Page 1

User's Guide
http://www.omega.com
e-mail: info@omega.com
PCI-DAS1602/16
Page 2

9
2
0
0
6
6
6
8
2
7
0
0
0
6
5
6
6
4
4
4
3
2
2
2
2
Table of Contents
1.0 INTRODUCTION
.0 INSTALLATION
2.1 Software Installation
.0 INSTACAL
3.2 Running InstaCal
3.3 Base I/O Address & Interrupt Level
.0 HARDWARE CONNECTIONS
4.1 Connector Pin Diagram
.0 FEATURES AND FUNCTIONS OVERVIEW
.0 PROGRAMMING & APPLICATIONS
6.1 Programming Languages
6.2 Packaged Applications Programs
...............................................................
.........................................................
..........................................................
......................................................
.....................................................
........................................................
..........................................
...................................................
.............................................................
..............................................
...................................................
...............................................
.......................................
.................................................
...........................................
....................................
..................................
Page
Page
Page
Page 3
Page 33.1 System Requirements
Page
Page
Page 53.4 Testing The Installation
Page 53.5 Calibration
Page
Page
Page 74.2 Connecting Signals to the PCI-DAS1602/16
Page 74.3 Analog Input Configurations
Page 9
Page 1
Page 1
Page 1
.0 SELF-CALIBRATION OF THE PCI-DAS1602/16
.................................................
7.2 Analog Output Calibration
.0 PCI-DAS1602/16 REGISTER DESCRIPTION
...............................................................
...............................................................
8.2.2 ADC Channel MUX And Control Register
...............................................................
8.4 BADR3
8.5 BADR4
................................................................
8.4.1 ADC Pacer Clock Data And Control Registers
...............................................................
8.5.1 DAC Data Register
8.5.2 DAC FIFO Clear Register
................................................
.................................
.....................................
.....................................
..............................................
.......................................
..............................................
.........................................
..............................................
.........................................
..............................
.............................
.........................
.....................
.........................
Page 11
Page 117.1 Analog Input Calibration
Page 1
Page 13
Page 138.1 BADR0
Page 138.2 BADR1
Page 138.2.1 Interrupt / ADC FIFO Register
Page 1
Page 188.2.3 Trigger Control/Status Register
Page 218.2.4 Calibration Register
Page 238.2.5 DAC Control/Status Register
Page 258.3 BADR2
Page 258.3.1 ADC Data Register
Page 258.3.2 ADC FIFO Clear Register
Page 2
Page 2
Page 278.4.2 High-Drive Digital I/O Data and Control Registers
Page 298.4.3 DAC Pacer Clock Data and Control Registers
Page 3
Page 3
Page 3
.0 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
..........................................
Page 33
Page 3

1.0 INTRODUCTION
The PCI-DAS1602/16 is a multifunction measurement and control board designed to operate in
computers with PCI bus accessory slots. The architecture of the boards is loosely based on the
original CIO-DAS16; the standard of ISA bus data acquisition. Much has changed though, and
all of it due to improvements in technology.
Higher quality analog components have made 16-bit measurements the standard. Dense packaging technology and custom ASICS allow a far greater range of control over programmable
options, such as calibration, triggering, synchronization and data transfer.
Even the connector has changed. New, denser connectors allow up to 100 signal lines where
once 37 was the the standard.
Because of the improvements in technology, the PCI-DAS1602/16 is easier to install and use
than any previous DAS16. There is not a single switch or jumper on the board, so go ahead and
install the PCI-DAS1602/16 into your computer then turn your computer on. Welcome to the
future!
2.0 INSTALLATION
2.1 Software Installation
2.1.1 Windows 95, 98, NT or above
If you will be installing the Universal Library with your board, insert the Universal Library
diskette or CD in an appropriate drive, run the program SETUP.EXE, and follow the installation
instructions provided. This program will install both Insta
test utility) and the Universal Library. If you are using Windows 95, you will have the option of
installing the 16-bit and/or 32-bit libraries. Unless you have a specific reason to use the 16-bit
library (e.g. compatibility with an exisiting program) install the 32-bit version.
If you are not using the Universal Library, insert the disk or CD labeled Insta
appropriate drive, and run SETUP.EXE. The install wizard will now launch and you will then be
prompted for additional information. Follow the instructions and, if possible, accept the defaults,
especially if this is your first installation. It will be easier for us to assist you in the unlikely event
of trouble during your system setup and operation.
2.1.2 UNIVERSAL LIBRARY INSTALLATION OPTIONS
The Universal Library provides example programs for a wide variety of programming languages.
If you are installing the Universal Library, an "Installation Options" dialog box will allow you to
select which languages' example programs are loaded onto your computer. Select the desired
example programs by checking the appropriate box(s).
Cal
TM
(setup and
Cal
TM
into an
Page 2
Page 4

2.1.3 FILE DEFAULT LOCATION
InstaCal will place all appropriate files in "C:CB" If you change this default location remember
where the installed files are placed as you may need to access them later.
2.1.4 INSTALLATION QUESTIONS
At the end of the installation process the installation wizard will ask a series of questions regarding updating your startup files. Unless you have knowledge to the contrary, simply accept the
default (YES) when prompted. You will also be asked if you would like to read an updated
README file. If possible, please choose yes and take a look at the information in the file. It will
include the latest information regarding the software you are installing.
2.1.5 INSTALLATION COMPLETION
After the installation of InstaCal is complete you should restart your computer to take advantage
of changes made to the system.
2.1.6 DOS and WINDOWS 3.x
Most users are now installing PCI Bus boards in systems with Windows operating systems (e.g.,
Windows 95, 98 or NT). If you are using Windows 3.x, the setup wizard will automatically
install the 16-bit version of the Universal Library and InstaCAL. These versions are compatible
with the DOS operating system.
If you need to install the software and do not have access to Windows, you will need to order the
special "DOS Only" version of the software. The part number for these products are
INSTACAL/DOS and Universal Library/DOS. Please contact the factory if you have any
questions regarding these special DOS only versions.
3.0 Insta
InstaCal is the Installation, Calibration and Test software supplied with all I/O
boards. After installing InstaCal you should re-start your computer to take advantage of changes
made to the AUTOEXEC and CONFIG files. The PCI-DAS1602/16 does not have to be installed
in order for InstaCal to run, but must be in order to test or calibrate the board.
Cal
3.1 System Requirements
Two versions of InstaCal are supplied with the PCI-DAS1602/16. The standard 32-bit version is
compatible with Windows 95, 98, NT and greater. For those using older operating systems, the
DOS based, 16-bit version is supplied and is compatible with DOS, Windows 3.x and Windows
95 (though we recommend Windows 95 users take advantage of the 32-bit version).
Page 3
Page 5

3.2 Running InstaCal
Be sure to restart your computer after the initial installation, and before running InstaCal. Run the
InstaCal program in order to test your board and configure it for run-time use. By configuring
the board, you add information to the configuration file, cb.cfg, that is used by the Universal
Library as well as third-party data acquisition packages that use the Universal Library to access
the board.
Launch InstaCal by going to your Start Menu then to Programs, then to CB, and
finally choosing Insta
launch the program by going to START>RUN and typing INSCAL32, or by finding the file
named "INSCAL32.exe" in your installation directory and double clicking it.
InstaCal will display a dialog box indicating the boards that have been detected in the system. If
there are no other boards currently installed by InstaCal, then the PCI-DAS1602/16 board will be
assigned board number 0. Otherwise it will be assigned the next available board number.
You can now view and change the board configuration by clicking the properties icon or selecting the Install\Configure menu.
Once done, exit InstaCal. This will update and save the configuration file, CBI.CFG in the
C:\CB directory.
Cal
(InstCAL 16 if you wish to run the 16-bit version). You may also
3.3 Base I/O Address & Interrupt Level
The PCI-DAS1602/16 uses a number of addresses and one interrupt. The addresses are allocated
by the PCI plug & play procedure and may not be modified. If you have installed ISA bus boards
in the past you are familiar with the need to select a base address and interrupt level. On PCI
systems this is not of concern to you. It is not up to you to select a base address and ensure that it
does not conflict with an installed port. In PCI systems, the operating software and installation
software do the selection and checking for you.
The computer BIOS selects and sets the I/O address and interrupt level from the range of available addresses. This address and other information is read by InstaCAL and stored in the configuration file CB.CFG. This file is accessed by the Universal Library for programmers. Note also
that the Universal Library is the I/O board in terface for packaged applications such as Labtech
Notebook and HP-VEE, therefore the InstaCal settings must be made in order for these and other
applications to run.
The base address and interrupt level are also stored in the system software. Once InstaCal installation software is run, other programming methods such as direct IN and OUT statements can
write and read the PCI-DAS1602/16 registers by reference to the base address and the offset from
base address corresponding to the chart of registers located elsewhere in this manual.
Page 4
Page 6

