
INDEX
1 HYSTORY
2 CONSTRUCTION
3 DIMENSIONS
4 PERFORMANCE
5 PANELS
6 FLYING
8 PREFLIGHT INSPECTION
9 PRE TAKEOFF CHECK
10 WINCH LAUNCHING
11 AEROTOW LAUNCHING
12 CLIMB
13 FREE FLIGHT
14 APPROACH AND LANDING
15 OFF-FIELD LANDING
16 STALL
17 BASIC AEROBATICS
18 LOOP
19 STALL TURN
20 IMMELMANN
21 SPLIT S
22 INVERSE FLIGHT
23 BARREL ROLL
24 ABOUT
3
3
4
4
5
6
6
7
8
8
9
9
9
9
10
11
11
12
13
14
14
14
15

HISTORY
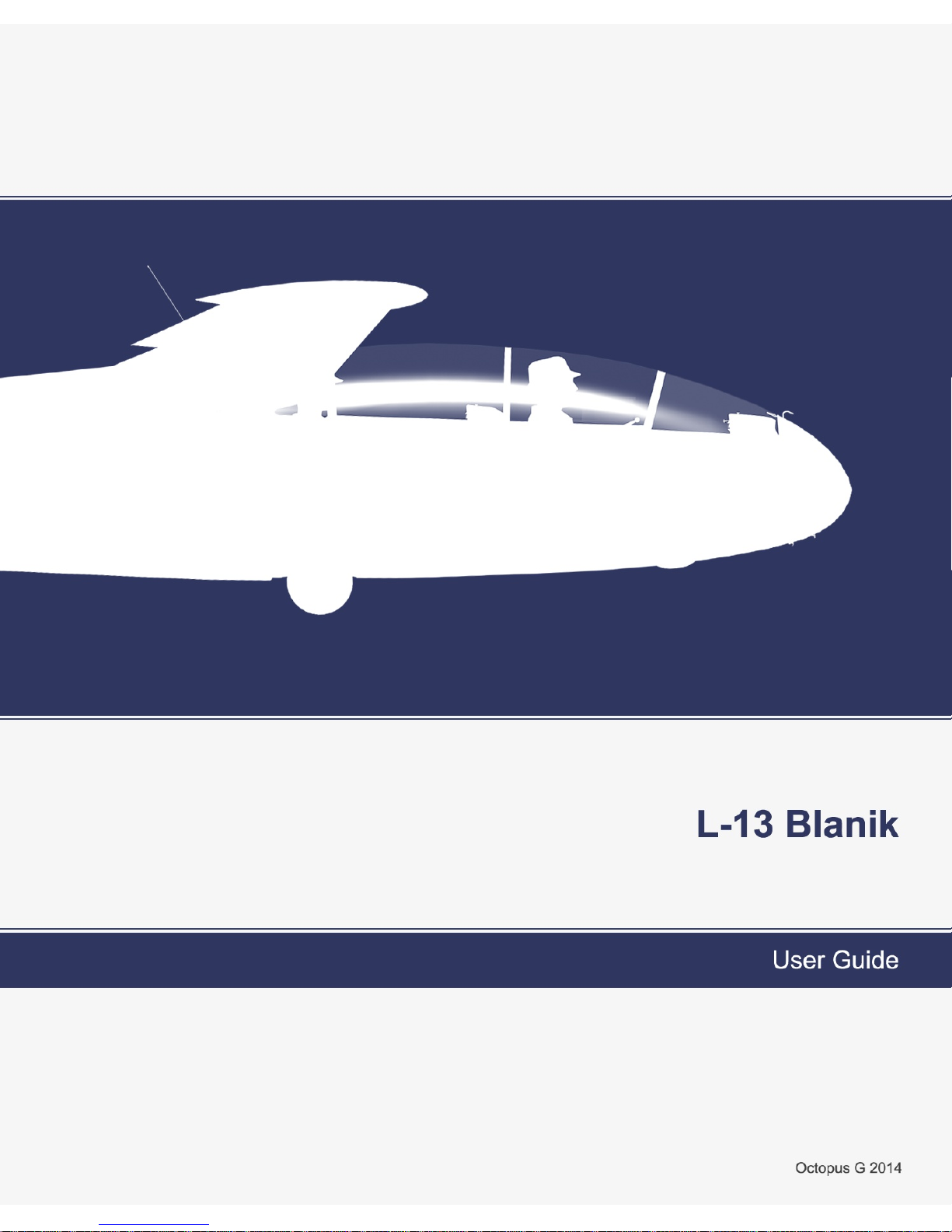
The L-13 Blanik is a two seater trainer glider produced by Let Kunovice since 1956. It is the
most numerous and widely used glider in the world. In United States Air Force Academy service, it is
designated TG-10C and is used for basic flight training.
The L-13 Blanik was designed by Karel Dlouhy of VZLÚ Letňany ca. 1956, building upon the
experience gained with the Letov XLF-207 Laminar, the first Czech glider to employ laminar flow wing
profiles. The L-13 was developed as a practical glider suitable for basic flight instruction, aerobatic
instruction and cross-country training. This design concept was combined with true and tested
technology: metal construction, NACA laminar profiles and many standard-issue components of the
Soviet aerospace industry.
The Blanik entered production in 1958 and quickly gained popularity as an inexpensive, rugged
and durable type, which was easy to fly and operate. It was widely adopted in the Soviet bloc and was
exported in large numbers to Western Europe and North America. Total production was in excess of
2650, or more than 3000 if variants are included. More than half a century after its first flight it is still the
most common glider in the World.
In the cross-country role the Blanik achieved many two-seater World distance records during
the 1960s in spite of having only fair performance. The Blanik inspired other designs, notably the
Démant and L-21 Spartak single-seaters developed to equip the Czechoslovak team in the 1956 and
1958 World Championships.
CONSTRUCTION
Fuselage of semi-monocoque construction employing longerons and bulkheads, with an ovoid
cross-section. The cockpit is covered with a two-part acrylic glass canopy.
• Trapezoidal single-taper wings with forward (negative) sweep, single-spar, all-metal
construction. Metal ‘torpedo’ tips. Flaps and ailerons have a metal frame and are covered in
fabric. Metal DFS type spoilers on the upper and lower wing surfaces.
• The horizontal tail surfaces fold up parallel to the fin for transportation and storage.
• The elevator and rudder are metal frames covered in fabric. The landing gear is semi-
retractable and sprung with an effective oleo-pneumatic shock absorber, excellent features
which assure landings with little or no damage even if the wheel is left (in error) in the raised
position.

