Page 1

Cat. No. I36I-E-01
MX2 EtherNet/IP Option Board
Born to drive machines
Model: 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
USER’S MANUAL
Page 2

Notice:
OMRON, 2011
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, or
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
OMRON products are manufactured for use according to proper procedures
by a qualified operator and only for the purposes described in this manual.
The following conventions are used to indicate and classify precautions in this
manual. Always heed the information provided with them. Failure to heed precautions can result in injury to people or damage to property.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The word "Unit" is also
capitalized when it refers to an OMRON product, regardless of whether or not
it appears in the proper name of the product.
Trademarks and Copyrights
EtherNet/IP is trademark of Open DeviceNet Vendor Association, Inc.
Other product names and company names in this manual are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective companies.
The copyright of the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option Board belongs to OMRON
Corporation.
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
• Personnel in charge of maintaining FA systems.
Page 3

About this Manual
This manual describes the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A EtherNet/IP Option Board for
OMRON's MX2-A@ Inverter. It also describes how to install and operate the
Unit.
Please read this manual carefully so that you understand the information provided before installing or using the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option Board. Start
with the precautions in the following section. They describe the operating
environment and application safety measures which must be observed prior
to and when using the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option Board.
Please be sure to read the related user manuals to use the 3G3AX-MX2-EIPA Option Board safely and properly. Be sure you are using the most current
version of the manual:
Manual Contents Cat No.
MX2 User's Manual Describes the installation and operation of the MX2-A@
EtherNet/IP Operation
Manual
EtherNet/IP CS/CJ Series
Units Operation Manual
Inverter
Describes the configuration and construction of a EtherNet/IP network, including installation procedures and
specifications for cables, connectors, and other connection devices, as well as information on functions, operating procedures, and applications.
Describes the models, specifications, functions, operating procedures, and applications of CS-series and
CJ-series EtherNet/IP Master Units.
I570
W420, W421
W342, W465
Page 4

Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials
and workmanship for a period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of
sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, REGARDING NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR
USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS
OF THEIR INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY
WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS, WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED
ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual
price of the product on which liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR,
OR OTHER CLAIMS REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS WERE PROPERLY HANDLED,
STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
Application Considerations
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to the combination of products in the customer's application or
use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification
documents identifying ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This
information by itself is not sufficient for a complete determination of the suitability of
the products in combination with the end product, machine, system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must
be given. This is not intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the
products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses listed may be suitable for the products:
o Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or uses not described in this manual.
o Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation
systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment,
and installations subject to separate industry or government regulations.
o Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS
RISK TO LIFE OR PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A
WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE
OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED FOR THE
INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
SUITABILITY FOR USE
iv
Page 5

Disclaimers
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable
product, or any consequence thereof.
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on
improvements and other reasons. It is our practice to change model numbers when
published ratings or features are changed, or when significant construction
changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be changed
without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix
or establish key specifications for your application on your request. Please consult
with your OMRON representative at any time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and does not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of
OMRON's test conditions, and the users must correlate it to actual application
requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON Warranty and Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be
accurate; however, no responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
v
Page 6

vi
Page 7

Table of contents
Safety Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
1 Hazardous High Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
2 General Precautions - Read These First! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
3 Installation Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
4 Configuration Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
6 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
7 Handling, Storage and Disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
8 Compliance with EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
SECTION 1
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-2 Option Board Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-3 Introduction to EtherNet/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SECTION 2
Option Board Mounting and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2-1 Orientation to Option Board Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2-2 Basic System Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2-3 Step-by-Step Basic Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
SECTION 3
Configuring Drive Parameters and Option Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3-1 Installation of EDS files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3-2 Configuring the Option Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3-3 Configuring the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3-4 IP Address Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
SECTION 4
Operations and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
4-1 Setting up inverter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4-2 Operating the Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4-3 Overriding Inverter inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4-4 Controlling Inverter Torque . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4-5 Faults and Trips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4-6 Accessing Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4-7 Flexible Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4-8 Limitations Caused by Inverter Mode and Rating Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4-9 Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
SECTION 5
Troubleshooting and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
5-1 Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
5-2 Other Error Causes and Error Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5-3 Maintenance and Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
APPENDIX A
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
vii
Page 8

Table of contents
APPENDIX B
Assembly Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
B-1 Basic Speed Control IO (20/70) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
B-2 Extended Speed Control IO (21/71) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
B-3 Extended Speed and Torque Control IO (123/173) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
B-4 Special IO (100/150) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
B-5 Extended Control IO (101/151/153) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
B-6 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
APPENDIX C
General Object Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
C-1 Identity Object (Class 0x01) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
C-2 Message Router Object (Class 0x02) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
C-3 Assembly Object (Class 0x04) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
C-4 Connection Manager (Class 0x06) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
C-5 Discrete Input Point Object (Class 0x08) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
C-6 Discrete Output Point Object (Class 0x09) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
APPENDIX D
AC Drive Object Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
D-1 Motor Data Object (Class 0x28) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
D-2 Control Supervisor Object (Class 0x29) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
D-3 AC/DC Drive Object (Class 0x2A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
APPENDIX E
EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
E-1 Function Code Object (Class 0x65) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
E-2 Modbus Register Object (Class 0x64) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
E-3 DLR Object (Class 0x47) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
E-4 QoS Object (Class 0x48) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
E-5 TCP/IP Object (Class 0xF5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
E-6 Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
E-7 Explicit Message Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
APPENDIX F
Flexible Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
viii
Page 9

Safety Messages
For the best results with the MX2-A@ Inverter, carefully read this manual and
all of the warning labels attached to the Inverter before installing and operating it, and follow the instructions exactly. Keep this manual handy for quick
reference.
Definitions and Symbols
A safety instruction (message) includes a "Safety Alert Symbol" and a signal
word or phrase such as WARNING or CAUTION. Each signal word has the
following meaning:
!HIGH VOLTAGE Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
in electric shock. It calls your attention to items or operations that could be
dangerous to you and other persons operating this equipment.
Read the message and follow the instructions carefully.
!WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
!Caution Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury, or property damage.
Step 1 Indicates a step in a series of action steps required to accomplish a goal. The
number of the step will be contained in the step symbol.
Note Notes indicate an area or subject of special merit, emphasizing either the
product's capability or common errors in operation or maintenance.
Tip Tips give a special instruction that can save time or provide other benefits
while installing or using the product. The tip calls attention to an idea that may
not be obvious if you are a first-time user of the product.
1 Hazardous High Voltage
!HIGH VOLTAGE Motor control equipment and electronic controllers are connected to hazard-
ous line voltages. When servicing drives and electronic controllers, there may
be exposed components with housing or protrusions at or above line potential. Extreme care should be taken to protect against shock.
Stand on an insulating pad and make it a habit to use only one hand when
checking components. Always work with another person in case an emergency occurs. Disconnect power before checking controllers or performing
maintenance. Be sure equipment is properly grounded. Wear safety glasses
whenever working on electronic controllers or rotating machinery.
ix
Page 10

General Precautions - Read These First!
2 General Precautions - Read These First!
!WARNING Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may
result in personal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure.
Please read each section in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and related sections before attempting any of
the procedures or operations given.
!WARNING This equipment should be installed, adjusted, and serviced by qualified elec-
trical maintenance personnel familiar with the construction and operation of
the equipment and the hazards involved. Failure to observe this precaution
could result in bodily injury.
!WARNING Wiring, maintenance or inspection must be performed by authorized person-
nel. Not doing so may result in electrical shock or fire.
!WARNING Hazard of electrical shock! Disconnect incoming power before working on the
OMRON 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A EtherNet/IP Option Board or the MX2-A@
Inverter.
!HIGH VOLTAGE Turn the power supply OFF and wait for the time specified on the Option
Board front cover before performing wiring, maintenance or inspection. Not
doing so may result in electrical shock.
The OMRON 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A EtherNet/IP Option Board is attached to an
MX2-A@ Inverter. Dangerous voltage exists until the MX2-A@ Inverter power
light is OFF.
!HIGH VOLTAGE Do not touch the conductive parts such as the internal PCB, terminals or con-
nector while power is being supplied. Doing so may result in electrical shock.
!WARNING Do not attempt to take an Option Board apart or touch any internal parts while
the power is being supplied. Doing so may result in electric shock.
!WARNING Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify an Option Board. Any
attempt to do so may result in malfunction, fire, or electric shock.
!WARNING Provide emergency stop circuits, interlock circuits, limit circuits and similar
safety measures in external circuits (NOT in the Option Board). This ensures
safety in the system if an abnormality occurs due to malfunction of the Option
Board or another external factor affecting the Option Board operation. Not
doing so may result in serious accidents.
!WARNING Fail-safe measures must be taken by the customer to ensure safety in the
event of incorrect, missing, or abnormal signals caused by broken signal
lines, momentary power interruptions, or other causes. Not doing so may
result in serious accidents.
!Caution Do not touch the Inverter during power on, and immediately after power off.
Hot surface may cause injury.
x
Page 11

Installation Precautions
!Caution The product will be used to control an adjustable speed drive connected to
high voltage sources and rotating machinery that is inherently dangerous if
not operated safely. Interlock all energy sources, hazardous locations, and
guards in order to restrict the exposure of personnel to hazards. The adjustable speed drive may start the motor without warning. Signs on the equipment
installation must be posted to this effect. A familiarity with auto-restart settings
is a requirement when controlling adjustable speed drives. Failure of external
or ancillary components may cause intermittent system operation, i.e., the
system may start the motor without warning or may not stop on command.
Improperly designed or improperly installed system interlocks and permissives may render a motor unable to start or stop on command.
3 Installation Precautions
!WARNING Always connect the grounding cable to one of the ground terminals of the
MX2-A@ Inverter. Failure to abide could lead to serious or possibly fatal injury.
!Caution Failure to observe these precautions could lead to faulty operation of the
Option Board or the Inverter, or could damage either of the two. Always read
these precautions.
• Install external breakers and take other safety measures against short-circuits in external wiring. Not observing this may result in burning.
• Be sure that all cable connector screws are tightened to the torque specified in the relevant manuals. Incorrect tightening torque may result in malfunction.
• Do not allow metal clippings to enter either Option Board or Inverter when
wiring or installing the unit.
• Follow the network configuration and wiring instructions provided in the
EtherNet//IP Operation Manual (Cat. No. W465):
• Wire the EtherNet/IP cables and connectors correctly. Incorrect wiring
may result in burning.
• Always connect a Terminating Resistor at the prescribed locations of
the EtherNet/IP network to ensure the quality of the transmission path.
Do not apply termination anywhere else.
• Be sure that the Option Board is mounted correctly. Improper mounting
may result in malfunction.
• Disconnect the grounding cable when performing withstand-voltage tests.
Not disconnecting the grounding cable may result in burning.
4 Configuration Precautions
!Caution Failure to observe these precautions could lead to unexpected operation of
the Option Board or the Inverter. Always read these precautions.
• Check the network related Inverter settings regarding EtherNet/IP node
address and EtherNet/IP remote I/O allocation. Not doing so may result in
unexpected operation.
• When replacing an Inverter be sure that all Inverter settings of the Inverter
being replaced are restored to the replacement.
xi
Page 12

Application Precautions
5 Application Precautions
!WARNING Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
!WARNING It is extremely important that the Unit is used for its specified purpose and
under the specified conditions, especially in applications that can directly or
indirectly affect human life. You must consult your OMRON representative
before using it in a system in the above-mentioned applications.
!WARNING Failure to observe these precautions could lead to serious or possibly fatal
injury. Always read these precautions.
• Check any user program in the system that acts as a EtherNet/IP Master
before actually running it. Not checking the program may result in unexpected operation.
• For safe operation clear the run command via EtherNet/IP as soon as a
trip condition is detected.
• In the event the Inverter is in a Trip state, be sure to investigate the cause
of this Trip state thoroughly before clearing the Trip. Not checking the
cause may result in unexpected operation.
!Caution Failure to observe these precautions could lead to faulty operation of the
Option Board or the Inverter, or could damage to either of the two. Always
read these precautions.
• Check the Inverter settings for proper Inverter behaviour before actually
operating the Inverter remotely via the EtherNet/IP network.
• Check the Inverter's EzSQ program and its interaction with the EtherNet/
IP Master before actually running it on the Inverter. Not checking the program may result in unexpected operation.
• Confirm that no adverse effect will occur at the moment the EtherNet/IP
Master stops communicating with the Inverter or at the moment the EtherNet/IP Master has not yet started communicating to the Inverter.
• Confirm that no adverse effect will occur in the Inverter before force-setting/force-resetting any bit in the system that acts as a EtherNet/IP Master.
xii
Page 13

Operating Environment Precautions
6 Operating Environment Precautions
!Caution Do not operate the MX2-A@ Inverter with a mounted 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
Option Board in the following locations (doing so may result in malfunction,
electric shock or burning):
• Locations subject to direct sunlight
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidity outside the range specified
in the specifications
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salts
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals
• Locations subject to shock or vibration
!Caution Take appropriate and sufficient countermeasures when installing systems in
the following locations (doing so may result in malfunction):
• Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radioactivity
• Locations close to power supplies
!Caution The operating environment of the MX2-A@ Inverter with a mounted
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E Option Board can have a large effect on the longevity and
reliability of the system. Improper operating environments can lead to malfunction, failure, and other unforeseeable problems with the system. Make
sure that the operating environment is within the specified conditions at installation and remains within the specified conditions during the life of the system.
7 Handling, Storage and Disposal
!Caution Failure to observe these precautions could lead to faulty operation of or dam-
age to the Option Board. Always read these precautions.
• Before touching the Option Board or Inverter, be sure to first touch a
grounded metallic object in order to discharge any static built-up. Not
doing so may result in malfunction or damage.
• When transporting or storing the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option Board, keep
the product within the specified storage temperature range.
!Caution Never dispose electrical components by incineration. Contact your state envi-
ronmental agency for details on disposal of electrical components and packaging in your area.
8 Compliance with EC Directives
This product complies with EC Directives when mounted to an MX2-A@
Inverter with the grounding cable connected.
xiii
Page 14

Compliance with EC Directives
xiv
Page 15

SECTION 1
Getting Started
1-1 Introduction
1-1-1 Main Features
The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A allows controlling, monitoring and parameterization
of an MX2-A@ Inverter via an EtherNet/IP network. The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
serves as a gateway that passes communicated register values from the EtherNet/IP network to the MX2-A@ Inverter and vice versa. The
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E adheres to the EtherNet/IP / CIP AC Drive profile.
The following functions are available via EtherNet/IP communication by
installing the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E:
Cyclic Data Exchange The EtherNet/IP Master and 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E can exchange data via an
EtherNet/IP Remote I/O connection:
• Output data (from EtherNet/IP Master to 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E):
E.g. Run/stop, Reference frequency and Fault reset.
• Input data (from 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E to EtherNet/IP Master):
E.g. Inverter status, Output frequency and Output current, etc.
Inverter Parameter Access The EtherNet/IP Master can read and write parameter data via the
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E using the explicit message communication.
The inverter parameters are accessible in multiple ways:
• Access based on Function code
• Access based on the Modbus register address
Several AC Drive profile attributes can also be accessed using the explicit
message mechanism.
Simplified Start-up The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E can be set up easily, just by connecting the Unit and
setting a drive parameter to configure the IP address (see 3-4 IP Address
Configuration).
1
Page 16

Introduction Section 1-1
1-1-2 Inverter Support
The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option board supports drives of revision 4264 4309
(for full support revision 4324 4413) . The revision of the drive can be
checked by using a web browser connected to the option board. The error
code E65 will be shown on the drive display if the revision of the drive is
incorrect.
If the revision of the Inverter does not support the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A, please
contact your local OMRON representative.
1-1-3 Inverter Safety (ISO 13849-1)
An MX2-A@ Inverter provides a Gate Suppress function to perform a safe
stop according to the EN60204-1, stop category 0. The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
Option Board has been designed not to interfere with this safety function.
Note The 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A is not a safety device and does not implement any
safety protocols.
2
Page 17

