Page 1

PC–600 Single Board Computer
Reference manual
Manual part #6437, rev. 0806
CONTACT INFORMATION
Front Desk: 303–430–1500
Technical Support: 303–426–4521
FastHelp@octagonsystems.com
www.octagonsystems.com
Page 2

Copyright
OS Embedder™ is a trademark, and Octagon Systems Corporation®,
and the Octagon logo are registered trademarks of Octagon Systems
Corporation. ROM–DOS™ is a trademark of Datalight. QNX® is a
registered trademark of QNX Software Systems Ltd. Windows 2000®,
Windows NT®, Windows XP® and Windows CE.net® are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. HyperTerminal ™ is a copyright
of Hilgraeve, Inc. CompactFlash™ is a trademark of San Disk
Corporation. Ethernet® is a registered trademark of Xerox
Corporation.
Disclaimer
Copyright 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006—Octagon Systems Corporation. All
rights reserved. However, any part of this document may be
reproduced, provided that Octagon Systems Corporation is cited as the
source. The contents of this manual and the specifications herein may
change without notice.
The information contained in this manual is believed to be correct.
However, Octagon assumes no responsibility for any of the circuits
described herein, conveys no license under any patent or other right,
and makes no representations that the circuits are free from patent
infringement. Octagon makes no representation or warranty that such
applications will be suitable for the use specified without further
testing or modification.
Octagon Systems Corporation general policy does not recommend the
use of its products in life support applications where the failure or
malfunction of a component may directly threaten life or injury. It is a
Condition of Sale that the user of Octagon products in life support
applications assumes all the risk of such use and indemnifies Octagon
against all damage.
Technical Support
Carefully recheck your system before calling Technical Support. Run
as many tests as possible; the more information you can provide, the
easier it will be for Technical Support staff to help you solve the
problem. For additional technical assistance, try the following:
Technical Support telephone: 303–426–4521
E-mail Technical Support:
Applications Notes (via web):
fasthelp@octagonsystems.com
www.octagonsystems.com
Page 3

IMPORTANT!
Please read the following section before installing your product:
Octagon’s products are designed to be high in performance while
consuming very little power. In order to maintain this advantage, CMOS
circuitry is used.
CMOS chips have specific needs and some special requirements that the
user must be aware of. Read the following to help avoid damage to your
card from the use of CMOS chips.
Using CMOS circuitry in industrial control
Industrial computers originally used LSTTL circuits. Because many PC
components are used in laptop computers, IC manufacturers are
exclusively using CMOS technology. Both TTL and CMOS have failure
mechanisms, but they are different. Described below are some of the
failures which are common to all manufacturers of CMOS equipment.
The most common failures on Single Board Computers are over voltage of
the power supply, static discharge, and damage to the serial and parallel
ports. On expansion cards, the most common failures are static discharge,
over voltage of inputs, over current of outputs, and misuse of the CMOS
circuitry with regards to power supply sequencing. In the case of the video
cards, the most common failure is to miswire the card to the flat panel
display. Miswiring can damage both the card and an expensive display.
Multiple component failures: The chance of a random component
failure is very rare since the average MTBF of an Octagon card is
greater than 11 years. In a 7 year study, Octagon has
single case where multiple IC failures were
accident. It is very probable that multiple component failures indicate
that they were user-induced.
not caused by misuse or
never found a
Testing “dead” cards: For a card that is “completely nonfunctional”,
there is a simple test to determine accidental over voltage, reverse
voltage or other “forced” current situations. Unplug the card from the
bus and remove all cables. Using an ordinary digital ohmmeter on the
2,000 ohm scale, measure the resistance between power and ground.
Record this number. Reverse the ohmmeter leads and measure the
resistance again. If the ratio of the resistances is 2:1 or greater, fault
conditions most likely have occurred. A common cause is miswiring
the power supply.
3
Page 4

Improper power causes catastrophic failure: If a card has had
reverse polarity or high voltage applied, replacing a failed component
is not an adequate fix. Other components probably have been partially
damaged or a failure mechanism has been induced. Therefore, a
failure will probably occur in the future. For such cards, Octagon
highly recommends that these cards be replaced.
Other over-voltage symptoms: In over-voltage situations, the
programmable logic devices, EPROMs and CPU chips, usually fail in
this order. The failed device may be hot to the touch. It is usually the
case that only one IC will be overheated at a time.
Power sequencing: The major failure of I/O chips is caused by the
external application of input voltage while the Micro PC power is off.
If you apply 5V to the input of a TTL chip with the power off, nothing
will happen. Applying a 5V input to a CMOS card will cause the
current to flow through the input and out the 5V power pin. This
current attempts to power up the card. Most inputs are rated at 25
mA maximum. When this is exceeded, the chip may be damaged.
Failure on power-up: Even when there is not enough current to
destroy an input described above, the chip may be destroyed when the
power to the card is applied. This is due to the fact that the input
current biases the IC so that it acts as a forward biased diode on
power-up. This type of failure is typical on serial interface chips but
can apply any IC on the card.
Under-rated power supply: The board may fail to boot due to an
under-rated power supply. It is important that a quality power supply
be used with the PC–600 SBC that has sufficient current capacity, line
and load regulation, hold up time, current limiting, and minimum
ripple. The power supply for the PC–600 must meet the startup
risetime requirements specified in the ATX Power Design Guide,
version 1.1, section 3.3.5. This assures that all the circuitry on the
CPU control card sequences properly and avoids system lockup.
Excessive signal lead lengths: Another source of failure that was
identified years ago at Octagon was excessive lead lengths on digital
inputs. Long leads act as an antenna to pick up noise. They can also
act as unterminated transmission lines. When 5V is switch onto a line,
it creates a transient waveform. Octagon has seen sub-microsecond
pulses of 8V or more. The solution is to place a capacitor, for example
0.1 µF, across the switch contact. This will also eliminate radio
frequency and other high frequency pickup.
4
Page 5

Avoiding damage to the heatsink or CPU
WARNING!
When handling any Octagon Single Board Computer,
extreme care must be taken not to strike the heatsink (if
installed) against another object, such as a table edge. Also,
be careful not to drop the Single Board Computer, since this
may cause damage to the heatsink or CPU as well.
Note Any physical damage to the CPU control card is not covered under
warranty.
Excessive Thermal Stress
This card is guaranteed to operate over the published temperature ranges
and relevant conditions. However, sustained operation near the maximum
temperature specification is not recommended by Octagon or the CPU
chip manufacturer due to well known, thermal related, failure
mechanisms. These failure mechanisms, common to all silicon devices,
can reduce the MTBF of the cards. Extended operation at the lower limits
of the temperature ranges has no limitations.
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Copyright.......................................................................................................................... 2
Disclaimer ........................................................................................................................ 2
Technical Support............................................................................................................ 2
Using CMOS circuitry in industrial control......................................................................3
Avoiding damage to the heatsink or CPU ......................................................................... 5
Excessive Thermal Stress ...............................................................................................5
Table of Contents ...............................................................................................................6
List of Figures...................................................................................................................12
List of Tables .....................................................................................................................13
Overview: Section 1 – Installation ..............................................................................15
Chapter 1: Overview.......................................................................................................16
Description ........................................................................................................................ 16
PC–600 major hardware features....................................................................................16
CPU ................................................................................................................................16
SDRAM........................................................................................................................... 16
On-board flash ...............................................................................................................16
Hard disk, CompactFlash, and floppy disk ports......................................................... 17
USB ports ....................................................................................................................... 17
Serial ports..................................................................................................................... 17
Digital I/O ...................................................................................................................... 17
Speaker, keyboard, and mouse ports............................................................................ 17
Video............................................................................................................................... 18
PC/104 and PC/104 Plus interface................................................................................ 18
Ethernet ......................................................................................................................... 18
Multifunctional printer port ......................................................................................... 18
Watchdog timer added for safety .................................................................................. 18
Real time calendar/clock with battery–backup............................................................ 18
Setup information stored in EEPROM for high reliability .........................................19
Hardware reset .............................................................................................................. 19
Temperature sensor....................................................................................................... 19
5 volt operation lowers system cost .............................................................................. 19
Rugged environmental operation.................................................................................. 20
Size .................................................................................................................................20
PC–600 major software features...................................................................................... 21
Diagnostic software verifies system integrity automatically ......................................21
Phoenix BIOS................................................................................................................. 21
Octagon BIOS extensions.............................................................................................. 21
Boot sequence................................................................................................................. 21
Chapter 2: Quick start ...................................................................................................22
Hardware installation ......................................................................................................22
Installing the PC–600.......................................................................................................27
Installation..................................................................................................................... 27
Hardware mounting ......................................................................................................28
Power connection ........................................................................................................... 29
6
Page 7

Monitor........................................................................................................................... 30
Keyboard and mouse .....................................................................................................30
Speaker........................................................................................................................... 30
Installing an operating system ........................................................................................30
OS on floppy onto a hard drive or CompactFlash ........................................................ 31
OS on CD-ROM onto a hard drive or CompactFlash................................................... 32
Power supply requirements .............................................................................................34
Power supply requirements .............................................................................................35
Chapter 3: Setup programs...........................................................................................36
Operating systems other than DOS.................................................................................36
Setup .................................................................................................................................36
Main menu ..................................................................................................................... 37
Hard drive submenus .................................................................................................... 38
Advanced menu.............................................................................................................. 39
Advanced Chipset Control submenu ............................................................................40
I/O Device Configuration submenu ..............................................................................41
Audio Options submenu ................................................................................................ 42
PCI Configuration submenu .........................................................................................43
PCI Configuration submenu .........................................................................................43
PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion submenu .......................................................... 44
PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion submenu ........................................................ 45
PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion submenu ...................................................... 45
Power menu ...................................................................................................................46
Boot menu ...................................................................................................................... 47
Expanded Boot screen ................................................................................................... 47
Exit menu....................................................................................................................... 48
Chapter 4: Save and run programs.............................................................................49
Save and run your programs on the PC–600 .................................................................. 49
Saving programs and support files..................................................................................49
Adding your application ................................................................................................ 49
Overriding the autoexecution of your application .......................................................50
Option 1.......................................................................................................................... 50
Option 2.......................................................................................................................... 50
Option 3.......................................................................................................................... 50
Option 4.......................................................................................................................... 50
Overview: Section 2 – Hardware .................................................................................51
Chapter 5: Serial ports...................................................................................................52
Description ........................................................................................................................ 52
Serial port configurations.................................................................................................53
Serial port configurations.................................................................................................54
Function and use of serial ports.......................................................................................56
COM1 as serial console device ...................................................................................... 56
Mating receptacle ..........................................................................................................56
COM Ports as RS–232 I/O............................................................................................. 57
COM3 and COM4 as RS–422 and RS–485 networks ..................................................57
RS–422 ...........................................................................................................................58
RS–485 ...........................................................................................................................58
Chapter 6: LPT1 parallel port, LCD and keypad.....................................................60
7
Page 8

LPT1 parallel port ............................................................................................................ 60
Installing a printer ...........................................................................................................60
Display ..............................................................................................................................61
Installing a display ........................................................................................................ 61
Keypad...............................................................................................................................62
Installing a keypad ........................................................................................................ 63
Chapter 7: Console devices ...........................................................................................64
Description ........................................................................................................................ 64
Selecting console devices .................................................................................................. 64
Monitor and keyboard console ......................................................................................64
Serial console .................................................................................................................65
Chapter 8: CompactFlash, SDRAM, and battery backup........................................68
Description ........................................................................................................................ 68
CompactFlash ...................................................................................................................68
Creating a bootable CompactFlash............................................................................... 69
SDRAM..............................................................................................................................69
Battery backup for real time calendar clock ................................................................... 70
Installing an AT battery................................................................................................ 70
Chapter 9: External drives............................................................................................71
Description ........................................................................................................................ 71
Floppy disk controller.......................................................................................................71
Power requirements ...................................................................................................... 71
Installing a floppy disk drive ........................................................................................71
Hard disk controller .........................................................................................................72
Master/slave designation for IDE devices .................................................................... 72
Installing a hard drive................................................................................................... 72
Chapter 10: Bit-programmable digital I/O ................................................................74
Description ........................................................................................................................ 74
Interfacing to switches and other devices ....................................................................... 75
Opto-module rack interface...........................................................................................75
Organization of banks ...................................................................................................... 78
Port addressing.............................................................................................................. 78
Base I/O address ............................................................................................................ 79
Pulling the I/O lines high or low......................................................................................79
Configuring and programming the digital I/O ports ......................................................80
Programming the I/O..................................................................................................... 80
Configuring the I/O........................................................................................................ 80
Writing and reading from I/O .......................................................................................81
Digital I/O output program examples........................................................................... 82
Digital I/O input program examples.............................................................................82
Enhanced INT 17h function definitions ..........................................................................83
Initialize I/O................................................................................................................... 83
Write I/O......................................................................................................................... 83
Read I/O.......................................................................................................................... 84
Chapter 11: CRTs and flat panels................................................................................86
Video features ...................................................................................................................86
Connecting a monitor .......................................................................................................87
Connecting a flat panel display .......................................................................................89
8
Page 9

Flat panels requiring bias voltage ................................................................................ 89
Connecting the flat panel to the PC–600 ..................................................................... 91
Programming the video BIOS .......................................................................................... 93
Additional notes on video BIOS .................................................................................... 93
Chapter 12: Ethernet......................................................................................................94
Description ........................................................................................................................ 94
Chapter 13: USB ..............................................................................................................95
Description ........................................................................................................................ 95
Chapter 14: Audio ...........................................................................................................96
Description ........................................................................................................................ 96
Chapter 15: PC/104 and PC/104 Plus expansion.......................................................98
Description ........................................................................................................................ 98
Overview: Section 3 – System management............................................................100
Chapter 16: Watchdog timer and hardware reset .................................................101
Description ...................................................................................................................... 101
Timeout period (ranges) .............................................................................................. 101
Booting, power down, and strobing the watchdog timer ........................................... 101
Watchdog function definitions using enhanced INT 17h handler ...............................102
Enable watchdog.......................................................................................................... 102
Strobe watchdog........................................................................................................... 102
Disable watchdog......................................................................................................... 103
Hardware reset ...............................................................................................................104
Chapter 17: Serial EEPROM.......................................................................................105
Description ...................................................................................................................... 105
Enhanced INT 17h function definitions ........................................................................105
Serial EEPROM..............................................................................................................105
Read a single word from the serial EEPROM............................................................ 105
Write a single word to the serial EEPROM ...............................................................106
Read multiple words from the serial EEPROM......................................................... 106
Write multiple words to the serial EEPROM............................................................. 107
Return serial EEPROM size .......................................................................................108
Chapter 18: Temperature sensor and user jumper ...............................................109
Description ...................................................................................................................... 109
Temperature sensor INT17h function definitions ........................................................ 109
Write TEMP SENSOR register pointer...................................................................... 109
Read TEMP SENSOR current register ......................................................................110
Write TEMP SENSOR current register .....................................................................111
Read TEMP SENSOR Int Status bit .......................................................................... 111
Read user jumper............................................................................................................112
Chapter 19: CPU clock, system jumpers, and BIOS recovery.............................113
Description ...................................................................................................................... 113
System jumper ............................................................................................................. 114
Extended BIOS jumper ...............................................................................................114
Video jumper................................................................................................................ 114
User jumper .................................................................................................................115
BIOS recovery jumper ................................................................................................. 115
BIOS programming using PHLASH.EXE .................................................................. 116
Chapter 20: Troubleshooting......................................................................................117
9
Page 10

