Page 1

F3G-C1R70
Safety Laser Scanner
Instruction Manual
April, 2003
© OMRON Corporation 2003 All Right Reserved.
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 2

Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
List of contents
List of contents
1 About this document .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 The function of this document..................................................................................3
1.2 The target group of this document ........................................................................... 3
1.3 Depth of information of this document.................................................................... 3
1.4 Abbreviations and terms...........................................................................................3
1.4.1 Abbreviations.................................................................................................3
1.4.2 Important terms ............................................................................................3
1.5 Symbols used.............................................................................................................4
2 On safety ................................................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Use of the device....................................................................................................... 6
2.2 Correct use of the device ..........................................................................................7
2.3 General safety information and protective measures.............................................7
2.3.1 Stationary application ................................................................................... 8
2.3.2 Application on automated guided vehicles (AGVs)....................................11
2.4 Protection of the environment................................................................................14
3 Product description...........................................................................................................................15
3.1 Construction of the device ......................................................................................15
3.2 Operating principles of the device..........................................................................18
4 Installation and mounting ...............................................................................................................20
4.1 Operating conditions ...............................................................................................20
4.2 Mounting the device................................................................................................20
4.3 Minimum distance from objects.............................................................................22
5 Electrical installation........................................................................................................................23
5.1 Integrating the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70’s outputs into the
machine control system..........................................................................................23
5.2 Connecting the power supply and signal cables....................................................25
5.3 Connecting the data cables ....................................................................................27
6 Configuration.......................................................................................................................................28
6.1 Delivery status .........................................................................................................28
6.2 Preparing the configuration ....................................................................................28
7 Commissioning ...................................................................................................................................29
7.1 Access authorization ...............................................................................................29
7.2 Testing the Monitor functions.................................................................................29
7.3 Regular examinations..............................................................................................30
8 Transport and storage ......................................................................................................................31
8.1 Transporting the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 ...............................................31
8.2 Storage.....................................................................................................................32
Page 3

Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
List of contents
9 Maintenance and care .....................................................................................................................33
10 Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................34
10.1 Correcting faults...................................................................................................... 34
10.2 System error indications......................................................................................... 34
11 Technical data ..........................................................................................................................35
11.1 Data sheet............................................................................................................... 35
11.2 Device accuracy and safety supplements .............................................................37
12 Order data...................................................................................................................................38
12.1 Delivery.................................................................................................................... 38
12.2 Optional accessories...............................................................................................38
13 Appendix.....................................................................................................................................39
13.1 Dimensional drawings, safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 .................................... 39
13.2 Standards and directives........................................................................................ 40
13.3 Checklist for the manufacturer ..............................................................................41
13.4 List of tables............................................................................................................ 42
13.5 List of illustrations...................................................................................................42
2
Page 4

Instruction Manual Chapter 1
F3G-C1R70
About this document
1 About this document
Please read this chapter carefully before working with this documentation and the safety
laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
1.1 The function of this document
This document provides information on the technical properties of the Safety Laser
Scanner F3G-C1R70 (Rotating Laser Scanner). You will find information on:
• Safety
• Structure and operation
• Planning
• Maintenance and care
1.2 The target group of this document
This document is intended for those persons who constructively integrate the safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70, and commission and operate it as a protective device.
ESPE
CSL
OSSD
Machine
Scanning range
1.3 Depth of information of this document
This document contains all the information necessary for planning, acquisition and
maintenance of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70. Information is provided on its
operating principle, possible uses and mounting.
More information is available from OMRON directly.
1.4 Abbreviations and terms
1.4.1 Abbreviations
Electro-sensitive protective equipment (e.g. safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70)
Configuration Software for Laserscanner. With a PC and the CSL, as a user, you can define
the monitored areas, and define or check the correct configuration of the safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70.
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 uses a reference target fixed to the F3G-C1R70 for
self-checking. Any change to this target is interpreted as a system error.
Output signal switching device
1.4.2 Important terms
Please distinguish between the following terms:
In this instruction manual,
dangerous state or a dangerous movement that rules out the presence of persons or
objects in the protective field is involved in the operation of the machine.
The maximum scanning range describes an arc of 300° around the sensor with a radius
of max. 7.5 m.
machine is used as a term for the system to be monitored. A
3
Page 5

Chapter 1 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
About this document
Protective field
Protective field size
Monitored areas
Warning field
Response time
Reactivation time
The safety area that, when infringed, results in the immediate shut down of the dangerous
movement is termed the protective field. If a person or object enters the protective field,
the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 provides a stop signal to the machine via the OSSD
switching outputs.
The maximum protective field size is defined by the distance of the safety laser scanner
scanning head to the most distant point of the protective field including the safety
supplement.
Monitored areas are a general term used for protective fields (up to 6 m) and/or warning
fields (up to 7.5 m). Monitored areas can have irregular shapes or shapes adapted to the
surroundings. The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 monitors them continuously by means
of individual radial laser beams.
The warning field is described as that safety area whose infringement causes an optical or
acoustic warning signal. If a person or object enters the warning field, the safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70 provides a signal to the monitored machine via the warning output.
The response time is maximum time between intrusion of objects in monitored areas and
making OSSDs into OFF-state (Open).
The reactivation time is time between removal of objects from monitored areas and
making OSSDs into ON-state (Close).
1.5 Symbols used
Recommendation
Note
, Red, + Yellow,
- Green
Action
%
WARNING
!
Particular emphasis is given to some information in this document to make it easier to find
quickly.
Recommendations are designed to give you assistance in your decision-making process
with respect to a function or a technical measure.
Such notes provide information on special device features.
LED symbols describe the state of a diagnostics LED. Examples:
, Red The red LED is illuminated constantly.
+ Yellow The yellow LED is flashing.
- Green The green LED is off.
An arrow indicates that some action is required. Carefully read and follow the instructions
for the action to be taken.
Warning!
A warning indicates an actual or potential risk or health hazard. They are designed to
prevent accidents.
Always read warnings attentively and follow instructions carefully!
Software notes show the location in the CSL (Configuration Software for Laserscanner)
where you can make the appropriate settings and adjustments.
The term “dangerous state”
The dangerous state (standard term)
diagrams of this document as a movement of a machine part. In practical operation, there
may be a number of different dangerous states:
• Machine movements
• Electrical conductors
• Visible or invisible radiation
• A combination of several hazards
of the machine is always shown in the drawings and
4
Page 6

Instruction Manual Chapter 2
F3G-C1R70
On safety
2 On safety
This chapter deals with your safety and the safety of the equipment operators.
Safety notes
%
WARNING
Please observe the following items in order to ensure the correct and safe use of the
safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
Prior to commissioning the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 for the first time, please read
this instruction manual and the users manual for the CSL (Configuration Software for
Laserscanner) carefully. Get to know the system and the CSL. Please contact your nearest
OMRON representative if you have any questions. We will be pleased to provide assistance.
All appropriate legal regulations, the requirements of the trade associations and the
instructions of the manufacturer of the machine to be monitored must be observed
without fail.
The protective function of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 depends on the correct
definition and programming of the warning field and protective field.
Installation of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70, definition and programming of the
areas to be monitored and integration in the machine control system, must be carried out
only by authorised personnel who are appropriately trained.
After completing the programming, the arrangement of the protective and warning fields
are to be tested on the machine while it is switched on, but not running. On this topic see
Section 7.2 "Testing the Monitor functions" on page 29.
5
Page 7

