OKI MSM7580GS-K Datasheet

E2U0031-39-61
¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Jun. 1999
Previous version: Aug. 1998
MSM7580
ITU-T G.721 ADPCM TRANSCODER
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM7580 is an ADPCM transcoder which is used by the new digital cordless system. It
converts 64 kbps voice PCM serial data to 32 kbps ITU-T G.721 ADPCM serial data, and vice
versa.
This device consists of two systems with full-duplex voice data channels and a data-through
mode.
The MSM7580 provides cost effective solutions for digital cordless office telephone systems
which are incorporated into PABXs and for the public base stations which are connected to the
central office through digital PSTNs.
FEATURES
• Conforms to ITU-T G.721
• Built-in Full-duplex Transcoder with Two Data channels
• PCM companding Law: A-law/µ-law selectable
• Synchronized Operation between coder and decoder, and between two channels.
• Serial PCM Data Transmission Speed: 64 kbps to 2048 kbps
• Serial ADPCM Data Transmission Speed: 32 kbps to 2048 kbps
• Hardware Reset – ITU-T G.721 Optional Reset – for each channel
• Power Down Control for each channel
• Decoder (ADPCM Æ PCM ) MUTE Mode and PAD Mode for each channel
• ADPCM Data-through Mode
• Capable of time slot conversion
• Special ADPCM Input Data Code (”0000”) Detector for each channel
