OMVC ATSC A/153 Profile Manuallines

ATSC Mobile DTV Receiver
Profile Guidelines
Final – December 2012
July 2013 version

OMVC – ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines Page i
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................. 1
Conditional Access ........................................................................................................... 1
Service/Audience Measurement ........................................................................................ 2
IP Connectivity ................................................................................................................. 2
ATSC MOBILE DTV RECEIVER PROFILE GUIDELINES TABLE ................................... 3
GLOSSARY OF KEY MDTV TERMS ......................................................................... 8
REFERENCE DOCUMENTS .................................................................................. 16

ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines
Introduction
Consumers increasingly demand access to local content and enhanced television services on
their portable devices, which makes Mobile DTV a great opportunity for consumer electronics
device manufacturers. By developing Mobile DTV receivers, manufacturers can tap into the
growing universe of consumers who want to tune in to live, local news, traffic information,
weather, sporting events and entertainment programs while on the go – in their car, on the
beach, or wherever they may be.
The Open Mobile Video Coalition (OMVC), working with device manufacturers through their
participation in the Mobile DTV Forum, and in collaboration with broadcasters and other
stakeholders in the Mobile DTV ecosystem, has developed these ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV
Receiver Profile Guidelines. They provide directional guidance to consumer electronics
manufacturers on the device features and functionalities that will help ensure that devices have
robust reception capability and interoperability with services offered by broadcasters – and
that consumers have an enjoyable and secure Mobile DTV experience.
These guidelines provide two Mobile DTV receiver profiles for illustrative purposes. The first
profile represents a basic Mobile DTV receiver that can receive broadcast transmissions and
that is interoperable with real-time linear Mobile DTV broadcast services. The second profile
represents an enhanced Mobile DTV receiver that includes all the basic elements plus many of
the advanced features and functionalities that many consumers will demand.
Consumer electronics manufacturers will be familiar with many elements of the ATSC A/153
Mobile DTV Receiver Profiles, such as digital recording and pausing functionality. However,
both profiles also address three new elements that OMVC believes are critical to Mobile DTV’s
success, conditional access, service/audience measurement and Internet Protocol (IP)
connectivity:
Conditional Access. The ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV standard incorporates a conditional
access system that is based on the OMA-DRM standard. Because we anticipate that
some Mobile DTV services will use service protection, both profiles require support for
conditional access. In both cases, registration with a Mobile DTV trust authority is
required so that unique digital certificates can be issued to each Mobile DTV receiver.
Short term keys are sent over the broadcast channel. In order to provide a Mobile DTV
system that can effectively handle a large volume of users, OMVC believes the Mobile
DTV service protection system must incorporate the use of an interaction channel.
OMVC – ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines Page 1

Service/Audience Measurement. To date, broadcasters have only been able to make
decisions using audience estimates based on sampling techniques. Mobile DTV’s new
service and audience measurement tools will enable broadcasters to identify which
channels are viewed, the duration and time of viewing, and channel changing and video
download activity from every viewer who agrees to share such information. This data
allows broadcasters to provide a more effective advertising-supported Mobile DTV
service.
IP Connectivity. To facilitate the operation of the conditional access system and the
transmission of service and audience data, the Mobile DTV receiver must offer IP
connectivity at least once every seven days using, for example, an Internet, Wi-Fi, 2G,
3G, 4G, USB, or Bluetooth connection.
Since the Advanced Television Systems Committee adopted the ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV
standard in 2009, broadcasters have developed new and innovative Mobile DTV services and
business models based on the standard. Ongoing innovation, in turn, drives the development
of features and functionalities that consumers will demand as part of the Mobile DTV
experience. These ATSC Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines are an important step in
helping consumer electronics device manufacturers predict and meet this demand.
OMVC encourages manufacturers to continue working closely with broadcasters and other
industry stakeholders not only in implementing the functionalities in these Receiver Profile
Guidelines but also in developing exciting new features that go beyond these baseline
requirements. Naturally, commercial Mobile DTV service providers may have additional device
requirements and should be contacted directly. We will continue to support all key
stakeholders as they work to advance Mobile DTV and ensure its commercial success.