But a word of warning is in order here. Direct writes to the addresses simply by reference to the
base address of the PCI-DAS1602/16 I/O registers is not advised. Since the addressess assigned
by the PCI plug & play software are not under your control, there is no way to guarantee that
your program will run in any other computer.
Not only that, but if you install another PCI board in a computer after the PCI-DAS1602/16
addresses have been assigned, those addresses may be moved by the plug & play software when
the second board is installed. It is best to use a library such as Universal Library or a program
such as HP-VEE to make measurements with your PCI-DAS1602/16.
3.4 Testing The Installation
After you have run the install program and set your address and interrupt with InstaCal, it is time
to test the installation. The following section describes the InstaCal procedure to test that your
board is properly installed. The procedure has you connect one of the outout channels to one of
the A/D channels, it then outputs a simple waveform and shows you the wavefrom monitored on
the selected A/D channel.
1. With InstaCal running, select the PCI-DAS1602/16.
2. Select the "TEST" function from the main menu
3. Follow the instructions provided
If you do not receive the expected results:
a. make certain you have connected the correct pins according to the connector diagram.
b. go back through the installation procedure and make sure you have installed the
board acording to the instructions.
If this does not get you to the desired display, please call us (or contact your local distributer) for
additional assistance.
3.5 Calibration
Selecting CALIBRATE from the InstaCal main menu runs a fully automated PCI-DAS1602/16
calibration program. The software controlled calibration of the PCI-DAS1602/16 is explained
extensively in the section on calibration.
Page 5
Page 7
4.0 HARDWARE CONNECTIONS
4.1 Connector Pin Diagram
The PCI-DAS1602/16 employs the new 100 pin connector. Please make accurate notes and pay
careful attention to wire connections. In a large system a misplaced wire may create hours of
work ‘fixing’ problems that do not exist before the wiring error is found.
A n a log In p u t C h 0 L o w / 8 High 3
A n a log In p u t C h 0 H ig h 2
Analog Input C h 1 High
A n a log In p u t C h 1 L o w / 9 High
Analog Input C h 2 High
A n a log In p u t C h 2 L o w / 1 0 H ig h
Analog Input C h 3 High
A n a log In p u t C h 3 L o w / 11 H ig h
Analog Input C h 4 High
A n a log In p u t C h 4 L o w / 1 2 H ig h
Analog Input C h 5 High
A n a log In p u t C h 5 L o w / 1 3 H ig h
A n a log In p u t C h 6 High
A n a log In p u t C h 6 L o w / 1 4 H ig h
Analog Input C h 7 High
A n a log In p u t C h 7 L o w / 1 5 H ig h
Analog Ground 1
Analog Ground 18
D/A GND 0 35
D/A OUT 0 36
D/A GND 1 37
D/A OUT 1 38
A/D External Pacer 42
Analog Trigger In 43
D/A External Pacer 44
A/D External Trigger 45
PC G round 50
NC 19
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
CLK 4 39
GATE 4 40
OU T 4 41
NC
NC
PC +5V 48
SSH OUT 49
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
46
47
51 Digital A0
D igita l A 1
52
D igita l A 2
53
D igita l A 3
54
D igita l A 4
55
D igita l A 5
56
D igita l A 6
57
D igita l A 7
58
D igita l B 0
59
D igita l B 1
60
D igita l B 2
61
D igita l B 3
62
D igita l B 4
63
D igita l B 5
64
D igita l B 6
65
D igita l B 7
66
Digital C0
67
Digital C1
68
Digital C2
69
Digital C3
70
Digital C4
71
Digital C5
72
Digital C6
73
Digital C7
74
75 NC
N C
76
N C
77
N C
78
N C
79
N C
80
N C
81
N C
82
N C
83
N C
84
N C
85
N C
86
N C
87
N C
88
P C Gro u nd
89
90 PC +12V
91 PC G round
92 P C -1 2 V
N C
93
N C
94
95 A /D Inte rn a l P a c e r O u tp u t
D /A In te rn al P a c e r Outp u t
96
E xte rn a l D /A Pac e r Ga te
97
N C
98
99 E x te rn a l Inte r ru pt
100 PC G round
PCI-D AS 1602/16 C onnector Diagram
Page 6
Page 8

4.2 Connecting Signals to the PCI-DAS1602/16
The 100 pin connector provides a far greater signal density than the traditional 37 pin D type
connector. In exchange for that density comes a far more complex cable and mating connector.
The C100-FF-2 cable is a pair of 50 pin ribbon cables. At one end they are joined together with a
100 pin connector. From the 100 pin connector designed to mate with the PCI-DAS1602/16
connector, the two 50 pin ribbon cables diverge and are terminated at the other end with standard
50 pin header connectors. A CIO-MINI50 screw terminal board is the ideal way to terminate real
word signals and route them into the PCI-DAS1602/16
Analog inputs to the PCI-DAS1600 may be connected in three different configurations. In order
of complexity, these are Single Ended, Floating Differential and Differential.
WARNING - PLEASE READ
Here is a good tip. Measure the voltage potential (difference) between the
ground signal at the signal source and the PC. Use a volt meter and place the
red probe on the PC ground and the black probe on the signal ground. If there
is a difference of more than 10 volts, do not connect the CIO-DAS1600 to this
signal source because you will not be able to make any reading. A difference
more than 30 volts will likely damage the board and possibly the computer.
4.3 Analog Input Configurations
SINGLE ENDED
Single ended inputs are most appropriate in systems where the signal source and the data acquisition board share a common ground. This is a very common scenario and includes almost all
systems where the data acquisition system is supplying either the power (+5V and GND) or the
excitation (from a D/A). In this case you may take advantage of the P CI-1602/16’s 16 channel
mode without affecting performance.
Single ended inputs are also useful the signal source is electrically isolated (also referred to as
floating) from the data acquisition board’s ground (e.g. connecting to the two terminals of a
battery). However, the use of differential input configuration will provide better noise immunity
than single ended when monitoring an isolated signal source. Unless you absolutely need more
than 8 channels, we recommend using the differential input mode for isolated input signals.
Please refer to the next paragraph for connection information for the connection of isolated
signals to differential inputs.
.
FLOATING DIFFERENTIAL
A floating differential input is two wires from the signal source and a 10K ground reference
resistor installed at the PCI-DAS1602/16 input. The two signals from the signal source are
Signal High (CH# HI) and Signal Low (CH# LO).
The reference resistor is connected between the PCI-DAS1602/16 CH# LO and LLGND pins.
Page 7
Page 9

