
BISON VI

The material in this manual is for information only and is subject to change without
notice.
REVISION: 1.1
IBM, IBM PC/XT/AT, PC-DOS, MS-DOS, OS/2, INTEL, AMI, Pentium ARE THE
TRADEMARKS OR REGISTERED TRADEMARKS OF THEIR RESPECTIVE
OWNERS.

RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE STATEMENT
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and
if not installed and used properly, that is, in strict accordance
with the manufacturer's instructions, may cause interference
with radio and television reception.
If this equipment does cause interference to radio or TV
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
* Reorient the receiving antenna.
* Relocate the computer away from the receiver.
* Move the computer away from the receiver.
* Plug the computer into a different outlet so that computer
and receiver are on different branch circuits.
* Ensure that card slot covers are in place when no card is
installed.
* Ensure that card mounting screws, attachment connector
screws, and ground wires are tightly secured.
* If peripherals are used with this system, it is suggested to
use shielded, grounded cables, with in-line filters if
necessary.
If necessary, the user should consult the dealer service
representative for additional suggestions.
The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV
interference caused by unauthorized modifications to this
equipment. It is the responsibility of the user to correct such
interference.

Note
1. Electronic components are sensitive to dust and dirt. Do
inspect and clean the computer system regularly.
2. Turn off the power whenever you install or remove any
connector, memory module and add-on card. Before
turning on the power, make sure that all the connectors,
memory modules and add-on cards are secured.
3. After power is on, wait for a minute. The system BIOS are
going through a self-test during this period and nothing is
shown on the screen. After the self-test, the system BIOS
will initialize the display adaptor and show messages.
4. The SIMM sockets are fragile device. Do not force the
SIMM modules into the sockets. It may break the locking
latches.

Table of Content
Chapter One INTRODUCTION
Chapter Two GENERAL FEATURES
Specifications ....................................................................2-1
The Central Processing Unit ............................................2-2
Cache Subsystem ...............................................................2-3
DRAM Subsystem ..............................................................2-3
PCI Bus .............................................................................2-4
Chapter Three CONFIGURING THE SYSTEM
Installing The Processor ...................................................3-1
Installing RAM Modules ...................................................3-2
Configuring The Cache Memory ......................................3-2
DRAM Configuration ........................................................3-3
Reset CMOS Setup Information ........................................3-4
PCI-Bus Adapter Installation ...........................................3-4
Board Layout .....................................................................3-5
System Board Jumper and Connector Summary ..............3-6
System Board Jumper Setting ...........................................3-7
System Board Connectors .................................................3-9

Table of Content
Chapter Four TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Memory Mapping ..............................................................4-1
I/O Address Map ...............................................................4-2
System Interrupts ...............................................................4-4
Direct Memory Access (DMA) ..........................................4-5
Real Time Clock and CMOS RAM ....................................4-6
System Expansion Bus .......................................................4-6
Appendix A OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
Static Electricity ............................................................... A-1
Keeping The System Cool ................................................ A-1
Cleaning The "Golden Finger" ........................................ A-2
Cleaning The Motherboard .............................................. A-2

Chapter One 1-1
Chapter One
Introduction
OCTEK BISON VI is a workstation class platform that can
meet the demand of most time critical applications nowadays.
With the Intel Pentium processor and 64 bit interleaved memory
system, it delivers higher performance among the PC/AT class
machines that ever been.
ISA bus are incorporated to adapt the most popular add-on card
standard. Latest local bus technology - Peripheral Component
Interconnect (PCI) is also implemented, that makes BISON VI
tremendous adaptability.
Next-generation design remains 100% binary and PC/AT
compatible that boosts up the existing applications without recompile.

1-2 Chapter One
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

Chapter Two 2-1
Chapter Two
General Features
Specifications
Processor : Pentium 75MHz, 90MHz or 100MHz CPU
I/O Slot : Four 16 bit ISA slots
Four PCI local bus slot (supporting
four bus masters)
Cache* :
Internal cache inside Pentium: 8K instruction cache
8K data cache
External cache: 256K external cache expandable to 2M
DRAM : Supports 3 banks of 32 bit wide SIMM
modules with 1MB, 2MB, 4MB, 8MB, 16MB,
32MB and 64MB DRAMs
Supports DRAM size from 2MB to
128MB
Two non-cacheable regions
DRAM post write buffer and Read buffer
Others : Fast Gate A20 and reset emulations.
* Both caches are in write back.

