
PERSONAL
ANDROID USER GUIDE

1
Thank you for purchasing Omegawave Personal!
Omegawave is the fastest and safest way to achieve your goals. Following the guidance of Omegawave
Personal you can rest assured your next training is the most effective for you that day. The ability to
quickly adapt your training plan based on daily changes in your body allows you to reach your training
goals safer and more effortlessly.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS ............................................................................................................................................ 1
GETTING STARTED ................................................................................................................................................. 2
LOGGING IN ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
MANAGING YOUR PERSONAL DATA .................................................................................................................... 5
MANAGING YOUR SUBSCRIPTIONS ..................................................................................................................... 6
USING THE MEASUREMENT HARDWARE ............................................................................................................ 8
PAIRING THE SENSOR WITH YOUR MOBILE DEVICE ........................................................................................ 11
MEASURING – QUICK GUIDE .............................................................................................................................. 13
MEASURING – DETAILS ........................................................................................................................................ 14
ANALYZING RESULTS ........................................................................................................................................... 16
FAQ ........................................................................................................................................................................ 26
REGULATORY INFORMATION ............................................................................................................................. 28

2
GETTING STARTED
Let’s start by reviewing what’s inside your package:
• Omegawave Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) sensor. Model name: OW-CB2.
Simultaneously measures both an electrocardiogram (ECG) and Direct Current (DC) Potential of
the Brain.
• ECG chest strap
• DC Potential cable
• Pre-gelled electrodes for DC Potential measurement
• Micro-USB charging cable

