Page 1

S12 MagniV
Microcontrollers
nxp.com
MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Reference Manual
Rev. 1.3
07 MAR 2017
MC9S12ZVMBRM
Page 2
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family is targeted for safety relevant systems and has been developed using
an ISO26262 compliant development system under the NXP Safe Assure program. For details of
device usage in safety relevant systems refer to the MC9S12ZVMB Safety Manual.
The document revision on the Internet is the most current. To verify this is the latest revision, refer to:
nxp.com
This document contains information for all modules except the CPU. For CPU information please refer to
the CPU S12Z Reference Manual. The following revision history table summarizes changes to this
document. The individual module sections contain revision history tables with more detailed information..
Table 0-1. Revision History
Date Revision Description
Updated family member comparison table
26 Nov 2015 1.1
24 Mar 2016 1.2
16 Sep 2016
07 Mar 2017 1.3
1.3
DRAFT A
Corrected Figure 1-10
Updated ordering information in Appendix K
Added Grade0 row to device summary Table 1-2
Corrected number of external ADC channels Section 1.4.11
Specified unused VSUPHS must be connected to VSUP or VDDX Section 1.7.3.6
Adjusted VREG temperature sensor electrical parameter valuesTa b le B -1
Changed ADC maximum frequency from 8.34MHz to 8MHz Table C-1
Adjusted HVI input resistance in PIM chapter Figure 2-42
Corrected pin name from VRH0 to VRH_0 Figure 1-4
Minor formating and error corrections (see PIM, GDU, SRAM_ECC revision histories)
Corrected write access limitations for GDU registers
Added bootstrap switch diode to GDU Figure 18-17
Added GDU current sense unity bandwidth and input resistance to Ta bl e E- 1
Changed RESET pin input pulse passed parameter minimum value Ta b le A -11
Added bootstrap diode resistance parameter Table E-1
Added to applications list in device overview
Added temperature sensor application information Section 1.13.1
Renamed CPMU alternate temperature sensor to DVBE temperature sensor
Enhanced power dissipation info Table A-7, Figure A-2
Updated PT2 leakage values Table A-10
Updated current consumption values Table A-16, Tab l e A -1 7
Updated DVBE temperature sensor values Ta bl e B - 1
Updated VBG temperature dependence value, Ta b le B -1
Added desaturation thresholds to GDU electrical specification Ta bl e E -1
Updated VLS current limit threshold Table E-1
Added parameter GHD division ratio through phase mux.Ta bl e E - 1
Clarified VDDX range for test and characterization Ta b le A -1 0, Ta bl e C - 1
Updated ISUPS values at 105C Ta b le A -1 7
Updated V
Updated temperature sensor application information Section 1.13.1
Updated GDU t
Added R
Updated gate drive footnote Ta bl e E -1
Updated current injection considerations C.1.1.4/C-692, Table A-12
parameter value Table B-1
DVBE
, t
delon
deloff
bsdon
and I
parameter values Table E-1
VBS
parameter values Tab le E -1
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
2 NXP Semiconductors
Page 3

Chapter 1
Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.2.1 MC9S12ZVMB-Family member comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.2.2 ADC module versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.2.3 S12ZVMBA versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.3 Chip-Level features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.4 Module features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.4.1 S12Z central processor unit (CPU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.4.2 Embedded memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.4.3 Clocks, reset & power management unit (CPMU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.4.4 External oscillator (XOSCLCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.4.5 4 channel timer (TIM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.4.6 Pulse width modulator with fault protection (PMF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.4.7 Programmable trigger unit (PTU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.4.8 LIN physical layer transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.4.9 Serial communication interface module (SCI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4.10 Serial peripheral interface module (SPI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4.11 Analog-to-digital converter module (ADC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4.12 Supply voltage sensor (BATS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.4.13 On-chip voltage regulator system (VREG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.4.14 Gate drive unit (GDU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.4.15 High side driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.6 Device memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.6.1 Part ID assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1.7 Signal description and device pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1.7.1 Pin assignment overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1.7.2 Detailed external signal descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1.7.3 Power supply pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
1.7.4 Package and pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
1.7.5 Pin and signal mapping overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
1.8 Internal signal mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.8.1 ADC connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.8.2 GDU timer connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
1.8.3 PTU connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
1.8.4 PMF connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
1.8.5 Motor control loop interface connectivity overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
1.8.6 BDC clock source connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
1.8.7 LINPHY connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
1.8.8 FTMRZ connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
1.8.9 CPMU connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
1.9 Modes of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
1.9.1 Chip configuration modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 3
Page 4

1.9.2 Debugging modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
1.9.3 Low power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
1.10 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
1.10.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
1.10.2 Securing the microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
1.10.3 Operation of the secured microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
1.10.4 Unsecuring the microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
1.10.5 Reprogramming the security bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
1.10.6 Complete memory erase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
1.11 Resets and interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
1.11.1 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
1.11.2 Interrupt vectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
1.11.3 Effects of reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
1.12 Module device level dependencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
1.12.1 CPMU COP and GDU GSUF configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
1.12.2 Flash IFR mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
1.12.3 BDC command restriction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
1.13 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
1.13.1 Temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
1.13.2 SCI baud rate detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
1.13.3 BDCM complementary mode operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
1.13.4 Power domain considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Chapter 2
Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
2.1.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
2.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
2.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
2.2.1 Internal Routing Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
2.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
2.3.1 Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
2.3.2 PIM Registers 0x0200-0x020F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
2.3.3 PIM Generic Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
2.3.4 PIM Generic Register Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
2.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
2.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
2.4.2 Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
2.4.3 Pin I/O Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
2.4.4 Pull Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
2.4.5 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
2.4.6 High-Voltage Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
2.5 Initialization and Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
2.5.1 Port Data and Data Direction Register writes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
2.5.2 SCI Baud Rate Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
4 NXP Semiconductors
Page 5

2.5.3 Over-Current Protection on PP0 (EVDD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
2.5.4 Over-Current Protection on PT2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
2.5.5 Open Input Detection on PL[2:0] (HVI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Chapter 3
Memory Mapping Control (S12ZMMCV1)
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
3.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.1.2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.1.3 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.1.4 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.1.5 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.3.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
3.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
3.4.1 Global Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
3.4.2 Illegal Accesses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
3.4.3 Uncorrectable ECC Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Chapter 4
Interrupt (S12ZINTV0)
4.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
4.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
4.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
4.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
4.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
4.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
4.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
4.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
4.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
4.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
4.4.1 S12Z Exception Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
4.4.2 Interrupt Prioritization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
4.4.3 Priority Decoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
4.4.4 Reset Exception Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
4.4.5 Exception Priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
4.4.6 Interrupt Vector Table Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
4.5 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
4.5.1 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
4.5.2 Interrupt Nesting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
4.5.3 Wake Up from Stop or Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 5
Page 6

Chapter 5
Background Debug Controller (S12ZBDCV2)
5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
5.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
5.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
5.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
5.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
5.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
5.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
5.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
5.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
5.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
5.4.1 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
5.4.2 Enabling BDC And Entering Active BDM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
5.4.3 Clock Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
5.4.4 BDC Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
5.4.5 BDC Access Of Internal Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
5.4.6 BDC Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
5.4.7 Serial Interface Hardware Handshake (ACK Pulse) Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.4.8 Hardware Handshake Abort Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
5.4.9 Hardware Handshake Disabled (ACK Pulse Disabled) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
5.4.10 Single Stepping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
5.4.11 Serial Communication Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
5.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
5.5.1 Clock Frequency Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Chapter 6
S12Z DebugLite (S12ZDBGV3) Module
6.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
6.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
6.1.2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
6.1.3 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
6.1.4 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
6.1.5 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
6.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
6.2.1 External Event Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
6.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
6.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
6.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
6.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
6.4.1 DBG Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
6.4.2 Comparator Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
6.4.3 Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
6.4.4 State Sequence Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
6 NXP Semiconductors
Page 7

6.4.5 Breakpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
6.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
6.5.1 Avoiding Unintended Breakpoint Re-triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
6.5.2 Breakpoints from other S12Z sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Chapter 7
ECC Generation Module (SRAM_ECCV3)
7.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
7.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
7.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
7.2.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
7.2.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
7.3 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
7.3.1 Aligned Memory Write Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
7.3.2 Non-aligned Memory Write Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
7.3.3 Memory Read Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
7.3.4 Memory Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
7.3.5 Interrupt Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
7.3.6 ECC Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
7.3.7 ECC Debug Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Chapter 8
S12 Clock, Reset and Power Management Unit (S12CPMU_UHV_V11)
8.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
8.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
8.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
8.1.3 S12CPMU_UHV_V11 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
8.2 Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.1 RESET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.2 EXTAL and XTAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.3 VSUP — Regulator Power Input Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.4 VDDA, VSSA — Regulator Reference Supply Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.5 VDDX, VSSX — Pad Supply Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
8.2.6 BCTL — Base Control Pin for external PNP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.7 VSS — Core Logic Ground Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.8 VDD — Internal Regulator Output Supply (Core Logic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.9 VDDF — Internal Regulator Output Supply (NVM Logic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.10 API_EXTCLK — API external clock output pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.11 TEMPSENSE — Internal Temperature Sensor Output Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
8.2.12 DVBE TEMPSENSE — DVBE Internal Temperature Sensor Output Voltage . . . . . . 230
8.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
8.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
8.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
8.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 7
Page 8

8.4.1 Phase Locked Loop with Internal Filter (PLL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
8.4.2 Startup from Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
8.4.3 Stop Mode using PLLCLK as source of the Bus Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
8.4.4 Full Stop Mode using Oscillator Clock as source of the Bus Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
8.4.5 External Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
8.4.6 System Clock Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
8.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
8.5.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
8.5.2 Description of Reset Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
8.5.3 Oscillator Clock Monitor Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
8.5.4 PLL Clock Monitor Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
8.5.5 Computer Operating Properly Watchdog (COP) Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
8.5.6 Power-On Reset (POR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
8.5.7 Low-Voltage Reset (LVR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
8.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
8.6.1 Description of Interrupt Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
8.7 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
8.7.1 General Initialization Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
8.7.2 Application information for COP and API usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
8.7.3 Application Information for PLL and Oscillator Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Chapter 9
Analog-to-Digital Converter
9.1 Differences ADC12B_LBA V1 vs V2 vs V3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
9.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
9.3 Key Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
9.3.1 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
9.3.2 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
9.4 Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
9.4.1 Detailed Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
9.5 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
9.5.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
9.5.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
9.6 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
9.6.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
9.6.2 Analog Sub-Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
9.6.3 Digital Sub-Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
9.7 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
9.8 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
9.8.1 ADC Conversion Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
9.8.2 ADC Sequence Abort Done Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
9.8.3 ADC Error and Conversion Flow Control Issue Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
9.9 Use Cases and Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
9.9.1 List Usage — CSL single buffer mode and RVL single buffer mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
8 NXP Semiconductors
Page 9

9.9.2 List Usage — CSL single buffer mode and RVL double buffer mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
9.9.3 List Usage — CSL double buffer mode and RVL double buffer mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
9.9.4 List Usage — CSL double buffer mode and RVL single buffer mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
9.9.5 List Usage — CSL double buffer mode and RVL double buffer mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
9.9.6 RVL swapping in RVL double buffer mode and related registers ADCIMDRI and
ADCEOLRI 352
9.9.7 Conversion flow control application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
9.9.8 Continuous Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
9.9.9 Triggered Conversion — Single CSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
9.9.10 Fully Timing Controlled Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
Chapter 10
Supply Voltage Sensor - (BATSV3)
10.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
10.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
10.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
10.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
10.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
10.2.1 VSUP — Voltage Supply Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
10.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
10.3.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
10.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
10.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
10.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
10.4.2 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
Chapter 11
Timer Module (TIM16B4CV3) Block Description
11.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
11.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
11.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
11.1.3 Block Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
11.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
11.2.1 IOC3 - IOC0 — Input Capture and Output Compare Channel 3-0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
11.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
11.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
11.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
11.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
11.4.1 Prescaler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 384
11.4.2 Input Capture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
11.4.3 Output Compare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
11.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
11.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
11.6.1 Channel [3:0] Interrupt (C[3:0]F) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 9
Page 10

11.6.2 Timer Overflow Interrupt (TOF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
Chapter 12
Pulse Width Modulator with Fault Protection (PMF15B6CV4)
12.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
12.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
12.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
12.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
12.2 Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.1 PWM0–PWM5 Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.2 FAULT0–FAULT5 Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.3 IS0–IS2 Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.4 Global Load OK Signal — glb_ldok . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.5 Commutation Event Signal — async_event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
12.2.6 Commutation Event Edge Select Signal — async_event_edge_sel[1:0] . . . . . . . . . . . 392
12.2.7 PWM Reload Event Signals — pmf_reloada,b,c . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
12.2.8 PWM Reload-Is-Asynchronous Signal — pmf_reload_is_async . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
12.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
12.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
12.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
12.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
12.4.1 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
12.4.2 Prescaler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
12.4.3 PWM Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
12.4.4 Independent or Complementary Channel Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
12.4.5 Deadtime Generators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
12.4.6 Top/Bottom Correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
12.4.7 Asymmetric PWM Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 440
12.4.8 Variable Edge Placement PWM Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
12.4.9 Double Switching PWM Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 442
12.4.10Output Polarity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
12.4.11Software Output Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
12.4.12PWM Generator Loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
12.4.13Fault Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 452
12.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
12.6 Clocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
12.7 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
12.8 Initialization and Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
12.8.1 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
12.8.2 BLDC 6-Step Commutation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
Chapter 13
Programmable Trigger Unit (PTUV3)
13.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 459
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
10 NXP Semiconductors
Page 11

13.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 459
13.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 459
13.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
13.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
13.2.1 PTUT0 — PTU Trigger 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
13.2.2 PTURE — PTUE Reload Event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
13.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
13.3.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
13.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
13.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 473
13.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 473
13.4.2 Memory based trigger event list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 474
13.4.3 Reload mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
13.4.4 Async reload event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 476
13.4.5 Interrupts and error handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 476
13.4.6 Debugging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
Chapter 14
Serial Communication Interface (S12SCIV6)
14.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 479
14.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 479
14.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 480
14.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
14.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
14.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
14.2.1 TXD — Transmit Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
14.2.2 RXD — Receive Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
14.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
14.3.1 Module Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
14.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
14.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
14.4.1 Infrared Interface Submodule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
14.4.2 LIN Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
14.4.3 Data Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
14.4.4 Baud Rate Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 496
14.4.5 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 498
14.4.6 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
14.4.7 Single-Wire Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
14.4.8 Loop Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
14.5 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
14.5.1 Reset Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
14.5.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 513
14.5.3 Interrupt Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 513
14.5.4 Recovery from Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 515
14.5.5 Recovery from Stop Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 515
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 11
Page 12

Chapter 15
Serial Peripheral Interface (S12SPIV5)
15.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 517
15.1.1 Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 517
15.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 517
15.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 517
15.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 518
15.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 519
15.2.1 MOSI — Master Out/Slave In Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 519
15.2.2 MISO — Master In/Slave Out Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
15.2.3 SS — Slave Select Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
15.2.4 SCK — Serial Clock Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
15.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
15.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
15.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
15.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 529
15.4.1 Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 530
15.4.2 Slave Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 531
15.4.3 Transmission Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 532
15.4.4 SPI Baud Rate Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
15.4.5 Special Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 538
15.4.6 Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
15.4.7 Low Power Mode Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
Chapter 16
High-Side Driver Module - HSDRV2C (HSDRV2CV3)
16.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
16.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
16.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 544
16.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 544
16.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
16.2.1 HS[0], HS[1] — High Side Driver Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
16.2.2 VSUPHS — High Side Driver Power Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
16.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
16.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
16.3.2 Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
16.3.3 Port HS Data Register (HSDR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
16.3.4 HSDRV2C Configuration Register (HSCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
16.3.5 HSDRV2C Slew Rate Control Register (HSSLR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
16.3.6 Reserved Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 550
16.3.7 HSDRV2C Status Register (HSSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
16.3.8 HSDRV2C Interrupt Enable Register (HSIE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
16.3.9 HSDRV2C Interrupt Flag Register (HSIF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
16.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
12 NXP Semiconductors
Page 13

16.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
16.4.2 Open Load Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
16.4.3 Over-Current Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
16.4.4 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
Chapter 17
LIN Physical Layer (S12LINPHYV2)
17.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
17.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
17.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 556
17.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
17.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
17.2.1 LIN — LIN Bus Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.2.2 LGND — LIN Ground Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.2.3 VLINSUP — Positive Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.2.4 LPTxD — LIN Transmit Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.2.5 LPRxD — LIN Receive Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
17.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
17.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 565
17.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 565
17.4.2 Slew Rate and LIN Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 565
17.4.3 Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 566
17.4.4 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 569
17.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
17.5.1 Module Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
17.5.2 Interrupt handling in Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
Chapter 18
Gate Drive Unit (GDU2PHV2)
18.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
18.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
18.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
18.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 577
18.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.1 GHD — High-Side Drain Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.2 VBS[1:0] — Bootstrap Capacitor Connection Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.3 GHG[1:0] — High-Side Gate Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.4 GHS[1:0] — High-Side Source Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.5 VLS[1:0] — Voltage Supply for Low-Side Pre-Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.2.6 GLG[1:0] — Low-Side Gate Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
18.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 579
18.3.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 580
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 13
Page 14

