Page 1

1 Introduction
The MPC560xP microcontrollers are members of the 32-bit
Qorivva microcontroller family built on the Power
Architecture® technology. The devices are targeted at the
chassis and safety market segment, especially the Electrical
Hydraulic Power Steering, low end Electrical Power Steering
and Airbag applications.
The purpose of this document is to describe hardware design
considerations when developing hardware for the MPC560xP
family of microcontrollers: 5604P, 5603P, 5602P, 5601P. It
will cover topics such as clock generation, decoupling,
Voltage regulator and power considerations. Detailed
reference design schematics and descriptions of the main
components are also contained within this document. Some
general hardware recommendations are also provided.
2 Power Supply
The MPC5604P has a single main/input voltage supply which
can be either 5 V or 3.3 V with a specified tolerance of ±10%
this is converted using the internal VREG to 1.2V ±10% for
the core logic. The user is not permitted to supply the core
logic via an external 1.2 V supply, they must always use the
on-chip voltage regulator (VREG).
Freescale Semiconductor
Document Number: MPC560xPQRUG
Design Guide
Rev. 0, 2012
Hardware Design Guide
MPC560xP devices
© 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Contents
1 Introduction................................................................1
2 Power Supply............................................................1
3 Clock Circuity...........................................................7
4 Analogue to Digital Convertor (ADC)......................9
5 Recommended debug connectors and
connector pin out definitions..................................11
6 MPC56xx high-speed parallel trace
connector.................................................................12
7 Minimum external circuitry....................................14
8 Example communication peripheral
connections..............................................................15
9 Pin Overview...........................................................21
Page 2