Option Board Specifications Section 1-2
1-2 Option Board Specifications
Table 1 Option Board Specification
Item Specification
Installation Unit type MX2 Series Option Board
Model 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
Dimensions (W x H x D) 68 x 58 x 45 mm
Weight 170g (typical)
Environment Ambient operating temperature -10 to 50°C (no icing or condensation)
Ambient operating humidity 20 to 90%RH
Ambient storage temperature -20 to 65°C (no icing or condensation)
Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s2 (0.6G) at 10…55 Hz
Dielectric strength 500 VAC (between isolated circuits)
EtherNet
Interface
EtherNet/IP
Configuration
EMC compliance (CE) and Electrical safety standards
cULus compliance Documented by UL in file E347728
Enclosure rating IP 20
Communications protocol EtherNet/IP
Certification EtherNet/IP Conformance Tested (ODVA)
EtherNet/IP Profile AC Drive (0x02)
Supported connections Remote I/O: Master-Slave connection
Communications ports 2
Communication speed 10 and 100 Mbps. Full and half duplex. Auto negotiation (default)
Supported Assemblies Basic Remote IO (Output assembly 20, Input assembly 70)
EDS file Depending on the MX2-A@ inverter model (see below)
EN61800-3: 2004 (2004/108/EC) Second environment, Category
C3
EN61800-5-1: 2007 (2006/95/EC) SELV
COS
Cyclic
Explicit Messages, UCMM and Class3
Conform to EtherNet/IP specifications
Announce-based DLR
or forced speed/duplex.
Extended Speed IO (21, 71)
Extended Speed and Torque Control (123, 173)
Special IO (100, 150)
Extended Control IO (101, 151)
Extended Control IO and Multi function IO monitor (101, 153)
Flexible Format (139, 159)
Extended Speed and Acceleration Control (110, 111)
Note 1 The derated- or ambient operating temperature of the MX2 Inverter takes pre-
cedence over that of the Option Board.
Note 2 In case the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A is connected to the MX2-A@ Inverter, it is not
supported to connect any external devices to the RS485 (Modbus) interface
and the RJ45 port (Optional operator port) of the inverter.
3
Page 18
Introduction to EtherNet/IP Section 1-3
The required EDS file for the option board depends on the model of the
MX2-A@ inverter.
Table 2 Device List
MX2-A@
Model name
MX2-AB001(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB001_A2001(-E).eds 1960 2000
MX2-A2001(-E)
MX2-AB002(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB002_A2002(-E).eds 1961 2001
MX2-A2002(-E)
MX2-AB004(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB004_A2004(-E).eds 1962 2002
MX2-A2004(-E)
MX2-AB007(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB007_A2007(-E).eds 1964 2004
MX2-A2007(-E)
MX2-AB015(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB015_A2015(-E).eds 1966 2006
MX2-A2015(-E)
MX2-AB022(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB022_A2022(-E).eds 1967 2007
MX2-A2022(-E)
MX2-A2037(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2037(-E).eds 1969 2009
MX2-A2055(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2055(-E).eds 1971 2011
MX2-A2075(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2075(-E).eds 1972 2012
MX2-A2110(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2110(-E).eds 1973 2013
MX2-A2150(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2150(-E).eds 1974 2014
MX2-A4004(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4004(-E).eds 1982 2022
MX2-A4007(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4007(-E).eds 1984 2024
MX2-A4015(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4015(-E).eds 1986 2026
MX2-A4022(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4022(-E).eds 1987 2027
MX2-A4030(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4030(-E).eds 1988 2028
MX2-A4040(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4040(-E).eds 1990 2030
MX2-A4055(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4055(-E).eds 1991 2031
MX2-A4075(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4075(-E).eds 1992 2032
MX2-A4110(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4110(-E).eds 1993 2033
MX2-A4150(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4150(-E).eds 1994 2034
Name of EDS file Product
Code (-E)
Product
Code (no -E)
1-3 Introduction to EtherNet/IP
1-3-1 Overview of EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP is a multi-bit, multi-vendor network that combines control and
monitoring on a machine/line-control level and that conforms to EtherNet/IP
open field network specifications. EtherNet/IP is a member of a family of networks that implements the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) at its upper layers.
Two types of communications are supported to provide a single point of connection for both control and configuration:
1. Time-critical control remote I/O communications that automatically transfer
between the Master Unit/CPU Unit and the remote Slave Units, and
2. Explicit message communications that read/write messages, control operation, or perform other functions to the Slave Units. Message communications are achieved by executing specific instructions from the program in
the CPU Unit to which the Master Unit is mounted.
4
Page 19

Introduction to EtherNet/IP Section 1-3
1-3-2 What is the AC Drive profile
Within EtherNet/IP/CIP standard, multiple device profiles have been defined.
Therefore the devices which adhere to a certain device profile are compatible
and replaceable in a multi-vendor environment.
The AC Drive device profile (profile code 0x02) supplements the EtherNet/IP/
CIP standard. It defines a unified behaviour and technique to access Inverter
and drive device data. All drives supporting the AC Drive profile respond the
same way to control instructions.
5
Page 20

Introduction to EtherNet/IP Section 1-3
6
Page 21

Option Board Mounting and Installation
Model
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
INSTRUCTION SHEET
Thank you for purchasing an OMRON product. Read this
thoroughly and familiarize yourself with the functions and
characteristics of the product before using it. Keep this
instruction sheet for future reference.
Option Board with
Grounding Cable and
EtherNet connector
Instruction Sheet Warning Labels
2-1 Orientation to Option Board Features
2-1-1 Unpacking and Inspection
Take a few moments to unpack your new 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A Option Board
and perform these steps:
1. Look for any damage that may have occurred during transportation.
2. Verify the contents of the box:
SECTION 2
OMRON Corporation
© 2011 OMRON Electronics LLC All rights reserved I37I-E-01
3. Inspect the markings on the Option Board. Make sure it matches the product part number you ordered.
7
Page 22
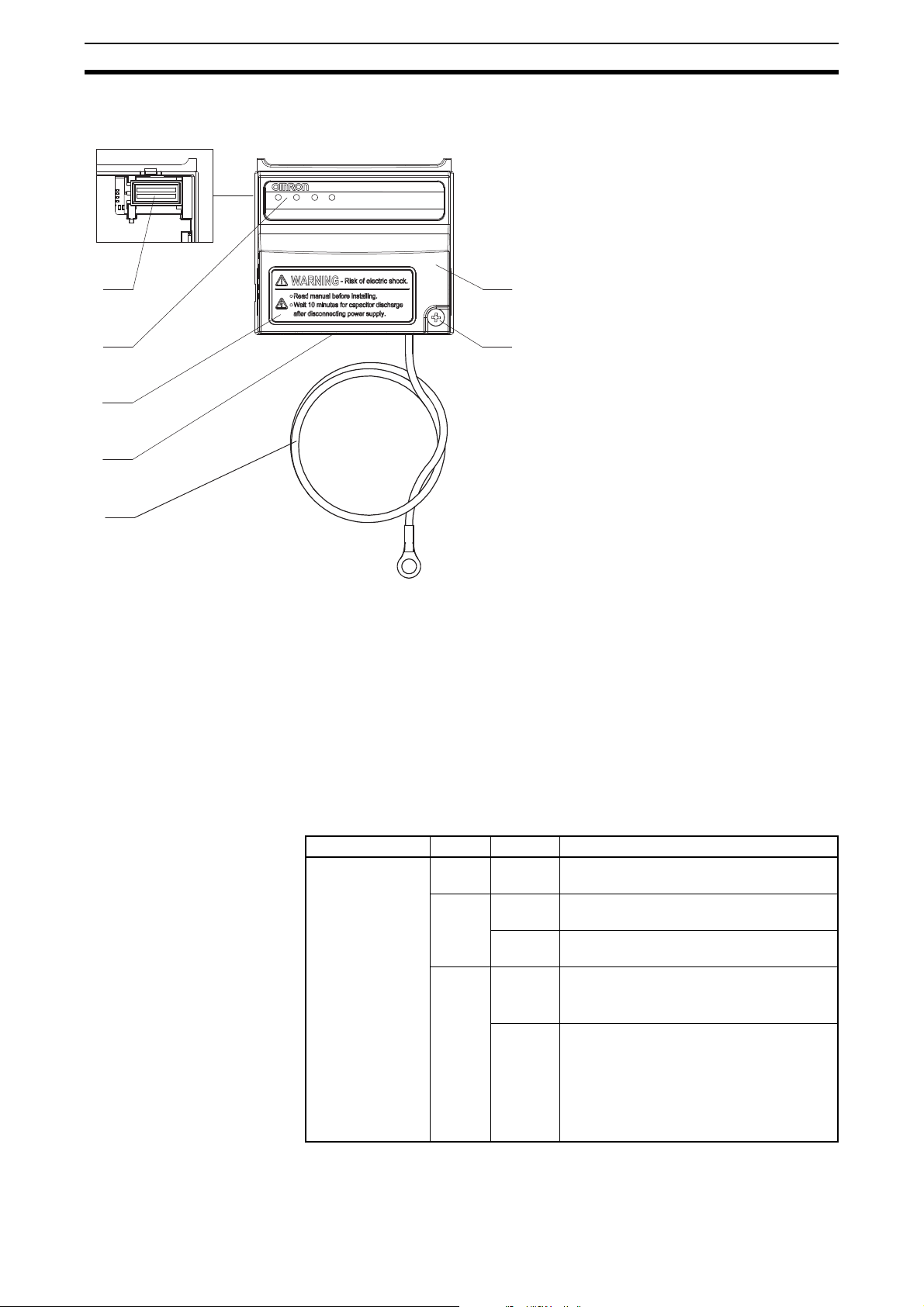
Orientation to Option Board Features Section 2-1
A
underside
C
G
F
D
B
E
MS
NS
LA1
LA2
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
EtherNet/IP
TM
A - Option board connector
B - LED indicators (MS, NS, LA1, LA2)
C - Warning label
D - Fieldbus connector
E - Grounding cable
F - Housing
G - Mounting screw
2-1-2 Main Physical Features
2-1-3 LED Indicators
8
The LED indicators (B) allow easy diagnosis. An attached grounding cable (E)
is sized to reach the ground terminals on all MX2-A Inverter models. A feature in the housing (F) will retain the mounting screw (G) when the Option
Board is not mounted to the Inverter. The orientation of the Fieldbus connector (D) allows unstrained connection and removal of the EtherNet connector.
Please pay special attention to the Option Board connector: It must be properly connected with the Inverter when the Option Board is mounted.
The LED indicators on the front indicate the operational mode and status of
the Option Board and the network.
Table 3 Led Indicators
Indicator Colour Status Meaning
MS
(Module status)
Green Lit Normal operation. Established I/O connec-
Red Lit Unrecoverable fault:
Not Lit • Power is not supplied to the Option Board
• Option Board is being reset
tion in RUN mode.
Flashing • No I/O connection
• I/O connection in IDLE
• Option Board hardware error
• Unsupported Inverter version
Flashing Recoverable fault:
• IP address conflict
• Illegal Flexible configuration
• Option Board parameters out of range or
cannot be read
• Option Board detects consecutive communication errors
Page 23
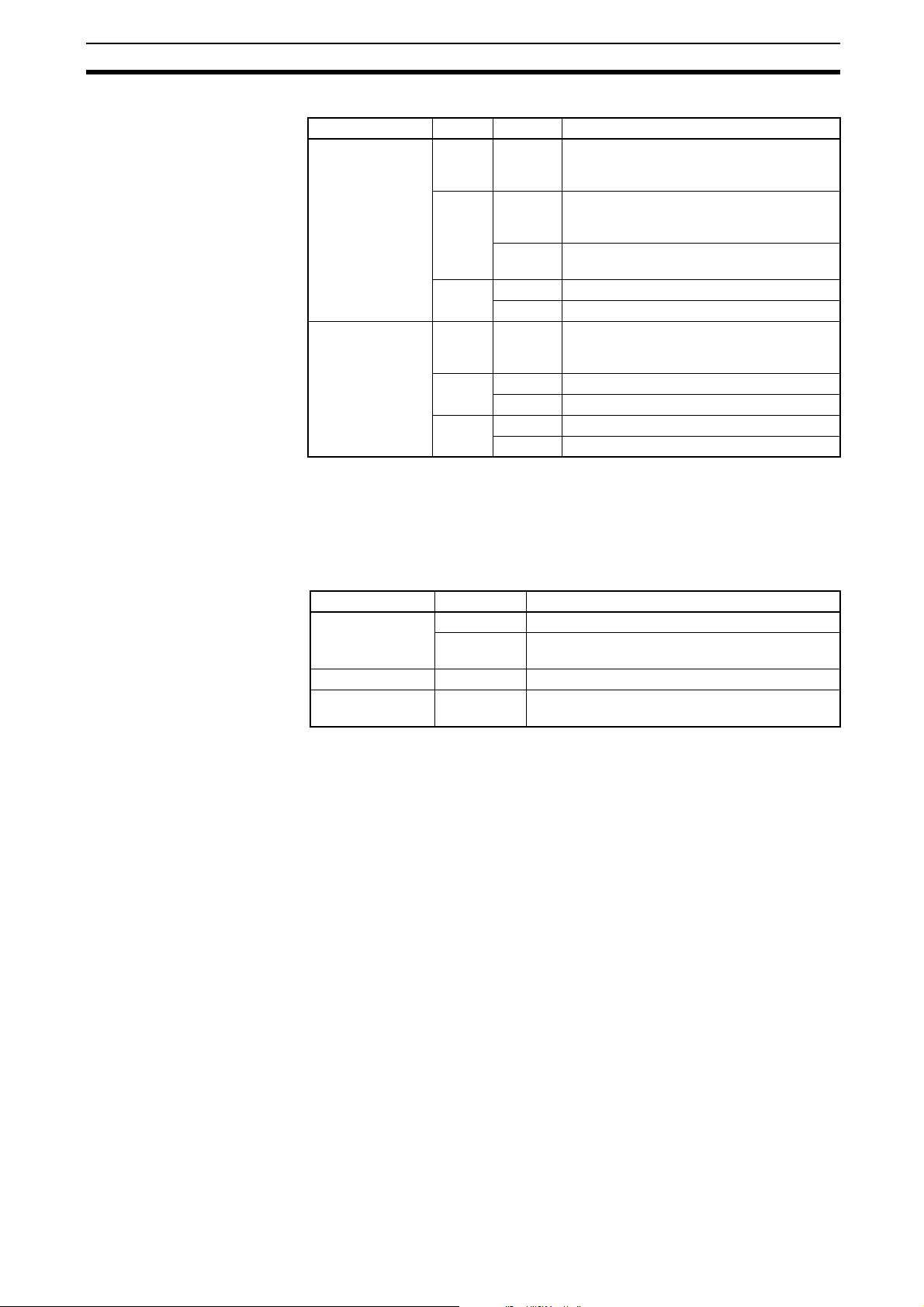
Orientation to Option Board Features Section 2-1
Table 3 Led Indicators
Indicator Colour Status Meaning
NS
(Network status)
Green Lit CIP connection established (any transport
Red Lit • Duplicate IP address detected
LA1, LA2
(Link Activity 1, 2)
Green Lit Link established, 100 Mb
Yellow Lit Link established, 10 Mb
Note Refer to section 5-1 for Troubleshooting using the LED indicators on page 33.
Not lit • Power not supplied (check Module Status
LED)
• No IP address configured
class. No timed out Exclusive Owner connection.
Flashing IP address configured and No CIP connec-
tions established
Flashing Exclusive owner connection timed out
Not lit • Power not supplied (check Module Status
LED)
• No link established
Flickering Activity, 100 Mb
Flickering Activity, 10 Mb
2-1-4 IP Settings
Note Both parameters are only read during power up.
Parameter P185 in the drive is used to determine IP address.
Table 4 Parameter Setting
Parameter Value Meaning
P185 0 (default) Use internally saved IP configuration.
1 - 127 The value of P185 sets the last byte (xyz) of the
IP address (192.168.250.xyz)
P186 0 Do nothing
1 Reset module to default settings, then set param-
eter to 0
9
Page 24

Basic System Description Section 2-2
Slave
PLC
EtherNet/IP Master
MX2-A@ Inverter
+
Option Board
Ethernet network
PC
2-2 Basic System Description
The Option Board connects to the Master via an Ethernet network cable.
Inverter I/O data is generally shared with the Master's I/O memory through the
EtherNet/IP network. Every EtherNet/IP communication cycle, Inverter I/O
data is collected by the Option Board and exchanged with the Master. The PC
(personal computer) allows you to configure, monitor, program, diagnose and
operate the system.
10
Page 25

Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
2-3 Step-by-Step Basic Installation
2-3-1 Option Board Mounting
Always switch OFF the mains power supply to the Inverter before removing
any covers. Wait for the time specified on the Inverter front cover for the
capacitors to discharge. Not doing so may result in electrical shock.
Step 1 Loosen the screw of the option board
cover, remove the cover and put the
cover aside.
Step 2 For Inverters up to 4.0 kW only:
loosen the screws of the terminal
block cover and remove the cover to
enable access to the chassis ground
terminal screws.
11
Page 26
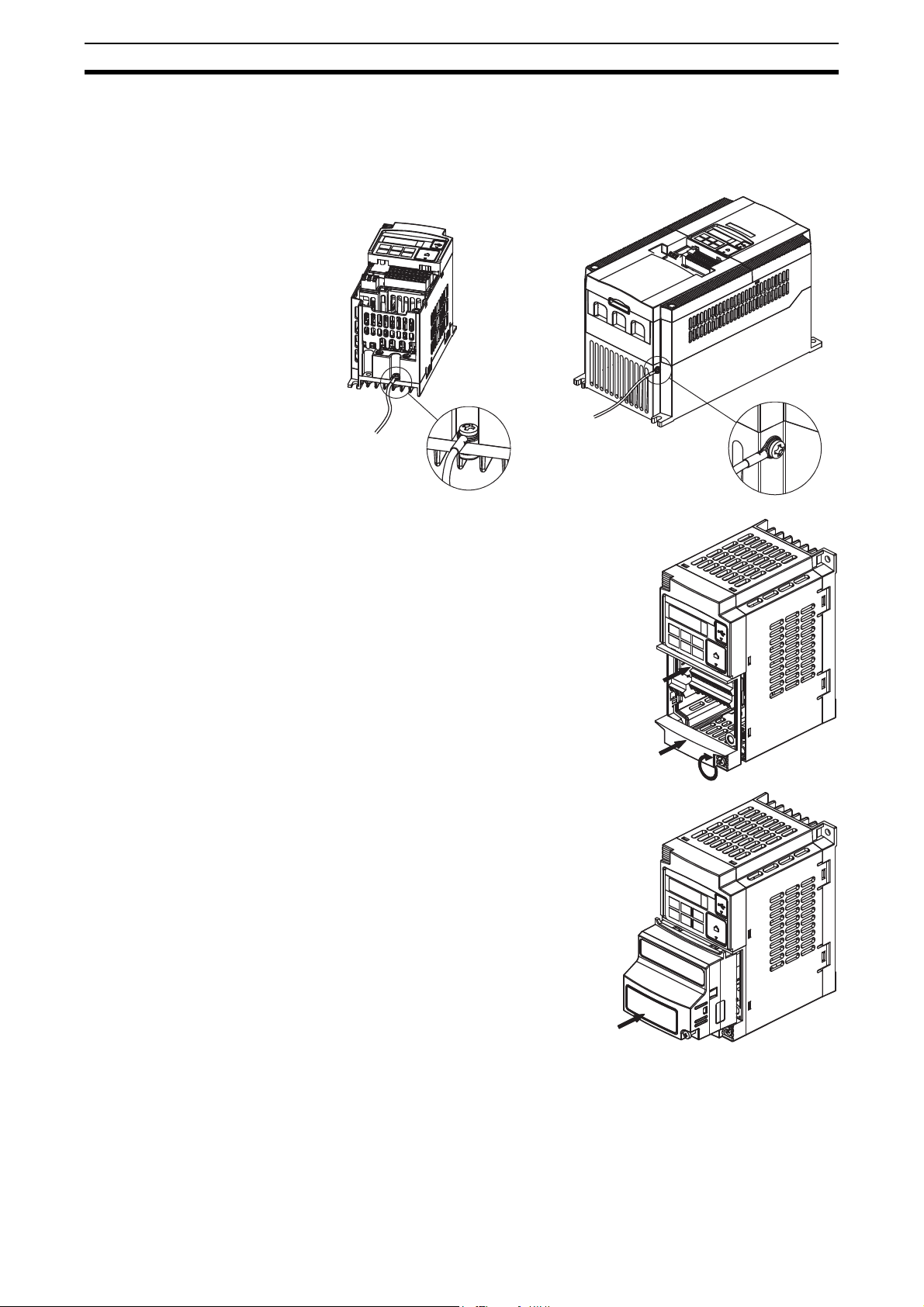
Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
Step 3 Secure the Option Board grounding cable to the MX2-A Inverter with a
mounting screw.
1-phase 200 V 0.1 - 2.2 kW
3-phase 200 V 0.1 - 3.7 kW
3-phase 400 V 0.4 - 4.0 kW
Step 4 If removed in Step 2, mount the termi-
nal cover again and tighten the
screw(s).
3-phase 200 V 5.5 - 15 kW
3-phase 400 V 5.5 - 15 kW
12
Step 5 Push the Option Board into the previ-
ous location of the option board cover
until it clicks into place
Page 27

Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
Step 6 Press down on the indicated corner
of the Option Board housing to
ensure proper connection of the
Option Board connector
Step 7 Check that there is
no gap between the
top edges of the
Option Board and
the Inverter casing.
Step 8 Secure the Option
Board in place with the mounting
screw (do not over-tighten).
Step 9 Select the right warning language from the warning label sheet and replace
the English warning if appropriate.
Note 1 Refer to section 2-1-3 in the MX2 User's Manual (Cat. No. I570) for operations
related to assembly and disassembly of the MX2-A Inverter:
Note 2 Some Inverter models do not include a screw for the grounding cable. Please
supply the recommended screw, lock-washer and washer to attach the
grounding cable.
Table 5 Ground cable screw selection
Inverter models Grounding Cable Attachment Screw
3-phase 200 V 5.5 – 7.5 kW M4 x 6
3-phase 400 V 5.5 – 7.5 kW
13
Page 28

Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
Table 5 Ground cable screw selection (continued)
Inverter models Grounding Cable Attachment Screw
3-phase 200 V 11 – 15 kW M5 x 6
3-phase 400 V 11 – 15 kW
Note 3 Illustrations are only provided for one Inverter size. The instructions however
are generic, and may be followed for all Inverter sizes. Make use of the
MX2-A Inverter manual.
Never operate the Inverter with the terminal block cover or backing plate
removed.
Always connect the grounding cable to one of the ground terminals of the
MX2-A Inverter. Failure to abide could lead to serious or possibly fatal injury.
Provide emergency stop circuits, interlock circuits, limit circuits and similar
safety measures in external circuits (NOT in the Option Board). This ensures
safety in the system if an abnormality occurs due to malfunction of the Option
Board or another external factor affecting the Option Board operation. Not
doing so may result in serious accidents.
Never touch the heat sink during or just after operation; it can be very hot.
Be sure that the Option Board is mounted correctly. Improper mounting may
result in malfunction.
Be sure that all cable connector screws are tightened to the torque specified
in the relevant manuals. Incorrect tightening torque may result in malfunction.
2-3-2 Installation Environment Clearance
Please adhere to the requirements of section 2-3-2 in the MX2 User's manual
(Cat. No. I570) on "Installation Environment clearance". In addition to this,
provide sufficient clearance to allow connection and removal of the Ethernet
connector. No unnecessary strain should be placed on the Ethernet cable or
connector that could be transferred to the Option Board.
14
Page 29
Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
d2
d4
d3
d
w
h
d1
MS
NS
LA1
LA2
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
EtherNet/IP
TM
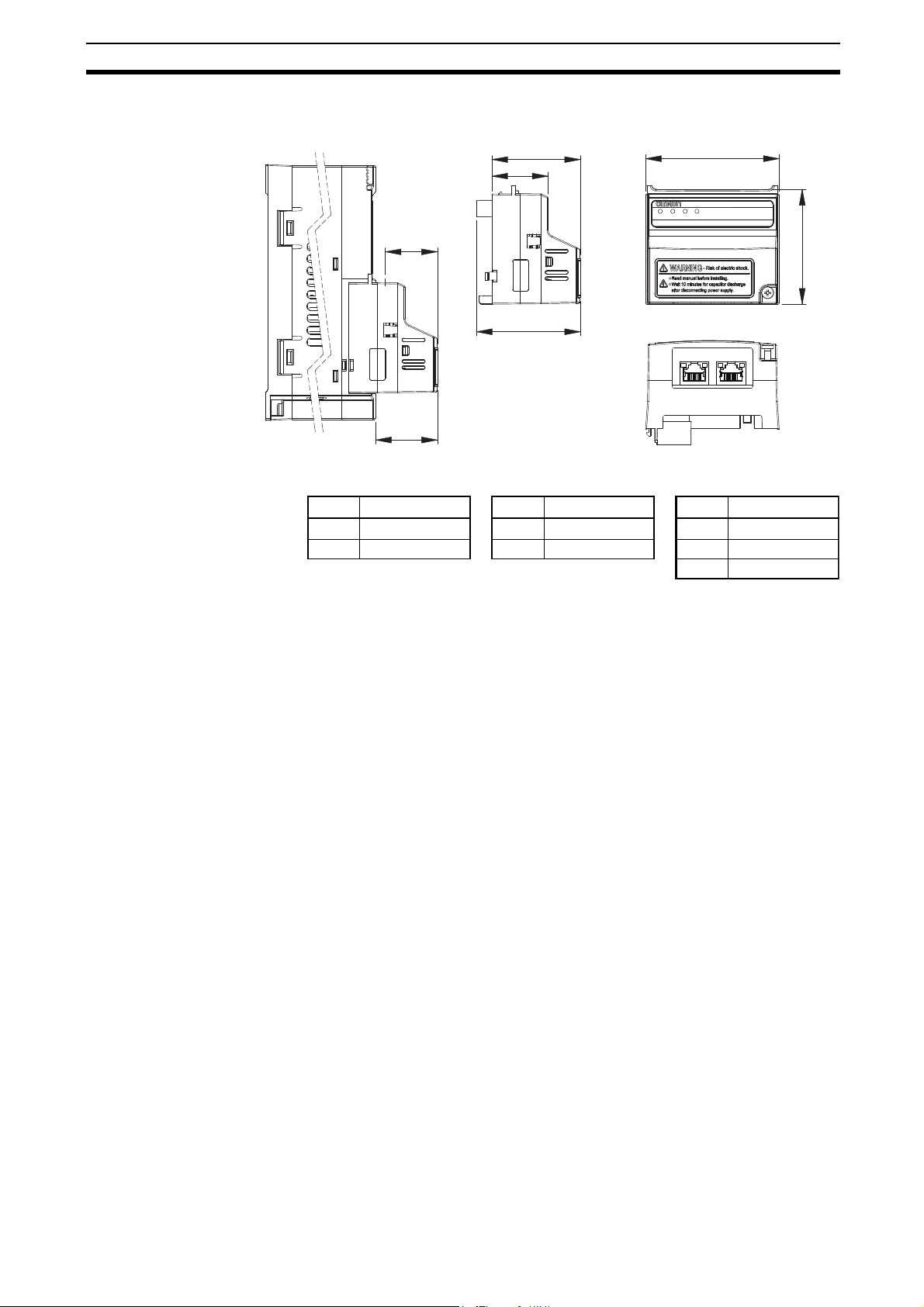
Table 6 Option Board Dimensions
Item Dimension Item Dimension Item Dimension
h 57.9 mm d 52.6 mm d2 31.3 mm
w 67.6 mm
d1
1
1. Dimension d1 gives the increase in MX2-A Inverter dimension D when the
Option Board is fitted. Please refer to section 2-3 of the MX2 User's manual
(Cat. No. I570).
26.4 mm d3 44.8 mm
d4 28.4 mm
2-3-3 Option Board Dimensions
15
Page 30

Step-by-Step Basic Installation Section 2-3
16
Page 31

Configuring Drive Parameters and Option Board
3-1 Installation of EDS files
For each of the MX2 Inverter models, a specific EDS file exists for the Option
Board. The EDS files contain specific parameter data (default, ranges)
depending on the model. Perform the following steps to install the EDS files
prior to configure the network.
Step 1 Download the EDS files named 3G3AX-MX2-EIP- -E.eds for the
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E Option Board via the Omron website (http://
industrial.omron.eu).
Step 2 Install / add these EDS files to the EtherNet/IP Master Unit configuration pro-
gram used to configure your EtherNet/IP master.
3-2 Configuring the Option Board
Step 3 Set inverter parameter B037 to 0 (Full display) to enable access to all inverter
parameters.
Step 4 Set the option board IP address, see 3-4 IP Address Configuration. Use either
the Inverter keypad or any other method of configuring the inverter parameters. See note 1.
SECTION 3
Step 5 It is recommended to set C102 = 3 to prevent the Inverter reset input and
Stop/reset button from interfering with Option Board during operation. Setting
C102 to another value causes the Option Board to reset when a trip condition
is cleared. See the MX2 User’s manual (Cat. No. I570) for details on this
parameter.
Table 7 Configuration of Inverter Reset Mode Selection
Param Description Setting
C102 Reset mode selection Set to 3 "Resetting only trip" (recommended setting)
Step 6 Inverter registers P044, P045 and P048 configure the EtherNet/IP network-
related parameters. Adjust these to configure required action in case a fieldbus network IDLE mode behaviour and/or a fieldbus failure occurs.
Table 8 Configuration of EtherNet/IP Parameters
Param Description Setting
P044 Network Error Timer Communication watchdog timer while running.
Note additional to EtherNet/IP inactivity / watch-
dog timer.
0 to 9999 in 0.1 s unit. Set to 0 to disable.
P045 Action on Network
Error
P048 Action on Network
Idle Mode
Set to 0 for inverter trip (Default)
Set to 1 for deceleration and trip
Set to 2 for no action
Set to 3 for stop due to free-run
Set to 4 for deceleration and stop
Set to 0 for inverter trip (Default)
Set to 1 for deceleration and trip
Set to 2 for no action
Set to 3 for stop due to free-run
Set to 4 for deceleration and stop
17
Page 32

Configuring the Option Board Section 3-2
Step 7 Registers A001 and A002 are used by the Inverter to adjust the frequency
source and control source. If the second motor parameter set is used, registers A201 and A202 also have to be set. Adjust these in accordance with the
following table:
Table 9 Configuration of Source Selection Parameters
Param Description Setting
A001 Motor 1
Frequency Source
A002 Motor 1 Run
Command Source
Step 8 Registers P033, P036, C021, C022 and C026 are used by the Inverter to
adjust some Inverter function sources. If required, adjust these in accordance
with the following table:
Table 10 Configuration of Other Selection Parameter
Param Description Setting
P033 Torque Command
Source
P036 Torque Bias Mode For option board as source:
C021 Output Terminal 11
Source
C022 Output Terminal 12
Source
C026 Alarm Relay Source Set to 63 for option board as source (optional)
For option board as source:
Set to 4 "Option Board input" for all assemblies
except Flexible format (P046 is not 6)
Set to 3 "Modbus network input" in case of Flexible
format (P046 is 6)
For option board as source:
Set to 6 "Option Board input" for all assemblies
except Flexible format (P046 is not 6)
Set to 3 "Digital Operator input" for Flexible format
(P046 is 6)
Set to 5 "Option Board input" for all assemblies
except Flexible format (P046 is not 6)
Set to 3 "Digital Operator input" for Flexible format
(P046 is 6)
Set to 63 for option board as source
Set to 63 for option board as source
Step 9 The Flexible format (assembly 139/159) gives you the freedom to select any
Inverter Modbus register for Cyclic Data Exchange. Inverter registers P160 –
P179 are used to configure and map the exchanged Modbus registers.
Please refer to APPENDIX F Flexible Format on page 77 for more detail.
Table 11 Configuration of Flexible Mapping
Param Description Setting
P160 Output Register 1
contents
P161 Output Register 2
contents
P162 Output Register 3
contents
P163 Output Register 4
contents
P164 Output Register 5
contents
P165 Output Register 6
contents
P166 Output Register 7
contents
P167 Output Register 8
contents
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 1
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 2
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 3
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 4
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 5
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 6
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 7
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 8
18
Page 33

Configuring the Option Board Section 3-2
Table 11 Configuration of Flexible Mapping
Param Description Setting
P168 Output Register 9
contents
P169 Output Register 10
contents
P170 Input Register 1 con-
tents
P171 Input Register 2 con-
tents
P172 Input Register 3 con-
tents
P173 Input Register 4 con-
tents
P174 Input Register 5 con-
tents
P175 Input Register 6 con-
tents
P176 Input Register 7 con-
tents
P177 Input Register 8 con-
tents
P178 Input Register 9 con-
tents
P179 Input Register 10
contents
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 9
Modbus register mapped into flexible output
word 10
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 1
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 2
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 3
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 4
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 5
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 6
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 7
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 8
Modbus register mapped into flexible input word 9
Modbus register mapped into flexible input
word 10
Step 10 Restart the MX2-A@ Inverter for the changes to take effect. See note 1 and 2.
Note 1 Alternative ways for configuring inverter parameters and resetting the inverter
are use the OMRON CX-Drive tool, use Network Configurator for EtherNetIP
with the unit’s EDS file (see SECTION 4 Operations and Monitoring on page
23), or use Explicit messages to access the parameters directly (refer to
APPENDIX E EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages on page 67).
Note 2 EtherNet/IP Master Units in market may send Idle messages during specific
events (start-up, PLC program mode, etc). In this case, consider to put Action
to Network Idle Mode (P048) to value 2 (no action).
The EDS file contains the access data for most of the Inverter’s parameters.
This enables EtherNet/IP configurators such as Network Configurator for EtherNetIP (in the CX-One Suite) to configure the Inverter.
The defaults of the parameters have been selected specifically for the Option
Board and not necessarily the same as the Inverter parameter's default value.
Please note that the write access of the Inverter parameters may depend on
the Inverter mode. Also make sure the Inverter is not in trip state before downloading the parameters.
!WARNING During the parameter initialisation (Inverter parameter b180), operating the
Inverter is not prevented automatically and doing so may lead to unpredicted
behaviour.
Be sure to not operate the Inverter and do not write any Inverter parameter
during the parameter initialisation by Option Board or any other interface.
19
Page 34

Configuring the Network Section 3-3
3-3 Configuring the Network
The EtherNet/IP Configurator software is used to allocate the slaves to the
memory in the Master PLC.
For details about configuring the OMRON CJ1W-EIP21, CS1W-EIP21, CJ2HCPU**-EIP and CJ2M-CPU3* Master Unit’s using the EtherNet/IP Configurator software, refer to EtherNet/IP Unit Operation Manuals (Cat. No. W465).
For details on configuring the drive slave modules refer to the corresponding
manuals (Cat. No. I361).
Step 1 Connect the module to the network.
Step 2 Turn on the power for the driver. Use the keypad to set parameter B037 to 0
(Full display) to enable access to all inverter parameters.
Step 3 Set the IP address of the driver as in the table below. Then turn the power on
for all drivers, communications and PLC or MTaster Unit. The method of IP
address configuration depends on the setting of the inverter parameters:
Table 12 Configuration of IP address
Parameter Description
P185 = 0 The drive will use what is already stored internally. Any previ-
ously stored IP address, e.g. using the web page
At delivery the drive is by default set to receive the IP address
from DHCP/BOOTP.
P185 =1 - 127 The IP address will be 192.168.250.xyz, where xyz is the value
of parameter P185.
P186 = 1 Cycle power. Set parameter P186 to 1 and cycle power again.
The option board will return to factory default settings and
parameter P186 will return to 0 automatically.
1. The web page can also be used to set the Subnet mask, the Gateway Address, Host
Name, DHCP ON/OFF, and Baud Rate for Port 1 and Port 2.
1
will be used.
Step 4 Start the Network Configurator for EtherNet/IP.
Step 5 Import the EDS files into the Network Configurator using the “EDS File” -
“Install Utility”.
Step 6 Go to “DeviceType Communication Adapter” and select the EIP master for
this project - CJ2B-EIP if it is the built-in EIP master in the CJ2H. Drag the
correct communications device into the right window (most likely labelled EtherNet/IP 1). Right click on the device and set “Node Address” to the correct IP
address.
Step 7 Go to “Vendor” - “AC Drives” <pick applicable drive> and drag the correct
drive into the right window (most likely labelled EtherNet/IP 1). Right click on
the device and set “Node Address” to the correct IP address.
Step 8 Attach the slave to the master. Click on the master. Right click “Parameter” -
“Edit”.
Step 9 Tag S e t s .
Start by creating some tags in the PLC. The input and output tags must be the
same size as the connection assemblies to be used in the drive. For example
an array of bits (16) for the control bits and a UINT tag for the speed set point
on the outputs and status bits (16) and speed feedback UINT for the inputs
(this would work for instances 20 and 70). You can either repeat this in the edit
tags window of the Network Configurator or use the “Import tags” button to
import them in the Configurator. Collect all the input tags in one Tag Set adn
all the output tags in another Tag Set.
20
Page 35

