Page 1

Odin TeleSystems Inc.
RTP Bridge
User’s Guide
Doc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1
Rev. 1.9
pyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc, 2010 www.odints.com
Co
December 20, 2010
Page 2

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 2(36)
Copyright
© Copyright 2010, Odin TeleSystems, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying,
recording or otherwise, without the prior written consent of Odin TeleSystems Inc., 800 East Campbell Road, Suite
334, Richardson, Texas 75081, U. S. A.
Trademarks
Odin TeleSystems, OTX, RTP Bridge, RTP Streamer, Alvis-CSI, Alvis-PBX, Alvis-PCIe, Alvis-ASM, the Odin
Logo, are trademarks of Odin TeleSystems Inc., which may be registered in some jurisdictions. Other trademarks
are the property of their respective companies.
Changes
The material in this document is for information only and is subject to change without notice. While reasonable
efforts have been made in the preparation of this document to assure its accuracy, Odin TeleSystems Inc., assumes
no liability resulting from errors or omissions in this document, or from the use of the information contained herein.
Odin TeleSystems Inc. reserves the right to make changes in the product design without reservation and notification
to its users.
Warranties
THE PRODUCT AND ITS DOCUMENTATION ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF
ANY KIND. ODIN TELESYSTEMS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL THE WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE. ODIN TELESYSTEMS DOES NOT WARRANT THAT THE
FUNCTIONALITY OF THE PRODUCT WILL MEET ANY REQUIREMENTS, OR THAT THE OPERATIONS
OF THE PRODUCT WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED OR ERROR-FREE, OR THAT DEFECTS WILL BE
CORRECTED. FURTHERMORE, ODIN TELESYSTEMS DOES NOT WARRANT OR MAKE ANY
REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF THE PRODUCT OR ITS DOCUMENTATION IN TERMS
OF THEIR CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY, OR OTHERWISE. NO ORAL OR WRITTEN
INFORMATION OR ADVISE GIVEN BY ODIN TELESYSTEMS OR ODIN TELESYSTEMS’ AUTHORIZED
REPRESENTATIVE SHALL CREATE A WARRANTY. SOME JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE
EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES, SO THE ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCE SHALL ODIN TELESYSTEMS INC., ITS OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES, OR
AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING
DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS, PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS
INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT AND ITS DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ODIN TELESYSTEMS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT WILL ODIN TELESYSTEMS’ LIABILITY FOR ANY REASON EXCEED THE
ACTUAL PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT AND ITS DOCUMENTATION. SOME JURISDICTIONS DO
NOT ALLOW THE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION OF LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL AND CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 3

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 3(36)
Table of Contents
1 Introduction.........................................................................................................................................4
1.1 Description .........................................................................................................................................4
1.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................. 5
2 T1/E1 Channels Configuration..........................................................................................................6
3 The RTP Bridge Installation and Running.......................................................................................9
4 Command Line Arguments..............................................................................................................10
5 The RTP Bridge Commands............................................................................................................11
5.1 Running RTP Bridge Commands from a Configuration File........................................................... 18
5.2 Running RTP Bridge Commands from a Command Line................................................................ 18
5.3 Running RTP Bridge Commands via Telnet Interface..................................................................... 18
6 Transcoding Operation.....................................................................................................................19
7 Multi-conferences support................................................................................................................22
8 Testing Verification Procedure........................................................................................................25
8.1 Testing Scheme 1 .............................................................................................................................25
8.2 Testing Scheme 2 .............................................................................................................................26
9 The RTP Bridge License...................................................................................................................29
10 References .......................................................................................................................................30
11 Product Versions History...............................................................................................................31
12 Document History...........................................................................................................................34
13 Glossary...........................................................................................................................................36
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 4
RTP Bridge User’s Guide 4(36)
1 Introduction
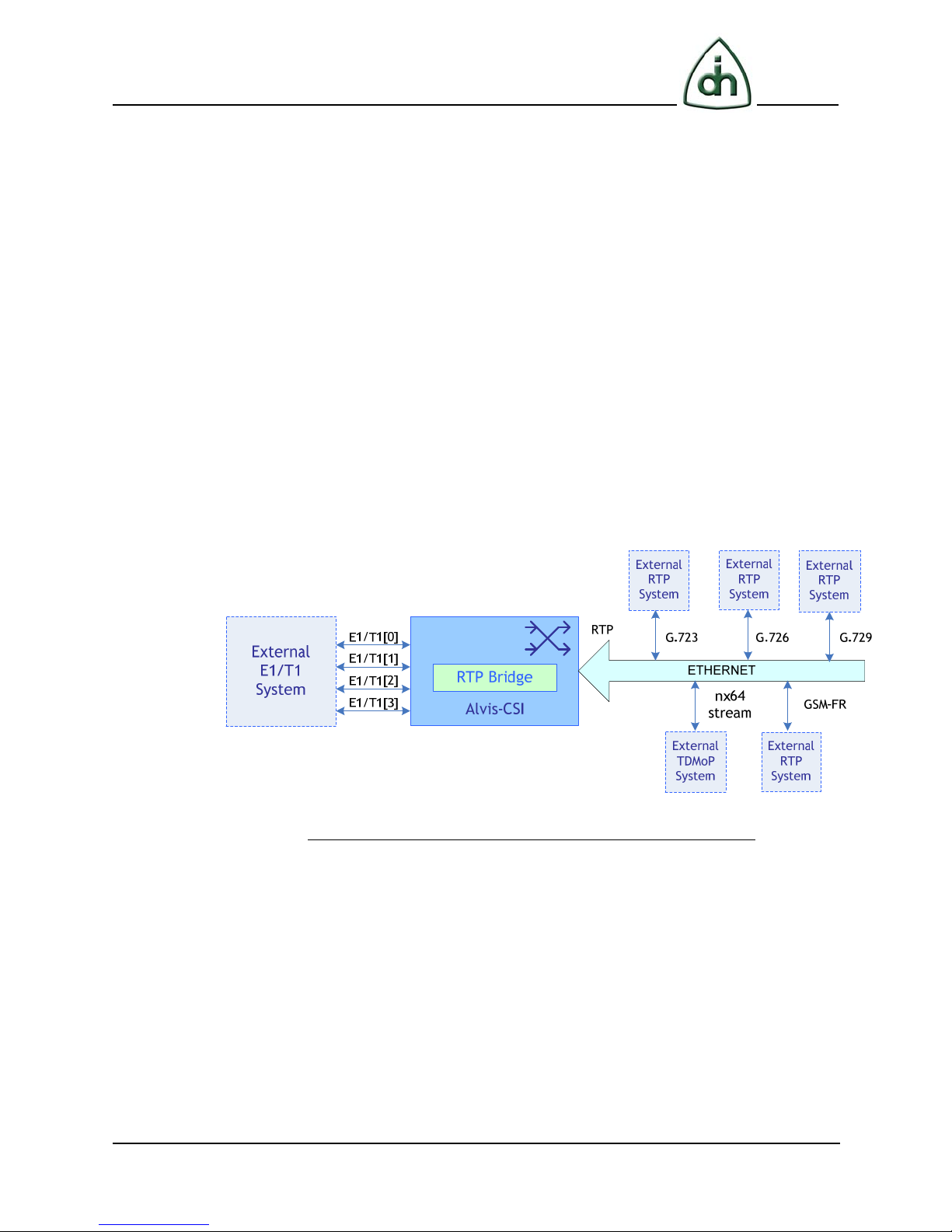
The RTP Bridge is a universal streaming media gateway application running on the top of
TDM (E1/T1) and RTP media streams designed for the industry's award-winning Odin
Telecom frameworX (OTX) hardware. This document provides detailed information
about the RTP Bridge product.
1.1 Description
The RTP Bridge solution provides data transfer between various E1/T1 timeslots and
RTP end-points in simplex or duplex directions. Voice data could be additionally
transcoded between each of G.711 (a-law, u-law) / G.711.1 / G.711.2 E1/T1 timeslots
and RTP end-points (G.711, G.723, G.726, G.729, GSM-FR, G.722 / G.722.1 / G.722.2
(AMR-WB)) in any order. (See Figure 1)
It is also possible to use the
case the RTP Bridge connects data from one IP-Address:Port to another IP-Address:Port,
with transcoding options.
RTP Bridge product without E1/T1 TDM streams. In that
Figure 1 The universal streaming media gateway on the OTX Hardware
The RTP Bridge is targeted to use DaVinci™-enabled products of Odin TeleSystems like
Alvis-CSI, Alvis-PBX, Alvis-PCIe, Alvis-ASM. It runs on the embedded TI DM64XX
SoC processors.
The RTP Bridge uses the OtxRtp Library on the DM6443 SoC ARM core. Also there are
Win32/64 and Linux versions of the OtxRtp Library available.
The RTP Bridge application could be remotely controlled in real-time by the Telnet
interface; it is possible to make connect / disconnect, status monitoring, etc. Connections
could be also taken from the configuration file at startup.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 5

