Page 1

iConverter® 10/100M Media Converter
and
Network Interface Device
STANDALONE AND PLUG-IN MODULE
USER MANUAL
Release 3.4
Page 2

Table of Contents
1.0 Overview ....................................................................................................................3
1.1 General Description....................................................................................................3
1.1.1 Advanced Features ....................................................................................................3
2.0 Port Structure .............................................................................................................4
2.1 Overview.....................................................................................................................4
2.1.1 Management Port.......................................................................................................4
2.1.2 UTP and Fiber Ports ..................................................................................................4
2.1.3 Backplane Ethernet Ports ..........................................................................................4
3.0 Installation Procedure ................................................................................................5
3.1 Overview.....................................................................................................................5
3.2 Configuring DIP-switches ...........................................................................................6
3.2.1 Board-Mounted Bank 1 Settings ................................................................................6
3.2.2 Board-Mounted Bank 2 Settings ................................................................................9
3.3 Installing Plug-in Modules and Connecting Cables ..................................................10
3.4 Configure the Module via Command Line Interface ................................................. 11
3.4.1 Setting IP and Control Preferences..........................................................................13
3.4.2 Setting SNMP Preferences ......................................................................................16
3.4.3 Management Processor VLAN Support ...................................................................19
3.4.4 Enabling/Disabling Soft-switch Reload.....................................................................19
3.4.5 Access the 10/100M Remotely ................................................................................21
3.5 Verify Operation........................................................................................................23
4.0 Detailed Module Configuration.................................................................................24
4.1 Overview...................................................................................................................24
4.2 Module Management Mode......................................................................................27
4.3 Port Configuration ....................................................................................................28
4.3.1 Port Access.............................................................................................................29
4.3.2 Bandwidth Control....................................................................................................29
4.3.3 SFP Information .......................................................................................................30
4.3.4 802.3ah Parameters .................................................................................................32
4.3.5 802.3ah Events .......................................................................................................34
4.3.6 Port VLAN ................................................................................................................35
4.3.7 Tagged VLAN...........................................................................................................37
4.3.8 VLAN Membership Table .........................................................................................39
4.3.9 cNode Loopback ......................................................................................................42
4.3.10 Port Statistics ...........................................................................................................43
5.0 10/100M Specifications ............................................................................................44
6.0 Troubleshooting Guide.............................................................................................45
6.1 Overview...................................................................................................................45
6.1.1 Power Issues............................................................................................................45
6.1.2 Fiber Issues..............................................................................................................45
6.1.3 UTP Issues...............................................................................................................45
7.0 Warranty...................................................................................................................47
Page 2
Page 3
1.0 OVERVIEW
This document describes the installation and configuration of the iConverter 10/100M standalone Network
Interface Device and plug-in modules. The difference between the module types are indicated using the
following legend throughout this User Manual:
1.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Omnitron iConverter®10/100M is a carrier-class media converter and a Network Interface Device (NID)
that provides 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX (10/100) to 100BASE-FX Fiber media conversion with integrated
management.
The 10/100M conforms to Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) fiber standards to support Fiber-to-the-X
(FTTX) Metropolitan access and Enterprise LAN networks. 10/100M media converters are used to provide
managed copper demarcation points at the customer premises and network edge, offering service provisioning
functions, such as, Quality of Service and Bandwidth Control (rate-limiting) capabilities.
®
The IP-based remote management of the 10/100M can be accessed by Omnitron’s NetOutlook
SNMP
Network Management Software, third-party SNMP clients and Telnet. The management IP address is
configured manually or as a DHCP client in the configuration menu. IP-less remote management is supported
via 802.3ah OAM or Secure OAM protocol. A menu-driven CLI is accessible via Telnet, serial console
port, or a modem connection to the serial console port.
IMPORTANT
This manual provides information on the installation and configuration of the module using the command
line interface (serial console). For ongoing network management, Omnitron Systems recommends
NetOutlook, an SNMP-based Network Management Software.
NetOutlook provides an efficient, user-friendly way to configure, monitor and manage devices installed
on a single network or on a series of networks by providing an intuitive graphical display with real-time
status and alarm (trap) information. The user can easily manage iConverter equipment on a large
Enterprise network or Metropolitan Area network (MAN) from a single location without the need of
additional resources.
The firmware of the Network Management Module (NMM) and NetOutlook must be the same or
greater than the firmware on the 10/100M for the module to be managed.
1.1.1 Advanced Features
The 10/100M features Port VLAN, Tag VLAN, Provider VLAN and QoS prioritization which are defined
in the IEEE 802.1Q, 802.1ad and 802.1p specifications.
Ethernet Virtual Connections can be configured with Provider VLAN to support E-Line and E-LAN
connections on Metro Ethernet Networks.
Access to the management control can be restricted with the Port VLAN and Tag VLAN features, helping
to prevent Denial-Of-Service (DoS) and unauthorized management access.
Other advanced features include:
• Bandwidth Control (Rate Limiting) • Real-time MIB statistics reporting (38 variables)
• Port Access Control • 802.3ah OAM and Extensions
• cNode Level 1 Agent • SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3
Refer to the appropriate sections for configuration information.
Page 3
Page 4
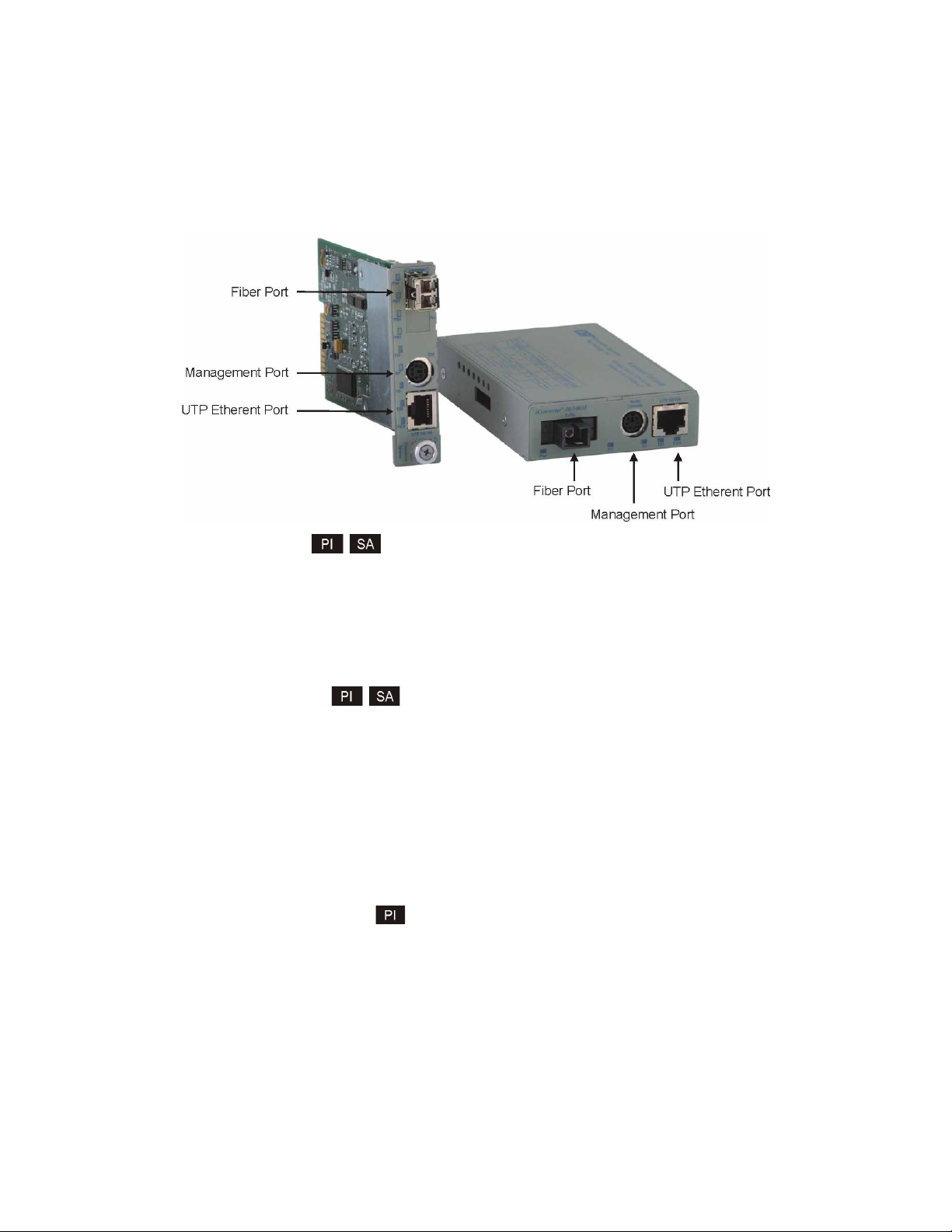
2.0 PORT STRUCTURE
2.1 OVERVIEW
The front panel of the 10/100M provides access to the management (serial console), UTP and fiber ports.
The fiber port will vary depending on the connector type; ST, SC, MT-RJ, LC or SFP supporting
100BASE-FX transceivers. The plug-in module features two additional Ethernet ports for connectivity
via the chassis backplane.
2.1.1 Management Port
The 10/100M features a Serial RS-232 Console Port (aka Craft Interface) which can be connected to a
computer for initial setup and configuration. The Serial Console Port is accessed through the mini DIN-6
female DCE interface. Connect the interface to a computer’s DB-9 serial port using the mini DIN-6 male
to DB-9 female cable adapter (Part # 8082-0), which is included with the 10/100M.
An optional DB-9 male to female straight-through serial cable is available for extension (Part # 8081-3).
2.1.2 UTP and Fiber Ports
The UTP Ethernet port supports 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX protocols, auto-negotiation and manual
forced modes for half and full duplex. The UTP port can be enabled or disabled via network management.
A port disabled with the Port Access Control feature will still connect and allow 802.3ah OAM or IP-less
(secure) OAM communication, but blocks normal data traffic.
The fiber interface supports the 100BASE-FX protocol. The fiber interface always operates in manual
mode and supports half or full duplex operation. The fiber port can be enabled or disabled via network
management. A port disabled with the Port Access Control feature will still connect and allow 802.3ah
OAM or IP-less (secure) OAM communication, but blocks normal data traffic.
2.1.3 Backplane Ethernet Ports
The plug-in module supports two additional 10/100Mbps Ethernet Backplane Ports. The Backplane Ports
A and B allow Ethernet data connectivity between adjacent modules in an iConverter chassis. The two
backplane ports can be disabled or enabled via a DIP-switch or network management.
The iConverter 19-Module, 5-Module, 2-Module and 1-Module Redundant Chassis backplanes provide