This floating configuration is appropriate when the signal source is floating with respect to
ground, (e.g. a battery or 4-20mA transmitter), the lead lengths are long, your system is subject to
substantial EMI interference.
WARNING!
Is that signal source really floating? Check it with a voltmeter before risking the
PCI-DAS1602/16 and PC! If you can measure a constant voltage between the
grounds of the PC and your signal source, it’s probably not floating.
DIFFERENTIAL
Proper measurement of a differential signal requires three wires from the signal source. The
signals are Signal High (CH# HI), Signal Low (CH# LO) and Signal Ground (LLGND).
A differential connection allows you to connect the PCI-DAS1602/16 to a signal source with a
ground that is different, but not isolated from the PC ground, but less than 10V difference, and
still make a true measurement of the signal between CH# HI and CH# LO.
EXAMPLE:
Non-Isolated laboratory instruments with three prong wall plug. There are usually differences in
wall GND potentials between outlets.
Page 8
Page 10
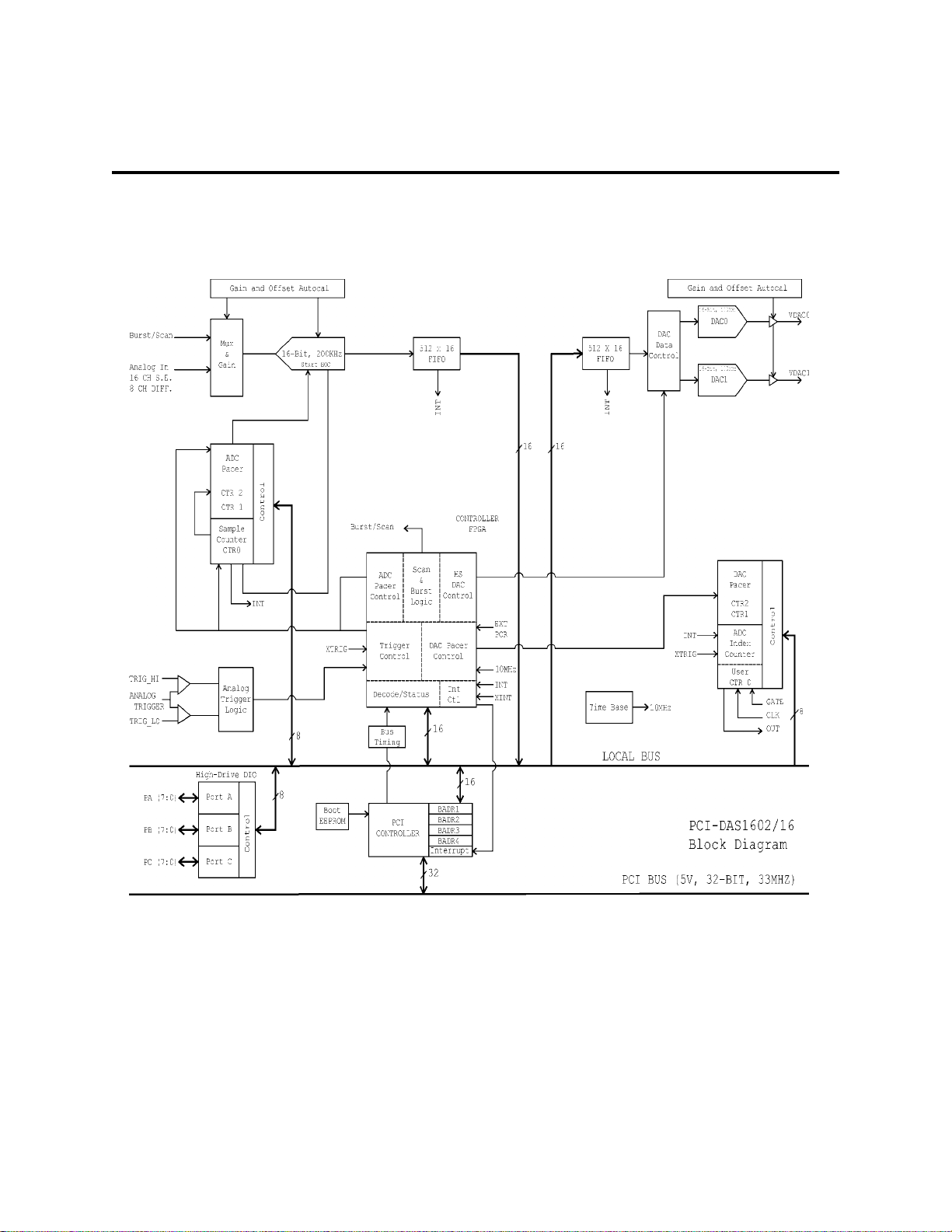
5.0 Features and Functions Overview
The PCI-DAS1602/16 is a multifunction measurement and control board. The design of the
board may be simplified into several blocks containg the major functions of the board. Please
take a moment to examine the diagram here.
Page 9
Page 11

