Page 1

Cat. No. W409-E2-04
SYSMAC CS/CJ-series
CS1W-PRM21
CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS Master Units
OPERATION MANUAL
Page 2

SYSMAC CS/CJ-series
CS1W-PRM21
CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS Master Units
Operation Manual
Revised May 29, 2006
Page 3

ii
Page 4

Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use by a trained operator and only for the purposes described
in this manual.
The following conventions are used to classify and explain the precautions in this manual. Always
heed the information provided with them.
!DANGER Indicates information that, if not heeded, is likely to result in serious injury or loss of life.
!WARNING Indicates information that, if not heeded, could possibly result in serious injury or loss of
life.
!Caution Indicates information that, if not heeded, could possibly result in minor or relatively serious
injury, damage to the product or faulty operation.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The first letter of the word Unit is also capitalized
when it refers to an OMRON product, regardless of whether it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation Ch appears in some displays and on some OMRON products. It often means word
and is abbreviated as Wd in the documentation.
The abbreviation PLC means Programmable Logic Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1, 2, 3...Indicates various lists such as procedures, checklists etc.
iii
Page 5

Trademarks and Copyrights
r
f
PROFIBUS, PROFIBUS FMS, PROFIBUS DP, PROFIBUS DP-V1, and PROFIBUS PA are trademarks of PROFIBUS International.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Explorer and ActiveX are
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Sycon and CIF are trademarks of Hilscher GmbH.
®
HART
Other product names and company names in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
The copyright of the PROFIBUS Master Unit belongs to OMRON Corporation.
is a registered trademark of HART Communication Foundation.
OMRON, 2006
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, o
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission o
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
iv
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
About this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
5 Application Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
SECTION 1
Features and Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-3 PROFIBUS Master Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1-4 CX-Profibus Configurator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
1-5 Basic Operating Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
SECTION 2
Installation and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2-1 Unit Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-2 Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-3 Initial Setup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2-4 Setting up a Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2-5 Defining PROFIBUS DP in the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
SECTION 3
Configuration Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3-1 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-2 CX-Profibus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-3 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3-4 C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3-5 Generic Slave Device DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
SECTION 4
Allocated CIO and DM Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
4-1 Overview of Word Allocations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
4-2 Allocated CIO Area Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
v
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5
FINS Commands and Responses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
5-1 FINS Commands and Responses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
5-2 Command / Response Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
SECTION 6
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
6-1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
6-2 Setting up a network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
6-3 Configuring the Slave Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
6-4 Configuring the Master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
6-5 I/O Communication Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
6-6 Operating the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
6-7 Monitoring the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
6-8 PROFIBUS DP-V1 Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
SECTION 7
Troubleshooting and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
7-1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
7-2 Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
7-3 Troubleshooting Using Error Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
7-4 Troubleshooting the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
7-5 Troubleshooting Using the Error Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
7-6 Troubleshooting FINS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
7-7 Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
7-8 Replacing the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Appendices
A Bus Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
B Slave Diagnostics Message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
C I/O Data Conversions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
D Configurator Error and Warning Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
E Memory Card Backup Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
F Application Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
G C200HW-PRM21 Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
vi
Page 8

Page 9

Page 10
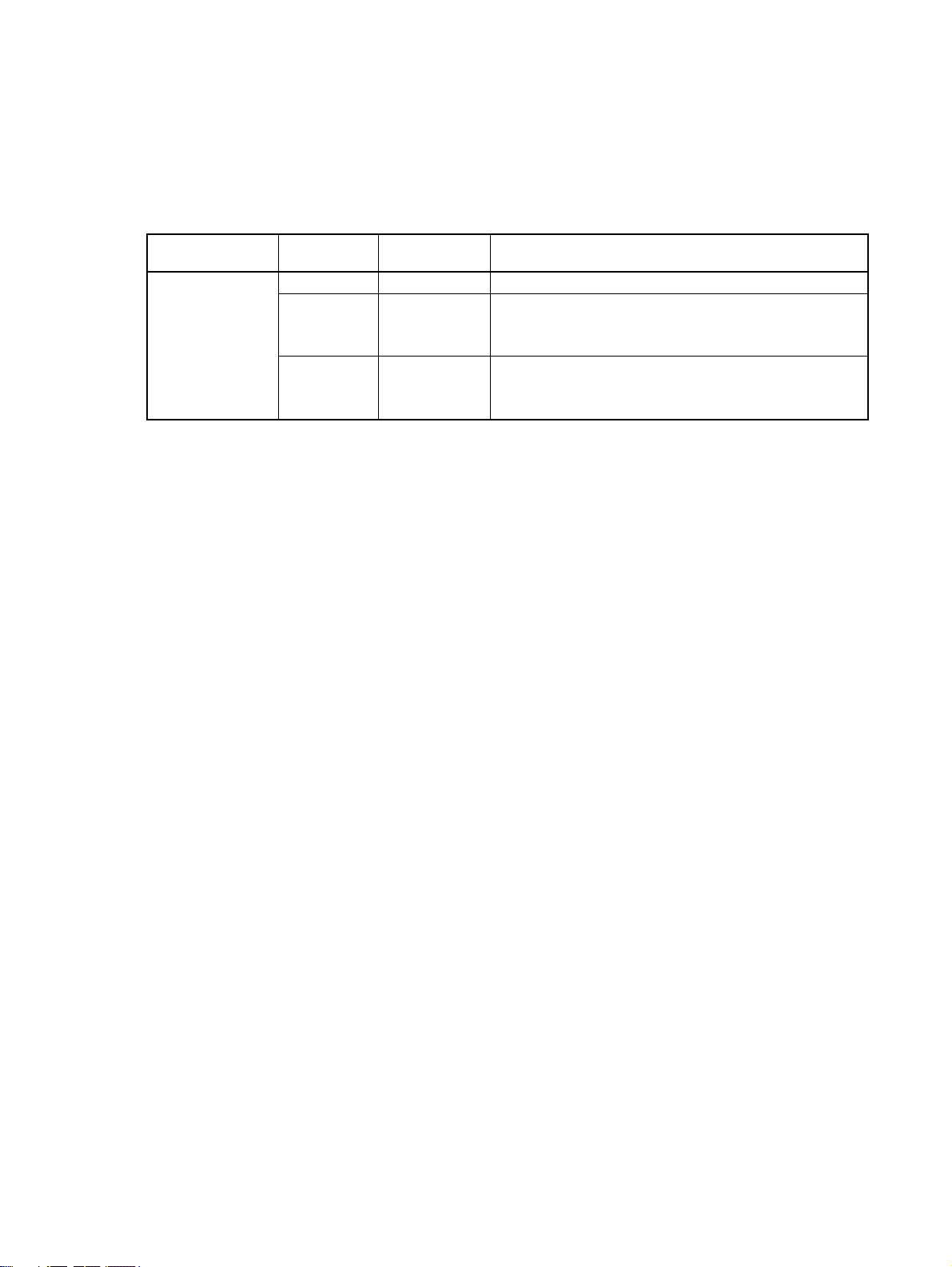
About this Manual
This manual describes the CS1W-PRM21 and CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS DP-V1
Master Units. The Unit version number on the side case of the housing indicates supported functionality. If no version number is shown, the version number is 1.0. The following table lists the functions supported per version number.
Unit name Unit Version Supporting
CJ1W-PRM21
CS1W-PRM21
Unit version 3.0 includes the same functions as Unit version 1.0 and 2.0, in addition to PROFIBUS DPV1 Class 2 related functions. Unit version 3.0 will eventually replace Unit version 1.0 and 2.0.
The DTM versions are downward compatible. Newer versions also support features of previous Unit
versions.
Note Unless stated otherwise, specifications, descriptions and images in this manual apply to all
Unit versions of the CS1W-PRM21 and CJ1W-PRM21 Units. The indication PROFIBUS Master Unit(s) will be used when referring to both unit types.
1.0 0.1.0.1 and up PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
2.0 0.2.0.0 and up PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
3.0 0.3.0.0 PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
Functions supported
DTM version
PROFIBUS DP-V1 (Class 1) Master
Additional PROFIBUS DP acyclic services
PROFIBUS DP-V1 (Class 1 and Class 2) Master
Additional PROFIBUS DP acyclic services
Note The basic functionality of PROFIBUS DP is sometimes referred to as PROFIBUS DP-V0. In
this document the term PROFIBUS DP will be used to indicate the basic functionality.
This manual describes how to install and operate the CS1W-PRM21 and CJ1W-PRM21 Units. Both
Units serve the same purpose: enable devices of various manufacturers to intercommunicate without
making any special interface adaptations. They are technically the same; they differ only in their physical dimensions and weight and the way they are connected to the backplane.
This manual also describes - to a lesser extent - how to configure the C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS
DP Master Unit using the CX-Profibus Configurator. For more information on the C200HW-PRM21
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit, refer to the C200H-series PROFIBUS DP Master Units Operation Manual
(W349-E2-@).
Please read this manual carefully so that you understand the information provided before installing or
using the PROFIBUS Master Unit. Start with the precautions in the following section. They describe
the operating environment and application safety measures which must be observed prior to and when
using the PROFIBUS Master Unit.
The sections of this manual are as follows:
Section 1 introduces the PROFIBUS Master Units and CX-Profibus.
Section 2 describes the installation and setup of the PROFIBUS Master Units.
Section 3 describes the installation of CX-Profibus and provides a overview.
Section 4 describes how the Units interface to the PLC CPU.
Section 5 describes the FINS commands supported by the PROFIBUS Master Units.
Section 6 describes the operational aspects of the PROFIBUS Master Units.
Section 7 provides procedures for troubleshooting the PROFIBUS network and the Units.
The Appendices contain information supplementary to the information in the main body of the manual. They are referred to in the various sections as required.
ix
Page 11
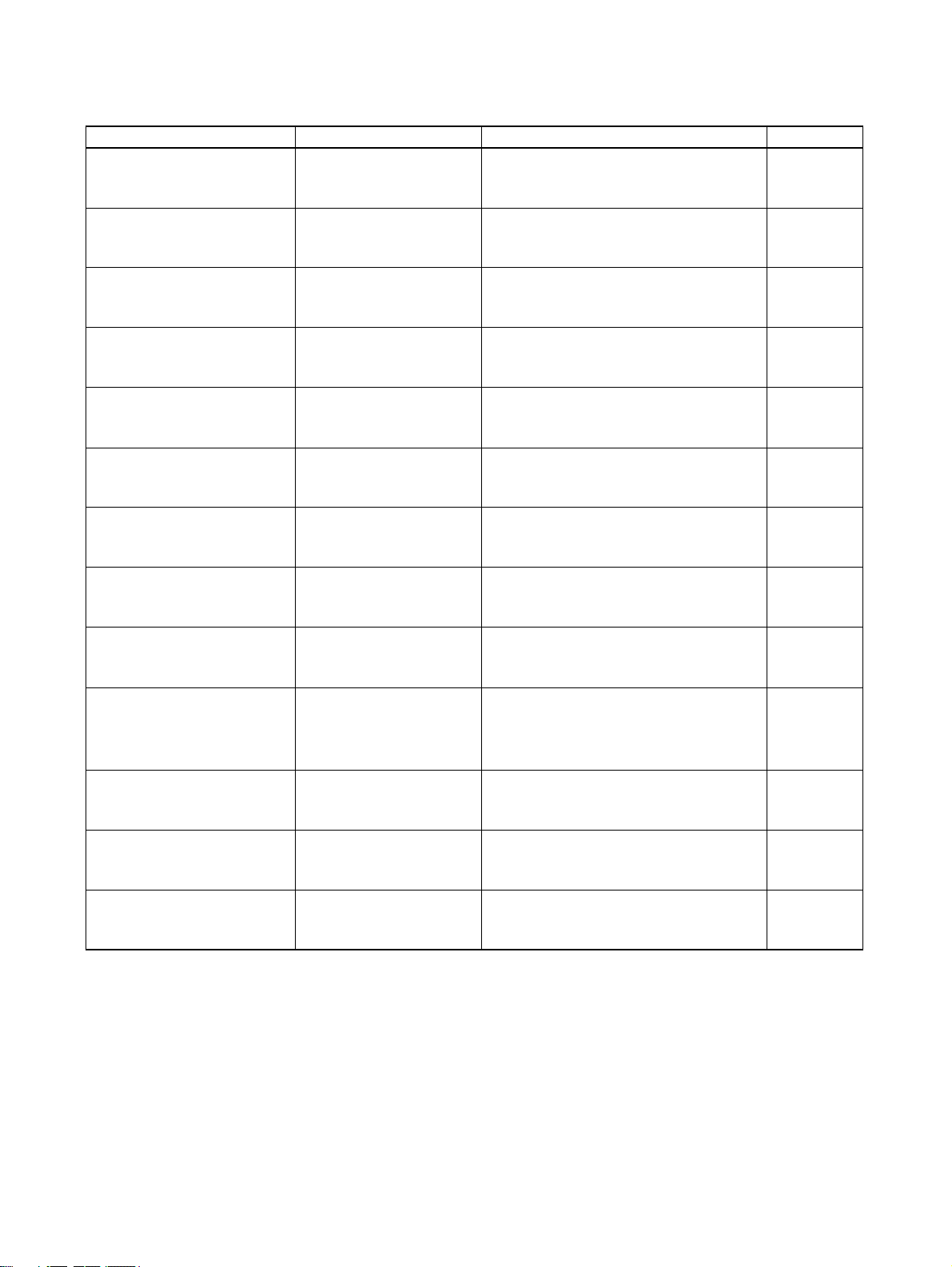
Manual Products Contents Cat. No.
CS-series
Programmable Controllers
Operation Manual
CJ-series
Programmable controllers
operation Manual
CS/CJ-series
Programmable Controllers
Programming Manual
CS/CJ-series
Programmable Controllers
Instructions Reference Manual
CS/CJ Series Communication
Commands Reference Manual
CX-Programmer
Operation Manual
CX-Server
Run Time User Manual
C200H-series PROFIBUS DP
Master Units
Operation Manual
CJ-series PROFIBUS DP
Slave unit
Operation Manual
SmartSlice GRT1-Series
PROFIBUS Communication
Unit Operation Manual
SYSMAC CS-series
CS1G/H-CPU@@-E
SYSMAC CJ-series
CJ1G-CPU@@
SYSMAC CS/CJ-series
CS1G/H-CPU@@-E, CJ1GCPU@@
SYSMAC CS/CJ-series
CS1G/H-CPU@@-E, CJ1GCPU@@
SYSMAC CS1G/HCPU@@-E CPU Units
SYSMAC WS02-CXP@@-E
CX-Programmer
CX-Server Provides information on how to use the CX-
SYSMAC C200H-series
C200HW-PRM21
SYSMAC CJ1-series
CJ1W-PRT21
Smar tSlice GRT1-Series
GRT1-PRT
Describes the installation and operation of
the CS-series PLCs.
Describes the installation and operation of
the CJ-series PLCs.
Describes the ladder diagram programming
instructions supported by CS/CJ-series
PLCs.
Describes the ladder diagram programming
instructions supported by CS-series and
CJ-series PLCs.
Describes the C-series (Host Link) and
FINS communications commands used
with CS/CJ-series PLCs.
Provides information on how to use the CXProgrammer, programming software which
supports CS1/CJ1-series PLCs.
Server communication driver software
which supports CS1/CJ1-series PLCs.
Describes the Installation and Operation of
the C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master Units.
Describes the Installation and Operation of
the CJ1W-PRT21 PROFIBUS DP Slave
Units.
Describes the Installation and Operation of
the SmartSlice GRT1_series GRT1-PRT
PROFIBUS Communication Unit.
W339-E1-@
W393-E1-@
W394-E1-@
W340-E1-@
W342-E1-@
W414-E1-@
W391-E2-@
W349-E2-@
W408-E2-@
W04E-EN-@
GT1-series PROFIBUS DP
Multiple I/O Terminal
Operation Manual
C200H-series PROFIBUS DP
Slave unit
Operation Manual
F150-series PROFIBUS DP
Vision Sensor
Operation Manual
PRT1-COM & GT1-series Describes the Installation and Operation of
the PROFIBUS DP PRT1-COM and GT1series I/O Units.
SYSMAC C200H-series
C200HW-PRT21 PROFIBUS DP Slave unit
F150-C15E-3-PRT21
PROFIBUS DP Vision Sensor
Describes the Installation and Operation of
the C200HW-PRT21 PROFIBUS DP Slave
Units.
Describes the Installation and Operation of
the F150 PROFIBUS Vision Sensor.
W900-E2-@
W901-E2-@
Z143-E1-@
!WARNING Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may result in per-
sonal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure. Please read each section
in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and
related sections before attempting any of the procedures or operations given.
x
Page 12

Read and Understand this Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON
representative if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE
PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS
DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES,
LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS,
WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT
LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual price of the product on which
liability is asser ted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO
CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
xi
Page 13

Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to the
combination of products in the customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying
ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a
complete determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end product, machine,
system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses
listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or
uses not described in this manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical
equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment, and installations subject to separate
industry or government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR
PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO
ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED
FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable product, or any
consequence thereof.
xii
Page 14

Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on improvements and other
reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or features are changed, or when
significant construction changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be changed
without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix or establish key
specifications for your application on your request. Please consult with your OMRON representative at any
time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when
tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and does
not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users must
correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON Warranty and
Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate; however, no
responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
xiii
Page 15

Page 16

PRECAUTIONS
This section provides general precautions for using the PROFIBUS Master Units, Programmable Controllers and related
devices.
The information contained in this section is important for the safe and reliable operation of the PROFIBUS Master
Units. You must read this section and understand the information contained before attempting to set up or operate
a PROFIBUS Master Unit and PLC system.
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
6-1 Applicable Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
6-2 Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
xv
Page 17

Intended Audience
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have a
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating OMRON
PROFIBUS Master Units. Be sure to read this manual before attempting to
use the Unit and keep this manual close at hand for reference during operation.
1
!WARNING It is extremely important that all PLC Units be used for their specified pur-
poses and under the specified conditions, especially in applications that can
directly or indirectly affect human life. You must consult your OMRON representative before using a PLC System in the above-mentioned applications.
3 Safety Precautions
!WARNING Do not attempt to take any Unit apart while the power is being supplied. Doing
so may result in electric shock.
!WARNING Never touch any of the terminals while power is being supplied. Doing so may
result in serious electrical shock or electrocution.
!WARNING Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any Units. Any attempt to do
so may result in malfunction, fire, or electric shock.
!WARNING Do not touch the Power Supply Unit while power is being supplied or immedi-
ately after power has been turned OFF. Doing so may result in electric shock.
!Caution Tighten the screws on the terminal block of the AC Power Supply Unit to the
torque specified in the operation manual. Loose screws may result in burning
or malfunction.
xvi
Page 18

Operating Environment Precautions
!WARNING The CPU Unit refreshes I/O even when the program is stopped (i.e., even in
PROGRAM mode). Confirm safety thoroughly in advance before changing the
status of any part of memory allocated to I/O Units, Special I/O Units, or CPU
Bus Units. Any changes to the data allocated to any Unit may result in unexpected operation of the loads connected to the Unit. Any of the following operation may result in changes to memory status.
• Transferring I/O memory data to the CPU Unit from a Programming
Device.
• Changing present values in memory from a Programming Device.
• Force-setting/-resetting bits from a Programming Device.
• Transferring I/O memory files from a Memory Card or EM file memory to
the CPU Unit.
• Transferring I/O memory from a host computer or from another PC on a
network.
!WARNING Execute online edits only after confirming that no adverse effects will be
caused by extending the cycle time. Otherwise, the input signals may not be
readable.
4
4 Operating Environment Precautions
!Caution Do not operate the Unit in the following places:
• Locations subject to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidities outside the range specified in the specifications.
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salt.
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
Provide proper shielding when installing in the following locations:
• Locations subject to static electricity or other sources of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radiation.
• Locations near to power supply lines.
!Caution The operating environment of the PLC system can have a large effect on the
longevity and reliability of the system. Unsuitable operating environments can
lead to malfunction, failure and other unforeseeable problems with the PLC
system. Ensure that the operating environment is within the specified conditions at installation time and remains that way during the life of the system.
Follow all installation instructions and precautions provided in the operation
manuals.
xvii
Page 19

