Page 1

Machine Automation Controller NJ-series
EtherCAT
Connection Guide
OMRON Corporation
E3X-ECT Sensor Communication Unit
(EtherCAT Slave)
P529-E1-01
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. Related Manuals........................................................................................ 1
2. Terms and Definition................................................................................. 2
3. Remarks..................................................................................................... 3
4. Overview .................................................................................................... 5
5. Applicable Devices and Support Software.............................................. 5
5.1. Applicable Devices............................................................................. 5
5.2. Device Configuration.......................................................................... 6
6. EtherCAT Settings..................................................................................... 7
6.1. EtherCAT Communications Settings .................................................. 7
6.2. Allocating the Global Variables .......................................................... 7
7. Connection Procedure.............................................................................. 9
7.1. Work Flow .......................................................................................... 9
7.2. Setting Up the Sensor Communication Unit..................................... 10
7.3. Setting Up the Controller.................................................................. 12
7.4. Checking the Connection Status...................................................... 23
8. Initialization Method................................................................................ 28
8.1. Controller ......................................................................................... 28
9. Revision History...................................................................................... 29
Page 3
1. Related Manuals
1
1. Related Manuals
The table below lists the manuals related to this document.
To ensure system safety, make sure to always read and heed the information provided in all
Safety Precautions, Precautions for Safe Use, and Precaution for Correct Use of manuals for
each device which is used in the system.
Cat.No. Model Manual name
W500 NJ501-[][][][] NJ-series CPU Unit Hardware User's Manual
W501 NJ501-[][][][] NJ-series CPU Unit Software User's Manual
W505 NJ501-[][][][] NJ-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherCAT Port User's Manual
W504 SYSMAC-SE2[][][] Sysmac Studio Version 1 Operation Manual
E413 E3X-ECT E3X-ECT EtherCAT Sensor Communications Unit Operation
Manual
Page 4
2. Terms and Definition
2
2. Terms and Definition
Te rm s Explanation and Definition
PDO
Communications
(Communications
using Process Data
objects)
This method is used for cyclic data exchange between the master unit
and the slave units.
PDO data (i.e., I/O data that is mapped to PDOs) that is allocated in
advance is refreshed periodically each EtherCAT process data
communications cycle (i.e., the period of primary periodic task).
The NJ-series Machine Automation Controller uses process data
communications for commands to refresh I/O data in a fixed control
period, including I/O data for EtherCAT Slave Units, and the position
control data for the Servomotors.
It is accessed from the NJ-series Machine Automation Controller in the
following ways.
•With device variables for EtherCAT slave I/O
•With Axis Variables for Servo Drive and encoder input slaves to which
assigned as an axis
SDO
Communications
(Communications
using Service Data
objects)
This method is used to read and write the specified slave unit data from
the master unit when required.
The NJ-series Machine Automation Controller uses SDO
communications for commands to read and write data, such as for
parameter transfers, at specified times.
The NJ-series Machine Automation Controller can read/write the
specified slave data (parameters and error information, etc.) with the
EC_CoESDORead (Read CoE SDO) instruction or the
EC_CoESDOWrite (Write CoE SDO) instruction.
Slave There are various types of slaves such as Servo Drives that handle
position data and I/O terminals that control the bit signals.
The slave receives output data sent from the master, and transmits
input data to the master.
Node address An address to identify the unit connected to EtherCAT.
ESI file
(EtherCAT Slave
Information file)
The ESI files contain information unique to the EtherCAT slaves in XML
format.
Install an ESI file into the Sysmac Studio, to allocate slave process data
and make other settings.
Page 5