6.0 Programming & Applications
Your PCI-DAS1602/16 is now installed and ready for use. Although the PCI-DAS1602/16 is
part of the larger DAS family, there is no correspondence between registers. Software written at
the register level for the other DAS's will not work with the PCI-DAS1602/16. This includes any
driver or library where the target board is other than a PCI-DAS1602/16.
6.1 Programming Languages
The UniversalLibrary provides complete access to the PCI-DAS1602/16
functions from a range of programming languages; both DOS and Windows. If you are planning
to write programs, or would like to run the example programs for Visual Basic or any other
language, please turn now to the UniversalLibrary manual.
VIX Components is a set of programming tools based on a DLL interface to Windows languages.
A set of VBX, OCX or ActiveX interfaces allows point and click construction of graphical
displays, analysis and control structures. Please see the cat alog for a complete description of the
package.
6.2 Packaged Applications Programs
Many packaged application programs, such as DAS Wizard, Labtech Notebook and HP-VEE
now have drivers for the PCI-DAS1602/16. If the package you own does not appear to have
drivers for the PCI-DAS1602/16 please fax or e-mail the package name and the revision number
from the install disks. We will research the package for you and advise how to obtain
PCI-DAS1602/16 drivers.
Some application drivers are included with the Universal Library package, but not with the
Application package. If you have purchased an application package directly from the software
vendor, you may need to purchase our Universal Library and drivers. Please contact us for more
information on this topic.
Page 10
Page 12
7.0 Self-Calibration of the PCI-DAS1602/16
The PCI-DAS1602/16 provides self-calibration of the analog source and measure systems
thereby eliminating the need for external equipment and user adjustments. All adjustments are
made via 8-bit calibration DACs or digital potentiometers referenced to an on-board factory
calibrated standard. The PCI-DAS1602/16 is shipped fully-calibrated from the factory with cal
coefficients stored in nvRAM. At run time, these calibration factors are loaded into system
memory and are automatically retrieved each time a different DAC/ADC range is specified. The
user has the option to recalibrate with respect to the factory-measured voltage standards at any
time by simply selecting the "Calibrate" option in InstaCal. Full calibration typically requires
less than two minutes and requires no user intervention.
7.1 Analog Input Calibration
A variety of methods are used to calibrate the different elements on the board. The analog frontend has several "knobs" to turn. Offset calibration is performed in both the instrumentation
amplifier gain stage and the ADC itself. Front-end gain adjustment is performed only via the
ADC reference. This strategy was chosen since the gain tolerance of the in-amp circuit is quite
good and there is adequate gain tuning range using only the ADC.
The analog output circuits are calibrated for gain and offset as well. Offset adj ustments for the
analog output are made in the output buffer section. The tuning range of this adjustment allows
for max DAC and output buffer offsets. Gain calibration of the analog outputs are performed via
DAC reference adjustments.
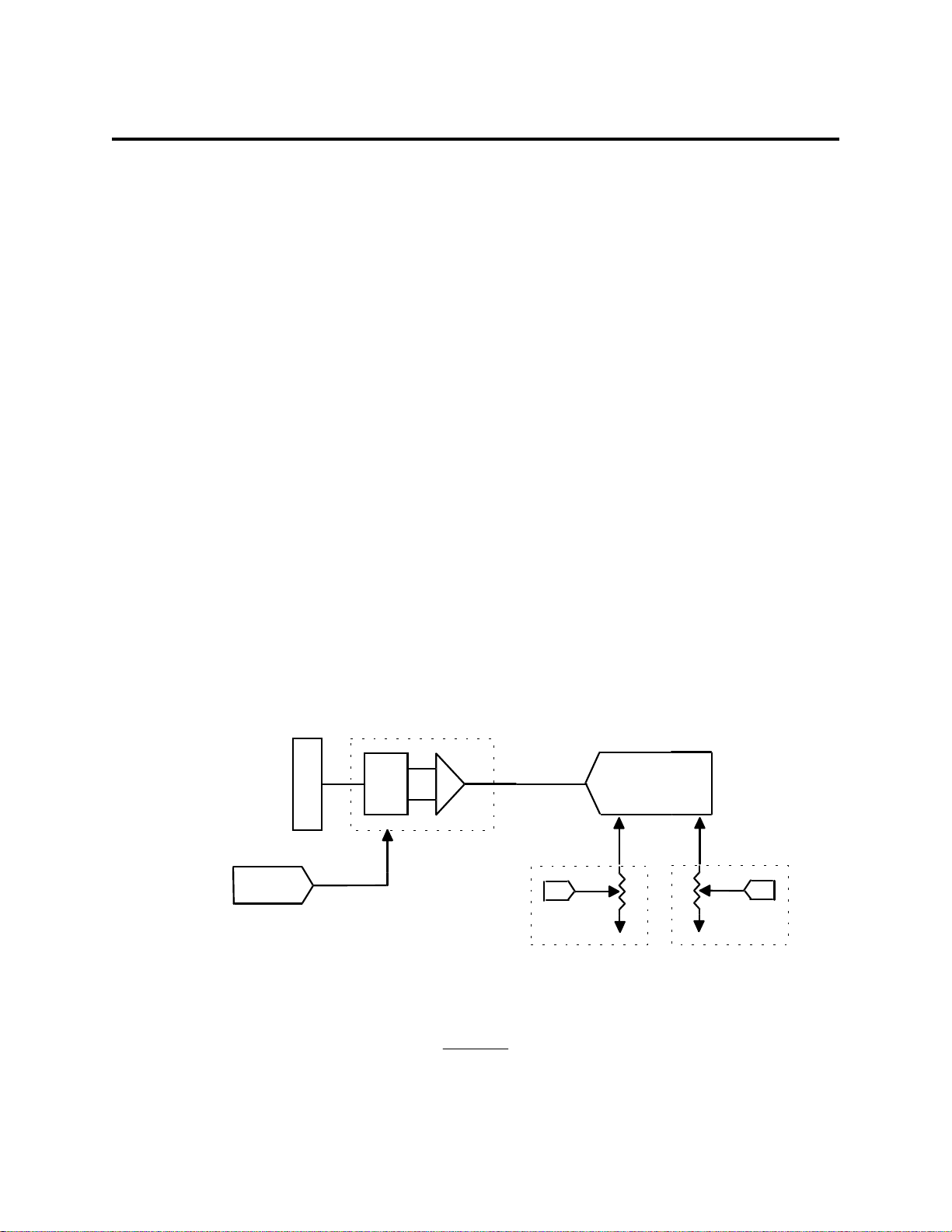
Figure 1 below is a block diagram of the analog front-end calibration system:
Cal
Ref
Analog-In
ADC
Offset Adj Uni/Bip
Trim Dac
Offset
Digital Offset Pot
Figure 1
RefOffset Adj
Digital Gain Pot
Page 11
Page 13

7.2 Analog Output Calibration
The analog output circuits are calibrated for both gain and offset. Coarse and Fine offset adjustments are made in the output buffer section. The tuning range of these adjustments allows for
maximum DAC and output buffer offsets. Coarse and Fine gain calibration is performed via
adjustments to the DAC reference.
Note that there are no references associated with the DAC calibration - a fully calibrated ADC set
to the respective DAC range is used as the m easurement system. Sub-ranging of the ADC i s used
to ensure highly accurate offset adjustments.
The calibration scheme for the Analog Out section is shown in Figure 2 below. This circuit is
duplicated for both DAC0 and DAC1 Figure 2
Analog-Out
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
16
Gain Adj
Gain Adj
Gain Adj
Ref
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
(Coarse)
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
Trim Dac
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
(Fine)
DAC
Analog Out
Offset Adj
Figure 2
Page 12
Page 14

8.0 PCI-DAS1602/16 Register Description
The PCI-DAS1602/16 operation registers are mapped into the PC I/O address space. Unlike its
ISA counterpart, this board has several base addresses each corresponding to a reserved block of
addresses in I/O space. Of six Base Address Regions (BADR) available in the PCI 2.1 specification, five are implemented in this design and are summarized as follows:
OperationsFunctionI/O Region
32-Bit DWORDPCI Controller Operation RegistersBADR0
16-Bit WORDGeneral Control/Status RegistersBADR1
16-Bit WORDADC Data, FIFO Clear RegistersBADR2
8-Bit BYTEPacer, Counter/Timer and DIO RegistersBADR3
16-Bit WORDDAC Data, FIFO Clear RegistersBADR4
BADRn will likely be different on different machines. Assigned by the PCI BIOS, these Base
Address values cannot be guaranteed to be the same even on subsequent power-on cycles of the
same machine. All software must interrogate BADR0 at run-time with a READ_CONFIGURATION_DWORD instruction to determine the BADRn values.
Please see the "AMCC S5933 PCI Controller Data Book, Spring 1996" for more information.
8.1 BADR0
BADR0 is reserved for the AMCC S5933 PCI Controller operations. This region supports 32-bit
DWORD operations
8.2 BADR1
The I/O region defined by BADR1 contains 5 control and status registers for ADC, DAC, interrupt and Autocal operations. This region supports 16-bit WORD operations.
8.2.1 Interrupt / ADC FIFO Register
BADR1+ 0
Interrupt Control, ADC status. A read/write register.
WRITE
0123456789101112131415
DAEMCL
-
INT0INT1INTEDAHFIEEOAIEDAHFCLEOACLINTCL----DAEMIEADFLCL
Write operations to this register allow the user to select interrupt sources, enable interrupts, clear
interrupts as well as ADC FIFO flags. The following is a description of the Interrupt/ADC FIFO
Register:
Page 13
Page 15

INT[1:0] General Interrupt Source selection bits.
SourceINT0 INT1
External 00
End of Channel Scan10
AD FIFO Half Full01
AD FIFO Not Empty11
INTE
Enables interrupt source selected via the INT[1:0] bits.
1 = Selected interrupt Enabled. 0 = Selected interrupt Disabled
DAHFIE
Enables DAC FIFO Half-Full signal as interrupt source. Used for high speed DAC operations.
1= Enable DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt. 0 = Disable DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt
EOAIE
Enables End-of-Acquisition interrupt. Used during FIFO'd ADC operations to indicate that the
desired sample size has been gathered.
1= Enable EOA interrupt. 0 = Disable EOA interrupt
DAHFCL
A write-clear to reset DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt status.
1 = Clear DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt. 0 = No effect.
EOACL
A write-clear to reset EOA interrupt status.
1 = Clear EOA interrupt. 0 = No effect.
INTCL
A write-clear to reset INT[1:0] selected interrupt status.
1 = Clear INT[1:0] interrupt 0 = No effect.
DAEMIE
Enables DAC FIFO Empty signal as an interrupt source.
1 = Enables DAC FIFO Empty interrupt. 0 = Disables DAC FIFO Empty interrupt.
ADFLCL
A write-clear to reset latched ADC FIFO Full status.
1 = Clear ADC FIFO Full latch. 0 = No Effect.
Page 14
Page 16

