Page 1

Cat. No. Z905-E1-07
DeviceNet Safety
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MANUAL
Page 2

Page 3

Page 4

Page 5

DeviceNet Safety System Configuration Manual
Revised July 2009
Page 6

iv
Page 7

Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use according to proper procedures by a qualified operator
and only for the purposes described in this manual.
The following conventions are used to indicate and classify precautions in this manual. Always heed
the information provided with them. Failure to heed precautions can result in injury to people or damage to property.
!WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in minor or
moderate injury, or may result in serious injury or death. Additionally, there may be significant property damage.
Indicates general prohibitions for which there is no specific symbol.
Indicates general mandatory actions for which there is no specific symbol.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The word “Unit” is also capitalized when it refers to
an OMRON product, regardless of whether or not it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation “PLC” means Programmable Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
IMPORTANT Indicates important information on what to do or not to do to prevent failure to
operation, malfunction, or undesirable effects on product performance.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1,2,3... 1. Indicates lists of one sort or another, such as procedures, checklists, etc.
v
Page 8

Trademarks and Copyrights
r
f
CIP, EtherNet/IP, DeviceNet and DeviceNet Safety are registered trademarks of the ODVA.
Other product names and company names in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
OMRON, 2005
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, o
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission o
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
vi
Page 9

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
1 Intended Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
4 Precautions for Safe Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xxi
SECTION 1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 DeviceNet Safety System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 Safety Network Controller Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-3 Network Configurator Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-4 Basic System Startup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
SECTION 2
Constructing a Safety Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2-1 Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
SECTION 3
Basic Operation of the Network Configurator . . . . . . . . . . 35
3-1 Network Configurator Startup and Main Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3-2 Menu List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-3 Connecting to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
3-4 Creating a Virtual Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
3-5 Saving and Reading Network Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3-6 Device Password Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3-7 Device Parameters and Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3-8 Parameter Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-9 Configuration Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3-10 Device Reset and Status Change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
SECTION 4
Editing Safety I/O Terminal Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
4-1 Editing Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
4-2 Editing Parameters for Logic Terminals (DST1-XD0808SL-1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
SECTION 5
Editing Safety Network Controller Parameters. . . . . . . . . . 115
5-1 Safety Connection Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
5-2 Safety Slave Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
5-3 Standard Slave Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
5-4 Setting the Controller as an EtherNet/IP Standard Target . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
vii
Page 10

TABLE OF CONTENTS
5-5 Local I/O Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
5-6 Setting the Operating Mode and Confirming the Cycle Time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
5-7 Extend Mode Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
5-8 Setting Maintenance Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
5-9 Displaying Memory Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
SECTION 6
Programming the Safety Network Controller . . . . . . . . . . . 157
6-1 Starting and Exiting the Logic Editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
6-2 Menu Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
6-3 Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
SECTION 7
Monitoring Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
7-1 Monitoring Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
7-2 Maintenance Functions (Unit Version 1.0 or Later) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
7-3 Displaying Safety Device Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
SECTION 8
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
8-1 Connection Status Tables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
8-2 Errors When Downloading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
8-3 Errors When Resetting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
8-4 Errors When Changing Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8-5 Errors That Can Be Found Using the Connection Check Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
SECTION 9
Maintenance Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
9-1 Overview of Maintenance Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
9-2 Starting and Exiting the Maintenance Tool and Version Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
9-3 Screen Names and Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
9-4 Setting the Monitor Refresh Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
9-5 Basic Online Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
9-6 Reading Device Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
9-7 Replacing a Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
9-8 Uploading to Individual Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
9-9 Downloading for Individual Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
9-10 Uploading (Network). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
9-11 Downloading (Network) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .266
9-12 Resetting a Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
9-13 Changing the Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
9-14 Locking/Unlocking Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
9-15 Change Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
viii
Page 11

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
ix
Page 12

Page 13

About this Manual:
This manual describes the configuration of the DeviceNet Safety system.
Please read this manual carefully and be sure you understand the information provided before
attempting to configure a DeviceNet Safety system. Be sure to read the precautions provided in the following section.
The following manuals provide information on the DeviceNet and DeviceNet Safety.
DeviceNet Safety System Configuration Manual (this manual) (Z905)
This manual explains how to configure the DeviceNet Safety system using the Network Configurator.
DeviceNet Safety NE1A Series Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z906-E1-07 or higher)
This manual describes the specifications, functions, and usage of the NE1A-series Controllers.
DeviceNet Safety I/O Terminal Operation Manual (Z904)
This manual describes the specifications, functions, and usage of the DST1 series.
DeviceNet Operation Manual (W267)
This manual describes the construction and connection of a DeviceNet network. It provides detailed
information on the installation and specifications of cables, connectors, and other peripheral equipment used in the network, and on the supply of communications power. Obtain this manual and gain a
firm understanding of its contents before using a DeviceNet system.
DeviceNet Safety Logic Simulator Operation Manual (Z910)
This manual describes the functions and operating procedures of the NE1A Logic Simulator.
DeviceNet Safety NE0A-series Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z916)
This manual describes the models, specifications, functions, and operating procedures of the NE0Aseries Safety Network Controllers.
!WARNING Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may result in per-
sonal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure. Please read each section
in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and
related sections before attempting any of the procedures or operations given.
xi
Page 14

xii
Page 15

Read and Understand this Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON
representative if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE
PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS
DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES,
LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS,
WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT
LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual price of the product on which
liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO
CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
xiii
Page 16

Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to the
combination of products in the customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying
ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a
complete determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end product, machine,
system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses
listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or
uses not described in this manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical
equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment, and installations subject to separate
industry or government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR
PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO
ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED
FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable product, or any
consequence thereof.
xiv
Page 17

Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on improvements and other
reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or features are changed, or when
significant construction changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be changed
without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix or establish key
specifications for your application on your request. Please consult with your OMRON representative at any
time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when
tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and does
not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users must
correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON Warranty and
Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate; however, no
responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
xv
Page 18

xvi
Page 19

PRECAUTIONS
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
3 Safety Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
4 Precautions for Safe Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxi
xvii
Page 20

Intended Audience 1
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must have knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of introducing FA and safety systems into production
facilities
• Personnel in charge of designing FA and safety systems
• Personnel in charge of managing FA facilities
• Personnel who have the qualifications, authority, and obligation to provide
safety during each of the following product phases: mechanical design,
installation, operation, maintenance, and disposal
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amuse-
ment machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating the Unit. Be
sure to read this manual before attempting to use the Unit and keep this manual close at hand for reference during operation.
!WARNING This is the System Configuration Manual for DeviceNet Safety Systems. Heed
the following items during system construction to ensure that safety-related
components are configured in a manner that allows the system functions to
operate sufficiently.
• Risk Assessment
The proper use of safety devices described in this Manual as it relates to
installation conditions and mechanical performance and functions is a prerequisite for their use. When selecting or using a safety device, risk assessment must be conducted with the aim of identifying potential danger factors
in equipment or facilities in which the safety device is to be applied, during
the development stage of the equipment or facilities. Suitable safety devices must be selected under the guidance of a sufficient risk assessment
system. An insufficient risk assessment system may lead to the selection
of unsuitable safety devices.
• Typical related international standards: ISO 14121, Safety of Machinery -- Principles of Risk Assessment
• Safety Measures
When using safety devices to build systems containing safety-related components for equipment or facilities, the system must be designed with the
full understanding of and conformance to international standards, such as
those listed below, and/or standards in related industries.
xviii
Page 21

General Precautions 2
• Typical related international standards: ISO/DIS 12100, Safety of Machinery -- Basic Concepts and General Principles for Design
IEC 61508, Safety Standard for Safety Instrumented Systems (Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safetyrelated Systems)
• Role of Safety Device
The safety devices are provided with safety functions and mechanisms as
stipulated in relevant standards, but suitable designs must be used to allow
these functions and mechanisms to operate properly inside system constructions containing safety-related components. Build systems that enable these functions and mechanisms to perform properly, based on a full
understanding of their operation.
• Typical related international standards: ISO 14119, Safety of Machinery -- Interlocking Devices Associated with Guards -- Principles of Design and Selection
• Installation of Safety Device
The construction and installation of systems with safety-related components for equipment or facilities must be performed by technicians who
have received suitable training.
• Typical related international standards: ISO/DIS 12100, Safety of Machinery -- Basic Concepts and General Principles for Design IEC
61508, Safety Standard for Safety Instrumented Systems (Functional
Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related
Systems)
• Complying with Laws and Regulations
The safety devices conform to the relevant regulations and standards, but
make sure that they are used in compliance with local regulations and
standards for the equipment or facilities in which they are applied.
• Typical related international standards: IEC 60204, Safety of Machinery -- Electrical Equipment of Machines
• Observing Precautions for Use
When putting the selected safety devices to actual use, heed the specifications and precautions in this Manual and those in the Operation Manuals
that comes with the products. Using the products in a manner that deviates
from these specifications and precautions will lead to unexpected failures
in equipment or devices, and to damages that result from such failures,
due to insufficient operating functions in safety-related components.
• Moving or Transferring Devices or Equipment
When moving or transferring devices or equipment, be sure to include this
Manual to ensure that the person to whom the device or equipment is being moved or transferred will be able to operate the system properly.
• Typical related international standards: ISO/DIS 12100 ISO, Safety of
Machinery -- Basic Concepts and General Principles for Design IEC
61508, Safety Standard for Safety Instrumented Systems (Functional
Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related
Systems)
xix
Page 22

Safety Precautions 3
3 Safety Precautions
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Do not use the test outputs of the products as safety outputs.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Do not use DeviceNet standard I/O data or explicit message data as safety signals.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Do not use the indicators on the products for safety operations.
Serious injury may possibly occur due to breakdown of safety outputs or test
outputs. Do not connect loads beyond the rated value to the safety outputs or
test outputs.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Wire the output lines and 24-VDC line so that they will not touch each other to
prevent a load from turning ON due to a short-circuit with the 24-VDC line.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Ground the 0-V side of the external power supply to prevent an output from turning ON due to a ground fault in a safety output or test output.
Safety functions may be impaired, and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, clear the previous configuration
data.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, configure the appropriate node
address and the baud rate.
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before operating the system, conduct user testing to confirm if the configuration data of all the devices and their operations are correct.
Safety functions may be impaired, and serious injury may occasionally occur.
When replacing a device, confirm that the replacement device is appropriately
configured and operates properly.
Serious injury may possibly occur due to loss of required safety functions. Use
appropriate components or devices according to the requirements given in the
following table.
Control device Requirements
Emergency stop switch Use approved devices with a direct opening mechanism compliant with IEC/
EN 60947-5-1.
Door interlocking switch or
limit switch
Safety sensor Use approved devices compliant with the relevant product standards, regula-
Relay with forcibly guided
contacts
Use approved devices with a direct opening mechanism compliant with IEC/
EN 60947-5-1 and capable of switching micro-loads of 4 mA at 24 VDC.
tions, and rules in the country where they are used.
Use approved devices with forcibly guided contacts compliant with EN
50205. For feedback, use devices with contacts capable of switching microloads of 4 mA at 24 VDC.
xx
Page 23

Precautions for Safe Use 4
Control device Requirements
Contactor Use contactors with a forcibly guided mechanism and monitor the auxiliary
Other devices Evaluate whether devices used are appropriate to satisfy the requirements of
NC contact to detect contactor failures. For feedback, use devices with contacts capable of switching micro-loads of 4 mA at 24 VDC.
the safety category level.
4 Precautions for Safe Use
■ Handling
Do not drop the products or subject them to excessive vibration or impact.
Doing so may result in error or malfunction.
■ Installation and Storage
Do not install or store the products in the following locations:
• Locations subject to direct sunlight
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidity outside the range specified
in the specifications
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salts
• Locations subject to water, oil, or chemicals
• Locations subject to shock or vibration outside the range specified in the
specifications
Take appropriate and sufficient measures when installing systems in the following locations. Inappropriate and insufficient measures may result in malfunction.
• Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radioactivity
• Locations close to power supplies
■ Mounting
Confirm the operating suggestions provided in the operation manual for each
product before installation and mounting.
■ Wiring
• Use the following wires to connect external I/O devices to the products.
Solid wire
Stranded
(flexible) wire
0.2 to 2.5 mm
0.34 to 1.5 mm
Stranded wires should be prepared by attaching ferrules with plastic insulation collars (DIN 46228-4 standard compatible) before
connecting them.
2
(AWG 24 to AWG 12)
2
(AWG 22 to AWG 16)
• Turn OFF the power supply before starting any wiring operations. Not
doing so may result in unexpected operation of external devices connected to the products.
• Properly apply the specified voltage to the product inputs. Applying an
inappropriate DC voltage or any AC voltage may cause reduced safety
functions, damage to the products, or a fire.
• Do not wire cables for communications and I/O signals near high-voltage
lines or power lines.
xxi
Page 24

Precautions for Safe Use 4
• Be careful not to get your fingers caught when attaching connectors to the
plugs on the products.
• Tighten the DeviceNet connector to the appropriate torque (0.25 to
0.3 N·m).
• Incorrect wiring may reduce safety functions. Perform all wiring correctly
and check operation prior to using the products.
• Remove the dust-preventive label after completing wiring to ensure
proper heat dissipation.
■ Selecting a Power Supply
Use a DC power supply satisfying the following requirements.
• The secondary circuits of the DC power supply must be isolated from the
primary circuit by double insulation or reinforced insulation.
• The DC power supply must satisfy the requirements for class 2 circuits or
limited voltage/current circuits defined in UL 508.
• The output hold time must be 20 ms or longer.
■ Periodic Inspections and Maintenance
• Turn OFF the power supply before replacing the products. Not doing so
may result in unexpected operation of external devices connected to the
products.
• Do not disassemble, repair, or modify the products. Doing so may impair
the safety functions.
■ Disposal
• If you disassemble the products for disposal, be careful not to injure yourself.
xxii
Page 25