3
In order to use the Omegawave Personal App, you will need to have a device with Android 4.3 or a
newer mobile operating system and have downloaded the Omegawave App from the Google Play.
Please check the following:
• Ensure that your device has an active Internet connection via WLAN or mobile data (3G/4G).
• Please fully charge the sensor before first use by connecting the micro-USB cable to a computer
or USB compatible power source and attaching it to the sensor.
o A red light on the sensor will appear to indicate that the sensor is being charged. Once
the light turns off, the sensor is fully charged. A full charge will take approximately one
hour.
o If charging via a wall outlet, use a USB compatible power adapter (not included with the
product). Make sure that the adapter is specified with the following voltage and current
values: "output 5V DC, 0.5A - 2A max".
IMPORTANT!
Please ensure that the white dot on the
charging cable aligns with the sensor LED
as illustrated.
Please do not force the cable into the
sensor, otherwise you may break the
sensor’s micro-USB connector.
Support
If you have any questions or need technical assistance, please contact us through our community
http://community.omegawave.com
4
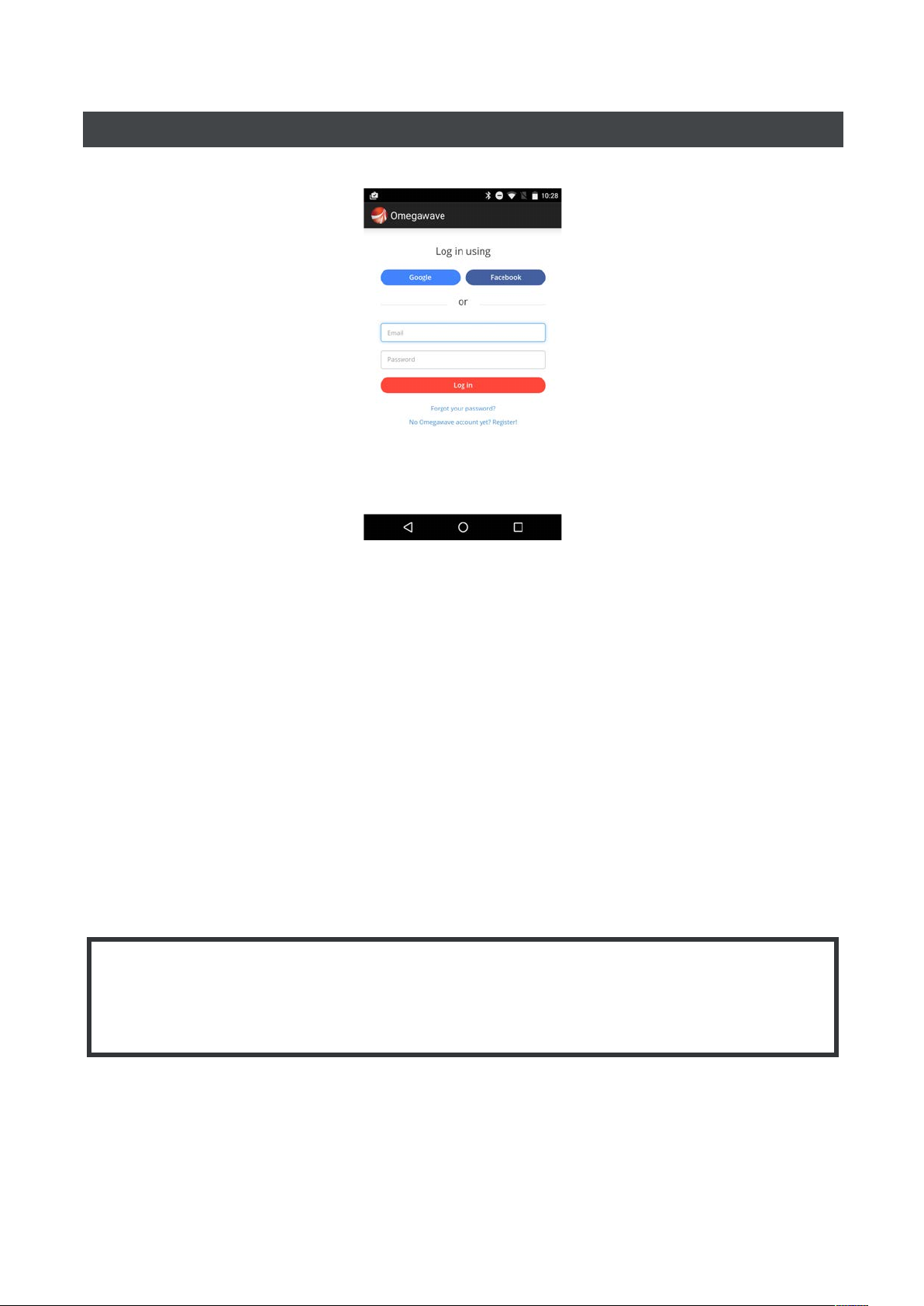
LOGGING IN
Open the Omegawave App and tap the Sign in options button.
If you made your purchase from the Omegawave web shop
Use the email address and password you set during the transaction to log in.
If you are an existing Omegawave user
Use the authentication type (Omegawave, Facebook or Google) that is linked to your account to log in.
If you do not have an Omegawave account yet
Use the Omegawave App to create an account if you do not already have one.
If you are an Omegawave Team athlete
Select “Team sign in” from the Omegawave app main screen and use the activation key sent by your
coach to sign in.
NOTE
If you forget your Omegawave account password, you can request a new one from the login screen
by tapping Forgot your password.