DAEMCL
A write-clear to reset DAEM interrupt status.
1= Clear DAEM interrupt. 0 = No effect.
NOTE: It is not necessary to reset any write-clear bits after they are set.
READ
0123456789101112131415
-----DAHFIEOAIINTXINTIEOBIADHFIADNEIADNELADFULDAEMI-
Write operations to this register allow you to check status of the selected interrupts and ADC
FIFO flags. The following is a description of Interrupt / ADC FIFO Register Read bits:
DAHFI
Status bit of DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt
1 = Indicates a DAC FIFO Half-Full interrupt has been latched. 0 = Indicates a DAHF interrupt
has not occurred.
EOAI
Status bit of ADC FIFO End-of-Acquisition interrupt.
1 = Indicates an EOA interrupt has been latched. 0 = Indicates an EOA interrupt has not
occurred.
INT
Status bit of General interrupt selected via INT[1:0] bits. This bit indicates that any one of these
interrupts has occurred.
1 = Indicates a General interrupt has been latched. 0 = Indicates a General interrupt has not
occurred.
XINTI
Status bit of External interrupt. External interrupt requires a rising TTL logic level input.
1 = Indicates an External interrupt has been latched. 0 = Indicates an interrupt has not occurred.
EOBI
Status bit ADC End-of-Burst interrupt. Only valid for ADC Burst Mode enabled.
1 = Indicates an EOB interrupt has been latched. 0 = Indicates an EOB interrupt has not
occurred.
ADHFI
Status bit of ADC FIFO Half-Full interrupt. Used during REP INSW operations.
1 = Indicates an ADC Half-Full interrupt has been latched. FIFO has been filled with more than
255 samples. 0 = Indicates an ADC Half-Full interrupt has not occurred. FIFO has not yet
exceeded 1/2 of its total capacity.
Page 15
Page 17

ADNEI
Status bit of ADC FIFO Not-Empty interrupt. Used to indicate ADC conversion complete in
single conversion applications.
1 = Indicates an ADC FIFO Not-Empty interrupt has been latched and that one data word may be
read from the FIFO. 0 = Indicates an ADC FIFO Not-Empty interrupt has not occurred. FIFO
has been cleared, read until empty or ADC conversion still in progress.
ADNE
Real-time status bit of ADC FIFO Not-Empty status signal.
1 = Indicates ADC FIFO has at least one word to be read. 0 = Indicates ADC FIFO is empty.
LADFUL
Status bit of ADC FIFO FULL status. This bit is latched.
1 = Indicates the ADC FIFO has exceeded full state. Data may have been lost. 0 = Indicates
non-overflow condition of ADC FIFO.
DAEMI
Status bit of DAC FIFO Empty interrupt. Used to indicate that a FIFO'd DAC Operation has
completed.
1 = DAC FIFO Empty interrupt condition has occurred. 0 = DAC FIFO Empty interrupt condition has not occurred.
8.2.2 ADC Channel MUX And Control Register
BADR1 + 2
This register sets channel mux HI/LO limits, ADC gain, offset and pacer source.
A Read/Write register.
WRITE
CHL8-CHL1,
CHH8-CHH1
When these bits are written, the analog input multiplexers are set to the channel specified by
CHL8-CHL1. After each conversion, the input multiplexers increment to the next channel,
reloading to the "CHL" start channel after the "CHH" stop channel is reached. LO and HI
channels are the decode of the 4-bit binary patterns.
GS[1:0]
These bits determine the ADC range as indicated below:
0123456789101112131415
CHL1CHL2CHL4CHL8CHH1CHH2CHH4CHH8GS0GS1SEDIFFUNIBIPADPS0ADPS1--
Page 16
Page 18

RangeGS0GS1
10V00
5V10
2.5V01
1.25V11
SEDIFF
Selects measurement configuration for the Analog Front-End.
1 = Analog Front-End in Single-Ended Mode. This mode supports up to 16 channels.
0 = Analog Front-End in Differential Mode. This mode supports up to 8 channels.
UNIBIP
Selects offset configuration for the Analog Front-End.
1 = Analog Front-End Unipolar for selected range
0 = Analog Front-End Bipolar for selected range.
The following table summarizes all possible Offset/Range configurations:
Input GainInput RangeGS0GS1UNIBIP
000
100
010
110
001
101
011
111
±
10V
± 5V
±
2.5V
±
1.25V
0-10V
0-5V
0-2.5V
0-1.25V
Measurement
Resolution
305uV1
153uV2
76uV4
38uV8
153uV1
76uV2
38uV4
19uV8
ADPS[1:0]
These bits select the ADC Pacer Source. Maximum Internal/External Pacer frequency is
200KHz.
Pacer SourceADPS0ADPS1
SW Convert00
82C54 Counter/Timer10
External Falling01
External Rising11
Page 17
Page 19

Note: For ADPS[1:0] = 00 case, SW conversions are initiated via a word write to BADR2 + 0.
Data is 'don't care.'
READ
0123456789101112131415
--------------EOC-
EOC
Real-time, non-latched status of ADC End-of-Conversion signal.
1 = ADC DONE
0 = ADC BUSY
8.2.3 Trigger Control/Status Register
BADR1 + 4
This register provides control bits for all ADC trigger modes. A Read/Write register.
WRITE
0123456789101112131415
TS0TS1TGPOLTGSELTGENBURSTEPRTRGXTRCLCLO_ENCHI_ENHMODEARMFFM0C0SRC--
TS[1:0]
These bits select one-of-three possible ADC Trigger Sources:
SourceTS0TS1
Disabled00
SW Trigger10
External (Digital)01
External (Analog)11
Note: TS[1:0] should be set to 0 while setting up Pacer source and count values.
TGPOL
This bit sets the polarity for the external trigger/gate. Internally, the ADC is triggered on a rising
edge or gated on with an active high signal. Use TGPOL to condition external trigger/gate for
proper polarity.
1 = External trigger/gate input inverted.
0 = External trigger/gate input not inverted.
TGSEL
Page 18
Page 20

This bit selects whether external ADC control signal is an edge or a level. Use TGPOL signal to
create rising edge or high level input.
1 = Edge triggered.
0 = Level triggered.
TGEN
This bit is used to enable External Trigger/Gate function
1 = Selected Trigger Source enabled.
0 = Selected Trigger Source has no effect.
Note that external trigger/gate requires proper setting of the TS[1:0],
TGPOL, TGSEL and TGEN bits.
Example: Application requires use of external falling edge to start acquisition. Set:
TS1 = 1, TS0 = 0 -> External Digital Trigger
TGPOL = 1 -> Invert falling edge
TGSEL = 1 -> Edge Triggered event
TGEN = 1 -> Enable External Trigger.
Once TGEN is set the next falling edge will start a Paced ADC conversion. Subsequent triggers
will have no effect until external trigger flop is cleared (XTRCL).
BURSTE
bit enables ADC Burst mode. Start/Stop channels are selected via the CHLx, CHHx bits in ADC
CTRL/STAT register at BADR1 + 2.
1 = Burst Mode enabled
0 = Burst Mode disabled
PRTRG
This bit enables ADC Pre-trigger Mode. This bit works with the ARM and FFM0 bits when
using Pre-trigger mode.
1 = Enable Pre-trigger Mode
0 = Disable Pre-trigger Mode
XTRCL
A write-clear to reset the XTRIG flip-flop.
1 = Clear XTRIG status.
0 = No Effect.
CHI_EN
These bits select the Analog Trigger/Gate Mode as described in the table below.
CLO_EN
Page 19
Page 21