2-2 Chapter Two
The Central Processing Unit
The Pentium processor is the next-generation member of 80486
family of microprocessors. It contains all of the features of the
80486 and provides significant enhancements and additions. It
is 100% binary compatible with the X86 CPU.
The superscalar architecture of the Pentium processor contains
two instruction pipelines and floating-point unit on the Pentium
processor are capable of independent operation. Each pipeline
issues hit instructions in a single clock. The dual pipes can issue
two integer instructions in one clock, or one floating-point
instruction in one clock.
The branch prediction unit includes two prefech buffers, one to
prefetch code in a linear fashion, and one to prefetch code
according to the Branch Target Buffer so that the needed code is
almost always prefetched before it is needed for execution.
The floating point unit is redesigned and runs at least three
times faster than 80486.
The Pentium processor includes separate 8K code cache and 8K
write-back data cache. Each cache is 32 byte line size and is 2way set associative. The data cache is configurable to be writeback or write-through on a line-by-line basis and follows the
MESI protocol. The code cache is a write-protected cache.
The Pentium processor has widen the data bus to 64 bits to
improve the data transfer rate. Burst read and burst writeback
cycles are supported by the Pentium processor.

Chapter Two 2-3
In summary, the Pentium processor provides an ultimate
performance levels and retains compatibility with the existing
applications.
Cache Subsystem
The external cache of BISON VI is write-back, direct-mapped
with sizes of 256K, 512K, 1M or 2M. It is organized by single
or dual bank mode. Dual bank mode is accessed in interleaved
manner and it can support 3-2-2-2 burst read cycle.
DRAM Subsystem
The memory controller is 64 bit wide and has the following
features:
Posted-Write to the DRAM improves the write-cycle timing.
One quad-word deep data buffer is used to hold the data from
the CPU without waiting for the external DRAM cycle.
Shadow RAM is available as an option. System BIOS and video
BIOS residing in slow EPROM can be copied to local DRAM
to speed up accesses to BIOS code. Video BIOS at C0000h C7FFFh can be cached in the external cache after shadowing.
Two DRAM control regions can be selected to adapt the bus
mastering add-on cards. For the memory region that bus master
would write to, set it to non-cacheable or write-through would
improve bus bandwidth owing to the elimination of the timeconsuming cache invalidation cycle. For the card with its own
memory mapped overlay to the system memory, memory holes
can be set to allow accessing to the memory.