5
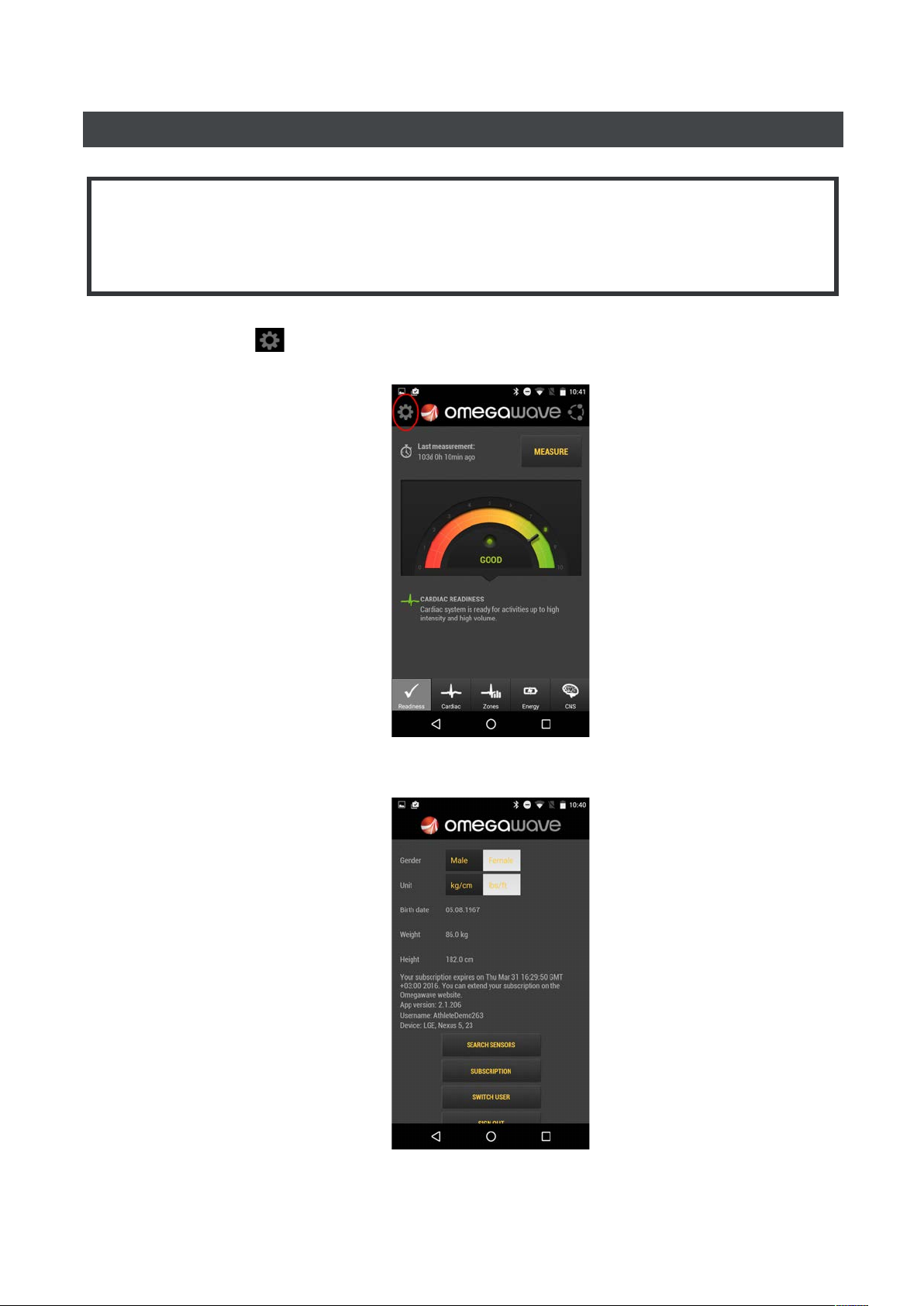
MANAGING YOUR PERSONAL DATA
IMPORTANT!
The App needs to know your gender, date of birth, height and weight in order to calculate accurate
results. It is important to always keep your personal data updated.
1. Go to Settings
2. Update your personal data and tap Done
6
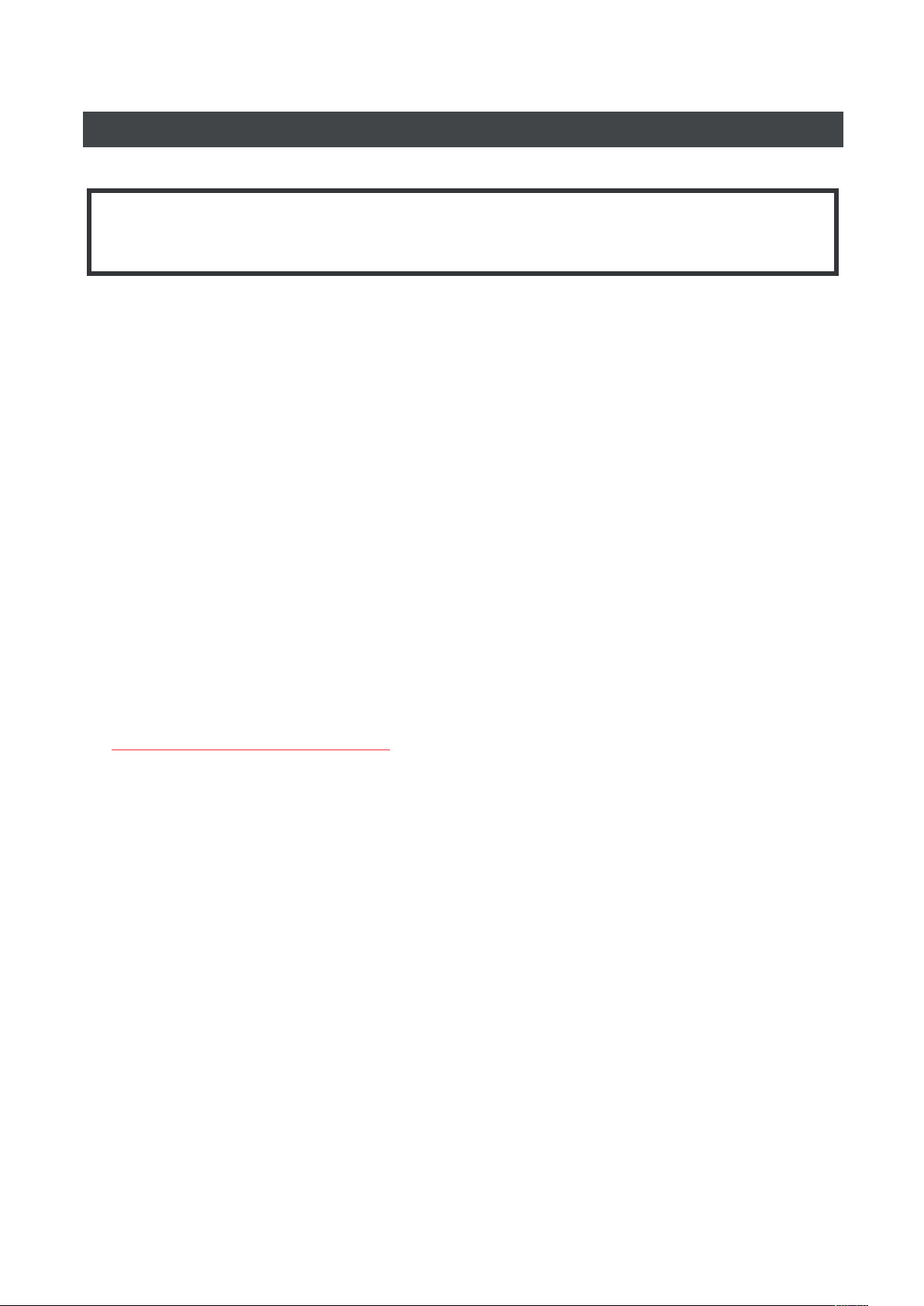
MANAGING YOUR SUBSCRIPTIONS
NOTE
To perform measurements, you need to have a valid subscription.
Valid subscription types:
• free trial
• fixed term subscription with defined start and end dates
• recurring subscription with monthly or yearly billing period
• team athlete subscription
Starting a free trial period
If you are a new user and have bought Omegawave without a subscription, you can activate a free trial
period in order to try the product. During the trial period you will have access to all Omegawave
Personal features including ECG and DC measurements.
How to start a trial?
• After successful sign in the application will ask you if you want to start your free trial.
Recurring subscription with monthly or yearly billing
If you want to make any modifications to your recurring subscription, please go to the My Account page
at: http://app.omegawave.com/#/account
Team athlete subscription
Your coach will manage your subscription.
Fixed term subscription
You can have a fixed term subscription if you have bought a subscription from an approved retailer.
Your subscription will be valid until the end date. You can extend your subscription at any time by
entering the new activation key purchased from your retail source. If you still have time left from your
previous subscription, the remaining time will be added to your new subscription.
How to use your fixed term subscription?
• If you are a new user and you do not have an old subscription, start your free trial (see
instructions above). Then use your activation key to convert your free trial to a fixed term
subscription.
• If you are a current user and you have a valid or expired fixed term subscription, use your
