Page 1

Installation Guide
Version 1.7
54M/150M/300Mbps
USB WIRELESS ADAPTER
1.Hard
2. Hardware Installation diagram------------------------------------------------ ---
3. Software Installation----------------------------------------------------------------
ware Photo-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 1
Page 2
Page 5
Page 2
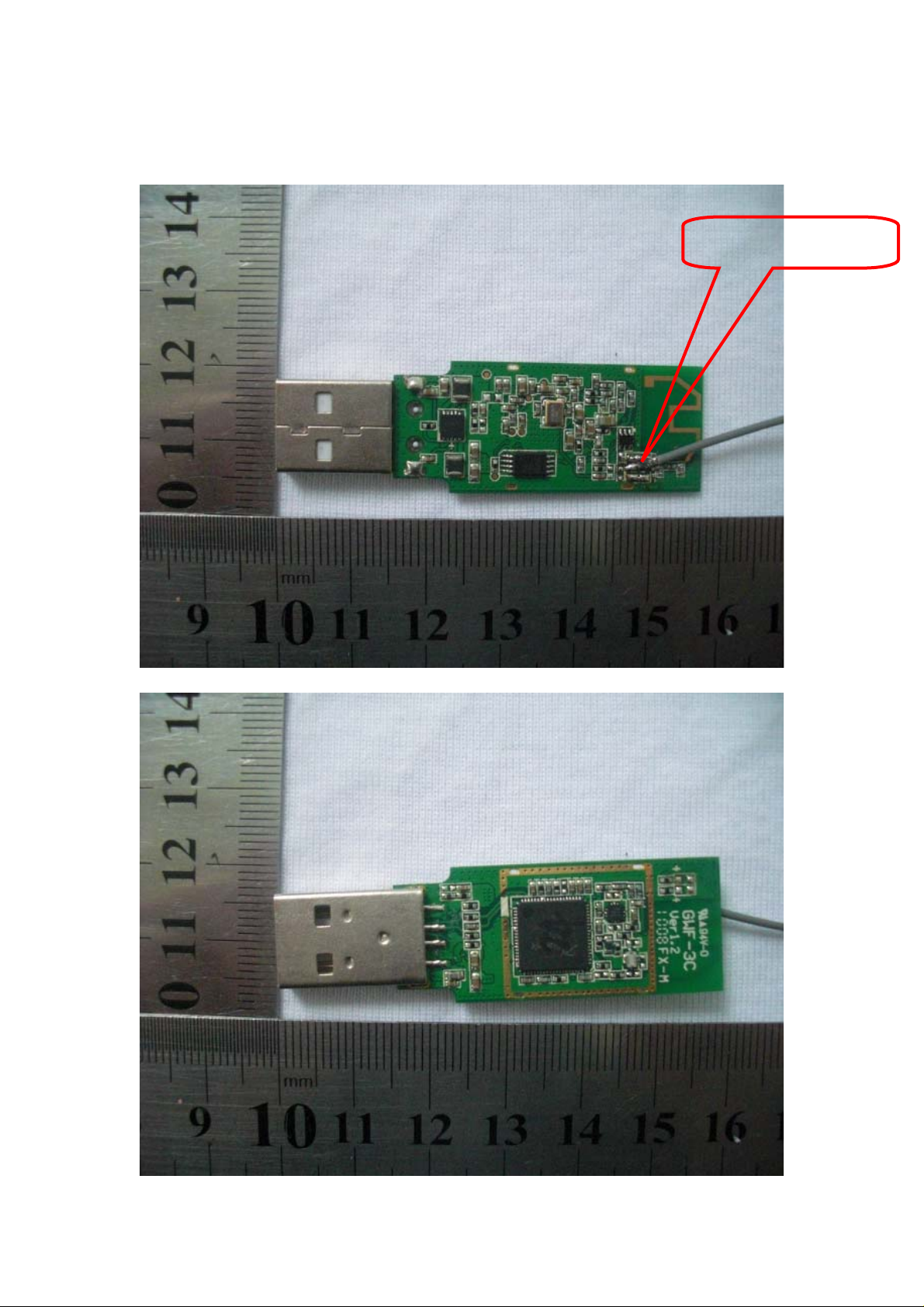
1. Hardware Photo
第 1/8页
Antenna interface
Page 3
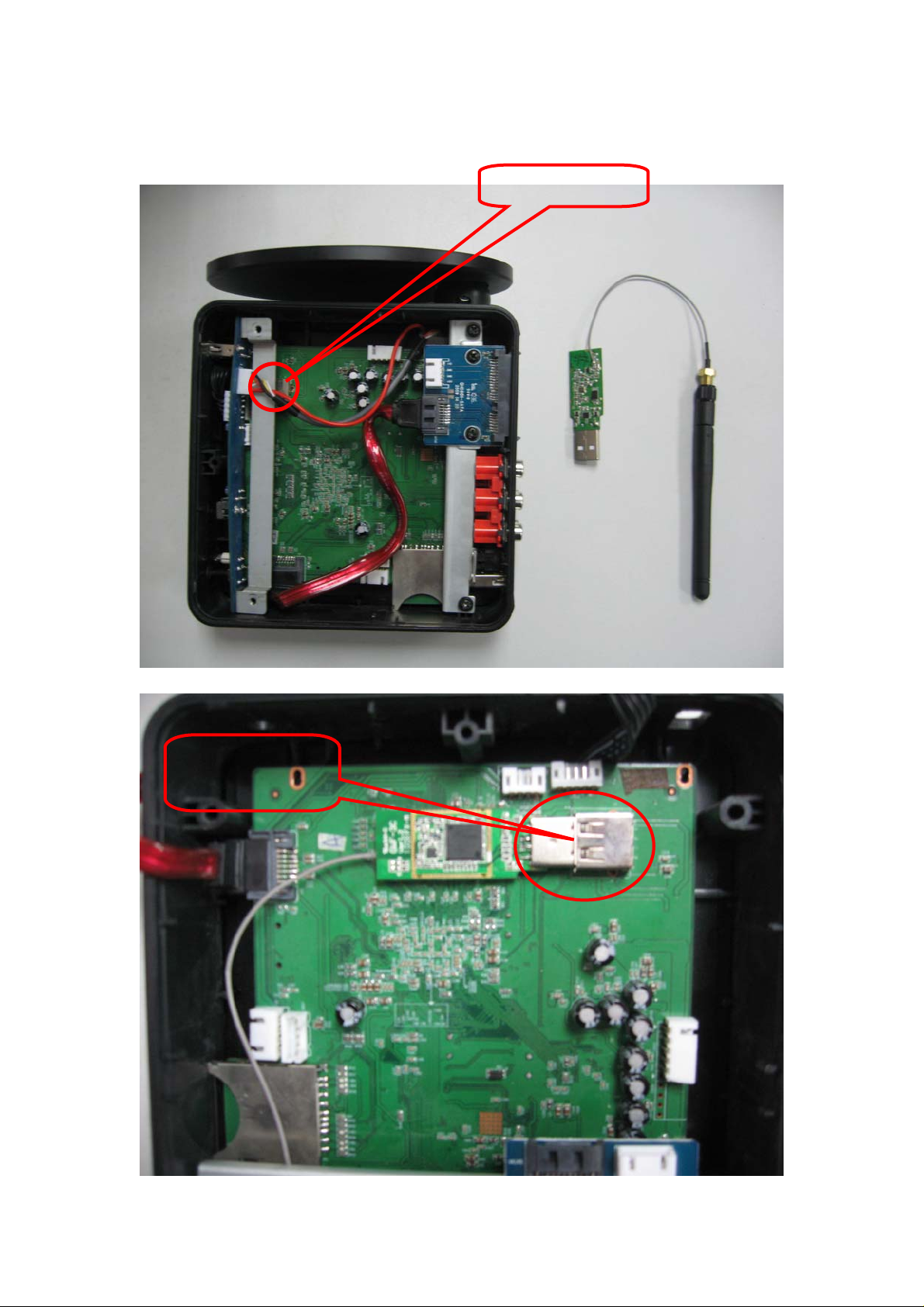
2. Hardware Installation diagram
第 2/8页
USB Interface
Inserted into the
USB interface
Page 4