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 5(36)
1.2 Features
Simultaneous bi-directional data transfer between E1/T1 spans and various RTP
remote nodes.
Uses a Telnet interface for E1/T1 timeslot–to-RTP endpoints mapping
configuration.
Transcoding of voice data between any of G.711 (a-law, u-law) / G.711.1 /
G.711.2, G.723, G.726, G.729, GSM-FR, G.722 / G.722.1 / G.722.2 (AMR-WB)
codecs.
Multi-party conferences support. (According to RFC 3550/3551 each RTP
session (listened port) could be connected to some other remote systems. I.e. we
could stream one E1/T1 timeslot to different remote locations at the same time.)
N64 Streaming support (The RTP Bridge allows to send E1 super channels over
UDP to PC, and backwards, to receive UDP packets with E1 data and to send
them to E1 as super channels).
Integrated SNMP monitoring
LED Alarms indication.
Possibility to send OTX Events over UDP.
DSP C64+ powered built-in configurable jitter buffer of incoming RTP packets.
TDM Passive monitoring provides the ability to stream E1/T1 spans to the RTP
end-points in a non-intrusive mode.
Optimized data processing using multi-core DaVinci™ architecture with
offloading of all real-time operations on the powerful C64+ DSP core.
Compatible with the OTX DaVinci driver.
Compatible with the OTX XDM SDK API.
Multi-session mode; the user can create any numbers of listening ports on one
system.
Real-time statistics for RTP sessions is available.
Customizable RTP streams parameters: packetizing time, packet size, adjustable
codec parameters, etc.)
Optimized RTP monitoring mode allows to listen RTP streams coming with
different IP-addresses and ports.
Supports IETF RFC 3550, RFC 3551 RTP/RTCP Transport protocols.
A variety of optional decoding / encoding Plugins are available (ATM/AAL5,
HDLC/SS7, TRAU, H.324M).
1
using the OtxSNMP Library (SNMP Layer1) and
1
For more detailed information on SNMP monitoring settings please refer to Alvis-CSI Technical
Description (version 1.5 and later), chapter 8.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 6