activation key to extend your subscription.
7
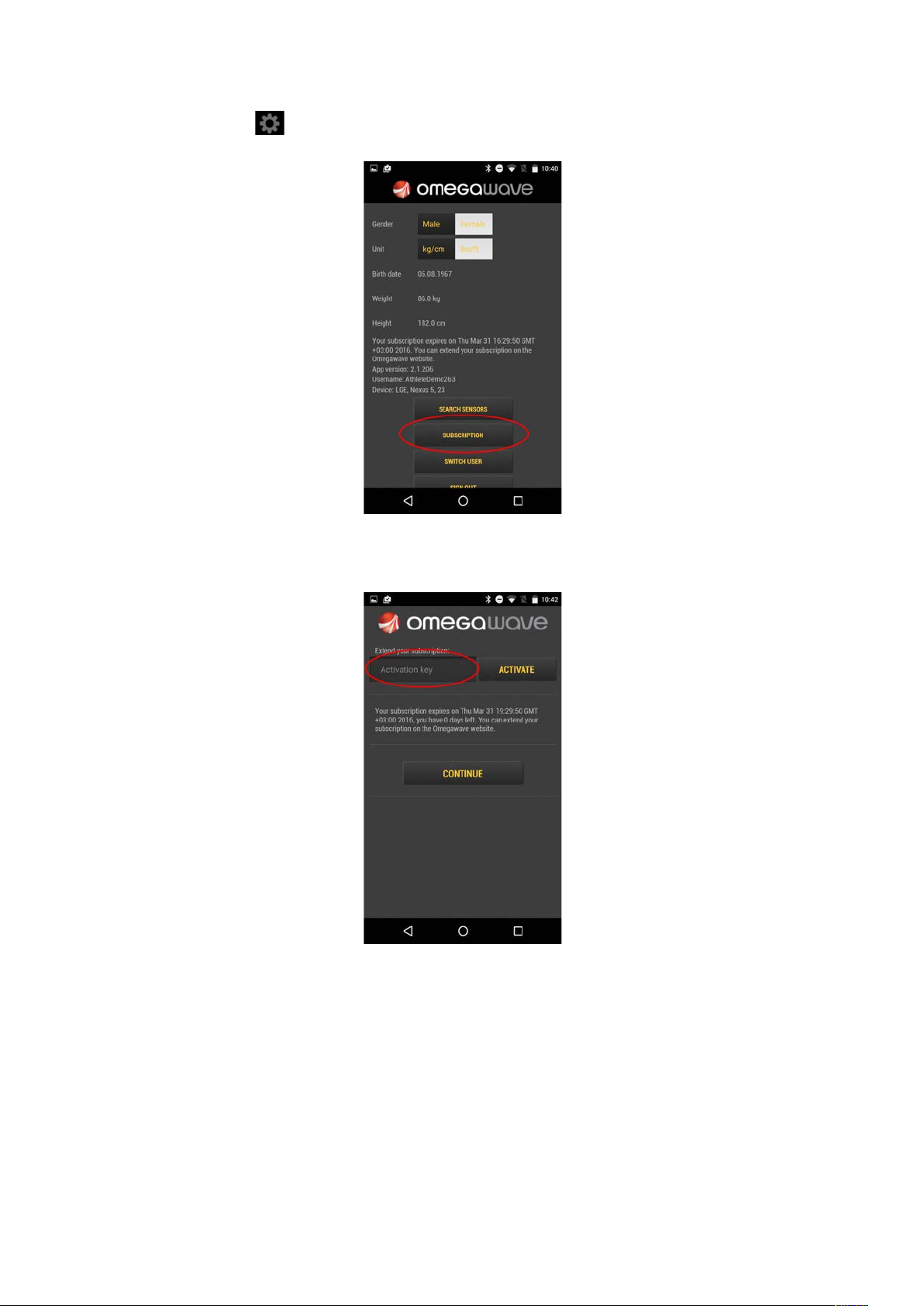
1. Go to Settings and look for Subscriptions
2. Fill in your activation key and tap Activate
If your activation key is valid, the application will extend your subscription and you will see a new
expiration date.
8
USING THE MEASUREMENT HARDWARE
ECG measurement
An ECG recording is used to assess your cardiac and metabolic state.
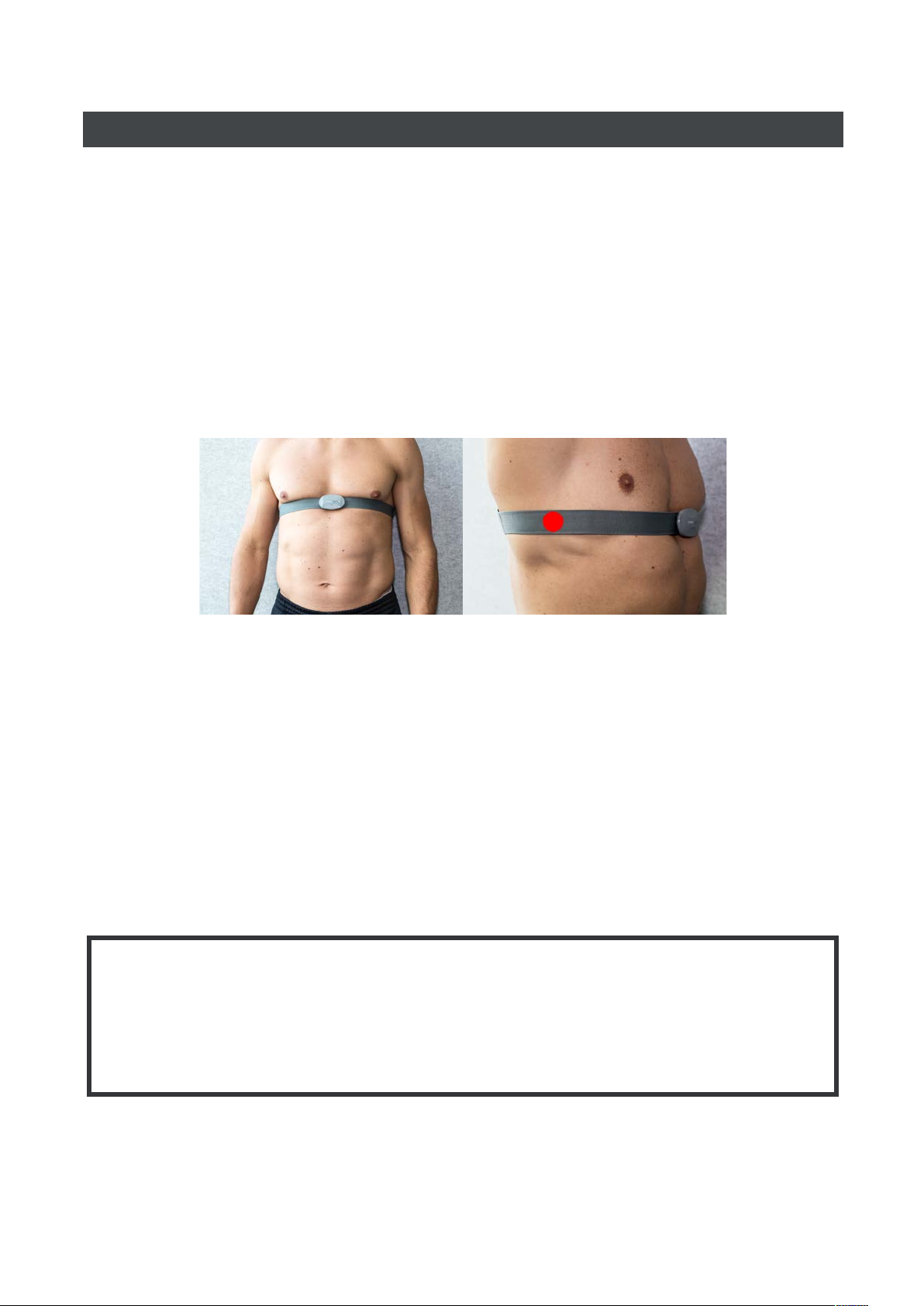
The sensor should be attached to the ECG chest strap and must be placed at the bottom of the
sternum. Soak the ECG chest strap electrode pads with water. The micro-USB port on the sensor needs
to be facing down; if you attach the sensor upside-down, your ECG will appear inverted and will cause
inaccurate assessment results.
The electrode pads on the inside of the chest strap must be aligned with the midaxillary line of the
body (position V6, shown as a red dot in the picture below). The chest strap should be tight around the
chest and it should not move out of position during normal breathing.
Female users should place the chest strap directly below or under a sports bra support band. When
possible, remove undergarments to ensure optimal placement of the chest strap.
DC Potential measurement
A DC Potential of the Brain recording is used to assess the state of your CNS.
One single-use, pre-gelled electrode should be used to connect the sensor to your forehead via the DC
Potential cable (please see the next page for illustrations). The other electrode should be attached to
the palm of your dominant hand at the base of the thumb, and also connected to the sensor via the DC
Potential cable. Each measurement requires a new set of gelled electrodes; using old or standard
ECG electrodes will result in inaccurate assessment results.
NOTE
Keep unused electrodes in their original pouch.
Always seal an opened pouch by tightly folding the top of the pouch to prevent the electrodes from
drying.

