Page 1
OECD.Stat Web Browser
User Guide
Release 1/1a
September 2008
Page 2

Page 3

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Table of Contents:
TUIntroductionUT ....................................................................................... 4
TUOECD.Stat ConceptsUT ............................................................................................. 4
TUData OrganisationUT ............................................................................................... 4
TUReference SeriesUT ................................................................................................. 5
TUSearchUT ............................................................................................................... 5
TUThe OECD.Stat Web BrowserUT ................................................................................. 5
TUUser GuideUT .......................................................................................... 6
TUGetting Started PageUT ........................................................................................... 6
TULanguage SelectionUT ............................................................................................. 7
TULocating Data through the OECD.Stat SearchUT ....................................................... 8
TULocating Data by Browsing ThemesUT ..................................................................... 9
TULocating a dataset or a query in the theme listUT .................................................. 10
TUUsing the Table FeaturesUT ................................................................................... 11
TUSelecting Dimensions and their VariablesUT ............................................................... 12
TUChanging the Time DimensionUT .............................................................................. 14
TURotating Dimensions by Adjusting the Dataset ViewUT ................................................ 17
TUFormatting OptionsUT ............................................................................................. 19
TUExporting to ExcelUT .............................................................................................. 22
TUExporting to a CSV fileUT ........................................................................................ 22
TUDownloading related files and large data selectionsUT ................................................. 23
TUExporting to PC-Axis TableUT ................................................................................... 25
TUCharting DataUT .................................................................................................... 26
TUViewing MetadataUT .............................................................................................. 28
TUOther Related MetadataUT....................................................................................... 28
TUFlagsUT ................................................................................................................ 28
TUWorking with QueriesUT ........................................................................................ 29
TUSaving a QueryUT .................................................................................................. 29
TUMerge QueriesUT ................................................................................................... 30
TUCreating a Merge QueryUT ...................................................................................... 30
TUViewing the QueryUT .............................................................................................. 31
TUChanging the QueryUT ............................................................................................ 32
TUSaving a Multi-Dataset QueryUT ............................................................................... 32
TUViewing Frequently Requested and Saved QueriesUT ............................................. 33
TUViewing the Country Statistical ProfilesUT ............................................................. 34
TUPrinting Data from the Browser UT ......................................................................... 37
TUProviding FeedbackUT .......................................................... ................ 38
09/2008 3 / 39
Page 4

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
0BIntroduction
TOECD.Stat provides a single online platfo rm where users can discover and access statistical da tabases
from the OECD. You will be able to build tables and extract data from across databases as well as work
within individual databases. Use Browse Themes or Search to find the statistical information you need.
Each database includes detailed metadata to help you understand the numbers.
OECD.Stat offers a number of opportunities for improving data management, in particular in
the following areas:
• General data identification, taxonomy and classification
• Data accessibility and security
• Data relevance by the provision of related metadata
• Fostering coherency of statistical data and metadata
• Eliminating duplication of effort by maintaining a single copy of key series
It also provides a common platform for future development and implementation of standards
for statistical data and metadata across the OECD.
3BOECD.Stat Concepts
OECD.Stat features the following main concepts:
• Catalogues of information on themes, datasets, dimensions, dimension
members and reference series
• Storage of metadata at all levels from dataset through to cell level
• Storage of numeric data figures, as well as cell-level flags
• A data warehouse searching mechanism
16BData Organisation
Datasets
Within OECD.Stat, statistical data are organised in the form of datasets. A dataset is a
collection of numerical values and their associated textual information, with all values sharing
a common set of dimensions. Each dataset is attached to a specific statistical activity or subactivity.
Dimensions
The dimensions of a dataset are the axes on which the data are described. Country and year
are two common examples of dimensions. Dimensions can be presented as either a flat list or
as a hierarchy.
Dimension Members
Every dimension contains a pre-defined list of items, called dimension members. In the
country dimension for example, the dimension members are the individual countries.
Metadata
09/2008 4 / 39
Page 5

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Qualitative data, attached to the quantitative data in OECD.Stat is called metadata. Metadata
can be found at various levels, ranging from an abstract found at the level of an entire
dataset, country- or series-level footnotes which apply to a broad selection of data within a
dataset, and down to the level of a single cell.
Flags
When a qualitative note is recurrent in a dataset, and the exact same note can be attached
to many individual data figures, this may be stored as a flag. A flag is a letter, which appears
alongside the numerical data in any table cell where it applies. A legend appears beneath the
table, explaining the signification of each flag present in the table. Flags are frequently used
to note general data properties such as “confidential”, “provisional” and “estimated”.
17BReference Series
A number of data series, identified by the OECD Statistics Directorate as being generally
useful in the calculation of indicators, are available via the Reference Series dataset. Data in
this dataset are linked dynamically to the source datasets from which they are taken, so that
there is no duplication of data and in order to ensure that the Reference Series contain the
most recent data a v ai l ab le.
18BSearch
A text-based search facility, which searches through dataset names, dimension names,
dimension member names and metadata, can be used to quickly locate relevant datasets and
view tables.
19BThe OECD.Stat Web Browser
The OECD.Stat Web Browser provides the online user environment to access OECD statistical
information. The browser has been designed to allow both experienced and new users to
rapidly locate and retrieve statistical data and related metadata.
Main features include:
• Links to frequently requested tables - access the latest versions of the most
frequently requested OECD Reference Series data (Exchange rates, GDP figures, etc.)
• “Table View” – view data, flags and metadata from a table that includes a number of
features for customising the layout of the data.
• “Data Basket” - save data queries for later viewing, and share them with others.
• Merge Queries – combine queries to allow cross-dataset comparisons along common
dimension(s).
• Metadata access - access all metadata from dataset level down to series footnotes
and data flags.
• Microdata viewer - access transaction-level microdata in addition to aggregate
macrodata.
• Full Text Search - rapidly locate series across data sets, data dimensions and
metadata.
• Dynamic graphics – visualize data dynamically in a line chart, bar chart or pie chart.
09/2008 5 / 39
Page 6

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
1BUser Guide
The OECD.Stat Web Browser has been designed to be straightforward and intuitive in use. It
does, however, contain a number of advanced features, which reflect the diversity of the
Organization’s statistical resources. This User Guide has been prepared to help acquaint
first-time users with these features, by stepping through them with the aid of selected screen
shots.
47B4BGetting Started Page
From the Getting Started page, the user has the option of finding OECD statistical data and
metadata through a number of different avenues.
Data can be located in various ways:
• OECD.Stat Search
• Browse Themes
• Browse Queries
Each of these options will be explained in more detail in the remainder of the User Guide.
The browser is best used in full-screen view at 1024x768 pixel screen resolution or higher.
Click here to open/close left
panel.
Click on arrow/dash to
expand or collapse the
respective panel.
Click on question mark for
contextual help.
Figure 1: OECD.Stat Browser Getting Started page
09/2008 6 / 39
Page 7