18.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
18.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
18.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
18.4.2 Low-Side FET Pre-Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
18.4.3 High-Side FET Pre-Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 596
18.4.4 Charge Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598
18.4.5 Desaturation Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 599
18.4.6 Phase Comparators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 600
18.4.7 Fault Protection Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 601
18.4.8 Current Sense Amplifier and Overcurrent Comparator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
18.4.9 GDU DC Link Voltage Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
18.4.10Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 606
18.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
18.5.1 FET Pre-Driver Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
18.5.2 GDU Intrinsic Dead Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 608
18.5.3 On Chip GDU tdelon and tdeloff Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610
Chapter 19
Flash Module (S12ZFTMRZ)
19.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
19.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 614
19.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 614
19.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
19.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 617
19.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 618
19.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 618
19.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 622
19.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 642
19.4.1 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 642
19.4.2 IFR Version ID Word . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 642
19.4.3 Flash Block Read Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 642
19.4.4 Internal NVM resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 643
19.4.5 Flash Command Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 644
19.4.6 Allowed Simultaneous P-Flash and EEPROM Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 648
19.4.7 Flash Command Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 649
19.4.8 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 665
19.4.9 Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
19.4.10Stop Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
19.5 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
19.5.1 Unsecuring the MCU using Backdoor Key Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
19.5.2 Unsecuring the MCU in Special Single Chip Mode using BDM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 667
19.5.3 Mode and Security Effects on Flash Command Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 667
19.6 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 667
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
14 NXP Semiconductors
Page 15

Appendix A
MCU Electrical Specifications
A.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 669
A.2 I/O Pin Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 679
A.3 Supply Currents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 681
Appendix B
CPMU Electrical Specifications (VREG, OSC, IRC, PLL)
B.1 VREG Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 685
B.2 Reset and Stop Timing Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 686
B.3 IRC and OSC Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 686
B.4 Phase Locked Loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 687
Appendix C
ADC Electrical Specifications
C.1 ADC Operating Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 691
Appendix D
LINPHY Electrical Specifications
D.1 Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 697
D.2 Static Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 697
D.3 Dynamic Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 698
Appendix E
GDU Electrical Specifications
E.1 Operating Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 701
Appendix F
HSDRV Electrical Specifications
F.1 Operating Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 705
F.2 Static Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 705
F.3 Dynamic Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 707
Appendix G
NVM Electrical Specifications
G.1 NVM Timing Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 709
G.2 NVM Reliability Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 710
G.3 NVM Factory Shipping Condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 711
Appendix H
BATS Electrical Specifications
H.1 Static Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 713
H.2 Dynamic Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 714
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 15
Page 16

Appendix I
SPI Electrical Specifications
I.1 Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 715
Appendix J
Package Information
J.1 64LQFP Package Mechanical Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 719
J.2 48LQFP Package Mechanical Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 722
Appendix K
Ordering Information
Appendix L
Detailed Register Address Map
L.1 0x0000–0x0003 Part ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 725
L.2 0x0010–0x001F S12ZINT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 725
L.3 0x0070-0x00FF S12ZMMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 727
L.4 0x0100-0x017F S12ZDBG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 727
L.5 0x0200-0x037F PIM Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730
L.6 0x0380-0x039F FTMRZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 735
L.7 0x03C0-0x03CF SRAM_ECC_32D7P. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 737
L.8 0x0400-0x042F TIM1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 738
L.9 0x0500-x053F PMF15B6C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740
L.10 0x0580-0x059F PTU. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 743
L.11 0x05C0-0x05EF TIM0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 745
L.12 0x0600-0x063F ADC0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 747
L.13 0x06A0-0x06BF GDU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 748
L.14 0x06C0-0x06DF CPMU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750
L.15 0x06F0-0x06F7 BATS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 751
L.16 0x0700-0x0707 SCI0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 752
L.17 0x0710-0x0717 SCI1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 753
L.18 0x0780-0x0787 SPI0. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 753
L.19 0x0980-0x0987 LINPHY0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 754
L.20 0x09C0-0x09C7 HSDRV0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 754
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
16 NXP Semiconductors
Page 17
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-1. Revision History
Version
Number
0.4 11.Jun.2015 General Initial version for S12ZVMB64 product
0.5 16.Jul.2015 General Removed async_event connections
0.6 17.Jul.2016 Section 1.1 Added applications
Revision
Date
Sections
Affected
Description of Changes
Added GDU to TIM1 IC2 connection
Changed pin order to improve VLS bond out
1.1 Introduction
The S12 MagniV product line is a highly optimized, automotive family of devices which integrate, beside
the typical digital peripherals, additional analog battery level (12 V) components.
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family is a new member of the S12 MagniV product line based on the enhanced
performance, linear address space S12Z core and delivers an optimized solution with the integration of
several key system components into a single device, optimizing system architecture and achieving
significant space savings.
The particular differentiating features of this family are the enhanced S12Z core, the combination of an
ADC synchronized to PWM signals using a Programmable Trigger Unit (PTU) and the integration of
“high-voltage” analog modules, including the voltage regulator (VREG), Gate Drive Unit (GDU) and a
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) physical layer. These features enable a fully integrated single chip
solution to drive external power MOSFETs for motor drive applications.
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family includes error correction code (ECC) on RAM and flash memory, EEPROM
for diagnostic or data storage, a fast analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a frequency modulated phase
locked loop (PLL) that improves the EMC performance. The MC9S12ZVMB-Family delivers all the
advantages and efficiencies of a 16-bit MCU while retaining the low cost, power consumption, EMC, and
code-size efficiency advantages currently enjoyed by users of existing S12 families. In addition to the
peripheral module I/O ports, further I/O ports are available with interrupt capability allowing wake-up
from stop or wait modes.
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family is a general-purpose family of devices suitable for a range of applications,
including:
• Brush DC motors that need driving in 2 directions, along with PWM control for
— Window lift
— Trunk opener
— Sun roof
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductor 17
Page 18
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
— Sliding doors
— Seat positioning
1.2 Features
This section describes the key features of the MC9S12ZVMB-Family.
1.2.1 MC9S12ZVMB-Family member comparison
Table 1-2 provides a summary of feature set differences within the MC9S12ZVMB-Family. All other
features are common to all family members.
Table 1-2. MC9S12ZVMB-Family devices
Feature S12ZVMBA S12ZVMB
Flash memory 64 KB 48 KB 64 KB 48 KB 64 KB 48 KB 64 KB 48 KB
Package option LQFP48 LQFP64 LQFP48 LQFP64
Grade 0 qualification
(Ta up to 150
EEPROM 512 Byte
RAM 4 KB
C)
Yes No Yes No
Physical Layer LIN
High Voltage Inputs 3
High Side Drivers 2
FET pre-driver (GDU) 2 HS + 2 LS
Max. PWM frequency 20 kHz
Integrated Current Sense Op-Amp 1
VREG ballast transistor support yes
SCI 2
SPI 1
16-Bit Timer channels 4+4
15-bit PMF channels
ADC channels mapped to pins 5 9 5 9
EVDD (20 mA source) 1
NGPIO (25 mA sink) 1
General purpose I/O 15 24 15 24
1. One SCI internally mapped to LIN physical layer
2. Four PWM channels internally mapped to GDU, 2 PWM channels for GPIO/HS
(2)
(1)
6
Max. PWM frequency 1 kHz
2 HS + 2 LS
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
18 NXP Semiconductors
Page 19

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.2.2 ADC module versions
This device family features ADC V3. The ADC module description includes a superset of features for V1,
V2 and V3. It also summarizes these minor version differences.
1.2.3 S12ZVMBA versions
The FET-Predriver on the S12ZVMB version cannot be driven directly from the PMF PWM channels at a
frequency of greater than 1KHz. Otherwise the S12ZVMB device is identical to the S12ZVMBA device.
1.3 Chip-Level features
On-chip modules available within the family include the following features:
• S12Z CPU core
• 64 KB or 48 KB on-chip flash with ECC
• 512 Byte EEPROM with ECC
• 4 KB on-chip SRAM with ECC
• Phase locked loop (IPLL) frequency multiplier with internal filter
• 1 MHz internal RC oscillator with +/-1.3% accuracy over junction temperature range up to 150C
• 4-20 MHz amplitude controlled pierce oscillator
• Internal COP (watchdog) module
• 6-channel, 15-bit pulse width modulator with fault protection (PMF)
• Low-side and High-side FET pre-drivers for each phase
— Gate drive pre-regulator (11 V LDO)
— High-side gate supply generated using bootstrap circuit with internal diode and external
capacitor
— Sustaining charge pump with two external capacitors and diodes
— High-side drain (GHD) monitoring on internal ADC channel using GHD/5 voltage
• Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with 10-bit resolution and up to 9 channels available on
external pins
• One serial peripheral interface (SPI) module
• One serial communication interface (SCI) module with interface to internal LIN physical layer
transceiver (with RX connected to a timer channel for frequency calibration purposes, if desired)
• One additional SCI (not connected to LIN physical layer)
• On-chip LIN physical layer transceiver fully compliant with the LIN 2.2 and SAE J2602-2
standards
• Two 4-channel timer modules (TIM) with input capture/output compare
• One programmable trigger unit (PTU) for ADC trigger synchronization
• On-chip voltage regulator (VREG) for regulation of input supply and all internal voltages
• One current sense circuit for over-current detection or torque measurement
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 19
Page 20

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
• Autonomous periodic interrupt (API)
• Two High-side Driver outputs
• Three High Voltage Input (HVI) pins
• One 20mA high-current output for use as Hall sensor supply
• Supply voltage sensor with low battery warning
• One high current (25 mA sink) NGPIO
• Chip temperature sensor
1.4 Module features
The following sections provide more details of the integrated modules.
1.4.1 S12Z central processor unit (CPU)
The S12Z CPU is a revolutionary high-speed core, with code size and execution efficiencies over the S12X
CPU. The S12Z CPU also provides a linear memory map eliminating the inconvenience and performance
impact of page swapping.
• Harvard Architecture - parallel data and code access
• 3 stage pipeline
• 32-Bit wide instruction and databus
• 32-Bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
• 24-bit addressing, of 16 MByte linear address space
• Instruction and addressing modes optimized for C-programming & compilation
— Multiply and accumulate (MAC) unit 32bit += 32bit*32bit
— Hardware divider
— Single cycle multi-bit shifts (Barrel shifter)
— Special instructions for fixed point math
• Unimplemented opcode traps
• Unprogrammed byte value (0xFF) defaults to SWI instruction
1.4.1.1 Background debug controller (BDC)
• Background debug controller (BDC) with single-wire interface
— Non-intrusive memory access commands
— Supports in-circuit programming of on-chip nonvolatile memory
1.4.1.2 Debugger (DBG)
• Three comparators (A, B and D)
— Comparator A compares the full address bus and full 32-bit data bus
— Comparators B and D compare the full address bus only
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
20 NXP Semiconductors
Page 21

— Each comparator can be configured to monitor PC addresses or addresses of data accesses
— Each comparator can select either read or write access cycles
— Comparator matches can force state sequencer state transitions
• Three comparator modes
— Simple address/data comparator match mode
— Inside address range match
— Outside address range match
• State sequencer control
— State transitions forced by comparator matches
— State transitions forced by software write to TRIG
— State transitions forced by an external event
• The following types of breakpoints
— CPU breakpoint entering active BDM on breakpoint (BDM)
— CPU breakpoint executing SWI on breakpoint (SWI)
1.4.2 Embedded memory
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.4.2.1 Memory access integrity
• Illegal address detection
• ECC support on embedded NVM and SRAM
1.4.2.2 Flash
On-chip flash memory features the following:
• Up to 64KB of program flash memory
— 32 data bits plus 7 syndrome ECC (error correction code) bits allow single bit fault correction
and double bit fault detection
— Erase sector size of 512 bytes
— Automated program and erase algorithm
— User margin level setting for reads
— Protection scheme to prevent accidental program or erase
1.4.2.3 EEPROM
• Up to 512 Bytes EEPROM
— 16 data bits plus 6 syndrome ECC bits
— Single bit error correction, double bit error detection
— Erase sector size 4 bytes, program with word resolution
— Automated program and erase algorithm
— User margin level setting for reads
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 21
Page 22

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.4.2.4 SRAM
• Up to 4 Kbytes of general-purpose RAM with ECC
— Single bit error correction and double bit error detection
1.4.3 Clocks, reset & power management unit (CPMU)
• Real time interrupt (RTI)
• Clock monitor, supervising the correct function of the oscillator (CM)
• Computer operating properly (COP) watchdog
— Configurable as window COP for enhanced failure detection
— Can be initialized out of reset using option bits located in flash memory
• System reset generation
• Autonomous periodic interrupt (API) (combination with cyclic, watchdog)
— Trimmable RC oscillator timebase that can remain active in STOP mode
• Low Power Operation
— RUN mode - main full performance operating mode with the entire device clocked
— WAIT mode - the internal CPU clock is switched off, so the CPU does not execute instructions
— Pseudo STOP - system clocks are stopped but the oscillator, RTI, COP, and API modules can
be enabled
— STOP - the oscillator is stopped in this mode, all clocks are switched off and all counters and
dividers remain frozen, with the exception of the COP and API which can optionally run from
ACLK
1.4.3.1 Internal phase-locked loop (IPLL)
• Phase-locked-loop clock frequency multiplier
— No external components required
— Reference divider and multiplier allow large variety of clock rates
— Automatic bandwidth control mode for low-jitter operation
— Automatic frequency lock detector
— Configurable option to spread spectrum for reduced EMC radiation (frequency modulation)
— Reference clock sources:
– Internal 1 MHz RC oscillator (IRC)
– External 4-20 MHz crystal oscillator/resonator
1.4.3.2 Internal RC oscillator (IRC)
• Trimmable internal 1 MHz reference clock.
— Trimmed accuracy for temperature options V, M: 1.3%max.
— Trimmed accuracy for temperature option W: 1.45%max
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
22 NXP Semiconductors
Page 23

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.4.4 External oscillator (XOSCLCP)
• Amplitude controlled Pierce oscillator using 4 MHz to 20 MHz crystal
— Current gain control on amplitude output
— Signal with low harmonic distortion
— Low power
— Good noise immunity
— Eliminates need for external current limiting resistor
— Trans conductance sized for optimum start-up margin for typical crystals
— Oscillator pins shared with GPIO functionality
1.4.5 4 channel timer (TIM)
• 4 x 16-bit channels Timer module for input capture or output compare
• 16-bit free-running counter with 8-bit precision prescaler
1.4.6 Pulse width modulator with fault protection (PMF)
• 6 x 15-bit channel PWM resolution
• Each pair of channels can be combined to generate a PWM signal (with independent control of
edges of PWM signal)
• Dead time insertion available for each complementary pair
• Center-aligned or edge-aligned outputs
• Programmable clock select logic with a wide range of frequencies
• Programmable fault detection
1.4.7 Programmable trigger unit (PTU)
• Synchronizes ADC triggers based on PMF signal edges
• One 16 bit counter as time base for all trigger events
• One trigger generator(TG0) Up to 32 trigger events per trigger generator
• Global Load OK support, to guarantee coherent update of all control loop modules
• Trigger values stored in system memory
• Software generated reload event and trigger event generation for debugging
1.4.8 LIN physical layer transceiver
• Compliant with LIN physical layer 2.2 specification
• Compliant with the SAE J2602-2 LIN standard
• Standby mode with glitch-filtered wake-up
• Slew rate selection optimized for the baud rates:
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 23
Page 24

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
— 10.4 kBit/s
— 20 kBit/s
— Fast Mode (up to 250 kBit/s)
• Selectable pull-up of 34 k or 330 k (in Shutdown Mode, 330 k only)
• Current limitation for LIN Bus pin falling edge.
• Over-current protection.
• LIN TxD-dominant timeout feature monitoring the LPTxD signal.
• Automatic transmitter shutdown in case of an over-current or TxD-dominant timeout.
• Fulfills the OEM “Hardware Requirements for LIN (CAN and FlexRay) Interfaces in Automotive
Applications” v1.3.
1.4.9 Serial communication interface module (SCI)
• Full-duplex or single-wire operation
• Standard mark/space non-return-to-zero (NRZ) format
• Selectable IrDA 1.4 return-to-zero-inverted (RZI) format with programmable pulse widths
• 16-bit baud rate selection
• Programmable character length
• Programmable polarity for transmitter and receiver
• Active edge receive wakeup
• Break detect and transmit collision detect supporting LIN
1.4.10 Serial peripheral interface module (SPI)
• Configurable 8- or 16-bit data size
• Full-duplex or single-wire bidirectional
• Double-buffered transmit and receive
• Master or slave mode
• MSB-first or LSB-first shifting
• Serial clock phase and polarity options
1.4.11 Analog-to-digital converter module (ADC)
• Selectable 10-bit or 8-bit resolution
• Up to 12 external channels & 8 internal channels
• 2.2us for single 10-bit resolution conversion
• Left or right aligned result data
• Continuous conversion mode
• Programmers model with list based command and result storage architecture
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
24 NXP Semiconductors
Page 25

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
• ADC directly writes results to RAM, preventing stall of further conversions
• Internal signals monitored by the ADC module
— VRH, VRL, (VRL+VRH)/2
— Vsup monitor
— VREG Vbg, and Temperature Sensor
— Delta VBE Temperature Sensor
— GDU phase, GDU DC-link
— High Voltage Inputs (PL[2:0])
• External pins can also be used as digital I/O with keyboard wake-up interrupt capability
1.4.12 Supply voltage sensor (BATS)
• Monitoring of supply (VSUP) voltage
• Internal ADC interface from an internal resistive divider
• Optional generation of low or high voltage interrupts
1.4.13 On-chip voltage regulator system (VREG)
• Voltage regulator
— Linear voltage regulator directly supplied by VSUP
— Low-voltage detect on VSUP
— Power-on reset (POR)
— Low-voltage reset (LVR) for VDDX domain
— Over-temperature interrupt
• Internal voltage regulator
— Linear voltage regulator with bandgap reference
— Low-voltage detect on VDDA
— Power-on reset (POR) circuit
— Low-voltage reset for VDD domain
1.4.14 Gate drive unit (GDU)
• Low-side and High-side FET pre-drivers for 2 phases of 2 half bridges
• Gate drive pre-regulator LDO (Low Dropout Voltage Regulator)
• High-side gate supply done via bootstrap circuit with internal diode and external capacitor
• Sustaining charge pump with two external capacitors and diodes
• FET-Predriver short circuit (desaturation) detection
• Over and under voltage detection and shutdown
• Over current monitor with optional shutdown
• Monitoring of FET High-side drain (GHD) voltage
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 25
Page 26