DIMENSIONS
Lenght, m 8,4
Wing span, m 16,2
Wing area, m2 19,5
PERFORMANCE
Vne, kmh: 253
Minimum vertical speed, m/sec: 0,82
Vne (air brakes extended), kmh: 253
Max. tow speed, kmh:
flaps down: 110
flaps up: 140
Max winch launch speed, kmh:
flaps down: 100
flaps up: 120

PANELS
1. ASI
2. Altimeter
3. Magnetic compass
4. VSI (for 5 m/s)
5. Turn coordinator
6. VSI VR-30
7. Trim lever
8. Air brakes lever
9. Flaps lever
10. Gear lever
11. Release handle
12. Ventilation lever
13. Canopy jettison
14. Brake lever
15. Radio bottom
16. Volume regulator
17. Noise switch
18. Frequency selection switch
19. Pedals regulator
20. Frequency selection switch
21. Frequency window
22. Frequency window

FLYING
PREFLIGHT INSPECTION
Examine the sailplane for external damage. Check that a wing and tai1p1ane attachment and
control assembly pins are secure
Check that the canopy jettison lever has not been operated accidentally. and that the sealing
wire is intact.
Inspect the cockpit hood for damage and, clean it and demist the interior if necessary.
Check the controls, flaps, air brakes, and trim control for full and free movement and operation
in the correct sense.
Inspect the cockpit, including instruments, for proper condition, and make sure that the safety