2-4 Chapter Two
PCI Bus
The Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) local bus was
specified to establish a high performance local bus standard for
several generations of product. It is a 32 bit wide, burst transfer
mode bus that is designed to allow glue-less interconnect of
component. The following is the features of the PCI :
High performance -
Synchronous bus with operation up to 33MHz
132Mbytes/sec substantial transfer rate.
Ease of use -
Enables full auto configuration support of PCI local
bus add-in boards and components. PCI devices contain
registers with the device information required for
configuration.
Features of the PCI bus in OCTEK BISON VI
* The PCI local bus is fully compliant to PCI V2.0
specification.
* Up to four PCI masters.
* Burst mode PCI accesses to local memory support.
* Combine host CPU sequential writes into PCI burst
write cycles.
Chapter Three 3-1
Chapter Three
Configuring The System
Important Note: Turn off the power before installing or
replacing any component.
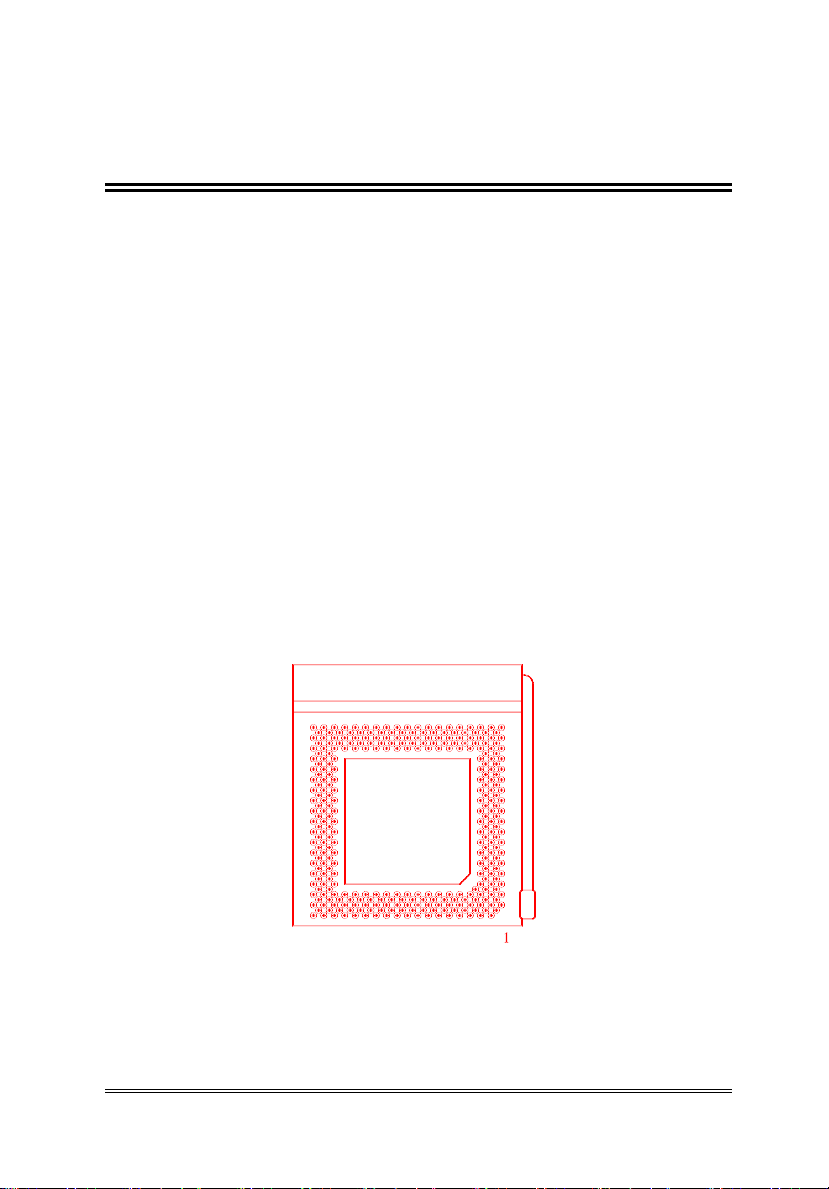
Installing The Processor
Pentium (75/90/100) is a 296 pin SPGA device. Make sure the
pin 1 of Pentium (with a notch at the corner) is line up with the
pin 1 of the socket.
Before installing the processor, make sure that all the pins are
straight. The pins are very fragile. Once these pins are bent, the
processor may be damaged.
PENTIUM 75/90/100 OVERDRIVE SOCKET

3-2 Chapter Three
Installing RAM Modules
BISON VI has three banks on board for 72-pin SIMM modules.
Bank 0 must be installed first. Make sure pin 1 of the SIMM
module inserted near the power connector. Lock it firmly with
the latches on the socket.
Extra SIMM module should be inserted at bank 2 and bank 3.
Configuring The Cache Memory
Note: If you have any question about the configuration of the
cache memory, consult your local dealer. Improper
configuration will cause the system malfunction.
The external cache is organized by single bank or dual banks
with sizes of 256KB to 2MB. Follow the tables below to
configure the system.
Cache
size
JP1
JP2
JP3
JP4
JP5
JP6
Type
(Data RAM)
Bank
256K
1-2
1-2
1-2
1-2
1-2, 3-4
2-3
32Kx8
0
512K
2-3
1-2
1-2
2-3
2-3, 4-5
2-3
32Kx8
0, 1
512K
2-3
1-2
1-2
1-2
1-2, 3-4
1-2
64Kx8
0
1M
2-3
2-3
1-2
2-3
2-3, 4-5
2-3
64Kx8
0, 1
1M
2-3
2-3
1-2
1-2
1-2, 3-4
2-3
128Kx8
0
2M
2-3
2-3
2-3
2-3
2-3, 4-5
2-3
128Kx8
0, 1