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
• Diagnostic failure management
• Integrated OP-amp functionality
1.4.15 High side driver
• Selectable gate control: HSDR[HSDRx] register bits or PWM or timer channels
• Open-load detection
• Slew rate control
• Over-current shutdown, comprising of:
— Interrupt flag generation
— Driver shutdown
— Optional masking window
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
26 NXP Semiconductors
Page 27
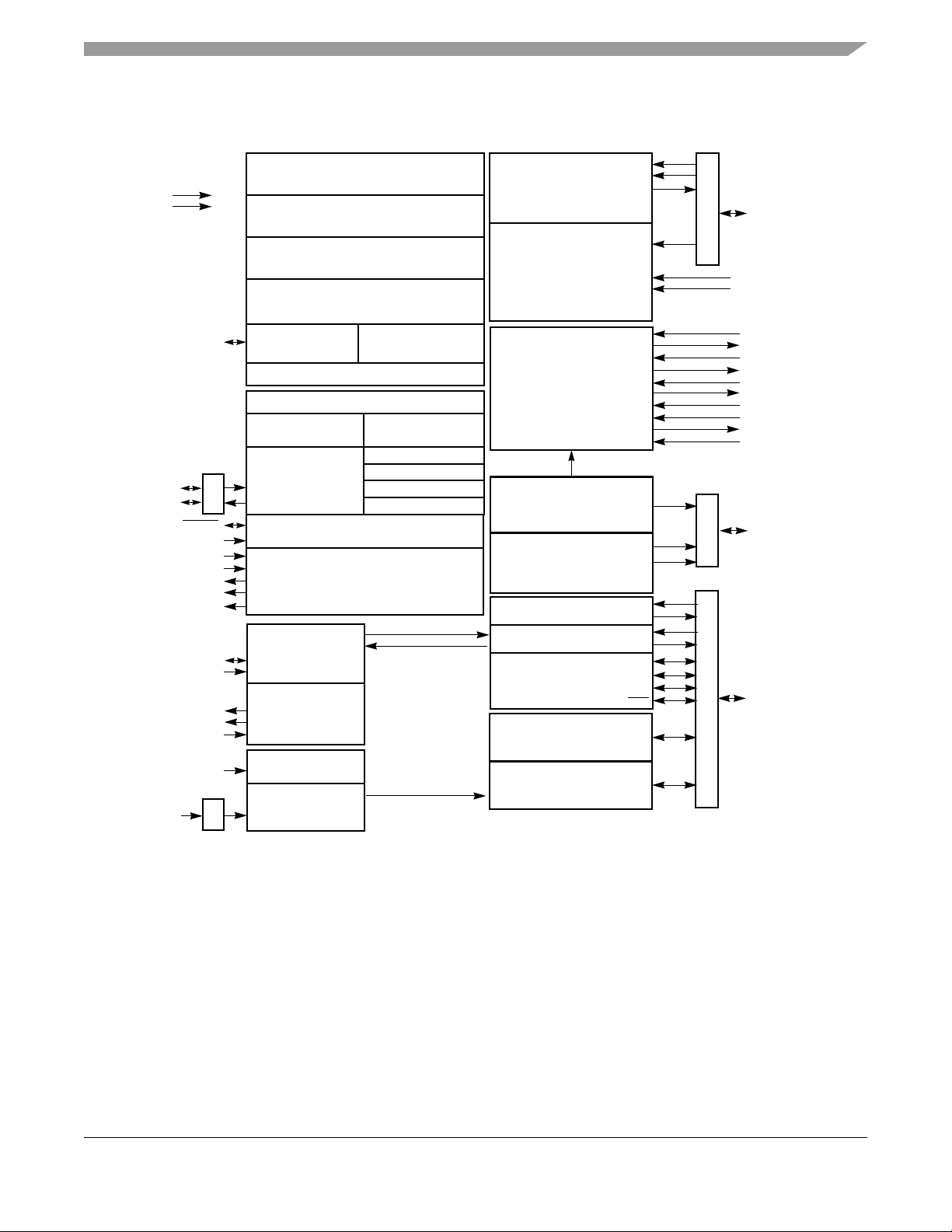
1.5 Block diagram
RESET
EXTAL
XTAL
BKGD
VSUP
Real Time Interrupt
Clock Monitor
Background
TEST
Debug Controller
Interrupt Module
PAD[8:0]/KWAD[8:0]
S12ZCPU
COP Watchdog
PLL with Frequency
Modulation option
Debug Module
Reset Generation
and Test Entry
Auton. Periodic Int.
MOSI0
SS0
SCK0
MISO0
SPI0
5V Voltage
(Nominal input 12V)
Block Diagram shows the maximum configuration
Not all pins or all peripherals are available on all devices and packages.
Rerouting options are not shown.
PE0
PE1
PTAD
IRC
BATS
Voltage Supply Monitor
BDC
DBG
VDDX
VSSX
VSS
High Voltage Input
HVI[2:0]
KWL[2:0]/PL[2:0]
VSUP
SCI1
RXD1
TXD1
PMF
PWM[5:4]
CPMU
ADC
AN[8:0]
VRH_[2:0]
VRL_0
VDDA
VSSA
LP Pierce Oscillator
10-bit
Analog-Digital
Converter
15-bit 6 channel
Pulse Width Modulator
PP[1:0]/KWP[1:0]
PTP
Asynchronous Serial IF
Synchronous Serial IF
Flash with ECC
48 K or 64 K bytes
EEPROM with ECC
512 bytes
RAM with ECC
4 K bytes
Clock Power Management Unit
Internal RC Oscillator
XOSCLCP
PTE
PTL
LIN
LINPHY
LIN
LGND
LGND
RXD0
TXD0
LPTXD
LPRXD
TIM0
IOC0[3:0]
16-bit 4-channel
Time r
PT[7:0]
PTT
GDU
Gate Drive Unit
GHD
CP
VCP
VLS_OUT
VBS[1:0]
GHG[1:0]
GHS[1:0]
VLS
GLG[1:0]
GLS[1:0]
GHD
CP
VCP
VLS_OUT
VBS[1:0]
GHG[1:0]
GHS[1:0]
VLS
GLG[1:0]
GLS[1:0]
High Side Driver
HSDRV
VSUPHS
HS0
HS1
GDU-AMP
Current Sense Circuit
AMPP0
AMPM0
AMP0
PWM[3:0]
PTU
PTURE
Programmable Trigger Unit
PTUT0
TIM1
IOC1[3:0]
16-bit 4-channel
Timer
SCI0
RXD0
TXD0
Asynchronous Serial IF
BCTL
Regulator
PWM[3:0]
IC1_[3,2,0]
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Figure 1-1. MC9S12ZVMB-Family block diagram
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 27
Page 28
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.6 Device memory map
Table 1-3 shows the device register memory map. All modules that can be instantiated more than once on
S12 devices are listed with an index number, even if they are only instantiated once on this device family.
Table 1-3. Module register address ranges
Address Module
0x0000–0x0003 Part ID Register Section 1.6.1 4
0x0004–0x000F
0x0010–0x001F INT 16
0x0020–0x006F Reserved 80
0x0070–0x008F MMC 32
0x0090–0x00FF MMC Reserved 112
0x0100–0x017F DBG 128
0x0180–0x01FF
0x0200–0x037F PIM 384
0x0380–0x039F FTMRZ 32
0x03A0–0x03BF
0x03C0–0x03CF SRAM ECC 16
0x03D0–0x03FF Reserved 48
0x0400–0x042F TIM1 48
0x0430–0x043F Reserved 16
0x0440–0x04FF
0x0500–0x053F PMF 64
Reserved 12
Reserved 128
Reserved 32
Reserved 192
Size
(Bytes)
0x0540–0x057F Reserved 64
0x0580–0x059F PTU 32
0x05A0–0x05BF
0x05C0–0x05EF TIM0 48
0x05F0–0x05FF
0x0600–0x063F ADC0 64
0x0640–0x067F Reserved 64
0x0680–0x069F
0x06A0–0x06BF GDU 32
0x06C0–0x06DF CPMU 32
0x06E0–0x06EF
0x06F0–0x06F7 BATS 8
0x06F8–0x06FF
0x0700–0x0707 SCI0 8
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
28 NXP Semiconductors
Reserved 32
Reserved 16
Reserved 32
Reserved 16
Reserved 8
Page 29
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-3. Module register address ranges
Address Module
0x0708–0x070F Reserved 8
0x0710–0x0717 SCI1 8
0x0718–0x077F Reserved 104
0x0780–0x0787 SPI0 8
0x0788–0x097F Reserved 504
0x0980–0x0987 LINPHY0 8
0x0988–0x09BF
0x09C0–0x09C7 HSDRV0 8
0x09C8–0x0FFF Reserved 1592
Reserved 56
Size
(Bytes)
NOTE
Reserved register space shown above is not allocated to any module. This
register space is reserved for future use. Writing to these locations has no
effect. Read access to these locations returns zero.
Table 1-4. MC9S12ZVMB-Family memory address ranges
Device Address Memory Block
MC9S12ZVB64 0x00_1000–0x00_1FFF SRAM 4K
MC9S12ZVB64 0x10_0000–0x10_01FF EEPROM 512 Bytes
MC9S12ZVB64 0xFF_0000–0xFF_FFFF Program Flash 64K
MC9S12ZVB48 0x00_1000–0x00_1FFF SRAM 4K
MC9S12ZVB48 0x10_0000–0x10_01FF EEPROM 512 Bytes
MC9S12ZVB48 0xFF_4000–0xFF_FFFF Program Flash 48K
Size
(Bytes)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 29
Page 30
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
0x00_1000
0x00_0000
0x10_0000
0x1F_4000
0x80_0000
0xFF_FFFF
RAM
EEPROM
Unmapped
Program NVM
Register Space
4 KByte
max. 8 KByte
max. 2 KByte
max. 128 KByte
6 MByte
High address aligned
Low address aligned
0x1F_8000
Unmapped
address range
0x1F_C000
Reserved (read only)
6 KByte
NVM IFR
256 Byte
Reserved
512 Byte
0x20_0000
30 NXP Semiconductors
Figure 1-2. MC9S12ZVMB-Family global memory map.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 31

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.6.1 Part ID assignments
The part ID is located in four 8-bit registers at addresses 0x0000-0x0003. The read-only value is a unique
part ID for each revision of the chip. Table 1-5 shows the assigned part ID number and mask set number.
Table 1-5. Assigned part ID numbers
Device Mask Set Number Part ID
MC9S12ZVMB64 N17S 0x06160000
1.7 Signal description and device pinouts
This section describes signals that connect off-chip. It includes pin out diagrams, a table of signal
properties, and detailed discussion of signals. Internal inter module signal mapping at device level is
described in 1.8 Internal signal mapping.
1.7.1 Pin assignment overview
Table 1-6 provides a summary of which ports are available.
Table 1-6. Port availability by package option
Port 64 LQFP 48 LQFP
Port AD PAD[8:0] PAD[4:0]
Port E PE[1:0] PE[1:0]
Port L (HVI) PL[2:0] PL[2:0]
Port P PP[1:0] PP[1:0]
Port T PT[7:0] PT[2:0]
sum of ports 24 15
NOTE
To avoid current drawn from floating inputs, all non-bonded pins should be
configured as output or configured as input with a pull up or pull down
device enabled
1.7.2 Detailed external signal descriptions
This section describes the properties of signals available at device pins. Signal names associated with
modules that can be instantiated more than once are indexed, even if the module is only instantiated once.
If a signal already includes a channel number, then the index is inserted before the channel number. Thus
TIMx_y corresponds to TIM instance x, channel number y.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 31
Page 32

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.1 RESET — External reset signal
The RESET signal is an active low bidirectional control signal. It acts as an input to initialize the MCU to
a known start-up state, and an output when an internal MCU function causes a reset. The RESET pin has
an internal pull-up device.
1.7.2.2 TEST — Test pin
This input only pin is reserved for factory test. This pin has an internal pull-down device.
NOTE
The TEST pin must be tied to ground in all applications.
1.7.2.3 MODC — Mode C signal
The MODC signal is used as an MCU operating mode select during reset. The state of this signal is latched
to the MODC bit at the rising edge of RESET. The signal has an internal pull-up device.
1.7.2.4 PAD[8:0] / KWAD[8:0] — Port AD, input pins of ADC
PAD[8:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals can be configured on per signal basis as
interrupt inputs with wake-up capability (KWAD[8:0]). These signals can have a pull-up or pull-down
device selected and enabled on per signal basis. During and out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
1.7.2.5 PE[1:0] — Port E I/O signals
PE[1:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals can have a pull-up or pull-down device,
enabled by on a per pin basis. Out of reset the pull-down devices are enabled.
1.7.2.6 PL[2:0] / KWL[2:0] — Port L input signals
PL[2:0] are the high voltage input signals. These signals can be configured on a per signal basis as interrupt
inputs with wake-up capability (KWL[2:0]). These signals can alternatively be used as analog inputs
measured by the ADC.
1.7.2.7 PP[1:0] / KWP[1:0] — Port P I/O signals
PP[1:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals can be configured on per signal basis as
interrupt inputs with wake-up capability (KWP[1:0]). They can have a pull-up or pull-down device
selected and enabled on per signal basis. During and out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
The PP0 pin features the EVDD option, for an increased high-side current drive with low voltage drop.
1.7.2.8 PT[7:0] — Port T I/O signals
PT[7:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. They can have a pull-up or pull-down device selected
and enabled on per signal basis. During and out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
The PT2 pin features the NGPIO option, for an increased Low-side current drive with low voltage drop.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
32 NXP Semiconductors
Page 33

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.9 AN0_[11:0] — ADC input signals
These are the analog inputs of the Analog-to-Digital Converter. ADC0 has up to 9 analog input channels
connected to PAD[8:0] port pins. The channels AN_[11:9] are connected to HVI[2:0] respectively.
1.7.2.10 VRH_0, VRL_0— ADC reference inputs
VRH_0 and VRL_0 are the reference voltage inputs for the analog-to-digital converter.
1.7.2.11 SPI0 signals
1.7.2.11.1 SS0 signal
This signal is associated with the slave select SS functionality of the serial peripheral interface SPI0.
1.7.2.11.2 SCK0 signal
This signal is associated with the serial clock SCK functionality of the serial peripheral interface SPI0.
1.7.2.11.3 MISO0 signal
This signal is associated with the MISO functionality of the serial peripheral interface SPI0. This signal
acts as master input during master mode or as slave output during slave mode.
1.7.2.11.4 MOSI0 signal
This signal is associated with the MOSI functionality of the serial peripheral interface SPI0. This signal
acts as master output during master mode or as slave input during slave mode
1.7.2.12 SCI[1:0] signals
1.7.2.12.1 RXD[1:0] signals
These signals are associated with the receive functionality of the serial communication interfaces
(SCI[1:0]).
1.7.2.12.2 TXD[1:0] signals
These signals are associated with the transmit functionality of the serial communication interfaces
(SCI[1:0]).
1.7.2.13 Timer IOC0_[3:0] signals
The signals IOC0_[3:0] are associated with the input capture or output compare functionality of the timer
(TIM0) module.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 33
Page 34

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.14 Timer IOC1_[3:0] signals
The signals IOC1_[3:0] are associated with the input capture or output compare functionality of the timer
(TIM1) module.
1.7.2.15 PWM[5:4] signals
The signals PWM[5:4] are associated with the PMF module digital channel outputs.
1.7.2.16 PTU signals
1.7.2.16.1 PTUT0 signal
This is the PTU trigger output signal, routed to a pin for debugging purposes.
1.7.2.16.2 PTURE signal
This signal is the PTU reload enable output signal. This signal is routed to a pin for debugging purposes.
1.7.2.17 Interrupt signals — IRQ and XIRQ
IRQ is a maskable level or falling edge sensitive input. XIRQ is a non-maskable level-sensitive interrupt.
1.7.2.18 Oscillator and clock signals
1.7.2.18.1 Oscillator pins — EXTAL and XTAL
EXTAL and XTAL are the crystal driver and external clock pins. On reset all the device clocks are derived
from the internal PLLCLK, independent of EXTAL and XTAL. XTAL is the oscillator output.
1.7.2.18.2 ECLK
This signal is associated with the output of the bus clock (ECLK).
NOTE
This feature is only intended for debug purposes at room temperature.
It must not be used for clocking external devices in an application.
1.7.2.19 BDC and debug signals
1.7.2.19.1 BKGD — Background debug signal
The BKGD signal is used as a pseudo-open-drain signal for the background debug communication. The
BKGD signal has an internal pull-up device.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
34 NXP Semiconductors
Page 35

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.19.2 DBGEEV — External event input
This signal is the DBG external event input. It is input only. Within the DBG module, it allows an external
event to force a state sequencer transition A falling edge at the external event signal constitutes an event.
Rising edges have no effect. The maximum frequency of events is half the internal core bus frequency.
1.7.2.20 FAULT5 — External fault input
This is the PMF fault input signal, with configurable polarity, that can be used to disable PMF operation
when asserted.
1.7.2.21 LIN Physical layer signals
1.7.2.21.1 LIN0
This pad is connected to the single-wire LIN data bus.
1.7.2.21.2 LP0TXD
This is the LIN physical layer transmitter input signal.
1.7.2.21.3 LP0RXD
This is the LIN physical layer receiver output signal.
1.7.2.21.4 LP0DR1
This is the LIN LP0DR1 register bit, visible at the designated pin for debug purposes.
1.7.2.22 HS[1:0] High-Side driver output signals
Outputs of the two high-side drivers.
1.7.2.23 Gate drive unit (GDU) signals
These are associated with driving the external FETs.
1.7.2.23.1 GHD — FET predriver high-side drain input
This is the drain connection of the external high-side FETs. The voltage present at this input is scaled down
by an internal voltage divider, and can be routed to the internal ADC.
1.7.2.23.2 VBS[1:0] - Bootstrap capacitor connections
These signals are the bootstrap capacitor connections for phases HS[1:0]. The capacitor connected
between HS[1:0] and these signals provides the gate voltage and current to drive the external FET.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 35
Page 36

