Page 1

User’s Manual
Wireless LAN PCI/CardBus Adapter
Model No.: SP906GK/SP908GK V3
http://www.micronet.info
Page 2

1. Introduction
1.1 Package Content
SP906GK/SP908GK V3 54M Wireless PCI/CardBus Adapter
Driver and Manual CD
Quick Installation Guide
External Antenna (SP906GK Only)
1.2 Features
Compliant with IEEE802.11g and IEEE802.11b wireless standards
Support modulation with Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
technology and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
technology for IEEE802.11b/g
PCI 2.1/2.0
32 bit CardBus interface
Operate in 2.4GHz frequency band
Support auto-data rate selection at 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 and 6M for
IEEE 802.11g
Interoperate with IEEE802.11b wireless networks at 11M
Support 64(40)/128 bit WEP for network security
Provide Window-based configuration utility
Support Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP
Support 802.11d regulatory domain
2
Page 3
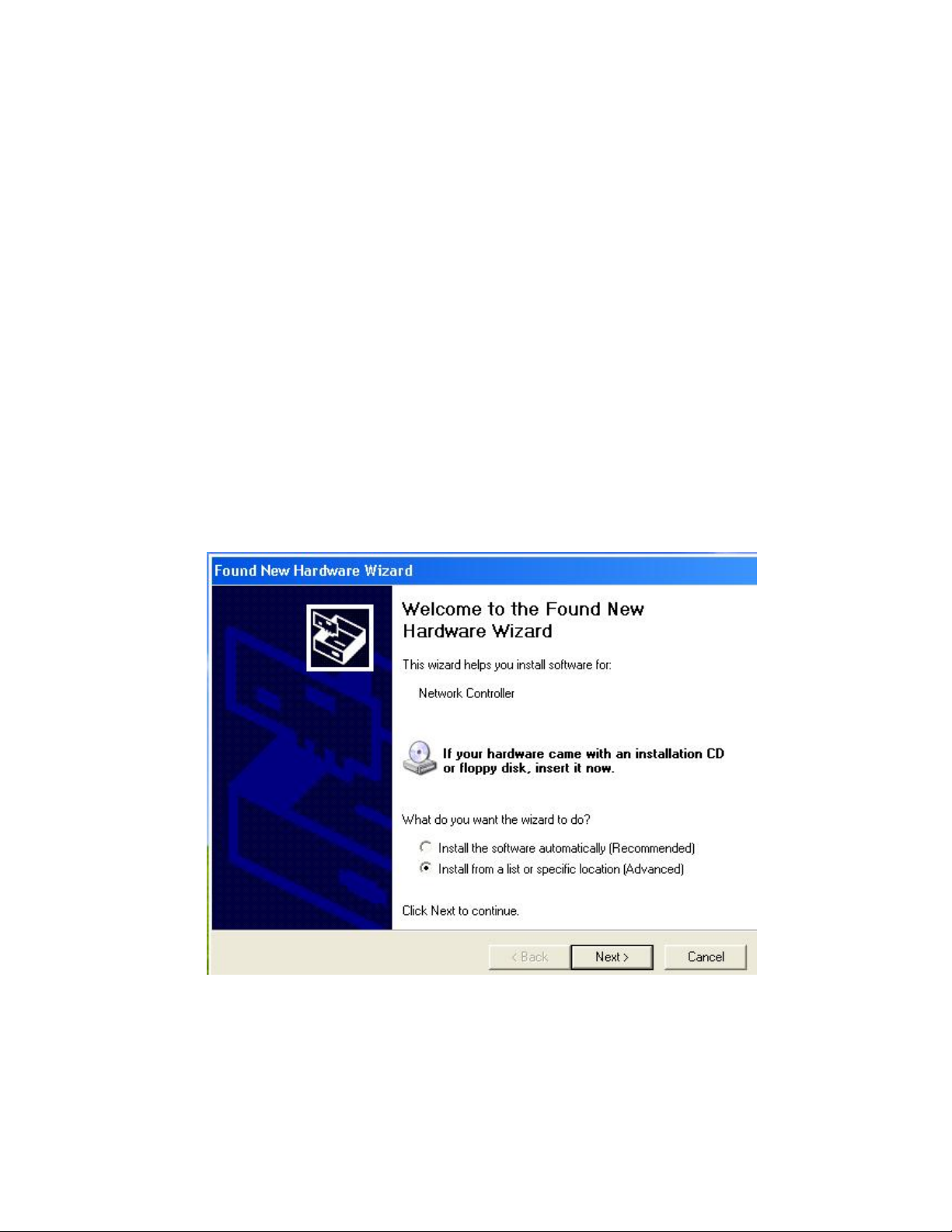
Installation
2.1 Driver Installation