Chapter 2 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
On safety
2.1 Use of the device
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has been developed and approved as a Type 3
electro-sensitive protective equipment according to the IEC/EN 61)496-1 standard.
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of
the monitored areas
Measuring range
Warning field (example)
Maximum protective field
Protective field (example)
6 m
7.5 m
60°
Test range
(reference target)
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has been designed for industrial use. Its task is to
detect access of persons to hazardous areas and stop the dangerous movement of a
machine in this area. A signal is triggered as soon as a person or object enters the
monitored area:
• If a person or object is present within the warning field, the safety laser scanner F3G-
C1R70 switches a relay contact at the corresponding signal output. This signal can be
used for acoustic and optical warnings. Warning is to indicate that the hazardous area is
to be left before the protective field is activated and the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70’s OSSDs issue a stop signal that triggers a machine stop.
• If a person or object is present within the protective field, the safety laser scanner F3G-
C1R70 switches two independent relay contacts, OSSDs. These signals must lead to an
immediate switching off of the dangerous machine movement.
The CSL (Configuration Software for Laserscanner) is included with the safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70 for the definition and testing of the protective field and warning field.
6
Page 8

Instruction Manual Chapter 2
F3G-C1R70
On safety
2.2 Correct use of the device
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 can only be used as protective equipment for
detecting persons or objects (horizontal protective field). Operation of the device is only
permissible according to the technical specifications. All warranty claims against OMRON
are forfeited in the case of any other use, or if alterations are made to devices, even as
part of their mounting or installation.
2.3 General safety information and protective measures
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must only be employed for monitoring tasks
%
WARNING
fulfilling all the following conditions:
• The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be able to terminate the dangerous state
within a defined time period by triggering the stop signal.
• The safety distance monitored by the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be smaller
than the maximum protective field.
• The maximum value of the machine’s stopping time plus the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70’s response time must be calculated so that nobody can gain access to the
hazardous point before the dangerous movement has come to a complete stop.
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is of laser safety class 1.
Additional measures for screening the laser radiation are not
necessary (eye safe).
LASER CLASS 1
7
Page 9

Chapter 2 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 2: Calculation of the
safety distance for a
stationary application
On safety
2.3.1 Stationary application
According to Chapter 6.2 of the EN 999 standard, the safety distance between the limit of
the protective field and the hazardous area of a stationary machine is calculated as
follows:
S
h
S = 1.6 × (t1 + t2) + (1200 – 0.4 h) + ZM
Please note: 1200 – 0.4 h ≥ 850
Here…
S = The safety distance (in mm)
= The response time of the F3G-C1R70 (in ms) (see Chapter 11 “Technical data” on
t
1
page 35)
= The machine stopping/run-down time (in ms)
t
2
h = Height of protective field above the floor (in mm) 300 ≤ h ≤ 1000
1.6 = The assumed approach speed (in m/s)
ZM = Maximum measuring error of the F3G-C1R70 (see Chapter 11 “Technical data” on
page 35)
%
WARNING
%
WARNING
Ensure that the correct mounting height is used!
When selecting the mounting height ensure that it is not possible to enter the hazardous
area from below the protective field.
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be supplemented by further safety devices if
one of the following situations applies:
• A hazardous point can be reached without passing through the monitored areas.
• The area monitored by the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 can be reached from above,
below or from the side.
• According to EN 999, possible access by crawling below the protective field must be
taken into account above the regulation minimum protective field height of 300 mm.
8
Page 10
Instruction Manual Chapter 2
F3G-C1R70
On safety
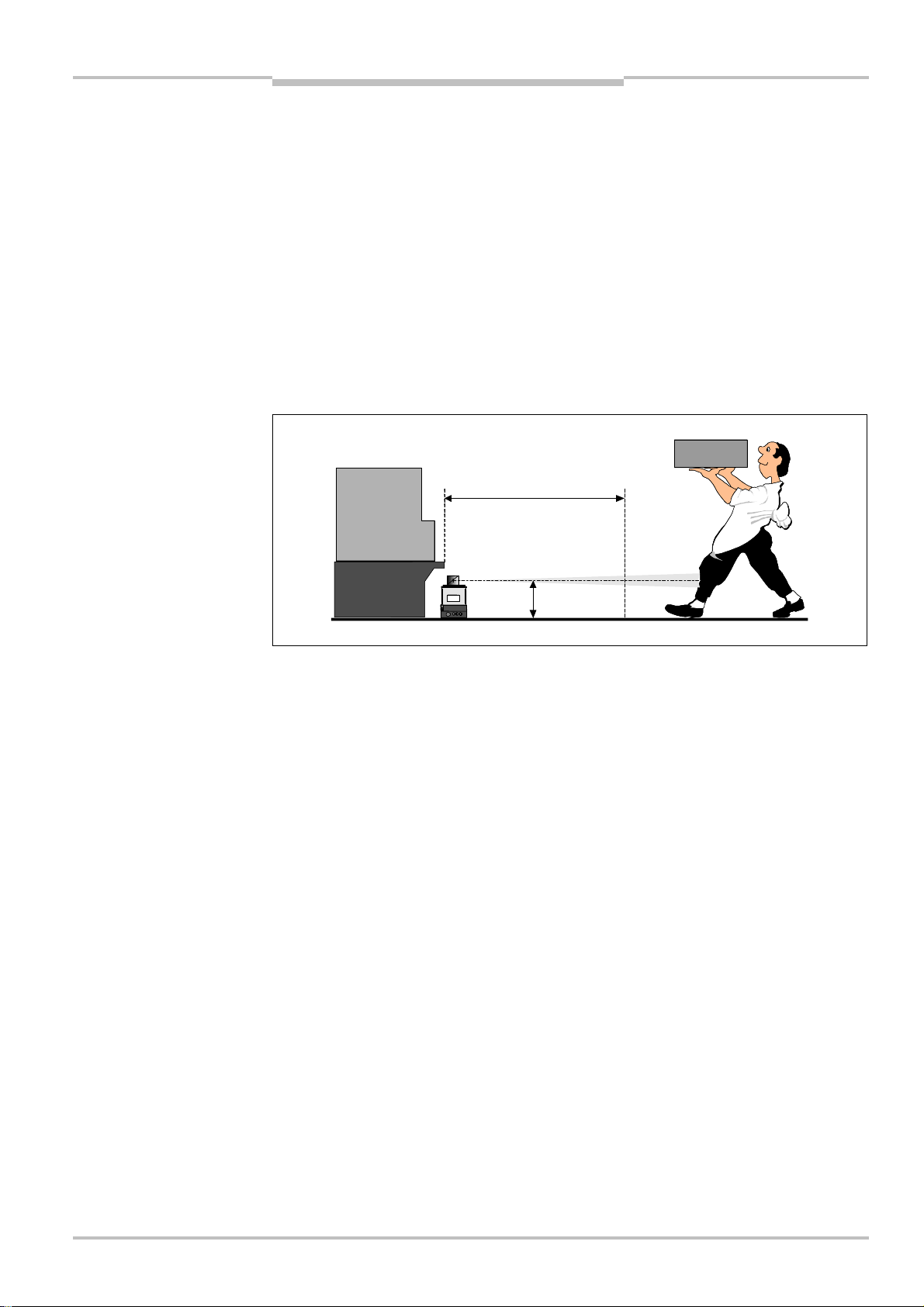
Example for a stationary application
Machine width M = 2.2 m = 2200 mm
Response time of the F3G-C1R70 = 280 ms
The machine stopping/run-down time = 300 ms
Height of protective field above the floor = 0.5 m = 500 mm
Maximum measuring error of the F3G-C1R70 = 350 mm
Protective field width = M + safety supplement left and right
S = 1.6 m/s × (280 ms + 300 ms) + (1200 mm – 0.4 × 500 mm) + 350 mm = 2278 mm
Protective field width = 2200 mm + 350 mm + 350 mm = 2900 mm
Maximum protective field size = (S
2
+ ½ protective field width2)½ = 2700 mm
Please note: The example only applies if no access from the side is possible. Access from
the side must be prevented either by a wider protective field and/or other measures.
Fig. 3: Example: minimum
distance for stationary
application
S = 2278 mm
500 mm
9
Page 11
Chapter 2 Instruction Manual
t
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 4: Example: maximum
protective field size and
safety supplements for
stationary applications
On safety
Machine to be
safeguarded
Safety supplement left
Maximum protective
field size
S
%
WARNING
Protective field
Safety supplement right
Safety supplements are to be determined for maximum protective field sizes.
The following applies if the access of persons from behind cannot be hindered by
appropriate sizing of the protective field:
• A manual restart interlock must be present in the machine control system (generally
necessary). The switch to reset the interlock condition must be installed so that the
entire hazardous area is visible and free of personnel, also the switch must not be able
to be operated from within the hazardous area.
• The width of the accessible, unmonitored area directly in front of the machine must be
smaller than 35 mm for a maximum protective field size of up to 3 m. For larger
maximum protective field sizes, the distance must be reduced to zero.
Safety supplement fron
10
Page 12