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 6(36)
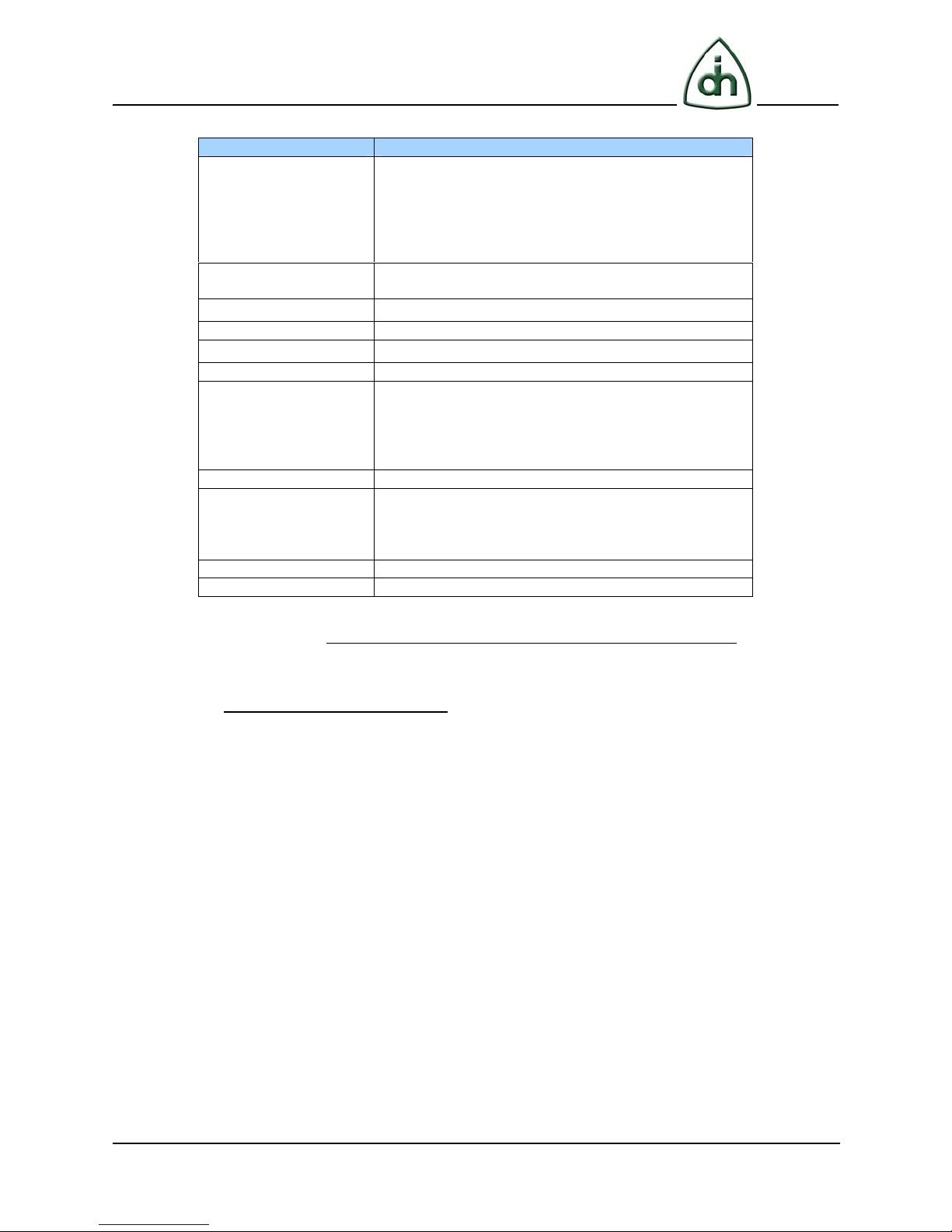
2 T1/E1 Channels Configuration
The T1/E1 channels configuration before running the RTP Bridge is optional. It is set in
“OtxHwLayer.conf” file in a case of RTP Bridge uses T1/E1 streams.
The structure of the OtxHwLayer configuration file should be composed from the
parameters provided by line. Each parameter is initialized with the name and the value
represented on a single line through any number of spaces.
Example: T1E1LiMode E1
The configuration file can also contain comments. The comment line begins with ‘#’
character and ends with the end of line. If you need to allocate a few lines for comment,
you should put a ‘#’ character at the beginning of each line.
Example: # Line termination mode
Most of the parameters are set by default; all you need is to define a number of key
parameters: the type of board (BoardType), the index of board (BoardNo), etc.
Please see the full list of configuration file parameters in Table 1.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 7
RTP Bridge User’s Guide 7(36)
Parameter Name
Termination OTX_T1E1_TERM_120_OHM,
OTX_T1E1_TERM_100_OHM,
OTX_T1E1_TERM_75_OHM,
OTX_T1E1_TERM_75_OHM_BALANCED,
OTX_T1E1_TERM_300_OHM,
OTX_T1E1_TERM_HIGHZ
RxThreshold
Positive integer, defaults to
OTX_HWLAYER_DEFAULT_RX_THRESHOLD: 500
SetMonitorMode
FrontEndAmplifier
BoardType
BoardNo
T1FrameFormat OTX_T1_FF_F12, OTX_T1_FF_F4,
T1LineCode
E1FrameFormat OTX_E1_FF_DOUBLE_FRAME,
Boolean value P_BOOL
Boolean value P_BOOL: OFF
A2, A2P, A4, A8, A4M, A8M, AA
The index of board, defaults to 0
OTX_T1_FF_ESF, OTX_T1_FF_F72,
OTX_T1_FF_F12_J1, OTX_T1_FF_F4_J1,
OTX_T1_FF_ESF_J1, OTX_T1_FF_F72_J1,
OTX_T1_FF_UNFRAMED
OTX_T1_LC_AMI, OTX_T1_LC_B8ZS
OTX_E1_FF_CRC4_MULTIFRAME,
OTX_E1_FF_CRC4_MULTIFRAME_G706,
OTX_E1_FF_UNFRAMED
E1LineCode
T1E1LiMode
OTX_E1_LC_AMI, OTX_E1_LC_HDB3
T1, E1
Possible Values
2
3
: NO
4
Table 1 The full list of OtxHwLayer configuration file parameters
Note: The default values are marked bold.
2
Line termination mode can be one of the following:
OTX_T1E1_TERM_120_OHM – Span is terminated for 120 ohm twisted pair (balanced
differential signal)
OTX_T1E1_TERM_100_OHM – Span is terminated for 100 ohm twisted pair (balanced
differential signal)
OTX_T1E1_TERM_75_OHM – Span is terminated for 75 ohm coax (unbalanced unipolar
signal)
OTX_T1E1_TERM_HIGHZ – Span is not terminated (Balanced, High impedance, for
monitoring scenarios when short (<2 meters) monitor taps are used)
OTX_T1E1_TERM_75_OHM_BALANCED – Span is terminated for 75 ohm balanced
differential signal (for special monitoring conditions)
OTX_T1E1_TERM_300_OHM – Span is terminated for 300 ohm twisted pair (balanced
differential signal)
3
Possible values for P_BOOL: TRUE, T, 1, YES, ON, FALSE, F, 0, NO, OFF.
4
Explanation of abbreviations for the BoardType parameter:
A2 - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_2_CSI,
A2P - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_2_PBX,
A4 - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_4_CSI,
A8 - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_8_CSI,
A4M - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_4M_CSI,
A8M - OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS_8M_CSI,
AA
- OTX_DEVICE_DMP_ALVIS.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 8

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 8(36)
Example (Alvis-4-CSI):
--------------------------------------------- OtxHwLayer.conf --------------------------------------
E1FrameFormat OTX_E1_FF_CRC4_MULTIFRAME
# Line termination mode
Termination OTX_T1E1_TERM_100_OHM
# Receive threshold (in mV)
RxThreshold 500
# Set Monitor (-20dB) mode (YES/NO)
SetMonitorMode NO
# Turning front end Amplifier ON/OFF
FrontEndAmplifier OFF
T1E1LiMode E1
# Board type
BoardType A4
# Board No
BoardNo 0
-------------------------------------------------- EOF --------------------------------------------------
Doc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 9