1. Before insert PCI/CardBus into the PC CardBus of your computer, please install
the Driver first. Make sure that the 802.11g wireless PCI/CardBus Adapter is
NOT inserted into the CardBus slot.
NOTE: all the snapped images of installation mentioned in this manual are based
on Windows XP. For other windows operating system, all the procedures are
the same but the screens are not the exactly same.
2. Turn on the computer. Insert the CD into the CD-ROM Drive. Please click
the “Next”.
3
Page 4
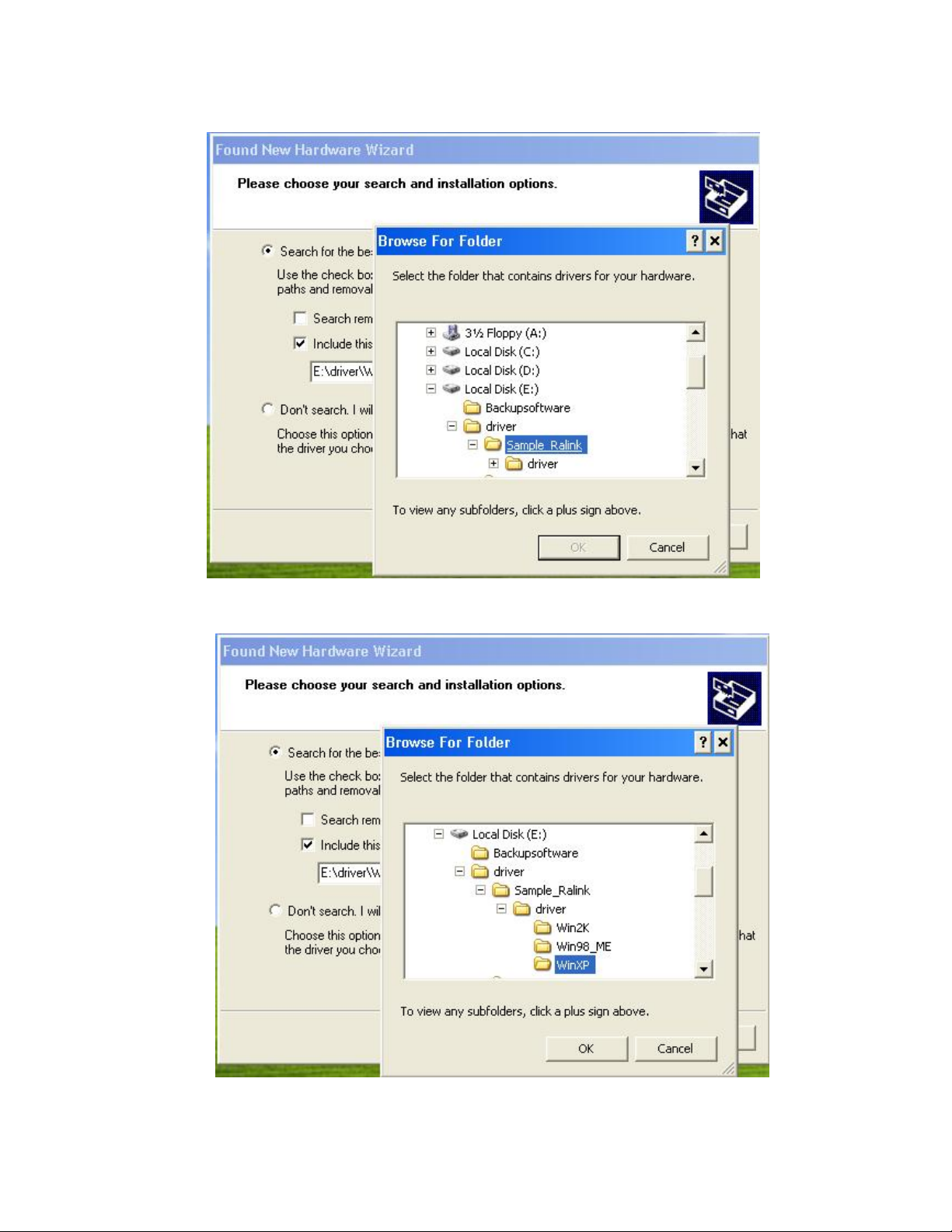
