Page 1

MKW01Z128
Sub 1 GHz Low Power Transceiver plus Microcontroller
Reference Manual
Document Number: MKW01xxRM
Rev. 3
04/2016
Page 2

Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
References. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Chapter 1
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
1.1 KW01 family introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.2 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.3 General platform features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.4 MCU features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.5 RF transceiver features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.6 Software solutions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.7 System overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.7.1 Transceiver overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.7.2 MCU overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.7.2.1 Module functional categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.7.2.2 ARM Cortex-M0 core modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.7.2.3 System modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
1.7.2.4 Memories and memory interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
1.7.2.5 Clock modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
1.7.2.6 Security and integrity module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
1.7.2.7 Analog modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
1.7.2.8 Timer modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
1.7.2.9 Radio. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
1.7.2.10 Communication interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
1.7.2.11 Human-machine interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
1.7.2.12 System Device Identification Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
Chapter 2
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
2.1 Device pin assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2 Pin definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.3 Internal Functional Interconnects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Chapter 3 Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 Signal Multiplexing Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2.1 Port control and interrupt module features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2.2 Clock gating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.2.3 Signal multiplexing contraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.3 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. iii
Page 3

Chapter 4
System Considerations
4.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 Power connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.3 System functional interconnects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.3.1 In-package Connections (SPI Channel and Status) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.3.2 System Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.3.2.1 MCU Reset pin (pin 33) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.3.2.2 Transceiver Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.3.2.3 MCU Control of Transceiver Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.3.3 External Clock Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.4 System Clock Sources and Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4.4.1 Additional Transceiver Status Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.4.2 Transceiver Oscillator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.4.2.1 Crystal Resonator Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.4.2.2 Transceiver ClkOut Output (DIO5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.4.3 MCU Clock Sources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
4.4.3.1 MCU External Clock Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
4.4.3.2 MCU External Crystal Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
4.4.3.3 MCU Internal Clock Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4.4.3.4 LPO 1 kHz Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4.4.4 System Clock Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4.4.4.1 Single crystal with ClkOut driving MCU EXTAL input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.4.4.2 Single Crystal with MCU Using Internal Clock Only . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.4.4.3 Dual Crystal Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.4.5 Debug Port Pin Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
4.5 MKW01Z128 GPIO (Mixed I/O from Transceiver and MCU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
4.5.1 MCU GPIO Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
4.5.2 Transceiver DIOX Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
4.6 Transceiver RF Configurations and External Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.6.1 RF Interface Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.6.2 Standard Output Power RF Configuration (Single, Bidirectional Port). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.6.3 Higher Output Power RF Configuration (Dual Port with Optional External Power Amplifier)
4-16
4.6.4 Filter and Matching Network Component Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
Chapter 5
Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
5.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.2 Simplified Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.3 Transceiver Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.4 Low Battery Detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.5 Frequency Synthesis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.5.1 Reference Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
iv Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 4

5.5.2 CLKOUT Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.5.3 PLL Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.5.3.1 VCO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.5.3.2 PLL Bandwidth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.5.3.3 Carrier Frequency and Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.5.4 Lock Time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.5.5 Lock Detect Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.6 Transmitter Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.6.1 Bit Rate Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5.6.2 FSK Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.6.3 OOK Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.6.4 Modulation Shaping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.6.5 Power Amplifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.6.6 Over Current Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.7 Receiver Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.7.1 LNA - Single to Differential Buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.7.2 Automatic Gain Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
5.7.2.1 RssiThreshold Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.7.2.2 AGC Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.7.3 Continuous-Time DAGC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.7.4 Quadrature Mixer - ADCs - Decimators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.7.5 Channel Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
5.7.6 DC Cancellation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-14
5.7.7 Complex Filter - OOK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
5.7.8 RSSI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
5.7.9 Cordic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-16
5.7.10 FSK Demodulator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-17
5.7.11 OOK Demodulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-17
5.7.11.1 Optimizing the Floor Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-18
5.7.11.2 Optimizing OOK Demodulator for Fast Fading Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-19
5.7.11.3 Alternative OOK Demodulator Threshold Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-19
5.7.12 Bit Synchronizer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-19
5.7.13 Frequency Error Indicator (FEI). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-21
5.7.14 Automatic Frequency Correction (AFC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-22
5.7.15 Optimized Setup for Low Modulation Index Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-22
5.7.16 Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-23
5.7.17 Timeout Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
5.8 High Bit Rate Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
5.8.1 500 kbps Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
5.8.2 600 kbps Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
Chapter 6
Transceiver Operating Modes
6.1 Basic Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. v
Page 5

6.2 Automatic Sequencer and Wake-Up Times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.2.1 Transmitter Startup Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.2.2 TX Start Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.2.3 Receiver Startup Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.4 RX Start Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.5 Optimized Frequency Hopping Sequences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.3 Listen Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
6.3.1 Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
6.3.2 Criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
6.3.3 End of Cycle Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
6.3.4 RC Timer Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.4 AutoModes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Chapter 7
Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.1.1 Data Operation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.2 Control Block Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.2.1 SPI Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.2.2 FIFO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.2.2.1 Overview and Shift Register (SR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.2.2.2 Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.2.3 Interrupt Sources and Flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.2.4 FIFO Clearing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
7.2.3 Sync Word Recognition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
7.2.3.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
7.2.3.2 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.2.4 Packet Handler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.2.5 Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.3 Digital IO Pins Mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.3.1 DIO Pins Mapping in Continuous Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.3.2 DIO Pins Mapping in Packet Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.4 Continuous Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
7.4.1 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
7.4.2 TX Processing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
7.4.3 RX Processing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.5 Packet Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.5.1 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.5.2 Packet Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
7.5.2.1 Fixed Length Packet Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
7.5.2.2 Variable Length Packet Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.5.2.3 Unlimited Length Packet Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.5.3 TX Processing (without AES) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.5.4 RX Processing (without AES) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
vi Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 6

7.5.5 AES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
7.5.5.1 TX Processing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
7.5.5.2 RX Processing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
7.5.6 Handling Large Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.5.7 Packet Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.5.7.1 Sync Word Based . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.5.7.2 Address Based. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.5.7.3 Length Based . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.5.7.4 CRC Based . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.5.8 DC-Free Data Mechanisms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
7.5.8.1 Manchester Encoding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
7.5.8.2 Data Whitening. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
7.6 Register Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
7.7 Common Configuration Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
7.8 Transmitter Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
7.9 Receiver Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-26
7.10 IRQ and Pin Mapping Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-29
7.11 Packet Engine Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-32
7.12 Temperature Sensor Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-36
7.13 Test Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-36
Chapter 8
MKW01Z128 Transceiver - MCU SPI Interface
8.1 SiP Level SPI Pin Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.3 SPI System Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.3.1 SPI Signal Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.1.1 Slave Select (SS or NSS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.1.2 SPI Clock (SCK or SPSCK). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.1.3 Master Out / Slave In (MOSI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.1.4 Master In / Slave Out (MISO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.2 MKW0xxx SPI Transaction Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3.3 MKW0xxx SPI Transaction Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
Appendix A
MKW01Z128 MCU Reference Manual
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. vii
Page 7

MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
viii Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 8
Contents
About This Book
This manual details the MKW01, which is a highly-integrated, cost-effective, system-in-package (SIP),
sub-1 GHz wireless node solution with an FSK, GFSK, MSK, or OOK modulation-capable transceiver and
low-power Kinetis microcontroller . The highly integrated RF trans cei ver operates over a wide frequency
range including 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 470 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, 928 MHz, and 955 MHz in the
license-free Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) frequency bands.
Audience
This manual is intended for system designers.
Revision History
The following table summarizes revisions to this document since the previous release (Rev 2.0).
Revision History
Location Revision
Chapter 1 • Corrected the package name from 56 LGA to 60-pin LGA
• Added the following paragraph in Section 1.7.1, “Transceiver overview
“The versatile RF Transceiver in the MKW01 can be configured to be compliant with
the relevant sections of numerous world-wide standards, including but not limited to:
ARIB-T108 and T67, FCC 15.231, 15.247 and 15.249, 802.15.4g, EN54-25 and ETSI
300 220.”
Chapter 2 • Updated Figure 2-1. MKW01Z128 pinout
• Updated Table 2-1. Pin Function Description
• Updated description of pin # 58 in Table 2-2 MKW01Z128 Internal Functional
Interconnects.
Chapter 3 • Updated Table 3-2 Reset State of PORTx_PCRn Register Bit Fields.
• Updated Table 3-3 MKW01 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing.
Chapter 4 • Added a note related to CLKOUT in Idle mode to Section 4.3.3, “External Clock
Connections.
Chapter 5 • Added a note to Section 5.5.5, “Lock Detect Indicator.
• Added a figure to show Pout vs. Programmed Power to Section 5.6.5, “Power
Amplifiers.
• Updated the following sentence in Section 5.7.3, “Continuous-Time DAGC from
“The DAGC is enabled by setting RegTestDagc to 0x10“ to “The DAGC is enabled by
setting RegTestDagc to 0x20“.
• Added Table 5-6. Available DCC Cutoff Frequencies Expressed as Percentage of
RXBW (continued) to Section 5.7.6, “DC Cancellation.
• Added RSSI chart and the notes following the figure to Section 5.7.8, “RSSI.
Chapter 6 • Added a note related to CLKOUT in Idle mode to Section 6.3, “Listen Mode.
Chapter 7 • Updated Reset value of RegVersion (at address 0x10) from 0x22 to 0x 23 in T able 7-4.
Registers Summary. Also added a line for register RegTestTcxo at address 0x59.
• Added a line for register RegTestTcxo at address 0x59 in Table 7-11 Test Registers.
Also updated description of RegTestDagc (0x6F) register.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. ix
Page 9

Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations
The following list defines the acronyms and abbreviations used in this document.
ACK Acknowledgement Frame
API Application Programming Interface
BB Baseband
CCA Clear Channel Assessment
CRC Cyclical Redundancy Check
DCD Differential Chip Decoding
DME Device Management Entity
FCS Frame Check Sequence
FFD Full Function Device
FFD-C Full Function Device Coordinator
FLI Frame Length Indicator
GTS Guaranteed Time Slot
HW Hardware
IRQ Interrupt Request
ISR Interrupt Service Routine
LO Local Oscillator
MAC Medium Access Control
MCPS MAC Common Part Sublayer
MCU Microcontroller Unit
MLME MAC Sublayer Management Entity
MSDU MAC Service Data Unit
NWK Network
PA Power Amplifier
PAN Personal Area Network
PANID PAN Identification
PHY PHYsical Layer
PIB PAN Information Base
PPDU PHY Protocol Data Unit
PSDU PHY Service Data Unit
RF Radio Frequency
RFD Reduced Function Device
SAP Service Access Point
SFD Start of Frame Delimiter
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
x Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 10

SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
SSCS Service Specific Convergence Layer
SW Software
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
References
The following sources were referenced to produce this book:
[1] IEEE 802.15.4 Standard
[2] Freescale
MKW01xx Data Sheet
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. xi
Page 11

MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
xii Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 12

Chapter 1 MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
Kinetis is the most scalable portfolio of low power, mixed-signal ARM®Cor tex™ MCUs in the industry.
Kinetis MCU families are peripheral- and software-compatible devices. Each family offers excellent
performance, memory and feature scalability with common peripherals, memory maps, and packages
providing easy migration both within and between families.
Kinetis MCUs are built from Freescale’ s innovative 90 nm thin film storage (TFS) flash technology with
unique FlexMemory. Kinetis MCU families combine the latest low-power innovations and high
performance, high precision mixed-signal capability with a broad range of connectivity, human-machine
interface, and safety & security peripherals.Kinetis MCUs are supported by a market-leading enablement
bundle from Freescale and numerous ARM 3rd party ecosystem partners.
Kinetis W-series devices all contain wireless connectivity options spanning across frequency bands and
standards.
T a ble 1-1. Kinetis W-Series devices
Family Frequency Band
KW0x Sub-Gigahertz
KW2x 2.4 GHz
KW3x Reserved
KW01 devices also have these features:
•Core:
— ARM Cortex-M0+ Cores delivering single-cycle access memories, 48 MHz CPU frequency
— Up to 16-channel DMA for peripheral and memory servicing with minimal CPU intervention
— Broad range of performance levels rated at maximum CPU frequencies starting at 48 MHz
• Ultra-low power:
— Multiple low power operating modes for optimizing peripheral activity and wakeup times for
extended battery life.
— Low–leakage wakeup unit, low power timer, and low power RTC for additional low power
flexibility
— Industry-leading fast wakeup times
• Memory: 16 KB RAM, 128 KB flash
• Mixed-signal analog:
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-1
Page 13

MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
— Fast, high precision 16-bit ADCs, 12-bit DACs, high speed comparators and an internal voltage
reference. Powerful signal conditioning, conversion and analysis capability with reduced
system cost
• Human Machine Interface (HMI):
— Capacitive Touch Sensing Interface with full low-power support and minimal current adder
when enabled
• Connectivity and Communications:
— UARTs with ISO7816, CEA709.1-B (LON), and IrDA support, I2C, and DSPI
• Reliability, Safety and Security:
— Hardware cyclic redundancy check engine for validating memory contents/ communication
data and increased system reliability
— Independent-clocked computer operating properly (COP) for protection against code runaway
in fail-safe applications
— External watchdog monitor
• Timing and Control:
— Programmable Interrupt Timer for RTOS task scheduler time base or trigger source for ADC
conversion and programmable delay block
•System:
— Wide operating voltage range from 1.8 V to 3.6 V with flash programmable down to 1.8 V with
fully functional flash and analog peripherals
— Ambient operating temperature ranges from –40°C to 85°C
1.1 KW01 family introduction
The KW01 family is the entry point into the Kinetis W-Series portfolio. The K01W is a single-chip
solution combining an ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller and a sub-GHz ISM band radio front-end
device.
Devices contain 128 KB of flash and 16 KB of SRAM in an 8 x 8 mm 60-pin LGA package. Standard
features include a rich suite of analog, communication, timing and control peripherals. Additionally,
flexible low-power capabilities and innovative FlexMemory help to solve many of the major pain points
for system implementation.
1.2 Ordering information
Table 1-2 lists the available devices in the MKW01 family.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 14
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
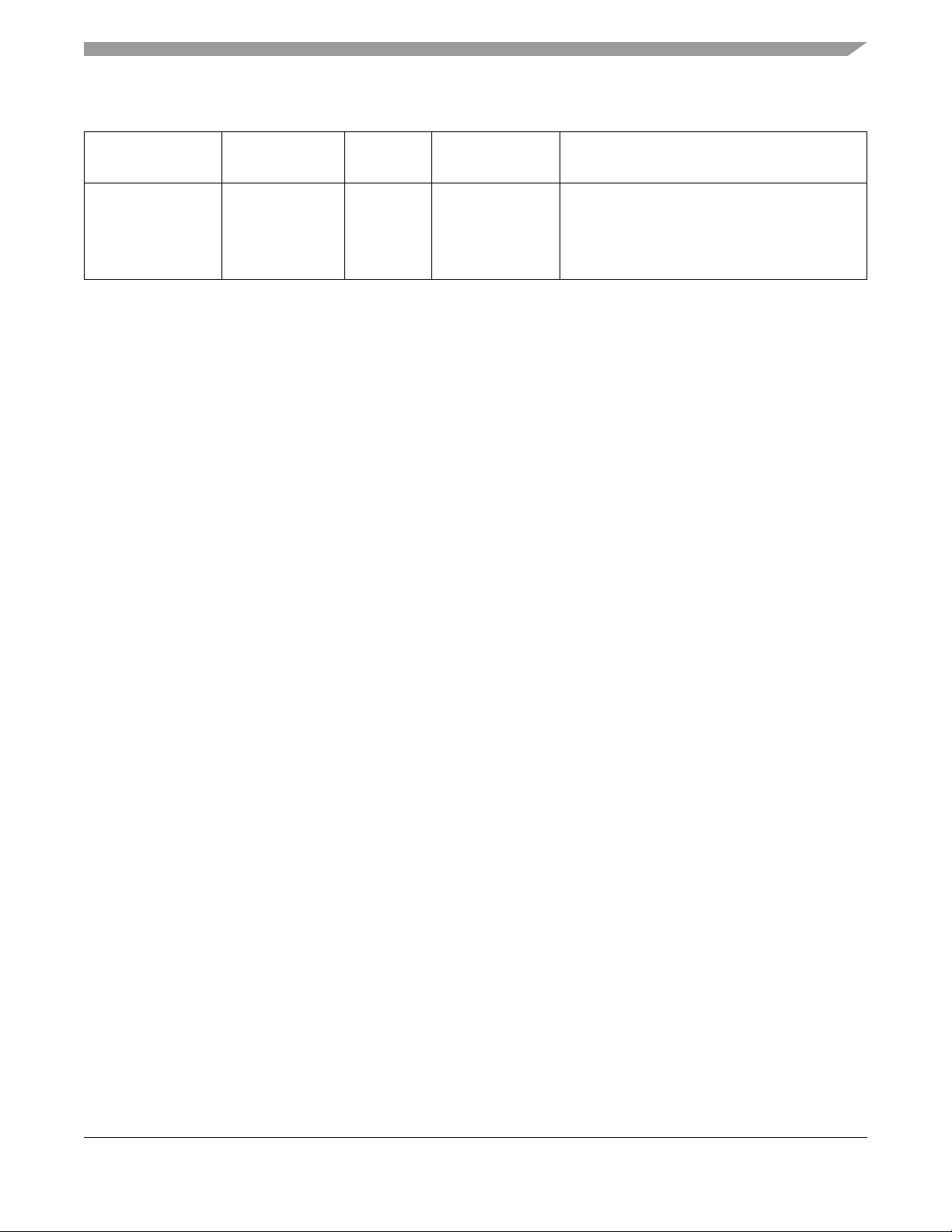
Table 1-2. Devices in the MKW01 Family
Device
MKW01Z128CHN –40° to 85° C 60 LGA 16 KB RAM,
Operating Temp
Range (TA.)
Package Memory Options Description
The primary target market is communications for
128 KB flash
last mile metering, sub metering and associated
devices such as concentrators. The feature set
will also allow it to serve for wireless sensor
networks in building control and automation.
1.3 General platform features
• ARM Cortex-M0+ Core
• Sub-1 GHz in-package transceiver
• Multiple power saving modes
• 1.8 V to 3.6 V operating voltage with on-chip voltage regulators
• –40°C to +85°C temperature range
• Low external component count
• Supports single crystal (32 MHz typical) clock source operation or dual crystal operation
• Versatile software solutions
• 60-pin LGA (8x8 mm) Package
1.4 MCU features
•Core:
— ARM Cortex-M0+ 1.77 CoreMark/MHz from single-cycle access memories, 48 MHz CPU
frequency
— 4-channel DMA for peripheral and memory servicing with minimal CPU intervention
— CPU frequencies up to 48 MHz
• Ultra-low power:
— Multiple low power operating modes for optimizing peripheral activity and wakeup times for
extended battery life.
— Low–leakage wakeup unit and low power timer for time keeping function
— Industry-leading fast wakeup times
• Memory:
— 128 KB Flash, 16 KB RAM
• Mixed-signal analog:
— Fast, high precision 16-bit ADCs, and internal high speed comparators. Powerful signal
conditioning, conversion and analysis capability with reduced system cost
• Human Machine Interface (HMI):
— Capacitive Touch Sensing Interface with full low-power support and minimal current adder
when enabled
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-3
Page 15

MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
• Connectivity and Communications:
— Three UARTs, two SPIs, and two I2C
• Reliability, Safety and Security:
— Hardware cyclic redundancy check engine for validating memory contents/ communication
data and increased system reliability
— Independent-clocked computer operating properly (COP) for protection against code runaway
in fail-safe applications
• Timing and Control:
— Powerful timer modules that support general-purpose, PWM, and motor control functions
— Programmable Interrupt Timer for RTOS task scheduler time base or trigger source for ADC
conversion and programmable delay block
•System:
— Wide operating voltage range from 1.8 V to 3.6 V with flash programmable down to 1.8 V with
fully functional flash and analog peripherals
— Ambient operating temperature ranges from –40°C to 85°C
1.5 RF transceiver features
• High Sensitivity: down to –120 dBm at 1.2 kbps
• High Selectivity: 16-tap FIR Channel Filter
• Bullet-proof front end: IIP3 = –18 dBm, IIP2 = +35 dBm, 80 dB Blocking Immunity, no Image
Frequency response
• Low current: RX = 16 mA, 100 nA register retention
• Programmable Pout : –18 to +17 dBm in 1 dB steps
• Constant RF performance over voltage range of chip
• FSK bit rates up to 600 kbps
• Fully integrated synthesizer with a resolution of 61 Hz
• FSK, GFSK, MSK, GMSK and OOK modulations
• Built-in Bit Synchronizer performing Clock recovery
• Incoming Sync Word Recognition
• Automatic RF Sense with ultra-fast AFC
• Packet engine with CRC, AES-128 encryption and 66-byte FIFO
• Built-in temperature sensor and Low battery indicator
• 32 MHz (typical) crystal oscillator clock source
1.6 Software solutions
Freescale will support the MKW01Z128 platform with several software solutions:
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 16

MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
• A radio utility GUI will be available that allows testing of various features and setting registers. A
firmware-based connectivity test will allow a limited set of testing controlled with a terminal
emulator on any computer.
• SMAC (Simple Media Access Controller) — This codebase provides simple communication and
test apps based on drivers/PHY utilities available as source code. This environment is useful for
hardware and RF debug, hardware standards certification, and developing proprietary applications.
• MAC/PHY (Media Access Control/Physical) for IEEE 802.15.4g/e — This release was developed
primarily for the ZigBee Alliance specified Home Energy Management Systems for the Japanese
application space.
• Additional software will be available through 3rd party providers.
1.7 System overview
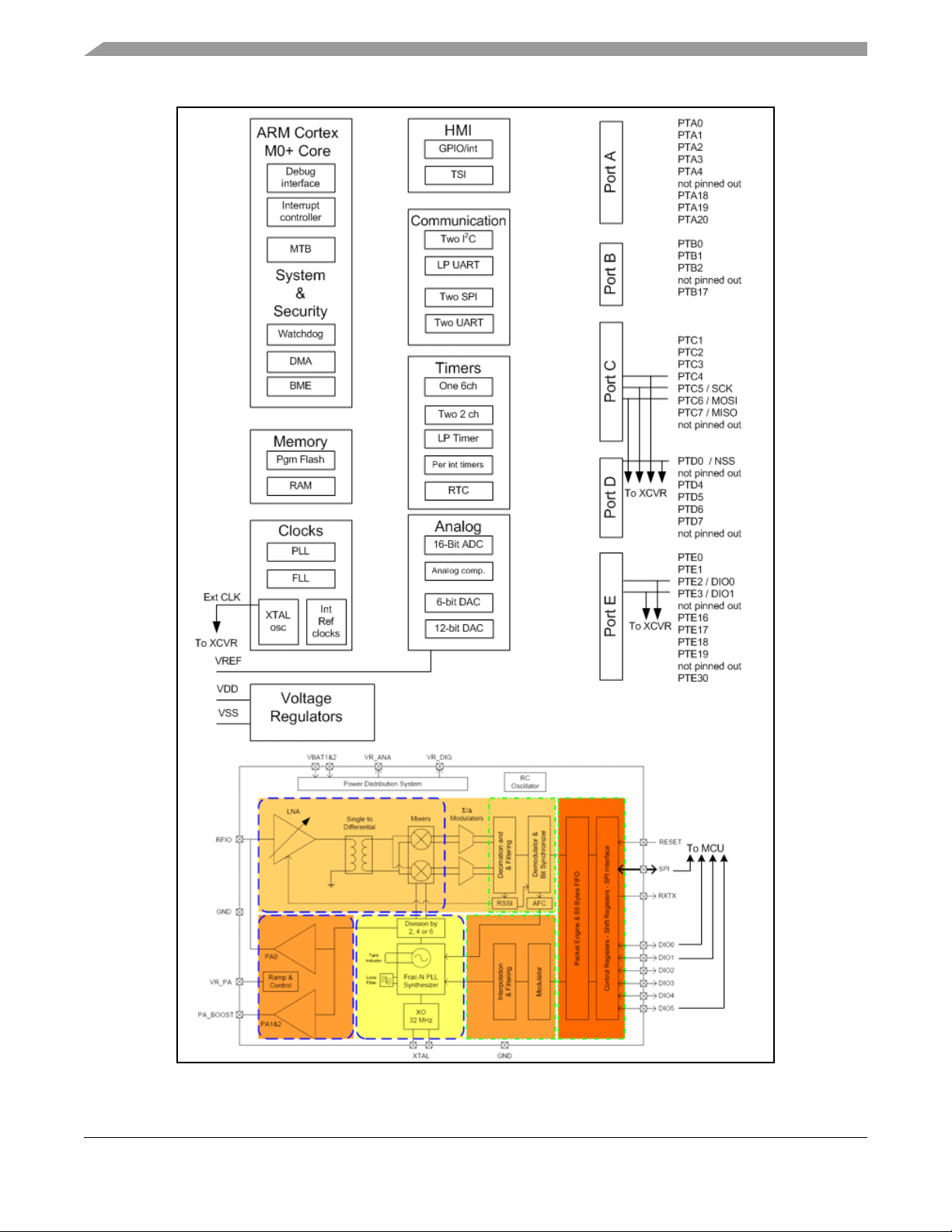
Figure 1-1 shows a simplified block diagram of the MKW01.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-5
Page 17
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
Figure 1-1. MKW01 system level block diagram
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 18

MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
1.7.1 Transceiver overview
The transceiver (see Figure 1-1) is a single-chip integrated circuit ideally suited for today's high
performance ISM band RF applications. Its advanced features set, including state of the art packet engine,
greatly simplifies system design while the high level of integration reduces the external RF component bill
of material (BOM) to a handful of passive de-coupling and matching components. It is intended for use as
a high-performance, low-cost FSK and OOK RF transceiver for robust, frequency agile, half-duplex
bidirectional RF links.
The MKW01 is intended for applications over a wide frequency range, including the 433 MHz and
868 MHz European and the 902–928 MHz North American and Japan ISM bands. Coupled with a link
budget in excess of 135 dB, the transceiver advanced system features include a 66 byte TX/RX FIFO,
configurable automatic packet handler, listen mode, temperature sensor and configurable DIOs which
greatly enhance system flexibility while at the same time significantly reducing MCU requirements. The
transceiver complies with both ETSI and FCC regulatory requirements.
The major RF communication parameters of the MKW0 1 transceiver are programmable and most can be
dynamically set. This feature offers the unique advantage of programmable narrow-band and wide-band
communication modes without the need to modify external components. The transceiver is also optimized
for low power consumption while offering high RF output power and channelized operation.
The versatile RF Transceiver in the MKW01 can be configured to be compliant with the relevant sections
of numerous world-wide standards, including but not limited to: FCC Part 15.247 and Part 15.249, ETSI
EN 300 220, ARIB STD-T108, IC RSS 210.
1.7.2 MCU overview
The in-package Kinetis L series 48 MHz MCU features an ARM Cortex M0+, 16 KB Ram and 128 KB
flash. The RF transceiver is controlled through the MCU SPI port which is dedicated to the RF device
interface. Two of the transceiver status IO lines are also directly connected to the MCU GPIO to monitor
the transceiver operation. In addition, the transceiver reset and additional status can be connected to the
MCU through external connections.
1.7.2.1 Module functional categories
The modules on this device are grouped into functional categories. The following sections describe the
modules assigned to each category in more detail.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-7
Page 19
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
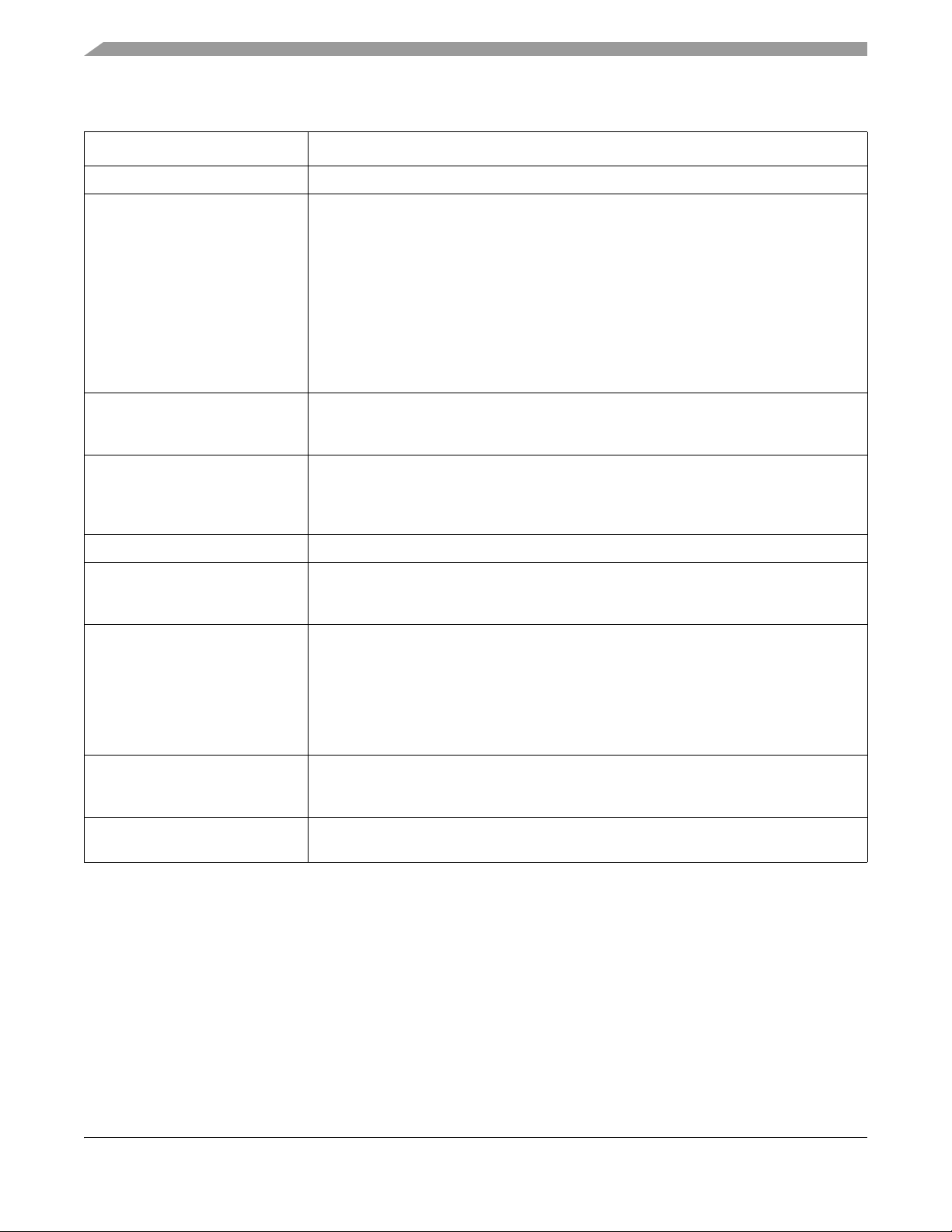
Table 1-3. Module functional categories
Module category Description
ARM Cortex-M0+ core
System • System integration module
• Power management and mode controllers — Multiple power modes available based on
run, wait, stop, and powerdown modes
• Low-leakage wakeup unit
• Miscellaneous control module
• Crossbar switch
• Peripheral bridge
• Direct memory access (DMA) controller with multiplexer to increase available DMA
requests
• External watchdog monitor
• Watchdog
Memories Internal memories include:
• Up to 128KB program flash memory
• Up to 16KB SRAM
Clocks • Multiple clock generation options available from internally- and externally-generated
clocks
• System oscillator from transceiver to provide clock source for the MCU
• 32 kHz RTC oscillator
Security • Cyclic Redundancy Check module for error detection
Analog • 16-bit analog-to-digital converter
• Internal Comparator with internal 6-bit DAC for reference
• 12-bit DAC with DMA support and two 16-bit buffers
Timers • Low Power Timer/PWM (TPM) modules
• One 6-channel TPM
• Two 2-channel TPMs
• 2-channel periodic interrupt timer
• Real-time clock
• Low-power timer
• System tick timer
Communications • 2x internal serial peripheral interface
• 2x inter-integrated circuit (I
•3x UART
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) • General purpose input/output controller
• Capacitive touch sense input interface enabled in hardware
2
C)
1.7.2.2 ARM Cortex-M0 core modules
The following core modules are available on this device.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 20
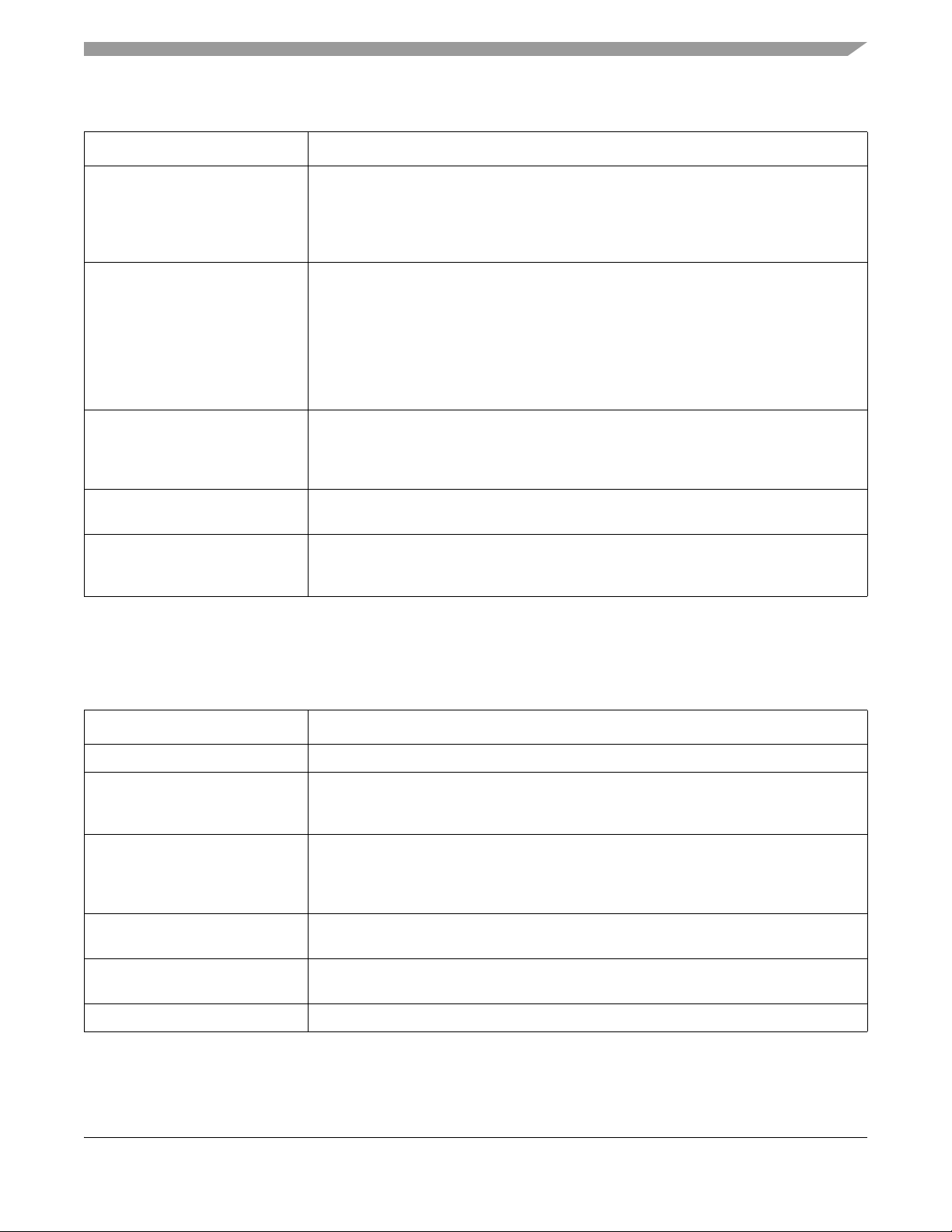
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
Table 1-4. Core modules
Module Description
ARM Cortex-M0+ The ARM Cortex-M0+ is the newest member of the Cortex M Series of processors
targeting microcontroller applications focused on very cost sensitive, deterministic,
interrupt driven environments. The Cortex M0+ processor is based on the ARMv6
Architecture and Thumb®-2 ISA and is 100% instruction set compatible with its
predecessor, the Cortex-M0 core, and upward compatible to Cortex-M3 and M4 cores.
NVIC The ARMv6-M exception model and nested-vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) implement
a relocatable vector table supporting many external interrupts, a single non-maskable
interrupt (NMI), and priority levels.
The NVIC replaces shadow registers with equivalent system and simplified
programmability. The NVIC contains the address of the function to execute for a particular
handler. The address is fetched via the instruction port allowing parallel register stacking
and look-up. The first sixteen entries are allocated to ARM internal sources with the others
mapping to MCU-defined interrupts.
AWIC The primary function of the Asynchronous Wake-up Interrupt Controller (AWIC) is to detect
asynchronous wake-up events in stop modes and signal to clock control logic to resume
system clocking. After clock restart, the NVIC observes the pending interrupt and performs
the normal interrupt or event processing.
Single-cycle I/O Port For high-speed, single-cycle access to peripherals, the Cortex-M0+ processor implements
a dedicated single-cycle I/O port.
Debug interfaces Most of this device's debug is based on the ARM CoreSight™ architecture. One debug
interface is supported:
• Serial Wire Debug (SWD)
1.7.2.3 System modules
The following system modules are available on this device.
Table 1-5. System modules
Module Description
System integration module (SIM) The SIM includes integration logic and several module configuration setti n gs.
System mode controller The SMC provides control and protection on entry and exit to each power mode, control
for the Power management controller (PMC), and reset entry and exit for the complete
MCU.
Power management controller
(PMC)
Low-leakage wakeup unit (LLWU) The LLWU module allows the device to wake from low leakage power modes (LLS and
Peripheral bridge The peripheral bridge converts the crossbar switch interface to an interface to access a
The PMC provides the user with multiple power options. Multiple modes are supported that
allow the user to optimize power consumption for the level of functionality needed. Includes
power-on-reset (POR) and integrated low voltage detect (LVD) with reset (brownout)
capability and selectable LVD trip points.
VLLS) through various internal peripheral and external pin sources.
majority of peripherals on the device.
DMA multiplexer (DMAMUX) The DMA multiplexer selects from many DMA requests down to 4 for the DMA controller.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-9
Page 21
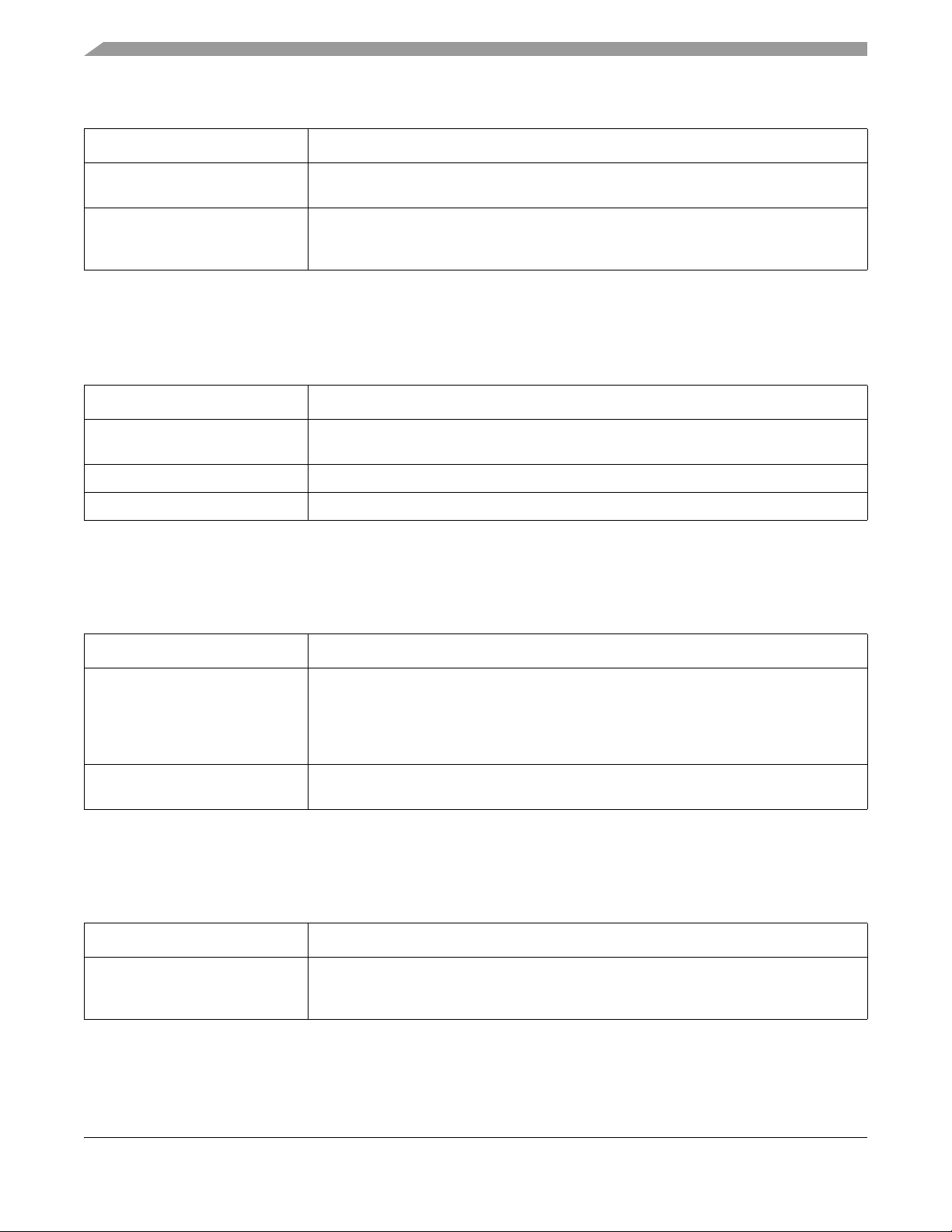
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
Table 1-5. System modules (continued)
Module Description
Direct memory access (DMA)
controller
Computer operating properly
watchdog (WDOG)
The DMA controller provides programmable channels with transfer control descriptors for
data movement via dual-address transfers for 8-, 16- and 32-bit data values.
The WDOG monitors internal system operation and forces a reset in case of failure. It can
run from an independent 1 kHz low power oscillator with a programmable refresh window
to detect deviations in program flow or system frequency.
1.7.2.4 Memories and memory interfaces
The following memories and memory interfaces are available on this device.
Table 1-6. Memories and memory interfaces
Module Description
Flash memory Program flash memory — up to 128 KB of the non-volatile flash memory that can
execute program code
Flash memory controller Manages the interface between the device and the on-chip flash memory.
SRAM Up to 16 KB internal system RAM.
1.7.2.5 Clock modules
The following clock modules are available on this device.
Table 1-7. Clock modules
Module Description
Multi-clock generator (MCG) The MCG , controlled by an internal or external (such as the CLKOUT from the transceiver)
reference oscillator, provides several clock sources for the MCU that include:
• Phase-locked loop (PLL). Voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO)
• Frequency-locked loop (FLL). Digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO)
• Internal reference clocks. Can be used as a clock source for other on-chip peripherals
System oscillator The system oscillator, in conjunction with an external crystal or resonator,
generates a reference clock for the MCU.
1.7.2.6 Security and integrity module
The following security and integrity module is available on this device.
Table 1-8. Security and integrity module
Module Description
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Hardware CRC generator circuit using 16-/32-bit shift register. Error detection for all single,
double, odd, and most multi-bit errors, programmable initial seed value, and optional
feature to transpose input data and CRC result via transpose register.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 22
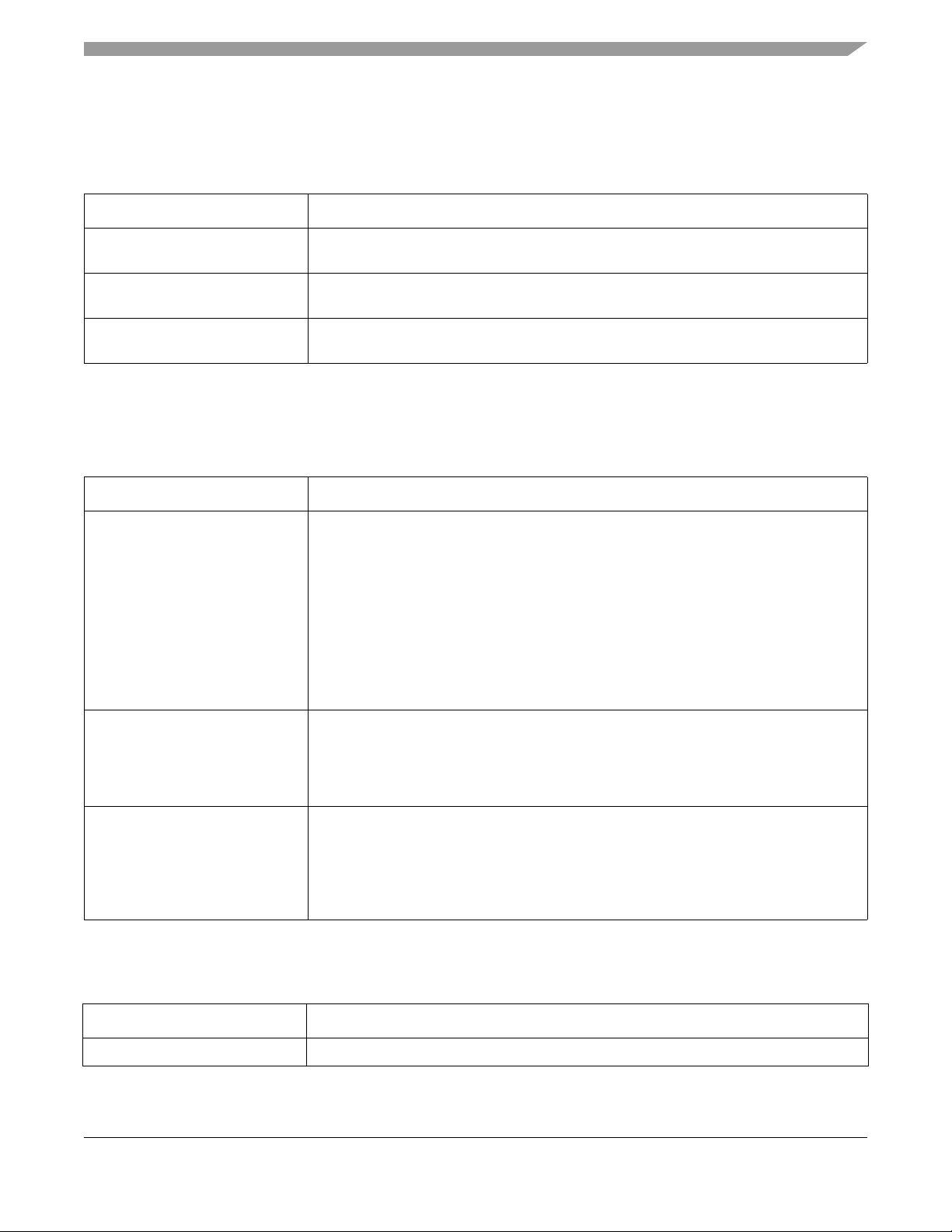
1.7.2.7 Analog modules
The following analog modules are available on this device.
T ab le 1-9. Analog Modules
Module Description
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
16-bit analog-to-digital converters
(ADC)
Internal analog comparators Compares two analog input voltages, one of which can be a reference provided by the
6-bit digital-to-analog converters
(DAC)
16-bit successive-approximation ADC
internal 6-bit DAC, across the full range of the supply voltage.
64-tap resistor ladder network which provides a selectable voltage reference for analog
comparator.
1.7.2.8 Timer modules
The following timer modules are available on this device.
Table 1-10. Timer modules
Module Description
Timer/PWM module (TPM) Selec table TPM clock mode
• Prescaler divide-by 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128
• 16-bit free-running counter or modulo counter with counting be up or updown
• Six configurable channels for input capture, output compare, or edge-aligned PWM
mode
• Support the generation of an interrupt and/or DMA request per channel
• Support the generation of an interrupt and/or DMA request when the counter overflows
• Support selectable trigger input to optionally reset or cause the counter to start
incrementing.
• Support the generation of hardware triggers when the counter overflows and per
channel
Periodic interrupt timers (PIT) • Four general purpose interrupt timers
• Interrupt timers for triggering ADC conversions
• 32-bit counter resolution
• Clocked by system clock frequency
• DMA support
Low-power timer (LPTimer) • Selectable clock for prescaler/glitch filter of 1 kHz (internal LPO), 32.768 kHz (external
crystal), or internal reference clock
• Configurable Glitch Filter or Prescaler with 16-bit counter
• 16-bit time or pulse counter with compare
• Interrupt generated on Timer Compare
• Hardware trigger generated on Timer Compare
1.7.2.9 Radio
Table 1-11. Radio transceiver
Module Description
Sub-GHz transceiver • A highly integrated ISM band transceiver for FSK and OOK packet or continuous data.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1-11
Page 23
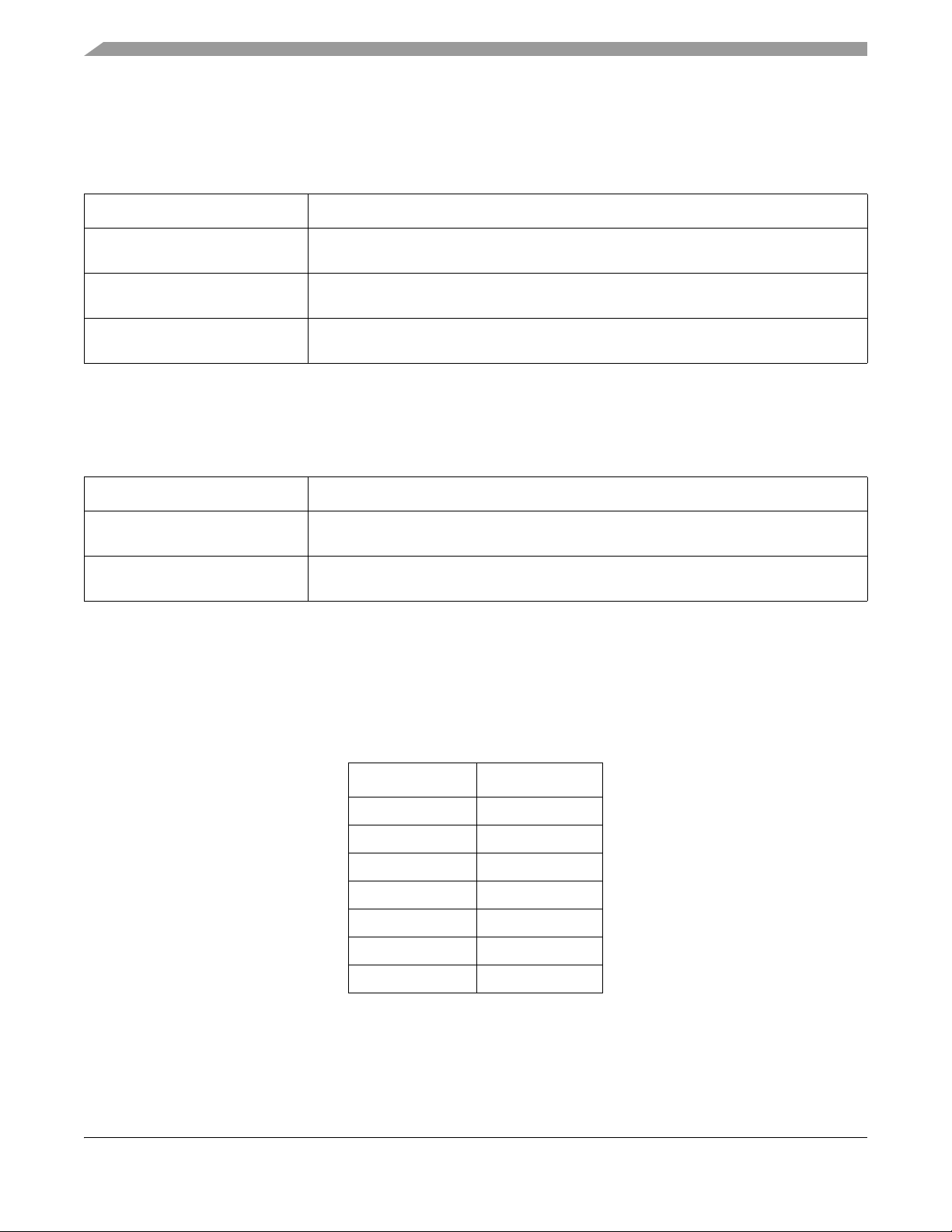
MKW01Z128 Introduction and Chip Configuration
1.7.2.10 Communication interfaces
The following wired communication interfaces are available on this device.
T able 1-12. Communication interfaces
Module Description
Internal serial peripheral interface
(SPI)
Inter-integrated circuit (I2C) Allows communication between a number of devices. Also supports the System
Universal asynchronous
receiver/transmitters (UART)
Synchronous serial bus for communication to an external device
Management Bus (SMBus) Specification, version 2.
Asynchronous serial bus communication interface with programmable 8- or 9-bit data
format
1.7.2.11 Human-machine interfaces
The following human-machine interfaces (HMI) are available on this device.
Table 1-13. HMI modules
Module Description
General purpose input/output
(GPIO)
Capacitive touch sense input (TSI) Contains up to 10 channel inputs for capacitive touch sensing applications. Operation is
All general purpose input or output (GPIO) pins are capable of interrupt and DMA request