ethernet data connectivity between adjacent slots or ports. The A and B backplane ports connect the slots
as illustrated.
Page 4
Page 5
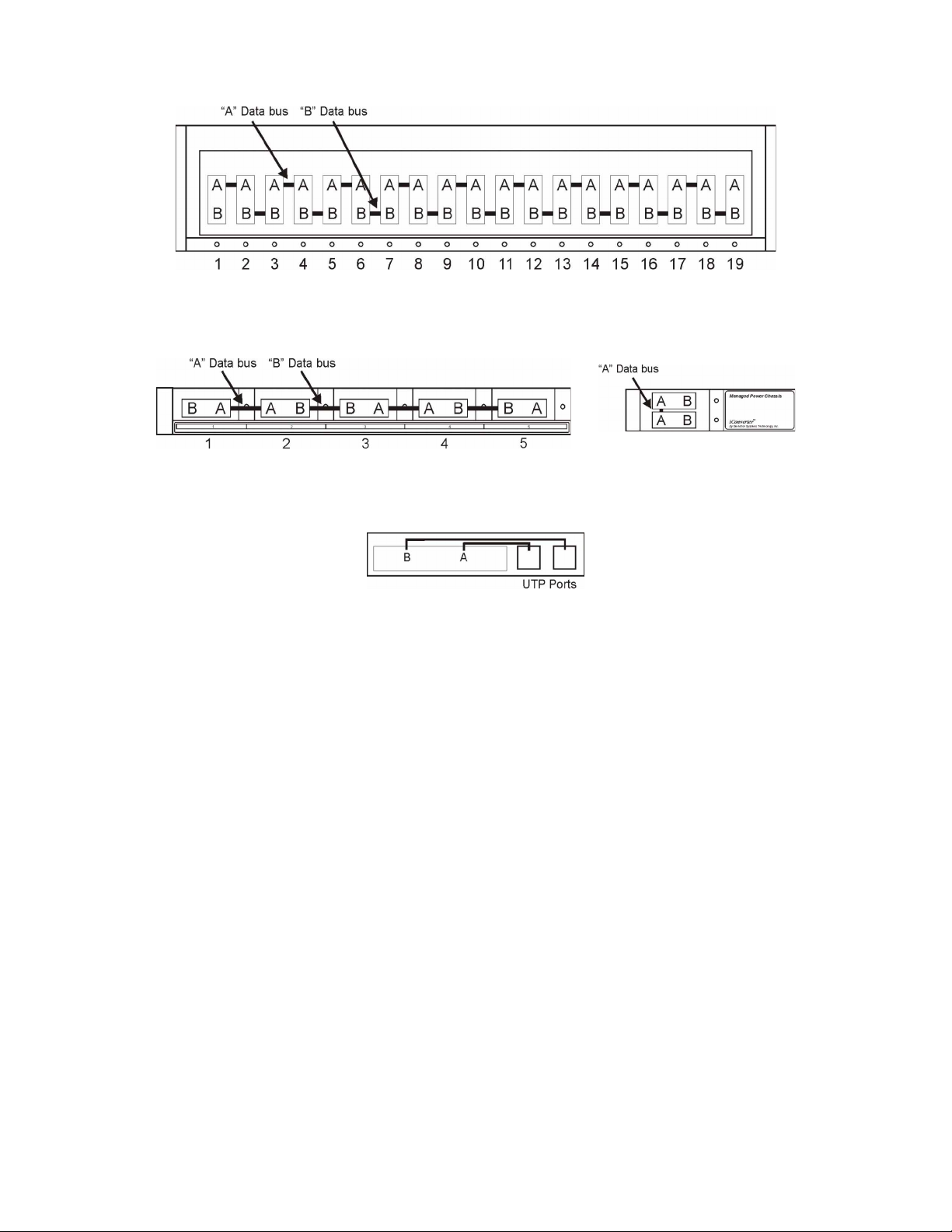
19-Module Chassis
5-Module Chassis 2-Module Chassis
1-Module Redundant Chassis
3.0 INST ALLA TION PROCEDURE
3.1 OVERVIEW
The following steps outline the installation and configuration procedures for the 10/100M. Refer to the
specified sections for detailed instructions.
• Configure DIP-switches (Section 3.2)
• Installing the Module and Connecting Cables (Section 3.3)
• Configure Module via Command Line Interface (Section 3.4)
• V erify Operation (Section 3.5)
When the setup and configuration procedures are completed, the 10/100M has been configured with the
basic setup requirement for standard operation. To configure the module with additional features, see
Section 4.0, “Detailed Module Configuration”.
Page 5
Page 6
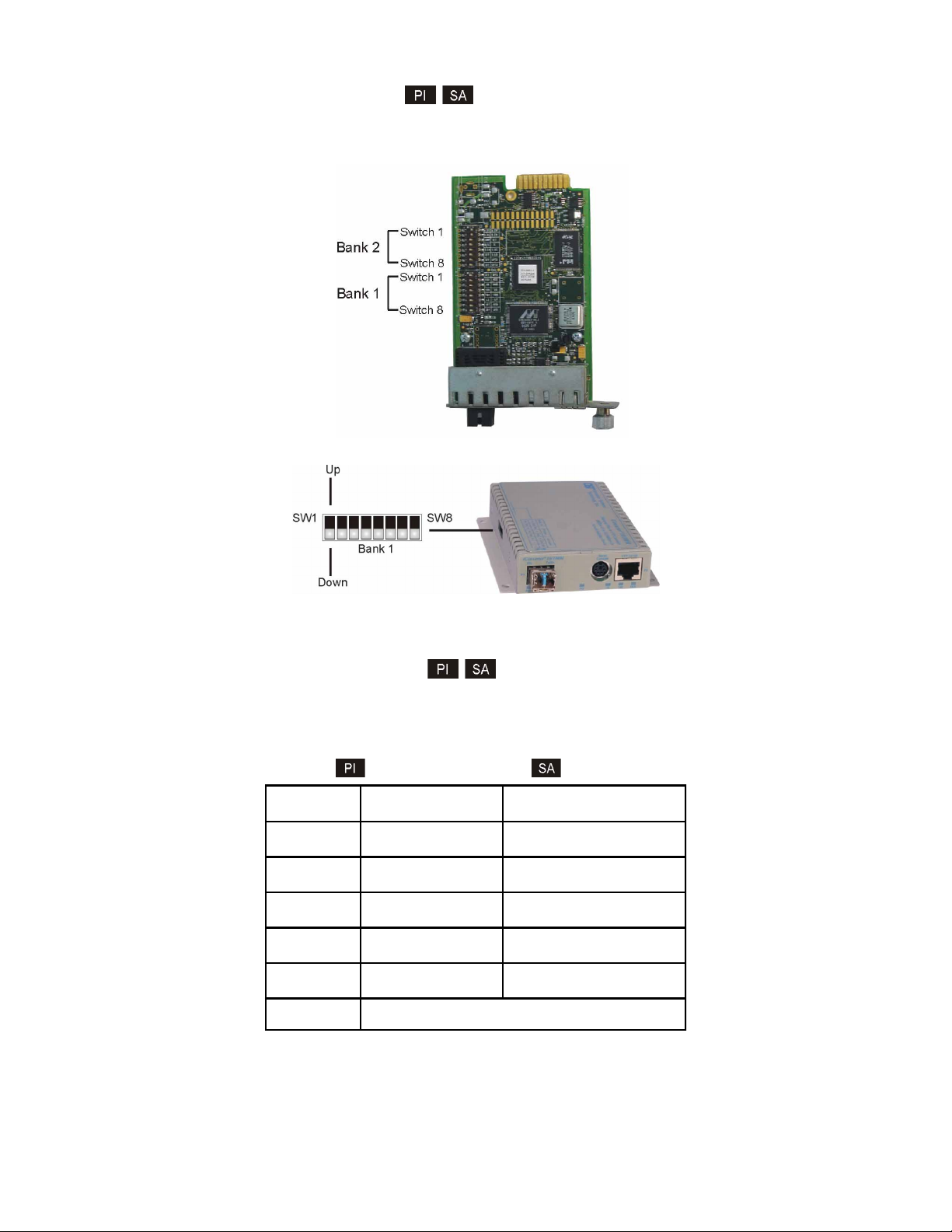
3.2 CONFIGURING DIP-SWITCHES
The 10/100M plug-in module has two board-mounted DIP-switches. The standalone unit has one bank of
DIP-switches. The locations of the DIP-switches are illustrated below.
DIP-switch Locations
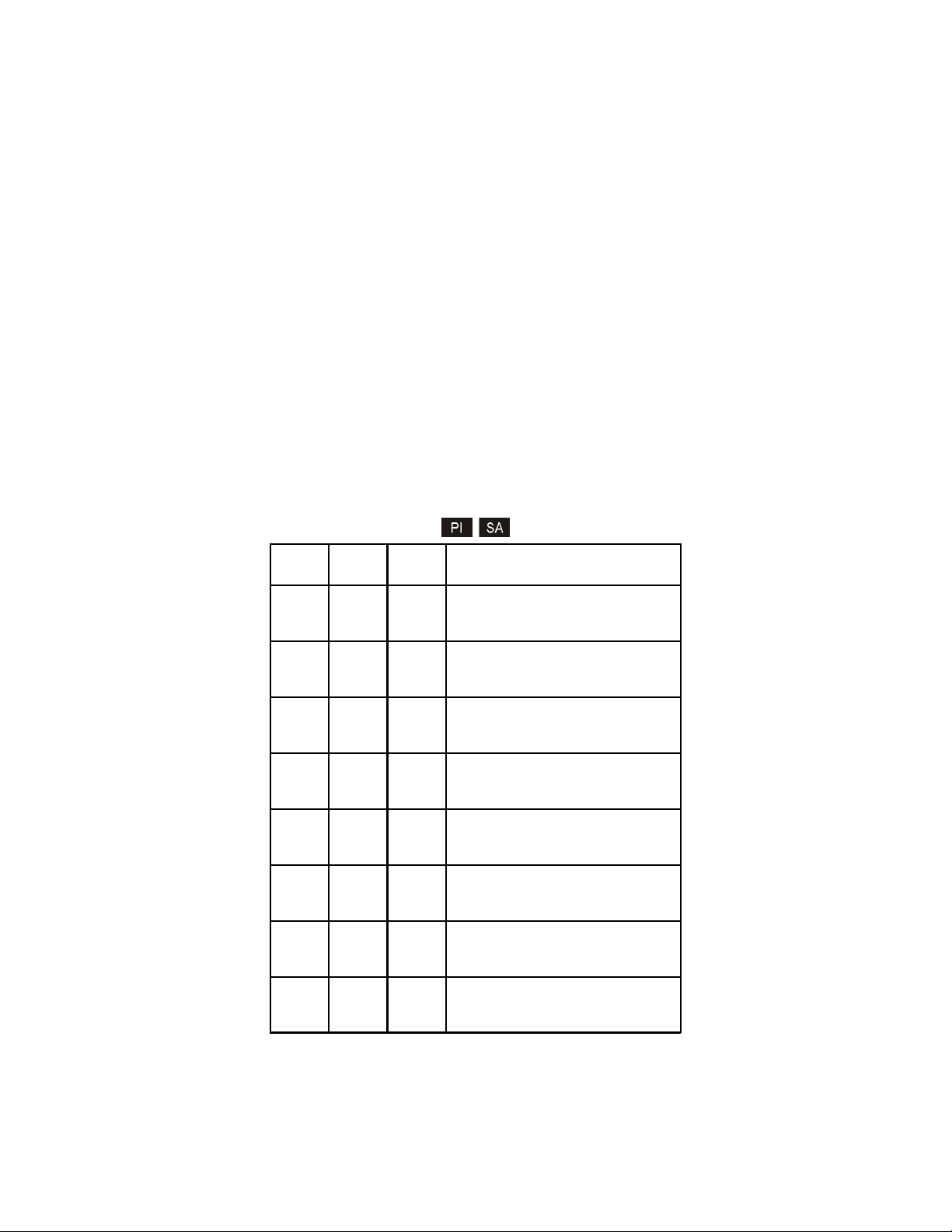
3.2.1 Board-Mounted Bank 1 Settings
DIP-switch Bank 1 is available on both the plug-in and standalone modules. The table indicates the position
of the switch; Left/Down or Right/Up. As indicated in the DIP-switch location diagram, Left and Right
refers to the plug-in module and Down and Up refers to the standalone module.
(Left/Right) (Up/Down)
Switch
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
SW5
SW6 - SW8 See Link Mode DIP-Switch Table in Section 3.2.1.6
3.2.1.1 SW1 - Pause Disable/Enable “Off/On”
Left/Down
(Factory Default)
Off:
Pause Disable
FDX:
Fiber Full-Dup lex
AN:
UTP Auto-Negotiate
100:
UTP 100Mbps
FDX:
UTP F ull-D uplex
Right/Up
On:
Pause Enable
HDX:
Fiber Half-Duplex
Man:
UTP Manual
10:
UTP 10Mbps
HDX:
UTP Half-D up le x
When a port is operating in auto-negotiation, its Pause operation mode is determined by the Pause capability
advertised during auto-negotiation between itself and the link partner. The port advertises its Pause capability
during auto-negotiation based on the Pause Disable/Enable DIP-switch setting. Setting the Pause DIP-switch to
Page 6
Page 7
the “Off” position (factory default) forces the port to negotiate to No Pause mode with its link partner.
Setting the Pause DIP-switch to the “On” position allows the port to negotiate to Symmetrical Pause, or No
Pause mode with its link partner.
When a port is operating in Manual mode, its Pause operation mode is based on the Pause Disable/Enable
DIP-switch setting. Setting the Pause DIP-switch to the “Off” position (factory default) forces the port to
operate in No Pause mode. Setting the Pause DIP-switch to the “On” position allows the port to operate in
Symmetrical Pause mode.
3.2.1.2 SW2 - Fiber Full/Half-Duplex “FDX/HDX”
When the DIP-switch is in the Full Duplex “FDX” position (factory default), the fiber port will facilitate a
connection that supports Full-Duplex operation. Setting this DIP-switch to Half-Duplex “HDX” facilitates
a connection that supports only Half-Duplex.
3.2.1.3 SW3 - UTP Auto/Manual Negotiate “AN/Man”
When the DIP-switch is in the UTP auto-negotiate “AN” position (factory default), the UTP port automatically
determines the speed and duplex mode of the connecting UTP device. If the connecting UTP device cannot
provide the proper signal to indicate its own mode of operation, this DIP-switch should be set to the UTP
Manual mode “Man” position. Manual mode requires manually configuring the UTP port to match the
speed and the duplex mode of the connecting UTP device using the “10/100” and UTP “FDX/HDX”
DIP-switches. Refer to the table below for a detailed explanation.
Switch
SW3
AN 100 FDX The UTP port is set to auto-negotiation
AN 100 HDX The UTP port is set to auto-negotiation
AN 10 FDX The UTP port is set to auto-negotiation
AN 10 HDX The UTP port is set to auto-negotiation
MAN 100 FDX The UTP por t is set to manual
MAN 100 HDX The U TP port is set to manual
MAN 10 FDX The UTP port is set to manual
MAN 10 HDX The UTP port is set to manual
Switch
SW4
Switch
SW5
Function
with the following modes advertised:
100F, 100H, 10F, 10H
with the following modes advertised:
100H, 10F, 10H
with the following modes advertised:
10F, 10H
with the following modes advertised:
10H
negotiation and is forced to:
100F
negotiation and is forced to:
100H
negotiation and is forced to:
10F
negotiation and is forced to:
10H
3.2.1.4 SW4 - UTP 10/100Mbps “10/100”
When the UTP “AN/Man” DIP-switch (described above) is in the manual “Man” position, the “10/100"
DIP-switch determines the speed of operation for the UTP port. Setting the “10/100” DIP-switch to UTP
Page 7
Page 8
100Mbps “100” position (factory default) forces the UTP port to operate at 100Mbps. Setting this DIP-switch
to UTP 10Mbps “10” position forces the UTP port to operate at 10Mbps. Adjust the “10/100” DIP-switch to
match the speed of the connecting UTP device.
When the UTP “AN/Man” DIP-switch is in the auto-negotiate “AN” position and the UTP 10/100
DIP-switch is in the “100” position, the UTP port auto-negotiates to 100Mbps or 10Mbps. When in the
“10” position, the UTP port only operates at 10Mbps. Refer to the table above for a detailed explanation.
3.2.1.5 SW5 - UTP Full/Half Duplex “FDX/HDX”
When the UTP “AN/Man” DIP-switch is in the manual “Man” position, the UTP Full/Half-Duplex
“FDX/HDX” DIP-switch determines the duplex operation mode of the UTP port. Setting the UTP
Full/Half-Duplex DIP-switch to UTP Full-Duplex “FDX” position (factory default) forces the UTP port to
operate in Full-Duplex. Setting this DIP-switch to UTP Half-Duplex “HDX” forces the UTP port to operate
in Half-Duplex. Adjust the UTP Half/Full-Duplex DIP-switch to match the duplex mode of the connecting
UTP device.
When the UTP “AN/Man” DIP-switch is in the auto-negotiate “AN” position, and the UTP Full/Half-Duplex
DIP-switch is in the Full-Duplex “FDX” position, the UTP port auto-negotiates to Full or Half-Duplex. When
in the Half-Duplex “HDX” position, the UTP port functions only in Half-Duplex for the speed selected.
Refer to the table on the previous page for a detailed explanation.
3.2.1.6 SW6, SW7, SW8 - Link Modes
These three DIP-switches configure the link mode settings. The following table details possible Link Mode
DIP-switch configurations.
SW6 SW7 SW8 Result
Left Left Left Enables Link Segment mode (LS).
Right Left Left Enables Link Propagate mode (LP).
Left Right Left
Right Right Left
Left Left Right Enables Symmetrical Fault Detect mode (SFD).
Right Left Right Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Left Right Right Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Right Right Right Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Enables Remote Fault Detection mode plus
Link Segment mode (RFD+LS).
Enables Remote Fault Detection mode plus
Link Propagation mode (RFD+LP).
SW6 SW7 SW8 Result
Down Down Down Enables Link Segment mode (LS).
Up Down Down Enables Link Propagate mode (LP).
Down Up Down
Up Up Down
Down Down Up Enables Symmetrical Fault Detect mode (SFD).
Up Down Up Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Down Up Up Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Up Up Up Illegal setting. LS mode is enabled.
Enables Remote Fault Detection mode plus
Link Segment mode (RFD+LS).
Enables Remote Fault Detection mode plus
Link Propagation mode (RFD+LP).
NOTE: Connecting two converters set to any of the RFD modes are illegal and will cause a “deadly
embrace” lockup.
NOTE: It is recommended to keep the LS setting (default) until initial configuration is complete.
For detailed information on the operation of the different Link Modes, download the application note
“iConverter Link Modes” available on Omnitron’s web page:
http://www.omnitron-systems.com/downloads.php
Page 8
Page 9
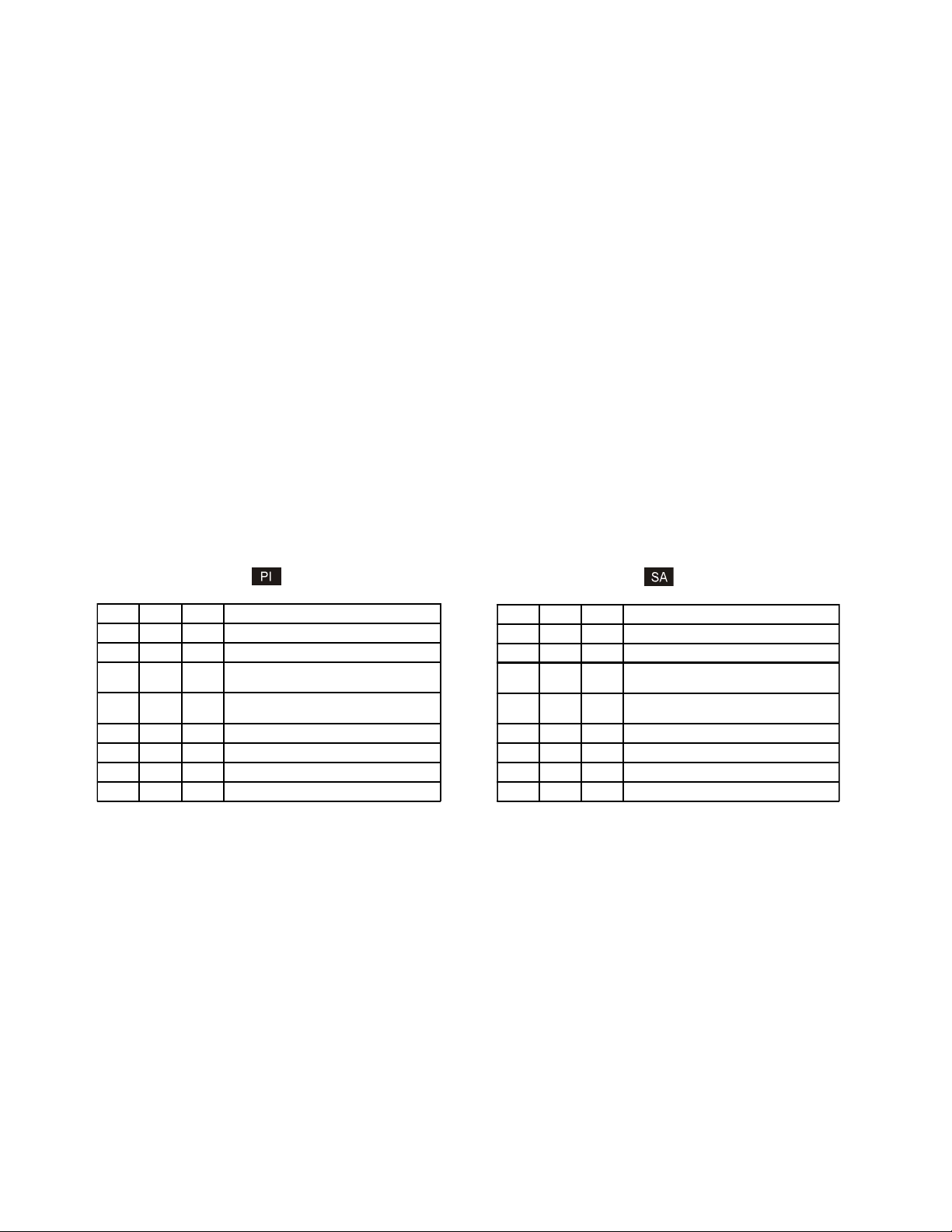
3.2.2 Board-Mounted Bank 2 Settings
DIP-switch Bank 2 is only available on the plug-in module.
Switc h Left (Factory Default) Right
SW1 A-DS:
Backplane Port A Disabled
SW2 B-DS:
Backplane Port B Disa bled
SW3 Re served Reserved
SW4 M/SL:
Mas ter/Sla ve Auto-Select
SW5 - SW8 R ese rved Reserved
3.2.2.1 SW1 - Backplane Port A Enabled “A-DS/A-EN”
A-EN:
Port A Enabled
B-EN:
Port B Enabled
SL:
Slave-Mode Only
When the DIP-switch is in the Left “A-DS” position (factory default), Backplane Port A of the 10/100M is
isolated from the chassis Backplane. When the DIP-switch is in the Right “A-EN” position, Backplane
Port A of the 10/100M is enabled. This port allows Ethernet Backplane connectivity to an adjacent module
via the chassis Backplane Port A. See the backplane illustrations in Section 2.1.3.
3.2.2.2 SW2 - Backplane Port B Enabled “B-DS/B-EN”
When the DIP-switch is in the Left “B-DS” position (factory default), Backplane Port B is isolated from the
chassis Backplane. When the DIP-switch is in the Right “B-EN” position, Backplane Port B is enabled.
This port allows Ethernet Backplane connectivity to an adjacent module via the chassis Backplane Port B.
See the backplane illustrations in Section 2.1.3.
3.2.2.3 SW4 - Master/Slave Auto-Select and Slave-Only “M/SL / SL
When multiple management modules such as the NMM and the 10/100M (or multiple self-managed modules
such as the 10/100M) are installed in the same chassis, only one management module can act as the chassis
master . The master management module has the ability to make changes to the settings of the other modules
in the chassis, while the slave management modules cannot make the changes. If an NMM is installed in
the chassis, the NMM will always be the master, otherwise the lowest slot number with a management
module installed will become chassis master.
When this DIP-switch is in the Left “M/SL” position (factory default), the assignment of mastership is
automatically negotiated by the installed management modules. T o designate a specific management module
as the master when no NMM is installed in the chassis, set the DIP-switch on the master module to the Left
“M/SL” position, and set the other installed management modules’ DIP-switches to the Right “SL” position
to enable Slave-Only mode.
Only the chassis master can change configuration settings of other modules.
3.2.2.4 SW3, SW5, SW6, SW7, SW8 - Reserved
These DIP-switches are for factory use only .
NOTE: DIP-switches marked Reserved must be kept in the Left (factory default) position.
Page 9
Page 10