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.23.3 GHG[1:0] - High-side gate signals
These pins are the gate drives for the high-side power FETs. The drivers provide a high current with low
impedance to turn on and off the high-side power FETs.
1.7.2.23.4 GHS[1:0] - High-side source signals
These pins are the source connection for the high-side power FETs and the drain connection for the lowside power FETs. The low voltage end of the bootstrap capacitor is also connected to this pin.
1.7.2.23.5 VLS - Voltage supply for low -side drivers
This pin is the voltage supply pin for the low-side FET pre-drivers. It should be connected to the voltage
regulator output pin VLS_OUT.
1.7.2.23.6 GLG[1:0] - Low-side gate signals
These pins are the gate drives for the low-side power FETs. The drivers provide a high current with low
impedance to turn on and off the low-side power FETs.
1.7.2.23.7 GLS[1:0] - Low-side source signals
These pins are the low-side source connections for the low-side power FETs. The pins are the power
ground pins used to return the gate currents from the low-side power FETs.
1.7.2.23.8 CP - Charge pump output signal
This pin is the switching node of the charge pump circuit. The supply voltage for charge pump driver is
the output of the voltage regulator VLS_OUT. The output voltage of this pin switches typically between
0V and 11V. This pin must be left unconnected if not used.
1.7.2.23.9 VCP - Charge pump input for high-side driver supply
This is the charge pump input for the FET high-side gate drive supply circuit. The pin must be left
unconnected if not used.
1.7.2.23.10 VLS_OUT - 11V Voltage regulator output
This pin is the output of the GDU integrated voltage regulator. The output voltage is typically 11V. The
input voltage to the voltage regulator is the VSUP pin.
1.7.2.23.11 AMPP0 - Current sense amplifier non-inverting input
This is the current sense amplifier non-inverting input.
1.7.2.23.12 AMPM0 - Current sense amplifier inverting input
This is the current sense amplifier inverting input.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
36 NXP Semiconductors
Page 37

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.2.23.13 AMP0 - Current sense amplifier output
This is the current sense amplifier output.
1.7.3 Power supply pins
The power and ground pins are described below. Because fast signal transitions place high, short-duration
current demands on the power supply, use bypass capacitors with high-frequency characteristics and place
them as close to the MCU as possible.
NOTE
All ground pins must be connected together in the application.
1.7.3.1 VDDX1, VSSX[5:1] — Digital I/O power and ground pins
VDDX1 is the voltage regulator output to supply the digital I/O drivers. The VSSX pins are the ground
pins for the output drivers and GDU drivers.
Bypass requirements on VDDX/VSSX depend on how heavily the MCU pins are loaded.
1.7.3.2 VDDA, VSSA — Power supply pins for ADC
These are the power supply and ground pins for the analog-to-digital converter and the voltage regulator.
1.7.3.3 VSS — Core ground pin
The voltage supply of nominally 1.8V is generated by the internal voltage regulator.
1.7.3.4 LGND — LINPHY ground pin
LGND is the ground pin for the LIN physical layer LINPHY.
1.7.3.5 VSUP — Voltage supply pin for voltage regulator
VSUP is the main supply pin typically coming from the car battery/alternator in the 12V supply voltage
range. This is the voltage supply input from which the voltage regulator generates the on-chip voltage
supplies. It must be protected externally against a reverse battery connection.
1.7.3.6 VSUPHS Voltage supply pin for high-side drivers
VSUPHS is the 12V/18V shared supply voltage pin for the high-side drivers. It must be protected
externally against a reverse battery connection.
NOTE
If not used VSUPHS must be connected either to VSUP or VDDX. It must
not be connected to VSSX
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 37
Page 38

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.7.3.7 EVDD
This is a high current, low voltage drop output intended for supplying external devices in a range of up to
20mA. Configuring the pin direction as output automatically enables the high current capability. It
includes an over current protection feature.
1.7.3.8 NGPIO
This is a high current, low voltage drop output intended for increased low side current driving capability
in a range of up to 25mA. Configuring the pin direction as output automatically enables the high current
capability. It includes an over current protection feature.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
38 NXP Semiconductors
Page 39

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1314151617181920212223
24
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
4847464544434241403938
37
MC9S12ZVMB-Family
48LQFP
GLS1
GLG1
VLS
VSSX4
VBS1
GHG1
GHS1
GHS0
GHG0
VBS0
VSSX3
GLG0
VSUPHS
BKGD
RESET
TEST
PAD 4
PAD 3
PAD 2
PAD 1
VDDA
VSSA
PAD 0
GLS0
VSUP
VLS_OUT
CP
VSSX1
VCP
GHD
PL2
PL1
PL0
HS1
VSSX2
HS0
PP0
VDDX1
PT2
VSS
PE0
PE1
PP1
PT1
PT0
BCTL
LIN0
LGND
1.7.4 Package and pinouts
The following package options are offered.
• 48LQFP
• 64LQFP
The pin outs are shown in the following diagrams. The signal to pin mapping is specified in Table 1-7
Pins specified as N.C. have no physical connection to silicon.
Figure 1-3. MC9S12ZVMB-Family 48-pin LQFP pin out
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 39
Page 40

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
PT4
PT5
PT6
PT7
GLS1
GLG1
VLS
VSSX4
VBS1
GHG1
GHS1
GHS0
GHG0
VBS0
VSSX3
GLG0
.BKGD
RESET
TEST
PAD8
PAD7
PAD6
PAD5
PAD 4
PAD 3
PAD 2
PAD 1
VRH_0
VDDA
VSSA
PAD 0
GLS0
VSUP
VLS_OUT
CP
VSSX1
VCP
GHD
N.C.
PL2
PL1
PL0
N.C.
HS1
VSSX2
HS0
VSUPHS
N.C.
N.C.
PP0
VDDX1
PT2
VSSX5
VSS
PE0
PE1
N.C
PP1
PT1
PT0
PT3
BCTL
LIN0
LGND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
171819202122232425262728293031
32
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
646362616059585756555453525150
49
MC9S12ZVMB
64-pin LQFP
Figure 1-4. MC9S12ZVMB-Family 64-pin LQFP pin out
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
40 NXP Semiconductors
Page 41

1.7.5 Pin and signal mapping overview
Please refer to the PIM chapter for priority and routing information.
Table 1-7. Pin summary (Sheet 1 of 3)
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
LQFP
Option
64 48 Pin
1st
Func.
2nd
Func.
Function
3rd
Func.
4th
Func.
5th
Func.
6th
Func.
Power
Domai
n
Internal Pull
Resistor
CTRL
Rese
t
State
11VSUP——————— ——
2 2 VLS_OU
——————— ——
T
33CP——————— ——
4 4 VSSX1 ——————— ——
55VCP——————— ——
66GHD——————— ——
7—N.C.——————— ——
8 7 PL2 HVI2 KWL2 IC1_2 AN0_11 — — — — —
9 8 PL1 HVI1 KWL1 IC1_1 AN0_10 — — — — —
10 9 PL0 HVI0 KWL0 IC1_0 AN0_9 — — — — —
11—N.C.——————— ——
1210HS1OC1_2PWM5————V
13 11 VSSX2 ——————V
1412HS0OC1_1PWM4————V
1513VSUPHS——————V
SUPHS
SUPHS
SUPHS
SUPHS
——
——
——
——
16—N.C.——————— ——
1714BKGDMODC—————V
18 15 RESET ——————V
DDX
DDX
—Up
TEST pin Up
1916TEST———————RESETDown
20—PAD8KWAD8AN0_8————V
DDA
PERADH/
Off
PPSADH
21—PAD7KWAD7AN0_7————V
DDA
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
22—PAD6KWAD6AN0_6————V
DDA
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 41
Page 42

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-7. Pin summary (Sheet 2 of 3)
LQFP
Option
Function
Power
Domai
64 48 Pin
1st
Func.
23—PAD5KWAD5AN0_5————V
24 17 PAD4 KWAD4 AN0_4 SS0 — — — V
25 18 PAD3 KWAD3 AN0_3 PTUT0 — — — V
26 19 PAD2 KWAD2 AN0_2 AMP0 — — — V
27 20 PAD1 KWAD1 AN0_1 AMPM0 — — — V
28—VRH_0——————V
—21VDDAVRH_0—————V
29—VDDA——————V
30 22 VSSA VRL_0 —————V
31 23 PAD0 KWAD0 AN0_0 AMPP0 — — — V
2nd
Func.
3rd
Func.
4th
Func.
5th
Func.
6th
Func.
n
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
Internal Pull
Resistor
Rese
CTRL
t
State
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
——
——
——
——
PERADL/
Off
PPSADL
3224GLS0——————— ——
3325GLG0——————— ——
34 26 VSSX3 ——————— ——
35 27 VBS0 ——————— ——
3628GHG0——————— ——
3729GHS0——————— ——
3830GHS1——————— ——
3931GHG1——————— ——
40 32 VBS1 ——————— ——
41 33 VSSX4 ——————— ——
4234VLS——————— ——
4335GLG1——————— ——
4436GLS1——————— ——
45—PT7IOC1_3—————V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
42 NXP Semiconductors
Page 43

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-7. Pin summary (Sheet 3 of 3)
LQFP
Option
Function
Power
Domai
64 48 Pin
1st
Func.
46—PT6IOC1_2—————V
2nd
Func.
3rd
Func.
4th
Func.
5th
Func.
6th
Func.
n
DDX
Internal Pull
Resistor
CTRL
PERT/
Rese
t
State
Off
PPST
47—PT5IOC1_1—————V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
48—PT4IOC1_0—————V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
4937LGND——————— ——
5038LIN0——————— —Up
(weak
)
5139BCTL——————— ——
52—PT3IOC0_3—————V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
53 40 PT0 IOC0_0 MOSI0 RXD0 RXD1 XIRQ — V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
54 41 PT1 IOC0_1 MISO0 PWM2 TXD0 TXD1 LP0DR1 V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
55 42 PP1 KWP1 PWM5 FAULT5 SCK0 — — V
DDX
PERP/
Off
PPSP
56—N.C.——————— ——
57 43 PE1 XTAL TXD1 PWM1 DBGEE
V
58 44 PE0 EXTAL RXD1 PWM0 — — V
——V
DDX
DDX
PERE/
PPSE
PERE/
Down
Down
PPSE
5945VSS——————— ——
60 — VSSX5 ——————— ——
61 46 PT2
(NGPIO)
6247VDDX1——————V
63 48 PP0
(EVDD)
IOC0_2 PWM3 LP0RXDFAULT5 ECLK — V
KWP0 PWM4 PTURE IRQ LP0TXD — V
DDX
DDX
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
——
PERP/
Off
PPSP
64—N.C.——————— ——
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 43
Page 44

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.8 Internal signal mapping
This section specifies the mapping of inter-module signals at device level.
1.8.1 ADC connectivity
1.8.1.1 ADC reference voltages
VRH_[2:1] are always mapped to VDDA, VRH_0 is mapped to VDDA in the 48LQFP package option
but mapped to a dedicated VRH_0 pin in the 64LQFP package option. The preferred reference is VRH_0.
VRL_0 is always mapped to VSSA.
1.8.1.2 ADC internal channels
The ADC0 internal channel mapping is shown in Table 1-8.
Table 1-8. Usage of ADC0 internal channels
ADCCMD_1 CH_SEL[5:0]
0 0 1 0 0 0 Internal_0 ADC0 temperature sensor
0 0 1 0 0 1 Internal_1 VREG temperature sensor or bandgap (V
0 0 1 0 1 0 Internal_2 GDU phase multiplexer voltage
0 0 1 0 1 1 Internal_3 GDU DC link voltage monitor
0 0 1 1 0 0 Internal_4 BATS VSUP sense voltage
0 0 1 1 0 1 Internal_5 Reserved
0 0 1 1 1 0 Internal_6 Reserved
0 0 1 1 1 1 Internal_7 Delta VBE temperature sensor
1. Selectable in CPMU
ADC Channel
Usage
BG
The PL[2:0] High Voltage Inputs are connected to ADC0 external channels, AN[11:9] respectively.
1.8.1.3 ADC digital input signals
The ADC input Seq_abort is unused and forced to an inactive state at device level
The ADC Restart input is connected to ptu_reload.
The ADC input LoadOK is connected to the glb_ldok at device level
The ADC Trigger input has routing options to the following sources:
(1)
)
• Internal TIM0 OC2
• Internal PTUT0 signal (Default)
• Internal PMF reload event (PWM generator A)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
44 NXP Semiconductors
Page 45

1.8.2 GDU timer connectivity
Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
TIM1 IC3 can be mapped to the GDU using PIM (see the PIM specification) in order to measure the t
and
tdeloff
times.
1.8.3 PTU connectivity
PTU reload_is_async is unused and forced to an inactive state at device level.
1.8.4 PMF connectivity
Table 1-9. Internal mapping of PMF signals
PMF Connection
PWM0 GDU HS driver GHG[0]
PWM1 GDU LS driver GLG[0]
PWM2 GDU HS driver GHG[1]
PWM3 GDU LS driver GLG[1]
FAULT5 External FAULT5 pin
FAULT4 GHD Over voltage (GOVA = 0) or GDU over current (GOCA = 0)
FAULT3 VLS under voltage
FAULT2 Tied to b0
FAULT1 GDU Desaturation[1] or GDU over current (GOCA = 1)
or GHD over voltage (GOVA =1)
FAULT0 GDU Desaturation[0] or GDU over current (GOCA = 1)
IS2 Tied to 0x1
IS1 GDU Phase Status[1]
IS0 GDU Phase Status[0]
async_event Tied to 0x0
async_event_edge_sel[1:0] Tied to 0x3(both edges active)
Usage
delon
1.8.5 Motor control loop interface connectivity overview
Table 1-10 and Figure 1-5 describe motor control loop connectivity that concerns device level inter
module operation specific for motor control.
.
Table 1-10. Control loop interface connectivity
Device Level Event PMF PTU ADC0 GDU
pmf_reload reloada
ptu_reload ptu_reload Restart reload
glb_ldok glb_ldok glb_ldok LoadOK Phase MUX
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 45
(1)
reload
selector
Page 46

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
PMF
ADC0
GDU
M
pmf_reload
dc_bus_voltage
sine/
sensor
cosine
reloada
Restart
PTU
ptu_reload
&
PTUE
Trigge r
OC2
glb_ldok
PTUT0
async_event
reload
Table 1-10. Control loop interface connectivity
Device Level Event PMF PTU ADC0 GDU
trigger_0 PTUT0 Trigger
1. PMF events reloadb and reloadc are not connected at device level
Figure 1-5. Motor control module interfaces
(MUX Option)
1.8.6 BDC clock source connectivity
The BDC clock, BDCCLK, is mapped to the IRCCLK generated in the CPMU module.
The BDC clock, BDCFCLK is mapped to the device bus clock, generated in the CPMU module.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
46 NXP Semiconductors
Page 47

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.8.7 LINPHY connectivity
The VLINSUP supply is internally connected to the device VSUP pin.
1.8.8 FTMRZ connectivity
The soc_erase_all_req input to the flash module is driven directly by a BDC erase flash request resulting
from the BDC ERASE_FLASH command.
The FTMRZ FCLKDIV register is forced to 0x05 by the BDC ERASE_FLASH command. This
configures the clock frequency correctly for the initial bus frequency on leaving reset. The bus frequency
must not be changed before launching the ERASE_FLASH command.
1.8.9 CPMU connectivity
The API_EXTCLK clock generated in the CPMU is not mapped to a device pin in the MC9S12ZVMBFamily.
The VDDF supply voltage is not mapped to device pins.
1.9 Modes of operation
The MCU can operate in different configuration modes, as described in 1.9.1 Chip configuration modes.
The MCU can operate in different power modes to facilitate power saving when full system performance
is not required. These are described in 1.9.3 Low power modes.
The MCU features a Background Debug Mode (BDM), as described in 1.9.2 Debugging modes.
1.9.1 Chip configuration modes
The different modes and the security state of the MCU affect the debug features (enabled or disabled).
The operating mode out of reset is determined by the state of the MODC signal during reset (Table 1-11).
The MODC bit in the MODE register shows the current operating mode and provides limited mode
switching during operation. The state of the MODC signal is latched into this bit on the rising edge of
RESET.
Table 1-11. Chip modes
Chip Modes MODC
Normal single chip 1
Special single chip 0
1.9.1.1 Normal single-chip mode
This mode is intended for normal device operation. The opcode from the on-chip memory is being
executed after reset (requires the reset vector to be programmed correctly). The processor program is
executed from internal memory.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 47
Page 48