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
5BLanguage Selection
The interface and data can be viewed in English or French. The language can be changed by
clicking on the language option, located at the top of the screen.
Figure 2: Changing the language of the browser
46B
09/2008 7 / 39
Page 8
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
6BLocating Data through the OECD.Stat Search
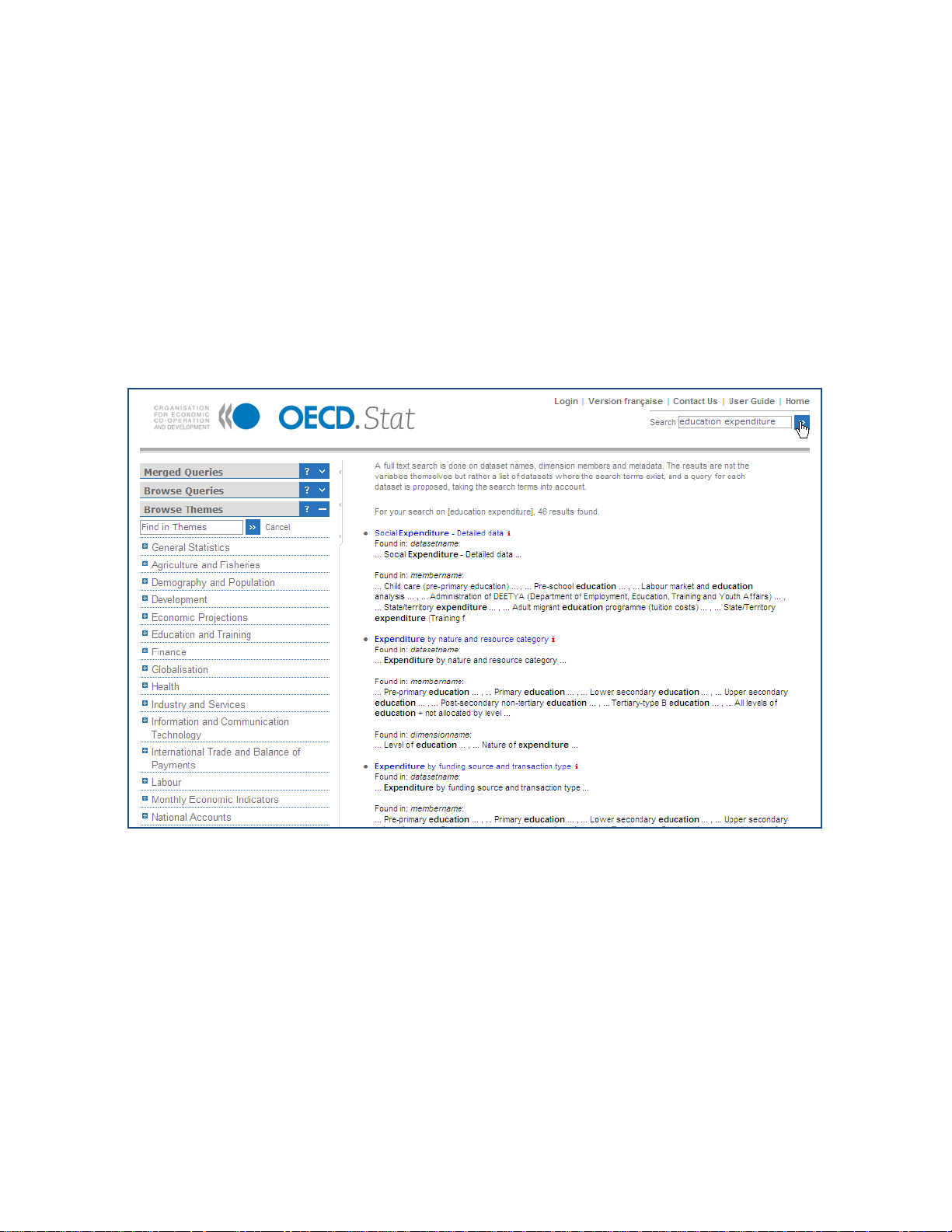
Data can be located by e ntering keywords in the OECD.Stat Search box, at the top right of
the page. This will return a list of links giving the name of each dataset in which the
keywords were found, and providing further details as to where the keywords are present
within each dataset. The most relevant links are shown first based on the frequency with
which the keywords appear in each dataset, and at which level they were found. A keyword
found in the name of a dataset is considered mo re relevant than a keyword found only in o ne
of the dimension members of a dimension of the dataset or in the metadata.
Clicking on the link will op en the datas et with the default view. If a country has been entered
as a keyword, the results will be filtered to reflect this. The tables resulting from a search will
contain any references to the search keywords entered that could be found in the data.
These tables can be modified and used as a starting point to find data related to the
keywords entered.
Figure 3: Results from the search ranked in order of relevance
45B
09/2008 8 / 39
Page 9
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
7BLocating Data by Browsing Themes
In the Browse Themes panel, click a theme title, click a sub-theme title and so forth, until
you can select a dataset. Datasets can be recognised by the table icon in front of their name.
A pre-defined, default view of the table will open. This view can be customized (see next
section).
Navigate through themes and
sub-themes down to a dataset.
Click the dataset title once to
open the default view.
Figure 4: Browsing through themes to view data
49B
09/2008 9 / 39
Page 10
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
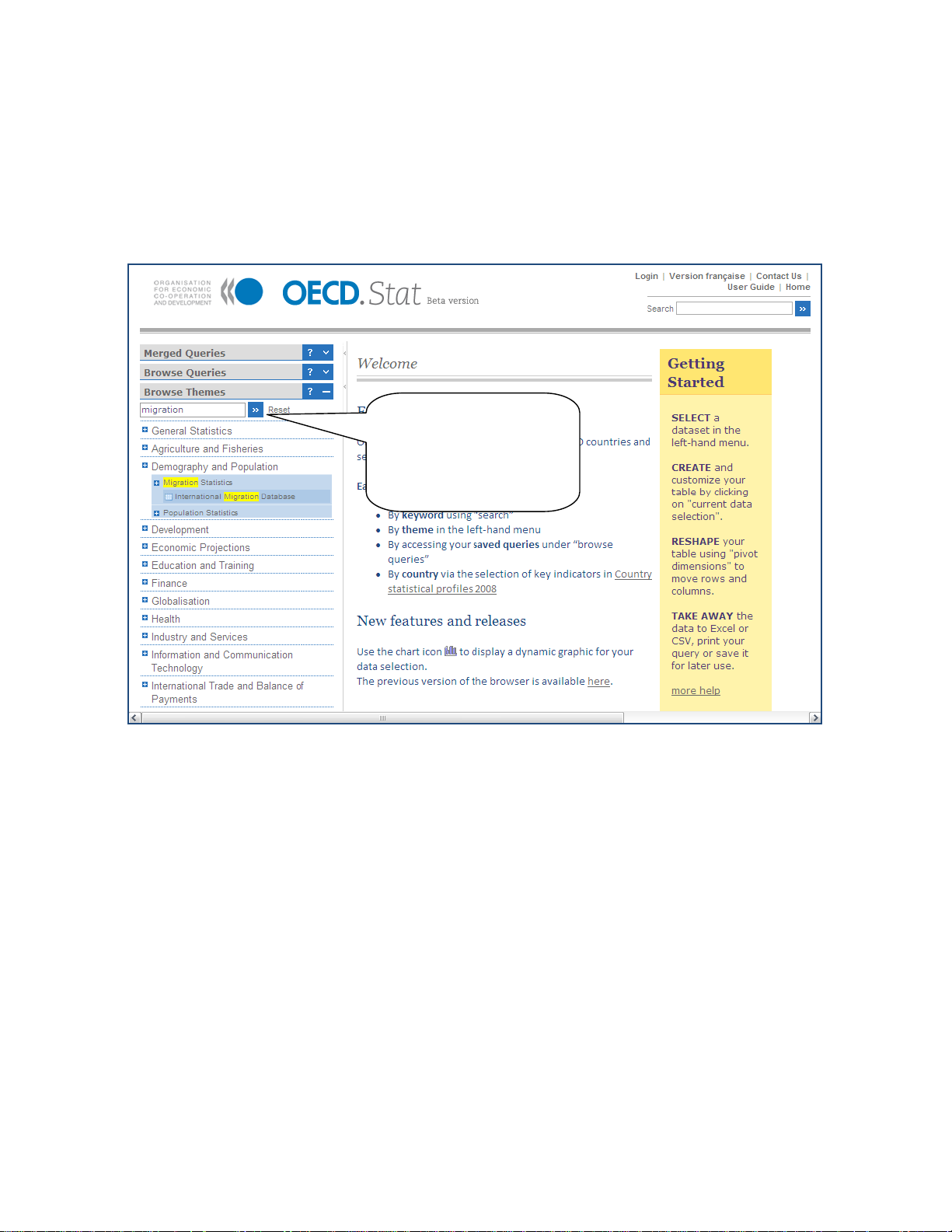
8BLocating a dataset or a query in the theme list
At the top of the Browse Themes panel click the text box and enter a key term to search for
within the theme and data set list. Click the “>>” sign or press Enter to execute the sear ch .
All found entries will be highlighted in yellow.
To start over, simply click Reset to the right of the text box and click the text box agai n in
order to enter a new key term.
Enter a key term and
search among the themes
and data sets in the
theme panel. Results will
be highlighted in the
panel.
Figure 5: Find a theme or data set
This search routine will look for exact matches of the entered text string, including spaces
but irrelevant of miniscule or majuscule characters.
This method also allows a quick lookup for well known OECD data sets by their acronym, e.g.
MEI, STAN, ITCS, etc.
09/2008 10 / 39
Page 11
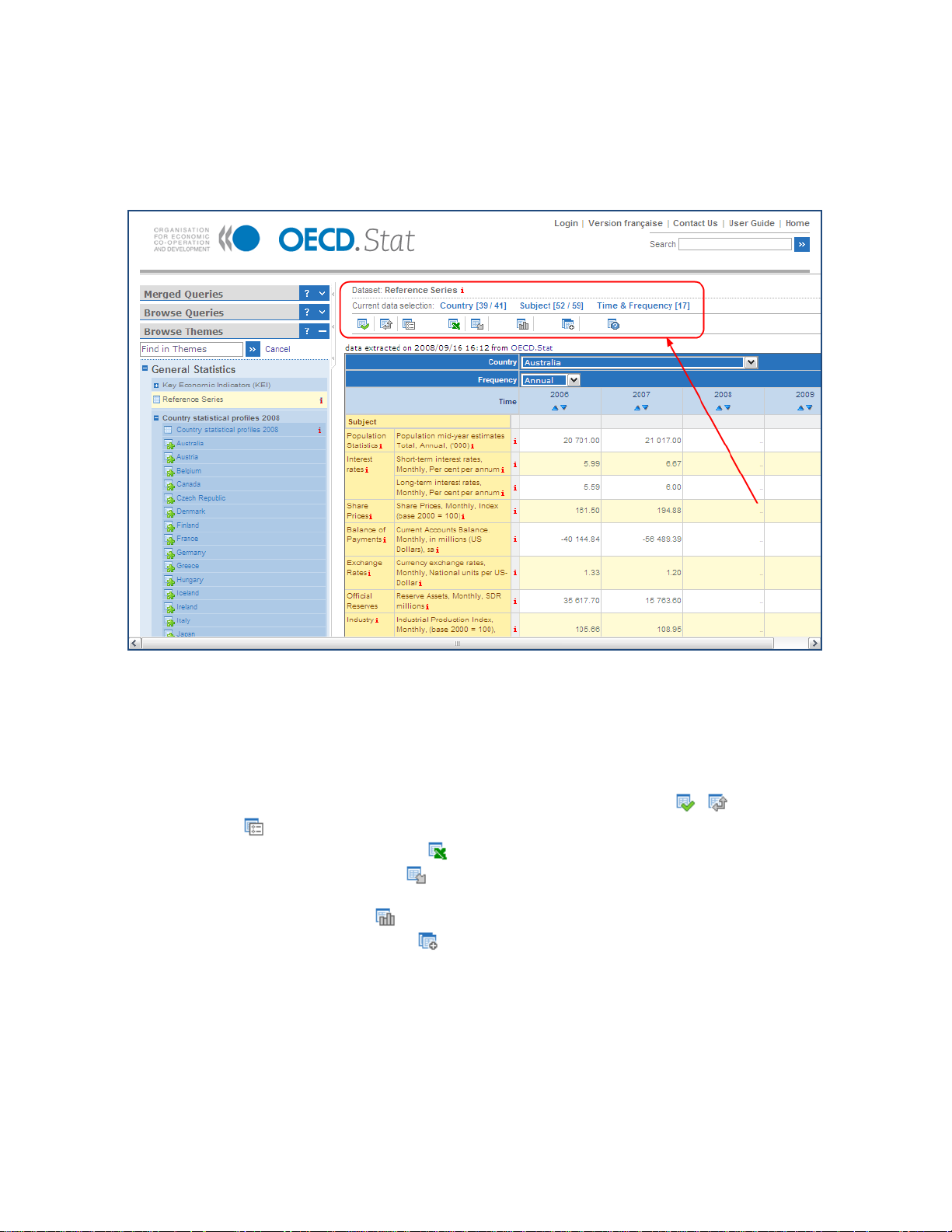
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
9BUsing the Table Features
When a dataset is first opened, a table in a default view is presented. This default data
selection can be modified using the features found atop the table.