Boot Block Recovery ....................................................................................................... 117
Memory conflicts using operating system other than DOS.......................................... 117
No system LED activity .................................................................................................117
No CRT or flat panel video.............................................................................................118
Video is present but is distorted ....................................................................................118
No serial console activity................................................................................................ 119
Garbled console screen activity......................................................................................119
System generates a BIOS message but locks up when booting ...................................120
System will not boot from CompactFlash .....................................................................120
System locks up on power–up; may or may not respond to reset switch..................... 120
System locks up after power–down/power–up ..............................................................121
LED signaling of “beep” codes........................................................................................ 121
Description ................................................................................................................... 121
Technical assistance ....................................................................................................... 124
Overview: Section 4 – Appendices.............................................................................125
Appendix A: PC–600 technical data ..........................................................................126
Technical specifications..................................................................................................126
CPU ..............................................................................................................................126
Bus clock....................................................................................................................... 126
BIOS ............................................................................................................................. 126
SDRAM......................................................................................................................... 126
On-board flash .............................................................................................................126
Hard drive .................................................................................................................... 126
CompactFlash socket................................................................................................... 126
Floppy drive .................................................................................................................126
USB ..............................................................................................................................126
Serial I/O ...................................................................................................................... 127
Parallel port ................................................................................................................. 127
Digital I/O .................................................................................................................... 127
Speaker, Keyboard, and Mouse ports ......................................................................... 127
Video............................................................................................................................. 127
Ethernet ....................................................................................................................... 127
Watchdog timer............................................................................................................ 127
Real time clock............................................................................................................. 127
Expansion..................................................................................................................... 127
Operating systems ....................................................................................................... 127
PCI bus mastering ....................................................................................................... 128
Power requirements .................................................................................................... 128
Environmental specifications...................................................................................... 128
Size ...............................................................................................................................128
Weight .......................................................................................................................... 128
Excessive Thermal Stress ...........................................................................................128
Mating connectors ..........................................................................................................129
Maps ................................................................................................................................130
Jumper settings ..............................................................................................................132
Connector pin-outs..........................................................................................................135
Appendix B: Software utilities...................................................................................145
Introduction ....................................................................................................................145
10
Page 11

Support commands ...................................................................................................... 145
I17HNDLR.EXE ............................................................................................................. 146
LPT1CON.COM..............................................................................................................146
PGMVIDEO.EXE............................................................................................................ 147
PHLASH.EXE.................................................................................................................148
RESET.COM...................................................................................................................148
Appendix C: Accessories..............................................................................................149
Warranty ..........................................................................................................................151
Limitations on warranty ............................................................................................. 151
Service policy ...............................................................................................................152
Returning a product for repair....................................................................................152
Returns......................................................................................................................... 153
Governing law .............................................................................................................. 153
11
Page 12

List of Figures
Figure 2–1 PC–600 connector and jumper diagram................................................ 23
Figure 2–2 PC–600 center-to-center hole dimensions (thousandths) ....................24
Figure 2–3 PC–600 center-to-center hole dimensions (millimeters)...................... 25
Figure 2–4 Basic hookup diagram ........................................................................... 28
Figure 2–5 Power connector: J9 ............................................................................... 29
Figure 2–6 Installing an operating system.............................................................. 34
Figure 5–1 COM ports .............................................................................................. 53
Figure 5–2 VTC–20F and VTC–20M cables ............................................................ 57
Figure 5–3 Typical RS–422 four-wire interface circuit........................................... 58
Figure 5–4 Typical RS–485 half duplex interface circuit ....................................... 59
Figure 5–5 Typical RS–485 full duplex interface circuit ........................................ 59
Figure 6–1 LPT1 as a printer port ........................................................................... 61
Figure 6–2 LPT1 as a display or keypad port.......................................................... 62
Figure 7–1 Monitor and keyboard console............................................................... 65
Figure 7–2 PC–600 and a serial console .................................................................. 67
Figure 7–3 VTC–20F cable and null modem adapter ............................................. 67
Figure 10–1 Typical digital I/O configurations ......................................................... 77
Figure 10–2 Organization of banks............................................................................ 78
Figure 11–1 PC–600 and a VGA monitor .................................................................. 88
Figure 11–2 PC–600 and a flat panel display ........................................................... 92
Figure 14–1 Audio cable ............................................................................................. 97
Figure 15–1 Typical PC/104 module stack ................................................................ 99
12
Page 13

List of Tables
Table 2–1 PC–600 connector functions .................................................................. 26
Table 2–2 PC–600 jumper functions ......................................................................26
Table 2–3 Power connector: J9 ............................................................................... 29
Table 5–1 Serial port configurations ...................................................................... 54
Table 5–2 COM1, COM2: J4 ................................................................................... 55
Table 5–3 COM3, COM4: J5 ................................................................................... 55
Table 5–4 COM3 and COM4 jumpers: W3, W5, W7, and W11............................. 56
Table 6–1 LPT1 connector: J8 ................................................................................ 60
Table 8–1 CompactFlash configuration jumper: W13 ........................................... 68
Table 8–2 Battery connector: J19........................................................................... 70
Table 10–1 Digital I/O connectors: J6 and J13 (arranged by function).................. 74
Table 10–2 Digital I/O connectors: J6 and J13 (arranged by pins) ........................ 75
Table 10–3 Digital I/O opto-rack interface............................................................... 76
Table 10–4 Digital I/O port addressing.................................................................... 79
Table 10–5 Digital I/O pull-up/pull-down jumpers: W2 and W4 ............................ 79
Table 10–6 Digital I/O port byte............................................................................... 81
Table 11–1 CRT connector: J18 ................................................................................ 88
Table 11–2 Display jumpers: W6, W9, and W12 ..................................................... 90
Table 11–3 Flat panel connector: J14 ...................................................................... 90
Table 11–4 Flat panel back-light connector: J16..................................................... 91
Table 12–1 Ethernet LEDs ....................................................................................... 94
Table 12–2 Ethernet IRQs ........................................................................................ 94
Table 13–1 USB connector: J3.................................................................................. 95
Table 14–1 Audio connector: J20.............................................................................. 96
Table 14–2 Audio connections .................................................................................. 97
Table 16–1 Reset connector: J7 .............................................................................. 104
Table 18–1 CPU clock speed jumper: W1............................................................... 113
Table 18–2 System jumpers: W12 .......................................................................... 114
Table 20–1 BIOS beep codes................................................................................... 122
Table A–1 Mating connectors................................................................................ 129
Table A–2 PC–600 DMA map................................................................................ 130
Table A–3 PC–600 I/O map ................................................................................... 130
Table A–4 PC–600 interrupt map ......................................................................... 131
Table A–5 PC–600 memory map........................................................................... 131
Table A–6 W1 – CPU clock speed ......................................................................... 132
Table A–7 W2, W4 – Digital I/O pull-up/pull-down jumpers............................... 132
Table A–8 W3, W5, W7, W11 – COM3 and COM4 jumper settings.................... 133
Table A–9 W6, W9, W12 – display jumpers ......................................................... 133
Table A–10 W12 – system jumpers......................................................................... 134
Table A–11 W13 – CompactFlash configuration jumper....................................... 134
Table A–12 J1, J2 – Ethernet connectors ............................................................... 135
Table A–13 J3 – USB connector.............................................................................. 135
Table A–14 J4 – COM1, COM2 connectors ............................................................ 136
Table A–15 J5 – COM3, COM4 connectors ............................................................ 136
13
Page 14

Table A–16 J6, J13 – Digital I/O connectors .......................................................... 137
Table A–17 J7 – reset connector .............................................................................137
Table A–18 J8 – LPT1 connector ............................................................................ 137
Table A–19 J9 – power connector............................................................................ 138
Table A–20 J10 – PS/2 keyboard/mouse connector ................................................ 138
Table A–21 J12 – floppy drive connector................................................................ 139
Table A–22 J14 – flat panel connector.................................................................... 140
Table A–23 J16 – flat panel back-light connector .................................................. 140
Table A–24 J17 – EIDE connector .......................................................................... 141
Table A–25 J18 – CRT connector ............................................................................ 141
Table A–26 J19 – battery connector ....................................................................... 142
Table A–27 J20 – audio connector .......................................................................... 142
Table A–28 J501 – PC/104 connector...................................................................... 143
Table A–29 J15 – PC/104 Plus connector ............................................................... 144
Table C–1 Cables and terminal board ..................................................................149
Table C–2 LCD displays and keypads .................................................................. 149
Table C–3 Miscellaneous part numbers ............................................................... 150
14
Page 15

Overview: Section 1 – Installation
Section 1 provides installation and programming instructions, startup
options, and system configuration program examples. The following
chapters are included:
Chapter 1: Overview
Chapter 2: Quick start
Chapter 3: Setup programs
Chapter 4: Save and run programs
15
Page 16

Chapter 1: Overview
Description
The PC–600 Single Board Computer is intended for higher-performance
embedded control applications. The PC–600 integrates serial
communication, IDE hard disk port, CompactFlash socket, floppy disk
port, a multifunctional parallel port, a keyboard/mouse port, a video
interface, two USB ports, an audio port, two 10/100BaseT Ethernet ports,
and 48 digital I/O lines. The PC–600 can be used in a stand-alone mode or
expanded through a PC/104 or PC/104 Plus interface.
The PC–600 comes with a BIOS loaded on a flash device for easy updates.
It is fully compatible with most popular operating systems.
PC–600 major hardware features
CPU
The CPU is a high-performance, low-power AMD Geode GX1 CPU with a
maximum clock speed of 300 MHz. It uses the CS5530A companion chip
for some of the peripherals. The PC–600 has an ISA bus speed of 8.33
MHz, and a PCI speed of 33 MHz.
SDRAM
The memory socket can accept up to 512 MB capacity SO-DIMM modules.
On-board flash
On board is a 512 KB SMT flash that contains the BIOS.
16
Page 17

Hard disk, CompactFlash, and floppy disk ports
The IDE hard drive port is terminated with a 44-pin, 2 mm connector and
supplies power to 2.5” hard drives. CompactFlash appears as an IDE
device and has a locking type interface. The BIOS supports up to three
IDE drives. The floppy drive port is terminated with a standard 34-pin
connector and up to two floppy drives are supported.
USB ports
The CS5530A companion chip supports two USB 1.1 channels, which are
available when using an operating system that supports USB. Both
channels are open HCI compliant.
Note that USB devices are hot-swappable when a device is plugged into a
standard USB connector, as pins on the connectors determine the order in
which they make contact. Devices are not hot-swappable when connected
to a non-standard header. You can hot swap a device through the USB
connector on the two-port USB cable, or through another USB connector
wired to the 10-pin header, but you cannot hot swap at the 10-pin header
itself.
Serial ports
The PC–600 has four serial ports with combinations of RS–232C, RS–422,
and RS–485 interfaces.
Digital I/O
The 48 digital I/O lines will interface with logic devices, switch inputs,
LEDs and industry standard opto module racks. The I/O lines are 0–5V
logic compatible. They can be individually programmed as inputs or
outputs.
Speaker, keyboard, and mouse ports
The audio connector has a speaker output, which is PC compatible. The
keyboard controller accepts an AT style keyboard and has a PS/2 type
connector. The mouse port is combined with the keyboard port and is
accessed with a “Y” cable. Note that with some “Y” cables you may have to
plug the mouse into the keyboard icon, and the keyboard into the mouse
icon; if the mouse and keyboard do not function at power up, try switching
them. A keyboard connects directly to the PC–600 while a mouse requires
the “Y” cable.
17
Page 18

Video
CRTs are supported up to 1280 x 1024 x 16 bits per pixel (bpp) resolution.
Flat panel displays are supported up to 1024 x 768 x 16 bpp resolution.
PC/104 and PC/104 Plus interface
The PC/104 interface accepts an 8- or 16-bit PC/104 expansion board. The
PC/104 Plus accepts industry-standard PC/104 Plus boards. PC/104
expansion boards are available from several manufacturers. PC/104 or
PC/104-Plus expansion boards may be stacked on the PC–600 SBC to
form a fully-integrated system.
Ethernet
The PC–600 provides two 10/100BaseT Ethernet ports and supports the
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard.
Multifunctional printer port
The PC–600 incorporates the latest enhanced parallel port and includes
unidirectional, bi-directional, ECP and EPP modes.
The following represent applications in the multifunctional parallel port:
LPT1 for PC compatible printers
17 general purpose digital I/O lines
Up to a 4 x 4 matrix keypad
4–line alphanumeric display
Watchdog timer added for safety
The watchdog timer resets the system if the program stops unexpectedly.
The watchdog is enabled, disabled, and strobed by software control; it can
also be enabled or disabled in Setup. The time-out period is
programmable from 2 ms to 120 seconds, with a variability of ±50%.
Real time calendar/clock with battery–backup
The real time clock is fully AT compatible and uses the standard DOS
calls. An optional off-card battery powers the real time clock when the 5
volt supply is removed. A connector is provided for the external battery.
18
Page 19

Setup information stored in EEPROM for high reliability
Loss of Setup data is serious in industrial applications. Most PCs store
Setup information in battery-backed CMOS RAM. If the battery fails or is
replaced during routine maintenance, this information is lost. Without a
keyboard and monitor in embedded applications, time consuming reinitialization is required. The PC–600 stores the system Setup
information in nonvolatile EEPROM so that it is still available if the
battery backup fails or is not used. There are 1024 words available to the
user. Software routines to use this available memory come with the PC–
600.
Hardware reset
A hardware reset ensures complete reset of the system and all attached
peripherals. A hardware reset can be done by any of the following:
An expired watchdog timer cycle
Depressing the reset switch or pulling the reset pin to ground
Cycling power
Power supervisor reset
Temperature sensor
A serial temperature sensor is located on the card. It is accessed through
INT17 calls.
5 volt operation lowers system cost
The PC–600 operates from a single 5V ±5% supply.
5V ±5%
+12V (if connected to power connector) supplied to PC/104
connector; not required for PC–600 operation
19
Page 20

Rugged environmental operation
Operating temperature –40° to 85°C @ 233 MHz
–40° to 70°C @ 300 MHz
Nonoperating temperature –55° to 95°C
Relative humidity 5% to 95% noncondensing
Shock 40g, 3 axis
Vibration 5g, 3 axis
Size
5.75" x 8.0" x 0.80", SBX form factor
20
Page 21

PC–600 major software features
Diagnostic software verifies system integrity automatically
The PC–600 has built–in diagnostic software that can be used to verify
on–card I/O and memory functions. On power-up, a series of tests is
performed. If a problem occurs, the failed test can be identified by a
flashing LED. The test is performed automatically every time the system
is reset or powered up. Memory verification does not require software,
test equipment, monitor, keyboard, disks, or test fixtures. See the
“Troubleshooting” chapter for a complete listing of tests and failures and
their descriptions.
Phoenix BIOS
The PC–600 has a Phoenix BIOS with Octagon BIOS extensions. The
BIOS extensions support the INT17 functions.
Octagon BIOS extensions
On–board BIOS extensions allow easy access to digital I/O, watchdog
timer functions, temperature sensor, etc.
Boot sequence
A PC–600 can be configured to boot from a CompactFlash, a floppy disk, a
hard disk, or a CD–ROM.
21
Page 22