3. Remarks
3
3. Remarks
(1) Understand the specifications of devices which are used in the system. Allow some
margin for ratings and performance. Provide safety measures, such as installing safety
circuit in order to ensure safety and minimize risks for abnormally occurrence.
(2) To ensure system safety, always read and heed the information provided in all Safety
Precautions, Precautions for Safe Use, and Precaution for Correct Use of manuals for
each device which is used in the system.
(3) The users are encouraged to confirm the standards and regulations that the system must
conform to.
(4) It is prohibited to copy, to reproduce, and to distribute a part of or whole part of this
document without the permission of OMRON Corporation.
(5) This document provides the latest information as of March 2013. The information on
this manual is subject to change for improvement without notice.
About Intellectual Property Right and Trademarks
Microsoft product screen shots reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the USA and other countries.
EtherCAT® is registered trademark and patented technology, licensed by Beckhoff Automation
GmbH, Germany.
Company names and product names in this document are the trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 6

3. Remarks
The following not
ation is used in this document.
Precautions for Safe Use
Indicates precautions on what to do and what not to do to ensure using the product safely.
Precautions for Correct Use
Indicates precautions on what to do and what not to do to ensure proper operation and
performance.
Additional Information
Provides useful information.
Additional information to increase understanding or make operation easier.
4
Page 7

4. Overview
4. Overview
This document describes the procedure for connecting the Sensor Communication Unit
(E3X-ECT) of OMRON Corporation (hereinafter referred to as OMRON) to NJ-series Machine
Automation Controller (hereinafter referred to as Controller) on EtherCAT and provides the
procedure for checking their connection.
Refer to Section 7 Connection Procedure to understand the setting method and key points to
connect the devices via EtherCAT.
5. Applicable Devices and Support Software
5.1. Applicable Devices
The following devices can be connected.
Manufacturer Name Model Version
OMRON NJ series CPU Unit NJ501-[][][][] -
OMRON Sensor Communications Unit
(EtherCAT slave)
E3X-ECT -
OMRON Standard Fiber Sensor E3X-HD0 OMRON 2CH Fiber Sensor E3X-MDA0 OMRON High-function Fiber Sensor E3X-DA0-S OMRON Laser Amplifier E3C-LDA0 OMRON Proximity Sensor Amplifier E2C-EDA0 -
Additional Information
As applicable devices above, the devices listed in Section 5.2. are actually used in this
document to check the connection. When using devices not listed in Section 5.2, check the
connection by referring to the procedure in this document.
Additional Information
This document describes the procedure to establish the network connection. It does not
provide information about operation, installation nor wiring method of each device.
For details on above products (other than communication connection procedures), refer to
the manuals for the corresponding products or contact your OMRON representative.
5
Page 8

5. Applicable Devices and Support Software
5.2. Device Configuration
The hardware components to reproduce the connection procedure of this document are as
follows.
E3X-ECT
Personal computer
(Sysmac Studio installed,
OS:Windows7)
6
Manufacturer Name Model Version
OMRON CPU Unit
(Built-in EtherCAT port)
NJ501-1500
OMRON Power Supply Unit NJ1W-PA3001
OMRON Sysmac Studio SYSMAC-SE2[][][] Ver.1.01
- Personal computer
(OS:Windows7)
- USB cable
(USB 2.0 type B connector)
OMRON Ethernet cable (with industrial
Ethernet connector)
XS5W-T421-[]M[]-K
OMRON Sensor Communications Unit
(EtherCAT slave)
E3X-ECT
OMRON Fiber Sensor
E3X-HD0
Precautions for Correct Use
The connection line of EtherCAT communication cannot be shared with other networks, such
as Ethernet or EtherNet/IP.
The switching hub for Ethernet cannot be used for EtherCAT.
Please use the cable of Category 5 or higher, double-shielded with aluminum tape and
braided shielding and the shielded connector of Category 5 or higher.
Connect the cable shield to the connector hood at both ends of the cable.
Additional Information
For information on the specifications of the Ethernet cable and network wring, refer to Section
4 EtherCAT Network Wiring in the NJ-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherCAT Port User's Manual
(Cat. No. W505).
Additional Information
The system configuration in this document uses USB for the connection between the
personal computer and the NJ-series CPU Unit. For information on how to install a USB
driver, refer to A-1 Driver Installation for Direct USB Cable Connection of the Sysmac Studio
Operation Manual (Cat.No. W504).
USB cable
NJ
501-1500
(Built-in EtherCAT port)
E3X-HD0 (3 units
)
Ethernet cable
Page 9