3. InstallShield Wizard will automatically start.
Select driver for your OS then click “ok” to continue.
4
Page 5
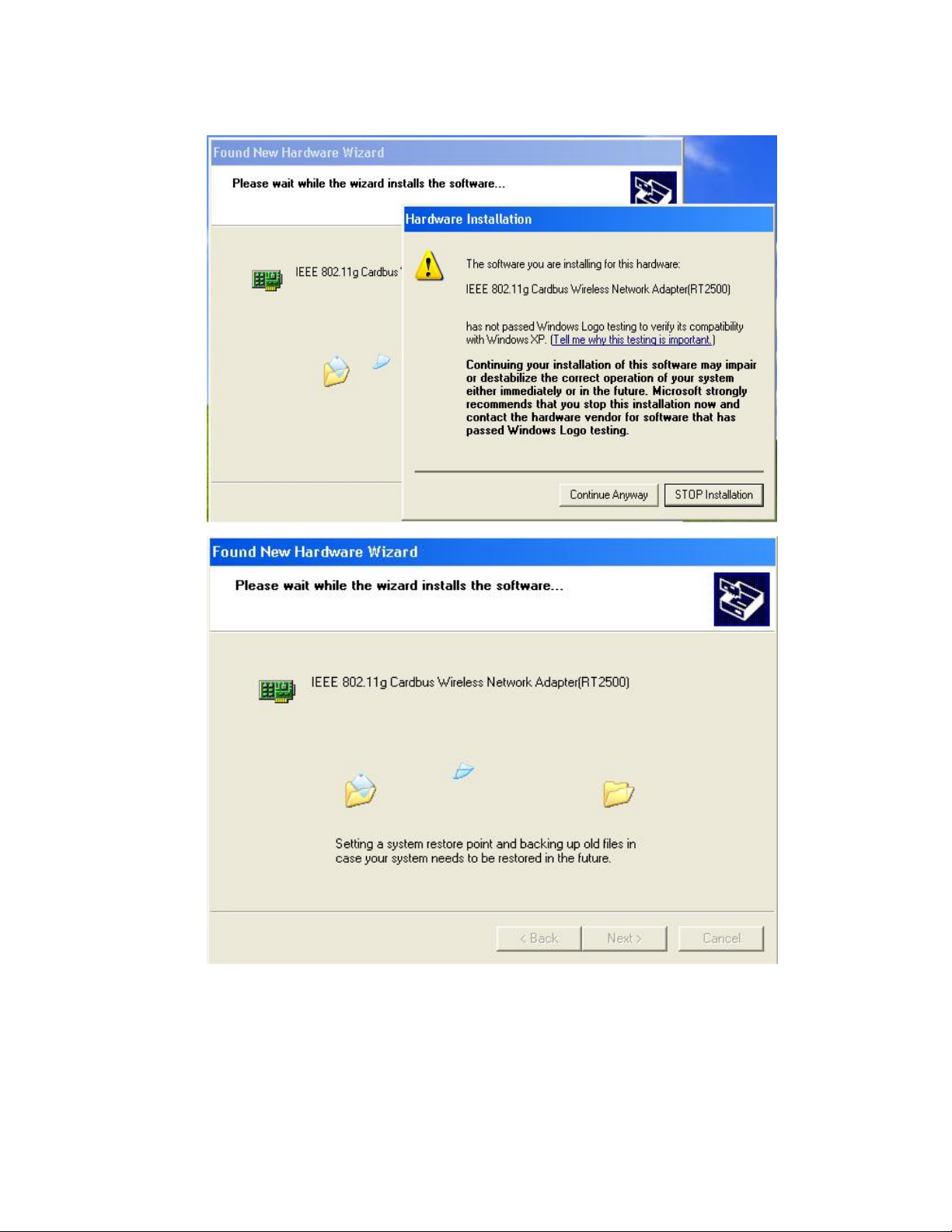
4. Please click “Continue Anyway”
5
Page 6
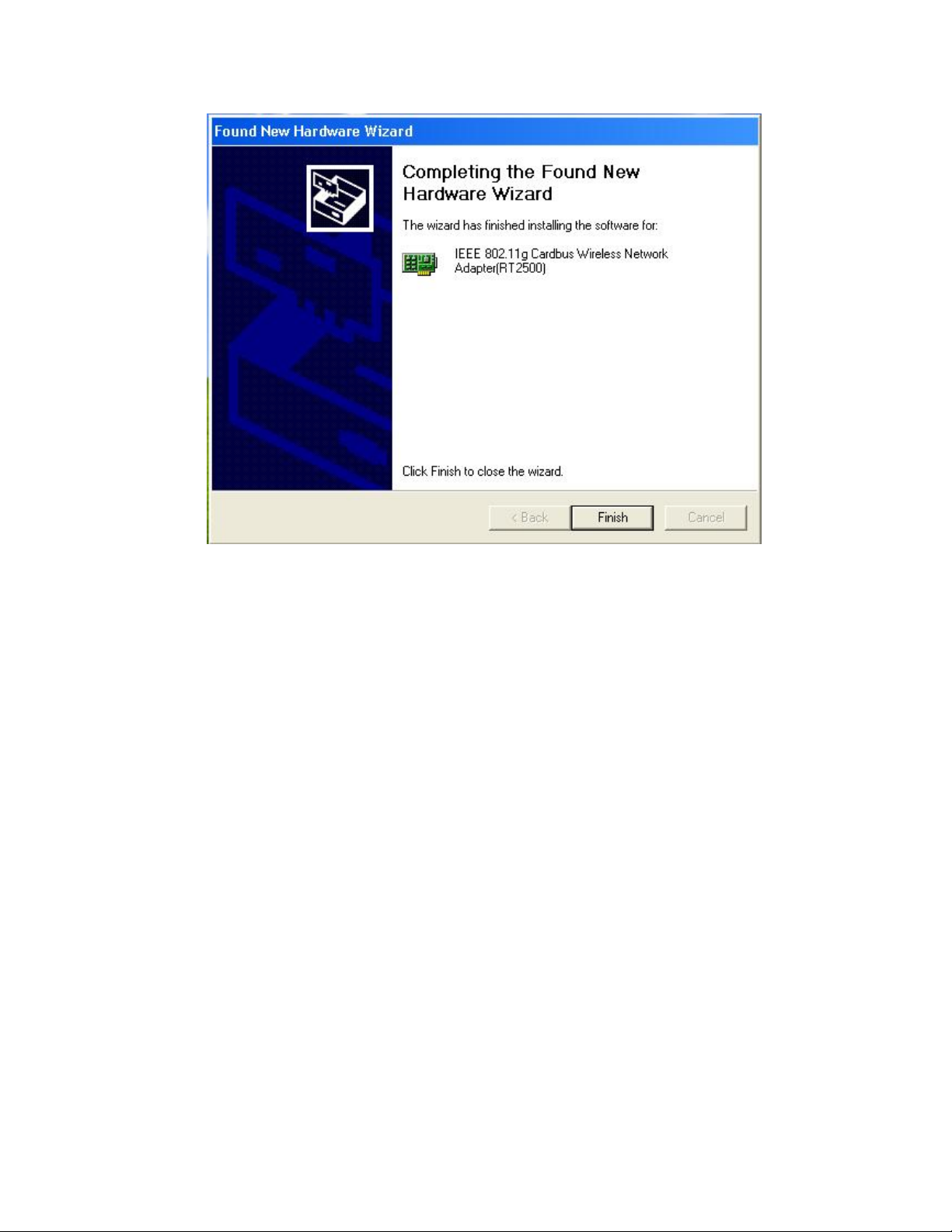
5. Please chick Finish then turn off your computer and then insert the PC card into
the card bus. Turn on your computer and start to install the driver.
2.2 Utility Installation
1. Please select the second option and click “Next”.
6
Page 7
2. Please click “Next”
7
Page 8