generation. All GPIO pins have 5 V tolerance.
available in low-power modes via interrupts.
1.7.2.12 System Device Identification Register
The system device identification register contains device specific information factory programmed into the
in-package MCU die.
Table 1-14. Device-Specific Values
Field ID Value
FAMID 0001
SUBFAMID 0111
SERIESID 0001
SRAMSIZE 0101
REVID 0001
DIEID 01010
PINID 0010
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
1-12 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 24
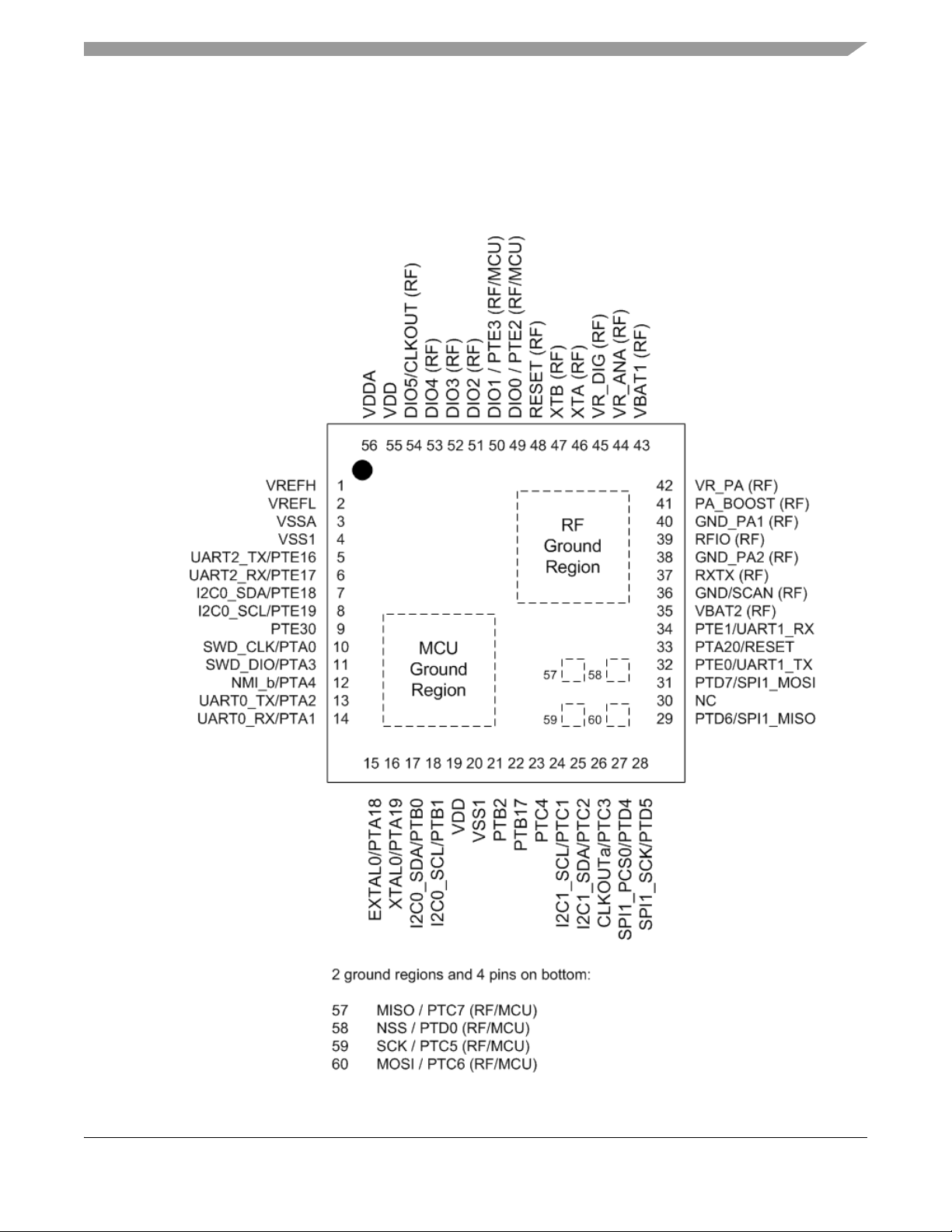
Chapter 2 MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
2.1 Device pin assignment
Figure 2-1. MKW01Z128 pinout
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2-1
Page 25
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
2.2 Pin definitions
Table 2-1 details the MKW01Z128 pinout and functionality.
Table 2-1. Pin Function Description (Sheet 1 of 5)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
1 VREFH Input MCU high reference voltage for ADC
2 VREFL Input MCU low reference voltage for ADC
3 VSSA Power Input MCU ADC Ground Connect to ground
4 VSS Power Input MCU Ground Connect to ground
5 PTE16/ADC0_DP1/ADCO_
SE1/SPI0_PCS0/TPM/
UART2_TX
6 PTE17/ADC0_DM1/ADCO_
SE5a/SPI0_SCK/ TPM_
CLKIN1/UART2_RX/
LPTMR0_ALT3
7 PTE18/ADC0_DP2/ADC0_
SE2/SPI0_MOSI/I2C0_SDA/
SPI0_MISO
8 PTE19/ADC0_DM2/ ADC0_
SE6a/SPI0_MISO /I2C0_SCL/
SPI0_MOSI
9 PTE30/DAC0_OUT/
ADCO_SE23/ CMP0_IN4/
TPM0_CH3/TPM_CLKIN1
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
Digit-l Input /
Output
MCU Port E Bit 16 / ADC0 positive
differential analog channel input DP1/
ADC0 Single Ended analog channel input
SE1 / SPI module 0 PCS0 / TPM module
Clock In 0 / UART2_TX
MCU Port E Bit 17 / ADC0 negative
differential analog channel input DM1/
ADC0 Single Ended analog channel input
5a / SPI module 0 SCK / TPM module
Clock In 1 / UART2_RX / Low Power Timer
Module 0 ALT3
MCU Port E Bit 18 / ADC0 positive
differential analog channel input DP2/
ADC0 Single Ended analog channel input
2 / SPI module 0 MOSI / I2C0 Bus Data /
SPI module 0 MISO
MCU Port E Bit 19 / ADC0 negative
differential analog channel input DM2/
ADC0 Single Ended analog channel input
6a / SPI module 0 MISO / I2C0 Bus Clock /
SPI module 0 MOSI
MCU Port E Bit 30 / DAC0 Output/ ADC0
Single Ended analog channel input 23 /
Comparator 0 Analog Voltage Input 4/ TPM
Timer module 0 Channel 3 / TPM module
Clock In 1
10 PTA0/SWD_CLK/TSI0_CH1/
TPM0_CH5
11 PTA3/SWD_DIO/TSI0_CH4/
I2C1_SCL/TPM0_CH0
12 PTA4/NMI_b/TSI0_CH5/
I2C1_SDA/TPM0_CH1
2-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
MCU Port A Bit 0 / Serial Wire Data Clock
/ Touch Screen Interface Channel 1/ TPM
module 0 Channel 5
MCU Port A Bit 3 / Serial Wire Data DIO /
Touch Screen Interface Channel 4 / I2C1
Bus Clock / TPM module 0 Channel 0
MCU Port A Bit 4/ / Non Maskable
Interrupt_ b/Touch Screen Interface
Channel 5 /I2C1 Bus Data / TPM module 0
Channel 1
Page 26
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
Table 2-1. Pin Function Description (Sheet 2 of 5)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
13 PTA2/TSI0_CH3/UART0_TX/
TPM2_CH1
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port A Bit 2/Touch Screen Interface
Channel 3/UART module 0 Transmit / TPM
module 2 Channel 1
14 PTA1/TSI0_CH2/UART0_RX/
TPM2_CH0
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port A Bit 1/Touch Screen Interface
Channel 2/UART module 0 Receive / TPM
module Channel 0
15 PTA18/EXTAL0/UART1_RX/
TPM_CLKIN0
16 PTA19/XTAL0/UART1_TX/
TPM_CLKIN1/LPTMR0_ALT1
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port A Bit 18 / EXTAL0/ UART
module 1 Receive / TPM module Clock In 0
MCU Port A Bit 19 / XTAL0/ UAR T module
1 Transmit / TPM module Clock In 1
/Low Power Timer module 0 ALT1
17 PTB0/ADC0_SE8/TSI0_CH0/
LL WU_P5/I2C0_SCL/ TPM1_
CH0
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port B Bit 0 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE8 / Touch Screen
Interface Channel 0/ Low Leakage Wake
Up Port 5 / I2C0 Bus Clock / TPM module
1 Channel 0
18 PTB1/ADCO_SE9/TSI0_CH6/
I2C0_SDA/ TPM1_CH1
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port B Bit 1 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE9 / Touch Screen
Interface Channel 6 / I2C0 Bus Data / TPM
module 1 Channel 1
19 VDD Power Input MCU VDD supply input Connect to system VDD
supply
20 VSS Power Input MCU Gro und Connect to ground
21 PTB2/ADC0_SE12/TSI0_
CH7/I2C0_SCL/TPM2_CH0
Digital Input/
Output
MCU Port B Bit 2 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE12 / T ouch Screen
Interface Channel 7 / I2C0 Bus Clock /
TPM Timer module 2 Channel 0
22 PTB17/TSI0_CH10/SPI1_
MISO/UART0_TX/TPM_
CLKIN1/SPI1_MOSI
23 PTC4/LLWU_P8/SPI0_PCS0/
UART1_TX/TPM0_CH3
Digital Input/
Output
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port B Bit 17 / T ouch Screen Interface
Channel 10/SPI1 MOSI or MISO/UART0
TX / TPM timer clock
MCU Port C bit 4 / Low leakage Wake Up
port 8 / SPI0 Chip Select / UART1 TX /
TPM Timer module 0 channel 3
24 PTC1/ADC0_SE15/TSI0_
CH14/LLWU_P6/R TC_CLKIN/
I2C1_SCL/TPM0_CH0
Digital Input
Output /
Analog Input
MCU Port C Bit 1 /ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE15/ Touch Screen
Interface Channel 14/ Low Leakage Wake
Up Port 6 / Real Time Counter Clock Input/
IC1 Bus Clock/ TPM module 0 Channel 0
25 PTC2/ADC0_SE11/TSI0_
CH15/I2C1_SDA/TPM0_CH1
Digital Input /
Output /
Analog Input
MCU Port C Bit 2 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE11/ / T ouch Screen
Interface Channel 15 / I2C1 Bus Data /
TPM module 0 Channel 1
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2-3
Page 27
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
Table 2-1. Pin Function Description (Sheet 3 of 5)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
26 PTC3/LLWU_P7/UART1_RX/
TPM0_CH2/CLKOUTa
Digital Input /
Output
MCU Port C Bit 3 / Low Leakage Wake Up
Port 7 / UART module 1 Receive / TPM
module 0 Channel 2/ Clock OutA
27 PTD4/LLWU_P14/SPI1_
PCS0/UART2_RX/TPM0_
CH4
28 PTD5/ADC0_SE6b/SPI1_
SCK/UART2_TX/TPM0_CH5
29 PTD6/ADC0_SE7b/LLWU_
P15/SPI1_MOSI/UART0_RX/
SPI1_MISO
Digital Input /
Output
Digital Input /
Output /
Analog Input
Digital Input /
Output /
Analog Input
MCU Port D Bit 4 / Low Leak Wake Up Port
14/ SPI module 1 PCS0 / UART2 Receiver
input / TPM module 0 Channel 4
MCU Port D bit 5 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE6b / SPI1 clock /
UART2 TX / TPM module 0 Channel 5
MCU Port D bit 6 / ADC0 Single Ended
analog channel input SE7b / Low leakage
Wake Up port 15 / SPI1 MOSI / UART0 RX
/ SPI module 1 MISO
30 NC No Connect
31 PTD7/SPI0_MISO/UART0_
TX/SPI1_MOSI
Digital Input/
Output
MCU Port D Bit 7 / SPI module 0 MISO /
UART module 0 Transmit / SPI module 1
MOSI
32 PTE0/SPI1_MISO/UART1_
TX/RTC_CLKOUT/CMP0_
OUT/ I2C1_SDA
Digital Input/
Output
MCU Port E Bit 0 / SPI module 1 MISO /
UART module 1 Transmit / Real Time
Counter Clock Output / Comparator 0
Analog voltage Output / I2C1 Bus Data
33 PT A20/RESETB Digital Input/
MCU Port A Bit 20/MCU RESET FTFA_FOPT[RESET_
Output
PIN_CFG] controls the
functionality of this pin.
34 PTE1 / SPI1_MOSI / UART1_
RX /SPI1_MISO / I2C1_SCL
Digital Input/
Output
MCU Port E Bit 1 / SPI module 1 MOSI /
UART module 1 RX / SPI1_MISO / I2C1_
SCL
35 VBAT2 (RF) Power Input Transceiver VDD Connect to system VDD
supply
36 GND/SCAN (RF) Power Input Transceiver Ground Connect to ground
37 RXTX (RF) Digital
Output
Transceiver RX / TX RF Switch Control
Output; high when in TX
38 GND_PA2 (RF) Power Input Transceiver RF Ground Connect to ground
39 RFIO (RF) RF Input /
Transceiver RF Input / Output
Output
40 GND_PA1 (RF) Power Input Transceiver RF Ground Connect to ground
41 PA_BOOST (RF) RF Output Transceiver Optional High-Power PA
Output
42 VR_PA (RF) Power
Output
Transceiver regulated output voltage for
VR_PA use.
De-coupling cap
suggested.
43 VBAT1 (RF) Power Input Transceiver VDD for RF circuitry Connect to system VDD
supply
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
2-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 28
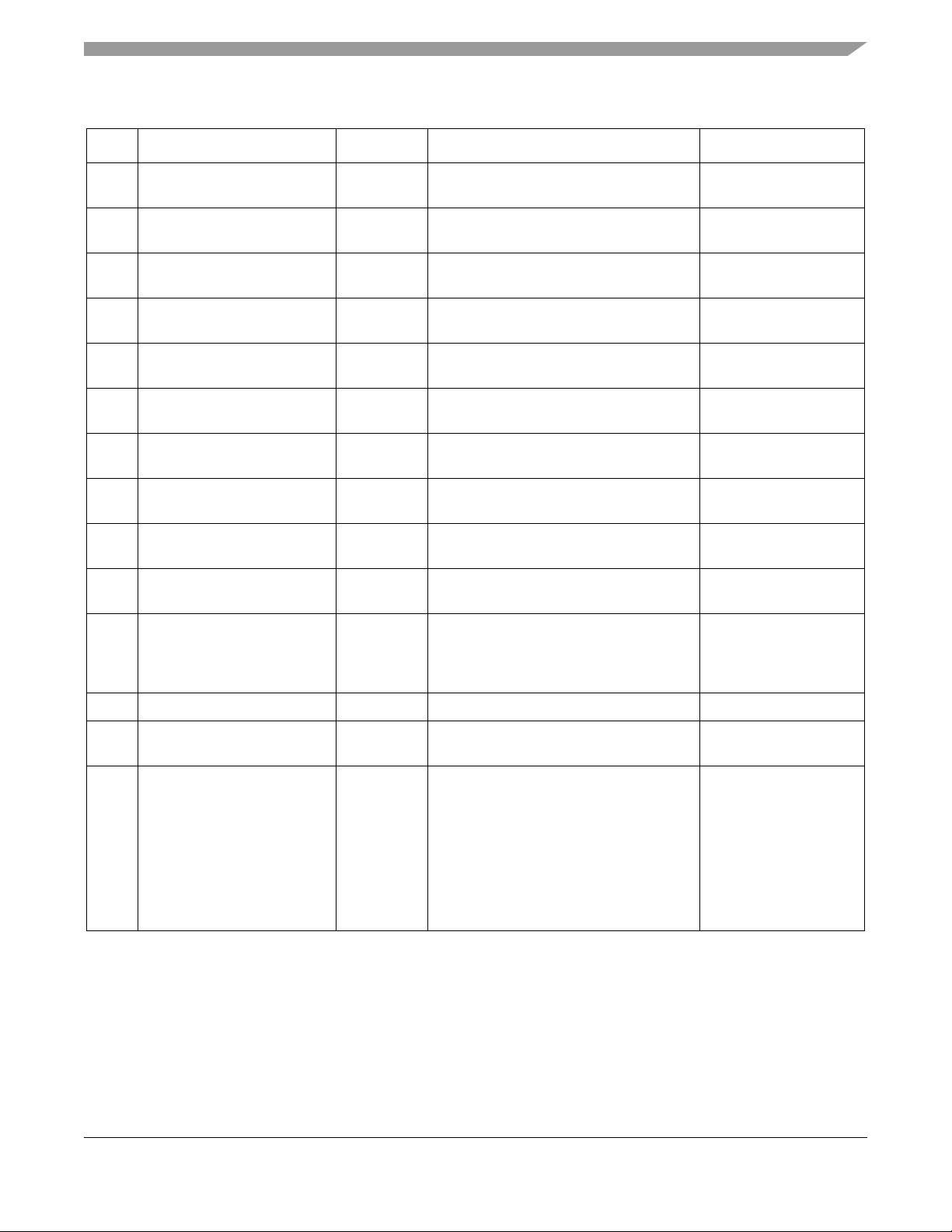
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
Table 2-1. Pin Function Description (Sheet 4 of 5)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
44 VR_ANA (RF) Power
Output
45 VR_DIG (RF) Power
Output
Transceiver regulated output voltage for
analog circuitry.
Transceiver regulated output voltage for
digital circuitry.
Decouple to ground with
100 nF capacitor
Decouple to ground with
100 nF capacitor
46 XTA (RF) Xtal Osc Transceiver crystal reference oscillator Connect to 32 MHz
crystal and load capacitor
47 XTB (RF) Xtal Osc Transceiver crystal reference oscillator Connect to 32 MHz
crystal and load capacitor
48 RESET (RF) Digital Input Transceiver hardware reset input Typically driven from
MCU GPIO
49 DIO0/PTE2/SPI1_SCK Digital Input/
Output
50 DIO1/PTE3/SPI1_MISO/
SPI1_MOSI
Digital Input/
Output
51 DIO2 Digital Input/
Internally connected to Transceiver GPIO
bit 0 and MCU Port E bit 2 / SPI1 clock
Internally connected to Transceiver GPIO
bit 1 and MCU Port E bit 3 /SPI1 in or out
Transceiver GPIO Bit 2
MCU IO and Transceiver
IO connected onboard
MCU IO and Transceiver
IO connected onboard
Output
52 DIO3 Digital Input/
Transceiver GPIO Bit 3
Output
53 DIO4 Digital Input/
Transceiver GPIO Bit 4
Output
54 DIO5/CLKOUT Digital Input/
Output
Transceiver GPIO Bit 5 / ClkOut Commonly programmed
as ClkOut to supply MCU
clock; connect to Pin 15
PTA18/EXTAL0.
55 VDD Power Input MCU VDD supply Connect to VDD supply
56 VDDAD Power Input MCU Analog supply Connect to Analog
supply
57 MISO/PTC7/SPI0_MISO/
SPI0_MOSI
Digital Input/
Output
Internal SPI data connection from
Transceiver MISO bit 1 to MCU SPI0 (Port
C bit 7 )
• MCU IO and
Transceiver IO
connected onboard
• MCU IO must be
configured for this
connection
• SPI0 is dedicated to
radio interface; not for
application usage
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2-5
Page 29
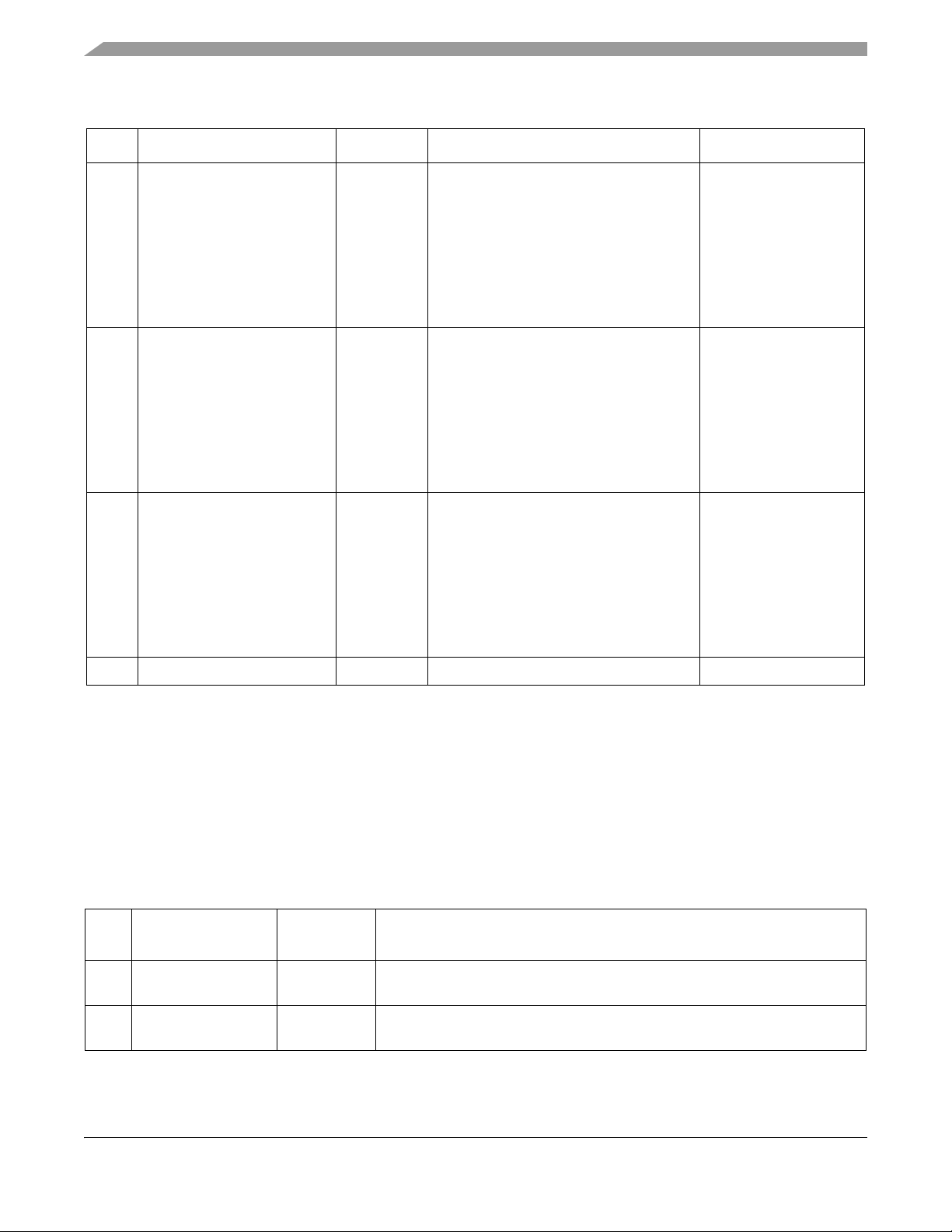
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
Table 2-1. Pin Function Description (Sheet 5 of 5)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
58 NSS/PTD0/SPI0_PCS0 Digital Input/
Output
59 SCK/PTC5/SPI0_SCK Digital Input/
Output
60 MOSI/PTC6/SPI0_MOSI/
SPI0_MISO
Digital Input/
Output
Internal SPI select connection between
Transceiver NSS and MCU SPI0 (Port D bit
0)
Internal SPI clock connection between
Transceiver SCK and MCU SPI0 (port C bit
5)
Internal SPI data connection to Transceiver
MOSI bit 1 to MCU SPI0 (Port C bit 6 )
• MCU IO and
Transceiver IO
connected onboard
• MCU IO must be
configured for this
connection
• SPI0 is dedicated to
radio interface; not for
application usage
• MCU IO and
Transceiver IO
connected onboard
• MCU IO must be
configured for this
connection
• SPI0 is dedicated to
radio interface; not for
application usage
• MCU IO and
Transceiver IO
connected onboard
• MCU IO must be
configured for this
connection
• SPI0 is dedicated to
radio interface; not for
application usage
FLAG VSS Power input External package flag. Common VSS Connect to ground.
2.3 Internal Functional Interconnects
The MCU provides control to the transceiver through the SPI0 Port and receives status from the transceiver
from the DIOx pins. Certain interconnects between the devices are routed in the package. In addition, the
signals are brought out to external pads for monitoring, but only SPI1 is intended for applications usage.
SPI0 is dedicated to the radio interface and should not be used for applications.
Table 2-2. MKW01Z128 Internal Functional Interconnects
Pin # MCU Signal
49
DIO0/PTE2/SPI1_
SCK
50 DIO1/PTE3/SPI1_
MISO/SPI1_MOSI
Transceiver
Signal
DIO0 Transceiver DIO0 can be programmed to provide status to the MCU
DIO1 Transceiver DIO1 can be programmed to provide status to the MCU
Description
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
2-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 30
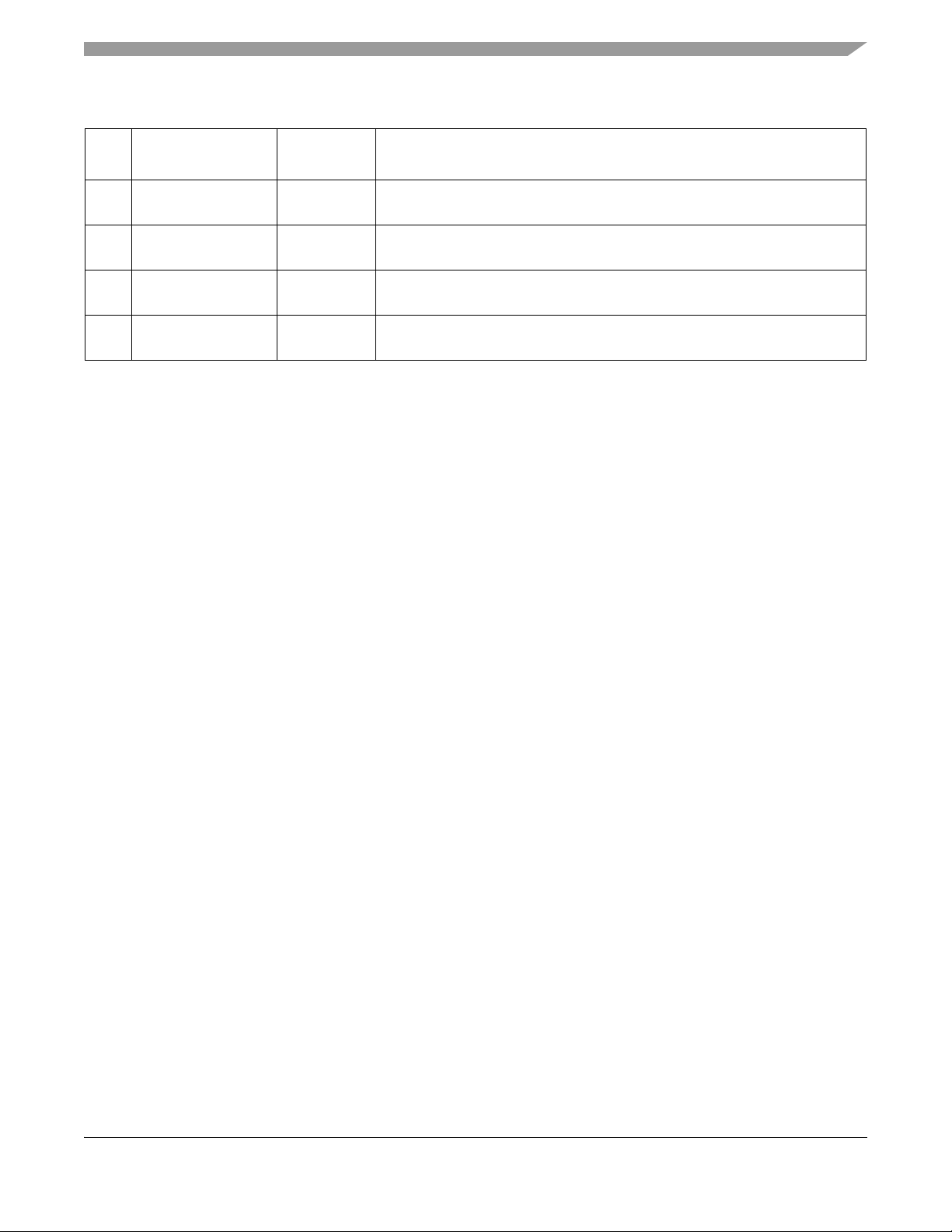
MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
Table 2-2. MKW01Z128 Internal Functional Interconnects
Pin # MCU Signal
57 MISO/PTC7/SPI0_
MISO/SPI0_MOSI
58 NSS/PTD0/SPI0_
PCS0
SCK/PTC5/SPI0_
59
SCK
60 MOSI/PTC6/SPI0_
MOSI/SPI0_MISO
• As shown in Table 2-2, the MCU SPI Port pin selection must be
configured by software by writing the corresponding port multiplex
control registers
• The transceiver DIO pins must be programmed to provide desired status
Transceiver
Signal
MISO SPI data from transceiver to MCU
NSS PTD0 programmed as SPI chip select
SCK SPI Clock
MOSI SPI data from MCU to transceiver
Description
NOTE
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2-7
Page 31