Chapter Three 3-3
DRAM Configuration
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 3
Total
Simm 5
Simm 6
Simm 3
Simm 4
Simm 2
Simm 1
1MB-S
1MB-S
2MB
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
4MB
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
12MB
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
1MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
36MB
2MB-D
2MB-D
4MB
2MB-D
2MB-D
2MB-D
2MB-D
8MB
2MB-D
2MB-D
4MB-S
4MB-S
12MB
2MB-D
2MB-D
8MB-D
8MB-D
20MB
2MB-D
2MB-D
16MB-S
16MB-S
36MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
8MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
16MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
24MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
8MB-D
8MB-D
32MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
48MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
4MB-S
32MB-D
32MB-D
80MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
40MB
4MB-S
4MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
72MB
8MB-D
8MB-D
16MB
8MB-D
8MB-D
4MB-S
4MB-S
24MB
8MB-D
8MB-D
8MB-D
8MB-D
32MB
8MB-D
8MB-D
16MB-S
16MB-S
48MB
8MB-D
8MB-D
32MB-D
32MB-D
80MB
16MB-S
16MB-S
32MB
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
64MB
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
8MB-D
8MB-D
80MB
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
16MB-S
96MB
32MB-D
32MB-D
64MB
32MB-D
32MB-D
4MB-S
4MB-S
72MB
32MB-D
32MB-D
16MB-S
16MB-S
96MB
32MB-D
32MB-D
32MB-D
32MB-D
128MB
64MB-S
64MB-S
128MB
Type S stands for single density DRAM module, type D stands for double
density. 70nS 72-pin 32-bit wide SIMM modules can be used.

3-4 Chapter Three
Reset CMOS Setup Information
Sometimes, the improper setting of system setup may make the
system malfunction. In this case, shorted JP16. The internal
CMOS status register is reset. The BIOS finds the CMOS
status register is reset and regards the setup information is
invalid. So it will prompt you to correct the information.
Before shorting JP16, please take note of the following.
If the U40 (Real time clock) is Benchmarq bq3287AMT, the
JP16 jumper must be shorted while the computer is powered
ON.
If the U40 (Real time clock) is Dallas DS12887A, the JP16
jumper must be shorted while the computer is powered
OFF.
PCI-Bus Adapter Installation
PCI-Bus adapters can be installed either at PCI1, PCI2, PCI3 or
PCI4. The corresponding PCI slot number of each physical slot
is listed in the following table :
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI Slot #
1 2 3
4

Chapter Three 3-5
Board Layout

3-6 Chapter Three
System Board Jumper and Connector
Summary
Description
J1
Keyboard Connector
J2
Power Supply Connector (5V)
J8
Power Supply Connector (3.3V)
JP1~JP6
Cache Size Selection
JP7~JP9
CPU Clock Speed Selection
JP12
Flash ROM Selector
JP13, JP15
CPU Internal Cache Write Back,
Write Through Selector
JP14
CPU Pipeline Selector
JP16
Reset CMOS
Key Lock
Power LED & Ext-Lock Connector
Speaker
Speaker Connector
Reset
Hardware Reset Connector
B-SW
Suspend Switch
S-LED
Suspend LED

Chapter Three 3-7
System Board Jumper Setting
There are several options which allows user to select by
hardware switches.
JP7~JP9 - CPU Clock Speed Selection
JP7
JP8
JP9
75MHz-CPU / 50MHz Bus
Open
Open
Short
90MHz-CPU / 60MHz Bus
Short
Open
Short
100MHz-CPU / 66MHz Bus
Short
Short
Short
JP12 - Flash ROM Selection
Pin
1-2
12-Volt Flash ROM
2-3
5-Volt Flash ROM
Pin
3-4
Flash ROM Programming Disable
(Default)
4-5
Flash ROM Programming
Enabled

3-8 Chapter Three
JP13 - CPU Internal Cache Write Back Selection
Pin
1-2
CPU Internal Cache Write Back
(Default)
2-3
CPU Internal Cache Write
Through
JP14 - CPU Pipeline Selection
Pin
1-2
CPU Pipeline Disabled
2-3
CPU Pipeline Enabled (Default)
JP15 - CPU Internal Cache Write Through Selection
Pin
1-2
For CPU Write Through
2-3
For CPU Write Back (Default)

Chapter Three 3-9
System Board Connectors
Under typical conditions, these connectors should be connected
to the indicators and switches of the system unit. The functions
and the pin assignment of the connectors on the motherboard
are listed below.
J1 - Keyboard Connector
Pin
Assignment
1
Keyboard Clock
2
Keyboard Data
3
Spare
4
Ground
5
+5 Vdc
J8 - Power Supply Connector (3.3V)
Pin
Assignment
1
Ground
2
Ground
3
Ground
4
3.3 Vdc
5
3.3 Vdc
6
3.3 Vdc