Application Precautions
5 Application Precautions
Observe the following precautions when using the PROFIBUS Master Unit.
!WARNING Failure to abide by the following precautions could lead to serious or possibly
fatal injury. Always heed these precautions.
5
• Always connect to a class-3 ground (100
Units.
!Caution Failure to abide by the following precautions could lead to faulty operation or
the PLC or the system or could damage the PLC or PLC Units. Always heed
these precautions.
• Install double safety mechanisms to ensure safety against incorrect signals that may be produced by broken signal lines or momentary power
interruptions.
• When adding a new device to the network, make sure that the baud rate
is the same as other nodes.
• When adding a new slave device to the network, make sure that the
PROFIBUS Master Unit is in the OFFLINE state, to prevent unexpected
results when starting up the slave device.
• Use specified communications cables.
• Do not extend connection distances beyond the ranges given in the specifications.
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the personal computer, Slaves, and
Communications Units before attempting any of the following.
• Mounting or dismounting the PROFIBUS Master Unit, Power Supply
Units, I/O Units, CPU Units, or any other Units.
• Assembling a Unit.
• Setting DIP switches or rotary switches.
• Connecting or wiring the cables.
• Connecting or disconnecting connectors.
• Be sure that the terminal blocks, connectors, Memory Units, expansion
cables, and other items with locking devices are properly locked into
place. Improper locking may result in malfunction.
• Be sure that all the mounting screws, terminal screws, Unit mounting
screws, and cable connector screws are tightened to the torque specified
in the relevant manuals. Incorrect tightening torque may result in malfunction.
• Leave the label attached to the Unit when wiring. Removing the label may
result in malfunction if foreign matter enters the Unit.
• Remove the label after the completion of wiring to ensure proper heat dissipation. Leaving the label attached may result in malfunction.
• Always use the power supply voltage specified in this manual.
• Double-check all the wiring and connection of terminal blocks and connectors before mounting the Units.
• Use crimp terminals for wiring. Do not connect bare stranded wires
directly to terminals.
Ω or less) when installing the
xviii
Page 20

Application Precautions
5
• Observe the following precautions when wiring the communications
cable.
• Separate the communications cables from the power lines or high-tension lines.
• Do not bend the communications cables.
• Do not pull on the communications cables.
• Do not place heavy objects on top of the communications cables.
• Be sure to wire communications cable inside ducts.
• Use appropriate communications cables.
• Take appropriate measures to ensure that the specified power with the
rated voltage and frequency is supplied in places where the power supply
is unstable. An incorrect power supply may result in malfunction.
• Install external breakers and take other safety measures against short-circuits in external wiring. Insufficient safety measures against short-circuits
may result in burning.
• Double-check all the wiring and switch settings before turning ON the
power supply.
• Check the user program for proper execution before actually running it on
the Unit. Not checking the program may result in an unexpected operation.
• When configuring a slave device on the network using PROFIBUS DP-V1
messaging services via the PROFIBUS Master Unit, make sure that the
PROFIBUS Master Unit is in the CLEAR state, to prevent unexpected
results when.
• Confirm that no adverse effect will occur in the system before attempting
any of the following. Not doing so may result in an unexpected operation.
• Changing the operating mode of the PC.
• Force-setting/force-resetting any bit in memory.
• Changing the present value of any word or any set value in memory.
• After replacing Units, resume operation only after transferring to the new
CPU Unit and/or Special I/O Units the contents of the DM Area, HR Area,
and other data required for resuming operation. Not doing so may result in
an unexpected operation.
• When transporting or storing the product, cover the PCBs with electrically
conductive materials to prevent LSIs and ICs from being damaged by
static electricity, and also keep the product within the specified storage
temperature range.
• When transporting the Unit, use special packing boxes and protect it from
being exposed to excessive vibration or impacts during transportation.
• Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any Units.
• Do not attempt to remove the cover over the non-used connector hole on
the front of the CS1W-PRM21 Unit.
xix
Page 21
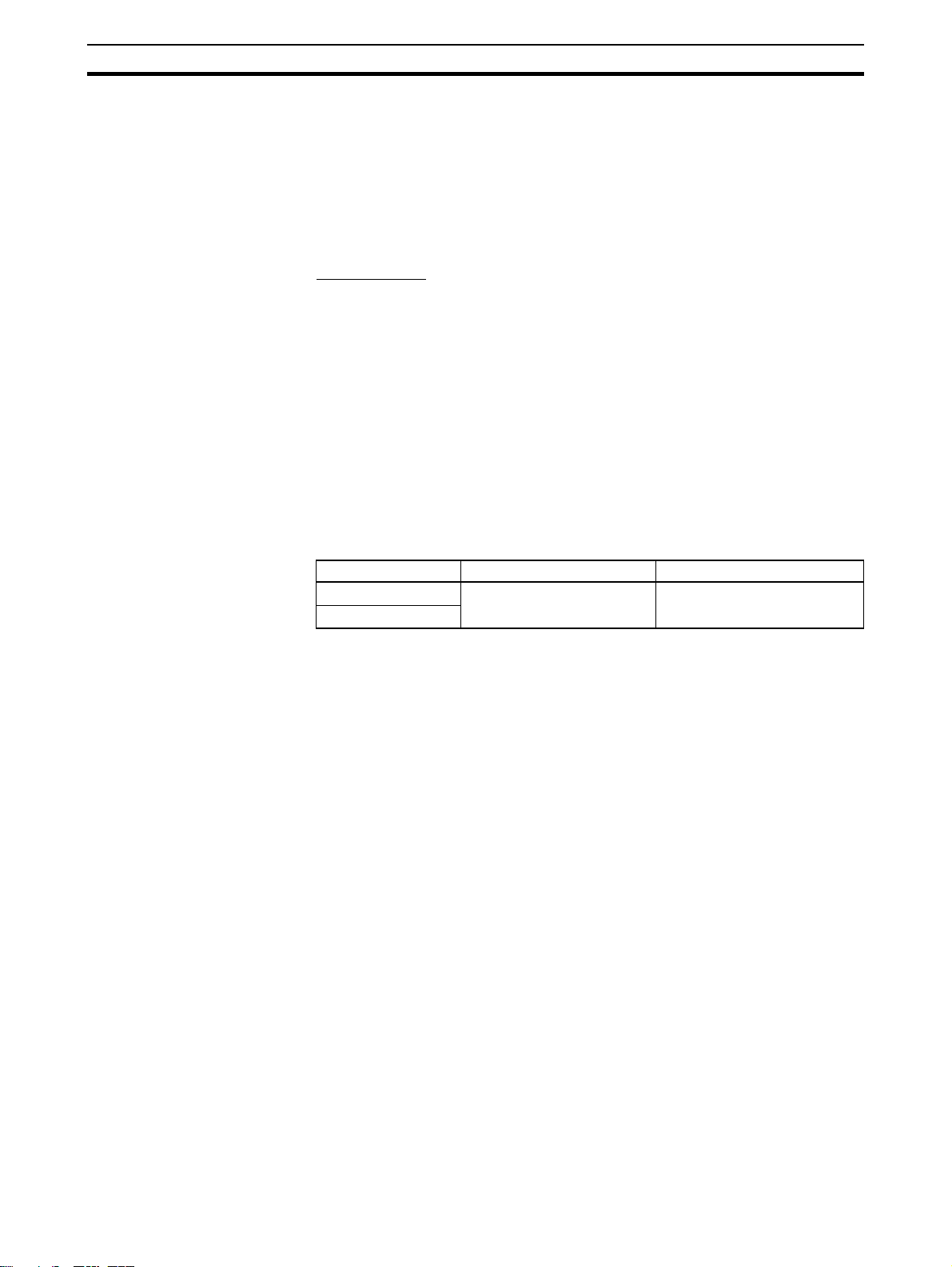
Conformance to EC Directives
6 Conformance to EC Directives
6-1 Applicable Directives
•EMC Directives
• Low voltage directive EN 61131-2:1994+A12:2000
6-2 Concepts
EMC Directives
OMRON Units complying with EC Directives also conform to related EMC
standards making them easier to incorporate in other Units or machines. The
actual products have been checked for conformity to EMC standards. (See
the following note.) Whether the products conform to the standards in the system used by the customer, however, must be checked by the customer.
EMC-related performance of OMRON Units complying with EC Directives will
vary depending on the configuration, wiring, and other conditions of the equipment or control panel in which OMRON devices are installed. The customer
must, therefore, perform final checks to confirm that units and the overall system conforms to EMC standards.
Note Applicable EMS (Electromagnetic Susceptibility) and EMI (Electromagnetic
Interference standards in the EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) standards
are as follows:
6
Unit EMS EMI
CS1W-PRM21 EN 61000-6-2:2001 EN 61000-6-2:2001
CJ1W-PRM21
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives
Units that meet EC directives also meet the common emission standard
(EN50081-2). The measures necessary to ensure that the standard is met will
vary with the overall configuration. You must therefore confirm that EC directives are met for the overall configuration, particularly any radiated emission
requirement (10 m).
xx
Page 22

SECTION 1
Features and Specifications
This section provides an introductory overview of PROFIBUS, its functions and how to setup and configure a network. It
also addresses the PROFIBUS Master Units and the configurator, their features and specifications.
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-2 PROFIBUS Communication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-3 Device Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-1-4 Bus Access Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-1-5 Diagnostic functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-1-6 Protection Mechanisms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-1-7 Network Operation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-2 Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-2-1 Configuring the PROFIBUS Master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-2-2 FDT/DTM Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-2-3 GSD file Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-3 PROFIBUS Master Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1-3-1 PROFIBUS Master Unit Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1-3-2 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1-3-3 Comparison with Previous Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1-4 CX-Profibus Configurator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1-4-1 CX-Profibus Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1-4-2 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1-5 Basic Operating Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1-5-1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1-5-2 Preparations for Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1-5-3 Procedures Prior to Starting Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1
Page 23

Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS
1-1-1 Introduction
Standard EN50170 PROFIBUS (PROcess FIeldBUS) is an open fieldbus standard for a wide
range of applications in manufacturing, processing and building automation.
The Standard, EN 50170 (the Euronorm for field communications), to which
PROFIBUS adheres, guarantees vendor independence and transparency of
operation. It enables devices of various manufacturers to intercommunicate
without having to make any special interface adaptations.
The PROFIBUS family comprises three mutually compatible versions: PROFIBUS FMS, PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS PA.
PROFIBUS FMS FMS means Fieldbus Message Specification. This version is the general-pur-
pose solution for high-level extensive and complex communication tasks.
Powerful services open up a wide range of applications and provide great flexibility.
PROFIBUS DP DP means Decentralized Periphery. PROFIBUS DP is optimized for high
speed and low-cost interfacing. It is specially designed for communication
between automation control systems and distributed I/O at the device level.
PROFIBUS PA PA means Process Automation. It permits sensors and actuators to be con-
nected to one common bus even in areas where intrinsically safe products are
required. It also permits data and power to be supplied over the bus using
2-wire technology according the international standard IEC 1158-2.
Uniform Bus Access
Protocol
!Caution It is not possible to exchange one of these family members by another family
PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS FMS use the same transmission technology
and uniform bus access protocol. Consequently, both versions can be operated simultaneously on the same bus. FMS field devices, however, cannot be
controlled by DP masters and vice versa.
member. This will cause faulty operation.
The rest of this section describes the PROFIBUS DP Protocol architecture.
1-1-2 PROFIBUS Communication Protocol
OSI reference model
ISO-7498
In general, the PROFIBUS communication protocol is based on the Open
System Interconnection (OSI) reference model in accordance with the international standard ISO-7498 (see the following illustration). The model defines
7 layers of communication functions, three of which - layers 1, 2, and 7 - are
used in PROFIBUS.
• Layer 1, the Physical Layer of this model, defines the physical transmission characteristics.
• Layer 2, the Data Link Layer of this model, defines the bus access protocol. This protocol also includes data security and the handling of transmission protocols and telegrams.
• Layer 7, the Application Layer of this model, defines the application functions. This Layer is only applicable to PROFIBUS FMS.
2
Page 24

Overview of PROFIBUS
.
DP-Profiles
DP-Extensions
User Interface Layer DP Basic Functions
(7) Application Layer
(6) Presentation Layer
(5) Session Layer NOT DEFINED
(4) Transport Layer
(3) Network Layer
(2) Data Link Layer Fieldbus Data Link (FDL)
(1) Physical Layer RS485 / Fibre Optics
PROFIBUS DP In the rest of this manual, only PROFIBUS DP is considered.
Section 1-1
OSI Layer 1, 2 and User
Interface
PROFIBUS DP uses layers 1 and 2, and the user interface. Layers 3 to 7 are
not defined for PROFIBUS DP. The user interface Layer defines the interface
functions for specific application areas, i.e. the PROFIBUS DP basic functions
and communication profiles.This streamlined architecture ensures fast and
efficient data transmission. The application functions which are available to
the user, as well as the system and device behaviour of the various PROFIBUS DP device types, are specified in the user interface.
OSI Layer 1: Transmission
Medium
RS-485 transmission technology or fibre optics are available for transmission.
RS-485 transmission is the most frequently used transmission technology. Its
application area includes all areas in which high transmission speed and simple inexpensive installation are required. PROFIBUS modules are interconnected by single twisted-pair shielded copper wires.
RS-485 Technology The RS-485 transmission technology is very easy to handle. Installation of the
twisted pair cable does not require expert knowledge. The bus structure permits addition and removal of devices or step-by-step commissioning of the
system without influencing the other devices. Later expansions have no effect
on devices which are already in operation.
RS-485 Transmission
Speed
Transmission speeds between 9.6 kbit/s and 12 Mbit/s can be selected as
shown in the table below. One unique transmission speed must selected for
all devices on the bus when the system is commissioned.
Baud rate (kbit/s) Distance / segment (m)
9.6 1200
19.2 1200
45.45 1200
93.75 1200
187.5 1000
500 400
1500 200
3000 100
6000 100
12000 100
Cable length The maximum cable length values depend on the transmission speed and are
based on type-A cable (see Cable Type on page 39). The length can be
increased by the use of repeaters.However, it is not recommended to use
more than three repeaters in series in a PROFIBUS network.
3
Page 25

Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
1-1-3 Device Types
PROFIBUS distinguishes between master devices and slave devices.
Master Devices Master devices determine the data communication on the bus. A Master can
send messages without an external request, as long as it holds the bus
access right (the token). Masters are also referred to as active devices in the
PROFIBUS standard.
There are two types of master devices:
Class 1 Master (DPM1) A PROFIBUS DP Class 1 Master (DPM1) device is a central controller, which
exchanges information with the decentralized devices (i.e. DP slaves) within a
specified message cycle.
Class 2 Master (DPM2) PROFIBUS DP class 2 Master (DPM2) devices are programmers, configura-
tion devices or operator panels. They are used during commissioning, for configuration of the DP system, or for operation and monitoring purposes.
As of Unit Version 3.0 the CS1W-PRM21 and the CJ1W-PRM21 are PROFIBUS DP Class 1 as well as Class 2 Master devices.
Slave Devices Slave devices are peripheral devices. Typical slave devices include input/out-
put devices, valves, drives, and measuring transmitters. They do not have bus
access rights and they can only acknowledge received messages or send
messages to the master when requested to do so. Slave devices are also
called passive devices
Device Profile To enable the exchange of devices from different vendors, the user data has
to have the same format. The PROFIBUS DP protocol does not define the format of user data, it is only responsible for the transmission of this data. The
format of user data may be defined in so called profiles. Profiles can reduce
engineering costs since the meaning of application-related parameters is
specified precisely. Profiles have been defined for specific areas like drive
technology, encoders, and for sensors / actuators.
PROFIBUS DP-V1 PROFIBUS DP-V1 is an extension to the PROFIBUS DP protocol standard. It
defines acyclic message services between a PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master and a
PROFIBUS DP-V1 slave device. These acyclic message services allow
exchange of extended parameter settings as well as extended diagnostics
and alarm information, during regular I/O data exchange. PROFIBUS DP-V1
devices must at least support PROFIBUS DP.
PROFIBUS DP-V1 services are designated as MSACn services (M
S
lave Acyclic, Class n), in which n designates the Master Class (i.e. 1 or 2).
The CS1W-PRM21 and the CJ1W-PRM21 both support PROFIBUS DP-V1
Class 1 and Class 2 Master functions as of Unit version 3.0.
aster-
1-1-4 Bus Access Protocol
OSI Layer 2: Bus Access
Protocol
The PROFIBUS bus access protocol is implemented by OSI layer 2. This protocol also includes data security and the handling of the transmission protocols and messages.
Medium Access Control The Medium Access Control (MAC) specifies the procedures which determine
when a device is permitted to transmit data. A token passing procedure is
used to handle the bus access between master devices, and a polling procedure is used to handle the communication between a master device and its
assigned slave device(s).
4
Page 26

Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
Token Passing The token passing procedure guarantees that the bus access right (the token)
is assigned to each master within a precisely defined time frame. The token
message, a special message for passing access rights from one master to the
next master, must be passed around the logical token ring - once to each
master - within a specified target rotation time. Each master executes this procedure automatically.
Polling Procedure The polling or master-slave procedure permits the master, currently in pos-
session of the token, to access its assigned slaves. The figure below shows a
possible configuration The configuration shows three active devices (masters)
and six passive devices (slaves).
Token Passing
DPM1 DPM2 DPM1
Active stations
Master devices
Passive stations
Slave devices
Polling
PROFIBUS
The three masters form a logical token ring. When an active device receives
the token message, it can perform its master role for a certain period of time.
During this time it can communicate with all assigned slave devices in a master-slave communication relationship, and a DPM2 master can take the initiative to communicate with DPM1 master devices in a master-master
communication relationship.
Multi-peer Communication In addition to logical peer-to-peer data transmission, PROFIBUS DP provides
multi-peer communication (broadcast and multicast).
Broadcast
Communication
In the case of broadcast communication a master device sends an unacknowledged message to all other devices (masters and slaves).
Multicast Communication In the case of multicast communication a master device sends an un-
acknowledged message to a predetermined group of slave devices.
1-1-5 Diagnostic functions
Extended Diagnostics Extended diagnostic functions defined in PROFIBUS DP enable the fast loca-
tion of error at slave devices. Diagnostic messages are transmitted over the
bus and collected at the master. Three diagnostic message types are defined:
Device Related
Diagnostics
• Messages concerning the general operational status of the whole device,
e.g. over temperature, low voltage.
Module Related
Diagnostics
Channel Related
Diagnostics
• Messages indicating that an error is present in a specific I/O range of a
device, e.g. an 8-bit output module.
• Messages indicating an error at a given input or output, e.g. short circuit
on Output 5.
5
Page 27

Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
1-1-6 Protection Mechanisms
Monitoring Time PROFIBUS DP provides effective protection functions against parameteriza-
tion errors or failure of the transmission equipment. Time monitoring is provided both at the master and the slave devices. The monitoring interval is
specified when the system is configured.
Monitoring at the Master The PROFIBUS Master monitors data transmission of the slaves with the
Data-Control-Timer. A separate control timer is used for each slave. This timer
expires if response data is not correctly transmitted by the slave within the
monitoring interval. The user is informed when this happens. If the automatic
error reaction (Auto-CLEAR) has been enabled, the PROFIBUS Master exits
its OPERATE state, switches the outputs of all assigned slaves to the fail-safe
status and changes to the CLEAR state.
Monitoring at the Slave Slave devices use a watchdog to detect failures of the master or the bus. If
data communication with the master does not occur within the set watchdog
time interval, a slave automatically switches its outputs to the fail-safe mode.
Also, access protection is provided for the inputs and outputs of the slaves
operating in multi-master systems. Only authorized masters can access their
slaves.
1-1-7 Network Operation Modes
PROFIBUS DP distinguishes four different network operation modes:
OFFLINE • Communication with all PROFIBUS DP participants (masters and slaves)
is stopped. The Master ceases to access the PROFIBUS network.
STOP • Cyclic communication as well as PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 1 communica-
tion between the master and its slaves is stopped. Only PROFIBUS DPV1 Class 2 communication and communication between the master and
other masters is still possible.
CLEAR • The master tries to set parameters, check the configuration, and perform
data exchange with its associated slaves. Data exchange involves reading
the inputs of the PROFIBUS DP slaves and writing zeros to the outputs of
the slaves.
OPERATE • The master exchanges data with its assigned slaves, inputs are read and
outputs are written. Also, the master cyclically sends its local status to all
its assigned PROFIBUS DP slaves (using a broadcast message).
The PROFIBUS Master Unit will always be in one of these four modes. Mode
transitions from one mode to another will be performed via intermediate
modes. For example, a mode transition from OFFLINE to OPERATE, will be
Auto-CLEAR
Fail-safe State
performed as OFFLINE
If an error occurs during the data exchange phase of the master, the ‘AutoCLEAR’ function determines the subsequent actions. If this function has been
disabled, the master remains in the OPERATE mode. If the function has been
enabled, the master automatically changes the network to the CLEAR mode,
in which the outputs of the assigned PROFIBUS DP slaves are switched to
zero, i.e. the ‘fail-safe’ state. The master continues to read the inputs of the
slaves.
→ STOP → CLEAR → OPERATE.
6
Page 28

Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network
Section 1-2
1-2 Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network
1-2-1 Configuring the PROFIBUS Master
In order to operate a PROFIBUS network, each master in the network needs
to be configured. This process of configuration involves
• setting up the network topology, i.e. assigning the slave devices with
which the master will be exchanging data,
• defining the parameterization data, which the master will send to each of
the slave devices, before process data exchange can commence
• defining the configuration data, i.e. defining the process data, which will
be exchanged,
• setting up the bus parameters, which define the baud rate and the bus
timing parameters.
• downloading the configuration setup to the master device.
Configuration Technology The configuration process is usually facilitated by a special Computer based
program, often referred to as a configurator. The configurator requires special
configuration files, defining the configuration options for each device, which is
to participate in data exchange. The files must be provided by the manufacturer of the device.
Two types of configuration technology exist:
• Configuration technology based on FDT/DTM technology
• Configuration technology based on GSD-files
1-2-2 FDT/DTM Technology
FDT/DTM Technology The newer configuration tools are based on FDT/DTM technology.
FDT/DTM Concept The FDT/DTM concept specifies the interfaces between the engineering sys-
tems called Field Device Tools (FDT), and the device-specific software components called Device Type Managers (DTM).
The FDT/DTM concept separates the device dependent functionality (which is
in the DTM) from the application. It provides separate interfaces for device
configuration, monitoring and maintenance solutions, which before largely
depended on the manufacturer of the application. Because of this concept,
FDT/DTM technology is not limited to PROFIBUS applications. In concept,
any type of network can be configured and accessed, provided the appropriate DTMs are available.
FDT Container Application A FDT container application facilitates configuration of network devices and
parameterizing and/or manipulating their operational modes. All device
dependent functionality is concentrated in the DTM.
FDT container applications can be stand-alone tools, or can be part of other
engineering tools such web browsers providing FDT interfaces.Since FDT
standardizes the interfaces, it allows devices from different manufacturers to
be integrated in any automation system, regardless of the fieldbus system.
CX-Profibus is an example of a FDT container application. It is described in
detail in the following sections.
Device DTM DTMs are provided by the manufacturer of the device. A DTM is comparable
to a printer driver, which allows interactive configuration and diagnostics.
7
Page 29

Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network
The DTM provides not only the configuration, manipulation and monitoring
functions for a device including the user interface functions, it also provides
the connection technology to the device.
DTM Properties In general, a DTM is a Microsoft COM-component, which can be executed
from within a FDT container application. A DTM is not a stand-alone tool, it
requires a FDT container application to be executed. The DTM provides a
number of interface functions, through which it can be controlled and
accessed in order to transfer data to or from the DTM.
A DTM provides all the options for configuration and monitoring of a device,
which it can present to the user through its own user interface.
ActiveX User Interface The user interface for a DTM is provided using ActiveX windows. Control of
these windows is done by the DTM, but the FDT container application can
request specific user input from the DTM, based on which the DTM will provide the necessary ActiveX windows. In general multi-language user interface
windows, including DTM specific Help files are supported by the DTM.
XML based Data Transfer Data transfer to and from a DTM is provided using XML-documents. The
XML-documents are standardized for the communication between the FDT
container application and for communication between DTMs.
An additional specification covers the definition of XML-data formats for the
transfer of application specific data, such as PROFIBUS data.
Section 1-2
Communication DTM In general, a device configuration DTM is accompanied by a communication
DTM. This specific DTM facilitates device specific communication, e.g. for
downloading a configuration to a PROFIBUS Master Unit and/or for retrieving
monitoring information from PROFIBUS Master Unit. It may incorporate the
specific communication protocol, or rely on other available drivers.
CX-Profibus CX-Profibus is a FDT container application. Together with this container appli-
cation, OMRON provides five DTMs:
• A DTM to facilitate configuration and operation of the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master Units (As of Unit version 2.0).
• A DTM to facilitate configuration of the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS
DP Master Units (Unit version 1.0).
• A DTM to facilitate configuration of the C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP
Master Unit.
• A DTM to facilitate configuration of the SmartSlice GRT1-series
GRT1-PRT PROFIBUS Communication Unit.
• A DTM to facilitate integration of GSD file based devices into CX-Profibus (see section 1-2-3 GSD file Technology for more information).
1-2-3 GSD file Technology
GSD file Technology The older and most commonly used configuration technology is the based on
GSD files (General Slave Data file). A GSD file is a text file, containing the
characteristic features and configuration options of a device. The device data
base file of each device is loaded in the configurator and downloaded to the
master device.
GSD files are usually supplied with a Unit, or can be downloaded from the
Internet, either from the manufacturer's site, or from the GSD library of the
PROFIBUS International at http://www.profibus.com.
8
Page 30

Setting up a PROFIBUS DP Network
GSD File Language The language used in the GSD file is indicated by the last letter of the file
extension, *.GS?:
Default = GSD
English = GSE
German = GSG
Italian = GSI
Portuguese = GSP
Spanish = GSS
The GSD files are prepared individually by the vendor for each type of device,
according to a fixed format. Some parameters are mandatory, some have a
default value and some are optional. The device data base file is divided into
three parts:
General Section • General specifications
This section contains the vendor name, the device name, hardware- and software release versions, device type and identification number, protocol specification and supported baud rates.
DP-master Section • DP master-related specifications
This section contains all parameters which only apply to DP master devices
(e.g. maximum memory size for the master parameter set, maximum number
of entries in the list of active devices, or the maximum number of slaves the
master can handle).
Section 1-2
DP-slave Section • DP slave-related specifications
This section contains all specification related to slaves (e.g. minimum time
between two slave poll cycles, specification of the inputs and outputs, and
consistency of the I/O data).
For PROFIBUS DP-V1 devices this section also specifies what services for
PROFIBUS DP-V1 are supported.
DTM versus GSD File When comparing the two configuration technologies, a GSD file only provides
information on the device characteristics and configuration options. It has no
GUI of its own, nor can it connect to the device itself. A GSD file always
requires a separate configurator program to interpret the data. In the FDT/
DTM concept all these device related functions are included in the DTM. The
DTM can be executed from any program, which provides FDT interfaces.
Sending PROFIBUS DP-V1 commands to a device from the configuration tool
is only possible using DTM technology. The GSD file does not provide this
means.
9
Page 31

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Section 1-3
1-3 PROFIBUS Master Unit
1-3-1 PROFIBUS Master Unit Features
PROFIBUS Master Unit The PROFIBUS Master Unit is a CPU Bus Unit, which can be installed on a
CS1/CJ1 PLC System. There are two available models of the PROFIBUS
Master Unit: the CS1W-PRM21 for connection to a CS1 PLC System and the
CJ1W-PRM21 for connection to a CJ1 PLC System. Both models provide
identical functionality.
CPU Bus Unit A total of up to 16 CPU Bus Units can be mounted on the CPU Rack or an
Expansion Rack. The total of 16 must include all PROFIBUS Master Units and
all other CPU Bus Units
Unit Control and Status Up to 25 words of control and status words are exchanged between the
PROFIBUS Master Unit and a dedicated CIO memory area, of which the location is related to the Unit Number. Control bits, allow the PLC program to
switch the Unit between OFFLINE, STOP, CLEAR and OPERATE mode,
which represent the main PROFIBUS DP modes of operation. The control
words also allow for user initiated transmission of a Global-Control message
over the PROFIBUS network to any group of slave devices.
The remaining CIO words provide status and diagnostics information on the
Unit itself, the PROFIBUS network and the slave devices.
I/O Data The total size of I/O data however, must not exceed the maximum I/O size of
up to 7168 words, which it can exchange with the PLC memory. The I/O data
can be distributed over up to two input areas and two output areas. Each of
the input and output areas can be mapped to any location in the DM Area,
CIO Area, WR Area, HR Area, or the EM banks.
FINS Messages The PROFIBUS Master Unit supports FINS message exchange with the PLC
CPU to allow the transfer of Slave diagnostics data, the Error log, or to enable
or disable communication with specific allocated slave devices, so that they
can temporarily be taken out of the network for maintenance, without the
PROFIBUS Master Unit reporting an error.
As of Unit version 2.0, FINS commands have been implemented to support
the transfer of data via acyclic PROFIBUS messages over the network. These
messages can be used to change a slave device address, read slave device
configuration, or to send and receive extended parameter data information.
As of Unit version 3.0, a FINS command containing CIP data can be sent to
other OMRON devices on the PROFIBUS network, using PROFIBUS DP-V1
Class 2 services. CIP or Common Industrial Protocol is protocol defined by
ODVA, the Open Devicenet Vendor Association. Refer to their website for
more information: http://www.odva.org/.
PROFIBUS DP Class 1
Services
The PROFIBUS Master Unit supports all mandatory Class 1 services defined
in the PROFIBUS DP standard EN50170, Volume 2 for Master - Slave Communication. These functions includes the following services:
• Set_Prm
• Chk_Cfg
• Slave_Diag
• Data_Exchange
• Global-Control (FREEZE, UNFREEZE, SYNC, UNSYNC, CLEAR)
The PROFIBUS Master Unit supports cyclic Master - Slave communications
for networks with up to 125 slave devices. With each slave device it can
exchange up to 244 bytes of input data and up to 244 bytes of output data.
10
Page 32

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Section 1-3
For diagnostics purposes the PROFIBUS Master Unit collects all Slave Diagnostics messages, which it can transfer to the PLC memory, using FINS commands. From every allocated slave device it can receive up to 244 bytes of
diagnostics data.
PROFIBUS DP Class 2
Services
PROFIBUS DP-V1
Services
Configuration Before the PROFIBUS Master Unit can control the PROFIBUS network, it
Troubleshooting
Functions
The PROFIBUS Master Unit also supports additional PROFIBUS DP Class 2
services defined in the PROFIBUS DP standard EN50170, Volume 2 for Master - Slave Communication. These functions includes the following services:
• Set_Slave_Addr
• Get_Cfg
• Rd_Inp
• Rd_Outp
These services can be invoked from the PLC CPU using FINS message communication.
The PROFIBUS Master Unit supports PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 1 and Class 2
services. Additional parameter data can be written/read to and from PROFIBUS DP-V1 compatible slave devices. These services can be initiate either
from the PLC CPU or from the associated DTM.
must be configured, using the dedicated configuration program CX-Profibus.
Without this configuration, the Unit will not be able to achieve data exchange,
neither to send any acyclic messages. The configurator is explained in section
1-4 CX-Profibus Configurator.
The PROFIBUS Master Unit is provided with a variety of troubleshooting functions for prompt recovery in case of errors:
• Extensive self-diagnostic function at startup
• Data exchange flags, indicating if I/O data is being exchanged with the
slave devices
• Diagnostics flags, indicating if new Slave diagnostics data is available
• Extensive status and error flags, indicating the status of the Unit and the
PROFIBUS network
• Error log for recording error history data.
11
Page 33

PROFIBUS Master Unit
1-3-2 Specifications
PROFIBUS Master Unit Model
Applicable
PLC
CS Series
CJ Series
Model name Unit
CS1W-PRM21
CJ1W-PRM21
CPU Bus Unit 1.0 0.1.0.1 and up • PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
Section 1-3
The CS1W-PRM21 and CJ1W-PRM21 are remote I/O Communication units
providing PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master capabilities. The
Unit version number on the side case of the housing indicates supported functionality. If no version number is shown, the version number is 1.0. The following table lists the functions supported per version number.
Alternatively, the PROFIBUS DP Master DTM can be used to obtain the Units
version number, refer to section 3-3-1 Configuration User Interface.
classification
Unit
Version
2.0 0.2.0.0 and up • PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
3.0 0.3.0.0 • PROFIBUS DP (Class 1) Master
Supporting
DTM version
Functions supported
• PROFIBUS DP (Class 2) Master
• PROFIBUS DP-V1 (Class 1) Master
• PROFIBUS DP (Class 2) Master
• PROFIBUS DP-V1 (Class 1) Master
• PROFIBUS DP-V1 (Class 2) Master
Note 1. Unit version 3.0 includes the same functions as Unit version 1.0 and 2.0,
in addition to new PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2 related functions, and is
backward compatible with Unit version 1.0 and 2.0. Unit version 3.0 will
eventually replace Unit version 1.0 and 2.0.
2. Unless stated otherwise, specifications, descriptions and images in this
manual apply to both Unit versions of the CS1W-PRM21 and CJ1WPRM21 Units. The indication PROFIBUS Master Unit(s) will be used when
referring to both unit types.
General Specifications General specifications of the CS/CJ-series PROFIBUS Master Units conform
to the general specifications for the SYSMAC CS/CJ-series CPU Units.
Functional Specifications
Item Specification
PROFIBUS Master Unit types CS1W-PRM21 CJ1W-PRM21
Applicable PLC series CS-series CJ-series
Mounting position • CPU Rack,
• CS Expansion Rack (Excluding
a C200H Expansion I/O Rack or
SYSMAC BUS Slave Rack.)
• CS1D Duplex
Unit classification CPU Bus Unit
Applicable unit numbers 0 to F (Hex)
Maximum number of Units per PLC 16
Current consumption 400 mA max at 5 Vdc
Dimensions (W x H x D) 35 x 130 x 101 mm 31 x 90 x 65 mm
Weight 187g (typical) 100g (typical)
Installation
•CPU Rack,
• CJ1 Expansion Rack
12
Page 34

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Item Specification
Ambient temperatures Operating temperature: 0 to 55°C
Ambient operating humidity 10% to 90% (with no condensation)
Vibration resistance Conforms to IEC60068-2-6, test Fc.
Shock resistance Conforms to IEC60068-2-27, test Ea.
Dielectric strength 600 VAC (between isolated circuits)
Conformance to EMC and Electrical
safety standards
Environment
Settings Unit Number rotary switch, range: 0 ~ F (Hex)
Indicators 7 LEDs, indicating Unit status and PROFIBUS status:
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC thread)
Front case
CIO Area words allocated for the CPU
Bus Unit
DM Area words allocated for the CPU
Bus Unit.
I/O Data allocations Maximum total size: 7168 words
PROFIBUS DP-V1 status flags DPV1 Connection/Abort status flags: 16 words.
Memory area allocation
Reading slave device diagnostics The MEMORY AREA READ (0101) FINS command can be used to
Reading and controlling the error log Catalogues the history of error events. The Unit supports the following
Device state changes Allocated slave devices can be disabled and enabled in order to tempo-
FINS messaging
Section 1-3
Storage temperature: –20 to 75°C
10 to 54.8Hz, 0.25-mm amplitude, 54.8 to 300Hz, acceleration:
29.4 m/s
(Total time: 12 linear sweeps x 10 minutes / sweep = 120 minutes)
196 m/s
EN61000-6-2: 2001
EN61000-6-4: 2001/CISPR11
EN61131-2:1994+a12:2000
Unit status: RUN (Green LED)
Host PLC status: ERH (Red LED)
Configuration status: PRM (Green LED)
PROFIBUS status: BST (Green LED)
Fixed allocation of 25 words per Unit.
CIO 1500 + (25 x Unit number)
CIO words provide:
• 2 words for software switches
• 1 word for the Global-Control
• 21 words for the Unit and Slave statuses
Fixed allocation of 100 words per Unit.
DM 30000 + (100 x Unit number)
DM Area allocated to the Unit is reserved for future use.
I/O Data can be allocated to up to 2 input areas and 2 output areas.
Input and output areas can be mapped to CIO, DM, WR, and HR Areas,
as well as EM banks. Mapping must be defined through configurator.
The status flags can be mapped to CIO, DM, WR, and HR Areas, as
well as EM banks. Mapping must be defined through configurator.
obtain the last received Slave Diagnostics message.
Error Log related FINS commands:
• ERROR LOG READ
• ERROR LOG CLEAR
rarily remove them from data exchange services. The Unit supports the
following FINS commands to implement this:
•RUN
•STOP
2
in X, Y, and Z directions for 120 minutes each.
2
three times each in X, Y, and Z directions
ERC (Red LED)
COMM (Green LED)
BF (Red LED)
13
Page 35

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Item Specification
PROFIBUS DP messages
(See Note 3)
Explicit messages
(See Note 3)
Error history size and storage The PROFIBUS Master Unit supports storage of up to 80 error events,
FINS messaging
Section 1-3
The PROFIBUS MESSAGE SEND (2809) FINS command can be used
to send PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS DP-V1 messages over the
PROFIBUS network from the CS1/CJ1 PLC CPU.The following services can be initiated:
PROFIBUS DP services:
•Get_Cfg
• Set_Slave_Add
• Rd_Inp
• Rd_Outp
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 1 services (See Note 1):
•MSAC1 - Read
•MSAC1 - Write
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2 services (See Note 2):
• MSAC2 - Initiate
•MSAC2 - Read
•MSAC2 - Write
• MSAC2 - Abort
The EXPLICIT MESSAGE SEND (2801) FINS command can be used
to send CIP based messages to OMRON slave devices using PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2 messages.
including time stamps in volatile memory.
16 error events can be logged in non-volatile memory
Protocol Specification
Item Specification
Applicable standards EN50170, Volume 2
Protocol type supported PROFIBUS DP, PROFIBUS DP-V1
PROFIBUS Unit types PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 1 and Class 2 Master
PROFIBUS Media type RS-485, galvanically isolated from the PLC
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC thread)
Unit device address range
Number of slave devices supported
baud rates supported Selectable through the configurator:
Bus timing definitions Calculated by the configurator
PROFIBUS interface
Termination according to EN50170 provided by the cable connector
0 ~ 125, set through the configurator (See Note 4)
125 max, address range
• 9.6 kbit/s
• 19.2 kbit/s
• 45.45 kbit/s
• 93.75 kbit/s
• 187 kbit/s
• 500 kbit/s
• 1.5 Mbit/s
• 3 Mbit/s
• 6 Mbit/s
• 12 Mbit/s
0 ~ 125
14
Page 36

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Item Specification
PROFIBUS DP Master Class 1 - Slave
cyclic services
PROFIBUS DP Master Class 2 - Slave
acyclic services available to the PLC
PROFIBUS DP Master - Master services Not supported
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master Class1 Slave acyclic message services
(See Note 1)
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master Class2 Slave acyclic message services
(See Note 2)
PROFIBUS Services
Number of I/O module definitions 4000 max. over all configured slave devices
Number of I/O data supported by Master Up to 244 bytes input and 244 bytes output max. per slave device
Number of diagnostics data supported
by Master
Additional status flags DPV1 Connection/Abort status flags.
I/O Data
Section 1-3
•Set_Prm
• Chk_Cfg
• Data_Exchange
• Slave_Diag
• Global-Control - CLEAR
Global-Control, initiated from CIO Word.
Can be addressed to all or a specified group of slave devices.
Supported commands:
• SYNC
• UNSYNC
• FREEZE
• UNFREEZE
Acyclic message services, initiated through FINS. Can be addresses to
one slave device at a time (See Note 1).
Supported PROFIBUS DP services:
•Get_Cfg
• Set_Slave_Add
• Rd_Inp
• Rd_Outp
• MSAC1 - Read
•MSAC1 - Write
• MSAC2 - Initiate
• MSAC2 - Read
•MSAC2 - Write
• MSAC2 - Abort
(defined by slave device)
Total sum of all I/O Data must not exceed 7168 words
Up to 244 bytes of diagnostics max. per slave device
Diagnostic data is collected at the Unit, and can be obtained from the
Unit using FINS messaging
The status flags - 16 words in total - can be mapped by the user to any
PLC CPU memory location.
Note 1. These functions are implemented as of Unit version 2.0.
2. These functions are implemented as of Unit version 3.0.
3. The maximum data length for FINS messages which are redirected to the
PROFIBUS network is 1004 bytes.
4. Although the Unit device address can be set to address 0, this number
should not be used, since this number is reserved in FINS communication.
15
Page 37