MKW01Z128 Pins and Connections
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
2-8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 32

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
Chapter 3 Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
3.1 Introduction
T o optimize functionality in small packages, pins have several functions available via signal multiplexing.
This chapter illustrates which of this device's signals are multiplexed on which external pin.
The Port Control block controls which signal is present on the external pin. Reference that chapter to find
which register controls the operation of a specific pin.
3.2 Signal Multiplexing Integration
This section summarizes how the module is integrated into the device. For a comprehensive description of
the module itself, see the module's dedicated chapter.
Figure 3-1. Signal Multiplexing Integration
Table 3-1. Reference Links to Related Information
T opic Related Module Reference
Full description Port control Section 3.2.1, “Port control and interrupt
module features ”
System memory map Section 1.7.2, “MCU overview”
Clocking Clock distribution
Register access Peripheral bus controller Peripheral bridge
3.2.1 Port control and interrupt module features
• 32-pin ports
NOTE
Not all pins are available on the device. See the following sections for
details.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 3-1
Page 33

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
• Port A and port D are each assigned one interrupt. For DMA requests, port A and port D each have
a dedicated input to the DMA multiplex.
• Port A is assigned a dedicated interrupt and port C and port D share an interrupt. For DMA
requests, port A, port C, and port D each have a dedicated input to the DMA multiplex.
The reset state and read/write characteristics of the bit fields within the PORTx_PCRn registers are
summarized in the table below.
Table 3-2. Reset State of PORTx_PCRn Register Bit Fiel d s
This field of
PORTx_PC Rn
PS 1 PTA0 0 Yes - All GPIO are configurable
PE 0 PTA0 and PTA2 1 Yes - All GPIO are configurable
DSE 0 No exceptions — 4 pins are configurable for High Drive
SRE 1 PTA3, PTA4, PTB17,
MUX 000 PTA0, PTA3, PTA4 111 Yes - All GPIO are configurable
PFE 0 PTA 20, all other PFE
IRQC 000 No exceptions - all are
ISF 0 No exceptions - all are
1
The RESET pin has the passive analog filter fixed enabled when functioning as the RESET pin (FOPT[RESET_PIN_CFG]
= 1) and fixed disabled when configured for its alternate function: PTA20 (FOPT[RESET_PIN_CFG] = 0).
Generally
resets to
Except for Resets to Configurability
(PTB0, PTB1, PTD6, PTD7). All others are
fixed for Normal Drive and the associated
DSE bit is read only.
0 Yes - All GPIO are configurable
PTC3, PTC4, PTC5,
PTC6, PTC7, PTD4,
PTD5, PTD6 PTD7
are cleared on reset.
cleared on reset.
cleared on reset.
1
— Only implemented for ports that support
— Only implemented for ports that support
The GPIO shared with NMI_b pin is
configurable. All other GPIO is fixed and
read only.
interrupt and DMA functionality.
interrupt and DMA functionality.
3.2.2 Clock gating
The clock to the port control module can be gated on and off using the SCGC5[PORTx] bits in the SIM
module. These bits are cleared after any reset, which disables the clock to the corresponding module to
conserve power . Prior to initializing the corresponding module, set SCGC5[POR Tx] in the SIM module to
enable the clock. Before turning off the clock, make sure to disable the module. For more details, refer to
the clock distribution chapter.
3.2.3 Signal multiplexing contraints
A given peripheral function must be assigned to a maximum of one package pin. Do not program the same
function to more than one pin.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
3-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 34

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
To ensure the best signal timing for a given peripheral's interface, choose the pins in closest proximity to
each other.
3.3 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing
The following table shows the signals available on each pin and the locations of these pins on the MKW01.
The Port Control Module is responsible for selecting which ALT functionality is available on each MCU
pin. Both MCU and transceiver pins are shown, for transceiver pin assignment see Section 7.3, “Digital
IO Pins Mapping”. For those package pins which are connected internally to both the MCU and the
transceiver, both devices must be configured in software for the appropriate function. Likewise where an
MCU pin is connected to a transceiver pin off-chip.
Table 3-3. MKW01 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing (Sheet 1 of 4)
Pin
No.
1 VREFH VREFH VREFH
2 VREFL VREFL VREFL
3 VSSA VSSA VSSA
4 VSS1 VSS1 VSS1
5 PTE16 PTE16 ADC0_
6 PTE17 PTE17 ADC0_
7 PTE18 PTE18 ADC0_
8 PTE19 PTE19 ADC0_
Pin
Name
MCU die
XCVR
die
Default alt 0 alt 1 alt 2 alt 3 alt 4 alt 5 alt 6 alt 7
DP1/
ADC0_
SE1
DM1/
ADC0_
SE5a
DP2/
ADC0_
SE2
DM2/A
DC0_S
E6a
ADC0_
DP1/
ADC0_
SE1
ADC0_
DM1/
ADC0_
SE5a
ADC0_
DP2/
ADC0_
SE2
ADC0_
DM2/A
DC0_S
E6a
PTE16 SPI0_
PCS0
PTE17 SPI0_
SCK
PTE18 SPI0_
MOSI
PTE19 SPI0_M
ISO
UART2
_TX
UART2
_RX
TPM_
CLKIN
0
TPM_
CLKIN
1
I2C0_
SDA
I2C0_
S CL
LPTM
R0
_AL T
3
SPI0_
MISO
SPI0_
M OSI
9 PTE30 PTE30 DAC0_
OUT/
ADC0_
SE23/
CMP0_
IN4
10 PTA0 PTA0 SWD_
CLK
11 PTA3
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 3-3
PTA3 SWD_
DIO
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
DAC0_
OUT/
ADC0_
SE23/
CMP0_
IN4
TSI0_
CH1
TSI0_
CH4
PTE30
PTA0 TPM0_
PTA3 I2C1_S
CL
TPM0_
CH3
CH5
TPM0_
CH0
TPM_
CLKIN
1
SWD_
CLK
SWD_
DIO
Page 35

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
Table 3-3. MKW01 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing (Sheet 2 of 4)
Pin
No.
12 PTA4
13 PTA2 PTA2 DISABL
14 PTA1 PTA1 DISABL
Pin
Name
MCU die
XCVR
die
Default alt 0 alt 1 alt 2 alt 3 alt 4 alt 5 alt 6 alt 7
PTA4 NMI_b TSI0_
CH5
TSI0_
ED
CH3
TSI0_
ED
CH2
PTA4 I2C1_S
DA
PTA2 UART0
_TX
PTA1 UART0
_RX
TPM0_
CH1
TPM2_
CH1
TPM2_
CH0
15 PTA18 PTA18 EXTAL0 EXTAL0 PTA18 UART1
_RX
16 PTA19 PTA19 XTAL0 XTAL0 PTA19 UART1
_TX
17 PTB0 PTB0 ADC0_
SE8/
TSI0_
CH0
18 PTB1 PTB1 ADC0_
SE9/TSI
0_CH6
ADC0_
SE8/
TSI0_
CH0
ADC0_
SE9/
TSI0_C
PTB0/
LLWU_
I2C0_
SCL
P5
PTB1 I2C0_
SDA
TPM1_
CH0
TPM1_
CH1
H6
TPM_
CLKIN
0
TPM_
CLKIN
1
NMI_
b
LPTM
R
0_AL
T1
19 VDD VDD VDD
20 VSS1 VSS1 VSS1
21 PTB2 PTB2 ADC0_
SE12/
TSI0_
CH7
22 PTB17 PTB17 TSI0_
CH10
23 PTC4 PTC4 DISABL
ED
24 PTC1 PTC1 ADC0_
SE15/
TSI0_
CH14
25 PTC2 PTC2 ADC0_
SE11/
TSI0_
CH15
ADC0_
SE12/
TSI0_
CH7
TSI0_
CH10
ADC0_
SE15/
TSI0_
CH14
ADC0_
SE11/
TSI0_
CH15
PTB2 I2C0_
SCL
PTB17 SPI1_
MISO
PTC4/
LLWU_
SPI0_
PCS0
P8
PTC1/
LLWU_
I2C1_S
CL
P6/RTC
_CLKIN
PTC2 I2C1_
SDA
TPM2_
CH0
UART0
_TX
UART1
_TX
TPM_
CLKIN
1
TPM0
_ CH3
TPM0
_ CH0
TPM0
_ CH1
SPI1_
MOSI
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
3-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 36

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
Table 3-3. MKW01 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing (Sheet 3 of 4)
Pin
No.
26 PTC3 PTC3 DISABL
Pin
Name
MCU die
XCVR
die
Default alt 0 alt 1 alt 2 alt 3 alt 4 alt 5 alt 6 alt 7
PTC3/
ED
LLWU_
P7
27 PTD4 PTD4 DISABL
ED
PTD4/
LLWU_
P14
28 PTD5 PTD5 ADC0_
SE6b
29 PTD6 PTD6 ADC0_
SE7b
ADC0_
SE6b
ADC0_
SE7b
PTD5 SPI1_
PTD6/
LLWU_
P15
30 NC NC
31 PTD7 PTD7 DISABL
PTD7 SPI1_
ED
32 PTE0 PTE0 DISABL
PTE0 SPI1_
ED
33 PTA20 PTA20 RESET _b PTA20
34 PTE1 PTE1 DISABL
PTE1 SPI1_
ED
SPI1_
PCS0
SCK
SPI1_
MOSI
MISO
MISO
MOSI
UART1
_RX
UART2
_RX
UART2
_TX
UART0
_RX
UART0
_TX
UART1
_TX
UART1
_RX
TPM0
_ CH2
TPM0
_ CH4
TPM0
_ CH5
RTC_
CLKO
UT
CLKO
UT
SPI1_
MISO
SPI1_
MOSI
CMP0_
OUT
SPI1_
MISO
I2C1_
SDA
I2C1_
SCL
35 VBAT2 VBAT2 VBAT2
36 GND/SC
A N
GND/
SCAN
GND/
SCAN
37 RXTX RXTX RXTX
38 GND_P
A2
GND_P
A2
GND_
PA2
39 RFIO RFIO RFIO
40 GND_P
A1
41 PA_BO
OS T
GND_P
A1
PA_
BOOST
GND_
PA1
PA_
BOOST
42 VR_PA VR_PA VR_PA
43 VBAT1 VBAT1 VBAT1
44 VR_AN
VR_ANA VR_ ANA
A
45 VR_DIG VR_DIG VR_DIG
46 XTA XTA XTA
47 XTB XTB XTB
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 3-5
Page 37

Signal Multiplexing and Signal Descriptions
Table 3-3. MKW01 Pin Assignments and Signal Multiplexing (Sheet 4 of 4)
Pin
No.
48 RESET
49 DIO0 /
50 DIO1 /
Pin
Name
PTE2
PTE3
MCU die
XCVR
die
Default alt 0 alt 1 alt 2 alt 3 alt 4 alt 5 alt 6 alt 7
RESET RESET
PTE2 DIO01DISABL
ED
PTE3 DIO11 DISABL
ED
51 DIO2 DIO21
52 DIO3 DIO31
53 DIO4 DIO41
54 DIO5 DIO51 CLKOU T
55 VDD VDD VDD
56 VDDA VDDA VDDA
57 MISO /
PTC7
58 NSS /
PTD0
59 SCK /
PTC5
PTC7 MISO CMP0_
IN1
PTD0 NSS DISABL
ED
PTC5 SCK DISABL
ED
CMP0_
IN1
PTE2 SPI1_
SCK
PTE3 SPI1_
MISO
SPI0_
MISO
PTD0 SPI0_
PCS0
PTC5/
LLWU_
SPI0_
SCK
P9
SPI1_
MOSI
60 MOSI /
PTC6
1
See Section 7.3, “Digital IO Pins Mapping” for DIO mapping.
PTC6 MOSI CMP0_
IN0
CMP0_
IN0
PTC6/
LLWU_
P10
SPI0_
MOSI
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
3-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 38

Chapter 4 System Considerations
4.1 Introduction
The MKW01Z128 is the embodiment of a sub-1 GHz wireless node in a single SiP package. All control
of the node is done through the in-package Kinetis KL26 48 MHz processor, and all MCU peripherals,
MCU GPIO, transceiver functionality , and transceiver GPIO are manipulated by the processor. The MCU
GPIO and MCU peripherals are accessed as ports from the MCU internal bus and can be programmed
directly.
Communication to the transceiver is through the common SPI0 bus and several MCU GPIO lines. Primary
interface with the transceiver is through the SPI command structure that allows reading/writing registers
and provides initialization of parameters, reading of status, and control of transceiver operation. The
transceiver also has two status signals tied to MCU GPIO internally and requires several others to be tied
externally.
This chapter presents information addressing application and operation of the node from a system level.
The areas considered here are also covered in greater detail in the following sections of the book. The book
is organized such that the first three chapters present the top-level view of the MKW01Z128 device and
the following chapters present individual functions in detailed descriptions.
4.2 Power connections
The MKW01Z128 power connections at the SiP level are listed in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. Power pin descriptions
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
3 VSSA Power Input MCU ADC Ground Connect to ground
4 VSS Power Input MCU Ground Connect to ground
19 VDD Power Input MCU VDD Connect to MKW01Z128 VDD
supply
20 VSS Power Input MCU Ground Connect to ground
35 VBAT2 Power Input Transceiver VDD Connect to MKW01Z128 VDD
supply
36 GND/SCAN Power Input Transceiver Ground Connect to ground
38 GND_PA2 (RF) Power Input Transceiver RF Ground Connect to ground
40 GND_PA1 (RF) Power Input Transceiver RF Ground Connect to ground
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-1
Page 39

System Considerations
Table 4-1. Power pin descriptions (continued)
Pin # Pin Name Type Description Functionality
42 VR_PA Power Output Transceiver regulated output voltage for
VR_PA use.
43 VBAT1 (RF) Power Input Transceiver VDD for RF circuitry Connect to MKW01Z128 VDD
supply
44 VR_ANA Power Output Transceiver regulated output voltage for
analog circuitry.
45 VR_DIG Power Output Transceiver regulated output voltage for
digital circuitry.
55 VDD Power Input MCU VDD supply Connect to MKW01Z128 VDD
56 VDDA Power Input MCU ADC VDD Connect to MKW01Z128 VDD
FLAG1VSS Power input External package flag. Common VSS Connect to ground.
1
Flags on bottom of package are electrically separate. Both must be connected to ground.
Decouple to ground with 100
nF capacitor
Decouple to ground with 100
nF capacitor
supply
supply
When designing power to the MKW01Z128 SiP, the following points need to be considered:
• The SiP package has two ground flags (VSS) on chip the package (pin 4 and pin 20). These are
separated and both must be connected to system ground.
• The MCU VDD power supply connections include
— VDD (Pin 19)
— VDD (Pin 55)
— The VDDA (Pin 56) analog supply to the MCU ADC is also normally wired to the common
source supply.
• For the transceiver the primary power inputs include
— VBAT2 (Pin 35)
— VBAT1 (Pin 43)
— Both VBAT1 and VBAT2 should be powered together from the same circuitry
• The transceiver provides on-chip voltage regulator outputs for bypassing — VR_ANA (Pin 44) regulated voltage to analog circuitry; bypass to ground
— VR_DIG (Pin 45) regulated voltage to digital circuitry; bypass to ground
• The transceiver provides a regulated output VR_PA (Pin 42) for with RF power boost mode.
• Additional system ground pins include — VSS (Pin 4 and Pin 20) - MCU ground
— VSSA (Pin 3) - MCU ATD ground
— GND (Pin 36) - transceiver ground
— GND_PA1 (Pin 40) and GND_PA2 (Pin 38) - transceiver RF grounds
Power supply connections are shown in Figure 4-1.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 40