Figure 6: Default dataset view and Current Selection values
The Current Data Selection information shows the dimensions of the dataset with an
indication, in parentheses, of the number of items, or members, selected in each dimension.
If you click a dimension title, a list of the members you can chose from will be shown.
Once you have made your data selection, you can:
• click on one of the several option buttons to customize the layout (
display (
• click the Export to Excel button (
• click the Other Export button (
) of the current table
) to save your selection as an MS Excel file
) to save your selection as a CSV file, PC-Axis table,
, ) and/or
or download related, ready-made files
• click on the Chart button (
• click the Merge Queries button (
) to dynamically graph the displayed data
) to add your current table view as a query for
further work. You will need to login first to take full advantage of all query features.
09/2008 11 / 39
Page 12
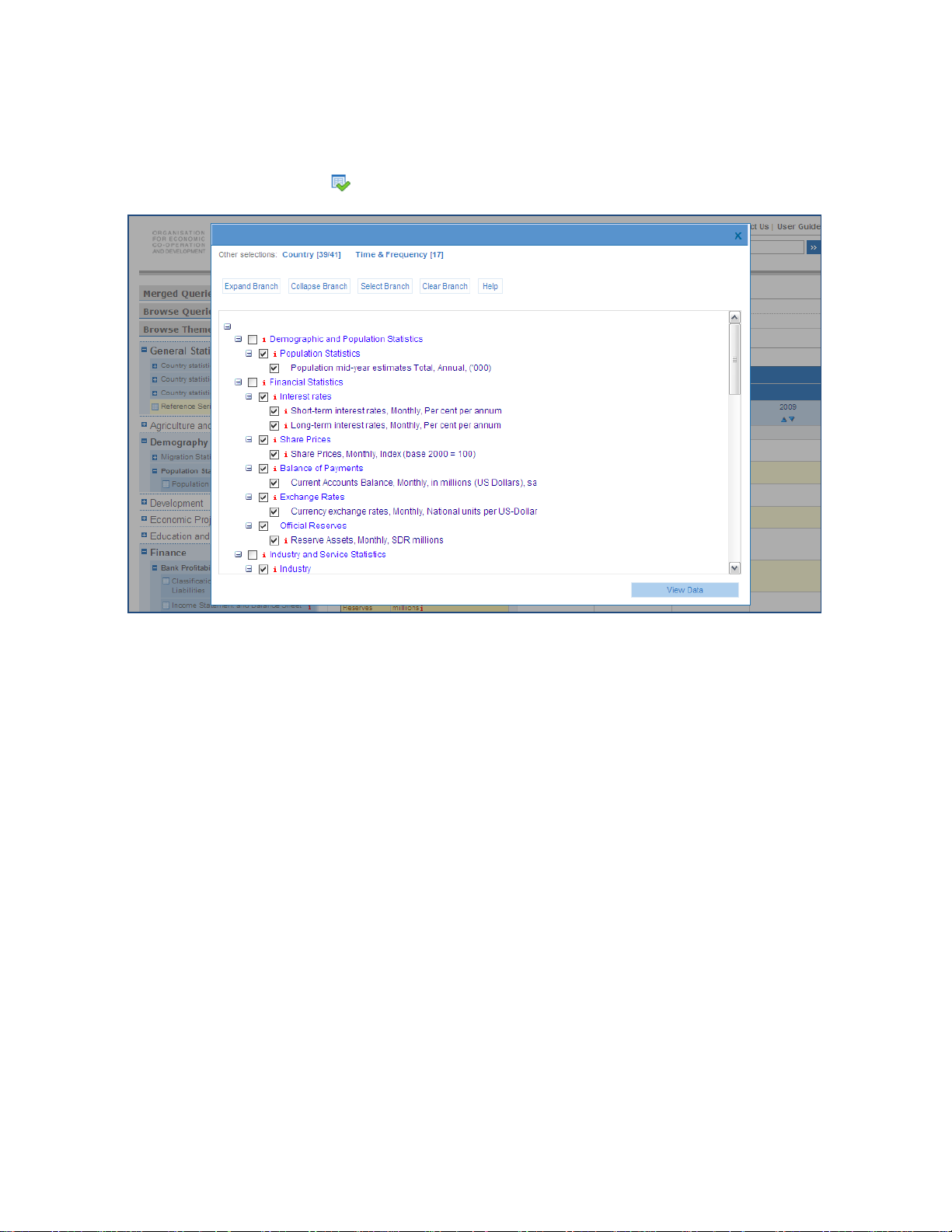
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
20BSelecting Dimensions and their Variables
The items selected for each dimension, often referred to as dimension members, can be
modified by clicking on the
button to Select Dimensions at the top of a tab l e.
Figure 7: Using the Dimension Selector
To select or deselect an item, click the check box to the left of the item. In hierarchical
dimensions, a plus or minus will appear next t o parent-level items. Clicking on this symbol
will allow you to show or hide the child items.
At the top of the screen, a series of options appear.
To apply your modified selection of items for the current dimension and see a table of data
corresponding to this new selection, click View Data. Alternatively, after changing the
selection for one dimension, you can click on another dimension to modify, before viewing
the new table of data.
For hierarchical dimensions, clicking on Expand Branch or Collapse Branch will show or hide
all the child-level items of the dimension.
Note: If all members of a hierarchical dimension are selected, the resulting table could
contain empty rows or columns corresponding to the higher levels (see below).
36BDimension Member Colour Coding
The OECD.Stat Web Browser uses colour coding to help you identify for which dimension
members data exists. This is especially important for sparse datasets where data can be
found in only a small proportion of dimension combinations. This function has be en provided
to save time by avoiding searching for non-existent data.
09/2008 12 / 39
Page 13
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
The colours for each dimension member indicate the following:
Based on the current selection for all other dimensions…
Dark Blue: The item has data.
Blue: The item has no data but some of its children have data.
Green: Item has no data at any level.
Remember: The colour coding takes into account the current select ion for al l ot her m em ber s.
In other words, the colours indicate the existence of data for the countries, years, etc.
currently selected.
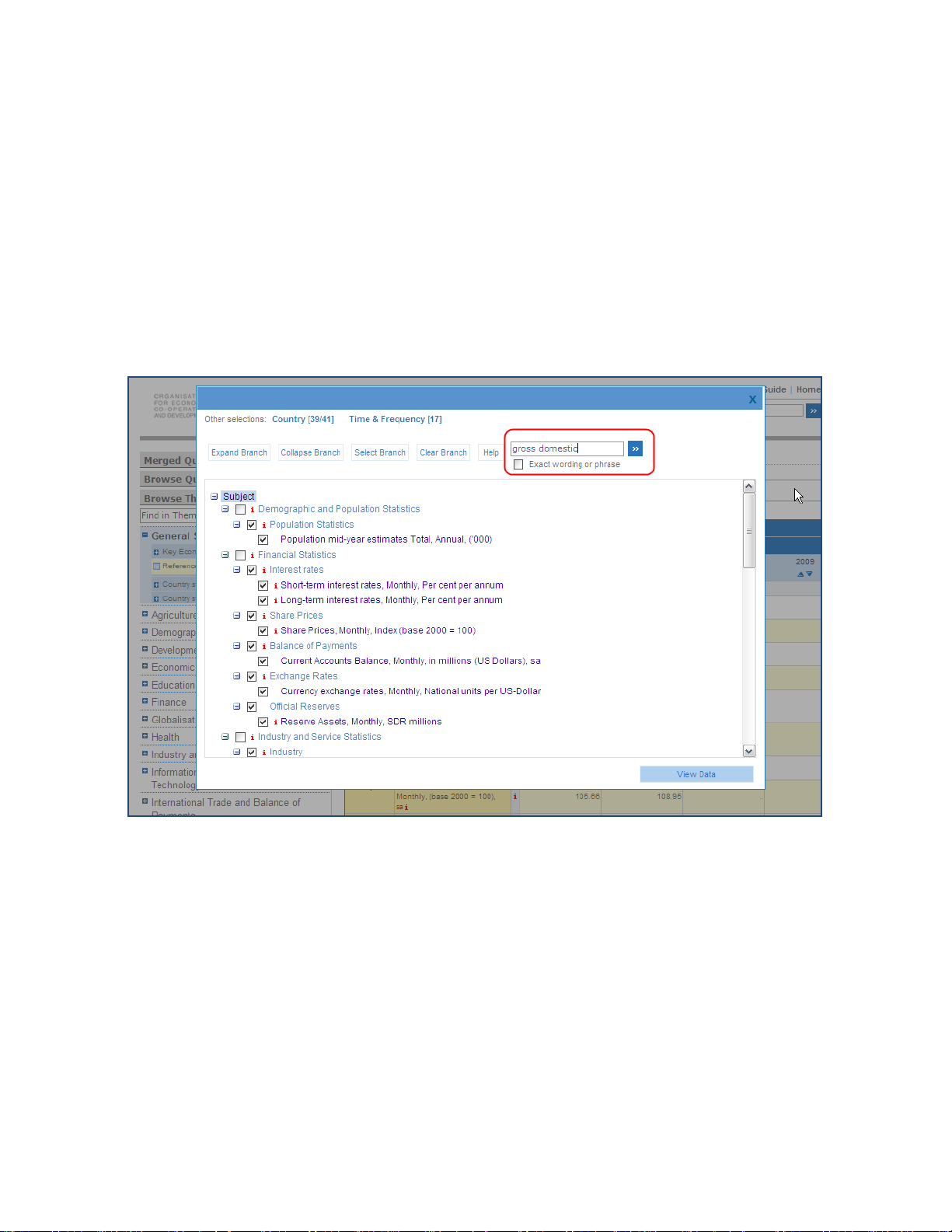
Another option is to search in the dimension selector to display dimension members
matching the search criteria.
Figure 8: Searching in the dimension selector
All matching dimension members will be displayed and automatically selected.
09/2008 13 / 39
Page 14