3. Please click “Next”
Please click “Next”
8
Page 9

Please chick Finish.
9
Page 10

4. To make sure if the installation is successful, you could check it through the
device management.
5. Once the installation is successful, a utility program icon will show on your Start
Menu->WLAN Monitor->WLANmon, just double click the icon.
10
Page 11

2. Configuration
The default page is as below after you launch the Utility program.
On the left side of the screen are Available WLANs, which you may connect to by first
selecting the WLAN (it will appear highlighted) and then clicking on Add. When you do so a
screen like the one below will pop up:
11
Page 12

In the Wireless Network Properties screen you may change the name of the WLAN. You
may also enter wireless network encryption keys by checking Network Authentication
(Shared mode) or Data encryption (WEP enabled). You may enter up to four keys of length
10 or 25 hexadecimal digits. You may also set one of the four keys as a default key.
Data Encryption:
Select Enabled or Disabled.
Authentication:
Open Authentication - The CardBus is visible to all devices on the network.
Shared Authentication – Allows communication only with other devices with identical
WEP settings.
Auto - Will automatically adjust to the Authentication mode of the wireless access point or
router.
If the network you are using is a computer-to-computer network or ad hoc network, no access
points are used. You may check the box “This is a computer to computer (ad hoc) network; no
access points are used” to enable this option.
On the Configuration T ab, click on Refresh to call up all the available WLANs. On the
right side of the screen is a list of Preferred WLANs. These are WLANs that have already
been added to the wireless network. Click New to rename the WLAN and reset its properties.
12
Page 13

You will see the Wireless Network Properties screen as displayed previously when you click
New. This is also the same screen that will appear when you click Properties on the right side
of the Configuration Tab screen. Click Remove to remove the connection.
On the right side of the screen you may click Move Up to move the selected WLAN up in the
order it is displayed on the Preferred WLANs screen. You may click Move Down to move the
selected WLAN down in the order in which it is displayed.
The Advance button allows the user to set the WLAN type to connect: infrastructure and ad
hoc network, in frastructure network only, or ad hoc network only. You may also automatically
connect to non-preferred networks by checking the option.
When you are done entering the settings and options for the wireless network click on OK,
Cancel, or Apply. OK places the settings into effect and closes the graphical user interface
(GUI). Cancel makes invalid all settings entered. Apply implements the setting entered, but
does not close the GUI.
Under the Status Tab you will find information on the connection state, hardware information,
and advanced state.
13
Page 14

3.1 S tatus Tab
After clicking on the Configuration Utility icon, the Status screen will display the settings for the
CardBus:
SSID:
The Service Set Identifier is the name assigned to the wireless network.
The factory SSID setting is default.
BSSID:
The CardBus hardware MAC address
Network Type:
The Network Type have three mode
(Please see the Getting Option section in this manual for an explanation of these three modes.)
Frequency:
802.11g indica tes that the CardBus is communicating in the 2.4GHz band.
Data Encryption:
You can see if WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is Enabled or Disabled here.
Speed:
This is display wireless and wireless connecting Speed.
Authentication State:
14
Page 15

This is display Authen t icati o n State, it’s to provide N/A and Conne cte d two state.
Signal Strength:
A colored bar shows the intensity of the radio signals in the network
Under Hardware Information the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the hardware
(WLAN CardBus card) is given. The MAC address is a factory given address that cannot be
changed.
Advanced State shows the Radio Status (ON or OFF).
Click OK to accept the connection status and exit the GUI. Click Cancel to not accept the
status settings and exit the GUI.
Under the Option Tab general settings and advanced settings are shown.
3.2 Option Tab
Under General Setting,
Auto launch when Windows starts up:
The WLAN automatically launches when Windows starts up.
Remember mini status position:
Resident in the memory
15
Page 16

Auto hide mini status:
Auto hide the tools
Set mini status always on top:
It will lock the station.
Enable IP setting and Proxy setting in profile:
The function will backup previous IP setting now
Under WLAN type to connect
Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc network:
Wireless mode used when connecting Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc two different access point
network environment
Infrastructure:
Connecting to the WLAN using an access point.(This is the default setting).
Ad-Hoc:
Wireless mode used when connecting directly to a computer equipped with a wireless adapter
in a Peer-to-Peer environment
Under Advance Setting :
Disable Radio:
Disable to send by radio
Fragmentation Threshold:
The size at which packets will be fragmented. Choose a setting within a range of 256 to
2346 bytes.
RTS Threshold:
Minimum packet size to require an RTS (Request To Send).For packets smaller than this
threshold, an RTS is not sent and the packet is transmitted directly to the WLAN. This is
the option for the RTS Threshold activation.
Ad-Hoc Channel:
All devices in the Ad-Hoc network must be set to the same channel.
Power save Mode:
Fast Save - This setting consumes the half power.
Max Save - This setting cons umes the least power.
Disable - This default setting consumes the most power
There power modes to provide 100%,50% , 25% , 12.5% and Lowest 5 modes.
16
Page 17