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 9(36)
3 The RTP Bridge Installation and Running
It is recommended to install the RTP Bridge on Alvis-4-CSI board with firmware
package version 2.11.12 or later. For more information of firmware upgrade, please refer
to Alvis-CSI Firmware Upgrade HOW TO
1.1).
To install the OTX RTP Bridge from rpm repository please follow these steps:
1. Update the rpm repository packets list:
apt-get update
2. Install RTP Bridge package with a command:
apt-get install rtpbridge
(Odin document #1712-1-HCA-1020-1.0-
3. Reboot the board (Alvis-CSI):
sync & reboot
The RTP Bridge will automatically start at system start-up (daemon mode). You can
connect it via Telnet. If you want to start with CLI, then issue the commands:
service rtpbridge stop
/opt/rtpbridge/rtpbridge
If you will get a “No license found” message please follow the instructions in Chapter 9 The RTP Bridge License.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 10

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 10(36)
4 Command Line Arguments
The RTP Bridge accepts several command line arguments:
--help or -h
Displays help with command line arguments available.
--daemon or -d
Runs the RTP Bridge in a daemon mode.
--pid <file_name> or -p <file_name>
Changes the name of pid-file (where process identifier is stored). By default it is
‘/var/run/rtpbridge.pid’.
--port or -P
Changes port for Telnet interface. By default it is 10000.
--burst or -b
Uses Burst events instead of Core-to-Core mechanism.
--packetsize <msec> or -s <msec>
Sets the default size of RTP packets (in milliseconds) in TDM->RTP Mode.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 11

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 11(36)
5 The RTP Bridge Commands
There are several commands available to control / get status of connections between the
RTP and TDM media streams (or mixed):
CONNECT
MCONNECT
LIST
DISCONNECT
DSP LOAD
DSP LOAD EX
BURST STATS
CONSTAT
JITTER BLOCKS
READCONFIG
SHOW LICENSE
PACKET SIZE
BENCH
TRACES
EVENTS
CONSOLE
CORE
Please see the detailed commands description below.
CONNECT <src_type>:<src_stream>:<src_idx>:[opt]
<dst_type>:<dst_stream>:<dst_idx>:[opt]
This command establish a simplex cross-connect between an incoming and outgoing
stream. To do a duplex connection, one more connection needs to be done separately.
The fields are:
src_type, dst_type:
RTP (RTP connection), TDM (TDM cross-connect), TDMOE (Pseudowire crossconnect)
src_stream, dst_stream:
For RTP: IP-address, for TDM: Span number
src_idx, dst_idx:
For RTP: Port number (local/remote), for TDM: Timeslot
opt:
Usually src_codec, dst_codec are voice codec used for the specified stream end, e.g.
alaw (or g711a), ulaw (or g711u), g729, g723, g726, etc.
Note:
If src_codec and dst_codec parameters are not specified, they take the default value.
Currently the default codec is alaw.
For the incoming RTP data src_codec can be overridden by the payload type of RTP
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
JITTER BLOCKS
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 12

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 12(36)
packet.
The abbreviations are: src is source, dst - destination, li - span, ts – timeslot, codec codec name, ip – IP-address, r_port – remote port number, l_port – local port number.
For span and timeslot parameters several formats are supported; you can skip li, ts
abbreviations and specify only span and timeslot numbers.
E.g.: li0:ts5 or 0:5.
Below there are several examples of the CONNECT command with some description:
1. TDM -> TDM Mode
connect tdm:<src_li#>:<src_ts#>[:src_codec] tdm: <dst_li#>:<dst_ts#>[:dst_codec]
Example: connect tdm:li0:ts5:ulaw tdm:li1:ts10:alaw
Note: src_codec and dst_codec will be used as a default TDM codec type specified in the
default configuration settings.
2. RTP -> TDM Mode
connect rtp:<src_ip>:<src_remote_port>:<src_local_port>[:src_codec] tdm:
<dst_li#>:<dst_ts#>[:dst_codec]
Example: connect rtp:192.168.102.70:5060:6060:g729 tdm:li0:ts10:alaw
Note: Omitted src_codec will be set according to the incoming RTP payload type
automatically. Omitted dst_codec will be substituted by the default RTP stream encoder
codec.
3. TDM -> RTP Mode
connect tdm:<src_li#>:<src_ts#>[:src_codec]
rtp:<dst_ip>:<dst_remote_port>:<dst_local_port>[:dst_codec]
Example: connect tdm:li0:ts10:alaw rtp:192.168.102.70:5060:6060:g729
4. RTP -> RTP Mode
connect rtp:<src_ip>:<src_remote_port>:<src_local_port>[:src_codec]
rtp:<dst_ip>:<dst_remote_port>:<dst_local_port>[:dst_codec]
Example: connect rtp:192.168.102.60:5060:6060:g726
rtp:192.168.102.70:5060:6060:g729
5. N64 Streaming
connect tdmli:<src_li#>[:format] tdmop:<dst_ip>:<dst_remote_port>:<dst_local_port>
connect tdmop:<src_ip>:<src_remote_port>:<src_local_port> tdmli:<dst_li#>
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 13

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 13(36)
The abbreviations are:
src_li, dst_li: source/destination E1/T1 span
src_ip, dst_ip: source/destination IP-address
src_remote_port, dst_remote_port: source/destination
src_local_port, dst_local_port: source/destination local port number
format - defines which timeslots to send/receive; can take following values:
number from 1 to 32 (32 connects 0-31 timeslots, 31 connects 1-31 timeslots, 30
connects 2-31 timeslots, etc)
string ‘raw’ (connects 0-31 timeslots)
mask [ts1,ts2,ts3,…] (defines the list of timeslots to connect)
Example: connect tdmli:0:mask[3,7,11] tdmop:192.168.102.60:5060:6060
Note: If format is not declared, timeslots 1-31 are connected.
Note: With the Alvis-PCIe board you can use only RTP -> RTP connection mode.
Also you can use the connection command with a conference mode. For more
information see chapter 7 Multi-conferences support.
To quickly create
many RTP connections please use the following command:
MCONNECT <num_of_conn>
rtp:<src_ip>:<src_remote_port+shift>:<src_local_port+shift>:[src_codec]
rtp:<dst_ip>:<dst_remote_port+shift>:<dst_local_port+shift>:[dst_codec]
The abbreviations are:
num_of_conn: number of connections
src_ip, dst_ip: source/destination IP-address
src_remote_port, dst_remote_port: source/destination remote port number
src_local_port, dst_local_port: source/destination local port number
shift: port’s shift
src_codec: source/destination voice codec used for the specified stream end, e.g. alaw (or
g711a), ulaw (or g711u), g723, g726, g729.
Note:
You can use this command only in the case of RTP Bridge commands run from a
configuration file (Refer to Chapter 5.1).
If src_codec and dst_codec para
meters are not specified, they take the default value.
Currently the default codec is alaw.
For the incoming RTP data src_codec can be overridden by the payload type of RTP
packet.
Example: mconnect 31 rtp:192.168.102.90:8002+4:7002+4:alaw
rtp:192.168.102.90:8002+4:9006+4:g729
(Creates 31 connections, See Figure 1Figure 2)
To see the list of existing c
onnections use the command (See Figure 2):
LIST
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 14