3-10 Chapter Three
J2 - Power Supply Connector (5V)
Pin
Assignment
1
POWERGOOD
2
+5 Vdc
3
+12 Vdc
4
-12 Vdc
5
Ground
6
Ground
Pin
Assignment
1
Ground
2
Ground
3
-5 Vdc
4
+5 Vdc
5
+5 Vdc
6
+5 Vdc
Key Lock - Power LED & Ex-Lock Connector
Pin
Assignment
1
+5 Vdc
2
Key
3
Ground
4
Keyboard Inhibit
5
Ground

Chapter Three 3-11
Speaker - Speaker Connector
Pin
Assignment
1
Data Out
2
+5 Vdc
3
Ground
4
+5 Vdc
Reset - Hardware Reset Connector
Pin
Assignment
1
Selection Pin
2
Ground

3-12 Chapter Three
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

Chapter Four 4-1
Chapter Four
Technical Information
This section provides technical information about BISON VI
and is intended for advanced users interested in the basic design
and operation of BISON VI.
Memory Mapping
Address
Range
Function
0000007FFFFF
000K-512K
System Board Memory
(512K)
08000009FFFF
512K-640K
System Board Memory
(128K)
0A00000BFFFF
640K-768K
Display Buffer (128K)
0C00000DFFFF
768K-896K
Adaptor ROM / Shadow
RAM (128K)
0E00000EFFFF
896K-960K
System ROM / Shadow
RAM (64K)
0F00000FFFFF
960K-1024K
System BIOS ROM /
Shadow RAM (64K)
1000007FFFFF
1024K-8192K
System Memory
800000FFFFFF
8192K-16318K
System Memory

4-2 Chapter Four
I/O Address Map
I/O Address Map on System Board
I/O address hex 000 to 0FF are reserved for the system board
I/O.
Address (Hex)
Device
000-01F
DMA Controller 1, 8237
020-03F
Interrupt Controller 1, 8259, Master
040-05F
Timer, 8254
060-06F
Keyboard Controller
070-07F
Real Time Clock, NMI
(non-maskable interrupt) mask
080-09F
DMA Page Register, 74LS612
0A0-0BF
Interrupt Controller 2, 8259
0C0-0DF
DMA Controller 2, 8237
0F0
Clear Math Coprocessor Busy
0F1
Reset Math Coprocessor
0F8-0FF
Math Coprocessor Port

Chapter Four 4-3
I/O address hex 100 to 3FF are available on the I/O channel.
Address (Hex)
Device
1F0-1F8
Fixed Disk
200-207
Game I/O
278-27F
Parallel Printer Port 2
2F8-2FF
Serial Port 2
300-31F
Prototype Card
360-36F
Reserved
378-37F
Parallel Printer Port 1
380-38F
SDLC, bisynchronous 2
3A0-3AF
Bisynchronous 1
3B0-3BF
Monochrome Display and Printer
Adapter
3C0-3CF
Reserved
3D0-3DF
Color Graphics Monitor Adapter
3F0-3F7
Diskette Controller
3F8-3FF
Serial Port 1
CF8
PCI Config-address Register +
CFC
PCI Config-data Register +
+ Double word I/O locations

4-4 Chapter Four
System Interrupts
Sixteen levels of system interrupts are provided on BISON VI.
The following shows the interrupt-level assignments in
decreasing priority.
Level Function
Microprocessor NMI Parity or I/O Channel Check
Interrupt Controllers
CTLR 1 CTLR 2
IRQ0 Timer Output 0
IRQ1 Keyboard
(Output Buffer Full)
IRQ2 Interrupt from CTLR 2
IRQ8 Real-time Clock Interrupt
IRQ9 Software Redirected to
INT 0AH (IRQ2)
IRQ10 Reserved
IRQ11 Reserved
IRQ12 Reserved
IRQ13 Coprocessor
IRQ14 Fixed Disk Controller
IRQ15 Reserved
IRQ3 Serial Port 2
IRQ4 Serial Port 1
IRQ5 Parallel Port 2
IRQ6 Diskette Controller
IRQ7 Parallel Port 1