Instruction Manual Chapter 2
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 5: Calculating the
minimum distance for
automated guided vehicles
On safety
2.3.2 Application on automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
Taking the regulations for automated guided vehicles (e.g. EN 1525: Safety of industrial
trucks - Driverless trucks and their systems) into account, the minimum distance between
the edge of the protective field and the hazardous area of the AGV is calculated as follows:
S
200 mm > h > 100 mm
%
WARNING
S = 1.1 × ((V
Here…
S = Minimum distance (in mm) = max. stopping distance of the AGV
= Response time of the F3G-C1R70 (in ms) (see Chapter 11 “Technical data”
t
1
t
= AGV control system reaction time (in ms)
2
= Maximum speed of the AGV (m/s)
V
max
B = Maximum braking path for the AGV (in mm)
ZM = Maximum measuring error of the F3G-C1R70 (see Chapter 11 “Technical
F = Foot clearance: 150 mm (for the AGV with a floor clearance of less than
h = Height of protective field above the floor (in mm)
1.1 = Safety supplement for possible brake wear
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be supplemented by further safety devices if
one of the following situations applies:
• A hazardous point can be reached without passing through the monitored areas.
• The area monitored by the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 can be reached from above,
below or from the side.
× (t1 + t2)) + B) + ZM + F1)
max.
on page 35)
data” on page 35)
120mm)
%
WARNING
Define protective field cover correctly!
The protective field must cover the entire width of the AGV. The protective field must be
increased at the sides by the safety supplements (see Chapter 11 “Technical data” on
page 35).
1)
F only applies when there is no foot clearance according to EN 1493.
11
Page 13

Chapter 2 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
%
WARNING
%
WARNING
Fig. 6: Prevent undercutting
of the AGV protective field
On safety
Define the protective field correctly where routes bisect each other!
At “crossroads” where there are “blind spots”, the protective field must have the same
configuration as in the direction of motion.
Avoid undercutting of the protective field!
The protective field must be configured in such a way that stepping between the protective
field and the AGV from behind in the direction of motion (undercutting) is not possible. The
safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has a maximum scanning angle of 300°.
The protective field is to be selected so that it is not possible for a person to pass
unnoticed between the protective field and vehicle.
%
WARNING
%
WARNING
AGV
The following must be considered!
• In cases where it is not possible to prevent undetected personnel from standing in front
of the AGV by appropriate sizing of the protective field, then a manual restart interlock
must be included in the AGV. The switch to reset the interlock condition must be
installed so that the entire hazardous area is visible and free of personnel, also the
switch must not be able to be operated from within the hazardous area.
• The width of the accessible area that is not monitored directly in front of the AGV must
be less than 35 mm for a maximum protective field size of up to 3 m. For larger
maximum protective field sizes, the distance must be reduced to zero.
Program reactivation delay!
In case of AGV applications, you must program a reactivation delay for the safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70. The reactivation delay defines the length of time [ms] before the
relay is reactivated after the monitored field is clear (automatic restart after time).
With automatic restart, the restart period must be set to a minimum of 2000 ms.
12
!
You can stipulate the reactivation delay independently for the warning field and the
protective field (Right-click on the device symbol in the navigation area > Configuration
draft > Edit parameters). The values permitted are between 200 and 5000 ms.
Page 14

Instruction Manual Chapter 2
t
d
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 7: Example: minimum
distance for automated
guided vehicles
On safety
Example for application on AGVs
AGV
Response time of the F3G-C1R70 = 280 ms
AGV control system reaction time = 300 ms
Maximum speed of the AGV = 1 m/s
Maximum braking distance for the AGV = 0.3 m = 300 mm
Maximum measuring error of the F3G-C1R70 = 250 mm
F unnecessary: the AGV has foot clearance
Safety supplement for possible brake wear = 1.1
Protective field width = AGV
S = 1.1 × ((1 m/s × (280 ms + 300 ms)) + 300 mm) + 250 mm = 1218 mm
Protective field width = 1600 mm + 250 mm + 250 mm = 2100 mm
Maximum protective field size = (S
= 1.6 m = 1600 mm
width
+ safety supplement left and right
width
2
+ ½ protective field width2)½ = 1608 mm
Fig. 8: Example: maximum
protective field size and
safety supplements for AGVs
S = 1218 mm
200 mm
Safety supplement left
Maximum protective
field size
S
AGV
Protective fiel
Safety supplement right
Safety supplement fron
13
Page 15

Chapter 2 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
On safety
2.4 Protection of the environment
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is constructed in such a way that it adversely affects
the environment as little as possible. It emits and contains no environmentally damaging
substances and requires only a minimum of energy and resources.
At work, always act in an environmentally responsible manner. For this reason, please note
the following information on disposal.
Disposal
Note
Always dispose of unusable or irreparable devices according to the particular waste
disposal regulations applicable in the country of use.
14
Page 16

Instruction Manual Chapter 3
l
F3G-C1R70
Product description
3 Product description
3.1 Construction of the device
The sensor of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is housed in a sturdy aluminum housing.
The housing is protected against water spray according to IP 65 (only applicable if the
connection sockets are equipped with plugs or covers).
Do not damage seals!
%
WARNING
Fig. 9: Construction of the
safety laser scanner F3GC1R70
The housing screws are sealed. Any damage to seals leads to forfeiture of the
manufacturer’s warranty.
The mirror and laser optics are located on the top of the housing in a rotating housing
component. The laser transmitter and receiver use the same lens. This complex co-axial
construction prevents angular error resulting from separate transmitter and receiver optics.
Rotating scanning
head
Optical surface
%
WARNING
Indicators
The invisible laser beams emitted conform to laser safety class 1. The measurement area
begins immediately in front of the optical surface.
Do not mount the device at eye level!
Fix the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 so that the measuring beam is not at eye level
during use.
Electrica
connections
15
Page 17