Network Configurator Version Upgrade
Upgrade from Version 1.6@ to Version 2.2@
The WS02-CFSC1-E Network Configurator has been upgraded from version
to 2.2@. The following changes have been made in line with the upgrade.
Item Ver. 1.6 @ Ver. 2.00 Ver. 2.01 Ver. 2.1@ Ver. 2.2@
Supported Devices Added
NE1A-EDR01 --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
NE0A-SCPU01 --- --- --- Supported Supported
NE1A-SCPU01-EIP
NE1A-SCPU02-EIP
Support for multiple networks in the
same file
I/O Parameter Wizard --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Configuration checking when down-
loading to networks
Batch mode changes for multiple
devices
Batch verification for multiple devices --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Batch registration to Safety Master --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Switching the display between expan-
sion and standard parameters on
DST1-series setting displays
Connection replacement --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
I/O connection batch replacement --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Device connection configuration dis-
play
Saving and reading design data for
individual networks in files
Moving network tabs --- --- Supported Supported Supported
Automatic update of the user-defined
function blocks
Setting parameters used in userdefined function blocks
Moving and saving connection positions
Improved method for changing the
number of function block I/O
Copying and pasting between different
programs
Page name printing at program printing
Applicable OS Windows 2000
Changes to restrictions when a network configuration file is opened in
Protect Mode (Downloading (when
changing parameters), resetting, locking and unlocking, and changing
modes are supported.)
Batch saving of device parameter files
with multiple devices selected
Displaying countermeasures in the
error history monitor
--- --- --- --- Supported
Network Setting Function
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- --- Supported Supported Supported
Programming Functions
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- --- Supported Supported Supported
Other Functions
Windows 2000
Windows XP
--- --- --- --- Supported
--- --- --- --- Supported
--- --- --- --- Supported
Windows XP
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows VISTA
xxiii
Page 26

Unit Versions of NE1A-series Controllers
Checking the Unit Version
A “unit version” has been introduced to manage NE1A-series Safety Network
Controllers according to differences in functionality accompanying Unit
upgrades, even though the model numbers are the same.
The unit version can be checked on the product itself or using the Network
Configurator.
Note The Network Configurator maintains a revision number to manage device
functions for DeviceNet and EtherNet/IP. Refer to “Checking the Unit Version
with the Network Configurator” on page xxiv for the relationship between
NE1A-series Controller unit versions and the revisions.
Checking the Unit
Version on the Product
Nameplate
The unit version (Ver. @.@) is listed near the lot number on the nameplate of
the products for which unit versions are being managed, as shown below.
• The unit versions of the NE1A-SCPU01, NE1A-SCPU02, NE1A-SCPU01EIP, and NE1A-SCPU02-EIP Controllers begin from Ver. 1.0.
• Controllers that do not have a unit version listed on the label are called
Pre-Ver. 1.0 Controllers.
Product Nameplate
The unit version is listed here.
(Example: Ver. 1.0)
Checking the Unit
Version with the
Network Configurator
xxiv
The following procedure can be used to check the unit version from the Network Configurator Ver. 1.6 or higher.
1. Select Network - Upload to upload the configuration information.
Page 27
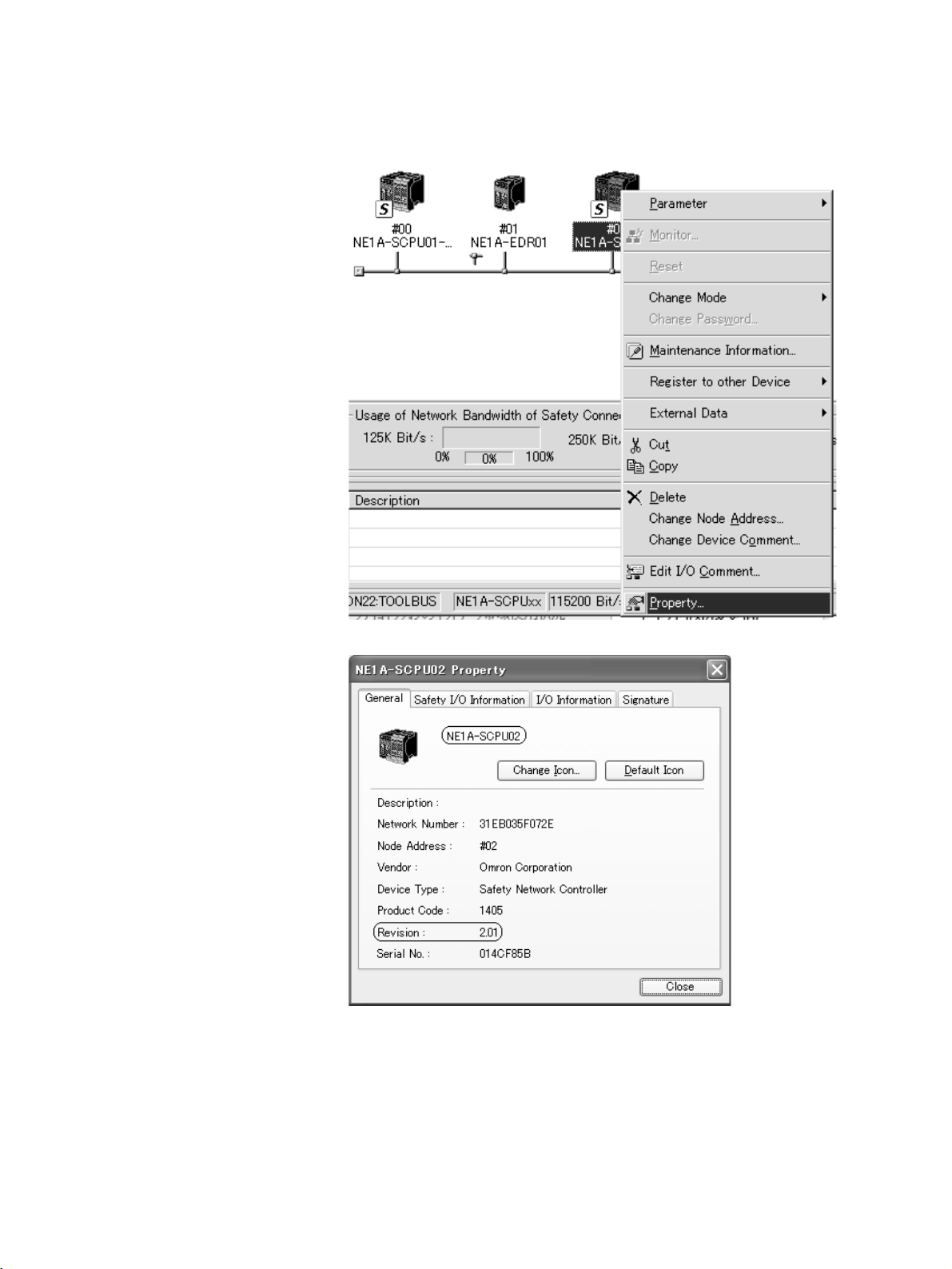
2. Right-click on the Controller's icon to display the popup menu shown below.
Select Property from the menu.
The Controller's Property Window will be displayed.
The Controller's model number (device name) and revision are displayed
in the Property Window. The NE1A-series Controllers supported by Network Configurator version 2.0@ are listed in the following table.
xxv
Page 28

• CPU Units without EtherNet/IP
Model Device name Revision Unit version
NE1A-SCPU01 NE1A-SCPU01 1.01 Pre-Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1 NE1A-SCPU01-V1 1.01 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1 NE1A-SCPU01-V1 2.01 2.0
NE1A-SCPU02 NE1A-SCPU02 1.01 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02 NE1A-SCPU02 2.01 2.0
• CPU Units with EtherNet/IP
Model Device name Revision Unit version
NE1A-SCPU01-EIP NE1A-SCPU01-EIP 1.01 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02-EIP NE1A-SCPU02-EIP 1.01 1.0
Checking the Unit Version on the Product Nameplate
The following unit version labels are provided with the Controller.
These labels can be attached to the front of the Controllers to differentiate
between Controllers with different unit versions from the front of the Controller.
xxvi
Page 29

Function Support by Unit Version
Model NE1A-SCPU01 NE1A-SCPU01-V1NE1A-SCPU02 NE1A-
Unit version
Function
Logic operations
Maximum program size
(total number of function blocks)
Added function blocks
• RS Flip-flop
• Multi Connector
•Muting
• Enable Switch
• Pulse Generator
• Counter
• Comparator
Selection of the rising edge of the reset
condition for the Reset and Restart
Function Blocks
Use local I/O status in logic programming
Use the Unit's general status in logic
programming
Program execution delay --- Supported
I/O control functions
Contact Operation Counter --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Total ON Time Monitor --- Supported Supported Supported Supported
DeviceNet communications functions
Number of safety I/O connections at the
Safety Master
Selection of operation of safety I/O
communications after a communications error
Add local output status to send data
during Slave operation.
Add local input monitoring to send data
during Slave operation.
Communications with devices on other
networks (off-link connections)
Functions supporting system startup and error recovery
Saving non-fatal error history in non-
volatile memory
Added function block errors to error his-
tory.
EtherNet/IP communications
I/O communications --- --- --- Supported Supported
Message communications --- --- --- Supported Supported
Routing between DeviceNet and EtherNet/IP
I/O routing --- --- --- Supported Supported
Message routing --- --- --- Supported Supported
Pre-Ver. 1.0 Ver. 1.0/Ver. 2.0 Ver. 1.0/Ver. 2.0 Ver. 1.0 Ver. 1.0
128 254 254 254 254
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
Supported
(Unit version 2.0
only)
16 32 32 32 32
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported
(Unit version 2.0
only)
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
--- Supported Supported Supported Supported
(Unit version 2.0
only)
Supported
(Unit version 2.0
only)
SCPU01-
EIP
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
NE1A-
SCPU02-
EIP
xxvii
Page 30

Unit Versions and Programming Devices
Network Configurator version 2.0@ or higher must be used when using a
NE1A-SCPU01-V1 or NE1A-SCPU02 Safety Logic Controller with unit version 2.0.
Network Configurator version 2.2@ or higher is required to use the NE1ASCPU01-EIP or NE1A-SCPU02-EIP.
The following table shows the relationship between unit versions and Network
Configurator versions.
Model number Network Configurator
Ver. 1.3@ Ver. 1.5 @ Ver. 1.6@ Ver. 2.0@/2.1@ Ver. 2. 2@
NE1A-SCPU01
Pre-Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1
Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02
Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1
Ver.2. 0
NE1A-SCPU02
Ver.2. 0
NE1A-SCPU01-EIP Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used.
NE1A-SCPU02-EIP Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used.
Can be used. Can be used. Can be used. Can be used. Can be used.
Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used. Can be used. Can be used.
Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used. Can be used. Can be used.
Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used.
(See note.)
Cannot be used. Cannot be used. Can be used.
(See note.)
Can be used. Can be used.
Can be used. Can be used.
Note Can be used as a Safety Logic Controller with unit version 1.0.
Note (1) Network Configurator version 1.5@ or lower can be upgraded to version
1.6@ free of charge.
(2) When using Network Configurator version 1.6@, there are no operational
differences in the NE1A-SCPU01-V1 and NE1A-SCPU02 Safety Logic
Controllers that derive from the unit version.
Unit Versions and Configuration Data
The following table shows the relationship between unit versions of NE1Aseries Controllers in network configuration files created with Network Configurator version 2.2@ and the unit version of NE1A-series Controllers to which
configuration files are downloaded.
Unit versions of NE1A-
series Controllers in
Network configuration
files created with
Network Configurator
version 2.2@
Pre-Ver. 1.0 CPU Unit Downloading is possi-
CPU Unit with unit version 1.0 that does not
support EtherNet/IP
CPU Unit with unit version 2.0
CPU Unit with unit version 1.0 that supports
EtherNet/IP
Pre-Ver. 1.0 CPU
ble.
Not possible. Downloading is possi-
Not possible. Not possible. Downloading is possi-
Not possible. Not possible. Not possible. Downloading is possi-
NE1A-series Controller to which configuration file is downloaded
Unit
CPU Unit with unit
version 1.0 that does
not support
EtherNet/IP
Not possible. (See
note 1.)
ble.
CPU Unit with unit
version 2.0
Not possible. (See
note 1.)
Downloading is possible. (See note 2.)
ble.
CPU Unit with unit
version 1.0 that
supports EtherNet/
IP
Not possible. (See
note 1.)
Not possible. (See
note 1.)
Not possible. (See
note 1.)
ble.
xxviii
Note (1) Downloading is possible if the device type is changed using the function
provided in Network Configurator version 2.2@. For details, refer to “Converting Systems to New Versions of the NE1A Controller” on page xxix.
Page 31