• Master Clock Signal : Not necessary
• Power supply voltage/Consumption current :
+5 V ±10%, 2.5 mA/channel
• Package :
28-pin plastic SOP (SOP28-P-430-1.27-K) (Product name : MSM7580GS-K)
1/17
2/17
¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
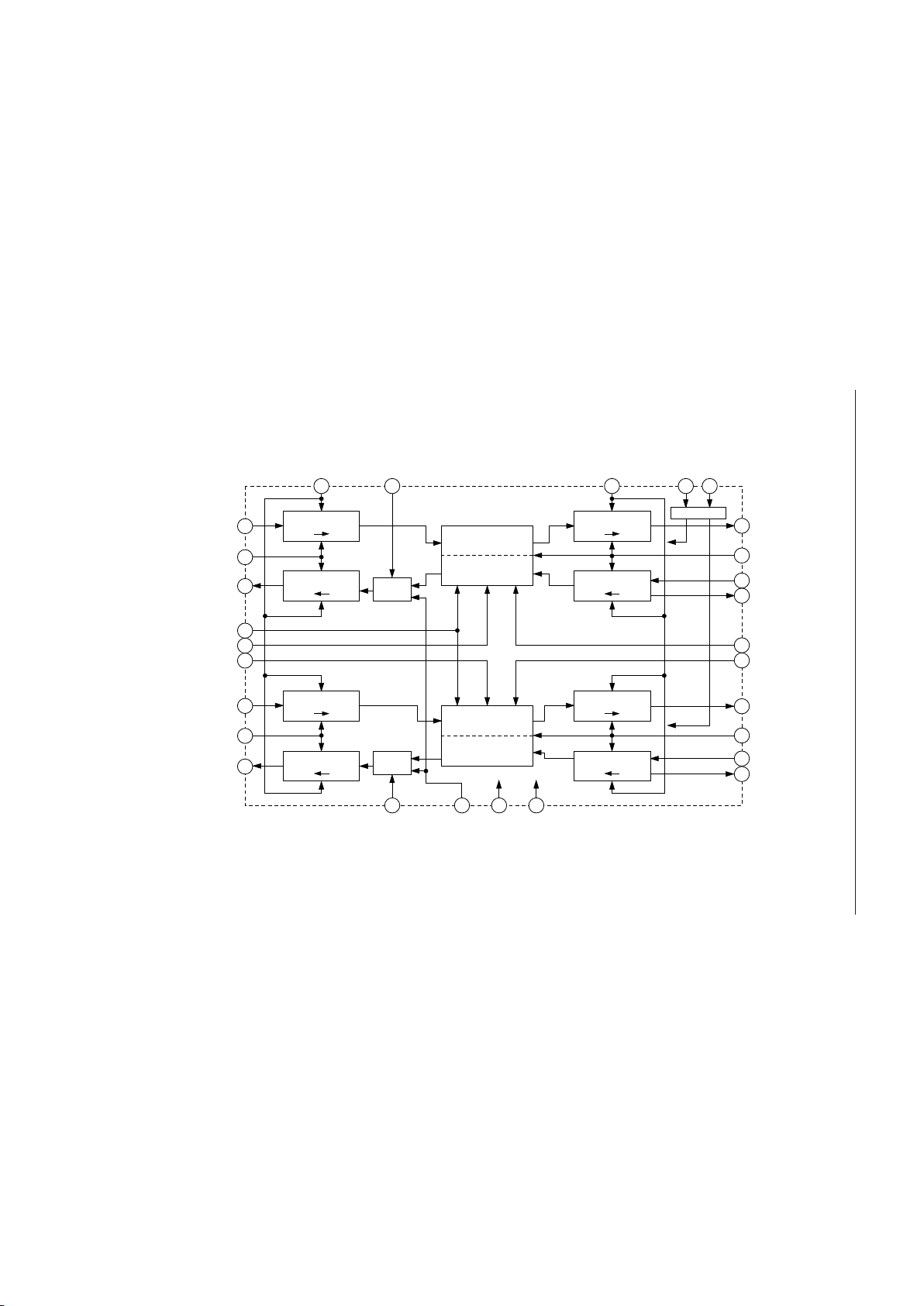
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SIP1
SYNCP1
SOP1
LAW
THR1
THR2
SIP2
SYNCP2
SOP2
SIA2
SYNCA2
SOA2
DET2
RES2
RES1
DET1
SIA1
SYNCA1
SOA1
BCLKP MUTE1 BCLKA PDN1 PDN2
MUTE2 PAD/
MUTE
VDDGND
CODER
P S
DECODER
P S
DECODER
P S
CODER
P S
CODER
DECODER
CODER
DECODER
CODER
S P
DECODER
S P
DECODER
S P
CODER
S P
MUTE
/
PAD
+5 V 0 V
MUTE
/
PAD
POWER DOWN
¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
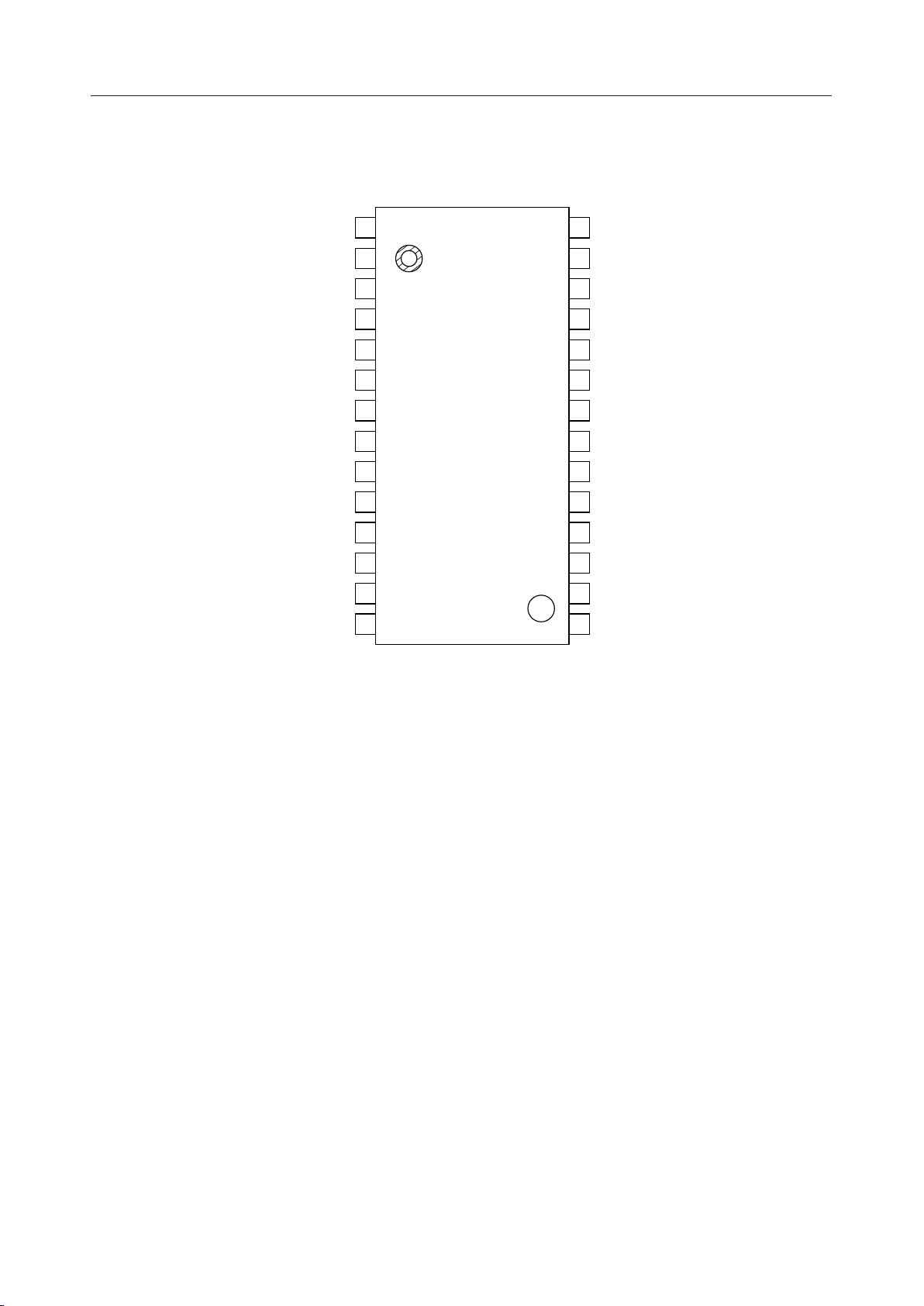
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
SIP2
SOP2
THR2
MUTE2
SYNCP2
PAD/MUTE
BCLKP
GND
LAW
SYNCP1
MUTE1
THR1
SOP1
SIP1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28-Pin Plastic SOP
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
SOA2
SIA2
SYNCA2
RES2
DET2
PDN2
V
DD
BCLKA
PDN1
DET1
RES1
SYNCA1
SIA1
SOA1
3/17

¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
PIN AND FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
GND
Ground, 0 V.
SIP1, SOP1
PCM serial data input (SIP1) and output (SOP1) for Channel 1.
SOP1 is an open-drain output, which goes into a high impedance state after a continuous 8-bit