Chapter 3 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Product description
There are four indicators on the side of the housing showing the state of the system.
Fig. 10: LEDs on the safety
laser scanner F3G-C1R70
Reference target
Rotating scanning head
Tab. 1: Status of the LEDs for
the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70
Green ON-state indictor
Red OFF-state indicator
Yellow Warning indicator
Yellow Diagnostic indicator
:Outputs for protective field (OSSDs) in ON state
:Outputs for protective field (OSSDs) in OFF state
:Outputs for warning field in OFF state
:System state
Indicator Status
ON OFF Warning Diag.
Green Red Yellow Yellow
Meaning
- - - - Device switched off
, , , , Test LEDs for 1 sec. after Power On2)
The system is ready for operation, the outputs for
, - - -
protective field (OSSDs) and for warning field are in
an ON state
- , - Outputs for protective field (OSSDs) are in OFF-state.
, - Output for warning field is in OFF-state.
- , , +)3)System error
2)
The diagnostic indicator lights up during the start-up test after Power On. During the last 5 seconds before
operational readiness is achieved and the release of the release of outputs for protective field (OSSDs), this
indicator blinks at 2 Hz.
3)
For more on this topic see Section 10.2 “System error indications” on page 34.
16
Page 18

Instruction Manual Chapter 3
t
A
s
r
g
F3G-C1R70
Product description
There are two connection sockets on the opposite side of the housing, indicated as
Interface and 24 V DC/signal.
Fig. 11: Housing
connection side
Rotating scanning head
Power supply connector
(24V DC/signal)
Interface connector
(Interface)
Reference targe
Fuse 3.15
low blow under cove
medium
with sealing rin
Protective cap
for interface
Earth terminal
• Interface connector
This connector is used for communication with the computer. At this connection, an
RS 232 interface is available.
• Power supply connector
This connector is used for connecting the power supply, the two outputs for protective
field, OSSD1 and OSSD2, and the output for warning field.
17
Page 19

Chapter 3 Instruction Manual
r
s
r
r
A
r
s
s
s
D =
2
Product description
F3G-C1R70
3.2 Operating principles of the device
Measurement principle
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 emits pulsed laser beams throughout a complete
360° with the help of a rotating mirror. The light pulses are reflected diffusely from objects
in the vicinity and received by a photodiode in the sensor. The safety laser scanner F3GC1R70 determines the distance to the object from the propagation time that the light
requires from emission to reception of the reflection at the sensor.
Fig. 12: Schematic diagram
of operating principle
Stopwatch
Sampling
∆ T × V
stop
start
Light
Rotating mirro
Laser optic
Laser receive
Laser sende
trigger
ngular encode
Motor
Laser reflection
Laser beam
The direction of each individual measurement beam is determined with the help of an
angular encoder.
The measurement data for distance and direction can be called up by a computer via the
interface.
18
Page 20

Instruction Manual Chapter 3
F3G-C1R70
Product description
Monitoring of protective field and warning field
Two distance limit values, representing the warning field and protective field, can be
defined for each measurement beam with the help of the CSL. While monitoring, the safety
laser scanner F3G-C1R70 compares the measured object distance with defined limit
values.
Fig. 13: Configuration of
monitored areas
Warning field
Protective field
F3G
°
60
F3G
Warning field
Protective
field
Possible configuration Impossible configuration
The tables of distance limit values are determined with a computer and laid down in the
safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70. The warning and protective field limits can be of any
shape and ideally adapted to the surroundings. The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must
therefore be within the limits of both the warning field and the protective field.
Self-testing
Comprehensive internal tests run continuously within the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
This ensures the system’s high level of operational reliability. All basic components are
either present in duplicate, or are monitored by testing logics that operate independently.
The so-called reference or test target is an important constituent of the self-testing
systems. This involves a stationary target firmly mounted on the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70, detected on each rotation. Any alteration in the measurement value indicates a
system error and leads to an error state.
During monitoring the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 checks that it is functioning
correctly.
The system sensitivity of the device is monitored through the measurement of the light
reflected from the reference target. Contamination of the optical surface or the reference
target can thus lead to the system error: Device insensitive/reference target error (LED
indicators). If this happens, clean the optical surface as well as the reference target as per
the instructions given in Section 9 “Maintenance and care” on page 33.
19
Page 21

Chapter 4 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Installation and mounting
4 Installation and mounting
4.1 Operating conditions
Please note the following points before using the device:
• The device is only for use in predominantly enclosed areas.
• The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is protected against water spray according to IP 65
and operates within a temperature range of 0 to 50 °C. Protect the system from
moisture and temperatures that are outside the temperature range.
• Protect the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 from continuous direct sunlight.
• To prevent condensation, do not expose the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 to rapidly
changing temperatures.
• Do not expose the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 to aggressive chemicals (detergents).
• Glass panes or reflective surfaces are not reliably detected by the safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70 as objects.
• The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 only detects objects that are visible from its
location and not covered up.
• Rain, snow, dust and smoke are detected as “objects” and may trigger warning field or
protective field states.
%
WARNING
4.2 Mounting the device
Observe the machine manufacturer’s safety regulations!
It is essential that the safety instructions for working on the machine, defined by the
machine manufacturer, are observed when mounting the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
Mounting of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 may only be carried out by qualified
personnel.
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 can be mounted in any orientation (standing, hanging,
lying).
20
Page 22

Instruction Manual Chapter 4
F3G-C1R70
%
WARNING
Fig. 14: Minimum distance to
the floor
Installation and mounting
The emitted laser beam has a divergence of ≤ 1°.
It is essential that during mounting a minimum distance of 100 mm to the floor must be
maintained.
Measuring range
Minimum distance to the floor
%
WARNING
Fig. 15: Mounting several
safety laser scanners
When installing several safety laser scanners, mounting must be carried out in a way
that does not allow any mutual interference.
h
Invalid configuration
min. 500 mm
Possible configuration
Possible configuration
Possible configuration
Screening
21
Page 23