Note that the CHI Threshold is set by DAC1, CLO Threshold is set by DAC0.
HMODE
CHI >= CLO by definition.
000
100
X10
X01
X11
Signal goes HIGH when ATRIG is more positive than
CHI. Signal goes low when ATRIG becomes more
negative than CLO. Hysteresis level is the difference
between CHI and CLO.
Signal goes HIGH when ATRIG is more negative than
CLO. Signal goes low when ATRIG becomes more
positive than CHI. Hysteresis level is the difference
between CHI and CLO.
Signal goes high when ATRIG more negative than
CLO.
CHI has no effect.
Signal goes high when ATRIG is more positive than
CHI.
CLO has no effect.
CHI-CLO. Signal is low outside this region.
ModeAnalog Trigger/Gate FunctionHMODECLO_ENCHI_EN
Negative
Hysteresis
Positive
Hysteresis
Negative
Slope
Positive
Slope
WindowSignal goes high when within region defined by
ARM, FFM0
These bits work in conjunction the PRTRG bit during FIFO'd ADC operations. Note that
1 FIFO = 512 samples.
Page 20
Page 22

FFM0PRTRG
00
Via SW when remaining
------------------------
Via SW immediately
10
01
Via SW immediately
Via SW when remaining
------------------------
Via SW after XTRIG has
is set...
count <1 FIFO
1/2 FIFO < # Samples < 1 FIFO
# Post-Trigger Samples >1 FIFO
count <1 FIFO
1/2 FIFO < # Post-Trigger Samples < 1 FIFO
been detected
(INDX_GT=1)
FIFO ModeARM
# Samples >1 FIFO
Normal Mode
----------------------------------
Normal Mode
# Samples <1/2 FIFO
Normal Mode
Pre-Trigger Mode
----------------------------------
Pre-Trigger Mode
Sample CTR
Starts on...
ADHF
ADC Pacer
ADHF
11
Via SW after XTRIG has
been detected
(INDX_GT=1)
# Post-Trigger Samples < 1/2 FIFO
Pre-Trigger Mode
Via SW after
INDX_GT=1
C0SRC
This bit allows the user to select the clock source for user Counter 0.
1 = Internal 10MHz oscillator
0 = External clock source input via
CTR0CLK
pin on 100p connector.
READ
XTRIG
1 = External Trigger flip-flop has been set. This bit is write-cleared.
0 = External Trigger flip-flop reset. No trigger has been received.
INDX-GT
1 = Pre Trigger index counter has completed its count
0 = Pre Trigger index counter has not yet been gated on, or has not yet completed its count.
0123456789101112131415
-------XTRIG----INDX-GT---
8.2.4 Calibration Register
BADR1 + 6
This register controls all autocal operations. A Write only register.
Page 21
Page 23

WRITE
CD0CD1CD2CD3CD4CD5CD6CD7SEL8800SEL8402SEL08CSRC0CSRC1CSRC2CALENSDI
CD[7:0]
These 8 bits are the D/A code inputs for the analog-front DAC08 offset calibration DAC.
Complimentary current outputs of the DAC08 are equal at mid-scale, 7Fh. This should be the
default, non-calibrated value.
SEL8800
This bit enables the 8-bit trim DACs for the following circuits:
Cal Function DAC Channel
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DAC0
DAC0
DAC0
DAC1
DAC1
DAC1
DAC0
DAC1
Fine Gain
Coarse Gain
Offset
Offset
Fine Gain
Coarse Gain
Fine Offset
Fine Offset
0123456789101112131415
SEL8402
This bit enables the 8-bit digital potentiometers (50KOhm) for the following circuits.
Cal Function Trimmer Channel
0
1
ADC
ADC
Gain Cal
Offset Cal
SEL08
This bit enables conversions on the 8-bit DAC08 for Analog Front-End offset calibration. Data
value is set via CD[7:0].
1 = Offset DAC conversions enabled.
0 = Offset DAC conversions disabled (last value held).
Page 22
Page 24

CSRC[2:0]
These bits select the different calibration sources available to the ADC front end.
Cal SourceCSRC0CSRC1CSRC2
AGND000
7.0V100
3.5V010
1.75V110
0.875V001
-10.0V101
VDAC0011
VDAC1111
CALEN
This bit is used to enable Cal Mode.
1 = Selected Cal Source, CSRC[2:0], is fed into Analog Channel 0.
0 = Analog Channel 0 functions as normal input.
SDI
Serial Data In. This bit is used to set serial address/data stream for the DAC8800 TrimDac and
8402 digital potentiometer. Used in conjunction with SEL8800 and SEL8402 bits.
8.2.5 DAC Control/Status Register
BADR1 + 8
This register selects the DAC gain/range, Pacer source, trigger and High-Speed Modes. In
addition, DAC FIFO status information is available. This is a Read/Write register.
WRITE
0123456789101112131415
LDAEMCL
DACENSTARTDAPS0DAPS1HS0HS1-DAC0R0DAC0R1DAC1R0DAC1R1----
LDAEMCL
This is a Write-clear bit to reset the latched EMPTY status flag of the DAC FIFO.
1 = Reset Empty Flag
0 = No Effect.
DACEN
Page 23
Page 25

This bit enables the Analog Out features of the board.
1 = DAC0/1 enabled.
0 = DAC0/1 disabled.
START
This bit starts FIFO'd DAC operations. If used with DAXTRG, the external trigger signal, the
START bit is used to arm the operation.
1 = Start/Arm FIFO operations.
0 = Disable FIFO'd DAC operations.
DAPS[1:0]
These bits select the DAC Pacer Source:
Pacer SourceDAPS0DAPS1
SW Convert00
10
Programmed via BADR3 + 9, + A
Internal 82C54
External Falling Edge01
External Rising Edge11
HS[1:0]
These bits select the High-Speed DAC Modes as follows:
DAC ModeHS0HS1
Disabled00
10
DAC0
DAC101
Simultaneous DAC0/111
DACnR[1:0]
These bits select the independent gains/ranges for either DAC0 or DAC1. n=0 for DAC0 and n=1
for DAC1.
LSB SizeRangeDACnR0DACnR1
153uVBipolar 5V00
305uVBipolar 10V10
76uVUnipolar 5V01
153uVUnipolar 10V11
Page 24
Page 26

READ
0123456789101112131415
---------------
LDAEM
LDAEM
This is the latched version of the DAC FIFO_EMPTY signal. This bit must be write-write
cleared with the DAEMCL bit.
1 = DAC FIFO was emptied at some point during FIFO'd operations. Incorrect data may have
been clocked into the selected DAC(s).
0 = DAC FIFO did not empty during FIFO'd operations. Status good.
8.3 BADR2
The I/O Region defined by BADR2 contains the ADC Data register and the ADC FIFO clear
register.
8.3.1 ADC Data Register
BADR2 + 0 ADC Data register.
WRITE
Writing to this register is only valid for SW initiated conversions. The ADC Pacer source must
be set to 00 via the ADPS[1:0] bits. A null write to BADR2 + 0 with begin a single conversion.
Conversion status may be determined in two ways. The EOC bit in BADR1 + 0 may be polled
until true or ADNEI (the AD FIFO not-empty interrupt) may be used to signal that the ADC
conversion is complete and the data word is present in the FIFO.
READ
0123456789101112131415
AD0AD1AD2AD3AD4AD5AD6AD7AD8AD9AD10AD11AD12AD13AD14AD15
MSB LSB
AD[15:0]
This register contains the current ADC data word. Data format is dependent upon offset mode:
Bipolar Mode: Offset Binary Coding
0000 h = -FS
7FFFh = Mid-scale (0V)
FFFFh = +FS - 1LSB
Unipolar Mode: Straight Binary Coding
0000 h = -FS (0V)
7FFFh = Mid-scale (+FS/2)
FFFFh = +FS - 1LSB
8.3.2 ADC FIFO Clear Register
Page 25
Page 27