6. EtherCAT Settings
7
6. EtherCAT Settings
This section describes the specifications such as communication parameters and variables
that are set in this document.
6.1. EtherCAT Communications Settings
The following is the setting of the destination device.
E3X-ECT
Node address 001
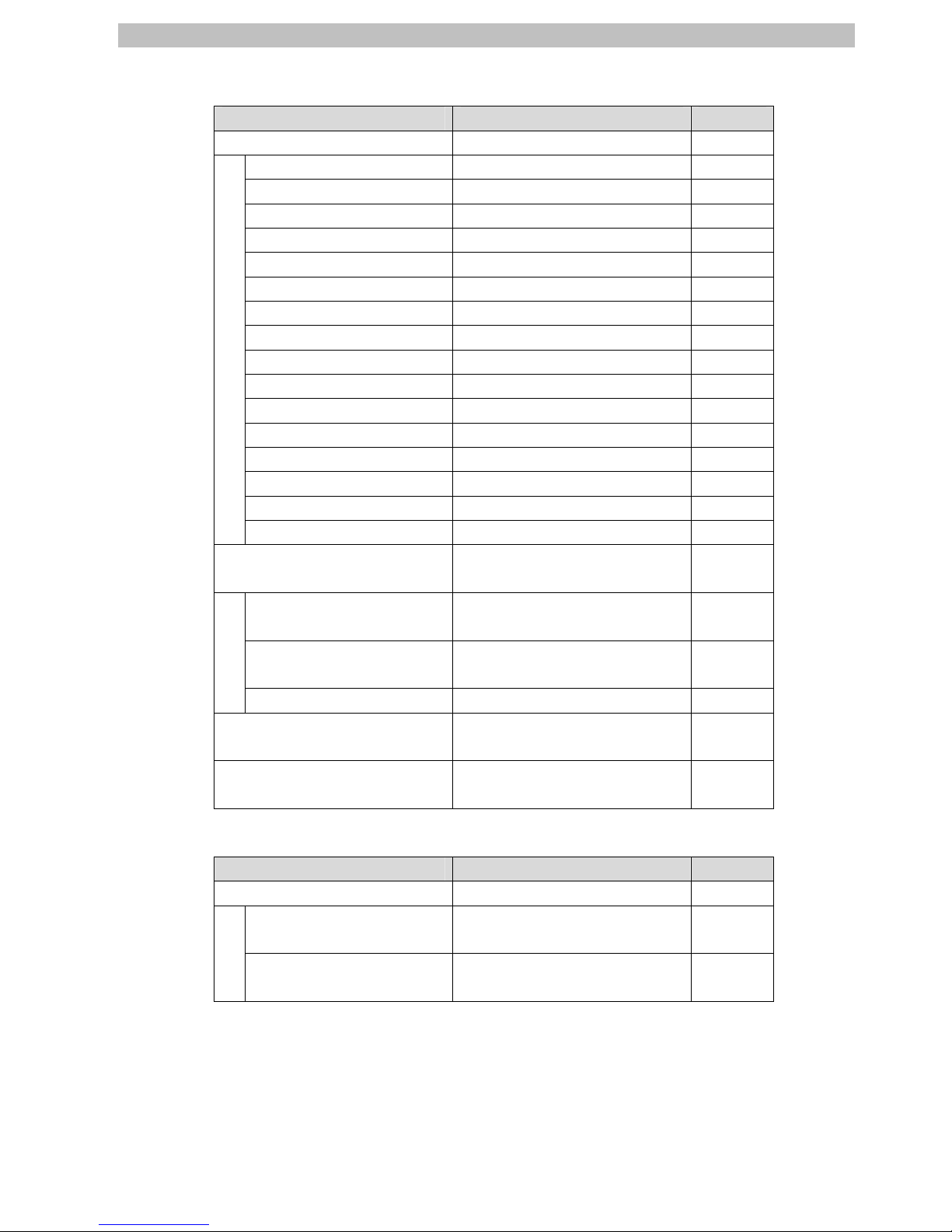
6.2. Allocating the Global Variables
The device variables of the destination device are allocated to the Controller's global
variables.
The relationship between the device data and the global variables is shown below.
■Input area (Controller ← Destination device)
Destination device data Global variable name Data type
Input bits 00 to 15 E001_Read_input_1st_word WORD
Sensor 1 output 1 E001_In_Bit00 BOOL
Sensor 1 output 2 E001_In_Bit01 BOOL
Sensor 2 output 1 E001_In_Bit02 BOOL
Sensor 2 output 2 E001_In_Bit03 BOOL
Sensor 3 output 1 E001_In_Bit04 BOOL
Sensor 3 output 2 E001_In_Bit05 BOOL
Sensor 4 output 1 E001_In_Bit06 BOOL
Sensor 4 output 2 E001_In_Bit07 BOOL
Sensor 5 output 1 E001_In_Bit08 BOOL
Sensor 5 output 2 E001_In_Bit09 BOOL
Sensor 6 output 1 E001_In_Bit00 BOOL
Sensor 6 output 2 E001_In_Bit11 BOOL
Sensor 7 output 1 E001_In_Bit12 BOOL
Sensor 7 output 2 E001_In_Bit13 BOOL
Sensor 8 output 1 E001_In_Bit14 BOOL
Sensor 8 output 2 E001_In_Bit15 BOOL
Page 10
6. EtherCAT Settings
8
Destination device data Global variable name Data type
Input bits 16 to 31 E001_Read_input_2nd_word WORD
Sensor 9 output 1 E001_In_Bit16 BOOL
Sensor 9 output 2 E001_In_Bit17 BOOL
Sensor 10 output 1 E001_In_Bit18 BOOL
Sensor 10 output 2 E001_In_Bit19 BOOL
Sensor 11 output 1 E001_In_Bit20 BOOL
Sensor 11 output 2 E001_In_Bit21 BOOL
Sensor 12 output 1 E001_In_Bit22 BOOL
Sensor 12 output 2 E001_In_Bit23 BOOL
Sensor 13 output 1 E001_In_Bit24 BOOL
Sensor 13 output 2 E001_In_Bit25 BOOL
Sensor 14 output 1 E001_In_Bit26 BOOL
Sensor 14 output 2 E001_In_Bit27 BOOL
Sensor 15 output 1 E001_In_Bit28 BOOL
Sensor 15 output 2 E001_In_Bit29 BOOL
Sensor 16 output 1 E001_In_Bit30 BOOL
Sensor 16 output 2 E001_In_Bit31 BOOL
Sensor Communications Status
8 bits
E001_Sensor_Communication_
Status
BYTE
Sensor communication
busy
E001_Sensor_Communication_
Busy
BOOL
Sensor communication
error
E001_Sensor_Communication_
Error
BOOL
Number of Sensors setting E001_Number_of_Sensors_Sett
ing
USINT
Number of Sensors (incl.
dummy)
E001_Number_of_Sensors_with
_Dummy
USINT
■Details of the status allocation (Controller ← Destination device)
Destination device data Global variable name Data type
Sysmac Error Status E001_Sysmac_Error_Status BYTE
Error information at
observation level
E001_Observation BOOL
Error information at minor
fault level
E001_Minor_Fault BOOL
Page 11