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 9: Results of a Search in the dimension selector
21BChanging the Time Dimension
The options available for changing the selected dates of a time dimension are different from
those presented for other dimensions. Dates can be selected either using the Date Range
Selection method or the Time Period Selection method.
37BDate Range Selection
All frequencies available for the selected dataset are shown on the screen. If the data is only
annual, for example, the controls for selecting quarters, semesters and months will not
appear.
First tick the boxes next to the frequencies to be included in the selection. Then choose
either a specific range of dates (from 1980 to 2000, for example) by clicking Select Date
Range, or indicate that you wish to have the most recent data available (last 5 years, for
example) by clicking Select Latest Data.
When selecting a date range, it is possible to select a start year, quarter, month, etc. and
automatically include all available data from that date onward by ticking the box next to
Latest Available Data.
09/2008 14 / 39
Page 15

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 10: Date Range Selection
38BTime Period Selection
It is also possible to select individual years, quarters, months, etc. by ticking the box next to
each item. This is necessary if t he selecti on of dates you wish to include is not a continuous
series, but instead contains breaks or time periods outside the main date range.
This works in a manner identical to the general dimension selector described ab ove.
09/2008 15 / 39
Page 16

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 11: Time Period Selection
Note: It is advisable to select a general range of dates using the Date Range Selection first,
and then include or exclude individual time periods using the Time Period Selection screen.
The inverse, making changes to a Time Period Selection using the Date Range Selection
screen, may result in some of the individual time periods selected being lost, as the Date
Range Selection screen is only able to manage continuous, non-broken series of dates.
09/2008 16 / 39
Page 17

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
22BRotating Dimensions by Adjusting the Dataset View
The different dimensions of a dataset can be displayed on either the horizontal or vertical
axis of a table, or in the filter area at the top of the table. To move a dimension from one
place to another, either click once on the name of the dimension within the table itself or
click the Pivot Dimensi ons button above the table. A dialog box will pop up that allows you to
visually drag and drop a dimension to the desired location.
Visual identification
when a dimension is
selected to be moved.
A place holder outline
will assist in ‘dropping’
Figure 12: Moving a dimension to rotate the data view
If a dimension for which more than one item has been selected is placed into the filter area
at the top of the page, a drop-down list will become available. To change the filter currently
applied to the data, simply select the appropriate value in the drop-down list.
If the dimension in question does not have a drop-down list, then only one item has been
selected. To include other items, click on the dimension name in the Current Data Selection
box on the left, and follow the instructions provided above to select more items.
09/2008 17 / 39
Page 18

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 13: Changing the view using Country drop-down list
09/2008 18 / 39
Page 19

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
23BFormatting Options
A set of options is available to allow you to format the view of the displayed table, e.g. you
can select the number of digits after the decimal point to be displayed, or select a “scaling”,
which allows you to display the figures in unit value, hundreds, thousands, hundredths,
thousandths, etc.
Figure 14: Formatt i ng Options Panel
39BShowing Codes Instead of Names
All datasets, dimensions and dimension members have short codes as well as names. If it is
useful, the codes can be displayed instead of names, by ticking the option Use Codes instead
of full descriptions.
09/2008 19 / 39
Page 20

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 15: Table showing codes instead of names
40BHiding Empty Rows or Columns
If a table of data has many rows or columns containing no data, it can be useful to hide
these rows or columns, in order to condense the table and improve readability.
09/2008 20 / 39
Page 21

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 16: Before using the Hide Empty Rows and Columns options
Figure 17: Dataset view with empty rows and columns hidden
09/2008 21 / 39
Page 22