3.3 About Tab:
Display the Utility Version and Driver Version 。
17
Page 18

3. Specification
Model SP906GK/SP908GK Wireless PCI/CardBus Adapter
Standard IEEE802.11b and 802.11g
Interface PCI/32bit CardBus
Frequency 2.4GHz
Data Rate 11/54M
Output Power (Max) 17dBm
Sensitivity –84dBm at < 8% BER
Antenna Type Built-in
Operation Channel 802.11d
Radio Modulation DSSS/OFDM
Security
Network Architecture Type Ad-hoc and Infrastructure
Driver Support Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP.
Dimension (mm)
Operating
Temperature (degree C)
Operating Humidity 20~95%, Non-condensing
Emission CE, FCC
64(40)/128bit WEP Encryption and WPA (Wi-Fi Protected
Access)
82(L) x 29(W ) x1 0( H )
0~40℃
18
Page 19

4. Glossary
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating
a standard for the industry.
Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless
networks together.
Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter,
connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad Hoc wireless LAN is
applicable at a
departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a
BSS must
be configured with the same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - a method in which IP addresses are
assigned
by server dynamically to clients on the network. DHCP is used for Dynamic IP
Addressing and requires a dedicated DHCP server on the network.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless cards use to transmit data over the frequency
spectrum. The other method is frequency hopping. Direct sequence spreads
the data
over one frequency range (channel) while frequency hopping jumps from one
narrow
frequency band to another many times per second.
ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile
19
Page 20

workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set
(ESS).
Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs while served as a
continuous
connection to the network wireless stations and Access Points within an ESS
must be
configured with the same ESSID and the same radio channel.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office wiring.
Users
must be wired to the network at all times to gain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar
systems,
such as a LAN and a mainframe. In Internet terminology, a gateway is another
name
for a router. Generally a gateway is used as a funnel for all traffic to the
Internet.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Infrastructure
An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration.
Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central
database,
or wireless application for mobile workers.
ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidt h
for
unlicensed use in the so-called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band.
Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available
worldwide.
This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed
wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the globe.
20
Page 21

Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network
adapter
card connected by cable/air, that share applications, data, and peripherals. All
connections are made via cable or wireless media, but a LAN does not use
telephone
services. It typically spans a single building or campus.
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and
messages can
be transmitted over this network. Networks may be local or wide area
networks.
PCMCIA
Personal Computer Memory Card International Association. Also a PCMCIA
card is
also referred to CardBus Adapter.
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation is to
take
place, including the format, timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that share
the same SSID are able to communicate with each other. This string is
case-sensitive.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol of
TCP/IP. In SNMP, agents-which can be hardware as well as soft ware-monitor
the activity in the various devices on the network and report to the network
console workstation. Control information about each device is maintained in a
structure known as a management information block.
21
Page 22

Static IP Addressing
A method of assigning IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks with
Static
IP address, the network administrator manually assigns an IP address to each
computer. Once a Static IP address is assigned, a computer uses the same IP
address every time it reboots and logs on to the network, unless it is manually
changed.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research Projects
Agency (ARPA). It is widely used in corporate Internet works, because of its
superior design for WANs. TCP governs how packet is sequenced for
transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to refer
to the entire suite of rel ated protoc ols.
Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone services
and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs may span a city, a state, a country, or even
the world.
Copyright S tatement
No part of this publication may be reproduced. Stored
22
Page 23

The information in this guide may change without notice. The manufacturer
assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this guide.
Ethernet is a trademark of XEROX Corporation. Microsoft, Windows and
Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corpor ation.
Copyright 2004, Manufacturer . All right reserv ed. No Part of the contents of this
guide maybe transmitted or reproduced in any form or by any means without
the written permission of manufacturer. Printed in Taiwan.
FCC Statement
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules . These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against such interference when operat ing in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used according to the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interfere nce
in which case the user, at his or her own expense will be required to take
whatever measures may be required to correct the interference.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause
radio interference in which case the user may be required t o take adequate
measures.
23
 Loading...
Loading...