7. Connection Procedure
9
7. Connection Procedure
This section describes how to connect the Sensor Communication Unit via EtherCAT.
This document explains the procedures for setting up the Controller and Sensor
Communication Unit from the factory default setting. For the initialization, refer to Section 8
Initialization Method.
7.1. Work Flow
The following is the procedure for connecting to EtherCAT.
7.2 Setting Up the Sensor
Communication Unit
Set up the Sensor Communication Unit.
↓
7.2.1 Hardware Settings Check the hardware switches on the Sensor
Communication Unit.
↓
7.3 Setting Up the Controller Set up the Controller.
↓
7.3.1 Starting the Sysmac Studio and
Setting the EtherCAT network
configuration
Start the Automation Software Sysmac Studio and
set the EtherCAT network configuration.
↓
7.3.2 Setting the Global Variables Set global variables to use for the EtherCAT Slave
Unit.
↓
7.3.3 Transferring the Project Data Transfer the project data from the Sysmac Studio to
the Controller.
↓
7.3.4 Setting the Number of
Connected Sensors
Set the number of Sensors connected to the Sensor
Communication Unit.
↓
7.4 Checking the Connection Status Check the EtherCAT network connection status.
↓
7.4.1 Checking the Connection Status Check that the EtherCAT communication is normally
performed.
↓
7.4.2 Checking Data that are Sent and
Received
Check if the correct data are sent and received.
Page 12