Chapter 2: Quick start
This chapter covers the basics of setting up a PC–600 system. Refer to
the PC–600 component diagram (Fig. 2–1) for the location of the various
connectors. The following topics are discussed:
Mounting the PC–600
Installing an operating system
Loading files to the PC–600 and running a program.
Hardware installation
WARNING!
The PC–600 contains static-sensitive CMOS components. To
avoid damaging your card and its components:
Ground yourself before handling the card
Disconnect power before removing or inserting a PC/104 or
PC/104 Plus expansion board.
22
Page 23
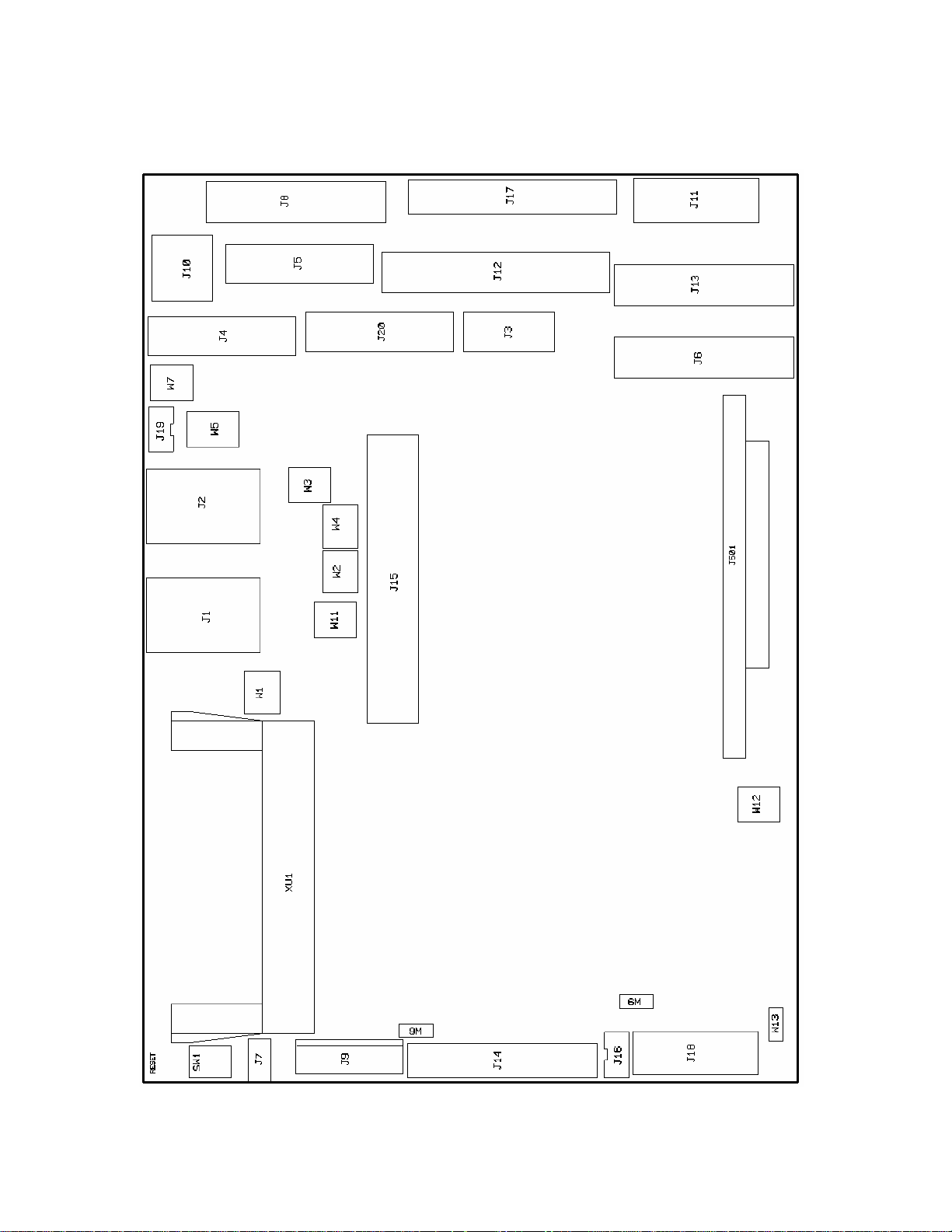
Figure 2–1 PC–600 connector and jumper diagram
23
Page 24
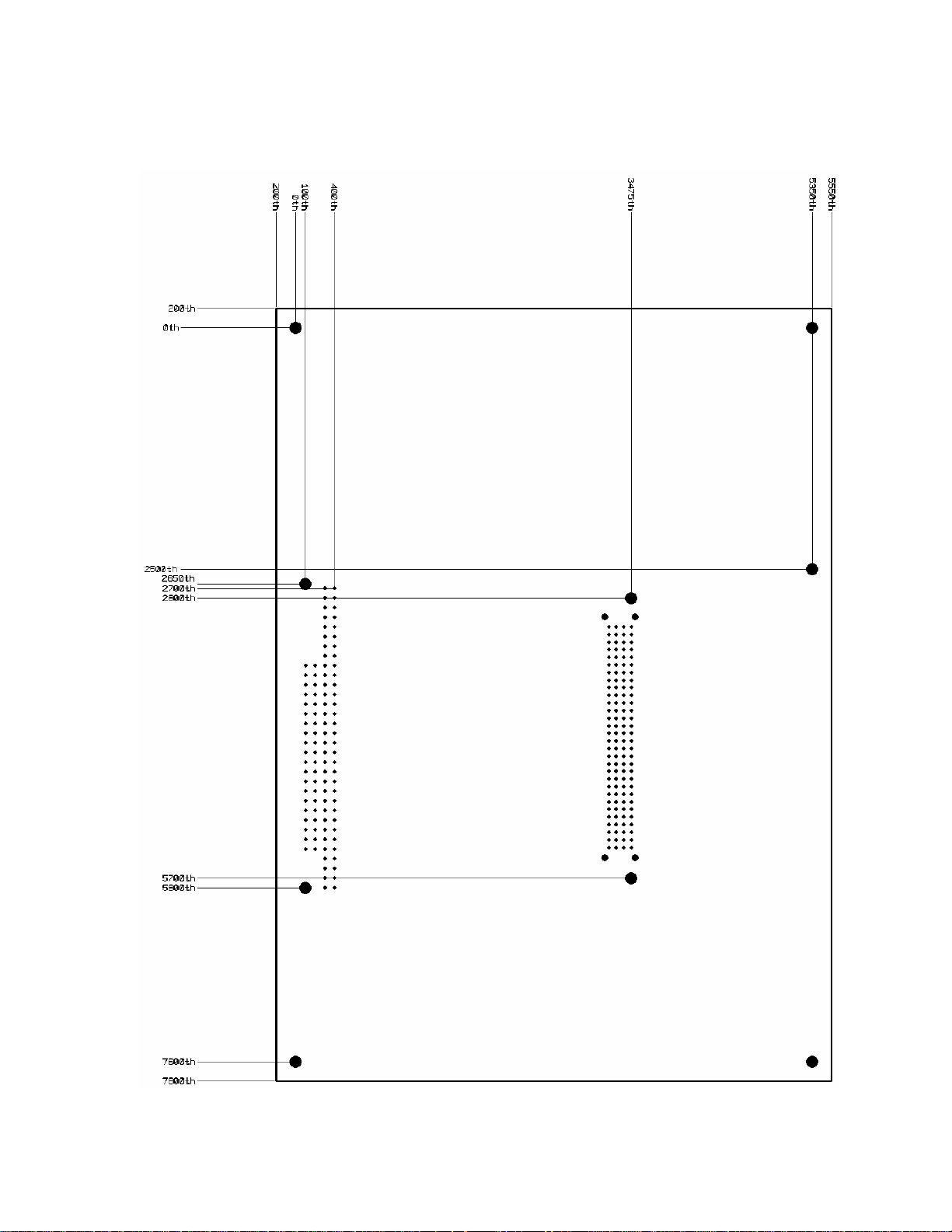
Figure 2–2 PC–600 center-to-center hole dimensions (thousandths)
24
Page 25
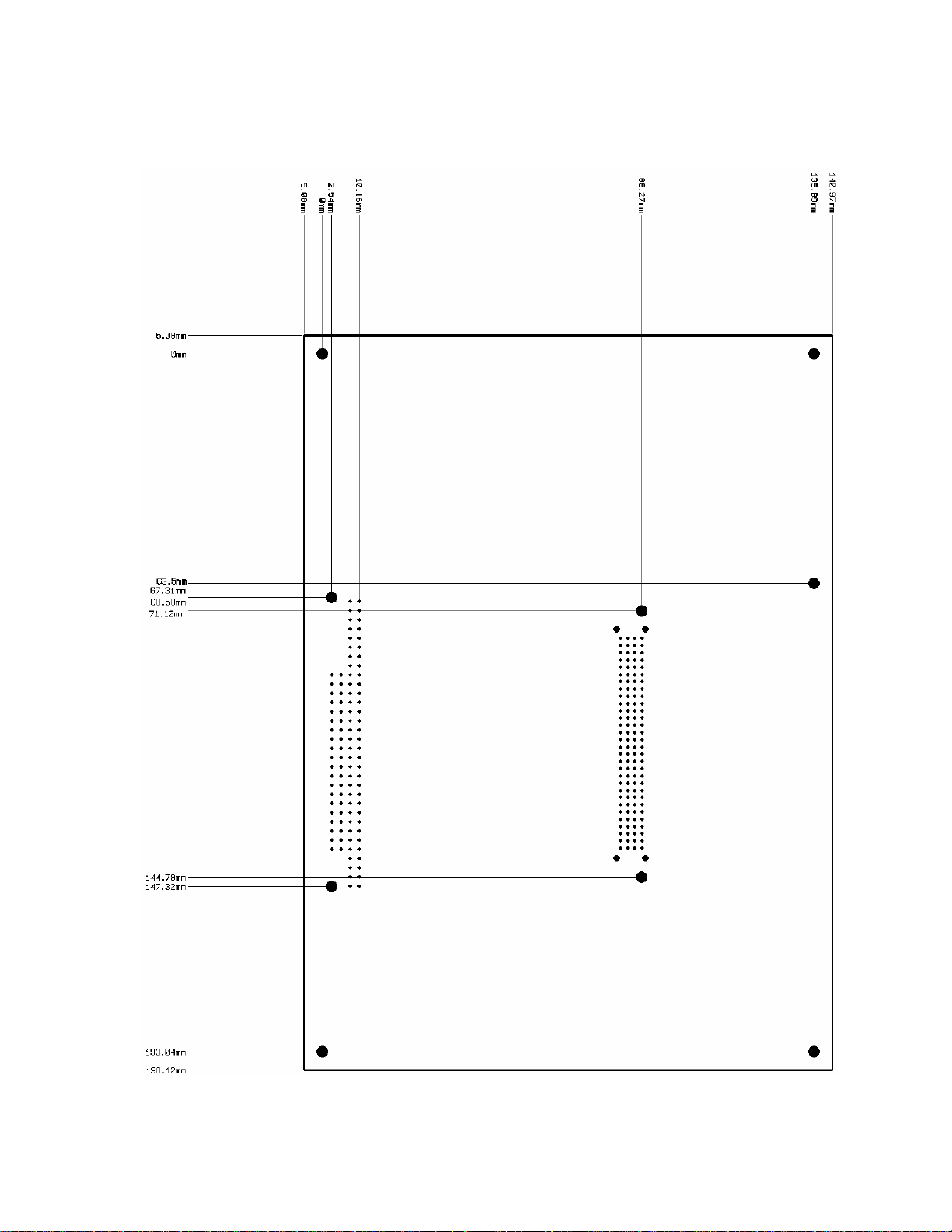
Figure 2–3 PC–600 center-to-center hole dimensions (millimeters)
25
Page 26
Table 2–1 PC–600 connector functions
Connector Function
J1 Ethernet 1
J2 Ethernet 2
J3 USB 1 and 2
J4 COM1/2
J5 COM3/4
J6 Digital I/O 1
J7 Reset
J8 LPT1
J9 Power
J10 PS/2 keyboard/mouse
J11 Future use
J12 Floppy drive
J13 Digital I/O 2
J14 Flat panel
J15 PC/104
J16 Flat panel back-light
J17 IDE (hard drive, CD ROM)
J18 CRT monitor
J19 AT Battery
J20 Audio
Table 2–2 PC–600 jumper functions
Jumper Function
W1 CPU clock speed jumper
W2 I/O pull-up/pull-down jumper
W3 COM3, COM4 jumper
W4 I/O pull-up/pull-down jumper
W5 COM3, COM4 jumper
W6 Display jumper
W7 COM3, COM4 jumper
W9 Display jumper
W11 COM3, COM4 jumper
W12 Display jumper / system jumper
W13 CompactFlash configuration
26
Page 27

Installing the PC–600
Installation
To install the PC–600 you will need the following equipment (or
equivalent):
PC–600 CPU card
VGA-12 video cable, p/n 4865
PC–600 power cable, p/n 6286
+5V power supply - see Power Supply Requirements section
PS/2 style keyboard
SVGA monitor
A device with an operating system. The device could be a
CompactFlash, floppy, hard disk, or CD ROM. The operating
system can be Windows NT, Windows CE.net, Linux, QNX, or
DOS. Note: Windows 2000 and Windows XP/XP Embedded
will run with known issues, however, new driver
development is not supported by the CPU manufacturer.
PC–600 Utilities zip file (see page 145)
Hardware components required to mount the PC–600 (not included):
9 threaded hex standoffs (4–40 x 3/8")
9 screws (4–40 x 1/4")
9 internal star lock washers (#4)
Refer to the PC–600 component diagram, figure 2–1 on page
location of various connectors, and to the mounting hole diagram, figure
2-2 on page
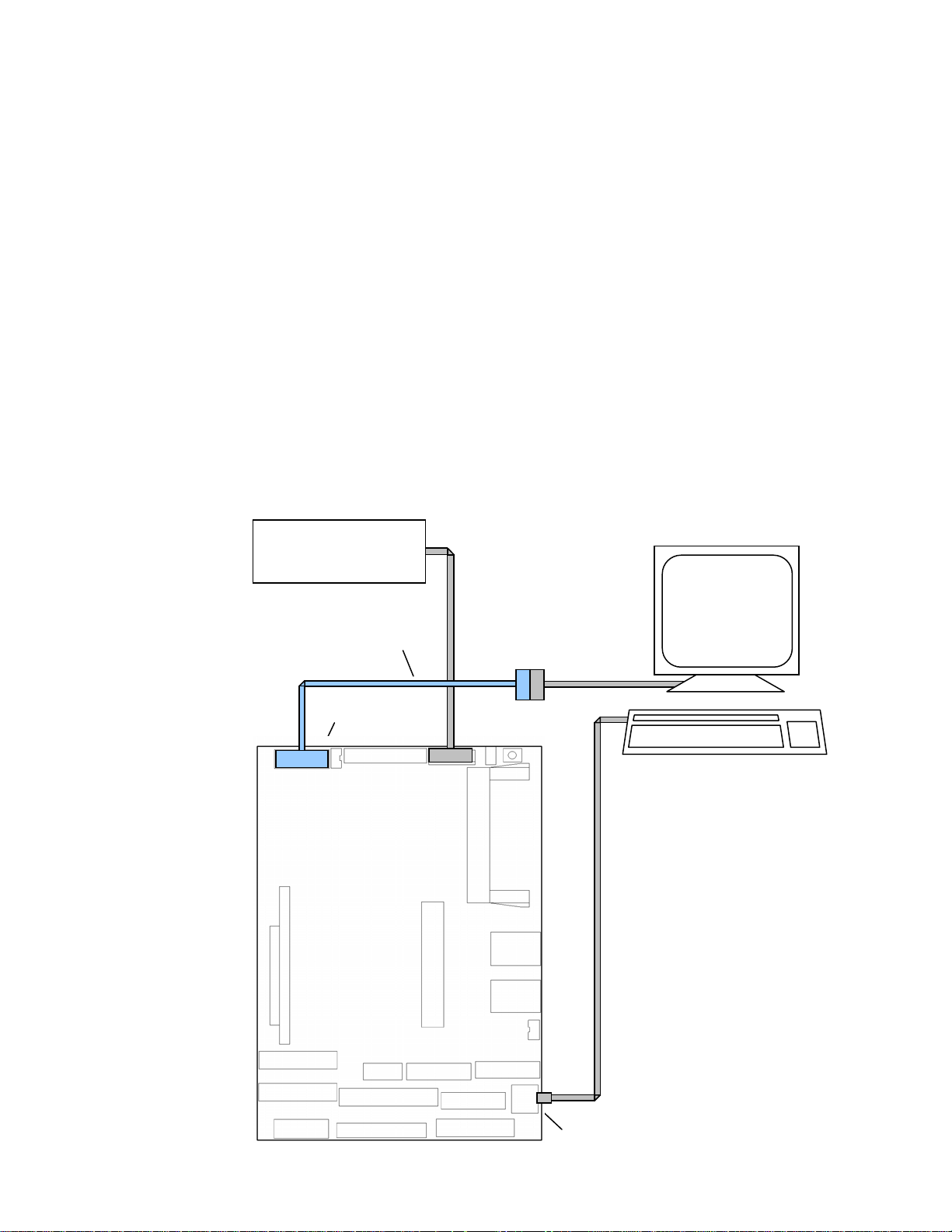
Refer to figure 2-4 for the basic hookup diagram.
24, for mounting the PC–600 system.
23, for the
27
Page 28
Hardware mounting
1. Use the standoffs, washers, and screws and place them in the 9 holes on
the PC–600 board. Refer to Figure 2–2 for the center-to-center mounting
hole dimensions and for the location of the designated holes used for
mounting the hardware.
All 9 standoffs, screws and washers must be used to secure
the PC–600. The standoffs will ensure full support not only
on all four sides, but also in the middle of the board. This will
reduce circuit board flex when a PC/104 expansion board or
other device is connected.
In high vibration and shock environments, the standoffs are
required to avoid damage to the electronic components and
circuit board traces.
Figure 2–4 Basic hookup diagram
WARNING!
Power Supply
VGA-12 video cable
CRT connector
VGA Monitor
PS/2 Keyboard
28
Keyboard connector
Page 29
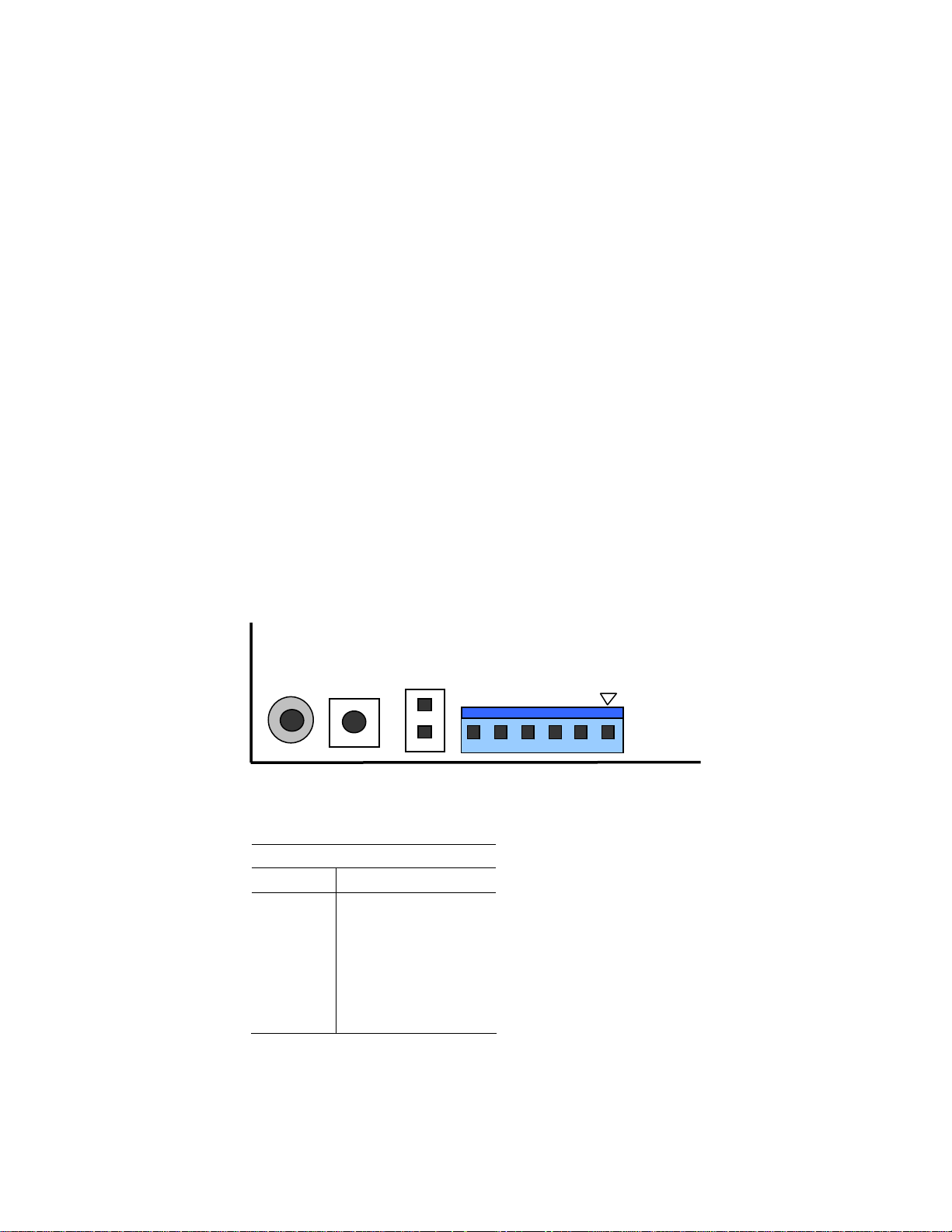
Power connection
1. Connect a 5V power source to the PC–600. Refer to the Power Supply
Requirements section on page
Plus expansion card, you may also require a +12V source.
2. The power supply connector is located at J9. Refer to Figure 2–5. Make
certain to use both +5V connections and both ground connections. This is
required for proper operation.
Make sure the power supply is OFF when connecting the
power cable to the PC–600 board. Damage to the PC–600 may
occur if the power is ON when connecting the power cable.
Accidentally crossing the wires, i.e., plugging +5V wires into
the ground connector or the ground wires into the +5V
connector will damage the PC–600 and void the warranty.
35. If you are using a PC/104 or PC/104
WARNING!
WARNING!
Figure 2–5 Power connector: J9
Table 2–3 Power connector: J9
J9 – power connector
Pin # Pin Name
1 Gnd
2 +5V
3 +12V
4 +12 V
5 +5V
6 Gnd
J9
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
29
Page 30