The internal regulator has 3 different domains:
• Low Voltage Domain for 1.2 V output to the core
• High Voltage Domain for 5 V supply
• High Voltage Domain for 3.3 V supply
MPC5604P has 6 different pin supply voltages:
Symbol Description
VDD_HV_REG Voltage regulator supply voltage
VDD_LV_COR 1.2v Core supply
VDD_HV_IO Input/Output supply voltage
VDD_HV_ADC ADC supply and high voltage reference
VDD_HV_OSC Crystal oscillator amplifier supply voltage
VDD_HV_FL Code and data flash supply voltage
HV: High Voltage external power supply for voltage regulator module. These pins must be connected to the power supply
(3.3 V or 5 V).
LV: Low Voltage (1.2 V) internal power supply for the Core, PLL. This voltage is generated by the internal voltage regulator
with external connections available for stability decoupling capacitors. It is further split into three main domains to ensure
noise isolation between critical LV modules within the device: Core, Flash , PLL
HV_ADC dedicated to the Analog to Digital Converter functions.
2.1 Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator on the MPC560xP converts the main input supply 3.3 V or 5.0 V ±10% to 1.2 V core logic level. The
internal voltage regulator requires an external capacitance to be connected to the device in order to provide a stable 1.2 V low
voltage digital supply to the device.
2.2 Ballast Transistor
The internal VREG requires an external NPN ballast transistor (BCP56, BCP68, BCX68 or BC817) to be connected as given
in Figure 1. The NPN provides a stable low voltage digital supply to the device and serves as the main current source for the
device.
Power Supply
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 3
Table 2. Recommended Ballast Transistors
Part Manufacturer Recommended derivative
BCP68 ON semi BCP68
Infineon BCP68-10
NXP BCP68-10; BCP68-25
Fairchild BCP68-10; BCP68-25
BCX68 Infineon BCX68-10;BCX68-16; BCX68-25
Fairchild BCX68
BC817 Infineon BC817-16; BC817-25; BC817SU
NXP BC817-16; BC817-25
Fairchild BC817-16;BC817-25; BC817-40
BCP56 ON semi BCP56-10
Infineon BCP56-10; BCP56-16
NXP BCP56-10; BCP56-16
Fairchild BCP56
ST BCP56-16
The ballast transistor provides regulator stability. Stability refers to the way which the regulator reacts to changes in the load.
An unstable circuit may enter a state of continuous oscillation.
Figure 1 represents a typical example of the ballast transistor circuitry.
Power Supply
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 3
Page 4
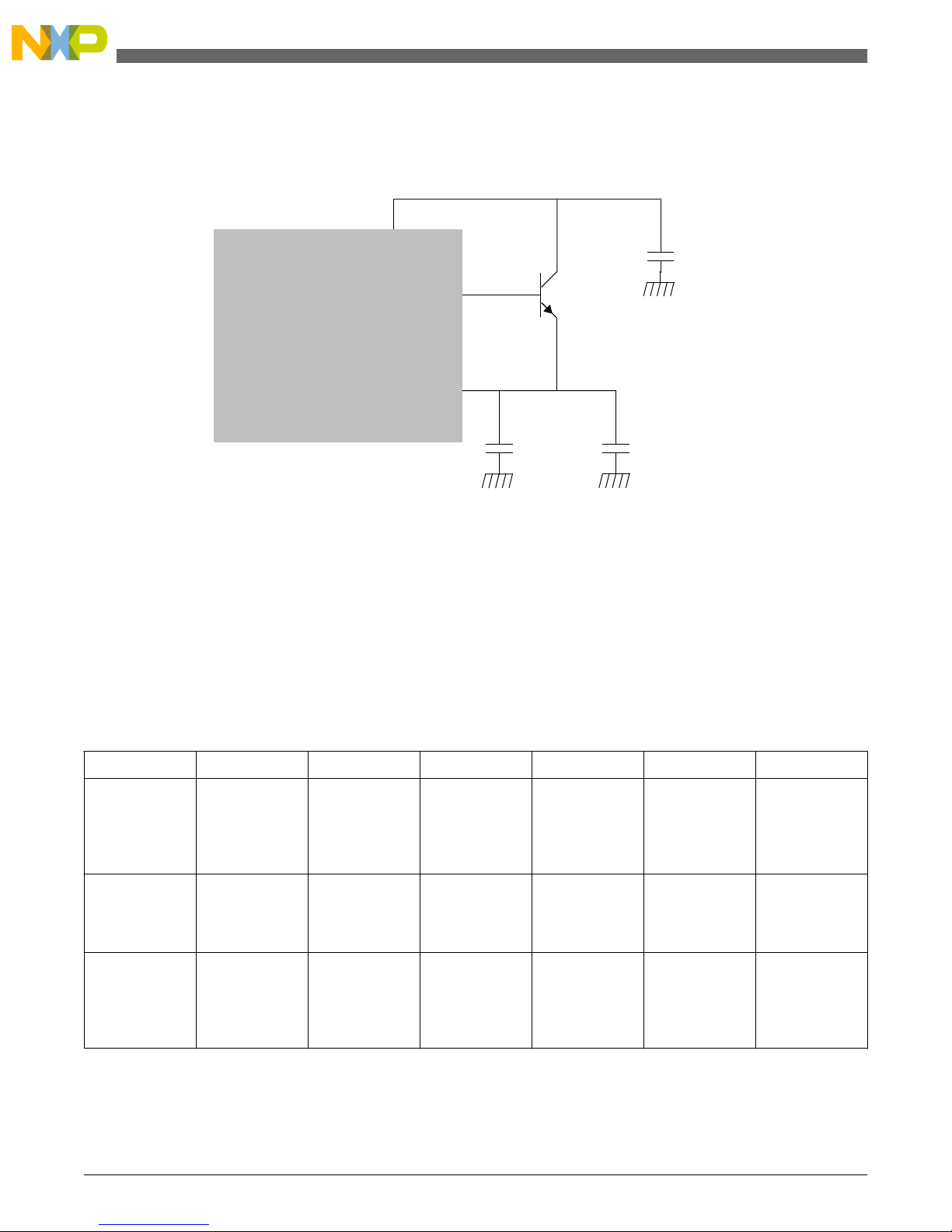
BCTRL
VDD_LV_COR
C
DEC3
C
DEC2
C
DEC1
VDD_HV_REG
BCP56,
BCP68,
BCX68,
BC817
MPC5604P
Figure 1. Configuration without base resistor
BCTRL - (Voltage Regulator external NPN Ballast base control pin) controls the current on the base of the transistor. The
current is increased to raise the voltage on the VDD and decreases to lower the voltage. The gain of the transistor controls the
maximum current available on the supply pin. The gain should be high enough to allow for startup and low enough to prevent
the regulator becoming unstable.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
DD_LV_REGCOR
Output voltage
under maximum
load run supply
current
configuration
Post-trimming 1.15 - 1.32 V
C
DEC1
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor
4 capacitances 40 56 - µF
R
REG
Resulting ESR
of all four C
DEC1
Absolute
maximum value
between 100
kHz and 10
MHz
- - 45 mΩ
Table continues on the next page...
Power Supply
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 5
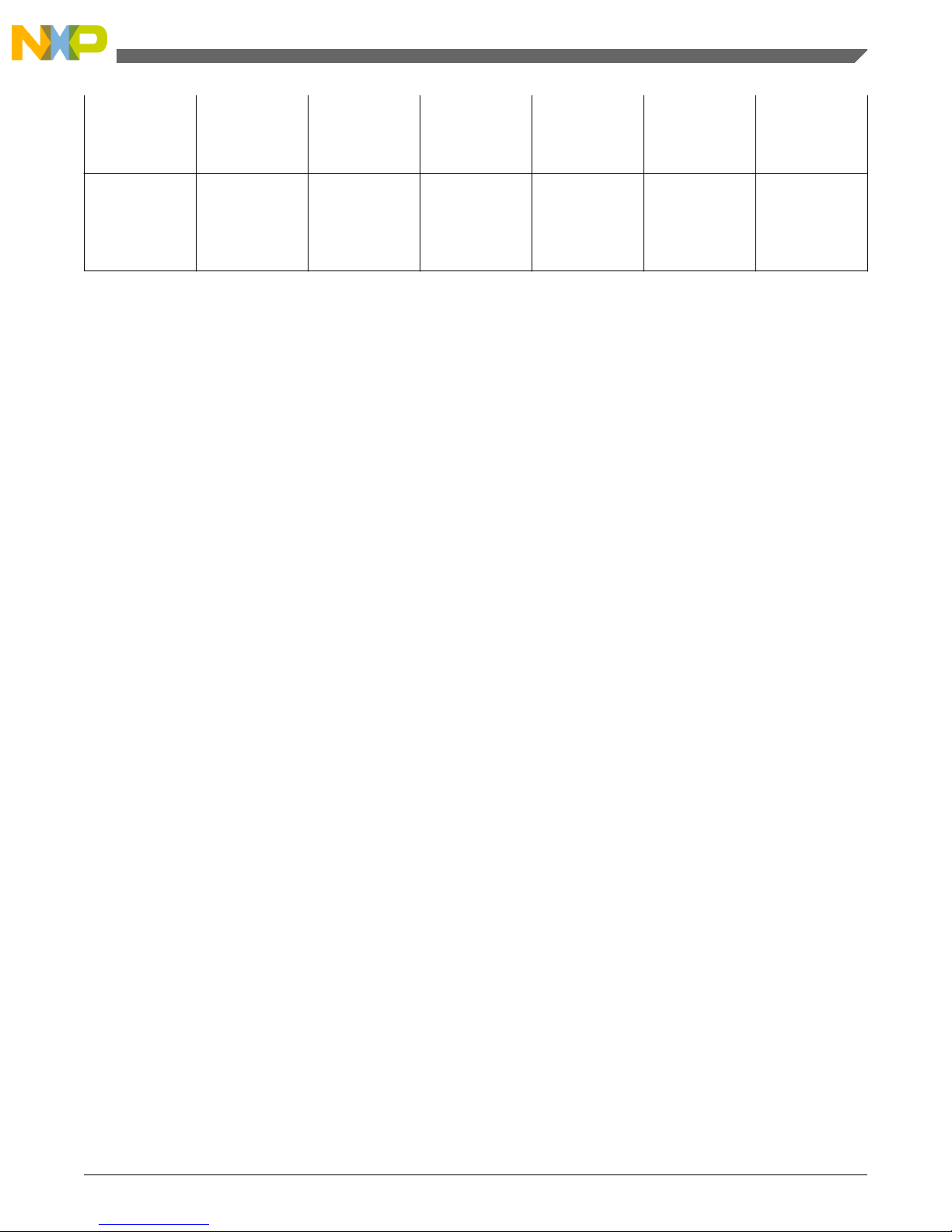
C
DEC2
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor
4 capacitances
of 100 nF each
400 - - nF
C
DEC3
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor on
V
DD_HV_REG
- 40 - - µF
2.3 Capacitors
The ballast transistor requires capacitors to be added for decoupling and stability. The number of capacitors is not important
— only the overall capacitance value and the overall ESR value are important.
• C1 – The capacitance on V
DD_LV
is determined by the stability requirement of the regulator. It is recommended that the
40µF value is split between the V
DD_LV_COR
/ V
SS_LV_COR
pair pins, 4x10µF capacitors placed as close as possibly to
the MCU pins.
• C2 – The 4 x100nF decoupling capacitors are required to filter high frequency noise and smooth the 5 V input signal,
again these should be placed as close as possible to the MCU pins.
• C3 – The 40µF capacitance value is required to meet the voltage drop on the collector and transient requirements,
especially during power-up. It is recommended to place the 40µF capacitor as close as possible to the ballast transistor
collector pin.
47 µF cap can be added to the VDD 5V as a bulk capacitance to reduce ripple from the input supply (optional).
The bypass capacitors serve two purposes:
• To provide (normally dominant) pole to ensure loop stability
• Used as a charge tank for load demand changes. This means if for example load suddenly drops, the cap on the collector
will consume the current until the regulator has adapted to the new situation (and vice versa)
NOTE
Required capacitor values listed in the table include a de-rating factor of 40%, covering tolerance, temperature, and aging