PROFIBUS Master Unit
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ISOM
CS
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ERH
PRM
COMM
External Dimensions (mm)
CS1W-PRM21
PRM21
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
130
35
UNIT
No.
ERH
PRM
COMM
Section 1-3
3
CS
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ISOM
94
101
BUS
25
11
CJ1W-PRM21
PRM21
31
RUN
ERC
COMM
PRM
BST
BF
ERH
UNIT
5
4
6
3
7
2
8
1
9
0
A
NO.
F
B
E
C
D
3
54
90
BUS
25
11
65
16
Page 38

PROFIBUS Master Unit
1-3-3 Comparison with Previous Model
The following table provides a comparison between the CS1W-PRM21/
CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master Units and their predecessor, the
PROFIBUS DP Master used in a CS-series PLC
Item C200HW-PRM21 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 (Unit version 3.0)
Unit classification C200H Special I/O Unit CPU Bus Unit
Mounting position • CPU Rack,
• C200H I/O Expansion Rack,
• CS-series Expansion Rack
Can not be mounted on a CS1D PLC
Applicable Unit numbers 0 to F (Hex) 0 to F (Hex)
Maximum number of Units
per PLC
Allocated CIO Area words 2,000 to 2,004 + (10 x unit number)
Allocated DM Area words D20000 to D20017 + (100 x unit number)
I/O Data allocations Maximum total size: 300 words per Unit
Message communications Message communication using IOWR and
16 16
Up to 4 CIO words contain:
• Command settings
• Unit Status and error flags
• Error reporting from the PROFIBUS interface
The area contains user defined memory
mapping of I/O data. At start up this area is
transferred to the Unit
I/O Data words can be allocated to up to 2
input areas and 2 output areas
I/O size per area: up to 200 words
Mapping / area size set in DM words:
CIO: CIO 0000 to CIO 0235
CIO: CIO 0300 to CIO 0511
CIO: CIO 1000 to CIO 1063
HR: HR000 to HR099
DM: D00000 to D05999
Default mapping (DM words contain 0000):
• Output area: CIO 0050 to CIO 0099
• Input area: CIO 0350 to CIO 0399
• Diagnostic flags: CIO 0200 to CIO 0215
IORD PLC instructions:
• IOWR to send Global-Control command
• IORD to read slave diagnostics
FINS message communication not supported
• CPU Rack,
• CS/CJ-series Expansion Rack
CS1W-PRM21 can be mounted on CS1D
1,500 to 1,524 + (25 x unit number)
Up to 25 CIO words contain:
• Command settings
• Unit Status and error flags
• PROFIBUS status and error flags
• Slave status flags
D30000 to D30099 + (100 x unit number)
Not used on the Unit. Reserved for future
use
Maximum total size: 7168 words per Unit
I/O Data words can be allocated to up to 2
input areas and 2 output areas
I/O size per area: up to 7168 words
Mapping and area size set by configurator:
CIO: CIO 0000 to CIO 6143
WR: W000 to W511
HR: HR000 to HR511
DM: D00000 to D32767
EM: E00000 to E32767 (Banks 0 to C)
Default mapping: Not supported
Note Diagnostics flags: available in allo-
cated CIO Area words
FINS message communication. Commands
supported:
• MEMORY AREA READ to read slave
device diagnostics message
• ERROR LOG READ, to read the Unit’s
error log
• ERROR LOG CLEAR to clear the Unit’s
error log
• RUN to enable communication with a
slave device
• STOP to disable communication with a
slave device
• PROFIBUS MESSAGE SEND to send
messages over PROFIBUS network
(Implemented as of Unit version 2.0).
• EXPLICIT MESSAGE SEND to send CIPbased messages over the PROFIBUS
network to OMRON slave devices (implemented as of Unit version 3.0)
Section 1-3
17
Page 39

PROFIBUS Master Unit
Item C200HW-PRM21 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 (Unit version 3.0)
Configuration connection
method
PROFIBUS Media type RS-485, galvanically isolated from the PLC RS-485, galvanically isolated from the PLC
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC
Unit device address range 0 ~ 125, set through the configurator 0 ~ 125, set through the configurator
Number of slave devices
supported on the network
Baud rates supported Selectable through the configurator:
Bus timing definitions Calculated by the configurator Calculated by the configurator
Master Class 1 - Slave cyclic
services
Master Class 1 - Slave services available to the PLC
Master Class 2 - Slave acyclic services
Master - Master services Not supported Not supported
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master
Class 1 - Slave services
PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master
Class 2 - Slave services
Error reporting Error numbers are transferred to CIO word
Serial connection (RS232) directly to connector on the front of the Unit
thread)
Termination provided through a switch on
the unit according to EN50170
125 max, address range 0 ~ 125 125 max, address range 0 ~ 125
• 9.6 kbit/s
• 19.2 kbit/s
• 93.75 kbit/s
• 187 kbit/s
• 500 kbit/s
• 1.5 Mbit/s
• 3 Mbit/s
• 6 Mbit/s
• 12 Mbit/s
• Set_Prm
•Chk_Cfg
• Data_Exchange
• Slave_Diag
• Global-Control - CLEAR
Global-Control, initiated from CIO Word:
Can be addressed to one or all slave
devices or a specified group of slaves
devices. Supported commands:
• SYNC
• UNSYNC
• FREEZE
• UNFREEZE
• CLEAR
• Get_Cfg
• Set_Slave_Add
• Rd_Inp
• Rd_Outp
Not supported • MSAC1 - Read
Not supported • MSAC2 - Initiate
Internal logging not supported
Serial connection directly via PLC CPU, or
via other I/O Units. No separate connector
on the front of the Unit
9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC
thread)
Termination must be provided by the cable
connector according to EN50170
Selectable through the configurator:
• 9.6 kbit/s
• 19.2 kbit/s
• 45.45 kbit/s
• 93.75 kbit/s
• 187 kbit/s
• 500 kbit/s
• 1.5 Mbit/s
• 3 Mbit/s
• 6 Mbit/s
• 12 Mbit/s
• Set_Prm
•Chk_Cfg
• Data_Exchange
• Slave_Diag
• Global-Control - CLEAR
Global-Control, initiated from CIO Word:
Can be addressed to all slave devices or a
specified group of slaves devices.
Supported commands:
• SYNC
• UNSYNC
• FREEZE
• UNFREEZE
• Get_Cfg
• Set_Slave_Add
• Rd_Inp
• Rd_Outp
(Implemented as of Unit version 2.0)
•MSAC1 - Write
(Implemented as of Unit version 2.0)
•MSAC2 - Write
• MSAC2 - Read
• MSAC2 - Abort
(Implemented as of Unit version 3.0)
Error numbers are logged internally and can
be retrieved through FINS messages
Section 1-3
18
Page 40

CX-Profibus Configurator
Section 1-4
1-4 CX-Profibus Configurator
1-4-1 CX-Profibus Features
CX-Profibus The PROFIBUS Master Unit requires a configuration before it can exchange
I/O data with the slave devices. For this purpose OMRON provides the CXProfibus Configuration program, which runs under Microsoft Windows™ NT
4.0, Windows™ 2000 or Windows™ XP
Together with CX-Profibus, OMRON provides five DTM COM Objects:
• A DTM to configure the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master
• A DTM to configure the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master
• A DTM to configure the C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master
• A DTM to configure the SmartSlice GRT1-series GRT1-PRT.
• A DTM to allow the handling of classic GSD files in CX-Profibus
The following provides a quick overview of the functions.
CX-Profibus FDT
Container Application
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 DTM The two CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 DTMs provided to configure the CS1/CJ1W-
CX-Profibus provides an FDT environment in which DTMs can be executed.
The main function of CX-Profibus is to facilitate the DTMs and the data
exchange between them. It provides:
• Network setup functions: A tree view shows the relations between the
DTMs, i.e. the relation between the Master and slave devices.
• Device Catalogue functions: A Device Catalogue containing the installed
DTMs is maintained, to which the user can add new DTMs or delete
them. Device DTMs can be added to the network from this Catalogue.
• Project maintenance functions: CX-Profibus provides the functions to create, save and open project files. It facilitates user access control, which
limits of use to authorized personnel only, using password protection.
• Additional functions: CX-Profibus provides additional functions like printing, error logging, FDT Communication logging and help files.
PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master Units and the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS
DP-V1 Master Units both provide the same basic PROFIBUS DP functions.
These DTMs consist of three parts:
• The Settings User Interface, which handles the configuration for the
PROFIBUS Master Unit. This includes the bus parameters settings, the
I/O data mappings and Master specific settings. The Settings DTM provides its own user interface.
• The Monitoring User Interface, which handles the status monitoring and
control over the PROFIBUS Master Unit, when it is on-line and communicating over the PROFIBUS network. It provides its own user interface to
read out Master status flags and Error log, as well as Slave status flags
and the Slave diagnostics messages received by the Unit. It also allows
the user to send Global-Control messages over the network and to
change the PROFIBUS Master Unit’s mode on the PROFIBUS network.
• The communication interface between the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 DTMs and
CX-Server. CX-Server, provided with the CX-Profibus package, is the
driver for communication between the PC and the PLC CPU.
19
Page 41

CX-Profibus Configurator
Section 1-4
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS DP-V1 DTM
C200HW-PRM21 DTM The C200HW-PRM21 DTM allows configuration of the C200HW-PRM21
In addition to the PROFIBUS DP functions, the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP-V1 DTM provides:
• A communication channel to the user to change a remote slave device
address. This channel has its own user interface.
• Communication channels to facilitate data transfer through PROFIBUS
DP-V1 MSAC1 acyclic message transfer between a PROFIBUS DP-V1
slave device DTM and the physical slave device.
• Communication channels to facilitate data transfer through PROFIBUS
DP-V1 Class 2 acyclic message transfer between a PROFIBUS DP-V1
slave device DTM and the physical slave device. This also allows direct
connection to third-party PROFIBUS slave devices supporting PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2, e.g. PROFIBUS PA devices.
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit. This predecessor of the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 can
be used on existing C200H PLC CPU Systems as well as CS1 PLC Systems,
except for the CS1D.
The C200HW-PRM21 DTM consist of three parts:
• The Settings User Interface, which handles the settings for the C200HWPRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master Unit, including the bus parameters settings, and the I/O data mappings.
• The Monitoring User Interface, to handle the Unit’s status monitoring. The
DTM’s user interface displays the Master status and Slave status.
• The communication interface between the two DTMs mentioned above
and the serial communication driver, to the C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS
DP Master Unit.
Note 1. This Operation Manual does not contain a detailed description of the
C200HW-PRM21 Unit, only a description of the DTM. For more details on
the C200HW-PRM21 refer to C200H-series PROFIBUS DP Master Units
Operation Manual (W349-E2-@).
2. The C200HW-PRM21 Unit and DTM do not support PROFIBUS DP-V1.
SmartSlice GRT1-series
GRT1-PRT DTM
Generic Slave DTM The Generic Slave DTM allows the handling of classic GSD files of up to GSD
SmartSlice GRT1-series GRT1-PRT DTM allows configuration of the GRT1PRT PROFIBUS Communication Unit and SmartSlice I/O Units. The DTM
provides the following user interfaces:
• The Configuration User interface to define the I/O configuration and
parameter setting for I/O data exchange with the PROFIBUS Master Unit.
• Configuration User Interfaces to configure individual SmartSlice I/O Units
attached to the GRT1-PRT.
• A monitoring User interface to monitor the status of the GRT1-PRT and
individual SmartSlice I/O Units.
revision 3 within CX-Profibus. Upon allocating a slave device, for which only a
GSD file is available to a Master Unit in the network, this DTM will be invoked.
This DTM consists of two parts:
• The Settings User Interface will provide the user interface to display the
device’s information and the selectable values, as defined in the GSD.
After making the necessary configuration settings, and saving them,
these will be transferred to the Master DTM.
• The Monitoring User Interface will provide a diagnostics interface to the
user, allowing him to check the Slave’s status. This DTM obtains the necessary information from the PROFIBUS Master Unit’s monitoring DTM.
20
Page 42

CX-Profibus Configurator
r
Note The Generic Slave DTM provides parameter settings related to PROFIBUS
Section 1-4
DP-V1. However, it does not support PROFIBUS DP-V1 communication.
Downloading the
Configuration
CS/CJ-series
ROFIBUS DP
Master Unit
After setting up the configuration, it must be downloaded to the PROFIBUS
Master Unit. The type of serial connection to use for downloading, depends
on the Unit:
• CS1/CJ1W-PRM21: Connection to the Unit is achieved through the serial
port of the PLC CPU, using CX-Server. CX-Server also allows routing the
download through multiple systems, if supported by these systems. The
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 does not support message routing.
• C200HW-PRM21: Connection to the C200HW-PRM21 is achieved
through a serial RS-232c Connection between one of the PC’s Serial
COM Ports and the dedicated configuration connector at the front of the
Unit. For details, refer to the C200HW-PRM21 Manual: W349-E2-2. The
figure below shows the connection methods, for both types.
Serial connection to CS/CJ-series
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit
COM Port on PC
Peripheral Bus or
Host LINK
CX-Profibus
Configurator
C200H-series
PROFIBUS DP
Master Unit
Serial connection to C200H-series
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit
COM Port on PC
CX-Profibus
Configurato
OMRON
SYSMAC CS1G
PROGRAMMABLE
CONTROLLER
PROFIBUS Network
Peripheral or RS232C
Port of CPU Unit
OMRON
SYSMAC CS1G
PROGRAMMABLE
CONTROLLER
PROFIBUS Network
Configuration Port on
PROFIBUS DP
Master Unit
21
Page 43

CX-Profibus Configurator
1-4-2 Specifications
Functional Specifications
Item Specification
Model number WS02-9094G
Hardware platform • Personal computer: IBM PC/AT or compatible
Operating System • MS Windows NT4.0, SP6
Connection to CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 • Peripheral or RS-232C port of PC with PLC CPU. Serial communica-
Connection to C200HW-PRM21 • RS-232C port of PC with Configuration port on the Unit.
Operating environment
General Project functions File handling: CX-Profibus supports overall handling of project files as
Network setup functions CX-Profibus provides network tree view, from which hierarchy between
Device Catalogue functions The Device Catalogue maintains the installed device DTMs. After instal-
Support functions CX-Profibus provides the following additional support functions:
CX-Profibus
Section 1-4
• Processor: Pentium 500 MHz or higher
• Memory: 256 Mbytes
• Hard disk: A minimum of 256 Mbytes
• CD-ROM drive
• Graphics resolution: 800 x 600 pixels minimum
• Serial port: RS-232C
• MS Windows 2000, SP2
• MS Windows XP
Note Internet Explorer 5.01 is also required.
tions mode: Peripheral bus, Host Link, Toolbus, supported by CXServer.
• Communication cable: Cable CS1W-CN226 to connect to the peripheral port on the CPU (Not included in package).
well as network data.
• New: Start a new project.
• Open: Open an existing project file.
• Save (As): Save a project file.
• Export: Export project data to HTML.
• Properties:Edit project property information.
User management: Functionality of CX-Profibus can be limited as
defined by several password protected access levels:
• Administrator
• Planning engineer
• Maintenance
•Operator
• Observer
Master and slave devices can clearly be distinguished.
The following network functions are available:
• Network DTMs (i.e. devices) can be added or deleted, using drag and
drop from the Device Catalogue.
• Network DTMs can be copied and moved from one location to
another in the network view.
• DTM names can be edited by the user.
• Any change to the parameters of a DTM is clearly marked in the tree
view, until the project is downloaded to the Master Unit.
lation of a new DTM, the user must refresh the database. The Device
Catalogue provides the following functions:
• Update Device Catalogue.
• Add device DTMs to the network directly.
• Install a GSD file. This function allows copying of GSD files to a specific directory, after which they are available for the Generic Slave
DTM.
• Context sensitive help functions.
• Error logging.
• Monitoring of FDT communication between DTMs.
• Multi-language support.
22
Page 44

CX-Profibus Configurator
Item Specification
Device setup Device setup allows the user to:
Master setup It allows enabling of Auto Addressing, to facilitate I/O data mapping, as
Bus parameter setup The bus parameter setup allows the selection of baud rate and calcula-
Slave area setup The Slave area setup allows the user to define the I/O Data mapping of
Monitoring functions • Master status read out.
Additional Master functions • Set remote slave address.
Support functions • Context sensitive help functions.
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 DTM
Bus parameter setup The bus parameter setup allows the selection of baud rate and calcula-
Address mapping setup The address mapping setup shows an overview of the mapping of the
Monitoring functions • Master status read out.
Support functions • Context sensitive help functions.
C200HW-PRM21 DTM
Support functions • Context sensitive help functions.
I/O configuration setup The I/O configuration setup function allows:
Parameter setup The Parameter setup function:
Group setting The Group setup function allows definition of the group to which the
Monitoring functions The Monitoring functions provides a display of
Support functions • Context sensitive help functions.
Generic Slave DTM
Section 1-4
• Select the PROFIBUS Master Unit’s unit number.
• Configure the communication link between the PC and the Unit. This
function invokes the user interface of CX-Server.
• Test the Units communication link and read out the Unit’s information.
well as defining the Unit’s behaviour in case of
• a network malfunction.
• PLC mode changes between PROGRAM and RUN/MONITOR mode.
tion and editing of specific bus parameters.
the I/O Data from each of the slave devices on to PLC memory areas.
• Slave status and slave diagnostics read-out.
• Read out of the Unit’s error log.
• Communication channels for PROFIBUS DP-V1 MSAC1 messages.
• Communication channels for PROFIBUS DP-V1 MSAC2 messages.
Note These functions are implemented as of Unit version 3.0.
• Multi-language support.
tion and editing of specific bus parameters.
I/O data of each Slave on to the Unit’s memory. The mapping can be
accomplished automatically, but the function also allows editing of individual address mappings.
• Slave status read-out.
• Multi-language support.
• Multi-language support.
• Selection of device address.
• Enable/disable watchdog.
• Overview of available I/O modules.
• Selection of I/O modules, including Addition, Insertion and Removal of
multiple modules.
• Setting of common as well as module dependent parameters.
• Setting of PROFIBUS DP Extension parameters.
• Setting of PROFIBUS DP-V1 dependent parameters.
associated slave device will belong.
• Standard Slave diagnostics flags.
• Extended diagnostics messages.
• Multi-language support.
Note For more information on the GRT1-PRT DTM, refer to the SmartSlice GRT1-
series GRT1-PRT PROFIBUS Communication Unit Operation Manual
(W04E-EN-@).
23
Page 45

Basic Operating Procedure
1-5 Basic Operating Procedure
1-5-1 Overview
The following diagram provides an overview of the installation procedures.
For experienced installation engineers, this may provide sufficient information. For others, cross-references are made to various sections of this manual
where more explicit information is given.
Mount the PROFIBUS Master Unit on
to the PLC
(See section 2-2 Installing the CS1/
CJ1W-PRM21 Units)
Select a unique Identity Number (0 - F)
for the Unit using the rotary switch on
the front of the Unit
(See section 2-3 Initial Setup
Procedure)
Section 1-5
Connect the PROFIBUS Master unit to
the PROFIBUS network
(See section 2-4 Setting up a Network)
Switch on the power supply for the PLC
and create a PLC I/O table in CXProgrammer. See CX-Programmer
User Manual (Reference No. W361).
Configure the PROFIBUS Master Unit
using CX-Profibus on the PC.
(See sections 3-3 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS Master DTM and 6-4
Configuring the Master)
Download configuration data to
PROFIBUS Master Unit.
(See sections 3-3-3 Connecting to the
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21) and 6-4-5
Downloading the Configuration)
PROFIBUS DP starts communicating,
confirmed by the COMM LED
continuously lit. Check status of other
LED Indicators (See sections 6-5 I/O
Communication Characteristics, 6-6
Operating the Network and 6-7
Monitoring the Network)
24
Page 46