(2) Only functions CPU Units with unit version 1.0 can be used.
Note The Configuration data created with unit version 1.0 can be downloaded to a
NE1A-series Controller with unit version 2.0. The data will be subsequently
treated as unit version 2.0 data if it is uploaded.
Converting Systems to New Versions of the NE1A Controller
Functions are added and functionality is expanded in various ways for the
NE1A-series Controllers. The device type in an existing network configuration
file can be changed to a higher version so that the new functionality can be
used.
The following table shows the NE1A-series Control device types in network
configuration files and the device types that they can be upgraded to.
Device type before
change
NE1A-SCPU01
Pre-Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1
Unit Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02
Unit Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1
Unit Ver. 2.0
NE1A-SCPU02
Unit Ver. 2.0
NE1A-SCPU01-EIP
Unit Ver. 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02-EIP
Unit Ver. 1.0
Device type after change
NE1A-SCPU01-V1 NE1A-SCPU02 NE1A-
SCPU01-EIP
Un it Ver. 1. 0 Un it Ver. 2. 0 Unit Ver. 1. 0 Un it Ver. 2. 0 Un it Ver. 1.0 Un i t Ver. 1.0
OK OK OK OK OK OK
--- OKOKOKOKOK
Not possible Not possible --- OK Not possible OK
Not possible --- Not possible OK OK OK
Not possible Not possible Not possible --- Not possible OK
Not possible Not possible Not possible Not possible --- OK
Not possible Not possible Not possible Not possible Not possible ---
NE1A-
SCPU02-EIP
1. Read the configuration data.
Use the following procedure to read the configuration data with Network
Configurator version 1.6@ or higher.
• Read configuration data that has been saved on the computer.
• Upload the configuration data from the network devices.
The display should appear as follows after then data has been read:
2. Convert the configuration data.
In the network configuration, right-click the NE1A-SCPU01 data to be con-
verted to NE1A-SCPU01-V1 or NE1A-SCPU02 data and select Change
Device Type from the pop-up menu.
xxix
Page 32

Select the device to which the data is to be converted in the New Device Field
and click the OK Button.
The data will be converted to configuration data for the new devices and the
model given on the display will change.
3. Expansion Functions
All the configuration data for the expansion functions will be set to the de-
fault settings. Change these settings as required for any expansion functions that are to be used.
xxx
Note (1) When changing the device type using Network Configurator version
1.6@, open the Edit Device Parameters Dialog Box of the Controller, select a connection on the Safety Connection Tab Page, and click the Up-
date Button.
(2) When changing the device type using Network Configurator version 2.@
or higher, the connection information will be updated automatically.
Page 33

Note Data cannot be converted to a lower version, such as from unit version 2.0 to
unit version 1.0.
Precautions Updating from Network Configurator Version 1.3@ to a Higher Version
Data Compatibility
Data created using Network Configurator version 1.3@ can be used with a
higher version without any problems if converted as outlined below. Data created with higher versions cannot be used with lower versions; the data upload
from the device will fail when loading the project file.
Procedure for Converting Data from Version 1.3@ to a Higher Version
Version 1.5@ and higher have improved safety check functions, so
version programs from lower versions will need to be checked for
safety. Use the following procedure to check programs.
a. Click the Logic Tab on the Edit Device Parameters Window of the
NE1A-series Controller and click the Edit Button to start the Logic Editor.
b. Select Edit - Find Function Blocks with Open Connections to
check that all function block I/O have connections.
c. Select File - Apply to save the logic program then exit the editing of
the logic program.
d. Return to the NE1A-series Controller's Edit Device Parameters Win-
dow and click the OK Button.
Note Data created using version 1.3@ cannot be monitored online.
Always convert the data to version 1.5@ and download it before
monitoring online.
Handling Function Blocks with Open I/O Connections
Function block outputs with open connections in version 1.3@ data could still
be downloaded (see following diagram).
Download cannot be executed with version 1.5@ or higher, however, if there
are outputs with open connections (to improve the program validity).
For this reason, data created using version 1.3@ cannot be downloaded as is
for use with version 1.5@ or higher. If open connections exist in version 1.3@
data, use the Search Open Connection function and use the Set Output Point
Tab Page in the Safety Gate Monitoring Window for the function block with
open connections to disable the outputs or connect the open connections to
output I/O tags.
Open connection
Note Versio ns 1.5@ and higher have functions for creating text boxes on program
screens and changing the I/O tag color. The text box and I/O color data is not
xxxi
Page 34

saved to the NE1A-series Controller, however, during download. For this reason, text box and I/O tag color data is not restored when the program is
uploaded.
xxxii
Page 35

1-1 DeviceNet Safety System Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-1 About DeviceNet Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 Safety Network Controller Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-2-1 About the NE1A-series Safety Network Controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-2-2 NE1A Series Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-2-3 Standard Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-3 Network Configurator Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-3-1 About the Network Configurator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-3-2 Network Configurator Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-3-3 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-3-4 Standard Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-4 Basic System Startup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-4-1 System Design and Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-4-2 Installation and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1-4-3 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1-4-4 User Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
SECTION 1
Overview
1
Page 36

DeviceNet Safety System Overview Section 1-1
1-1 DeviceNet Safety System Overview
1-1-1 About DeviceNet Safety
DeviceNet is an open-field, multi-vendor, multi-bit network, which combines
the controls in the machine and line control levels with information. The
DeviceNet Safety network adds safety functions to the conventional standard
DeviceNet communications protocol. The DeviceNet Safety concept has been
approved by a third-party organization (TÜV Rhineland).
Just as with DeviceNet, DeviceNet Safety-compliant devices from third-party
vendors can be connected to a DeviceNet Safety network. Also, DeviceNetcompliant devices and DeviceNet Safety-compliant devices can be combined
and connected on the same network.
By combining DeviceNet Safety-compliant products, a user can construct a
safety control/network system that meets the requirements for Safety Integrity
Level (SIL) 3 according to IEC 61508 (Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems) and the requirements for Safety Category 4 according to EN 954-1.
Safety Control performed by the
Safety Network Controller
Safety remote I/O communications
-
Safety Network Controller
-
Safety Master functions
-
Standard Slave functions
Safety communications
Safety I/O Terminal
-
Safety Slave functions
-
Standard Slave functions
Network Configurator
Safety
configuration
Safety Network Controller
-
Safety Slave functions
-
Standard Slave functions
Standard Control and Monitoring by
the Standard PLC
-
-
Standard
configuration
Standard communications
Standard remote I/O communications
Explicit message communications
Standard PLC and Master
Standard Slave
2
Page 37

Safety Network Controller Overview Section 1-2
1-2 Safety Network Controller Overview
1-2-1 About the NE1A-series Safety Network Controllers
The NE1A-series Safety Network Controllers provide various functions, such
as safety logic operations, safety I/O controls, and a DeviceNet Safety protocol. The NE1A-series Controllers allow the user to construct a safety control/
network system that meets the requirements for Safety Integrity Level (SIL) 3
according to IEC 61508 (Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/ Program-
mable Electronic Safety-related Systems) and the requirements for Safety
Category 4 according to EN 954-1.
In the example system shown below, the safety control system implemented
with the NE1A-series Controller and the monitoring system implemented with
the standard PLC are realized on the same network.
• As a Safety Logic Controller, the NE1A-series Controller executes safety
logic operations and controls local I/O.
• As a Safety Master, the NE1A-series Controller controls the remote I/O of
Safety Slaves.
• As a Standard Slave, the NE1A-series Controller communicates with the
Standard Master.
Safety Logic Operations
and Safety I/O Control
PLC
DeviceNet Standard Master
DeviceNet
Standard Slave
The NE1A PLC system monitors the
SNC (i.e., the safety control system)
using DeviceNet I/O communications
and explicit messages.
Network Configurator
SNC
DRT1-series
DeviceNet Safety Slave
Safety-related Control Non-safety-related Control
The DeviceNet Safety
System controls remote I/O.
3
Page 38

Safety Network Controller Overview Section 1-2
1-2-2 NE1A Series Features
Safety Logic Operations
In addition to basic logic functions, such as AND and OR, the NE1A-series
Controllers also support application function blocks, such as Emergency Stop
Pushbutton Monitoring and Safety Gate Monitoring, that enable various safety
applications.
User-defined Function Blocks
Previously prepared logic functions and function blocks can be combined to
create a user-defined function block using the Network Configurator version
1.5@ or higher. This can be used to standardize functions that are used frequently to facilitate reusing them. Passwords can also be used to protect the
programming inside the function blocks by making them “black boxes.”
Local Safety I/O
• A total of 24 local safety I/O points are supported by NE1A-SCPU01(V1)(-EIP): 16 input terminals and 8 output terminals.
• A total of 48 local safety I/O points are supported by NE1A-SCPU02(EIP): 40 input terminals and 8 output terminals.
• Faults in external wiring can be detected.
• Dual Channel Mode can be set for pairs of related local inputs.
When Dual Channel Mode is set, the NE1A-series Controller can evaluate
the input data patterns and the time discrepancy between input signals.
• Dual Channel Mode can be set for pairs of related local outputs. When
Dual Channel Mode is set, the NE1A-series Controller can evaluate the
output data patterns.
DeviceNet Safety Communications
• As a Safety Master, a Pre-Ver. 1.0 NE1A-series Controller can perform
safety I/O communications with up to 16 connections using up to 16 bytes
per connection.
• As a Safety Master, any NE1A-series Controller other than a Pre-Ver. 1.0
NE1A-series Controller can perform safety I/O communications with up to
32 connections using up to 16 bytes per connection.
• As a Safety Slave, the NE1A-series Controller can perform safety I/O
communications with a maximum of four connections using up to 16 bytes
per connection.
DeviceNet Standard Communications
As a Standard Slave, the NE1A-series Controller can perform standard I/O
communications with one Standard Master for up to two connections using up
to 16 bytes per connection.
EtherNet/IP Standard Communications (Controllers that Support EtherNet/IP Only)
As an EtherNet/IP Target, the NE1A-series Controller can perform standard
I/O communications with one EtherNet/IP originator for up to two connections
using up to 16 output bytes and 128 input bytes per connection.
Disabling DeviceNet Communications (Standalone)
An NE1A-series Controller can be used as a Standalone Controller by using a
setting to disable the Controller's DeviceNet communications.
Configuration with a Graphical Tool
• A graphical tool is provided for both network configuration and logic pro-
4
gramming. It enables easy configuration and programming.
Page 39

Safety Network Controller Overview Section 1-2
• A Logic Editor can be activated from the Network Configurator.
• Configuration data can be downloaded and uploaded, and devices can be
monitored online via DeviceNet, USB, or EtherNet/IP.
System Startup and Error Recovery Support
• Error information can be checked by using the error history or the indicators on the front of the NE1A-series Controller.
• The NE1A-series Controller’s internal status information can be monitored from a standard PLC by allocating the information in the Standard
Master. In the same way, the information can be monitored from a safety
PLC by allocating the information in the Safety Master.
• The NE1A-series Controller's internal status information can be monitored from a standard PLC by allocating the information in an EtherNet/IP
Originator.
Access Control with a Password
• NE1A-series Controller configuration data is protected by a password.
• Network configuration files (project files) created with the Network Configurator are also password protected.
• Programs and user-defined function blocks can be password-protected
using the Network Configurator version 1.5@ or higher.
1-2-3 Standard Models
Normal Controllers
Model number Name Number of I/O points
Safety inputs Test outputs Safety outputs
NE1A-SCPU01 Safety Network Controller 16 inputs 4 outputs 8 outputs
NE1A-SCPU01-V1, unit
version 1.0
NE1A-SCPU02,
unit version 1.0
NE1A-SCPU01-V1, unit
Ver.2. 0
NE1A-SCPU02, unit
Ver.2. 0
Controllers That Support EtherNet/IP
Model number Name Number of I/O points
NE1A-SCPU01-EIP Safety Network Controller 16 inputs 4 outputs 8 outputs
NE1A-SCPU02-EIP Safety Network Controller 40 inputs 8 outputs 8 outputs
Safety Network Controller 16 inputs 4 outputs 8 outputs
Safety Network Controller 40 inputs 8 outputs 8 outputs
Safety Network Controller 16 inputs 4 outputs 8 outputs
Safety Network Controller 40 inputs 8 outputs 8 outputs
Safety inputs Test outputs Safety outputs
5
Page 40

Network Configurator Overview Section 1-3
1-3 Network Configurator Overview
1-3-1 About the Network Configurator
The WS02-CFSC1-E Network Configurator Support Software is used to configure, set, and manage a DeviceNet Safety network with graphical window
operations.
The Network Configurator can be used to configure a virtual DeviceNet Safety
network (in the Network Configuration Window) and monitor the configuration
and parameters of each safety device and standard device.
1-3-2 Network Configurator Features
Compliant with Standard and Safety DeviceNet Networks
The Network Configurator can configure and monitor devices that support
DeviceNet Safety or EtherNet/IP as well as existing standard DeviceNet
devices. It can thus support building systems for standard control, safety control, or mixed standard/safety control.
Multiple Network Configurations Supported (Version 2.0@ or Later)
Multiple DeviceNet network configurations can be made in one project. Starting with version 2.2@, it is also possible to build multiple EtherNet/IP networks
in one project.
Safety Network Controller Programming
The Network Configurator provides built-in programming tools for the safety
logic of the NE1A-series Controllers and thus enables building DeviceNet
Safety applications using only the Network Configurator.
• Previously prepared function blocks can be incorporated in logic.
AND/OR and other logic functions and emergency stop button/safety
door/light curtain monitoring, and other previously prepared function
blocks can be selected from the function block list and placed in the Workspace to create software connections in the logic of the Network Controller.
6
Page 41