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 14(36)
Figure 2 List of RTP connections created using mconnect command
To disconnect a certain connection please see the number of this connection in the list
and type the command (See Figure 3):
DISC
ONNECT <connection_number>
Also for disconnection you can use a command similar to CONNECT:
DISCONNECT <src_type>:<src_stream>:<src_idx>:[opt]
dst_type>:<dst_stream>:<dst_idx>:[opt]
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 15

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 15(36)
Figure 3 List of connections after disconnection of one stream
To test the DSP core load you can use the following commands (See Figure 4):
DSP LOAD
Output the DSP load once.
DSP LOAD EX
Output the DSP load in a loop.
Figure 4 DSP core load output
Note: These DSP LOAD commands are available only from console.
To display the Burst statistics use the following command (See Figure 5):
BURST STATS
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 16

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 16(36)
Figure 5 Burst statistics output
Note: This command can be run only from console. This command is deprecated. It is
applicable in non Core-2-Core mode of RTP Bridge only.
To display channel statistics (is channel incoming or outgoing, TDM or RTP, payload
type, Jitter statistics for RTP connections) use the command (See Figure 6):
CONS
TAT <connection_number>
To set the jitter blocks parameters (size and delay) use the following command:
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Figure 6 RTP connection statistics
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 17

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 17(36)
JITTER BLOCKS:<max>:<min>
The abbreviations are: max - jitter size, min - jitter delay in 10ms blocks.
Note: New jitter blocks values do not apply to previously created connects. Thus you
should create connects only after jitter blocks command input. This command can not be
run from a configuration file.
Example: jitter blocks:500:30
(jitter time is 5 seconds, jitter delay is 300 milliseconds)
SHOW LICENSE – displays information on RTP Bridge license (customer name,
software version, board serial number, and expiration date).
PACKET SIZE <msec> - sets the default size of RTP packets (in milliseconds) in
TDM->RTP Mode.
Note: This command is only applicable if no connection exists.
BENCH <codec> enc|dec [test_num] - executes codec benchmark.
The abbreviations are:
codec: codec name (e.g. g723)
enc|dec: choose one option to test (encoder or decoder)
test_num - number of tests to run
Note: This command is not applicable to alaw, ulaw and for some decoders. Command is
available only from console. This command is only applicable if no connection exists.
TRACES on|off - switches DSP traces (on/off).
Note: This command can be executed from consolу only.
EVENTS udp:<dst_ip>:<dst_port>:[<src_port>] - sets up event sending over UDP.
The abbreviations are:
dst_ip: destination IP-address
src_port, dst_port: source/destination port number to send UDP packets
Note: src_port = dst_port by default. This command can be executed from consolу only.
CONSOLE <cmd> - executes console command.
Note: This command can be executed from configuration file or Telnet interface only.
Example: console traces on
(executes traces on command in console)
CORE <cmd> - executes Telnet interface command.
Note: This command can be executed from consolу only.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 18

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 18(36)
Example: core readconfig my.conf
5.1 Running RTP Bridge Commands from a Configuration File
To run the RTP Bridge commands from a configuration file please input appropriate
commands in a ‘cfg’ file and place it in a /root directory. The commands will run at RTP
Bridge start-up.
Also to read the commands from the configuration file you can type in Telnet:
READCONFIG <file_name>
5.2 Running RTP Bridge Commands from a Command Line
The RTP Bridge commands can be run from a command line (CLI). Type the appropriate
commands after running of RTP Bridge.
5.3 Running RTP Bridge Commands via Telnet Interface
If the RTP Bridge is already running, you can use the Telnet Interface for dynamic
configuration (real-time control commands). The default port is 10000.
You can restrict access to RTP Bridge via the Telnet interface using White List feature.
For this please create ‘allow.conf’ file in /opt/rtpbridge directory at Alvis board. Specify
the list of allowed IP addresses there. If this file is empty, no one address is allowed. If
‘allow.conf’ does not exist, any IP address has permission to connect to the RTP Bridge.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 19

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 19(36)
6 Transcoding Operation
Odin provides boards with pre-installed and pre-configured vocoders. They are also
available with the OTX XDM SDK.
The RTP Bridge supports the transcoding operation (data converting from one codec to
another as softswitch) by the following scheme:
CodecA -> linear PCM16 -> CodecB.
The RTP Bridge allows to implement transcoding operation of the following codecs:
G.711 (a-law, u-law) / G.711.1 / G.711.2
G.723
G.726
G.729
GSM-FR
G.722 / G.722.1 / G.722.2 (AMR-WB).
Note that it is possible any combination between these codecs as in RTP channels so in
TDM channels.
The transcoding operations are offloaded to powerful C64+ DSP core (4700 MIPS) of the
TI DM64XX SoC processors without increasing the load of ARM core. So the total
number of transcoding channels can be determined by resource-intensiveness of encoding
/ decoding algorithms in accordance with the selected pair of codecs. Below are the
benchmark results to judge the availability and number of channels and CPU. (See Table
2, Table 3)
Doc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 20