9
The DC Potential cable
with a head symbol
connects to your
forehead.
The DC Potential cable
with a hand symbol
connects to the base
of the thumb of your
dominant hand.
The DC Potential cable
connects to the microUSB port of the
sensor. Please ensure
that the white dot on
the cable aligns with
the sensor LED as
illustrated.

10
NOTE
Follow this protocol when dressing the chest strap, sensor and DC electrodes to avoid bending the
micro-USB connector:
1. Thoroughly wet the chest strap electrodes and wear it
2. Attach the DC electrodes to the hand and the forehead
3. Attach the DC cable to the DC electrodes on the body
4. Attach the DC cable to the sensor
5. Go to Measure view
6. Optional: Update your weight, mark whether the measurement was taken “Before” or “After”
training and record additional notes
7. Attach the sensor to the chest strap
8. Wait until the application detects data from the sensor
9. Lay down
10. Start the measurement immediately
11. After the measurement is done, take the sensor from the chest strap before standing up
12. Remove the DC cable from the sensor
The picture below shows an athlete with the hardware properly attached (left hand dominant).

11
PAIRING THE SENSOR WITH YOUR MOBILE DEVICE
NOTE
Before proceeding with the following steps, please put on the chest strap and attach the sensor to
the strap as previously described. Please ensure that your device’s Bluetooth is switched on. The
sensor’s Bluetooth connection will be activated and the LED will start blinking blue only when the
sensor is connected to the chest strap.
1. Open the Omegawave App and go to the Settings.
2. Tap Search Sensors.

12
3. The Omegawave sensor should now become visible: “Not set” text changes to green
text indicating sensor ID. Tap Done in order to complete the pairing process.
Now the Omegawave sensor is paired to the application.
IMPORTANT!
If you have an old black sensor, pairing requires the PIN code: 0000

13
MEASURING – QUICK GUIDE
Conditions
• To achieve comparable results, measure yourself in the same way each time.
• If interrupted for any reason, cancel the measurement.
• If measuring after exercise, wait at least 30 minutes.
Measurement instructions
1. Pair the Omegawave sensor in the application (needs to be done only once).
2. Thoroughly wet the ECG chest strap pads with water and only use new gelled electrodes.
3. Attach the belt and sensor as instructed.
4. Lie down flat on your back, relax and breathe normally.
5. Begin the measurement immediately upon lying down.
6. The application will sound when the measurement is complete.
NOTE
There are two measurement types available:
- ECG only
- ECG + DC Potential (requires a subscription that allows you to measure DC Potential)
Completing only a DC Potential measurement is not supported.
NOTE
You can do measurements without Internet connection, but the results will be calculated only when
the connection is available. When you start the application, it will briefly show a notification text
indicating that you have done measurement(s) which are not yet calculated. The application will try
to calculate these measurement(s) automatically.

14
MEASURING – DETAILS
1. Make sure that you have an active Internet connection via Wi-Fi or mobile data.
2. Make sure that your device has the volume switched on.
3. Make sure that you are correctly wearing the chest strap, sensor and electrodes as previously
described.
4. Tap the Measure button.
The application will automatically find the paired Omegawave sensor. If the sensor does not
appear, the most common reason is that the ECG chest strap electrodes have not been
properly moistened. See also FAQ section for additional troubleshooting information.
Screenshot below shows the case when both ECG and DC Potential measurements are ready
to be started.
If you want to do an ECG only measurement, do not connect the DC cable. In this case Omega
part remains in “connecting…” phase.

15
5. When the sensor is ready to start a measurement, the “Start measurement” button becomes
visible. To begin the measurement, tap Start measurement button.
a. If the “Start measurement” button is not appearing, check FAQ section for additional
troubleshooting information.
6. The measurement will take approximately 4 minutes. In the beginning of the measurement
application waits until your ECG signal has stabilized, then the actual ECG data collection is
started.
a. If the application detects any errors or connectivity issues with the sensor, you will hear
a sound and the measurement will be cancelled. Review the error message and follow
the instructions provided then initiate a new measurement according to the protocol.
7. You will hear a sound when the measurement is complete. Please ensure that your device’s
volume is switched on.
8. After the data collection is complete, the assessment results will be calculated automatically.
a. If the application detects problems with your Internet connection, you will see an error
message. Make sure that your device has a working Internet connection and try again.
9. After the measurement, remove the sensor from the ECG chest strap and the DC cable from the
sensor to prevent battery drain. The sensor should be charged approximately once a month.
You can also check the battery level from the measurement screen.
IMPORTANT!
Please wait at least 10 minutes before initiating a new measurement. During this time stand up and
continue your daily activities to return your body’s functional state back to an active level of
wakefulness. If you maintain a resting position and initiate a new measurement without following
this protocol, your functional state will change from active to reduced wakefulness. Omegawave’s
algorithms are designed to analyze your functional state at an active level of wakefulness. Doing a
measurement while in a state of reduced wakefulness will therefore distort your measurement
results.

16
ANALYZING RESULTS
From the main view, you can:
• See when your last measurement was done
• See cardiac readiness results of your last measurement
• Access to a detailed breakdown of Cardiac and Energy Supply and Central Nervous System
indices as well as their historical data
• Access to training zones view
• Start a new measurement
• Access to settings and share your results
CNS, Cardiac and Energy Supply System views allow you to analyse trends over the last 10
measurements. If you want to analyse trends over a longer period, you can use Omegawave web app:
http://app.omegawave.com

17
Training zones view
Training zones view shows the suggested heart rate training zones as those levels relate to cardiac and
metabolic training. The numerical heart rate values in these training zones can change from one
measurement to the next, reflecting changes in your current functional state.
IMPORTANT!
The height of the green bar will indicate all of the training zones you are ready to train in at that
moment in time – the highest zone in green is the maximum recommended training zone. In
general, whenever multiple zones are in the green, it is up to you to choose the intensity-level of
your next training session.
If you want to see a definition for each heart rate zone, tap the info button of the individual zone.