serial data output.
SIP2, SOP2
PCM serial data input (SIP2) and output (SOP2) for Channel 2.
SOP2 is an open-drain output, which goes into a high impedance state after a continuous 8-bit
serial data output.
PAD/ MUTE
Control input for the selection of PAD or MUTE mode.
When digital "1" is input, the PAD mode is selected and when digital "0" is input, the MUTE mode
is selected.
THR1, THR2
Control pins for the data through modes.
THR1 and THR2 are for Channel 1 and Channel 2, respectively. The data-through mode is
selected when digital “1” is applied to THR1 and THR2. In this mode, 8-bit serial input data
applied to SIA1 and SIA2 (ADPCM data input) is passed to the PCM serial data output pins,
SOP1 and SOP2, without any data modification. SOP1 and SOP2 go to the high impedance state
after the output of 8-bit data has been applied to SIA1 and SIA2.
Conversely 8-bit serial input data applied to SIP1 and SIP2 (PCM data input) is passed to
ADPCM serial data output pins, SOA1 and SOA2, without any data modification.
SOA1 and SOA2 go to the high impedance state after the output of 8-bit data has been applied
to SIP1 and SIP2.
Since ADPCM and PCM data interfaces have the mutually independent signal input pins for
synchronizing signals the time slots for data input and output can be exchanged between them.