Codec
name
Enc / Dec
Number
of test
iterations
Bytes processed Milliseconds Bytes output N5
G.723 enc 350 11256000 7270 562800 97
G.723 dec 500 20040000 2657 40080000 943
G.726 enc 120 3859200 6099 964800 40
G.726 dec 60 1200000 7191 4800000 42
G.729 enc 350 11256000 6047 703500 117
G.729 dec 850 4250000 7220 68000000 588
Table 2 Synthetic testing results of encoding / decoding operations
Codec
name
Enc / Dec
G.711 - 30 10 1.63 28-30 1.9
G.723 enc 35 57 0.43 65-70 1.37
G.723 dec 35 15 3.2 45-50 2.0
G.726 enc 20 64 2.55 38-40 2.15
Number of
connections
DSP Load
%
DSP Load
per channel
ARM Load
%
ARM Load
per channel
G.726 dec 20 51 1.53 40-45 1.73
G.729 enc 30 46 0.73 52 1.6
G.729 dec 30 22 0.53 50-55 2.43
Table 3 Overall testing results with account of incoming and outgoing RTP connections and jitter6
The Alvis powered by the RTP Bridge can successfully offload x86 servers increasing
the compactness of solution. This makes possible to create low power-consumption
devices as a breeze. (See Table 4)
Codec
name
Number of
encoding
channels
G.723 63 318
G.726 32 39
G.729 63 188
Table 4 Number of encoding / decoding channels
Number of
decoding
channels
5
The number of voice channels that can handle the codec.
6
The testing was performed with 20ms RTP packets stream.
pyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc, 2010 www.odints.com
Co
Page 21

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 21(36)
Enc / Dec
Scenario
Encoding: TDM(A-law)->encoding->RTP
Decoding: RTP->decoding->TDM(A-law)
Encoding+Decoding: TDM(A-law)->encoding->
RTP(127.0.0.1)->decoding->TDM(A-law)
Encoding+Decoding: RTP->decoding->encoding->RTP
Table 5 TI C64+ DSP Core Load Tests in various Encoding/Decoding Scenarios
GSM G.723.1 G.729
129 67 77
124 200 144
62 51 49
93 62 62
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 22

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 22(36)
7 Multi-conferences support
The RTP Bridge supports a multi-conference mode. It is possible to create any number of
conference participants. The number of conferences is unlimited and mixing operations
are offloaded on the DSP C64x+ core simultaneously with transcoding and RTP
packetizing.
Conference connections are created by several usual connects (conference input and
output). The syntax of the commands is similar to common RTP Bridge commands
syntax with adding the conference identifier. Please see the commands of conference
connection below.
CONNECT <src_type>:<src_stream>:<src_idx>:[opt] conf:<conf_id>
CONNECT conf:<conf_id> <dst_type>:<dst_stream>:<dst_idx>:[opt]
The fields are:
src_type, dst_type:
RTP (RTP connection), TDM (TDM cross-connect), TDMOE (Pseudowire crossconnect)
src_stream, dst_stream:
For RTP: IP-address, for TDM: Span number
src_idx, dst_idx:
For RTP: Port number (local/remote), for TDM: Timeslot
opt:
Usually src_codec, dst_codec are voice codec used for the specified stream end, e.g.
alaw (or g711a), ulaw (or g711u), g729, g723, g726, etc.
conf_id:
Conference identifier (any string to identify the conference)
The abbreviations are: src is source, dst - destination, li - span, ts – timeslot, codec codec name, ip – IP-address, r_port – remote port number, l_port – local port number.
Note:
If src_codec and dst_codec parameters are not specified, they take the default value.
Currently the default codec is alaw.
For the incoming RTP data src_codec can be overridden by the payload type of RTP
packet.
Various conference connection schemes are available. Please see some examples below.
Scheme1: connect rtp:<src_ip_1>:<src_r_port_1>:<src_l_port_1>:[src_codec_1] conf:1
connect rtp:<src_ip_2>:<src_r_port_2>:<src_l_port_2>:[src_codec_2] conf:1
connect conf:1 tdm:<dst_li#>:<dst_ts#>:[dst_codec]
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 23

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 23(36)
Figure 7 RTP-to-TDM conference connection scheme
Scheme2: connect tdm:<src_li#_1>:<src_ts#_1>:[src_codec_1] conf:2
connect tdm:<src_li#_2>:<src_ts#_2>:[src_codec_2] conf:2
connect conf:2 rtp:<dst_ip>:<dst_r_port>:<dst_l_port>:[dst_codec]
Figure 8 TDM-to-RTP conference connection scheme
Scheme3: connect tdm:<src_li#>:<src_ts#>:[src_codec_1] conf:3
connect rtp:<src_ip>:<src_port>:[src_codec_2] conf:3
connect conf:3 rtp:<dst_ip>:<dst_port>:[dst_codec]
TDM
RTP 2
RTP 1
Figure 9 TDM+RTP-to-RTP conference connection scheme
Scheme4: connect rtp:<src_ip_1>:<src_port_1>:[src_codec_1] conf:4
connect rtp:<src_ip_2>:<src_port_2>:[src_codec_2] conf:4
connect conf:4 rtp:<src_ip_3>:<src_port_3>:[src_codec_3]
Figure 10 RTP-to-RTP conference connection scheme
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 24

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 24(36)
Example:
connect rtp:192.168.102.9:8002:7002 conf:test1
connect rtp:192.168.102.9:8004:7004 conf:test1
connect conf:test1 rtp:192.168.102.9:8006:7006:alaw
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 25

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 25(36)
8 Testing Verification Procedure
8.1 Testing Scheme 1
To test RTP Bridge please use the following connection scheme (See Figure 11):
Figure 11 RTP Bridge Testing Scheme 1
Notes to the scheme:
a. The T1/E1Analyzer is run on an OTX board (e.g., on t2pp) connected to Li0 of
the Alvis Board.
b. The RTP Bridge sets RTP connection on a loopback IP-address 127.0.0.1.
c. Alvis Board should be one of the following OTX boards:
Alvis-2-CSI
Alvis-4-CSI
Alvis-4M-CSI
Alvis-8-CSI
Alvis-8M-CSI
Alvis-ASM
Alvis-PCIe
Alvis-2-PBX
1. Update the rpm repository packets list at Alvis Board:
apt-get update
2. Install RTP Bridge package at Alvis Board with a command:
apt-get install rtpbridge
3. Reset Linux file buffers at Alvis Board with a command:
sync
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 26