effects. These factors are taken into account to assure proper operation under worst case conditions. X7R type materials are
recommended for all capacitors, based on ESR characteristics.
2.4 Additional design option
The output stage for the power transistor is a class A stage, PMOS power device, loaded with a bit current towards ground.
Thus only the current source towards ground can remove charge in the base of the power transistor, so the turn off delay is
not acceptable. Adding an external resistor base to ground improves the situation and decreases the max available base
current. Using this approach it is possible to reduce load capacitance from 40μF to 20μF as shown in Figure 2. This is
achieved through the addition of an external 20 kresistor added to the base of the transistor. Addition of this pull-down
resistor reduces the response rate of the regulation loop, and therefore reduces the amount of reserve required to respond to
changes in the load. This option may reduce component cost.
Power Supply
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5
Page 6
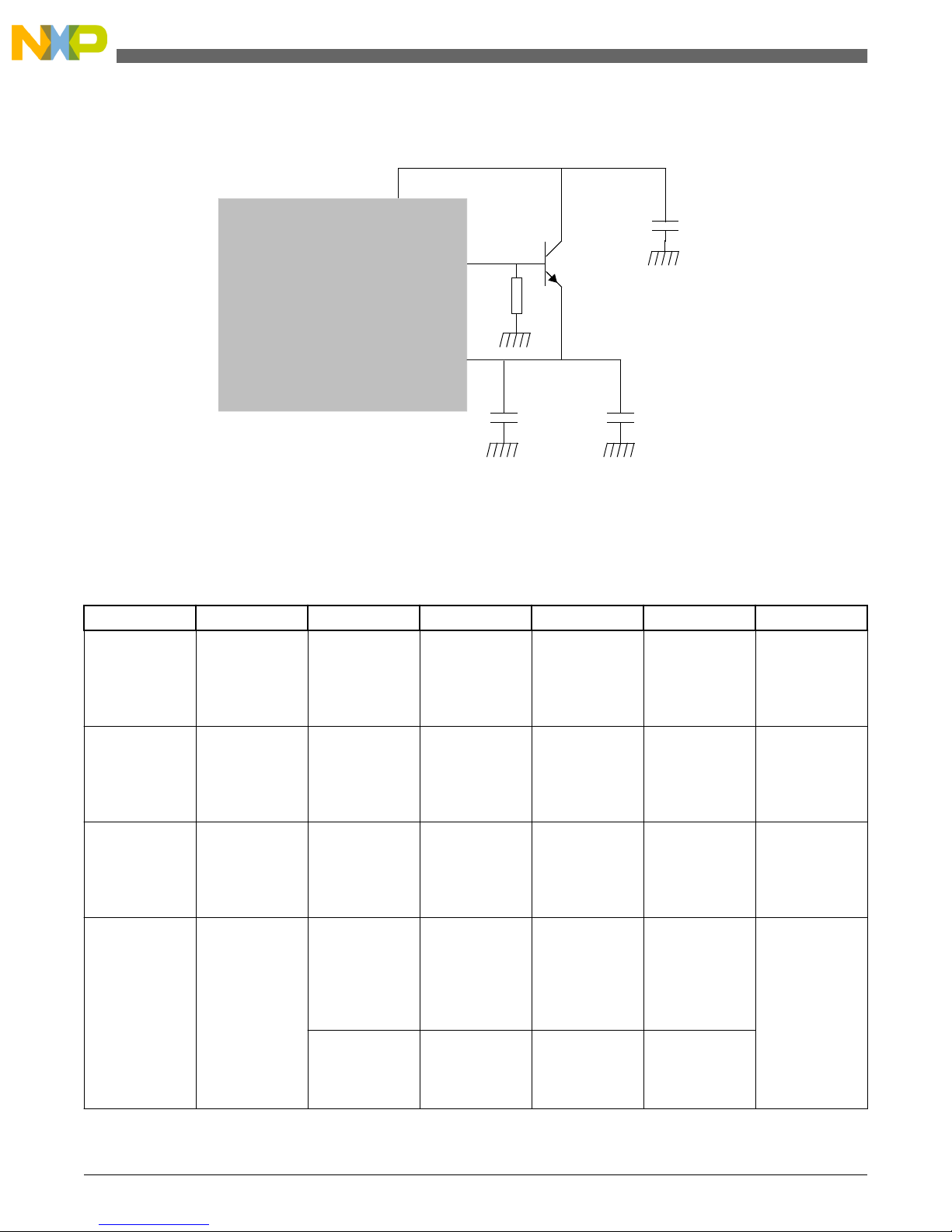
BCTRL
VDD_LV_COR
C
DEC3
C
DEC2
C
DEC1
VDD_HV_REG
BCP68,
BCX68,
BC817SU
MPC5604P
R
B
Figure 2. Configuration with base resistor
Note: For 5601P and 5602P the 20k base resistor has been integrated into the MCU and additional component is not required.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
VDD_LV_REG
COR
Output voltage
under maximum
load run supply
current
configuration
Post-trimming 1.15 ˉ 1.32 V
R
B
External
resistance on
bipolar junction
transistor (BJT)
base
Bipolar BCP68
or BCX68 or
BC817. Three
capacitance s of
10µF
19.5 30 ˉ µF
R
REG
Resulting ESR
of either one or
all three CDEC1
Absolute
maximum value
between 100
kHz and 10
MHz
ˉ ˉ 45 m
C
DEC1
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor
Bipolar BCP68
or BCX68 or
BC817SU
Three
capacitances of
10 μF
19.5 30 ˉ µF
Bipolar BC817
One
capacitance of
22 μF
14.3 22 ˉ
Table continues on the next page...
Power Supply
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 7
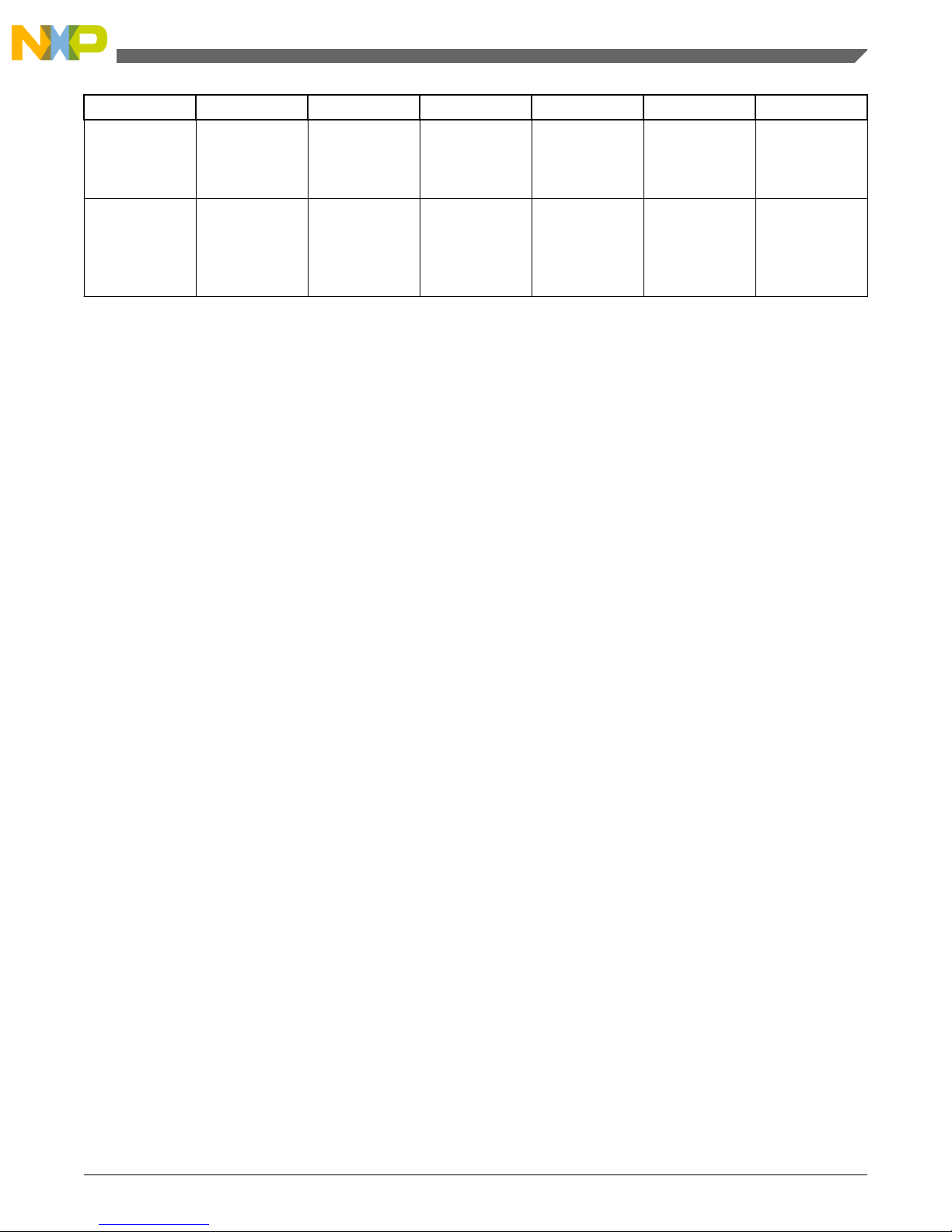
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
C
DEC2
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor
Four
capacitances of
440 nF each
1200 1760 ˉ nF
C
DEC3
External
decoupling/
stability ceramic
capacitor on
V
DD_HV_REG
Two
capacitances of
10 μF each
2 x 10µF ˉ ˉ µF
3 Clock Circuity
The MPC5604P has 4 clock sources.
• IRC— internal RC oscillator
• XOSC — external oscillator clock
• FMPLL_0 - 64 Mhz PLL (max) for System clock
• FMPLL_1 - 120 Mhz PLL (max) for Motor control peripherals
The IRC is internal and does not have to be considered from a hardware design perspective. The FMPLL is described in
Section 3.1.
The XOSC external crystal oscillator works in a range from 4 MHz to 40 MHz. The crystal oscillator circuit includes an
internal oscillator driver and an external crystal circuitry. It provides an output clock that can be provided to PLL or used as a
reference clock to specific modules depending on system requirements.
Referring to the schematic of the on-chip oscillator (Figure 3: Reference oscillator circuit), the key items are described in the
following section. The oscillator circuit provides a reference clock signal to the on-chip PLL. The oscillator circuit consists
of:
• the crystal
• two capacitors
• The external bias resistor (R1) is not required as there is an internal bias resistor within the recommended crystals.
However, it is recommended to leave space for one on the PCB to accommodate different crystal configurations in the
future.
Clock Circuity
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7
Page 8
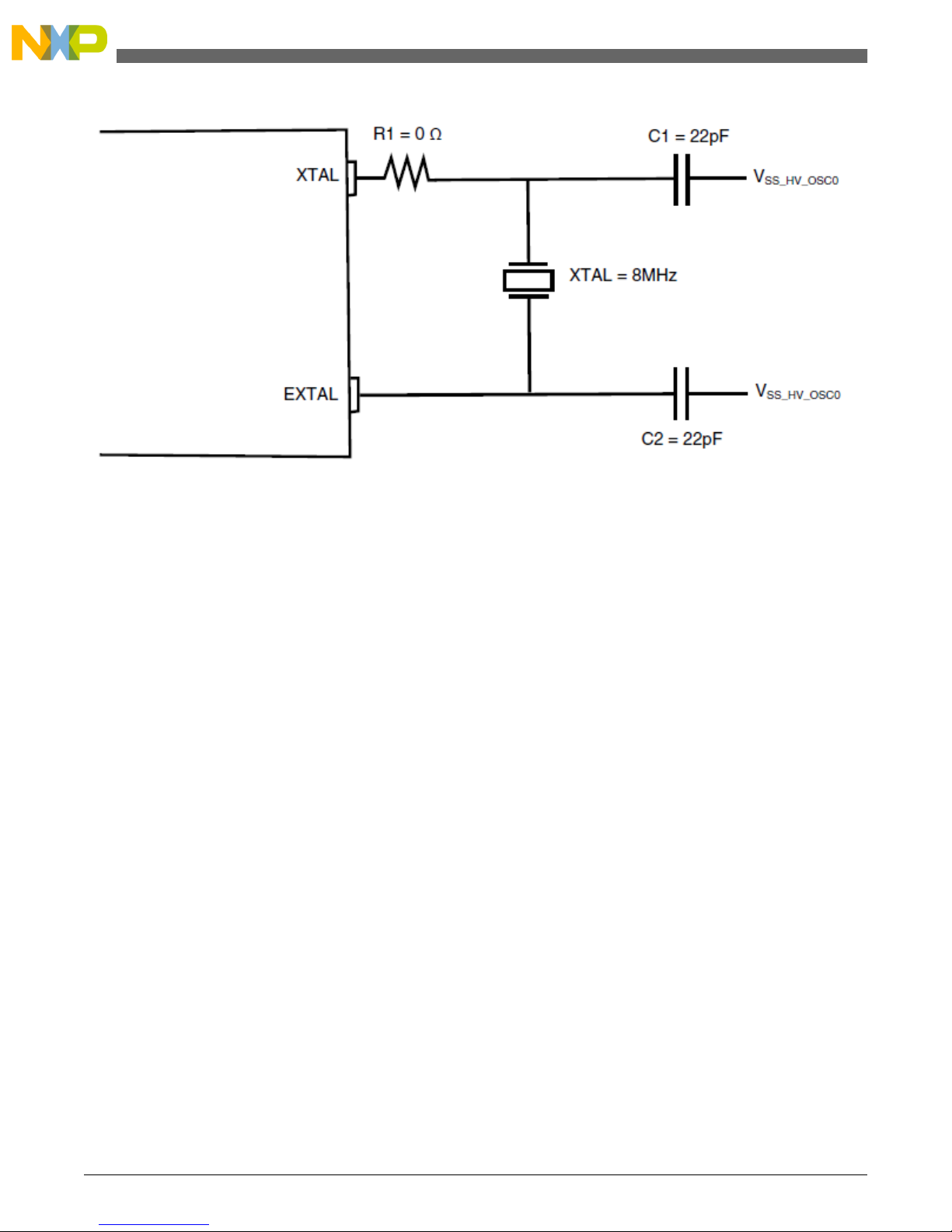
Figure 3. External crystal circuit
The load capacitors are dependent on the specifications of the crystal and on the board capacitance. It is recommended to
have the crystal manufacturer evaluate the crystal on the evaluation board / PCB.
3.1 Frequency Modulated PLL (FMPLL)
The FMPLL allows the user to generate high speed system clocks from a 4MHz to 40MHz input clock. Futhermore, the
FMPLL supports programmable frequency modulation of the system clock. The PLL has the following major features:
• Input clock frequency from an 4MHz to 40MHz
• Voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) range from 256MHz to 512MHz
• Reduced frequency divider (RFD) for reduced frequency operation without forcing the PLL to re-lock
• Frequency modulated PLL
• Modulation enabled/disabled through software
• Triangle wave modulation
• Programmable modulation depth (±0.25% to ±4% deviation from center frequency)
• Programmable modulation frequency dependent on reference frequency
• Self-clocked mode (SCM) operation
• Input supply : same as core supply : 1.2V
The MPC56xx devices can use either the on-chip oscillator with an external crystal or an external reference clock as the
reference clock to the device. This reference is qualified in multiple manners before the PLL will begin lock operation. The
“pre” FMPLL circuitry consists of an automatic level-controlled amplifier, a comparator, a loss of clock detector, and a
predivider.
Clock Circuity
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 9