IP Address Configuration Section 3-4
Step 10 Select the Connections Tab. The top window will show the drives that are
available on the network.
• Using the down arrow button, move the drive you are configuring to the
bottom window.
• Double click on the drive.
• Choose connection type in the top part of the page.
• Select tags and connection instance from the drive. Connection type will
most likely be “Point to Point” to reduce traffic on the network.
• Set your connection interval and name.
• Click “Regist” button to finish
• Close the window and download the configuration to the master.
Step 11 Once the network is re-started with the new settings, check that the Option
Board LED indicators indicate proper operation: If everything is correctly configured, both the MS (Module Status) LED and the NS (Network Status) LED
will be Green. Please refer to section 5-1 Troubleshooting Using the LED Indi-
cators for troubleshooting any configuration errors if the LED indicators are
displaying a different pattern.
Tip In case of any errors during configuring the network, please refer to SECTION
5 Troubleshooting and Maintenance.
For the user-set allocation, the EtherNet/IP configurator is used. The output
and input data assemblies of the slaves can be allocated freely to the Master
Units IO blocks. Also specific connection variants (COS, Cyclic) can be
selected based on the settings in the EDS file.
3-4 IP Address Configuration
There are different methods to set the IP address of the Option Board:
Table 13 IP address configuration
Method Description
DHCP IP address is obtained from a DHCP server (enabled by default)
Inverter parameters
Web page The IP address can be set on the internal web page of the
TCP/IP object
The IP address is set to 192.168.250.xyz, where xyz is given by
parameter P185 in the drive.
If P185 is set to 0, the Option Board will use the internally saved
IP address.
Setting parameter P186 to 1 will return the Option Board to its
factory settings. (Set P186 to 1, cycle power, P186 will auto
change back to 0.)
Option Board, see
Page
The IP address can be set in the TCP/IP object, see
IP Object (Class 0xF5)
3-4-1 IP Address Configuration Web
E-5 TCP/
21
Page 36

IP Address Configuration Section 3-4
3-4-1 IP Address Configuration Web Page
The IP address of the Option Board can be set on the internal web page.
Table 14 IP address configuration, internal web page
Parameter Description
IP address Enter IP address to be saved internally (will be used after restart
Subnet mask Enter subnet mask to be saved internally (will be used after
Gateway Enter gateway number
Host Name Enter Host Name
DHCP Enable/disable DHCP (will be used after restart if P185 = 0)
if P185 = 0)
restart if P185 = 0)
22
Page 37

This section provides some common usage examples to help you get started.
Table 15 Extended Speed I/O Output Words
Word Bit Allocation
76543210
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Instance ID 21: Extended Speed Control Output
n - REF CTR - - RST REV FWD
--------
n + 1 Rotational Speed Reference (default [0.01 Hz])
Rotational Speed Reference
Bit Name Description
FWD Forward/Stop 0: Stop
1: Forward
REV Reverse/Stop 0: Stop
1: Reverse
RST Fault Reset Reset Fault/Trip condition on transi-
tion from 0 to 1
CTR NetCtrl Run command selection.
0: Setting of A002
1: Network controlled
REF NetRef Speed reference selection.
0: Setting of A001
1: Network controlled
Table 16 Extended Speed I/O Input Words
Word Bit Allocation
76543210
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Instance ID 71: Extended Speed Control Input
n ARF RFN CFN RDY DRR DFR WR FLT
Drive State (see far right)
n + 1 Rotational Speed Monitor (default [0.01 Hz])
Rotational Speed Monitor
Bit Name Description
FLT Fault 0: Normal
1: Fault/Trip
WR Warning 0: Normal
1: Warning
DFR During forward run 0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DRR During reverse run 0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
RDY Inverter ready 0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
CFN Ctrl from Net Run command input selection
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
RFN Ref from Net Speed reference input selection
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
ARF At reference 0: Accel/decel phase
1: At reference
Drive State
Value Description
1Startup
2 Not ready
3 Ready
4 Enabled
5 Stopping
6 Fault/Trip Stop
7 Faulted/Tripped
4-1 Setting up inverter
Unless otherwise specified, all usage examples make use of the Extended
Speed IO format as the connection path (Refer to section 3-1 Installation of
EDS files, Step 2). Prepare the Inverter and Option Board before starting with
the usage examples:
Step 1 Initialize the Inverter mode to Std. IM by first setting b171 = 1 and then
b180 = 1 (Refer to MX2 User’s manual (Cat. No. I570) section 3-6-24).
Step 2 Set the Inverter rating to CT (constant torque) by setting b049 = 0 (Refer to
the MX2 User’s manual section 3-2-5).
Step 3 Configure the Option Board and Network as explained in sections 3-1 Installa-
tion of EDS files and 3-2 Configuring the Option Board with Extended Speed
IO (Output assembly 21, Input assembly 71).
• Select the two Extended Speed IO assemblies.
If you configured everything correctly, your output and input I/O words should
contain the following data:
SECTION 4
Operations and Monitoring
!Caution Check the Inverter settings for proper Inverter behaviour before actually oper-
ating the Inverter remotely via the network.
23
Page 38

Operating the Motor Section 4-2
The product will be used to control an adjustable speed drive connected to
high voltage sources and rotating machinery that is inherently dangerous if
not operated safely. Interlock all energy sources, hazardous locations, and
guards in order to restrict the exposure of personnel to hazards. The adjustable speed drive may start the motor without warning.
Signs on the equipment installation must be posted to this effect. A familiarity
with auto-restart settings is a requirement when controlling adjustable speed
drives. Failure of external or ancillary components may cause intermittent
system operation, i.e., the system may start the motor without warning or may
not stop on command. Improperly designed or improperly installed system
interlocks and permissions may render a motor unable to start or stop on
command.
4-2 Operating the Motor
4-2-1 Starting the Motor
Step 1 Set A001 = 4 and A002 = 4 so that the Inverter can be controlled using the
EtherNet/IP Option Board.
Note The net control (CTR) and net reference (REF) override bits in the 1
word can be used to override A001 and A002.
When these bits are set, it has the same effect as temporarily setting
A001 = 4 and A002 = 4. Clearing these bits removes the override, and the
Inverter sources are once again determined by these registers.
Step 2 Set F002 and F003 for adjusting the acceleration and deceleration time of the
motor. Refer to MX2 User’s manual (Cat. No. I570) section B-4.
Step 3 Set the Rotation Speed Reference (see Appendix B) of the Inverter in the 2
I/O output word to 10.00 Hz.
Step 4 Set the FWD bit to put the Inverter in run mode. The RUN indicator on the
Inverter should light up at this point. If this is not the case, check your source
selection (please refer to section 3-2 step 5).
The motor accelerates until it reaches the desired frequency. Notice that the
ARF bit is set once the inverter has reached the desired Rotation Speed Reference.
4-2-2 Changing Direction
Step 5 Clear the FWD bit and set the REV bit.
The motor decelerates stops and then accelerates in the opposite direction.
ARF bit clears as soon as the Rotation Speed Reference is changed. Once
the new Rotation Speed Reference is reached, ARF bit is set again.
st
output
nd
4-2-3 Stopping the Motor – Decelerated stop
Step 6 Clear the run bits (FWD or REV) to bring the motor to a controlled (deceler-
ated) stop.
The motor decelerates, and comes to a stop. ARF bit clears as soon as the
run bit is cleared.
Before continuing set Rotation Speed Reference to 0 Hz.
Note The motor can also be brought to a stop by setting Rotation Speed Reference
to 0 Hz and leaving the run bits set. The Inverter will however stay in run
mode once the motor has reached 0 Hz.
24
Page 39

Overriding Inverter inputs Section 4-3
4-2-4 Stopping the Motor – Free-running
An alternative to Clear the run bits (FWD or REV) to bring the motor to a controlled (decelerated) stop of step 6 is a free-run stop. The Inverter stops controlling the motor, and the motor coasts to a stop. Set C001 = 11 (FRS: freerun stop) to assign intelligent input terminal 1 as free-run stop enable. Restart
the Inverter or reset the Option Board for the new settings to take effect. Set
the terminal input 1 to ON to enable free-run stop. During a free-run stop,
Rotation Speed Monitor immediately drops to 0 and ARF bit is cleared.
4-2-5 Changing Speed Reference and Speed Monitor Scaling
Rotational Speed Reference and Rotational Speed Monitor are word registers. The scaling of these values depend on the inverter's Motor poles setting
P049:
1. In case P049 has non-zero value, the Unit is RPM.
2. In case P049 is set to zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode. If the
inverter is in High Frequency (HF) mode, the Unit is 0.1 Hz. The unit will
be 0.01 Hz in other modes.
For the second option (Unit is either 0.1 Hz or 0.01 Hz), the maximum frequency which can be set is 400.00 Hz. Please refer to 3&3MX2 User's manual (Cat. No. I570) for instructions about inverter modes and parameter P049.
4-3 Overriding Inverter inputs
By using the Option Boards input override functionality, the Inverter Intelligent
Terminal Functions can be controlled from the network.
The following example explains how to make use of the Option Board to override the input function Free Run Stop (FRS) using the IO data.
Step 1 Configure the Option Board and Network as explained in sections 3-1 Installa-
tion of EDS files on page 17 and 3-2 Configuring the Option Board on page 17
with Extended Control IO and Multi-function IO monitor (Output assembly
101, Input assembly 151).
Step 2 Set C003 = 11 (FRS: Free Run Stop) to assign intelligent input terminal 3.
Step 3 The output words of assembly 101 contain the CI3 bit (see table 16), which
overrides input terminal 3. Set this bit to enable the free run stop.
Please note that as an alternative to override inputs using this assembly with
bits CI3 to CI7, also the explicit message writing the Discrete Input Point
Object (0x08) can be used. Please refer to APPENDIX B Assembly Specifica-
tion on page 43 and APPENDIX E EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages on page
67).
4-4 Controlling Inverter Torque
In addition to Speed control, the MX2-A@ Inverter allows direct control of the
motor torque.
!Caution Before following this example, disconnect your motor from any load to prevent
injury or damage to property.
The following example explains how to make use of the Option Board to control the motor torque:
Step 1 Configure the Option Board and Network as explained in sections 3-1 Installa-
tion of EDS files and 3-2 Configuring the Option Board with Control IO and
Multi function IO monitor (Output assembly 101, Input assembly 151).
25
Page 40

Controlling Inverter Torque Section 4-4
Table 17 Extended Speed Torque I/O Output Words
Word Bit Allocation
76543210
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Instance ID 101:
Extended Control IO Output
n - CI7 CTR CI5 CI4 CI3 REV FWD
CO2 CO1 CR - - - RST FFL
n + 1 Rotational Speed Reference (default [0.01 Hz])
Rotational Speed Reference
n + 2 Torque Reference [1 %]
Torque Reference
n + 3 Torque Compensation Bias [1 %]
Torque Compensation Bias
Bit Name Description
FWD Forward/Stop 0: Stop
1: Forward
REV Reverse/Stop 0: Stop
1: Reverse
RST Fault Reset Reset Fault/Trip condition on transi-
tion from 0 to 1
FFL Force Fault Force external fault/trip from network
CI3 to
CI7
Control/Override
Input
0: Reset 1: Set override for Multi
Function input 3 to 7.
CO1,
CO2,
CR
Set (Relay) Output 0: Reset 1: Set Multi Function 1 to 2
or Relay Output (CR).
Table 18 Extended Speed Torque I/O Input Words
Word Bit Allocation
76543210
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Instance ID 151: Extended Control IO Input
n FLT WR RDY ARF - DRR DZS DFR
- - MO2 MO1 MR CFN - -
n + 1 Rotational Speed Monitor (default [0.01 Hz])
Rotational Speed Monitor
n + 2 Torque actual [1 %]
Torque actual
n + 3 Output current monitor [0.1 A]
Output current monitor
n + 4 - MI7 MI6 MI5 MI4 MI3 MI2 MI1
--------
Bit Name Description
DFR During forward run 0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DZS During zero speed 0: Non-zero speed
1: During zero speed
DRR During reverse run 0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
ARF At reference 0: Accel/decel phase
1: At reference
RDY Inverter ready 0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
WR Warning 0: Normal
1: Warning
FLT Fault 0: Normal
1: Fault/Trip
CFN Control from net Run command input selection
(0: local, 1: EtherNet/IP)
MO1,
MO2,
MR
Monitor (Relay)
outputs
0: OFF
1: ON
Step 2 Set C003 = 52 (ATR: permission of torque command input) to assign intelli-
gent input terminal 3 as torque enable. See also section 4-3 Overriding
Inverter inputs
Step 3 Set parameter A044=3 to enable Sensorless Vector Control (SLV).
Step 4 Set parameter P033=6 to assign Torque command input selection to Option
Board.
Step 5 Restart the Inverter or reset the Option Board for the new settings to take
effect.
Note The Inverter will only allow setting of torque related registers if it is configured
to operate with CT rating in Std. IM mode.
Your input and output process areas should now have the following layout:
Step 6 Set the maximum allowable output frequency in torque mode by configuring
P039 and P040 for the forward- and reverse run directions. Be careful to
select safe limits for your test setup.
26
Step 7 Set the Rotation Speed Reference (see APPENDIX B Assembly Specification
Step 8 Set the Torque Reference of the Inverter in the 3
Step 9 Set the FWD bit to put the Inverter in run mode. The motor will accelerate to a
Step 10 Override the input terminal 3 (CI3) to enable torque command input.
on page 43) of the Inverter in the 2
constant forward output frequency.
nd
I/O output word to 10.00 Hz.
rd
I/O output word to 20%.
Page 41

Faults and Trips Section 4-5
The motor either accelerates or decelerates depending on the load. The output frequency is limited by the P039 setting. The output torque is given by
d012.
Step 11 To change the torque command direction, clear the FWD bit and set the REV
bit.
The motor decelerates and accelerates in the opposite direction. The output
frequency is limited by the P040 setting.
Note As an alternative for the overriding of input terminal 3 from the network at step
10, also the physical input terminal can be used.
4-5 Faults and Trips
4-5-1 External Trip
You may want to trip the Inverter from your PLC program. Not all assemblies
support setting the external trip by using a bit in IO Data. Basically there are
two options:
• Select an assembly which support this trip set in the output data.
• Using explicit message to set the Force Fault/Trip attribute in the Control
Supervisor Object ( Class 29 Hex, Instance 01 Hex, Attribute 11 Hex).
The two Extended Control IO assemblies (Output 101, Input 151) contains the
FFL (Force Fault/Trip) bit and can be used for this feature.
Step 1 Follow the instructions sections 3-1 Installation of EDS files and 3-2 Configur-
Step 2 Set bit 8 (FFL) of the first word of the output data to trip the Inverter.
4-5-2 Clearing a Trip
!WARNING In the event the Inverter is in a Trip state, be sure to investigate the cause of
Step 1 Please clear the FWD and REV bits in your PLC program when a rising edge
Step 2 Set the RST bit of the output assembly to clear the trip.
ing the Option Board to configure the assemblies.
The alternative is to use the explicit message mechanism to generate the
external trip. Please refer to APPENDIX E EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages
example 3 for a description how to do this.
When the inverter trips due to a fault condition first analyse the trip cause as
explained in section 5-1 Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators on page 33
or section 5-3 Maintenance and Inspection on page 38.
Notice that the FLT bit is set (present in all output assemblies) when the
Inverter trips.
this Trip state thoroughly before clearing the Trip. Not checking the cause may
result in unexpected operation.
is detected on FLT.
!WARNING Always clear the run bits FWD and REV in your PLC program on the rising
edge of the FLT bit. Not doing so may result in the motor starting unexpectedly when the trip is cleared via EtherNet/IP or the „Stop/reset“ button on the
Inverter
27
Page 42

Accessing Parameters Section 4-6
4-6 Accessing Parameters
EtherNet/IP explicit messages sent from the Master Unit to the
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E Unit can be used to access any parameter from the Unit
or the MX2-A@ Inverter. Please refer to the APPENDIX E EtherNet/IP Explicit
Messages on page 67 for details and examples.
Refer to the EtherNet/IP Master Units Operation manual (Cat. No. W465) for
details on how to send the explicit messages to the 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A.
Below are examples for usage of the OMRON CJ1W-EIP21 Master Unit with
the FINS Explicit Message Send command (2801).
4-7 Flexible Format
The Flexible format lets you operate the Inverter either from the web page or
by using the Modbus registers directly. Parameters P160 to P169 and P170 to
P179 can be used to map Modbus registers into the cyclically exchanged IO
data. User parameters P160 to P169 configure the output data words where
parameters P170 to P179 configure the input data words.
Please refer to the APPENDIX F Flexible Format on page 77 for details on the
flexible mode.
4-7-1 Typical Configuration
Step 1 Configure the Option Board and Network as explained in sections 3-1 Installa-
tion of EDS files and 3-2 Configuring the Option Board.
Step 2 Set parameters P160 to 1F01h to map coil data 0 as the first output word.
Step 3 Set parameters P161 and P162 to 0001h and 0002h to map the Modbus fre-
nd
quency reference (F001) as the 2
Step 4 Set parameter P170 to 0005h to map Inverter status C as the first input word.
Step 5 Set parameter P171 to 1E01h to map coil data 1 (coil no 0010h to 001Fh) into
the second input word.
Step 6 Set parameters P172 and P173 to 1001h and 1002h to map the Modbus fre-
quency monitor (d001) as the third and fourth input word.
Step 7 Restart the Inverter or reset the Option Board for the new settings to take
effect.
If you configured everything correctly, your output and input words should
have the following mapping:
and 3rd output words.
28
Page 43