Network Configurator Overview Section 1-3
• User-defined function blocks can be easily created and reused using the
Network Configurator version 1.5@ or higher.
New user-defined function blocks can be created. These can be used
simply by selecting them from the function block list and placing them in
the Workspace. Created user-defined function blocks can be saved to file
and installed on another computer to use with the Network Configurator
on that computer.
• Editing of user-defined function blocks can be password-protected.
Upward Compatibility with DeviceNet Configurator
All the functions of DeviceNet Configurator are supported. Also, all of the files
created by the DeviceNet Configurator can be used as they are.
1-3-3 System Requirements
The following computer system is required in order to use the Network Configurator.
Item Requirement
OS (English or
Japanese)
Computer IBM PC/AT or compatible with a
Memory At least 256 MB of physical
Hard disk At least 200 MB of available space is required.
Monitor Monitor with a high-resolution display of SVGA 800 x 600 or bet-
Disk drives CD-ROM drive
Communications
port for connection
Microsoft Windows 2000 (Service Pack 3 or higher) or XP
Pentium II 333-MHz processor
or better
A Pentium III 1-GHz processor
is recommended.
memory is required.
At least 512 MB is recom-
mended.
ter and at least 256 colors
At least one of the following communications ports is required.
• USB port: To go via a NE1A-series or NE0A-series USB port
(USB 1.1).
• Ethernet port: To online via Ethernet.
• DeviceNet Interface Card (3G8F7-DRM21 or 3G8E2-DRM21V1): To go online via DeviceNet.
Note At least one USB port is required as the communications
port of the Maintenance Tool.
Microsoft Windows Vista
(except for 64-bit version)
IBM PC/AT or compatible with a
processor recommended by
Microsoft
A speed of 1 GHz or higher is
recommended.
At least 512 MB of physical
memory is required.
At least 1 GB is recommended.
1-3-4 Standard Models
Model number Name Component Compatible
WS02-CFSC1-E
(Version 2.2@)
Network Configurator Installation disk
(CD-ROM)
IBM PC/AT or compatible
OS
computer
Windows 2000 or
Windows XP
Windows Vista (Network
Configurator version 2.2@
or higher)
7
Page 42

Basic System Startup Procedure Section 1-4
1-4 Basic System Startup Procedure
This manual introduces the basic steps that are needed to make the safety
system operational, with particular focus on the following steps.
• System Design and Programming
• Configuration
• User Test
1. System Design
&
Programming
2. Installation and Wiring
3. Configuration
4. User Test
1-4-1 System Design and Programming
In this step, the optimum safety system is determined by the following procedures:
1. Based on the required safety system specifications, select and arrange the
safety devices and determine the safety functions to be allocated to each
device.
2. Configure the network system as a virtual network in the Network Configurator.
• Register all of the devices. If the system is a mixed safety control and
standard control system, register both the safety devices and standard
devices.
• Set the parameters of all the devices.
• Check the percentage of the network bandwidth being used and review the parameters.
• Create the program for the NE1A-series Controller.
• Verify the system reaction time of all the safety chains.
The network bandwidth usage and the system reaction time are affected by
several factors, including the network configuration, NE1A-series Controller
and Safety I/O Terminal parameter settings, and NE1A-series Controller program, so repeat the steps above to determine a system configuration which
meets the users’ requirements.
Please refer to the following sections for the operating instructions of the Network Configurator.
• Device Registration
Refer to 3-4 Creating a Virtual Network.
5. System Operation
8
Page 43

Basic System Startup Procedure Section 1-4
• Editing Device Parameters
Refer to 3-7 Device Parameters and Properties.
Refer to SECTION 5 Editing Safety Network Controller Parameters.
• Checking the Usage Rate of Network Bandwidth
Refer to 2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the
Best EPI.
• Calculating the Reaction Time
Refer to 2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time.
IMPORTANT Allocate a unique safety network number to each safety network or safety
subnetwork.
1-4-2 Installation and Wiring
In this step, install and wire each device as shown below:
• Install all of the devices and set node addresses and baud rates.
• Connect to I/O devices.
• Wire the power supplies.
• Wire the DeviceNet.
• Wire the USB.
• Wire the EtherNet/IP.
Please refer to the following related manuals for details:
Item Manual name Cat. No.
DeviceNet installation DeviceNet Operation Manual W267
EtherNet/IP installation DeviceNet Safety System Configuration
NE1A-series Controller installation
DeviceNet Safety I/O Terminal
installation
Installation of other devices Operation manual for each device ---
Manual
DeviceNet Safety Safety Network Controller
Operation Manual
DeviceNet Safety I/O Terminal Operation
Manual
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, clear the previous configuration
data.
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, set the appropriate node address
and baud rate.
Z905
Z906
Z904
9
Page 44

Basic System Startup Procedure Section 1-4
1-4-3 Configuration
In this step, transfer the parameters for each device created by the Network
Configurator to the actual device to make the system operative.
Use the Network Configurator to perform the following operations:
1. Download
The parameters set in the Network Configurator's virtual network are transferred to the actual device and stored in each device.
2. Verification
Verify the safety device settings.
The user confirms that the parameters and safety signatures stored in
each device are correct.
Please refer to the following sections for the operating instructions of the Network Configurator.
• Download
Refer to 3-7 Device Parameters and Properties.
• Verification
Refer to 3-8 Parameter Verification.
IMPORTANT • After downloading the device parameters, verify the parameters to con-
firm that the parameters and the safety signature saved in the devices are
correct.
• When selecting Open Only in the Open Type setting for the safety connection, check that the Safety Master and Safety Slave are correctly configured.
1-4-4 User Test
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before operating the system, perform user testing to confirm that the configuration data of all the devices is correct and that they are operating correctly.
IMPORTANT • After configuring all the devices, user testing must be performed to check
In this step, the user himself confirms the program operation and performs
functional tests.
Always perform the user test, because it is the user’s responsibility to verify
the system operation. The user test verifies the correctness of all parameters
downloaded to each safety device, as well as each device’s safety signature.
To demonstrate that all parameters and safety signatures are correct after
completing the user test, perform a Configuration Lock operation on all of the
safety devices.
Refer to 3-9 Configuration Lock for details on performing a Configuration Lock
from the Network Configurator.
!WARNING
if the configuration data and device operation of each device are correct.
User testing is performed to verify the safety signature for each device.
• The configuration must be locked after the user testing has completed.
10
Page 45

Constructing a Safety Network
2-1 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-1-1 Establishing a New Safety Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-1-2 Changing an Established Safety Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI . . . . . . 19
2-2-1 Checking the Network Bandwidth Used for Safety
I/O Communications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2-2-2 Displaying Device Bandwidth Usage Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2-2-3 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage Rates and
Calculating Best EPI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2-2-4 Example of EPI Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-3-1 Concept of Reaction Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-3-2 Calculating the Maximum Reaction Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2-3-3 Verifying the Maximum Reaction Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
SECTION 2
11
Page 46

Applications Section 2-1
2-1 Applications
This section describes how to construct a DeviceNet Safety Network in the
following two cases.
1. Establishing a new Safety Network
2. Changing an established Safety Network
2-1-1 Establishing a New Safety Network
This section describes the procedure for establishing a system by designing a
new Safety Network using the Network Configurator and then downloading
the parameters to the network devices.
System Design and Programming
1. Starting the Network Configurator
Start the Network Configurator.
Refer to 3-1-1 Starting and Exiting the Network Configurator.
2. Creating the Virtual Network
Create the virtual network by adding a device from the Hardware List. If the
user is to specify the network number, set the network number as well.
Refer to 3-4 Creating a Virtual Network.
3. Editing and Programming Device Parameters
Set the parameters of the NE1A-series Controller configured in the virtual
network.
Refer to SECTION 5 Editing Safety Network Controller Parameters
and to the Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z906).
Program the NE1A-series Controllers configured in the virtual network.
Refer to SECTION 6 Programming the Safety Network Controller and
to the Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z906).
4. Verifying the Network Bandwidth to Use
Confirm that the bandwidth used in the safety I/O communications does
not exceed the acceptable bandwidth in the network. If exceeded, re-examine the procedure from network configuration in step 2.
Refer to 2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the
Best EPI.
5. Calculating and Verifying the Maximum Reaction Time
Calculate the maximum reaction time of all the safety chains and check if
the requirement specifications are met. If the requirement specifications
are not met, re-examine the procedure from network configuration in step
2.
Refer to 2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time.
6. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the network configuration file with the completed design.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
7. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
The following operations are performed by connecting the Network Config-
urator to the network after the network installation and wiring.
12
IMPORTANT Allocate a unique safety network number to each safety network or safety
subnetwork.
Page 47

Applications Section 2-1
Configuration
8. Starting the Network Configurator and Connecting to the Network
Start the Network Configurator and connect it to the network via the USB
port on the NE1A-series Controller or via DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP.
Refer to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
9. Reading the Network Configuration File
Read the saved network configuration file with the completed design.
Refer to 3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File.
10. Resetting a Device
When changing the configuration because of user testing results or when
downloading the parameters again, it is necessary to clear the previous
configuration before downloading the new parameters. Reset the device by
setting the reset type to Return to the out-of-box configuration, and then
emulate cycling power.
Refer to 3-10-2 Resetting Devices.
11. Downloading Device Parameters
Download the parameters to all the devices.
Refer to 3-7-3 Downloading Device Parameters.
12. Confirming the Downloaded Device Parameters and Safety Signatures
Verify the parameters for all the devices and check if the device parameters
and program that the user input have been correctly downloaded and
saved in the devices.
Refer to 3-8 Parameter Verification.
13. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the network configuration file in which parameter verification of all the
devices has been completed.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
14. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
User Testing
IMPORTANT • After downloading the device parameters, verify the parameters to con-
firm that the parameters and the safety signature saved in the devices are
correct.
• When selecting Open Only in the Open Type setting for the safety connection, check that the Safety Master and Safety Slave are correctly configured.
15. User Testing
The user himself must verify device parameters and operation to confirm
that safety system requirement specifications are met.
16. Starting the Network Configurator and Connecting to the Network
Start the Network Configurator and connect it to the network via the USB
port on the NE1A-series Controller or via DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP. Refer
to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
17. Reading the Network Configuration File
Read the saved network configuration file with parameters that are already
verified.
13
Page 48

Applications Section 2-1
Refer to 3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File.
18. Configuration Lock
Lock the configuration of all the devices to indicate that they have been verified as well as to prevent parameters from being mistakenly rewritten.
Refer to 3-9-1 Locking the Device Configuration.
19. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the network configuration file of the virtual network in which the configuration is locked.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
20. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before operating the system, perform user testing to confirm that the configuration data of all the devices is correct and that they are operating correctly.
IMPORTANT • After configuring all the devices, user testing must be performed to check
if the configuration data and device operation of each device are correct.
User testing is performed to verify the safety signature for each device.
• The configuration must be locked after the user testing has completed.
Running the System
21. Running the System
Run the system.
14
Page 49

Applications Section 2-1
2-1-2 Changing an Established Safety Network
This section describes procedure to change the Safety Network after the system is running.
Changing the System
1. Stopping the System
Turn OFF the power supplies to moving parts, such as motors, and stop
the system. Continue supplying power to the network and the NE1A-series
Controller.
2. Starting the Network Configurator and Connecting to the Network
Start the Network Configurator and connect it to the network via the USB
port on the NE1A-series Controller or via DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP.
Refer to 3-1-1 Starting and Exiting the Network Configurator and 3-3
Connecting to the Network.
3. Uploading the Network Configuration
Upload the network to obtain the current network configuration.
Refer to 3-4 Creating a Virtual Network.
4. Unlocking the Configurations
Unlock the configurations of all the devices to enable changing the network
configuration.
Refer to 3-9-2 Unlocking the Device Configuration.
5. Resetting a Device
Before changing device parameters and node address, clear the configuration of the device. Reset the device by setting the reset type to Return to
the out-of-box configuration, and then emulate cycling power.
Refer to 3-10-2 Resetting Devices.
6. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
7. Changing the System
Change the network, wiring, and node addresses and add or delete devices according to the specified system changes. Safety devices that are being newly added must be configured in advance.
Refer to 3-10-2 Resetting Devices.
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, clear the previous configuration
data.
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before connecting a device to the network, set the appropriate node address
and baud rate.
Note There is no need to use the saved network configuration file, because the pur-
pose of this procedure is to unlock the device configurations and reset devices
to the default configurations.
15
Page 50

Applications Section 2-1
Redesigning the System
8. Starting the Network Configurator
Start the Network Configurator to redesign the network.
9. Reading the Network Configuration File
Read the saved network configuration file with a locked configuration.
Refer to 3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File.
10. Changing the Virtual Network
Add or delete the devices and change the node addresses according to
specified changes.
Refer to 3-4 Creating a Virtual Network.
11. Changing the Device Parameters and Program
Set and change the parameters of the NE1A-series Controllers configured
in the virtual network according to specified changes.
Refer to SECTION 5 Editing Safety Network Controller Parameters
and to the Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z906).
Create and change the programs of the NE1A-series Controllers configured in the virtual network according to specified changes.
Refer to SECTION 6 Programming the Safety Network Controller and
to the Safety Network Controller Operation Manual (Z906).
12. Verifying the Network Bandwidth to Use
Confirm that the bandwidth used in the safety I/O communications does
not exceed the acceptable bandwidth in the network. If exceeded, re-examine the specified changes.
Refer to 2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the
Best EPI.
13. Recalculating and Verifying the Maximum Reaction Time
Calculate the maximum reaction time of all the safety chains and check if
the requirement specifications are met. If the requirement specifications
are not met, re-examine the specified changes.
Refer to 2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time.
14. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the network configuration file with the completed changes.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
15. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
The following operations are performed by connecting the Network Config-
urator to the network after the actual system changes have been completed.
16
IMPORTANT • Allocate a unique network number when establishing a network or sub-
network.
• If the parameters of a Safety Slave or Standard Slave are changed, the
parameter information will not match in the Safety Master or Standard
Master in which the Slave is registered. Therefore, a yellow [ ! ] symbol
will be displayed next to the slave icon. If this symbol is displayed, check
the slave information by opening the Edit Parameter Window of the Master. Allocate a unique network number when establishing a network or
subnetwork with Safety Slaves.
Page 51