7. Connection Procedure
7.2. Setting Up the Sensor Communication Unit
Set up the Sensor Communication Unit.
7.2.1. Hardware Settings
Check the hardware switches on the Sensor Communication Unit.
Precautions for Correct Use
Make sure that the power supply is OFF when you perform the settings.
1
Make sure that the power supply
of the Sensor Communication
Unit is turned OFF.
*If the power supply is turned
ON, settings may not be
applicable as described in the
following procedure.
2
Mount the Sensor
Communication Unit and Sensor
Amplifier.
*For information on mounting
method, refer to 4-1-1 Mounting
Method in the E3X-ECT
EtherCAT Sensor
Communications Unit
Operation Manual (Cat. No.
E413).
10
Page 13

7. Connection Procedure
3
Refer to the right figure and
check the hardware switches
located on the front panel of the
Sensor Communication Unit.
Set the NODE ADDRESS
switches as follows:
x 100 to 0
x 10 to 0
x 1 to 1
Set the node address to 001.
4
Connect the Ethernet
Communication cable to the
built-in EtherCAT port on the
front panel of the Sensor
Communication Unit.
Connect the power supply to the
power supply connector.
11
Page 14

7. Connection Procedure
7.3. Setting Up the Controller
Set up the Controller.
7.3.1. Starting the Sysmac Studio and Setting the EtherCAT Network
Configuration
Start the Automation Software Sysmac Studio and set the EtherCAT network configuration.
Install the software and USB driver beforehand.
1
Start the Sysmac Studio.
Click the New Project Button.
2
The Project Properties Window
is displayed. Check that
Controller is selected from the
category and NJ501 is selected
from the device in the Select
Device Field. Then, click the
Create Button.
*In this document, New Project
is set as the project name.
3
The New Project is displayed.
There are Menu Bar and Toolbar