Flexible Format Section 4-7
dec
hex
1514131211109876543210
-
- In7 In6 In5 In4 In3 In2 In1 - - RS EXT Dir Opr -
0000000000000000
In4
In5
In6
Value
Name
Bit
EXT
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0
---
000
Word offset
+1+0+2
+3-+4
-
-+9-
+8+5+6
+7
Value
F001 (0001h/0002h)
0
Register
0
0000
Opr
Operation command
Intelligent input terminal [3]
In3
0
0000
0000
0000
0
0
External Trip
Intelligent input terminal [5]
RS
Trip reset
Intelligent input terminal [6]
Dir
Rotation direction command
Intelligent input terminal [4]
In2
Intelligent input terminal [2]
In1
Intelligent input terminal [1]
In7
Intelligent input terminal [7]
Coil data 0
(see note)
dec
hex
1514131211109876543210
ONT RNT TRQ UV - OTQ FA3 AL OD OL FA2 FA1 RUN - Rdy Dir
0000000000000010
FA3
OTQ
UV
RNT
ONT
Invstat C
Inverter status C (Refer to Inverter Manual section B-4-2)
OL
Overload advance notice
OD
Output deviation for PID control
FA2
Set frequency overreached
TRQ
Torque limited
Operation time over
Plug-in time over
RUN
Running
Over-torque
FA1
Constant-speed reached
Undervoltage
Dir
Rotation direction
AL
Alarm signal
Rdy
Inverter ready
Set frequency reached
-+4-
-+9-
+8+5+7
-
Value
+6+2+3
Coil data 1
Register
Word offset
+1
+0
Invstat C
d001 (1001h/1002h)
0
0000
-
000
0002
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0
0
Value
0
Name
2
Bit
1
0001
0000
dec
hex
1514131211109876543210
-
*1
- In7 In6 In5 In4 In3 In2 In1 - - RS EXT Dir Opr -
000000000000001 0
000000000
0000
0000
000000000
0000
Value
F001 (0001h/0002h)
+1000
Register
2
0002
0000
03E8
-+4-
-+9-
+8+5+6
+7
0
0
---
0
0
Value
Name
Bit
+2
+30Word offset
+1
+0
Coil data 0
Table 19 Flex Mode Output Area with Typical Configuration
Table 20 Flex Mode Input Area with Typical Configuration
Confirm the Output has a data size of 3 words and the Input has 4 words. This
is because P163 to P169 and P174 to P179 are all set to zero.
Note Do not set bit 15 of the Coil data 0 to ON. The operation status coil (000Fh)
cannot be used in the output process area.
4-7-2 Operating the Motor
Step 8 Set A001 = 3 and A002 = 3 so that the Inverter can be controlled using the
Modbus registers in Flexible mode.
Step 9 Set the Opr bit to put the Inverter in run mode. The RUN indicator on the
Inverter should light up at this point. If this is not the case, check your source
selection.
Step 10 Change F001 in the Output data to the desired frequency (E.g. 1000 for
10.00 Hz)
Table 21 Flex Mode Output Area with Motor Running Forward
The motor accelerates until it reaches the desired frequency. Notice that the
FA1 bit is set once the inverter has reached the desired reference frequency.
29
Page 44

Flexible Format Section 4-7
dec
hex
1514131211109876543210
ONT RNT TRQ UV - OTQ FA3 AL OD OL FA2 FA1 RUN - Rdy Dir
0000000000011010
-+4-
-+9-
+8+5+7
-
Value
+6+2+3
Coil data 1
Register
Word offset
+1
+0
Invstat C
d001 (1001h/1002h)
0
03E8
-
000
001A
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0
0
Value
+1000
Name
26
Bit30003
0000
Table 22 Flex Mode Input Area with Motor Running Forward
Step 11 Set Dir to reverse the direction of the motor. The motor decelerates, stops and
then accelerates in the opposite direction. The FA1 bit clears as soon as the
reference frequency is changed. Once the new reference frequency is
reached, the FA1 bit is once again set.
Step 12 Clear the Opr bit to stop the motor. The motor decelerates and comes to a
halt.
4-7-3 Faults and Trips
User trips can be generated by setting the EXT bit in coil data 0. You must
always immediately clear the Opr bit in your PLC program when the Unit indicates it is in Trip status (for example when AL bit is set ON). If the Opr bit is
set when the trip condition is cleared, the Inverter will immediately start running!
!WARNING Always clear the Opr bit in your PLC program when the AL bit is set ON by the
Inverter. Not doing so may result in the motor starting unexpectedly when the
trip is cleared.
Set and clear the RS bit in coil data 0 to clear a trip.
!WARNING Always clear the RS bit after setting it. Not doing so will result in new trip con-
ditions automatically being cleared.
30
Page 45

Limitations Caused by Inverter Mode and Rating Selection Section 4-8
4-8 Limitations Caused by Inverter Mode and Rating Selection
The Inverter mode and rating selection directly affects several aspects of the
Option Board usage. Refer to the MX2 User’s manual section 3-6-24. The following table lists the most common consequences of the various Inverter
modes and ratings:
Table 23 Limitations Caused by Inverter Mode and Rating Selection
Inverter Mode and
Rating
d060 0 (1-C) 1 (1-v) 2 (H-1) 3 (P)
Rotational speed scaling 0.01 Hz 0.1 Hz 0.01 Hz
Torque-related registers Available Not available (see note 1)
Note 1 The Inverter will trip due to a cyclic mapping fault if you use torque-related
registers in the process area when not available.
Standard Induction Motor High
Constant
Torq ue
Varia ble
Torq ue
Frequency
Permanent
Magnet
4-9 Connections
I/O data can be transferred via Class 1 connections that are established to the
assembly object instances. The total number of connections can be no more
than three. Each connection supports data transfer in both directions.
There are three kinds of Class 1 connections, exclusive-owner, input-only and
listen-only.
There can be only one exclusive-owner connection for each module. It controls the output of the module and does not depend on any other connection.
The input-only connection is used to read data from the module without affecting the output. If an exclusive-owner connection is open, it will tune in on that
connection and will time out with it as well. A properly closed exclusive-owner
connection will not affect an input-only connection.
The listen-only connection depends on another connection for its existence,
and will be closed if the other connection is closed.
For more information see C-4 Connection Manager (Class 0x06).
31
Page 46

Connections Section 4-9
32
Page 47

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
MSMSMSMSMS
5-1 Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators
The four bi-color LED indicators on
the Option Board provide information
on the Option Board mode and status and the network status.
When an error occurs, the Option
Board trips the Inverter so that an
error code is displayed on the fourdigit display of the Inverter. Use the
error code to help troubleshoot the
error.
In the following sections typical LED
indicator and four-digit Inverter display patterns are provided to assist
in troubleshooting. To show the status of the indicators, the following
conventions are used:
MS
NS
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A
SECTION 5
LA2
LA1
EtherNet/IP
TM
OFF
RED
GREEN
Flashing
Not important (Ignore)
Inverter error code
Not important (Ignore)
Tip Do not clear the trip before you are finished troubleshooting an error. When
you clear the trip, the error code is cleared from the four-digit display. You may
therefore lose the error information before you are able to start troubleshooting. Checking data in trip history is still an option in this case.
33
Page 48

Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators Section 5-1
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
5-1-1 Option Board or Inverter Errors
During the Initialization process the MS and NS indicator shortly blink GREEN
and RED to show correct operation of the indicator. Please refer to 2-1-3 LED
Indicators for behaviour at normal operation.. The table below shows the indicator and display patterns caused by Option Board or Inverter Errors.
Table 24 Option Board or Inverter Errors
Display &
Indicators
The Inverter does not power up. Follow the instruction provided in the MX2 User’s manual (Cat.
The Option Board connector is damaged Replace the Option Board.
No IP address Establish IP address, see 3-4 IP Address Configuration
The Inverter RS input is ON Switch the Inverter RS input OFF.
The Option Board encountered a fatal
error during Power-on
The Inverter does not support a 3G3AXMX2-EIP-A (Refer to section 5-1-2 Con-
figuration Errors)
The Option Board connector is damaged Replace the Option Board.
The Option Board encountered a fatal
error during Operation.
Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
No. I570) section 6-1-4 to troubleshoot.
Check that the Option Board is mounted properly and restart
the Option Board. If the problem persists, replace the Option
Board.
Replace the Inverter with a later version.
Check that the option is mounted properly and restart the Option
Board. If the problem persists, replace the Option Board
The Inverter is tripped with the Force
Clear the FFL Force external fault bit and reset the trip.
external Fault/Trip through the fieldbus.
The Inverter detected a fatal error in the
operation of the Option Board.
Check that the option is mounted properly and restart the
Option Board. If the problem persists, replace the Option Board
34
Page 49

Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators Section 5-1
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
5-1-2 Configuration Errors
If the Option Board is correctly configured, the MS indicator will lit or flash
GREEN The table below shows the indicator and display patterns caused by
configuration errors.
Table 25 Configuration Errors
Display &
Indicators
One of the configuration parameters
P160 – P179 has been rejected by the
Inverter.
Your Inverter settings are not compatible
with this version of the 3G3AX-MX2-EIPA.
The option board has failed to read its
internally stored configuration
Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
Check (and correct) the following items:
STEP I:
• Is one of the parameters P160 – P179 specifying a Modbus
register that does not exist?
• If one of the parameters P160 – P169 is specifying a doubleword Modbus register: Are both the low- and high-words
specified in sequence by two consecutive parameters?
• If one of the parameters P170 – P179 is specifying a doubleword Modbus register: Are both the high- and low-words
specified in sequence by two consecutive parameters?
• Is a specific Modbus register specified twice in the output
parameter registers P160 – P169?
• Is one of the output parameters P160 – P169 specifying a
Modbus register that is read only? (A register is read-only if it
has an ‘R’ in the ‘R/W’ column in section B-4-2 of the MX2
User’s manual (Cat. No. I570).)
• Is one of the output parameters P160 – P169 specifying a
Modbus register of which the parameter is not run-mode editable? (A parameter is not run-mode editable if it has an ‘’ in
the ‘Run Mode Edit’ column in section 3 of the MX2 User’s
manual.)
STEP II:
Restart the system by one of the following method
• Power OFF and ON
• Press the stop button on the Operator panel.
• Use the RS function of the intelligent input terminal.
Recovery via the fieldbus:
• Use Modbus Class Object to set the Trip reset coil (04h) in
coil register 0x1F01.
• Check P045 value in range [0..4] and restart unit.
• Check P046 value in range [0..7] and restart unit.
• Check P048 value in range [0..4] and restart unit.
• Reset the Inverter to factory defaults. If the problem persists,
contact your local OMRON representative for assistance.
• Reset the Inverter to factory defaults. If the problem persists,
contact your local OMRON representative for assistance.
35
Page 50

Troubleshooting Using the LED Indicators Section 5-1
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
MS NS
5-1-3 EtherNet/IP Errors
If the EtherNet/IP master is correctly configured and there are no wiring
errors, the NS indicator will lit GREEN. The table below shows the indicator
patterns caused by configuration EtherNet/IP errors.
Table 26 EtherNet/IP Errors
Display &
Indicators
Waiting for connection -
Duplicate IP address detected. Does the Master Unit or any other slave device on the Ether-
Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
Net/IP network also have the same IP address?
Remove conflict and restart.
The Option Board detects: communication idle or communication timeout
(P044).
An exclusive owner EtherNet/IP connection has timed out. The Option Board
detects communication lost.
5-1-4 Commissioning Mode
When using one of the OMRON tools during commissioning time, the
3G3AX-MX2-EIP-E can be set into commissioning mode. A clear indication
will be given by the tool.
Commissioning mode is NOT an error, but it can influence normal system
operation. During commissioning mode, Inverter parameter access takes priority over cyclic data exchange. Accessing Inverter parameters will therefore
delay cyclic data exchange causing unexpected latencies.
!Caution Make sure that commissioning mode is disabled before operating the system.
Check (and correct) the following items:
• Is the EtherNet/IP master sending IDLE messages? Check
P048 to select the Action on Network Idle.
• Increase the value of P044, the timeout value. (COS/Cyclic
connections require the P044 time-out to be set to a value
larger than the heartbeat timer).
• Set P044 to 0. (Turns off the watchdog timer)
• Set P045 to select the action on network timeout,
Check (and correct) the following items:
• is the EtherNet/IP Master operating correctly?
• Is the network topology between Master and network ok?
• Check P045 to select the action on netw0rk timeout.
36
Page 51

Other Error Causes and Error Procedures Section 5-2
5-2 Other Error Causes and Error Procedures
This section explains about errors which are not shown as specific LED
indicator states.
Table 27 Other errors
Error event Possible cause and procedure
Within Network Configurator for EtherNetIP, the download or upload of the
parameters of the Unit fail.
Explicit message access of the
parameters (using Function Code object
or Modbus Register object) fail.
The Inverter may have limited write access to the parameters
based on the Inverter mode selected.
The Inverter may be in Trip state, which prevents parameters to
be downloaded.
Check the proper Inverter mode and state before attempting
downloading again.
The Inverter may have limited write access to the parameters
based on the Inverter mode selected.
The Inverter may be in Trip state, which prevents parameters to
be downloaded.
Check the proper Inverter mode and state before attempting
downloading again.
37
Page 52

Maintenance and Inspection Section 5-3
5-3 Maintenance and Inspection
5-3-1 Replacing the Option Board
!HIGH VOLTAGE Always Switch OFF the mains power supply to the Inverter before removing
the Option Board. Wait for the time specified on the Inverter front cover for the
capacitors to discharge. Not doing so may result in electrical shock.
Step 1 Loosen the faulty Option Board
mounting screw.
Step 2 Pull the faulty Option Board straight
out of the Inverter while pushing
down on the indicated sides to
release the snap-fits.
Step 3 For Inverters up to 4.0 kW only:
loosen the screw(s) of the terminal
block cover and remove the cover to
enable access to the chassis ground
terminal screws.
38
Page 53

Maintenance and Inspection Section 5-3
Step 4 Unscrew and remove the faulty Option Board grounding cable. Keep the
screw and washers, but set the faulty Option Board aside.
1-phase 200 V 0.1 - 2.2 kW
3-phase 200 V 0.1 - 3.7 kW
3-phase 400 V 0.4 - 4.0 kW
Step 5 Secure the replacement Option Board grounding cable to the MX2-A@
Inverter using the mounting screw saved in .Unscrew and remove the faulty
Option Board grounding cable. Keep the screw and washers, but set the
faulty Option Board aside.
3-phase 200 V 5.5 - 15 kW
3-phase 400 V 5.5 - 15 kW
Step 6 If removed in Step 3, mount the termi-
nal cover again and tighten the
screw(s).
Step 7 Push the replacement Option Board
into Inverter to replace the removed
Option Board until it clicks into place
39
Page 54

Maintenance and Inspection Section 5-3
Step 8 Press down on the indicated corner
of the replacement option board
housing to ensure proper connection
of the option board connector
Step 9 Check that there is
no gap between the
top edges of the
replacement Option
Board and the
Inverter casing.
Step 10 Secure the replacement Option
Board in place with the mounting
screw (do not over-tighten).
!Caution When replacing an Inverter be sure that all Inverter settings of the Inverter
being replaced are restored to the replacement.
40
Page 55

APPENDIX A
Glossary
Change of state (COS) In case a Slave unit is configured for change of state data exchange, it will
send data immediately when its data has changed. This mechanism reduces
the network traffic as unchanged data does not need to be transmitted.
The mechanism does have a maximum time interval after which unchanged
data will be transferred.
Cyclic I/O In case a Slave unit is configured for cyclic I/O data exchange, it will send
data at a fixed user-configurable time interval.
Electronic Data Sheet
(EDS) Files
Explicit Messaging Explicit messages are acyclic communication messages used for configura-
Inverter A device that electronically changes DC to AC current through an alternating
Torque The rotational force exerted by a motor shaft. The units of measurement con-
Trip event An event that causes the inverter to stop operation is called a "trip" event (as
Text files which are used by network configuration tools such as CX-Integrator
to configure the system. The configuration consists of EtherNet/IP network
related settings and may contain additional configurable parameters.
tion or monitoring the devices over EtherNet/IP
process of switching the input to the output, inverted and non-inverted. It contains three inverter circuits to generate 3-phase output to the motor.
sist of the distance (radius from shaft center axis) and force (weight) applied
at that distance. Units are usually given as pound-feet, ounce-inches, or Newton-meters.
in tripping a circuit breaker). The inverter keeps a history log of trip events.
They also require an action to clear.
41
Page 56

APPENDIX A
42
Page 57

B-1 Basic Speed Control IO (20/70)
APPENDIX B
Assembly Specification
Assembly ID 20: Basic
Speed Control Output
Table B-1 Basic Speed Control Output - Assembly 20 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n0-----RST-FWD
1--------
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Reference (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Reference (High Byte)
Table B-2 Basic Speed Control Output - Assembly 20 Description
Name Description
FWD Forward run command
RST Fault reset
Rotational
Speed Reference
0: Stop
1: Forward run
Reset fault / trip condition on transition from 0 to 1
Reference rotational speed. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Note For safety reasons, the FWD, REV and RST command operation requires a
rising edge (0 to 1 transition) after power on and fault/trip reset.
Assembly ID 70: Basic
Speed Control Input
Table B-3 Basic Speed Control Input - Assembly 70 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n0-----DFR-FLT
1--------
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
Table B-4 Basic Speed Control Input - Assembly 70 Description
Name Description
FLT Fault
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
Rotational
Speed Monitor
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
43
Page 58

Extended Speed Control IO (21/71) APPENDIX B
B-2 Extended Speed Control IO (21/71)
Assembly ID 21: Extended
Speed Control Output
Table B-5 Extended Speed Control Output - Assembly 21 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 - REF CTR - - RST REV FWD
1--------
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Reference (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Reference (High Byte)
Table B-6 Extended Speed Control Output - Assembly 21 Description
Name Description
FWD Forward run command
0: Stop
1: Forward run
REV Reverse run command
0: Stop
1: Reverse run
RST Fault reset
CTR NetCtrl run command selection
REF NetRef speed reference selection
Rotational
Speed Reference
Reset fault / trip condition on transition from 0 to 1
0: Setting of inverter parameter A002
1: Network controlled
0: Setting of inverter parameter A001
1: Network controlled
Reference rotational speed. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Note For safety reasons, the FWD, REV and RST command operation requires a
Assembly ID 71: Extended
Speed Control Input
rising edge (0 to 1 transition) after power on and fault/trip reset.
Table B-7 Extended Speed Control Input - Assembly 71 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 ARF RFN CFN RDY DRR DFR WR FLT
1 Drive state
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
Table B-8 Extended Speed Control Input - Assembly 71 Description
Name Description
FLT Fault
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
WR Warning
0: Normal
1: Warning
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DRR During reverse run
0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
44
Page 59