18
Cardiac System view
Cardiac System Readiness
Description:
The level of functioning and tension of the cardiac system at a specific moment in time.
Guidance:
The functional state of the cardiac system reflects the current integrated response of the multi-level
system that regulates cardiac function in the process of adapting to training loads.
The role of the cardiac system is to form critical and useful adaptations that lead to an improved
trained-state of the athlete. The level of the functional state is an indicator of the cardiac system’s
capability to perform this role. From assessment data the levels of stress, adaptation reserves, and the
recovery pattern of the cardiac system are identified – reflecting an accurate picture of it's Readiness
for training loads.
Resting heart rate
Description:
Resting heart rate (RHR) varies from 60 to 90 bpm for normal individuals. A lower RHR can be an
indicator of better cardiac efficiency. Measured in beats per minute.
Guidance:
An integrative physiological indicator of the functional state of the cardiac system. The norm for
untrained individuals is between 60-90 bpm; known as normocardia. Under adverse conditions (i.e.
illness, chronic excessive exercise, etc.) the RHR may rise significantly, up to 100 bpm or more; known
as tachycardia. Trained individuals, particularly those involved in cyclical sports, can experience a RHR
of below 60 bpm; known as bradycardia. This is a normal result and is brought on by adaptive
responses resulting in a high vagal tone.
Recovery pattern
Description:
Current activation level of the parasympathetic regulation of the cardiac system. Serves to maintain
homeostasis and restore the functionality of the body after load. Measured in seconds.
Guidance:
Reflects the quality of the recuperative processes in the cardiac system in response to training loads.
Optimal values range from 0.16 to 0.41 seconds. High or low values indicate that the cardiac system is
functioning outside established norms, reflecting a state of high tension during adaptation to training
loads and an incomplete recovery process. Fluctuations within the optimal zone are acceptable.
However, a higher value within the optimal zone is indicative of a more efficient recovery process.
Trained individuals often exhibit higher values compared to untrained individuals (within the optimal
zone). Also, endurance athletes exhibit higher values than sprinters. Regardless of the sport, most
athletes exhibit a high activity of the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system – as
indicated by high values of the recovery pattern – and a low activity of the sympathetic branch.

19
Causes of a low recovery pattern:
• Overload of physical and/or mental stimuli
• Unbalanced ratio between work and rest
• Illness and/or intoxication
• Unbalanced or irregular meals
• Lack of or inadequate recovery
Risks associated with prolonged excessively low values:
• Increased risk of illness
• Increased probability of overtraining
• Increased probability of injury
• Increased probability of poor performance
• Reduced likelihood of effective recovery
Risks associated with prolonged excessively high values:
• Increased probability of injury
• Increased probability of poor performance
• Increased probability of onset of arrhythmia
Undesired recovery pattern be avoided by:
• Selection of appropriate aerobic training loads
• Customization of recovery activities
• Balanced and regular meals
• Balanced ratio between work and rest
Positive effects of maintaining an ideal recovery pattern:
• Increased rate of recovery
• Increased work capacity
• Normalization of excitation and inhibition in the nervous system
• Decreased likelihood of prolonged stress
• Decreased risk of injury and illness
Stress
Description:
Tension level in the cardiac system in response to physical and mental loads.
Guidance:
A key component in managing the training process is to monitor the effect of prescribed doses of
stress in the cardiac system over time. The level of stress in the cardiac system determines its readiness
for upcoming training loads. A state of excessive stress (fatigue) in the cardiac system can be caused by
prolonged and improper management of training loads.

20
In order to identify a state of excessive fatigue, Omegawave quantifies the level of stress in the cardiac
system on a scale of 1 to 7; 1 being very high tension and 7 being very low tension. With this
information, training and recovery activities can be customized to the needs of the athlete.
Causes of excessive stress include:
• Prolonged physical and mental loads
• Inadequate recovery
• Unbalanced and irregular meals
• Unbalanced ratio between work and rest
• Poor environmental conditions
Consequences of unmanaged stress include:
• Decreased adaptation reserves of the cardiac system
• Unpredictable training effect
• Onset of chronic stress
• Onset of overtraining
• Onset of illness and injury
• Decreased work capacity and performance results
Excessive stress can be avoided by:
• Proper selection and application of physical and mental loads with sufficient recovery
• Balanced and regular meals
• Balanced ratio between work and rest
• Improved environmental conditions
Positive results of proper stress management:
• Control of the training process
• Reduced likelihood of excessive stress
• Increased work capacity and performance results
• Reduced likelihood of overtraining
• Reduced risk of illness and injury
Adaptation reserves
Description:
A measure of how long and effectively the cardiac system can express the ability to adapt to external
stimuli.
Guidance:
Adaptation reserves reflect the capacity of the cardiac system to form a positive, useful adaptive
response to training. The athlete's cardiac system is able to effectively adapt to the effects of training
and withstand stress when the reserves are between 3 and 7. If the reserves are exhausted (a value of
1 or 2), the cardiac system will not be able to adequately compensate for the physiological changes

21
caused by stress; therefore, the athlete will be unable to form a useful adaptive result. Trained
individuals often exhibit higher adaptation reserves than untrained individuals.
Causes of low adaptation reserves include:
• Chronic physical, psychological, and emotional stress
• Chronic training strain, overreaching, and overtraining
• Inadequate recovery
• Chronic illness
• Unbalanced or irregular meals
Prolonged low adaptation reserve values are indicative of a state of chronic stress and overtraining.
Associated risks of this condition include:
• Increased likelihood of sub-par performance results
• Increased likelihood of injury and illness
Low adaptation reserves can be avoided by:
• Proper management of physical, psychological, and emotional stress.
• Individualization of training loads
• Sufficient recovery activities
• Reducing the risk of injury or illness
• Proper diet management
Positive effects of maintaining high adaptation reserves:
• Increased capacity to handle physical, psychological, and emotional loads
• Increased capability to handle greater training loads
• Decreased risk of overreaching and overtraining
• Increased likelihood of successful performance results
• Decreased risk of injury or illness
Increasing the athlete’s adaptation reserves allows the volume of resources in the cardiac system to be
developed, providing the body with an additional opportunity to effectively manage useful adaptations
in the development of a sport-specific functional system. This effect benefits training by allowing the
athlete to significantly diversify the means and methods of preparation.