Applications Section 2-1
Note If device parameters with a locked configuration are changed, the color of the
key icon will change to yellow.
Re-configuration
16. Starting the Network Configurator and Connecting to the Network
Start the Network Configurator and connect it to the network via the USB
port on the NE1A-series Controller or via DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP.
Refer to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
17. Reading the Network Configuration File
Read the saved network configuration file with the completed design
changes.
Refer to 3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File.
18. Downloading Device Parameters
Download the parameters to all the devices.
Refer to 3-7-3 Downloading Device Parameters.
19. Confirming the Downloaded Device Parameters and Safety Signature
Verify the parameters for all devices with an icon indicating pre-verification
and check if the device parameters and program that the user input are
correctly downloaded and saved to the devices.
Refer to 3-8 Parameter Verification.
20. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the configuration file for a network in which parameter verifications of
all the devices have been completed.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
21. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
IMPORTANT • After downloading the device parameters, verify the parameters to con-
Note • In the Network Configuration Pane, the device will be displayed as
Additional User Testing
firm that the parameters and the safety signature saved in the device are
correct.
• When selecting Open Only in the Open Type setting for the safety connection, check that the Safety Master and Safety Slave are correctly configured.
locked, but the actual device has already been unlocked. Therefore, the
parameters can be downloaded.
• If downloading to a device with a key icon color that has changed to yellow because of parameter changes, the icon must be returned to the state
before verification (white [ S ] symbol).
• If downloading to a device with a key icon color that has not changed
because parameters have not been changed, the icon must be returned
to the state indicating that verification has been completed (green [ S ]
symbol).
22. User Testing
The user himself must verify device parameters and operation to confirm
that the safety system requirement specifications are met.
23. Starting the Network Configurator and Connecting to the Network
17
Page 52

Applications Section 2-1
Start the Network Configurator and connect it to the network via the USB
port on the NE1A-series Controller or via DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP.
Refer to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
24. Reading the Network Configuration File
Read the saved network configuration file with verified parameters.
Refer to 3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File.
25. Configuration Lock
Lock the configuration of all the devices to indicate that they have been verified as well as to prevent parameters from being mistakenly rewritten.
Refer to 3-9-1 Locking the Device Configuration.
26. Saving the Network Configuration File
Save the file of a virtual network with a locked configuration.
Refer to 3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File.
27. Exiting the Network Configurator
Exit the Network Configurator.
!WARNING
Safety functions may be impaired and serious injury may occasionally occur.
Before operating the system, perform user testing to confirm that the configuration data of all the devices is correct and that they are operating correctly.
IMPORTANT • After configuring all the devices, user testing must be performed to con-
Restarting the System
firm that the configuration data and operation of each device are correct.
User testing is performed to verify the safety signature for each device.
• The configuration must be locked after user testing has been completed.
28. Running the System
Run the system.
18
Page 53

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
2-2 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the
Best EPI
Almost all of the DeviceNet network bandwidth can be used for safety I/O and
standard I/O communications.
Communications may time out, however, if the connection settings exceed the
acceptable bandwidth usage for each type of communications.
Check the connection settings and, if a setting is found to exceed the acceptable bandwidth usage rate, the setting must be changed to the value outlined
in the following table.
• Safety I/O
communications
• Standard I/O
communications
The network configuration may need to be changed if the settings exceed the
acceptable bandwidth usage rate as a result of securing the required communications performance (i.e., the required network reaction time for safety I/O
communications).
This section describes how to check the network bandwidth used for safety
I/O communications in the designed network, how to calculate the best EPI
from the set bandwidth usage rate, and how to re-set the value.
EPI (Expected Packet Interval) setting for safety connections
Master communications cycle time
2-2-1 Checking the Network Bandwidth Used for Safety I/O
Communications
The actual network bandwidth usage rate for safety I/O communications for
the connections set in the virtual network is displayed at the bottom of the
Network Configuration Window under Usage of Network Bandwidth for Safety
Connections. The network bandwidth usage rate is displayed for each baud
rate, as shown in the following diagram.
When a virtual network (including programming) is created, the network bandwidth usage conditions of safety connections at
each baud rate are displayed.
As shown in the diagram, the faster the baud rate, the lower the bandwidth
usage rate.
IMPORTANT Keep 10% or more of the network bandwidth available for establishing con-
nections and for explicit message communications with the Network Configurator, whether using only safety I/O communications or using both safety I/O
and standard I/O communications.
Even if 10% or more is available, however, safety or standard communications
might time out, depending on the Network Configurator operation (e.g., monitoring or other operations that create a load on the network) or if the user
19
Page 54

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
application uses explicit message communications. If timeouts occur, reduce
the network bandwidth usage rate (i.e., increase the unused bandwidth).
Performing Only Safety I/O Communications
When performing only safety I/O communications, there is no problem if the
network bandwidth used for safety I/O communications is approximately 90%.
If the bandwidth exceeds 90%, obtain the best average EPI for all connections
by referring to 2-2-3 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage Rates and Calculat-
ing Best EPI and change the EPI setting for each connection.
Performing Safety I/O Communications and Standard I/O Communications
When both safety I/O communications and standard I/O communications are
used on one network, it is necessary to determine the network bandwidth to
use for each type of communications. Problems will occur if only the network
bandwidth for safety I/O communications is determined, because some network bandwidth is required for standard I/O communications.
Refer to 2-2-3 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage Rates and Calculating
Best EPI and enter the network bandwidth used for each type of communications and set the best average EPI for each safety connection and the communications cycle time of the Standard Master.
2-2-2 Displaying Device Bandwidth Usage Conditions
The conditions of bandwidth used in the EtherNet/IP network can be displayed. The function applies to all EtherNet/IP devices and can be used if the
EtherNet/IP network is displayed.
1. Click the tab for the EtherNet/IP Network Configuration Window.
2. Click the Detail Button. The Usage of Device Bandwidth Dialog Box will be
displayed.
20
Page 55

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
Display Details and Operation
Item Description
# IP address
Comment Device name
Usage of Capacity Displays the present percentage of the send/
receive packet processing capacity that the device
supports.
Mbit/s Number of bits presently processed per seconds
Usage of IP multicast addresses Number of multicast addresses used.
Set Packet Interval (RPI) Button This button is not used for DeviceNet Safety-Ether-
Close Button Closes the Usage of Device Bandwidth Dialog Box.
by the Ethernet port for a device.
Net/IP systems.
2-2-3 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage Rates and Calculating Best
EPI
The average EPIs for safety I/O communications and standard I/O communications and the best communications cycle time are calculated by entering
the network bandwidth usage rate for each type of communications into the
Network Configurator.
Calculate the best average EPIs and the best communications cycle using the
following procedure. The network configuration might need to be changed if
the required communications characteristics cannot be achieved.
1. Make the required settings for the virtual network on the Network Configu-
rator, including creating programs for the Safety Network Controller.
2. Click the Calculate EPI Button at the bottom of the Network Configuration
Window. The Calculate EPI Dialog Box will be displayed.
3. Input the network bandwidth used in safety I/O communications and the
bandwidth used in standard I/O communications.
• If using only safety I/O communications:
Input the network bandwidth used by the safety connections as 90%
or less and input 0% for the network bandwidth used by standard connections.
21
Page 56

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
If using both safety and standard I/O communications:
Input the total network bandwidth used for safety and standard connections as 90% or less, e.g., 40% for safety connections and 30% for standard connections.
Safety and standard I/O communications will use the bandwidth based on
the rates specified here.
4. Click the Calculate Button.
5. The best average EPI of all the connections in the safety I/O communica-
tions and the optimum Master communications cycle time in the standard
I/O communications will be displayed for each baud rate.
6. Perform the following trial calculation.
• When using safety I/O communications only
Increase the network bandwidth for safety connections to 90%. If the
desired best EPI for each safety connection cannot be calculated, try
increasing the EPI for connections that need faster speeds (EPI settings,
step 9 as described later).
• When using a mixture of safety and standard I/O communications:
Try changing the network bandwidth usage rate and calculating the EPI,
as described below.
• Increase the usage rate for safety connections to shorten the EPI for
safety I/O communications and lengthen the communications cycle time
for standard I/O communications.
• Conversely, increase the usage rate for standard communications to
shorten the cycle time for standard I/O communications and increase the
EPI for safety I/O communications.
7. Check the Safety Network Controller cycle time.
Next, check that the cycle times calculated in the previous steps are longer
than the Safety Network Controller cycle time. If they are shorter, the Safety Network Controller cycle time will be the minimum that can be set for the
EPI. The Safety Network Controller cycle time can be checked offline after
creating the program, under Cycle Time on the Mode/Cycle Time Tab in
the Edit Device Parameters Dialog Box. Refer to 5-6 Setting the Operating
Mode and Confirming the Cycle Time.
22
Page 57

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
IMPORTANT The minimum possible EPI setting is larger value of either the Safety Network
Controller cycle time or the Safety Slave cycle time (fixed at 6 ms). The minimum possible EPI will be affected, therefore, if the Safety Network Controller
cycle time is longer than 6 ms.
8. Reconsider the network configuration itself if you have performed the test
calculation as outlined above and either of the following occur, i.e.,
• the desired best average EPI for each safety connection and the best
communications cycle time for the Standard Master cannot be calculated,
or
• the Safety Network Controller cycle time is longer than the best average
EPI.
Consider adjusting the following aspects of the network configuration.
• Reducing the number of nodes or I/O points.
• Splitting the network
• If using both safety and standard I/O communications, split the network into a DeviceNet Safety network and a standard DeviceNet network.
• If using only safety I/O communications, split the network into two DeviceNet Safety networks.
9. Change the EPI settings for each safety connection and the Standard Master communications cycle time setting to suit the desired baud rate.
• Changing the EPI Settings for Each Safety I/O Connection
The best average EPI calculated is the best average of all safety connec-
tions.
The following method is used for setting the calculated EPI as the EPI in
the parameters for all safety connections.
• Method for batch setting the best EPI to devices
a. Click the Update Device Configuration Button.
The Update Device Configuration Dialog Box will be displayed.
b. Select the baud rate to be used and click the OK Button.
The calculated best average EPI value will be batch set as the EPI in
the safety connection parameters for all devices.
c. If required, adjust the EPI settings for the whole network, making the
EPI smaller for those connections that need a faster response time
(e.g., for safety curtain connections) and making the EPI larger for
23
Page 58

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
those connections that do not need a fast response (e.g., for door
switches not used in hazardous areas).
Refer to the reaction time listed in the EPI field to check what the reaction time will be for each safety connection EPI setting.
Note Set the EPI for each safety connection longer than Safety Network
Controller cycle time. If the EPI is shorter, errors will occur when the
safety connection parameters are downloaded and the download
will fail.
• Changing Standard Master Communications Cycle Times
The value calculated as the best average cycle time is the best communi-
cations cycle time for the Standard Master.
Set the calculated value as the Standard Master communications cycle
time.
10. Reconfirm the bandwidth usage rate.
If the EPI settings in the safety connection parameters or the Standard
Master communications cycle time setting has been changed based on the
calculation results, check that the network bandwidth usage when safety
connections are used, displayed at the bottom of the Network Configuration Window, is less than the value input in the Calculate EPI Dialog Box.
It is particularly important to check the bandwidth usage rate if the best average EPI has been adjusted for each connection rather than applied as a
batch setting.
Note The EPI is set in 1-ms units, so the network bandwidth usage rate
may be smaller than the input value if the calculation result is input
directly.
11. Perform a test to ensure that there are no problems with the set values.
24
Page 59

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
2-2-4 Example of EPI Calculations
The following network configuration is used for an example of calculating the
EPI.
Conditions
The baud rate is 500 Kbit/s.
■ Safety I/O Communications
Example: The NE1A-series Controller sets safety connections between six
DST1-ID12SL-1 Input Terminals and five DST1-MD16SL-1 I/O Terminals. The
default set values are used for all the safety connections, and the EPI is
10 ms.
■ Standard I/O Communications
Example: The CJ1W-DRM21 sets the standard connections between six
DRT2-ID16 Input Terminals and five DRT2-OD16 Output Terminals. The
default set values are used, and the communications cycle of the CJ1WDRM21 is automatically set but it attempts to operate at a cycle time of about
3.2 ms.
25
Page 60

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
Calculations
Here, we allocate 70% network bandwidth usage rate to safety connections
and 20% to standard connections.
Click the Calculate Button and from the calculation results, you can see the
EPI for the safety connections can be set to 7 ms and the communications
cycle of the Standard Master can be set to 6 ms.
Checking the Safety Network Controller Cycle Time
If, for example, the Safety Network Controller cycle time was 6 ms, it is shorter
than the calculation result of 7 ms which means the result can be set as the
EPI.
Changing Settings
Changing the EPI Settings for Each Safety I/O Connection
Set the EPI of all safety connections set in the NE1A-series Controller to 7 ms
according to the calculation results.
26
Page 61

Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage and Calculating the Best EPI Section 2-2
Click the Update Device Configuration Button to batch set the calculation
result of 7 ms as the EPI for all safety connections by selecting the baud rate
to be used.
Refer to 2-2-3 Allocating Network Bandwidth Usage Rates and Calculating
Best EPI.
Changing Standard Master Communications Cycle Time Settings
Set the communications cycle of the CJ1W-DRM21 to 6 ms.
27
Page 62