Extended Speed and Torque Control IO (123/173) APPENDIX B
Table B-8 Extended Speed Control Input - Assembly 71 Description (continued)
Name Description
RDY Inverter ready status
CFN Ctrl from net: run command input selection
RFN Ref from net: speed reference input selection
ARF At reference
Drive State Drive State
Rotational
Speed Monitor
0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
0: Acceleration or deceleration phase
1: At reference
1: Startup
2: Not ready
3: Ready
4: Enabled
5: Stopping
6: Fault / trip stop
7: Faulted / tripped
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
B-3 Extended Speed and Torque Control IO (123/173)
Assembly ID 123:
Extended Speed and
Torque Control Output
Table B-9 Extended Speed and Torque Control Output - Assembly 123 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 - REF CTR - - RST REV FWD
1--------
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Reference (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Reference (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Torque Reference (Low Byte)
5 Torque Reference (High Byte)
Table B-10 Extended Speed and Torque Control Output - Assembly 123 Description
Name Description
FWD Forward run command
0: Stop
1: Forward run
REV Reverse run command
0: Stop
1: Reverse run
RST Fault reset
Reset fault / trip condition on transition from 0 to 1
CTR NetCtrl run command selection
0: Setting of inverter parameter A002
1: Network controlled
REF NetRef speed reference selection
0: Setting of inverter parameter A001
1: Network controlled
45
Page 60

Extended Speed and Torque Control IO (123/173) APPENDIX B
Table B-10 Extended Speed and Torque Control Output - Assembly 123 Description
Name Description
Rotational
Speed Reference
Torque Reference
Note For safety reasons, the FWD, REV and RST command operation requires a
rising edge (0 to 1 transition) after power on and fault/trip reset.
Reference rotational speed. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Reference torque. Unit: [%]
Assembly ID 173:
Extended Speed and
Torque Control Input
Table B-11 Extended Speed and Torque Control Input - Assembly 173 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 ARF RFN CFN RDY DRR DFR WR FLT
1 Drive state
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Torque Actual (Low Byte)
5 Torque Actual (High Byte)
Table B-12 Extended Speed and Torque Control Input - Assembly 173 Description
Name Description
FLT Fault
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
WR Warning
0: Normal
1: Warning
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DRR During reverse run
0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
RDY Inverter ready status
0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
CFN Ctrl from net: run command input selection
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
RFN Ref from net: speed reference input selection
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
ARF At reference
0: Acceleration or deceleration phase
1: At reference
Drive State Drive State
1: Startup
2: Not ready
3: Ready
4: Enabled
5: Stopping
6: Fault / trip stop
7: Faulted / tripped
46
Page 61

Special IO (100/150) APPENDIX B
Table B-12 Extended Speed and Torque Control Input - Assembly 173 Description
Name Description
Rotational
Speed Monitor
Torque Actual Actual torque monitor. Unit: [%]
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
B-4 Special IO (100/150)
Assembly ID 100:
Special Output
Table B-13 Special Output - Assembly 100 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 Function Code
1-
n + 1 2 Register Number (Low Byte)
3 Register Number (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Register Data Word 0 (Low Byte)
5 Register Data Word 0 (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Register Data Word 1 (Low Byte)
7 Register Data Word 1 (High Byte)
Table B-14 Special Output - Assembly 100 Description
Name Description
Function Code Special IO function code (in Hex):
03 Read single word
10 Write single word
43 Read double word
50 Write double word
Note these codes are not the same as the explicit message service
code.
Register Number
Register Data
Word 0 / 1
The modbus register number corresponding to a specific inverter
parameter to be written.
The data to write to the specified register. Word 0 is the least significant word. Word 1 is the most significant word (zero in case of single word write).
Assembly ID 150:
Special Input
Table B-15 Special Input - Assembly 150 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 Function Code
1-
n + 1 2 Register Number (Low Byte)
3 Register Number (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Register Data Word 0 (Low Byte)
5 Register Data Word 0 (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Register Data Word 1 (Low Byte)
7 Register Data Word 1 (High Byte)
47
Page 62

Extended Control IO (101/151/153) APPENDIX B
Table B-16 Special Input - Assembly 150 Description
Word Byte Write success Read success Failure
n 0 0x10 / 0x50 0x03 / 0x43 Function code OR'ed
1---
n + 1 2 Register Number (Low Byte)
3 Register Number (High Byte)
n + 2 4 - Register Data Word
0 (Low Byte)
5 - Register Data Word
0 (High Byte)
n + 3 6 - Register Data Word
7 - Register Data Word
1 (Low Byte)
1 (High Byte)
The error codes for the Special IO operation are listed here below.
Table B-17 Special Input - Assembly 150 Errors
Fault
code
01 Hex Function code error A code other than 03 / 10 / 43 or 50 Hex has
02 Hex Register number error The specified register number does not
04 Hex Slave device failure Option inverter communication failure
21 Hex Data setting error An upper or lower limit for the write data set-
22 Hex Writing mode error The inverter is in the wrong mode
23 Hex Register size error. Used 2 bytes read/write on 4 bytes register
Name Description
been set as function code.
exist.
ting range was exceeded
or 4 bytes read/write on 2 bytes register
with 0x80
Fault code
-
-
-
B-5 Extended Control IO (101/151/153)
Assembly ID 101:
Extended Control Output
Table B-18 Extended Control Output - Assembly 101 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 - CI7 CI6 CI5 CI4 CI3 REV FWD
1 CO2 CO1 CR - - - RST FFL
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Reference (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Reference (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Torque Reference (Low Byte)
5 Torque Reference (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Torque Compensation Bias (Low Byte)
7 Torque Compensation Bias (High Byte)
Table B-19 Extended Control Output - Assembly 101 Description
Name Description
FWD Forward run command
0: Stop
1: Forward run
REV Reverse run command
0: Stop
1: Reverse run
CI3 - CI7 Control / override for multi function input terminal [3] to [7]
0: Reset
1: Override input
48
Page 63

Extended Control IO (101/151/153) APPENDIX B
Table B-19 Extended Control Output - Assembly 101 Description (continued)
Name Description
FFL Force external fault/trip
RST Fault reset
C01, C02, CR Set (relay) output
Rotational
Speed Reference
Torque Reference
Torque Compensation Bias
Note For safety reasons, the FWD, REV and RST command operation requires a
rising edge (0 to 1 transition) after power on and fault/trip reset.
Set external fault / trip state on transition from 0 to 1
Reset fault / trip condition on transition from 0 to 1
0: Reset
1: Set multi function output [1] to [2] or relay output (CR)
Reference rotational speed. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Reference torque. Unit [%]
Compensation bias torque. Unit: [%]
Assembly ID 151:
Extended Control Input
Table B-20 Extended Control Input - Assembly 151 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 FLT WR RDY ARF - DRR DZS DFR
1--MO2MO1MRCFN- -
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Torque Actual (Low Byte)
5 Torque Actual (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Output Current Monitor (Low Byte)
7 Output Current Monitor (High Byte)
Table B-21 Extended Control Input - Assembly 151 Description
Name Description
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DZS During zero speed
0: Non-zero speed
1: During zero speed
DRR During reverse run
0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
ARF At reference
0: Acceleration or deceleration phase
1: At reference
RDY Inverter ready status
0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
WR Warning
0: Normal
1: Warning
FLT Fault
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
49
Page 64

Extended Control IO (101/151/153) APPENDIX B
Table B-21 Extended Control Input - Assembly 151 Description (continued)
Name Description
CFN Ctrl from net: run command input selection
MO1, MO2, MRMonitor (relay) outputs
Rotational
Speed Monitor
Torque Actual Actual torque monitor. Unit: [%]
Output current
monitor
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
0: OFF
1: ON
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Output current monitor. Unit: [0.1 A]
Assembly ID 153:
Extended Control + Multi
Function Input
Table B-22 Extended Control + Multi Function Input - Assembly 153 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 FLT WR RDY ARF - DRR DZS DFR
1--MO2MO1MRCFN- -
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Torque Actual (Low Byte)
5 Torque Actual (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Output Current Monitor (Low Byte)
7 Output Current Monitor (High Byte)
n + 4 8 - MI7 MI6 MI5 MI4 MI3 MI2 MI1
Table B-23 Extended Control + Multi Function Input - Assembly 153 Description
Name Description
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DZS During zero speed
0: Non-zero speed
1: During zero speed
DRR During reverse run
0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
ARF At reference
0: Acceleration or deceleration phase
1: At reference
RDY Inverter ready status
0: Inverter not ready
1: Inverter ready
WR Warning
0: Normal
1: Warning
FLT Fault
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
CFN Ctrl from net: run command input selection
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
50
Page 65

Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111) APPENDIX B
Table B-23 Extended Control + Multi Function Input - Assembly 153 Description
Name Description
MO1, MO2, MRMonitor (relay) outputs
Rotational
Speed Monitor
Torque Actual Actual torque monitor. Unit: [%]
Output current
monitor
MI1 to MI7 Monitor multi function inputs [1] to [7]
0: OFF
1: ON
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Output current monitor. Unit: [0.1 A]
0: OFF
1: ON
B-6 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111)
Assembly ID 110:
Extended Speed and
Acceleration Control
Output
Table B-24 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Output - Assembly 110
Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
n 0 - REF CTR - FRS RST REV FWD
1--------
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Reference (Low Byte)
3 Rotational Speed Reference (High Byte)
n + 2 4 Acceleration Time (Low Byte)
5 Acceleration Time (High Byte)
n + 3 6 Deceleration Time (Low Byte)
7 Deceleration Time (High Byte)
Table B-25 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Output - Assembly 110
Description
Name Description
FWD Forward run command
0: Stop
1: Forward run
REV Reverse run command
RST Fault reset
FRS Activate Free run stop (coasting)
CTR NetCtrl run command selection
REF NetRef speed and acceleration/deceleration reference selection
Rotational
Speed Reference
0: Stop
1: Reverse run
Reset fault / trip condition on transition from 0 to 1
0: No action
1: Free run stop
0: Setting of inverter parameter A002
1: Network controlled
0: Setting of inverter parameters A001, F002 and F003
1: Network controlled
Reference rotational speed. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
51
Page 66

Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111) APPENDIX B
Table B-25 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Output - Assembly 110
Description (continued)
Name Description
Note For safety reasons, the FWD, REV and RST command operation requires a
Assembly ID 111:
Extended Speed and
Acceleration Control Input
Acceleration
time
Deceleration
time
rising edge (0 to 1 transition) after power on and fault/trip reset.
Table B-26 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Input - Assembly 111 Allocation
Word Byte Bit Allocation
n 0 MI3 MI2 MI1 ARF - FLT DRR DFR
n + 1 2 Rotational Speed Monitor (Low Byte)
n + 2 4 Output Current Monitor (Low Byte)
n + 3 6 Trip Cause
Reference acceleration time. Unit: [0.1 s]
Range of setting [0.1 to 3600.0]
Be sure to set the REF bit to control the acceleration or deceleration
time using this assembly. Otherwise the F002 and F003 will be
used independent of parameter A001.
Reference deceleration time. Unit: [0.1 s]
Range of setting [0.1 to 3600.0]
Be sure to set the REF bit to control the acceleration or deceleration
time using this assembly. Otherwise the F002 and F003 will be
used independent of parameter A001.
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Drive state
3 Rotational Speed Monitor (High Byte)
5 Output Current Monitor (High Byte)
7 RFN CFN - - MI7 MI6 MI5 MI4
Table B-27 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Input - Assembly 111
Description
Name Description
DFR During forward run
0: Stop/reverse
1: During forward run
DRR During reverse run
0: Stop/forward
1: During reverse run
FLT Fault
ARF At reference
MI1 to MI7 Monitor multi function inputs [1] to [7]
CFN Ctrl from net: run command input selection
RFN Ref from net: speed reference input selection
0: Normal
1: Fault/trip
0: Acceleration or deceleration phase
1: At reference
0: OFF
1: ON
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
0: Local
1: EtherNet/IP reference
52
Page 67

Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111) APPENDIX B
Table B-27 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Input - Assembly 111
Description (continued)
Name Description
Drive State Drive State
1: Startup
2: Not ready
3: Ready
4: Enabled
5: Stopping
6: Fault / trip stop
7: Faulted / tripped
Rotational
Speed Monitor
Output current
monitor
Trip Cause Returns direct trip cause. Value 1 to 99 decimal correspond to trip
Actual rotational speed monitor. Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter P049 is set to
zero, the Unit depends on the inverter mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Output current monitor. Unit: [0.1 A]
E01 to E99.
53
Page 68

Extended Speed and Acceleration Control IO (110/111) APPENDIX B
54
Page 69

General Object Specification
C-1 Identity Object (Class 0x01)
Supported Service Codes Table C-1 Identity Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
05 Reset (return to initial status)
Object Details
Table C-2 Identity Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
01 01 Vendor ID Indicates the manufacturer's ID ---- 47 (OMRON
Attribute
(hex)
02 Device Type Indicates the EtherNet/IP profile
03 Product Code Product code depending on the
04 Revision Indicates overall major and minor
Name Content Setting
classification
MX2-A@ inverter model. See note.
software revision for EtherNet/IP
Option Board and Inverter
Default Get Set Size
range
Corporation)
---- 2 (AC Drive) Yes No UINT
---- Depending
on inverter
---- Depending
APPENDIX C
Yes N o U IN T
Yes N o U IN T
Yes N o WO RD
on unit
Note this attribute depends on
both the Option Board and the
Inverter. Be sure to match the correct EDS file to this revision for
configuration.
05 Status Indicates communications status
for EtherNet/IP Option board
Bit allocation, see
Table C-4 Sta-
tus Attribute Description
06 Serial Number Indicates the serial number of the
EtherNet/IP Option board
07 Product Name Product name depending on the
09 Configuration
Consistency
Val ue
64 Protocol Ver-
sion
65 Firmware Revi-
sion Option
Board
MX2-A@ inverter model. See note.
Indicates the consistency value
which is incremented if an inverter
or option board parameter is
changed and stored to EEPROM
through the Option Board interface.
Please note changes using the
other Inverter interfaces (Serial,
Digital operator) will not influence
this attribute.
Writing to EEPROM save (Modbus
address 0900 Hex, class 64 Hex,
instance 09 Hex, attribute 0 Hex)
will also increment this value.
Version of the EtherNet/IP stack
used in the option board
Indicates software version of the
EtherNet/IP Option board.
---- 0 Hex Yes No WORD
---- Unique for
each unit
---- Depending
on inverter
---- 0 Hex Yes No UINT
---- Depending
on unit
---- Depending
on unit
Yes N o L ON G
Yes N o U IN T
Yes N o WO RD
Yes N o WO RD
55
Page 70

Identity Object (Class 0x01) APPENDIX C
The product code and the product name depend on the MX2-A@ of inverter
being used, as shown in the following table.
Table C-3 Device List
MX2-A@
Model name
MX2-AB001(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB001_A2001(-E).eds 1960 2000
MX2-A2001(-E)
MX2-AB002(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB002_A2002(-E).eds 1961 2001
MX2-A2002(-E)
MX2-AB004(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB004_A2004(-E).eds 1962 2002
MX2-A2004(-E)
MX2-AB007(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB007_A2007(-E).eds 1964 2004
MX2-A2007(-E)
MX2-AB015(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB015_A2015(-E).eds 1966 2006
MX2-A2015(-E)
MX2-AB022(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-AB022_A2022(-E).eds 1967 2007
MX2-A2022(-E)
MX2-A2037(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2037(-E).eds 1969 2009
MX2-A2055(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2055(-E).eds 1971 2011
MX2-A2075(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2075(-E).eds 1972 2012
MX2-A2110(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2110(-E).eds 1973 2013
MX2-A2150(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A2150(-E).eds 1974 2014
MX2-A4004(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4004(-E).eds 1982 2022
MX2-A4007(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4007(-E).eds 1984 2024
MX2-A4015(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4015(-E).eds 1986 2026
MX2-A4022(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4022(-E).eds 1987 2027
MX2-A4030(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4030(-E).eds 1988 2028
MX2-A4040(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4040(-E).eds 1990 2030
MX2-A4055(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4055(-E).eds 1991 2031
MX2-A4075(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4075(-E).eds 1992 2032
MX2-A4110(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4110(-E).eds 1993 2033
MX2-A4150(-E) 3G3AX-MX2-EIP-A4150(-E).eds 1994 2034
Name of EDS file Product
Code (-E)
Product
Code (no -E)
56
Page 71

Identity Object (Class 0x01) APPENDIX C
Table C-4 Status Attribute Description
Bit Description
0 Owned, shall be set when at least one connection is configured
1 Reserved, set to 0
2 Configured, shows if the product is configured to other settings than “out-of-the-box”
3 Reserved, set to 0
4 - 7 Extended device status:
0000: Unknown
0001: Firmware update in progress
0010: Faulted I/O connection
0011: No I/O connection established
0100: Non volatile configuration bad
0101: Major fault
0110: Connection in run mode
0111: Conneciton in idle mode
8 Minor recoverable faults IP address conflict
9 Minor unrecoverable faults
10 Major recoverable faults Failed to read stored configuration or internal communication prob-
11 Major unrecoverable faults Hardware error, unrecognized or no MX2 inverter
12 - 15 Reserved
lem
57
Page 72

Message Router Object (Class 0x02) APPENDIX C
C-2 Message Router Object (Class 0x02)
Object Details No vendor specific attributes are supported.
C-3 Assembly Object (Class 0x04)
Supported Service Codes Table C-5 Assembly Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table C-6 Assembly Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
14 03 Remote I/O
15 03 Remote I/O
46 03 Remote I/O
47 03 Remote I/O
64 03 Remote I/O
65 03 Remote I/O
6E 03 Remote I/O
6F 03 Remote I/O
7B 03 Remote I/O
8B 03 Remote I/O
96 03 Remote I/O
97 03 Remote I/O
99 03 Remote I/O
9F 03 Remote I/O
AD 03 Remote I/O
C6 03 Heartbeat Input Only ---- ---- Yes No 0
Attribute
(hex)
Name Content Setting
Data same as Basic Speed IO
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
(Output)
Data same as Extended Speed IO
(Output)
Data same as Basic Speed IO
(Input)
Data same as Extended Speed IO
(Input)
Data same as Special IO (Output) ---- 00 00 00 00
Data same as Extended Control IO
(Output)
Data same as Extended Speed
and Acceleration Control (Output)
Data same as Extended Speed
and Acceleration Control (Input)
Data same as Extended Speed
and Torque Control (Output)
Flexible IO (Output) ---- 00 00 00 00
Data same as Special IO (Input) ---- 00 00 00 00
Data same as Extended Control IO
(Input)
Data same as Extended Control IO
and Multi-Function monitor (Input)
Flexible IO (Input) ---- 00 00 00 00
Data same as Extended Speed
and Torque Control (Input)
Default Get Set Size
range
---- 00 00 00 00 Yes Yes BYTE x
---- 00 00 00 00 Yes Yes BYTE x
---- 00 00 00 00 Yes No BYTE x
---- 00 00 00 00 Yes No BYTE x
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00
---- 00 00 00 00
00 00
Yes Yes BYTE x
Yes Yes BYTE x
Yes Yes BYTE x
Yes No BYTE x
Yes Yes BYTE x
Yes Yes BYTE x
20 max
(see
note 2)
Yes No BYTE x
Yes No BYTE x
Yes No BYTE x
Yes No BYTE x
20 max
(see
note 2)
Yes No BYTE x
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
6
8
8
9
6
C7 03 Heartbeat Listen Only ---- ---- Yes No 0
58
Page 73