BADR2 + 2 ADC FIFO Clear register. A Write-only register. A write to this address location
clears the ADC FIFO. Data is don't care. The ADC FIFO should be cleared before all new
ADC operations.
8.4 BADR3
The I/O Region defined by BADR3 contains data and control registers for the ADC Pacer, DAC
Pacer, Pre/Post-Trigger Counters and High-Drive Digital I/O bytes. The PCI-DAS1602/16 has
two 8254 counter/timer devices. These are referred to as 8254A and 8254B and are assigned as
shown below:
FunctionCounter #Device
ADC Post-Trigger Sample Counter08254A
ADC Pacer Lower Divider18254A
ADC Pacer Upper Divider28254A
ADC Pre-Trigger Index/UserCounter08254B
DAC Pacer Lower Divider18254B
DAC Pacer Upper Divider28254B
All reads/writes to BADR3 are byte operations.
8.4.1 ADC Pacer Clock Data And Control Registers
8254A COUNTER 0 DATA - ADC RESIDUAL SAMPLE COUNTER
BADR3 + 0
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
Counter 0 is used to stop the acquisition when the desired number of samples have been
gathered. It is gated on when a 'residual' number of conversions remain. Counter 0 will be
enabled by use of the ARM bit (BADR1 + 4).
Counter 0 is to operated in Mode 0.
8254A COUNTER 1 DATA - ADC PACER DIVIDER LOWER
BADR3 + 1
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
8254A COUNTER 2 DATA - ADC PACER DIVIDER UPPER
Page 26
Page 28

BASE + 2
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
Counter 1 provides the lower 16 bits of the 32-bit pacer clock divider. Its output is fed to the
clock input of Counter 2 which provides the upper 16-bits of the pacer clock divider. The clock
input to Counter 1 is a precision 10MHz oscillator source.
Counter 2 output is called the 'Internal Pacer' and can be selected by software to the be the ADC
Pacer source. Counters 1 & 2 should be configured to operate in 8254 Mode 2.
ADC 8254 CONTROL REGISTER
BADR3 + 3
WRITE ONLY
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
The control register is used to set the operating Modes of 8254 Counters 0,1 & 2. A counter is
configured by writing the correct Mode information to the Control Register followed by count
written to the specific Counter Register.
The Counters on the 8254 are 16-bit devices. Since the interface to the 8254 is only 8-bits wide,
Count data is written to the Counter Register as two successive bytes. First the low byte is
written, then the high byte. The Control Register is 8-bits wide. Further information can be
obtained on the 8254 data sheet, available from Intel or Harris.
8.4.2 High-Drive Digital I/O Data and Control Registers
The 24 High-Drive DIO lines on the PCI-DAS1602/16 are grouped as three byte-wide
I/O ports. Port assignment and functionality is identical to that of the industry standard 8255
Peripheral Interface operating in Mode 0. Please see the Intel or Harris data sheets for more
information. Drive capability of each line is -15mA in the TTL HI state and 24mA in the TTL
LO state.
HDIO PORT A DATA
BADR3 + 4
PORT A may be configured as an 8-bit I/O channel.
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
Page 27
Page 29

HDIO PORT B DATA
BADR3 + 5
PORT B may be configured as an 8-bit I/O channel. Its functionality is identical to that of
PORT A.
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
HDIO PORT C DATA
BADR3 + 6
PORT C may be configured as an 8-bit port of either input or output, or it may be split into two
independent 4-bit ports of input or output. When split into two 4-bit I/O ports, D[3:0]
make up the lower nibble, D[7:4] comprise the upper nibble. Although it may be split, every
write to Port C is a byte operation. Unwanted information must be ANDed out during reads
and writes must be ORd with current value of the other 4-bit port.
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
HDIO CONTROL REGISTER
BADR3 + 7
The HDIO Control register is used configure Ports A,B and C as inputs or outputs. Operation is
identical to that of the 8255 in Mode 0.
WRITE
01324567
D0D10D3D4001
Note: Bits 3,5-7 are hardwired to the values shown (Mode 0). Actual writes to these bit
positions are "don't care."
The following table summarizes the possible I/O Port configurations for the PCI-DAS1602/16
HDIO:
Page 28
Page 30

PORT AD0D1D3D4
UPPER
PORT BPORT C
PORT C
LOWER
OUTOUTOUTOUT0000
INOUTOUTOUT1000
OUTINOUTOUT0100
ININOUTOUT1100
OUTOUTINOUT 0010
INOUTINOUT1010
OUTININOUT0110
INININOUT1110
OUTOUTOUTIN0001
INOUTOUTIN1001
OUTINOUTIN0101
ININOUTIN1101
OUTOUTININ0011
INOUTININ1011
OUTINININ0111
ININININ1111
8.4.3 DAC Pacer Clock Data and Control Registers
8254B COUNTER 0 DATA
- ADC PRE-TRIGGER INDEX COUNTER
BADR3 + 8
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
Counter 0 of the DAC 8254 device is actually used as the ADC Pre-Trigger index counter.
This counter serves to mark the boundary between pre- and post-trigger samples when the ADC
is operating in Pre-Trigger Mode. The External ADC Trigger flip flop gates Counter 0 on;
the ADC FIFO Half-Full signal gates it off. Knowing the desired number of post-trigger
samples, software can then calculate how may 1/2 FIFO data packets need to be collected
and what corresponding residual sample count needs to be written to BADR3 + 0.
8254B COUNTER 1 DATA
- DAC PACER DIVIDER LOWER
BADR3 + 9
READ/WRITE
Page 29
Page 31

01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
8254B COUNTER 2 DATA
- DAC PACER DIVIDER UPPER
BADR3 + Ah
READ/WRITE
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
Counter 1 provides the lower 16 bits of the 32-bit pacer clock divider. Its output is fed to the
clock input of Counter 2 which provides the upper 16-bits of the pacer clock divider. The clock
input to Counter 1 is a precision 10MHz oscillator source.
Counter 2's output is called the 'Internal Pacer' and can be selected by software to the be the
ADC Pacer source. Counters 1 & 2 should be configured to operate in 8254 Mode 2.
8254B CONTROL REGISTER
BADR3 + Bh
WRITE ONLY
01324567
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
The control register is used to set the operating Modes of 8254 Counters 0,1 & 2. A counter is
configured by writing the correct Mode information to the Control Register, then the proper
count data must be written to the specific Counter Register.
The Counters on the 8254 are 16-bit devices. Since the interface to the 8254 is only 8-bits wide,
Count data is written to the Counter Register as two successive bytes. First the low byte is
written, then the high byte. The Control Register is 8-bits wide. Further information can be
obtained on the 8254 data sheet, available from Intel or Harris.
8.5 BADR4
The I/O Region defined by BADR4 contains the shared DAC data register and the DAC FIFO
clear register.
8.5.1 DAC Data Register
BADR4 + 0
DAC Data register. A Write-only register.
Page 30
Page 32

WRITE
0123456789101112131415
DA0DA1DA2DA3DA4DA5DA6DA7DA8DA9DA10DA11DA12DA13DA14DA15
MSB LSB
DA[15:0]
These bits represent the DAC data word. Format is dependent upon offset mode as described
below:
Bipolar Mode: Offset Binary Coding
0000 h = -FS
7FFFh = Mid-scale (0V)
FFFFh = +FS - 1LSB
Unipolar Mode: Straight Binary Coding
0000 h = -FS (0V)
7FFFh = Mid-scale (+FS/2)
FFFFh = +FS - 1LSB
Paced DAC operations require that the FIFO be loaded with the appropriate data. A REP
OUTSW instruction to this address will do this. It is important to note that the FIFO is the
shared data source between DAC0 and DAC1. Care must be taken to ensure that DAC0
data always precedes DAC1 data during simultaneous operations. Target DAC selection is
made via the HS[1:0] bits described earlier.
FIFO DATALOCATION #SELECTED DAC(S)HS0HS1
DAC010
DAC101
DAC0 & DAC111
0
1
2
3
|
0
1
2
3
|
0
1
2
3
|
NOTE: FIFO location #0 is the first value written to the Cleared DAC FIFO.
Page 31
N/AN/ANone00
DAC0
DAC0
DAC0
DAC0
|
DAC1
DAC1
DAC1
DAC1
|
DAC0
DAC1
DAC0
DAC1
|
Page 33