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
2-3 Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time
The last step in designing the network is calculating the reaction time of safety
chains. The user must check that the reaction time in all the safety chains
meets the requirement specifications.
2-3-1 Concept of Reaction Time
Reaction time is the worst down time among the running devices considering
faults and failures in safety chains. The safety distance is calculated from
reaction time.
The reaction time is calculated for each safety chain. The typical combinations
of safety chains are as follows:
1. Standalone NE1A-series Controller (DeviceNet Communications Disabled)
Safety
sensor/switch
NE1A -SCPU01
Actuator
2. Remote Input – NE1A-series Controller Output
Network
Safety
sensor/switch
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
NE1A-SCPU01
Actuator
3. NE1A-series Controller Input – Remote Output
Network
Safety
sensor/switch
NE1A-SCPU01
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Actuator
4. Remote Input – Remote Output
Safety
sensor/switch
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Network
NE1A-SCPU01
Network
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Actuator
Note Even if a fault or failure occurs in a safety chain, the output shutoff time is
ensured as the maximum reaction time.
28
Page 63

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
2-3-2 Calculating the Maximum Reaction Time
Reaction Time Components
Reaction time components are displayed for each safety chain.
1. Standalone NE1A-series Controller (DeviceNet Communications Disabled)
Safety
sensor/switch
Sensor/switch
reaction time
NE1A-SCPU01
Local input/local
output
reaction time
Actuator
Actuator
reaction time
(A)
2. Remote Input – NE1A-series Controller Output
Safety
sensor/switch
Sensor/switch
reaction time
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Input
reaction time
(E)
Network
reaction time
(G)
NE1A-SCPU01
Remote
input/local
output
reaction time
(B)
3. NE1A-series Controller Input – Remote Output
Safety
sensor/switch
Sensor/switch
reaction time
NE1A-SCPU01
Local
input/remote
output
reaction time
(C)
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Network
reaction time
(G)
Output
reaction time
(F)
4. Remote Input – Remote Output
Actuator
Actuator
reaction time
Actuator
Actuator
reaction time
Safety
sensor/switch
Sensor/switch
reaction time
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Input reaction
time
(E)
Network
reaction time
(G)
NE1A-SCPU01
Remote input/
remote output
reaction time
(D)
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Network
reaction time
(G)
Output
reaction time
(F)
Actuator
Actuator
reaction time
29
Page 64

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
Maximum Reaction Time Formula
Item Time formula
A Local input/local output reaction time of the
NE1A-series Controller (ms)
B Remote input/local output reaction time of the
NE1A-series Controller (ms)
C Local input/remote output reaction time of the
NE1A-series Controller (ms)
D Remote input/remote output reaction time of the
NE1A-series Controller (ms)
E Input reaction time of the DST1-series I/O Termi-
nal (ms)
F Output reaction time of DST1-series I/O Terminal
(ms)
G Network reaction time (ms) Use the Network Configurator calculation result.
IMPORTANT In the SNC program, add the time for the NE1A-series Controller cycle time to
the reaction time of the safety chain when the output from a function block is
fed back to the input side of the function block.
Check the NE1A-series Controller cycle time, I/O refresh cycle time, and network reaction time in the Network Configurator.
Check the NE1A-series Controller cycle time and I/O refresh time in Mode/
Cycle Time Tab of the Edit Device Parameters Window.
ON/OFF delay + I/O refresh cycle time
+ NE1A-series Controller cycle time × 2 + 2.5
NE1A-series Controller cycle time + 2.5
ON/OFF delay time + I/O refresh cycle time
+ NE1A-series Controller cycle time × 2
NE1A-series Controller cycle time
ON/OFF delay time + 16.2
6.2 + Relay reaction time
(DST1-MRD08SL-1 only)
30
Page 65

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
Check the network reaction time in the Safety Connection Tab of the Edit
Device Parameters Window.
31
Page 66

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
Example of Maximum Reaction Time Calculation
Example 1: Remote Input – NE1A-series Controller Output
SNC cycle time = 6 ms
I/O refresh cycle = 6 ms
NE1A-SCPU01
DST1-series
I/O Terminal
Safety connection (EPI = 6 ms)
network reaction time = 24 ms
Switch
Actuator
DeviceNet
Maximum reaction time (ms)
= Switch reaction time
+ DST1-series I/O Terminal input reaction time
+ Network reaction time
+ NE1A-series Controller remote input/local output reaction time
+ Actuator reaction time
= Switch reaction time
+ ON/OFF delay (DST1-series I/O Terminal) + 16.2
+ 24
+
6 + 2.5
+ Actuator reaction time
= 48.7 + ON/OFF delay + Switch reaction time + Actuator reaction time
32
Page 67

Calculating and Verifying the Reaction Time Section 2-3
Example 2: Local Input – Remote Output
NE1A-series Controller cycle time = 6 ms
I/O refresh cycle
time
= 6 ms
NE1A-series Controller cycle time = 7 ms
I/O refresh cycle
time
= 3.5 ms
Switch
NE1A-SCPU01
A
Safety connection (EPI = 7 ms)
network reaction time = 28 ms
NE1A-SCPU01
B
Actuator
DeviceNet
Maximum reaction time (ms)
= Switch reaction time
+ NE1A-series Controller-A local input/remote output reaction time
+ Network reaction time
+ NE1A-series Controller-B remote input/local output reaction time
+ Actuator reaction time
= Switch reaction time
+ ON/OFF delay (NE1A-series Controller) + 6 + 6 × 2
+ 28
+
7 + 2.5
+ Actuator reaction time
= 55.5 + ON/OFF delay + Switch reaction time + Actuator reaction time
2-3-3 Verifying the Maximum Reaction Time
Check that the calculated maximum reaction time meets the required specifications in all safety chains. If the reaction time exceeds the required specifications, re-examine the network design, taking into consideration the following
points for the maximum reaction time to meet the requirement specifications:
• Shortening the EPI will shorten the network reaction time. Shortening the
EPI, however, narrows the network bandwidth that can be used for other
connections.
• The NE1A-series Controller cycle time is automatically calculated based
on the program size, the number of connections, etc. It is also possible to
use different NE1A-series Controller Controllers for safety chains that
require a high-speed reaction time and other safety chains.
33
Page 68

Page 69

Basic Operation of the Network Configurator
3-1 Network Configurator Startup and Main Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3-1-1 Starting and Exiting the Network Configurator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3-1-2 Checking the Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3-1-3 Main Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3-2 Menu List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2-1 File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2-2 Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2-3 View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2-4 Network Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3-2-5 Device Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3-2-6 EDS File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3-2-7 Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3-2-8 Option Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3-2-9 Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-3 Connecting to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-3-1 Network Connection via USB Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-3-2 Network Connection via DeviceNet Interface Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3-3-3 Network Connection via Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-3-4 Connecting to a Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-3-5 Changing a Connected Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3-4 Creating a Virtual Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3-4-1 Creating a New Virtual Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3-4-2 Network Numbers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3-4-3 Adding Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3-4-4 Deleting Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3-4-5 Changing the Node Address or IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3-4-6 Changing Device Comments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3-4-7 Creating a Connected Network from a Device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3-5 Saving and Reading Network Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3-5-1 Password Protection of the Network Configuration File . . . . . . . . . 65
3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3-5-4 Protect Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
3-6 Device Password Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3-6-1 Setting a Device Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3-6-2 Forgotten Device Passwords. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
SECTION 3
35
Page 70

3-7 Device Parameters and Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3-7-1 Editing Device Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3-7-2 Uploading Device Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3-7-3 Downloading Device Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3-7-4 Device Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
3-8 Parameter Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-8-1 Device Parameter Verification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-9 Configuration Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3-9-1 Locking the Device Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3-9-2 Unlocking the Device Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
3-10 Device Reset and Status Change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
3-10-1 Reset Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
3-10-2 Resetting Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
3-10-3 Reset Types and Device Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
3-10-4 Changing Device Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
36
Page 71

Network Configurator Startup and Main Window Section 3-1
3-1 Network Configurator Startup and Main Window
This section describes methods for starting and exiting the Network Configurator, describes how to check the Network Configurator version and describes
the Main Window.
3-1-1 Starting and Exiting the Network Configurator
Starting
Select Program -OMRON Network Configurator for DeviceNet Safety -
Network Configurator from the Windows Start Menu (when using the default
program folder name).
The Network Configurator will start, and the following window will be dis-
played.
Exiting
Select File -Exit in the Main Window.
The Network Configurator will close.
37
Page 72

Network Configurator Startup and Main Window Section 3-1
3-1-2 Checking the Version
The procedure to check the Network Configurator version is as follows:
Windows XP or Windows 2000
1. For Windows XP, select Control Panel - Add or Remove Programs from
the Windows Start Menu.
For Windows 2000, select Setting - Control Panel - Add/Remove Pro-
grams from the Windows Start Menu.
2. Select the Network Configurator for DeviceNet Safety from the installed
program list, and then refer to the support information by following each
display.
3. The version will be displayed as support information.
Windows Vista
1. Select Control Panel - Programs from the Start Menu.
2. Select Network Configurator for DeviceNet Safety from the list of in-
stalled programs.
The version is displayed in the details pane.
38
Page 73

Network Configurator Startup and Main Window Section 3-1
3-1-3 Main Window
The Main Window consists of the Hardware List, the Network Configuration
Pane, Maintenance Pane, and the Message Pane.
Network Configuration Pane:
Hardware List:
Displays the devices
that can be added to
the network.
Maintenance Pane:
Maintenance information
for the devices on the
network will be displayed.
Displays virtual networks.
Message Report Pane:
Display information such as
communications errors.
39
Page 74

Menu List Section 3-2
3-2 Menu List
This section describes the function of each menu command of the Network
Configurator.
“Online” is the state in which the Network Configurator is connected to the
network. “Offline” is the state in which the Network Configurator is disconnected from the network.
3-2-1 File Menu
O: Supported ×: Not supported
Submenu Description Offline Online
New Creates a new network configuration. O O
Open Opens an existing network configuration file. O O
Save Saves the current network configuration to a file. O O
Save As Names and saves the current network configuration. O O
External Data Export
Device
List Export
Export Exports a network configuration file that can be used with Network
Import Imports a network configuration file created in DeviceNet Configura-
Change Password Changes the password of the network configuration file.
Report Creates a report on a specified device.
Print Prints the device parameters and I/O comment list.
Setup Printer Sets up the printer. O O
Exit Exits the Configurator. O O
Exports in CSV format a file with the contents displayed in the
detailed display.
Configurator version 2.1@ or lower.
tor version 1 or version 2.
Refer to 3-5-1 Password Protection of the Network Configuration
File.
Refer to 3-8 Parameter Verification.
(Use the report function to print information for a safety device.)
OO
OO
OO
OO
OO
OO
3-2-2 Edit Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Cut Deletes selected devices and copies them to the clipboard. O O
Copy Copies selected devices to the clipboard. O O
Paste Pastes a device on the clipboard to the cursor position. O O
Delete Deletes selected devices. O O
Select All Selects all the devices. O O
Clear Message Report Clears a message in the Message Pane. O O
3-2-3 View Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Toolbar Displays or hides the toolbar. O O
Status Bar Displays or hides the status bar. O O
Message Report Displays or hides the Message Pane. O O
Maintenance Displays or hides the Maintenance Pane. O O
Large Icons Switches to network display.
Large Icons - Maintenance Mode
Display Mode 1 Switches to the detailed display mode 1, which displays the configu-
Refer to 3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes.
Displays or hides maintenance information.
Refer to 3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes.
ration based on the master device.
Refer to 3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes.
OO
OO
OO
40
Page 75

Menu List Section 3-2
Submenu Description Offline Online
Display Mode 2 Switches to the detailed display mode 2, which displays the configu-
ration based on the slave devices.
Refer to 3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes.
Open All Devices Displays all of the devices set for communications with the device
that the configuration is based on. This function can be used only in
Detailed Display Mode 1 or 2.
Close All Devices Hides all of the devices set for communications with the device that
the configuration is based on. This function can be used only in
Detailed Display Mode 1 or 2.
Hardware List Displays or hides the Hardware List. O O
Network Structure Displays or hides the Network Configuration Window.
Refer to Network Structure in 3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes.
OO
OO
OO
OO
3-2-4 Network Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Connect Connects the Network Configurator to the network.
Refer to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
Disconnect Disconnects the Network Configurator from the network.
Refer to 3-3 Connecting to the Network.
Change Connect Network Port Changes the destination network port.
Refer to 3-3-5 Changing a Connected Network.
Move Network Switches the network to connect.
(Not normally used for DeviceNet Safety.)
Wireless Network
Upload Uploads all the device parameters in the network to the
Download Downloads all the device parameters in the Network Con-
Verify Structure Verifies the current network configuration in the Network
I/O Connection
Update Maintenance Information Updates the maintenance information of each device to the
Update Device Status Updates the status information for each device to the most
View Device’s Connection Structure
Tr ee
Check Connection Checks the consistency of all the connections. O O
Edit All Connections Makes batch settings for all connections in the system.
Add DeviceNet Adds a DeviceNet network in the Network Configuration
Copy Copies the selected network configuration. O O
Move to Upper Network
Move to Lower Network
Start Establishes an I/O connection for the specified device.
Stop Stops the I/O connection for the specified device. (Can be
EtherNet/IP Adds an EtherNet/IP network in the Network Configuration
Displays the network one layer above the current network
in the wireless networks.
(Not normally used for DeviceNet Safety.)
Displays the network one layer below the current network
in the wireless networks.
(Not normally used for DeviceNet Safety.)
Network Configurator.
Refer to Uploading the Network Configuration from the
Actual Network (Network Upload) in 3-4 Creating a Virtual
Network.
figurator to the devices in the network.
Refer to 3-7-3 Downloading Device Parameters.
Configurator with the actual network configuration of the
destination online connection.
(Can be used only with EtherNet/IP.)
used only with EtherNet/IP.)
latest information.
recently updated information.
Displays the connection configuration of the entire system.
Refer to Device’s Connection Structure Tree Display in 3-2-
10 Main Window Display Modes.
Refer to 5-1-4 Listing and Setting Connection Parameters.
Window.
Window.
O×
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
OO
OO
OO
OO
41
Page 76

