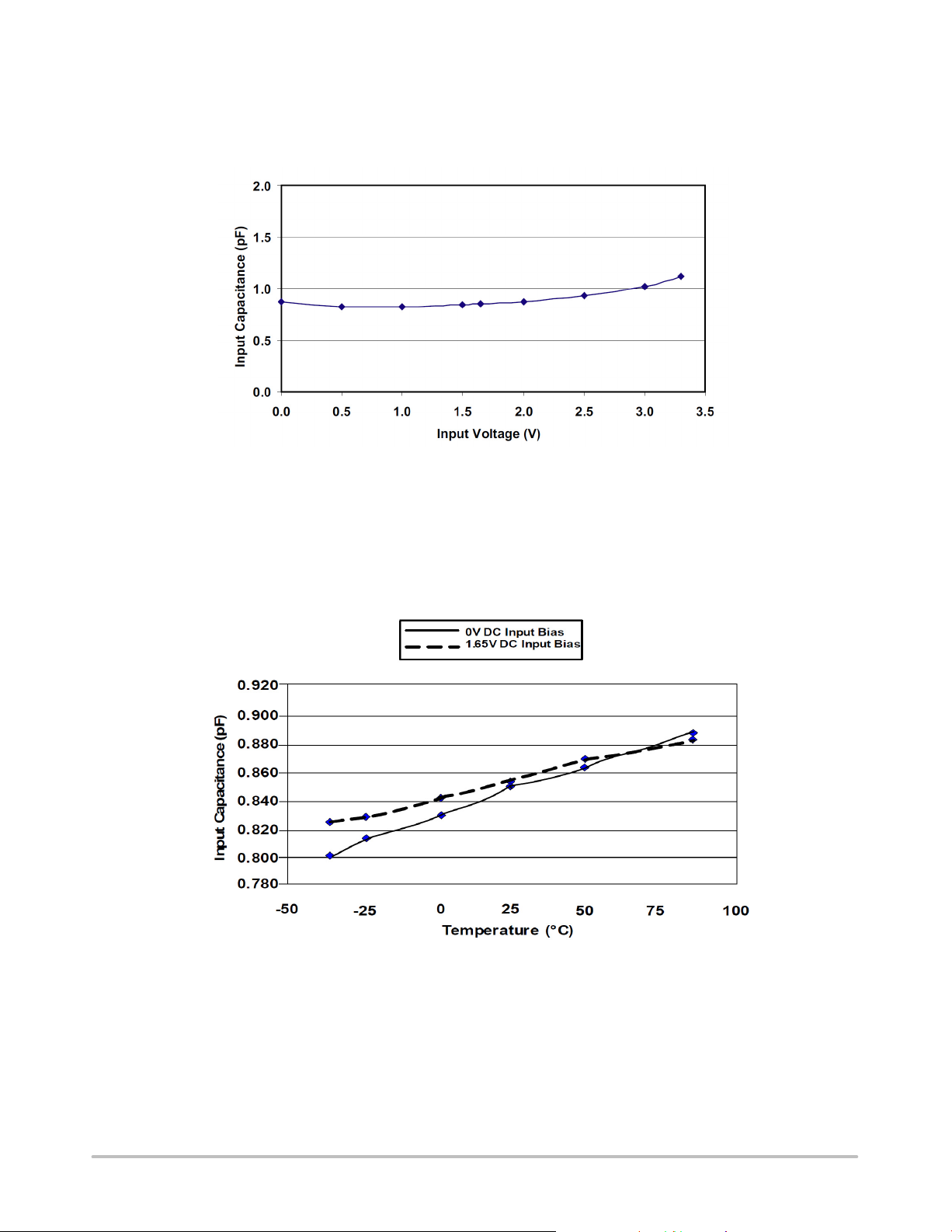
Input Channel Capacitance Performance Curves
Figure 1. Typical Variation of CIN vs. V
IN
(f = 1 MHz, VP = 3.3 V, VN = 0 V, 0.1 F Chip Capacitor between VP and VN, 255C)
(f = 1 MHz, V
Figure 2. Typical Variation of C
= 30 mV, VP = 3.3 V, VN = 0 V, 0.1 F Chip Capacitor between VP and VN)
IN
vs. Temp
IN
http://onsemi.com
3
Page 4

CM1293A−04SO
PERFORMANCE INFORMATION (Cont’d)
Typical Filter Performance (nominal conditions unless specified otherwise, 50 Environment)
Figure 3. Insertion Loss (S21) vs. Frequency (0 V DC Bias, V
= 3.3 V)
P
Figure 4. Insertion Loss (S21) vs. Frequency (2.5 V DC Bias, V
http://onsemi.com
4
= 3.3 V)
P
Page 5

CM1293A−04SO
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Design Considerations
In order to realize the maximum protection against ESD pulses, care must be taken in the PCB layout to minimize parasitic
series inductances on the Supply/Ground rails as well as the signal trace segment between the signal input (typically a
connector) and the ESD protection device. Refer to Figure 5, which illustrates an example of a positive ESD pulse striking an
input channel. The parasitic series inductance back to the power supply is represented by L
line being protected is:
and L2. The voltage VCL on the
1
V
where I
= Fwd voltage drop of D
CL
is the ESD current pulse, and V
ESD
1
+ V
SUPPLY
SUPPLY
+ L1 x d(I
) / dt+ L2 x d(I
ESD
is the positive supply voltage.