System Considerations
43
100 nF
56
19
4
20
3
FLAG
VSS
VSSAD
MKW01
VBAT1
VBAT2
VR_DIG
VR_ANA
GND_PA2
GND_PA1
GND
35
45
44
38
40
36
100 nF
100 nF100 nF
100 nF
55
FLAG
VSS
VSS
VSS
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDDA
Figure 4-1. MKW01Z128 power supply connections
NOTE
Depending on the application, the VREFH high reference voltage for the
ADC module is commonly also tied to the VDD common supply and the
VREFL low reference voltage is tied to ground.
4.3 System functional interconnects
The MKW01Z128 comprises two separate devices in a single package. The MCU controls the transceiver
and there are connections between the devices for several functions.
• Some connections are provided on chip
• Additional external connections may also be used depending on the application needs.
— Transceiver reset
— Clock interconnect
— Additional transceiver status
— Enhanced packet performance
4.3.1 In-package Connections (SPI Channel and Status)
The internal (in-package) device connections are listed in Table 2-2. These include:
• SPI communication channel - see Chapter 8, “MKW01Z128 Transceiver - MCU SPI Interface”
• Transceiver DIO0 and DIO1 outputs as status - these status outputs are used to manage the data
• flow and transceiver sequencer during radio packet mode operation. Enhanced performance can be
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-3
obtained by additionally connecting these pins externally to other GPIO pins described below.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 41

System Considerations
4.3.2 System Reset
The MKW01Z128 system does not have a master input that resets the entire SiP:
• The MCU reset input is pin 33, RESET_b — use of this pin as an external reset is optional, and the
MCU has a separate power-on reset (POR).
• The transceiver has an independent reset pin (RESET), pin 48 — this signal is typically connected
to an MCU GPIO to provide total software control of the transceiver
NOTE
It is recommended that the MCU be connected to the transceiver reset via
an MCU GPIO pin to provide best overall hardware control.
4.3.2.1 MCU Reset pin (pin 33)
On this device, RESET is a dedicated input pin for which filtering can be enabled. This pin is open drain
and has an internal pullup device. This pin can be disabled or configured as a GPIO (PTA20). Asserting
RESET (low) wakes the device from any mode. During a pin reset, the RCM's SRS0 PIN bit is set. The
MCU's Low Voltage Detect (LVD) can also generate a reset.
4.3.2.2 Transceiver Reset
The transceiver can be reset via two means:
• A power-on reset (POR) of the MKW01Z128 transceiver is triggered when VDD is applied to
VBAT1 and VBAT2.
• A hardware reset can be issued by controlling Pin 48 (transceiver RESET).
4.3.2.2.1 Transceiver POR
Similar to the MCU, a transceiver POR is internally generated when power is applied to VDD. See
Figure 4-2 for the transceiver POR timing diagram.
• The transceiver hardware RESET pin is bidirectional and is first driven to high as the result of the
POR.
• The RESET signal is then driven low , and the application must wait for 10 ms from the end of the
POR cycle before commencing communications over the SPI bus.
• RESET should be left floating during the POR sequence.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 42

System Considerations
Figure 4-2. POR Timing Diagram
NOTE
Any CLKOUT activity can also be used to detect when the chip is ready.
4.3.2.2.2 Transceiver Hardware Reset
A hardware reset of the transceiver on MKW01Z128 is also possible by asserting RESET high for a
minimum of one hundred microseconds, and then releasing. The application must wait 5 ms before using
the chip.
Figure 4-3. Manual Reset Timing Diagram
NOTE
While RESET is driven high, additional current consumption of up to ten
milliamps may be seen on VDD.
4.3.2.3 MCU Control of Transceiver Reset
It is recommended to provide hardware reset capability of the transceiver via an MCU GPIO externally
connected to the transceiver RESET pin. For Freescale applications software, MCU signal PTE30 is the
preferred GPIO to control the RESET.
4.3.3 External Clock Connections
It is possible that the transceiver can supply a clock source to the MCU through external connections. The
transceiver can output a clock signal on pin 54 DIO5/CLKOUT. The transceiver can be configured (via
the SPI) to select various clock frequencies that are divided from the transceiver external crystal frequency
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-5
Page 43

System Considerations
being applied to XTA and XTB pins. This output clock can be connected to pin 15 PTA18/EXTAL0 ,
externally , and provide the clock source to the MCU's MCG module, thus providing the CPU and System
clock of the MCU.
NOTE
From POR and from an MCU reset (on pin 33) the MCU will by default
select the internal RC oscillator as the clock source to the CPU.
In Idle mode (a phase of Listen mode), the 32 MHz crystal oscillator of the
transceiver is disabled. If this signal, or a derivative thereof, is used as the
MCU clock via CLKOUT to EXT A L0, care should be taken in firmware to
configure the MCU clock to an internal low-power clock immediately prior
to asserting Listen mode to prevent loss of clock affecting MCU
performance.
4.4 System Clock Sources and Configurations
The MKW01Z128 clock connections are shown in Figure 4-4. The device allows for a wide array of
system clock configurations.
• Pins are provided for a separate external clock source for the CPU. The external clock source can
by derived from a crystal oscillator or from an external clock source
• The transceiver optionally provides a ClkOut programmable frequency clock output that can be
used as an external source to the CPU. As a result, a single crystal system clock solution is possible.
This is the preferred configuration
• Pins are provided for a 32 MHz crystal for the transceiver reference oscillator (crystal can be 28 to
33 MHz but all frequencies derived from Fref must be appropriately calculated)
• The MCU contains an internal nominal 32 kHz clock oscillator (which can be trimmed) that can
be used to run the MCU
• Out of reset, the MCU uses the internal oscillator and the on-chip FLL to generate an
approximately 20 MHz clock for start-up. This allows recovery from stop or reset without a long
crystal start-up delay
In addition, the transceiver has an on-chip RC oscillator that is used only internally for triggering periodic
listen modes.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 44

System Considerations
Figure 4-4. MKW01Z128 Clock Connections (Upper figure is the preferred configuration.)
4.4.1 Additional Transceiver Status Signals
The MKW01Z128 transceiver has a total of six outputs (DIO5:DIO0) that can be programmed as status
indicators:
• DIO1 and DIO0 are connected to MCU GPIOs, PTE3 & PTE2, internally to the package. For
certain software configurations, improved performance can be obtained by connecting to
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-7
Page 45

System Considerations
additional GPIOs, P TC4, and P TC3, of f chip. These connections are used by applications software
in packet mode.
• At the user’s discretion, the additional DIO5:DIO2 can be connected externally to the MCU GPIO
and programmed as status indicators -
— Use of selected signals must be programmed on the transceiver
— If interrupt request (IRQ) capability is desired, any status signal must be connected to an IRQ
capable GPIO pin.
4.4.2 Transceiver Oscillator
The transceiver crystal oscillator is the main timing reference of the device. The transceiver oscillator
source must always be present and an external crystal is typically used to implement the oscillator,
although an external TCXO may also be used (see Section 5.5.1, “Reference Oscillator”). The source
frequency is normally 32 MHz.
In Figure 4-4 crystal Y1 and two capacitors form the transceiver crystal oscillator circuit. An off board
feedback resistor between input XTA and output XTB is not required. An important parameter for the
crystal Y1 is the load capacitance. The oscillator needs to see a balanced load capacitance at each terminal,
and as a result, the sum of the stray capacitance of the pcb board, device pin (XTA or XTB), and load
capacitor at each terminal should be equal. The amount of external load capacitance is determined by the
specific crystal specification.
NOTE
• There is no on-chip trim capacitance, therefore the user should evaluate
and size the external load capacitors to center the oscillator frequency
within the cut tolerance of the crystal.
• The frequency accuracy of the crystal (cut tolerance plus temperature
variation) must be matched to the required specification of the
application.
• T o compensate for reference error , actual RF frequency can be adjusted
to the desired frequency by offsetting of the PLL control word, Frf.
4.4.2.1 Crystal Resonator Specification
Table 4-2 shows the crystal resonator specification for the crystal reference oscillator circuit of the
MKW01Z128 transceiver. This specification covers the full range of operation and is employed in the
reference design.
Table 4-2. Crystal Specification
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
FXOSC XTAL Frequency 26 32 33 MHz
Rs XTAL Serial Resistance - 30 140 ohms
C0 XTAL Shunt Capacitance - 2.8 7 pF
CLOAD External Foot Capacitance On each pin XTA and XTB 8 16 22 pF
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 46

System Considerations
NOTE
• The initial frequency tolerance (cut tolerance), temperature stability and
aging performance should be chosen in accordance with the target
operating temperature range and the receiver bandwidth selected.
• The loading capacitance should be applied externally , and adapted to the
actual C
specification of the crystal.
load
• A minimum crystal frequency of 28 MHz is required to cover the
863-870 MHz band and 29 MHz for the 902-928 MHz band.
4.4.2.2 Transceiver ClkOut Output (DIO5)
The reference frequency, or a fraction of it, can be provided as an output on DIO5. Use of the ClkOut
output allows:
• Driving the clock source to the MCU — Saves the cost of an additional crystal.
— ClkOut can be made available in any operation mode except Sleep mode and is automatically
enabled at power-on reset.
• Trimming of the reference oscillator frequency - ClkOut can be provided as a test point for a
frequency counter to allow trimming of the external load capacitance during design/evaluation.
The ClkOut functionality is controlled by programming transceiver Register RegDioMapping2 (0x26)
(see Section 7.10, “IRQ and Pin Mapping Registers”):
• Bits 5:4 - control the function of DIO5 and enable ClkOut. See Table 7-2 and Table 7-3.
• Bits 2:0 - control the ClkOut frequency.
Table 4-3 lists ClkOut frequency versus Bits 2:0 setting using a 32 MHz reference source.
Table 4-3. ClkOut Frequency Using 32 MHz Reference Oscillator
ClkOut
Bits 2:0
000 1 32
001 1/2 16
010 1/4 8
011 1/8 4
100 1/16 2
101 1/32 1
110 RC 62.5 kHz
111 - OFF
Divide
Ratio
ClkOut Frequency
(MHz)
(Automatically enabled)
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-9
Page 47

System Considerations
4.4.3 MCU Clock Sources
The MCU has several options for its primary clock source depending on its mode of operation as well as
its hardware configuration.
• The ICS module has an on-chip 32 kHz (nominal) oscillator and FLL — Provides start-up run clock
— The oscillator can be used with or without the FLL
— The FLL can be used with an external clock/crystal
• External pins are provided to accommodate an external crystal, resonator, or clock source.
• A separate low power 1 kHz oscillator (LPO) can be used for the real time counter (RTC) or the
COP timer.
4.4.3.1 MCU External Clock Source
As shown in Figure 4-4, the external pins associated with the MCU clock source are output XTAL and
input EXT AL. (External pin names are XTAL0 and EXT AL0.) An external clock source (such as ClkOut)
can have a frequency as high as 40 MHz with no minimum frequency. The external source must have
compatible logic levels and drive input EXTAL. Note that no external components are required for the
clock oscillator if an external source is used.
4.4.3.2 MCU External Crystal Oscillator
Referring again to Figure 4-4, another choice is the use of an external crystal or ceramic resonator, shown
as Y2. The MCU oscillator is a Pierce type that can accommodate crystals or resonators in any of four
modes:
• 30 to 40 kHz low frequency range crystal — low power
• 30 to 40 kHz low frequency range crystal — high gain
• 3~32 MHz high frequency range crystal — low power
• 3~32 MHz high frequency range crystal — High gain
RF must be a low-inductance resistor such as carbon composition. Wire-wound resistors, and some metal
film resistors, have too much inductance. Cy and Cx normally must be high-quality ceramic capacitors
specifically designed for high-frequency applications.
is used to provide a bias path to keep the EXT AL input in its linear range during crystal startup; its value
R
F
is not generally critical. T ypical systems use 1 M to 10 M. Higher values are sensitive to humidity and
lower values reduce gain and (in extreme cases) could prevent startup. With the low-power mode, the
oscillator has the internal feedback resistor RF. Therefore, the feedback resistor must not be externally
Cy and Cx are typically not used when a low frequency crystal is chosen. With a high frequency range
crystal, these capacitors will be in the 5 pF to 25 pF range and are chosen to match the requirements of a
specific crystal or resonator. Take into account printed circuit board (PCB) capacitance and MCU pin
capacitance when selecting Cy and Cx. The crystal manufacturer typically specifies a load capacitance
which is the series combination of Cy and Cx (which are usually the same size). As a first-order
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 48

System Considerations
approximation, use 10 pF as an estimate of combined pin and PCB capacitance for each oscillator pin
(EXTAL and XTAL).
When using the oscillator in low frequency range modes, the external components Cx and Cy are not
required.
When using the oscillator in low power modes, the external RF is not required and should not be used.
4.4.3.3 MCU Internal Clock Source
The MKW01 has an internal reference clock (nominally 32 kHz) that is used in a number of ways:
• Default MCU clock out of reset - the internal ICS clock module defaults to the internal oscillator
enabled and the FLL engaged. The resulting default CPU clock frequency is a nominal 20 MHz
(10 MHz bus clock).
• Programmable system clock - either used with or without the FLL, the internal oscillator can
remain as the normal RUN frequency source
— Nominal maximum CPU clock of 48 MHz
— Total trimmed frequency deviation of +/-2% maximum
• Wake-up clock for low power modes - the internal oscillator can be enabled to clock the RTC to
provide a wake-up timer from Stop2 or Stop3
4.4.3.4 LPO 1 kHz Oscillator
The LPO is independent of the ICS module and can be used to clock the R TC or COP. Its period can vary
greatly from 0.7–1.3 ms.
4.4.4 System Clock Configurations
Because of the multiple clock configurations of the MCU, the availability of external clock source pins of
both the transceiver and the MCU, and the ClkOut output from the transceiver, there are a number of
variations for MKW01Z128 system clock configurations. Key considerations for any system clock
configuration are:
• The transceiver 32 MHz source (typically the reference crystal oscillator) must always be present.
• Battery-operated application requirements for low power can impact the choices for MCU clock
source.
• The system clock configuration will impact system initialization procedures.
• Software requirements can impact MCU processor and bus speed - The user must be aware of the
performance requirements for the MCU. The CPU clock is always 2X the internal bus speed, and
the application software may impact the required system clock rate.
As far as external connections are concerned, there are three possibilities which are covered in the
following sections.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-11
Page 49

System Considerations
NOTE
In the following sub-sections, it is assumed that the MCU GPIO is
connected to drive the transceiver reset.
4.4.4.1 Single crystal with ClkOut driving MCU EXTAL input
The single crystal (transceiver) with ClkOut driving the MCU EXTAL input (external clock) is the most
common configuration for low cost and excellent frequency accuracy. The ClkOut frequency is
programmable but setting the divide ratio to 1 resulting in a 32 MHz CLKOUT (with a 32 MHz crystal) is
recommended to drive the MCU external source.
In this configuration, clock start-up from a reset condition involves:
• MCU reset is released and MCU starts on internal 20 MHz clock, which is derived internally via
the FLL from the slow IRC 32 kHz clock.
• Initialization software should reset and then release reset to the transceiver (MCU still running on
start-up clock)
• Wait for transceiver start-up.
• Program ClkOut to desired frequency (clkout to 000, divide by 1, recommended)
• Wait for the ClkOut source plus PLL to lock, and then switch MCU clock to external source
If the transceiver is forced to a low power condition, the MCU can revert to the internal oscillator and FLL.
4.4.4.2 Single Crystal with MCU Using Internal Clock Only
The single crystal (transceiver) with the MCU using internal clock only has no real advantage over using
the ClkOut output, except for slightly lower power.
In this configuration, clock start-up from a reset condition involves:
• MCU reset is released and MCU starts on internal 20 MHz clock, which is derived internally via
the FLL from the slow IRC 32 kHz clock
• Initialization software should assert reset and then release reset to the transceiver (MCU still
running on start-up clock)
• Program MCG to desired clock rate if the default is not the preferred choice
• Program transceiver to disable ClkOut.
The MCU does not have a high accuracy time base when using the internal reference.
4.4.4.3 Dual Crystal Operation
The transceiver crystal can be augmented by the use of a second crystal on the MCU. The typical
application would use a 32.768 kHz crystal that would allow an accurate time base in the MCU for long
power down delays. The obvious disadvantage of this configuration is additional cost.
In this configuration, clock start-up from a reset condition involves:
• MCU reset is released and MCU starts on internal 20 MHz clock, which is derived internally via
the FLL from the slow IRC 32 kHz clock
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-12 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 50

System Considerations
• Initialization software should assert reset and then release reset to the transceiver (MCU still
running on start-up clock)
• The MCU clock can be switched to the OSC
• Program transceiver to disable ClkOut
The second crystal is justified when accurate power down time periods are required. The external clock
with the 32.768 kHz crystal allows an accurate time tick for the RTC at very low power.
4.4.5 Debug Port Pin Descriptions
The debug port pins default after POR to their SWD functionality.
Table 4-4. Serial wire debug pin description
Pin Name Type Description
SWD_CLK Input Serial wire clock. This pin is the clock for debug logic when in the Serial Wire
Debug mode. This pin is pulled down internally.
SWD_DIO Input/Output Serial wire debug data input/output. This pin is used by an external debug
tool for communication and device control. This pin is pulled up internally.
4.5 MKW01Z128 GPIO (Mixed I/O from Transceiver and MCU)
The MKW01Z128 SiP supports a total of 43 GPIO pins that originate from the transceiver and/or the
MCU:
• The transceiver provides six pins (DIO5-DIO0) that can be programmed as status — Use of the DIOX are programmed as listed in Table 7-2 and Table 7-3
— DIO1 and DIO0 are connected internally to MCU GPIOs, PTE3, PTE2, as well as routed to
package pins. Enhanced performance can be achieved by routing them externally to other
GPIO pins, PTC4 and PTC3.
— Freescale software commonly uses DIO4 externally connected to PTD4.
— DIO5 is also ClkOUT and most commonly externally connected to EXTAL0 for the MCU
clock source
— DIO2 often used for DATA out, in conjuction with DIO1 DCLK.
— DIO3 is uncommitted.
• Four-signal SPI Bus port connected internally and reserved for MCU and transceiver use. On
bottom pins 57–60. (PTC7, PTD0, PTC5, PTC6)
• PTE30 is typically used to drive the RESET on the transceiver.
• PTA1 and PTA2 are used for UART0 RXD & TXD.
• PTC1 and PTC2 are typically used for I2C.
• PTE17 is used as a software PN output for testing in some Freescale applications.
— If a crystal is used with the MCU, PTA19/XT AL0 and PTA18/EXTAL0 pins cannot be used as
GPIO. These are available only using the internal clock reference.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-13
Page 51

System Considerations
— If ClkOut is used to drive the external clock source to the MCU, EXTAL (PTA18) is not
available as GPIO.
— PTA20 can be used as MCU reset.
• fourteen additional MCU GPIO are available for use in the SiP package. Four of them (PTB0,
PTB1, PTD6, PTD7) have 20mA drive capability and can drive LEDs directly.
NOTE
Unused GPIO pins should be disabled and if possible left unconnected.
NOTE
Four additional MCU GPIO are not pinned-out and cannot be used.
However, they must be initialized for low power operation.
— If a crystal is used with the MCU, PTA19/XT AL0 and PTA18/EXTAL0 pins cannot be used as
GPIO. These are available only using the internal clock reference.
— If ClkOut is used to drive the external clock source to the MCU, EXTAL0 is not available as
GPIO.
— PTA0, PTA3 and PTA20 are not commonly used as GPIOs because they are dedicated to the
MCU debug port (SWD).
4.5.1 MCU GPIO Characteristics
The internal MCU GPIO hardware consists of 5 ports with 32 signals per port for a total of 160 signals
(not all are available on the MKW01Z128). There are 8 signals from P T A, 5 from P TB, 9 from P TC, 5 from
PTD and 9 from PTE, many of which are dedicated to some function. This can be seen in Figure 1-1.
NOTE
To avoid extra current drain, all unused signals should be disabled. This
includes signals not pinned-out on the package.
• The GPIO ports share the pins with other modules and selection of either GPIO or a selection of
altenative modules signals are configured via the PORT control module. The PORT control
module provides up to 7 possible options for each external pin, and also provides optional
pull-up/pull-down devices when GPIO pin is input, and interrupt capability where available. See
section 7 of the MCU portion of this reference manual, Port Control.
• For information about how and when on-chip peripheral systems use these pins, refer to the
appropriate peripheral chapter of this document
4.5.2 Transceiver DIOX Characteristics
The transceiver status/GPIO consists of 6 signals total (DIO5-DIO0). DIO2 is bidirectional and all others
are output only . Immediately after reset, all the DIO are configured as outputs. Use of the DIO is controlled
by transceiver registers RegDioMapping1 and RegDioMapping2, see Section 7.10, “IRQ and Pin
Mapping Registers”.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-14 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 52

System Considerations
4.6 Transceiver RF Configurations and External Connections
The MKW01Z128 transceiver radio has features that allow for a flexible as well as low cost RF interface:
• Sensitivity down to -120 dBm at 1.2 kbps
• High selectivity w/16-tap FIR channel filter
• Robust receiver front end:
— IIP3 = -18 dBm
— IIP2 = +35 dBm
— 80 dB blocking immunity
— No image frequency response
• Programmable Pout from -18 to +17 dBm in 1 dB steps
• FSK bit rates up to 600 kbps
• FSK, GFSK, MSK, GMSK, and OOK modulators
• Two TX output power configurations
4.6.1 RF Interface Pins
The MKW01Z128 transceiver has the following pins associated with the RF interface:
• VR_PA - regulated voltage supply to the internal PA circuit, to be routed through the matching
network
• PA_BOOST - optional secondary high-power TX PA
• RFIO - RF bidirectional input/output; used as input only for PA boost mode
• RXTX - digital output to control RF switch
• GND_PA1- RF ground
• GND_PA2 - RF ground
NOTE
The following descriptions for RF operation are not meant as complete
applications information, but rather general information. Freescale supplies
evaluation boards as well as complete reference designs, and the user is
directed to these designs upon which to build target systems.
There are two basic RF configurations as described in the following sections.
4.6.2 Standard Output Power RF Configuration (Single, Bidirectional Port)
The standard RF configuration for the transceiver is a single, bidirectional port mode (shown in
Figure 4-5):
• Only the bidirectional RF pin RFIO is used
• Maximum output power of typically +13 dBm into a 50 ohm load.
• The output power is programmable in approximately 1 dB steps.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-15
Page 53

System Considerations
C17
C18
A2
ANT
C19
L5
L6 L7
C20 C21
C22 C23
C24
L8
U2
MC13213
RXTX
37
GND_PA2
38
VR_PA
42
PA _BOOST
41
RFIO
39
GND_PA1
40
AC Blocking Netw ork
• Inductor L8 and capacitor C19 provide an ac blocking network for the PA power supply.
• The remaining external components are a generalized RF network — Provides impedance match between the antenna and the transceiver RFIO
— Supports an elliptic-function low pass filter to provide TX harmonic trapping and out-of-band
suppression
— The topology for the RF matching network can be used over the various bands of interest with
changes in component values. Not all indicated components are used at all frequencies
Figure 4-5. Single Port RF Schematic (+13dBm)
4.6.3 Higher Output Power RF Configuration (Dual Port with Optional External Power Amplifier)
The secondary RF configuration for the transceiver is a dual port mode (shown in Figure 4-6):
• Secondary P A output (PA_BOOST) is used as the TX port and the standard RFIO pin is used as the
RX port.
• Maximum output power from the PA_BOOST output is typically +17 dBm into a 50 ohm load.
• Inductor L1 and capacitor C1 provide an ac blocking network for the PA_BOOST power supply.
• An external RF switch is required to enable the appropriate path to the antenna — The TX port (PA_BOOST network) is selected for transmit
— The RFIO port network is selected for receive
— Device control output RXTX can used to control the antenna switch
• An optional external power amplifier can be inserted between the device TX output and the
antenna switch to increase transmitted power up to typically about 1 W maximum.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
4-16 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 54