Menu List Section 3-2
Submenu Description Offline Online
Delete Deletes the selected network configuration. O O
Change View Switches the displayed network. O O
Property Displays the network properties. The network name and
safety network number can be set.
This function can also get network numbers from actual
networks. This function is enabled only when on online.
OO
3-2-5 Device Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Parameter Wizard Configures the device parameters in a wizard format. This func-
tion is not supported by all devices.
Edit Edits the device parameters. O O
Read Reads the parameters from the device parameter file. O O
Save As Saves the device parameters to a file. O O
Upload Uploads the device parameters from a device in the network.
Download Downloads the device parameters to a device in the network.
Verify Verifies the device and the device parameters in the network. × O
Lock Locks the configuration of a device in the network.
Refer to 3-9-1 Locking the Device Configuration.
Unlock Unlocks the locked configuration of a device in the network.
Refer to 3-9-2 Unlocking the Device Configuration.
Monitor Monitors the parameters and status of a device in the network.
Not all devices support this function.
Reset Resets a device in the network.
Refer to 3-10 Device Reset and Status Change.
Change Mode Changes the status of a device in the network. Not all devices
support this function.
Refer to 3-10-4 Changing Device Status.
Change Password Changes the password of a device in the network.
Refer to 3-6 Device Password Protection.
Maintenance Information Displays the maintenance information of a device in the net-
work.
This function is enabled only for devices that support it.
Register to Another Device Registers a device to another device. O O
External Data Export Exports I/O comments or device parameters to another file for-
mat. Not all devices support this function.
Import Imports a device parameter file created with DeviceNet Config-
urator (version 1 or version 2). Not all devices support this func-
tion.
Change Node Address Changes a device node address. O O
Change Device Comment Changes a device name. O O
Change Device Converts configuration data for the NE1A-SCPU01 to configu-
ration data for the NE1A-SCPU01-V1 or E1A-SCPU02.
Edit I/O Comment Edits the I/O comment. O O
Identity Synchronization Acquires identity information from a device and save it to a file. × O
Register To Routing Network Creates a new network (or selects from existing networks) and
specifies the routing destination network.
Display Routing Network Displays the routing network if a device that supports routing is
selected (NE1A-SCPU01-EIP, NE1A-SCPU02-EIP, or NE1A-
EDR01).
Property Displays the properties of a device. O O
OO
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
×O
OO
OO
OO
OO
OO
42
Note The Device Menu and Edit Menu can be partially displayed by right-clicking in
the Network Configuration Pane.
Page 77

Menu List Section 3-2
3-2-6 EDS File Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Install Installs an EDS file and adds a device to the Hardware
List.
(Normally there is no need to install the EDS files.)
Create Creates a new EDS file and adds a device to the Hard-
ware List.
Delete Deletes a device from the Hardware List. The installed
EDS file is also deleted.
Save As Names and saves the EDS file of a device on the Hard-
ware List.
Find Searches for a specified EDS file from the Hardware List. O O
Add to Network Adds a device on the Hardware List to the virtual network. O O
Property Displays the properties of an EDS file. O O
OO
OO
OO
OO
Note The EDS File Menu can be displayed by right-clicking in the Hardware List
Window.
3-2-7 Tools Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Setup Parameters Sets parameters by using explicit message communica-
Setup Node Address/Baud Rate
(only when DeviceNet is selected)
Setup TCP/IP Configuration (only
when EtherNet/IP is selected)
tions.
Sets the node address or baud rate of a device in the
DeviceNet network.
Makes TCP/IP settings, such as the IP address and sub-
net mask of a device on the EtherNet/IP network.
×O
×O
×O
3-2-8 Option Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Select Interface Selects an interface for the Network Configurator to use for
Edit Configuration File Edits various configuration files.
Setup Monitor Refresh Timer Sets the monitor refresh timer values (monitoring cycles in
Install Extend Module Installs an Expansion Module.
Install Interface Module Installs an Interface Module.
Parameter Auto Update when Configuration Changed
Device Status Auto Update When
Connected Online
the network connection.
(Normally not required.)
device monitoring).
(Normally not required.)
(Normally not required.)
The slave parameters registered in the Master will be
updated automatically when a slave parameter is
changed. The default is OFF (do not update). Under normal conditions, leave this option set to OFF. If slave information registered in the Master does not match with the
slave information, an exclamation mark [!] will be displayed
below the device icon. (Refer to 2-1-2 Changing an Estab-
lished Safety Network.)
When this option is ON, if the device is online, its status
will be automatically detected and displayed.
O×
OO
OO
OO
O×
OO
O×
43
Page 78

Menu List Section 3-2
3-2-9 Help Menu
Submenu Description Offline Online
Topic Searches the help topics. O O
About Displays the version information of the Network Configura-
tor.
OO
3-2-10 Main Window Display Modes
The Main Window display can be changed. Any of the following display modes
can be selected: Communications Mode, Maintenance Mode, Detailed Display 1, Detailed Display 2, Network Configuration Window, or Device’s Connection Structure Tree.
Communications Mode
This is the normal display mode. A device list, node addresses, and device
names are displayed.
Maintenance Mode
44
Page 79

Menu List Section 3-2
In this mode, in addition to the information displayed in Communications
Mode, the devices required for maintenance can be checked at a glance and
device status can be displayed at the same time.
Detailed Display 1 (Based on Master Devices)
The following items are displayed in list format in this mode: Comments added
to devices, device names, node addresses, device node addresses registered
to master devices, header names, device types, product names, and revisions.
Detailed Display 2 (Based on Slave Devices)
The following items are displayed in list format in this mode: Comments
attached to devices, device names, MAC IDs, device MAC IDs registered to
slave devices, header names, device types, product names, and revisions.
45
Page 80

Menu List Section 3-2
Network Structure
Select View - Network Structure to display the following window.
This window displays a list of virtual networks created with the Network Configurator and the structure of those networks. Double-click the network name
to switch the Main Window display to the corresponding network.
The toolbar at the top of the Network Structure Window includes the following
functions.
Icon Description
Hide router devices.
Hides router devices in the network structure list.
Display router devices.
Note An exclamation mark [!] may be displayed below the device icon on the Net-
work Configurator. This indicates that the information in the Slave and the
information in the Master do not match.
If an exclamation mark is displayed, update the information by opening the
Property Dialog Box of the Master that the Slave is registered with. (If the
Slave is registered with the Standard Master, check the Standard Master.)
Displays router devices in the network structure list.
Open all.
Opens items displayed in trees and displays all items.
Close all.
Closes items displayed in trees and displays only the top network.
46
Page 81

Menu List Section 3-2
Device’s Connection Structure Tree Display
Select Network - Device’s Connection Structure Tree to display the following window.
This window displays a list of the networks. Under each network is displayed a
list of master devices in that network. The devices registered to a master
device and displayed under the master device. Registered devices can also
be displayed in the same way via the NE1A-EDR01.
The display type can be switched between the master device-based mode
(displaying devices connected to master devices) and the slave device-based
mode (displaying devices connected to slave devices).
In addition, the Display Route Path and Display Connection Details are sup-
ported as display options.
Select the Display Route Path option to display a route (EtherNet/IP if registered via the NE1A-EDR01).
If the Display Route Path option is not selected, only the networks on which
master devices and slave devices exist will be displayed, and not the route.
If the Display Connection Details option is selected, an asterisk (*) is displayed at the connected master device.
“R” and “F” indicate the number of resources required for communications.
“R” indicates the number of communications resources required by each
device. “F” indicates the number of communications required by each device.
Users do not normally need to be aware of the these values because they are
calculated automatically by the Network Configurator.
47
Page 82

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
3-3 Connecting to the Network
The Network Configurator must be connected to the network to perform operations that are valid only when online, such as obtaining the network configuration from an actual network or downloading the configured device
parameters to actual devices.
This section describes the procedure for connecting to the network via the
USB port on the NE1A-series Controller, a DeviceNet Interface Card installed
in a computer, and Ethernet (only when using the NE1A-SCPU01-EIP, NE1ASCPU02-EIP, or NE1A-EDR01).
Refer to the Appendix for other network connection procedures.
3-3-1 Network Connection via USB Port
1. Turn ON the power supply to the NE1A-series Controller and connect it to
a USB port on the computer.
2. Select Option - Select Interface - NExA USB Port followed by the desired
mode from the menu bar.
3. Select Network - Connect from the menu bar.
The Select Connect Network Port Dialog Box will be displayed.
48
When connecting to a network for the first time, this dialog box will be displayed and a network search will be performed automatically. Wait until the
search has been performed for all addresses. After the search, the networks that can be connected will be displayed.
From the second time onwards, the network search will not be performed
automatically.
4. Select the network to connect to and click the OK Button.
If an online connection is made normally, On-line will be displayed in the
status bar at the bottom of the window.
Page 83

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
3-3-2 Network Connection via DeviceNet Interface Card
1. Select Option - Select Interface - DeviceNet I/F.
2. Select Network - Connect.
The Select Interface Dialog Box will be displayed.
3. Select the interface card, and click the OK Button.
The Setup Interface Dialog Box will be displayed.
This window varies depending on the type of interface card. In this exam-
ple, a DeviceNet PCMCIA Card (3G8E2-DRM21-V1) is used. If you use
another interface card, refer to the operation manual for the card.
4. Set the MAC ID (node address) and baud rate, and click the OK Button.
The Select Connect Network Port Dialog Box will be displayed.
49
Page 84

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
In the first network connection, a network search is performed automatically with this dialog box displayed. Wait until the search has been performed
for all addresses. After the search, the networks that can be connected will
be displayed.
Automatic searching for networks will not be performed the second time or
after.
5. Select the network to connect to, and click the OK Button.
If is online connection is made normally, On-line will be displayed in the
status bar at the bottom of the window.
3-3-3 Network Connection via Ethernet
This section describes the procedures for connecting to the network via Ethernet (enabled only when using the NE1A-SCPU01-EIP, NE1A-SCPU02-EIP, or
NE1A-EDR01).
1. Select Option - Select Interface.
2. Select Network - Connect.
The Select Interface Dialog Box will be displayed.
3. Click the OK Button.
The Select Connect Network Port Dialog Box will be displayed.
50
Page 85

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
4. Select the network to be connected, and then click the OK Button.
The Select Connected Network Dialog Box will be displayed.
5. Select the network to be connected, and then click the OK Button. If an online connection is made normally, On-line will be displayed in the status bar
at the bottom of the window.
A tab for the network to be connected will be displayed in blue as in the following figure.
3-3-4 Connecting to a Network
This section describes the basic concept of connecting the Network Configurator to an actual network.
As shown in the following figure, the description will use an example with multiple networks in a system. In the example in the figure, the networks are
DeviceNet_1, EtherNet_1, and DeviceNet_2.
51
Page 86

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
(1)
DeviceNet_1
NE1A-series Controller
EtherNet_1
(3)
(2)
NE1A-EDR01
DeviceNet_2
There are three ways to connect the Network Configurator to the network.
a. Connection via a USB port (connection to an NE1A-series Controller)
b. Connection via a DeviceNet Interface Card
c. Connection via Ethernet (NE1A-EDR01: Network Configurator version
2.0@ or higher, NE1A-SCPU01-EIP or NE1A-SCPU02-EIP: Network
Configurator version 2.2@ or higher)
With Network Configurator version 1.6@ or earlier, operations (e.g., downloading and uploading) can be performed only for networks that have devices
connected. In the figure above, if a connection is made at network 1, only
devices on DeviceNet_1 can be accessed, and if connection is made at network 2, only devices on DeviceNet_2 can be accessed.
When using Network Configurator version 2.0@ or higher with a network that
contains the NE1A-EDR01, CPU Units with unit version 2.0, and CPU Units
that support EtherNet/IP (see note 2), uploading, downloading, and other
online operations can be performed for networks other than the network to
which the connected device belongs. If a connection is made to the NE1ASCPU01 Controller (pre-version 1.0) in network 1, operations can be performed only for the DeviceNet_1 network.
Note (1) For CPU Units with unit version 1.0 or earlier, uploading and downloading
can be performed only for devices that are connected to the network to
which the CPU Unit belongs.
(2) CPU Units (with EtherNet/IP) support the Network Configurator of version
2.2@ or higher.
When the Network Configurator is connected to the network, a blue icon will
be displayed on the tab of a destination network, and a green icon will be displayed on the tab of an operable network, as in the following figure.
The tab may remain grey after a network has been set to online. This indicates that the network is inoperable at the present online destination. The
connection destination must be changed to operate the network. Change the
connection destination using the procedure described in 3-3-5 Changing a
Connection Destination.
3-3-5 Changing a Connected Network
This section describes how to change a connection destination.
Note This function is enabled only when connection is made to the NE1A-EDR01
via Ethernet, connection is made to the NE1A-SCPU02 (unit version 2.0) via
52
Page 87