ESD
) / dt
An ESD current pulse can rise from zero to its peak value in a very short time. As an example, a level 4 contact discharge
per the IEC61000−4−2 standard results in a current pulse that rises from zero to 30 Amps in 1 ns. Here d(I
approximated by DI
increment in V
CL
/Dt, or 30/(1x10−9). So just 10 nH of series inductance (L
ESD
!
Similarly for negative ESD pulses, parasitic series inductance from the V
1
pin to the ground rail will lead to drastically
N
and L
combined) will lead to a 300 V
2
)/dt can be
ESD
increased negative voltage on the line being protected.
The CM1293 has an integrated Zener diode between V
L
on VCL by clamping VP at the breakdown voltage of the Zener diode. However, for the lowest possible VCL, especially when
2
V
is biased at a voltage significantly below the Zener breakdown voltage, it is recommended that a 0.22 F ceramic chip
P
capacitor be connected between V
and the ground plane.
P
and VN. This greatly reduces the effect of supply rail inductance
P
As a general rule, the ESD Protection Array should be located as close as possible to the point of entry of expected
electrostatic discharges. The power supply bypass capacitor mentioned above should be as close to the V
pin of the Protection
P
Array as possible, with minimum PCB trace lengths to the power supply, ground planes and between the signal input and the
ESD device to minimize stray series inductance.
L
2
V
P
PATH OF ESD CURRENT PULSE I
POSITIVE SUPPLY RAIL
ESO
V
CC
D
0.22 mF
V
N
1
D
2
ONE
CHANNEL
Figure 5. Application of Positive ESD Pulse between Input Channel and Ground
FireWire is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
i.LINK is a trademark of Sony Corporation.
L
1
CHANNEL
INPUT
0 A
25 A
LINE BEING
PROTECTED
V
CL
GROUND RAIL
SYSTEM OR
CIRCUITRY
BEING
PROTECTED
CHASSIS GROUND
http://onsemi.com
5
Page 6

MECHANICAL CASE OUTLINE
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
6
1
SCALE 2:1
D
456
E
b
A
0.05 (0.002)
H
E
1
23
e
A1
SOLDERING FOOTPRINT*
2.4
0.094
SC−74
CASE 318F−05
ISSUE N
c
L
DATE 08 JUN 2012
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
3. MAXIMUM LEAD THICKNESS INCLUDES LEAD FINISH
THICKNESS. MINIMUM LEAD THICKNESS IS THE MINIMUM
THICKNESS OF BASE MATERIAL.
4. 318F−01, −02, −03, −04 OBSOLETE. NEW STANDARD 318F−05.
DIMAMIN NOM MAX MIN
A1 0.01 0.06 0.10 0.001
b 0.25 0.37 0.50 0.010
c 0.10 0.18 0.26 0.004
D 2.90 3.00 3.10 0.114
q
E 1.30 1.50 1.70 0.051
e 0.85 0.95 1.05 0.034
L
H
E
q
MILLIMETERS
0.90 1.00 1.10 0.035
0.20 0.40 0.60 0.008
2.50 2.75 3.00 0.099 0.108 0.118
0° 10° 0° 10°
− −
INCHES
NOM MAX
0.039 0.043
0.002 0.004
0.015 0.020
0.007 0.010
0.118 0.122
0.059 0.067
0.037 0.041
0.016 0.024
GENERIC
MARKING DIAGRAM*
XXX MG
G
0.95
1.9
0.074
0.7
0.037
0.95
0.037
0.028
1.0
0.039
SCALE 10:1
ǒ
inches
mm
Ǔ
*For additional information on our Pb−Free strategy and soldering
details, please download the ON Semiconductor Soldering and
Mounting Techniques Reference Manual, SOLDERRM/D.