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
ootnotes
24BExporting to Excel
Click on the Export to Excel button (
) to export your data selection to a MS Excel file. You
will be prompted to either save the MS Excel file to disk or open it directly. As your computer
settings may not allow for the file to be directly opened, it is recommended that you save the
file to your desktop and then open it from there.
Data flags saved
as Excel
f
Figure 18: Using the Export to Excel option to save data in Excel format
25BExporting to a CSV file
Larger tables can be saved to a CSV file; to do so simply click on the Other Export button
(
) above the table.
09/2008 22 / 39
Page 23

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 19: Using the Other Export option to save data as a CSV file
You will be prompted to select a dimension label format and a column separator. The
dimension label format determines what information will be included in your file for each
country, variable, etc. The column separator determines which character will be used to
separate columns in the file.
Enter your e-mail address in the box in the middle of the dialog box and click the Export to
Text file button. The file will be created and an e-mail sent to you informing you how to
retrieve it. The file will not be included as an attachment to the e-mail, as it could potentially
be very large. Instead the e-mail will contain a link allowing you to download the file.
26BDownloading related files and large data selections
Any number of documents related to a given dataset may be available for download through
the data browser. To view the list of files, click on the dataset name, either in the Browse
Themes list on the left, or in the list of recently-updated datasets visible in the centre of the
Getting Started page.
09/2008 23 / 39
Page 24

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 20: Finding files related to a dataset
The Related Files button (
list of files related to the dataset.
) at the top of the table will be displayed. Click on it to view a
09/2008 24 / 39
Page 25

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 21: Selecting a file to download
The list of files may contain documents in any format, or large prepared selections of the
data in text format. Click on the name of a file to begin downloading.
27BExporting to PC-Axis Table
Click on the Export to PC-Axis button to export your data selection to a PC-Axis table file.
You will be prompted to either save the table file to disk or open it directly. As your computer
settings may not allow for the file to be directly opened, it is recommended that you save the
file to your desktop and then open it from there.
Figure 22: Exporting to PC-Axis table
09/2008 25 / 39
Page 26
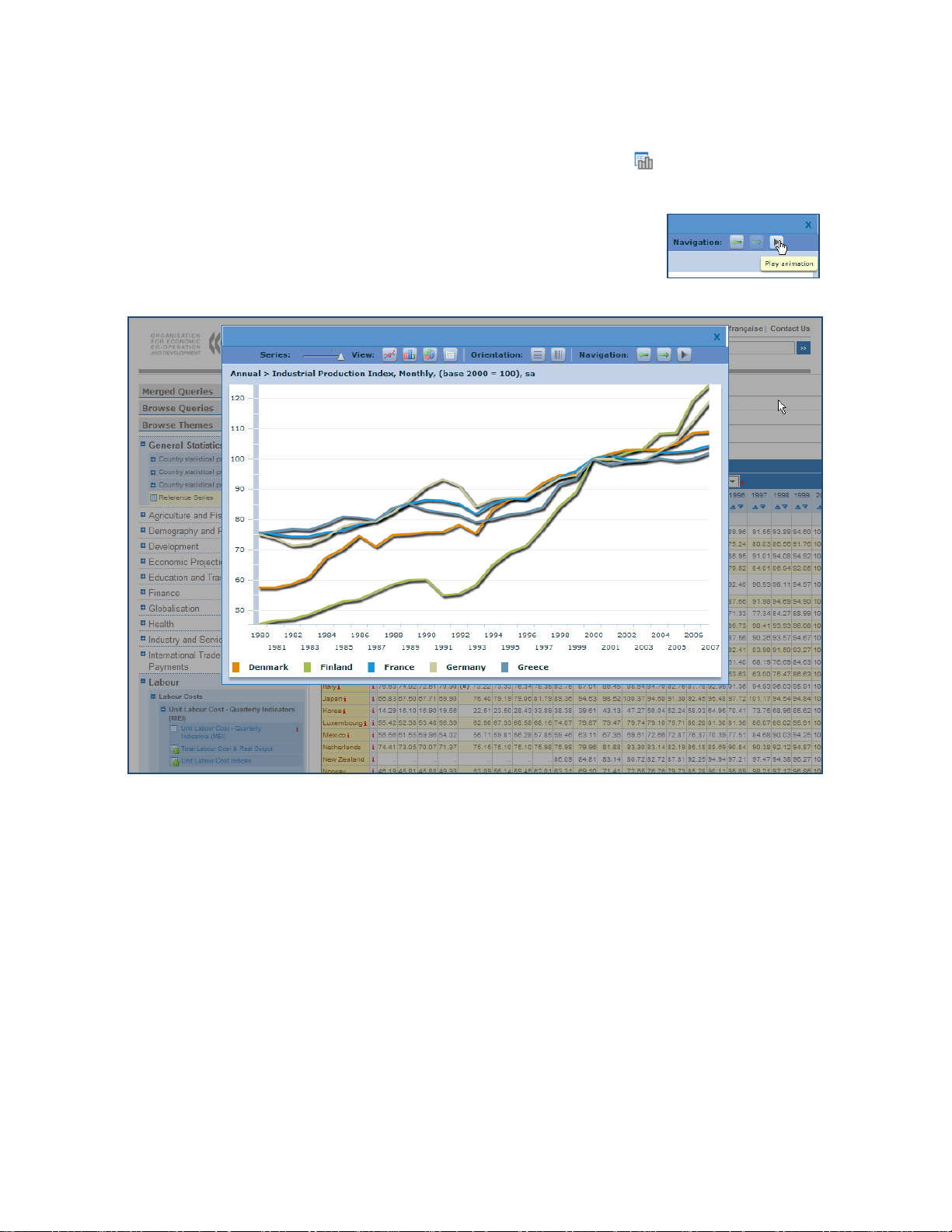
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
44B28BCharting Data
The OECD.Stat web browser includes a dynamic charting feature (
) enabling the display
and animation of line charts, bar charts and pie charts based on the current data selection.
The navigation options of the chart dialog box include a button to
animate the displayed chart, advancing it in even intervals.
Figure 23: Charting – Line chart
09/2008 26 / 39
Page 27

