OKI MSM7602-001GS-K, MSM7602-011GS-2K Datasheet

E2U0037-28-82
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Aug. 1998
Previous version: Nov. 1996
MSM7602
Echo Canceler
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM7602 is an improved version of the MSM7520 with the same basic configuration. The
MSM7602 uses a 19.2 MHz clock frequency to meet PHS, the 3 V power supply (2.7 V to 5.5 V),
and compact packaging. Also, this device adds the howling detecter control pins and main clook
output pins. (See the Appendix)
The MSM7602 is a low-power CMOS IC device for canceling echo (in an acoustic system or
telephone line) generated in a speech path.
Echo is canceled, in digital signal processing, by estimating the echo path and generating a
pseudo echo signal.
When used as an acoustic echo canceler, the device cancels the acoustic echo between the loud
speaker and the microphone which occurs during hands free communication such as with a
cellular phone or a conference system phone.
When used as a line echo canceler, the device cancels the line echo caused by impedance
mismatching in a hybrid.
In addition, the MSM7602 makes possible a quality conversation by controlling the noise level
and preventing howling with howling detector, double talk detector, attenuation function, and
a gain control function. The devise also controls the low level noise with a center clipping
function.
Further, the MSM7602 I/O interface supports m-law PCM . The use of a single chip CODEC, such
as the MSM7566/7704 (3 V) or MSM7543/7533 (5 V), allows an economic and efficient echo
canceler configuration.
FEATURES
• Handles both acoustic echoes and telephone line echoes.
• Cancelable echo delay time:
MSM7602-001 ................. For a single chip: 23 ms (max.)
MSM7602-011 ................. For a cascade connection (can also be used for a single chip)
Master chip: 23 ms (max.)
Slave chip: 31 ms (max.)
Cancelable up to 209 ms (1 master plus 6 slaves)
For a single chip: 23 ms (max.)
• Echo attenuation : 30 dB (typ.)
• Clock frequency : 19.2 MHz