Basic Operating Procedure
1-5-2 Preparations for Communications
1,2,3... 1. Mount the Master Unit on the PLC system (refer to 2-2 Installing the CS1/
CJ1W-PRM21 Units).
• Treat the Unit as a CPU Bus Unit.
• It can be mounted to a CPU Rack or Expansion Rack.
• Number of Units: 16 (Max).
2. Set the Unit No. (UNIT No.) for the PROFIBUS Master Unit (refer to 2-3-1
Selecting a unit number).
3. Connect a PC or a Programming Device to the PLC and turn ON the power
supply to the PLC.
4. Generate the I/O tables and restart the PLC (refer to 2-3-2 Creating an I/O
table).
5. Install CX-Profibus, and the DTMs on to the PC.
1-5-3 Procedures Prior to Starting Communications
Use the following procedure to configure the Unit using CX-Profibus:
1,2,3... 1. Wire the network, to connect the PROFIBUS Master Unit to the slave de-
vices.
2. Turn ON the PLC power supply and the power supplies of the slave device
on the network.
3. In CX-Profibus, create a network and define the parameters and I/O configurations for the PROFIBUS Master Unit settings and the allocated slave
devices. Determine the baud rate and the bus parameter setup. Make sure
that the “Go to OPERATE mode“ option is selected, to force the Unit to OPERATE mode upon a PLC mode change to RUN / MONITOR mode.
4. Download the network configuration to the PROFIBUS Master Unit. After
downloading the configuration, CX-Profibus will restart the PROFIBUS
Master Unit.
5. After restarting the PROFIBUS Master Unit it will automatically start communication.
Section 1-5
25
Page 47

Basic Operating Procedure
Section 1-5
26
Page 48

SECTION 2
Installation and Wiring
This section shows the PROFIBUS device and identifies its controls and indicators. It contains the procedures for installing
the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit on the PLC System and setting up the PROFIBUS network.
2-1 Unit Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-1-1 Nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-1-2 Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2-1-3 Switch Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-1-4 PROFIBUS Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2-2 Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-2-1 Handling Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-2-2 Mounting the CS1W-PRM21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-2-3 Mounting the CJ1W-PRM21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-3 Initial Setup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2-3-1 Selecting a unit number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2-3-2 Creating an I/O table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2-4 Setting up a Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2-4-1 Network Structure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2-4-2 Bus Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2-4-3 PROFIBUS Cable Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2-4-4 Shielding Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2-5 Defining PROFIBUS DP in the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
27
Page 49

Unit Components
CS
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ERH
PRM
COMM
2-1 Unit Components
2-1-1 Nomenclature
The illustration below shows the Status LED indicators, the Unit number
selector switch, and a 9-pin female sub-D connector on the front side of the
CS1W-PRM21 and the CJ1W-PRM21 Units. Each of these components are
explained in the following sections
CS1W-PRM21
Section 2-1
PRM21
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
UNIT
No.
ERH
PRM
COMM
CS
Indicators
Unit number switch
This switch sets the Unit Number of the
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit as a one-digit
hexadecimal number
PROFIBUS DP Connector
BUS
9-Pin Sub-D, female connector, #4/40 UNC thread
Connect the PROFIBUS DP network cable to this
connector. Termination must be provided with the
cable connector
CJ1W-PRM21
PRM21
RUN
ERC
COMM
PRM
BST
BF
ERH
UNIT
4
5
3
6
2
7
1
8
0
9
F
NO.
A
E
B
D
C
Indicators
Unit number switch
This switch sets the Unit Number of the
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit as a one-digit
hexadecimal number
BUS
PROFIBUS DP Connector
9-Pin Sub-D, female connector, #4/40 UNC thread
Connect the PROFIBUS DP network cable to this
connector. Termination must be provided with the
cable connector
28
Page 50

Unit Components
CS
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ERH
PRM
COMM
2-1-2 Indicators
The CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Units are each fitted with seven
LEDs to indicate the operational mode and status of the Unit and the PROFIBUS network
CJ1W-PRM21CS1W-PRM21
PRM21
RUN
ERC
COMM
PRM21
RUN
ERC
BST
BF
ERH
PRM
COMM
CS
Indicator Specifications
Indicator Colour Status Meaning
RUN Green Not lit • Startup test failed, Unit not operational.
• Operation stopped, due to a fatal error.
Lit Initialization successful, Unit is in normal operation.
ERC
(PROFIBUS Master Unit
Error)
ERH
(PLC Error)
PRM
(Parameter database)
BST
(Bus status)
COMM
(I/O Data communication)
BF
(Bus Fail)
Red Not lit Unit is in normal operation.
Lit One of the following errors occurred:
• Startup error.
• Non-volatile memory error (checksum failed, write-verify failed).
• Invalid PROFIBUS parameter configuration setting.
• Fatal error in program execution.
Red Not lit PLC CPU in normal operation.
Lit One of the following errors occurred:
• PLC CPU Bus error.
• Cyclic Refresh Monitor Time-out.
• Routing table error.
Green Not lit PROFIBUS Parameter configuration is not available or incorrect.
Flashing PROFIBUS Parameter configuration is being transferred to the Unit
and is not yet available.
Lit PROFIBUS Parameter configuration is correct, and operational.
Green Not lit The PROFIBUS Master Unit is in OFFLINE or STOP mode.
Flashing The PROFIBUS Master Unit is in CLEAR mode.
Lit The PROFIBUS Master Unit is in OPERATE mode.
Green Not lit No PROFIBUS data exchange with any of the allocated slaves.
Flashing Fatal error occurred (ERC LED is ON). Unit initialization failed.
Lit PROFIBUS data exchange ongoing with at least one allocated slave.
Red Not lit No PROFIBUS communication errors occurred.
Flashing At least one allocated slave is not in data exchange with the Unit.
Lit An error occurred in the PROFIBUS interface of the Unit (see section 7-
2 Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators).
ERH
PRM
BST
BF
Section 2-1
Note Unless otherwise specified, the frequency of a flashing LED is 1 Hz (50% duty
cycle).
29
Page 51

Unit Components
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Section 2-1
2-1-3 Switch Settings
Setting the Unit Number The unit number is used to identify individual CPU Bus Units when more than
one CPU Bus Unit is mounted to the same PLC. The unit number must be
unique for each CPU Bus Unit. Selecting a non-unique number for a CPU Bus
Unit will prevent the PLC System from starting correctly.
Note Always turn OFF the power to the PLC CPU before changing the Unit number
Note If the unit number is being set for the first time or changed, then an I/O table
Unit Number and CPU Bus
Unit Word Allocations
CS1W-PRM21
CJ1W-PRM21
Setting range:
0 ~ F (Hexadecimal)
UNIT
UNIT
5
4
6
3
No.
1. Turn OFF the power supply before setting the Unit number.
2. Set the switch to the new Unit number. Use a small screwdriver to make
the setting, taking care not to damage the rotary switch. The unit number
is factory-set to 0.
3. Turn ON the power again.
setting. The Unit only reads the Unit number setting during the initialization
following a power-up, but not following a software reset.
must be created for the PLC.
With CS/CJ-series PLCs, words are automatically allocated in the CIO Area
and the DM Area. The PROFIBUS Master Unit uses these words for receiving
control data from the CPU Unit and for notifying the CPU Unit of PROFIBUS
Master Unit and communications status. The word addresses in the allocated
areas for the CPU Bus Unit are important when creating the user program for
using the PROFIBUS Master Unit. This must be considered when setting the
unit number.
The CIO and DM Word allocations are discussed in detail in 4-2 Allocated
CIO Area Words. The tables below show the relation between the unit number
and the allocated CIO Area and DM Area words.
7
2
8
1
9
0
A
NO.
F
B
E
C
D
Unit No.
(decimal)
0 (0) CIO1500 to CIO1524 8 (8) CIO1700 to CIO1724
1 (1) CIO1525 to CIO1549 9 (9) CIO1725 to CIO1749
2 (2) CIO1550 to CIO1574 A (10) CIO1750 to CIO1774
3 (3) CIO1575 to CIO1599 B (11) CIO1775 to CIO1799
4 (4) CIO1600 to CIO1624 C (12) CIO1800 to CIO1824
5 (5) CIO1625 to CIO1649 D (13) CIO1825 to CIO1849
6 (6) CIO1650 to CIO1674 E (14) CIO1850 to CIO1874
7 (7) CIO1675 to CIO1699 F (15) CIO1875 to CIO1899
30
Allocated words Unit No.
(decimal)
Allocated words
Page 52

Unit Components
DM Area Allocations
Unit No.
(decimal)
0 (0) D30000 to D30099 8 (8) D30800 to D30899
1 (1) D30100 to D30199 9 (9) D30900 to D30999
2 (2) D30200 to D30299 A (10) D31000 to D31099
3 (3) D30300 to D30399 B (11) D31100 to D31199
4 (4) D30400 to D30499 C (12) D31200 to D31299
5 (5) D30500 to D30599 D (13) D31300 to D31399
6 (6) D30600 to D30699 E (14) D31400 to D31499
7 (7) D30700 to D30799 F (15) D31500 to D31599
2-1-4 PROFIBUS Connector
The PROFIBUS connector on the font of the Unit is a 9-pin female sub-D connector, as recommended by the PROFIBUS standard EN 50170.
Pin No. Signal Description
9
6
5
1
1 Shield Shield/protective ground
2--
3 RxD/TxD-P Receive/Transmit data - plus (B wire)
4 RTS Control signal for repeaters (direction control) (TTL)
5 DGND Data ground (reference potential for VP)
6 VP Supply voltage of the terminator resistance (5 Vdc)
7--
8 RxD/TxD-N Receive/Transmit data - minus (A wire)
9--
Allocated words Unit No.
(decimal)
Section 2-1
Allocated words
The signal RTS (TTL signal) is for the direction control of repeaters, which do
not have a self-controlling capability.
The signals DGND and VP are used to power the bus terminator located in
the cable connector.
Note The orientation of the sub-D connector allows the use of PROFIBUS connec-
tors with a 90° angle cable outlet, e.g ERNI, Delconec and Phoenix.
Note The 9-pin sub-D connector uses #4/40 UNC thread, for mechanical fixation of
the cable connector. Make sure that if non-standard PROFIBUS connectors
are used, the corresponding thread is used on the cable connector.
31
Page 53

Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units
pply
2-2 Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units
2-2-1 Handling Precautions
When installing the PROFIBUS Master Unit on the PLC system, observe the
following handling precautions
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the PLC before mounting or dismounting a Unit or connecting or disconnecting cables.
• Provide separate conduits or ducts for the I/O lines to prevent noise from
high-tension lines or power lines.
• Leave the label on top of the Unit attached when wiring. Removing the
label prior to wiring may result in malfunction if foreign matter enters the
Unit.
• Remove the label after the completion of wiring to ensure proper heat dissipation. Leaving the label attached may result in malfunction.
2-2-2 Mounting the CS1W-PRM21
The CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit can be mounted to any slot in
either a CS-series CPU Rack, a CS-series Expansion CPU Rack or a CS1
Duplex CPU Rack. The CS-series PLC supports up to 7 Expansion CPU
Racks, in addition to the CPU rack.
The number of slots to which PROFIBUS Master Unit can be mounted
depends on the Backplane. Up to 16 PROFIBUS Master Units can be
mounted to a single PLC system. If it is mounted in combination with other
CPU Bus Units (e.g., Ethernet Units), the maximum total number of CPU Bus
Units that can be mounted is 16.
.
CS1W-BC023 / BC033 / BC053 / BC083 / BC103 CPU Backplane
CS-series CPU Rack
Can mount to any position,
with 2, 3, 5, 8, or 10 slots.
CPU
PS
Section 2-2
32
2, 3, 5, 8, or 10 slots
(Expansion Backplane not possible with 2-slot CPU Backplane.)
CS1W-BI033 / BI053 / BI083 / BI103 CS-series Expansion Backplane
CS-series Expansion Rack
Can mount to any position,
PS
with 3, 5, 8, or 10 slots.
3, 5, 8, or 10 slots
C200H Expansion I/O Backplane
C200H Expansion Rack
PROFIBUS DP Master Unit cannot be
PS
mounted to any slots.
CPU: CPU Unit
PS: Power Su
Note The CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit’s maximum current consumption
is 400 mA. Make sure that the total current consumption of all the Units connected to the same CPU Backplane or Expansion Backplane does not exceed
the output capacity of the Power Supply Unit.
Up to 16 Units can be mounted
to the slots shown in the diagrams
on the left.
Unit
Page 54

Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units
Section 2-2
Mounting Procedure Mount the CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit to the Backplane using the
following procedure.
!Caution Always turn OFF the power supply to the PC before mounting or dismounting
a Unit or connecting or disconnecting cables.
1,2,3... 1. Hook the claw on the top of the Unit onto the Backplane.
Claw
Backplane
2. Insert the Unit into Backplane connectors and securely tighten the screw
at the bottom of the Unit. Tighten the screws to a torque of 0.4 N•m.
3. When removing the Unit, first loosen the screw at the bottom of the Unit.
Fixing screws
Note When mounting the Unit, provide the clearance shown below to facilitate easy
mounting or dismounting.
Duct
Duct
Philips screwdriver
20 mm min.
Backplane
20 mm min.
33
Page 55

Installing the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Units
/O
ace Unit
2-2-3 Mounting the CJ1W-PRM21
The PROFIBUS Master Unit can be mounted to any slot in either a CJ-series
CPU Rack, or a CJ-series Expansion CPU Rack. The CJ-series PLC supports
up to 4 Expansion CPU Racks, in addition to the CPU rack.
The number of slots to which PROFIBUS Master Unit can be mounted in any
of the positions shown below using the sliders on the top and bottom of the
Unit. Up to 16 PROFIBUS Master Units can be mounted to a single PLC. If it
is mounted in combination with other CPU Bus Units (e.g., Ethernet Units),
the maximum total number of CPU Bus Units that can be mounted is 16.
Section 2-2
PLC CPU rack
P
SIC
Expansion Backplane
PSI
Expansion Backplane
PSI
Expansion Backplane
10 Units max.
C
P
U
10 Units max.
I
10 Units max.
I
10 Units max.
End cover
End cover
End cover
End cover
Up to 16 PROFIBUS DP
Master Units can be
mounted.
34
PSI
I
PS: Power Supply Unit
CPU: CPU Unit
IC: I/O Control Unit
Interf
II: I
Note The CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit’s maximum current consumption
is 400 mA. Make sure that the total current consumption of all the Units connected to the same CPU Backplane or Expansion Backplane does not exceed
the output capacity of the Power Supply Unit.
Page 56

Initial Setup Procedure
Section 2-3
Mounting Procedure Mount the CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit to the PLC using the follow-
ing procedure.
1. Carefully align the connectors to mount the PROFIBUS Master Unit.
Connector
PA205R
POW
ER
L1
AC100-240V
INPUT
L2/N
RUN
OUTPUT
AC240V
DC24V
2. Move the yellow sliders on the top and bottom of the Unit until they click
into position, to lock.
SYSMAC
CJ1G-CPU44
PR
O
G
R
A
M
M
A
C
O
N
TR
O
L
L
ER
B
O
MCPWR
BUSY
LE
P
E
N
PERIPHE
PORT
ERR/ALM
RUN
INH
PRPHL
COMM
RAL
PRM21
RUN
E
R
C
P
R
M
C
O
M
M
E
R
H
BS
T
B
F
UNIT
5
4
6
3
7
2
8
1
9
NO.
0
A
F
B
E
C
D
BUS
PA205R
POWER
L1
AC100-240V
INPUT
L2/N
RUN
OUTPUT
AC240V
DC24V
Note If the sliders are not securely locked, the PROFIBUS Master Unit functions
may not operate correctly.
To dismount the Unit, move the sliders to the “Release” direction.
2-3 Initial Setup Procedure
After mounting the PROFIBUS Master Unit to its PLC System, the following
Initial Setup Procedure must be applied to allow the Unit to start up properly
and to be configured for operation.
• A unique unit number must be selected, before the PLC’s power supply is
turned on.
• An I/O table must be created in the PLC, in order to register the Unit on
the PLC CPU.
SYSMAC
CJ1G-C
PROGRAMM
CONTROLLER
PU44
ABLE
OPEN
MCPWR
BUSY
ERR/ALM
PRPHL
COMM
PERIPHERAL
PORT
Slider
RUN
INH
PRM21
R
U
N
ERC
P
R
M
COMM
E
R
H
BST
B
F
UNIT
5
4
6
3
7
2
8
1
9
NO.
0
A
F
B
E
C
D
BUS
BUS
Release
Lock
35
Page 57

Initial Setup Procedure
2-3-1 Selecting a unit number
1. Make sure that the PLC Power Supply is turned OFF before setting the
Unit number.
2. Set the switch to the desired unit number. Use a small screwdriver to make
the setting, taking care not to damage the rotary switch. The unit number
is factory-set to 0. Make sure that the unit number is unique on the PLC,
i.e. there must be no other CPU Bus Units with the same unit number.
3. Turn ON the PLC Power Supply.
After setting the unit number, the PLC CPU must now register the PROFIBUS
Master Unit, by creating an I/O table.
2-3-2 Creating an I/O table
An I/O table is used to identify Units connected to the PLC and to allocate I/O
to them. The I/O table is stored within the PLC CPU, and loaded at start up. If
any change is made to the Unit configuration of a CS/CJ-series PC, the I/O
table must be created again to register the Units to the CPU Unit.
Section 2-3
Connecting a
Programming Device
Applicable Programming
Devices
Connecting Programming
Devices
Procedure for Creating an
I/O Table
To create the I/O table, connect a Programming Device (such as a Programming Console or CX-Programmer) to the PLC.
The following Programming Devices can be used with CS/CJ-series PLCs.
Programming Console
Model number Key Sheet (required) Recommended cable (required)
C200H-PRO27-E CS1W-KS001-E CS1W-CN224 (cable length: 2.0 m)
CS1W-CN624 (cable length: 6.0 m)
CX-Programmer and CX-Net
Model number: WS02-CXP@@-EV2
The operations are explained here using a Programming Console. For details
regarding the CX-Programmer and the CX-Net, refer to the CX-Programmer
User’s Manual.
CX-Net is software that comes with CX-Programmer and is automatically
installed when CX-Programmer is installed.
To connect a Programming Console, attach a CS/CJ-series Key Sheet and
then connect the Console to the CPU Unit’s peripheral port. (It cannot be connected to the RS-232C port.)
The procedure for creating an I/O table is shown here, taking as an example
an I/O table that is generated automatically for a PLC connected online. In this
example, a Programming Console is used for creating the I/O table. For an
explanation of how to create an I/O table using a CX-Programmer, refer to the
CX-Programmer User’s Manual.
Use the following procedure to create the I/O table.
36
Page 58

Setting up a Network
Initial screen
000000 I/O TBL ?
CHG
000000 I/O TBL
WRIT ????
000000CPU BU ST?
0:CLR 1:KEEP
SHIFT
Passw ord
CH
*DM
Section 2-4
WRITE
or
000000 I/O TBL
WRIT OK
(Save or clear the CPU Bus Unit System Setup.)
After creating the I/O table, the Unit is ready to be configured for first use on
the PROFIBUS network.
Note After mounting the Unit and starting it up for the first time, the Unit’s Configu-
ration is empty. This will cause the red ERC LED on the front of the Unit to be
switched ON. In this situation, the Unit can still be configured.
2-4 Setting up a Network
2-4-1 Network Structure
Communication Medium The PROFIBUS standard defines the use of EIA RS-485 as the main commu-
nication transport medium. The PROFIBUS Master Unit is designed to interface directly to this type of medium. This section will discuss the setup of
networks based on this medium.
Note The other communication medium specified for PROFIBUS is optical fibre.
The PROFIBUS Master Units does not provide a direct interface to this type of
medium. However, by using third party couplers an interface between EIA RS485 and optical fibre networks can be made.
Linear Bus Topology PROFIBUS DP defines the use of the Linear Bus Network Topology. The Bus
must be terminated at both ends, and must not contain network branches.
The total cable length of the bus depends on the cable and the selected baud
rate. Also, RS-485 specifies a maximum of up to 32 devices - master and
slave devices - per line segment. If more than 32 devices are to be connected, or if the total length of the segment must be extended beyond its maximum, repeaters must be used to link the separate segments.
37
Page 59