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.9.1.2 Special single-chip mode
This mode is used for debugging operation, boot-strapping, or security related operations.The background
debug mode (BDM) is active on leaving reset in this mode.
1.9.2 Debugging modes
The background debug mode (BDM) can be activated by the BDC module or directly when resetting into
Special Single-Chip mode. Detailed information can be found in the BDC module section.
Some modules feature a software programmable option to freeze the module status whilst the background
debug mode is active to facilitate debugging. This is referred to as freeze mode at module level.
Writing to internal memory locations using the debugger, whilst code is running or at a breakpoint, can
change the flow of application code.
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family supports BDC communication throughout the device Stop mode. During
Stop mode, writes to control registers can alter the operation and lead to unexpected results. It is thus
recommended not to reconfigure the peripherals during STOP using the debugger.
1.9.3 Low power modes
The device has two dynamic-power modes (run and wait) and two static low-power modes (stop and
pseudo stop). For a detailed description refer to the CPMU section.
• Dynamic power mode: Run
— Run mode is the main full performance operating mode with the entire device clocked. The user
can configure the device operating speed through selection of the clock source and the phase
locked loop (PLL) frequency. To save power, unused peripherals must not be enabled.
• Dynamic power mode: Wait
— This mode is entered when the CPU executes the WAI instruction. In this mode the internal
CPU clock is switched off. All peripherals can be active in system wait mode. For further
power consumption the peripherals can individually turn off their local clocks. Asserting
RESET
, XIRQ, IRQ, or any other interrupt that is not masked, either locally or globally by a
CCR bit, ends system wait mode.
• Static power modes:
Static power (Stop) modes are entered following the CPU STOP instruction. If NVM commands
are being processed then Stop mode entry is delayed, until they have been completed, then the Stop
request is acknowledged and the device enters either Stop or Pseudo Stop mode.
— Pseudo-stop: In this mode the system clocks are stopped but the oscillator is still running and
the real time interrupt (RTI), watchdog (COP) and Autonomous Periodic Interrupt (API) may
be enabled. Other peripherals are turned off. This mode consumes more current than system
STOP mode but, as the oscillator continues to run, the full speed wake up time from this mode
is significantly shorter.
— Stop: In this mode, if the BDC is disabled, the oscillator is stopped, clocks are switched off and
the VREG enters reduced power mode (RPM). The counters and dividers remain frozen. The
autonomous periodic interrupt (API) may remain active but has a very low power consumption.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
48 NXP Semiconductors
Page 49

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
The key pad and SCI transceiver modules can be configured to wake the device, whereby
current consumption is negligible.
If the BDC is enabled, when the device enters Stop mode, the VREG remains in full
performance mode. With BDC enabled and BDCCIS bit set, then all clocks remain active to
allow BDC access to internal peripherals. If the BDC is enabled and BDCCIS is clear, then the
BDCSI clock remains active to allow further BDC communication, but other clocks (with the
exception of the API) are switched off. With the BDC enabled during Stop, the VREG full
performance mode and clock activity lead to higher current consumption than with BDC
disabled.
If the BDC is enabled in Stop mode, then the BATS voltage monitoring remains enabled.
1.10 Security
The MCU security mechanism prevents unauthorized access to the flash memory. It must be emphasized
that part of the security must lie with the application code. An extreme example would be application code
that dumps the contents of the internal memory. This would defeat the purpose of security. Also, if an
application has the capability of downloading code through a serial port and then executing that code (e.g.
an application containing bootloader code), then this capability could potentially be used to read the
EEPROM and flash memory contents even if the microcontroller is in the secure state. In this example, the
security of the application could be enhanced by requiring a response authentication before any code can
be downloaded.
Device security details are also described in the flash block description.
1.10.1 Features
The security features of the S12Z chip family are:
• Prevent external access of the non-volatile memories (flash, EEPROM) content
• Restrict execution of NVM commands
• Prevent BDC access of internal resources
1.10.2 Securing the microcontroller
The chip can be secured by programming the security bits located in the options/security byte in the flash
memory array. These non-volatile bits keep the device secured through reset and power-down.
This byte can be erased and programmed like any other flash location. Two bits of this byte are used for
security (SEC[1:0]). The contents of this byte are copied into the flash security register (FSEC) during a
reset sequence.
The meaning of the security bits SEC[1:0] is shown in Table 1-12. For security reasons, the state of device
security is controlled by two bits. To put the device in unsecured mode, these bits must be programmed to
SEC[1:0] = ‘10’. All other combinations put the device in a secured mode. The recommended value to put
the device in secured state is the inverse of the unsecured state, i.e. SEC[1:0] = ‘01’.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 49
Page 50

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-12. Security bits
SEC[1:0] Security State
00 1 (secured)
01 1 (secured)
10 0 (unsecured)
11 1 (secured)
NOTE
Please refer to the flash block description for more security byte details.
1.10.3 Operation of the secured microcontroller
By securing the device, unauthorized access to the EEPROM and Flash memory contents is prevented.
Secured operation has the following effects on the microcontroller:
1.10.3.1 Normal single chip mode (NS)
• .Background debug controller (BDC) operation is completely disabled
• Execution of flash and EEPROM commands is restricted (described in flash block description).
1.10.3.2 Special single chip mode (SS)
• Background debug controller (BDC) commands are restricted
• Execution of flash and EEPROM commands is restricted (described in flash block description).
In special single chip mode the device is in active BDM after reset. In special single chip mode on a secure
device, only the BDC mass erase and BDC control and status register commands are possible. BDC access
to memory mapped resources is disabled. The BDC can only be used to erase the EEPROM and flash
memory without giving access to their contents.
1.10.4 Unsecuring the microcontroller
Unsecuring the microcontroller can be done using three different methods:
1. Back-door key access
2. Reprogramming the security bits
3. Complete memory erase
1.10.4.1 Unsecuring the MCU using the back-door key access
In normal single chip mode, security can be temporarily disabled using the back-door key access method.
This method requires that:
• The back-door key has been programmed to a valid value
• The KEYEN[1:0] bits within the flash options/security byte select ‘enabled’.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
50 NXP Semiconductors
Page 51

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
• The application program programmed into the microcontroller has the capability to write to the
back-door key locations
The back-door key values themselves should not normally be stored within the application data, which
means the application program would have to be designed to receive the back-door key values from an
external source (e.g. through a serial port).
The back-door key access method allows debugging of a secured microcontroller without having to erase
the flash. This is particularly useful for failure analysis.
NOTE
No back-door key word is allowed to have the value 0x0000 or 0xFFFF.
1.10.5 Reprogramming the security bits
Security can also be disabled by erasing and reprogramming the security bits within the flash
options/security byte to the unsecured value. Since the erase operation will erase the entire sector
(0x7F_FE00–0x7F_FFFF) the back-door key and the interrupt vectors will also be erased; this method is
not recommended for normal single chip mode. The application software can only erase and program the
flash options/security byte if the flash sector containing the flash options/security byte is not protected (see
flash protection). Thus flash protection is a useful means of preventing this method. The microcontroller
enters the unsecured state after the next reset following the programming of the security bits to the
unsecured value.
This method requires that:
• The application software previously programmed into the microcontroller has been designed to
have the capability to erase and program the flash options/security byte.
• The flash sector containing the flash options/security byte is not protected.
1.10.6 Complete memory erase
The microcontroller can be unsecured by erasing the entire EEPROM and flash memory contents. If
ERASE_FLASH is successfully completed, then the flash unsecures the device and programs the security
byte automatically.
1.11 Resets and interrupts
1.11.1 Resets
Table 1-13. lists all reset sources and the vector locations. Resets are explained in detail in the S12CPMU
module description.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 51
Page 52

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-13. Reset sources and vector locations
Vector Address Reset Source
0xFFFFFC Power-On Reset (POR) None None
Low Voltage Reset (LVR) None None
External pin RESET None None
Clock monitor reset None OSCE Bit in CPMUOSC register
COP watchdog reset None CR[2:0] in CPMUCOP register
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
OMRE Bit in CPMUOSC2 register
1.11.2 Interrupt vectors
Table 1-14 lists all interrupt sources and vectors in the default order of priority. The interrupt module
description provides an interrupt vector base register (IVBR) to relocate the vectors.
Table 1-14. Interrupt vector locations (Sheet 1 of 4)
Vector Address
Vector base + 0x1F8 Unimplemented page1 op-code trap
Vector base + 0x1F4 Unimplemented page2 op-code trap
Vector base + 0x1F0 Software interrupt instruction (SWI) None None - -
Vector base + 0x1EC System call interrupt instruction
Vector base + 0x1E8 Machine exception None None - -
Vector base + 0x1E4
(1)
Interrupt Source
(SPARE)
(TRAP)
(SYS)
CCR
Mask
None None - -
None None - -
None None - -
Reserved
Local Enable
Wake up
from STOP
Wake up
from WAIT
Vector base + 0x1E0
Vector base + 0x1DC Spurious interrupt — None - -
Vector base + 0x1D8 XIRQ
Vector base + 0x1D4 IRQ
Vector base + 0x1D0 RTI time-out interrupt I bit CPMUINT (RTIE)
Vector base + 0x1CC TIM0 timer channel 0 I bit TIM0TIE (C0I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x1C8 TIM0 timer channel 1 I bit TIM0TIE (C1I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x1C4 TIM0 timer channel 2 I bit TIM0TIE (C2I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x1C0 TIM0 timer channel 3 I bit TIM0TIE (C3I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x1BC
to
Vector base + 0x1B0
Vector base + 0x1AC TIM0 timer overflow I bit TIM0TSCR2(TOI) No Yes
Vector base + 0x1A8 Reserved
52 NXP Semiconductors
interrupt request X bit None Yes Yes
interrupt request I bit IRQCR(IRQEN) Yes Yes
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Reserved
Reserved
See CPMU
section
Yes
Page 53

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-14. Interrupt vector locations (Sheet 1 of 4)
Vector Address
(1)
Vector base + 0x1A4
Interrupt Source
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
Reserved
Wake up
from STOP
Wake up
from WAIT
Vector base + 0x1A0 SPI0 I bit SPI0CR1 (SPIE, SPTIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x19C SCI0 I bit SCI0CR2
No Yes
(TIE, TCIE, RIE, ILIE)
SCI0ACR1(RXEDGIE) Yes Yes
Vector base + 0x198 SCI1 I bit SCI1CR2
No Yes
(TIE, TCIE, RIE, ILIE)
SCI0ACR1(RXEDGIE) Yes Yes
Vector base + 0x194 Reserved
Vector base + 0x190
Vector base + 0x18C ADC0 Error I bit ADC0EIE (IA_EIE, CMD_EIE,
Reserved
No Yes
EOL_EIE, TRIG_EIE,
RSTAR_EIE, LDOK_EIE)
ADC0IE(CONIF_OIE)
Vector base + 0x188 ADC0 sequence abort done I bit ADC0IE(SEQAD_IE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x184 ADC0 conversion complete I bit ADC0CONIE[15:0] No Yes
Vector base + 0x180
Oscillator status interrupt
I bit CPMUINT (OSCIE)
No
Yes
Vector base + 0x17C PLL lock interrupt I bit CPMUINT (LOCKIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x178
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x174
Vector base + 0x170 RAM error I bit EECIE (SBEEIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x16C
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x168
Vector base + 0x164 FLASH error I bit FERCNFG (SFDIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x160 FLASH command I bit FCNFG (CCIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x15C
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x148
Vector base + 0x144 LINPHY over-current interrupt I bit LPIE (LPERR) No Yes
Vector base + 0x140 BATS supply voltage monitor
I bit BATIE (BVHIE,BVLIE) No Yes
interrupt
Vector base + 0x13C GDU Desaturation Error I bit GDUIE (GDSEIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x138 GDU Voltage/Current Limit Detected I bit GDUIE (GOCIE[0],
No Yes
GHHDFIE, GLVLSFIE)
Vector base + 0x134 HSDRV over-current interrupt I bit HSIE (HSOCIE) No Yes
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 53
Page 54

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-14. Interrupt vector locations (Sheet 1 of 4)
Vector Address
(1)
Interrupt Source
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
Wake up
from STOP
Wake up
from WAIT
Vector base + 0x130
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x114
Vector base + 0x110 NGPIO over-current (Port T) I bit OCIET[2] No Yes
Vector base + 0x10C Port P interrupt I bit PIEP[1:0] Yes Yes
Vector base + 0x108 EVDD over-current I bit OCIEP[0] No Yes
Vector base + 0x104
Vector base + 0x100
Low-voltage interrupt (LVI)
Autonomous periodical interrupt
(API)
I bit
I bit
CPMUCTRL (LVIE)
CPMUAPICTRL (APIE)
No Yes
Yes Yes
Vector base + 0x0FC High temperature interrupt I bit CPMUHTCTL(HTIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0F8
Vector base + 0x0F4 Port AD interrupt I bit PIEADH(PIEADH0)
Reserved
Yes Yes
PIEADL(PIEADL[7:0])
Vector base + 0x0F0 PTU Reload Overrun I bit PTUIEH(PTUROIE) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0EC PTU Trigger0 Error I bit PTUIEL(TG0AEIE,TG0REIE,
No Yes
TG0TEIE)
Vector base + 0x0E8
Reserved
Vector base + 0x0E4 PTU Trigger0 Done I bit PTUIEL[TG0DIE] No Yes
Vector base + 0x0E0
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x0D4
Vector base + 0x0D0 PMF Reload A I bit PMFENCA(PWMRIEA) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0CC PMF Reload B I bit PMFENCB(PWMRIEB) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0C8 PMF Reload C I bit PMFENCC(PWMRIEC) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0C4 PMF Fault I bit PMFFIE(FIE[5:0]) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0C0 PMF Reload Overrun I bit PMFROIE(PMFROIEA,PMF
No Yes
ROIEB,PMFROIEC)
Vector base + 0x0BC Port L interrupt I bit PIEL[2:0] Yes Yes
Vector base + 0x0B8
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x0B0
Vector base + 0x0AC TIM1 timer channel 0 I bit TIM1TIE (C0I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0A8 TIM1 timer channel 1 I bit TIM1TIE (C1I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0A4 TIM1 timer channel 2 I bit TIM1TIE (C2I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x0A0 TIM1 timer channel 3 I bit TIM1TIE (C3I) No Yes
Vector base + 0x09C
to
Reserved
Vector base + 0x090
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
54 NXP Semiconductors
Page 55

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Table 1-14. Interrupt vector locations (Sheet 1 of 4)
Vector Address
Vector base + 0x08C TIM1 timer overflow I bit TIM1TSCR2(TOI) No Yes
Vector base + 0x088
to
Vector base + 0x010
1. 15 bits vector address based
(1)
Interrupt Source
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
Reserved
Wake up
from STOP
Wake up
from WAIT
1.11.3 Effects of reset
When a reset occurs, MCU registers and control bits are initialized. Refer to the respective block sections
for register reset states.
On each reset, the flash module executes a reset sequence to load flash configuration registers.
1.11.3.1 Flash configuration reset sequence phase
On each reset, the flash module will hold CPU activity while loading flash module registers from the flash
memory If double faults are detected in the reset phase, flash module protection and security may be active
on leaving reset. This is explained in more detail in the flash module description.
1.11.3.2 Reset while flash command active
If a reset occurs while any Flash command is in progress, that command will be immediately aborted. The
state of the word being programmed or the sector/block being erased is not guaranteed.
1.11.3.3 I/O pins
Refer to the PIM section for reset configurations of all peripheral module ports.
1.11.3.4 RAM
The system RAM arrays, including their ECC syndromes, are initialized following a power on reset. All
other RAM arrays are not initialized out of any type of reset.
With the exception of a power-on-reset the RAM content is unaltered by a reset occurrence.
1.12 Module device level dependencies
1.12.1 CPMU COP and GDU GSUF configuration
The COP time-out rate bits CR[2:0] and the WCOP bit in the CPMUCOP register are loaded from the flash
configuration field byte at global address 0xFF_FE0E during the reset sequence. The GSUF bit in the
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 55
Page 56

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
GDUF register is also loaded from the Flash configuration field byte at global address 0xFF_FE0E during
the reset sequence. See Table 1-15 , Table 1-17 and Table 1-17 for coding.
Table 1-15. Initial COP rate configuration
NV[2:0] in
FOPT Register
000 111
001 110
010 101
011 100
100 011
101 010
110 0 01
111 000
CR[2:0] in
CPMUCOP Register
Table 1-16. Initial WCOP configuration
NV[3] in
FOPT Register
10
01
WCOP in
CPMUCOP Register
Table 1-17. Initial GSUF configuration
NV[7] in
FOPT Register
10
01
GSUF in
GDUF Register
1.12.2 Flash IFR mapping
Table 1-18. Flash IFR mapping
1514131211109876543210 IFR Byte Address
DVBE Temperature sensor ADC result (probe) 0x1F_C054 & 0x1F_C055
1.12.3 BDC command restriction
The BDC command READ_DBGTB returns 0x00 on this device because the DBG module does not
feature a trace buffer.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
56 NXP Semiconductors
Page 57

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
1.13 Application information
1.13.1 Temperature sensor
The DVBE temperature sensor output is mapped to the ADC internal channel 7. It is tested in production
at 26C, using conversions of ADC internal channel 7 and storing the result to the flash location
0x1F_C054, 0x1F_C055 as a 12-bit right aligned value.
The accuracy of the controlled production test temperature is 26 C +/-3 °C.
The slope is linear over the device operating temperature range.
The accuracy of the slope dV/dT is 6 mV/C +/-0.2 mV/C.
The typical application is to use the temperature sensor to warn if device or application temperature is
approaching the maximum limit in order to take precautionary measures.
The following example uses an application aiming to detect a maximum temperature of 126°C, whereby
the difference between the maximum level and tested level is 100C (for calculation simplicity)
Figure 1-6 illustrates the effect of the slope variation alone.
Typically a 100C difference corresponds to 600 mV (100 x 6 mV) change in the DVBE output compared
to the stored value from 26C production test (V26). Thus the application could be configured to detect a
600 mV change with respect to V26.
Considering the dV/dT slope minimum/maximum specification, an inaccuracy of +/-20 mV may exist
over the 100C range, whereby +/-20 mV corresponds to a +/-3.3C. Thus, if configured to detect V26 +
600 mV, the detection could occur at 129.3C, as shown by the red 5.8 mV/C slope of Figure 1-6.
To compensate for the minimum dV/dT the application could be configured to detect a 580 mV change
with respect to V26.
Note that the result stored in flash is a 12-bit value. However the ADC is only specified to 10-bit accuracy
for applications. Thus the full 12-bit value in flash should be considered for V26 calculation.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 57
Page 58

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Voltage (V)
Temperature (C)
26
V
26
126
6 mV/C
5.8 mV/C
6.2 mV/C
0.6 V
0.58 V
129.3
Figure 1-6. DVBE effect of slope inaccuracy
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
58 NXP Semiconductors
Page 59