3.2 Approved crystals
Following is a list of crystals that have been tested and approved by Freescale. If you wish to use a crystal not on this list
please work with the crystal manufacturer to ensure compatibility.
Table 5. Approved crystals
Nominal
frequency
Crystal info Crystal
equivalent
series
resistance ESR
Crystal motional
capacitance
(CI) fF
Crystal motional
inductance (LI)
mH
Load on xtalin/
xtalout
C1=C2(pF)
Shunt
capacitance b/w
xtalout and
xtalin C0(pF)
4.0 NX8045GB 300 2.68 591.0 21.0 2.93
8.0 NX5032GA 300 2.46 160.7 17.0 3.01
10.0 NX5032GA 150 2.93 86.6 15.0 2.91
12.0 NX5032GA 120 3.11 56.5 15.0 2.93
16.0 NX5032GA 120 3.90 25.3 10.0 3.00
40.0 NX5032GA 50 6.18 2.56 8.0 3.49
the CERALOCK resonators listed below have also been approved for use on all MPC560xP devices based on the e200z0
core.
Table 6. Approved resonators
Part
number
vibrationFr[kHz[ Fa[kHz] Fa-
Fr(dF)
[kHz]
Ra[ohm]R1[ohm]L1[mH] C1[pF] Co[pF] Qm CL1(No
minal)p
F
CL2(no
minal)p
F
CSTCR
4M00G
53-R0
Funda
mental
3929.504163.25233.75 372.41 12.78 0.844431.9426815.857301630.9315 15
CSTCR
4M00G
55-R0
Funda
mental
3898.004123.00225.00 465.03 11.38 0.882441.8891715.905371899.7739 39
4 Analogue to Digital Convertor (ADC)
The ADC module has an independent A/D converter supply and reference voltage which allows for an isolated analog
voltage supply input pin VDD_HV_ADC, resulting in a low noise voltage source. The VDD_HV_ADC must be at the same
voltage as the digital voltage supply VDD_HV, in addition to the VSS_HV_ADC analog ground in for further supply
isolation.
Analog signals should not run parallel to clock or any noisy signals such as XTAL and EXTAL and should cross at right
angles if necessary.
Symbol Description
VDD_HV_AD0 ADC0 supply and high reference voltage
VSS_HV_AD0 ADC0 ground and low reference voltage
VDD_HV_AD1 ADC1 supply and high reference voltage
VSS_HV_AD1 ADC1 ground and low reference voltage
Analogue to Digital Convertor (ADC)
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 9
Page 10