External input and internal oscillator circuit are provided.
• Power supply voltage : 2.7 V to 5.5 V
• Package options:
28-pin plastic SSOP (SSOP28-P-485-0.65-K) (Product name : MSM7602-001GS-K)
56-pin plastic QFP (QFP56-P-910-0.65-2K) (Product name : MSM7602-011GS-2K)
1/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
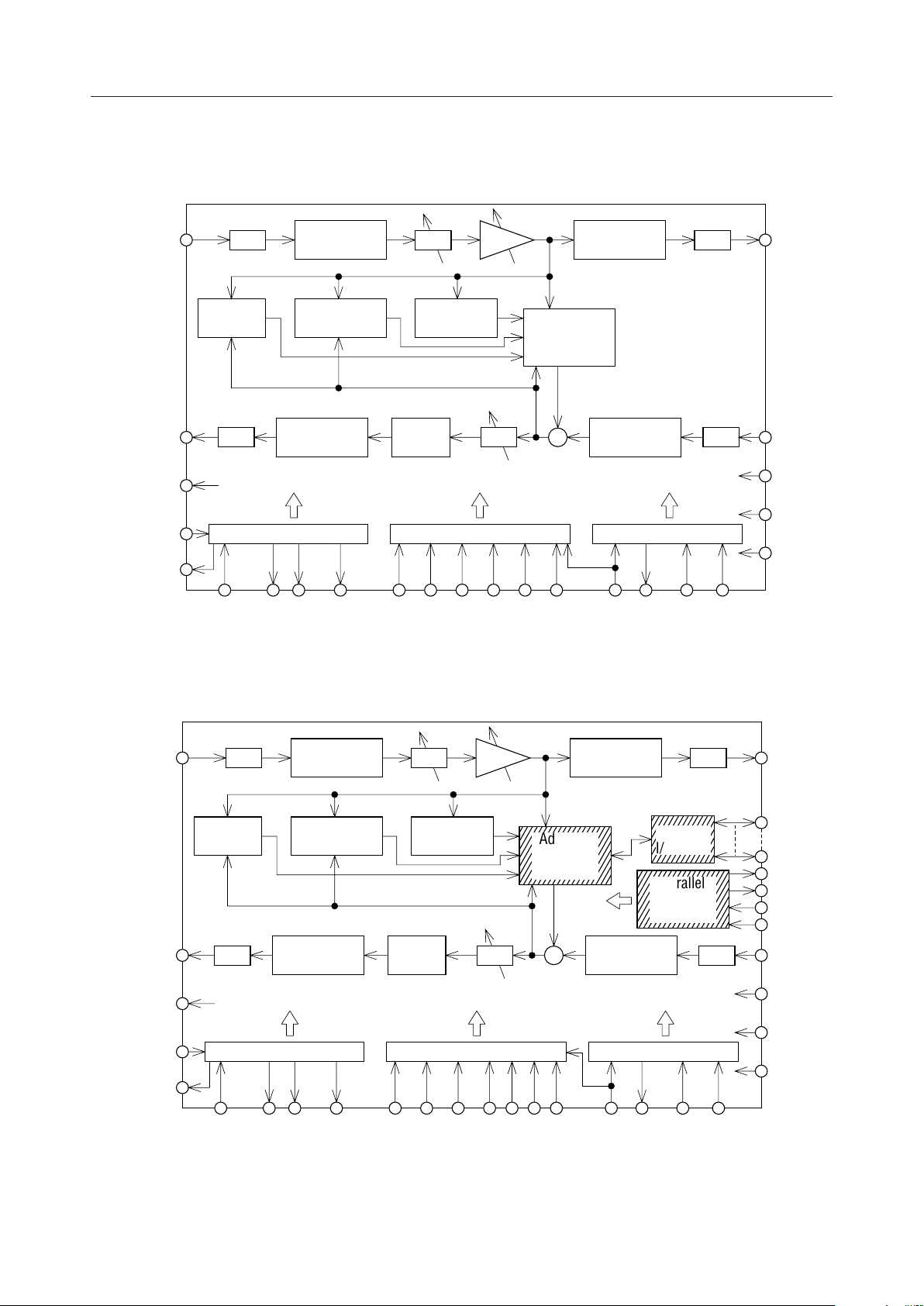
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MSM7602-001 (Single chip only)
RIN ROUT
S/P ATT Gain
Howling
Detector
Non–linear/
Linear
Double Talk
Detector
Power
Calculator
Linear/
Non–linear
Adaptive
FIR Filter
(AFF)
P/S
–
+
SOUT SIN
WDT
PWDWN
MCKO
P/S
*
Linear/
Non–linear
Clock Generator Mode Selector I/O Controller
Center
Clip
ATT
+
HD
Non–linear/
Linear
INT IRLD SCK SYNCNLP HCL ADP ATT GCSYNCOSCKOX2X1/CLKIN
S/P
RST
V
DD
V
SS
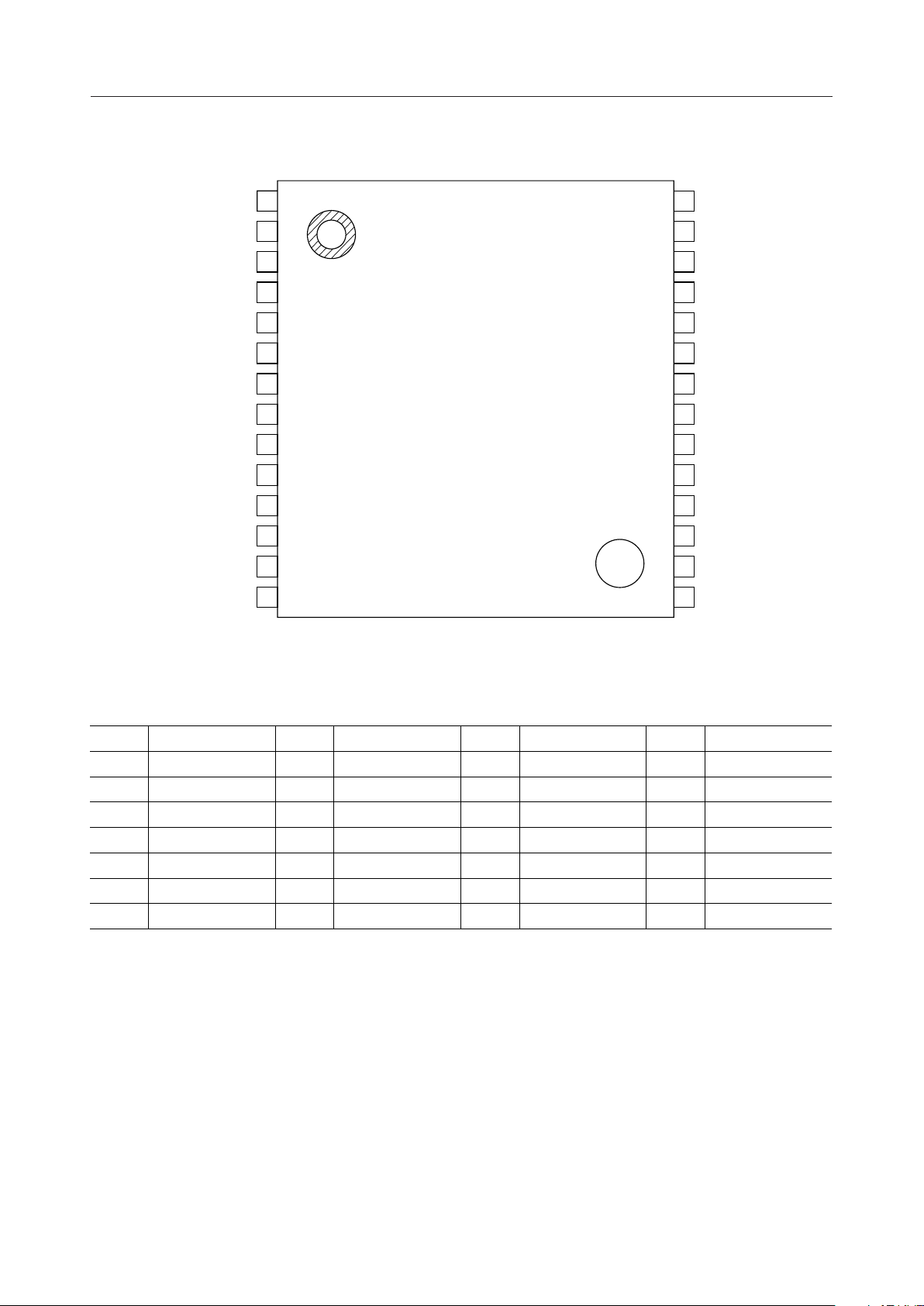
MSM7602-011 (Cascade connection or single chip)
RIN ROUT
SOUT SIN
WDT
* PWDWN
MCKO
* If the MSM7602-011 is used in the slave mode, only the diagonally hatched blocks and
the pins marked with * are used.