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
Voltage (V)
Temperature (C)
29
V
26
126
6 mV/C
5.8 mV/C
0.6 V
0.562 V
129 26
Typical slope from V
26
Typical offset slope from V
26
Minimum dV/dT offset slope from V
26
132.3
Furthermore the production test temperature control accuracy is limited to +/-3C. Figure 1-7 illustrates
the effect of this limitation, whereby the value V26 actually corresponds to a test temperature of 29C.
Thus, if configured to detect V26 + 600mV, the detection could be offset by 3C and in this case would
occur at 129C for a typical slope. Considering further inaccuracy for the minimum slope results in an
actual temperature limit detection at 132.3C as shown in Figure 1-7. Further compensation can be
applied, if necessary by adjusting the detection level.
Figure 1-7. Effect of slope plus V
reference inaccuracy
26
The ADC uses the on chip generated VDDA as the VRH reference. The accuracy of VRH can also be
considered. In order to compensate for VRH load variation, the reference voltage can be indirectly
measured using the internal reference voltage V
VRH reference can be obtained by applying a clean, unloaded VRH and converting V
ADC conversion result of V
BG can be stored to flash for reference.
BG. VBG is mapped to ADC channel internal_1. Thus a
BG. The resulting
By measuring the voltage VBG in the application environment and comparing the result to the reference
value stored in flash, it is possible to determine the current ADC reference voltage V
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
RH:
NXP Semiconductors 59
Page 60

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
VRH = (StoredReference/ConvertedReference) x 5V Eqn. 1-1
The absolute value of the DVBE conversion can be determined as follows:
V
DVBE
= ConvertedDVBE x (StoredReference/ConvertedReference) x 5V/2
n
Eqn. 1-2
ConvertedDVBE: Result of the analog to digital conversion of the DVBE
ConvertedReference: Result of internal channel conversion
StoredReference: Reference value from clean, unloaded VRH, V
conversion
BG
n: ADC resolution (10 bit)
VRH variation over temperature can also be considered, whereby the maximum VRH differential between
26C and 126C is typically -46mV (126C value is always less than the 26C value).
This correlates to a maximum VRH induced error of -4C when applied to the V
of Equation 1-2.
DVBE
1.13.2 SCI baud rate detection
The baud rate for SCI0 and SCI1 is achieved by using a timer channel to measure the data rate on the RXD
signal.
1. Establish the link:
— For SCI0: Set [T0IC3RR1:T0IC3RR0]=0b01 to reroute TIM0 input capture channel 3 (IC0_3)
to the RXD0 signal of SCI0.
— For SCI1: Set [T0IC3RR1:T0IC3RR0]=0b11 to reroute TIM0 input capture channel 3 (IC0_3)
to the RXD1 signal of SCI1.
2. Determine pulse width of incoming data: Configure TIM0 IC3 to measure time between incoming
signal edges.
1.13.3 BDCM complementary mode operation
This section describes BDCM control using center aligned complementary mode with deadtime insertion.
The brushed DC motor power stage topology is a classical full bridge as shown in Figure 1-8. The brushed
DC motor is driven by the DC voltage source. A rotational field is created by means of commutator and
brushes on the motor.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
60 NXP Semiconductors
Page 61

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
PWM
0
PWM
2
PWM
3
PWM
1
+ 1/2 U
- 1/2 U
A
B
PWM0
PWM1
PWM2
PWM3
T
PWM
PWM0, PWM1 base
PWM2, PWM3 base
Figure 1-8. DC brushed motor external configuration
Usually the control consists of an outer, speed control loop with inner current (torque) control loop. The
inner loop controls DC voltage applied onto the motor winding. The control loop is calculated regularly
within a given period. In most cases, this period matches the PWM reload period.
Driving the DC motor from a DC voltage source, the motor can work in all four quadrants. The
complementary mode of operation with deadtime insertion is needed for smooth reversal of the motor
current (motor torque), hence smooth full four quadrant control. Usually the center-aligned PWM is
chosen to lower electromagnetic emissions.
The PWM frequency selection is always a compromise between audible noise, electromagnetic emissions,
current ripples and power switching losses.
The BDCM control loop goal is to provide a controlled DC voltage to the motor winding, whereby it is
controlled cycle-by-cycle using a speed, current or torque feedback loop.
The center aligned PWM waveforms generated by the PMF module are applied to the bridge as shown in
Figure 1-9 whereby the base waveform for PWM0 and PWM1 is depicted at the top and the
complementary PWM0 and PWM1 waveforms are shown with deadtime insertion depicted by the gray
phases before the rising edges.
Figure 1-9. BDCM complementary mode waveform
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 61
Page 62

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
PWM with
PWM base
PWM cycle
deadtime
GDU
propagation
FET
turn on
Current sense
settling time
ADC delay
T
DEAD_x
t
delon
t
HGON
(tcslsst)
Assuming first quadrant operation, forward accelerating operation, the applied voltage at node A must
exceed the applied voltage at node B (Figure 1-8). Thus the PWM0 duty cycle must exceed the PWM2
duty cycle.
The PWM duty cycle of PWM0 defines the voltage at the first power stage branch.
The PWM duty cycle of PWM2 defines the voltage at the second power stage branch.
Modulating the PWM duty cycle every period using the function F
PWM0 duty-cycle = 0.5 + (0.5 * F
PWM2 duty-cycle = 0.5 - (0.5 * F
); For -1<=F
PWM
)
PWM
PWM
<= 1;
then the duty cycle is expressed as:
PWM
1.13.3.1 Control loop timing considerations
Delays within the separate control loop elements require consideration to ensure correct synchronization.
Regarding the raw PWM signal as the starting point and stepping through the control loop stages, the
factors shown in Figure 1-10 contribute to delays within the control loop, starting with the deadtime
insertion, going through the external FETs and back into the internal ADC measurements of external
voltages and currents.
Figure 1-10. Control loop delay overview
The PWM deadtime (T
DEAD_X
) is an integral number of bus clock cycles, configured by the PMF
deadtime registers.
The GDU propagation delays (t
The FET turn on times (t
parameter Table E-1.
GHGON
, t
delon
) are load dependent but are specified for particular loads in the electrical
) are specified in the electrical parameter Table E- 1.
deloff
The current sense amplifier delay is highly dependent on external components.
The ADC delay until a result is available is specified as the conversion period N
62 NXP Semiconductors
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
in Table C-1.
CONV
Page 63

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
GHHDF
CORE
RAM’s
PLL
IRC
OSC
FLASH
PAD S
GDU
LDO
LINPHY
VREG_AUTO
1.8 V
2.8 V
5 V
VDDA
VSSA
VSS
VLS_OUT
GHD
GLG
GLS
GPIO
VSSX
VSUP (12 V/18 V)
VDDX
LIN
LGND
GFDE
PORF
LVRF
GLVLSF
CPS
INT
INT
RES
RES
BATS
INTADC
VRH_SEL
VRL_SEL
VRH
VRL
VSSA
VDDA
ADC
GCPE
VLS
(11V)
CP
VCP
VRBATP
VSUPHS (12 V/18 V)
HS
VDD
VDDF
VRH_0
1.13.4 Power domain considerations
The MC9S12ZVMB-Family power domains are illustrated in Figure 1-11. More detailed information is
included in the individual module descriptions.
Figure 1-11. Power domain overview
The system supply voltage VRBATP is a reverse battery protected input voltage. It must be protected
against reverse battery connections and must not be connected directly to the battery voltage (VBAT).
The device supply voltage VSUP provides the input voltage for the internal regulator, VREG_AUTO, and
to the GDU LDO. The VDDX domain supplies the device I/O pins, VDDA supplies the ADC and internal
bias current generators. The VDDA and VDDX pins must be connected at board level, they are not
NXP Semiconductors 63
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 64

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
connected directly internally. ESD protection diodes exist between VDDX and VDDA, therefore forcing
a common operating range.
The VDD domain supplies the internal device logic. The VDDF domain supplies sections of the internal
Flash NVM circuitry.
The LINPHY pull-up resistor is internally connected to the VSUP voltage. The external connections for
the VSUP pin must ensure a reverse battery protection.
The High-side driver supply, VSUPHS, also requires an external reverse battery protection.
1.13.4.1 Voltage domain monitoring
The BATS module monitors the voltage on the VSUP pin, providing status and flag bits, an interrupt and
a connection to the ADC, for accurate measurement of the scaled VSUP level.
The POR circuit monitors the VDD (internal) and VDDA domains, ensuring a reset assertion until an
adequate voltage level is attained. The LVR circuit monitors the VDD, VDDF and VDDX domains,
generating a reset when the voltage in any of these domains drops below the specified assert level. The
VDDX LVR monitor is disabled when the VREG is in reduced power mode. A low voltage interrupt circuit
monitors the VDDA domain.
The GDU High-side drain voltage, pin GHD, is monitored within the GDU and mapped to an interrupt. A
connection to the ADC is provided for accurate measurement of a scaled GHD level.
1.13.4.2 FET-predriver (GDU) supplies
A dedicated low drop regulator is used to generate the VLS_OUT voltage from VSUP. The VLS_OUT
voltage is used to supply the Low-side drivers and can be externally, directly connected to the VLS input.
1.13.4.3 Bootstrap precharge
The FET-predriver High-side driver must provide a sufficient gate-source voltage and sufficient charge for
the gate capacitance of the external FETs. A bootstrap circuit is used to provide sufficient charge, whereby
the capacitor CBS is first charged to VLS_OUT via an internal diode, when the Low-side driver is active
Figure 1-12. When the High-side driver switches on, the charge on this capacitor, supplies the FET-
predriver via the VBSx pin. The C
a long period of inactivity of the Low-side driver, the CBS capacitor becomes discharged. In this case, the
Low-side driver must be switched on to charge C
takes to discharge the bootstrap capacitor CBS can be calculated from the size of the bootstrap capacitor
C
and the leakage current on VBSx pin.
BS
The bootstrap capacitors must be precharged before turning on the high-side drivers for the first time. This
can be done by using the PMF software output control mechanism:
PMFOUTC = 0x0F; // SW control on all outputs
PMFOUTB = 0x0A; // All high-sides off, all low-sides on
capacitor can only be charged if the Low-side driver is active, so after
BS
before commencing High-side driving. The time it
BS
The PWM signals should be configured to start with turning on the low-side before the high-side drivers
in order to assure precharged bootstraps. Therefore invert the PWM signals:
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
64 NXP Semiconductors
Page 65

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
PMFCINV = 0x0F; // Invert all channels to precharge bootstraps
1.13.4.4 High-side charge pump for 100% duty cycle
A charge pump voltage is used to supply the High-side FET-predriver with enough current to maintain the
gate source voltage. To generate this voltage an external charge pump is driven by the pin CP, switching
between 0 V and 11 V. The pumped voltage is then applied to the pin VCP.
At 100% duty cycle operation the low-side turn on time is zero, which can cause bootstrap charge to decay.
In order to speed-up the high-side gate voltage level directly after commutation, the software should drive
the first PWM cycle with a duty cycle meeting an on-time of at least t
minpulse
then switch back to 100% again.
The GDU High-side drain voltage, pin GHD, is supplied from VBAT through a reverse battery protection
circuit. In a typical application the charge pump is used to switch on an external NMOS, N1, with source
connected to VBAT, by generating a voltage of VBAT+VLS-(2 x Vdiode). In a reverse battery scenario,
the external bipolar turns on, ensuring that the GHD pin is isolated from VBAT by the external NMOS, N1.
for the low-side drivers and
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 65
Page 66

Chapter 1 Device Overview MC9S12ZVMB-Family
GCPE
VLS_OUT
(11 V)
CP
VCP
VBSx
0 V
11 V
1000 uF
(Motor Dependent)
S
D
1 nF
N1
GHSx
GHD
High-side
Low-side
VBAT
C
BS
10 nF
Diode voltage drop = Vdiode
GCPCD
GHGx
Figure 1-12. High-side supply and charge pump concept
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
66 NXP Semiconductors
Page 67

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-1. Revision History
Rev. No.
(Item No.)
V03.00 19 Jun 2015 • Initial release for S12ZVMB-family
V03.01 7 Jul 2015 • Incorporated feedback from review
V03.02 14 Jul 2015 2.3.2.6/2-87 • Added TIM1 IC0 routing option
V03.03 22 Jul 2015 • Typos and formatting
V03.04 24 Jul 2015 2.3.2.5/2-86 • Changed write restrictions of MODRR4 register
V03.05 30 Jul 2015 • Typos and formatting
V03.06 5 Aug 2015 2.1.1/2-68
V03.06 5 Aug 2015 2.1.1/2-68
Date (Submitted
By)
Sections
Affected
2.2/2-71
2.3.1/2-77
2.3.2.6/287
2.2/2-71
2.3.1/2-77
2.3.2.6/287
Substantial Change(s)
• Typos and formatting
• Added PT7
• Typos and formatting
• Added PT7
• Typos and formatting
V03.07 13 Aug 2015 Table 2-4
Ta bl e 2 - 44
V03.08 28 Aug 2015 2.1.1/2-68
2.3.1/2-77
2.3.2.1/2-
83Table 2-
5
Table 2-6
V03.09 1 Sep 2015 2.3.4.5/2-
99
Ta bl e 2 - 45
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductor 67
• Typos and formatting
• Changed SPI0 (SCLK) routing
• Corrections
Page 68

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Rev. No.
(Item No.)
V03.10 16 Sep 2015 2.1.1/2-68
V03.11 23 Nov 2015 2.4.6/2-
V03.12 23 Mar 2016 • Corrections
Date (Submitted
By)
Sections
Affected
2.2/2-71
110
Substantial Change(s)
• Corrections
• Corrections
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Overview
The S12ZVMB-family port integration module establishes the interface between the peripheral modules
and the I/O pins for all ports. It controls the electrical pin properties as well as the signal prioritization and
multiplexing on shared pins.
This document covers:
• Port E
GPIO DBG SCI1 PMF
PTE1
DBGEE
V
TXD1 PWM1 XTAL PE1
External
Oscillator
Pins
PTE0 RXD1 PWM0 EXTAL PE0
•Port AD
GPIO/KWU ADC0 SPI0 GDU PTU Pins
PTADH0 AN0_8 PAD 8
PTADL7 AN0_7 PAD7
PTADL6 AN0_6 PAD6
PTADL5 AN0_5 PAD5
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
68 NXP Semiconductors
Page 69

PTADL4 AN0_4 SS0 PAD4
PTADL3 AN0_3 PTUT0 PAD3
PTADL2 AN0_2 AMP0 PAD2
PTADL1 AN0_1 AMPM0 PAD 1
PTADL0 AN0_0 AMPP0 PAD0
•Port T
GPIO TIM0 TIM1 PMF SPI0 SCI0 SCI1 LINPHY0 PMF
PTT7 IOC1_3 PT7
PTT6 IOC1_2 PT6
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
ECLK/
XIRQ Pins
PTT5 IOC1_1 PT5
PTT4 IOC1_0 PT4
PTT3 IOC0_3 PT3
PTT2 IOC0_2 PWM3 LP0RXD FAULT5 ECLK PT2
PTT1 IOC0_1 PWM2 MISO0 TXD0 TXD1 LP0DR1 PT1
PTT0 IOC0_0 MOSI0 RXD0 RXD1 XIRQ
• Port P
GPIO/KWU PMF SPI0 PTU PMF LINPHY0 IRQ Pins
PTP1 PWM5 SCK0 FAULT5 PP1
PTP0 PWM4 PTURE LP0TXD IRQ
PT0
PP0
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 69
Page 70

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
• Port L
HVI/KWU ADC0 TIM1 Pins
PTIL2 AN0_11 IC1_2 PL2
PTIL1 AN0_10 IC1_1 PL1
PTIL0 AN0_9 IC1_0 PL0
Most I/O pins can be configured by register bits to select data direction and to enable and select pullup or
pulldown devices.
NOTE
This document shows the superset of all available features offered by the
S12ZVMB device family. Refer to the package and pinout section in the
device overview for functions not available for a particular device or
package option.
2.1.2 Features
The PIM includes these distinctive registers:
• Data registers for ports E, AD, T, P when used as general-purpose I/O
• Data direction registers for ports E, AD, T, P when used as general-purpose I/O
• Control registers to enable pull devices on ports E, AD, T, P
• Control registers to select pullups or pulldowns on ports E, AD, T, P
• Control register to enable digital input buffers on port AD and L
• Interrupt enable register for pin interrupts and key-wakeup (KWU) on port AD, P and L
• Interrupt flag register for pin interrupts and key-wakeup (KWU) on port AD, P and L
• Control register to configure IRQ pin operation
• Control register to enable ECLK output
• Routing registers to support signal relocation on external pins and control internal routings:
— 2 PWM channels to alternative pins (1 option each)
— 4 TIM0 channels to alternative pins
— Various SCI0-LINPHY0 routing options for standalone use and conformance testing
— SCI1 to alternative pins (1 option)
— HSDRV control selection from PWMTIM OC or related register bit
— Internal RXD0 and RXD1 link to TIM0 input capture channel (IC0_3) for baud rate detection
— Internal ACLK link to TIM0 input capture channel (IC0_2) for calibration and clock
monitoring purposes
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
70 NXP Semiconductors
Page 71

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
A standard port pin has the following minimum features:
• Input/output selection
• 5V output drive
• 5V digital and analog input
• Input with selectable pullup or pulldown device
Optional features supported on dedicated pins:
• Interrupt input with glitch filtering
• High current drive strength from VDDX with over-current protection
• High current drive strength to VSSX with over-current protection
• Selectable drive strength for high current capable outputs
2.2 External Signal Description
This section lists and describes the signals that do connect off-chip.
Table 2-8 shows all pins with the pins and functions that are controlled by the PIM. Routing options are
denoted in parentheses.
If there is more than one function associated with a pin, the output priority
is indicated by the position in the table from top (highest priority) to bottom
(lowest priority). Inputs do not arbitrate priority unless noted differently in
Table 2-45.
Table 2-2. BKGD Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
BKGDBKGD MODC
1. Function active when RESET asserted
Pin Function
& Priority
(1)
BKGD I/O S12ZBDC communication —
NOTE
I/O Description
I MODC input during RESET
Routing
Register Bit
— BKGD
Func.
after
Reset
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 71
Page 72