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 24: Charting – Bar chart
Figure 25: Charting – Pie chart
09/2008 27 / 39
Page 28
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
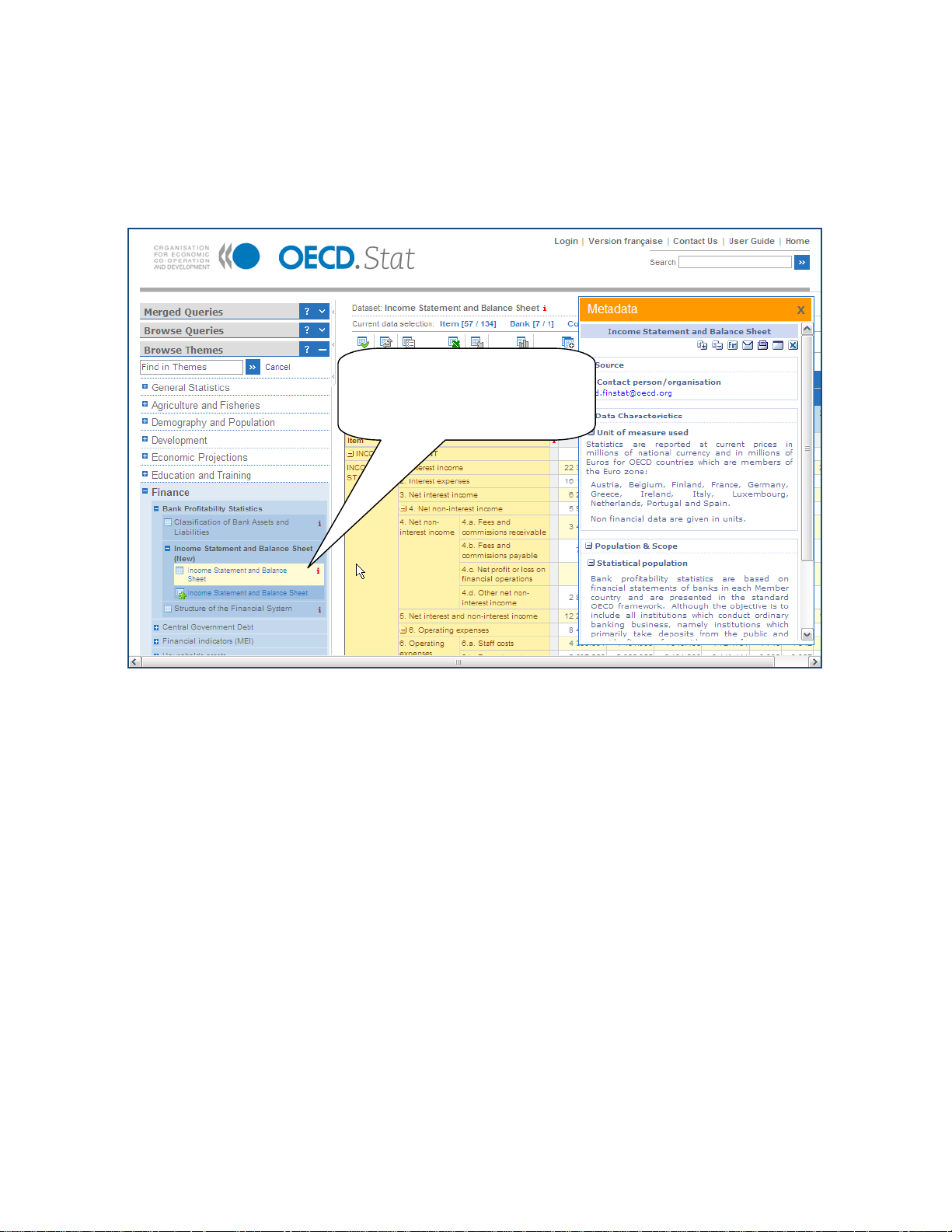
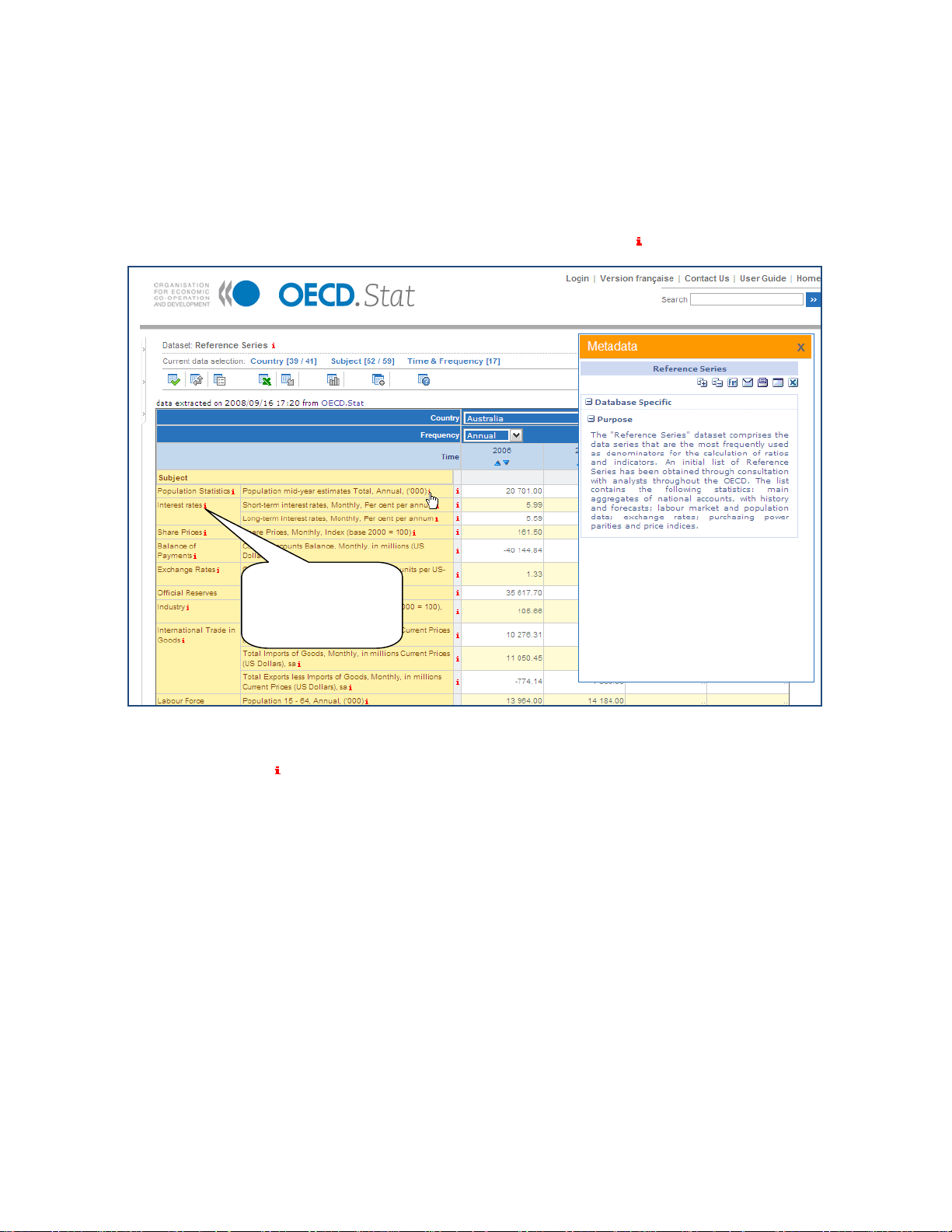
10BViewing Metadata
Metadata can be viewed at all levels, from the dataset-level abstract down through to cell
level footnotes. The presence of metadata is flagged by a small, red
.
Click on metadata
indicator to open
window displaying
metadata.
Figure 26: Footnotes and Dataset-level metadata
Clicking on the red
will bring up the related metadata window in the right-hand area of the
screen. The window can be moved around and closed by clicking on the “x” in the top right
corner of the window.
29BOther Related Metadata
If there are other metadata available in the data sets, which are closely related to the
metadata displayed on screen, a set of links to these other metadata will appear in the
metadata window, below the metadata text.
30BFlags
Certain pieces of metadata, which are recurrent within the dataset, are treated differently by
the system and referred to as flags. These flags appear as letters in parentheses in the cell
alongside the piece of data to which they correspond. Below any data table containing flags
will appear a legend, explaining the meaning of each letter used as a flag in the table.
09/2008 28 / 39
Page 29