8.5.2 DAC FIFO Clear Register
BADR4 + 2
DAC FIFO Clear register. A Write-only register. A write to this address location clears
the DAC FIFO. Data is don't care. The DAC FIFO should be cleared before all new
DAC operations.
Page 32
Page 34

9.0 Electrical Specifications PCI-DAS1602/16
Typical for 25 DegC unless otherwise specified.
Analog input section
A/D converter type AD976ABN
Resolution 16 bits
Programmable ranges ±10V, ±5V, ±2.5V, ±1.25V, 0 - 10V, 0 - 5V, 0 - 2.5V, 0 - 1.25V
A/D pacing Programmable: internal counter or external source
Data transfer From 512 sample FIFO via REPINSW, int, software polled
Bust mode Programmable option at 5us samples intervals during burst
Polarity Unipolar/Bipolar SW selectable
Number of channels 8 differential or 16 single-ended, SW selectable
Interrupts INTA# - mapped to IRQn via PCI BIOS at boot-time
Interrupt enable Programmable
A/D conversion time 5µs
Throughput 200KHz min
Differential Linearity error (Bipolar) ±1 LSB
Integral Linearity error (Bipolar)
Differential Linearity error (Unipolar) ±1 LSB
Integral Linearity error (Unipolar)
Gain Error ±10V, 0-10V Ranges: 22.5ppm Max
No missing codes guaranteed 16 bits
Gain drift (A/D specs) ±20ppm/°C, all ranges
Zero drift (A/D specs) ±10ppm/°C, all ranges
1
2
±1.5 LSB
±1.5 LSB
±5V, 0-5V Ranges: 22.5ppm Max
±2.5V, 0-2.5V Ranges: 22.5ppm Max
±1.25,V 0-1.25V Ranges: 22.5ppm typical, 45ppm Max
Input leakage current (@25 Deg C) 200nA
Input impedance Min 10Meg Ohms
Absolute maximum input voltage ±15V
A/D Triggering Modes Digital:
SW configurable for Edge (triggered) or level-activated (gated).
Programmable polarity (rising/falling edge trigger, high/low gate).
Analog:
SW configurable for above/below reference, in/out window and
hysteresis.
Programmable polarity (rising/falling edge trigger, high/low gate).
Trigger levels set by DAC0 and/or DAC1.
Pre-trigger:
Unlimited pre- and post-trigger samples. Total # of samples must
be > 256. Compatible with both Digital and Analog trigger
options.
1
Integral linearity for 1.25V bipolar is specified at +/- 3LSB max
2
Integral linearity for 1.25V unipolar is specified at +/- 3LSB max
Page 33
Page 35

Analog Output:
Resolution 16 bits
Number of channels 2
D/A type AD669BR
Voltage Ranges ±10V, ±5V, 0-5V, 0-10V. Independently selectable between channels.
Offset error ±100uV max, all ranges (calibrated)
Gain error ±30.5ppm max (calibrated)
Differential nonlinearity ±1LSB max
Integral nonlinearity ±1LSB max
Monotonicity 16 bits at 25 DegC
D/A Gain drift ±15 ppm/°C max
D/A Bipolar offset drift ±5 ppm/°C max
D/A Unipolar offset drift ±3 ppm/°C max
Output Coupling DC
Amp Output Impedance 0.1 Ohms max
Data transfer From 512 sample FIFO via REPOUTSW or programmed I/O.
Throughput 100KHz, 2 channels simultaneous.
Settling time (20V step to .0008%) 13 µs max
Settling time (10V step to .0008%) 6µs typ
Slew Rate 10V Ranges: 6V/uS
D/A trigger modes SW or external gate.
Current Drive ±5 mA min
Output short-circuit duration 25 mA indefinite
Data interleaved for dual analog output mode.
5V Ranges: 3V/uS
Miscellaneous Double buffered input latches
Update DACs individually or simultaneously (SW selectable)
Power up and reset, all DAC's cleared to 0 volts
Digital Input / Output
Digital Type 8255 emulation
Output: 74LS244
Input: 74LS373
Configuration 2 banks of 8, 2 banks of 4, programmable by bank as input or
output
Number of channels 24 I/O
Output High 2.4 volts @ -15mA min
Output Low 0.5 volts @ 64 mA min
Input High 2.0 volts min, 7 volts absolute max
Input Low 0.8 volts max, -0.5 volts absolute min
Power-up / reset state Input mode (high impedance)
Interrupts INTA# - mapped to IRQn via PCI BIOS at boot-time
Interrupt enable Programmable
Interrupt sources External (rising TTL edge event), Residual counter, A/D End-of-
conversion, A/D End-of-channel-scan, A/D FIFO-not-empty, A/D
FIFO-half-full, D/A FIFO-not-empty, D/A FIFO-half-full
Page 34
Page 36

Counter section
Counter type 82C54
Configuration Two 82C54 devices. 3 down counters per 82C54, 16 bits each
82C54A: (Counters 1, 2, & 3)
Counter 0 - ADC residual sample counter.
Source: ADC Clock.
Gate: Programmable source.
Output: End-of-Acquisition interrupt.
Counter 1 - ADC Pacer Lower Divider
Source: 10 MHz oscillator
Gate: Tied to Counter 2 gate, programmable source.
Output: Chained to Counter 2 Clock.
Counter 2 - ADC Pacer Upper Divider
Source: Counter 1 Output.
Gate: Tied to Counter 1 gate, programmable source.
Output: ADC Pacer clock (if software selected), available at user
connector.
82C54B: (Counters 4, 5 &6)
Counter 0 - Pretrigger Mode
Source: ADC Clock.
Gate: External trigger
Output: End-of-Acquisition interrupt.
Counter 0 - Non-Pretrigger Mode: User counter 4
Source: User input at 100pin connector or internal 10MHz
(software selectable)
Gate: User input at 100pin connector.
Output: Available at 100pin connector.
Counter 1 - DAC Pacer Lower Divider
Source: 10 MHz oscillator
Gate: Tied to Counter 2 gate, programmable source.
Output: Chained to Counter 2 Clock.
Counter 2 - DAC Pacer Upper Divider
Source: Counter 1 Output.
Gate: Tied to Counter 1 gate, programmable source.
Output: DAC Pacer clock, available at user connector.
Clock input frequency 10Mhz max
High pulse width (clock input) 30ns min High, 50ns min Low
Gate width high 50ns min (high or low)
Input low voltage 0.8V max
Input high voltage 2.0V min
Output low voltage 0.4V max
Output high voltage 3.0V min
Environmental
Operating temperature range 0 to 70°C
Storage temperature range -40 to 100°C
Humidity 0 to 90% non-condensing
Power consumption
Icc: Operating (A/D converting to FIFO) 2.0A typical, 2.1A max
Page 35
Page 37

For Your Notes
Page 36
Page 38

EC Declaration of Conformity
High speed analog I/O board for the PCI busPCI-DAS1602/16
DescriptionPart Number
to which this declaration relates, meets the essential requirements, is in conformity with, and CE marking has been
applied according to the relevant EC Directives listed below using the relevant section of the following EC standards
and other normative documents:
EU EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
EU 55022 Class B
technology equipment.
EN 50082-1
IEC 801-2
IEC 801-3
equipment.
IEC 801-4
Carl Haapaoja, Director of Quality Assurance
: EC generic immunity requirements.
: Electrostatic discharge requirements for industrial process measurement and control equipment.
: Radiated electromagnetic field requirements for industrial process measurements and control
: Electrically fast transients for industrial process measurement and control equipment.
: Limits and methods of measurements of radio interference characteristics of information
: Essential requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility.
Page 37
Page 39

 Loading...
Loading...