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-3. Port E Pin Functions and Priorities
Func.
Reset
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
E PE1 XTAL — CPMU OSC signal — GPIO
(PWM1) O PWM channel 1 P0C1RR
(TXD1) I/O SCI1 transmit SCI1RR
DBGEEV I DBG external event —
PTE[1] I/O GPIO —
PE0 EXTAL — CPMU OSC signal —
(PWM0) O PWM channel 0 P0C0RR
(RXD1) I SCI1 receive SCI1RR
PTE[0] I/O GPIO —
after
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
72 NXP Semiconductors
Page 73

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-4. Port AD Pin Functions and Priorities
Func.
after
Reset
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
AD PAD8 AN8 I ADC0 analog input — GPIO
PTADH[0]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADH[0]
PAD7-5 AN7-5 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[7:5]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[7:5]
PAD4 S S0
I/O SPI0 slave select —
AN4 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[4]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[4]
PAD3 PTUT0 O PTU trigger 0 —
AN3 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[3]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[3]
PAD2 AMP0 O GDU AMP0 output —
AN2 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[2]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[2]
PAD1 AMPM0 I GDU AMP0 inverting input (-) —
AN1 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[1]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[1]
PAD0 AMPP0 I GDU AMP0 non-inverting input (+) —
AN0 I ADC0 analog input —
PTADL[0]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWADL[0]
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 73
Page 74

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-5. Port T Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
T PT7 IOC1_3 I/O TIM1 channel 3 T1IC3RR GPIO
PTT[7] I/O GPIO —
PT6 IOC1_2 I/O TIM1 channel 2 T1IC2RR,T1OC2RR
PTT[6] I/O GPIO —
PT5 IOC1_1 I/O TIM1 channel 1 T1IC1RR,T1OC1RR
PTT[5] I/O GPIO —
PT4 IOC1_0 I/O TIM1 channel 0 T1IC0RR
PTT[4] I/O GPIO —
PT3 IOC0_3 I/O TIM0 channel 3 T0IC3RR1-0
PTT[3] I/O GPIO —
PT2
(1)
ECLK O Free-running clock —
FAULT5 I PMF fault FAULT5RR
(LP0RXD) O LINPHY0/HVPHY0 receive output S0L0RR2-0
(PWM3) O PMF channel 3 P0C3RR
IOC0_2 I/O TIM0 channel 2 T0IC2RR
PTT[2]/
I/O GPIO —
NGPIO
PT1 (LP0DR1) O LPTXD0 direct control by LP0DR[LP0DR1] S0L0RR2-0
TXD1 I/O SCI1 transmit SCI1RR
(TXD0) I/O SCI0 transmit S0L0RR2-0
MISO0 I/O SPI0 master in/slave out —
(PWM2) O PMF channel 2 P0C2RR
IOC0_1 I/O TIM0 channel 1 —
PTT[1] I/O GPIO —
PT0 XIRQ
(2)
I Non-maskable level-sensitive interrupt —
RXD1 I SCI1 receive SCI1RR
(RXD0) I SCI0 receive S0L0RR2-0
MOSI0 I/O SPI0 master out/slave in —
IOC0_0 I/O TIM0 channel 0 —
PTT[0] I/O GPIO —
1. High current capable low-side output with over-current interrupt and protection for all sources (see 2.4.5.3/2-110)
Func.
after
Reset
2. The interrupt is enabled by clearing the X mask bit in the CPU CCR. The pin is forced to input upon first clearing of the X bit and
is held in this state until reset. A stop or wait recovery using XIRQ with the X bit set is not available.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
74 NXP Semiconductors
Page 75

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-6. Port P Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
P PP1 (FAULT5) I PMF fault FAULT5RR GPIO
SCK0 I/O SPI0 serial clock —
PWM5 O PMF channel 5 P0C5RR
PTP[1]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWP[1]
PP0
(1)
IRQ I Maskable level- or falling edge-sensitive
—
interrupt
(LP0TXD) I LINPHY0/HVPHY0 transmit input S0L0RR2-0
PTURE O PTU reload event with over-current interrupt;
—
high-current capable (20 mA)
PWM4 O PMF channel 4 with over-current interrupt;
P0C4RR
high-current capable (20 mA)
PTP[0]/
KWP[0]/
EVDD
I/O General-purpose; with interrupt and wakeup
Switchable external power supply output with
over-current interrupt; high-current capable
—
(20 mA)
1. High current capable high-side output with over-current interrupt and protection for all sources (see 2.4.5.3/2-110)
Func.
after
Reset
Table 2-7. Port L Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
L PL2 IOC1_2 I TIM1 input capture channel 2 T1IC2RR HVI
AN11 I ADC0 analog input AN11
PTIL[2]/
I HVI with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWL[2]
PL1 IOC1_1 I TIM1 input capture channel 1 T1IC1RR
AN10 I ADC0 analog input AN10
PTIL[1]/
I HVI with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWL[1]
PL0 IOC1_0 I TIM1 input capture channel 0 T1IC0RR
AN9 I ADC0 analog input AN9
PTIL[0]/
I HVI with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWL[0]
Routing
Register Bit
Func.
after
Reset
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 75
Page 76

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-8. HSDRV Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
N/A
(1)
1. Not a PIM port. Listed here for priority information only. Refer to section S12HSDRV.
HS1 (PWM5) O PMF channel 5 P0C5RR HSDRV
HS0 (PWM4) O PMF channel 4 P0C4RR
Pin Function
& Priority
(OC1_2) O TIM1 output compare channel 2 T1OC2RR
HSDR[HSDR1] O High-side driver 1 —
(OC1_1) O TIM1 output compare channel 1 T1OC1RR
HSDR[HSDR0] O High-side driver 0 —
I/O Description
2.2.1 Internal Routing Options
The following table summarizes the internal routing options.
Table 2-9. Internal Routing Options
Internal Signal Connects to Routing Bits
ACLK IC0_2 T0IC2RR
RXD0, RXD1 IC0_3 T0IC3RR1-0
Routing
Register Bit
Func.
after
Reset
TIM0 OC2 ADC0 Trigger TRIG0RR1-0
PMF reload
PTU trigger 0
HVI0 IC1_0 T1IC0RR
HVI1 IC1_1 T1IC1RR
HVI2 IC1_2 T1IC2RR
2.3 Memory Map and Register Definition
This section provides a detailed description of all port integration module registers. Subsection 2.3.1
shows all registers and bits at their related addresses within the global SOC register map. A detailed
description of every register bit is given in subsections 2.3.2 to 2.3.4.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
76 NXP Semiconductors
Page 77

2.3.1 Register Map
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
0x0200 MODRR0
0x0201 MODRR1
0x0202 MODRR2
0x0203 MODRR3
0x0204 MODRR4
0x0205 MODRR5
0x0206–
0x0207
Register
Name
Reserved
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R0 0
W
R000000
W
R00000000
W
R000
W
R
FAULT5R
R
W
R
T1IC3RR T1IC2RR T1IC1RR T1IC0RR
W
R00000000
W
0
Reserved
P0C5RR P0C4RR P0C3RR P0C2RR P0C1RR P0C0RR
0
T0IC3RR1-0 T0IC2RR
SCI1RR S0L0RR2-0
0
T1OC2RR T1OC1RR
TRIG0RR1-0
00
0
0x0208 ECLKCTL
0x0209 IRQCR
0x020A–
0x020C
0x020D Reserved
0x020E Reserved
0x020F Reserved
0x0210–
0x025F
0x0260 PTE
Reserved
Reserved
R
NECLK
W
R
IRQE IRQEN
W
R00000000
W
R00000
W
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
R00000000
W
R000000
W
0000000
000000
Reserved
0
PTE1 PTE0
Reserved
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 77
Page 78

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x0261 Reserved
0x0262 PTIE
0x0263 Reserved
0x0264 DDRE
0x0265 Reserved
0x0266 PERE
0x0267 Reserved
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R00000000
W
R000000PTIE1PTIE0
W
R00000000
W
R000000
W
DDRE1 DDRE0
R00000000
W
R000000
W
PERE1 PERE0
R00000000
W
0x0268 PPSE
0x0269–
0x027F
Reserved
0x0280 PTADH
0x0281 PTADL
0x0282 PTIADH
0x0283 PTIADL
0x0284 DDRADH
0x0285 DDRADL
R000000
W
PPSE1 PPSE0
R00000000
W
R0000000
W
R
PTADL7 PTADL6 PTADL5 PTADL4 PTADL3 PTADL2 PTADL1 PTADL0
W
PTADH0
R0000000PTIADH0
W
R PTIADL7 PTIADL6 PTIADL5 PTIADL4 PTIADL3 PTIADL2 PTIADL1 PTIADL0
W
R0000000
W
R
DDRADL7 DDRADL6 DDRADL5 DDRADL4 DDRADL3 DDRADL2 DDRADL1 DDRADL0
W
DDRADH0
0x0286 PERADH
R0000000
W
PERADH0
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
78 NXP Semiconductors
Page 79

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x0287 PERADL
0x0288 PPSADH
0x0289 PPSADL
0x028A–
0x028B
Reserved
0x028C PIEADH
0x028D PIEADL
0x028E PIFADH
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R
PERADL7 PERADL6 PERADL5 PERADL4 PERADL3 PERADL2 PERADL1 PERADL0
W
R0000000
W
R
PPSADL7 PPSADL6 PPSADL5 PPSADL4 PPSADL3 PPSADL2 PPSADL1 PPSADL0
W
PPSADH0
R00000000
W
R0000000
W
R
PIEADL7 PIEADL6 PIEADL5 PIEADL4 PIEADL3 PIEADL2 PIEADL1 PIEADL0
W
R0000000
W
PIEADH0
PIFADH0
0x028F PIFADL
0x0290–
0x0297
Reserved
0x0298 DIENADH
0x0299 DIENADL
0x029A–
0x02BF
Reserved
0x02C0 PTT
0x02C1 PTIT
0x02C2 DDRT
R
PIFADL7 PIFADL6 PIFADL5 PIFADL4 PIFADL3 PIFADL2 PIFADL1 PIFADL0
W
R00000000
W
R0000000
W
R
DIENADL7 DIENADL6 DIENADL5 DIENADL4 DIENADL3 DIENADL2 DIENADL1 DIENADL0
W
DIENADH0
R00000000
W
R
PTT7 PTT6 PTT5 PTT4 PTT3 PTT2 PTT1 PTT0
W
R PTIT7 PTIT6 PTIT5 PTIT4 PTIT3 PTIT2 PTIT1 PTIT0
W
R
DDRT7 DDRT6 DDRT5 DDRT4 DDRT3 DDRT2 DDRT1 DDRT0
W
0x02C3 PERT
R
PERT7 PERT6 PERT5 PERT4 PERT3 PERT2 PERT1 PERT0
W
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 79
Page 80

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x02C4 PPST
0x02C5–
0x02C8
Reserved
0x02C9 OCPET
0x02CA OCIET
0x02CB OCIFT
0x02CC Reserved
0x02CD RDRT
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R
PPST7 PPST6 PPST5 PPST4 PPST3 PPST2 PPST1 PPST0
W
R00000000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
OCPET2
OCIET2
OCIFT2
00
00
00
R00000000
W
R00000
W
RDRT2
00
0x02CE–
0x02CF
0x02D0–
0x02EF
Reserved
Reserved
0x02F0 PTP
0x02F1 PTIP
0x02F2 DDRP
0x02F3 PERP
0x02F4 PPSP
0x02F5 Reserved
R00000000
W
R00000000
W
R000000
W
PTP1 PTP0
R000000PTIP1PTIP0
W
R000000
W
R000000
W
R000000
W
DDRP1 DDRP0
PERP1 PERP0
PPSP1 PPSP0
R00000000
W
0x02F6 PIEP
R000000
W
PIEP1 PIEP0
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
80 NXP Semiconductors
Page 81

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x02F7 PIFP
0x02F8 Reserved
0x02F9 OCPEP
0x02FA OCIEP
0x02FB OCIFP
0x02FC Reserved
0x02FD RDRP
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R000000
W
PIFP1 PIFP0
R00000000
W
R0000000
W
R0000000
W
R0000000
W
OCPEP0
OCIEP0
OCIFP0
R00000000
W
R0000000
W
RDRP0
0x02FE–
0x02FF
0x0300–
0x032F
Reserved
Reserved
0x0330 Reserved
0x0331 PTIL
0x0332 Reserved
0x0333 PTPSL
0x0334 PPSL
0x0335 Reserved
R00000000
W
R00000000
W
R00000000
W
R00000PTIL2PTIL1PTIL0
W
R00000000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
PTPSL2 PTPSL1 PTPSL0
PPSL2 PPSL1 PPSL0
R00000000
W
0x0336 PIEL
R00000
W
PIEL2 PIEL1 PIEL0
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 81
Page 82

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Global
Address
0x0337 PIFL
0x0338–
0x0339
0x033A PTABYPL
0x033B PTADIRL
0x033C DIENL
0x033D PTAENL
0x033E PIRL
Register
Name
Reserved
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R00000
W
R00000000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
R00000
W
PIFL2 PIFL1 PIFL0
PTABYPL2 PTABYPL1 PTABYPL0
PTADIRL2 PTADIRL1 PTADIRL0
DIENL2 DIENL1 DIENL0
PTAENL2 PTAENL1 PTAENL0
PIRL2 PIRL1 PIRL0
0x033F PTTEL
0x0340–
0x037F
Reserved
R00000
W
R00000000
W
PTTEL2 PTTEL1 PTTEL0
2.3.2 PIM Registers 0x0200-0x020F
This section describes registers implemented in address range 0x0200-0x020F. These registers serve for
specific PIM related functions not part of the generic port registers.
• If not stated differently, writing to reserved bits has no effect and read returns zero.
• All register read accesses are synchronous to internal clocks.
• Register bits can be written at any time if not stated differently.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
82 NXP Semiconductors
Page 83

2.3.2.1 Module Routing Register 0 (MODRR0)
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address 0x0200 Access: User read
76543210
R0 0
W
Routing
Option
Reset00000000
— — — — SCI1 SCI0-LINPHY0 interface
Reserved
0
SCI1RR S0L0RR2-0
Figure 2-1. Module Routing Register 0 (MODRR0)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
Table 2-10. MODRR0 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
3
SCI1RR
2-0
S0L0RR2-0
Module Routing Register — SCI1 routing
1 TXD1 on PE1; RXD1 on PE0
0 TXD1 on PT1; RXD1 on PT0
Module Routing Register — SCI0-LINPHY0 routing
Selection of SCI0-LINPHY0 interface routing options to support probing and conformance testing. Refer to
Figure 2-2 for an illustration and Table 2-11 for preferred settings.
Note: SCI0 must be enabled for TXD0 routing to take effect on pin. LINPHY0 must be enabled for LPRXD0 and
LPDR[LPDR1] routings to take effect on pins.
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 83
Page 84

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
LPRXD0
LPTXD0
TXD0 / LPDR1
RXD0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
TIM0 input
capture
channel 3
S0L0RR2S0L0RR1S0L0RR0
SCI0 LINPHY0
TXD0
RXD0
LPTXD0
LPRXD0
LPDR1
LIN
Figure 2-2. SCI0-to-LINPHY0 Routing Options Illustration
Table 2-11. Preferred Interface Configurations
S0L0RR[2:0] Description
000 Default setting:
SCI0 connects to LINPHY0, interface internal only
001 Direct control setting:
LP0DR[LPDR1] register bit controls LPTXD0, interface internal only
100 Probe setting:
SCI0 connects to LINPHY0, interface accessible on 2 external pins
110 Conformance test setting:
Interface opened and all 4 signals routed externally
NOTE
For standalone usage of SCI0 on external pins set S0L0RR[2:0]=0b110 and
disable LINPHY0 (LPCR[LPE]=0). This releases the LINPHY0 associated
pins to other shared functions.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
84 NXP Semiconductors
Page 85

2.3.2.2 Module Routing Register 1 (MODRR1)
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address 0x0201 Access: User read/write
76543210
R000000
W
— — — — — — ADC0 trigger
Reset00000000
TRIG0RR2-0
Figure 2-3. Module Routing Register 1 (MODRR1)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-12. MODRR1 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
1-0
TRIG0RR
1-0
1. Output compare function on pin remains active unless disabled in timer config register TIM0OCPD[OCPD2]=1
Module Routing Register — ADC0 trigger source
11 R e s e r ved
10 TIM0 output compare channel 2 connected to ADC0 trigger input
01 PMF reload connected to ADC0 trigger input
00 PTU trigger 0 connected to ADC0 trigger input
(1)
(1)
2.3.2.3 Module Routing Register 2 (MODRR2)
Address 0x0202 Access: User read/write
76543210
R00000000
W
————————
Reset00000000
Figure 2-4. Module Routing Register 2 (MODRR2)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Never
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 85
Page 86

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.2.4 Module Routing Register 3 (MODRR3)
Address 0x0203 Access: User read/write
76543210
R000
T0IC3RR1-0 T0IC2RR
W
— — — IC0_3 IC0_2 — —
Reset00000000
00
Figure 2-5. Module Routing Register 3 (MODRR3)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-13. MODRR3 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
4-3
T0IC3RR1
-0
Module Routing Register — IC0_3 routing
If timer channel is not used with a pin (T0IC3RR0=1) then one out of two internal sources can be selected as input.
11 TIM0 input capture channel 3 connected to RXD1
10 Reserved
01 TIM0 input capture channel 3 connected to RXD0
00 TIM0 input capture channel 3 connected to PT3
(1)
2
T0IC2RR
Module Routing Register — IC0_2 routing
1 TIM0 input capture channel 2 connected to ACLK
0 TIM0 input capture channel 2 connected to PT2
2.3.2.5 Module Routing Register 4 (MODRR4)
Address 0x0204 Access: User read
76543210
R
FAULT5RR
W
Routing
Option
Reset00000000
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
FAULT5 — PWM5 PWM4 PWM3 PWM2 PWM1 PWM0
0
P0C5RR P0C4RR P0C3RR P0C2RR P0C1RR P0C0RR
Figure 2-6. Module Routing Register 4 (MODRR4)
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
86 NXP Semiconductors
Page 87