Connection Manager (Class 0x06) APPENDIX C
Note 1 The data allocation of the assembly in this objects are the same as defined in
Appendix B.
Note 2 The size of the Flexible IO assemblies are depending on the actual configura-
tion.
C-4 Connection Manager (Class 0x06)
Supported Service Codes Table C-7 Connection Manager - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
54 Forward Open
4E Forward Close
C-4-1 Class 1 Connection Details
Class 1 connections are used to transfer I/O data, and can be established to
instances in the Assembly Object. Each Class 1 connection will establish two
data transports; one consuming and one producing. The heartbeat instances
can be used for connections that shall access only inputs. Class 1 connections use UDP transport.
• Total number of supported class 1 connections: 3
(Exclusive-Owner + Input-Only + Listen-Only connections)
• Supported API: 2... 3200 ms
• T
O Connection type: Point-to-point, Multicast
T Connection Type: Point-to-point
•O
• Supported trigger type: Cyclic, Change-of-state
Connection Types Exclusive-Owner connection
This type of connection controls the outputs of the module and does not
depend on other connections.
• Max. no. of Exclusive-Owner connections: 1
• Connection point O
• Connection point T
Input-Only connection
This type of connection is used to read data from the module without controlling the outputs. It does not depend on other connections.
• Max. no. of Input-Only connections: 3
• Connection point O
Only heartbeat
• Connection point T
Note If an Exclusive-Owner connection has been opened towards the module and
times out, the Input-Only connection times out as well. If the Exclusive-Owner
connection is properly closed, the Input-Only connection remains unaffected.
Listen-Only connection
This type of connection requires another connection in order to exist. If that
connection (Exclusive-Owner or Input-Only) is closed, the Listen-Only connection will be closed as well.
• Max. no. of Listen-Only connections: Up to 3
• Connection point O
Only heartbeat
• Connection point T
T: Output Assembly Object instance
O: Input Assembly Object instance
T: Assembly Object, instance C6h (Input-
O: Input Assembly Object instance
T: Assembly Object, instance C7h (Listen-
O: Input Assembly Object instance
59
Page 74

Discrete Input Point Object (Class 0x08) APPENDIX C
C-4-2 Class 3 Connections Details
Class 3 connections are used to establish connections towards the message
router. Thereafter, the connection is used for explicit messaging. Class 3 connections use TCP connections.
Explicit message connection
• No. of simultaneous Class 3 connections: 6
• Supported API: 100 - 10000 ms
• T->O Connection type: Point-to-point
• O->T Connection Type: Point-to-point
• Supported trigger type: Application
C-5 Discrete Input Point Object (Class 0x08)
Supported Service Codes Table C-8 Discrete Input Point Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table C-9 Discrete Input Point Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
01 to 07
(See
Note)
Attribute
(hex)
03 Value Read input point value
69 Override Override input point value
Name Content Setting
0: Off
1: On
0: Off
1: On
Default Get Set Size
range
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- ---- Yes Yes BOOL
Note The instance 1 to 7 correspond to the MX2-A inverter input terminal [1] to
[7].
C-6 Discrete Output Point Object (Class 0x09)
Supported Service Codes Table C-10 Discrete Output Point Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table C-11 Discrete Output Point Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
01 to 03
(See
note)
Attribute
(hex)
03 Value Control the output point value
Name Content Setting
0: Off
1: On
range
Default Get Set Size
---- ---- Yes Yes BOOL
60
Note The instance 1 to 3 correspond to the MX2-A inverter output terminals
respectively output [11], output [12] and alarm relay contacts (AL0,1,2).
Page 75

AC Drive Object Specification
D-1 Motor Data Object (Class 0x28)
Supported Service Codes Table D-1 Motor Data Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table D-2 Motor Data Object - Object Details
Instance
01 03 Motor Type Depends on the motor control mode which is
(hex)
Attribute
(hex)
06 Rated Current Motor rated current. Unit: [0.1 A] ---- Depend-
07 Rated Voltage Motor rated voltage. Unit: [V]
08 Rated Power Motor rated power. Unit: [W]
09 Rated Frequency Motor rated frequency. Unit: [Hz]. 300 - MaxSpeed 50 Yes Yes UINT
11 MaxSpeed Maximum allowed motor speed. Unit: [RPM] Depending on
12 PoleCount Number of poles in the motor.
Name Content Setting
selected for the inverter. The motor control mode
can be read by inverter parameter d060.
Get values:
3: PM synchronous motor (d060 = 3)
7: Squirrel cage induction motor (d060 != 3)
Set values:
3: in case inverter control mode is not in this mode,
the inverter will be set to PM synchronous mode
(d060 = 3).
7: in case inverter control mode is PM synchronous
mode (d060 = 3), the inverter will be set to ND
mode (d060 = 1).
See note
Set: Only defined set of values as indicated for
inverter parameter A082 (AVR voltage select) are
accepted.
Set: Only defined set of values as indicated for
inverter parameter H003 (Squirrel cage induction
motor) or H103 (PM Synchronous mode) are
accepted.
(speed conversion only)
Only even number of poles are valid.
range
---- 7 Yes Yes US
---- Depend-
---- Depend-
motor control
mode
0 - 38 0 Yes Yes UINT
APPENDIX D
Default Get Set Size
INT
ing on
inverter
type
ing on
inverter
type
ing on
inverter
type
50 Yes Yes UINT
Yes Yes UINT
Yes Yes UINT
Yes Yes UINT
Note A change of the Motor Type value will cause an inverter and EtherNet/IP
option board reset. This is equivalent to setting inverter parameters b171
(Inverter mode selection) and b180 (Parameter initialisation trigger).
61
Page 76

Control Supervisor Object (Class 0x29) APPENDIX D
D-2 Control Supervisor Object (Class 0x29)
Supported Service Codes Table D-3 Control Supervisor Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
05 Reset
Object Details
Table D-4 Control Supervisor Object - Object Details
Instance
01 03 Run1 Run Forward
01 64 Drive State Detail Drive State Detail value:
Attribute
(hex)
(hex)
04 Run2 Run Reverse
05 Net Ctrl Run command input is set
06 State Drive status. See Appendix B for details. ---- ---- Yes No UINT
07 Running1 Forward Running
08 Running2 Reverse Running
09 Ready Inverter ready
0A Faulted Inverter fault / trip
0B Warning Inverter warning
0C Fault Rst Reset fault / trip state of inverter when written to 1. ---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
0D Fault Code Current fault / trip state code. See note. ---- ---- Yes No UINT
0F Ctrl From Net Run command input selection
10 Net Fault Mode Inverter action on network error
11 Force Fault Force external fault / trip state for inverter on rising
12 Force Status Status external fault forced
14 Net Idle Mode Inverter action on network idle mode
65 Trip Cause Returns direct trip cause (E01 to E99) ---- ---- Yes No USINT
66 Free Run Activate Free run stop (coasting)
Name Content Setting
0: Stop
1: Run Forward
0: Stop
1: Run Reverse
0: Setting of inverter parameter A002
1: EtherNet/IP reference
0: Stop
1: Forward Running
0: Stop
1: Reverse Running
0: Not ready
1: Ready
0: No inverter fault / trip
1: Inverter fault / trip
0: No inverter warning
1: Inverter warning
0: Setting of A002
1: EtherNet/IP controlled
0: Inverter fault / trip and stop (P045 = 1)
1: Ignore (P045 = 2)
2: Vendor specific.
edge.
0: Fault not forced
1: Fault forced
0: Stop (P048 = 4)
1: Ignore (P048 = 2)
2: Vendor specific.
0: Stopping
1: Running
2: Jogging
3: Free running (coasting)
4: Direct current DC braking
5: Pickup (Decelerated stop)
7: During pickup (Retry)
8: Waiting (Retry)
10: Trip condition
11: Under-voltage condition
0: No action
1: Free run stop
range
---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- ---- Yes No UINT
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
---- 2 Yes Yes UINT
---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
---- 0 Yes No BOOL
---- 2 Yes Yes USINT
---- ---- Yes No USINT
---- 0 Yes Yes BOOL
Default Get Set Size
62
Page 77

Control Supervisor Object (Class 0x29) APPENDIX D
Note The following table shows the conversion between the MX2 Error or Trip code
and the CIP Fault and Warning codes.
Table D-5 Error Code Conversion
MX2 Error/Trip code CIP Fault and Warning Code
Code Name Code Name
E01 Over-current event while at con-
stant speed
E02 Over-current event during deceler-
ation
E03 Over-current event during acceler-
ation
E04 Over-current event during other
E05 Overload protection 2220 Continuous Overcurrent
E06 Braking resistor overload protec-
E07 Over-voltage protection 3210 Overvoltage inside the device
E08 EEPROM error 6320 Parameter Error
E09 Under-voltage error 3220 Undervoltage inside the Device
E10 Current detection error 5210 Measurement Circuit
E11 CPU error 6100 Internal Software
E12 External trip 9000 External Malfunction
E13 USP 9000 External Malfunction
E14 Ground fault 2120 Short to Earth
E15 Input over-voltage 3110 Mains overvoltage
E16 Momentary electricity failure pro-
E20 Temperature error with cooling fan
E21 Inverter thermal trip 4200 Device Temperature
E22 CPU error 5000 Device Hardware
E24 Phase Failure 3130 Phase Failure
E25 Main circuit error 5410 Output Stages
E30 Driver error 5400 Power section
E35 Thermistor 7300 Sensor
E36 Braking error 9000 External Malfunction
E37 Safe Stop 9000 External Malfunction
E38 Low-speed overload protection 2221 Continuous Overcurrent no1
E40 Operator connection 5300 Operator control circuit
E41 Modbus communication error 7500 Communication
E43 EzSQ invalid instruction 6200 User Software
E44 EzSQ nesting count error 6200 User Software
E45 EzSQ instruction error 6200 User Software
E50
…59
E60 Option error (inverter communica-
E61 Option error (Duplicated MAC ID) 7510 Serial Interface No 1
E62 Option error (External trip) 7510 Serial Interface No 1
E63 Communication lost between
E64 Illegal flexible mapping 6320 Parameter error
E65
…68
conditions
tion
tection
frequency lowering
EzSQ user trip (0 to 9) 6200 User Software
tions error)
module and drive
Option error (reserved) 7510 Serial Interface No 1
2200 Current Inside the Device
2214 Overcurrent during Slowdown
2213 Overcurrent during Startup
2200 Current Inside the Device
7112 Brake Chopper overcurrent
3120 Mains undervoltage
4000 Temperature
7510 Serial Interface No 1
7510 Serial Interface No 1
63
Page 78

Control Supervisor Object (Class 0x29) APPENDIX D
Table D-5 Error Code Conversion (continued)
MX2 Error/Trip code CIP Fault and Warning Code
Code Name Code Name
E69 Option error (inverter communica-
tion lost error)
E80 Encoder disconnection 7305 Incremental Encoder 1 Defective
E81 Excessive speed 8401 Velocity following error
E82 Positioning error 8500 Position
E83 Position control range error 8501 Position Following Error
7510 Serial Interface No 1
64
Page 79

AC/DC Drive Object (Class 0x2A) APPENDIX D
D-3 AC/DC Drive Object (Class 0x2A)
Supported Service Codes Table D-6 AC/DC Drive Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table D-7 AC/DC Drive Object - Object Details
Instance
1 03 At Reference Status indication for at reference
(hex)
Attribute
(hex)
04 Net Ref Speed reference selection
06 Drive Mode Fixed to value:
07 Speed Actual Actual rotational speed monitor.
08 Speed Ref Reference rotational speed.
09 Current Actual Output current monitor. Unit: [0.1 A] ---- ---- Yes No INT
0F Power Actual Output power monitor. Unit: [W] ---- ---- Yes No INT
11 Output Voltage Output voltage monitor. Unit: [V] ---- ---- Yes No INT
12 Accel Time Acceleration time. Unit: [ms] 10 - 3600000 10000 Yes Yes UINT
13 Decel Time Deceleration time. Unit: [ms] 10 - 3600000 10000 Yes Yes UINT
1D Ref From Net Speed reference input selection monitor:
77 Torque Actual
78 Torque Ref Rel Reference torque. Unit [%] 0 - 200 0 Yes Yes INT
79 Torque
7A At Zero Speed Status indication at zero speed
Name Content Setting
0: Stopped, accelerating or decelerating
1: At reference
0: Setting of inverter parameter A002
1: Network controlled
0: Vendor specific mode
Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter
P049 is set to zero, the Unit depends on the inverter
mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
Unit: [RPM]/[0.1 Hz]/[0.01 Hz].
If Motor poles setting for RPM (inverter parameter
P049 is set to zero, the Unit depends on the inverter
mode (d060):
d060 = 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.1 Hz]
d060 != 2 (High Frequency mode): Unit is [0.01 Hz]
0: Local
1: Network reference
Rel
Compensation
Bias Rel
Actual torque monitor. Unit: [%] ---- ---- Yes Yes INT
Compensation bias torque. Unit: [%] -200 - 200 0 Yes Yes INT
0: Non-zero speed
1: Zero speed
range
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
0 - 1 0 Yes Yes BOOL
00YesYesUSINT
---- ---- Yes No INT
0 - Max Speed 0 Yes Yes INT
0 - 1 0 Yes Yes BOOL
---- ---- Yes No BOOL
Default Get Set Size
65
Page 80

AC/DC Drive Object (Class 0x2A) APPENDIX D
66
Page 81

EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages
XX YY
Instance I D X X
Attribute ID YY
Funct ion Code
Object
Inverter function
code
E-1 Function Code Object (Class 0x65)
5-1-1 Supported Service Codes
Table E-1 Function Code Object (Class 0x65) Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
5-1-2 Supported Instance and Attribute Codes
The inverter parameter Function code are mapped to the object's instance
and attributes.
APPENDIX E
The instance and attribute are calculated using a sequence number of the
function group (A = 0, B = 1, etc) * 1000 plus the function code value. The
resulting value is allocated to the instance (high byte) and attribute (low byte).
Table E-2 Function Code Object (Class 0x65) Supported Instance and Attribute
Codes
Function Code Decimal base Decimal range Hexadecimal range
A001 - A999 0 1 - 999 0001 - 03E7
b001 - b999 1000 1000 - 1999 03E9 - 07CF
C001 - C999 2000 2001 - 2999 07D1 - 0BB7
d001 - d999 3000 3001 - 3999 0BB9 - 0F9F
F001 - F999 5000 5001 - 5999 1389 - 176F
H001 - H999 7000 7001 - 7999 1B59 - 1F3F
P001 - P999 15000 15001 - 15999 3A99 - 3E7F
U001 - U999 20000 20001 - 20999 4E21 - 5207
Note 1 Please refer to Appendix B of the MX2 User's Manual (Cat. No. I570) for
details about Function code references and data sizes.
Note 2 All data written by Function Code or Modbus Register object are stored tem-
porary in the memory of the inverter. Be sure to execute the ENTER command at the end of writing sequence to store the value in EEPROM.
Note 3 Function code F001 can not be written using the Function code object. The
Function code B127 has a data size of 2 words (different from the Modbus
register size of 1 word).
The ENTER command is executed by:
• enable the EEPROM write mode (write 01 Hex to Modbus address
0902 Hex)
• write to EEPROM (write 01 Hex to Modbus address 0900 Hex)
67
Page 82

Function Code Object (Class 0x65) APPENDIX E
Both operation can be performed by using Modbus Register Object Class.
68
Page 83

Modbus Register Object (Class 0x64) APPENDIX E
E-2 Modbus Register Object (Class 0x64)
5-2-1 Supported Service Codes
Table E-3 Modbus Register Object (0x64) Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
5-2-2 Supported Instance and Attribute Codes
For this Object, the corresponding Modbus register of the inverter parameter
are mapped to the object's instance and attribute.
Modbus Register
Object
Instance ID XX
High byte Low byte
Attribute ID YY
In case of the Modbus Address XXYY Hex, the instance of the object is
mapped to XX and the attribute is mapped to YY.
Note 1 Please refer to Appendix B of the MX2 User's Manual (Cat. No. I570) for
details about Modbus registers and data sizes.
Note 2 All data written by Function Code or Modbus Register object are stored tem-
porary in the memory of the inverter. Be sure to execute the ENTER command at the end of writing sequence to store the value in EEPROM.
The ENTER command is executed by:
• enable the EEPROM write mode (write 01 Hex to Modbus address
0902 Hex)
• write to EEPROM (write 01 Hex to Modbus address 0900 Hex)
Both operation can be performed by using Modbus Register Object Class.
Modbus register address .
XXYY Hex
69
Page 84