Chapter Four 4-5
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
BISON VI supports seven DMA channels.
Channel
Function
0
Spare (8 bit transfer)
1
SDLC (8 bit transfer)
2
Floppy Disk (8 bit transfer)
3
Spare (8 bit transfer)
4
Cascade for DMA Controller 1
5
Spare (16 bit transfer)
6
Spare (16 bit transfer)
7
Spare (16 bit transfer)
The following shows the addresses for the page register.
Page Register
I/O Address (HEX)
DMA Channel 0
0087
DMA Channel 1
0083
DMA Channel 2
0081
DMA Channel 3
0082
DMA Channel 5
008B
DMA Channel 6
0089
DMA Channel 7
008A
Refresh
008F

4-6 Chapter Four
Real Time Clock and CMOS RAM
Real time clock and CMOS RAM are contained on board. Real
time clock provides the system date and time. CMOS RAM
stores system information. Both are backed up by battery and
will not lose information after power off
System Expansion Bus
BISON VI provides four 16-bit ISA slots.
The I/O channel supports:
* I/O address space from hex 100 to hex 3FF
* Selection of data access (either 8 or 16 bit)
* 24 bit memory addresses (16MB)
* Interrupts
* DMA channels
* Memory refresh signal

Chapter Four 4-7
The following figure shows the pin numbering for I/O channel
connectors (A-side and B-side).

4-8 Chapter Four
The following figure shows the pin numbering for I/O channel
connectors (C-side and D-side).

Chapter Four 4-9
The following tables summarize pin assignments for the I/O
channel connectors.
I/O Channel (A-Side)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
I/O
A1
-I/O CH CK
I
A2
SD7
I/O
A3
SD6
I/O
A4
SD5
I/O
A5
SD4
I/O
A6
SD3
I/O
A7
SD2
I/O
A8
SD1
I/O
A9
SD0
I/O
A10
-I/O CH RDY
I
A11
AEN
O
A12
SA19
I/O
A13
SA18
I/O
A14
SA17
I/O
A15
SA16
I/O
A16
SA15
I/O
A17
SA14
I/O
A18
SA13
I/O
A19
SA12
I/O
A20
SA11
I/O
A21
SA10
I/O
A22
SA9
I/O
A23
SA8
I/O
A24
SA7
I/O
A25
SA6
I/O
A26
SA5
I/O
A27
SA4
I/O
A28
SA3
I/O
A29
SA2
I/O
A30
SA1
I/O
A31
SA0
I/O

4-10 Chapter Four
I/O Channel (B-Side)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
I/O
B1
GND
Ground
B2
RESET DRV
I
B3
+5 Vdc
Power
B4
IRQ9
I
B5
-5 Vdc
Power
B6
DRQ2
I
B7
-12 Vdc
Power
B8
0WS I B9
+12 Vdc
Power
B10
GND
Ground
B11
-SMEMW
O
B12
-SMEMR
O
B13
-IOW
I/O
B14
-IOR
I/O
B15
-DACK3
I
B16
DRQ3 O B17
-DACK1
I
B18
DRQ1 O B19
-Refresh
I/O
B20
CLK O B21
IRQ7 I B22
IRQ6
I
B23
IRQ5
I
B24
IRQ4
I
B25
IRQ3
I
B26
-DACK2
O
B27
T/C
O
B28
BALE O B29
+5 Vdc
Power
B30
OSC O B31
GND
Ground

Chapter Four 4-11
I/O Channel (C-Side)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
I/O
C1
SBHE
I/O
C2
LA23
I/O
C3
LA22
I/O
C4
LA21
I/O
C5
LA20
I/O
C6
LA19
I/O
C7
LA18
I/O
C8
LA17
I/O
C9
-MEMR
I/O
C10
-MEMW
I/O
C11
SD8
I/O
C12
SD9
I/O
C13
SD10
I/O
C14
SD11
I/O
C15
SD12
I/O
C16
SD13
I/O
C17
SD14
I/O
C18
SD15
I/O

4-12 Chapter Four
I/O Channel (D-Side)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
I/O
D1
-MEM CS16
I
D2
-I/O CS16
I
D3
IRQ10
I
D4
IRQ11
I
D5
IRQ12
I
D6
IRQ15
I
D7
IRQ14 I D8
-DACK0
O
D9
DRQ0
I
D10
-DACK5
O
D11
DRQ5
I
D12
-DACK6
O
D13
DRQ6
I
D14
-DACK7
O
D15
DRQ7
I
D16
+5 Vdc
Power
D17
-MASTER
I
D18
GND
Ground