The Open Mobile Video Coalition
These guidelines are based on our understanding of current industry practices and technology. They are provided
“as is” and without warranty of any kind. The user is responsible for obtaining any applicable licenses or
authorizations to use the technologies, standards, and specifications referenced in the guidelines.
OMVC – ATSC A/153 Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines Page 2
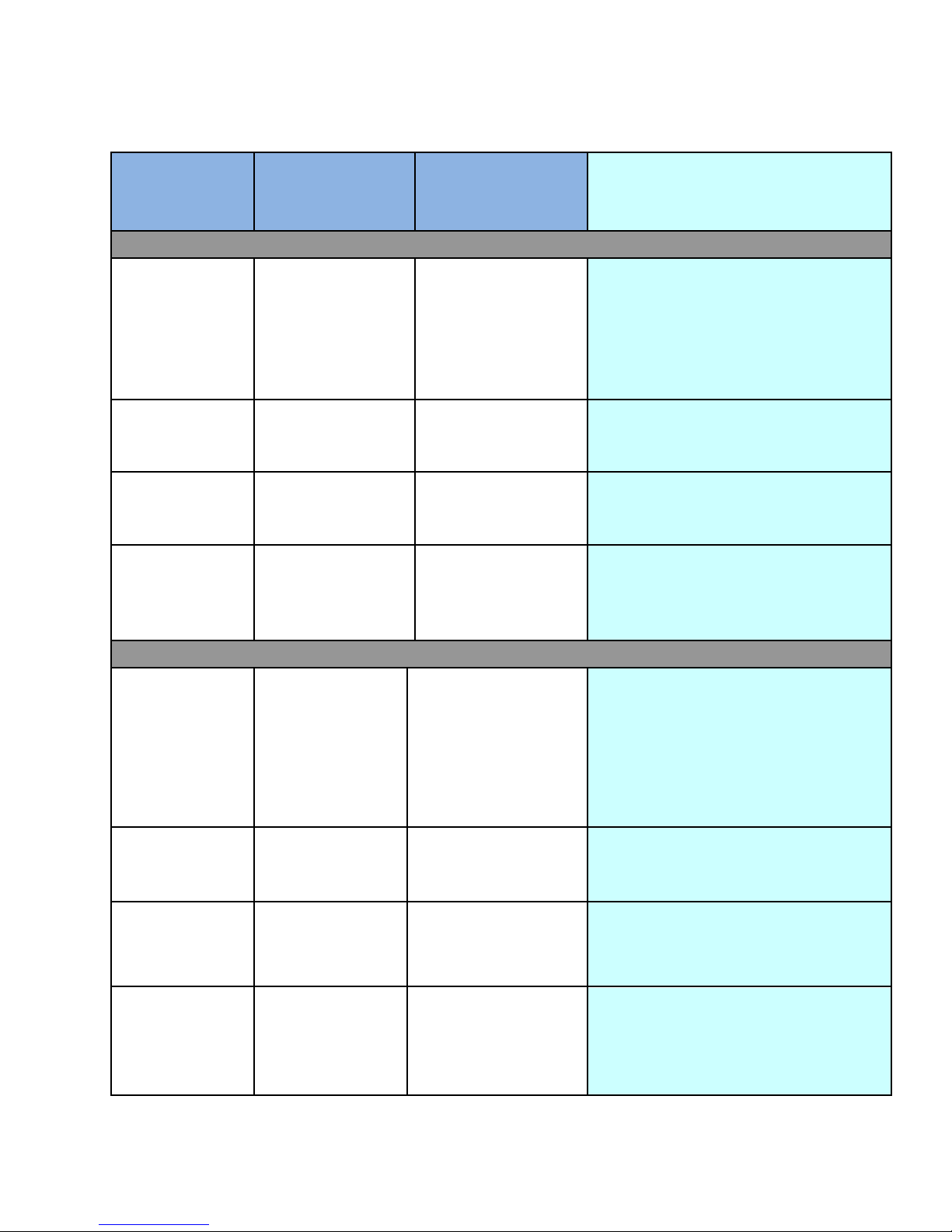
Functions &
Features
Base Profile
(Required)
Enhanced
Profile
(Optional)
OMVC Comments and
Rationale
RF
Channel tuning
US Channels 7-56
US Channels 7-56
Both profiles should tune Ch. 7-56.