Monitor
The PC–600 interfaces to a standard SVGA monitor through the J18
connector using a VGA-12 cable. Connect one end of the VGA-12 cable
into J18 and connect the other end to a SVGA monitor cable.
Keyboard and mouse
The PC–600 accepts an AT style keyboard and has a PS/2 type connector,
located at J10. The mouse port shares the keyboard connector.
To use a keyboard, plug the keyboard directly into J10.
To connect a mouse, use a laptop style “Y” cable, available at computer
stores, that splits the J10 signals into keyboard and mouse connectors.
Note With some “Y” cables you may have to plug the mouse into the
keyboard icon, and the keyboard into the mouse icon; if the
mouse and keyboard do not function at power up, try switching
them.
Speaker
If required, you can interface a speaker via the 20–pin audio connector at
J20. You may use any external speaker from 8–50 ohms. Refer to Figure
2–1 for the location of J20.
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
Installing an operating system
The PC–600 does not come with an installed operating system. You can
install an operating system onto a hard drive or CompactFlash. Octagon
Systems has OS Embedder kits available for several operating systems.
These kits directly support the unique features of Octagon products, such
as digital I/O, watchdog timer, etc., eliminating the need to write special
drivers. Contact Octagon Systems for information concerning the software
development kits.
To install an operating system you will need:
VGA–12 video cable, #4865
30
PS/2 style keyboard
VGA monitor
Page 31

Floppy drive or CD-ROM drive, depending on the operating system
media to be used
Operating system media
Hard drive or CompactFlash to install the operating system onto.
OS on floppy onto a hard drive or CompactFlash
Refer to Figure 2–6 on page 34 for the following:
1. Attach the VGA–12 video cable to J18.
2. Connect the PS/2 keyboard to J10, a VGA monitor to the VGA–12 video
cable, and a floppy drive to J12.
3. If using a hard drive, configure it as a master device and install it on J17.
Note IDE devices have a jumper or a switch that designates whether the device
is a master or a slave device. If only one device is connected to a port, it
must be configured as a master. If two devices are connected, one must be
configured as a master and one as a slave. The PC–600 does not use the
CS signal (Cable Select) to designate master or slave on a multi-connector
cable. You can use BIOS Setup to designate either the master or the slave
as a boot device.
4. If using a CompactFlash, install it into the CompactFlash socket.
5. Apply power to the PC–600 system. A logon message similar to the one
below will appear on your PC monitor:
Copyright 1985-2003 Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
Octagon Systems: PC–600 V1.00
Build Time: 01/27/03 16:59:27
CPU = Cyrix MediaGXm300 MHz
638K System RAM Passed
130048K Extended RAM Passed
System BIOS shadowed
31
Page 32

6. Enter Setup by pressing the F2 key during BIOS POST sequence (this
occurs between the memory test and bootup).
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Boot Exit
System Time:
System Date:
Legacy Diskette A:
Legacy Diskette B:
> Primary Master
> Primary Slave
> Secondary Master
> Secondary Slave
>Memory Cache:
>Boot option:
System Memory:
Extended Memory:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[00:00:36]
[01/01/1988]
[1.44/1.25 MB 3 1/2"]
[Disabled]
[None]
[None]
[3253MB]
[None]
640 KB
130048 KB
Item Specific Help
<Tab>, <Shift-Tab>, or
<Enter> selects field.
Note Your display message may be slightly different
7. Change the boot sequence to floppy drive first.
8. Insert the operating system media into the floppy drive.
9. Reboot the system. The system should boot to the floppy drive.
10. Refer to the OS documentation to load the operating system.
OS on CD-ROM onto a hard drive or CompactFlash
Refer to Figure 2–6 on page 34 for the following:
1. Attach the VGA–12 video cable to J18.
2. Connect the PS/2 keyboard to J10, a VGA monitor to the VGA–12 video
cable, and a CD-ROM drive to J17. Configure the CD-ROM drive as a
master.
3. If using a hard drive, configure it as a slave device and install it on the
IDE cable connected to J17.
Note IDE devices have a jumper or a switch that designates whether the device
is a master or a slave device. If only one device is connected to a port, it
must be configured as a master. If two devices are connected, one must be
configured as a master and one as a slave. The PC–600 does not use the
CS signal (Cable Select) to designate master or slave on a multi-connector
cable. You can use BIOS Setup to designate either the master or the slave
as a boot device.
32
4. If using a CompactFlash, install it into the CompactFlash socket.
Page 33

5. Apply power to the PC–600 system. A logon message similar to the one
below will appear on your PC monitor:
Copyright 1985-2003 Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
Octagon Systems: PC–600 V1.00
Build Time: 01/27/03 16:59:27
CPU = Cyrix MediaGXm300 MHz
638K System RAM Passed
130048K Extended RAM Passed
System BIOS shadowed
6. Enter Setup by pressing the F2 key during BIOS POST sequence (this
occurs between the memory test and bootup).
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Time:
System Date:
Legacy Diskette A:
Legacy Diskette B:
> Primary Master
> Primary Slave
> Secondary Master
> Secondary Slave
>Memory Cache:
>Boot option:
System Memory:
Extended Memory:
[00:00:36]
[01/01/1988]
[1.44/1.25 MB 3 1/2"]
[Disabled]
[None]
[None]
[3253MB]
[None]
640 KB
130048 KB
Item Specific Help
<Tab>, <Shift-Tab>, or
<Enter> selects field.
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Note Your display message may be slightly different
7. Configure the CD–ROM as a master device, and change the boot sequence
to CD-ROM drive first.
8. Insert the operating system media into the CD-ROM drive.
9. Reboot the system. The system should boot to the CD-ROM.
10. Follow the on-screen dialog to load the operating system. Refer to the OS
documentation for further information.
33
Page 34

Figure 2–6 Installing an operating system
Power Supply
VGA–12 video cable
CRT connector
VGA Monitor
PS/2 Keyboard
CompactFlash installed into
CompactFlash socket
J12, Floppy drive connector
Keyboard connector
IDE ribbon cable for two devices, or one device directly into J17
CD-ROM
and / or
Hard Drive
34
Page 35

Power supply requirements
The PC–600 is designed to operate from a single +5 VDC supply,
connected at J9. The typical current requirements for the PC–600 is listed
in the Technical data appendix. If you are using the PC/104 interfaces,
you may also require +12 VDC. Make sure that you utilize both +5 VDC
conductors and both ground conductors.
You should also consider other factors such as the power cable conductor
gauge, number and length of conductors, mating connectors, and the
power supply to external devices such as hard drives, floppy drives,
displays, mouse, and keyboard.
It is important that a quality power supply be used with the PC–600 that
has sufficient current capacity, line and load regulation, hold up time,
current limiting, and minimum ripple.
The power supply for the PC–600 must meet the startup risetime
requirements specified in the ATX Power Design Guide, version 1.1,
section 3.3.5. This assures that all the circuitry on the PC–600 sequences
properly and avoids system lockup.
Also, select a power supply that discharges quickly. If large power supply
output capacitors are used, powering the system down and then up may
lock up the PC–600. If the power supply does not drain below 0.7V, the
CMOS components on the PC–600 will act like diodes and forward bias,
potentially damaging the PC–600 circuitry.
The proper selection of a quality power supply ensures reliability and
proper functioning of the PC–600.
35
Page 36

Chapter 3: Setup programs
This chapter discusses running the Setup configuration program on the
PC–600 CPU card. Setup configures devices set up by the BIOS such as
serial ports, floppy drives, etc.
Operating systems other than DOS
If you are using an operating system other than DOS the X jumper should
be removed. The X jumper maps the INT17 extended BIOS into the
0xD8000-0xDFFFF memory. This can cause problems with applications or
hardware running on other operating systems if they attempt to use this
memory range. Removing the X jumper frees this memory for use by other
operating systems.
Setup
Setup can be entered by pressing the “F2” key during the BIOS POST
sequence (this occurs between the memory test and boot).
Also, by removing the USER Setup jumper from the “S” position at
W12[1–2], you may force the setup to temporarily revert to the defaults
shown in the following menus, which allows the user to reconfigure the
setup.
Note The Setup defaults might vary slightly from those shown in the following
menus depending on the BIOS revision on your card.
The system will display the PC–600 PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility Main
menu. Select the submenu by using the up/down arrows, then press
<ENTER> (when using a monitor connected to the PC–600). For a serial
console configuration, Ctrl + E is up and Ctrl + X is down.
36
Page 37

Main menu
The Main menu allows you to set the basic system configuration.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Time:
System Date:
Legacy Diskette A:
Legacy Diskette B:
> Primary Master
> Primary Slave
> Secondary Master
> Secondary Slave
>Memory Cache:
>Boot options:
System Memory:
Extended Memory:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[00:00:36]
[01/01/1988]
[1.44/1.25 MB 3 1/2"]
[Disabled]
[None]
[None]
[3253MB]
[None]
640 KB
130048 KB
System Time: Sets the time for the system clock.
System Date: Sets the date for the system clock.
Legacy Diskette A: Enables or disables a legacy floppy disk drive. Choices are
Disabled, 360 KB 5 ¼”, 1.2 MB 5 ¼”, 720 KB 3 ½”, 1.44/1.25
MB 3 ½”, 2.88 MB 3 ½”.
Legacy Diskette B: Enables or disables a second legacy floppy disk drive. Note
that Diskette A must be enabled before Diskette B is
accessible.
> Primary Master Accesses submenu for a Primary Master disk drive. Options
are None, CD-ROM, ATAPI Removable, Other ATAPI,
User, and Auto. This channel is hardwired to Compactflash
and cannot be used for other devices.
> Primary Slave Same as Primary Master. This channel is reserved.
> Secondary Master Same as Primary Master. Note that the PC–600 only
supports three IDE devices (one Primary and two
Secondary.)
> Secondary Slave Same as Primary Master. Note that the PC–600 only
supports three IDE devices (one Primary and two
Secondary.)
>Memory Cache: Enables or Disables the memory cache.
>Boot options: Enables or Disables the following features: Quickboot
Mode, Summary Screen, Floppy Check, Hard disk PreDelay. Skipping these tests during boot will decrease the
time needed to boot the system.
System Memory: Displays the amount of system memory which is on
the card.
Extended Memory: Displays the amount of extended memory on the card.
Item Specific Help
<Tab>, <Shift-Tab>, or
<Enter> selects field.
37
Page 38

Hard drive submenus
The Hard drive submenus allow you to set the
primary/secondary/master/slave parameters. Except for older disk drives,
the Auto selection will detect and display the correct parameters.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main
Primary Master [3253MB] Item Specific Help
Type:
Multi-Sector Transfers:
LBA Mode Control:
32 Bit I/O:
Transfer Mode:
Ultra DMA Mode:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Auto]
[16 Sectors]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Fast PIO 4]
[Disabled]
User = you enter
parameters of hard-disk
drive installed at this
connection.
Auto = autotypes
hard-disk drive
installed here.
1-39 = you select
pre-determined type of
hard-disk drive
installed here.
CD-ROM = a CD- ROM drive
is installed here.
ATAPI Removable =
removable disk drive is
installed here.
Note UltraDMA modes are not supported directly by the PC–600. These modes
require an 80-pin connector, and there is no adapter available for the 44pin, 2mm IDE connector used on the PC–600.
38
Page 39

