
Contents
QUICK START FOR WINDOWS 95...........................................I
CHANGING SETTINGS FROM THE DEFAULT....................................II
INTRODUCTION.....................................................................1
OVERVIEW..................................................................................1
WHAT’S INCLUDED .....................................................................1
CARD SETUP .........................................................................2
PHOENIX TECHNOLOGIES PHOENIXCARD MANAGER PLUS™.......3
PhoenixCARD Manager Utility Programs...............................3
SYSTEMSOFT CARDSOFT™ PCMCIA .........................................4
CardSoft™ PCMCIA Utility ...................................................4
INSTALLATION......................................................................5
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION....................................................6
MODEM CONTROL SIGNAL CONSIDERATIONS...............................6
CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENTS...................................................7
RS-232....................................................................................7
RS-422/485/530......................................................................7
SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................8
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS...............................................8
POWER CONSUMPTION ................................................................8
MEAN TIME BETWEEN FAILURES (MTBF)....................................8
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS ...............................................................8
APPENDIX A - TROUBLESHOOTING ......................................9
APPENDIX B - HOW TO GET ASSISTANCE..........................12
APPENDIX C - SEAPC AND SSENABLE SOFTWARE ............13
SEAPC .....................................................................................13
SeaPC System Requirements................................................. 13
Installation of SeaPC.............................................................14
Executing the Driver............................................................. 14
SSENABLE................................................................................16
APPENDIX D - ELECTRICAL INTERFACE ............................17
RS-232.....................................................................................17
RS-422.....................................................................................17
RS-485.....................................................................................18
RS-530.....................................................................................18

APPENDIX D - COMPLIANCE NOTICES ............................... 19
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION STATEMENT..............19
CANADIAN RADIO INTERFERENCE REGULATIONS........................20
EMC DIRECTIVE STATEMENT....................................................20
WARRANTY......................................................................... 21
© 1997j Omega Engineering, Incorporated. All rights reserved.

Quick Start for Windows 95
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page i
Quick Start for Windows 95
Installing Asynchronous Serial ports under Windows 95 is not as arduous
a task as it may seem. If the steps are followed in the correct order, the
installation is quite easy. One of the most important issues is to make sure
that the Windows 95 Card and Socket services have been installed
properly. These services must be installed before any PCMCIA adapters
can be configured. After that the card almost installs itself.
With the first insertion of the PC Card, Win 95 will pop up a window:
‘Windows has found new Hardware and is installing software for it’
Then the next screen display:
Select ‘Driver from disk provided by hardware manufacturer’

Quick Start for Windows 95
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page ii
The next step is to place the Serial Utility Diskette (shipped with your
adapter) into a floppy drive (in the example below drive A:.)
Select the browse key and locate the \Windows\95\Inf sub-directory.
Click the “OK” command button and your installation is complete.
Changing settings from the Default
Now that the OMG-P232/P422 has been added to the system using the
previous steps, the resources (i.e. I/O address and IRQ) can be changed
using the following steps:
1.) Select the Control Panel folder and select the System icon.
2.) Select the Device Manager tab and click on the ‘+’ symbol next to the
Ports (COM & LPT) selection. Choose the port that corresponds to
the OMG-P232/P422
3.) Click the Properties button and then select the Resources tab.
4.) Select Basic Configuration 8, this will allow you to customize both
the IRQ and I/O settings.
5.) If the message "This resource setting cannot be modified." is
displayed, make sure you have selected a Base Configuration which
allows this resource to be changed and that the ‘Use Automatic
Settings’ checkbox is not selected.
6.) When the ‘OK’ button is pressed Windows 95 will automatically
update your settings. It will not be necessary to re-boot.
Refer to the Card Setup section for tips on installing the OMG-
P232/P422 with DOS Card and Socket Services.