DLR Object (Class 0x47) APPENDIX E
E-3 DLR Object (Class 0x47)
Supported Service Codes Table E-4 DLR Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
01 Get attribute All
0E Get attribute single
Object Details
Table E-5 DLR Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
Attribute
Name Content Default Get Set Size
(hex)
101Network Topol-
ogy
02 Network Status Network status information
0A Active supervisor Active ring supervisor address informa-
IP Address IP address of active ring supervisor - Yes No UDINT
MAC Address MAC address of active ring supervisor - Yes No Array of 6
0C Capability flags Announce-based ring node 0x00000001 Yes No DWORD
Network topology information
1: Linear/Star
2: Ring
0: Normal
1: Ring Fault
tion
- Yes No USINT
- Yes No USINT
- Yes No Struct of:
USINT
Note Refer to the vendor of the network configuration software for details on config-
uring the DLR function.
E-4 QoS Object (Class 0x48)
Supported Service Codes Table E-6 QoS Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute Single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table E-7 QoS Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
Attribute
Name Content Default Get Set Size
(hex)
1 01 802.1Q Tag
Enable
4 DSCP Urgent CIP transport class 1 messages with
5 DSCP Scheduled CIP transport class 1 messages with
DSCP High CIP transport class 1 messages with
6
DSCP Low CIP transport class 1 messages with
7
8 DSCP Explicit CIP UCMM and CIP class 3 27 No Yes USINT
Enables or disables sending 802.1Q
frames
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
Urgent prority
Scheduled priority
High priority
Low priority
0NoYesUSINT
55 No Yes USINT
47 No Yes USINT
43 No Yes USINT
31 No Yes USINT
70
Page 85

TCP/IP Object (Class 0xF5) APPENDIX E
E-5 TCP/IP Object (Class 0xF5)
Supported Service Codes Table E-8 TCP/IP Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
Object Details
Table E-9 TCP/IP Object - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
Attribute
Name Content Default Get Set Size
(hex)
1 01 Status Interface Configuration status:
Bits 0-3: Indicate the status of the Interface Configuration attribute.
0: The Interface Configuration attribute has not been configured
1: The Interface Configuration attribute contains valid configuration
obtained from DHCP or non-volatile
storage.
Bit 4: Mcast Pending. Indicates a pending configuration change in the TTL
Value and/or Mcast Config attributes.
This bit shall be set when either the
TTL Value or Mcast Config attribute is
set, and shall be cleared the next time
the device starts.
Bits 5 - 31: Reserved, set to 0.
02 Configuration
03 Configuration
04 Physical Link
05 Interface Config-
06 Host Name Host Name, max length 64 characters. - Yes Yes STRING
08 TTL Value Time to Live value for EtherNet/IP mul-
09 Multicast Config Multicast configuration:
Capability
Control
Object
uration
See Table E-10 on page 72 0x000000F4 Yes No DWORD
0: Use configuration stored in non-volatile memory
2: Obtain configuration using DHCP
No link path due to multiple physical
interfaces.
Contains information about the interface configuration:
IP Address
Subnet mask
Gateway Address
Primary DNS (0.0.0.0)
Secondary DNS (0.0.0.0)
Domain Name (Max len 64 char)
ticast packets.
Allocation Control
Reserved
Multicast addresses (Value = 1)
Multicast starting address
See EtherNet/IP Specification
-YesNoDWORD
-YesNoDWORD
0 Yes No Struct of:
- Yes Yes Struct of:
1YesYesUSINT
- Yes Yes Struct of:
UINT
Padded
EPAT H
UDINT
UDINT
UDINT
UDINT
UDINT
STRING
USINT
USINT
UINT
UDINT
0A SelectACD Enable/disable Adress Conflict Detec-
0B LastConflictDe-
tected
tion
Contains information related to the last
conflict detected:
AcdActivity: state of ACD activity when
last conflict detected
RemoteMAC: MAC address of remote
node from the ARP PDU in which a
conflict was detected
ArpPdu: Copy of the raw ARP PDU in
which a conflict was detected
1 Yes Yes BOOL
Yes Yes Struct of:
0
0
0
USINT
array of 6
USINT
array of
28 USINT
71
Page 86

TCP/IP Object (Class 0xF5) APPENDIX E
Table E-10 Configuration Capability
Configuration capability Description
DHCP capable The device is capable of obtaining its network configuration via DHCP.
Configuration settable Interface Configuration attribute is settable.
Keypad configuration of IP address IP address of Interface Configuration attribute can be set by assigning
Interface configuration change
requires reset attribute to take effect
AcdCapable The device is ACD capable (Address Conflict Detection).
values to inverter parameters using the keypad.
The device requires a restart in order for a change to the Interface Configuration attribute to take effect.
72
Page 87

Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6) APPENDIX E
E-6 Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6)
Supported Service Codes Table E-11 Ethernet Link Object - Supported Service Codes
Service Code No. (hex) Service
0E Get attribute single
10 Set attribute single
4C Get and Clear
Object Details
Table E-12 EtherNet Link - Object Details
Instance
(hex)
1, 2 01 Interface Speed 10 or 100 Mbps - Yes No UDINT
Attribute
Name Content Default Get Set Size
(hex)
02 Interface Flags See Table E-13 on page 74 - Yes No DWORD
03 Physical Address Module MAC address MAC
04 Interface Coun-
ters
05 Media Counters Counters that register the following
06 Interface Control Optional.
0A Interface Label Instance 1: “Port 1”
Counters that register the following
events:
In Octets
In Ucast packets
In NUcast packets
In Discards
In Errors
In Unknown Protos
Out Octets
Out Ucast packets
Out NUcast packets
Out Discards
Out Errors
events:
Alignment Errors
FCS Errors
Single Collisions
Multiple Collissions
SQE Test Errors
Deferred Transmits
Late Collisions
Excessive Collisions
MAC Transmit Errors
Carrier Sense Errors
Frame Too Long
MAC Receive Errors
Control bits
Forced Interface Speed
Instance 2: “Port 2”
address
- Yes No Struct of 11
- Yes No Struct of 12
- Yes Yes Struct of
-YesNoSHORT_S
Yes No Array of 6
USINTs
UDINTs
UDINTs
WORD
UINT
TRING
Note This object has two instances, one for each port.
73
Page 88

Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6) APPENDIX E
Table E-13 Interface Flags
Bit(s) Interface Flags Definition
0 Link Status 0: Indicates an inactive link
1: Indicates an active link
1 Half/Full Duplex 0: Indicates half duplex operation
1: Indicates full duplex operation
Note: If the Link Status flag is 0, the value of the Half/Full Duplex flag
is indeterminate.
2-4 Negotiation Status 0: Auto-negotiation in progress
1: Auto-negotiation and speed detection failed. Using default values
for speed and duplex.
2: Auto negotiation failed but detected speed. Duplex was defaulted.
3: Successfully negotiated speed and duplex.
4: Auto-negotiation not attempted. Forced speed and duplex.
5 Manual Setting Requires
Reset
6 Local Hardware Fault 0: Indicates that the interfac detects no local hardware fault
7-31 Reserved
0: Indicates that the interface can activate changes to link parameters
(auto-negotiate, duplex mode, interface speed) automatically.
1: Indicates that the device requires a Reset service to be issued to
its Identity Object in order for the changes to take effectl
1: Indicates that a local hardware fault is detected.
74
Page 89

Explicit Message Error Codes APPENDIX E
E-7 Explicit Message Error Codes
When an error response has been returned for the executed explicit message, this response will include on of the following error codes..
Table E-14 Error Response
Response
Code
02 Resource unavailable An internal communication error between
05 Path destination unknown The specified class or instance does not
08 Service not supported The service code is incorrect.
09 Invalid attribute value The specified attribute / inverter parame-
0C Object state conflict The specified command cannot be exe-
0E Attribute not settable An attribute ID supported only for reading
10 Device state conflict The specified command cannot be exe-
13 Not enough data The data is smaller than the specified
14 Attribute not supported The attribute or inverter parameter does
15 Too much data The data is larger than the specified size
16 Object does not exist The specified Instance ID is not sup-
1F Vendor specific This code is returned in case of an
20 Invalid parameter The specified operation command data is
Error Name Cause
Option Board and Inverter
exist.
ter value is not supported. The data written is outside range.
cuted due to an internal error.
has been executed for a write service
code.
cuted in this inverter mode.
size (accessing only high word of double
word).
not exists.
(accessing single word with double word
data).
ported.
Inverter error.
not supported.
75
Page 90

Explicit Message Error Codes APPENDIX E
76
Page 91

APPENDIX F
Flexible Format
The Flexible Format implements I/O data exchange that supports direct mapping of MX2-A Inverter Modbus registers in the I/O area. The Flexible Format provides
1. User configurable allocation of the IO Data to any Modbus register
2. Flexibility to set the size of the IO data to only transfer the necessary data,
minimising fieldbus traffic.
This offers fieldbus- and profile-independent control of the MX2-A Inverter.
The exchanged registers are configured by setting Inverter registers P160 –
P179 to the appropriate Inverter Modbus addresses.
Note The MX2-A Inverter places some restrictions on the Modbus register selec-
tion.
• For a Modbus Register to be mapped for output data exchange, it must
be both run-mode editable and writable.
• MX2-A Inverter parameters may not be accessible depending on the
Inverter’s mode (High frequency mode, Permanent magnet mode, Torque
mode, etc).
Flexible I/O Mapping
Tip Refer to section B-4-2 of the MX2 User’s manual for a listing of Modbus regis-
ters.
Tip Refer to section 3-2-3 of the MX2 User’s manual.
Tip The MX2-A Inverter parameter B031 (Sofware Lock Mode) determines the
various protection levels. Be sure to set the appropriate value B031 = 10 to be
able to set parameter during run-mode.
Tip When using Flexible Format, the Inverter is controlled via Modbus registers.
Set A001/A201 = 3 and A002/A202 = 3 to make use of the Modbus control
registers for typical Flexible Format use.
Table F-1 Flexible Format I/O Mapping
Word
Offset
+0 Modbus register set by P160 Modbus register set by P170
+1 Modbus register set by P161 Modbus register set by P171
+2 Modbus register set by P162 Modbus register set by P172
+3 Modbus register set by P163 Modbus register set by P173
+4 Modbus register set by P164 Modbus register set by P174
+5 Modbus register set by P165 Modbus register set by P175
+6 Modbus register set by P166 Modbus register set by P176
+7 Modbus register set by P167 Modbus register set by P177
+8 Modbus register set by P168 Modbus register set by P178
+9 Modbus register set by P169 Modbus register set by P179
Output Area Input Area
Content
Flexible I/O Settings Please consider the following notes when setting the parameters P160 to
P179.
Note 1 The parameters P160 to P179 determine the size of the input and output data.
The IO size is determined by the highest non-zero parameter. For example for
77
Page 92

APPENDIX F
output: if P164 is the highest non-zero parameter, the output data size will be
5 words.
Both output as input size should have a minimum size of 1 word.
Note 2 Setting specific parameters in the range to 0 (not at the end), can be used to
reserve IO memory. If set to 0 (zero), an output register is ignored and a 0
(zero) is mapped into an input register.
Note 3 Double-word MX2 registers should be mapped with two modbus registers in
sequence: high-word following low-word.
Mapping only the low word in output data will write zero in the high word of the
MX2 register.
Mapping only the low word in input data is not allowed.
Note 4 It is not allowed to map the same register more than once in the output area.
Note 5 An incorrect setting of P160 to 179 will lead to a Major Recoverable Fault (MS
blinking Red) and inverter trip state E64. In such case, correct the parameter
values and restart (or reset, see APPENDIX E EtherNet/IP Explicit Messages)
the Unit.
Tip In case the trip state E64 is generated, multiple incorrect settings in range
P160 - 179 can have caused this error. If the error persists after some
changes: it would be convenient to start with a small configuration which is
correct and add a new register one by one (checking by restarting the Unit).
Tip Set the following register values:
• P160 = 1F01h: This gives you control over Modbus Coils 0000h through
000Fh using the first output word. These coils implement all the important
control functions of the MX2-A Inverter.
• P161 = 0001h and P162 = 0002h: This gives you control over the frequency reference using output words 2 and 3.
• P170 = 1E01h: This allows you to monitor Modbus Coils 0010h through
001Fh as the first input word. These coils implement the most important
status information of the MX2-A Inverter.
• P171 = 1001h and P172 = 1002h: This allows you to monitor the output
frequency using input words 2 and 3.
The Modbus coil definitions for the MX2-A Inverter are listed in section B-41 of the MX2 User's manual (Cat. No. I570).
In case the output data is required to be as small as possilbe, please consider
to only use register 0002h (instead of both 0001h and 0002h) as frequency
reference. The resulting configuration is P160 = 1F01h and P161 = 0002h.
78
Page 93

Table index
Table 1 Option Board Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Table 2 Device List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Table 3 Led Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4 Parameter Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 5 Ground cable screw selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6 Option Board Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 7 Configuration of Inverter Reset Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 8 Configuration of EtherNet/IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 9 Configuration of Source Selection Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 10 Configuration of Other Selection Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 11 Configuration of Flexible Mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 12 Configuration of IP address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 13 IP address configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 14 IP address configuration, internal web page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 15 Extended Speed I/O Output Words. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 16 Extended Speed I/O Input Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 17 Extended Speed Torque I/O Output Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 18 Extended Speed Torque I/O Input Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 19 Flex Mode Output Area with Typical Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 20 Flex Mode Input Area with Typical Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 21 Flex Mode Output Area with Motor Running Forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 22 Flex Mode Input Area with Motor Running Forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 23 Limitations Caused by Inverter Mode and Rating Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 24 Option Board or Inverter Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 25 Configuration Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 26 EtherNet/IP Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 27 Other errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table B-1 Basic Speed Control Output - Assembly 20 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table B-2 Basic Speed Control Output - Assembly 20 Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table B-3 Basic Speed Control Input - Assembly 70 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table B-4 Basic Speed Control Input - Assembly 70 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table B-5 Extended Speed Control Output - Assembly 21 Allocation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table B-6 Extended Speed Control Output - Assembly 21 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table B-7 Extended Speed Control Input - Assembly 71 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table B-8 Extended Speed Control Input - Assembly 71 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table B-9 Extended Speed and Torque Control Output - Assembly 123 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table B-10 Extended Speed and Torque Control Output - Assembly 123 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table B-11 Extended Speed and Torque Control Input - Assembly 173 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table B-12 Extended Speed and Torque Control Input - Assembly 173 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table B-13 Special Output - Assembly 100 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table B-14 Special Output - Assembly 100 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table B-15 Special Input - Assembly 150 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table B-16 Special Input - Assembly 150 Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table B-17 Special Input - Assembly 150 Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table B-18 Extended Control Output - Assembly 101 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table B-19 Extended Control Output - Assembly 101 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table B-20 Extended Control Input - Assembly 151 Allocation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table B-21 Extended Control Input - Assembly 151 Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table B-22 Extended Control + Multi Function Input - Assembly 153 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table B-23 Extended Control + Multi Function Input - Assembly 153 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table B-24 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Output - Assembly 110 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table B-25 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Output - Assembly 110 Description. . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table B-26 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Input - Assembly 111 Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table B-27 Extended Speed and Acceleration Control Input - Assembly 111 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table C-1 Identity Object - Supported Service Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
79
Page 94

Table index
Table C-2 Identity Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table C-3 Device List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table C-4 Status Attribute Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table C-5 Assembly Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table C-6 Assembly Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table C-7 Connection Manager - Supported Service Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table C-8 Discrete Input Point Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table C-9 Discrete Input Point Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table C-10 Discrete Output Point Object - Supported Service Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table C-11 Discrete Output Point Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table D-1 Motor Data Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table D-2 Motor Data Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table D-3 Control Supervisor Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table D-4 Control Supervisor Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table D-5 Error Code Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table D-6 AC/DC Drive Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table D-7 AC/DC Drive Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table E-1 Function Code Object (Class 0x65) Supported Service Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table E-2 Function Code Object (Class 0x65) Supported Instance and Attribute Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table E-3 Modbus Register Object (0x64) Supported Service Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table E-4 DLR Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table E-5 DLR Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table E-6 QoS Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table E-7 QoS Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table E-8 TCP/IP Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table E-9 TCP/IP Object - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table E-10 Configuration Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Table E-11 Ethernet Link Object - Supported Service Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Table E-12 EtherNet Link - Object Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Table E-13 Interface Flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Table E-14 Error Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table F-1 Flexible Format I/O Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
80
Page 95

A manual revision code appears as a suffix to the catalog number on the front
Cat. No. I36I-E-01
Revision code
cover of the manual.
The following table outlines the changes made to the manual during each revision. Page numbers refer to the previous version.
Revision code Date Revised content
01 July 2011 Original production
Revision history
81
Page 96

OMRON INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION • THE AMERICAS HEADQUARTERS • Schaumburg, IL USA • 847.843.7900 • 800.556.6766 • www.omron247.com
OMRON CANADA, INC. • HEAD OFFICE
Toronto, ON, Canada • 416.286.6465 • 866.986.6766 • www.omron247.com
OMRON ELECTRONICS DE MEXICO • HEAD OFFICE
México DF • 52.
OMRON ELECTRONICS DE MEXICO • SALES OFFICE
Apodaca, N.L. • 52.81.11.56.99.20 • 001.800.556.6766 • mela@omron.com
OMRON ELETRÔNICA DO BRASIL LTDA • HEAD OFFICE
São Paulo, SP, Brasil • 55.11.2101.6300 • www.omron.com.br
OMRON EUROPE B.V. •
55.59.01.43.00
Wegalaan 67-69, NL-2132 JD, Hoofddorp, The Netherlands.
• 001.800.556.6766 • mela@omron.com
Authorized Distributor:
OMRON ARGENTINA • SALES OFFICE
Cono Sur • 54.11.4783.5300
OMRON CHILE • SALES OFFICE
Santiago • 56.9.9917.3920
OTHER OMRON LATIN AMERICA SALES
54.11.4783.5300
•
Tel: +31 (0) 23 568 13 00
•
Fax: +31 (0) 23 568 13 88
•
www.industrial.omron.eu
Automation Systems
• Programmable logic controllers (PLC) • Human machine interfaces (HMI) • Remote I/O
• Industrial PC’s • Software
Motion & Drives
• Motion controllers • Servo systems • AC drives
Control Components
• Temperature controllers • Power supplies • Timers • Counters • Programmable relays
• Digital panel indicators • Electromechanical relays • Monitoring products • Solid-state relays
• Limit switches • Pushbutton switches • Low voltage switch gear
Sensing & Safety
• Photoelectric sensors • Inductive sensors • Capacitive & pressure sensors
• Cable connectors • Displacement & width-measuring sensors • Vision systems
• Safety networks • Safety sensors • Safety units/relay units • Safety door/guard lock switches
I36I-E-01 Note: Specifications are subject to change. © 2011 Omron Electronics LLC Printed in U.S.A.
Printed on recycled paper.
 Loading...
Loading...