3.3 INSTALLING PLUG-IN MODULES AND CONNECTING CABLES
a. Carefully slide the module into an open slot in the chassis. Align the module with the installation
guides and ensure that the module is firmly seated against the backplane. Secure the module by
fastening the front panel thumbscrew (push in and turn clockwise to tighten) to the chassis front.
Verify the “Pwr” LED is ON (indicating the chassis is powered).
a. The 10/100M standalone Network Interface Device (NID) is available in tabletop and wall-mounting
models. For wall-mounting, attach the NID to a wall, backboard or other flat surfaces. For tabletop
installations, place the unit on a flat level surface. Attach the rubber feet to the bottom of the NID to
prevent the unit from sliding. Make sure the unit is placed in a safe, dry and secure location.
To power the unit using the AC/DC adapter, connect the AC/DC adapter to the AC outlet. Then
connect the barrel plug at the end of the wire on the AC/DC adapter to the 2.5mm DC barrel connector
(center-positive) on the unit. Confirm that the unit has powered up properly by checking the power
status LED located on the front of the unit.
To power the unit using a DC power source, prepare a power cable using a two-conductor insulated
wire (not supplied) with a 14 AWG gauge minimum. Cut the power cable to the length required.
Strip approximately 3/8 of an inch of insulation from the power cable wires. Connect the power
cables to the 10/100M standalone unit by fastening the stripped ends to the DC power connector.
Connect the power wires to the DC power source. The Power LED should indicate the presence of
power.
WARNING: Note the wire colors used in making the positive and negative connections. Use
the same color assignment for the connection at the DC power source.
NOTE: If mounting with a safety ground attachment, use the safety ground screw at the rear
of the unit.
b. When using a 10/100M SFP model, insert the SFP Fiber transceiver into the Port 1 SFP receptacle on
the 10/100M.
NOTE: The release latch of the SFP Fiber transceiver must be in the closed (up) position before
insertion.
c. Connect the UTP port via a Category 5 or better cable to a 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX Ethernet
device.
d. Connect the appropriate multimode or single-mode fiber cable to the fiber port of the installed module.
It is important to ensure that the transmit (Tx) is attached to the receive side of the device at the other
end and the receive (Rx) is attached to the transmit side. Single-fiber (SF) media converter models
operate in pairs. The Tx wavelength must match the Rx wavelength at the other end and the Rx
wavelength must match the Tx wavelength at the other end.
Page 10
Page 11

3.4 CONFIGURE THE MODULE VIA COMMAND LINE INTERF ACE
To configure, attach the 10/100M to a DB-9 serial (RS-232) equipped computer with terminal emulation
software such as HyperT erminal. The 10/100M Serial Console Port (DCE) is a mini DIN-6 female connector
which can be changed to a DB-9 connector with the included adapter (Part #8082-0). Attach the ends of a
serial cable to the serial port of the PC and the Serial Console Port of the 10/100M. This is a standard
asynchronous serial interface. The pin-outs are illustrated below.
Serial Connector Pin Outs
Start HyperTerminal and select the correct COM Port in the HyperTerminal “Connect To:” window.
Set the PC’s serial port to the following:
Bits Per Second: 57,600
Stop Bits: 1
Data Bits: 8
Parity: NONE
Hardware Flow Control: NONE
Power the chassis containing the 10/100M module and press <ENTER> to bring up a command line prompt
on the attached PC.
The module is configured with the following defaults:
IP
IP Address: 192.168.1.220
IP Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Passwords
Serial: No password assigned
FTP: No password assigned
Telnet: public
SNMPv1/v2c Communities
READ: public
WRITE: public
SNMPv3 Parameters
User 1 name (read only): guest
User 2 name (read/write): admin
User 1 Privacy pwd: publicguest User 1 Authen pwd: publicguest
User 2 Privacy pwd: privateadmin User 2 Authen pwd: privateadmin
Page 11
Page 12
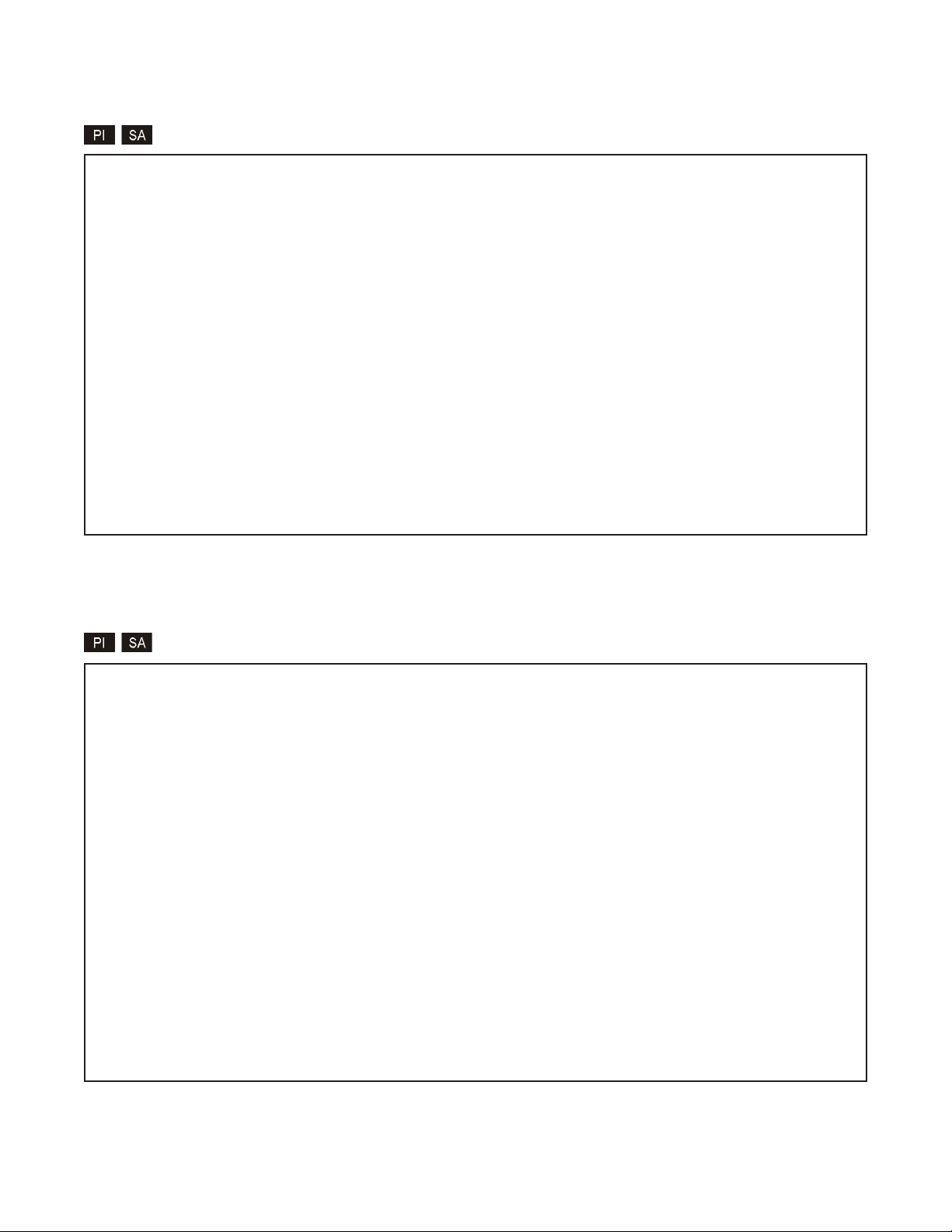
The Management Options screen will be displayed.
Management Options iConverter, Serial Agent
Network Management
1: Chassis and Module Management
2: Set Module Identifier
Management Module Preferences
3: IP and Control Preferences
4: SNMP Preferences
5: Abandon Preference Changes
6: Save Preference Changes
7: Restore to Factory Defaults
8: Restart Management Module
9: Other Networking Features
Management Module Maintenance
10: Firmware Update
11: Set Date/Time
IP Address = 192.168.1.220
Chassis Number = 1
Enter Choice, (H)elp, E(x)it >
A new 10/100M module does not have a password, and will skip the Password Entry screen and go straight
to the Management Options screen. If a password has been set, the Password Entry screen will be displayed.
T ype the password and press <ENTER>, the 10/100M will respond with the Management Options screen.
Omnitron Systems Technology, Inc. iConverter, Serial Agent
Copyright 2001-2007 OST, Inc. Password Entry
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------Omnitron Systems Technology Technical Support: (949) 250-6510
140 Technology #500 Sales/Products: (800) 675-8410
Irvine, CA 92618 On the web at: www.omnitron-systems.com
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IP Address 192.168.1.220
MAC 00:00:00:00:00:00
[xxxxxxxx]
Please enter the password >
Page 12
Page 13
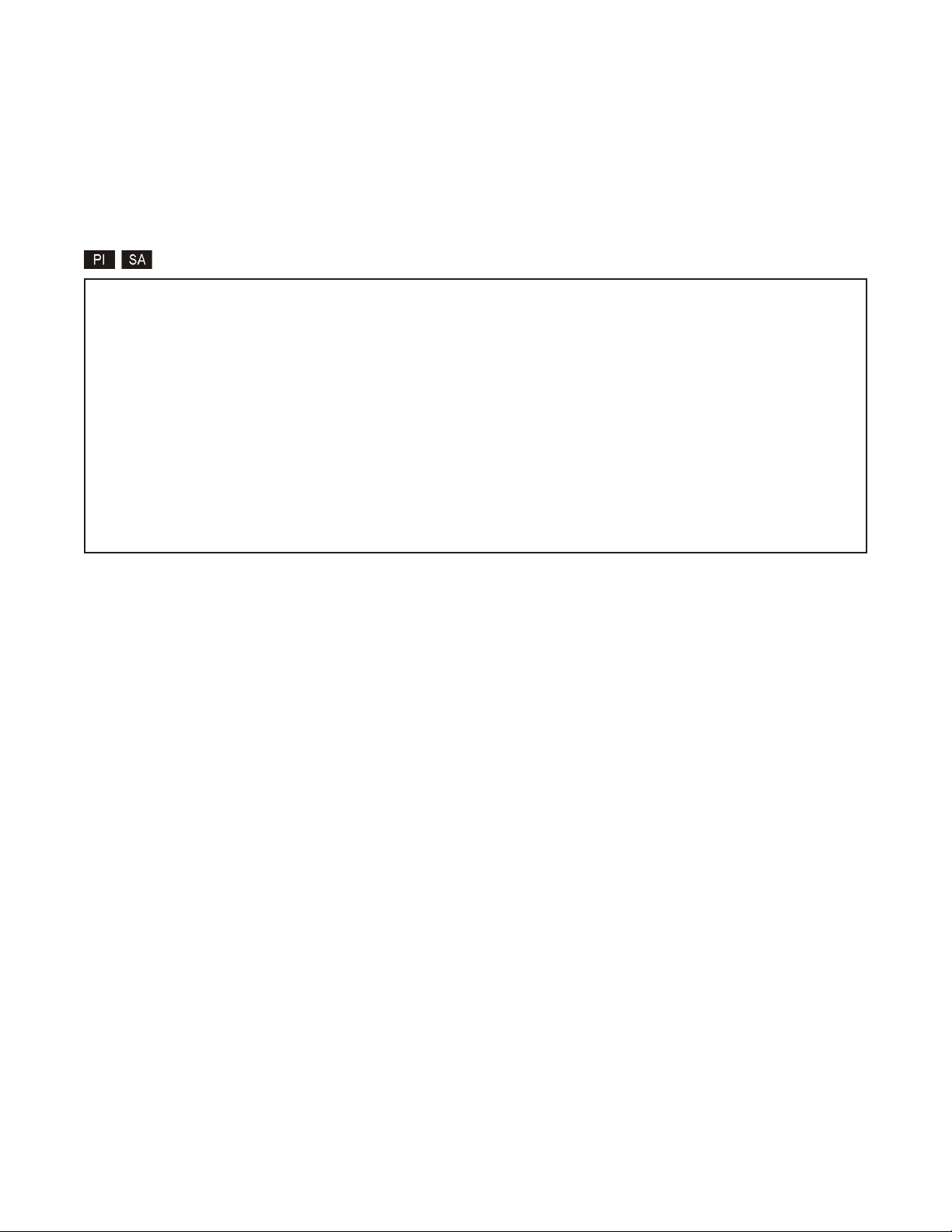
3.4.1 Setting IP and Control Preferences
An IP address is required for the SNMP manager to address the 10/100M. The factory default setting is
192.168.1.220. The IP address can be configured manually or automatically as a DHCP client.
3.4.1.1 Setting IP Parameters Manually
To manually configure the IP address and control parameters, select 3 from the Management Options
screen. The IP and Control Preferences screen will appear.
IP and Control Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Set IP 192.168.1.220
2: Set Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
3: Set Gateway 192.168.1.1
4: Chassis Number 1
5: Chassis Name (also sysName) 10/100M
6: Enable/Disable TELNET Enabled
7: Enable/Disable FTP Disabled
8: Enable/Disable Soft Switch Reload Disabled
9: TELNET Password *****
10: FTP Password
11: Serial Password
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To configure the IP address of the 10/100M, select 1 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, and press
<ENTER>. Backspace over the existing value, type the new value (in x.x.x.x format), and press <ENTER>.
T o configure the subnet mask of the 10/100M, select 2 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, and press
<ENTER>. Backspace over the existing value, type the new value (in x.x.x.x format), and press <ENTER>.
To configure the gateway of the 10/100M, select 3 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, and press
<ENTER>. Backspace over the existing value, type the new value (in x.x.x.x format), and press <ENTER>.
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.1.2 Setting IP Parameters as DHCP Client
To configure the IP automatically as a DHCP client, select 9 from the Management Options screen. The
Other Networking Features screen will appear.
Page 13
Page 14