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 26(36)
4. Run RTP Bridge at Alvis Board with the command:
/opt/rtpbridge/rtpbridge
If you will get a “No license found” message please follow the instructions in
Chapter 9 - The RTP Bridge License.
1. In CLI of RTP Bridge issue the co
mmands:
connect tdm:li0:ts1:g711a rtp:127.0.0.1:7000:8000:g711a
connect rtp:127.0.0.1:8000:7000:g711a tdm:li0:ts1:g711a
where 127.0.0.1 is the loopback IP-address.
2. Make sure that connections are created, type:
list
3. Run the T1/E1 Analyzer. Play audio file in a-law format with T1/E1 Analyzer on
TS1.
4. The RTP Bridge should put a-law data to Li0:TS1 that you can listen with the
T1/E1 Analyzer.
8.2 Testing Scheme 2
Note: For testing by this scheme, you should have RTP Streamer software with valid
license.
To test RTP Bridge in conjunction with RTP Streamer please use the following
connection scheme (See Figure 12):
Figure 12 RTP Bridge Testing Scheme 2
Notes to the scheme:
a. The T1/E1Analyzer is run on an OTX board (e.g., on t2pp) connected to Li0 of
the Alvis Board #1.
b. Alvis Board #1 and Alvis Board #2 are connected via LAN.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 27

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 27(36)
c. Alvis Board #1 should be one of the following OTX boards:
Alvis-4-CSI
Alvis-8-CSI
Alvis-ASM
d. Alvis Board #2 should be one of the following OTX boards:
a. Alvis-2-CSI
b. Alvis-4-CSI
c. Alvis-4M-CSI
d. Alvis-8-CSI
e. Alvis-8M-CSI
f. Alvis-ASM
g. Alvis-PCIe
h. Alvis-2-PBX
5. Update the rpm repository packets list at Alvis Board #2:
apt-get update
6. Install RTP Bridge package at Alvis Board #2 with a command:
apt-get install rtpbridge
7. Reset Linux file buffers at Alvis Board #2 with a command:
sync
8. Run RTP Bridge at Alvis Board #2 with the command:
/opt/rtpbridge/rtpbridge
If you will get a “No license found” message please follow the instructions in
Chapter 9 - The RTP Bridge License.
9. In CLI of RTP Bridge at Alvis Board #2 issue the command:
connect rtp:10.0.1.2:5002:6002 rtp:10.0.1.2:5004:6004:g711u
where 10.0.1.2 is the IP-address of the Alvis Board #1.
10. Update the rpm repository packets list at Alvis Board #1:
apt-get update
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 28

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 28(36)
11. Install RTP Streamer package at Alvis Board #1 with a command:
apt-get install rtpstreamer
12. Edit config file /opt/rtpstreamer/OtxRtpStreamer.conf. E.g.:
-------------------- OtxRtpStreamer.conf --------------------
connect tdm:li0:ts1:alaw rtp:10.0.1.100:6002:5002
connect rtp:10.0.1.100:6004:5004 tdm:li0:ts1:ulaw
---------------------------- EOF ----------------------------
where 10.0.1.100 is the IP-address of the Alvis Board #2.
13. Run the RTP Streamer with the command:
/opt/rtpstreamer/OtxRtpStreamer /TD /ME /P128
The arguments can be one of the following:
/T[D|K|X|Q|A] - Board Type used for the demo, where
D – use Alvis-4-CSI board,
K – use Alvis-4M-CSI board,
X – use Alvis-8-CSI board,
Q – use Alvis-8M-CSI board,
A – use Alvis-DMP (hosted on ASM or PCIe).
/ME – use E1 Li mode,
/MT – use T1 Li mode.
/P<bytes> – set RTP packets payload size (in bytes).
14. Run the T1/E1 Analyzer. Play the file alaw.bin with T1/E1 Analyzer on TS1.
So:
a. The RTP Streamer should get TDM data from Li0:TS1 and send RTP packets
with G.711 (a-law) payload to the RTP Bridge.
b. The RTP Bridge should decode this G.711 (a-law) encoded data and return it in
RTP packets with G.711 (u-law) payload to the RTP Streamer.
c. The RTP Streamer should put u-law data to Li0:TS1 that you can listen with the
T1/E1 Analyzer.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 29

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 29(36)
9 The RTP Bridge License
To successfully run the OTX RTP Bridge you should have a license (.lic file) in the
“/opt/rtpbridge” directory of installed software. Please perform these steps:
1. Get a board serial number. To do this, run the RTP Bridge with a key:
rtpbridge --getsn
The “sn.txt” file in the “/tmp” folder will be generated.
2. Send by the email the "sn.txt” file to Odin's Distributor to acquire the license. A
list of Distributors is available on http://odints.com/pages/dist/distfs.htm
3. After valid license receiving, put the “RtpBridge.lic” file in “/opt/rtpbridge”
directory on the Alvis-CSI and run the RTP Bridge. See Chapter 3 The RTP
Bridge Installation and Ru
nning.
.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 30

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 30(36)
10 References
Alvis-CSI Technical Description (Odin document # 1111-1-HCA-1020-1-1.0-
1.5)
Alvis-PCIe Technical Description
(Odin document # 1111-1-HCA-1021-1-1.0-
1.1)
Alvis-ASM Technical Description
(Odin document #1111-1-HCA-1018-1-1.0-
1.0)
RTP Streamer User’s Guide (Odin document #1412-1-SMA-1035-1-1.0-1.1)
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 31

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 31(36)
11 Product Versions History
Legend:
[+] New features
[–] Removed functionality
[*] Bugs fixed
[. ] Other things
15/11/2010 V.1.9.1 Internal Beta release
[+] Added initial support for N64 Streaming (31 timeslots, no headers).
[. ] Changed DSP implementation of GSM-FR codec (was trial).
19/10/2010 V.1.9.0
[-] SNMP monitoring support disabled for this release.
[. ] libOtxHw.so is used instead of static library.
[+] Added partial support of GSM-FR codec.
[*] Fixed false error signaling that was possible for simple connections
when payload change event occurs without actual change of payload.
[*] Fixed alignment issues in ARM<->DSP data exchange.
[+] DSP firmware is embedded into application.
[+] Added RTP aggregation support. -u (--udpagg) command line argument turns
UDP-based aggregation on. -e (--ethagg) command line argument turns
Eth-based aggregation on. Aggregation must be supported by libOtxRtp.so
to work properly.
[+] Added -t (--testrtp) command line argument that turns on check for RTP
sequences (for debug purposes).
[+] Added dummy connection point ("null[:codec]").
[+] Added partial support of Alvis-ASM. Host(x86)-based application is
necessary for TDM to work properly.
[. ] Improved ARM<->DSP interconnection.
[. ] Unified command handling for console, telnet interfaces and config file (/root/cfg).
[*] Fixed "mconnect" command handling in console interface.
[. ] Max amount of RTP connections increased to 512.
[+] Added support of Alvis-2-CSI.
09/08/2010 V.1.8.0 Internal beta release
[+] Added support of SNMP monitoring.
[+] Added -s <num> (--packetsize <num>) command line argument and
"packet size <num>" command that controls the packetization (set in ms).
[*] Fixed false error signaling for the conferences that have no outputs
(all outputs have been disconnected or have not been connected yet).
[*] Fixed attenuation of signal in TDM-to-TDM connections.
[. ] Changed default pid file name to /var/run/rtpbridge.pid
(was /var/run/rtpstreamer.pid).
24/06/2010 V.1.7.0 Internal release
[*] Fixed several alignment traps.
[. ] Used OTX XdmLink Layer API v.1.7.0.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 32