System Considerations
RFIO_EXT
VDD
TX_OUT
ANT_TXTX_OUT
ANT_TXTX_OUT ANT_TX
AC Blocking Network
Optional External PA
C12C12
C1C1
C10C10
L3L3
C13C13
C8C8
C5C5
L2L2
External PAExternal PA
RF_IN1RF_OUT
2
C2C2
C6C6
L6L6
1 2
L1L1
C4C4
C11C11
Ant SWAnt SW
VDD
6
IN
5
VCONT
4
OUT1
1
OUT2
3
GND
2
C7C7
C3C3
MC13213MC13213
RXTX
37
GND_PA2
38
VR_PA
42
PA_BOOST
41
RFIO
39
GND_PA1
40
C9C9
L5L5
1 2
A1
ANTA1ANT
L4L4
1 2
L4L4
• Similar to the single-port configuration, generalized RF circuit topologies are shown for both the
TX and RX paths -
— The TX path network provides both impedance matching and low pass filtering for TX
harmonic trapping and out-of-band suppression
— The RX path network typically provides only impedance match between the antenna and the
transceiver RFIO and can normally be greatly simplified
— The topology for the RF matching networks can be used over the various bands of interest with
changes in component values. Not all indicated components are used at all frequencies.
w
Figure 4-6. Dual Port RF Schematic (+17dBm to 1W)
4.6.4 Filter and Matching Network Component Values
The generalized filter/matching network shown in Figure 4-5 and Figure 4-6 must be evaluated and tuned
to its application use and frequency:
• Impedance matching is always required
• Only a transmission path typically uses any low pass filtering elements
• Not all indicated components are used at all frequencies
T o provide an initial design configuration for several popular frequency bands, Table 4-5 lists component
values versus frequency and use for the generalized component topology of Figure 4-7. For each
frequency, the filter components for the PA_BOOST output filter (Dual Port TX) and the Single Port
(TX/RX) are given.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 4-17
Page 55

System Considerations
ANT_RF
VR_PA
DEVICE_RF
AC Blocking Network
C1C1
L1L1
L3L3
C6C6 C7C7
C2C2
C4C4
C5C5
L4L4
L2L2
C3C3
These component values are given only as suggested initial design values.
The user must evaluate his particular design and adjust/change components
as required to meet targeted specifications.
Figure 4-7. General RF Filter/Matching Network Topology
NOTE
Table 4-5. RF Component Values vs. Frequency Band
434 or 490 MHz 868 MHz or 915 MHz
Component
Designation
L1 22 nH 33 nH 33 nH 33 nH
L2 Short Short 2 nH 4.7 nH
L3 12 nH 12 nH 5.6 nH 6.8 nH
L4 12 nH 10 nH 5.6 nH 6.8 nH
C2 10 pF 10 pF 47 pF 6.8 pF
C3 2.4 pF 2.4 pF dnp or open dnp or open
C4 dnp dnp dnp or open dnp or open
C5 15 pF 15 pF 6.8 pF 2 pF
C6 15 pF 15 pF 6.8 pF 7.5 pF
C7 8.2 pF 8.2 pF 3.3 pF 5.6 pF
4-18 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Dual Port
TX
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Single Port
TX/RX
Dual Port
TX
Single Port
TX/RX
Page 56

Chapter 5 Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
This chapter describes the architecture and operation of the MKW01Z128 low-power, highly integrated
transceiver chip.
5.1 Overview
The MKW01Z128 transceiver is a single-chip integrated circuit ideally suited for today's high
performance ISM band RF applications. The transceivers's advanced features set, including state of the art
packet engine greatly simplifies system design while the high level of integration reduces the external
BOM to a handful of passive decoupling and matching components. It is intended for use as
high-performance, low-cost FSK and OOK RF transceiver for robust frequency agile, half-duplex
bidirectional RF links, and where stable and constant RF performance is required over the full operating
voltage range of the device.
The transceiver is intended for applications over a wide frequency range, including the 433 MHz and
868 MHz European and the 902-928 MHz North American ISM bands. Coupled with a link budget in
excess of 135 dB, the advanced system features include a 66-byte TX/RX FIFO, configurable automatic
packet handler, listen mode, temperature sensor and configurable DIOs which greatly enhance system
flexibility whilst at the same time significantly reducing MCU requirements.
The transceiver complies with both ETSI and FCC regulatory requirements
5.2 Simplified Block Diagram
Figure 5-1 shows a simplified block diagram of the MKW01Z128 transceiver.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-1
Page 57

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Figure 5-1. MKW01Z128 Transceiver Block Diagram
5.3 Transceiver Power Supply
The MKW01Z128 has separate power pins for both the MCU and the transceiver. The transceiver employs
on-chip regulation and management that provides stable operating characteristics over the full temperature
and voltage range of operation. This includes the full output power of +17dBm which is maintained from
1.8 to 3.6 V.
The transceiver voltage source is supplied via pins VBAT1 and VBAT2. See Section 4.2, “Power
connections” for power supply connection and bypassing details. Freescale recommends that the MCU and
transceiver be powered together from the same supply.
5.4 Low Battery Detector
A low battery detector is also included allowing the generation of an interrupt signal in response to passing
a programmable threshold adjustable through the register RegLowBat. The interrupt signal can be mapped
to any of the DIO pins, through the programming of RegDioMapping.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 58

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
5.5 Frequency Synthesis
The LO generation on the MKW01Z128 transceiver is based on a state-of-the-art fractional-N PLL. The
PLL is fully integrated with automatic calibration.
5.5.1 Reference Oscillator
The crystal oscillator is the main timing reference of the MKW01Z128. It is used as a reference for the
transceiver frequency synthesizer and as a clock for the digital processing. In turn, the transceiver ClkOut
signal can be used to provide an external reference clock for the MCU (see Section 4.4, “System Clock
Sources and Configurations”).
The XO startup time, TS_OSC, depends on the actual XTAL being connected on pins XTA and XTB.
When using the built-in sequencer, the device optimizes the startup time and automatically triggers the
PLL when the XO signal is stable. To manually control the startup time, the user should either wait for
TS_OSC max, or monitor the signal CLKOUT which will only be made available on the output buffer
when a stable XO oscillation is achieved.
An external clock can be used to replace the crystal oscillator, for instance a ti ght tolerance TCXO. To do
so, Bit 4 at transceiver Address 0x59 should be set to 1, and the external clock has to be provided on XTA
(Pin 4). XTB (pin 5) should be left open. The peak-peak amplitude of the input signal must never exceed
1.8 V. Please consult your TCXO supplier for an appropriate value of decoupling capacitor, CD.
XTA XTB
OP
Vcc
NC
Vcc
C
D
TCXO
32MHz
GND
Figure 5-2. TCXO Connection
5.5.2 CLKOUT Output
The reference frequency, or a fraction of it, can be provided on DIO5 (pin 54) by modifying bits ClkOut
in RegDioMapping2. Two typical applications of the CLKOUT output include:
• Provide a clock output for the MCU (see Section 4.4, “System Clock Sources and Configurations”)
- saves the cost of an additional crystal. CLKOUT can be made available in any operation mode
except Sleep mode and is automatically enabled at power-on reset.
• Provides an oscillator reference output - allows simple software trimming of the initial crystal
tolerance.
If the transceiver is put into low power mode, ClkOut may be disabled for lowest power.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-3
Page 59

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
F
STEP
F
XOSC
2
19
---------------- -
=
F
RFFSTEP
Frf 230(,)=
5.5.3 PLL Architecture
The frequency synthesizer generating the LO frequency for both the receiver and the transmitter is a
fractional-N sigma-delta PLL. The PLL incorporates a third order loop capable of fast auto-calibration,
and it has a fast switching-time. The VCO and the loop filter are both fully integrated, removing the need
for an external tight-tolerance, high-Q inductor in the VCO tank circuit.
5.5.3.1 VCO
The VCO runs at 2, 4 or 6 times the RF frequency (respectively in the 915, 434 and 315 MHz bands) to
reduce any LO leakage in receiver mode, to improve the quadrature precision of the receiver, and to reduce
the pulling effects on the VCO during transmission.
The VCO calibration is fully automated. A coarse adjustment is carried out at power-on reset, and fine
tuning is performed each time the transceiver PLL is activated. Automatic calibration times are fully
transparent to the end-user, as this processing time is included in the TS_TE and TS_RE specifications.
5.5.3.2 PLL Bandwidth
The bandwidth of the Fractional-N PLL is wide enough to allow for:
• High speed FSK modulation, up to 600 kb/s, inside the PLL bandwidth
• Very fast PLL lock times - enabling both short startup and fast hop times required for frequency
agile applications
5.5.3.3 Carrier Frequency and Resolution
The transceiver PLL embeds a 19-bit sigma-delta modulator and its frequency resolution, constant over
the whole frequency range, and is given by:
The carrier frequency is programmed through RegFrf, split across Addresses 0x07 to 0x09:
NOTE
The Frf setting is split across 3 bytes. A change in the center frequency will
only be taken into account when the least significant byte FrfLsb in
RegFrfLsb is written. This allows for more complex modulation schemes
such as m-ary FSK, where frequency modulation is achieved by changing
the programmed RF frequency.
5.5.4 Lock Time
PLL lock time TS_FS is a function of a number of technical factors, such as synthesized frequency,
frequency step, etc. When using the built-in sequencer, the transceiver optimizes the startup time and
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 60

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
T
PLLAFC
5
PLLBW
---------------------
=
PLLBW default = Varies by region; see Table 7-11 for settings.
LNA
Receiver Chain
RFIO
Local
Oscillator
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA_BOOST
automatically starts the receiver or the transmitter when the PLL has locked. To manually control the
startup time, the user should either wait for TS_FS max given in the specification, or monitor the signal
PLL lock detect indicator, which is set when the PLL has is within its locking range.
When performing an AFC, which usually corrects very small frequency errors, the PLL response time is
approximately:
In a frequency hopping scheme, the timings TS_HOP given in the table of specifications give an order of
magnitude for the expected lock times.
5.5.5 Lock Detect Indicator
A lock indication signal can be made available on some of the DIO pins, and is toggled high when the PLL
reaches its locking range. Refer to Table 7-2 and Table 7-3 to map this interrupt to the desired pins.
NOTE
The lock detect block may indicate an unlock condition (signal toggling
low) when the transmitter is FSK modulated with large frequency deviation
settings.
5.6 Transmitter Description
The transmitter of MKW01Z128 transceiver is comprised of the frequency synthesizer, modulator and
power amplifier blocks.
Figure 5-3. Transmitter Block Diagram
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-5
Page 61

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
BR
F
XOSC
BitRate
------------------- -
=
5.6.1 Bit Rate Setting
When using the transceiver in Continuous mode, the data stream to be transmitted can be input directly to
the modulator via pin DIO2/DATA in an asynchronous manner , unless Gaussian filtering is used, in which
case the DCLK signal on pin 10 (DIO1/DCLK) is used to synchronize the data stream.
In Packet mode or in Continuous mode with Gaussian filtering enabled, the Bit Rate (BR) is controlled by
bits BitRate in RegBitrate:
Among others, the following Bit Rates are accessible:
Table 5-1. Bit Rate Examples (for 32 MHz reference)
Type
Classical transceiver baud
rates (multiples of 1.2 kbps)
Classical transceiver baud
rates (multiples of 0.9 kbps)
Round bit rates
(multiples of 12.5, 25 and
50 kbps)
BitRate
(15:8)
0x68 0x2B 1.2 kbps 1.2 kbps 1199.985
0x34 0x15 2.4 kbps 2.4 kbps 2400.060
0x1A 0x0B 4.8 kbps 4.8 kbps 4799.760
0x0D 0x05 9.6 kbps 9.6 kbps 9600.960
0x06 0x83 19.2 kbps 19.2 kbps 19196.16
0x03 0x41 38.4 kbps 38415.37
0x01 0xA1 76.8 kbps 76738.61
0x00 0xD0 153.6 kbps 153846.15
0x02 0x2C 57.6 kbps 57553.96
0x01 0x16 115.2 kbps 115107.9
0x0A 0x00 12.5 kbps 12.5 kbps 12500.00
0x05 0x00 25 kbps 25 kbps 25000.00
0x02 0x80 50 kbps 50000.00
0x01 0x40 100 kbps 100000.0
0x00 0xD5 150 kbps 150234 .74
BitRate
(7:0)
(G)FSK
(G)MSK
OOK
Actual BR
(b/s)
0x00 0xA0 200 kbps 200000.0
0x00 0x80 250 kbps 250000.0
0x00 0x6B 300 kbps 299065.4
0x00 0x40 500 kbps
0x00 0x35 600 kbps
Watch Xtal frequency 0x03 0xD1 32.768 kbps 32.768 kbps 32753.33
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 62

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
F
DEVFSTEP
Fdev 13 0(,)=
F
DEV
BR
2
------- -
500kHz+
5.6.2 FSK Modulation
FSK modulation is performed inside the PLL bandwidth, by changing the fractional divider ratio in the
feedback loop of the PLL. The large resolution of the sigma-delta modulator, allows for very narrow
frequency deviation. The frequency deviation F
is given by:
DEV
To ensure a proper modulation, the following limit applies:
NOTE
No constraint applies to the modulation index of the transmitter, but the
frequency deviation F
must exceed 600 Hz.
DEV
5.6.3 OOK Modulation
OOK modulation is applied by switching on and off the Power Amplifier. Digital control and smoothing
are available to improve the transient power response of the OOK transmitter.
5.6.4 Modulation Shaping
Modulation shaping can be applied in both OOK and FSK modulation modes, to improve the narrowband
response of the transmitter. Both shaping features are controlled with PaRamp bits in RegPaRamp.
• In FSK mode, a Gaussian filter with BT = 0.3, 0.5 or 1 is used to filter the modulation stream, at
the input of the sigma-delta modulator. If the Gaussian filter is enabled when the MKW01Z128 is
in Continuous mode, DCLK signal on pin 10 (DIO1/DCLK) will trigger an interrupt on the MCU
each time a new bit has to be transmitted.
• When OOK modulation is used, the PA bias voltages are ramped up and down smoothly when the
PA is turned on and off, to reduce spectral splatter.
NOTE
The transmitter must be restarted if the ModulationShaping setting is
changed, in order to recalibrate the built-in filter.
5.6.5 Power Amplifiers
Three power amplifier blocks are embedded in the transmitter . The first one (PA0) can generate up to +13
dBm into a 50 Ohm load. PA0 shares a common front-end pin RFIO with the receiver LNA.
PA1 and PA2 are both connected to pin PA_BOOST, allowing for two distinct power ranges:
• Low power mode - where power out is -18 dBm < Pout < 13 dBm, with PA1 enabled
• Higher power mode - when PA1 and PA2 are combined, providing up to +17 dBm to a matched
load.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-7
Page 63

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
NOTE
When PA1 and PA2 are combined to deliver +17 dBm to the antenna, a
specific impedance matching / harmonic filtering design is required to
ensure impedance transformation and regulatory compliance.
All PA settings are controlled by RegPaLevel, and the truth table of settings is given in Table 5-2.
Table 5-2. Power Amplifier Mode Selection Truth Table
Pa0On Pa1On Pa2On Mode Power Range Pout Formula
1 0 0 PA0 output on pin RFIO -18 to +13 dBm -18 dBm + OutputPower
0 1 0 PA1 enabled on pin PA_BOOST -18 to +13 dBm -18 dBm + OutputPower
0 1 1 PA1 and PA2 combined on pin PA_BOOST +2 to +17 dBm -14 dBm + OutputPower
Other combinations Reserved
1
Output power should be used only for the 16 steps from 0x10 to 0x1F . The range of 0x00 to 0x0F puts PA1 on the lower
half of its 32 step range but PA2 has only 16 steps in the upper half of the power curve regardless of the state of bit 4.
NOTE
• T o ensure correct operation at the hi ghest power levels, adjust the Over
Current Protection Limit accordingly in RegOcp.
• If PA_BOOST pin is not used, the pin can be left floating.
1
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 64

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Imax 45 5 OcpTrim mA+=
LNA
Single to
Differential
Mixers Modulators
Decimator
RSSI
AFC
RFIO
FSK
Demodulator
From
PA1
Local
Oscillator
Channel
Filter
DC
Cancellation
Rx Calibration
Reference
Bypassed
in FSK
Phase
Output
Module
Output
Complex
Filter
CORDIC
OOK
Demodulator
Processing
AGC
5.6.6 Over Current Protection
An over-current protection block is built-in the chip that helps prevent surge curr ents when the transmitter
is used at its highest power levels, thus protecting the battery that may power the application. The current
clamping value is controlled by OcpTrim bits in RegOcp, and is calculated with the following formula:
NOTE
Imax sets the maximum current drawn by the final PA stage, and does not
account for the PA drivers and frequency synthesizer. Global current drain
on Vbatt will be higher
5.7 Receiver Description
The MKW01Z128 transceiver features a digital receiver with the analog to digital conversion process
being performed directly following the LNA-Mixers block. The zero-IF receiver is able to handle (G)FSK
and (G)MSK modulation. ASK and OOK modulation is, however, demodulated by a low-IF architecture.
All the filtering, demodulation, gain control, synchronization and packet handling is performed digitally,
and this allows a very wide range of bit rates and frequency deviations to be selected. The receiver is also
capable of automatic gain calibration in order to improve precision of RSSI measurements.
Figure 5-4. Receiver Block Diagram
The following sections give a brief description of each of the receiver blocks.
5.7.1 LNA - Single to Differential Buffer
The LNA uses a common-gate topology, which allows for a flat characteristic over the whole frequency
range. It is designed to have an input impedance of 50 Ohms or 200 Ohms (as selected with bit LnaZin in
RegLna), and the parasitic capacitance at the LNA input port is cancelled with an external RF choke. A
single to differential buffer is implemented to improve the second order linearity of the receiver.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-9
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 65

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
NOTE
Due to circuit specifics and matching topology, optimum performance in
any given design may be achieved with LNA Zin set to either 50 or 200 .
Both settings should be tested for sensitivity in the actual system in
development.
The LNA gain, including the single-to-differential buffer, is programmable over a 48 dB dynamic range,
and control is either manual or automatic with the embedded AGC function.
NOTE
In the specific case where the LNA gain is manually set by the user, the
receiver will not be able to properly handle FSK signals with a modulation
index smaller than 2 at an input power greater than the 1dB compression
point (P1dB), described in Table 5-4.
Table 5-3. LNA Gain Settings
LnaGainSelect LNA Gain Gain Setting
000 Any of the below, set by the AGC loop 001 Max gain G1
010 Max gain - 6 dB G2
011 Max gain - 12 dB G3
100 Max gain - 24 dB G4
101 Max gain - 36 dB G5
110 Max gain - 48 dB G6
111 Reserved -
5.7.2 Automatic Gain Control
By default (LnaGainSelect = 000), the LNA gain is controlled by a digital AGC loop in order to obtain the
optimal sensitivity/linearity trade-off.
Regardless of the data transfer mode (Packet or Continuous), the following series of events takes place
when the receiver is enabled:
• The receiver stays in WAIT mode, until RssiValue exceeds RssiThreshold for two consecutive
samples. Its power consumption is the receiver power consumption.
• When this condition is satisfied, the receiver automatically selects the most suitable LNA gain,
optimizing the sensitivity/linearity trade-off.
• The programmed LNA gain, read-accessible with LnaCurrentGain in RegLna, is carried on for the
whole duration of the packet, until one of the following conditions is fulfilled:
— Packet mode:
if AutoRxRestartOn = 0, the LNA gain will remain the same for the reception of
the following packet. If AutoRxRestartOn = 1, after the controller has emptied the FIFO the
receiver will re-enter the WAIT mode described above, after a delay of InterPacketRxDelay,
allowing for the distant transmitter to ramp down, hence avoiding a false RSSI detection. In
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 66

both cases (AutoRxRestartOn=0 or AutoRxRestartOn=1), the receiver can also re-enter the
Towards
- 125dBm
A
G
C
R
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
A
g
c
T
h
r
e
s
h
1
A
g
c
T
h
r
e
s
h
2
A
g
c
T
h
r
es
h
3
A
g
c
T
h
r
e
s
h
4
Pin[dBm]
A
g
c
T
h
r
e
s
h
5
16dB 7dB 11dB 9dB 11dB
G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6
Higher Sensitivity
Lower Linearity
Lower Noise Figure
Lower Sensitivity
Higher Linearity
Higher Noise Figure
WAIT mode by setting RestartRx bit to 1. The user can decide to do so, to manually launch a
new AGC procedure.
— Continuous mode: upon reception of valid data, the user can decide to either leave the receiver
enabled with the same LNA gain, or to restart the procedure, by setting RestartRx bit to 1,
resuming the WAIT mode of the receiver, described above.
NOTE
• The AGC procedure must be performed while receiving preamble in
FSK mode.
• In OOK mode, the AGC will give better results if performed while
receiving a constant “1” sequence
The following figure illustrates the AGC behavior:
Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Figure 5-5. AGC Thresholds Settings
The following table summarizes the typical performance of the complete receiver:
T ab le 5-4. Receiver Performance Summary
Receiver Performance (typ)
Input Power
Pin
Pin < AgcThresh1 G1 -37 7 -18 +35
AgcThresh1 < Pin < AgcThresh2 G2 -31 13 -15 +40
AgcThresh2 < Pin < AgcThresh3 G3 -26 18 -8 +48
AgcThresh3 < Pin < AgcThresh4 G4 -14 27 -1 +62
AgcThresh4 < Pin < AgcThresh5 G5 >-6 36 +13 +68
AgcThresh5 < Pin G6 >0 44 +20 +75
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-11
Gain
Setting
P
-1dB
[dBm]
NF
[dB]
IIP3
[dBm]
IIP2
[dBm]
Page 67

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
5.7.2.1 RssiThreshold Setting
For correct operation of the AGC, RssiThreshold in RegRssiThresh must be set to the sensitivity of the
receiver. The receiver will remain in WAIT mode until RssiThreshold is exceeded.
NOTE
When AFC is enabled and performed automatically at the receiver startup,
the channel filter is used by the receiver during the AFC and the AGC is
RxBwAfc instead of the standard RxBw setting. This may impact the
sensitivity of the receiver, and the setting of RssiThreshold accordingly.
5.7.2.2 AGC Reference
The AGC reference level is automatically computed in the transceiver according to:
AGC Reference [dBm] = -174 + NF + DemodSnr +10*log(2*RxBw) + FadingMargin [dBm]
With:
• NF = 7dB : LNA’s Noise Figure at maximum gain
• DemodSnr = 8 dB : SNR needed by the demodulator
• RxBw : Single sideband channel filter bandwidth
• FadingMargin = 5 dB : Fading margin
5.7.3 Continuous-Time DAGC
In addition to the automatic gain control described in Section 5.7.2, “Automatic Gain Control”, the
transceiver is capable of continuously adjusting its gain in the digital domain, after the analog to digital
conversion has occurred. This feature, named DAGC, is fully transparent to the end user. The digital gain
adjustment is repeated every 2 bits, and has the following benefits:
• Fully transparent to the end user
• Improves the fading margin of the receiver during the reception of a packet, even if the gain of the
LNA is frozen
• Improves the receiver robustness in fast fading signal conditions, by quickly adjusting the receiver
gain (every 2 bits)
• Works in Continuous, Packet, and unlimited length Packet modes
The DAGC is enabled by setting RegTestDagc to 0x20 for low modulation index systems (i.e. when
AfcLowBetaOn=1) and 0x30 for other systems. It is recommended to always enable the DAGC.
5.7.4 Quadrature Mixer - ADCs - Decimators
The mixer is inserted between output of the RF buffer stage and the input of the analog to digital converter
(ADC) of the receiver section. This block is designed to translate the spectrum of the input RF signal to
baseband, and offer both high IIP2 and IIP3 responses.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-12 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 68

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
RxBw
FXOSC
RxBwMant 2
RxBwExp 2+
--------------------------------------------------------------------
=
RxBw
FXOSC
RxBwMant 2
RxBwExp 3+
--------------------------------------------------------------------
=
In the lower bands of operation (290 to 510 MHz), the multi-phase mixing architecture with weighted
phases improves the rejection of the LO harmonics in receiver mode, hence increasing the receiver
immunity to out-of-band interferers.
The I and Q digitalization is made by two 5th order continuous-time Sigma-Delta Analog to Digital
Converters (ADC). Their gain is not constant over temperature, but the whole receiver is calibrated before
reception, so that this inaccuracy has no impact on the RSSI precision. The ADC output is one bit per
channel. It needs to be decimated and filtered afterwards. This ADC can also be used for temperature
measurement; please refer to Section 5.7.16, “Temperature Sensor” for more details.
The decimators decrease the sample rate of the incoming signal in order to optimize the area and power
consumption of the following receiver blocks.
5.7.5 Channel Filter
The role of the channel filter is to filter out the noise and interferers outside of the channel. Channel
filtering on the transceiver is implemented with a 16-tap Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter, providing
an outstanding Adjacent Channel Rejection performance, even for narrowband applications.
NOTE
To respect oversampling rules in the decimation chain of the receiver, the
Bit Rate cannot be set to a value higher than 2 times the single-side receiver
bandwidth (BitRate < 2 * RxBw)
The single-side channel filter bandwidth RxBw is controlled by the parameters RxBwMant and RxBwExp
in RegRxBw:
• When FSK modulation is enabled:
• When OOK modulation is enabled:
NOTE
The following channel filter bandwidths are accessible (oscillator is mandated at 32 MHz):
Table 5-5. Available RxBw Settings
RxBw (kHz)
RxBwMant
(binary/value)
10b / 24 7 2.6 1.3
01b / 20 7 3.1 1.6
RxBwExp
(decimal)
FSK
ModulationType=00
OOK
ModulationType=01
00b / 16 7 3.9 2.0
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-13
Page 69