Table 2-14. MODRR4 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
7
FAULT5RR
5
P0C5RR
4
P0C4RR
3
P0C3RR
2
P0C2RR
1
P0C1RR
0
P0C0RR
Module Routing Register — FAULT5 routing
1 FAULT5 connected to PT2
0 FAULT5 connected to PP1
Module Routing Register — PWM5 routing
1 PWM5 connected to HS1
0 PWM5 connected to PP1
Module Routing Register — PWM4 routing
1 PWM4 connected to HS0
0 PWM4 connected to PP0
Module Routing Register — PWM3/GDU probe routing
1 PWM3/GDU signal visible at PT2
0 PWM3/GDU internal only
Module Routing Register — PWM2/GDU probe routing
1 PWM2/GDU signal visible at PT1
0 PWM2/GDU internal only
Module Routing Register — PWM1/GDU probe routing
1 PWM1/GDU signal visible at PE1
0 PWM1/GDU internal only
Module Routing Register — PWM0/GDU probe routing
1 PWM0/GDU signal visible at PE0
0 PWM0/GDU internal only
2.3.2.6 Module Routing Register 5 (MODRR5)
Address 0x0205 Access: User read/write
76543210
R
T1IC3RR T1IC2RR T1IC1RR T1IC0RR
W
IC1_3 IC1_2 IC1_1 IC1_0 — OC1_2 OC1_1 —
Reset00000000
Figure 2-7. Module Routing Register 1 (MODRR5)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
0
T1OC2RR T1OC1RR
0
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 87
Page 88

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-15. MODRR5 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
T1IC3RR
6
T1IC2RR
5
T1IC1RR
4
T1IC0RR
2
T1OC2RR
1
T1OC1RR
Module Routing Register — IC1_3 routing
1 TIM1 input capture channel 3 connected to GDU dead time measurement feature
0 TIM1 input capture channel 3 connected to PT7
Module Routing Register — IC1_2 routing
1 TIM1 input capture channel 2 connected to HVI2
0 TIM1 input capture channel 2 connected to PT6
Module Routing Register — IC1_1 routing
1 TIM1 input capture channel 1 connected to HVI1
0 TIM1 input capture channel 1 connected to PT5
Module Routing Register — IC1_0 routing
1 TIM1 input capture channel 0 connected to HVI0
0 TIM1 input capture channel 0 connected to PT4
Module Routing Register — OC1_2 routing
1 TIM1 output compare channel 2 connected to HS1
0 TIM1 output compare channel 2 connected to PT6
Module Routing Register — OC1_1 routing
1 TIM1 output compare channel 1 connected to HS0
0 TIM1 output compare channel 1 connected to PT5
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
88 NXP Semiconductors
Page 89

2.3.2.7 ECLK Control Register (ECLKCTL)
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address 0x0208 Access: User read/write
76543210
R
NECLK
W
Reset:10000000
0000000
(1)
Figure 2-8. ECLK Control Register (ECLKCTL)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-16. ECLKCTL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
NECLK
No ECLK — Disable ECLK output
This bit controls the availability of a free-running clock on the ECLK pin. This clock has a fixed rate equivalent to the
internal bus clock.
1 ECLK disabled
0 ECLK enabled
2.3.2.8 IRQ Control Register (IRQCR)
Address 0x0209 Access: User read/write
(1)
76543210
R
IRQE IRQEN
W
Reset00000000
000000
Figure 2-9. IRQ Control Register (IRQCR)
1. Read: Anytime
Write:
IRQE: Once in normal mode, anytime in special mode
IRQEN: Anytime
Table 2-17. IRQCR Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
IRQE
6
IRQEN
IRQ select edge sensitive only —
pin configured to respond only to falling edges. Falling edges on the IRQ pin are detected anytime when
1 IRQ
IRQE=1 and will be cleared only upon a reset or the servicing of the IRQ
0 IRQ configured for low level recognition
IRQ enable —
pin is connected to interrupt logic
1 IRQ
0 IRQ
pin is disconnected from interrupt logic
interrupt.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 89
Page 90

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.2.9 Reserved Register
Address 0x020D Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
Resetxxxxxxxx
Figure 2-10. Reserved Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode.
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and is not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the modules functionality.
2.3.2.10 Reserved Register
Address 0x020E Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
(1)
(1)
Resetxxxxxxxx
Figure 2-11. Reserved Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and is not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the modules functionality.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
90 NXP Semiconductors
Page 91

2.3.2.11 Reserved Register
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address 0x020F Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
Resetxxxxxxxx
Figure 2-12. Reserved Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode
NOTE
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and is not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the modules functionality.
2.3.3 PIM Generic Registers
This section describes the details of all PIM registers.
• Writing to reserved bits has no effect and read returns zero.
• All register read accesses are synchronous to internal clocks.
(1)
• All registers can be written at any time, however a specific configuration might not become active.
E.g. a pullup device does not become active while the port is used as a push-pull output.
• General-purpose data output availability depends on prioritization; input data registers always
reflect the pin status independent of the use.
• Pull-device availability, pull-device polarity, wired-or mode, key-wake up functionality are
independent of the prioritization unless noted differently.
• For availability of individual bits refer to Section 2.3.1, “Register Map” and Table 2-44.
NOTE
This is a generic description of the standard PIM registers. Refer to Table 2-
44 to determine the implemented bits in the respective register.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 91
Page 92

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.3.1 Port Data Register
Address 0x0260 PTE
0x0280 PTADH
0x0281 PTADL
0x02C0 PTT
0x02F0 PTP
76543210
R
PTx7 PTx6 PTx5 PTx4 PTx3 PTx2 PTx1 PTx0
W
Reset00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-13. Port Data Register
1. Read: Anytime. The data source is depending on the data direction value.
Write: Anytime
Table 2-18. Port Data Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PTx7-0
Port Data — General purpose input/output data
This register holds the value driven out to the pin if the pin is used as a general purpose output.
When not used with the alternative function (refer to Ta b le 2 -8 ), these pins can be used as general purpose I/O.
If the associated data direction bits of these pins are set to 1, a read returns the value of the port register, otherwise
the buffered pin input state is read.
(1)
2.3.3.2 Port Input Register
Address 0x0262 PTIE
0x0282 PTIADH
0x0283 PTIADL
0x02C1 PTIT
0x02F1 PTIP
0x0331 PTIL
76543210
R PTIx7 PTIx6 PTIx5 PTIx4 PTIx3 PTIx2 PTIx1 PTIx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-14. Port Input Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write:Never
Table 2-19. Port Input Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PTIx7-0
Port Input — Data input
A read always returns the buffered input state of the associated pin. It can be used to detect overload or short circuit
conditions on output pins.
Access: User read only
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
92 NXP Semiconductors
Page 93

2.3.3.3 Data Direction Register
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address 0x0264 DDRE
0x0284 DDRADH
0x0285 DDRADL
0x02C2 DDRT
0x02F2 DDRP
76543210
R
DDRx7 DDRx6 DDRx5 DDRx4 DDRx3 DDRx2 DDRx1 DDRx0
W
Reset00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-15. Data Direction Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-20. Data Direction Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
DDRx7-0
Data Direction — Select general-purpose data direction
This bit determines whether the pin is a general-purpose input or output. If a peripheral module controls the pin the
content of the data direction register is ignored. Independent of the pin usage with a peripheral module this register
determines the source of data when reading the associated data register address.
Note: Due to internal synchronization circuits, it can take up to two bus clock cycles until the correct value is read on
port data and port input registers, when changing the data direction register.
1 Associated pin is configured as output
0 Associated pin is configured as input
(1)
2.3.3.4 Pull Device Enable Register
Address 0x0266 PERE
0x0286 PERADH
0x0287 PERADL
0x02C3 PERT
0x02F3 PERP
76543210
R
PERx7 PERx6 PERx5 PERx4 PERx3 PERx2 PERx1 PERx0
W
Reset
Ports E:00000011
Others:00000000
Figure 2-16. Pull Device Enable Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 93
Access: User read/write
(1)
Page 94

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Table 2-21. Pull Device Enable Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PERx7-0
Pull Enable — Activate pull device on input pin
This bit controls whether a pull device on the associated port input or open-drain output pin is active. If a pin is used
as push-pull output this bit has no effect. The polarity is selected by the related polarity select register bit. On opendrain output pins only a pullup device can be enabled.
1 Pull device enabled
0 Pull device disabled
2.3.3.5 Polarity Select Register
Address 0x0268 PPSE
0x0288 PPSADH
0x0289 PPSADL
76543210
R
PPSx7 PPSx6 PPSx5 PPSx4 PPSx3 PPSx2 PPSx1 PPSx0
W
Reset
Ports E:00000011
Others:00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-17. Polarity Select Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
(1)
Table 2-22. Polarity Select Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PPSx7-0
Pull Polarity Select — Configure pull device and pin interrupt edge polarity on input pin
This bit selects a pullup or a pulldown device if enabled on the associated port input pin.
If a port has interrupt functionality this bit also selects the polarity of the active edge.
1 Pulldown device selected; rising edge selected
0 Pullup device selected; falling edge selected
2.3.3.6 Port Interrupt Enable Register
Address 0x028C PIEADH
0x028D PIEADL
0x02F6 PIEP
0x0336 PIEL
76543210
R
PIEx7 PIEx6 PIEx5 PIEx4 PIEx3 PIEx2 PIEx1 PIEx0
W
Reset00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-18. Port Interrupt Enable Register
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
94 NXP Semiconductors
Page 95

1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-23. Port Interrupt Enable Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
7-0
PIEx7-0
Port Interrupt Enable — Activate pin interrupt (KWU)
This bit enables or disables the edge sensitive pin interrupt on the associated pin. An interrupt can be generated if
the pin is operating in input or output mode when in use with the general-purpose or related peripheral function.
1 Interrupt is enabled
0 Interrupt is disabled (interrupt flag masked)
2.3.3.7 Port Interrupt Flag Register
Address 0x028E PIFADH
0x028F PIFADL
0x02F7 PIFP
0x0337 PIFL
76543210
R
PIFx7 PIFx6 PIFx5 PIFx4 PIFx3 PIFx2 PIFx1 PIFx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-19. Port Interrupt Flag Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime, write 1 to clear
Table 2-24. Port Interrupt Flag Register Field Descriptions
Access: User read/write
(1)
Field Description
7-0
PIFx7-0
NXP Semiconductors 95
Port Interrupt Flag — Signal pin event (KWU)
This flag asserts after a valid active edge was detected on the related pin (see Section 2.4.5.2, “Pin Interrupts and
Key-Wakeup (KWU)”). This can be a rising or a falling edge based on the state of the polarity select register. An
interrupt will occur if the associated interrupt enable bit is set.
Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 Active edge on the associated bit has occurred
0 No active edge occurred
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 96

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.3.8 Digital Input Enable Register
Address 0x0298 DIENADH
0x0299 DIENADL
76543210
R
DIENx7 DIENx6 DIENx5 DIENx4 DIENx3 DIENx2 DIENx1 DIENx0
W
Reset00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-20. Digital Input Enable Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-25. Digital Input Enable Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
DIENx7-0
Digital Input Enable — Input buffer control
This bit controls the digital input function. If set to 1 the input buffers are enabled and the pin can be used with the
digital function. If a peripheral module is enabled which uses the pin with a digital function, the input buffer is activated
and the register bit is ignored. If the pin is used with an analog function this bit shall be cleared to avoid shoot-through
current.
1 Associated pin is configured as digital input
0 Associated pin digital input is disabled
(1)
2.3.3.9 Reduced Drive Register
Address 0x02CD RDRT
0x02FD RDRP
76543210
R
RDRx7 RDRx6 RDRx5 RDRx4 RDRx3 RDRx2 RDRx1 RDRx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-21. Reduced Drive Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-26. Reduced Drive Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
RDRx7-0
Reduced Drive Register — Select reduced drive for output pin
This bit configures the drive strength of the associated output pin as either full or reduced. If a pin is used as input
this bit has no effect. The reduced drive function is independent of which function is being used on a particular pin.
1 Reduced drive selected (approx. 1/10 of the full drive strength)
0 Full drive strength enabled
Access: User read/write
(1)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
96 NXP Semiconductors
Page 97

2.3.3.10 PIM Reserved Register
Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
Address (any reserved) Access: User read
76543210
R00000000
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-22. PIM Reserved Register
1. Read: Always reads 0x00
Write: Unimplemented
2.3.4 PIM Generic Register Exceptions
This section lists registers with deviations from the generic description in one or more register bits.
2.3.4.1 Port T Polarity Select Register (PPST)
Address 0x02C4 PPST Access: User read/write
76543210
R
PPST7 PPST6 PPST5 PPST4 PPST3 PPST2 PPST1 PPST0
W
(1)
(1)
Reset00000000
Figure 2-23. Port T Polarity Select Register (PPST)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-27. Port T Polarity Select Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-3
PPST7-3
2
PPST2
1-0
PPST1-0
See Section 2.3.3.5, “Polarity Select Register”.
Pull Polarity Select — Configure pull device and pin interrupt edge polarity on input pin
This bit selects a pullup or a pulldown device if enabled on the associated port input pin.
If a port has interrupt functionality this bit also selects the polarity of the active edge.
This bit selects whether a high or a low level on FAULT5 generates a fault event in PMF, if FAULT5RR is set.
1 Pulldown device selected; rising edge selected; active-high level selected on FAULT5 input
0 Pullup device selected; falling edge selected; active-low level selected on FAULT5 input
See Section 2.3.3.5, “Polarity Select Register”.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 97
Page 98

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.4.2 Port T Over-Current Protection Enable Register (OCPET)
Address 0x02C9 Access: User read/write
76543210
R00000
OCPET2
W
Reset00000000
00
Figure 2-24. Over-Current Protection Enable Register (OCPET)
1. Read: Anytime
Write:Anytime
Table 2-28. OCPET Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
2
OCPET2
Over-Current Protection Enable — Activate over-current detector on PT2
Refer to Section 2.5.3, “Over-Current Protection on PP0 (EVDD)”
1 PT2 over-current detector enabled
0 PT2 over-current detector disabled
2.3.4.3 Port T Over-Current Interrupt Enable Register (OCIET)
Address 0x02CA Access: User read/write
(1)
(1)
76543210
R00000
OCIET2
W
Reset00000000
00
Figure 2-25. Port T Over-Current Interrupt Enable Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-29. OCIET Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
2
OCIET2
Over-Current Interrupt Enable —
This bit enables or disables the over-current interrupt on PT2.
1 PT2 over-current interrupt enabled
0 PT2 over-current interrupt disabled (interrupt flag masked)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
98 NXP Semiconductors
Page 99

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.4.4 Port T Over-Current Interrupt Flag Register (OCIFT)
Address 0x02CB Access: User read/write
76543210
R00000
OCIFT2
W
Reset00000000
00
Figure 2-26. Port T Over-Current Interrupt Flag Register (OCIFT)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime, write 1 to clear
Table 2-30. OCIFT Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
2
OCIFT2
Over-Current Interrupt Flag —
This flag asserts if an over-current condition is detected on PT2 (Section 2.4.5.3, “Over-Current Interrupt and
Protection”). Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 PT2 over-current event occurred
0 No PT2 over-current event occurred
2.3.4.5 Port P Polarity Select Register (PPSP)
Address 0x02F4 Access: User read/write
(1)
(1)
76543210
R000000
W
Reset00000000
PPSP1 PPSP0
Figure 2-27. Port P Polarity Select Register (PPSP)
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-31. Port P Polarity Select Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
1
PPSP1
0
PPSP0
Pull Polarity Select — Configure pull device and pin interrupt edge polarity on input pin
This bit selects a pullup or a pulldown device if enabled on the associated port input pin.
If a port has interrupt functionality this bit also selects the polarity of the active edge.
This bit selects whether a high or a low level on FAULT5 generates a fault event in PMF, if FAULT5RR is cleared
1 Pulldown device selected; rising edge selected; active-high level selected on FAULT5 input
0 Pullup device selected; falling edge selected; active-low level selected on FAULT5 input
See Section 2.3.3.5, “Polarity Select Register”.
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 99
Page 100

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12ZVMBPIMV3)
2.3.4.6 Port P Over-Current Protection Enable Register (OCPEP)
Address 0x02F9 Access: User read/write
76543210
R0000000
W
Reset00000000
OCPEP0
Figure 2-28. Over-Current Protection Enable Register (OCPEP)
1. Read: Anytime
Write:Anytime
Table 2-32. OCPEP Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
0
OCPEP0
Over-Current Protection Enable — Activate over-current detector on PP0
Refer to Section 2.5.4, “Over-Current Protection on PT2”
1 PP0 over-current detector enabled
0 PP0 over-current detector disabled
2.3.4.7 Port P Over-Current Interrupt Enable Register (OCIEP)
Address 0x02FA Access: User read/write
(1)
(1)
76543210
R0000000
W
Reset00000000
OCIEP0
Figure 2-29. Port P Over-Current Interrupt Enable Register
1. Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-33. OCIEP Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
0
OCIEP0
Over-Current Interrupt Enable —
This bit enables or disables the over-current interrupt on PP0.
1 PP0 over-current interrupt enabled
0 PP0 over-current interrupt disabled (interrupt flag masked)
MC9S12ZVMB Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
100 NXP Semiconductors
 Loading...
Loading...