in the upper part of the pane.
The left pane is called Multiview
Explorer, the right pane is called
Toolbox and the middle pane is
called Edit Pane.
Multiview
Explorer
Edit Pane Toolbox
Menu Bar Toolbar
12
Page 15
7. Connection Procedure
4
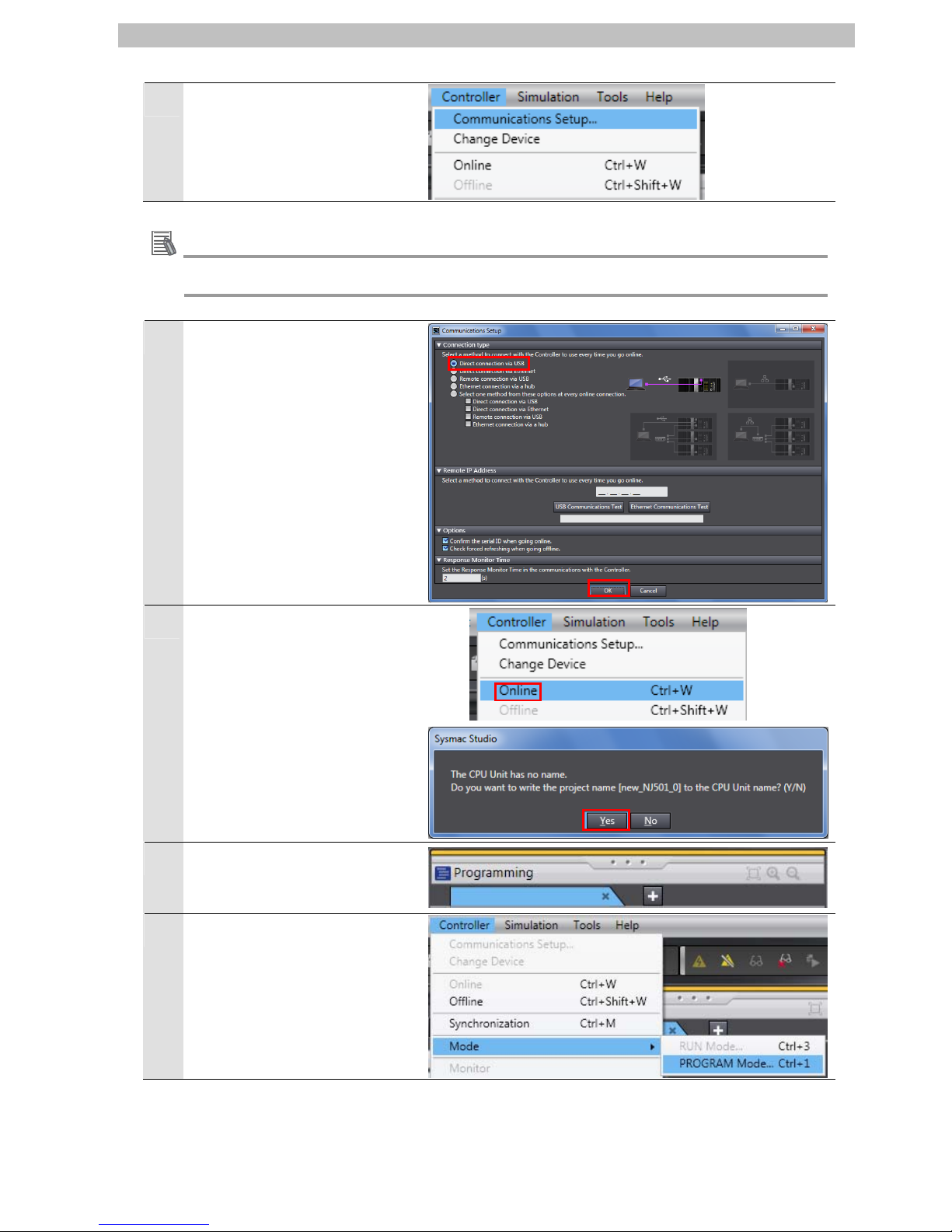
Select Communications Setup
from the Controller Menu.
Additional Information
For details on the online connections to a Controller, refer to Section 5 Going Online with a
Controller in the Sysmac Studio Version 1.0 Operation Manual (Cat. No. W504).
5
The Communications Setup
Dialog Box is displayed.
Select Direct Connection via
USB from Connection Type.
Click the OK Button.
6
Select Online from the
Controller Menu.
A confirmation dialog is
displayed. Click the Yes Button.
*A displayed dialog depends on
the status of the Controller
used. Select the Yes Button or
other button to proceed with the
processing.
7
When an online connection is
established, a yellow bar is
displayed on the top of the Edit
Pane.
8
Select Mode - PROGRAM
Mode from the Controller Menu.
13
Page 16

7. Connection Procedure
9
A confirmation dialog is
displayed. Click the Yes Button.
Check that the controller status
on the Toolbox is changed to the
PROGRAM mode.
10
Double-click EtherCAT under
Configurations and Setup in the
Multiview Explorer.
Or, right-click EtherCAT under
Configurations and Setup and
select Edit.
11
The EtherCAT Tab Page is
displayed in the Edit Pane.
12
Right-click the Master Icon and
select Compare and Merge
with Actual Network
Configuration.
A screen is displayed stating
"Get information is being
executed".
13
The Compare and Merge with
Actual Network Configuration
Pane is displayed.
Node address 1 and E3X-ECT
Rev:1.0 are added to the Actual
network configuration after the
comparison.
Click the Apply actual network
configuration Button.
14
Page 17