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
fc
4RxBw
2 2
DccFreq 2+
-----------------------------------------
=
Table 5-5. Available RxBw Settings
10b / 24 6 5.2 2.6
01b / 20 6 6.3 3.1
00b / 16 6 7.8 3.9
10b / 24 5 10.4 5.2
01b / 20 5 12.5 6.3
00b / 16 5 15.6 7.8
10b / 24 4 20.8 10.4
01b / 20 4 25.0 12.5
00b / 16 4 31.3 15.6
10b / 24 3 41.7 20.8
01b / 20 3 50.0 25.0
00b / 16 3 62.5 31.3
10b / 24 2 83.3 41.7
01b / 20 2 100.0 50.0
00b / 16 2 125.0 62.5
10b / 24 1 166.7 83.3
01b / 20 1 200.0 100.0
00b / 16 1 250.0 125.0
10b / 24 0 333.3 166.7
01b / 20 0 400.0 200.0
00b / 16 0 500.0 250.0
5.7.6 DC Cancellation
DC cancellation is required in zero-IF architecture transceivers to remove any DC offset generated through
self-reception. It is built into the device and its adjustable cutoff frequency fc is controlled in RegRxBw:
Table 5-6. Available DCC Cutoff Frequencies Expressed as Percentage of RXBW
DccFreq in RegRxBw fc in % of RxBw
000 16
001 8
010 (default) 4
011 2
100 1
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-14 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 70

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Table 5-6. Available DCC Cutoff Frequencies Expressed as Percentage of RXBW (continued)
DccFreq in RegRxBw fc in % of RxBw
101 0.5
110 0.25
1 11 0.125
The default value of DccFreq cutof f frequency is typically 4% of the RxBw (channel filter BW). The cutoff
frequency of the DCC can however be increased to slightly improve the sensitivity under wider
modulation conditions. It is advised to adjust the DCC setting while monitoring the receiver sensitivity.
5.7.7 Complex Filter - OOK
In OOK mode the receiver is modified to a low-IF architecture. The IF frequency is automatically set to
half the single side bandwidth of the channel filter (FIF = 0.5 * RxBw). The Local Oscillator is
automatically offset by the IF in the OOK receiver. A complex filter is implemented on the chip to
attenuate the resulting image frequency by typically 30 dB.
NOTE
This filter is automatically bypassed when receiving FSK signals
(ModulationType = 00 in RegDataModul).
5.7.8 RSSI
The RSSI block evaluates the amount of energy available within the receiver channel bandwidth. Its
resolution is 0.5 dB, and it has a wide dynamic range to accommodate both small and large signal levels
that may be present. Its acquisition time is very short, taking only 2 bit periods. The RSSI sampling must
occur during the reception of preamble in FSK, and constant “1” reception in OOK.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-15
Page 71

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
NOTE
• The receiver is capable of automatic gain calibration in order to improve
the precision of its RSSI measurements. This function injects a known
RF signal at the LNA input, and calibrates the receiver gain accordingly .
This calibration is automatically performed during the PLL start-up,
making it a transparent process to the end-user
• RssiValue can only be read when it exceeds RssiThreshold
• RSSI accuracy depends on all components located between the antenna
port and pin RFIO, and is therefore limited to a few dB. Board-level
calibration is advised to further improve accuracy.
• RssiStart command and RssiDone flags are not usable when DAGC is
turned on, see Section 5.7.3, “Continuous-Time DAGC”.
5.7.9 Cordic
The Cordic task is to extract the phase and the amplitude of the modulation vector (I+j.Q). This
information, still in the digital domain is used as follows:
• Phase output - used by the FSK demodulator and the AFC blocks.
• Amplitude output - used by the RSSI block, for FSK demodulation, AGC and automatic gain
calibration purposes.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-16 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 72

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
I(t)
Q(t)
Real-time Phase
Real-time
Magnitude
0.5
2F
DEV
BR
---------------------- -
10=
Figure 5-6. Cordic Extraction
5.7.10 FSK Demodulator
The FSK demodulator of the receiver is designed to demodulate FSK, GFSK, MSK and GMSK modulated
signals. It is most efficient when the modulation index of the signal is greater than 0.5 and below 10:
The output of the FSK demodulator can be fed to the Bit Synchronizer (described in Section 5.7.12), to
provide the companion processor with a synchronous data stream in Continuous mode.
5.7.11 OOK Demodulator
The OOK demodulator performs a comparison of the RSSI output and a threshold value. Three different
threshold modes are available, configured through bits OokThreshType in RegOokPeak.
The recommended mode of operation is the "Peak" threshold mode, illustrated in Figure 5-7:
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-17
Page 73

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Figure 5-7. OOK Peak Demodulator Description
In peak threshold mode the comparison threshold level is the peak value of the RSSI, reduced by 6dB. In
the absence of an input signal, or during the reception of a logical "0", the acquired peak value is
decremented by one OokPeakThreshStep every OokPeakThreshDec period.
When the RSSI output is null for a long time (for instance after a long string of "0" received, or if no
transmitter is present), the peak threshold level will continue falling until it reaches the "Floor Threshold",
programmed in OokFixedThresh.
The default settings of the OOK demodulator lead to the performance stated in the electrical specification.
However, in applications in which sudden signal drops are awaited during a reception, the three parameters
should be optimized accordingly.
5.7.11.1 Optimizing the Floor Threshold
OokFixedThresh determines the sensitivity of the OOK receiver, as it sets the comparison threshold for
weak input signals (i.e., those close to the noise floor). Significant sensitivity improvements can be
generated if configured correctly.
Note that the noise floor of the receiver at the demodulator input depends on:
• The noise figure of the receiver.
• The gain of the receive chain from antenna to base band.
• The matching - including SAW filter if any.
• The bandwidth of the channel filters.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-18 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 74

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
Set SX1231 in OOK Rx mode
Adjust Bit Rate, Channel filter BW
Default OokFixedThreshsetting
No input signal
Continuous Mode
Optimizationcomplete
Glitch activity
on DATA?
Monitor DIO2/DATA pin
Increment
OokFixedThresh
MKW01
It is therefore important to note that the setting of OokFixedThresh will be application dependant. The
following procedure is recommended to optimize OokFixedThresh.
Figure 5-8. Floor Threshold Optimization
The new floor threshold value found during this test should be used for OOK reception with those receiver
settings.
5.7.11.2 Optimizing OOK Demodulator for Fast Fading Signals
A sudden drop in signal strength can cause the bit error rate to increase. For applications where the
expected signal drop can be estimated, the following OOK demodulator parameters OokPeakThreshStep
and OokPeakThreshDec can be optimized as described below for a given number of threshold decrements
per bit. Refer to RegOokPeak to access those settings.
5.7.11.3 Alternative OOK Demodulator Threshold Modes
In addition to the Peak OOK threshold mode, the user can alternatively select two other types of threshold
detectors:
• Fixed Threshold: - The value is selected through OokFixedThresh
• A verage Threshold - Data supplied by the RSSI block is averaged, and this operation mode should
only be used with DC-free encoded data.
5.7.12 Bit Synchronizer
The Bit Synchronizer is a block that provides a clean and synchronized digital output, free of glitches. Its
output is made available on pin DIO1/DCLK in Continuous mode and can be disabled through register
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-19
Page 75

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
settings. However, for optimum receiver performance its use when running Continuous mode is strongly
advised.
The Bit Synchronizer is automatically activated in Packet mode. Its bit rate is controlled by BitRateMsb
and BitRateLsb in RegBitrate.
Figure 5-9. Bit Synchronizer Description
To ensure correct operation of the Bit Synchronizer, the following conditions have to be satisfied:
• A preamble (0x55 or 0xAA) of 12 bits is required for synchronization (from the RxReady interrupt)
• The subsequent payload bit stream must have at least one transition form '0' to '1' or '1' to '0 every
16 bits during data transmission
• The bit rate matching between the transmitter and the receiver must be better than 6.5 %.
NOTE
• If the Bit Rates of transmitter and receiver are known to be the same, the
receiver will be able to receive an infinite unbalanced sequence (all “0s”
or all ”1s”) with no restriction.
• If there is a difference in Bit Rate between TX and RX, the amount of
adjacent bits at the same level that the BitSync can withstand can be
estimated as follows:
• This implies approximately 6 consecutive unbalanced bytes when the
Bit Rate precision is 1%, which is easily achievable (crystal tolerance is
in the range of 50 to 100 ppm).
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-20 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 76

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
BW
20dB
2F
DEV
BR
2
------- -
+
=
FEI F
STEP
FeiValue=
MKW01
5.7.13 Frequency Error Indicator (FEI)
This function provides information about the frequency error of the local oscillator (LO) compared with
the carrier frequency of a modulated signal at the input of the receiver. When the FEI block is launched,
the frequency error is measured and the signed result is loaded in FeiValue in RegFei, in 2’s complement
format. The time required for an FEI evaluation is 4 times the bit period.
To ensure a proper behavior of the FEI:
• The operation must be done during the reception of preamble
• The sum of the frequency offset and the 20 dB signal bandwidth must be lower than the base band
filter bandwidth
The 20 dB bandwidth of the signal can be evaluated as follows (double-side bandwidth):
The frequency error, in Hz, can be calculated with the following formula:
SX1231 in Rx mode
Preamble-modulated input signal
Signal level > Sensitivity
Set FeiStart
= 1
FeiDone
= 1
Yes
No
Read
FeiValue
Figure 5-10. FEI Process
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-21
Page 77

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
5.7.14 Automatic Frequency Correction (AFC)
The AFC is based on the FEI block, and therefore the same input signal and receiver setting conditions
apply. When the AFC procedure is done, AfcValue is directly subtracted to the register that defines the
frequency of operation of the chip, FRF. The AFC can be launched:
• Each time the receiver is enabled, if AfcAutoOn = 1
• Upon user request, by setting bit AfcStart in RegAfcFei, if AfcAutoOn = 0
When the AFC is automatically triggered (AfcAutoOn = 1), the user has the option to:
• Clear the former AFC correction value, if AfcAutoClearOn = 1
• Start the AFC evaluation from the previously corrected frequency. This may be useful in systems
in which the LO keeps on drifting in the “same direction”. Aging compensation is a good example.
The receiver offers an alternate receiver bandwidth setting during the AFC phase, to accommodate large
LO drifts. If the user considers that the received signal may be out of the receiver bandwidth, a higher
channel filter bandwidth can be programmed in RegAfcBw, at the expense of the receiver noise floor, which
will impact sensitivity.
5.7.15 Optimized Setup for Low Modulation Index Systems
The following apply for optimizing low modulation index systems:
• For wide band systems, where AFC is usually not required (XTAL inaccuracies do not typically
impact the sensitivity), it is recommended to offset the LO frequency of the receiver to avoid
desensitization. This can be simply done by modifying Frf in RegFrfLsb. A good generalization is
to offset the receiver’s LO by 10% of the expected transmitter frequency deviation.
• For narrow band systems, it is recommended to perform AFC. The receiver has a dedicated AFC,
enabled when AfcLowBetaOn in RegAfcCtrl is set to 1. A frequency offset, programmable through
LowBetaAfcOffset in RegTestAfc, is added and is calculated as follows:
Offset = LowBetaAfcOffset * 488 Hz
The user should ensure that the programmed offset exceeds the DC canceller’s cutoff frequency, set
through DccFreqAfc in RegAfcBw.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-22 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 78

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
f
TXRX
f
RX & TX
Standard AFC
AfcLowBetaOn = 0
f
TXRX
TX RX
LowBetaAfcOffset
f
AfcValue
AfcValue
FeiValue
FeiValue
Optimized AFC
AfcLowBetaOn = 1
Before AFC After AFC
-40°C
+85
°
C
TempValue
Ambient
Returns150d(typ.)
Needs calibration
tt+1
TempValue(t)
TempValue(t)-1
-1°C/Lsb
Figure 5-11. Optimized AFC (AfcLowBetaOn=1)
As shown on Figure 5-11, a standard AFC sequence uses the result of the FEI to correct the LO frequency
and align both local oscillators. When the optimized AFC is enabled (AfcLowBetaOn=1), the receiver’s
LO is corrected by “FeiValue + LowBetaAfcOffset”.
When the optimized AFC routine is enabled, the receiver startup time can be computed as follows:
TS_RE_AGC&AFC (optimized AFC) = Tana + 4*Tcf + 4*Tdcc + 3*Trssi + 2*Tafc + 2*Tpllafc
5.7.16 Temperature Sensor
When temperature is measured, the receiver ADC is used to digitize the sensor response. Most receiver
blocks are disabled, and temperature measurement can only be triggered in Standby or Frequency
Synthesizer modes.
The response of the temperature sensor is -1°C / Lsb. A CMOS temperature sensor is not accurate by
nature, therefore it should be calibrated at ambient temperature for precise temperature readings.
Figure 5-12. Temperature Sensor Response
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5-23
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 79

Sub 1 GHz Transceiver Architecture Description
It takes less than 100 microseconds for the transceiver to evaluate the temperature (from setting
TempMeasStart to 1 to TempMeasRunning reset).
5.7.17 Timeout Function
The MKW01Z128 includes a Timeout function, which allows it to automatically shut-down the receiver
after a receive sequence and therefore save energy.
• Timeout interrupt is generated TimeoutRxStart * 8 * Tbit after switching to RX mode if
RssiThreshold flag does not raise within this time frame
• Timeout interrupt is generated TimeoutRssiThresh * 8 * Tbit after RssiThreshold flag has been
raised.
This timeout interrupt can be used to warn the MCU to shut down the receiver and return to a lower power
mode.
5.8 High Bit Rate Operations
High Bit rate operation is available in FSK mode. For operations in high bit rate, the frequency deviation
should respect thefollowing equation: FDA + BRF/2 =<500kHz, where FDA is the Frequency Deviation
and BR is the Bit Rate.
5.8.1 500 kbps Operation
For operation at 500 kbps, the following settings are recommended:
• FDA = 250kHz, where FDA is the Frequency Deviation (FSK operation with a Modulation index
of 1)
• Crystal should be selected for a maximum of +/- 20ppm frequency stability.
• Carrier frequency of the receiver should be programmed with 50kHz offset from the programmed
carrier frequency of transmitter. This offset takes into account the possible +/-20ppm drifts of
Crystals. No AFC is needed.
5.8.2 600 kbps Operation
For operation at 600kbps, the following settings are recommended:
• FDA = 150kHz, where FDA is the Frequency Deviation (FSK operation with a Modulation index
of 0.5)
• Crystal should be selected for a maximum of +/- 15ppm frequency stability.
• Carrier frequency of the receiver should be programmed with 40kHz offset from the programmed
carrier frequency of transmitter. This offset takes into account the possible +/-15ppm drifts of
Crystals. No AFC is needed.
NOTE
For both 500 and 600 kbps operations, RegTestPll must be set to 0x0C.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
5-24 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 80

Chapter 6 Transceiver Operating Modes
This chapter describes the operating modes of the MKW01Z128 transceiver.
6.1 Basic Modes
The transceiver can be programmed to 5 different basic modes which are described in Table 6-1.
By default, when switching from a mode to another one, the sub-blocks are woken up according to a
pre-defined and optimized sequence. Alternatively, these operating modes can be selected directly by
disabling the automatic sequencer (SequencerOff in RegOpMode = 1).
Table 6-1. Basic Transceiver Modes
ListenOn
in RegOpMode
0 0 0 0 Sleep Mode None
0 0 0 1 Stand-by Mode Top regulator and crystal oscillator
0 0 1 0 FS Mode Frequency synthesizer
0 0 1 1 Transmit Mode Frequency synthesizer and transmitter
0 1 0 0 Receive Mode Frequency synthesizer and receiver
1 x Listen Mode See Listen Mode, section Section 6.3, “Listen Mode”
Mode
in RegOpMode
Selected mode Enabled blocks
6.2 Automatic Sequencer and Wake-Up Times
By default, when switching from one operating mode to another, the circuit takes care of the sequence of
events in such a way that the transition timing is optimized. For example, when switching from Sleep mode
to Transmit mode, the device goes first to S tandby mode (XO started), then to frequency synthesizer mode,
and finally, when the PLL has locked, to transmit mode. Entering transmit mode is also made according
to a predefined sequence starting with the wake-up of the PA regulator before applying a ramp-up on the
PA and generating the DCLK clock.
• The crystal oscillator wake-up time, TS_OSC, is directly related to the time for the crystal
oscillator to reach its steady state. It depends notably on the crystal characteristics.
• The frequency synthesizer wake-up time, TS_FS, is directly related to the time needed by the PLL
to reach its steady state. The signal PLL_LOCK, provided on an external pin, gives an indication
of the lock status. It goes high when the PLL reaches its locking range.
Four specific cases can be highlighted:
• Transmitter Wake Up time from Sleep mode = TS_OSC + TS_FS + TS_TR
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 6-1
Page 81

Transceiver Operating Modes
Analog
group delay
0.5 x Tbit
1.25 x PaRamp
( only in FSK
mode)
XO Started and PLL is locked
5us
Transmission of Packet
ModeReady
TxReady
TS_TR
Tx startup request
( sequencer or user)
• Receiver Wake Up time from Sleep mode = TS_OSC + TS_FS + TS_RE
• Receiver Wake Up time from Sleep mode, AGC enabled = TS_OSC + TS_FS + TS_RE_AGC
• Receiver Wake Up time from Sleep mode, AGC and AFC enabled = TS_OSC + TS_FS +
TS_RE_AGC&AFC
In applications where the target average power consumption, or the target startup time, do not require
setting the transceiver in the lowest power modes (Sleep or Standby), the respective timings TS_OSC and
TS_FS in the former equations can be omitted.
6.2.1 Transmitter Startup Time
The transmitter wake-up time, TS_TR, is given by the sequence controlled by the digital part. It is a pure
digital delay which depends on the bit rate and the ramp-up time. In FSK mode, this time can be derived
from the following equation.
,
where PaRamp is the ramp-up time programmed in RegPaRamp and Tbit is the bit time.
In OOK mode, this equation can be simplified to the following:
6.2.2 TX Start Procedure
As described in the former section, ModeReady and TxReady interrupts warn the MCU that the transmitter
is ready to transmit data:
• In Continuous mode
pin immediately after any of these interrupts have fired. The DCLK signal, activated on pin
6-2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
DIO1/DCLK can also be used to start toggling the DATA pin, as described on Figure 6-2.
Figure 6-1. TX Startup, FSK and OOK
- the preamble bits preceding the payload can be applied on the DIO2/DATA
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 82

Transceiver Operating Modes
Analog FE’s
group delay
Channel Filter’s
group delay
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
RSSI
sampling
XO Started and PLL is locked
Tana
RSSI
sampling
Tcf Tdcc Trssi Trssi
Reception of Packet
ModeReady
RxReady
Channel Filter’s
group delay
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
RSSI
sampling
Tcf Tdcc Trssi
The LNA gain is adjusted by
the AGC, according to the
RSSI result
TS_RE_AGC
Rx startup request
( sequencer or user)
Analog FE’s
group delay
Channel Filter’s
group delay
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
RSSI
sampling
XO Started and
PLL is locked
Tana
RSSI
sampling
Tcf Tdcc Trssi Trssi
Reception of Packet
ModeReady
RxReady
Channel Filter’s
group delay
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
RSSI
sampling
Tcf Tdcc Trssi
AFC
Tafc
PLL
lock
Tpllafc
Channel Filter’s
group delay
Tcf
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
Tdcc
TS_RE_AGC&AFC
Rx startup request
( sequencer or user)
The LNA gain is adjusted by
the AGC, according to the
RSSI result
Carrier Frequency is adjusted
by the AFC
• In Packet mode - the transmitter will automatically modulate the RF signal with preamble bytes as
soon as TxReady or ModeReady happen. The actual packet transmission (starting with the number
of preambles specified in PreambleSize) will start when the TxStartCondition is fulfilled.
6.2.3 Receiver Startup Time
It is highly recommended to use the built-in sequencer of the transceiver to optimize the delays when
setting the chip in receive mode. It guarantees the shortest startup times, hence the lowest possible ener gy
usage, for battery operated systems.
The startup times of the receiver can be calculated from the following:
Rx startup request
( sequencer or user)
TS_RE
XO Started and PLL is locked
ModeReady
RxReady
Analog FE’s
group delay
Tana
Channel Filter’s
group delay
DC Cutoff’s
group delay
RSSI
sampling
Tcf Tdcc Trssi Trssi
Figure 6-2. RX Startup - No AGC, no AFC
Figure 6-3. RX Startup - AGC, no AFC
RSSI
sampling
Reception of Packet
Figure 6-4. RX Startup - AGC and AFC
The different timings shown above are as follows:
• Group delay of the analog front end - Tana = 20 us
• Channel filter’s group delay in FSK mode - Tcf = 21 / (4 * RxBw)
• Channel filter’s group delay in OOK mode - Tcf = 34 / (4 * RxBw)
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 6-3
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 83

Transceiver Operating Modes
• DC Cutoff’s group delay - Tdcc = max(8 , 2^(round(log2(8 * RxBw * Tbit)+1)) / (4 * RxBw)
• PLL lock time after AFC adjustment - Tpllafc = 5 / PLLBW (PLLBW default = 300 kHz, see
Table 7-11 for settings)
• AFC sample time - Tafc = 4 * Tbit (also denoted TS_AFC in the general specification)
• RSSI sample time - Trssi = 2 * int(4 * RxBw * Tbit)/(4 * RxBw) (aka TS_RSSI)
NOTE
The above timings represent maximum settling times, and shorter settling
times may be observed in real cases
6.2.4 RX Start Procedure
As described in the former sections, the RxReady interrupt warns the MCU that the receiver is ready.
• In Continuous mode with Bit Synchronizer, the receiver will start locking its Bit Synchronizer on
a minimum or 12 bits of received preamble, before the reception of correct Data, or Sync Word (if
enabled) can occur.
• In Continuous mode without Bit Synchronizer, valid data will be ava ilable on DIO2/DATA right
after the RxReady interrupt.
• In Packet mode, the receiver will start locking its Bit Synchronizer on a minimum or 12 bits of
received preamble, before the reception of correct Data, or Sync Word (if enabled) can occur.
•See Section 5.7.12, “Bit Synchronizer”, for details.
6.2.5 Optimized Frequency Hopping Sequences
In a frequency hopping-like application, it is required to turn off the transmitter when hopping from one
channel to another, to avoid spectral splatter and obtain the best spectral purity.
• Transmitter hop from Ch A to Ch B - it is advised to step through the RX mode:
1.Transceiver is in TX mode in Ch A
2.Program the MKW01Z128 in RX mode
3.Change the carrier frequency in the RegFrf registers
4.Turn the transceiver back to TX mode
5.Respect the TX start procedure
• Receiver hop from Ch A to Ch B -
1.Transceiver is in RX mode in Ch A
2.Change the carrier frequency in the RegFrf registers Program the transceiver in FS mode
3.Program the MKW01Z128 in FS mode
4.Turn the transceiver back to RX mode
5.Respect the RX start procedure
NOTE
All sequences described above are assuming that the sequencer is turned on
(SequencerOff=0 in RegOpMode).
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
6-4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 84

Transceiver Operating Modes
time
t
ListenIdle
t
ListenRx
t
ListenRx
Idle
Rx
Rx
6.3 Listen Mode
The receiver can be set to Listen mode, by setting ListenOn in RegOpMode to 1 while in Standby mode.
In this mode, transceiver spends most of the time in Idle mode, during which only the RC oscillator runs.
Periodically the receiver is awakened and listens for an RF signal. If a wanted signal is detected, the
receiver is kept on and the data is demodulated.
Otherwise, if a wanted signal hasn't been detected after a pre-defined period of time, the receiver is
disabled until the next time period.
This periodical RX wake-up requirement is very common in low power applications. On the transceiver it
is handled locally by the Listen mode block without using the MCU resources.
The simplified timing diagram of this procedure is illustrated in Figure 6-5.
Figure 6-5. Listen Mode Sequence (no wanted signal is received)
NOTE
In Idle mode (a phase of Listen mode), the 32 MHz crystal oscillator of the
transceiver is disabled. If this signal, or a derivative thereof, is used as the
MCU clock via CLKOUT to EXT A L0, care should be taken in firmware to
configure the MCU clock to an internal low-power clock immediately prior
to asserting Listen mode to prevent loss of clock affecting MCU
performance.
6.3.1 Timing
The duration of the Idle phase is given by t
a signal is given by t
t
ListenRx
includes the the wake-up time of the receiver, described in Section 6.2.3, “Receiver Startup
ListenRx
.
ListenIdle
Time”. This duration can be programmed in the configuration registers via the SPI.
Both time periods t
parameters from the configuration register and are calculated as follows:
ListenRx
and t
ListenIdle
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
(denoted t
. The time during which the receiver is on and waits for
ListenX
in the following text) are fixed by two
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 6-5
Page 85