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 27: Viewing the Data Flag Legend
11BWorking with Queries
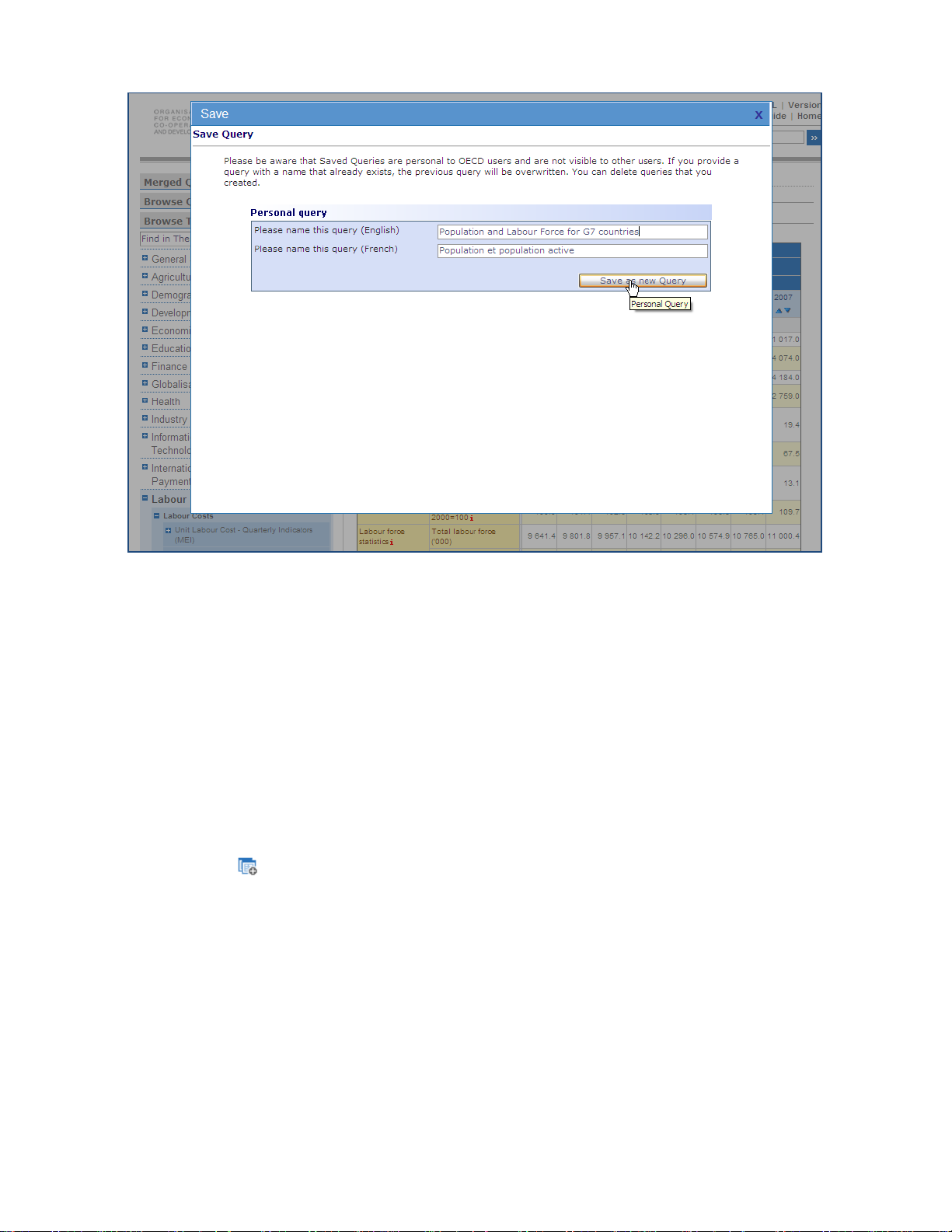
31BSaving a Query
When working with queries most features require you to log in, e.g. the Save Query button is
only displayed when you logged in via the Login link at the top right of the page. Once logged
in your name will be displayed at the top right of the page.
Your data selection, or query, can be saved at any time by clicking the Save Query button
) above the table, typing the name of the query, and then clicking the Save Query button
(
in the centre area of the screen. On subsequent visits to the browser, this saved query can
be opened to view the latest data availabl e within the selection.
Figure 28: Saving a Query
09/2008 29 / 39
Page 30
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 29: Saving a query with optional renaming
12BMerge Queries
Data from two or more datasets can be viewed in a combined table, using the Merge Query
function. Any common dimensions between the different datasets should be automatically
combined, provided that the data has been correctly entered into the system. Other
dimensions will automatically be displayed along the vertical axis, underneath section
headings indicating which dataset they come from.
32BCreating a Merge Query
To create a Merge Query, first create a customized view in one dataset. Then click the Merge
Query button (
) above the table to put this query into your “data basket”.
09/2008 30 / 39
Page 31

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 30: Adding a selection of data to a Multi-Dataset Query
Repeat this for each dataset that you wish to include in the multi-dataset query.
33BViewing the Query
When all selecti ons of data have been adde d, expand the Merged Queries panel in the lefthand area of the screen and click View to see the combined data table.
09/2008 31 / 39
Page 32

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 31: Viewing a Merge Query
34BChanging the Query
41BModify a selection
To modify any of the selections of data in the view, click the name of the dataset in the
Merged Queries panel, and then click Edit. The selection will appear on screen in the same
format as a single-dataset query. Make your changes and click once again on the Merge
Query button. Click View in the Merged Queries panel to see the modified query.
42BRemove a selection
To remove one of the selections in a Merged Query, click the name of the dataset in the
Merged Queries panel, and then cli ck Remove. Click View in the Merged Queries panel to see
the modified query.
35BSaving a Multi-Dataset Query
You can save your Multi-Dataset Query by clicking Save in the Merged Queries panel; typing
a name and then clicking Save once again.
09/2008 32 / 39
Page 33

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
53B
13BViewing Frequently Requested and Saved Queries
You have access to a set of public pre-defined queries through the Browse Queries panel.
There, you will also find your saved queries.
Open a public predefined query from
here
Click here to access
your Saved Queries
and view Recent
Queries
Figure 32: Using the Browse Queries panel to select a frequent ly requested table
Clicking on My Query Manager in the left panel display s the list of al l querie s which you hav e
personally saved together with a list of recent queries. This feature requires the u ser to login.
09/2008 33 / 39
Page 34

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 33: Viewing saved and recent queries
The Query Manager allows you to re-sort and save the list of queries as well as open and
delete any of them.
Figure 34: Sharing Saved Queries
Additionally, clicking the Share button displays a reference URL pointing to your saved query
which can be shared with colleagues, e.g. sent via email. Appropriate access rights will be
required to view the query.
50B14BViewing the Country Statistical Profiles
The Country Statistical Profiles are a special set of data that can be accessed through the
General Statistics theme. The data tables for these datasets include links on the right-hand
side to comparative views (graphs and tables) with other OECD countries.
09/2008 34 / 39
Page 35
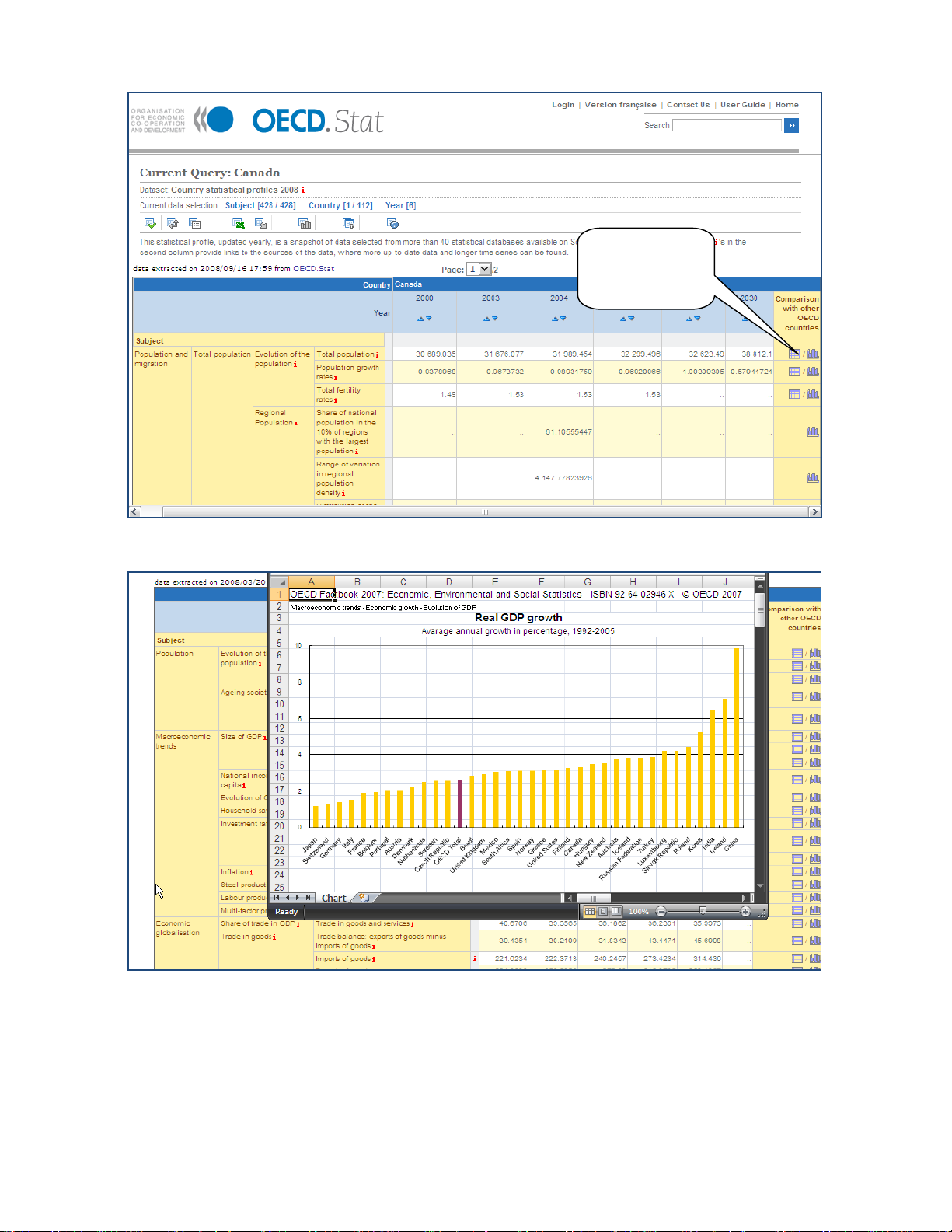
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Click to view
comparative
graphs and
tables
Figure 35: Viewing a Country Statistical Profile
Figure 36: Viewing the comparative country chart
09/2008 35 / 39
Page 36
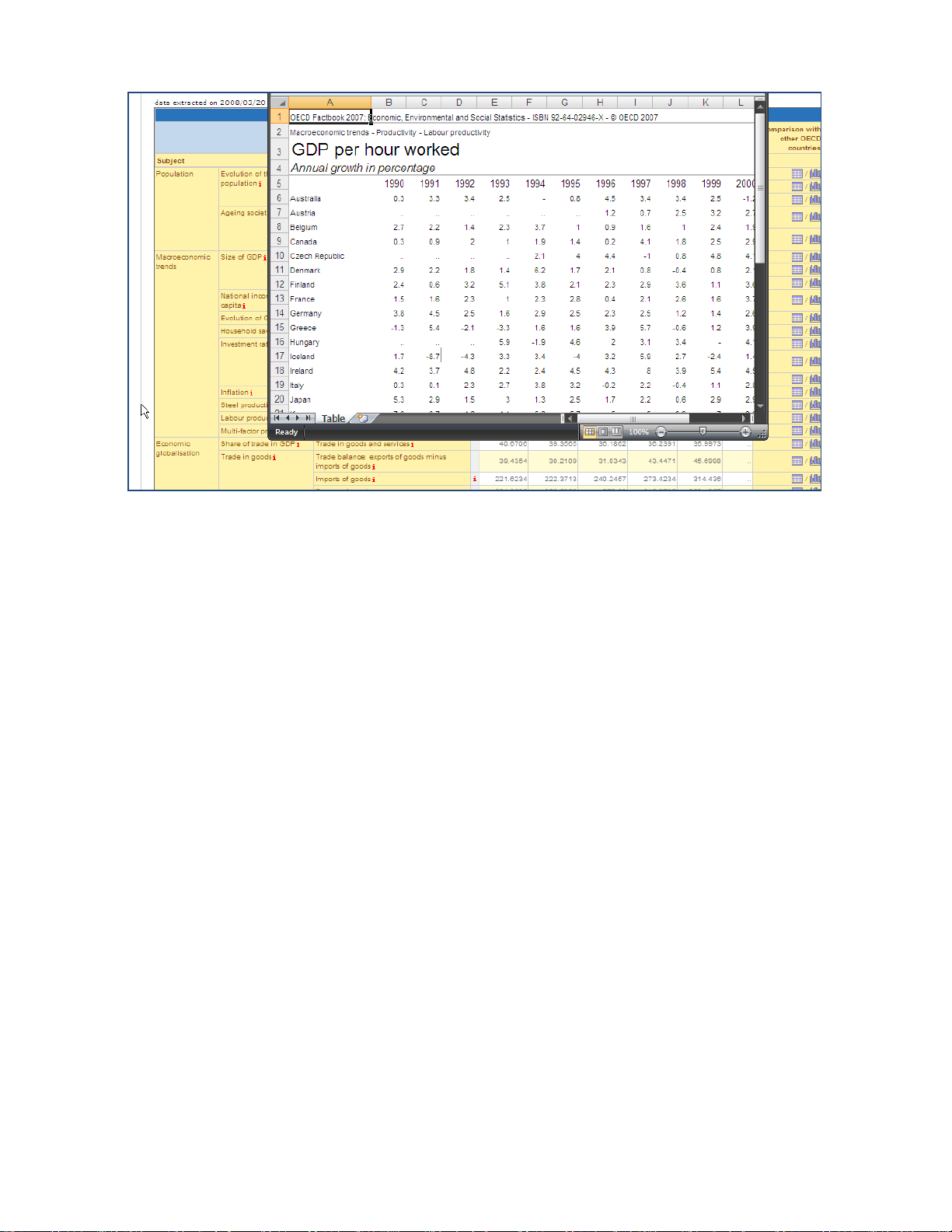
OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Figure 37: Viewing the comparative country table
51B
09/2008 36 / 39
Page 37