Chapter 4 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Installation and mounting
The followings are required for mounting the device:
• 4 M4 bolts
• 4 washers and locking washers
• If necessary, a spirit level for ensuring level mounting
Fit safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 to machine:
1. Turn off the machine and check that you are not taking any risks!
2. Turn the mounting screws (with the washers and locking washers in place) and tighten
them finger tight.
3. When attaching to non-mobile machines, it is recommended that the spirit level is
used in two axes to ensure level mounting.
4. Tighten the screws.
– Tightening torque: 2.6 N·m
– Minimum meshing length: 8mm
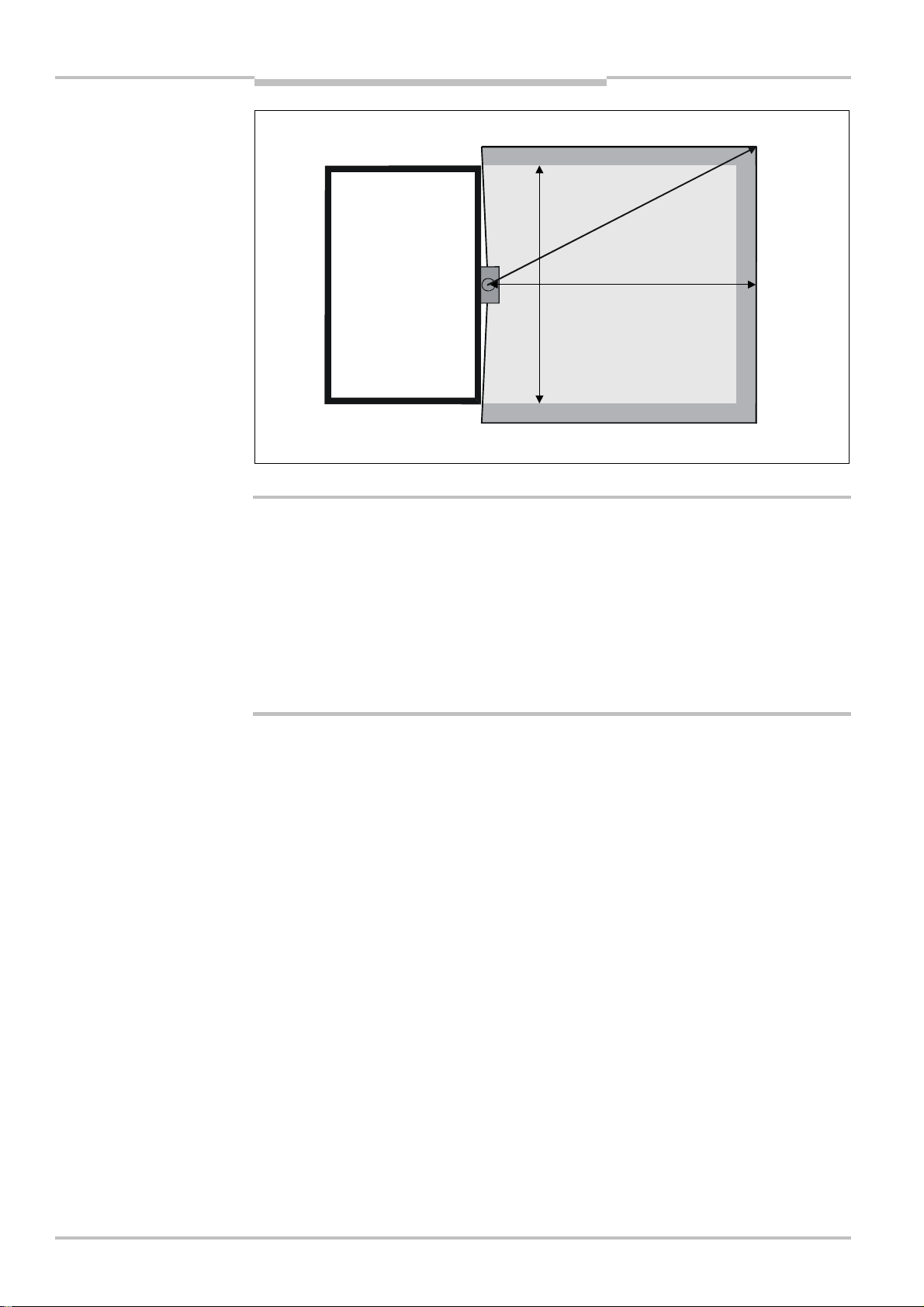
4.3 Minimum distance from objects
Fig. 16: Minimum distance of
the area monitored by the
safety laser scanner F3GC1R70 from surrounding
objects
When mounting in front of a wall, for reasons of availability, the programmed monitored
areas may not be closer than 25 cm to the wall.
Wall
Minimum distance
Monitored areas
F3G
Machine to be
safeguarded
22
Page 24

Instruction Manual Chapter 5
F3G-C1R70
Electrical installation
5 Electrical installation
5.1 Integrating the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70’s
outputs into the machine control system
Connection only by qualified personnel!
%
WARNING
Fig. 17: Example of
integration of the
warning field signal
Connection of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 to the machine may only be carried out
by appropriately qualified personnel.
These persons must have all the information provided by the suppliers of the machine.
30 V max. L
Warning field1.1
Warning field1.2
0 V N
Three potential-free switching outputs are available for connection to the machine for
warning field and protective field states. The outputs are designed as N.)O. contacts.
Switching output for warning field (Non-safety output)
The switching output for warning field can be used for the output of a warning signal. The
switching output for warning field is opened when the warning field is activated, or when
there is a safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 fault.
If an object is again removed from the warning field, its switching output closes after an
adjustable time between 200 and 5000 ms (reactivation delay).
The switching output for warning field can be switched with a maximum of 30 Volts and is
internally fuse-protected with 2 Amps.
23
Page 25

Chapter 5 Instruction Manual
-
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 18: Example of
integration of OSSDs. The
wiring is to be laid down in
such a way that it is
protected against mechanical
effects.
* = Screen to rule out crosscircuits
Electrical installation
24 V
OSSD2.1
OSSD2.2
Monitoring of K1
and K2
K1
K2
!
OSSD1.1
OSSD1.2
Suppression diode Suppression diode
*
K1 K2
0 V
*
Relay with positively
K1
K2
driven contacts
Safe controller as a
minimum category3
in accordance with
the EN 954-1
OSSD switching outputs (Safety outputs)
The OSSD switching outputs can be used as emergency stop trips in the system controller.
The OSSD switching outputs are open if
• the protective field has been activated
or
• the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has a fault.
The switching output closes after a programmable time of between 200 and 5000 ms
(reactivation delay), assuming that there is no system fault.
You can stipulate the reactivation delay independently for the warning field and the
protective field (Right-click on the device symbol in the navigation area > Configuration
draft > Edit parameters).
The OSSD1 and OSSD2 outputs can be wired with a maximum of 30 Volts and are
internally fuse-protected with 2 Amps.
24
Page 26

Instruction Manual Chapter 5
F3G-C1R70
Electrical installation
5.2 Connecting the power supply and signal cables
Electrical work is to be carried out only by appropriately trained electrical specialists!
%
WARNING
Fig. 19: Plug allocation for
connection of the power
supply and the signal cables
Electrical connection of the power supply and connection of the signal cables for the
warning field, OSSD1 and OSSD2 take place together via the middle socket on the right-
hand side of the housing. The power supply cable F39-JG5A (optional) is available for those
electrical connections.
2
4
1
5
8
3
Tab. 2: Plug allocation for
connection of the power
supply and the signal cables
Fig. 20: Dimension of the
power supply cable
6
Pin Signal Explanation Colour Marking
1 +24 V DC 24 V DC supply Brown +
2 0 V Ground Blue –
3 OSSD2.1 White S2
4 OSSD2.2
5 OSSD1.1 Black S1
6 OSSD1.2
7 Warning output1.1 Red A
8 Warning output1.2
FE Functional earth (shield) Black FE
Relay contact of the OSSD 2
Relay contact of the OSSD 1
Relay contact of the warning
output
7
Grey S2
Green S1
Pink A
18
±10
150
±100
5000
55
Unit: mm
25
Page 27