Management Options iConverter, Serial Agent
Network Management
1: Chassis and Module Management
2: Set Module Identifier
Management Module Preferences
3: IP and Control Preferences
4: SNMP Preferences
5: Abandon Preference Changes
6: Save Preference Changes
7: Restore to Factory Defaults
8: Restart Management Module
9: Other Networking Features
Management Module Maintenance
10: Firmware Update
11: Set Date/Time
IP Address = 192.168.1.220
Chassis Number = 1
Enter Choice, (H)elp, E(x)it > 9
Other Networking Features Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Enable/Disable DHCP Client Disabled
2: Enable/Disable Keep Alive Trap Disabled
3: Keep Alive Trap interval (10-600 secs) 10
4: Enable/Disable SW1 Switch Block Enabled
5: Serial Baud Rate 57600 bps
6: Enable/Disable VLAN Support Disabled
7: VLAN ID (0-4095) 2
8: VLAN Priority (0-7) 7
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To enable DHCP client, select 1 at the Other Networking Features screen and follow the screen prompts
to enable DHCP.
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.1.3 Setting the Chassis Number and Name
A Chassis Name, or sysName, can be assigned for identification of the 10/100M in the SNMP client. The
name can be any 1-32 character alphanumeric string.
The Chassis Number can remain as 1 (factory default) when the 10/100M is installed without an iConverter
NMM in the same chassis. When the 10/100M is installed in the same chassis as an NMM, then the 10/100M
must be set to the Chassis Number of the NMM.
T o set the Chassis Number , select 4 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and follow
the instructions to enter the chassis number.
To set the Chassis Name, select 5 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and follow
the instructions to enter the chassis name.
Page 14
Page 15

NOTE: When the NMM is installed into the chassis and is set to Remote OAM, the chassis number
of the 10/100M is automatically assigned by the NMM.
IP and Control Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Set IP 192.168.1.220
2: Set Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
3: Set Gateway 192.168.1.1
4: Chassis Number 1
5: Chassis Name (also sysName) 10/100M
6: Enable/Disable TELNET Enabled
7: Enable/Disable FTP Disabled
8: Enable/Disable Soft Switch Reload Disabled
9: TELNET Password *****
10: FTP Password
11: Serial Password
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.1.4 Setting 10/100M Passwords
The 10/100M is shipped from the factory without password protection on the Serial Console Port. It is
highly recommended that the network administrator set a password in order to prevent unauthorized access
to the unit. The password can be any 1-32 character alphanumeric string.
The 10/100M is shipped from the factory with T elnet enabled and FTP disabled. From the IP and Control
Preferences screen, select 6 to enable or disable Telnet, and select 7 to enable or disable FTP.
To set the password for Telnet access, select 9 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER>
and then follow the screen prompts to enter and verify the password. The default password for Telnet
access is “public”.
To set the password for FTP access, select 10 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER>
and then follow the screen prompts to enter and verify the password.
T o set the password for serial access, select 11 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER>
and then follow the screen prompts to enter and verify the password.
Page 15
Page 16

IP and Control Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Set IP 192.168.1.220
2: Set Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
3: Set Gateway 192.168.1.1
4: Chassis Number 1
5: Chassis Name (also sysName) 10/100M
6: Enable/Disable TELNET Enabled
7: Enable/Disable FTP Disabled
8: Enable/Disable Soft Switch Reload Disabled
9: TELNET Password *****
10: FTP Password
11: Serial Password
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.2 Setting SNMP Preferences
To set the SNMP Preferences for the 10/100M module, select 4 from the Management Options screen,
press <ENTER> to enter the SNMP Preferences screen.
Management Options iConverter, Serial Agent
Network Management
1: Chassis and Module Management
2: Set Module Identifier
Management Module Preferences
3: IP and Control Preferences
4: SNMP Preferences
5: Abandon Preference Changes
6: Save Preference Changes
7: Restore to Factory Defaults
8: Restart Management Module
9: Other Networking Features
Management Module Maintenance
10: Firmware Update
11: Set Date/Time
IP Address = 192.168.1.220
Chassis Number = 1
Enter Choice, (H)elp, E(x)it > 4
Page 16
Page 17

SNMP Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
Chassis Number = 1 SNMP Engine ID 80001CAE03000687003B19
1: sysContact Omnitron (949) 250-6510
2: sysLocation Irvine, CA USA
3: SNMP Writes Enabled
SNMP v1/v2c ------------------------------------------------------------------ 4: Read Community *****
5: Write Community *****
6: Agent Enabled
SNMP V3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 7: Agent Enabled
8: User 1 name (read only) guest
9: User 2 name (read/write) admin
10: User 1 Security noAuthNoPriv 13: User 2 Security noAuthNoPriv
11: User 1 Privacy pwd ***** 14: User 2 Privacy pwd *****
12: User 1 Authen. pwd ***** 15: User 2 Authen. pwd *****
Traps Hosts ------------------------------------------------------------------ 16: Address 1 255.255.255.255 20: Address 5 255.255.255.255
17: Address 2 255.255.255.255 21: Address 6 255.255.255.255
18: Address 3 255.255.255.255 22: Address 7 255.255.255.255
19: Address 4 255.255.255.255 23: Address 8 255.255.255.255
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
3.4.2.1 Setting SNMPv1/v2c Read and Write Community Names
The 10/100M is shipped from the factory with the SNMP agent enabled with the default SNMP Read and
Write Community name as “public”. See Section 3.4 for all factory default settings.
The SNMP Read Community Name is necessary for reading data from the 10/100M. The name can be any
1-32 character alphanumeric string. To set the SNMP Read Community Name, select 4 at the SNMP
Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts.
The SNMP Write Community Name is necessary for writing data to the 10/100M. The name can be any
1-32 character alphanumeric string. To set the SNMP Write Community Name, select 5 at the SNMP
Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts.
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.2.2 Setting SNMPv3 Parameters
SNMPv3 implements a security model that provides for message integrity , authentication, and encryption.
Authentication for SNMPv3 is provided through a unique User Name and Authentication Password for
each access level.
T wo access levels or accounts are available; Read-Only Level (User 1) and Read and W rite Level (User 2).
User 1 is allowed to request information from the module. User 2 is allowed to request information from
and set configuration to the module. To set the User 1 name, select 8 at the SNMP Preferences screen,
press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts. To set the User 2 name, select 9 at the SNMP
Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts. The 10/100M is shipped with
default values pre-assigned. See Section 3.4 for all factory default settings.
The module supports the three levels of Authentication and Encryption (Security Levels) for User 1 and
User 2; noAuthNoPriv, authNoPriv and authPriv. noAuthNoPriv uses username for authentication,
Page 17
Page 18

authNoPriv provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 algorithm and authPriv provides
DES 56-bit encryption based on the HMAC-MD5 algorithm.
To set User 1 security, select 10 at the SNMP Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and then follow the
screen prompts. T o set the User 2 security , select 13 at the SNMP Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and
then follow the screen prompts.
To set User 1 privacy password, select 11 at the SNMP Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and then
follow the screen prompts. T o set the User 2 privacy password, select 14 at the SNMP Preferences screen,
press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts.
To set User 1 authentication password, select 12 at the SNMP Preferences screen, press <ENTER> and
then follow the screen prompts. T o set the User 2 authentication password, select 15 at the SNMP Preferences
screen, press <ENTER> and then follow the screen prompts.
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
Community name and User name can be any 1-32 character alphanumeric string
Authentication Password and Privacy Password can be any 1-16 character alphanumeric string.
3.4.2.3 Setting the SNMP Trap IP Host Addresses
SNMP traps are used to report events that occur during the operation of a network, and may require the
attention of the network administrator. The 10/100M is capable of sending SNMP traps to up to eight
different SNMP Traphosts.
T o enter the IP address of the first T raphost Address, select 4 at the Management Options screen to access
the SNMP Preferences screen. Select 16 at the SNMP Preferences screen and press <ENTER>. Then
backspace over the existing value, type the new value (in x.x.x.x format), and press <ENTER>. To enter
the IP addresses of additional trap-receiving Traphost Addresses, repeat this process for T raphost Addresses
2-8 (menu options 17-23).
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.2.4 Enabling/Disabling SNMPv1/v2c Agent
To disable/enable SNMPv1/v2c agent, select 4 at the Management Options screen to access the SNMP
Preferences screen. Select option 6 to disable/enable SNMPv1/v2c agent. When disabled, the module
will not respond to any requests via the SNMPv1/v2c protocol.
3.4.2.5 Enabling/Disabling SNMPv3 Agent
To disable/enable SNMPv3 agent, select 4 at the Management Options screen to access the SNMP
Preferences screen. Select option 7 to disable/enable SNMPv3 agent. When disabled, the module will not
respond to any requests via the SNMPv3 protocol.
Note: Both SNMPv1/v2c and SNMPv3 agents can be enabled at the same time.
Page 18
Page 19