Setting up a Network
Section 2-4
Note Repeaters are devices which connect two segments. They do not have a
device address of their own, but they do count in the total number of devices
in a segment.
Repeaters A maximum of up to three repeaters between two devices in a network can be
used, i.e. a network can consist of up to 4 segments. The maximum number
of PROFIBUS devices in such a network is then 122. The figure below shows
an example of a two-segment network.
OMRON
SYSMAC CS1G
PROGRAMMABLE
CONTROLLER
Termination
Station 1
Termination
Termination
Repeater
Station 2 Station 3 Station 31
Station 63 Station 33 Station 32
Termination
Tree Topology The use of repeaters allows the extension of three or more Linear Bus seg-
ments into a Tree topology. In a tree topology more than three repeaters are
allowed, provided that there are no more than three repeaters between any
two devices in the network. The following figure presents an example of a network with more than three segments and repeaters.
Segment 1
Max. 31 stations
M / S
Segment 2
Max. 31 stations
M / S
38
R
Segment 4
Max. 31 stations
M / S
M / S
Master or slave station
R
Repeater
Termination
Max. total number of stations = 126
R
Segment 3
Max. 28 stations
Segment 5
Max. 30 stations
R
R
M / S
R
Segment 6
Max. 31 stations
M / S
M / S
Page 60

Setting up a Network
k
Section 2-4
Cable Type The PROFIBUS standard EN 50170 specifies Type A shielded, twisted- pair
cable as the recommended cable type for use in an RS-485 based PROFIBUS network. This cable type has the following characteristics:
Characteristic Value
Impedance 135 - 165 ohms
Capacitance per unit length < 30 pF/m
Loop resistance 110 ohms/km
Core diameter 0.64 mm
Core cross section
0.34 mm
2
Note The PROFIBUS standard EN 50170 also specifies a Type B cable with differ-
ent cable characteristics. Use of Type B cable is no longer recommended.
Maximum PROFIBUS
Cable Length
The transmission speed defines the maximum advised cable distance or
cable segment in metres before the use of a repeater is recommended. The
cable lengths specified in the following table are based on PROFIBUS type A
cable.
Baud rate
(kbit/s)
9.6 1200 500 400
19.2 1200 1500 200
45.45 1200 3000 100
93.75 1200 6000 100
187.5 1000 12000 100
Distance/segment
(m)
Baud rate
(kbit/s)
Distance/segment
(m)
Note 1. If network extension beyond the range of the advised cable length is re-
quired, the use of fibre optic cable to cross the larger distance should be
considered.
2. The recommended minimum cable length is 1 m.
Stub Lines Passive Stub lines (branches from the main line) should be avoided for data
transmission speeds of more than 500 kbit/s. Except at end devices with termination, it is recommended to always use plug connectors that permit two
data cables to be connected directly to the plug. This method allows the bus
connector to be plugged and unplugged at all times without interrupting data
communication between other devices.
2-4-2 Bus Termination
Termination Resistors In order to minimize cable reflections and ensure a defined signal level on the
VP
B-Line
A-Line
DGND
390 Ohm
220 Ohm
390 Ohm
Networ
data lines, the data transfer cable must be terminated at both ends with a terminating resistor combination. The bus termination diagram is shown on the
left.
The bus terminator connects the two data lines via a 220 ohm resistor which,
in turn, is connected to VP 5Vdc and DGND via two 390 ohm resistors. Powering the terminator resistor via VP 5V and DGND ensures a defined idle state
potential on the data lines.
To ensure the correct functioning up to the highest baud rate, the bus cable
must be terminated at both its ends.
A missing bus termination can cause errors during data transfer. Problems
can also arise if too many bus terminators are fitted, since each bus terminator represents an electrical load and reduces the signal levels and thus the
signal-to-noise ratio. Too many or missing bus terminators can also cause
39
Page 61

Setting up a Network
Section 2-4
intermittent data transfer errors, particularly if the bus segment is operated
close to the specified limits for maximum numbers of devices, maximum bus
segment length and maximum data transfer rate.
Inductors In addition to the bus termination, additional precautions must be taken to
ensure proper operation at high baud rates, i.e. baud rates of 500 kbit/s and
higher. Due to the capacitive load of the device and the resulting cable reflec-
B-Line
A-Line
110 mH
Network
110 mH
tions, bus connectors must be provided with built-in series inductors, of 110
mH each, as shown in the figure on the left.
Installing the inductors applies to all devices on the network, and not only to
the devices at both ends of the bus cable.
2-4-3 PROFIBUS Cable Connector
Bus Cable Connector The plug connector to be used on the CS/CJ-series PROFIBUS Master Unit is
a 9-pin male sub-D type, preferably encased in metal and having a facility to
connect the shield of the cable to the case or to pin 1. The cable should be
connected to the receive / transmit lines, pin 3 (B-line) and pin 8 (A-line).
The use of special PROFIBUS DP cable connectors, which are available from
several manufacturers, is highly recommended. Various models are widely
available, with or without the bus termination and inductors built-in. If provided
in the connector, the Bus termination can often be enabled or disabled
through a switch on the connector.
The special PROFIBUS DP cable connectors often provide a convenient way
of connecting the cables. The figure on the left, provides an example of such
a bus cable connector.
A standard 9-pin sub-D plug can only be used if the PROFIBUS Master Unit is
not at the start or the end of a bus segment, or on a stub line at a baud rate of
500 kbit/s or less.
To next
station
From
previous
station
The two PROFIBUS data lines are designated A and B. There are no regulations on which cable core colour should be connected to which of the two data
terminals on each PROFIBUS device; the sole requirement is to ensure that
the same core colour is connected to the same terminal (A or B) for all
devices throughout the entire system (across all devices and bus segments).
The PROFIBUS Organization recommends the following rule for data line
colour codes: PROFIBUS cables in general will use the colours red and green
for the data lines, with the following assignment:
• Data cable wire A - green
• Data cable wire B - red
This rule applies to both the incoming and the outgoing data lines.
40
Page 62

Defining PROFIBUS DP in the Software
Section 2-5
2-4-4 Shielding Precautions
Cable Shield Connection To ensure electro-magnetic compatibility (EMC), the shield of the cable
should be connected to the metal case of the plug connector.
Inside cabinet
Ground Rail
Outside cabinet
If the Unit is installed in a control cabinet, the bus cable shield should be
brought into physical contact with a grounding rail using a grounding clamp or
similar device. The cable shield should continue in the cabinet right up to the
PROFIBUS device.
Ensure that the PLC and the control cabinet in which it is mounted have the
same ground potential by providing a large-area metallic contact to ground,
e.g. galvanized steel to ensure a good electrical connection. Grounding rails
should not be attached to painted surfaces.
For further information regarding PROFIBUS network installation, please refer
to “Installation Guideline for PROFIBUS DP/FMS” (PNO Order No. 2.112),
which is available at every regional PROFIBUS Organization. The information
covers:
• Commissioning of PROFIBUS equipment.
• Testing the PROFIBUS cable and bus connectors.
• Determining loop resistance.
• Testing for correct bus termination.
• Determining the segment length and cable route.
• Other test methods.
• Example of an equipment report in the PROFIBUS guideline.
2-5 Defining PROFIBUS DP in the Software
Defining the Configuration After making the physical connections of the network, the configuration then
has to be defined in the software. OMRON provides a dedicated PC-based
configuration program, called CX-Profibus, as well as the required DTMs for
this purpose. It can be used to:
• Define the master(s).
• Assign slaves to their respective master(s).
• Define I/O Configuration and parameters of individual slave devices.
• Define bus parameters, e.g. baud rate, target rotation time etc.
Downloading the
Configuration
The system must be downloaded to the Master Unit after configuring it at the
PC. This is made possible by either connecting the serial COM port of the PC
to the CS1/CJ1 PLC with a serial interface cable, or use an ethernet connection between the PC and the CS1/CJ1 PLC via an ethernet unit or Controller
Link unit.
41
Page 63

Page 64

SECTION 3
Configuration Software
This section contains the procedures for installing the configuration software. It also presents an overview of the
Configuration software and discusses the main aspects of defining a PROFIBUS configuration. A more detailed description
of the use of the Configuration software can be found in SECTION 6 Operation.
3-1 Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-1-1 Installation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-1-2 Installation Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-1-3 Installing the C200HW-PRM21 DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3-2 CX-Profibus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-2-1 Starting CX-Profibus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-2-2 CX-Profibus Main Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3-2-3 Device Catalogue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3-2-4 Updating the Device Catalogue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3-2-5 Adding Devices to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3-2-6 Saving and Opening Projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3-2-7 Exporting to HTML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3-2-8 Error Logging and FDT Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3-2-9 Access Control and User Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3-3 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3-3-1 Configuration User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3-3-2 Diagnostics User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-3-3 Connecting to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
3-4 C200HW-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3-4-1 Configuration User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3-4-2 Diagnostics User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
3-4-3 Connecting to the C200HW-PRM21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
3-5 Generic Slave Device DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
3-5-1 Configuration User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
3-5-2 Diagnostics User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
43
Page 65

Installation
3-1 Installation
3-1-1 Installation Requirements
CX-Profibus Configuration software is required to configure the PROFIBUS
Master Unit before operating the network. Without a valid configuration the
PROFIBUS Master Unit will not be able to achieve data communication with
the slave devices on the network.
The following are the minimum requirements for a PC to install the CX-Profibus configurator software:
• PC Pentium III or higher, 500 MHz minimum
• Operating System: Windows 2000 SP2 / Windows NT 4.0, SP6 /
• RAM: 256 MB minimum
• Hard disk space: 256 MB minimum
• Graphics resolution: 1024 x 768 pixels minimum
• Serial port: RS-232C; COM1 to COM4 supported
• CD-ROM drive
• Communication cable: Cable CS1W-CN226 to connect to the peripheral
port on the CPU (Not included with CX-Profibus)
Section 3-1
Windows XP
3-1-2 Installation Procedure
This section explains how to install the CX-Profibus Configuration software
and its components for the PROFIBUS Master Unit.
CX-Profibus CD-ROM CX-Profibus is provided on a CD-ROM, which contains the following compo-
nents:
• Microsoft .NET Framework
• CX-Profibus FDT Container application.
• CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Configuration DTMs.
• CX-Server, to allow communication between the PC and the PLC.
• C200HW-PRM21 Configuration DTM.
• Generic Slave Device DTM, to allow slave configuration using GSD files.
• Additional GSD files for several OMRON slave devices.
Note 1. Any older version of CX-Profibus installed on the system, must be unin-
stalled, prior to installing the newer version.
2. Provided with the CD-ROM is a 16-digit installation key, which can be
found on a label on the CD-ROM box. The key is unique to the CD-ROM
and is required to allow full installation of the software. The key is also used
as reference when registering the purchased software with OMRON.
3. If during installation the 16-digit License code was not entered, the program will run in demo mode, i.e. it provides all functionality, but for a limited
period of 30 days. After this period has expired, the License code must be
provided to the program, to allow continuation of use.
4. During the limited period of 30 days, the valid License code, as shown on
the CD-ROM case can be entered at anytime when the program is running,
by selecting the License button in the About dialog window.
5. Administrator rights are required to install CX-Profibus.
44
Page 66

Installation
Section 3-1
6. The operations and displays shown in the following procedure may differ
slightly depending on the version of Windows software being used. The
displays for Windows 2000 are shown here.
1,2,3... 1. Exit all other Windows-based programs.
2. Insert the setup disk (CD-ROM) into the CD-ROM drive.
3. Double-click Setup.exe.
The setup program for CX-Profibus will start. A progress dialog window is displayed, indicating progress of the setup as the program is loaded.
4. During the preparation, the InstallShield wizard will determine if the Microsoft .NET framework needs to be installed. This package is required
during installation and for executing CX-Profibus. If already installed, the
installation will be skipped, and the process will proceed with step 7. Installation of the Microsoft .NET framework first displays the License statement
(shown below) to which the user must agree. Next, press the Install button
to continue.
45
Page 67

Installation
Section 3-1
5. After starting the Microsoft .NET framework installation process, a window
will be displayed showing the progress of this installation.
6. Completion of the Microsoft .NET framework installation is indicated by
displaying the message window below.
7. After installing the Microsoft .NET framework, CX-Profibus and its components will be installed. The installation welcome window as shown below
will be displayed. Click the Next button to continue.
8. After the welcome window the window containing the License statement
for CX-Profibus is displayed. The License window is shown below. Please
read the License carefully, before selecting the Ye s button to accept the
46
Page 68

Installation
Section 3-1
License. If the License is not accepted - by selecting the No button -, the
installation will be terminated.
9. After accepting the License statement, the window below is displayed to
allow you to enter your name, your Company name and the 16-digit License key provided on the back side of the CD-ROM case.
Note 1) If an incorrect 16-digit License code is entered, the program will
display an error message, after which it allows you to re-enter the
number again.
2) If no License code is entered, the program will still be installed, but
it will run only for 30 days after installation. After this 30-day trial
period, you will have to enter the required 16-digit License code in
order to be able to run the program.
10. After entering the information a window will be displayed, allowing you to
verify the entered information before installation commences. If the infor-
47
Page 69

Installation
Section 3-1
mation is correct, select the Yes button. Selecting the No button will revert
you to the previous window.
11. After entering the correct License code, the installation process will first require you to select the language to be installed for CX-Profibus and its
components. The windows shown below will be displayed, offering the
choice of available languages. Select the desired language package and
press the Next button.
48
12. You are now required to specify the destination directory for the configurator files. If the default directory shown in the window is acceptable, click the
Next Button. To specify a different directory, click the Browse Button,
specify the desired directory, and click the Next Button. If a new directory
is specified, the software will create it automatically.
Page 70

Installation
Section 3-1
13. Specify a Program Folder to which a shortcut to the program will be added.
The default Program Folder is OMRON\CX-Profibus. You can specify any
one of the other available Program Folders listed in the Existing Folders
frame. After making the desired selection, select the Next button. The installation will now be performed, the files will be copied to the destination
folder and the necessary registry entries will be made...
14. A window is displayed showing the progress of the installation.,
15. After completing the CX-Profibus installation, the setup program will
launch the CX-Server installation. The window shown below will be displayed. Select the Yes button to continue.
16. The CX-Server installation program will detect whether CX-Server has
been installed or not on the PC. If a newer version of CX-Server has been
installed by another CX-Suite application program, the installation of CXServer for CX-Profibus will be skipped. If an older CX-Server version has
been installed, the installation will be performed. The window shown below
49
Page 71

Installation
Section 3-1
will be displayed, prompting the user for a selection of language to be used
with CX-Server.
17. After selecting the language and pressing the OK button, the welcome
window shown below will be displayed. Please take note of the recommendations, and make sure all other windows programs are closed before continuing.
18. After pressing the Next button, the user is prompted for the directory in
which to install CX-Server. Press the Next button to continue with the default directory, or the Browse button to select another directory.
19. Next the user is prompted to select the additional driver software for CXServer. None of these additional drivers are required to accomplish serial
communication between the PC and the PLC CPU. Whether or not to in-
50
Page 72

Installation
Section 3-1
stall additional components, depends on hardware installed on your PC.
Press the Next button to continue. The installation will now be performed.
20. After completing the installation, a notification will be displayed, providing
access to CX-Server release notes. Press the Finish button when done.
21. Finally, CX-Profibus installation is complete. The window shown below is
displayed, to notify the user. Click the Finish Button to finalize installation
and view the readme.txt file for CX-Profibus, containing last minute information on the installed program components
51
Page 73

Installation
22. In order to be ensured of OMRON support for the program as well as information on updates, please register the program via the OMRON website http://softwaredownload.europe.omron.com.
Alternatively, fill out the registration card enclosed with the software package and return it to the OMRON regional sales office or to your local OMRON representative.
3-1-3 Installing the C200HW-PRM21 DTM
The first version of CX-Profibus, i.e. CX-Profibus 1.0 did not include the
C200HW-PRM21. Instead, this component could be downloaded from the
OMRON Internet website. To install the C200HW-PRM21 separately from
CX-Profibus perform the following procedure:
1,2,3... 1. Select from the task bar the Start - Run option and browse for the down-
loaded setup file, named OMRON C200HW-PRM21 DTM setup.exe.
2. Press the OK button to run the setup and follow the instructions as presented during the installation.
Section 3-1
52
Page 74

CX-Profibus
Section 3-2
3-2 CX-Profibus
3-2-1 Starting CX-Profibus
Starting CX-Profibus Select Program, OMRON, and CX-Profibus, from the Start Menu if the
default program folder name is used.
At startup, the CX-Profibus splash screen will appear, on top of which a login
window as shown below will be displayed.
Login Window The Login window provides the selection of the access level as well as the
entry of the password belonging to the access level selected.
Default Password The default password at the first start up of CX-Profibus is “password” and is
applicable to all access levels. Type in “password” (without the quotes) at the
password entry line and select OK.
!Caution If access limitation to CX-Profibus is required by the application, the password
Generating the Device
Catalogue
should be changed as soon as possible. Changing passwords is only possible
on the Administrator level. Refer to Changing the Passwords for an explanation on how to change passwords.
After entering the correct password, CX-Profibus will start up and open. The
first time CX-Profibus is started, the Device Catalogue will still be empty.
Therefore, the following window will be displayed on top of the CX-Profibus
application window.
Select Yes to generate the Device Catalogue for the first time. This action
may take several minutes depending on the number of installed DTMs.
After updating the Device Catalogue, it will open in the CX-Profibus application window.
53
Page 75

CX-Profibus
3-2-2 CX-Profibus Main Window
The main application window of CX-Profibus will open with a New Project.
After the first start up, the Device Catalogue will be opened automatically. If
not, the Device Catalogue may be opened from the menu.
The figure below shows the opened CX-Profibus application window with a
Project already containing a network, and the Device Catalogue window
opened.
Section 3-2
Tool Bar
Network view Device Catalogue
Error Log and FDT Monitoring view DTM view
The main components in this window are
• The Network view.
• The DTM / Catalogue view.
• The Error Log view.
• The FDT Monitoring view (not shown in the figure above).
• The Main menu.
• The Tool Bar and the Status Bar.
Network view The Network view displays the structure of the PROFIBUS network in a tree
view format. The tree has at least three levels:
• The Project Level.
• The master level.
• The slave level.
Status Bar
54
Page 76

CX-Profibus
Section 3-2
The highest level of the tree is the project. The next level is the PROFIBUS
Master level. On this level one or more PROFIBUS Master devices can be
allocated. The third level contains the slave DTMs.
The PROFIBUS network must be assembled in the Network view, i.e. the various DTMs are added to the network via this window. From the Network view
the individual DTM User Interfaces can be opened, and accessed.
CX-Profibus supports context menu in the Network view, which are made visible when selecting a device DTM and right clicking the mouse. The contents
of the menu may depend on the functionality supported by the DTM.
DTM / Device Catalogue
Window
The DTM / Device Catalogue window will hold the Device Catalogue as well
as every opened DTM User Interface. The window is an MDI type window, or
Multiple Document Interface. One or more user interface windows can be
opened, re-sized and moved inside this window.
Error Log view The Error Log view at the bottom of the CX-Profibus application window dis-
plays the error messages reported by DTMs to CX-Profibus. A Time stamp, a
Date stamp and the DTM name are added to the message.
The contents of the window can be cleared, or copied to the clipboard, to
allow pasting it into another document.
The Error Log view is opened by default, when starting CX-Profibus.
FDT Monitoring view The FDT Monitoring view at the bottom of the CX-Profibus application window
displays the FDT-DTM communication function calls between CX-Profibus
and the DTMs. A Time stamp, a Date stamp, the type of information and the
DTM name are added to the message.
The sequence of messages can be used to troubleshoot problems that may
occur when using third party DTMs in CX-Profibus.
The contents of the window can be cleared, or copied to the clipboard, to
allow pasting it into another document.
The FDT Monitoring view is not opened by default, when starting CX-Profibus.
It can be opened through the View - FDT Monitoring menu option.
Main Menu The main menu of CX-Profibus, provides all the necessary functionality to
handle a complete project. The table below lists the main menu and their sub
menu items.
Menu Command Short Key Description
File New CTRL-N Creates a new Project.
Open CTRL-O Opens an existing Project.
Save CTRL-S Saves the displayed Project to a file.
Save As... --- The Save as command is the same as Save, but the Filename Specifi-
cation Window is always displayed.
Export Project to HTML --- Exports Project data in HTML format and launches the browser.
Project Properties... --- Opens an edit window to add or edit Project information.
Recently used File List --- Lists the recently used Project files.
Exit --- Exits CX-Profibus.
Edit Cut CTRL-X Cuts devices and pastes them to the clipboard.
Copy CTRL-C Copies devices to the clipboard.
Paste CTRL-V Copies devices from the clipboard to the cursor position.
55
Page 77