Connecting to the Network Section 3-3
USB, or connection is made to the NE1A-SCPU01-EIP or NE1A-SCPU02-EIP
via USB or Ethernet.
1. Select Network - Select Connect Network Port. The Select Connect Net-
work Port Dialog Box will be displayed.
2. Select the network to be connected, and then click the OK Button. The Select Connected Network Dialog Box will be displayed.
3. Select the network to be connected, and then click the OK Button.
If an online connection is made normally, On-line will be displayed in the
status bar at the bottom of the window.
A tab for the network to be connected will be displayed in blue as in the
following figure.
Note Until Select Connect Network Port is used again to change the con-
nection destination, the network selected in step 3 (displaying a
blue icon) and related networks (displaying a green icon) will be operable.
53
Page 88

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
3-4 Creating a Virtual Network
To set device parameters and to program NE1A-series Controllers, create a
virtual network in the Network Configurator, set the device parameters in the
virtual network, and then download the parameters to the actual devices.
This section describes how to create a virtual network.
3-4-1 Creating a New Virtual Network
When the Network Configurator is started, a new virtual network can be created.
Use one of the following methods to create a new virtual network.
1. Select File - New from the menu bar.
2. Click the New Button on the toolbar.
Alternatively, select Network - Add from the menu bar to add another new virtual network.
Note When a new virtual network is created with unit version 1.6@ or higher, the vir-
tual network information that was displayed until then will be deleted. If the
previous virtual network information is required, save the data before creating
a new virtual network.
3-4-2 Network Numbers
The DeviceNet Safety System can be used to build multiple networks. Network numbers are used in combination with node addresses to specify unique
devices and confirm communicating nodes in this kind of multi-network configuration. This value is called a TUNID (Target Unique Network Identifier) and is
stored in the non-volatile memory of each device.
Setting TUNIDs
The TUNID is automatically set when parameters are first downloaded from
the Network Configurator to a device in out-of-the-box configuration. (See
note.)
Note “Out-of-the-box configuration” indicates the status when a reset-type device is
returned to its default status and restarted.
Users do not normally need to be aware of the existence of network numbers
because they can visually identify a device on the Network Configurator.
The default network number is automatically generated based on the date
and time the Network Configurator created the network configuration, but it
can also be specified by the user.
Cases Where the User Needs to Specify Network Numbers
The automatically generated network numbers will be sufficient when the Network Configurator is used to set all the devices on the network. In the following cases, however, the user must set a different network number for each
network.
1. When multiple Network Configurators are used to set individual devices:
When more than one Network Configurator is used to make settings on the
same network, the same network number must be set for each device.
2. When more than one type of setting software is used:
When setting software other than Network Configurator is used because
devices made by other manufacturers are being used, specify the same
network number with each type of setting software.
54
Page 89

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
Precautions When Downloading to Existing Networks
The following precautions must be heeded because parameters cannot be
downloaded to devices if the new automatically generated TUNID to be transmitted is different from the TUNID in the device memory.
Always use one of the four methods listed below when downloading parameters to a device that has already had parameters downloaded to it.
If the download is executed using a different method, the download will fail
because the transmitted TUNID and the TUNID in the device memory are different. A “Different TUNID” error message will appear in the error history.
Method 1: Download the parameters using the previously created net-
work configuration file.
Method 2: Download the parameters based on the configuration
obtained from a network upload.
Method 3: If using a newly created network configuration file, get the
network number from the actual network (a function of Network Configurator version 1.50 or higher; see note). Make the
virtual network number in Network Configurator the same as
the actual network number and then download the parameters.
Note Use the following procedure to get the network number.
(a) Select Network – Property or right-click the Network Configura-
tion Window and select Property. Click the Get from the actual
network Button in the Network Number Area in the Network
Property Dialog Box.
(b) The network number of the real number that you want to down-
load will be read to the personal computer.
(c) Click the OK Button and update the network number, and then re-
execute the download.
Method 4: If using a device that has been used in another location, reset
the device to out-of-the-box configuration (see note) and
download using methods 1, 2, or 3.
Note Select Device – Reset or click the right mouse button and select
Reset to display the Reset Device Dialog Box. Set the reset type to
Return to the out-of-box configuration, and then emulate cycling power and click the OK Button.
Generally, method 1 should be used, i.e., save the master network configuration file and use it to make any network configuration or parameter changes.
Then download parameters using that master file.
When connecting a new device to the network, use method 4 and reset the
device to initial status before downloading.
Note When the parameters are downloaded to the devices, the network number is
transferred with the parameters as the UNID and saved in the devices. Therefore, when using a device whose parameters have already been downloaded
to another domain, set the reset type to Return to the out-of-box configuration,
and then emulate cycling power and perform a reset to clear the UNID.
55
Page 90

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
Use the following procedure to set the network number.
1. Select Network - Property from the menu bar.
2. In the Network Number Field, select the Manual Option and enter the val-
ue.
IMPORTANT Always allocate a unique network number when a network or subnetwork is
established.
If the network number is not set correctly, a connection may be opened to a
different device. A different network number must be set for each network
domain, and the same network number must be set for all the devices on the
same domain.
If the network number is set by the user, click the Get from the actual net-
work Button in the Network Number Field on the Network Property Dialog
Box to check the network number set for the target actual network. The network number set to the target network will be read and displayed in the Man-
ual Field.
56
Page 91

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
3-4-3 Adding Devices
There are three ways to add a device to the virtual network.
1. Add from the Hardware List.
2. Upload the network configuration from the actual network.
3. Select EDS File – Add to Network from the menu.
Adding Devices from the Hardware List
There are two ways to add a device to the virtual network from the Hardware
List.
1. Double-click the selected device in the Hardware List.
2. Select the device from the Hardware List and drag it to the Network Configuration Pane.
When a device has been registered, it will be displayed as follows:
57
Page 92

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
Uploading the Network Configuration from the Actual Network (Network Upload)
The network configuration can be read from the actual network and to create
the same configuration in the virtual network. Connect the Network Configurator to the network, and then upload the network configuration using any of the
following methods.
1. Select Network - Upload from the menu bar.
2. Click Upload from Network on the toolbar. Uploading will start, and the
detected devices will be displayed sequentially.
3. Right-click without selecting any device in the Network Configuration Pane
and select Upload.
If the network device configuration that is currently displayed is the same as
the configuration of the connection destination network, a dialog box will be
displayed to check if the configuration can be uploaded with the current device
configuration.
• Click the Yes Button to start uploading with the current device configuration.
• Click the No Button to delete the current device configuration, and then
start uploading.
The following dialog box will be displayed if the currently displayed network is
different from the connection destination network.
• Uploading will be cancelled if the No Button is clicked.
• The following dialog box will be displayed if the Yes Button is clicked.
58
Page 93

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
• Select the network port to be connected, and then click the OK Button.
Uploading will start.
• After uploading has been completed, the following dialog box will be displayed if there is a NE1A-SCPU01-EIP, NE1A-SCPU02-EIP, or NE1AEDR01 in the network.
• The following dialog box will be displayed if the Yes Button is clicked here.
• Uploading for the target network will start if the Yes Button is clicked here.
If there is another device that must be added after the upload has completed,
add the device following the same procedure as in Adding Devices from the
Hardware List, above.
IMPORTANT If there is a CS/CJ-series DeviceNet Unit in the network, disable the master
function of the CS/CJ-series DeviceNet Unit, or disable I/O communications
from the DeviceNet Unit monitor window, and then do the upload. If I/O communications are enabled, uploading the device parameters may fail.
Note • When uploading the network configuration from a network, it can be
uploaded as the configuration or the current network or as a new network.
• When data is uploaded as a new network, the virtual network information
that was displayed until will be deleted. If the previous virtual network
information is required, save the data before the uploading the network.
59
Page 94

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
• When a network in which devices already have a set network number is
uploaded, the value that is already set in the devices will be used for the
network number.
Reusing Network Configurations
Network configurations can be reused starting from version 2.01. Use the following procedures.
1,2,3... 1. Open the project file from which the configuration information is to be re-
used.
2. Select File - Save As from the menu bar. The following dialog box will be
displayed.
3. A Select target network Check Box will be displayed in the Option Area. If
this check box is not selected, the configuration information for all networks
will be saved.
4. Select the check box and click the Save Button. The following dialog box
will be displayed.
5. Select the networks for which the configuration information is to be saved
and click the OK Button. The configuration information for the selected networks will be saved in a file.
The configuration information on devices on the selected networks in the virtual networks has now been saved. Use the following procedure to reuse the
configuration information in the file.
60
Page 95

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
1,2,3... 1. Select File - Open from the menu bar. The Open Dialog Box will be dis-
played. (You can also select project files saved from the previous version
of the Network Configurator.)
2. Two check boxes will be displayed in the Option Area: Select target net-
work and Add to current network. If neither of these check boxes is selected, a file can be selected using the same procedure as for version 2.0.
3. As an example, select the Select target network Check Box and click the
Open Button. The following dialog box will be displayed.
4. The networks with configuration information saved in the file will be displayed. Select the networks for which the configuration information is to be
reused and click the OK Button. The configuration information for only the
selected networks will be read.
5. If the Add to current network Check Box is selected in the Open Dialog Box
before the Open Button is clicked, the configuration information read from
the file will be added to the current network.
Note Starting from version 2.01, the network tabs that are displayed can be moved
by dragging and dropping them.
61
Page 96

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
3-4-4 Deleting Devices
There are three ways to delete a device from a virtual network.
1. Select a device, and then select Edit - Delete from the menu bar.
2. Select a device, and then click the Delete Button on the toolbar.
3. Select a device, and then right-click the selected device and select Delete.
A confirmation dialog box will be displayed before the deletion. Click the
Delete Button to delete the device.
3-4-5 Changing the Node Address or IP Address
When a device is added from the Device List, an unused node address or IP
address is automatically allocated sequentially in the order the device is
added.
There are two ways to change the allocated node address or IP address.
1. Select a device, and select Device - Change Node Address from the
menu bar.
2. Select a device, and then right-click the device and select Change Node
Address.
The following dialog box will be displayed. Change the node address or IP
address and click the OK Button.
■ DeviceNet Device
■ EtherNet/IP Device
Note (1) The above method is used to change the node address or IP address of
devices on a virtual network.
(2) For information on changing the node address or IP address of devices
that are online, refer to A-5-2 Setting the Node Addresses and Baud
Rates via the Network and A-5-3 Setting TCP/IP Over a Network.
3-4-6 Changing Device Comments
When a device is added from the Device List, the displayed comment is the
device type. Device comments can be set in the following two ways.
1. Select a device, and then select Device - Change Device Comment from
the menu bar.
62
Page 97

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
2. Select a device, and then right-click the device and select Change Device
Comment.
The following dialog box will be displayed. Enter the device name and click the
OK Button.
3-4-7 Creating a Connected Network from a Device
When the NE1A-SCPU01-EIP, NE1A-SCPU02-EIP, or NE1A-EDR01 is registered, either of the following methods can be used to create a new virtual network.
1. Select the device, and then select Device - Register to Routing Network
from the menu.
2. Right-click the device and select Register to Routing Network from the
pop-up menu.
The following dialog box will be displayed.
Click the Yes Button.
63
Page 98

Creating a Virtual Network Section 3-4
A new connected network will be created as shown below.
64
Page 99

Saving and Reading Network Configuration Files Section 3-5
3-5 Saving and Reading Network Configuration Files
The created network configuration of the virtual network can be saved in a file.
Also, you can open the saved file, modify it, or download it to the devices by
connecting to the network.
3-5-1 Password Protection of the Network Configuration File
A password can be set for the network configuration file. The set password is
encrypted and saved in the file. By setting the password for the network configuration file, the file is protected from unintended or unauthorized access.
The network configuration file password must be entered when the following
operations are performed in the Network Configurator:
• Saving the network configuration file
• Reading the network configuration file
• Changing the network configuration file password
The passwords must match to save the file. If the password does not match
when opening a file, Protect Mode is started. In Protect Mode, some Network
Configurator operations are restricted.
The password for the network configuration file is set when the file is saved for
the first time. The password must be from 6 to 16 alphanumeric characters. If
you do not want to set a password, enter nothing and click the OK Button.
To change the password for a network configuration file, select File - Change
Password from the menu bar. After changing the password, however, the file
and the password must be saved.
IMPORTANT • For security purposes, it is recommended to set a password for network
for network configuration files.
• Do not forget the set password. You can open a network configuration file
only in read-only mode if the password is forgotten, i.e., the file cannot be
edited.
65
Page 100

Saving and Reading Network Configuration Files Section 3-5
3-5-2 Saving the Network Configuration File
The network configuration can be saved using either of the following methods.
1. Select File - Save or File - Save As from the menu bar.
2. Click the Save Button on the toolbar.
Either way, the standard Windows dialog box for saving will be displayed.
Select the saving location, name the file, and then click the Save Button.
When saving the file for the first time, the Assign Password Dialog Box will be
displayed. Enter the password to set for the network configuration file.
When saving the second time or after, the Password Confirmation Dialog Box
will be displayed. Enter the password set when the network configuration file
was initially saved.
When saving has completed successfully, the following message will be displayed in the Message Pane:
3-5-3 Reading a Network Configuration File
The saved network configuration file can be read for use by the Network Configurator using either of the following methods.
1. Select File - Open from the menu bar.
2. Click the Open Button on the toolbar.
Either way, the standard Windows Open File Dialog Box will be displayed.
Select the file to open, and click the Open Button.
Next, the Check Password Dialog Box will be displayed. Enter the password
set when the network configuration file was saved.
When reading has completed successfully, the following message will be dis-
played in the Message Pane:
Note If the password does not match, the Network Configurator will open the file in
Protect Mode. In Protect Mode, operations such as saving the file and changing device status are prohibited. Refer to 3-5-4 Protect Mode for details.
66
 Loading...
Loading...