22
Energy Supply System view
Aerobic readiness
Description:
Reflects the current state of the aerobic metabolic pathway and the ability to perform aerobic work in
training.
Guidance:
Training loads of an aerobic nature are characterized by a long duration of exertion at a high or
moderate power output, during which the body is mainly fueled by aerobic sources of energy supply.
For endurance activities (such as running 5 km or swimming 1.5 km), the aerobic system produces at
least 70% of the required energy. Aerobic sources of energy supply are the basis for the development
of endurance and reflect the ability to resist stress and fatigue while allowing for an increase in
adaptation reserves.
Factors which may significantly lower aerobic readiness:
• Aerobic loads of large volume or intensity
• Lack of or insufficient recovery
• Unbalanced or irregular meals, especially a lack of carbohydrates
• Illness and intoxication
Risks associated with low aerobic readiness:
• Reduced level of trainability
• Reduced resistance to stress
• Accumulation of fatigue
• Reduced adaptation reserves
• Onset of illness and/or injury
• Decreased work capacity and performance
Factors that may increase aerobic readiness:
• Selection of appropriate aerobic training loads
• Adequate and complete recovery
• Balanced and regular meals
• Training at mid-range altitudes
Positive effects of maintaining an ideal aerobic readiness:
• Increased resistance to stress
• Reduced risk of overreaching and overtraining
• Increased adaptation reserves
• Decreased risk of illness and injury
• Increased work capacity

23
Anaerobic readiness
Description:
The current ability to perform muscle work using the glycolytic energy system while withstanding a high
level of lactate in the blood.
Guidance:
Training loads of an anaerobic nature are characterized by physical exercises where anaerobic
glycolytic processes account for over 60 % of the energy supply (for example, the 100-800m events in
track & field). Mixed anaerobic-aerobic loads are considered exercises where the anaerobic and aerobic
processes contribute an approximately equal amount (for example, a 1 - 3 km run).
Anaerobic Readiness also reflects the anaerobic energy supply system’s ability to compensate for an
inadequacy of the aerobic system’s energy production during strenuous muscle work.
Factors which may significantly lower anaerobic readiness:
• Excessive load (large volume and intensity) performed using the anaerobic glycolytic system
• Lack of or insufficient recovery
• Unbalanced or irregular meals, particularly a lack of glycogen and protein
Risks associated with low anaerobic readiness:
• Reduced level of speed & power endurance
• Reduced ability to perform high intensity exercises between 0.5 - 2.5 minutes
• Reduced capacity of anaerobic reserves
• Reduced ability to withstand hypoxia
Factors that may increase anaerobic readiness:
• Regular and optimal loads of an anaerobic nature
• Customization of nutrition and supplementation
Positive effects of maintaining an ideal anaerobic readiness:
• Increased speed & power endurance
• Faster activation of glycolytic processes resulting in the maximal output being reached in a
shorter amount of time (from 20 seconds to 5 seconds)
• Increased power and capacity of the anaerobic glycolytic system

24
Central Nervous System view
CNS Readiness
Description:
The level of activation and intensity of functioning at a specific moment in time.
Guidance:
A comprehensive indicator of the current state of the CNS presented on a scale of 1 to 7; 1 being a very
poor state of Readiness and 7 being an excellent state of Readiness. The current state of the CNS
determines its ability to effectively regulate the functions of the body in order to achieve useful
adaptive results from training.
To assess the functional state of the CNS, Omegawave utilizes the Direct Current Potential method to
record and analyze the super slow bioelectric activity of the athlete's brain. The behavior of this activity
over the course of a 4-minute assessment taken at rest indicates the Readiness of the CNS to regulate
bodily functions.
More specifically, the assessment identifies the quality of adaptations, and the stability and Readiness
of the CNS for upcoming training loads.
DC Potential
Description:
The current activation level of the frontal brain systems that comprise the integrative center. Measured
in millivolts.
Guidance:
Based upon psychophysiological characteristics, DC Potential can be categorized into the following
zones:
Increased zone of DC Potential at rest (above the green zone)
• Increased alertness and mental activation
• Psycho-emotional tension and/or instability
• Suboptimal functioning of central brain mechanisms due to a high state of tension in the
process of regulating the transition from active wakefulness to operational rest
• Low adaptive capacity of the body
• Limited cognitive activity and decreased learning ability
• Inappropriate reactions to certain physical, mental, social or other stimuli
• Low stress resistance
Optimal zone of DC at rest (the green zone)
• Optimal level of wakefulness and mental activation
• Optimal, balanced, steady state of central brain mechanisms regulating the level of active
wakefulness and operative rest
• Higher adaptive capacity of the body
• High productivity of cognitive activity and a high ability to learn

25
• Adequate response to any external influence: physical, mental, social and others
• High stress resistance
• The ability to spontaneously relax during the transition from a state of active wakefulness
to a state of operational rest
• Psycho-emotional stability
Reduced zone of DC Potential at rest (below the green zone)
• Decreased alertness and mental activation
• Suboptimal functioning of central brain mechanisms due to a state of exhaustion (of
varying intensities) in the process of regulating the transition from active wakefulness to
operational rest
• Limited adaptive capacity of the body
• Reduced efficiency of cognitive activity and decreased learning ability
• Reduced adaptive reserves of the body
• Inappropriate reactions to certain physical, mental, social or other stimuli
• Reduced stress resistance
• Psycho-emotional instability
To properly incorporate the use of DC Potential into a training plan, it is crucial to manage training
loads in a way that allows the athlete to remain within the optimal zone. The athlete should not
maintain measurements in a reduced or increased zone of DC Potential for extended periods of time.
The optimal zone of DC Potential at rest reflects the most favorable time to apply training loads.