Introduction
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page 1
Introduction
Overview
Congratulations! You have now entered the world of mobile
communications via the Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Serial
Interface.
In the last few years, the portable and notebook market has grown by leaps
and bounds. Most early laptops and notebooks handled I/O expansion
through proprietary expansion slots. These slots provided limited
expansion for specific peripherals such as modems and FAX peripherals.
Mass storage peripherals were factory installed and could not be easily
changed. Interconnectivity through local area networks offered limited
performance through slow parallel port network interfaces.
During this time period two standards organizations, JEIDA and
PCMCIA, were working on the standardization of memory IC cards.
These cards were designed as strictly non-volatile silicon storage. JEIDA
was the first to propose the 68 pin connector standard for memory cards.
In 1989, PCMCIA adopted the JEIDA 68 pin standard and worked with
JEIDA on further developments.
As the notebook market grew, the need for a standard I/O bus was seen.
The PCMCIA groups saw an opportunity to meet this need with an
expanded version of the 68 pin interface. Further development occurred
and within one year, release 2.0 of the standard was completed. Release
2.0 was a major update to Release 1.0 and included full hardware support
for I/O devices. Release 2.0 coincided with JEIDA’s 4.1 release and is
identical.
The OMG-P232/P422 continues the Omega Engineering tradition of an
easy to use, highly reliable, and technically advanced serial I/O solution.
What’s Included
The OMG-P232/P422 is shipped with the following items. If any of
these items are missing or damaged, contact the supplier.
• OMG-P232/P422 PCMCIA Serial Interface Adapter
• DB-25 cable assembly
• DB25 to DB9 Adapter (P/N 3601 only)
• Impact Resistant Carrying Case (Jewel Case)
• 3.5″ Serial Utility Diskette
• User Manual