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
15BPrinting Data from the Browser
Without exporting data as an MS Excel spreadsheet, the OECD.Stat Web Browser allows the
printing of a table via the Print command of the contextual menu (right-click).
The metadata window fe atures a dedicated pr int option via one of the buttons at the top of
the window.
Right-Click to print
table using the web
browser print
options.
Click to print out
displayed metadata.
Figure 38: Printing data and other information from the Web Browser
09/2008 37 / 39
Page 38

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
2BProviding Feedback
The OECD.Stat Project Team can be contacted via E-mail using the Contact Us link, at the
top of the screen.
Please note that in order to address your concerns in a timely manner, we have set up two
separate e-mail accounts. The first address,
HTUOECDdotStat@oecd.orgUTH, is accessible by clicking
the upper link of the contacts page. This address should be used for any technical questions
or bugs that you encounter.
The second address,
HTUOECDdotContent@oecd.orgUTH, can be contacted by the second link on this
page. This address will provide responses to questions regarding the actual data content of
OECD.Stat (e.g., Do you have data on shoe manufacturing? What units are your data on
domestic animal sales provided in?).
Figure 39: Creating an E-mail to the OECD.Stat Pro j ect Team
09/2008 38 / 39
Page 39

OECD.Stat Web Browser User Guide
Table of Figures used in this Guide:
Figure 1: OECD.Stat Browser Getting Started page ........................................................ 6
Figure 2: Changing the language of the browser ............................................................ 7
Figure 3: Results from the search ranked in order of relevance ........................................ 8
Figure 4: Browsing through themes to view data............................................................ 9
Figure 5: Find a theme or data set .............................................................................. 10
Figure 6: Default dataset view and Current Selection values ........................................... 11
Figure 7: Using the Dimension Selector ....................................................................... 12
Figure 8: Searching in the dimension selector ............................................................... 13
Figure 9: Results of a Search in the dimension selector .................................................. 14
Figure 10: Date Range Selection ................................................................................. 15
Figure 11: Time Period Selection ................................................................................ 16
Figure 12: Moving a dimension to rotate the data view .................................................. 17
Figure 13: Changing the view using Country drop-down list ............................................ 18
Figure 14: Formatting Options Panel ........................................................................... 19
Figure 15: Table showing codes instead of names ......................................................... 20
Figure 16: Before using the Hide Empty Rows and Columns options ................................. 21
Figure 17: Dataset view with empty rows and columns hidden ........................................ 21
Figure 18: Using the Export to Excel option to save data in Excel format .......................... 22
Figure 19: Using the Other Export option to save data as a CSV file ................................. 23
Figure 20: Finding files related to a dataset .................................................................. 24
Figure 21: Selecting a file to download ........................................................................ 25
Figure 22: Exporting to PC-Axis table .......................................................................... 25
Figure 23: Charting – Line chart ................................................................................. 26
Figure 24: Charting – Bar chart .................................................................................. 27
Figure 25: Charting – Pie chart ................................................................................... 27
Figure 26: Footnotes and Dataset-level metadata ......................................................... 28
Figure 27: Viewing the Data Flag Legend ..................................................................... 29
Figure 28: Saving a Query ......................................................................................... 29
Figure 29: Saving a query with optional renaming ......................................................... 30
Figure 30: Adding a selection of data to a Multi-Dataset Query ....................................... 31
Figure 31: Viewing a Merge Query .............................................................................. 32
Figure 32: Using the Browse Queries panel to select a frequently requested table .............. 33
Figure 33: Viewing saved and recent queries ................................................................ 34
Figure 34: Sharing Saved Queries ............................................................................... 34
Figure 35: Viewing a Country Statistical Profile ............................................................. 35
Figure 36: Viewing the comparative country chart ......................................................... 35
Figure 37: Viewing the comparative country table ......................................................... 36
Figure 38: Printing data and other information from the Web Browser .............................. 37
Figure 39: Creating an E-mail to the OECD.Stat Project Team ......................................... 38
09/2008 39 / 39
Page 40

Tools to access Merged Queries, Saved
Queries and Frequently Requested Tables
Dimension Selection Tools - Selecting Variables | Moving Dimensions | Data Viewing Options
Data Export Tools - MS Excel | CSV/Text format
Full-Text Search tool
Search themes, datasets and
data queries exactly as they
appear in the theme panel
Dynamic Data Graphics Tool
Query Management Tools - Merge Query | Save Query
Help - User Guide
Collapsible Theme panel with drill-down
list of themes and datasets
www.SourceOECD.org/database/OECDStat
Collapsible/Movable Metadata window
Data View panel
 Loading...
Loading...