7. Connection Procedure
14
A confirmation dialog box is
displayed. Click the Apply
Button.
Check that node address 1 and
E001 E3X-ECT Rev:1.0 are
added to the Network
configuration on Sysmac Studio.
15
Node address 1 and E001
E3X-ECT Rev:1.0 are added to
the EtherCAT Tab Page in the
Edit Pane.
15
Page 18

7. Connection Procedure
7.3.2. Setting Global Variables
Set global variables to use for the EtherCAT Slave Unit.
1
Select Offline from the
Controller Menu.
2
Double-click I/O Map under
Configurations and Setup on the
Multiview Explorer, or right-click
I/O Map and select Edit.
3
The I/O Map Tab is displayed on
the Edit Pane.
Click a column under Variable to
enter a new variable.
4
Right-click the row for Node1
and E3X-ECT. Then, select
Create Device Variable.
16
Page 19

7. Connection Procedure
5
The Variable names and
Variable Types are automatically
set.
Additional Information
The device variable names are created automatically from a combination of the device
names and the I/O port names.
For slave units, the default device names start with an "E" followed by a sequential number
starting from "001".
Additional Information
In the example above, a device variable name is automatically created for each slave.
However, a name can also be automatically created for each I/O port.
Also, you can set any device variables.
17
Page 20

7. Connection Procedure
7.3.3. Transferring Project Data
Transfer the project data from the Sysmac Studio to the Controller.
1
Select Online from the
Controller Menu.
When an online connection is
established, a yellow bar is
displayed on the top of the Edit
Pane.
2
Select Synchronization from
the Controller Menu.
3
The Synchronization Dialog Box
is displayed.
Check that the data to transfer
(NJ501 in the right figure) is
selected. Then, click the
Transfer to Controller Button.
4
A confirmation dialog is
displayed. Click the Yes Button.
A screen stating "Synchronizing"
is displayed.
18
Page 21

7. Connection Procedure
5
Check that the synchronized
data is displayed with the color
specified by “Synchronized”,
and that a message is displayed
stating "The synchronization
process successfully finished".
If there is no problem, click the
Close Button.
*If the synchronization fails,
check the wiring and repeat the
procedure described in this
section.
19
Page 22

7. Connection Procedure
7.3.4. Setting the Number of Sensors to Connect
Set the number of Sensors connected to the Sensor Communication Unit
1
Double-click the Parameter
under Configurations and Setup
- EtherCAT -
Node1:E3X-ECT(E001) in the
Multiview Explorer or right-click
Parameter and select Edit from
the menu.
2
Node1:E3X-ECT(E001) Tab
Page is displayed in the Edit
Pane.
In the 0x3001:01 Number of
Sensors/Number of Sensors
Setting, set the number of
Sensors connected to the
Sensor Communication Unit (in
this document, 3 is set).
Click the Transfer to Slave
Button.
20
Page 23

7. Connection Procedure
3
A confirmation dialog box is
displayed. Click the Transfer
Button.
A screen is displayed indicating
the transfer is being performed.
A screen is displayed indicating
the setting was written in the
salve. Click the Close Button.
4
After the transfer is completed,
click the OK Button.
Turn OFF the power supply to
the Sensor Communication Unit.
Turn ON the power supply
again.
5
Clear a Link OFF error that
occurs when communications
with the Sensor Communication
Unit is disconnected.
Select Troubleshooting from
the Tools Menu.
21
Page 24

7. Connection Procedure
6
The Troubleshooting Dialog Box
is displayed.
A link OFF error is occurring.
Click the Reset All Button.
7
A confirmation dialog is
displayed. Click the Yes Button.
8
Check that a message stating
No error is displayed. Click the
button to exit.
22
Page 25

7. Connection Procedure
7.4. Checking the Connection Status
Check the EtherCAT network connection status.
7.4.1. Checking the Connection Status
Check that the EtherCAT communication is normally performed.
1
Check the LED indicators on the
Controller and confirm that the
EtherCAT communications are
performed normally.
LED indicators in normal status.
[NET RUN]: Lit green
[NET ERR]: Not lit
[LINK/ACT]: Flashing yellow
2
Check the indicators on the Sensor
LED indicators in normal status:
[SS] :Lit green
Communication Unit.
[L/A IN] :Flashing
[PWR]: :Lit green
[RUN]: :Lit green
[ERR]: :Not lit
23
Page 26