CX-Profibus
Menu Command Short Key Description
View Network view --- Hides or un-hides the Network view.
Device Catalogue --- Opens or closes the Device Catalogue.
Tool Bar --- Hides or un-hides the Tool Bar.
Status Bar --- Hides or un-hides the Status Bar.
Error Logging --- Hides or un-hides the Error Logging window.
FDT Monitoring --- Hides or un-hides the FDT Monitoring view.
Device Add Device... --- Opens up the Device Catalog Add window, from which devices can be
added to the selected network tree.
Upload Parameters --- Uploads the parameters from a device to its associated DTM.
Download Parameters --- Downloads the parameters from DTM to its associated device.
Export to HTML --- Exports the properties and parameters of the selected DTM, or the net-
work to a HTML file and opens the default browser.
Properties --- Displays the properties of the selected DTM, or the network.
Tools User Management... --- Displays the user management (i.e password management) window.
Window Cascade --- Cascades all open DTM User Interfaces.
Tile Horizontally --- Tiles all open DTM User Interfaces horizontally.
Tile Vertically --- Tiles all open DTM User Interfaces vertically.
Close All --- Closes all open DTM User Interfaces.
Help Contents --- Opens the Help dialog and lists the Help file contents.
Index --- Opens the Help dialog and lists the Help Index.
About CX-Profibus... --- Opens the About dialog window for CX-Profibus.
Section 3-2
Tool Bar The tool bar provides quick access buttons to the user for frequently used
menu commands. The table below lists the toolbar buttons.
Icon Description Equivalent menu command
Creates a new project. File-New
Opens an existing project file. File-Open
Saves the displayed project to a file. File-Save
Connects the configurator to the selected devices. Device-Go Online
Downloads the parameters to the device. Device-Download Parameters
Uploads the parameters from the device. Device-Upload Parameters
Opens the Device Catalogue. View-Device Catalogue
Status Bar The status bar displays the current user role, i.e. the login level.
In case the Error Log view has been closed, the status bar will additionally
display a symbol to indicate that new errors are available in the Error Log
view. Double-clicking the symbol will open the Error Log view.
56
Page 78

CX-Profibus
3-2-3 Device Catalogue
Section 3-2
Device Catalogue Main
Components
The Device Catalogue is one of the main components in CX-Profibus. Its
main functions are
• to maintain a list of installed DTM and GSD files.
• to provide convenient sorting and categorizing of the list.
• to allow updating the list, after installation of new DTMs or GSD files.
• to provide detailed information on selected DTMs
The main layout of the Device Catalogue is shown below.
DTM categories
Device name
Version number
File date
Vendor name
Update Device Catalogue
Install a new GSD file
Add selected device to the network
Invoking the Device
Catalogue
The Device Catalogue window is opened by either selecting the icon in
the CX-Profibus toolbar or by selecting the View - Device Catalogue menu
option. Both options have toggle function: selecting one of them again will
close the Device Catalogue.
DTM view Layout The left view allows selection of specific groups of DTMs to be displayed. The
right view lists the DTMs, which are installed on the PC and which are available for setting up a network. A selection of DTMs is made by selecting a specific group in the left view.
Note The list makes no distinction between normal DTMs and GSD files which
have been loaded through the Generic Slave Device DTM.
57
Page 79

CX-Profibus
Section 3-2
DTM List Window The list items in the right view are described in the following table.
DTM Group Selection
Window
Column
Device The Device column contains the names of the DTMs, as provided by
the DTM or the GSD file. If the device is defined by a GSD file, the
Generic Slave Device DTM reads out the GSD file entry “Model
Name”. The string provided by this variable is the name displayed in
the list.
Version The version number defines the revision number of the device. If the
device is defined by a GSD file, the Generic Slave Device DTM reads
out the GSD file entry “Revision”. The string provided by this variable is
the version number displayed in the list.
Date For DTMs, Date is the date associated with the revision. For GSD file
based slaves, the date listed in this column is the date the GSD file
was last modified.
Vendor The Vendor name is provided by the DTM or the GSD files.
Description
The left view allows selection of specific groups of device DTMs with common
attributes, e.g. Vendor name, Protocol type etc. If a group is selected, all
device DTMs which belong to that group will be listed in the right view. The
table below lists the possible groups that can be selected.
List item
Device
Ty pe s
Vendors Sub groups, which can be selected are all available vendors. This infor-
Groups Sub groups are the device types, e.g. digital I/O, analog I/O etc.
Protocols Sub groups which can be selected are all the communication protocols
Sub groups, which can be selected are:
• Communication DTMs, e.g. PROFIBUS Master devices
• Gateways, e.g. to another network type
• Modular devices
• Other devices, e.g. slave devices
mation is provided by each DTM. It allows the user to select a group of
devices from one vendor.
found in the Device Catalogue.
Description
Additional DTM
Information
58
Note 1. The sub groups will be displayed by clicking on the + sign next to each
main group
2. Selecting the main group displays all devices in the group.
In order to obtain more information of a specific DTM, right-click the DTM in
the list, and from the pop-up menu, select DTM Information. This opens a
Page 80

CX-Profibus
window with additional DTM information. The figure below provides an example for the CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM.
3-2-4 Updating the Device Catalogue
If a new DTM has been installed, it will not automatically be included in the
Device Catalogue. In order to add newly installed DTMs to the list, the Device
Catalogue must be updated by selecting the Update button at the bottom of
the window.
Section 3-2
Updating the Device
Catalogue
Installing GSD Files The Device Catalogue also allows the installation, i.e. copying of new GSD
Note 1. Updating the Device Catalog after copying GSD file can only be done if
Updating the Device Catalogue may take some time, depending on the
amount of DTMs installed. A dialogue window with a progress bar will be
shown during the update process. After updating the Device Catalogue, it will
be stored on hard disk. The next time CX-Profibus is started the updated list
will be used.
files into the GSD directory for the Generic Slave Device DTM. Selecting the
Install GSD Files... button displays the standard Windows File selection window. After selecting the GSD file, and selecting the Open button in the File
selection window, the GSD file will be copied to the GSD file directory under
CX-Profibus.
After copying the GSD file, a warning window will be displayed, indicating that
the Device Catalogue needs to be updated. This can be accomplished by
selecting the Yes button in the warning window.
there is a new project opened, i.e. with no DTMs allocated to the network.
This is to prevent corruption of an existing network in case a GSD file is
removed or replaced.
2. The Install GSD Files... option allows installation of more than one file at
the same time.
59
Page 81

CX-Profibus
3-2-5 Adding Devices to the Network
Setting up a network in CX-Profibus involves adding and configuring single
device DTMs. The device DTMs as listed in the Device Catalogue can be
added to the network in three ways:
• Using the context menu
A context menu will pop up when selecting the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS Master DTM and right clicking the mouse. By selecting the
menu option Add Device, a simplified Device Catalogue is displayed,
allowing only a selection of DTMs which can be added to the PROFIBUS
Master DTM.
• Using the Drag & Drop function
A Device DTM listed in the standard Device Catalogue window can be
dragged and dropped from the Device Catalogue to a desired position in
the Network view.
• Using the Add Device button
A device DTM selected in the Device Catalogue can be added to a
selected Master DTM in the Network view by clicking the Add Device button in the Device Catalogue window.
Section 3-2
3-2-6 Saving and Opening Projects
A project, containing various DTMs can be saved and opened to and from
hard disk. Saving a project file is accomplished by selecting the File - Save or
File - Save As... menu option. This will display the standard Windows File
selection window, allowing the user to enter a file name.
The Project File is saved with the extension *.CPR.
Saving the data is initiated from CX-Profibus, but every DTM must support the
save function as well. The settings of each DTM are added to the Project file
by the DTM itself.
A Project file can be opened using the File - Open menu option. This will
open the standard Windows File selection window, after which the Project file
can be selected and opened.
Note When opening a Project file, the network tree view is constructed. However,
for performance reasons, the DTMs are not directly instantiated. The advantage is that the tree view is constructed fast, but opening a DTM from the tree
view may take longer, depending on the performance of the PC used.
A Project File can also be opened from Windows Explorer. Double-clicking a
file with extension *.CPR will invoke CX-Profibus and open the selected file.
3-2-7 Exporting to HTML
CX-Profibus provides automatic generation of project documentation upon
command of the user. The documentation is generated in HTML format, and
can cover either single DTMs or the whole project. After generation of the
HTML document, it will automatically launch the default Internet browser, to
display the result.
Exporting Project to HTML Exporting the project information to HTML can be achieved in two ways.
• Select the main menu File - Export Project as HTML option.
A window will pop up displaying the progress of the export process.
60
Page 82

CX-Profibus
Section 3-2
• select Export to HTML option from the context menu
First select the project level in the Network view, then right click the
mouse to display the context menu. A window will pop up displaying the
progress of the export process.
After exporting the information, the default browser is launched, showing the
result of the export process. Links are available to open the information pages
for the individual DTMs.
The extent of the information made available depends on the individual
DTMs. This can range from device type and version information up to all settings and selections made for the device.
Exporting DTM
Information to HTML
1,2,3... 1. Select the DTM in the Network view.
Exporting single DTM information to HTML is achieved by the following
sequence.
2. Right click the mouse to bring up the context menu.
3. Select the Export to HTML option from the context menu.
A window will pop up displaying the progress of the export process. When finished, CX-Profibus will launch the default browser to display the result. In this
case however, no links will be available to other DTMs in the network.
3-2-8 Error Logging and FDT Monitoring
CX-Profibus provides two logging windows at the bottom of the application
window. Both windows are used for displaying events.
Error Log view The Error Log view displays error messages reported by the DTMs and by the
CX-Profibus FDT container application. All messages include the Time and
Date of occurrence, as well as the DTM Name, as shown in the Network view.
Purpose of the Error Log The purpose of the Error Log view is error reporting as well as troubleshoot-
ing. The contents of the window can be copied to the clipboard, to allow it to
be pasted into another document or into an E-mail. The errors themselves as
well as the sequence of errors may hold additional clues in case of problems.
Error Log Format The format used in the Error Log view is
Time: <Time> Date: <Date> - <DTM name> <message>
The message displayed, originates from the DTM in which the error occurred.
The figure below shows an example of an error message sequence. This
example sequence is generated after attempting to change a slave address to
that of another slave already assigned to the same Master Unit.
By right-clicking the mouse cursor in the Error Log view, a context menu is
displayed. This context menu provides the options listed below.
61
Page 83

CX-Profibus
Section 3-2
Error Log view Context Menu
Menu item
Clear all entries Clears the entire Error Log view. ---
Copy to clipboard Copies the entire contents of the Error Log view to the clipboard. ---
Hide Hides the Error Log view. View - Error Logging
Description
Equivalent menu command
FDT Monitoring view The FDT Monitoring view displays the communication between the FDT Con-
tainer application (i.e. CX-Profibus) and any of the DTMs. The communication
is listed as a sequence of function calls from the CX-Profibus to a DTM and
vice versa.
Note The FDT Monitoring view is hidden by default. After starting CX-Profibus, the
window will be displayed, by selecting the View - FDT Monitoring option from
the main menu.
The purpose of the FDT Monitoring view is troubleshooting in case problems
occur with third party DTMs. The contents of the window can be copied to the
clipboard, to allow it to be pasted into another document or into an E-mail.
The messages themselves as well as the sequence of messages may hold
additional clues in case of problems.
The format used in the FDT Monitoring view is
Time: <Time> Date: <Date> - <Information Type> <message>
The message may include the name of the DTM involved in the communication.
The figure below shows an example of an FDT Monitoring message
sequence. This example sequence is generated when opening a CJ1WPRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit DTM.
By right-clicking the mouse cursor in the FDT Monitoring view, a context
menu is displayed. This context menu provides the options listed below.
FDT Monitoring view Context Menu
Menu item
Clear all entries Clears the entire FDT Monitoring view. ---
Copy to clipboard Copies the entire contents of the FDT Monitoring view to the clip-
board.
Hide Hides the FDT Monitoring view. View - FDT Monitoring
Description
Equivalent menu command
---
62
Page 84

CX-Profibus
3-2-9 Access Control and User Management
The FDT Standard defines four access levels and two attributes for FDT Container applications, which can be used to restrict access to the program or
certain features thereof for unauthorized personnel. The actual use of the
restrictions also depends on the application.
CX-Profibus implements the four levels as well as one of the attributes. These
levels are listed below.
• Observer
• Operator
• Maintenance
• Planning Engineer
• Administrator
The access rights per level are defined in the table below.
Section 3-2
Project File
Device
PROFIBUS Master DTM
Generic
Network
Function Observer Operator Maintenance Planning
New file Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Open file Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Save File Not allowed Not allowed Not Allowed Allowed Allowed
Save As... Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Properties View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Export to HTML Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
access
Open Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Add GSD files Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed
Update Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed
Catalogue
Open Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Master settings View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Communication
settings
Go online Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Monitoring Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Change state and
send commands
Export to HTML Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Properties View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Open Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Device settings View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Go online Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Monitoring Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Slave DTM
Add DTMs Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed
Delete DTMs Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed
Properties View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Export to HTML Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Change password Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed Allowed
View only View only Edit Edit Edit
Not allowed Not allowed Allowed Allowed Allowed
Engineer
Administrator
User
Management
63
Page 85

CX-Profibus
User Management To change access rights or to change the passwords for the various access
levels, first login into the Administrator level. This allows you to select the
Tools - User Management option from the main menu in CX-Profibus. Other
access levels do not have access to this menu option. The selection opens
the User Accounts window, as shown below.
Changing Access Rights By selecting the check box next to a level, the Administrator can grant access
rights to CX-Profibus, i.e. the checked levels can start and access CX-Profibus. If a check box is not selected, the corresponding level can not be used to
start CX-Profibus, and it will not appear in the drop down list in the login window.
For example, in the window below the Observer and Maintenance levels are
unchecked.
Section 3-2
The next time CX-Profibus is started, the Observer and Maintenance access
levels are not available in the login window, as shown below.
The Administrator level has always access and can not be disabled in the
User Accounts window.
Changing the Passwords In order to change a specific password, select the Change password button
in the User Account window, next to the related access level. The level must
be enabled by selecting the check box to the left of it. Pressing the Change
password button opens a window allowing the entry of a new password. As
an example the window below shows the Change password window for the
64
Page 86

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Planning Engineer. You can now enter the new password, confirm it by re-typing the password and select the OK button to activate the new password.
Note If access protection is not important for the application, you can define an
empty string as a password, i.e. when entering the new password, simply
press the return button on your PC. When starting CX-Profibus, the login window can be passed by pressing the return button on your PC, without entering
a password.
3-3 CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Master
DTM
To allow configuration and data monitoring from within CX-Profibus two CS1/
CJ1 PROFIBUS Master DTMs are installed, together with CX-Profibus. Each
DTM shows up in the Device Catalogue under two different names.
DTM Name Functions
CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master • I/O Configuration of PROFIBUS DP
CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master
CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master • I/O Configuration of PROFIBUS DP
CS1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP-V1 Master
The PROFIBUS Master DTM has two main user interface components.
• DTM Configuration User Interface
This user interface facilitates configuration of the Master Unit.
• DTM Diagnostics User Interface
The DTM Diagnostics User Interface facilitates Unit status determination,
slave status determination and changing the Unit’s PROFIBUS operational mode.
This section provides an overview of the PROFIBUS Master DTM, and discusses both user interfaces.
and PROFIBUS DP-V1 master Units
• Monitoring of PROFIBUS DP and
PROFIBUS DP-V1 master Units
and PROFIBUS DP-V1 master Units
• Monitoring of PROFIBUS DP and
PROFIBUS DP-V1 master Units
• Provide an Acyclic communication
channel with PROFIBUS DP-V1 slave
devices.
3-3-1 Configuration User Interface
Opening the
Configuration DTM
The configuration DTM is opened by
• Selecting the Master DTM in the Network view, and double-clicking the
left mouse button.
• Selecting the Master DTM in the Network view, and right-clicking the
mouse. From the context menu, select Configuration. The Master DTM
Configuration User Interface, which is displayed in the CX-Profibus DTM
view is shown below.
65
Page 87

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Note The Configuration User Interface for each of the two CS1/CJ1 PROFIBUS
Master DTM Configuration
User Interface
Configuration Interface
Buttons
Master DTMs contains the same views and setting options.
The Master DTM Configuration User Interface contains four tabs:
• Device Setup tab
• Master Setup tab
• Bus Parameters tab
• Slave Area tab
The four tabs are discussed below.
The Master DTM Configuration User Interface contains four general buttons.
They are listed in the table below, together with the action taken when pressing them.
Button Action
OK Evaluate, and save the changes made (if any) and close the user
interface.
Note If any invalid settings have been made, a warning message
will be displayed, allowing cancellation of the command.
Cancel Closes the user interface without saving.
Note If any changes were made, a warning message is displayed,
allowing cancellation of the command.
Help Launch context sensitive Help for the Active tab.
Save Evaluate changes and save them.
66
!Caution Save in the context of the buttons means that the changes made by the user
are saved in the DTM only, i.e. the changes are not permanently saved in the
Project yet. This is indicated by the asterisk next to the DTM in the Network
view. The next time in the same session the GUI is opened, the changes will
still be there. In order to save the changes permanently, e.g. to hard disk,
Click the File - Save option from the main menu of CX-Profibus.
Page 88

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Device Setup Tab The Device setup tab (see figure above) provides the controls to achieve
communication between the PC and the PROFIBUS Master Unit. It allows
setting of the unit number to identify it on the PLC system and the device
address to identify it on the PROFIBUS network. It also will invoke the CXServer interface to setup and test the communication between the PC and the
PLC to which the Unit is attached.
The Device Setup tab has the following components.
Settings Box The Settings box contains the setting the user must make before setting up
the communication and before testing the communication.
Control Description
Station Address Address of the Unit in the PROFIBUS network. Default value is
1, but it should be changed if there is already another device
with that number.
Unit Number This number must be the same as the number selected with the
Configure Button The Configure button invokes the CX-Server communications settings dia-
log. CX-Server is the driver software, providing the communication functionality between a PC and the PLC CPU. It is the basis for the OMRON’s CX-One
programs.
CX-Server is provided with CX-Profibus, but it may already be installed on the
PC, if other programs, for example CX-Programmer have been installed.
Unit Number Selector switch on the front of the Unit (refer to
2-3-1 Selecting a unit number). This number is used in the communication between the PC and the PLC to transmit the messages to the targeted PROFIBUS Master Unit
Note The CX-Server is designed to manage the communication between the PC
and the PLC and also configure the connected PLC. CX-Server currently supports CS1G-H, CS1H, CS1H-H, CJ1G-H, CJ1H-H CJ1M and CS1G/CJ1G
PLC types.
Section 3-3-3 Connecting to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 will provide more details
on how to configure CX-Server.
Test Button The purpose of the Te st button is to test the communication setup, after CX-
Server has been configured. If the PC and the PLC are connected, selecting
the Test button, will invoke a FINS request message to the PROFIBUS Master Unit via the PLC, to read its name and firmware version. If the request succeeds, both will be displayed in the Device Information Box.
If the FINS request fails (no response), an error message will be displayed in
the Error Log view. In this case the Firmware version field will revert back to
its default contents, i.e. “--- “.
67
Page 89

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Device Information Box The Device Information Box contains information obtained from the PROFI-
BUS Master Unit, through the communication.
Item Description
OMRON Corporation This is fixed text, indicating the Manufacturer of the PROFIBUS
Master Unit.
Description This string will contain the name of the Unit, i.e. CJ1W-PRM21
or CS1W-PRM21.
Firmware Version This string displays the firmware version, currently in the
Ident number The PROFIBUS Ident number (Hex) for the Unit:
PROFIBUS Master Unit.
• CJ1W-PRM21: 07C4
• CS1W-PRM21: 0742
Master Setup Tab The Master Setup tab contains settings regarding the behaviour of the
PROFIBUS Master Unit itself. The Master Setup tab is shown below.
Action to PLC Mode
Transition Box
Change PLC to RUN/
MONITOR Mode
68
The Action to PLC Mode Transition Box defines the behaviour of the Unit on
the PROFIBUS network, in case a PLC mode change occurs. The check
boxes define how the Unit should behave in case the PLC mode is changed
from RUN / MONITOR mode to PROGRAM mode, or vice versa. Refer to
section 1-1-7 Network Operation Modes for more information on PROFIBUS
operational modes.
The table below defines the behaviour in case the PLC changes to RUN /
MONITOR mode.
Control Description
Keep Current Mode Unit keeps the current mode if the PLC goes to RUN /
Go to OPERATE Mode
(default setting)
MONITOR mode (e.g. stay in CLEAR mode).
The Unit goes to the OPERATE mode whenever the PLC
goes to the RUN / MONITOR mode.
Page 90