Because of the physics of the receive
system, the general power levels allowed
in Low-band VHF, and the noise
environment in that band, we are
excluding Low-band VHF
External
Antenna
Connection
Desirable
Desirable
An external antenna connection is
desirable in both profiles where it is
practical in a specific device
Second tuner
Not Required
Desirable
In either profile the mix of capabilities is
left up to the receiver designers'
assessment of the market
SFCMM
Not Required
Desirable
SCFMM is acceptable in both profiles,
but the mix of capabilities is left up to
the receiver designers' assessment of the
market
Essence (Video / Audio) Decoding
H.264 profile
Base profile v1.3
& Main profile up
to v3.1
Base profile v1.3 &
Main profile up to
v3.1
The standard specifies Main Profile,
Level 3.1 for resolutions greater than
416x240, but using SVC. Since SVC is not
commercially available, OTAG
recommends AVC at Main Profile, Level
3.1. This capability needs to be in both
profiles.
SVC
Not Used
Not Used
SVC has not appeared in the marketplace
and since H.264 Level 3.1 can replace it,
there is no plan to use SVC
Audio
HE-AAC V2
(w/SBR) as
constrained in
A/153 Part 8
HE-AAC V2 (w/SBR)
as constrained in
A/153 Part 8
HE-AAC V2 with SBR is part of the
standard and is required in both profiles.
Note that A/153 requires the average
loudness of the audio to be -14 LKFS.
Multiple audio
services
Required
Required
The capability to receive different audio
services (one at a time) is required in
both profiles. Second language and
Descriptive Video Services are two
currently available services
ATSC MOBILE DTV RECEIVER PROFILE GUIDELINES TABLE
OMVC – ATSC Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines Page 3
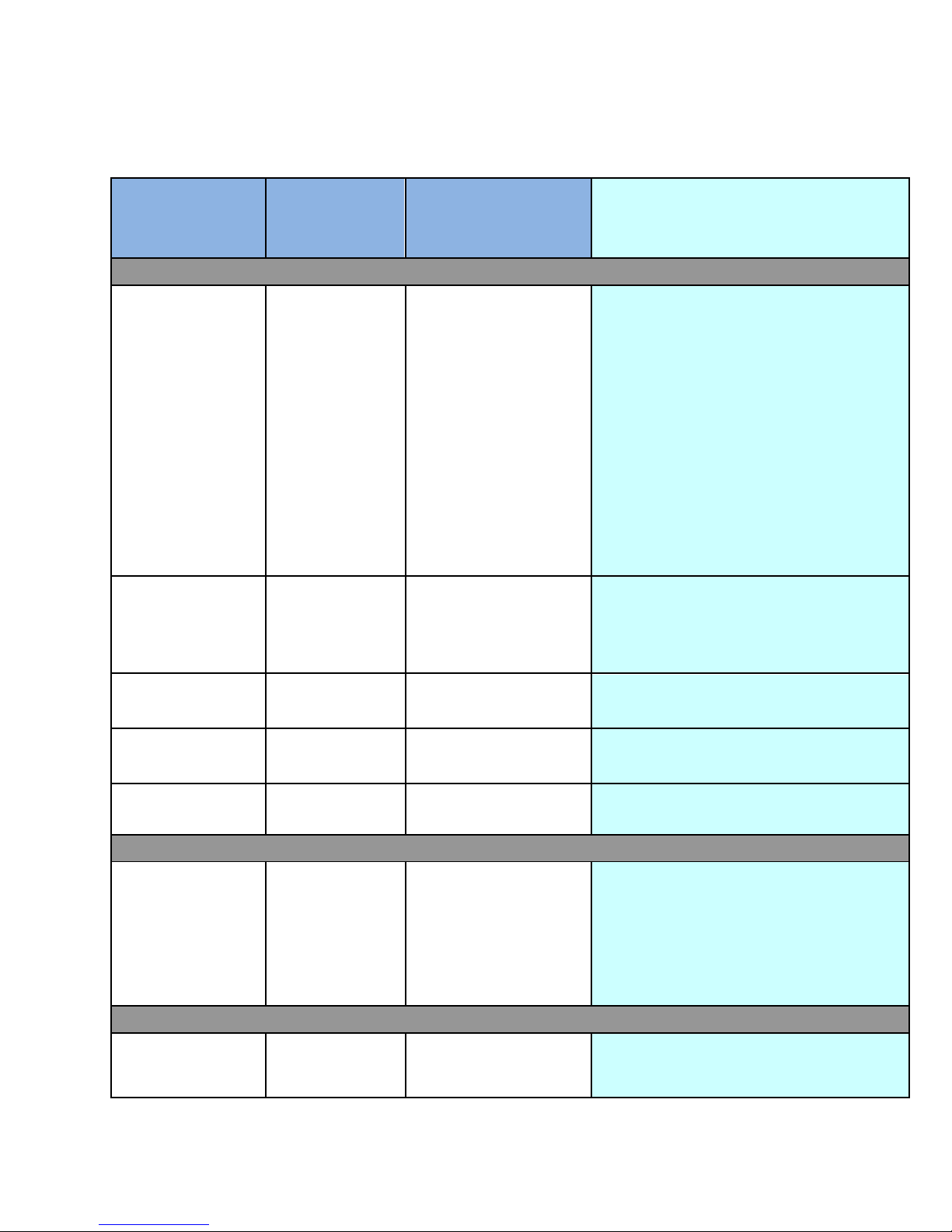
Functions &
Features
Base Profile
(Required)
Enhanced Profile
(Optional)
OMVC Comments and Rationale
Conditional Access/Service Protection
CA Type
ATSC-MH
Compliant-
Broadcast &
Interactive
mode
Note: See the
OMVC Service
Protection White
Paper for
additional details
on ATSC MDTV
Conditional
Access
Required
*Note: Some
commercial MDTV