Advanced menu
The Advanced menu allows you to set advanced system configuration. Note
that if items are incorrectly set in this menu, the system might malfunction.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Item Specific Help
Setup Warning
Setting items on this menu to incorrect
values may cause your system to malfunction.
Serial Video:
Baud Rate:
POST Video Mode:
>Advanced Chipset Control
>I/O Device Configuration
>Audio Options Menu
>PCI Configuration
Secured Setup Configurations
Installed O/S:
Reset Configuration Data:
Large Disk Access Mode:
Watchdog:
PCI IRQ Routing:
[Disabled]
[38.4K]
[Text]
[No]
[Other]
[No]
[DOS]
[Disabled]
[Method 1]
Enables redirection of
video and keyboard to
serial port COM1.
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Serial Video: Enabled, Disabled. Enables redirection of video and
keyboard to COM1.
Baud Rate: 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K, 115K. Selects baud rate
for serial console.
Post Video Mode: Text, Graphical. Selects which video mode to display
during POST.
Secured Setup Configurations: Yes or No. Yes prevents the operating system from
overriding selections you have made in Setup.
Installed O/S: Other, Win95. Selects the operating system you use
most often.
Reset Configuration Data: Yes or No. Yes erases all configuration data in a section
of memory for ESCD (Extended System Configuration
Data) which stores the configuration settings for nonPnP plug in devices. Select Yes when required to restore
the manufacturer’s defaults.
Large Disk Access Mode: DOS, Other. Select DOS if you have DOS. Select
Other for another operating system such as Unix.
Watchdog: Enabled, Disabled. Enables watchdog timer.
PCI IRQ Routing: Method 1, 2.
39
Page 40

Advanced Chipset Control submenu
The Advanced Chipset Control submenu allows you to set the video and
PS/2 mouse configurations.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
Advance Chipset Control Item Specific Help
Memory speed:
Video Resolution:
PS/2 Mouse:
Multiple Monitor Support:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Low]
[High]
[Enabled]
[Motherboard
Primary]
Memory speed: Low, Medium, High. Configures DRAM performance
options. High is a 100 MHz memory clock, Medium is an
80 MHz memory clock, and Low is a 66 MHz memory
clock. Low is recommended for Industrial Temperature
Range Applications
Video Resolution: Low, Medium, High, Super.
PS/2 Mouse: Disabled, Enabled, Auto Detect. Frees up IRQ12 if
disabled.
Multiple Monitor Support: Motherboard Disabled, Motherboard Primary, Adapter
Primary.
40
Page 41

I/O Device Configuration submenu
The I/O Device Configuration submenu allows you to set the I/O configurations.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
I/O Device Configuration Item Specific Help
Serial port A:
Base I/O address:
Interrupt:
Serial port B:
Mode
Base I/O address:
Interrupt:
Serial port C:
Serial port D:
Parallel port:
Mode:
Base I/O address:
Interrupt:
DMA Channel:
Floppy disk controller:
Local Bus IDE Adapter:
Digital I/O:
Base I/O address:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Enabled]
[3F8]
[IRQ 4]
[Enabled]
[Normal]
[2F8]
[IRQ 3]
[3E8]
[2E8]
[Enabled]
[ECP]
[378]
[IRQ 7]
[DMA 3]
[Enabled]
[Both]
[Enabled]
[120h]
Serial port A: Enabled, Disabled, Auto, OS controlled
Base I/O address: 3F8*, 2F8, 3E8, 2E8
Interrupt: IRQ3, IRQ4*
Serial port B: 3F8, 2F8*, 3E8, 2E8
Mode: IrDA, Ask-IR, Midi, Normal (only Normal supported)
Interrupt: IRQ3*, IRQ4
Serial port C: Enabled, Disabled, Auto. If enabled, base addresses are listed.
Serial port D: Enabled, Disabled, Auto. If enabled, base addresses are listed.
Parallel port: Disabled, Enabled, Auto. Enabled allows user to set
configuration, while Auto uses the BIOS or OS configuration.
Mode: Output only, Bi-directional, EPP, ECP
Base I/O address: 378, 278, 3BC
Interrupt: IRQ5, IRQ7
DMA Channel: DMA1, DMA3. Do not change this setting unless you are
experienced in modifying operating system parameters.
Floppy disk controller: Disabled, Enabled.
Local Bus IDE Adapter: Disabled, Primary, Secondary, Both. Enables the
integrated local bus IDE adapter.
Digital I/O: Enabled, Disabled. Selects whether the onboard digital
I/O is enabled or not.
41
Page 42

Base I/O address: 120h, 180h, 320h, 380h. Sets base address for digital I/O.
* defaults
Audio Options submenu
The Audio Options submenu allows you to set the audio configurations.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
I/O Device Configuration Item Specific Help
Sound:
Base I/O address:
MPU I/O address:
Interrupt:
8-bit DMA channel:
16-bit DMA channel:
Joystick:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Enabled]
[220 - 22F]
[330 - 331]
[IRQ 5]
[DMA 1]
[DMA 5]
[Disabled]
Configure sound device
using options:
Sound: Enabled, Disabled, Auto.
Base I/O address: 220–22F*, 240–24F, 260–26F, 280–28F.
MPU I/O address: 300-301*, 330-331.
Interrupt: IRQ2, IRQ5, IRQ7, IRQ10.
8-bit DMA channel: DMA 0, DMA1*, DMA 3. Do not change this setting
unless you are experienced in modifying operating
system parameters.
16-bit DMA channel: DMA 5*, DMA6, DMA 7. Do not change this setting
unless you are experienced in modifying operating
system parameters.
Joystick: Enabled, Disabled (Joystick is not supported)
* default
42
Page 43

PCI Configuration submenu
The I/O Device Configuration submenu allows you to set the PCI
configurations.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
PCI Configuration Item Specific Help
>PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion
>PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion
>PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion
ISA graphics device installed:
PCI IRQ line 1:
PCI IRQ line 2:
PCI IRQ line 3:
PCI IRQ line 4:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[No]
[Auto Select]
[Auto Select]
[Auto Select]
[Auto Select]
Reserve specific
upper memory blocks
for use by legacy ISA
devices
PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion See submenu
PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion See submenu
PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion See submenu
ISA graphics device installed: Yes, No.
PCI IRQ line 1/2/3/4: Disabled, Auto Select, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12,
14, 15. Specifies IRQ for use. PCI cannot use an
interrupt that is being used by an ISA or EISA
device. Select Auto only if no ISA or EISA
devices are on the system.
43
Page 44
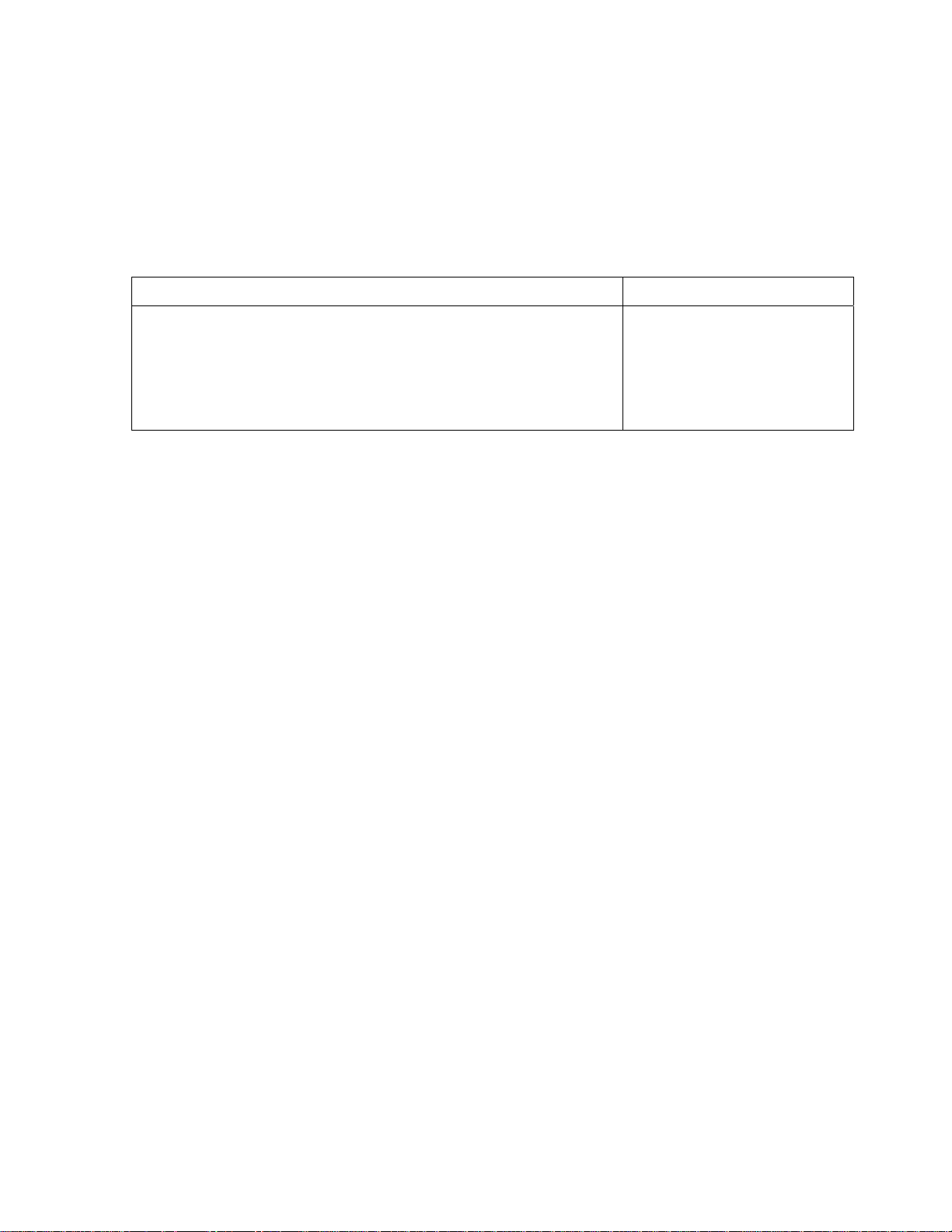
PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion submenu
The PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion submenu reserves the specified
block of upper memory for use by legacy ISA devices. Options are
Available or Reserved.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
PCI/PNP ISA UMB Region Exclusion Item Specific Help
C800 - CBFF:
CC00 - CFFF:
D000 - D3FF:
D400 - D7FF:
D800 - DBFF:
DC00 - DFFF:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Available]
[Reserved]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
Reserves the specified
block of upper memory
for use by legacy ISA
devices
Available means the operating system is free to configure or
use the region for automatic assignment during start-up
operations.
Reserved means the operating system cannot automatically
use or assign the region. The region will be assigned later
by the function or device attached.
If you experience problems with an auxiliary card, consult
the manual for the card and use this screen to reserve the
regions required by the card.
44
Page 45

PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion submenu
The PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion submenu reserves the
specified IRQ for use by legacy ISA devices. Options are Available or
Reserved.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
PCI/PNP ISA IRQ Resource Exclusion Item Specific Help
IRQ 3:
IRQ 4:
IRQ 5:
IRQ 7:
IRQ 9:
IRQ 10:
IRQ 11:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
Reserves the specified
IRQ for use by legacy
ISA devices
PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion submenu
The PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion submenu reserves the
specified DMA channels for use by legacy ISA devices. Options are
Available or Reserved.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
PCI/PNP ISA DMA Resource Exclusion Item Specific Help
DMA 0:
DMA 1:
DMA 2:
DMA 3:
DMA 5:
DMA 6:
DMA 7:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
[Available]
Reserves the specified
DMA channel for use by
non-Plug-and-Play ISA
devices.
45
Page 46

Power menu
The Power menu allows you to set the power management configuration.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Power Savings:
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
[Disabled]
When Power Savings is enabled, the following options and defaults appear:
Item Specific Help
Maximum Power Savings
conserves the greatest
amount of system power.
Maximum Performance
conserves power but
allows greatest system
performance. To alter
these settings, choose
Customized. To turn off
power management,
choose Disabled.
Power Savings: [Enabled] Disabled, Enabled. Disabled disables all power
management, Enabled allows you to set parameters
in the pop-up menu (see following).
Standby Timeout: [4 minutes] Off, 1 minute, 2 minutes, 4 minutes, 5 minutes, 10
minutes, 20 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour. Amount of
time the system needs to be in Idle mode before
entering the Standby mode.
Suspend Timeout: [4 minutes] Same as Standby Timeout. Amount of
time the system needs to be in Standby mode before
entering the Suspend mode.
Hard Disk Timeout: [Off] Same as Standby Timeout.
Video Timeout: {Off] Same as Standby Timeout.
Wakeup on Keyboard: [Yes] Yes, No.
Wakeup on Mouse: [Yes] Yes, No.
Wakeup on Modem: [Yes] Yes, No.
Wakeup on COM1: [Yes] Yes, No.
46
Page 47

Boot menu
K
<
c
<
a
<
<
d
D
<
The Boot menu allows you set the order of drives for booting.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
Boot Order Item Specific Help
+Removable Devices
+Hard Drive
CD-ROM Drive
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
eys used to view or
configure devices:
Enter> expands or
ollapses devices with
a + or -
Ctrl+Enter> expands
ll ³
Shift + 1> enables or
disables a device.
<+> and <-> moves the
device up or down.
n> May move removable
evice between Hard
isk or Removable Disk
d> Remove a device
that is not installed.
Expanded Boot screen
The expanded screen allows you set the order of drives for booting.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Advanced
Boot Order Item Specific Help
-Removable Devices
Legacy Floppy Drives
-Hard Drive
Bootable Add-in Cards
CD-ROM Drive
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Same description as
Boot menu.
47
Page 48

Exit menu
The Exit menu allows you to save or discard changes made during Setup.
Esc does not exit this menu, you must select one of the menu items and
press Enter. You can also press F9 or F10 at any time to exit Setup. When
using the serial console F9 and F10 are not available; you must press
down/up arrow to get to the proper option then press enter.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Exit Saving Changes
Exit Discarding Changes
Load Setup Defaults
Discard Changes
Save Changes
F1 Help ^v Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit <> Select Menu Enter Select > Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Item Specific Help
Exit System Setup and
save your changes to
CMOS.
48
Page 49

Chapter 4: Save and run programs
Save and run your programs on the PC–600
Once you have written, tested and debugged your application, you can
then save it to a hard drive or CompactFlash device. When you reboot the
PC–600, your program can automatically load and execute. This chapter
describes the following:
Saving an application program to hard disk or CompactFlash
Autoexecuting the program from the PC–600
Overriding autoexecution of your program.
The examples in this chapter are for ROM–DOS – the procedures will
vary for different operating systems. Some Microsoft programs make
undocumented DOS calls. With ROM–DOS, an error returns when an
undocumented DOS call is made, causing your program to operate
erratically. We recommend using Microsoft’s MSDOS when using
programs with undocumented DOS calls.
Saving programs and support files
A disk drive or CompactFlash must contain proper formatting. To format
the CompactFlash or to add your own operating system, please refer to
the Compact Flash, SDRAM, and battery backup chapter.
WARNING!
Reformatting the CompactFlash requires the use of a floppy
or a hard disk to restore system files.
Adding your application
1. To add your application to your CompactFlash use the DOS COPY
command
2. Add or remove any device drivers for your application. You may want
to do the same for the CONFIG.SYS file on the CompactFlash.
Remember to add these drivers to your drive as well.
49
Page 50

3. To autoexecute your application, add your application name to the
AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
Overriding the autoexecution of your application
You may stop the autoexecution of your application by doing one of the
following options:
Option 1
1. Press F5 or F8 on your local keyboard. For more information, see your
ROM–DOS manual.
Option 2
1. Press Ctrl–C when the system is first starting. This halts all batch files.
2. Change AUTOEXEC.BAT and/or CONFIG.SYS to not call out your
program.
Option 3
1. Install a floppy.
st
2. Change Setup option “Boot Order” to “Boot 1
: Drive A:”.
3. Change Setup to enable the floppy.
4. Boot from floppy.
5. Change AUTOEXEC.BAT on C:.
Option 4
1. Remove CompactFlash from target system.
2. Install CompactFlash in host system CompactFlash adapter.
3. Edit Config.sys and/or Autoexec.bat.
4. Reinstall CompactFlash in target system.
50
Page 51