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Change PLC to PROGRAM
Mode
The table below defines the behaviour in case the PLC changes to PROGRAM mode.
Control Description
Keep Current Mode Unit keeps the current mode if the PLC goes to PRO-
GRAM modem (e.g. stay in OPERATE mode).
Go to CLEAR Mode
(default setting)
The Unit goes to the CLEAR mode whenever the PLC
goes to the PROGRAM mode.
Auto-CLEAR Box Auto-CLEAR defines the Unit’s behaviour in case an error occurs in one of the
allocated slave devices, which causes it to stop data exchange with the Master Unit. If Auto-CLEAR is enabled, the Unit will automatically transition to the
CLEAR state and force all its allocated slave devices to the ‘safe’ state, i.e. all
outputs are set to 0, using the Global-Control CLEAR command.
Control Description
Auto-CLEAR Mode ON Selected Unit transitions to the CLEAR mode in the event
of a network error, e.g. because one or more configured
slaves are not in the Data Exchange mode.
Auto-CLEAR Mode OFF
(default setting)
Selected Unit does not transition to CLEAR mode, but
attempts to re-parameterize the slave device.
Support Box The Auto Addressing in the Support Box defines the I/O Mapping process
when adding/removing I/O modules or when editing an existing I/O Mapping.
Refer to section 6-5-2 Mapping I/O Data for more details on I/O mapping.
Control Description
Auto Addressing enabled I/O data mapping will be done by the Master DTM by allo-
cating the I/O data in ascending order of slave device
address and selected I/O modules. No memory allocation
gaps are left behind.
Auto Addressing
disabled
New I/O modules are appended to the existing mapping.
Changed I/O modules will be re-allocated to the end of the
list. Memory allocation gaps can be left behind.
Bus Parameters Tab The Bus Parameters tab contains the parameters for the communication on
the PROFIBUS network. The Bus Parameters tab is shown below.
The Bus Parameters are a number of settings which define the communication behaviour and timing on the PROFIBUS network. The Bus Parameters
depend on the selected baud rate, certain slave communication parameters
as well as the number of I/O data bytes exchanged between the Master Unit
and each of the slave devices.
The required combination of Bus Parameters is calculated by the program,
based on the dependencies mentioned above. However, the user can change
selected Bus Parameter manually if the application requires this.
69
Page 91

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
!Caution Changing the calculated Bus Parameters manually is not recommended, and
should only be performed if this is really necessary. Changing the Bus Parameters to an invalid combination, may result in Unit malfunctioning and unexpected behaviour.
Note When making changes to Bus Parameters, selecting the Optimize buttons,
allows toggling between the optimized values and the changed values.
Selecting another baud rate after changing parameters, will reset the Bus
Parameters to default values for the new baud rate.
The table below lists the parameters, shown in the Bus Parameter tab.
Item Description Unit Editable
by User
Baud rate Defines the transmission rate on the PROFIBUS DP Network. The following baud
rate values are defined by the PROFIBUS DP standard:
• 9.6 kBits/s
• 19.2 kBits/s
• 45.45 kBits/s
• 93.75 kBits/s
• 187.5 kBits/s
• 500 kBits/s
• 1500 kBits/s (default value)
• 3000 kBits/s
• 6000 kBits/s
• 12000 kBits/s
-- Yes
70
Page 92

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Item Description Unit Editable
by User
Optimize The Optimize setting defines whether parameters can be changed by the user.
-- Yes
• By Standard
Forces the user to use the default (optimized) settings.
•By User
Makes selected fields editable.
Note 1. If the By User option is selected and changes have been made, it is
still possible to switch between Optimize settings, without the changes
being lost.
2. If the By User option is selected and the baud rate is changed, the parameters will be optimized to the new baud rate.
Slot Time The maximum time a Master Unit must wait for a response to a request message. t
Min. Station Delay
of Responders
Max. Station Delay
of Responders
The minimum allowed time for a slave device before it will generate a response to
a request message.
The maximum allowed time for a slave device to generate a response to a request
message.
Quiet Time The time a transmitting device must wait after the end of a message frame, before
enabling its receiver.
Setup Time The time between an event and the necessary reaction. t
Min. Slave Interval The Minimum Slave Interval defines the poll cycle, i.e. the minimum time between
two consecutive Data_Exchange Cycles to the same slave device. The Minimum
t
t
t
t
BIT
BIT
BIT
BIT
BIT
BIT
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
No
No
Ye s
Slave Interval must be smaller than the Target Rotation Time.
Calculated Minimum Slave Interval in milliseconds. ms No
Target Rotation
Time
The anticipated time for one token cycle, including allowances for high and low
priority transactions, errors and GAP maintenance. Do not change the value
t
BIT
Ye s
below the calculated value, to avoid bus communication interruptions.
Max Retry Limit Maximum number of request transmission retries by this master if a device does
-- Yes
not reply to a request.
Highest Station
Address
The HSA defines the Highest Station Address of Master devices on the network,
of which the Master device will request the FDL status, when updating the active
-- Yes
device list (See GAP Update Factor).
If new slaves are added to the network, this field shows the highest device
address. The Master will periodically check whether new active devices have
been added between its own address and the Highest Station Address. If any
devices are detected, GAP is updated.
Permissible values are in the range of 0 to 126.
GAP Update
Factor
The GAP update factor defines the amount of updates of the active devices (i.e.
Master devices) list times during one token rotation cycle.
-- No
To update the list, the Master device will transmit FDL_Status_request messages
to ascending device addresses until it finds a next Master device, or until it
reaches the Highest Station Address (See HSA above).
The GAP Update Factor is fixed to 1.
Poll Timeout The maximum time interval that this master device may need for the execution of
ms No
a master-master function.
Data Control Time The cycle time in which the master updates its Data Transfer List, in which it
ms No
keeps an overview of all slave states. Data Control Time is based on the
Watchdog time T
Watchdog Control The Watchdog Control Time defines the time for a slave device to set its outputs
: Data Control Time = 7*TWD.
WD
ms Yes
to a fail-safe state, if during that time no communication between the Master
device and that slave device was detected. The Watchdog is automatically set for
all configured slaves, based on the value of T
TR
.
71
Page 93

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Slave Area Tab The Slave Area tab displays the mapping of the I/O data from/to the allocated
slave devices on to the PLC memory areas. The mapping can be made automatically, but can also be changed by the user, before downloading.
The Slave Area tab is shown below. Only the Output Allocation tab is shown.
Allocation Areas The Slave Area allocation tabs define how the I/O data of each of the slave
devices is mapped on to the PLC memory. The Slave area tab contains two
tabs, one for Output Allocation and one for Input Allocation. Each tab contains
an overall module list, showing all the output or input data per slave, along
with the Module names, sizes, data types and start addresses. This data has
been transferred to the Master DTM by each of the allocated slave DTMs. If
no slave devices have been allocated, or configured, the list will be empty.
Module List Box The Module List Box list contains the following information (refer to figure
above, the table applies to the lists in the Input and Output Allocation tabs).
Column Description
#Addr. Station address on the network, obtained from the slave DTM.
Index Index number of the I/O module.
Device Device name, obtained from DTM.
Module System generated name.
Size Module data size, unit of type mentioned in next column.
Type Module data type, e.g. Byte, Word etc.
Addr Mapped address area in PLC memory. For example: CIO3200,
equals CIO Area, start address 3200.
I/O Mapping Areas Each Output/Input Allocation tab also contains two areas on to which the I/O
data can be mapped. The areas will in turn be mapped to the PLC memory.
By default all data is mapped to Area 1, in order of ascending slave device
address.
72
Note 1. When mapping, the modules are copied from the module list to the map-
ping Area and not moved. This means that the module list acts as a resource for the two Mapping Areas, below the module list.
Page 94

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
2. When adding/removing slaves/modules, and Auto Addressing has been
enabled, the modules in the Areas will be remapped. This usually results in
I/O data being re-mapped. Therefore it is recommended to select all slaves
and modules, before setting up the PLC memory mapping configuration.
!Caution The default mapping of areas on to the PLC memory is the same default map-
ping as used in the CS1/CJ1W-DRM21 Devicenet Master/Slave Unit. Care
should be taken to avoid data overlap, if such a Unit is part of the same PLC
CPU system as the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master Unit.
Mapping Area Controls Each mapping Area in the Allocation tab is equipped with four controls and an
information field located below the Area. The controls and information field
are listed and explained in the table below.
Control Description
Area Selects the PLC memory area to which the associated
Start Address In this field the user can enter the start address in the
Length The length box allows the user to select the number of
Occupied This field display the actual length of the data block (not
Compress button Pressing the Compress button will compress the Area list
I/O Area will be mapped. Possible options are:
• Not Used (List must be empty).
•CIO
•DM
•Work
•HR
• EM Bank 0 to 12 (Decimal)
(See Note 1).
PLC memory of the mapped data block.
visible rows. The minimum and the default value is 100
words. If more than 100 words are configured, the minimum Length value will be that number.
The user can set the Length value to up to 7168 words.
necessarily the same as the amount of data in it). This
length includes both data and any gaps between modules. Gaps may only be there if Auto-Addressing option
in the Master Setup tab is disabled (See also Note 2).
associated with it, i.e. this action will remove all gaps
from the mapping list by moving all mapped I/O modules
as close to the start of the memory area as possible.
(See Notes 3 and 4).
Note 1. If the selected PLC memory area, on to which the data must be mapped is
not supported by the PLC CPU, a warning message will be displayed upon
downloading the configuration.
2. If an invalid setting is made the Occupied length value will change its colour to red, indicating an invalid setting. In addition, a warning message will
be displayed, upon saving the changes. Invalid settings are for example
• The start address and length definitions of the data block will cause it
to exceed the area in the PLC.
• The data mapping of two or more I/O Areas (Output and/or Input) will
be overlapping each other partly or totally in the PLC memory.
3. The Compress button will be disabled, i.e. grayed out, when Auto-Addressing (see Master Setup Tab on page 68) has been enabled.
4. Before Compressing, the Master DTM will display a warning message
prompting the user for confirmation of the action.
73
Page 95

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Changing Mapped Data
Allocations
1,2,3... 1. Find the module which must be mapped to a desired Area in the module
Note 1. If Auto-Addressing is enabled (see Master Setup tab in this section), any
By default, the data is mapped to Area 1 in both the Output and Input Allocation tabs. It is however possible to map a part of the data to the second area in
the same tab. For example, an application may require to store all byte data in
one location and all word data in another.
Moving data mapped in one Area to another Area is done from the module
list. The procedure is as follows.
list, and select it.
2. Left-click the module and drag it, while holding the Left mouse button, to
the desired Area. This can be the end of the list or any empty space in the
list in which it will fit (See Note).
3. Release the mouse button. The module data is copied in the desired Area
and appended to the already existing list. The same entry in the other list
is now deleted.
4. Finally, the PLC memory address to which the module is mapped is now
updated in the module list.
empty spaces evolving out of moving of modules to another Area will be
removed by compressing the list. Modules located to a higher address will
be moved to a lower address to fill up the gap.
2. If Auto-Addressing is disabled, compressing the list can be accomplished
by pressing the Compress button, after all modifications to the mapping
have been made.
Advanced Tab The Advanced tab displays the settings required for PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class
2 communication with Slave devices. The Advanced tab is shown below.
Acyclic Connection/Abort
Status Box
74
The Acyclic Connection/Abort status box contains settings, which allow the
user to define where in the PLC CPU memory the Connection/Abort status bit
fields must be mapped. These bits indicated the open/closed PROFIBUS DPV1 Class 2 connections between the Master Unit and individual slave devices.
Page 96

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
The Acyclic Connection/Abort status box contains the following information.
Control Description
Area Selects the PLC memory area to which the Acyclic Con-
Start Address In this field the user can enter the start address in the
Length The length value is a fixed number. The total number of
Note 1. If the selected PLC memory area, on to which the data must be mapped is
not supported by the PLC CPU, a warning message will be displayed upon
downloading the configuration.
2. If an invalid setting is made the Length value will change its colour to red,
indicating an invalid setting. In addition, a warning message will be displayed, upon saving the changes. Invalid settings are for example
• The start address and length definitions of the data block will cause it
to exceed the area in the PLC.
• The mapping overlaps with one or more of the I/O Areas (Output and/
or Input) mappings.
Section 3-3
nection/Abort status bits will be mapped. Possible
options are (See Note):
• Not Used (Default setting, Start Address and Length
will be set to 0).
•CIO
•DM
•Work
•HR
• EM Bank 0 to 12 (Decimal)
PLC memory of the mapped data block.
words is 16.
Acyclic Connection Status
The 8 word Acyclic Connection bit flags are shown below.
Flags
1514131211109876543210
Word n
Word n+1
Word n+2
Word n+3
Word n+4
Word n+5
Word n+6
Word n+7
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32
63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48
79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64
95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
111 110 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 100 99 98 97 96
Note In the above figure, n is the start address of the memory locations, defined by
the Area and Start Address setting in the Acyclic Connection/Abort Status
Box.
Bit Name Status Controlled
– Acyclic Connection
ON Unit If the bit corresponding to a slave device address is ON, it indicates that
flags
OFF Unit If the bit corresponding to a slave device address is OFF, it indicates
by
Slave station 00 ~ 15
Slave station 16 ~ 31
Slave station 32 ~ 47
Slave station 48 ~ 63
Slave station 64 ~ 79
Slave station 80 ~ 95
Slave station 96 ~ 111
125 124 123 122 121 120 119 118 117 116 115 114 113 112
Slave station 112 ~ 125
Unit operation
the PROFIBUS Master Unit has established a PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class
2 type connection.
that there is no open PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2 type connection with
the specific slave device.
75
Page 97

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Acyclic Connection Abort
The 8 word Acyclic Abort bit flags are shown below.
Status Flags
1514131211109876543210
Word n+8
Word n+9
Word n+10
Word n+11
Word n+12
Word n+13
Word n+14
Word n+15
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32
63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48
79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64
95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
111 110 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 100 99 98 97 96
Note In the above figure, n is the start address of the memory locations, defined by
the Area and Start Address setting in the Acyclic Connection/Abort Status
Box.
Bit Name Status Controlled
– Acyclic Connection
Abort flags
ON Unit If the bit corresponding to a slave device address is ON, it indicates that
OFF Unit If the bit corresponding to a slave device address is OFF, it indicates
by
Slave station 00 ~ 15
Slave station 16 ~ 31
Slave station 32 ~ 47
Slave station 48 ~ 63
Slave station 64 ~ 79
Slave station 80 ~ 95
Slave station 96 ~ 111
125 124 123 122 121 120 119 118 117 116 115 114 113 112
Unit operation
the PROFIBUS Master Unit has aborted a PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2
type connection.
that no abort action of a PROFIBUS DP-V1 Class 2 type connection
has been performed.
Slave station 112 ~ 125
Slave Timeouts The Acyclic Slave Timeout defines the timeout value for PROFIBUS DP-V1
Class 2 connections to slave devices. If a PROFIBUS DP-V1 message is sent
to a specific slave device, the timeout is used to monitor the response from
the slave device. If a response is not received with the specified timeout interval, the connection will be aborted by the Master unit.
The value can be set in the range of 1 to 32767, and is expressed in units of
10 ms.
Additional functions Two additional functions are provided to the user, via the DTM context menu:
• Slave DTM Address Assignment.
• Set Device Station Address (only available on DTM version 0.2.0.0 or
higher and for CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Unit versions 2.0 or higher).
To select these options perform the following steps:
1,2,3... 1. Select the Master DTM in the Network view.
2. Right click the mouse, and select the Additional functions entry from the
context menu.
3. Select the desired function.
76
Page 98

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
Section 3-3
Slave DTM Address
Assignment
Selecting the Slave DTM Address Assignment displays a list of DTMs
assigned to the PROFIBUS Master DTM, together with their Station address:
When assembling the network, the PROFIBUS Master DTM will automatically
assign a station address to each new slave DTM. The purpose of the Slave
DTM Address Assignment function is to allow the user to change the DTM
address of one or more devices, to make it the same as the actual physical
address of the device on the network.
In order to change an address perform the following steps:
1,2,3... 1. Select the slave device in the list.
2. Enter the new address in the field Address in the lower right corner of the
window.
3. Press the Set button. The Status field will display the status of this service,
i.e. whether or not the slave device responded without error.
Set Device Station
Address
The Set Device Station Address function is provided for slave devices of
which the PROFIBUS address is not set through switches, but by using the
PROFIBUS DP Set Slave Address service. Slave devices which support this
service also provide a means to store the address in internal non-volatile
memory. In case this non-volatile memory does not contain an entry, the
slave device will assume the default address 126.
Note 1. The PROFIBUS DP Set Slave Address service is supported by the CS1/
CJ1W-PRM21 Units as of Unit version 2.0.
2. In order to be able to change a device’s address, the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21
PROFIBUS Master DTM must be on-line.
Selecting the Set Device Station Address displays the window shown below:
77
Page 99

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
In order to change the address of a slave device perform the following steps
(Make sure that the DTM is on-line with the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Unit):
1,2,3... 1. Enter the device’s current address and its PROFIBUS Ident Number.
The PROFIBUS Ident Number can be found in the Generic Slave DTM or
through the device’s documentation. By default the device’s current address will be 126. If necessary, change this to the actual current address.
2. Enter the new device address in the New Address field.
3. Optionally, select the Lock checkbox, if the address change must be made
permanent.
4. Press the Set button to invoke the PROFIBUS DP Set Slave Address service. The Status field will display the status of this service, i.e. whether or
not the slave device responded without error.
!WARNING Selecting the Lock option makes any future changes of the address impossi-
ble, even after power-down/power-up of the slave device.
Note After successful completion of the address change, the device DTM address
in the Network view has to be changed as well.
Section 3-3
3-3-2 Diagnostics User Interface
Diagnostics User Interface The PROFIBUS Master DTM provides a second user interface, to display the
Diagnostics information available in the PROFIBUS Master Unit. This information concerns
• Unit and PROFIBUS DP Interface status flags.
• Slave status flags and common slave diagnostics.
• The Unit’s Error Log.
Furthermore, the Diagnostics User Interface allows changing the Master’s
PROFIBUS operational mode and the transmission of Global-Control messages.
In order to access the Diagnostics User Interface, the DTM has to be on-line,
i.e. a communication channel between the DTM and the PROFIBUS Master
Unit must have been established.
Opening the DTM
Diagnostics User Interface
1,2,3... 1. To go on line, perform one of the following actions.
In order to open the DTM Diagnostics User Interface perform the following
sequence.
• Select the DTM in the Network view.
• Select the Device - Go Online option from the main menu, or from the
DTM context menu, or
• Select the button from the Tool Bar.
78
2. A communication channel will be opened through CX-Server. The name of
the DTM in the Network view, will turn to Italic font, to indicate that the Unit
is on-line.
3. Select the Device - Diagnosis option from the main menu, or from the
DTM context menu. The Diagnostics User Interface will now be displayed.
Page 100

CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master DTM
The figure below shows an example of the DTM Diagnostics User Interface.
Section 3-3
The DTM Diagnostics User Interface contains two tabs:
• The Monitor tab
This tab displays all Master Unit status and error information as well the
overall slave status information, which resides in the Master Unit.
• The Online Operations tab
This tab contains controls to initiate state changes in the Master Unit as
well as transmit Global-Control messages over the PROFIBUS network.
Monitor Tab The DTM Diagnostics User Interface - Monitor tab contains three sub-tabs:
• Master Status tab.
• Slave Status tab.
• Error History tab.
Also, the Diagnostics data refreshing mode can be selected.
• Automatic
The Diagnostics data is constantly retrieved from the Unit.
• Manual
The Diagnostics data is retrieved only once from the Unit, when pressing
the Manual button.
Master Status Tab The Master Status tab (shown in the figure above) contains Diagnostics infor-
mation regarding the Master Status. Each of the four status boxes, is related
to one of the Unit’s status words in the PLC CIO Area Memory (see sections
4-2-3 Unit Status (Word n+4) to 4-2-6 Slave Status (Word n+7)).
The status is indicated by red or green LED indicators. Red indicates an error
situation, green indicates a status indication. The LED indicators are listed in
the table below.
79
 Loading...
Loading...