第 3/8页
SMA antenna cable
into the casing head
Lock screw
Page 5

Screw on the antenna
Complete
Installation Steps:
1.Open the cover,can see the USB connector and antenna installation mouth in the mainboard.
2.Plug the WIFI ADAPTER in the USB connector.
3.Plug the antennaSMA connector in antenna installation mouth,than fasten the screw.
4.connect up the external antenna.
5.installation complete.
第 4/8页
Page 6

第 5/8页
3.Software Installation
identify the chipset type applied in the adapter you have.
the driver of the USB adapter, please use administrator user account to login before the following steps:
To install
Tips: the latest original drivers can be down loaded from the website of Ralink chipset manufacturer. The current website is http://www.ralink.com.tw/support.php.
1. For a 54Mbps 802.11b/g or a 150Mbps or 300Mbps 802.11n adapter, double click Ralink_***.exe program, which is located in the driver folder in the installation disc. Such as: G:\WiFi
Driver\Windows Driver\ RT20 70_ RT307X.exe.
Notes: Because Ralink often updates software, the drivers contained in the disc might be changed without prior notice.
2. Follow the instructions and prompts of the “InstallShield Wizard” to finish the driver installation:
a. Select the “I accept the terms of the license agreements ”, then click the “Next”.
b. There s
hows a setup type window, you can select “Install driver only” or “Install driver and Ralink WALN utility” and then click the “Next”.
To find a
correct driver, please
ps:
Ti
1).
The Windows XP uti lizes a "Wireless Zero Configuration( WZC)" Service built into the operating system. Many wireless network adapter cards utilize this service.
2). Ralink- the chipset manufacturer has developed an utility for setting up wireless connection. If you select this item, you can switch between the Windows XP’s WZC service and the Ralink
WLAN utility service later.
c. Click the “Install” to confirm the installation, there shows the installation progress.
d. Click “f
inish” to finish the driver installation.
Page 7

Wireless Con
d
第 6/8页
1. After fini
Remarks: Make sure to connect the adapter to an USB port on your computer directly rather than an USB hub. Although it might work when connecting with an USB hub, the likelihood of
configuration problems will be higher.
2. The system shows a wireless utility icon in the Windows system tray, which locates in the bottom-right corner of your computer screen, and pops up a message that indicates a new hardware is
found and installed, something like this:
nection
shing driver installation, insert the USB adapter to Notebook or PC that supports USB 2.0/1.1 interface.
Should the
2. If you don't see your network, click “Refresh network list” in the upper left corner. If you are locating within the valid range of hotspots or wireless routers, all available networks will be recognized and
3. If the net
service " Wireless Zero
Should the serv
Configuration ( WZC)" be applie
Notes: Before
router, ask your network administrator to get the information.
listed automatically. Click your preferred network, and then click “Connect” in the lower right corner.
work security key hasn’t been inputted before, Windows XP prompts you to enter the network’s security key to access the wanted SSID. Type the encryption key that you wrote down earlier
in both the Network key and Confirm network key boxes, and then click “Connect”.
ice " Wireless Zero
configuring your WiFi access, you need to have your network’s SSID (service set identifier), security key and authentication type handy. Check the documentation coming with your
.
1. Double-click the utility icon or right click the icon and then select “View Available Wireless Networks” to launch the utility, the Wireless
Network Connection window appears and displays your wireless network listed with the SSID you chose.
Tips:
If there
are free hotspots, simply select the network you want from the list displayed, then click Connecting. It tries to launch your Internet browser —you should be connected to the Internet.
If there is a pay hotspot, signing in or up will require either to enter your login information-if you‘re an existing customer, or to enter your credit card information for payment, it is just decided by you.
Then clicking the Connecting, your default Internet browser will launch and take you to the service provider’s login page. Most providers have very simple and step-by-step instructions for you to sign
up and then to be connected. Another way to access the service provider’s login page is to simply launch your Internet browser, if there’s a pay network available, you’ll be take n directly to the login
page.
Should the s
After the installation of Ralink utility, the system shows a special wireless utility icon in the Windows system tray, which locates in the bottom-right corner of your c o mp u ter screen:
The icon chan
1. Double-click the icon or right click the icon and then select “Launch Config Utility” to launch the utility, the RaUI window appears like:
The Ralin
Wi-Fi setup, Cisco compatible extensions (CCX), call admission control (CAC), radio controls, Ralink driver/utility information, and help functions.
2. Clicking the expanding icon
ervice of Ralink wireless
connection utility be applied.
ges colors according to the wireless signal quality,when an USB wireless adapter is inserted into an USB 2.0/1.1 port of No tebook or PC.
k wireless utility starts in compact mode as shown above, provides profile management, the available networks listing, a statistical counter display, Wi-Fi multimedia (WMM), protected
ange to the full mode as shown below:
can ch
Page 8