3.4.3 Management Processor VLAN Support
The 10/100M Management Processor can independently transmit and receive Management Data with an
IEEE 802.1Q tag. To enable and configure this feature, type 9 from the Management Options screen to
access the Other Networking Features screen.
Management Options iConverter, Serial Agent
Network Management
1: Chassis and Module Management
2: Set Module Identifier
Management Module Preferences
3: IP and Control Preferences
4: SNMP Preferences
5: Abandon Preference Changes
6: Save Preference Changes
7: Restore to Factory Defaults
8: Restart Management Module
9: Other Networking Features
Management Module Maintenance
10: Firmware Update
11: Set Date/Time
IP Address = 192.168.1.220
Chassis Number = 1
Enter Choice, (H)elp, E(x)it > 9
Other Networking Features Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Enable/Disable DHCP Client Disabled
2: Enable/Disable Keep Alive Trap Disabled
3: Keep Alive Trap interval (10-600 secs) 10
4: Enable/Disable SW1 Switch Block Enabled
5: Serial Baud Rate 57600 bps
6: Enable/Disable VLAN Support Disabled
7: VLAN ID (0-4095) 2
8: VLAN Priority (0-7) 7
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To configure the VLAN management ID, select option 7. To configure the priority setting for the VLAN
management channel, select option 8. To enable or disable VLAN management support, select option 6.
Once VLAN support is enabled, IP management support will only be accessible using the configured
VLAN ID.
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
3.4.4 Enabling/Disabling Soft-switch Reload
The Soft-switch Reload function controls the configurations of the 10/100M and other iConverter modules
managed by the 10/100M following a power up.
When the Soft-switch Reload is disabled, the configurations of the 10/100M and the other managed modules
Page 19
Page 20

(non-management modules) are determined by their hardware DIP-switch settings following a return of
power.
When the Soft-switch Reload is enabled, the configurations of the 10/100M and the other managed modules
are determined by the previous software settings stored in the FLASH memory of the 10/100M following
a return of power. Each of the hardware DIP-switch settings on the module are ignored until a change is
made to the DIP-switch, then the hardware settings will take effect.
T o set the Soft-switch Reload function, select 8 at the IP and Control Preferences screen, press <ENTER>
and then follow the screen prompts to change the setting.
IP and Control Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Set IP 192.168.1.220
2: Set Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
3: Set Gateway 192.168.1.1
4: Chassis Number 1
5: Chassis Name (also sysName) 10/100M
6: Enable/Disable TELNET Enabled
7: Enable/Disable FTP Disabled
8: Enable/Disable Soft Switch Reload Disabled
9: TELNET Password *****
10: FTP Password
11: Serial Password
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
Page 20
Page 21

3.4.5 Access the 10/100M Remotely
Remote access to the 10/100M is provided via SNMP, Telnet, FTP or an external serial modem connected
to the Serial Console Port.
3.4.5.1 Accessing the 10/100M via NetOutlook (SNMP)
The 10/100M module can be remotely accessed by SNMP-client software such as NetOutlook or thirdparty SNMP management software. See Setting SNMP Preferences Section 3.4.2, on how to configure the
required parameters.
NetOutlook Chassis View and Trap Log Screens
3.4.5.2 Accessing the 10/100M via T elnet
The 10/100M is shipped from the factory with T elnet enabled. The default Telnet password is “public”. It
is highly recommended that the network administrator set a new Telnet password in order to prevent
unauthorized access to the unit. Telnet configuration parameters are available from the IP and Control
Preferences screen, option 6.
Page 21
Page 22
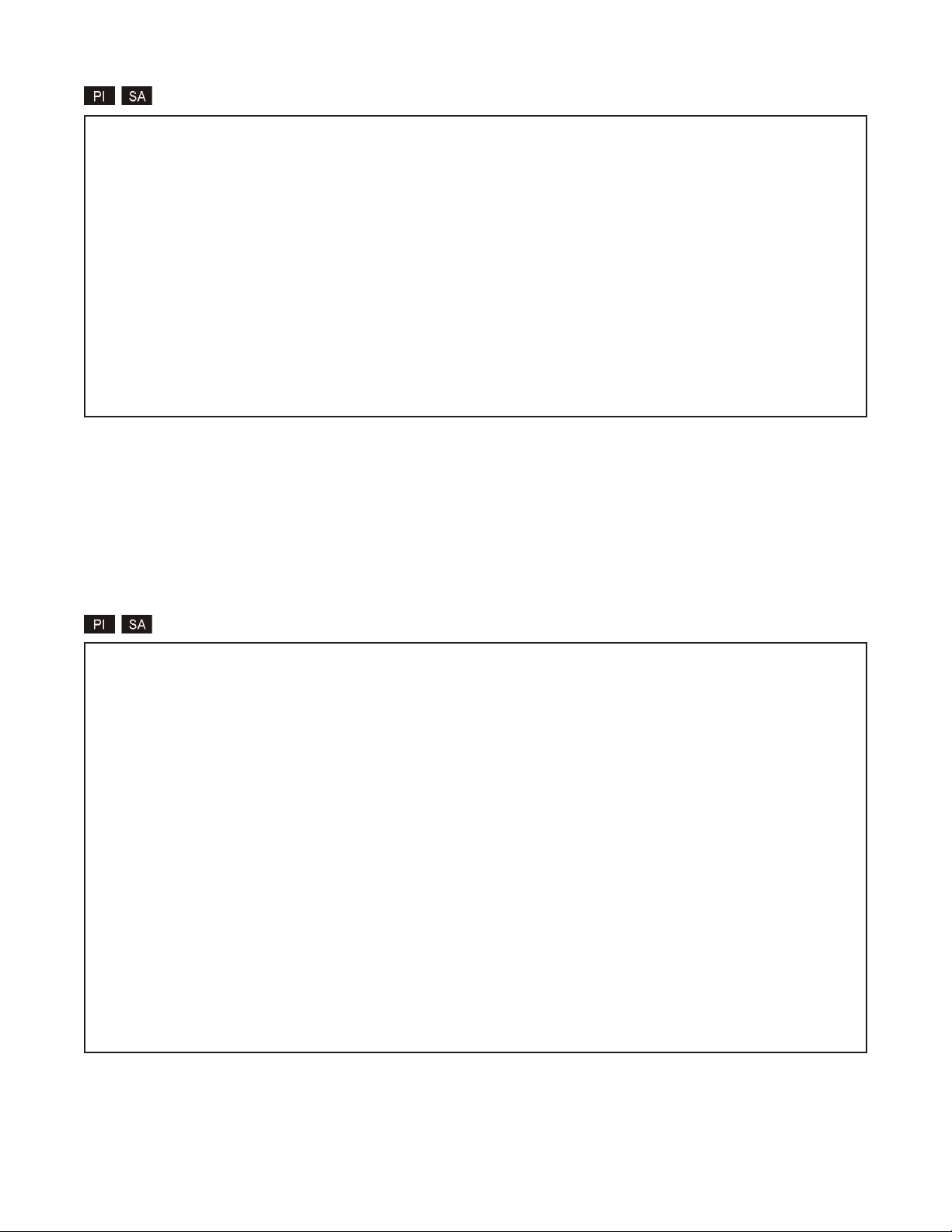
IP and Control Preferences Screen iConverter, Serial Agent
1: Set IP 192.168.1.220
2: Set Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
3: Set Gateway 192.168.1.1
4: Chassis Number 1
5: Chassis Name (also sysName) 10/100M
6: Enable/Disable TELNET Enabled
7: Enable/Disable FTP Disabled
8: Enable/Disable Soft Switch Reload Disabled
9: TELNET Password *****
10: FTP Password
11: Serial Password
Enter Choice, Management Options Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >6
Disable TELNET (Y/N)?>
To save the new values, select 0 and press <ENTER> to return to the Management Options screen, then
select 6 and press <ENTER> to Save Preference Changes.
The 10/100M may be accessed and configured via T elnet using any standard T elnet client. Only one T elnet
session can be active at a time. An inactive Telnet session terminates automatically after 5 minutes.
3.4.5.3 Updating the 10/100M Firmware via the Serial Console Port
To update the 10/100M firmware from the Serial Console Port, select 10 at the Management Options
screen, press <ENTER>. The 10/100M will display the following:
Management Options iConverter, Serial Agent
Network Management
1: Chassis and Module Management
2: Set Module Identifier
Management Module Preferences
3: IP and Control Preferences
4: SNMP Preferences
5: Abandon Preference Changes
6: Save Preference Changes
7: Restore to Factory Defaults
8: Restart Management Module
9: Other Networking Features
Management Module Maintenance
10: Firmware Update
11: Set Date/Time
IP Address = 192.168.1.220
Chassis Number = 1
Enter Choice, (H)elp, E(x)it > 10
UPDATE: Are you sure? (Y/N) > Y
Please Xmodem file now:
From the terminal program, use the Xmodem protocol to send the new 10100M-xxx.bin firmware file to
the 10/100M module (where xxx represents the release level of the software).
Once the file transfer begins, the data uploads to the 10/100M. The process takes about five minutes over
a serial connection.
Page 22
Page 23

When the upload is complete, the 10/100M displays the update status and then automatically restarts with
the newly loaded firmware.
3.4.5.4 Updating the 10/100M Firmware via FTP
Using an FTP application, upload the new firmware into the FTP root directory of the 10/100M. When the
file transfer is complete, the 10/100M verifies the file and then automatically restarts with the newly loaded
firmware.
For detailed instructions on updating the management modules and other modules in the same chassis via
FTP, download the application note “iConverter Management: Updating Modules via FTP” available on
Omnitron’s web page:
http://www.omnitron-systems.com/downloads.php
See Setting 10/100M Passwords Section 3.4.1.4, on how to configure FTP.
3.5 VERIFY OPERA TION
Once the module has been installed and configured, per Sections 3.2 - 3.4, verify the module is operational
by viewing the status of the LED indicators. The table below provides a description for each LED indicator .
The Power LED indicates the module is receiving power from the chassis or power cord. The plug-in
modules has an LED indicator for each available power supply in the chassis (the 19-Module Chassis has
three, the 5-Module Chassis has two).
The Fiber Optic “FO” LED indicates the fiber optic connection between the modules has been established.
A blinking LED indicates the presence of data.
The UTP “10/100” LED indicates the module has established a connection across its UTP port. A blinking
LED indicates the presence of data.
Refer to Section 6.0, Troubleshooting Guide, for help in determining possible fault conditions.
LED Function
"Legend"
Power "Pwr" Amber No power On: Module has power On: Module has power
Power Supply
Status #X
100Mbps Fiber
Opti c s "FO"
Chassis
Management
Master/Slave
"BP"
UTP port
10Mbps "10"
UTP port
100Mbps "100"
UTP port FullDuplex "FDX"
Co lo r Off State
Amber
Green No Fiber Link
Green
Green 10Mbps not active
Green 100Mbps not active
Green
Chassis Power
Supply not installed
Chassis Slave
Mode
Half-Duplex when
any UTP link is
active
On / B linking State On / B linking State
On: Power available from
installed Power Supply #X
Blinking: No power avai lable
from installed Power Supply #X
On: Fiber link is active
Blinki ng : F iber Data A c tivity
On: Chassis Master Mode
Blinking: Operating in OAM
Mode
On: 10Mbps UTP link is active
Blinking: UTP Data Activity
On: 100Mbps UTP link is active
Blinking: UTP Data Activity
Full-Duplex when any UTP link
is active
Not available on standalone
On: Fiber link is active
Blinking: Fiber Data A c tivity
Not available on standalone
On: 10Mbps UTP link is active
Blinking: UTP Data A c tivity
On: 100Mbps UTP link is active
Blinking: UTP Data A c tivity
Full-Duplex when any UTP link
is active
Note: On some models the fiber optic LED is referred to as ‘P1’.
Page 23
Page 24
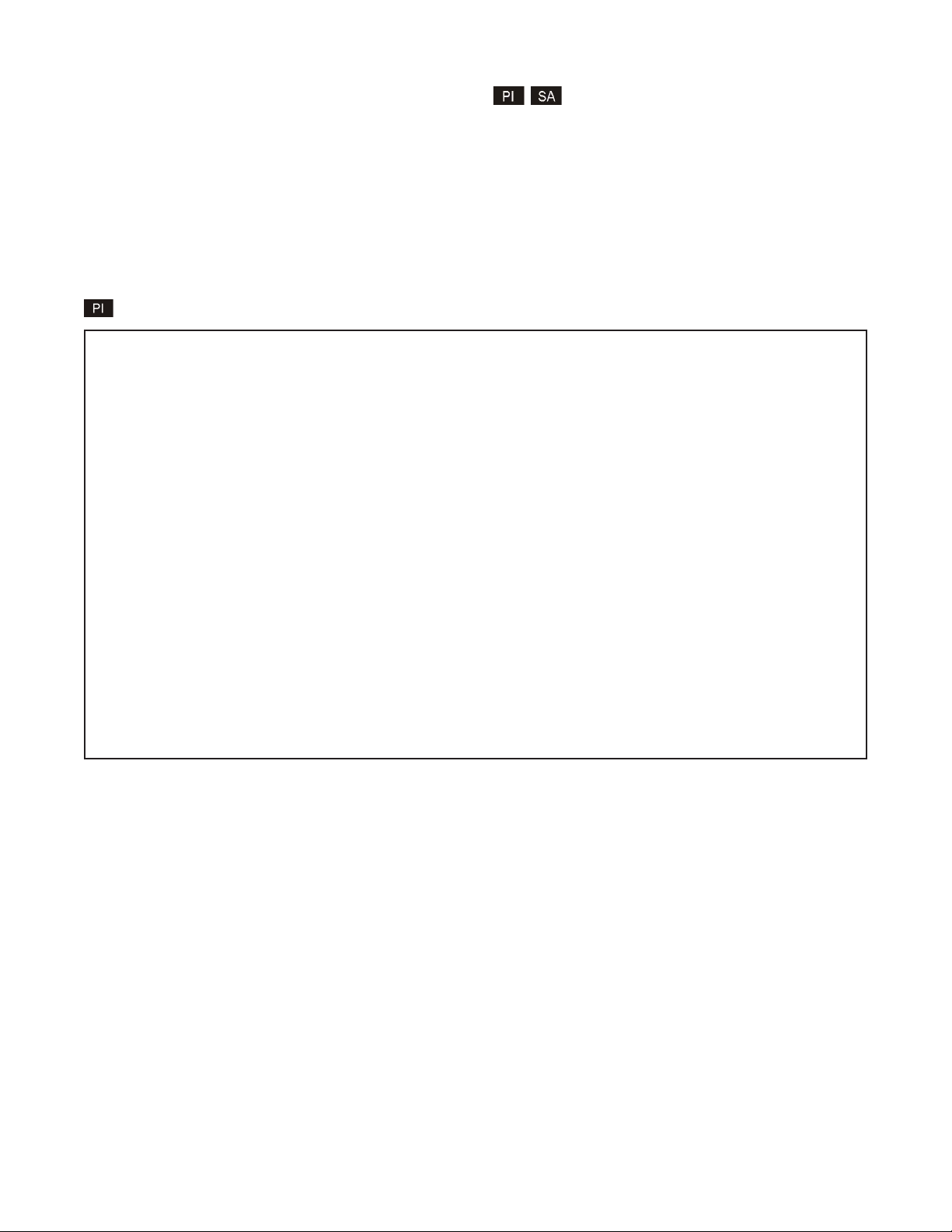
4.0 DET AILED MODULE CONFIGURATION
4.1 OVERVIEW
The 10/100M has module parameters that require configuration depending on the application. The Module
configuration screen is accessible by selecting the module slot number from the Chassis View screen. To
access the Module configuration menu, select 1 at the Management Options screen, press <ENTER>. The
Chassis Selection screen will be displayed. From the Chassis Selection screen, select the chassis number
where the 10/100M module is installed.
NOTE: Module configuration is also available using NetOutlook.
Chassis Selection iConverter, Serial Agent
Number Chassis Name
1 NMM
2 Not Available
3 Not Available
4 Not Available
5 Not Available
6 Not Available
7 Not Available
8 Not Available
9 Not Available
10 Not Available
11 Not Available
12 Not Available
13 Not Available
14 Not Available
15 Not Available
16 Not Available
17 Not Available
18 Not Available
19 Not Available
Connected to Chassis Number 1
Chassis Number(1-19), Management Options(0), (H)elp, E(x)it > 1
By selecting Chassis Number 1, from the Chassis Selection screen, the Chassis V iew screen will be displayed.
Page 24
Page 25
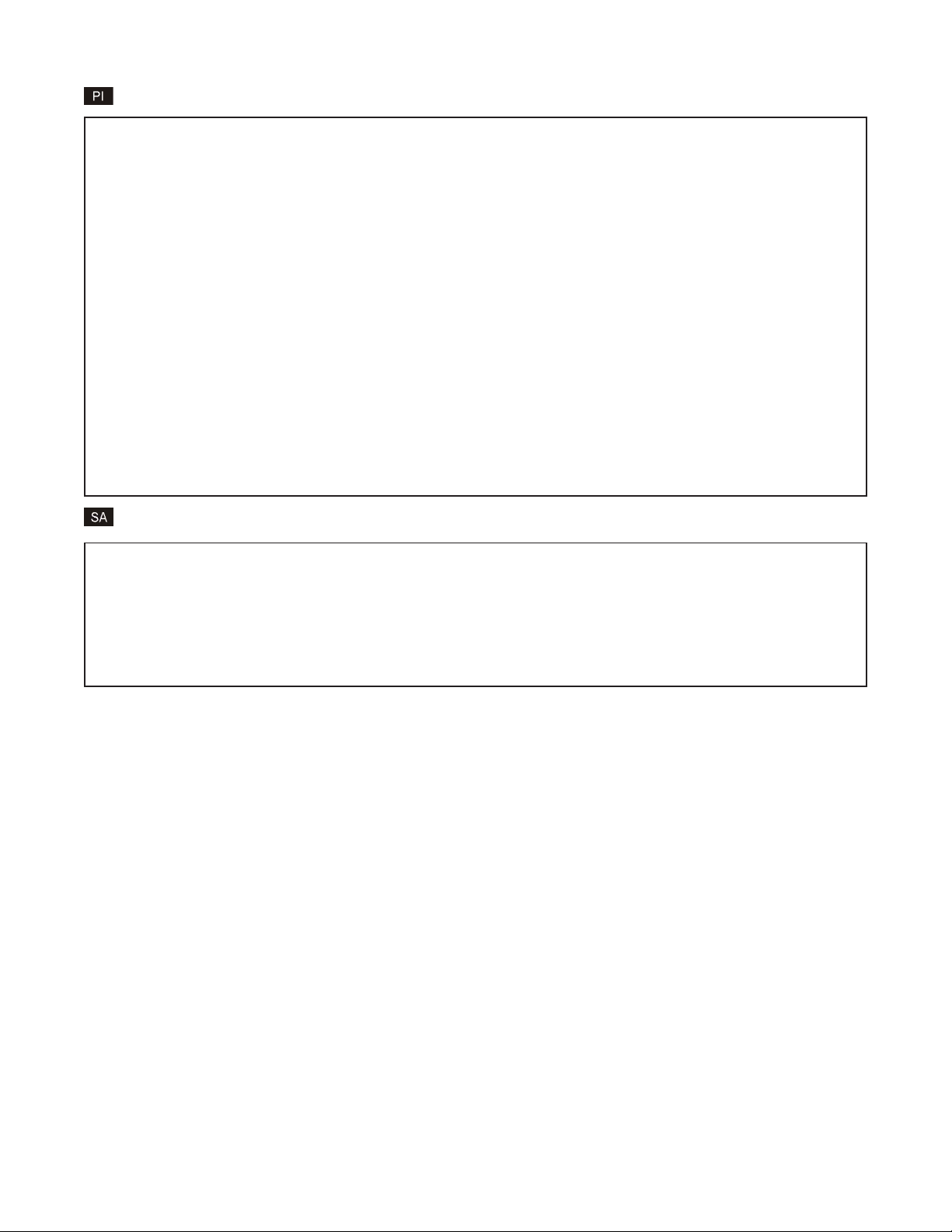
Chassis View 19 Slot iConverter, Serial Agent
Chassis Number = 1
Slot Model Type | Slot Model Type
1 8000-0 NMM | 16 N/A
2 8903-1 10/100M | 17 N/A
3 8911-1 10/100M | 18 N/A
4 N/A | 19 N/A
5 8919-0 10/100M | 20 N/A
6 N/A | 21 8200-9 Power Supply
7 N/A | 22 N/A
8 N/A |
9 N/A |
10 N/A |
11 N/A |
12 N/A |
13 N/A |
14 N/A |
15 N/A |
Module to View(1-22), Chassis Selection(0), (R)eset, (H)elp, E(x)it > 5
Chassis View 1 Slot iConverter, Serial Agent
Chassis Number = 1
Slot Model Type Module Identifier
1 8919-0 10/100M
Module to View(1), Management Options(0), (R)eset, (H)elp, E(x)it >1
From the Chassis View menu, select the desired module (select 1 or 5), press <ENTER>. The Module
configuration screen will be displayed.
Page 25
Page 26

Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Switch ON Condition OFF Condition H/W Actual
Slot Number = 1 1: Pause Enabled Pause Disabled Off Off
Model Number = 8919-0 2: Fiber HDX Fiber FDX Off Off
3: UTP Manual UTP Auto-Neg Off Off
Serial Number = xxxxxxxx 4: UTP 10 Mbps UTP 100 Mbps Off Off
Manufacturing Date = xxxxxxxx 5: UTP HDX UTP FDX Off Off
Product Revision = x 6: Link Propagate Link Segment Off Off
Software Revision = xx 7: Remote Fault Normal Off Off
8: Symm Fault Det Normal Off Off
LED 9: BP A Enabled BP A Disabled On On
1: Power = On 10: BP B Enabled BP B Disabled On On
2: Power Supply 1 = Off 11: Not Available
3: Power Supply 2 = Off 12: Slave Only Master/Slave Off Off
4: Power Supply 3 = Off 13: Not Available
5: Fiber Link = Off 14: Not Available
6: BP Master = On 15: Not Available
7: UTP 10 Link = Off 16: Not Available
8: UTP 100 Link = Off OAM settings:
9: UTP FDX = Off 17: IP Protocol State On
18: Management Mode Secure OAM
Toggle Switch(1-16), (I)dentifier, (R)eset, (H)elp, (P)ortStat, Port(C)tl >
The Module configuration screen provides general information concerning the configuration and status of
the module. The screen displays the model and serial numbers, hardware and software revisions, as well as
the condition of the LEDs and DIP-switches. The DIP-switches can be re-configured (options 1 - 10, 12)
without removing the module from the chassis. Select the appropriate option to change the DIP-switch
setting. Selecting DIP-switch options 1 - 10 and 12, will cause the selection to change states under the
‘Actual’ heading.
NOTE: The Plug-In Module configuration screen is shown. The standalone Module configuration
screen will display LED 2, 3, 4, and 6 and DIP-switches 9, 10 and 12 as NOT AVAILABLE.
Page 26
Page 27

4.2 MODULE MANAGEMENT MODE
From the Module configuration screen, the management mode can be changed. Select option 18 to change
the mode. The management mode options will be displayed.
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Switch ON Condition OFF Condition H/W Actual
Slot Number = 1 1: Pause Enabled Pause Disabled Off Off
Model Number = 8919-0 2: Fiber HDX Fiber FDX Off Off
3: UTP Manual UTP Auto-Neg Off Off
Serial Number = xxxxxxxx 4: UTP 10 Mbps UTP 100 Mbps Off Off
Manufacturing Date = xxxxxxxx 5: UTP HDX UTP FDX Off Off
Product Revision = x 6: Link Propagate Link Segment Off Off
Software Revision = xx 7: Remote Fault Normal Off Off
8: Symm Fault Det Normal Off Off
LED 9: BP A Enabled BP A Disabled On On
1: Power = On 10: BP B Enabled BP B Disabled On On
2: Power Supply 1 = Off 11: Not Available
3: Power Supply 2 = Off 12: Slave Only Master/Slave Off Off
4: Power Supply 3 = Off 13: Not Available
5: Fiber Link = Off 14: Not Available
6: BP Master = On 15: Not Available
7: UTP 10 Link = Off 16: Not Available
8: UTP 100 Link = Off OAM settings:
9: UTP FDX = Off 17: IP Protocol State On
18: Management Mode Secure OAM
Toggle Switch(1-16), (I)dentifier, (R)eset, (H)elp, (P)ortStat, Port(C)tl >
Mode (1=OAM Off, 2=Auto Secure OAM, 3=Auto ah OAM, 4=Secure OAM, 5=ah OAM): 3
The 10/100M module supports several management options. Option 18 configures how the module will
communicate to its remote partner. ‘Auto Secure OAM’ (option 2) and ‘Secure OAM’ (option 4) uses
Omnitron’s proprietary secure encrypted management channel. ‘Auto Secure OAM’ will force the remote
partner to communicate using the Secure OAM protocol while ‘Secure OAM’ will only attempt to
communicate with the remote partner over the secure protocol. The management channel can support IP or
IP-less connectivity based on the configuration of the ‘IP Protocol State’, option 17. ‘Auto ah OAM’
(option 3) and ‘ah OAM’ (option 5)’ conforms to the IEEE 802.3ah specification. ‘Auto ah OAM’ will
force the remote partner to communicate using the ah OAM protocol while ‘ah OAM’ will only attempt to
communicate with the remote partner over the ah protocol. This option provides an industry standard
method of fault detection and monitoring. The management channel supports both IP and IP-less connectivity
based on the configuration, option 17 and 18.
NOTE: See NetOutlook User Manual for complete information on the management modes.
Page 27
Page 28

4.3 PORT CONFIGURATION
The Port configuration screen provides access to the port level configuration parameters, such as, Port
Access, Bandwidth Control, SFP information, 802.3ah, Port VLANs, T agged VLANs and cNode Loopback.
T o access the Port configuration screen, select C from the Module configuration screen and press <ENTER>.
The Port configuration screen will appear.
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Port VLAN Path Setup
Slot Number = 11 --------------------------------- Model Number = 8919-0 11: Fiber to UTP Enable On
12: Fiber to BP A Enable On
Port Access Control Setup 13: Fiber to BP B Enable On
---------------------------------- 14: UTP to BP A Enable On
1: Fiber Enable On 15: UTP to BP B Enable On
2: UTP Enable On 16: BP A to BP B Enable On
17: Fiber to Mngmnt Enable On
Enhanced Features 18: UTP to Mngmnt Enable On
---------------------------------- 19: BP A to Mngmnt Enable On
3: 802.1Q Processing Enable Off 20: BP B to Mngmnt Enable On
4: Configure Tag VLAN Control
5: Configure VLAN Membership Bandwidth Control
6: Save TAG VLAN parameters ------------------------------- 7: Configure 802.3ah parameters 21: Ingress rate Fiber No Limit
8: Configure 802.3ah events 22: Egress rate Fiber No Limit
9: SFP Information 23: Ingress rate UTP No Limit
10: cNode Loopback 24: Egress rate UTP No Limit
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Port VLAN Path Setup
Slot Number = 11 --------------------------------- Model Number = 8919-0 11: Port1 to Port2 Enable On
12: Port1 to Mngmnt Enable On
Port Access Control Setup 13: Port2 to Mngmnt Enable On
--------------------------------- 1: Fiber Enable On Bandwidth Control
2: UTP Enable On --------------------------------
14: Ingress rate Fiber No Limit
Enhanced Features 15: Egress rate Fiber No Limit
---------------------------------- 16: Ingress rate UTP No Limit
3: 802.1Q Processing Enable Off 17: Egress rate UTP No Limit
4: Configure Tag VLAN Control
5: Configure VLAN Membership
6: Save TAG VLAN parameters
7: Configure 802.3ah parameters
8: Configure 802.3ah events
9: SFP Information
10: cNode Loopback
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 28
Page 29

4.3.1 Port Access
The Port Access option allows the ports to be disabled/enabled while maintaining the port configuration
and network link
To configure Port Access, select option 1 for the Fiber port and option 2 for the UTP port from the Port
configuration screen.
4.3.2 Bandwidth Control
The 10/100M Bandwidth Control is accessed by selecting options 21 - 24 or 14 - 17 depending on the
module type; plug-in or standalone.
The 10/100M provides separate ingress and egress rate control on each port.
Ingress values will be displayed when the option is selected. Values of 128Kbps, 256Kbps, 512Kbps,
1Mbps, 2Mbps, 4Mbps, 8Mbps and Full bandwidth are available.
Egress values will be displayed when the option is selected. Values of 128Kbps, 256Kbps, 512Kbps,
1Mbps, 2Mbps, 4Mbps, 8Mbps and Full bandwidth are available.
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Port VLAN Path Setup
Slot Number = 11 --------------------------------- Model Number = 8919-0 11: Fiber to UTP Enable On
12: Fiber to BP A Enable On
Port Access Control Setup 13: Fiber to BP B Enable On
---------------------------------- 14: UTP to BP A Enable On
1: Fiber Enable On 15: UTP to BP B Enable On
2: UTP Enable On 16: BP A to BP B Enable On
17: Fiber to Mngmnt Enable On
Enhanced Features 18: UTP to Mngmnt Enable On
---------------------------------- 19: BP A to Mngmnt Enable On
3: 802.1Q Processing Enable Off 20: BP B to Mngmnt Enable On
4: Configure Tag VLAN Control
5: Configure VLAN Membership Bandwidth Control
6: Save TAG VLAN parameters ------------------------------- 7: Configure 802.3ah parameters 21: Ingress rate Fiber No Limit
8: Configure 802.3ah events 22: Egress rate Fiber No Limit
9: SFP Information 23: Ingress rate UTP No Limit
10: cNode Loopback 24: Egress rate UTP No Limit
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >21
New Rate (0= No Limit, 1=128Kbps, 2=256Kbps, 3=512Kbps,
4=1Mbps, 5=2Mbps, 6=4Mbps, 7=8Mbps) > 0
Page 29
Page 30