Overview: Section 2 – Hardware
Section 2 discusses usage, functions, and system configurations of the
PC–600 major hardware features. The following chapters are included:
Chapter 5: Serial ports
Chapter 6: LPT1 parallel port, LCD and keypad
Chapter 7: Console devices
Chapter 8: CompactFlash, SDRAM, and battery backup
Chapter 9: External drives
Chapter 10: Bit-programmable digital I/O
Chapter 11: CRTs and flat panels
Chapter 12: Ethernet
Chapter 13: USB
Chapter 14: Audio
Chapter 15: PC/104 and PC/104 Plus expansion
51
Page 52

Chapter 5: Serial ports
Description
The PC–600 has four serial ports, COM1 through COM4. These serial
ports interface to a printer, terminal, or other serial device. All ports
support 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-bit word lengths, 1, 1.5, or 2 stop bits, and baud
rates up to 115.2K.
All four ports are 8-wire interfaces. COM3 and COM4 can be jumpered as
RS–232, RS–422, or RS–485 interfaces.
All serial ports have the following specifications:
16550 compatible
16-byte FIFO buffers
IEC 1000, level 3, ESD protection
— Contact discharge ±6 kV
— Air–gap discharge ±8 kV
Backdrive protection
Up to 115.2k Baud operation
The following sections describe these ports in more detail.
52
Page 53

Figure 5–1 COM ports
COM1/COM2 connector
Serial device
COM3/COM4 connector
Serial device
Serial device
Serial device
53
Page 54

Serial port configurations
COM1 and COM2 share J4, and COM3 and COM4 share J5.
COM3 and COM4 can be jumpered as either 8-wire RS–232 or 4-wire
RS–422/485 interfaces.
COM3 and COM4 share IRQ9. When IRQ9 occurs, you must access the
COM ports to determine which one caused the interrupt.
The COM ports are defined in Table 5–1. Table 5–2 shows the pin-outs
for J4 and J5. Table 5–3 shows the jumper settings for COM3 and COM4.
Table 5–1 Serial port configurations
COM
Port
COM1 3F8h IRQ4 or
COM2 2F8h IRQ3 or
COM3 3E8h IRQ9 RS–232 - 8 wire
COM4 2E8h IRQ9 RS–232 - 8 wire
* configurable in Setup.
** configurable in Setup. For serial console on COM1 this must be set
for IRQ4.
Address IRQ Interface Connector
RS–232 - 8 wire
IRQ3 **
RS–232 - 8 wire
IRQ4 *
RS–422 - 4 wire
RS–485 - 2 or 4 wire
RS–422 - 4 wire
RS–485 - 2 or 4 wire
J4
J5
54
Page 55

Table 5–2 COM1, COM2: J4
COM1 COM2
RS-232 RS-232
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 DCD 11 DCD
2 DSR 12 DSR
3 RxD 13 RxD
4 RTS 14 RTS
5 TxD 15 TxD
6 CTS 16 CTS
7 DTR 17 DTR
8 RI 18 RI
9 Gnd 19 Gnd
10 Nc 20 nc
Table 5–3 COM3, COM4: J5
COM3 COM4
RS-232 RS-232
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 DCD 11 DCD
2 DSR 12 DSR
3 RxD 13 RxD
4 RTS 14 RTS
5 TxD 15 TxD
6 CTS 16 CTS
7 DTR 17 DTR
8 RI 18 RI
9 Gnd 19 Gnd
10 Nc 20 nc
COM3 COM4
RS-422 RS-485
Pin # Signal Signal Pin # Signal Signal
1 TX+ DATA+ 11 TX+ DATA+
2 TX– DATA– 12 TX– DATA–
3 13
4 14
5 15
6 16
7 RX+ 17 RX+
8 RX– 18 RX–
9 Gnd Gnd 19 Gnd Gnd
10 nc nc 20 nc nc
J4 – COM1/COM2 connector
J5 – COM3/COM4 connector
RS-422 RS-485
55
Page 56

Table 5–4 COM3 and COM4 jumpers: W3, W5, W7, and W11
W3, W5, W7, and W11 – COM3, COM4 jumpers
COM Port Interface Jumper Settings
RS–232* W11[1–2]*
W5[4–6]* , W5[10–12]*
W7[1–2]* , W7[4–6]*, W7[5–7]*
RS–422
no termination
RS–422
COM3
COM4
* Default
** This jumper terminates the network. If the PC–600 is not at an end of the
network, leave these jumpers off .
with termination
RS–485
no termination
RS–485
with termination
RS–232 W11[7–8]*
RS–422
no termination
RS–422
with termination
RS–485
no termination
RS–485
with termination
W11[1–3]
W7[1–2]* , W7[4–6]*, W7[5–7]*
W11[1–3]
W7[1–2]* , W7[4–6]*, W7[5–7]*
W5[2–4]** , W5[8–10]**
W11[2–4]
W7[1–3], W7[7–9]
W11[2–4]
W7[1–3], W7[7–9]
W7[8–10]**
W5[3–5]* , W5[9–11]*
W3[1–2]* , W3[4–6]*, W3[5–7]*
W11[7–9]
W3[1–2]* , W3[4–6]*, W3[5–7]*
W11[7–9]
W3[1–2]* , W3[4–6]*, W3[5–7]*
W5[1–3]** , W5[7–9]**
W11[8–10]
W3[1–3], W3[7–9]
W11[8–10]
W3[1–3], W3[7–9]
W3[8–10]**
56
Function and use of serial ports
COM1 as serial console device
You can use COM1 as a console device to communicate with another PC.
For COM1 to be a serial console, the video jumper W12[5–6] must be
removed. See the Console devices chapter for more information.
Mating receptacle
Use a VTC–20F or VTC–20M cable to connect the COM ports to external
serial equipment. The P2 and P3 connectors are DB–9 female (VTC–20F)
Page 57

or DB–9 male (VTC–20M) connectors which plug directly into a 9–pin PC
serial cable.
Note When interfacing the PC–600 to your desktop PC, you must use a null
modem adapter.
Figure 5–2 VTC–20F and VTC–20M cables
P1
VTC-20F and VTC-20F Cables
P2
P3
COM Ports as RS–232 I/O
COM1, COM2, COM3 and COM4 are 8-wire RS–232 interfaces. You can
connect four serial devices. Note that COM3 and COM4 share IRQ9. You
must access the COM ports to determine which generated the interrupt.
In the default configuration, the Video jumper W12[5–6] is installed. This
jumper automatically disables the Serial Video option in the Advance
menu in Setup, and both COM ports are available for serial I/O devices.
In some instances, such as running a program on the PC–600 that will
ultimately be used on another card without on-board video, you might
want to remove the Video jumper and still use COM1 as a COM port
instead of a serial console. In this instance, you must go into Setup and
set Serial Video in the Advanced menu to Disabled.
COM3 and COM4 as RS–422 and RS–485 networks
COM3 and COM4 can be used as RS–422 or RS–485. RS–422 and RS–
485 use differential signaling to communicate between the devices on a
network. Differential signal reduces the effect of environmental noise,
allowing communication over distances up to 1200 meters.
RS–422 is a point-to-point configuration, RS–485 is a multi-node
configuration that allows up to 32 nodes on a network. COM3 and COM4
can be configured as either RS–232, RS–422, or RS–485. Refer to Tables
5–1 and 5–3.
57
Page 58

RS–422
–
Ω
RS–422 is typically point to point configuration. RS–422 is also specified
for multi-drop (party-line) applications where only one driver is connected
to, and transmits on, a “bus” of up to 10 receivers. The device at the end
of an RS–422 network must be terminated. The PC–600 optionally
terminates with a 100 ohm resistor. Refer to Table 5–3. Figure 5–3
shows a typical RS–422 four wire interface circuit.
Figure 5–3 Typical RS–422 four-wire interface circuit
TX +
TX –
RX +
100 Ω
RX –
Receiver Transmitter
RX + TX +
Receiver
100 Ω
RX
100 Ω
Gnd
Transmitter
TX –
100
RS–485
An application may implement a node as either the “host” node or as a
“remote” node in an RS–485 network. There can be as many as 32 nodes
without any bus repeaters in the network. A host is referred to as the
node that initiates communication; while a remote is referred to as a node
that is addressed by the host.
In any given communication sequence in an RS–485 network, there can
only be one host. The host is responsible for initiating communication,
maintaining network registration, and providing housekeeping tasks with
other nodes. Remotes, however, cannot initiate a communication. They
can only respond to messages that are addressed to them from the host.
The devices at each end of an RS–485 network must be terminated. Any
node located between the end points should not be terminated. The PC–
600 optionally terminates with a 100 ohm resistor. Refer to Table 5–3.
Figures 5–4 and 5–5 show typical RS–485 networks.
58
Page 59

Figure 5–4 Typical RS–485 half duplex interface circuit
–
DE
DI
RE
RO
TX +
Transmitter
TX –
Receiver
RX +
RX –
Receiver Receiver
Transmitter
Transmitter
DE
DI
RE
RO
DE
DI
Figure 5–5 Typical RS–485 full duplex interface circuit
DE
DI
RE
RO
TX +
Transmitter
TX –
Receiver
100 Ω
RX +
RX –
100 Ω 100 Ω
RO
2E
100 Ω 100 Ω
100 Ω
RX +
RX –
RX +
RX –
TX +
Transmitter
Receiver
Receiver
TX +
Transmitter
TX
DE
DI
120
RE
RO
RE
RO
DE
DI
DE
Transmitter
DI
Receiver
RE
RO
DE
Transmitter
DI
Receiver
RE
RO
59
Page 60

Chapter 6: LPT1 parallel port, LCD and
keypad
LPT1 parallel port
LPT1 uses a 26-pin connector. It supports the unidirectional standard
mode, bi-directional mode, enhanced parallel port (EPP) mode, and
extended capabilities port (ECP) mode. The default I/O address for LPT1
is 378h, with the default interrupt is IRQ7. You can choose the addresses
278h to 27Bh, or interrupt IRQ5, in Setup.
The LPT1 port supports a number of devices including a PC compatible
printer, an LCD display, or a keypad.
Table 6–1 LPT1 connector: J8
J8 – LPT1 connector
Pin # Pin Name Pin Name Pin #
1 STB* AFD* 2
3 PD[0] ERR* 4
5 PD[1] INIT* 6
7 PD[2] SLIN* 8
9 PD[3] Gnd 10
11 PD[4] Gnd 12
13 PD[5] Gnd 14
15 PD[6] Gnd 16
17 PD[7] Gnd 18
19 ACK* Gnd 20
21 BUSY Gnd 22
23 PE Gnd 24
25 SLCT VCC5S 26
* = active low
Installing a printer
60
1. Make sure that the LPT1 port is in standard or bi-directional mode.
2. Connect an Octagon VTC–5/IBM cable from the LPT1 port (J8) to the 25pin connector on your printer cable.
3. Connect the cable to your printer.
Page 61

Figure 6–1 LPT1 as a printer port
LPT1 connector
Display
The LPT1 port supports either a 4 x 20 or a 4 x 40 liquid crystal display
(LCD). To interface the displays to the PC–600, use the Octagon 2010
interface board. A CMA–26 cable is required to connect the interface
board to the PC–600. The program DISPLAY.EXE in the Utilities zip file
(see page
file DISPLAY.TXT for information on initializing and using the display.
Also, refer to the 2010 product sheet for more information on the interface
board.
Installing a display
145) provides an easy method to use the display. Refer to the
1. Connect a CMA–26 cable from the LPT1 port on the PC–600 (J8) to J3 on
the 2010. See Figure 6–2.
2. Connect the display cable to either the 14-pin or 16-pin header on the
2010. The size of the display will determine which header to use.
3. Refer to the file DISPLAY.TXT for more information on initializing and
using the display.
61
Page 62

Figure 6–2 LPT1 as a display or keypad port
LPT1 connector
2010 Interface
LCD display
4x4 Keypad
Keypad
LPT1 also supports 4 x 4 matrix keypads. To interface the keypad to the
PC–600, use the Octagon 2010 interface board. A CMA–26 cable is
required to connect the interface board to the PC–600. The program
DISPLAY.EXE in the Utilities zip file provides an easy method to use the
keypad. Refer to the file DISPLAY.TXT for information on initializing
and using the keypad. Also, refer to the 2010 product sheet for
information on the interface board.
62
Page 63

Installing a keypad
1. Connect a CMA–26 cable from the LPT1 port on the PC–600 (J8) to J1 on
the 2010. See Figure 6–2.
2. Connect the keypad cable to the 10-pin header on the 2010.
3. Refer to the DISPLAY.TXT file for more information on reading the
keypad.
63
Page 64

Chapter 7: Console devices
Description
The PC–600 has three options for console devices. You can use a monitor
and a keyboard as your console. You can use COM1 as the console, or you
can run the system without a console device.
Selecting console devices
The following represent the options on the PC–600 for console devices:
A standard VGA/SVGA monitor and a keyboard.
Serial console from COM1. A serial cable/null modem adapter plugged
into a host PC running HyperTerminal (or equivalent) provides both
input and output. The local keyboard also allows input but is not
required.
No console device means no video output, either from a monitor or the
serial console. A local keyboard allows input but is not required.
Monitor and keyboard console
To use a monitor and keyboard as the console, you will need the following
equipment (or equivalent):
PC–600 CPU card
PS/2 style keyboard
VGA/SVGA monitor
VGA–12 video cable, #4865
1. Refer to Figure 2–1 on page
jumpers before installing the PC–600.
2. Make sure that jumper the “V” video jumper, W12[5-6], is installed.
3. Connect the VGA–12 video cable into J18 and connect a VGA monitor to
the VGA–12 cable.
4. Connect a PS/2 style keyboard into J10.
23 for the location of various connectors and
64
Page 65

Figure 7–1 Monitor and keyboard console
VGA–12 video cable
VGA Monitor
CRT connector
PS/2 Keyboard
Keyboard connector
Serial console
COM1 is used as the console device if the serial console is enabled in
Setup.
To use COM1 as the console, you will need the following equipment (or
equivalent):
PC–600 CPU card
VTC–20F cable, #4866
Null modem adapter, #2470 (9-pin to 9-pin)
65
Page 66

Host computer running HyperTerminal (or equivalent)
Serial cable to connect PC–600 COM1 to host computer serial port
PS/2 style keyboard (optional)
1. Refer to Figure 2–1 on page
23 for the location of various connectors and
jumpers before installing the PC–600.
For the following, refer to Figures 7–2 and 7–3.
2. Connect a VTC–20F cable to J4 of the PC–600.
3. Connect P2 of the VTC–20F cable (COM1) to the 9-pin null modem adapter.
4. Connect the serial cable between the null modem adapter and the serial port
(COM1–COM4) of the host computer.
5. Remove the Video jumper, W12[5–6].
Follow these steps to use the serial console:
6. Start HyperTerminal or an equivalent terminal emulator.
7. For communication on the host computer, the following settings for the
terminal emulator must be used:
66
Connect using:
Direct to COM1, COM2, COM3, or COM4
(select the port the serial cable is connected to)
Baud rate:
38400
Communications
no parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
parameters:
Flow control:
none
Terminal support:
ANSI
ANSI terminal
Yes (uncheck box)
option– Wrap lines
that exceed
terminal width:
You are now ready to establish communications between the host PC and the
PC–600.
8. Power on the PC–600. Console data will be redirected to COM1 and will be
Page 67

displayed on the host computer.
9. If you do not get the proper logon message check the HyperTerminal serial
parameters of the host PC to make sure they match the settings in step 7.
Figure 7–2 PC–600 and a serial console
COM1/COM2 connector
VTC–20F cable
Serial cable
Figure 7–3 VTC–20F cable and null modem adapter
P2
Null modem adapter
HyperTerminal
or other
terminal emulator
COM
port
Desktop PC
P1
P3
RS–232 Null Modem Configuration
67
Page 68

Chapter 8: CompactFlash, SDRAM, and
battery backup
Description
The PC–600 is shipped with a 512 KB SMT flash which is soldered
directly onto the PCB board. This flash contains the BIOS.
CompactFlash
The CompactFlash appears to the system as an IDE device. It is
automatically detected and configured as a hard drive during bootup. To
configure the PC–600 to boot from a CompactFlash, refer to the following
section Creating a Bootable CompactFlash.
The CompactFlash socket is connected to the primary IDE channel. This
channel is configured for a Master device only. Therefore, if a
CompactFlash device is installed, it will show up as a master on the
primary IDE channel. Any additional IDE devices will show up as
secondary IDE devices.
The CompactFlash can be configured for 3V or 5V operation using jumper
W13. Table 8–1 shows the jumper settings.
Note Octagon Systems only recommends Industrial Grade CompactFlash
(NAND technology) that implements ECC error code correction, and wear
level technology.
Table 8–1 CompactFlash configuration jumper: W13
W13 – CompactFlash configuration jumper
Configuration Jumper
5V W13[2–4] *
3V W13[1–3]
* = default
68
Page 69