Chapter 5 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Electrical installation
Connecting the power supply to the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70:
1. Wiring is to be protected.
2. Turn off the machine and make sure that you are not exposed to any danger.
3. Avoid short-circuits.
4. Earth the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 from the earth terminal
– cross-section for functional earth/ground 1 … 2 mm
2
5. Prepare the power supply:
– operating voltage for the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70: 24 V DC ± 25)%
– power consumption in operation: typically 750 mA at 24 V DC (switch on current:
2 A for 100 ms)
6. Connect the plug of the power supply cable to the power supply connector of the
safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and tighten the screw.
7. Connect safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and computer.
8. Switch on safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
9. The rotating scanning head starts to rotate. After a few seconds the diagnostic
indicator goes out and the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is ready for configuration
of the areas to be monitored.
Notes
• On connecting the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70, it is imperative to ensure that the
earth is connected correctly. The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be provided with
a safety insulating transformer according to IEC 742 or equivalent means of isolation.
This also applies for the charging devices for vehicle batteries, if charging is to take
place on the vehicle.
• For stationary applications, the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be earthed (for
more on earth connection, see Section 3.1 “Construction of the device” on page 15).
• The functional earth is to be connected with ground potential for installation on
transport vehicles. For applications with battery-powered vehicles, a DC voltage
transformer must be connected in series before the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70. On
request, please consider a relevant protection against “low dump” (voltage drop).
Fig. 21: Example of the power
supply and grounding of
stationary applications
Fig. 22: Example of the power
supply and grounding on a
transport vehicle
26
24 V DC
0 V
FE
24 V DC
On-board voltage
0V
Page 28

Instruction Manual Chapter 5
F3G-C1R70
Electrical installation
5.3 Connecting the data cables
The interface cable F39-JG5R (optional) is available to connect the safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70 to the PC.
Fig. 23: Pin allocation of the
interface cable
Tab. 3: Pin allocation of the
interface cable
Fig. 24: Dimension of the
interface cable
J
Pin Signal Explanation Direction Level
A GND Ground, RS 232 --- --C RTS RS 232: Ready to send Output 24 V
E CTS RS 232: Clear to send Input 24 V
G TxD RS 232: Transmit data Output 24 V
J RxD RS 232: Receive data Input 24 V
L --- Do not connect! --- --M RES Reset (active LOW) Input 24 V
N --- Do not connect! --- --O --- Do not connect! --- ---
P --- Do not connect! --- ---
R --- Do not connect! --- ---
S --- Do not connect! --- ---
T --- Do not connect! --- ---
U --- Do not connect! --- ---
E
G
P
R
S
T
I
O
C
N
MU
A
55
±100
5000
Unit: mm
Connecting the interface cable between the PC and the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70:
1. Prevent short-circuits and switch off the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and the PC.
2. Connect the interface cable to the interface connector of the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70 and the serial interface port of the PC.
3. Make sure to screw connectors tight.
The device only conforms to enclosure rating IP65 if the interface connector is
connected with the interface cable, or covered with a cap.
27
18
Page 29

Chapter 6 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Configuration
6 Configuration
6.1 Delivery status
Protective field and warning field are set for maximum size in the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70 as a default when supplied. The relay reactivation delay is set to the standard
value of 200 ms. Prior to commissioning, the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must be
configured for the planned application with the aid of the CSL (Configuration Software for
Laserscanner) supplied.
6.2 Preparing the configuration
How to prepare the configuration:
Make sure that the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has been properly mounted, and
that the electrical connections are correct and in place.
Plan all necessary settings (warning field, protective field, reactivation delay, etc.).
To configure the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70, you need:
– CSL (Configuration Software for Laserscanner) on CD-ROM
– Users manual for CSL on CD-ROM
– PC/Notebook with Windows 9x/NT 4/2000 Professional/XP with a serial interface (RS
232) (PC/Notebook is not included.)
– Interface cable F39-JG5R for communication between PC and safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70 (Interface cable is not included.)
To configure the device, please read the users manual for the CSL (Configuration
Software for Laserscanner) and use the online help in the program.
28
Page 30

Instruction Manual Chapter 7
F3G-C1R70
Commissioning
7 Commissioning
7.1 Access authorization
Access to the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is password protected.
• The password is F3GC on delivery.
• The user (Safety Officer) must ensure that the password is known only by authorized
persons.
Recommendation
!
It is recommended that the F3GC password is replaced by a new password that you
select.
Right-click on the device symbol in the navigation area > Access rights > Change
password
• Without a password, it is possible to select the Monitor function on the PC and edit
protective fields, but it is not possible to change the protective field or parameters.
• Using a password, it is possible to change the protective field and parameters.
7.2 Testing the Monitor functions
After you have defined the monitored areas with the CSL, you must check and accept the
installation. For this purpose, proceed in two steps:
• First, check the definition of the protective field with a computer connected, and
document the test.
• Then, connect to the machine and repeat the test.
Check definition of the protective field and document:
Insert a dark test object with a diameter of about 70 mm from all sides into the
protective field. Check every section of the protective field limit.
The ON-state indicator (green LED) must go out, and the OFF-state indicator (red LED) on
the front of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 must light up.
Add test-results to your documentation.
Check installation of the safety system to the machine:
When you are sure that the definition of the protective field is correct, connect the safety
laser scanner F3G-C1R70 signal cables to the machine control system. Repeat the test
with the machine switched on, but not running. Check as far as possible the behaviour
of the protective device.
Also, check the behavior when the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is switched off.
Switch on the machine. Carefully insert an object, e.g. a box, into the monitored areas.
Observe the machine’s reaction.
Prepare a report.
29
Page 31

Chapter 7 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Commissioning
Before accepting the system, consider the following points:
Test to ensure that no dangerous state can be set in motion as long as an object is
present in the hazardous area.
Ensure that the dangerous state or the dangerous movement comes to a stop before
any part of a person’s body can reach the hazardous point. When defining the protective
field, take the machine stopping/run-down time and the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70’s response time into account.
Ensure that the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and other protective devices monitor all
access points to the hazardous areas.
Check that the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 is firmly mounted. Check that the
system doesn’t move under normal operating conditions and that its position cannot be
changed.
Train the machine operating personnel to operate the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
Explain its design and how to use the system (Indicators, faults).
7.3 Regular examinations
%
WARNING
Carry out regular tests!
Daily tests can be carried out by the machine’s operating personnel.
The six-monthly maintenance (see below) and testing of the monitored areas must only be
carried out by authorised Safety Officers.)
Daily tests
Check the state and installation of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 for any changes.
If in doubt, switch off the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and immediately inform the
Safety Officer.
Keep the optics clean. Only use a soft brush or optical cloth for cleaning the optics.
Check the surroundings for changes (e.g. structural alterations) that may have taken
place since configuration.
Six-monthly tests
Check the definition of the protective field at least every six months.
Follow the regulation procedure described in Section 7.2 "Testing the Monitor functions"
on page 29.
30
Page 32

Instruction Manual Chapter 8
F3G-C1R70
Transport and storage
8 Transport and storage
8.1 Transporting the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70
Adhere to the following instructions when transporting the safety laser scanner F3GC1R70:
Notes
Fig. 25: Place F3G-C1R70 on
its side in the original
packaging
1. Remove all plugs to prevent buckling of the cable.
2. Fix rotating parts with adhesive tape to prevent scratching of the optics.
3. Do not allow any mechanical loads to affect the rotating parts.
4. Use the original packaging.
This is how you pack the safety laser scanner in its original packaging:
1. Place the lower membrane cushion upright in the box and lay the safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70 on it on its side.
Fig. 26: Place the upper
membrane cushion on top of
the F3G-C1R70
2. Place the upper membrane cushion on top of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70.
31
Page 33

Chapter 8 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Fig. 27: Put the accessories
in the original packaging
Transport and storage
3. Finally, place the accessories in the box.
4. Before sending the package label it clearly: “Sensitive measurement device – fragile!”
8.2 Storage
Adhere to the following instructions when storing the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70:
Notes
Carefully dry the system before storage. Condensation can damage optical parts.
Do not store the system in closed airtight containers, so that any remaining dampness
can evaporate. If possible, use the original packaging.
Store with an air humidity of 5 to 95)%RH (without condensation)
Storage temperature –20 to +70 °C
32
Page 34