S/P ATT Gain
Howling
Detector
P/S
*
Clock Generator Mode Selector I/O Controller
*
Non–linear/
Linear
Double Talk
Detector
Linear/
Non–linear
Power
Calculator
Center
Clip
ATT
Adaptive
FIR Filter
(AFF)
–
+
+
MS
HD
*
Linear/
Non–linear
Non–linear/
Linear
INT *IRLD SCK SYNCNLP HCL *ADP ATT GCSYNCOSCKOX2X1/CLKIN
P/S
Parallel
I/O Port
Parallel
I/O
Controller
S/P
PD15
–
PD 0
OF1 *
OF2 *
SF1 *
SF2 *
RST *
VDD *
VSS *
*
*
2/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
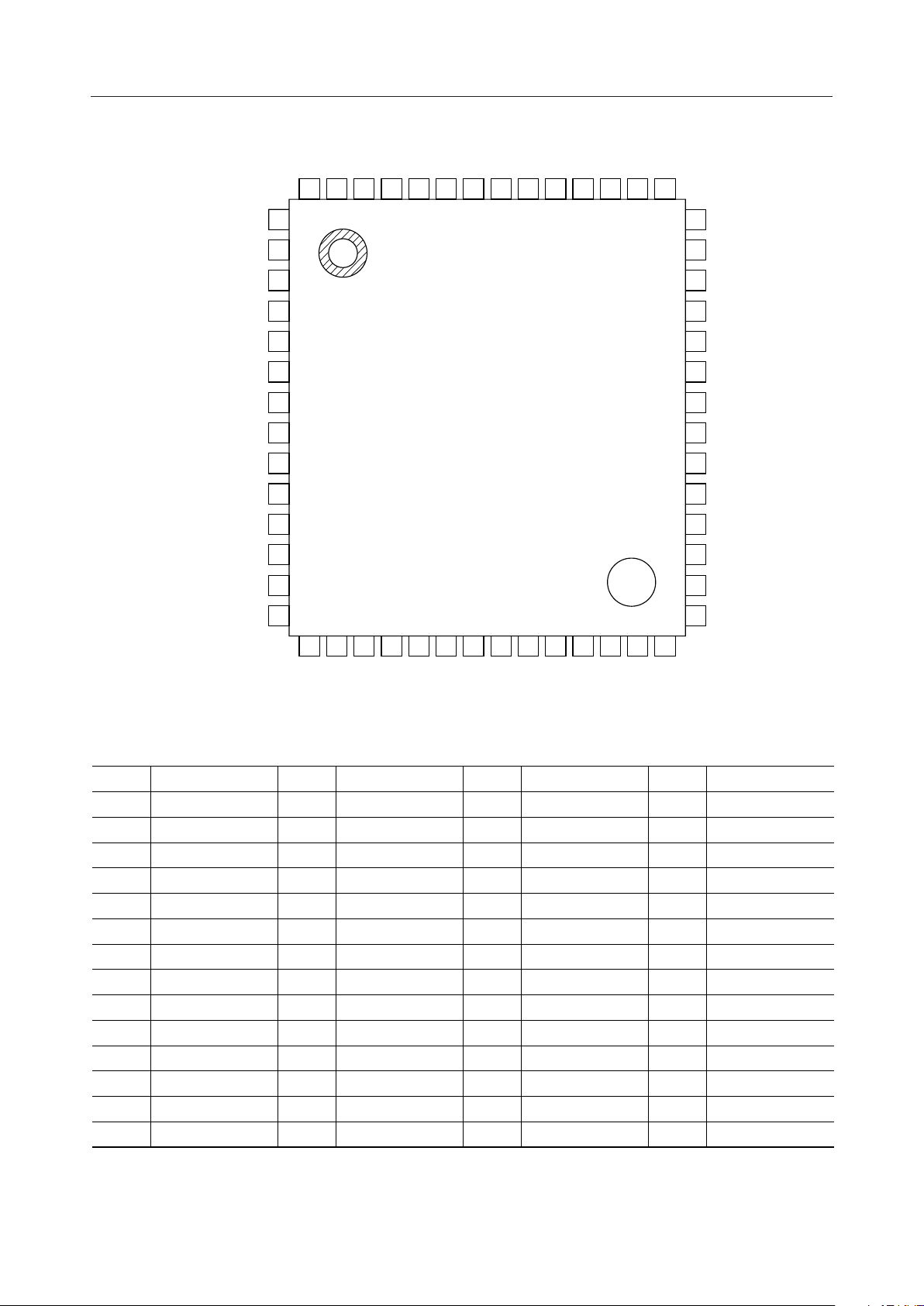
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
28-Pin Plastic SSOP
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Symbol
NLP
HCL
ADP
V
DD
ATT
INT
IRLD
Pin
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Symbol
SIN
RIN
SCK
SYNC
SOUT
ROUT
V
SS
Pin
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Symbol
V
SS
HD
X1/CLKIN
X2
V
DD
PWDWN
V
SS
Pin
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
Symbol
SYNCO
SCKO
RST
WDT
GC
V
DD
MCKO
3/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