services require an
additional application to
deliver Conditional
Access key source
information. These
applications should be
deployed in addition to
the standardized
method.
Note that the standard requires
implementation of a key delivery over an
interaction channel if an interaction channel
exists.
We believe that the most likely business reality
will dictate that at least some services using
Mobile DTV will use service protection. We
have concluded that the only large scale (10^5
and up units) practical way to implementation
of a usable service protection scheme will
require that key exchange happen over an
interaction channel. This is due to the
constraints on over-the-air channel capacity.
Therefore we advise device manufacturers that
devices without any kind of interaction channel
will most likely not be able to receive at least
some services that may be made available.
Long term key
delivery
For practical
implementation,
Interaction
channel is
required
For practical
implementation,
Interaction channel is
required
OMVC members need the interaction
channel for long term key delivery
especially as volume scales to large values
Short term key
delivery
In Band from
broadcast
service
In Band from
broadcast service
Required for business plans
Trust Authority
Registration
(Neustar)
Required
Required
Required for business plans
Clear-to-air (no
encryption)
Supported
Supported
Required for business plans
Additional Connectivity (interaction channel)
Periodic IP
Connectivity,
such as
connected
Internet, WIFI, 2G,
3G 4G, others or
USB or Bluetooth
via helper device
Required from
one
Required from one
Periodic IP Connectivity is required from at
least one of the following: Internet, WIFI,
2G, 3G 4G, others or USB or Bluetooth via
helper device. How periodic needs to be
defined, but no longer than seven days.
Electronic Service Guide
Type
OMA-BCAST, as
constrained by
A/153
OMA-BCAST, as
constrained by A/153
OMVC members plan to use the OMABCAST for Service Guides delivered in
band.
OMVC – ATSC Mobile DTV Receiver Profile Guidelines Page 4
 Loading...
Loading...