STYLE 1:
PIN 1. CATHODE
2. ANODE
3. CATHODE
4. CATHODE
5. ANODE
6. CATHODE
STYLE 7:
PIN 1. SOURCE 1
2. GATE 1
3. DRAIN 2
4. SOURCE 2
5. GATE 2
6. DRAIN 1
STYLE 2:
PIN 1. NO CONNECTION
2. COLLECTOR
3. EMITTER
4. NO CONNECTION
5. COLLECTOR
6. BASE
STYLE 8:
PIN 1. EMITTER 1
2. BASE 2
3. COLLECTOR 2
4. EMITTER 2
5. BASE 1
6. COLLECTOR 1
STYLE 3:
PIN 1. EMITTER 1
2. BASE 1
3. COLLECTOR 2
4. EMITTER 2
5. BASE 2
6. COLLECTOR 1
STYLE 9:
PIN 1. EMITTER 2
2. BASE 2
3. COLLECTOR 1
4. EMITTER 1
5. BASE 1
6. COLLECTOR 2
*This information is generic. Please refer to
STYLE 4:
PIN 1. COLLECTOR 2
2. EMITTER 1/EMITTER 2
3. COLLECTOR 1
4. EMITTER 3
5. BASE 1/BASE 2/COLLECTOR 3
6. BASE 3
STYLE 10:
PIN 1. ANODE/CATHODE
2. BASE
3. EMITTER
4. COLLECTOR
5. ANODE
6. CATHODE
XXX = Specific Device Code
M = Date Code
G = Pb−Free Package
(Note: Microdot may be in either location)
device data sheet for actual part marking.
Pb−Free indicator, “G” or microdot “ G”,
may or may not be present.
STYLE 5:
PIN 1. CHANNEL 1
2. ANODE
3. CHANNEL 2
4. CHANNEL 3
5. CATHODE
6. CHANNEL 4
STYLE 11:
PIN 1. EMITTER
2. BASE
3. ANODE/CATHODE
4. ANODE
5. CATHODE
6. COLLECTOR
STYLE 6:
PIN 1. CATHODE
2. ANODE
3. CATHODE
4. CATHODE
5. CATHODE
6. CATHODE
DOCUMENT NUMBER:
DESCRIPTION:
ON Semiconductor and are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC dba ON Semiconductor or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
ON Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. ON Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does ON Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically
disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation special, consequential or incidental damages. ON Semiconductor does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the
rights of others.
© Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2019
98ASB42973B
SC−74
Electronic versions are uncontrolled except when accessed directly from the Document Repository.
Printed versions are uncontrolled except when stamped “CONTROLLED COPY” in red.
PAGE 1 OF 1
www.onsemi.com
Page 7

ON Semiconductor and are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC dba ON Semiconductor or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
ON Semiconductor owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of ON Semiconductor’s product/patent
coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marking.pdf
ON Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does ON Semiconductor assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation special, consequential or incidental damages.
Buyer is responsible for its products and applications using ON Semiconductor products, including compliance with all laws, regulations and safety requirements or standards,
regardless of any support or applications information provided by ON Semiconductor. “Typical” parameters which may be provided in ON Semiconductor data sheets and/or
specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer
application by customer’s technical experts. ON Semiconductor does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. ON Semiconductor products are not
designed, intended, or authorized for use as a critical component in life support systems or any FDA Class 3 medical devices or medical devices with a same or similar classification
in a foreign jurisdiction or any devices intended for implantation in the human body. Should Buyer purchase or use ON Semiconductor products for any such unintended or unauthorized
application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold ON Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and
expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such
claim alleges that ON Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. ON Semiconductor is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer. This
literature is subject to all applicable copyright laws and is not for resale in any manner.
. ON Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein.
PUBLICATION ORDERING INFORMATION
LITERATURE FULFILLMENT:
Email Requests to: orderlit@onsemi.com
ON Semiconductor Website: www.onsemi.com
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
North American Technical Support:
Voice Mail: 1 800−282−9855 Toll Free USA/Canada
Phone: 011 421 33 790 2910
Europe, Middle East and Africa Technical Support:
Phone: 00421 33 790 2910
For additional information, please contact your local Sales Representative
◊
www.onsemi.com
1
 Loading...
Loading...