4.3.3 SFP Information
The 10/100M module installed with an SFP will provide general and specific information on the SFP. This
information is best viewed with SNMP management software. The following is the information available:
4.3.3.1 SFP A0 Information Display
This section displays fixed SFP Module information for the following areas.
• Identifier V alues • Extended Identifier
• Connector Values • Transceiver Codes
• Encoding Rules • Normal Bit Rate
• Link Length • Vendor Name
• Vendor OUI • Vendor Revision Number
• Laser W avelength • Options
• Vendor Serial Number • Date Code
• Diagnostic Monitoring T ype • Enhanced Options
• SFF-8472 Compliance
4.3.3.2 SFP A2 Information Display
This section displays decoded SFP data collected for the following statistics.
• Measured Temperature • Measured Vcc
• Measured Bias • Measured Tx Power
• Measured Rx Power • Temperature High Alarm Setting
• Temperature Low Alarm Setting • Temperature High Warning Setting
• Temperature Low Warning Setting • Vcc High Alarm Setting
• Vcc Low Alarm Setting • Vcc High Warning Setting
• Vcc Low W arning Setting • Bias High Alarm Setting
• Bias Low Alarm Setting • Bias High Warning Setting
• Bias Low Warning Setting • Tx Power High Alarm Setting
• Tx Power Low Alarm Setting • Tx Power High Warning Setting
• Tx Power Low Warning Setting • Rx Power High Alarm Setting
• Rx Power Low Alarm Setting • Rx Power High W arning Setting
• Rx Power Low Warning Setting
Page 30
Page 31

SFP information can be obtained by selecting option 9 from the Port configuration screen.
SFP Information - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0 Port = 1
Address A0 Page Contents
===================================================
00: 03 04 07 00 10 02 00 00 00 00 00 01 03 00 14 C8 ................
10: 37 37 00 00 43 4F 52 45 54 45 4B 20 20 20 20 20 77..xxxxxxx
20: 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 00 43 54 2D 30 31 35 35 53 ....xxxxxxxx
30: 53 50 2D 4D 42 35 4C 44 30 30 30 30 05 1E 00 84 xxxxxxxxxxxx....
40: 00 1A 00 00 41 31 36 37 45 43 35 30 30 30 30 30 ....A167EC500000
50: 36 20 20 20 30 35 31 32 30 37 20 20 68 90 01 A4 6 051207 h...
60: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
70: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
80: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
90: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
A0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
B0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
C0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
D0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF................
E0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
F0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
Enter Previous Screen(0), (n)ext page, (H)elp, E(x)it > n
SFP Information - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0 Port = 1
Address A2 Page Contents
===================================================
00: 64 00 F6 00 5A 00 FB 00 8C A0 75 30 88 B8 79 18 d...Z.....u0..y.
10: 9C 40 03 E8 88 B8 07 D0 09 D0 00 FB 07 CB 01 3C .@.............<
20: 18 A6 00 05 13 94 00 06 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
30: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
40: 00 00 00 00 3F 80 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 ....?...........
50: 01 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 AE ................
60: 24 A8 80 78 17 14 03 F0 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 F8 $..x............
70: 00 40 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 .@...@..........
80: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
90: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
A0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
B0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
C0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
D0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
E0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
F0: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF ................
Enter Previous Screen(0), (b) previous page, (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 31
Page 32

4.3.4 802.3ah Parameters
The 802.3ah parameters can be monitored and/or configured in the 802.3ah Control screen.
• 802.3ah OAM State - The 802.3ah OAM State turns 802.3ah processing on or of f for the selected port.
When the port is configured as “Disabled” it will not respond to OAMPDUs (OAM Protocol Data
Units). They will be dropped by the processor and not acted upon. When the port is configured as
“Enabled”, it will respond to and be involved in the Discovery process and other supported 802.3ah
OAM functions.
• 802.3ah OAM Mode - The 802.3ah OAM Mode sets the selected port to “Passive” or “Active”
configuration mode. In “Passive” mode the port cannot initiate Discovery, send Variable Requests or
initiate Loopback Mode. It can observe and report only the port status of its 802.3ah enabled remote
partner . An “Active” port can initiate Discovery, send Variable Requests and initiate loopback mode.
• Loopback Mode - The Loopback Mode turns loopback operations “On” or “Off”. When Loopback
Mode is set to “Off”, the port of the 802.3ah enabled local device will not initiate Loopback operations.
It can respond to loopback commands from its 802.3ah enabled remote partner if set to “Passive” or
“Active”. When Loopback Mode is set to “On”, the port of the 802.3ah enabled local device will
initiate Loopback operations and set the 802.3ah enabled remote partner into loopback. In this mode,
the 802.3ah enabled local device will not respond to any other configuration changes until its port is set
to “Off.”
• Loopback Mode Timeout (sec) - The Loopback Mode T imeout field controls the length of time that the
port will be set to Loopback “On” mode. Loopback can be set between 0 and 300 seconds. The 0
setting disables the timer.
4.3.4.1 Local Status Section
The Local Status section displays the status of the Fiber and UTP ports of the 802.3ah enabled local device.
The local device is controlled directly by SNMP, Telnet or via the Serial Port and has the ability to
communicate with an 802.3ah enabled remote partner.
• Discovery State - Indicates the Discovery state (“Complete”, “In Process” or “Incomplete”) of the
local ports. If “Complete” is displayed, Discovery has been completed. If “In Process”, Discovery has
been initiated but no response from the 802.3ah enabled remote partner has been received by the local
device. If “Incomplete”, Discovery has received a response from the 802.3ah enabled remote partner
but the Discovery process is not yet completed.
• Multiplexer State - Indicates the Multiplexer state (“Discard” or “Forward”) of the local ports. If
“Forward” is displayed, the local device is forwarding non-OAMPDU network frames to the lower
sublayer. If “Discard”, the local device is discarding non-OAMPDU network frames.
• Parser Action - Indicates the Parser Action (“Discard”, “Forward” or “Loopback”) of the local ports. If
“Forward” is displayed, the local device is forwarding non-OAMPDU network frames to the higher
sublayer. If “Loopback”, the local device is looping back non-OAMPDUs network frames. If “Discard”,
the device is discarding non-OAMPDUs network frames.
4.3.4.2 Remote Status Section
The Remote Status section displays the status of the ports of the 802.3ah enabled remote partner. These
remote ports are connected to the Fiber and UTP ports of the local device. The remote partner is managed
by the local device via the 802.3ah OAM channel.
• Discovery State - Indicates the Discovery state (“Complete”, “In Process” or “Incomplete”) of the
remote ports. If “Complete” is displayed, Discovery has been completed. If “In Process”, Discovery
has been initiated but no response from the local device has yet been received by the remote partner. If
“Incomplete”, Discovery is in process, but is not yet completed.
Page 32
Page 33

• Multiplexer State - Indicates the Multiplexer state (“Discard”, “Forward” or “Unknown”) of the remote
ports. If “Forward” is displayed, the remote partner is forwarding non-OAMPDUs to the lower sublayer.
If “Discard”, the remote partner is discarding non-OAMPDUs network frames. If “Unknown”, the
Multiplexer state of the remote partner is indeterminate.
• Parser Action - Indicates the Parser Action state (“Discard”, “Forward” or “Loopback”) of the remote
ports. If “Forward” is displayed, the remote partner is forwarding non-OAMPDUs network frames to
the higher sublayer. If “Loopback” is displayed, the remote partner is looping back non-OAMPDUs
network frames. If “Discard” is displayed, the remote partner is discarding non-OAMPDUs network
frames.
• Critical Event - Indicates the Critical Event state (“Yes” or “No”) of the remote partner. If “Yes” is
displayed, the local device has detected a Critical Event. If “No”, the local device has not detected a
critical event.
• Link Fault - Indicates the remote partner has detected a fault in the receive direction (“Y es” or “No”). If
“Yes” is displayed, the receive link is down. If “No”, the receive link is up.
• OAM Mode - Indicates the OAM mode (“Active” or “Passive”) of the remote partner .
• Supports - Indicates the supported options (Variable Access “Var”, Link Event Notification “Event”,
Loopback “LB” or blank if no options are supported) of the remote partner.
• OUI - Indicates the three hex byte IEEE organizational specific identifier (or blank if unknown) of the
remote partner.
802.3ah parameters can be accessed by selecting options 7 from the Port configuration screen. The fiber
configuration screen is displayed.
802.3ah Control - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0 Port # = 1
1: 802.3ah OAM State Enabled Local Status
2: OAM Mode Active Discovery State Incomplete
3: Loopback Mode Disabled Multiplexer State Forward
4: Loopback Timeout 30 sec Parser Action Forward
5: Unidirectional Mode Not Available
Remote Status
Discovery State Incomplete
Critical Event No
Link Fault No
Multiplexer State Unknown
Parser Action Unknown
Mode Unknown
Supports Unknown
OUI: Unknown
Enter, Previous Screen (0), (n)ext page, (H)elp, E(x)it >
To configure the 802.3ah parameters for the UTP port, type an n and press <ENTER>.
Page 33
Page 34

4.3.5 802.3ah Events
802.3ah events can be accessed by selecting options 8 from the Port configuration screen.
802.3ah Event - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
Port 1
1: Symbol Period Window 0 second < 0 symbols>
2: Symbol Period Threshold 0 symbols
3: Frame Window 0 seconds
4: Frame Threshold 0 frames
5: Frame Period Window 0 second < 0 frames>
6: Frame Period Threshold 0 frames
7: Frame Seconds Summary Window 0 seconds
8: Frame Seconds Summary Threshold 0 seconds
UTP
9: Symbol Period Window 0 second < 0 symbols>
10: Symbol Period Threshold 0 symbols
11: Frame Window 0 seconds
12: Frame Threshold 0 frames
13: Frame Period Window 0 second < 0 frames>
14: Frame Period Threshold 0 frames
15: Frame Seconds Summary Window 0 seconds
16: Frame Seconds Summary Threshold 0 seconds
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 34
Page 35

4.3.6 Port VLAN
The flow of data on the module is controlled by configuring the Port VLAN settings. The block diagram
illustrates the flow of both the management traffic and the data traffic for a plug-in module (standalone
modules do not have backplane access). The data traffic is controlled by a switch matrix which provides
complete control of the data traffic. The management traffic is simply enabled or disabled at each port. By
default traffic flows between all ports on the module.
Using the Port VLAN settings, data will only be forwarded across the enabled path, unless blocked by one
of the other features (Port Access or Tag VLAN). Secure OAM and ah OAM Management data will pass
to and from the Management port even if the path has been “disabled”. This allows OAM maintenance
functions to always be enabled. Port VLAN control is inactive when Tag VLAN processing is turned on.
Port VLAN Block Diagram
Page 35
Page 36

Port VLAN is access by selecting options 11 - 20 or 11 - 13 depending on the module type; plug-in or
standalone.
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Port VLAN Path Setup
Slot Number = 11 --------------------------------- Model Number = 8919-0 11: Fiber to UTP Enable On
12: Fiber to BP A Enable On
Port Access Control Setup 13: Fiber to BP B Enable On
---------------------------------- 14: UTP to BP A Enable On
1: Fiber Enable On 15: UTP to BP B Enable On
2: UTP Enable On 16: BP A to BP B Enable On
17: Fiber to Mngmnt Enable On
Enhanced Features 18: UTP to Mngmnt Enable On
---------------------------------- 19: BP A to Mngmnt Enable On
3: 802.1Q Processing Enable Off 20: BP B to Mngmnt Enable On
4: Configure Tag VLAN Control
5: Configure VLAN Membership Bandwidth Control
6: Save TAG VLAN parameters ------------------------------- 7: Configure 802.3ah parameters 21: Ingress rate Fiber No Limit
8: Configure 802.3ah events 22: Egress rate Fiber No Limit
9: SFP Information 23: Ingress rate UTP No Limit
10: cNode Loopback 24: Egress rate UTP No Limit
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Port VLAN Path Setup
Slot Number = 11 --------------------------------- Model Number = 8919-0 11: Port1 to Port2 Enable On
12: Port1 to Mngmnt Enable On
Port Access Control Setup 13: Port2 to Mngmnt Enable On
--------------------------------- 1: Fiber Enable On Bandwidth Control
2: UTP Enable On --------------------------------
14: Ingress rate Fiber No Limit
Enhanced Features 15: Egress rate Fiber No Limit
---------------------------------- 16: Ingress rate UTP No Limit
3: 802.1Q Processing Enable Off 17: Egress rate UTP No Limit
4: Configure Tag VLAN Control
5: Configure VLAN Membership
6: Save TAG VLAN parameters
7: Configure 802.3ah parameters
8: Configure 802.3ah events
9: SFP Information
10: cNode Loopback
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 36
Page 37

4.3.7 T agged VLAN
The 10/100M supports the IEEE 802.1Q tag VLAN packet tagging and un-tagging and the 802.1p Quality
of Service priority standards.
The following parameters are configured for each port:
4.3.7.1 Port Priority (PRI)
This (IEEE 802.1p based) user-specified value of 0 through 7 can be assigned as a QoS priority level (0
being lowest and 7 being highest) to packets ingressing (entering) a port. If no value is specified by the
user, a default priority value of “0” is assigned.
The PRI value is always assigned to all untagged packets. T agged packets are assigned the PRI value when
the “PVID” option is selected in the “Tagged Packet Use” section.
4.3.7.2 Port VLAN ID (PVID)
This (IEEE 802.1Q based) user-specified value of 0 through 4094 can be assigned as a Port VLAN ID
(PVID) to packets ingressing a port. If no value is specified by the user a default PVID value of “2” is
assigned.
The PVID value is always assigned to untagged packets. Tagged packets are assigned the PVID value
when the “PVID” option is selected in the “Tagged Packet Use” section.
4.3.7.3 T agged Packet Use
This section defines how tagged packets ingressing a port are processed.
Selecting the “PVID” option causes the PRI and PVID user-specified values to be used as the packet’s
VLAN ID (VID) for processing of the packet.
Selecting the “TVID” (Tagged VLAN ID) option causes the packet’s original Tag VLAN ID (TVID) and
priority level to be used as the packet’s VLAN ID (VID) for processing of the packet.
NOTE:Untagged packets are always assigned the port’s PRI and PVID values as their VID.
4.3.7.4 Ingress Security
This section selects the ingress security level of a port.
Selecting the “Low” option allows any packet to ingress a port.
Selecting the “High” option allows only packets that are assigned a VLAN ID (VID) value of which this
port is a member (according to the Membership Table) to ingress a port.
4.3.7.5 Egress Policy
This section defines the egress policy .
Selecting the “untag” option defines how a tagged or untagged packet is processed. A tagged packet will
have the top tag removed and an untagged packet will be passed unmodified.
Selecting the “tag” option will tag an untagged packet with the PVID and PRI of the ingress port or add a
tag to an already tagged packet with the PVID and PRI of the ingress port.
Selecting the “pass” option, a packet tagged or untagged will be passed unchanged as it egresses out of the
port.
Page 37
Page 38