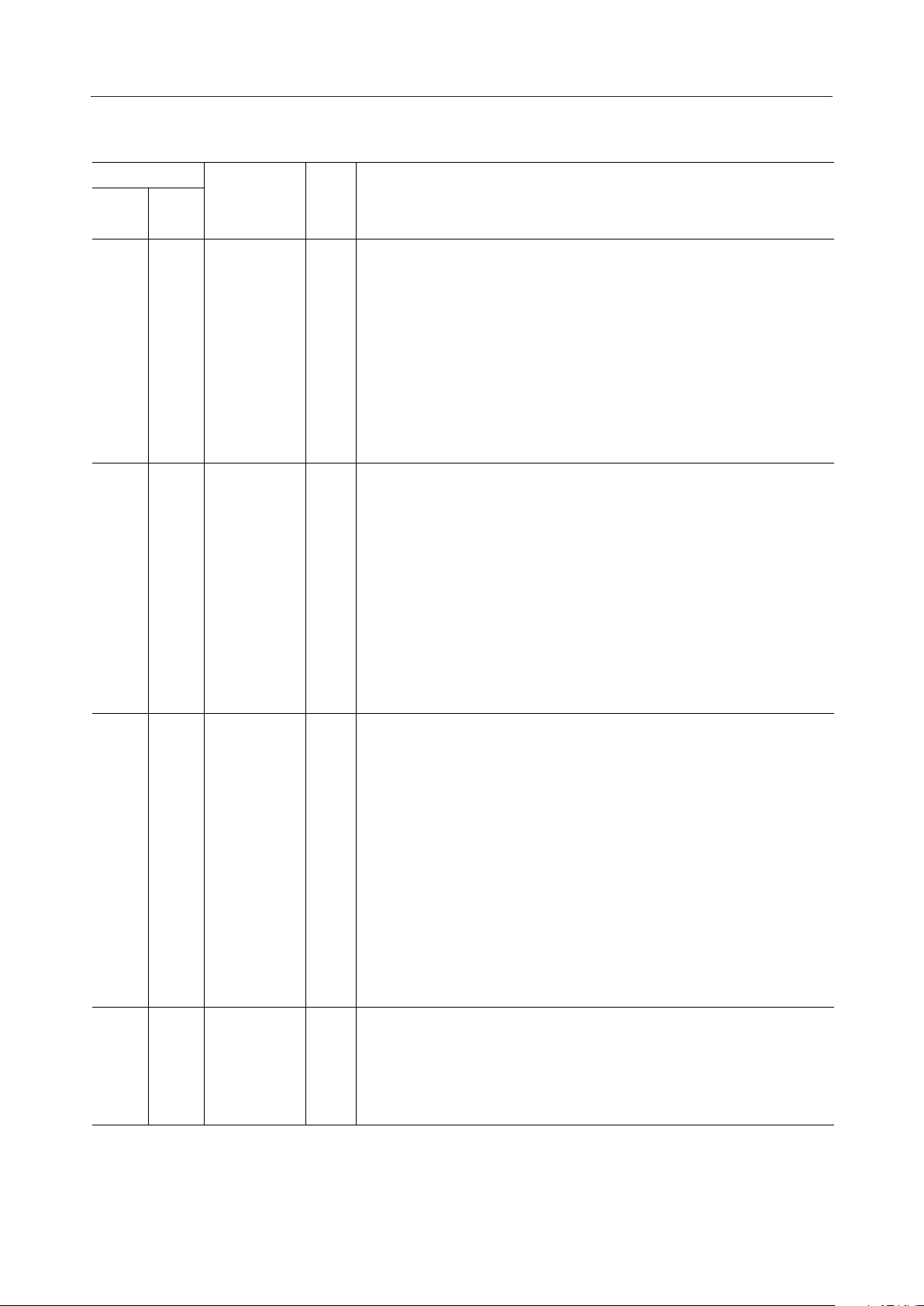
56 4355 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 2816 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
56-Pin Plastic QFP
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 22 PD6 36
9 23 PD7 37
11 25 PD9 39
12 26 PD10 40 54 V
14 28 HD 42 V
Symbol
NLP
HCL
ADP
MS
ATT
INT
IRLD
Pin
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Symbol
PD0
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
PD5
V
SS
Pin
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
SIN
RIN
SCK10 24 PD8 38
SYNC
SOUT
ROUT13 27 PD11 41 V
V
SS
Symbol
PD12
PD13
X1/CLKIN
X2
V
DD
PWDWN
V
SS
SYNCO
SCKO
RST
WDT
GC
DD
DD
Pin
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50 *
51 V
52 SF1
53 OF2
55 V
56 *
*: No connect pin
Symbol
*
PD14
PD15
MCKO
SF2
OF1
V
SS
SS
DD
DD
4/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
PIN DESCRIPTIONS (1/5)
Pin
28-pin
SSOP
56-pin
QFP
1 1 NLP I
2 2 HCL I
3 3 ADP I
— 4 MS I
Symbol Type Description
Control pin for the center clipping function.