1uF
10nF
VDD_HV_ADC0
VSS_HV_ADC0
C1
C2
Figure 4. ADC voltage supply connection
To preserve the accuracy of the A/D converter, it is necessary that analog input pins have low AC impedance. Placing a
capacitor with good high frequency characteristics at the input pin of the device can be effective: the capacitor should be as
large as possible, ideally infinite. This capacitor contributes to attenuating the noise present on the input pin; further, it
sources charge during the sampling phase, when the analog signal source is a high-impedance source.
A real filter can typically be obtained by using a series resistance with a capacitor on the input pin (simple RC filter). The RC
filtering may be limited according to the value of source impedance of the transducer or circuit supplying the analog signal to
be measured. The filter at the input pins must be designed taking into account the dynamic characteristics of the input signal
(bandwidth) and the equivalent input impedance of the ADC itself. For more information read MPC560xP datasheet.
Figure 5. Input equivalent circuit
Analogue to Digital Convertor (ADC)
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 11

5 Recommended debug connectors and connector pin out
definitions
The table below shows the recommended connectors for different applications for the MPC560xP.
Table 8. Recommended connectors
Connector style Target system part number Connector type
14-pin BERG JTAG only 3M 2514-6002UB JTAG-only configuration
25-position (2 × 25, 50-pin) Samtec Samtec ASP-148422-01 Full Nexus configuration
NOTE
Whichever connector is chosen, "keep-out" areas may be required by some tools. Consult
the preferred tool vendor to determine any area that must remain clear around the debug
connector. Some tool vendors may include an extension cable to minimize "keep-out"
areas, but use of an extension will degrade the signal. In many cases, this degradation will
be insignificant, but the amount of degradation depends on many factors, including clock
frequency and target board layout.
5.1 MPC5600 JTAG connector
The figure below shows the pinout of the recommended JTAG connector to support the MPC5600 devices. If there is enough
room allowed in the target system, a full Nexus connector is preferred over the simple 14-pin JTAG connector since it allows
a higher degree of debug capability. It can be used as a minimum debug access or for BSDL board testing.
The recommended connector for the target system is the Tyco part number 2514-6002UB.
NOTE
This pinout is similar to the Freescale MCORE and DSP JTAG/OnCE connector
definitions.
Table 9. Recommended JTAG connector pinout
Description Pin Pin Description
TDI 1 2 GND
TDO 3 4 GND
TCK 5 6 GND
EVTI
1
7 8 —
RESET 9 10 TMS
VREF 11 12 GND
RDY
2
13 14 JCOMP
1. EVTI is optional and was not included in the original (very early) definitions of the JTAG-only connector.
2. The RDY signal is not available on all packages or on all devices. Check the device pinout specification. In general it is not
available in packages with 208 signals or less.
Recommended debug connectors and connector pin out definitions
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 11
Page 12

NOTE
Freescale recommends that a full Nexus connector be used for all tool debug connections,
regardless of whether Nexus trace information is needed. Adapters for a JTAG class 1
14-pin connector (tool side) to the full Nexus MICTOR connectors (board side) are
available from P&E Microcomputer Systems (http://www.pemicro.com ), part number
PE1906, and from Lauterbach (http://www.lauterbach.com ), order number LA-3723
(CON-JTAG14-MICTOR). Lauterbach also has an adapter that will connect a MICTOR
connector (tool side) to a 14-pin JTAG connector (board side). This adapter is order
number LA-3725 (CON-MIC38-J14-5500).
6 MPC56xx high-speed parallel trace connector
For high-speed trace applications, the MICTOR-38 connector is not optimized for best signal integrity when using more than
eight Message Data Out signals (MDO). Twelve MDO pins push the capability of the connector from a signal integrity
standpoint. When moving to devices that support the full 16-bit MDO, a Samtec ERF8 series connector is highly
recommended. The part number of the Samtec connector is shown in the following table.
Table 10. Recommended high-speed parallel trace connector part number
Connector Part number
(Samtec)
Style Description
HP50 ASP-148422-01 Samtec ERF8 series, 25 position by 2
row
Vertical mount for MCU module
The Samtec ERF8 series of connectors is intended for high-speed applications requiring a minimal footprint with a reliable,
latching connection. The recommended connector has two rows of twenty-five contacts each with a spacing of 0.8 mm. The
connector provides isolation between the high-speed trace signals and the low-speed JTAG and control signals. It also
provides ample ground connections to ensure signal integrity.
The following picture is courtesy of Samtec U.S.A (http://www.samtec.com/search/NEXUS.aspx ).
Figure 6. HP50 (ASP-148422-01) connector
MPC56xx high-speed parallel trace connector
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
12 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 13