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 32(36)
[+] Added command "constat <num>" that prints information about connection.
[+] Added command "jitter blocks:<max>:<min>" that sets jitter time and jitter delay in 10ms blocks.
11/06/2010 V.1.6.1 Internal release
[. ] Used OTX XdmLink Layer API v.1.6.0
[. ] Some internal changes.
04/06/2010 V.1.6.0 Internal release
[+] Added handling of "Disconnect by timeout" event from OTX RTP Library.
[+] Added command "traces on|off" that turns DSP traces on/off.
[+] Added -b (--burst) command line argument parameters that disables DSP Core-to-Core optimization
and uses traditional burst events instead.
[. ] Improved quality of conference mode.
27/05/2010 V.1.5.1 Internal release
[.] Increased amount of DSP logical devices that could be created in runtime.
24/05/2010 V.1.5.0 Internal release
[+] RTP-to-TDM functionality is added.
[+] TDM-to-RTP functionality is added.
[+] TDM-to-TDM functionality is added.
20/04/2010 V.1.4.1 Internal release
[+] Buffers handling in asynchronous transcoding are enhanced.
[. ] DSP jitter is enhanced.
[*] Timestamps are fixed.
[*] Source clock frequency for some RTP payload types is fixed.
06/04/2010 V.1.4.0 Internal release
[+] Multi-party conferences support is added.
18/03/2010 V.1.3.1 Internal release
[+] New Telnet interface is added.
[+] Some internal changes and stability fixes.
05/03/2010 V.1.3.0 Internal release
[+] DSP jitter functionality is added.
[+] Many internal improvements are added.
16/02/2010 V.1.2.1 Internal release
[+] Buffering in asynchronous transcoding is changed.
[+] Performance gains and several stability fixes.
12/02/2010 V.1.2.0 Internal release
[+] Asynchronous transcoding is added.
[+] Performance gains.
27/01/2010 V.1.1.0 Internal release
[+] Many internal changes are added.
15/01/2010 V.1.0.1 Internal release
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 33

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 33(36)
[*] Timestamps calculation for outgoing RTP packets is fixed.
[*] Telnet interface is fixed.
29/12/2009 V.1.0.0 Initial internal alpha release
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 34

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 34(36)
12 Document History
Rev. 1.9 December, 20, 2010
Added new Board Types in Chapter 2 T1/E1 Channels Configuration.
Added new commands (BENCH, TRACES, EVENTS, CONSOLE, CORE) in
Chapter 5 The RTP Bridge Commands. Updated some commands.
Updated Chapter 8 Testing Verification Procedure.
Added V.1.9.1 in Chapter 11 Product Version History.
Rev. 1.8 December, 6, 2010
Added new features - GSM-FR codec and N64 Streaming support - in Chapter
1.2 Features.
Updated Chapter 3 The RTP Bridge Installation and Running.
Added connect command format - N64 Streaming.
Added benchmark table “TI C64+ DSP Core Load Tests in various
Encoding/Decoding Scenarios”.
Added V.1.8.0, V.1.9.0 description in Chapter 11 Product Versions History.
Rev. 1.7 July, 22, 2010
Added Chapter 4 Command Line Arguments.
Added a note on SNMP monitoring feature.
Added a ‘SHOW LICENSE’ and ‘PACKET SIZE’ commands.
Product Versions History was moved down to the Chapter 10.
Rev. 1.6 July, 1, 2010
Updated Product Revisions History (changed history order, added V.1.6.1 and
V.1.7.0 descriptions).
Updated Figure 1.
Updated list of features in Chapter 1.2.
Updated Chapter 2 (edited Table 1 and example of configuration file).
Added Chapter 3 The RTP Bridge Installation and Running..
Updated Chapter 4 The RTP Bridge Commands (added Commands Quick
Reference, added JITTER BLOCKS command).
Added Chapter 8 The RTP Bridge Commands.
Rev. 1.5 June, 23, 2010
Added command line screenshots.
Added an example of how to see board serial number in the case of RTP
Streamer.
Rev. 1.4 June, 18, 2010
Added ‘constat’ command description in Chapter 3 The RTP Bridge Commands.
Added a note about license generating in Chapter 6 Testing Procedure.
Added documents links in Chapter 7 References.
Rev. 1.3 June, 9, 2010
Added RTP Bridge versions 1.5.0, 1.5.1, 1.6.0 in Product Versions History.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 35

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 35(36)
Updated Chapter 2 OtxHwLayer Configuration.
Changed the title of Chapter 3 to The RTP Bridge Commands.
Added 3 sub-chapters in Chapter 3: how-to run RTP Bridge commands.
Refreshed benchmark tables.
Updated Chapter 6 testing Procedure.
Rev. 1.2 June, 7, 2010
Added Chapter 2 OtxHwLayer Configuration.
Updated 1.2 Features.
Updated Linux command line format.
Rev. 1.1 May, 13, 2010
Updated Table 3 in Chapter 4 (new codec benchmark).
Added warning in Chapter 6 (testing scheme).
Rev. 1.0 Apr, 22, 2010 A First Version.
oc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
D
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
Page 36

RTP Bridge User’s Guide 36(36)
13 Glossary
OTX – Odin Telecom FrameworX
CSI – Complete System Integration
DSP – Digital Signal Processor
SDK – Software Development Kit
API – Application Programmer Interface
RTP – Real-time Transport Protocol
TDM – Time-division multiplexing
SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
LED – Light-emitting diode
Doc. No. 1412-1-SAA-1020-1 www.odints.com Rev. 1.9
Copyright © Odin TeleSystems Inc., 2010
 Loading...
Loading...