This pin forces the SOUT output to a minimum value when the SOUT
signal is below –54 dBm0. Effective for reducing low-level noise.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"H": Center clip ON
"L": Center clip OFF
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "L"
This input signal is loaded in synchronization with the falling edge of the
INT signal or the rising edge of the RST signal.
Through mode control.
When this pin is in the through mode,
RIN and SIN data is output to ROUT and SOUT. At the same time, the
coefficient of the adaptive FIR filter is cleared.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"H": Through mode
"L": Normal mode (echo canceler operates)
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Same as master
This input signal is loaded in synchronization with the falling edge of the
INT signal or the rising edge of the RST signal.
AFF coefficient control.
This pin stops updating of the adaptive FIR filter (AFF) coefficient and sets
the coefficient to a fixed value, when this pin is configured to be the
coefficient fix mode.
This pin is used when holding the AFF coefficient which has been once
converged.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"H": Coefficient fix mode
"L": Normal mode (coefficient update)
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "L"
This input signal is loaded in synchronization with the falling edge of the
INT signal or the rising edge of the RST signal.
Select signal.
This pin selects between the master chip and slave chip when
used in a cascade connection.
"L": Single chip or master chip
"H": Slave chip
5/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
(2/5)
Pin
28-pin
SSOP
56-pin
QFP
5 5 ATT I
Symbol Type Description
Control for the ATT function.
This pin prevents howling by attenuators (ATT) for the RIN input and SOUT
output.
If there is input only to RIN, the ATT for the SOUT output is activated.
If there is no input to SIN, or if there is input to both SIN and RIN, the ATT
for the RIN input is activated.
Either the ATT for the RIN output or the ATT for the SOUT is always
activated in all cases, and the attenuation of ATT is 6 dB.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"H": ATT OFF
"L": ATT ON
"L" is recommended if performing echo cancellation.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "L"
This input signal is loaded in synchronization with the falling edge of the
INT signal or the rising edge of the RST signal.
66 INT I
77 IRLD O
8 8 SIN I
9 9 RIN I
Interrupt signal which starts 1 cycle (8 kHz) of the signal processing.
Signal processing starts when "H"-to-"L" transition is detected.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect the IRLD pin.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect the IRLD pin of the master chip.
INT input is invalid for 100 ms after reset due to initialization.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
Load detection signal output when the SIN and RIN serial input data is
loaded in the internal registers.
• Single Chip
Connect to the INT pin.
• Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect to the INT pin of the master chip and all the slave chips.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection Leave open.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
Transmit serial data.
Input the PCM signal synchronized to SYNC and SCK. Data is read in at
the falling edge of SCK.
Receive serial data.
Input the PCM signal synchronized to SYNC and SCK. Data is read at the
falling edge of SCK.
10 10 SCK I
Clock input for transmit/receive serial data.
This pin uses the external SCK or the SCKO.
Input the PCM CODEC transmit/receive clock (64 to 2048 kHz).
6/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
(3/5)
Pin
28-pin
SSOP
56-pin
QFP
11 11 SYNC I
Symbol Type Description
Sync signal for transmit/receive serial data.
This pin uses the external SYNC or SYNCO.
Input the PCM CODEC transmit/receive sync signal (8 kHz).
12 12 SOUT O
13 13 ROUT O
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
16 28 HD I
17 31 X1/CLKIN I
15
—
20
22
—
27
29
30
44
45
PD0
—
PD5
PD6
—
PD11
PD12
PD13
PD14
PD15
I/O
Transmit serial data.
Outputs the PCM signal synchronized to SYNC and SCK.
This pin is in a high impedance state during no data output.
Receive serial data.
Outputs the PCM signal synchronized to SYNC and SCK.
This pin is in a high impedance state during no data output.
This is the bidirectional bus pin for parallel data transfer between the
master chip and slave chip when used in a cascade connection.