26
FAQ
The Omegawave App cannot find the BLE sensor when trying to pair?
Pre-condition: Verify that the sensor is fully charged and the device’s Bluetooth is on.
• Verify that your device has the latest Android version.
• The sensor’s Bluetooth activates only when attached to the ECG chest strap and when the strap
is placed around your chest. Verify that the ECG chest strap is properly moisturized and that the
sensor is correctly attached to the strap. When the sensor’s Bluetooth is activated, the LED
starts to blink blue a light at a fast pace. When the sensor is connected to Omegawave App and
is ready for a measurement, the LED blinks slower.
• Connect the sensor to a power supply using the micro-USB charging cable for a few seconds.
Check that the sensor’s LED light turns red. This will reset the sensor. à Try to set the sensor
again.
• If that doesn’t work, shut down the App completely. à Repeat the steps above and try to set the
sensor again.
• If that doesn’t work, turn off Bluetooth from the Settings menu, and then turn it back on. à
Repeat the steps above and try to set the sensor again.
• If that doesn’t work, repeat all the steps above first, reboot your device. à Try to set the sensor
again.
Application cannot find the BLE sensor when in measurement view?
• Verify that the sensor is charged and that the device’s Bluetooth is on.
• Verify that you have configured the BLE sensor via the Omegawave App settings.
• The sensor’s Bluetooth activates only when attached to the ECG chest strap and the strap is
properly placed around your chest. Verify that the ECG chest strap is properly moisturized and
that the sensor is attached to the strap.
I’m getting really low scores for metabolic values compared to old ones?
Ensure that you have placed the sensor the right way up in relation to the ECG chest strap; the MicroUSB port needs to be facing down.
Results cannot be calculated because not a valid measurement?
Omegawave’s algorithms analyse the quality of the data, if issues are detected in relation to the
measurement, results cannot be calculated. Often, the underlying reason is that the ECG chest strap is
the wrong size or the strap’s electrodes are not properly moisturized with water. Also, if you did not
follow the measurement protocol (for example moving excessively or coughing during the
measurement), it may cause an invalid measurement.

27
You have completed a measurement but cannot see results?
A working Internet connection is required in order for the measurement results to be calculated. One
reason could also be that measurement data was too low quality and calculation engine rejected the
measurement.
Measurement was cancelled because the DC Potential values were out of range?
This may happen if you are reusing old electrodes or they have dried due to improper storage. Always
use unused electrodes and make sure that you properly seal the electrode bag to prevent drying.
DC Potential signal is not detected?
Ensure that you are using unused electrodes and that you have connected the DC cable to your
forehead and palm electrodes. If the application still indicates that it is unable to detect the DC
Potential signal, it can mean that the micro-USB connector of the sensor may be broken. In this case,
contact Omegawave support for further assistance: http://community.omegawave.com
The sensor cannot be charged?
If you cannot see the LED light turning red when the sensor is connected to a power supply with the
micro-USB cable, it means that the sensor is already fully charged. It can also mean that the micro-USB
connector of the sensor may be broken. In this case contact Omegawave support for further
assistance: http://community.omegawave.com
How can I cancel my recurring subscription?
Please contact us by sending an email to: support@omegawave.com
Can I wash the ECG chest strap?
Yes, and it’s recommended to do so regularly. The washing recommendations are printed on the strap
care label (40°C / 104°F, no fabric softener).
Sensor operating temperature?
0 °C to +40 °C / 32 °F to 104 °F

28
REGULATORY INFORMATION
OMEGAWAVE HAS NOT APPROVED ANY CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS TO THIS DEVICE BY THE USER. ANY CHANGES OR
MODIFICATIONS COULD VOID THE USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
OMEGAWAVE N’A APPROUÉ AUCUNE MODIFICATION APPORTÉE À L’APPAREIL PAR L’UTILISATEUR, QUELLE QU’EN SOIT LA
NATURE. TOUT CHANGEMENT OU TOUTE MODIFICATION PEUVENT ANNULER LE DROIT D’UTILISATION DE L’APPAREIL PAR
L’UTILISATEUR.
FCC REGULATORY INFORMATION
THIS DEVICE COMPLIES WITH PART 15 OF THE FCC RULES. OPERATION IS SUBJECT TO THE FOLLOWING TWO CONDITIONS: (1)
THIS DEVICE MAY NOT CAUSE HARMFUL INTERFERENCE, AND (2) THIS DEVICE MUST ACCEPT ANY INTERFERENCE RECEIVED,
INCLUDING INTERFERENCE THAT MAY CAUSE UNDESIRED OPERATION.
INDUSTRY CANADA (IC) REGULATORY INFORMATION
THIS DEVICE COMPLIES WITH INDUSTRY CANADA LICENCE-EXEMPT RSS STANDARD(S). OPERATION IS SUBJECT TO THE
FOLLOWING TWO CONDITIONS: (1) THIS DEVICE MAY NOT CAUSE INTERFERENCE, AND (2) THIS DEVICE MUST ACCEPT ANY
INTERFERENCE, INCLUDING INTERFERENCE THAT MAY CAUSE UNDESIRED OPERATION OF THE DEVICE.
AVIS DE CONFORMITÉ À LA RÉGLEMENTATION D’INDUSTRIE CANADA
LE PRÉSENT APPAREIL EST CONFORME AUX CNR D’INDUSTRIE CANADA APPLICABLES AUX APPAREILS RADIO EXEMPTS DE
LICENCE. L’EXPLOITATION EST AUTORISÉE AUX DEUX CONDITIONS SUIVANTES : (1) L’APPAREIL NE DOIT PAS PRODUIRE DE
BROUILLAGE, ET (2) L’UTILISATEUR DE L’APPAREIL DOIT ACCEPTER TOUT BROUILLAGE RADIOÉLECTRIQUE SUBI, MÊME SI LE
BROUILLAGE EST SUSCEPTIBLE D’EN COMPROMETTRE LE FONCTIONNEMENT.
CLASS B DIGITAL DEVICE NOTICE
THIS CLASS B DIGITAL APPARATUS COMPLIES WITH CANADIAN ICES-003, RSS-GEN AND RSS-210.
CET APPAREIL NUMERIQUE DE LA CLASSE B EST CONFORME A LA NORME NMB-003, CNR-GEN ET CNR-210 DU CANADA.
 Loading...
Loading...