Introduction
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page 2

Card Setup
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page 3
Card Setup
Card and Socket Services must be loaded on the system prior to installing
the OMG-P232/P422 card. Card and Socket Services are typically
supplied by the PCMCIA slot provider (i.e. the computer manufacturer or
the PC adapter manufacturer).
Socket Services are the lowest level of the PCMCIA Software hierarchy.
Socket Services provide a standard interface to the higher level drivers
and isolate the socket controller’s specific hardware details. Socket
Services provide the ‘BIOS’ interface to the socket controller hardware.
Socket Services are typically hidden under Card Services and are rarely
directly accessible by application software.
Card Services provide the interface to application software and drivers.
Card Services are responsible for allocating card resources and ensuring
that card resources do not interfere with other existing system resources.
Card Services are typically implemented as a driver and loaded via
CONFIG.SYS during boot up. Almost all PCMCIA type cards require
some sort of software driver. In the case of the OMG-P232/P422, the
generic Card Services driver supplied with the computer system should
provide adequate support for most applications. If the generic Card
Services are not sufficient, an ‘Enabler’ is provided with the OMG-
P232/P422 that will address unique interfacing requirements (i.e. non
standard I/O addressing, different IRQ selection etc.). Please refer to
Appendix C for information on the SEAPC enabler and the diagnostic
tool SSEnable.
The following pages present a few examples of main stream Card and
Socket Services and their implementation (including Windows 95).
Card Setup
Omega Engineering OMG-P232/P422 Page 4
Phoenix Technologies PhoenixCARD Manager Plus™
The PhoenixCARD Manager is shipped with several PC card compatible
Notebook and Laptop computers, as well as IBM PCDOS 6.1
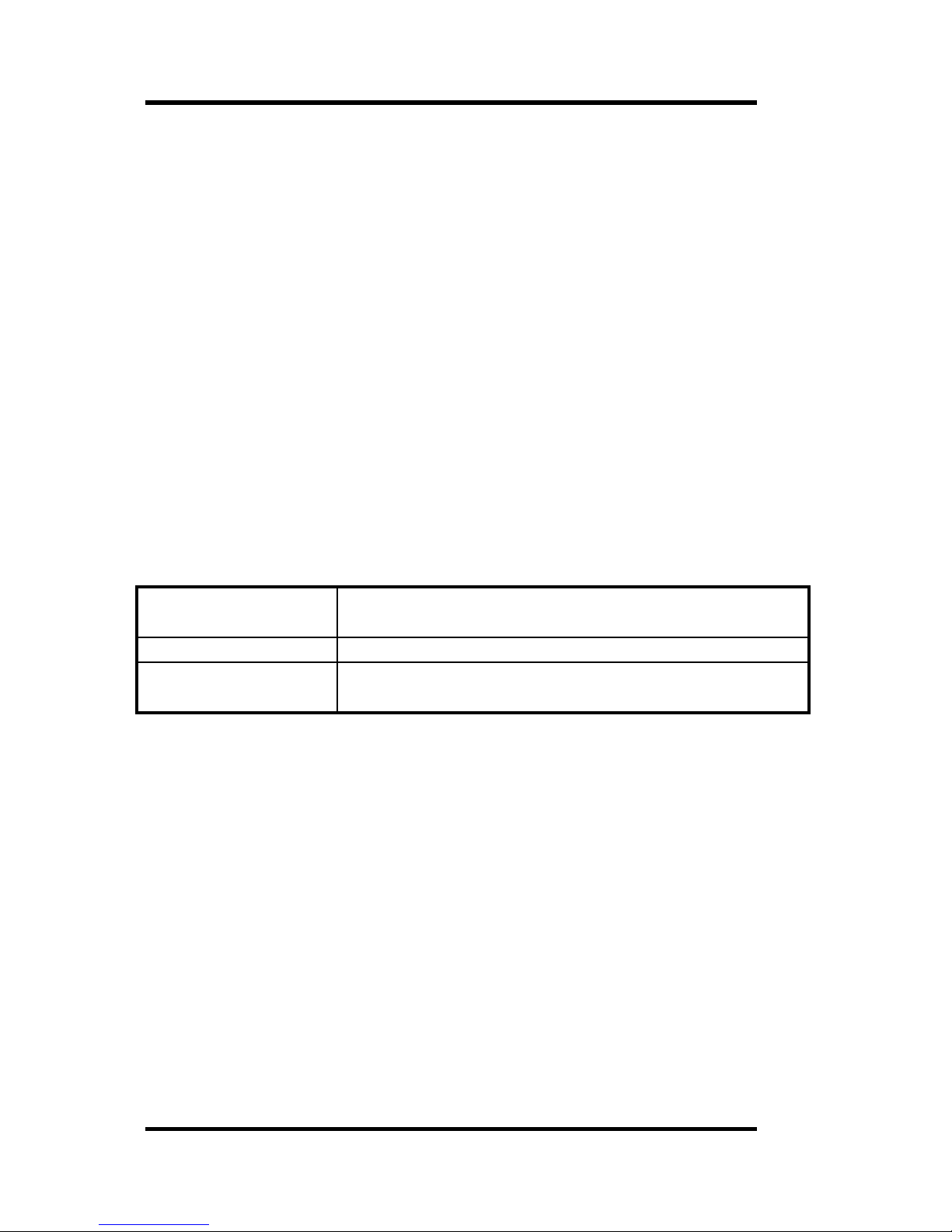
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS\PCMSS.EXE
Socket Services Driver
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS\PCMCS.EXE /WAIT=20 /ADDR=C8 /IRQ=10 /FLASH
Card Services
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS\PCMMTD.EXE
Memory Technology Driver
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS\PCMSCD.EXE /BEEP /COM=4 /RS=4
Phoenix Super Client Driver. Generic enabler to configure I/O Cards
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS\PCMATA.SYS /O
ATA Fixed Disk and SRAM cards in a DOS FAT structured format
PhoenixCARD Manager Utility Programs
PCMINFO.EXE Provides information about each PCMCIA socket and
any cards that are inserted
WPCMINFO.CPL Windows version of PCMINFO
PCMVCD.386 Windows Device Driver. Provides support for FAX
and Modem Cards
 Loading...
Loading...