Instruction Manual Chapter 9
F3G-C1R70
Maintenance and care
9 Maintenance and care
The safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 requires no maintenance apart from the regular
examinations already mentioned. No adjustments or calibration is necessary.
Please observe the following general instructions for handling the safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70:
Notes
To ensure the error-free operation of the sensor, clean the optical surface of the
scanning head as soon as there is evidence of visible contamination. Do not touch the
optical surface directly when cleaning. Use a plastic cleaner with a soft optical cloth to
clean the optical surface. Never use rough cloths or aggressive detergents such as
acetone.
Clean the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70’s housing with a soft, damp cloth. Do not use
aggressive detergents.
Protect the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 from continuous direct sunlight.
Do not expose the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 to rapid temperature changes to
prevent the formation of condensation.
Never open the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70! The system does not contain any
components that can be repaired or maintained by the operator.
If errors occur or you have difficulty using the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70, contact
your nearest OMRON representative.
%
WARNING
Never open the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70. The system does not contain any
components that can be repaired or maintained by the operator.
33
Page 35

Chapter 10 Instruction Manual
t
F3G-C1R70
Troubleshooting
10 Troubleshooting
10.1 Correcting faults
All the indicators are off and the rotating scanning head is not rotating:
• Power supply 18 … 30 V (24 V ± 25)%) present?
• Fuse intact?
• Plug correctly mounted on the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 and tightly connected?
• Connect the power supply with correct polarity?
The ON-state indicator (green LED) does not light up, Output contacts are open:
• Clean the optical surface (see Section 7.3 “Regular examinations” on page 30).
• Check power supply for high current.
• Connect the computer and display the CSL diagnosis.
Right-click on the device symbol in the navigation area > Diagnosis > Show.
!
• If you cannot solve the problem, please contact to your nearest OMRON representative.
Fig. 28: System error
indications
!
Objects within the monitored areas are not detected:
• Is the diagnostic indicator (yellow LED) lit or blinking?
– Yes: the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 has found an error: Check the optical surface
and the reference target.
– No: With the aid of the computer and the CSL, check the definitions for the protective
and warning field.
Right-click on the device symbol in the navigation area > Configuration draft > Edit field
setting…
Objects are reported within the monitored areas without actually existing:
• Check the surroundings for changes (e.g. structural alterations) that may have taken
place since configuration.
• Rain, snow, smoke and dust could be the cause of the spurious object detection!
10.2 System error indications
Diagnostic indicator (Yellow LED) Meaning
No error
Error at reference target
Rotational frequency error
Comparison error
Relay error
0.5 s 0.5 s
ON OFF
Error, self-
No configured fields
Repetition 8 sRepetition 8 s
est
34
Page 36

Instruction Manual Chapter 11
F3G-C1R70
Technical data
11 Technical data
11.1 Data sheet
Tab. 4: Technical data for
the safety laser scanner
F3G-C1R70
Safety classes
Safety category Type 3 ESPE acc. to EN/IEC 61)496-1
error-proof acc. to EN/IEC 61)496-1
Laser protection class Laser Class 1 acc. to EN60825-1, IEC825-1,
Laser Class I of FDA (21 CFR1040.10)
Characteristic data for the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70
Measurement and tolerance
range
Range for a safe detection of
the “nominal leg”4)
Detection capability Non-transparent:
Response time 280 ms
Reactivation time 200 to 5000 ms (adjustable)
Maximum scanning angle 300°
Laser and angular measurement
Laser diode Infrared laser diode (Avalanche Photo Diode)
Wavelength 905 nm
Pulse frequency 5.76 KHz + 5)%
0 to 7.5 m
0 to 6 m (incl. safety supplement)
70 mm min. in diameter (with 1.8% min. reflectivity)
Scanning frequency 8 Hz + 5)%
Scanning angle 300°
Angle encoder resolution 360)×)4 increments
Point resolution 0.5°
Optics (co-axial transmitter and receiver optics)
Laser beam divergence 15 mrad
Focal length 30 mm
Optical surface diameter 30 mm
Power supply
Supply voltage 24 V DC ± 25)% (ripple 5Vp-p max.) without voltage
drop due to cable, (via a safety insulating transformer
acc. to IEC 742, see section 5.2 “Connecting the
power supply and signal cable” on page 25).
Current uptake Approx. 1 A at 24 V DC
Switch on current 2 A for 100 ms
Power consumption 24 W total
Circuit protection Fuse 3.15 A medium slow blow
4)
Definition of the “nominal leg”: black cylinder with 70 mm diameter and 1.8)% reflectivity. This corresponds
approximately to a leg in child’s clothing made of black corduroy.
35
Page 37

Chapter 11 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Technical data
Tab. 4: Technical data for the
safety laser scanner F3GC1R70 (continued)
Housing and environmental resistance
Material Housing: Aluminum
Optical surface, Indicator: Glass
Degree of protection IP 65 (IEC 60529)
Length 168 mm
Width 108 mm
Height 176 mm
Weight 3.5 kg
Ambient temperature During operation: 0 to 50 °C
During storage: -20 to 70 °C
Ambient humidity During operation: 5 to 95 %RH (without condensation)
During storage: 5 to 95 %RH (without condensation)
Vibration resistance Normal operation: 10 to 55 Hz,
double amplitude 0.7 mm,
X, Y and Z directions 20 sweeps
Shock resistance Normal operation: 100 m/s2,
X,Y and Z directions 1000 times
Interfaces
Data interfaces to computer RS 232: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity
Signal outputs for warning field,
OSSD1, OSSD2
Cable Connection
Interface connection 14-pin circular connector (Binder: Series 423)
24 V DC/signal connection 8-pin circular connector (Binder: Series 423)
Cable
(optional)
Accessories
Accessories Instruction manual, CSL on CD-ROM, Mounting screws
for power supply
and output
for PC interface 5 m max., allowable bending radius: 112 mm
Potential-free relay outputs, max. 2 A, max. 30 V,
purely Ohmic load, number of operations 2 million,
Self-resetting fuse (2 A)
0.5 mm2 x 8 cores, with braided wire shield,
20 m max., allowable bending radius: 90 mm
36
Page 38

Instruction Manual Chapter 11
F3G-C1R70
Technical data
11.2 Device accuracy and safety supplements
The accuracy of the device depends on distance. Accuracy is as follows:
Tab. 5: Accuracy of the
F3G-C1R70 in relation to
distance
Distance up to Safety supplement
2 metres5) 25 cm
3 metres5) 35 cm
4 metres5) 45 cm
5 metres5) 55 cm
6 metres5) 70 cm
All possible influences, and particularly the reflective properties of the materials that could
come into question and all background effects, have been taken into consideration in
these tolerances.
Please note that when programming the device the safety supplement must be calculated
in.
5)
All distance figures include safety supplement.
37
Page 39

Chapter 12 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Order data
12 Order data
12.1 Delivery
The following components are included in the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 package:
• Safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 qty. 1
• Instruction manual (this manual) qty. 1
• Notes to user qty. 1
• CD-ROM including CSL (Configuration Software for Laserscanner) and the users manual
for the CSL qty. 1
• Mounting screw set
– 4 bolts (M)4)×)10)
– 4 washers
– 4 locking washers
12.2 Optional accessories
• Power supply cable F39-JG5A (5m)
• Interface cable F39-JG5R (5m)
38
Page 40