For more
第 7/8页
details about the RaUI utility, please read the help information of the utility by clicking the
tab
Tips for
Wi-Fi users
ith a W
i-Fi connection, you can roam about 150 m around the access point (depends on different environment), so find a spot where you can work without any interruption. Then see how mu ch
W
work you can do, such as:
and quickly receive and transmit files within your local network — no problem for big files.
Easily
z
z
z
z
Warning
you'll undoubtedly notice that you need to recharge mor e often. If you need to conserve ba ttery life — on a long trip for example — turn off your Wi-Fi connection when you don't act ually need it.
Security
be protected in order to be secure.
an effort to make it easy for anyone to connect. It may be found that some pay hotspots administered by service providers offer have some level of security, however, when using a hotspot, it’s
always a good idea to be proactive and to employ security measures of your own.
Key terms
Wi-Fi: Short for “wire
Hotspot: A specific geographic location in which an access point provides publi c wi reless broadband network servic es to mob ile vi sitors through a WLAN.
your email and surf the web with the same speed as that connected with network cables.
Access
Sync
hronize data between devices.
Take ad
Wi-Fi offers
Because wir
There are many security measures to safeguard wireless networks, protect the data, and keep unauthorized users out. Hotspots, on the other hand, are often free of standard security practices in
vantage of wireless printing — send files directly from your laptop PC to a wireless printer over Wi-Fi connection.
greater speed and range than Bluetooth, but it drains your portable device batteries a lot faster than Bluetooth does. In fact, if you use a Wi-Fi connecti on re gu larly on your laptop PC,
eless networks rely on radio signals to transmit data, they are not as secure as wire network. Wireless networks are susceptible to viruses and breaches like eavesdropping and need to
less fidelity,” a generic label that refers to wir el ess n etworks or networking.
Page 9

Throughput: The am
第 8/8页
Bandwidth: the amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period (usually a second).
Chipset: A group of microchips that execute various functions (like memory) to support the CPU.
Specifica
tions (Typical):
Protocol and
tandards
S
ount of data transmitted in a set amount of time.
IEEE 802.11b/g or 802.11n
Interface USB1.1, USB2.0
y
Frequenc
Band
Data Rat
Transmi
Power
Data Se
Power
umption
Cons
Transm
Distance
Environment
Operati
System
device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
This
undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential in stallation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
-- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
-- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different
from that to which the receiver is connected.
-- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
2.412~2.4835GHz (Depends on
different countries’ regulation)
For 802.11b/g:
Peak rate 54Mbps, Peak
throughput: 27Mbps.
For 802.11n
1T1R. Peak rate: 150Mbps, Peak
e
throughput: 90Mbps
1T2R. Peak rate: 300Mbps, Peak
throughput: Rx 160Mbps
2T2R. Peak rate: 300Mbps,
Peak throughput: Rx 260Mbps
t
802.11b: 19dBm; 802.11g:15dBm ;
802.11n: 14dBm.
curity WEP 64/128 , WPA, WPA2, 802.1X
It depends on different adapter
models, there are two typical
values: 330mA and 110mA in full
Transmit (TX), 290mA and 95mA in
full Receive (RX) .
Indoor up to 100m, outdoor up to
300m (Standard transmission
ission
distance, it is affected depending
on different environment).
Operating Temperature: 0°C~50°C
Storage Temperature: -20~70°C
Operating Humidity: 10%~90%
non-condensing.
Storage Humidity: 5%~95%
non-condensing.
It supports Windows
CE/2000/XP/Vista/7; Linux; Mac
ng
OS X.
The drivers might be supplied
basing on one or two system.
 Loading...
Loading...