Table 11 shows the recommended pinout for the Samtec connector.
Table 11. MPC56xx high-speed parallel trace connector
Position Signal
Direction
1
Pin
number
Pin
number
Direction
1
Signal IEEE-5001-2011 GEN_IO
signal name
GND
2
GND
2
1 MSEO0 Out 1 2
Out
3
VREF
2 MSEO1 Out 3 4 In TCK
3 GND 5 6 In TMS
4 MDO0 Out 7 8 In TDI
5 MDO1 Out 9 10 Out TDO
6 GND 11 12 In JCOMP
7 MDO2 Out 13 14 Out RDY
8 MDO3 Out 15 16 In EVTI
9 GND 17 18 Out EVTO
10 MCKO Out 19 20 In RESET
11 MDO4 Out 21 22 Out RSTOUT GEN_IO0
12 GND 23 24 GND
13 MDO5 Out 25 26 Out CLKOUT
14 MDO6 Out 27 28 In/Out TD/WDT GEN_IO1
15 GND 29 30 GND
16 MDO7 Out 31 32 In/Out DAI1 GEN_IO2
17 MDO8 Out 33 34 In/Out DAI2 GEN_IO3
18 GND 35 36 GND
19 MDO9 Out 37 38 ARBREQ GEN_IO4
20 MDO10 Out 39 40 ARBGRT GEN_IO5
21 GND 41 42 GND
22 MDO11 Out 43 44 Out MDO13
23 MDO12 Out 45 46 Out MDO14
24 GND 47 48 GND
25 MDO15 Out 49 50
N/C
4
GND
2
GND
2
1. Viewed from the MCU.
2. The connector locking mechanism provides additional ground connections on each end of the connector.
3. This is an output from the connector standpoint. It may or may not be from the MCU.
4. No connection — should be left open. Reserved for MDO16 on devices with more than sixteen MDO signals (future
compatibility). In some applications this may be used as an SRAM voltage detect to determine when voltage for a standby
SRAM is disconnected.
MPC56xx high-speed parallel trace connector
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 13
Page 14

7 Minimum external circuitry
In general, other than the connector, no additional circuitry is required for the Nexus/JTAG debug circuitry. The MPC5600
devices include internal pull devices that ensure the pins remain in a safe state; however, if there is additional circuitry
connected to the Nexus/JTAG pins, or long traces that could be affected by other signals (due to crosstalk from high-current
or high-speed signals), a minimum number of external pull resistors can be added to insure proper operation under all
conditions.
Table 12. Optional minimum debug port external resistors
Nexus/JTAG signal Resistor direction and value Description
JCOMP 10 kΩ pulldown Holds debug port in reset and prevents
any debug commands from interfering
with the normal operation of the MCU.
RESET 4.7 kΩ pullup The RESET input should be driven from
an open collector output; therefore, it
requires a pullup resistor for the MCU.
TD/WDT
1
10 kΩ pulldown With no tool attached, this signal should
be held low and may or may not be
connected to a pin of the MCU,
depending on the system definition.
EVTI 10 kΩ pullup A pullup resistor prevents debug mode
from being forced after reset if debug
mode is enabled (JCOMP = high). It
also prevents breakpoints from being
forced if debug mode is enabled.
NOTE: In almost all situations, a
resistor is not required on this
signal.
1. This is an optional signal and is not actually required for the MCU.
In addition to the pullup and pulldown resistors, some systems may want to use buffers between the Nexus/JTAG connector
inputs and the MCU. This will prevent over-voltage conditions from causing damage to the MCU signals. Normal systems
should not require this circuitry, but it is helpful in systems that can be exposed to improper connections that provide voltages
that are outside the operating conditions of the MCU. A common circuit to use is the Texas Instruments SN74CBTLV38611.
This device is a bus switch that implements a bidirectional interface between two terminals with less than 5 Ω of resistance. It
should be powered by the same supply that powers the debug port. The device enable should be connected to ground for the
interface to be enabled whenever the debug port on the MCU is powered. This circuit provides a high impedance to the tool
when the debug port is powered off.
NOTE
It is recommended that at least the reduced port configuration Nexus signals be made
available (somewhere) on production boards. This facilitates debugging of new boards
and analysis of errors in software, even on boards that have restricted space and normally
provide a JTAG-only connection. If the Nexus signals are available on the production
board, an adapter could be built to provide a Nexus connection on boards that do not have
a complete footprint for one of the standard Nexus connectors. Likewise, the JTAG
connector does not have to be populated on production boards and could even utilize a
smaller connector footprint that could be used with an adapter to the standard debug
connections.
1. SN74CBTLV3861-Q1 is automotive qualified if required.
Minimum external circuitry
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
14 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 15

8 Example communication peripheral connections
There are a wide range of peripheral pins available on the MCU. Many of these have fairly standard definitions for their use.
This section provides example connections for some of the most commonly used communications peripherals, such as LIN,
CAN, Ethernet, and RS-232 communication interfaces.
Table 13 summarizes the maximum communication speed and general overview information for the different types of
interfaces.
Table 13. Communication module comparison
Common
name
Standard Distributed
timebase
Speed
(maximum
supported)
Channels Time triggered Arbitration
RS-232D EIA RS-232
revision D
No 115.2 kbit/s Single No None (optional
flow control)
LIN LIN 1.0, LIN
2.0, and LIN
2.1
1
No
100 kbit/s
2
Single No None (master/
slave)
CAN Bosch 2.0B
ISO11898
No
1 Mbit/s
3
Single No (additional
function)
CSMA (Carrier
Sense Multiple
Access)
Ethernet IEEE 802.3
No
4
100 Mbit/s Single No CSMA/CD
1. Many Freescale devices only support the LIN 1.0 and 2.0 standards. LIN2.1 requires a different sampling scheme.
2. Typical speed is 10 or 20 Kbps, but supports a fast mode of 100 Kbps.
3. Two different speed classes are supported by CAN, a fast (250K to 1M bps) and a low speed CAN (5K to 125K bps).
4. Distributed timebase is not native by IEEE802.3 but there is hardware support for a PTP protocol that allows a distributed
timebase to be used.
In a typical system, the battery reverse bias and over-voltage protection may be shared between all of the communication
devices in the target system. Figure 7 shows a typical protection.
SMCJ24CA 100nF
VBAT
Protected Battery Voltage
100nF
MBRA140T3
100uF 35V
Ground Return
Figure 7. Typical protection circuit
8.1 Example RS-232 interface for LINFlex
The RS-232 (TIA/EIA-232-F) standard is a fairly common interface that was once available on nearly all computers. While
this interface is disappearing, adapters are available to allow the use of RS-232 peripherals through other interfaces, such as
USB. RS-232 was intended to be a very low-cost, low-performance interface. This interface was originally specified with
signal voltages of +12 V and –12 V typically. However, this has been lowered to a typical minimum voltage of +5 V and –5
V in recent years.
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 15
Page 16