harnesses are not damaged and are securely attacked to the glider. Remove all loose articles not
wanted in flight and, if the sailplane is to be flown solo, secure the rear safety harness and seat
cushions.
PRE TAKEOFF CECK
Safety Harness: Enter the cockpit and fasten the safety harness, insuring that it is fully and
tightly fitted.
Rudder controls: The position of the rudder pedals should be adjusted with the pilot fully
strapped in so "that each pedal can be moved comfortably to the full extent of its travel without either
foot having to be removed from the pedals.
The position of the rudder pedals in the front cockpit can be adjusted by means of the handle
(19) on the cockpit floor just in front of the base of the control column. In the rear cockpit, adjustment to
one of three possible positions may be obtained by first removing the locking pin on the back of each
pedal
Trim: Check the trim tab control (7) for full and free movement, and set to a position slightly
forward of neutral or as otherwise may be determined by experience.
Flaps and Air Brakes: Check the air brakes (8) and flaps (9) for full and free movement,
ensuring that the air brakes are fully retracted and the flaps set to the desired position for take-off.
Cable Release: Check the cable release mechanism for proper functioning by operating the
release handle (11).
Instruments: Set the barometric pressure scale on the altimeter (2). Check that the variometers
(4 and 6) read zero.

Flight Controls: Both the control column and the ruder pedals should be checked again for and
free movement in all directions. When checking the aileron controls, the wing tip should be lifted clear of
the ground so as to prevent damage to the aileron.
Wheel Brake: Check the wheel brake lever (6) for free move ment, and ensure that it is in the
fully off position.
Cockpit hood: Check that the cockpit hood is properly closed and locked.
WINCH LAUNCHING
If original towing-bridle is used, the maximum weak link strength is 2,000 1b. - (910 kp). For
maximum launch height, the side-towing bridle should be used. To reduce the possibility of “whip-ping"
the towing-bridle should be laid out in front ofthe sailplane before launching. During take-off, as the
control loads are very light, care should be taken not to climb too steeply at a low airspeed, and. it is
important when releasing the cable to pull the release handle fully so as to allow the cable hooks to fall
off.
The nose hook, which embodies a back release mechanism, also may be used for winch
launching. Partial flap may be used during winch launching, if desired, in order to reduce the take-off
run. A.speed of 54 knots (100 km/hr.) should not be exceeded if the flaps are extended, or 65 knots
(120 km/hr.) with the flaps retracted.
The recommended speed for winch launching is 43-54 knots (80--100 km,'hr.).
AEROTOW LAUNCHING
For the take-off by aerotow push Ctrl+Shift+Y. After this the aerotow aircraft appears and in
some seconds starts to run. The elevator and rudder efficiency is high enough during the initial stages
of the take-off run, that it is easy to prevent directional or roll oscillations by use of rudder or ailerons.
Hold the control stick in order to keep the sailplane in horizontal position on the landing gear and at
liftoff speed pull the control stick gently to unstick the sailplane. Hold the sailplane in horizontal flight at
a height of 3 ft (1 m ) until the towing airplane starts to climb. The take-off with cross wind is different
from the normal take-off. It is necessary to bank the wing into the wind ( in proportion to the wind
speed) and to unstick the sailplane at a higher speed. The tow rope should be attached to the front
hook only.
CLIMB
Retract and lock the landing gear (by pulling the handle in your direction) when above a
minimum safe height of 20 m (66 ft). Trim the sailplane for the climb speed. Smoothly moving the stick
and pedals keep the sailplane behind the aircraft or slightly at the side, but do not allow too large
deviations to avoid aerotow brake. At the needed height free the aerotow by X or Ctrl+Y.
Note: in simulator aerotow aircraft is flying with the speed 160 km/h while the maximum speed for the
aerotow is 140 km/h.
FREE FLIGHT
For the best gliding keep the speed of about 85-90 km/h. The sailplane is very manoeuvreable
and controllable and its behaviour is very good in turns with angles bank up to 60°.
APPROACH AND LANDING
The following approach speeds are recommended:
Descent Air brakes Flaps Approach speeds
Normal Retracted Extended 70-85 km/h
Normal Extended Extended 80-95 km/h
Steep Extended Extended 95-110 km/h
LANDING AT THE AIRPORT
The landing manoeuvre is entirely conventional. Use small elevator inputs at the flare. The
sailplane should touch down with the landing gear and with the tail wheel simultaneously. Do not flare
prematurely in order to prevent the sailplane from droping from a higher height.
OFF-FIELD LANDING
It is recommended to land with the landing gear retracted if landing on a soft ground. In this
case extend the wheel before the next flight.
Use of air brakes
It is recommended to use the air brakes in following cases :
1. To reduce landing especially roll on rough ground.
2. To increase accuracy of the landing manoeuvre.