Tagged VLAN is accessed by selecting option 4 from the Port configuration screen. The Tag VLAN
Control screen will be displayed.
Tag VLAN Control - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
Fiber1: Port Priority (PRI) 0 BP B 16: Port Priority (PRI) 0
2: PVID (Port VLAN ID 2 17: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
3: Tagged Packets Use PVID 18: Tagged Packets Use PVID
4: Ingress Security Low 19: Ingress Security Low
5: Egress Policy Pass 20: Egress Policy Pass
UTP 6: Port Priority (PRI) 0 Mngmnt 21: Port Priority (PRI) 0
7: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2 22: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
8: Tagged Packets Use PVID 23: Tagged Packets Use PVID
9: Ingress Security Low 24: Ingress Security Low
10: Egress Policy Pass 25: Egress Policy Pass
BP A 11: Port Priority (PRI) 0
12: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
13: Tagged Packets Use PVID
14: Ingress Security Low
15: Egress Policy Pass
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Tag VLAN Control - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
Fiber 1: Port Priority (PRI) 0
2: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
3: Tagged Packets Use PVID
4: Ingress Security Low
5: Egress Policy Pass
UTP 6: Port Priority (PRI) 0
7: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
8: Tagged Packets Use PVID
9: Ingress Security Low
10: Egress Policy Pass
Mngmnt 11: Port Priority (PRI) 0
12: PVID (Port VLAN ID) 2
13: Tagged Packets Use PVID
14: Ingress Security Low
15: Egress Policy Pass
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 38
Page 39
4.3.8 VLAN Membership T able
The VLAN Membership Table lists the permitted VLAN ID (VID) for each egress port on the module.
Only packets that are assigned a VID value that matches one of the egress port’s VID memberships are
allowed to egress through the port.
When the Ingress Security is set to High for a specific port, the membership table is used to list the VIDs of
the packets that are allowed to ingress that port.
VLAN Membership is accessed by selecting option 5 from the Port configuration screen. The VLAN
Membership screen will be displayed.
VLAN Membership - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN ID (VID) Fiber UTP BP A BP B Mngmnt
VLAN TABLE IS EMPTY
Add new entry (a), Delete entry (d), Edit entry (e), Clear table (c)
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
VLAN Membership - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN ID (VID) Fiber UTP Mngmnt
VLAN TABLE IS EMPTY
Add new entry (a), Delete entry (d), Edit entry (e), Clear table (c)
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 39
Page 40

Initially the table is empty. To configure the ports with VLAN IDs, select option (a) from the VLAN
Membership configuration screen.
Membership Entry - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN Table Membership Entry 1
------------------------------
1: VLAN ID 2
2: Fiber Port Membership No
3: UTP Port Membership No
4: BP A Port Membership No
5: BP B Port Membership No
6: Mngmnt Port Membership No
7: Submit Entry As Defined
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Membership Entry - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN Table Membership Entry 1
------------------------------
1: VLAN ID 2
2: Fiber Port Membership No
3: UTP Port Membership No
4: Mngmnt Port Membership No
5: Submit Entry As Defined
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 40
Page 41
T o add a VLAN ID to the membership table, select option 1 and enter the ID #. To associate the VLAN ID
to a port, select the appropriate port option (2 - 6 or 2 - 4) depending on the module type; plug-in or
standalone.
Membership Entry - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN Table Membership Entry 1
------------------------------
+1: VLAN ID 100
+2: Fiber Port Membership Yes
3: UTP Port Membership No
4: BP A Port Membership No
5: BP B Port Membership No
6: Mngmnt Port Membership No
*7: Submit Entry As Defined
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Membership Entry - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN Table Membership Entry 1
------------------------------
+1: VLAN ID 100
+2: Fiber Port Membership Yes
3: UTP Port Membership No
4: Mngmnt Port Membership No
*5: Submit Entry As Defined
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
Page 41
Page 42

Once all the VLAN IDs have been assigned, select option 7 or 5 to save the entries.
VLAN Membership - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 1 Model Number = 8919-0
VLAN ID (VID) Fiber UTP BP A BP B Mngmnt
1: 100 Yes No No No No
Add new entry (a), Delete entry (d), Edit entry (e), Clear table (c)
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
The VLAN membership entries are saved from the Port configuration screen, option 4.
4.3.9 cNode Loopback
The 10/100M has implemented Iometrix cNode Level 1 agent for testing performance metrics. The agent
recognizes measurement packets and loops them back to the sending cNode device. Iometrix cNode
equipment is required to obtain performance metrics.
cNode configuration is accessed by selecting option 10 from the Port configuration screen.
cNode Control -iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Slot Number = 2 Model Number = 8919-0
1: cNode Loopback Disabled
2: cNode Rate Limit 64 Kbps
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
From the menu, loopback can be enabled or disabled and the rate limit can be selected.
Page 42
Page 43

4.3.10 Port Statistics
The 10/100M module provides port statistics on both the fiber and UTP port.
The Port Statistics can be viewed by selecting option P from the Module configuration screen.
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1 Switch ON Condition OFF Condition H/W Actual
Slot Number = 1 1: Pause Enabled Pause Disabled Off Off
Model Number = 8919-0 2: Fiber HDX Fiber FDX Off Off
3: UTP Manual UTP Auto-Neg Off Off
Serial Number = xxxxxxxx 4: UTP 10 Mbps UTP 100 Mbps Off Off
Manufacturing Date = xxxxxxxx 5: UTP HDX UTP FDX Off Off
Product Revision = x 6: Link Propagate Link Segment Off Off
Software Revision = xx 7: Remote Fault Normal Off Off
8: Symm Fault Det Normal Off Off
LED 9: BP A Enabled BP A Disabled On On
1: Power = On 10: BP B Enabled BP B Disabled On On
2: Power Supply 1 = Off 11: Not Available
3: Power Supply 2 = Off 12: Slave Only Master/Slave Off Off
4: Power Supply 3 = Off 13: Not Available
5: Fiber Link = Off 14: Not Available
6: BP Master = On 15: Not Available
7: UTP 10 Link = Off 16: Not Available
8: UTP 100 Link = Off OAM settings:
9: UTP FDX = Off 17: IP Protocol State On
18: Management Mode Secure OAM
Toggle Switch(1-16), (I)dentifier, (R)eset, (H)elp, (P)ortStat, Port(C)tl > P
Port Statistic
Module - iConverter 10/100M iConverter, Serial Agent
Identifier -
Chassis Number = 1
Slot Number = 1
Model Number = 8919-0
Port Statistics
-------------------------------------------
Fiber UTP
Rx Bytes 0 0
Rx Packets 0 0
Rx Total Packets 0 0
Tx Bytes 0 0
Tx Packets 0 0
Enter Choice, Previous Screen(0), (H)elp, E(x)it >
To refresh the Port Statistic screen, press <ENTER>.
Page 43
Page 44
5.0 10/100M SPECIFICATIONS
Plug-in Module S tandalone Tabletop Standalone Wall-Mount
Description 10/100BAS E -TX UTP to 100BASE-F X F i b er Medi a Converter with integrated management
Protocols 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX,100BASE-FX with 1536 bytes max. frame size
Cable Types
UTP EIA/TIA 568A/B, Category 5 and higher
Fiber Multimode: 50/125, 62.5/125, 100/140 um,
Serial RS-23 2 , 22 to 24 AWG, 12 to 50 p F/ft.
Connector Types
UTP RJ45
Fiber
SFP:
Dual Fiber:
Single Fiber:
Seria l Mini DIN-6 female,
mini DIN-6 male to DB-9 female adapter included
Controls DIP-Switches and LEDs
802.1p Priority Levels and
VID Priority Level Groups
Power Requirements
DC Power 1.0A @ 3.3VDC Nominal: 0.6A @ 9VDC
DC Power Connector Power supplied by backplane 2.5mm Barrel Connector or Terminal Connector
AC Power Adapter [US] N/A 100-120VAC/60Hz
AC Power Adapter
N/A 100-240VAC/50-60Hz
[Universal]
Dimensions W: 2.8" x D: 4.5 "x H: 0.85" W: 3.1" x D: 4.8" x H :1.0" W: 3.8" x D: 4.8" x H: 1.0"
Weight
without power adapter 8 oz. 1 lb.
with power adapter N/A 1.5 lb.
Compliance UL, CE, FCC Class A
IP-Based Manag emen t Telnet; SNMPv1, S NMPv2c, S NMPv3
Temperature
Operational - Commercial 0 to +50
Operational - Wide Range -40 to +60
Operational - Extended -40 to +75
Storage -40 to +80
Humidity (non-condensing) 5 to 95%
Altitude (Opera tio nal) -100m to 4,000m
MTB F [hr s ]
without powe r a dapter 600 ,0 00
with power adapter [US] N/A 250,000
with powe r a dap te r [Unv] N/A 100,000
Single-mode: 9/125 um
LC
SC , ST, LC, MT-RJ
SC
4 Levels
(PRI 0-1, 2-3, 4-5, 6-7)
Voltage Range: 8 - 15VDC
o
C
o
C
o
C
o
C
0.07A @ 120VAC
0.07A @ 120VAC
Page 44
Page 45

6.0 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
6.1 OVERVIEW
The 10/100M module has several LED indicators available to assist in the determination of problems.
Refer to Section 3.5, Verify Operation, for LED definitions.
6.1.1 Power Issues
Problem:
The Power LED does not illuminate after installation is complete or no LED indicators are ON
Possible Causes:
A. For standalone modules, confirm that the power supply is connected to both the module and the AC or
DC power source. If Power LED is still not illuminated, use a voltmeter and check the voltage of the power
source (AC/DC converter used with the standalone unit should measure between 8 -15 VDC no load at the
barrel connector).
B. For plug-in module, confirm that the chassis is connected to an AC or DC power source. If the Power
LED is still not illuminated, remove the module and verify the operation of other modules in the chassis. If
power is present and the module will not turn ON, replace the module.
C. The plug-in module requires ~ 3.3 watts (3.3VDC @ 1.0 amps) for normal operation. The AC Power
Supply in a 19-Module Chassis can supply ~ 60 watts (3.3VDC @ 18amp). A fully loaded 19-Module
chassis of 10/100M modules will require two power supplies for standard operation. This condition will
cause the power LED not to illuminate.
6.1.2 Fiber Issues
Problem:
The Fiber Optic link LED does not illuminate after installation is complete.
Possible Causes:
A. Verify the Link Mode selection is set to Link Segment (LS). Until a stable link is established, leave the
Link Mode configured for LS. After a Link presence is established, the Link Mode selection can be modified.
B. Confirm that the fiber optic cable is properly connected to the iConverter 10/100M and the remote fiber
optic device. Connecting the fiber between the Tx of the far end to the Rx on the near end will cause the P1
LED on the near end to illuminate (only when the link mode is configured for Link Segment). Completing
the connection will cause the far end P1 LED to illuminate.
C. Confirm that the fiber cable type matches the fiber transceiver type (multimode, single-mode) on the
iConverter 10/100M.
D. If using a dual-fiber model, confirm that the transmitter (Tx) is attached to the receiver side of its link
partner, and that the receiver (Rx) is attached to the transmitter. A optical power meter will assist in
determining which cable should be connected to the Tx and Rx of the module. To insure proper operation,
a minimum of -30dBm must be present at the fiber optic receiver.
E. If using a single-fiber model, confirm that the Tx wavelength on the iConverter 10/100M matches the
Rx of the connected fiber optic device. Single-fiber units transmit and receive at different wavelengths
(1510nm/1310nm). Verify the model numbers to insure proper compatibility.
6.1.3 UTP Issues
Problem:
The UTP link LED does not illuminate after installation is complete.
Page 45
Page 46

Possible Causes:
A. Confirm that the UTP cable is connected properly to the iConverter 10/100M and the attached UTP
device. Once a connection has been established between the iConverter and its link partner (switch or
workstation), the UTP “10/100” LED should illuminate. If the LED does not illuminate, check the Link
Mode configuration. A link mode other than Link Segment may cause the UTP “10/100” LED not to turn
ON.
B. Verify the iConverter 10/100M UTP port is configured with the proper settings based on the attached
device (AN or MAN, 10 or 100, HD or FD).
C. Verify the distance between the iConverter and the link partner is within 100 meters.
D. Confirm that the UTP cable pin-out is correct (EIA/TIA-568-A). The module has auto-crossover
capability , so it will accept either a straight-through or crossover cable.
NOTE: If corrective actions do not resolve your situation, please contact Omnitron Systems Technical
Support.
Page 46
Page 47

7.0 WARRANTY
This product is warranted to the original purchaser against defects in material and workmanship for a
period of TWO YEARS from the date of shipment. A LIFETIME warranty may be obtained by the original
purchaser by REGISTERING this product with Omnitron within 90 days from the date of shipment. TO
REGISTER, COMPLETE AND MAIL OR FAX THE ENCLOSED REGISTRATION FORM TO THE
INDICATED ADDRESS. Or you may register your product on the Internet at http://www.omnitronsystems.com. During the warranty period, Omnitron will, at its option, repair or replace a product which is
proven to be defective.
For warranty service, the product must be sent to an Omnitron designated facility, at Buyer’s expense.
Omnitron will pay the shipping charge to return the product to Buyer’s designated US address using
Omnitron’s standard shipping method.
Limitation of Warranty
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper or inadequate use and/or
maintenance of the equipment by Buyer, Buyer -supplied equipment, Buyer-supplied interfacing, unauthorized
modifications or
tampering with equipment (including removal of equipment cover by personnel not specifically authorized
and certified by Omnitron), or misuse, or operating outside the environmental specification of the product
(including but not limited to voltage, ambient temperature, radiation, unusual dust, etc.), or improper site
preparation or maintenance.
No other warranty is expressed or implied. Omnitron specifically disclaims the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for any particular purpose.
Exclusive Remedies
The remedies provided herein are the Buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. Omnitron shall not be liable for
any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages, whether based on contract, tort, or any
legal theory .
Technical Support
140 T echnology Dr . #500
Irvine, CA 92618
949-250-6510 tel
949-250-6514 fax
email: support@omnitron-systems.com
web: www.omnitron-systems.com
041-08900-001 D 7/08
Page 47
 Loading...
Loading...