Figure 8 shows the typical connections between the serial port of an MCU and the MAX3232-EP RS-232D transceiver from
Texas Instruments (http://www.ti.com/ ). The transceiver operates from either a 3.3-V or a 5-V supply and includes two
charge pumps to generate the required output voltages. This device contains two transmit drivers and two receivers. The
charge pumps require four external capacitors.
NOTE
The commercial grade MAX3232 device is not rated for the full automotive temperature
of -40 to +125° C and is not intended for automotive applications. This circuit should not
be used or populated in a production module intended for automotive use. However, in
many cases, the RS-232 interface is intended only as a development interface; therefore,
the commercial device can be used for prototyping purposes. TI does offer a device
option with an operating temperature range of –40 to +85° C. TI has an enhanced version
of the device, MAX3232-EP, that is intended for aerospace, medical, and defense
applications. This version is available with an operating temperature range of –55 to
+125° C.
+
0.47uF
+
0.1uF
3.3V or 5V
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
DB9F
FB
1
V+
C1-
C2+
C2-
V-
DOUT2
8
Vcc
16
GND
15
DOUT1
RIN1 ROUT1
DIN1
DIN2
ROUT2
0.1uF
eSCI_TXDA
eSCI_RXDA
MAX3232
eSCI_RXDA2
HOST-R2
eSCI_TXDA2
HOST-T2
9
HOST-R1
HOST-T1
+
0.47uF
+
0.47uF
+
10
11
12
7
RIN2
14
13
2
4
C1+
3
6
5
Figure 8. Typical LINFlex to RS-232D circuit
Table 14. Typical RS-232D connector definition
1 Connect to pin 4 and 6
6 Connect to pin 1 and 4
2 RS-232 TX (transmit)
7 N/C
3 RS-232 RX (receive)
8 N/C
4 Connect to pin 1 and 6
9 N/C
5 GND
NOTE
N/C pins are not connected.
The connector's shell should be connected through a ferrite bead to ground.
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
16 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 17

8.2 CAN interface circuitry
Controller Area Network (CAN) is commonly used in almost all automotive applications to allow communication between
various microchips in the car.
The number of CAN modules on-chip vary from device to device. A separate CAN transceiver is required for each CAN
module, although some CAN transceivers may have more than one on a single chip.
Freescale CAN modules conform to CAN protocol specification version 2.0B, and the transceivers shown in this Hardware
design guide comply with ISO11898 physical layer standard.
Typically, CAN is used at either a low speed (5 Kbps to 125 Kbps) or a high speed (250 Kbps to 1 Mbps). Power train
applications typically use a high speed (HS) CAN interface to communicate between the engine control unit and the
transmission control unit. Body and chassis applications typically use a low speed (LS) CAN interface. In the dashboard of a
vehicle, there is typically a gateway device that interfaces between HS and LS CAN networks.
Popular CAN transceivers include the NXP devices in the table below. Example TJA1050 HS and TJA1054 LS circuits are
shown in this Hardware design guide .
Table 15. NXP CAN transceiver comparison
TJA1050 TJA1054 TJA1040 TJA1041
Bit-rate (Kbps) 1000 125 1000 1000
Modes of operation Normal, listen only Normal, standby, sleep Normal, standby Normal, listen only,
standby, sleep
8.2.1 High-speed CAN TJA1050 interface
Figure 9 shows the typical connections for the physical interface between the MCU and the CAN bus for HS applications
using the NXP TJA1050 HS CAN transceiver.
MCU_CAN_TXD
VREF
MCU_CAN_RXD
CANH
CANL
+5V
60 Ω
60 Ω
60 Ω
60 Ω
10K
4700 pF
U1
TJA1050T
U1
TJA1050T
GND
2
VCC
3
CANH
7
CANL
6
S
8
TXD
1
RXD
4
VREF
5
4700 pF
4700 pF
++
10 uF
Figure 9. Typical high-speed CAN circuit using TJA1050
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 17
Page 18

NOTE
Decoupling shown as an example only.
TXD/RXD pullup/pulldown may be required, depending on device implementation.
Table 16. TJA1050 pin definitions and example system connections
Pin
number
Pin name Pin
direction
Full pin
name
MCU or system
connection
Description
1 TXD Input Transmit
Data
MCU CAN TXD CAN transmit data input from the MCU.
2 GND Output Ground Ground Ground return termination.
3 VCC Input 5 V Voltage supply input (5 V).
4 RXD Output Receive
Data
MCU CAN RXD CAN receive data output to the MCU.
5 VREF Output Reference
voltage
Output
Not used Mid-supply output voltage. This is
typically not used in many systems, but
can be used if voltage translation needs
to be done between the CAN
transceiver and the MCU.
6 CANL Input/
Output
CAN Bus
Low
CAN Bus Connector CAN bus low pin.
7 CANH Input/
Output
CAN Bus
High
CAN Bus Connector CAN bus high pin.
8 S Input Select Grounded or MCU GPIO Select for high-speed mode or silent
mode. Silent mode disables the
transmitter, but keeps the rest of the
device active. This may be used in the
case of an error condition.
8.2.2 Low-speed CAN TJA1054 interface
Figure 10 shows the typical connections for the physical interface between the MCU and the CAN bus for LS applications
using the NXP TJA1054 LS CAN transceiver. Optionally, the standby and enable pins can be connected to MCU GPIO pins
for additional control of the physical interface.
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
18 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 19

MCU_CAN_TXD
MCU_CAN_RXD
MCU_GPIO
INH
CANH
CANL
Vbatt +5V
+5V
10K Ω
10K Ω
TJA1054
INH
1
WAKE
7
STB
5
EN
6
TXD
2
ERR
4
RXD
3
GND
13
RTL
9
CANH
11
CANL
12
RTH
8
BAT
14
VCC
10
4700 pF
++
10 uF
4700 pF
++
10 uF
511 Ω
120 Ω
511 Ω
MCU_GPIO
MCU_GPIO
Isolation and protection circuitry is not shown
in this drawing,only a termination resistor is shown.
Figure 10. Typical low-speed CAN circuit using TJA1054
NOTE
Decoupling shown as an example only.
STB and EN should be pulled high for Normal mode. These signals can optionally be
connected to MCU GPIO pins to allow MCU control of the the physical interface.
Table 17. TJA1054 pin definitions and example system connections
Pin
number
Pin name Pin
direction
Full pin
name
MCU or system
connection
Description
1 INH Input Inhibit Typically not connected Inhibit output for control of an external
power supply regulator if a wake up
occurs.
2 TXD Input Transmit
Data
MCU CAN TXD CAN transmit data input from the MCU.
3 RXD Output Receive
Data
MCU CAN RXD CAN receive data output to the MCU.
4 ERR Output Error MCU GPIO The error signal indicates a bus failure
in normal operating mode or a wake up
is detected in standby or sleep modes.
5 STB Input Voltage
Supply for
IO
MCU GPIO Standby input for device. It is also used
in conjunction with the EN pin to
determine the mode of the transceiver.
Table continues on the next page...
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 19
Page 20

Table 17. TJA1054 pin definitions and example system connections (continued)
Pin
number
Pin name Pin
direction
Full pin
name
MCU or system
connection
Description
6 EN Input Enable MCU GPIO Enable input for the device. It is also
used in conjunction with the STB pin to
determine the mode of the transceiver.
7 WAKE Input Wake Typically not connected Wake input (active low), both falling and
rising edges are detected.
8 RTH Input Termination
Resistor
High
Resistor to CANH Termination resistor for the CAN bus
high
1
9 RTL Input Termination
Resistor
Low
Resistor to CANL Termination resistor for the CAN bus
low
1
10 VCC Input Voltage
Supply
5 volts Digital IO supply voltage, 5 volts.
11 CANH Output CAN Bus
High
CAN Bus Connector CAN bus high pin.
12 CANL Input/
Output
CAN Bus
Low
CAN Bus Connector CAN bus low pin.
13 Ground Output Ground Ground Ground return termination path.
14 BAT Input Standby Battery voltage Battery supply pin, nominally 12 V.
1. This allows the transceiver to control the CAN bus impedance under an error condition.
8.2.3 Recommended CAN connector
Generally, DB9 connectors are used for evaluation boards to connect CAN modules together, whereas there are various
connectors used for production hardware. Figure 11 and Table 18 show a typical example of the connector pinout. A male
type connector is used on the evaluation board and a female type cable connects with it.
Example communication peripheral connections
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
20 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 21