Creating a bootable CompactFlash
A CompactFlash as shipped from the factory may or may not be
formatted; even if formatted, it may or may not be bootable. The following
sequence shows how to create a bootable CompactFlash, and how to
configure the PC–600 to boot from the CompactFlash.
CAUTION
You must use an external drive such as a hard drive, floppy,
or CD to sys the CompactFlash. The following instructions
are shown for DOS.
1. Create a bootable external device.
Note Octagon offers OS Embedders that include a CD boot disk for a variety of
operating systems. Contact your Octagon representative for additional
information.
2. Change the boot sequence in Setup so the PC–600 boots from the external
drive first. Reboot from the external device.
3. Use FDISK to create partitions on the CompactFlash. Refer to your
operating system manual for the appropriate parameters for using
FDISK. You might also have to refresh the MBR (Master Boot Record).
4. Reboot, using the external device.
5. Format the CompactFlash.
6. Copy your operating system from the external device to the
CompactFlash.
7. Change the boot sequence in Setup so that the CompactFlash (hard drive)
is first. Remove the external device and power off the PC–600.
8. Reboot.
SDRAM
The memory socket can accept up to 512 MB capacity SO-DIMM modules
using PC100 or PC133 memory sticks. Note that if the memory Speed in
BIOS is set to High, you must use PC133 memory sticks.
69
Page 70

Battery backup for real time calendar clock
An AT battery can be installed to back up the CMOS real time clock.
Installing an AT battery
1. Power off the PC–600.
2. Install the 3.6V AT clock battery at the J19 connector. Refer to the
component diagram on page
Table 8–2 Battery connector: J19
J19 – battery connector
Pin # Pin Name
1 Battery+
2 Key
3 Gnd
4 Battery–
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
23 for the location of J19.
70
Page 71

Chapter 9: External drives
Description
The PC–600 is compatible with any standard IDE hard drive that has a
16-bit IDE interface. The BIOS extension ROM for the hard drive is
supplied on the card so that no additional software is needed. The floppy
drives use DMA channel 2.
UltraDMA modes are not supported directly by the PC–600. These modes
require an 80-pin connector, and there is no adapter available for the 44pin, 2mm IDE connector used on the PC–600.
Floppy disk controller
The PC–600 can interface directly to one or two 3.5 in. or 5.25 in. floppy
drives via the connector at J12.
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information. If you wish to add a
second floppy drive to your system, you must use a floppy drive cable
which has two connectors and swaps the select lines.
Power requirements
The PC–600 requires +5V for operation. You must also supply power to
the floppy drive(s) through an external source. Refer to your floppy drive
manual for specific instructions.
Installing a floppy disk drive
1. Disconnect power to the PC–600.
2. Insert one end of your cable into the rear of the floppy drive. Make sure
pin 1 on the cable is connected to pin 1 on the drive.
3. Insert the other end of the cable into J12 on the PC–600.
4. Connect power to the floppy drive.
5. Enter Setup to set up the BIOS. You can execute this program by
pressing “F2” during system bootup. The system steps you through the
configuration. Also, refer to the Setup programs chapter for more
information on the BIOS Setup program.
71
Page 72

Hard disk controller
The PC–600 supports three 16-bit IDE devices. Since the CompactFlash is
connected to the primary IDE channel with a dedicated IDE controller,
additional IDE devices connected through J17 will show up in Setup as
secondary IDE devices (master and slave).
Standard IDE devices such as hard drives and CD-ROM drives are
interfaced via a 44-pin connectors at J17. For those IDE devices that use
a 40-pin interface, use the Octagon Systems IDE cable, #4080 or #6246.
UltraDMA modes are not supported directly by the PC–600. These modes
require an 80-pin connector, and there is no adapter available for the 44pin, 2mm IDE connector used on the PC–600.
IDE combinations:
2 hard drives
1 hard drive and 1 CD-ROM drive
CompactFlash and either of the above combinations
Master/slave designation for IDE devices
IDE devices have a jumper or a switch that designates whether the device
is a master or a slave device. If only one device is connected to a port, it
must be configured as a master. If two devices are connected, one must be
configured as a master and one as a slave. The PC–600 does not use the
CS signal (Cable Select) to designate master or slave on a multi-connector
cable. You can use BIOS Setup to designate either the master or the slave
as a boot device.
Installing a hard drive
1. Disconnect power to the PC–600.
2. Insert one end of the Octagon hard drive adapter cable into the rear of the
hard drive. Make sure pin 1 on the cable is connected to pin 1 on the
drive.
3. Insert the other end of the IDE cable into J17 on the PC–600. Make sure
pin 1 on the cable is connected to pin 1 on the PC–600.
4. Execute the BIOS Setup program to configure your system for a hard
drive. You can execute this program by pressing “F2” during system
bootup. The system steps you through the configuration. Also, refer to the
72
Page 73

Setup programs chapter for more information on the BIOS Setup
program.
5. If you want to boot the system from the hard drive, you need to format the
drive accordingly.
73
Page 74

Chapter 10: Bit-programmable digital I/O
Description
The bit-programmable digital I/O lines can be used to sense switch
closures, turn on lamps and LEDs, and interface with other devices that
have TTL input or output such as printers and scales. The digital I/O
lines drive the Octagon MPB series opto-isolation module racks directly,
controlling AC and DC loads to 240V at 3A. Figure 10–1 shows typical
I/O configurations. The digital I/O ports have the following specifications:
Each I/O chip has 24 I/O lines, grouped into 3 ports of 8 bits
Each bit is programmable as either 5V input or 5V output
Read back state of each pin
Easy-to-program
Each line can sink and source 15 mA
Table 10–1 Digital I/O connectors: J6 and J13 (arranged by function)
J6 – Digital I/O 1, J13 – Digital I/O 2
Pin # Port A Pin # Port B Pin # Port C
19 Bit 0 10 Bit 0 13 Bit 0
21 Bit 1 8 Bit 1 16 Bit 1
23 Bit 2 4 Bit 2 15 Bit 2
25 Bit 3 6 Bit 3 17 Bit 3
24 Bit 4 1 Bit 4 14 Bit 4
22 Bit 5 3 Bit 5 11 Bit 5
20 Bit 6 5 Bit 6 12 Bit 6
18 Bit 7 7 Bit 7 9 Bit 7
2 +5V safe
26 Gnd
* +5V safe is fused through a 750 mA automatic, resetting
fuse
74
Page 75

Table 10–2 Digital I/O connectors: J6 and J13 (arranged by pins)
J6 – Digital I/O 1, J13 – Digital I/O 2 connectors
Pin # Pin Name Pin Name Pin #
1 Port B, bit 4 Vcc (+5V safe)* 2
3 Port B, bit 5 Port B, bit 2 4
5 Port B, bit 6 Port B, bit 3 6
7 Port B, bit 7 Port B, bit 1 8
9 Port C, bit 7 Port B, bit 0 10
11 Port C, bit 5 Port C, bit 6 12
13 Port C, bit 0 Port C, bit 4 14
15 Port C, bit 2 Port C, bit 1 16
17 Port C, bit 3 Port A, bit 7 18
19 Port A, bit 0 Port A, bit 6 20
21 Port A, bit 1 Port A, bit 5 22
23 Port A, bit 2 Port A, bit 4 24
25 Port A, bit 3 Gnd 26
* +5V safe is fused through a 750 mA automatic, resetting fuse
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
Interfacing to switches and other devices
The STB–26 terminal board provides a convenient way of interfacing
switches or other digital I/O devices to the digital I/O port. I/O lines at
the digital I/O connector can be connected to an STB–26 with a CMA–26
cable. Parallel I/O devices are then connected to the screw terminals on
the STB–26. The illustration on page
board connected to the digital I/O. Refer to the STB–26 product sheet for
more information.
Opto-module rack interface
You can interface digital I/O lines to an 8-, 16-, or 24-position opto-module
rack. One end of the CMA-26 cable plugs into the I/O connector and the
other plugs into an MPB–8, MPB–16, or an MPB–24 opto rack. Refer to
the MPB opto racks data sheet for more information.
You can also use a CMA–26 cable to connect the I/O port to an STB–26
terminal board and then to the opto rack. The STB–26 has two 26-pin
connectors, one of which would connect to the I/O port, the other would
connect to the opto rack. Refer to the illustration on page
configuration, run a separate power line to +5V and ground on the optorack.
77 shows an STB–26 terminal
77. For either
Use the following table to determine the corresponding opto-channel
75
Page 76

position for ports A, B, and C for digital I/O.
Table 10–3 Digital I/O opto-rack interface
Digital I/O opto-rack interface
MPB opto rack I/O port Connector pin
Opto-module position Port C
0 Bit 0 13
1 Bit 1 16
2 Bit 2 15
3 MPB-08
4 MPB-16
5 MPB-24
Bit 3 17
Bit 4 14
Bit 5 11
6 Bit 6 12
7 Bit 7 9
Port A
8 Bit 0 19
9 Bit 1 21
10 Bit 2 23
11 MPB-16
12 MPB-24
Bit 3 25
Bit 4 24
13 Bit 5 22
14 Bit 6 20
15 Bit 7 18
Port B
16 Bit 0 10
17 Bit 1 8
18 Bit 2 4
19 MPB-24
Bit 3 6
20 Bit 4 1
21 Bit 5 3
22 Bit 6 5
23 Bit 7 7
76
Page 77

Figure 10–1 Typical digital I/O configurations
CMA-26 cable
MPB Opto Rack
J 2
J 2
MPB Opto Rack
CMA-26 cable
MPB Opto Rack
J 2
STB-26
CMA-26 cable
J 2
MPB Opto Rack
STB-26
77
Page 78

Organization of banks
Each I/O digital bank has a total of 24 I/O lines connected to a 26-pin
header. The lines are configured into three groups: ports A, B and C, each
group consisting of 8 bits. Any of the lines at ports A, B or C can be
configured individually as inputs or outputs.
Figure 10–2 Organization of banks
or Base A 8
or Base + 1 B 8
or Base + 2 C 8
Base + 3
Control
Register
Digital I/O chip
26-pin I/O connector
Port addressing
Ports A, B, C and the control register are addressable.
78
Page 79

Table 10–4 Digital I/O port addressing
I/O 1 base address I/O port Port I/O address
120h* A Base address
180h** B Base address + 1
320h** C Base address + 2
380h** Control Register Base address + 3
I/O 2 base address I/O port Port I/O address
124h* A Base address
184h** B Base address + 1
324h** C Base address + 2
384h** Control Register Base address + 3
* = default
** = selected in Setup
Base I/O address
The default base I/O address for digital I/O1 is 120h and is 124h for
digital I/O2.
Digital I/O1 always uses [base through base +3], and digital I/O2 uses
[base + 4 through base + 7]. Ports A, B, C and the control register are
addressable, with reference to the base address. These addresses can be
changed through Setup to one of four addresses.
Pulling the I/O lines high or low
Jumper blocks W2 and W4 pull the I/O lines at ports A, B, and C high or
low. This allows a known state upon power-up. The default configuration
pulls all of the I/O lines high. Note that 10K ohm resistor networks are
used to configure the I/O lines as high or low.
Table 10–5 Digital I/O pull-up/pull-down jumpers: W2 and W4
W2, W4 –I/O pull-up/pull-down jumpers
I/O Lines Pull UP (+5V) Pull DOWN Gnd)
I/O
Bank 1
I/O
Bank 2
0-7 W2[2–4]* W2[4–6]
8-15 W2[1–3]* W2[3–5]
16-23 W2[9–10]* W2[7–9]
0-7 W4[2–4]* W4[4–6]
8-15 W4[1–3]* W4[3–5]
16-23 W4[9–10]* W4[7–9]
79
Page 80

Configuring and programming the digital I/O
ports
The digital I/O chip has three ports with eight parallel I/O lines (bits) per
port. This chip can use one of four base I/O addresses. All lines can be
individually programmed as all inputs, all outputs or individually as
inputs or outputs. You can alter which bits are inputs or outputs by
writing a control command to the control register of the digital I/O. When
a line is configured as an output, it can sink a maximum of 15 mA at 0.4V
or can source 15 mA at 2.4V. On power-up and software or hardware
reset, all digital I/O lines at J6 and J13 are reset as inputs.
Programming the I/O
Follow these steps to program the I/O chip:
1. Configure the I/O port bit directions, either as inputs or outputs.
2. Write to port A, B, or C with the desired level or read the bit level from
the desired port.
Configuring the I/O
Follow these steps to configure the I/O chip.
Note In the following examples, “base” for I/O1 always refers to the starting
address selected in Setup (120h default). For I/O2, “base” is four greater
than I/O1.
1. Write a "2" to the control register (base address + 3). This places the I/O
chip in “direction” mode:
(default base address = 120h)
OUT 123h, 2 (control register, direction mode)
2. Set the direction of each bit. A "0" written to the corresponding line
indicates an input and a "1" bit indicates an output. Each bit corresponds
to the equivalent I/O line.
80
Page 81

Table 10–6 Digital I/O port byte
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Port I/O Line
X 7
X 6
X 5
X 4
X 3
X 2
X 1
X 0
For example, writing 00011100 to port C (base address + 2) will configure
port C I/O lines 0, 1, 5, 6, and 7 to be inputs and lines 2, 3, and 4 to be
outputs:
OUT 122h, 1Ch (00011100 binary = 1C hexadecimal)
3. Write a "1" to the control register (base register + 3). This places the I/O
chip into “preset” mode:
OUT 123h, 1 (control register, preset mode)
4. Write a bit pattern to appear at the outputs of the desired I/O port when
the I/O chip is put in “operation” mode; all input bits are unaffected.
5. Write a "3" to the control register (base register + 3). This places the I/O
chip back into “operation” mode:
OUT 123h, 3 (control register, operation mode)
Writing and reading from I/O
Writing to or reading from the desired I/O port is accomplished with
single program statements:
1. To write a bit pattern to the desired I/O port:
OUT 122h, FFh
All output bits of port C go high; all input bits are unaffected.
2. To read a bit pattern from the desired I/O port:
PORTC = INP(122h)
The byte read from port C is assigned to variable PORTC.
81
Page 82

Digital I/O output program examples
To configure ports A, B, and C as all outputs, issue the commands:
OUT 123h, 2 ‘Direction’ Mode
OUT 120h, FFh ‘PortA’
OUT 121h, FFh ‘PortB’
OUT 122h, FFh ‘PortC’
OUT 123h, 3 ‘Operation’ Mode
Ports A, B, and C will now output all "1"s after issuing the following
commands:
OUT 120h, FFh (portA)
OUT 121h, FFh (portB)
OUT 122h, FFh (portC)
or all "0"s after:
OUT 120h, 0 (portA)
OUT 121h, 0 (portB)
OUT 122h, 0 (portC)
Digital I/O input program examples
To configure ports A and C as inputs and port B as outputs, issue the
following commands:
OUT 123h, 2 'Direction Mode'
OUT 120h, 0 'Port A data'
OUT 121h, FF 'Port B data'
OUT 122h, 0 'Port C data'
OUT 123h, 3 'Operation Mode'
To read ports A and C, issue the following commands:
PORTA = INP(120h) (Port A)
PORTC = INP(122h) (Port C)
82
Page 83

Enhanced INT 17h function definitions
This section provides definitions for the following functions: Initialize
I/O, Write I/O, and Read I/O.
Initialize I/O
Function: efh
Subfunction: 00h
Purpose: To set the directions and to program the
initial values of an I/O port.
Calling registers: Ah efh
AL 00h (03h for I/O2)
DI Port A configuration
Initial Data Direction Mask
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
direction: 1=output, 0=input
BX Port B configuration
Initial Data Direction Mask
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
direction: 1=output, 0=input 0->input
CX Port C configuration
Initial Data Direction Mask
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
direction: 1=output, 0=input
DX ffffh
Return registers: Carry flag cleared if successful
Carry flag set if error
AL Error code
Comments: This function is used to initialize the
I/ before normal use.
Programming example:
/* Inline assembly code for Borland C++ 3.1 */
asm {
mov ax,0ef00h
mov di,00ffh /*port A all outputs,
init data=all 0’s */
mov bx,55ffh /*port B all outputs,
init data=55h*/
mov cx,0000h /*port C all inputs*
mov dx,0ffffh
int 17h
}
Write I/O
Function: efh
Subfunction: 01h
Purpose: To write a value of an I/O port.
Calling registers: AH efh
83
Page 84