Some timing at which data may be deleted or duplicated as described in "Notes on Usage" should
not be used.
MUTE1, MUTE2
Setting a digital "1"at these pins sets the PCM output to the idle pattern state regardless of the
ADPCM input data, when the MUTE mode is selected by the PAD/MUTE pin.
When the PAD mode is selected, the PCM output has a 12 dB loss.
Normally, these pins are set to a digital "0".
When the data through mode is selected, the function of these pins is invalid.
4/17

¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
SYNCP1, SYNCP2
Synchronous signal input.
SYNCP1 and SYNCP2 control the PCM data input/output timing for Channel 1 (SIP1, SOP1)
and Channel 2 (SIP2, SOP2), respectively.
Since other synchronous signal input pins SYNCA1 and SYNCA 2 for ADPCM interfaces are also
provided, the PCM and ADPCM data can be input or output with different timing.
PCM and ADPCM data interfaces can be used at a mutually independent timing except same
timing.
Note: When PCM and ADPCM data interfaces are used at a mutually independent timing, the
timing described in "Notes on Usage" should not be used.
BCLKP
Bit clock input.
This signal defines the PCM data transmission speed at the PCM data input/output pins.
BCLKP is used for Channels 1 and 2. Since BCLKA defines the data rate of the ADPCM data
interface, the PCM and ADPCM data can be input or output at different speeds.
LAW
PCM data companding law (A-law/m-law) selection.
Digital “1” and “0” correspond to A-law and µ-law, respectively.
PDN1, PDN2
Power down mode selection.
PDN1 and PDN2 can be independently set to power down mode. When a digital “0” is applied,
these pins are in the power-down mode.
SIA1, SOA1
ADPCM serial data input (SIA1) and output (SOA1) pins for Channel 1.
SOA1 is an open-drain pin and enters to the high impedance state after outputting a continuous
4-bit serial data stream. When the data-through mode is selected, SOA1 enters to the high
impedance state after outputting an 8-bit serial data stream.
SIA2, SOA2
ADPCM serial data input (SIA2) and output (SOA2) pins for Channel 2.
These pins function the same as SIA1 and SOA1.
5/17

¡ Semiconductor MSM7580
SYNCA1 , SYNCA2
Synchronous signal input pins.
SYNCA1 and SYNCA 2 control the ADPCM data input/output timing for Channel 1 (SIA1,
SOA1) and Channel 2 (SIA2, SOA2), respectivery.
The ADPCM data can be input or output with timing other than the PCM data interface.
Therefore PCM and ADPCM interfaces can be used at a mutually independent timing except
some timing.
Since master clocks are generated by the internal PLL using SYNCA, a synchronous signal
should be input to there pins.
Note: When PCM and ADPCM data interfaces are used at a mutually independent timing, the
timing described in "Notes on Usage" should not be used.
DET1, DET2
Special ADPCM input data pattern detect pins.
When a 4-bit continuous "0" pattern at the ADPCM input pins Channel 1 (STA1) and Channel 2
(SIA2) is detected, DET1 and DET2 go from a digital "0" to a digital "1" state.
A digital "1" is output at the rising edge of the clock.
The fourth data bit (LSB) is clocked into the register by the bit clock (BCLKA) and the held there
until the rising edge in the next time frame.
When detecting the special data pattern in the next time frame, the digital "1" on the pins DET
(1, 2) is remains. When the THR1 pin or THR2 pin is at digital "1" level, the functions of these pins
are invalid.
RES1, RES2
Algorithm reset signal input pins for Channel 1 (RES1) and Channel 2 (RES2).
When a digital “0” is applied, the entire transcoder goes to its initial state.
This reset is defined by ITU-T G.721 and is an optional reset.
BCLKA
Bit clock input pin used to define the data transmission speed at the ADPCM interface.
This pin can be used for Channels 1 and 2, which allows the ADPCM data interface speed to be
defined differently than the PCM data interface speed.
V
DD
Power supply.
The device must operate at +5 V ±10%.
6/17
 Loading...
Loading...