Instruction Manual Chapter 13
Appendix
F3G-C1R70
13 Appendix
13.1 Dimensional drawings, safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70
Approx. 60
Interface cable
Bending radius 90 mm min.
Bending radius 112 mm min.
Power cable
Min. 175 distance
56.5
115
±1
137.5
Diagnostic indicator
Warning indicator
OFF-state indicator
ON-state indicator
176
11
Mounting area
Interface protective cap
176
Interface connector
±1
±1
178
158
10
Power supply connector
Fuse 3.15 A
Earth terminal
15.5
19
15
Holes diagram, four-point fastening
+0.2
4 × 4.5
Fig. 29: Dimensional
drawings, safety laser
scanner F3G-C1R70
mm
115
144
±0.2
Fastening thread M 4 × 10 deep
±0.2
86
Mounting area
Unit: mm
39
Page 41

Chapter 13 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Appendix
13.2 Standards and directives
The most important standards and directives, valid for the use of opto-electronic protective
devices in Europe, are listed below. Further regulations may be of importance to you,
depending on the type of use. Further information on device-specific standards can be
obtained from the authorities responsible, or from your trade association.
If the machine or vehicle is to be operated in a country that does not belong to the
European Union, we recommend that you contact the plant operator or local authorities.
On the application and installation of protective equipment
• The Machinery Directive 98/37/EC
• Safety of machinery – Basic concepts, general principles for design (EN 292-1, -2)
• The safety of integrated production systems (DIN EN 1921)
• Safety of machinery – Electrical machine equipment – Part 1: General requirements
(EN 60)204)
• Safety of machinery – Safety distances to prevent danger zones being reached by the
upper limbs (EN 294)
• Safety requirements for robots (EN 775)
• Safety rules for electro-sensitive protective equipment on power-driven equipment
(ZH 1/597)
• Safety of machinery – The positioning of protective equipment in respect of approach
speeds of parts of the human body (EN 999)
• Safety of machinery – Principles for risk assessment (EN 1050)
On the construction and equipping of protective equipment
• Safety of machinery – Electro-sensitive protective equipment – Part 1: General
requirements (IEC/EN 61)496-1 as well as based on IEC/EN 61)496-3)
• Basic safety considerations for MCR safety systems (DIN V 19)250)
• Safety of machinery – Electrical equipment of machines – Part 1: General requirements
(EN 60)204)
• Safety of machinery – Safety-related parts of control systems – General principles for
design (EN 954)
40
Page 42

Instruction Manual Chapter 13
F3G-C1R70
Appendix
13.3 Checklist for the manufacturer
PNSPO!
Check list for the manufacturer/OEM for the installation of
electro-sensitive protective equipment (ESPE).
The details on the items listed below must be available at the latest when the system is commissioned for the first
time, depending, however, on the various applications the requirements of which must be reviewed by the
manufacturer/OEM.
This checklist should be retained and kept with the machine documentation to serve as reference during recurring
tests.
1. Have the safety rules and regulations been observed in compliance with the
directives/standards applicable to the machine?
2. Are the applied directives and standards listed in the declaration of conformity? Yes No
3. Does the protective device comply with the required safety category? Yes No
4. Is the access to the hazardous area/ hazardous point only possible through the protective field
of the ESPE?
5. Have appropriate measures been taken to prevent (mechanical point-of-operation guarding) or
monitor unprotected presence in the hazardous area when protecting a hazardous
area/hazardous point and have these been secured against removal?
6. Are additional mechanical protective measures fitted and secured against manipulation, which
prevent reaching below, above or around the ESPE?
7. Has the maximum shutdown and/or stopping/run-down time of the machine been measured,
specified and documented (at the machine and/or in the machine documentation)?
8. Has the ESPE been mounted such that the required safety distance from the nearest hazardous
point has been achieved?
9. Are the ESPE devices properly mounted and secured against manipulation after adjustment? Yes No
10. Are the required protective measures against electric shock in effect (protection class)? Yes No
11. Is the command unit for resetting the protective equipment (ESPE) or restarting the machine
present and correctly installed?
12. Are the outputs of the ESPE (OSSDs) integrated in compliance with the required safety category
and does the integration comply with the circuit diagrams?
13. Has the protective function been checked in compliance with the test notes of this
documentation?
14. Are the given protective functions effective at every setting of the operating mode selector
switch?
15. Are the switching elements activated by the ESPE, e.g. contactors, valves, monitored? Yes No
16. Is the ESPE effective over the entire period of the dangerous state? Yes No
17. Once initiated, will a dangerous state be stopped when switching the ESPE on or off and when
changing the operating mode, or when switching to another protective device?
This checklist does not replace the initial commissioning, or the regular inspection by specialist personnel.
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
41
Page 43

Chapter 13 Instruction Manual
F3G-C1R70
Appendix
13.4 List of tables
Tab. 1: Status of the LEDs for the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 ...............................16
Tab. 2: Plug allocation for connection of the power supply and the signal cables.......... 25
Tab. 3: Pin allocation of the interface cable ......................................................................27
Tab. 4: Technical data for the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70...................................... 35
Tab. 5: Accuracy of the F3G-C1R70 in relation to distance.............................................. 37
13.5 List of illustrations
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of the monitored areas............................................................ 6
Fig. 2: Calculation of the safety distance for a stationary application.............................. 8
Fig. 3: Example: minimum distance for stationary application.......................................... 9
Fig. 4: Example: maximum protective field size and safety supplements for
stationary applications............................................................................................10
Fig. 5: Calculating the minimum distance for automated guided vehicles..................... 11
Fig. 6: Prevent undercutting of the AGV protective field.................................................. 12
Fig. 7: Example: minimum distance for automated guided vehicles ..............................13
Fig. 8: Example: maximum protective field size and safety supplements for AGVs....... 13
Fig. 9: Construction of the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 .......................................... 15
Fig. 10: LEDs on the safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 ...................................................... 16
Fig. 11: Housing connection side ....................................................................................... 17
Fig. 12: Schematic diagram of operating principle.............................................................18
Fig. 13: Configuration of monitored areas .......................................................................... 19
Fig. 14: Minimum distance to the floor............................................................................... 21
Fig. 15: Mounting several safety laser scanners................................................................ 21
Fig. 16: Minimum distance of the area monitored by the safety laser scanner F3G-
C1R70 from surrounding objects........................................................................... 22
Fig. 17: Example of integration of the warning field signal............................................... 23
Fig. 18: Example of integration of OSSDs. The wiring is to be laid down in such a
way that it is protected against mechanical effects. ............................................ 24
Fig. 19: Plug allocation for connection of the power supply and the signal cables..........25
Fig. 20: Dimension of the power supply cable.................................................................... 25
Fig. 21: Example of the power supply and grounding of stationary applications ............. 26
Fig. 22: Example of the power supply and grounding on a transport vehicle ...................26
Fig. 23: Pin allocation of the interface cable ......................................................................27
Fig. 24: Dimension of the interface cable...........................................................................27
Fig. 25: Place F3G-C1R70 on its side in the original packaging........................................ 31
Fig. 26: Place the upper membrane cushion on top of the F3G-C1R70........................... 31
Fig. 27: Put the accessories in the original packaging....................................................... 32
Fig. 28: System error indications......................................................................................... 34
Fig. 29: Dimensional drawings, safety laser scanner F3G-C1R70 .................................... 39
42
 Loading...
Loading...