The PD15 pin corresponds to MSB.
This pin is in a high impedance state during no data
output. Data is loaded in at the falling edge of SFx.
Controls the howling detect function.
generated during hand-free talking for acoustic system.
This function is used to cancel acoustic echoes.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"L": Howling detector ON
"H": Howling detector OFF
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "L"
External input for the basic clock (17.5 to 20 MHz) or for the crystal
oscillator.
When the internal sync signal (SYNCO, SCKO) is used, input the basic
clock of 19.2 MHz.
This pin detets and cancels a howling
18 32 X2 O
Crystal oscillator output.
Used to configure the oscilation circuit.
Refer to the internal clock generator circuit example.
When inputting the basic clock externally, insert a 5 pF capacitor with
excellent high frequency characteristics between X2 and GND.
7/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
(4/5)
Pin
28-pin
SSOP
56-pin
QFP
20 34 PWDWN I
Symbol Type Description
Power-down mode control when powered down.
"L": Power-down mode
"H": Normal operation mode
During power-down mode, all input pins are disabled and output pins are
in the following states :
High impedance : SOUT, ROUT, PD0 to 15
"L": SYNCO, SCKO, MCKO
"H": OF1, OF2, X2
Holds the last state : WDT, IRLD
Reset after the power-down mode is released.
22 36 SYNCO O
23 37 SCKO O
24 38 RST I
25 39 WDT O
26 40 GC I
8 kHz sync signal for the PCM CODEC.
Connect to the SYNC pin and the PCM CODEC transmit/receive sync pin.
Leave it open if using an external SYNC.
Transmit clock signal (256 kHz) for the PCM CODEC.
Connect to the SCK pin and the PCM CODEC transmit/receive clock pin.
Leave it open if using an external SCK.
Reset signal.
"L": Reset mode
"H": Normal operation mode
Due to initialization, input signals are disabled for 100 ms after reset
(after RST is returned from L to H).
Input the basic clock during the reset.
Output pins during the reset are in the following states :
High impedance: SOUT, ROUT, PD0 to 15
"L": WDT
"H": OF1, OF2
Not affected: X2, SYNCO, SCKO, IRLD, MCKO
Test program end signal.
This signal is output when the one cycle (8kHz) of processing is completed.
Leave it open.
Input signal by which the gain controller for the RIN input is
controlled and the RIN input level is controlled and howling is
prevented.
The gain controller adjusts the RIN input level when it is –20 dBm0 or
above. RIN input levels from –20 to –11.5 dBm0 will be suppressed to
–20 dBm0 in the attenuation range from 0 to 8.5 dB.
RIN input levels above –11.5 dBm0 will always be attenuated by 8.5 dB.
• Single Chip or Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
"H": Gain control ON
"L": Gain control OFF
"H" is recommended for echo cancellation.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "L"
This pin is loaded in synchronization with the falling edge of the INT signal
or the rising edge of RST.
8/29
¡ Semiconductor MSM7602
(5/5)
Pin
28-pin
SSOP
56-pin
QFP
Symbol Type Description
28 46 MCKO O
—47 SF2 I
—48 OF1 O
—52 SF1 I
Basic clock (19.2 MHz).
Parallel data transfer flag.
• Single Chip
Fixed at "H"
• Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Fixed at "H"
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect OF2 of the master chip to the 1st stage slave chip.
Connect OF1 of the previous stage slave chip to the 2nd and later
stage slave chips.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
Parallel data transfer flag.
• Single Chip
Leave open.
• Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect to the SF1 of all slaves.
• Slave chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect to the SF2 of the next stage slave chip.
Connect the last stage slave chip to the SF1 of the master chip.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
Parallel data transfer flag.
• Single Chip
Connect OF2.
• Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect OF1 of the last stage slave chip.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect OF1 of master chip for all slave chips.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
—53 OF2 O
Parallel data output flag.
• Single Chip
Connect to SF1.
• Master Chip in a Cascade Connection
Connect to SF2 of the 1st stage slave chip.
• Slave Chip in a Cascade Connection
Leave open.
Refer to the control pin connection example.
9/29
 Loading...
Loading...