7. Connection Procedure
24
■LED indicators on the Sensor Communication Unit
Color
Status Description
Color
Status Description
Color
Status Description
[PWR] indicator [L/A IN] indicator [L/A OUT] indicator
- Not lit Unit power OFF state - Not lit
Link not established in
physical layer
- Not lit
Link not established in
physical layer
Green
Lit
The unit power (24 VDC)
is supplied to the Slave
Unit.
Flashing
In operation after
establishing link
Flashing
In operation after
establishing link
[ERR] indicator
Green
Lit
Link established in physical
layer
Green
Lit
Link established in physical
layer
- Not lit No error [RUN] indicator [SS] indicator
Blinking
Communications Setting
Error
- Not lit
Link not established in
physical layer
- Not lit
Power OFF or power
supply ON is being initial
confirmed.
Single flash
Communications data
error
Blinking Pre-Operational state
Green
Lit
Normal: The number of
connected Sensors agrees
with the setting.
Double
flash
Application WDT timeout Single flash Safe-Operational state
Red
Lit
Sensor Error: The number
of connected Sensors is
different from the setting.
Flashing Boot error
Green
Lit Operational state
Red
Lit PDI WDT timeout
Page 27

7. Connection Procedure
7.4.2. Checking Data That Are Sent and Received
Check if the correct data are sent and received.
1
Select Mode - RUN Mode from the
Controller Menu.
2
A confirmation dialog is displayed.
Click the Yes Button.
Check that the controller status on
the Toolbox is changed to the RUN
mode.
25
Page 28

7. Connection Procedure
3
Check the Monitor Button and Stop
Monitoring Button on the toolbar of
the Sysmac Studio to see if the
Controller is in monitor status.
Check that the Monitor Button is
selected and is not selectable and
that the Stop Monitoring Button is
selectable (monitor status) as
shown in the right figure.
*If the Controller is not in monitor
status, select Monitor from the
Controller Menu of the Sysmac
Studio.
*If the Sysmac Studio is offline, go
online by following steps 4 to 7 of
7.3.1.
Monitor
Stop Monitoring
4
Select Watch Tab Page from the
View Menu.
5
The Watch Window (Controller) Tab
Page is displayed in the lower
section of the Edit Pane.
6
Click the cell that states Input Name
at the bottom of the Watch Tab
Page.
26
Page 29

7. Connection Procedure
7
Now, characters can be entered.
Enter the device variable name.
Enter E001_In_Bit00 (input 00).
Type the first character E. A list of
device variables starting with E is
displayed.
Double-click E001_In_Bit00.
E001_In_Bit00 is entered in the
Name Column.
8
Click the cell that states Input Name
at the bottom of the Watch Tab
Page. Enter E001_In_Bit02 (input
02), E001_In_Bit04 (input 04),
E001_Number_of_Sensors_Setting
(number of Sensors setting), and
E001_Number_of_Sensors_with_D
ummy (number of Sensors (incl.
dummy).
Check the status of the inputs and
the number of the Sensors.
In this example, the number of
Sensors is 3 and all inputs are
TRUE (ON).
9
Operate the Sensor (Sensor 1) on
the far left.
In the example on the right, OUT is
turned OFF.
10
Check that the online value of
E001_In_Bit00 (input 00) is
changed from True to False.
27
Page 30

8. Initialization Method
8. Initialization Method
This document explains the setting procedure from the factory default setting.
If the device settings have been changed from the factory default setting, some settings may
not be applicable as described in this procedure.
8.1. Controller
To initialize the settings of the Controller, select Clear All Memory from the Controller Menu
of the Sysmac Studio.
28
Page 31

9. Revision History
29
9. Revision History
Revision
code
Date of revision Revision reason and revision page
01 Mar. 26, 2013 First edition
Page 32

2013
0911(-)
P529-E1-01
 Loading...
Loading...