Chapter Four 4-13
The following table summarizes pin assignments for PCI local
bus connector.
PCI Bus Pinout (side A)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
A1
TRST#
A2
+12V
A3
Reserved
A4
Reserved
A5
+5V
A6
INTA#
A7
INTC#
A8
+5V
A9
Reserved
A10
+5V
A11
Reserved
A12
Ground
A13
Ground
A14
Reserved
A15
RST#
A16
+5V
A17
GNT#
A18
Ground
A19
Reserved
A20
AD[30]
A21
Reserved
A22
AD[28]
A23
AD[26]
A24
Ground
A25
AD[24]
A26
IDSEL
A27
Reserved
A28
AD[22]
A29
AD[20]
A30
Ground

4-14 Chapter Four
PCI Bus Pinout (side A)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
A31
AD[18]
A32
AD[16]
A33
Reserved
A34
FRAME#
A35
Ground
A36
TRDY#
A37
Ground
A38
STOP#
A39
Reserved
A40
SDONE
A41
SBO#
A42
Ground
A43
PAR
A44
AD[15]
A45
Reserved
A46
AD[13]
A47
AD[11]
A48
Ground
A49
AD[09]
A50
C/BE[0]#
A51
Reserved
A52
AD[06]
A53
AD[04]
A54
Ground
A55
AD[02]
A56
AD[00]
A57
+5V
A58
REQ64#
A59
+5V
A60
+5V

Chapter Four 4-15
PCI Bus Pinout (side B)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
B1
-12V
B2
TCK
B3
Ground
B4
Reserved
B5
+5V
B6
+5V
B7
INTB#
B8
INTD#
B9
PRSNT1#
B10
Reserved
B11
PRSNT2#
B12
Ground
B13
Ground
B14
Reserved
B15
Ground
B16
CLK
B17
Ground
B18
REQ#
B19
+5V
B20
AD[31]
B21
AD[29]
B22
Ground
B23
AD[27]
B24
AD[25]
B25
Reserved
B26
C/BE[3]#
B27
AD[23]
B28
Ground
B29
AD[21]
B30
AD[19]

4-16 Chapter Four
PCI Bus Pinout (side B)
I/O Pin
Signal Name
B31
Reserved
B32
AD[17]
B33
C/BE[2]#
B34
Ground
B35
IRDY#
B36
Reserved
B37
DEVSEL#
B38
Ground
B39
LOCK#
B40
PERR#
B41
Reserved
B42
SERR#
B43
Reserved
B44
C/BE[1]#
B45
AD[14]
B46
Ground
B47
AD[12]
B48
AD[10]
B49
Ground
B50
AD[08]
B51
AD[07]
B52
Reserved
B53
AD[05]
B54
AD[03]
B55
Ground
B56
AD[01]
B57
Reserved
B58
ACK64#
B59
+5V
B60
+5V

Appendix A A-1
Appendix A
Operation and Maintenance
Static Electricity
When installing or removing any add-on card, DRAM module
or processor, you should discharge the static electricity on your
body. Static electricity is dangerous to electronic device and
can build-up on your body. When you touch the add-on card or
motherboard, it is likely to damage the device. To discharge the
static electricity, touch the metal of your computer. When
handling the add-on card, don't contact the components on the
cards or their "golden finger". Hold the cards by their edges.
Keeping The System Cool
The motherboard contains many high-speed components and
they will generate heat during operation. Other add-on cards
and hard disk drive can also produce a lot of heat. The
temperature inside the computer system may be very high. In
order to keep the system running stably, the temperature must
be kept at a low level. A easy way to do this is to keep the cool
air circulating inside the case. The power supply contains a fan
to blow air out of the case. If you find that the temperature is
still very high, it would be better to install another fan inside the
case. Using a larger case is recommended if there are a number
of add-on cards and disk drives in the system.

A-2 Appendix A
Cleaning The "Golden Finger"
Whenever inserting an add-on card to the motherboard, make
sure that there is no dirt on the "golden finger" of the add-on
card. If not, the contact between the "golden finger" and the
slot may be poor and thus the add-on card may not work
properly. Use a pencil eraser to clean the "golden finger" if dirt
is found.
Cleaning The Motherboard
The computer system should be kept clean. Dust and dirt is
harmful to electronic devices. To prevent dust from
accumulating on the mother-board, installing all mounting
plates on the rear of the case. Regularly examine your system,
and if necessary, vacuum the interior of the system with a
miniature vacuum.

Chapter Four 4-1
 Loading...
Loading...