Note:
In case of using air brakes during landing, it is necessary to maintain an approach speed of
about 10 km/h (5 kts) higher, because the stall speed with fully opened air brakes is about 5-7 km/h (3-
4 kts) higher.
3. To avoid exceeding the never exceed speed V
NE
during unusual attitude recoveries (for
example during aerobatics).
It is recommended to use the air brakes in any case when the sailplane starts to increase the
speed and the pilot is uncertain of his orientation or how to manage the situation. Configuration with “air
brakesextended” will ensure that VNE is not exceeded.Use of air brakes will enhance the safety and
makes handling easier because the extended air brakes tend to stabilize the sailplane. The control
lever should be held firmly when operating the air brakes to ensure smooth deployment and retraction.
STALL
Slow and continuous pulling aft on the control stick causes the sailplane to stall near the speed
60 km/h without flaps (55 km/h with flaps). Ailerons and rudder should be used to control bank, if any.
When stalled, the sailplane settles with a gentle pitching. Move the control stick forward and start the
stall recovery.

BASIC AEROBATICS
Table of speeds for basic aerobatics (km/h)
Solo Dual
Barrel roll 150 forbidden
Loop 160 180
Stall turn 170 180
Immelmann 180-190 190-200
Split S 130 140
Inverse flight Above 130 forbidden
LOOP
Enter a moderate dive with slight forward movement of the control stick to gain a speed of 160
km/h (86 KIAS) when flying solo or 180 km/h (97 KIAS) when flying dual. Raise the nose of the
sailplane by slight backward movement of the control stick, taking care not to apply excessive "g"
forces, and maintain this rate of backward stick movement throughout the first half of the loop, but do

not use more than about 60 % of the control stick full deflection. The load factor must drop in the
inverted position. After passing the inverted position the speed will increase and the control stick must
be eased forward gradually until the sailplane is flying level again. Before and during this manoeuvre
rudder should be used to prevent yaw and ailerons used to keep the wings level. Maintain precise
directional control for proper completion.
STALL TURN
This manoeuvre should be begun at the speed of 170 km/h (92 KIAS) when flying solo or 180
km/h (97 KIAS) when flying dual. Pull the control stick gently backward to bring the nose to a position of
about 60° to 70° above the horizon. Ease the control stick forward slightly to maintain this attitude. As
the speed falls to 130-140 km/h (70 - 76 KIAS), start to apply rudder in the required direction of turn.
The ailerons should be used against the direction of turn as necessary to prevent the sailplane rolling to
the inverted position. As the nose approaches the reciprocal heading, neutralize the rudder, keep the
wings level by use of the ailerons, and ease out of the resulting dive, taking care not to apply excessive
"g".

IMMELMANN
The initial speed for Immelmann is of about 180-190 km/h when flying solo or 190-200 km/h
when flying dual. Raising the nose of the sailplane is faster with respect to loop. After distinguishing of
the top point return the stick to have weightless state. Then deflect tne ailerons to turn in normal
position. At the bank 90° it is necessary to push upper pedal to maintain sailplane nose in horizon and
to prevent sailplane turn. To keep the sailplane nose in horizon in the last phase of the turn it is
recommended to push stick forward.

SPLIT S
At the beginning of this figure the speed should be 130 km/h when flying solo or 140 km/h when
flying dual. Rise the nose of the glider till 25° above horizon. Then push the stick forward for direct flight
and deflect the ailerons. To keep sailplane in horizontal position during the turn help by rudder pushing
upper pedal and in the last phase by moving the stick forward. When the glider is in the inverse position
the ailerons and rudder put in the neutral position. After this pull the stick as at the second phase of the
loop.
INVERSE FLIGHT
The inverse flight is allowed when flying solo only. We recommend to put sailplane to the
inverse position according to the description of the first part of the split S. The recommended speed is
130 km/h.
BARREL ROLL
It is allowed to do barrel roll flying solo only. After distinguishing the speed of 150 km/h rise the
nose of the sailplane by about 25° above the horizon returning the stick for direct flight. Then turn the

sailplane with full deflection of the ailerons. At the bank 90° push the upper rudder if the sailplane nose
goes down. In the inverse position push the stick forward to keep the axis of the fuselage. During the
roll the ailerons are always fully deflected. At the second phase of the roll use rudder and elevator to
prevent non desirable turns of the sailplane: the upper pedal at about 90° of the bank and the stick
forward close to the direct position.
ABOUT
 Loading...
Loading...