Transceiver Operating Modes
:
where ListenResolX is the RX or Idle resolution and is independently programmable on three values (64us,
4.1ms or 262ms), whereas ListenCoefX is an integer between 1 and 255. All parameters are located in
RegListen registers.
The timing ranges are tabulated in Table 6-2 below.
Table 6-2. Range of Durations in Listen Mode
ListenResolX
01 64 us 16 ms
10 4.1 ms 1.04 s
11 0.26 s 67 s
Min duration
( ListenCoef = 1 )
Max duration
( ListenCoef = 255 )
NOTE
• The accuracy of the typical timings given in Table 6-2 will depend in the
RC oscillator calibration
• RC oscillator calibration is required, and must be performed at power
up. See Section 6.3.4, “RC Timer Accuracy” for details
6.3.2 Criteria
The criteria taken for detecting a wanted signal and hence deciding to maintain the receiver on is defined
by ListenCriteria in RegListen1.
Table 6-3. Signal Acceptance Criteria in Listen Mode
ListenCriteria
Input Signal Power
>= RssiThreshold
SyncAddressMatch
0 Required Not Required
1 Required Required
6.3.3 End of Cycle Actions
The action taken after detection of a packet, is defined by ListenEnd in RegListen3, as described in the
table below.
Table 6-4. End of Listen Cycle Actions
ListenEnd Description
00
6-6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Chip stays in RX mode. Listen mode stops and must be disabled.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 86

Table 6-4. End of Listen Cycle Actions
Transceiver Operating Modes
01
10
Chip stays in RX mode until PayloadReady or Timeout interrupt occurs. It then goes to the mode defined
by Mode. Listen mode stops and must be disabled.
Chip stays in RX mode until PayloadReady or Timeout interrupt occurs. Listen mode then resumes in Idle
state. FIFO content is lost at next RX wakeup.
Upon detection of a valid packet, the sequencing is altered, as shown below:
PayloadReady
ListenCriteria
passed
Idle
ListenEnd=00
Listen Mode
Idle
ListenEnd=01
Listen Mode
Rx
Rx
Mode
Idle
ListenEnd=10
Listen Mode
Rx
Idle Rx
Figure 6-6. Listen Mode Sequence (wanted signal is received)
Listen mode can be disabled by writing ListenOn to 0.
6.3.4 RC Timer Accuracy
All timings of the Listen Mode rely on the accuracy of the internal low-power RC oscillator. This oscillator
is automatically calibrated at the device power-up, and it is a user-transparent process.
For applications enduring large temperature variations, and for which the power supply is never removed,
RC calibration can be performed upon user request. RcCalStart in RegOsc1 can be used to trigger this
calibration, and the flag RcCalDone will be set automatically when the calibration is over.
6.4 AutoModes
Automatic modes of packet handler can be enabled by configuring the related parameters in
RegAutoModes. The intermediate mode of the chip is called IntermediateMode and the enter and exit
conditions to/from this intermediate mode can be configured through the parameters EnterCondition &
ExitCondition. The enter and exit conditions cannot be used independently of each other i.e. both should
be enabled at the same time.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 6-7
Page 87

Transceiver Operating Modes
Initial state defined
By Mode in RegOpMode
Intermediate State
defined by IntermediateMode
ExitCondition
EnterCondition
Final state defined
By Mode in RegOpMode
The initial and the final state is the one configured in Mode in RegOpMode. The initial & final states ca n
be different by configuring the modes register while the chip is in intermediate mode. The pictorial
description of the auto modes is shown below.
Figure 6-7. Auto Modes of Packet Handler
Some typical examples of AutoModes usage are described below:
• Automatic transmission (AutoTx) : Mode = Sleep, IntermediateMode = TX, EnterCondition =
FifoLevel, ExitCondition = PacketSent
• Automatic reception (AutoRx) : Mode = RX, IntermediateMode = Sleep, EnterCondition = CrcOk,
ExitCondition = falling edge of FifoNotEmpty
• Automatic reception of acknowledge (AutoRxAck): Mode = TX, IntermediateMode = RX,
EnterCondition = PacketSent, ExitCondition = CrcOk
6-8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 88

Chapter 7 Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.1 Overview
The following figure shows the MKW01Z128 data processing circuit. Its role is to interface the data
to/from the modulator/demodulator and the MCU access points (SPI and DIO pins). It also controls all the
configuration registers.
The circuit contains several control blocks which are described in the following paragraphs.
Figure 7-1. MKW01Z128 Data Processing Conceptual View
The MKW01Z128 implements several data operation modes, each with their own data path through the
data processing section. Depending on the data operation mode selected, some control blocks are active
whilst others remain disabled.
7.1.1 Data Operation Modes
The MKW01Z128 has two different data operation modes selectable by the user:
• Continuous mode:
This mode may be used if adequate external signal processing is available.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-1
each bit transmitted or received is accessed in real time at the DIO2/DATA pin.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 89

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
• Packet mode (recommended): user only provides/retrieves payload bytes to/from the FIFO. The
packet is automatically built with preamble, Sync word, and optional AES, CRC, and DC-free
encoding schemes The reverse operation is performed in reception. The MCU processing overhead
is hence significantly reduced compared to Continuous mode. Depending on the optional features
activated (CRC, AES, etc) the maximum payload length is limited to FIFO size, 255 bytes or
unlimited.
Each of these data operation modes is described fully in the following sections.
7.2 Control Block Description
7.2.1 SPI Interface
The SPI interface gives access to the configuration register via a synchronous full-duplex protocol
corresponding to CPOL = 0 and CPHA = 0 in Motorola/Freescale nomenclature. Only the slave side is
implemented.
Three access modes to the registers are provided:
• SINGLE access: an address byte followed by a data byte is sent for a write access whereas an
address byte is sent and a read byte is received for the read access. The NSS pin goes low at the
begin of the frame and goes high after the data byte.
• BURST access: the address byte is followed by several data bytes. The address is automatically
incremented internally between each data byte. This mode is available for both read and write
accesses. The NSS pin goes low at the beginning of the frame and stay low between each byte. It
goes high only after the last byte transfer.
• FIFO access: if the address byte corresponds to the address of the FIFO, then succeeding data byte
will address the FIFO. The address is not automatically incremented but is memorized and does
not need to be sent between each data byte. The NSS pin goes low at the beginning of the frame
and stay low between each byte. It goes high only after the last byte transfer.
Figure below shows a typical SPI single access to a register.
Figure 7-2. SPI Timing Diagram (single access)
MOSI is generated by the master on the falling edge of SCK and is sampled by the slave (i.e. this SPI
interface) on the rising edge of SCK. MISO is generated by the slave on the falling edge of SCK.
A transfer always starts by the NSS pin going low. MISO is high impedance when NSS is high.
The first byte is the address byte. It is made of:
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-2 Freescal e Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 90

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
• wnr bit, which is 1 for write access and 0 for read access
• 7 bits of address, MSB first
The second byte is a data byte, either sent on MOSI by the master in case of a write access, or received by
the master on MISO in case of read access. The data byte is transmitted MSB first.
Proceeding bytes may be sent on MOSI (for write access) or received on MISO (for read access) without
rising NSS and re-sending the address. In FIFO mode, if the address was the FIFO address then the bytes
will be written / read at the FIFO address. In Burst mode, if the address was not the FIFO address, then it
is automatically incremented at each new byte received.
The frame ends when NSS goes high. The next frame must start with an address byte. The SINGLE access
mode is actually a special case of FIFO / BURST mode with only 1 data byte transferred.
During the write access, the byte transferred from the slave to the master on the MISO line is the value of
the written register before the write operation.
7.2.2 FIFO
7.2.2.1 Overview and Shift Register (SR)
In packet mode of operation, both data to be transmitted and that has been received are stored in a
configurable FIFO (First In First Out) device. It is accessed via the SPI interface and provides several
interrupts for transfer management.
The FIFO is 1 byte wide hence it only performs byte (parallel) operations, whereas the demodulator
functions serially. A shift register is therefore employed to interface the two devices. In transmit mode it
takes bytes from the FIFO and outputs them serially (MSB first) at the programmed bit rate to the
modulator. Similarly, in RX the shift register gets bit by bit data from the demodulator and writes them
byte by byte to the FIFO. This is illustrated in figure below.
Figure 7-3. FIFO and Shift Register (SR)
NOTE
When switching to Sleep mode, the FIFO can only be used once the
ModeReady flag is set (quasi immediate from all modes except from TX)
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-3
Page 91

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.2.2.2 Size
The FIFO size is fixed to 66 bytes.
7.2.2.3 Interrupt Sources and Flags
• FifoNotEmpty: FifoNotEmpty interrupt source is low when byte 0, i.e. whole FIFO, is empty.
Otherwise it is high. Note that when retrieving data from the FIFO, FifoNotEmpty is updated on
NSS falling edge, i.e. when FifoNotEmpty is updated to low state the currently started read
operation must be completed. In other words, FifoNotEmpty state must be checked after each read
operation for a decision on the next one (FifoNotEmpty = 1: more byte(s) to read; FifoNotEmpty =
0: no more byte to read).
• FifoFull: FifoFull interrupt source is high when the last FIFO byte, i.e. the whole FIFO, is full.
Otherwise it is low.
• FifoOverrunFlag: FifoOverrunFlag is set when a new byte is written by the user (in TX or Standby
modes) or the SR (in RX mode) while the FIFO is already full. Data is lost and the flag should be
cleared by writing a 1, note that the FIFO will also be cleared.
• PacketSent: PacketSent interrupt source goes high when the SR's last bit has been sent.
• FifoLevel: Threshold can be programmed by FifoThreshold in RegFifoThresh. Its behavior is
illustrated in figure below.
Figure 7-4. FifoLevel IRQ Source Behavior
NOTE
FifoLevel interrupt is updated only after a read or write operation on the
FIFO. Thus the interrupt cannot be dynamically updated by only changing
the FifoThreshold parameter.
FifoLevel interrupt is valid as long as FifoFull does not occur. An empty
FIFO will restore its normal operation
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-4 Freescal e Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 92

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.2.2.4 FIFO Clearing
Table below summarizes the status of the FIFO when switching between different modes.
Table 7-1. Status of FIFO when Switching Between Different Modes of the Chip
From To FIFO status Comments
Stdby Sleep Not cleared
Sleep Stdby Not cleared
Stdby/Sleep TX Not cleared To allow the user to write the FI FO i n Stdby/Sleep before TX
Stdby/Sleep RX Cleared
RX TX Cleared
RX S tdby/Sleep Not cleared To allow the user to read FIFO in Stdby/Sleep mode after RX
TX Any Cleared
7.2.3 Sync Word Recognition
7.2.3.1 Overview
Sync word recognition (also called Pattern recognition) is activated by setting SyncOn in RegSyncConfig.
The bit synchronizer must also be activated in continuous mode (automatically done in Packet mode) .
The block behaves like a shift register; it continuously compares the incoming data with its internally
programmed Sync word and sets SyncAddressMatch when a matc h is detected. This is illustrated in
Figure 7-5 below.
Figure 7-5. Sync Word Recognition
During the comparison of the demodulated data, the first bit received is compared with bit 7 (MSB) of
RegSyncValue1 and the last bit received is compared with bit 0 (LSB) of the last byte whose address is
determined by the length of the Sync word.
When the programmed Sync word is detected the user can assume that this incoming packet is for the node
and can be processed accordingly.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-5
Page 93

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
SyncAddressMatch is cleared when leaving RX or FIFO is emptied.
7.2.3.2 Configuration
• Size: Sync word size can be set from 1 to 8 bytes (i.e. 8 to 64 bits) via SyncSize in RegSyncConfig.
In Packet mode this field is also used for Sync word generation in TX mode.
• Error tolerance: The number of errors tolerated in the Sync word recognition can be set from 0 to
7 bits to via SyncTol.
• Value: The Sync word value is configured in SyncValue(63:0). In Packet mode this field is also
used for Sync word generation in TX mode.
NOTE
SyncValue choices containing 0x00 bytes are not allowed.
7.2.4 Packet Handler
The packet handler is the block used in Packet mode. Its functionality is fully described in section 7.5.
7.2.5 Control
The control block configures and controls the full chip's behavior according to the settings programmed in
the configuration registers.
7.3 Digital IO Pins Mapping
Six general purpose IO pins are available on the MKW01Z128, and their configuration in Continuous or
Packet mode is controlled through RegDioMapping1 and RegDioMapping2.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-6 Freescal e Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 94

7.3.1 DIO Pins Mapping in Continuous Mode
Mode Diox
Mapping
DIO5 DIO4 DIO3 DIO2 DIO1 DIO0
00-----01-----10 LowBat LowBat AutoMode - LowBat LowBat
11 ModeReady - - - - ModeReady
00 ClkOut - - - - 01-----10 LowBat LowBat AutoMode - LowBat LowBat
11 ModeReady - - - - ModeReady
00 ClkOut - - - - PllLock
01-----10 LowBat LowBat AutoMode - LowBat LowBat
11 ModeReady PllLock - - PllLock ModeReady
00 ClkOut Timeout Rssi Data Dclk SyncAddress
01 Rssi RxReady RxReady Data RxReady Timeout
10 LowBat SyncAddress AutoMode Data LowBat Rssi
11 ModeReady PllLock Timeout Data SyncAddress ModeReady
00 ClkOut TxReady TxReady Data Dclk PllLock
01 ClkOut TxReady TxReady Data TxReady TxReady
10 LowBat LowBat AutoMode Data LowBat LowBat
11 ModeReady PllLock TxReady Data PllLock ModeReady
Tx
FS
Rx
Sleep
Stdby
Mode Diox
Mapping
DIO5 DIO4 DIO3 DIO2 DIO1 DIO0
00 - - FifoFull FifoNotEmpty FifoLevel 01 - - - - FifoFull 10 LowBat LowBat LowBat LowBat FifoNotEmpty LowBat
11 ModeReady - - AutoMode - 00 ClkOut - FifoFull FifoNotEmpty FifoLevel 01 - - - - FifoFull 10 LowBat LowBat LowBat LowBat FifoNotEmpty LowBat
11 ModeReady - - AutoMode - 00 ClkOut - FifoFull FifoNotEmpty FifoLevel 01 - - - - FifoFull 10 LowBat LowBat LowBat LowBat FifoNotEmpty LowBat
11 ModeReady PllLock PllLock AutoMode PllLock PllLock
00 ClkOut Timeout FifoFull FifoNotEmpty FifoLevel CrcOk
01 Data Rssi Rssi Data FifoFull PayloadReady
10 LowBat RxReady SyncAddress LowBat FifoNotEmpty SyncAddress
11 ModeReady PllLock PllLock AutoMode Timeout Rssi
00 ClkOut ModeReady FifoFull FifoNotEmpty FifoLevel PacketSent
01 Data TxReady TxReady Data FifoFull TxReady
10 LowBat LowBat LowBat LowBat FifoNotEmpty LowBat
11 ModeReady PllLock PllLock AutoMode PllLock PllLock
Tx
FS
Rx
Sleep
Stdby
Table 7-2. DIO Mapping, Continuous Mode
Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.3.2 DIO Pins Mapping in Packet Mode
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-7
Table 7-3. DIO Mapping, Packet Mode
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 95

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
NOTE
Received Data is only shown on the Data signal between RxReady and
PayloadReady’s rising edges
7.4 Continuous Mode
7.4.1 General Description
As illustrated in Figure 7-6, in Continuous mode the NRZ data to (from) the (de)modulator is directly
accessed by the MCU on the bidirectional DIO2/DAT A pin. The FIFO and packet handler are thus inactive.
Figure 7-6. Continuous Mode Conceptual View
7.4.2 TX Processing
In TX mode, a synchronous data clock for an external MCU is provided on DIO1/DCLK pin. Clock timing
with respect to the data is illustrated in Figure 7-7. DA T A is internally sampled on the rising edge of DCLK
so the MCU can change logic state anytime outside the grayed out setup/hold zone.
Figure 7-7. TX Processing in Continuous Mode
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-8 Freescal e Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 96

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
NOTE
The use of DCLK is required when the modulation shaping is enabled.
7.4.3 RX Processing
If the bit synchronizer is disabled, the raw demodulator output is made directly available on DA TA pin and
no DCLK signal is provided.
Conversely, if the bit synchronizer is enabled, synchronous cleaned data and clock are made available
respectively on DIO2/DATA and DIO1/DCLK pins. DATA is sampled on the rising edge of DCLK and
updated on the falling edge as illustrated below.
Figure 7-8. RX Processing in Continuous Mode
NOTE
In Continuous mode it is always recommended to enable the bit
synchronizer to clean the DATA sig nal even if the DCLK signal is not used
by the MCU (bit synchronizer is automatically enabled in Packet mode).
7.5 Packet Mode
7.5.1 General Description
In Packet mode the NRZ data to (from) the (de)modulator is not directly accessed by the MCU but stored
in the FIFO and accessed via the SPI interface.
In addition, the MKW01Z128 packet handler performs several packet oriented tasks such as Preamble and
Sync word generation, CRC calculation/check, whitening/dewhitening of data, Manchester
encoding/decoding, address filtering, AES encryption/decryption, etc. This simplifies software and
reduces MCU overhead by performing these repetitive tasks within the RF chip itself.
Another important feature is ability to fill and empty the FIFO in Sleep/Stdby mode, ensuring optimum
power consumption and adding more flexibility for the software.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-9
Page 97

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
Figure 7-9. Packet Mode Conceptual View
The Bit Synchronizer is automatically enabled in Packet mode.
NOTE
7.5.2 Packet Format
7.5.2.1 Fixed Length Packet Format
Fixed length packet format is selected when bit PacketFormat is set to 0 and PayloadLength is set to any
value greater than 0.
In applications where the packet length is fixed in advance, this mode of operation may be of interest to
minimize RF overhead (no length byte field is required). All nodes, whether TX only , RX only, or TX/RX
should be programmed with the same packet length value.
The length of the payload is limited to 255 bytes if AES is not enabled else the message is limited to 64
bytes (i.e. max 65 bytes payload if Address byte is enabled).
The length programmed in PayloadLength relates only to the payload which includes the message and the
optional address byte. In this mode, the payload must contain at least one byte, i.e. address or message
byte.
An illustration of a fixed length packet is shown below. It contains the following fields:
• Preamble (1010...)
• Sync word (Network ID)
• Optional Address byte (Node ID)
• Message data
• Optional 2-bytes CRC checksum
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 98

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
Message
Up to 255 bytes
Address
byte
CRC
2-bytes
Sync Word
0 to 8 bytes
Preamble
0 to 65535
bytes
Payload
(min 1 byte)
CRC checksum calculation
DC free Data encoding
Fields added by the packet handler in Tx and processed and removed in Rx
Optional User provided fields which are part of the payload
Message part of the payload
AES Enc/Dec
Message
Up to 255 bytes
Address
byte
Length
byte
CRC
2-bytes
Sync Word
0 to 8 bytes
Preamble
0 to 65535
bytes
Payload
(min 2 bytes)
CRC checksum calculation
DC free Data encoding
Fields added by the packet handler in Tx and processed and removed in Rx
Optional User provided fields which are part of the payload
Message part of the payload
AES Enc/Dec
Figure 7-10. Fixed Length Packet Format
7.5.2.2 Variable Length Packet Format
Variable length packet format is selected when bit PacketFormat is set to 1.
This mode is useful in applications where the length of the packet is not known in advance and can vary
over time. It is then necessary for the transmitter to send the length information together with each packet
in order for the receiver to operate properly.
In this mode the length of the payload, indicated by the length byte, is given by the first byte of the FIFO
and is limited to 255 bytes if AES is not enabled else the message is limited to 64 bytes (i.e. max 66 bytes
payload if Address byte is enabled). Note that the length byte itself is not included in its calculation. In this
mode, the payload must contain at least 2 bytes, i.e. length + address or message byte.
An illustration of a variable length packet is shown below. It contains the following fields:
• Preamble (1010...)
• Sync word (Network ID)
• Length byte
• Optional Address byte (Node ID)
• Message data
• Optional 2-bytes CRC checksum
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-11
Figure 7-11. Variable Length Packet Format
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Page 99

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
7.5.2.3 Unlimited Length Packet Format
Unlimited length packet format is selected when bit PacketFormat is set to 0 and PayloadLength is set to 0.
The user can then transmit and receive packet of arbitrary length and PayloadLength register is not used
in TX/RX modes for counting the length of the bytes transmitted/received.
In TX the data is transmitted depending on the TxStartCondition bit. On the RX side the data processing
features like Address filtering, Manchester encoding and data whitening are not available if the sync
pattern length is set to zero (SyncOn = 0). The filling of the FIFO in this case can be controlled by the bit
FifoFillCondition. The CRC detection in RX is also not supported in this mode of the packet handler,
however CRC generation in TX is operational. The interrupts like CrcOk & PayloadReady are not
available either.
An unlimited length packet is made up of the following fields:
• Preamble (1010...).
• Sync word (Network ID).
• Optional Address byte (Node ID).
• Message data
• Optional 2-bytes CRC checksum (TX only)
Figure 7-12. Unlimited Length Packet Format
7.5.3 TX Processing (without AES)
In TX mode the packet handler dynamically builds the packet by performing the following operations on
the payload available in the FIFO:
• Add a programmable number of preamble bytes
• Add a programmable Sync word
• Optionally calculating CRC over complete payload field (optional length byte + optional address
byte + message) and appending the 2 bytes checksum.
• Optional DC-free encoding of the data (Manchester or whitening)
Only the payload (including optional address and length fields) is required to be provided by the user in
the FIFO.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
7-12 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Page 100

Transceiver Digital Control and Communications
The transmission of packet data is initiated by the Packet Handler only if the chip is in TX mode and the
transmission condition defined by TxStartCondition is fulfilled. If transmission condition is not fulfilled
then the packet handler transmits a preamble sequence until the condition is met. This happens only if the
preamble length
0, otherwise it transmits a zero or one until the condition is met to transmit the packet
data.
The transmission condition itself is defined as:
•if TxStartCondition = 1, the packet handler waits until the first byte is written into the FIFO, then
it starts sending the preamble followed by the sync word and user payload
•If TxStartCondition = 0, the packet handler waits until the number of bytes written in the FIFO is
equal to the number defined in RegFifoThresh + 1
• If the condition for transmission was already fulfilled i.e. the FIFO was filled in Sleep/Stdby then
the transmission of packet starts immediately on enabling TX
7.5.4 RX Processing (without AES)
In RX mode the packet handler extracts the user payload to the FIFO by performing the following
operations:
• Receiving the preamble and stripping it off
• Detecting the Sync word and stripping it off
• Optional DC-free decoding of data
• Optionally checking the address byte
• Optionally checking CRC and reflecting the result on CrcOk.
Only the payload (including optional address and length fields) is made available in the FIFO.
When the RX mode is enabled the demodulator receives the preamble followed by the detection of sync
word. If fixed length packet format is enabled then the number of bytes received as the payload is given
by the PayloadLength parameter.
In variable length mode the first byte received after the sync word is interpreted as the length of the
received packet. The internal length counter is initialized to this received length. The PayloadLength
register is set to a value which is greater than the maximum expected length of the received packet. If the
received length is greater than the maximum length stored in PayloadLength register the packet is
discarded otherwise the complete packet is received.
If the address check is enabled then the second byte received in case of variable length and first byte in
case of fixed length is the address byte. If the address matches to the one in the NodeAddress field,
reception of the data continues otherwise it's stopped. The CRC check is performed if CrcOn = 1 and the
result is available in CrcOk indicating that the CRC was successful. An interrupt (PayloadReady) is also
generated on DIO0 as soon as the payload is available in the FIFO. The payload available in the FIFO can
also be read in Sleep/Standby mode.
If the CRC fails the PayloadReady interrupt is not generated and the FIFO is cleared. This function can be
overridden by setting CrcAutoClearOff = 1, forcing the availability of PayloadReady interrupt and the
payload in the FIFO even if the CRC fails.
MKW01xxRM Reference Manual, Rev. 3, 04/2016
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7-13
 Loading...
Loading...