AL 01h (04h for I/O2)
DI Port A mask and data
Mask Data
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
Mask: 1=bit to be changed
BX Port B mask and data
Mask Data
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
Mask: 1=bit to be changed
CX Port C mask and data
Mask Data
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxB
Mask: 1=bit to be changed
DX ffffh
Return registers: Carry flag cleared if successful
Carry flag set if error
AL Error code
Comments: This function is used to initialize the
I/O.
Programming example:
/* Inline assembly code for Borland C++ 3.1 */
asm {
mov ax,0ef01h
mov di,00ffh /*Port A: no change */
mov bx,8000h /*Port B: bit 7 set to 0*/
mov cx,0202h /*Port C: bit 1 set to 1*/
mov dx,0ffffh
int 17h
}
Read I/O
Function: efh
Subfunction: 02h
Purpose: To read from an I/O port.
Calling registers: AH efh
AL 02h (05h for I/O2)
DX ffffh
Return registers: AL Port A data
Ah Port B data
BL Port C data
Carry flag cleared if successful
Carry flag set if error
AL Error code
Comments: This function is used to read from the
I/O.
84
Page 85

Programming example:
/* Inline assembly code for Borland C++ 3.1 */
asm {
mov dx,0ffffh
int 17h
mov aData,al
mov bData,ah
mov ax,0efoch
mov cData,bl
}
85
Page 86

Chapter 11: CRTs and flat panels
The video system on the PC–600 is implemented with the CS5530A
companion chip. It supports CRTs and TFT flat panel displays. Displays
from CGA through XVGA are supported. Since the video circuitry
operates on the PCI bus at the full PCI bus speed, programs like Windows
execute very rapidly. The PC–600 supports 3V and 5V flat panel displays.
Standard VGA monitors with analog inputs are connected using a
VGA–12 cable (p/n 4865) connected to J18. Flat panel displays are
connected using a 40-pin 2mm connector at J14. There is an additional
connector at J16 to support a back-light for flat panels.
Note EL panels, and quarter VGA panels are not supported.
Video features
Below is a list of standard video features installed on the PC–600:
CRT support with resolutions to 1280 x 1024 x 16 bpp at 60 Hz
Flat panel support with the following resolutions:
— 640 x 480 x 24 bpp
— 800 x 600 x 24 bpp
— 1024 x 768 x 16 bpp
Support for plasma and TFT flat panel displays
— 3V and 5V flat panel support
— Flat panel power sequencing
86
Page 87

Connecting a monitor
To use a monitor or a flat panel, the Video jumper (W12[5–6]) must be
installed. This is the default configuration. The 16–pin connector at J18
supports an analog VGA/SVGA/XVGA CRT color or monochrome monitor.
Refer to figure 11–1 for a diagram of connecting a CRT, and table 11–1 for
the pin-out for J18.
The PC–600 supports both an analog monitor and/or a flat panel display.
The CT.COM and FP.COM programs allow you to toggle between the
monitor and the flat panel. If the flat panel supports simultaneous mode,
the SM.COM program will allow you to display images from both the
monitor and the flat panel at the same time. These programs are in the
Utilities zip file along with other diagnostic and configuration utilities
(see page
To connect a monitor to the PC–600 you will need the following
equipment (or equivalent):
PC–600 CPU card
VGA-12 video cable, p/n 4865
145). Refer to the README file.
VGA/SVGA monitor
To connect a monitor:
1. Plug the VGA–12 adapter cable into J18 on the PC–600.
2. Plug the DB–15 end of the VGA–12 cable into the VGA cable of the
monitor.
Refer to Figure 11-1.
87
Page 88

Figure 11–1 PC–600 and a VGA monitor
VGA-12 video cable
CRT connector
VGA Monitor
Table 11–1 CRT connector: J18
J18 – CRT connector
Pin # Pin Name Pin Name Pin #
1 RD GR 2
3 BL NC 4
5 Gnd Gnd 6
7 Gnd Gnd 8
9 +5V Gnd 10
11 NC DDC SDA 12
13 HSYNCOUT VSYNCOUT 14
15 DDC SCL Gnd 16
88
Page 89

Connecting a flat panel display
The PC–600 is factory configured and programmed for a 640 x 480 CRT
monitor. If you wish to use a flat panel, you must reprogram the video
BIOS with the appropriate flat panel driver. To reprogram your video
BIOS refer to Programming the video BIOS in this chapter. Note that
both 3V and 5V flat panels are supported. Jumper W6 selects the flat
panel voltage. Flat panel displays are connected using a 40-pin 2mm
connector at J14.
The connector at J16 provides the control signals for back-light for flat
panels. The jumper at W9 selects 5V or 12V for back-light voltage.
Tables 11–2, 11–3, and 11–4 show the jumper settings and connectors for
flat panels.
The Utilities zip file contains text files for each of the supported flat
panels (see page
individual flat panels. Refer to the specific text file associated with your
flat panel to build an interface cable, and to determine the correct settings
for the flat panel jumpers.
To connect a flat panel to the PC–600 you will need the following
equipment (or equivalent):
145). These text files include wiring diagrams specific to
PC–600 CPU card
Flat panel
Custom flat panel to PC–600 cable
Flat panels requiring bias voltage
Some flat panels require a bias voltage. To determine if your flat panel
requires bias voltage refer to your flat panel information. If your flat
panel requires a bias voltage, refer to the manufacturer’s documentation
for procedures on supplying the proper bias voltage.
WARNING!
Since improper voltage levels can severely damage the flat
panel, make sure the bias voltage is correct before the flat
panel is connected to the PC–600.
89
Page 90

Table 11–2 Display jumpers: W6, W9, and W12
W6, W9, W12 – display jumpers
Function Voltage Jumper
Flat panel voltage select
Flat panel back-light voltage
Video enable/disable
3V panel W6[1–3]*
5V panel W6[2–4]
12V back-light W9[1–3]
5V back-light W9[2–4]*
Video enabled W12[5–6]*
Video disabled W12[5–6] jumper off
* = default
Table 11–3 Flat panel connector: J14
J14 – flat panel connector
Pin # Pin Name Pin Name Pin #
1 FPCLK Gnd 2
3 Gnd FPDATA[12] 4
5 FPDATA[0] FPDATA[13] 6
7 FPDATA[1] FPDATA[14] 8
9 FPDATA[2] SCL 10
11 FPDATA[3] SDA 12
13 Gnd FPDATA[15] 14
15 FPDATA[4] FPDATA[16] 16
17 FPDATA[5] FPDATA[17] 18
19 FPDATA[6] Gnd 20
21 FPDATA[7] FPDISPEN 22
23 Gnd FPV** 24
25 FPDATA[8] FPV** 26
27 FPDATA[9] FPVSYNC 28
29 FPDATA[10] Gnd 30
31 FPDATA[11] FPHSYNC 32
33 Gnd FPV** 34
35 PCIRST* FPV** 36
37 Gnd Gnd 38
39 Gnd Gnd 40
* active low
** flat panel voltage, selected with jumper W6
90
Page 91

Table 11–4 Flat panel back-light connector: J16
J16 – back-light connector
Pin # Pin Name
1 FPBV*
2 NC
3 NC
4 Gnd
* flat panel back-light voltage,
selected with jumper W9
Connecting the flat panel to the PC–600
Text files are located in the Utilities zip file. These text files include
wiring diagrams specific to individual flat panels. Refer to the specific
text file associated with your flat panel to build your cable. The maximum
recommended cable length is 18 in.
1. Refer to the text file associated with your flat panel to determine the
supply voltage for your panel, and whether a bias voltage is required.
2. Connect a cable from the flat panel to the flat panel connector located at
J14 on your PC–600. If your flat panel uses back-light, connect another
cable to the back-light connector at J16. Refer to Figure 11–2.
WARNING!
Improper wiring or connection from the flat panel to the PC–
600 can damage the PC–600 and the flat panel. Verify the flat
panel cable connections before connecting the cable to the
PC–600 and applying power to the system.
91
Page 92

Figure 11–2 PC–600 and a flat panel display
Custom flat panel cable
Flat panel connector
Bias connector
Flat panel
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
92
Page 93

Programming the video BIOS
The PC–600 BIOS is factory configured and programmed for a 640 x 480
CRT monitor. If you wish to use a flat panel, you must reprogram the
video BIOS with the appropriate flat panel driver. To reprogram your
video BIOS, load the appropriate driver from the Utilities zip file.
Note Refer to the README file for a list of the supported flat panel displays. If
your particular display is not currently listed, contact Octagon Technical
Support (303–426–4521) for assistance.
To load a new BIOS to support a different flat panel:
1. Attach a CRT monitor, a PS/2 compatible keyboard, and a floppy drive to
the PC–600.
Note If a monitor and keyboard are not available, connect the PC–600 to your
PC by using a remote serial console. Refer to the Serial Console section in
the Console devices chapter.
2. Power on the PC–600.
3. Select the correct .DAT file. Example: LQ15X015.DAT
3. Run PGMVIDEO. Example:
PC–600 C:\> PGMVIDEO \PC600\BIOS\LQ15X015.DAT
4. Power off the PC–600.
5. Install the flat panel cable into connector J14 and then apply power to the
system.
Additional notes on video BIOS
The video BIOS is stored in EEPROM. If this BIOS should become
corrupted, you will have to reprogram it. To do so, remove the Video
jumper W12[5–6] and the “S” jumper W12[1–2]. Connect a serial console
to COM1 to establish communication with the PC–600. Repeat the
procedure above to program the video BIOS.
93
Page 94

Chapter 12: Ethernet
Description
The PC–600 provides two 10/100BaseT Ethernet ports and supports the
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard. The PC–600 uses the Intel 82551ER
Ethernet chips. These chips are fully Plug-N-Play compatible. The
Ethernet controller IC chips provide the following:
8K x 16 SRAM buffer
Integrated 10/100 BaseT transceiver interface
Two LEDs for link and traffic status integrated into connector
The PC–600 Ethernet uses twisted–pair wiring cable, which is built in a
star configuration. The interface terminates at the standard, 8-position,
RJ–45 latching jack.
CAUTION
Use a strain relief loop when connecting to the PC–600
Ethernet connector to avoid damaging the connector.
For more information on programming the Ethernet ports, see the
README file in the Ethernet directory in the Utilities zip file (see page
145).
Table 12–1 Ethernet LEDs
Function Color Description
Activity LED Amber Activated by access to I/O space
Link LED Green Activated by network link
Table 12–2 Ethernet IRQs
Port IRQ
Ethernet 1 11* (shared with USB)
Ethernet 2 10*
* = default, can be changed in Setup
Ethernet LEDs
Ethernet IRQs
94
Page 95

Chapter 13: USB
Description
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a hardware interface for low-speed
peripherals such as the keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner, printer, and
telephony devices. USB 1.1 has a maximum transfer rate of 12 Mbits/sec.
Peripherals can be plugged in and unplugged while power is applied to
the system. The PC–600 contains two 1.1 compliant USB ports.
The two USB ports are accessed via a 10-pin, 0.1” pitch connector at J3.
Octagon provides a cable that routes the J3 signals to standard USB
connectors (Octagon p/n 6288). This cable consists of two five-pin
connectors that mate with the J3 connector on one end, and two USB
connectors at the other end. Ensure that the arrow on the five-pin
connectors is matched to the pin 1 end of J3. Any USB device can then
plug into either USB interface on the USB adapter cable, or into a multiport hub that then plugs into the USB adapter cable.
An operating system capable of utilizing the USB ports and USB devices
is required for USB operation.
USB devices are hot-swappable when a device is plugged
into a standard USB connector, as pins on the connectors
determine the order in which they make contact. Devices are
not hot-swappable when connected to a non-standard header
(J3). You can hot swap a device through the USB Adapter
cable connected to J3, or through another USB connector
wired to the 10-pin header, but you cannot hot swap at the
10-pin header itself.
Table 13–1 USB connector: J3
J3 – USB connector
Pin # Pin Name Pin Name Pin #
1 USB1 power USB2 power 2
3 USB1 – USB2 – 4
5 USB1 + USB2 + 6
7 Gnd Gnd 8
9 Gnd Gnd 10
Caution
95
Page 96

Chapter 14: Audio
Description
The audio feature provides microphone in, stereo line in and line out, PC
beep speaker, and stereo speaker. Audio is accessed via a 20-pin, 0.1”
pitch connector at J20. Octagon provides a cable that routes these
functions out to industry-standard connectors (Octagon p/n 6279). Figure
14–1 shows the audio cable.
Table 14–1 Audio connector: J20
J20 – audio connector
Pin # Pin Name
1 VCC5
2 Gnd
3 PC beep speaker
4 Gnd
5 Line-in Right
6 AGnd
7 Line-in Left
8 AGnd
9 Microphone power, 5V
10 AGnd
11 Microphone In
12 AGnd
13 Line-out R
14 AGnd
15 Line-out L
16 AGnd
17 Speaker-out R
18 AGnd
19 Speaker-out L
20 AGnd
96
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
Page 97

Figure 14–1 Audio cable
PC-600 Audio Cable
Table 14–2 Audio connections
Function Pin # Pin Name
PC beep speaker
Stereo line-in
Mike-in
Stereo line-out
Stereo speaker-out
"Beep" Speaker
Stereo line Input, Left/Right
Microphone Input
Line Output, Left/Right
Speaker Output, Left/Right
Audio connections
1 VCC5
3 PC beep speaker
5 Line-in Right
6 AGnd
7 Line-in Left
8 AGnd
9 Microphone power, 5V
10 AGnd
11 Microphone In
12 AGnd
13 Line-out R
14 AGnd
15 Line-out L
17 Speaker-out R
18 AGnd
19 Speaker-out L
20 AGnd
97
Page 98

Chapter 15: PC/104 and PC/104 Plus
expansion
Description
The PC/104 and PC/104 Plus connectors allow you to interface expansion
modules such as A/D converters, CardBus, digital I/O, serial ports, etc.
Modules can be stacked to form a highly integrated control system. The
PC/104 Plus expansion bus supports mastering devices.
Note The actual maximum number of modules in a stack is limited primarily to
the capacitive loading on the bus and the electrical noise environment.
This is especially true when wide temperature operation is required. Good
design practice dictates that the modules present only one load to each
bus signal. Unfortunately, there are modules on the market that violate
this practice by loading the bus more heavily. Typically, it is the IOW*,
IOR*, MEMW*, and RSTDRV* lines. For example, if the IOW* line is
routed to four ICs on the module without a buffer, then the loading is
equivalent to four PC/104 modules. Stacks with three or more expansion
modules should be carefully tested under all environmental conditions. If
possible, query the manufacture of the expansion module regarding
loading. All Octagon products present one load.
The situation is even more critical for the PC/104 Plus connector since the
bus speed is four times faster. The PC/104 Plus connector and the PC/104
Plus module represent one load each. Adding more than one PC/104 Plus
module (two loads) should trigger the same testing as discussed in the
previous paragraph.
98
Page 99

Figure 15–1 Typical PC/104 module stack
PC/104 expansion card
PC-600 card
WARNING!
When installing any PC/104 module, avoid excessively flexing
the PC–600 card. Excessive flexing may damage the PC–600
card. Mate pins correctly and use the required mounting
hardware.
Note See Appendix A - Connectors for mating information.
99
Page 100

Overview: Section 3 – System management
Section 3 provides information on managing the PC–600 in the areas of
internal control and troubleshooting. The following chapters are
included:
Chapter 16: Watchdog timer and hardware reset
Chapter 17: Serial EEPROM
Chapter 18: Temperature sensor and user jumper
Chapter 19: CPU clock, system jumpers, and BIOS recovery
Chapter 20: Troubleshooting
100
 Loading...
Loading...