1
5
6 9
Male
1
5
6
9
Female
Figure 11. DB9 Connector Types
Table 18. DB9 connector mapping
Pin number Signal name
1 N/C
2 CAN_L
3 GND
4 N/C
5 CAN_SHIELD (OPTIONAL)
6 GND
7 CAN_H
8 N/C
9 CAN_V+ (OPTIONAL)
NOTE
The metal shell of the connector should be connected through a ferrite bead to the chassis
ground.
9 Pin Overview
Since there are many different requirements for the input and output signals of the MCU, several types of pin types are used.
The following table summarizes the types of pins/pads available on the MCU. Information on the pad types and signal
multiplexing is available in the device Reference Manual and the device Data Sheet. This section helps interpret this
information.
Pin Overview
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 21
Page 22

NOTE
This document uses the terms pins, balls, and pads interchangeably when referencing the
external signals of the device.
Table 19. Pad Types
Pad type Abbreviation Description
Slow Speed pads Slow Most of the peripheral signals are slow
(or medium if available depending on
the device definition) speed pads. The
Slow speed pads have slew rate control
and may implement digital input
circuitry, digital output circuitry or both.
Slow pads can be powered by 3.3 volts.
Medium Speed pads Medium Most of the peripheral signals are
medium (or medium if available
depending on the device definition)
speed pads. The Medium speed pads
have slew rate control and may
implement digital input circuitry, digital
output circuitry or both. Medium pads
can be powered by 3.3 volts.
Fast pads Fast The fast pads are digital pads that allow
high speed signals. Generally, these are
used for the external bus interface.
Each of these pad types have programmable features that are controlled in a pin or pad configuration register (PCR). All pin,
except single purpose pins without special properties that need to be controlled, on the device have a PCR. In a few cases,
some signals are grouped together and a PCR controls multiple pins. The PCR is identified by the GPIO number. The PCR
controls the pin function, direction, and other capabilities of the pin.
9.1 Pad slew rate
The slow, medium and high speed pads implement a slew rate control (SRC) selection in the Pad Configuration Register
(PCR). Slew rate is used to slow down the time it takes for the signal to switch from a low to a high or from a high to a low.
The table below shows the different slew rate settings that are available.
Table 20. Slew Rate settings
Pad type Load drive (pF) Frequency of Operation
(MHz) (max)
Slope at rising/falling edge
(ns) (min/max)
Slow Speed Pad 25 4 4/40
50 2 6/50
100 2 10/75
200 2 14/100
Medium Speed Pad 25 40 2/12
50 20 4/25
100 13 8/40
200 7 14/70
Table continues on the next page...
Pin Overview
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
22 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 23

Table 20. Slew Rate settings (continued)
Pad type Load drive (pF) Frequency of Operation
(MHz) (max)
Slope at rising/falling edge
(ns) (min/max)
Fast Speed Pad 25 72 1/4
50 55 1.5/7
100 40 3/12
200 25 5/18
9.2 Injection Current
All pins implement protection diodes that protect against electrostatic discharge (ESD). In many cases, both digital and
analog pins need to be connected to voltages that are higher than the operating voltage of the device pin. In addition to
providing protection from ESD, these diode structures will also clamp the voltage to a diode drop above the supply of that pin
segment. This is permissible, as long as the current injection is limited as defined in the device specification. Current can be
limited by adding a series resistor on the signal. The input protection diodes will keep the voltage at the pin to a safe level
(per the absolute maximum ratings of the device) as long as it is less than the maximum injection current specification.
Additional circuits on the pins can be enabled only by fast ESD transients. In normal operation, these circuits have no effect
on the pin characteristics and are triggered by fast high voltage transients. To prevent turning on these circuits during normal
power-up sequences, the ramp rate of the power supplies (all external supplies, 5V, and if the internal regulators are not used,
3.3V and 1.2V) should not exceed 25 V/ms.
Below is an extract from the MPC5604P Data Sheet revision 7 dated 04/2011. These specifications may change. Consult the
latest revision of the data sheet to determine if there have been updates to these specifications.
NOTE
Applying signals to pins (~3.3V) during power-off (VDD ~0V) must be considered as a
kind of overload conditions. Series resistors between signal sources and pins may be
needed to limit injection current.
NOTE
Any overload conditions (positive or negative voltage out of VIH and VIL spec applied to
the pins) should be avoided.
Table 21. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
V
IN
Voltage on any pin with
respect to ground
(V
SS_HV
)
V
SS_HV_IO
-0.3 V
DD_HV_IO
+0.3 V
I
INJPAD
Input current on any
pin during overload
condition
-10 10 mA
I
INJSUM
Absolute sum of all
input currents during
overload condition
-50 50 mA
Pin Overview
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 23
Page 24

Table 22. ADC conversion characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Value Unit
Min Typ Max
I
INJ
Input current
injection
Current
injection on one
ADC input,
different from
the converted
one. Remains
within TUE
specification
-5 5 mA
TUE Total
unadjusted
error without
current injection
- -2.5 - 3 LSB
TUE Total
unadjusted
error with
current injection
- -3 - 3 LSB
NOTE
In case overload condition can not be avoided, injection current specification (I
INJPAD
,
I
INJSUM
, I
INJ
) can be applied which limits the current at internal clamp by using an
external series resistor, however, current injection should be minimized because it causes
degradation of ADC accuracy.
9.3 Handling unused pins
In some applications, not all pins of the device may be needed. Good CMOS handling practices state that all unused pins
should be tied off and not left floating. On the MCU, unused digital pins can be left open in the target system. Almost all pins
have internal pull devices (either pullup or pulldown devices2 ). For unused digital pins, it is recommended that software
disable both the input buffers and the output buffers of the pads in the Pad Control Register for the ball. In addition, the weak
pulldown device should be enabled. This keeps the pad in a safe state under all conditions.
For analog pins, it is recommended that they be pulled down to VSSA (the analog return path to the MCU).
2. Technically, these devices are not resistors. They are active weak transistors that pull the input either up or down.
Pin Overview
Hardware Design Guide, Rev. 0, 2012
24 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 25

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
Web Support:
http://www.freescale.com/support
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, EL516
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
www.freescale.com/support
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
www.freescale.com/support
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor China Ltd.
Exchange Building 23F
No. 118 Jianguo Road
Chaoyang District
Beijing 100022
China
+86 10 5879 8000
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
1-800-441-2447 or +1-303-675-2140
Fax: +1-303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Document Number: MPC560xPQRUG
Rev. 0, 2012
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductors products. There are no express or implied
copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated circuits or
integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any
products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation, or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any liability, including without limitation
consequential or incidental damages. "Typical" parameters that may be provided in
Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different
applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters,
including "Typicals", must be validated for each customer application by customer's
technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license under its patent
rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed,
intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant
into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other
application in which failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product could create a
situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use
Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or unauthorized application,
Buyer shall indemnify Freescale Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries,
affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury
or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claims alleges
that Freescale Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of
the part.
RoHS-compliant and/or Pb-free versions of Freescale products have the functionality and
electrical characteristics as their non-RoHS-complaint and/or non-Pb-free counterparts.
For further information, see http://www.freescale.com or contact your Freescale
sales representative.
For information on Freescale's Environmental Products program, go to
http://www.freescale.com/epp.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...